⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-30 更新
Masked Language Prompting for Generative Data Augmentation in Few-shot Fashion Style Recognition
Authors:Yuki Hirakawa, Ryotaro Shimizu
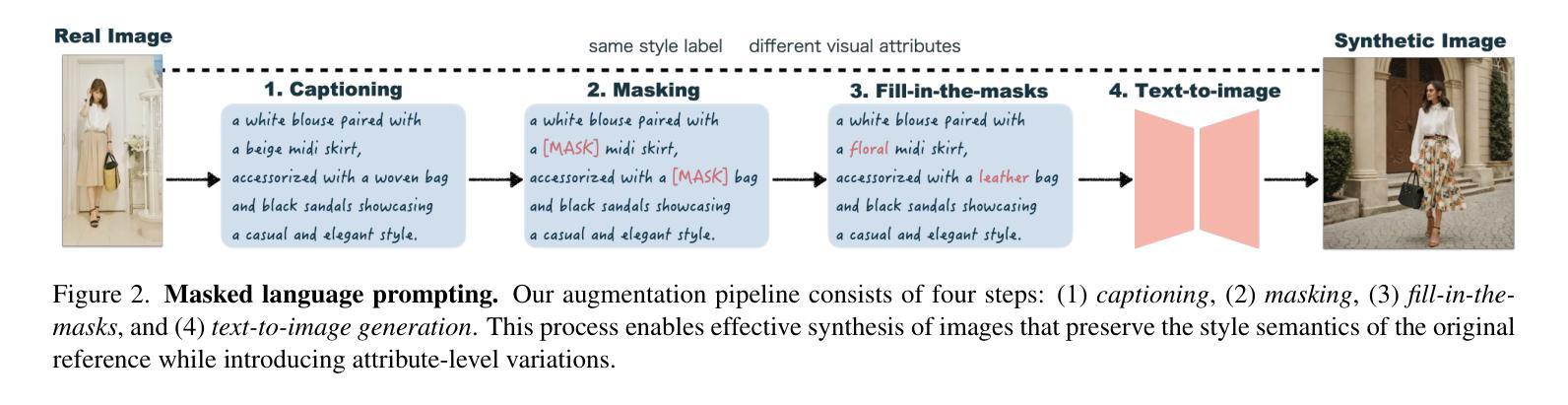
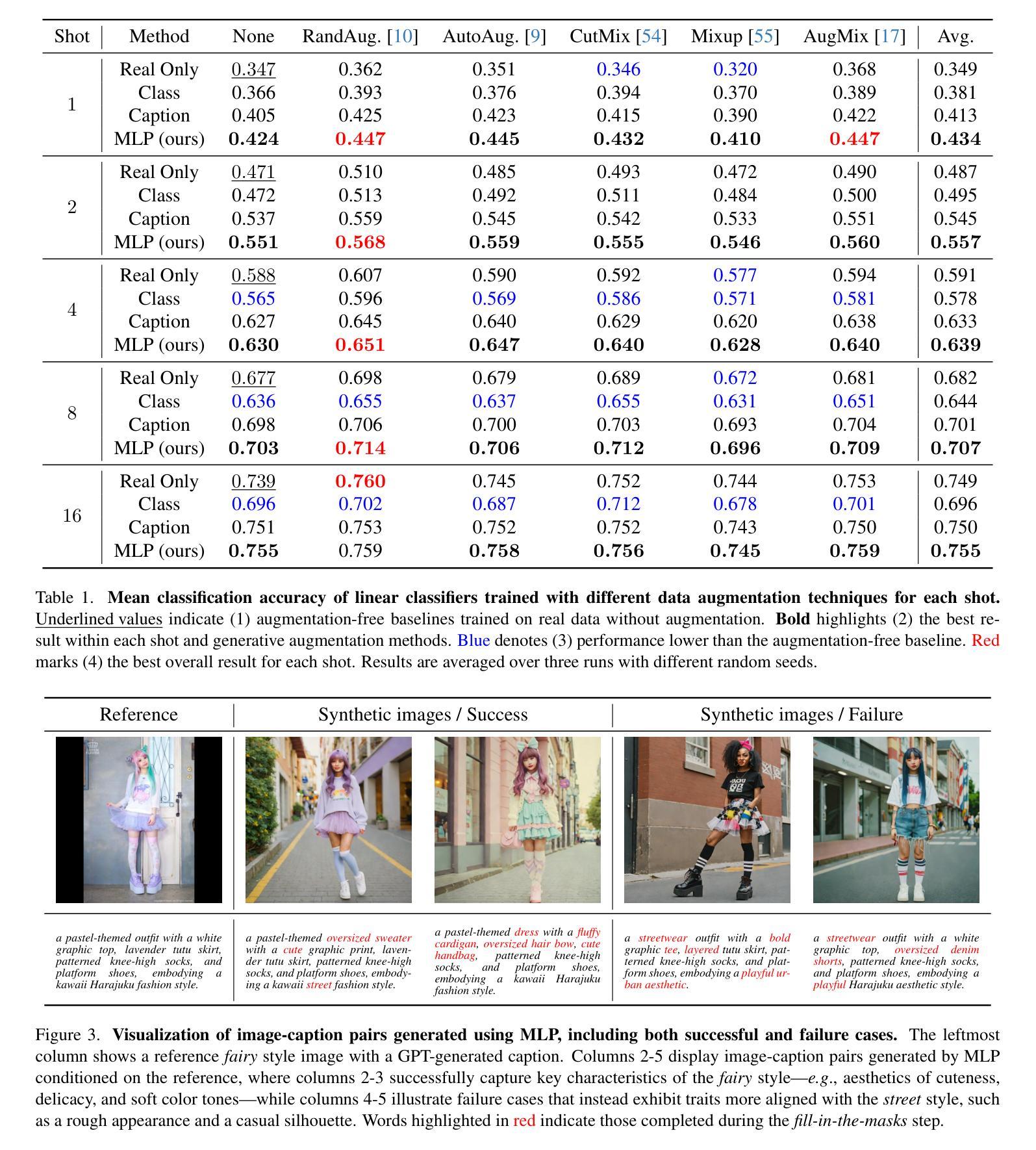
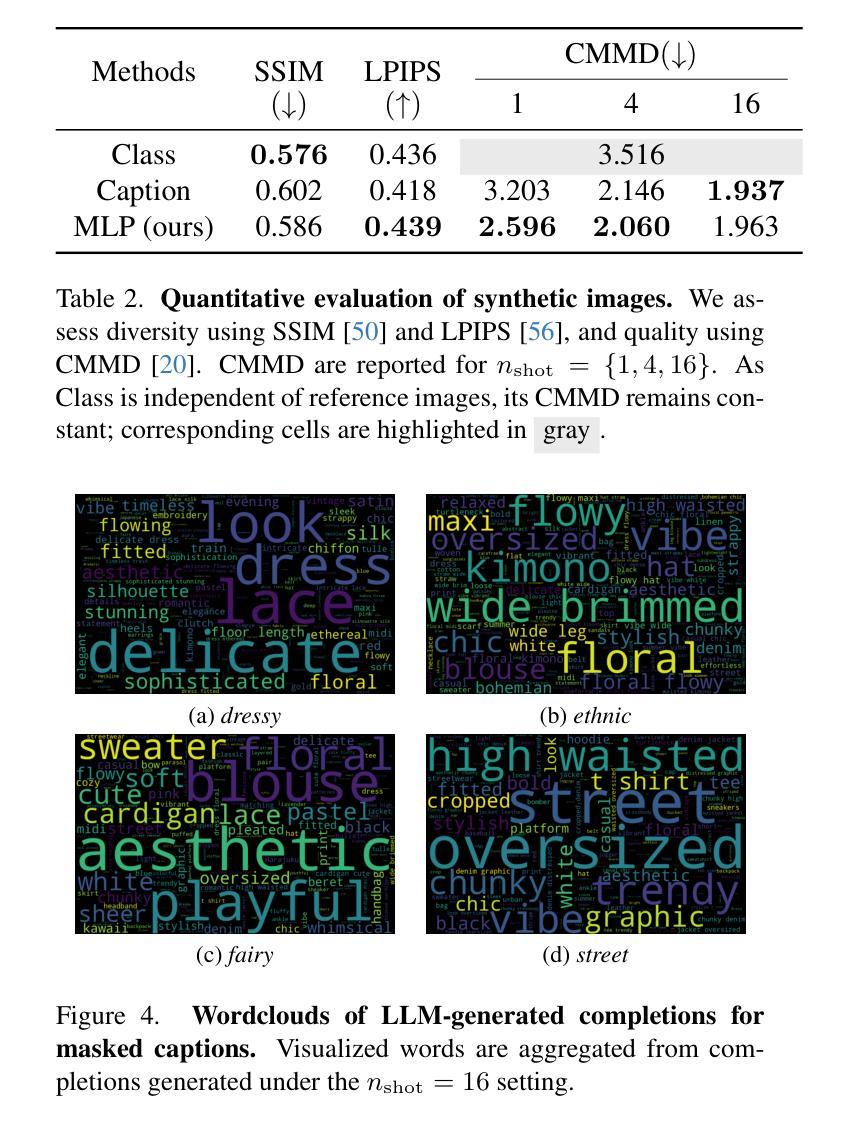
Constructing dataset for fashion style recognition is challenging due to the inherent subjectivity and ambiguity of style concepts. Recent advances in text-to-image models have facilitated generative data augmentation by synthesizing images from labeled data, yet existing methods based solely on class names or reference captions often fail to balance visual diversity and style consistency. In this work, we propose \textbf{Masked Language Prompting (MLP)}, a novel prompting strategy that masks selected words in a reference caption and leverages large language models to generate diverse yet semantically coherent completions. This approach preserves the structural semantics of the original caption while introducing attribute-level variations aligned with the intended style, enabling style-consistent and diverse image generation without fine-tuning. Experimental results on the FashionStyle14 dataset demonstrate that our MLP-based augmentation consistently outperforms class-name and caption-based baselines, validating its effectiveness for fashion style recognition under limited supervision.
构建用于时尚风格识别的数据集具有挑战性,因为风格概念具有固有的主观性和模糊性。最近的文本到图像模型的进步通过从标记数据中合成图像促进了生成数据增强,但现有方法仅基于类名或参考字幕往往无法在视觉多样性和风格一致性之间取得平衡。在这项工作中,我们提出了Masked Language Prompting(MLP),这是一种新的提示策略,它掩盖了参考字幕中的选定单词,并利用大型语言模型生成多样但语义连贯的补全。这种方法保留了原始字幕的结构语义,同时引入了与既定风格一致的属性级别变化,能够在不进行微调的情况下生成风格一致且多样的图像。在FashionStyle14数据集上的实验结果表明,我们基于MLP的增强方法一直优于基于类名和字幕的基线方法,验证了其在有限监督下对时尚风格识别的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
时尚风格识别数据集构建具有挑战性,因为风格概念具有主观性和模糊性。最近文本到图像模型的进步通过合成图像简化了生成数据增强。然而,现有方法往往无法平衡视觉多样性和风格一致性。本研究提出一种名为Masked Language Prompting(MLP)的新提示策略,它通过掩盖参考字幕中的选定词汇并利用大型语言模型生成多样且语义连贯的补全内容来实现风格一致且多样化的图像生成。在FashionStyle数据集上的实验结果表明,基于MLP的增强方法优于基于类别名称和标题的基线方法,证明了它在有限监督下的时尚风格识别的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 时尚风格识别数据集构建具有挑战性,因为风格概念具有主观性和模糊性。
- 当前文本到图像模型的方法有助于生成数据增强。
- 现有方法难以平衡视觉多样性和风格一致性。
- Masked Language Prompting(MLP)是一种新的提示策略,利用大型语言模型生成多样且语义连贯的补全内容。
- MLP通过掩盖参考字幕中的词汇来保留原始字幕的结构语义,同时引入与预期风格一致的属性级别变化。
- 基于MLP的增强方法在FashionStyle数据集上表现出优异性能,优于基于类别名称和标题的基线方法。
点此查看论文截图

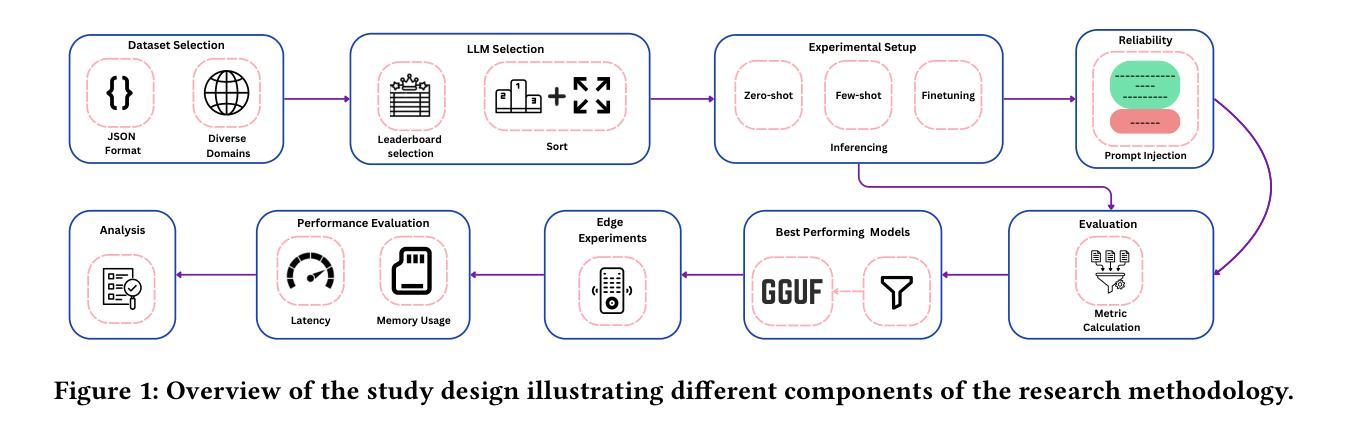
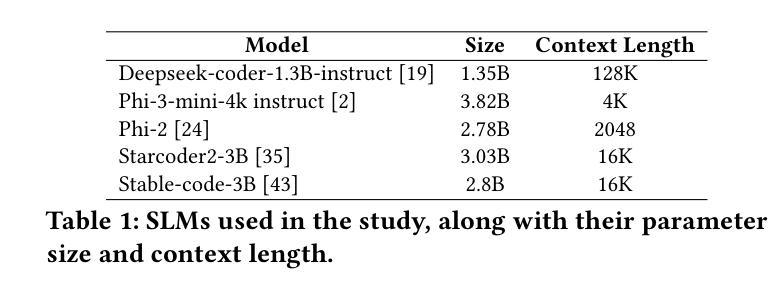
Small Models, Big Tasks: An Exploratory Empirical Study on Small Language Models for Function Calling
Authors:Ishan Kavathekar, Raghav Donakanti, Ponnurangam Kumaraguru, Karthik Vaidhyanathan
Function calling is a complex task with widespread applications in domains such as information retrieval, software engineering and automation. For example, a query to book the shortest flight from New York to London on January 15 requires identifying the correct parameters to generate accurate function calls. Large Language Models (LLMs) can automate this process but are computationally expensive and impractical in resource-constrained settings. In contrast, Small Language Models (SLMs) can operate efficiently, offering faster response times, and lower computational demands, making them potential candidates for function calling on edge devices. In this exploratory empirical study, we evaluate the efficacy of SLMs in generating function calls across diverse domains using zero-shot, few-shot, and fine-tuning approaches, both with and without prompt injection, while also providing the finetuned models to facilitate future applications. Furthermore, we analyze the model responses across a range of metrics, capturing various aspects of function call generation. Additionally, we perform experiments on an edge device to evaluate their performance in terms of latency and memory usage, providing useful insights into their practical applicability. Our findings show that while SLMs improve from zero-shot to few-shot and perform best with fine-tuning, they struggle significantly with adhering to the given output format. Prompt injection experiments further indicate that the models are generally robust and exhibit only a slight decline in performance. While SLMs demonstrate potential for the function call generation task, our results also highlight areas that need further refinement for real-time functioning.
函数调用是一项具有广泛应用的复杂任务,在信息检索、软件工程和自动化等领域都有涉及。例如,要查询1月15日从纽约到伦敦的最短航班,需要识别正确的参数来生成准确的函数调用。大型语言模型(LLM)可以自动化这个过程,但在资源受限的环境中,它们计算成本高昂,不太实用。相比之下,小型语言模型(SLM)可以高效运行,提供更快的响应时间和更低的计算需求,使其成为边缘设备上函数调用的潜在候选者。在这项探索性实证研究中,我们评估了SLMs在跨不同领域生成函数调用时的有效性,采用了零样本、少样本和微调方法,有/无提示注入,同时提供微调模型以促进未来应用。此外,我们通过分析一系列指标的模型响应,捕捉函数调用生成的各个方面。另外,我们在边缘设备上进行实验,以评估其在延迟和内存使用方面的性能,为实际应用提供有用见解。我们发现,虽然SLMs从零样本到少样本有所提升,并在微调时表现最佳,但它们在很大程度上难以遵循给定的输出格式。提示注入实验进一步表明,这些模型通常很稳健,性能只有轻微下降。虽然SLM在函数调用生成任务中显示出潜力,但我们的结果也强调了需要进一步完善以实现实时功能的领域。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at EASE 2025 AI Models and Data Evaluation track
Summary
此文本探讨了小型语言模型(SLMs)在生成函数调用方面的效能。该研究评估了SLMs在不同领域生成函数调用的效果,采用了零样本、少样本和微调方法,同时分析了模型响应的各种指标。此外,该研究还在边缘设备上进行了实验,以评估其延迟和内存使用情况。研究发现,SLMs从零样本到少样本有所提升,在微调后表现最佳,但在遵循输出格式方面存在困难。同时,实验显示模型通常很稳健,性能略有下降。虽然SLMs在函数调用生成任务上展现出潜力,但仍需要进一步改进以适应实时应用。
Key Takeaways
- SLMs在函数调用生成方面展现出了潜力,尤其是在资源受限的边缘设备上。
- 研究评估了SLMs在多种领域生成函数调用的效能,采用了零样本、少样本和微调方法。
- SLMs在零样本到少样本的表现有所提升,经过微调后表现最佳。
- 模型在遵循输出格式方面存在困难。
- 通过实验发现,SLMs通常很稳健,性能略有下降。
- 在边缘设备上进行的实验评估了SLMs的延迟和内存使用情况。
点此查看论文截图


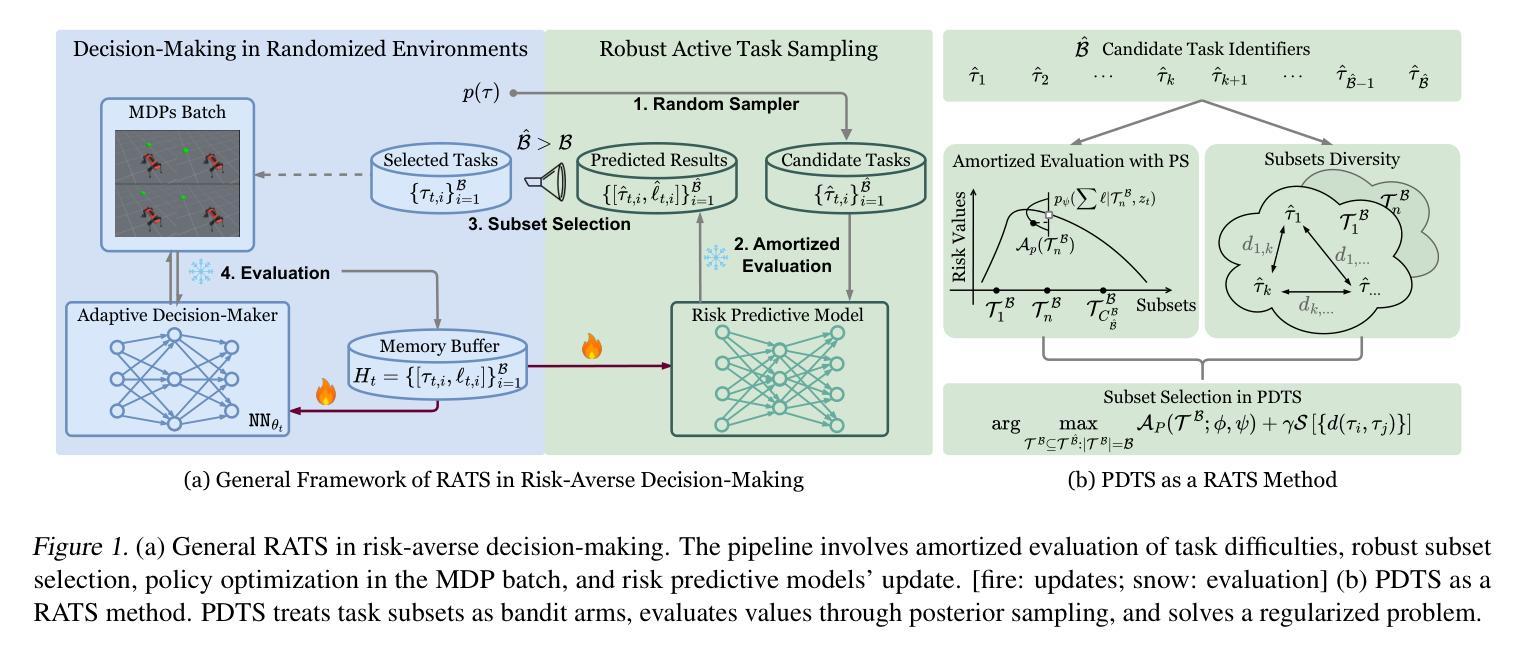
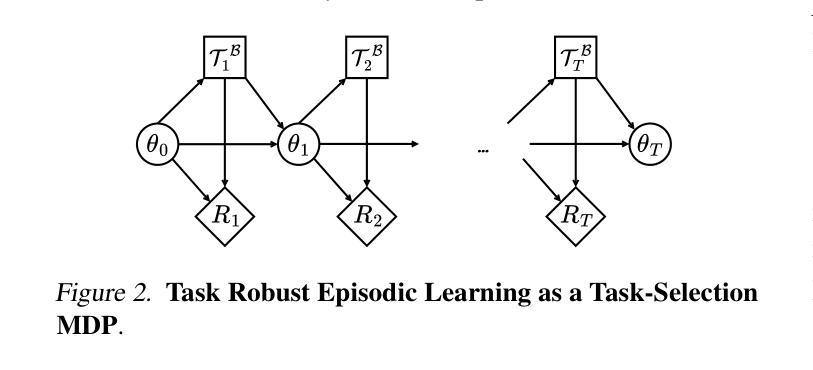
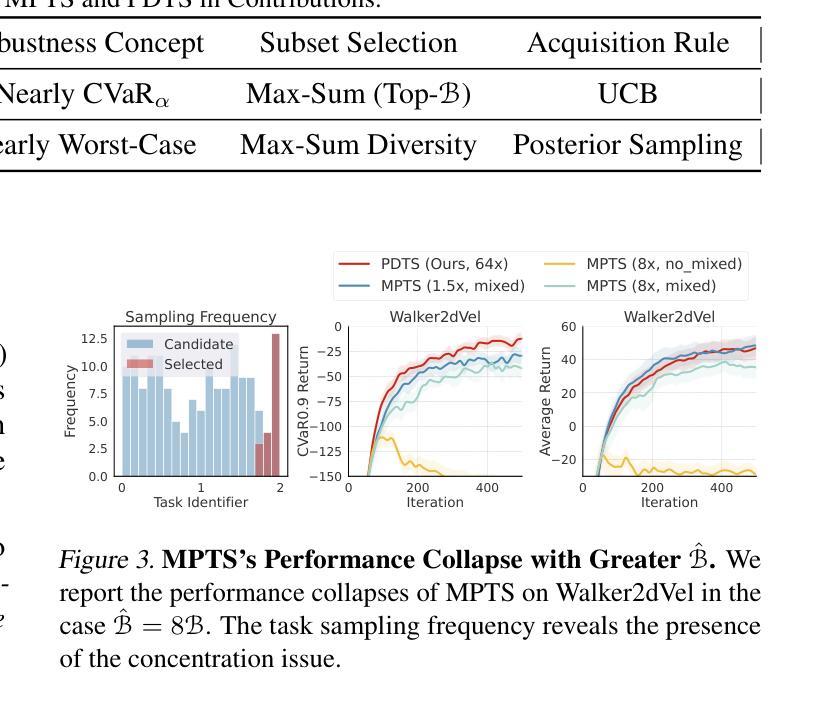
Fast and Robust: Task Sampling with Posterior and Diversity Synergies for Adaptive Decision-Makers in Randomized Environments
Authors:Yun Qu, Qi, Wang, Yixiu Mao, Yiqin Lv, Xiangyang Ji
Task robust adaptation is a long-standing pursuit in sequential decision-making. Some risk-averse strategies, e.g., the conditional value-at-risk principle, are incorporated in domain randomization or meta reinforcement learning to prioritize difficult tasks in optimization, which demand costly intensive evaluations. The efficiency issue prompts the development of robust active task sampling to train adaptive policies, where risk-predictive models are used to surrogate policy evaluation. This work characterizes the optimization pipeline of robust active task sampling as a Markov decision process, posits theoretical and practical insights, and constitutes robustness concepts in risk-averse scenarios. Importantly, we propose an easy-to-implement method, referred to as Posterior and Diversity Synergized Task Sampling (PDTS), to accommodate fast and robust sequential decision-making. Extensive experiments show that PDTS unlocks the potential of robust active task sampling, significantly improves the zero-shot and few-shot adaptation robustness in challenging tasks, and even accelerates the learning process under certain scenarios. Our project website is at https://thu-rllab.github.io/PDTS_project_page.
任务鲁棒性适应是序列决策制定中一个长期追求的目标。一些风险规避策略,例如条件风险价值原则,被纳入领域随机化或元强化学习中,以优化中的优先处理困难任务,这些任务需要进行昂贵的密集评估。效率问题促使开发稳健的活动任务采样来训练自适应策略,其中风险预测模型用于替代策略评估。这项工作将稳健活动任务采样的优化管道特征化为马尔可夫决策过程,提供了理论和实践见解,并构成了风险规避场景中的稳健性概念。重要的是,我们提出了一种易于实施的方法,称为“后验和多样性协同任务采样(PDTS)”,以实现快速和稳健的序列决策制定。大量实验表明,PDTS释放了稳健活动任务采样的潜力,显著提高了挑战性任务的零样本和少样本适应稳健性,甚至在特定场景下加速了学习过程。我们的项目网站是https://thu-rllab.github.io/PDTS_project_page。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于序贯决策制定的任务稳健适应是一项长期追求。本研究将风险规避策略融入领域随机化或元强化学习中,优先处理优化中的困难任务,同时解决效率问题。研究发展出稳健的任务主动采样方法,用以训练适应性政策,并用风险预测模型替代政策评估。提出一种简单实用的方法——后验与多样性协同任务采样(PDTS),实现快速稳健的序贯决策制定。大量实验表明,PDTS解锁了稳健主动任务采样的潜力,显著提高了挑战性任务的零样本和少样本适应稳健性,并在某些场景下加速了学习过程。
Key Takeaways
- 任务稳健适应是序贯决策中的长期目标。
- 风险规避策略被融入领域随机化或元强化学习中以处理困难任务。
- 效率和优化中的挑战促使发展稳健的任务主动采样方法。
- 风险预测模型用于替代政策评估。
- 提出了一种简单实用的方法——后验与多样性协同任务采样(PDTS)。
- PDTS显著提高了在挑战性任务中的零样本和少样本适应稳健性。
点此查看论文截图

Towards Robust Dialogue Breakdown Detection: Addressing Disruptors in Large Language Models with Self-Guided Reasoning
Authors:Abdellah Ghassel, Xianzhi Li, Xiaodan Zhu
Large language models (LLMs) are rapidly changing various domains. However, their capabilities in handling conversational breakdowns still require an in-depth exploration. This paper addresses the challenge of detecting and mitigating dialogue breakdowns within LLM-driven conversational systems. While powerful models from OpenAI and Anthropic excel in many dialogue tasks, they can still produce incoherent or contradictory responses, commonly referred to as breakdowns, which undermine user trust. To tackle this, we propose an approach that combines specialized fine-tuning with advanced prompting strategies, including few-shot learning, chain-of-thought reasoning, and analogical prompting. In particular, we fine-tune a small 8B model and demonstrate its robust classification and calibration capabilities in English and Japanese dialogue. We also validate its generalization on the BETOLD dataset, achieving a 7% accuracy improvement over its base model. Furthermore, we introduce a real-time deployment architecture that selectively escalates suspicious responses to more resource-intensive frontier models only when breakdowns are detected, significantly cutting operational expenses and energy consumption. Experimental results show our method surpasses prior state-of-the-art specialized classifiers while also narrowing performance gaps between smaller open-source models and large proprietary ones. Our approach offers a scalable solution for robust conversational AI in high-impact domains by combining efficiency, interpretability, and reliability.
大型语言模型(LLM)正在迅速改变各个领域。然而,它们在处理对话中断方面的能力仍然需要深入研究。本文旨在解决在LLM驱动的对话系统中检测和缓解对话中断的挑战。虽然来自OpenAI和Anthropic的强大模型在许多对话任务中表现出色,但它们仍然可能产生不连贯或矛盾的回应,通常被称为中断,这会破坏用户信任。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种结合专业微调与先进提示策略的方法,包括小样本学习、思维链推理和类比提示。特别是,我们对一个小型8B模型进行了微调,并展示了其在英语和日语对话中的稳健分类和校准能力。我们在BETOLD数据集上验证了其泛化性,相比基础模型实现了7%的准确率提升。此外,我们引入了一种实时部署架构,该架构仅在检测到中断时选择将可疑的响应升级到更耗费资源和计算资源的尖端模型,从而显著降低了运营成本并减少了能源消耗。实验结果表明,我们的方法超越了现有的最先进的专用分类器,同时缩小了开源小型模型和大型专有模型之间的性能差距。通过结合效率、可解释性和可靠性,我们的方法为高影响力领域提供稳健的对话AI的可扩展解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在对话任务中展现出强大能力,但在处理对话崩溃方面仍存在挑战。本文提出一种结合专门微调与先进提示策略的方法,包括小样本学习、链式思维推理和类比提示,以检测和减轻LLM驱动对话系统中的对话崩溃问题。通过精细调整8B模型,并在英语和日语对话中进行演示,以及在实际部署架构中选择性升级可疑响应,仅在检测到崩溃时才使用更多资源密集型前沿模型,从而降低成本和能耗。实验结果表明,该方法优于先前的最新专用分类器,并缩小了开源小型模型与大型专有模型之间的性能差距。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在对话任务中具有巨大潜力,但处理对话崩溃仍需深入研究。
- 论文提出了一种结合专门微调与先进提示策略的方法,旨在检测和减轻LLM在对话中的崩溃问题。
- 通过精细调整模型,论文展示了在英语和日语对话中的稳健分类和校准能力。
- 论文介绍了一种实时部署架构,该架构能够选择性升级可疑响应,仅在必要时使用更多资源,从而提高效率并降低成本。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在检测对话崩溃方面优于之前的专用分类器。
- 该方法缩小了开源小型模型与大型专有模型之间的性能差距。
点此查看论文截图


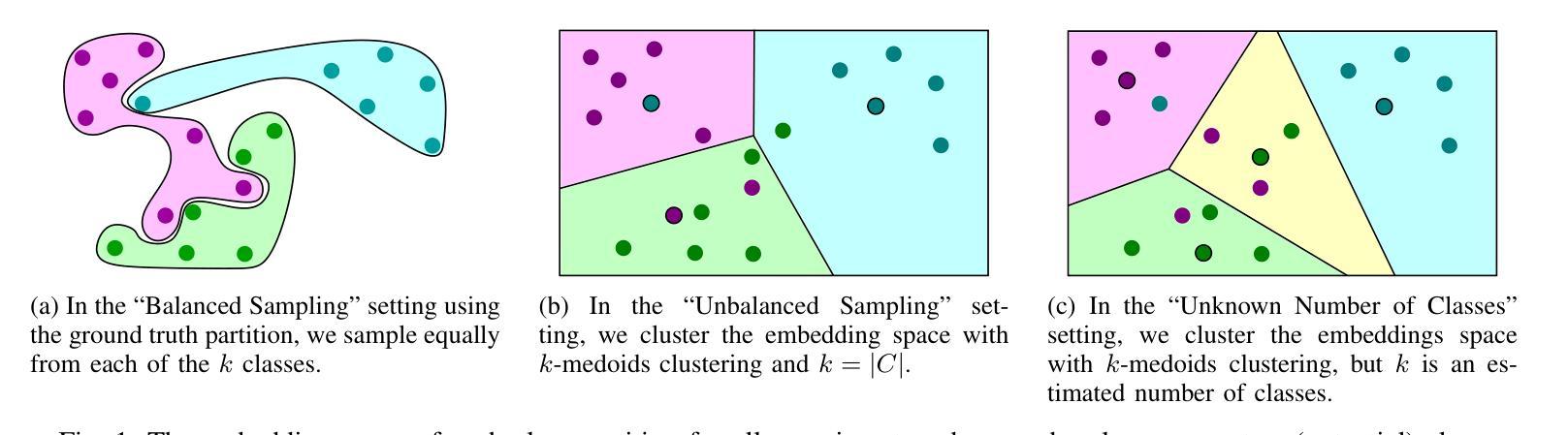
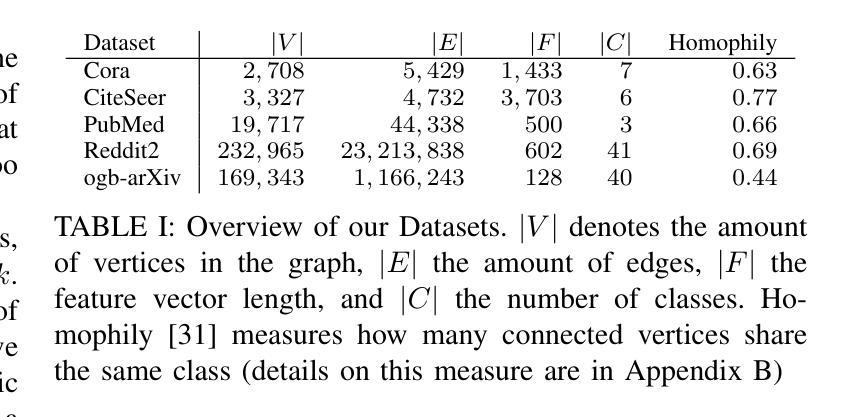
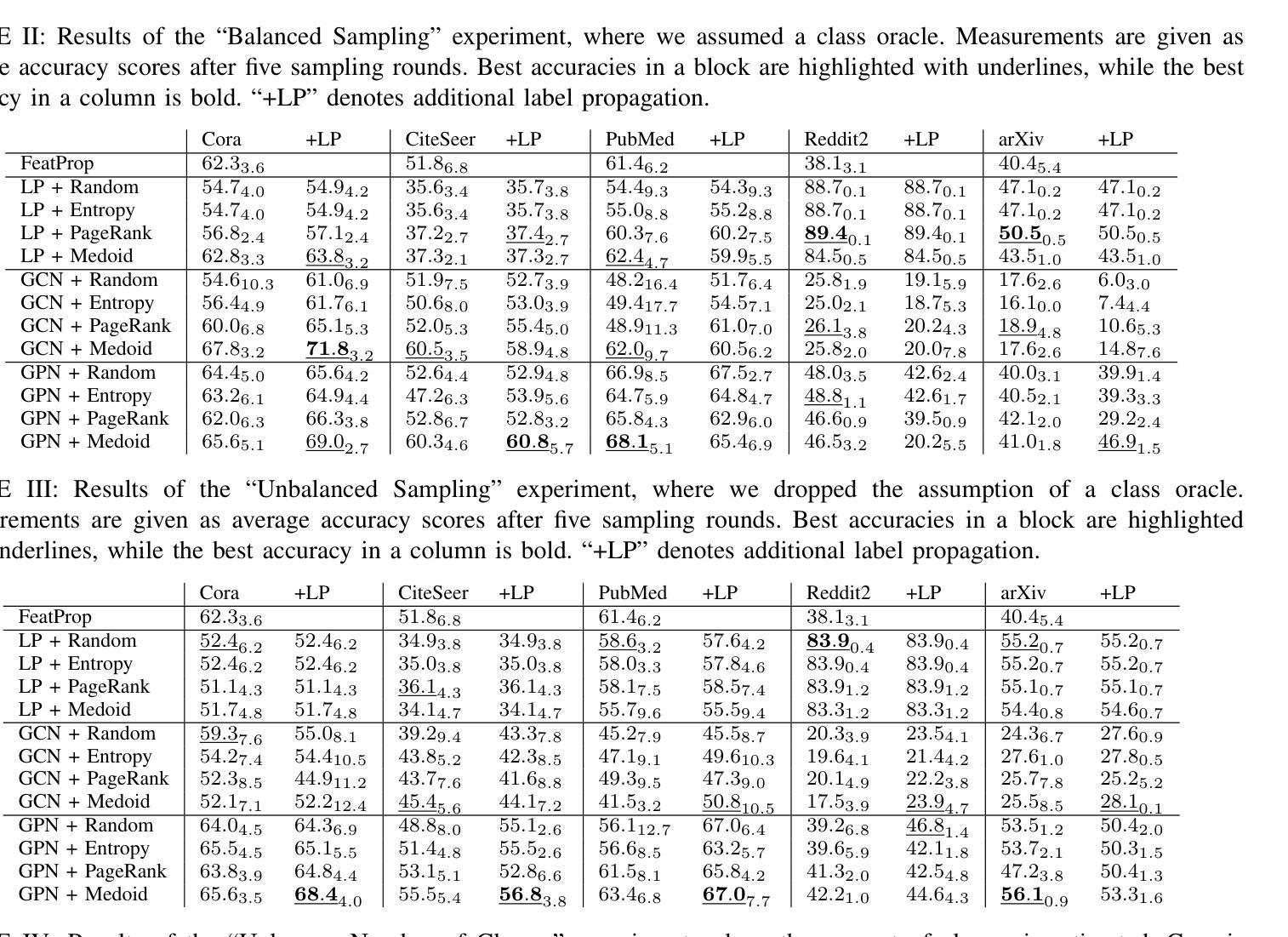
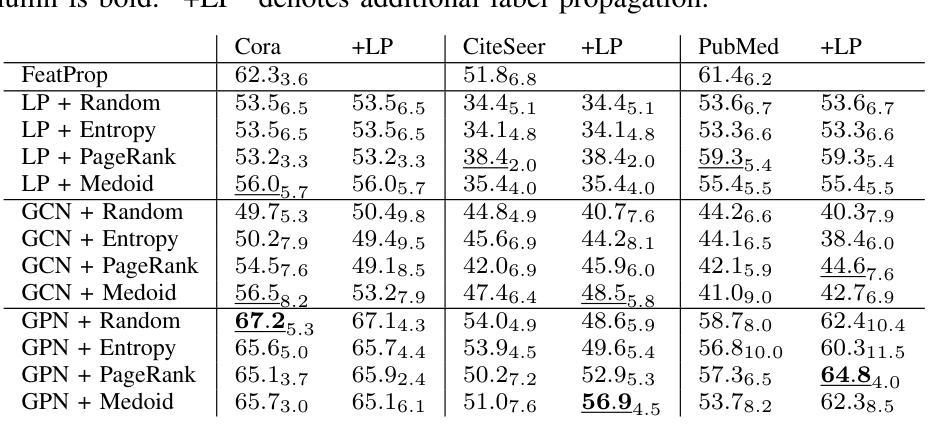
Active Few-Shot Learning for Vertex Classification Starting from an Unlabeled Dataset
Authors:Felix Burr, Marcel Hoffmann, Ansgar Scherp
Despite the ample availability of graph data, obtaining vertex labels is a tedious and expensive task. Therefore, it is desirable to learn from a few labeled vertices only. Existing few-shot learners assume a class oracle, which provides labeled vertices for a desired class. However, such an oracle is not available in a real-world setting, i.e., when drawing a vertex for labeling it is unknown to which class the vertex belongs. Few-shot learners are often combined with prototypical networks, while classical semi-supervised vertex classification uses discriminative models, e.g., Graph Convolutional Networks (GCN). In this paper, we train our models by iteratively prompting a human annotator with vertices to annotate. We perform three experiments where we continually relax our assumptions. First, we assume a class oracle, i.e., the human annotator is provided with an equal number of vertices to label for each class. We denote this as “Balanced Sampling’’. In the subsequent experiment, “Unbalanced Sampling,’’ we replace the class oracle with $k$-medoids clustering and draw vertices to label from the clusters. In the last experiment, the “Unknown Number of Classes,’’ we no longer assumed we knew the number and distribution of classes. Our results show that prototypical models outperform discriminative models in all experiments when fewer than $20$ samples per class are available. While dropping the assumption of the class oracle for the “Unbalanced Sampling’’ experiment reduces the performance of the GCN by $9%$, the prototypical network loses only $1%$ on average. For the “Unknown Number of Classes’’ experiment, the average performance for both models decreased further by $1%$. Source code: https://github.com/Ximsa/2023-felix-ma
尽管存在大量的图形数据,但获取顶点标签是一项既繁琐又昂贵的任务。因此,只需从少数标记的顶点中学习即可。现有的小样学习者假设存在一个类oracle(为所需类别提供标记顶点的工具),但在现实世界的场景中,当绘制顶点进行标记时,并不知道该顶点属于哪个类别。小样学习者通常与原型网络相结合,而经典的半监督顶点分类则使用判别模型,例如图卷积网络(GCN)。在本文中,我们通过不断提示人类注释者进行顶点标注来训练我们的模型。我们进行了三项实验,不断放宽我们的假设。首先,我们假设存在一个类oracle,即人类注释者被提供数量相等的每个类别的顶点进行标注。我们将其称为“平衡采样”。在随后的实验“不平衡采样”中,我们用k-medoids聚类替换类oracle,并从聚类中抽取顶点进行标注。在最后一个实验“未知类别数量”中,我们不再假设我们知道类别的数量和分布。我们的结果表明,在所有实验中,当每个类别的样本少于20个时,原型模型在性能上优于判别模型。在“不平衡采样”实验中放弃类oracle的假设使GCN的性能降低了9%,而原型网络的平均性能仅下降了1%。对于“未知类别数量”实验,两个模型的平均性能进一步下降了1%。源代码:https://github.com/Ximsa/2023-felix-ma
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at IJCNN 2025
Summary
本文探讨了从少量标记顶点学习的问题。现有方法依赖于类oracle来提供标记顶点,但在现实世界中这一假设不成立。本文通过迭代提示人类注释者进行标注来训练模型,并进行了三个实验来逐步放宽假设。实验结果表明,在样本数量较少的情况下,原型模型的表现优于判别模型。当不再假设类oracle时,GCN的性能下降了9%,而原型网络的平均性能仅下降了1%。
Key Takeaways
- 获取顶点标签是一个繁琐且昂贵的任务,因此从少量标记顶点学习是理想的。
- 现有方法依赖于类oracle提供标记顶点,这在现实世界中不可行。
- 本文通过迭代提示人类注释者进行标注来训练模型。
- 进行了三个实验来逐步放宽假设,包括平衡采样、不平衡采样和未知类别数量。
- 原型模型在样本数量较少时表现较好。
- 当不再假设类oracle时,GCN的性能大幅下降,而原型网络的性能相对更稳定。
点此查看论文截图

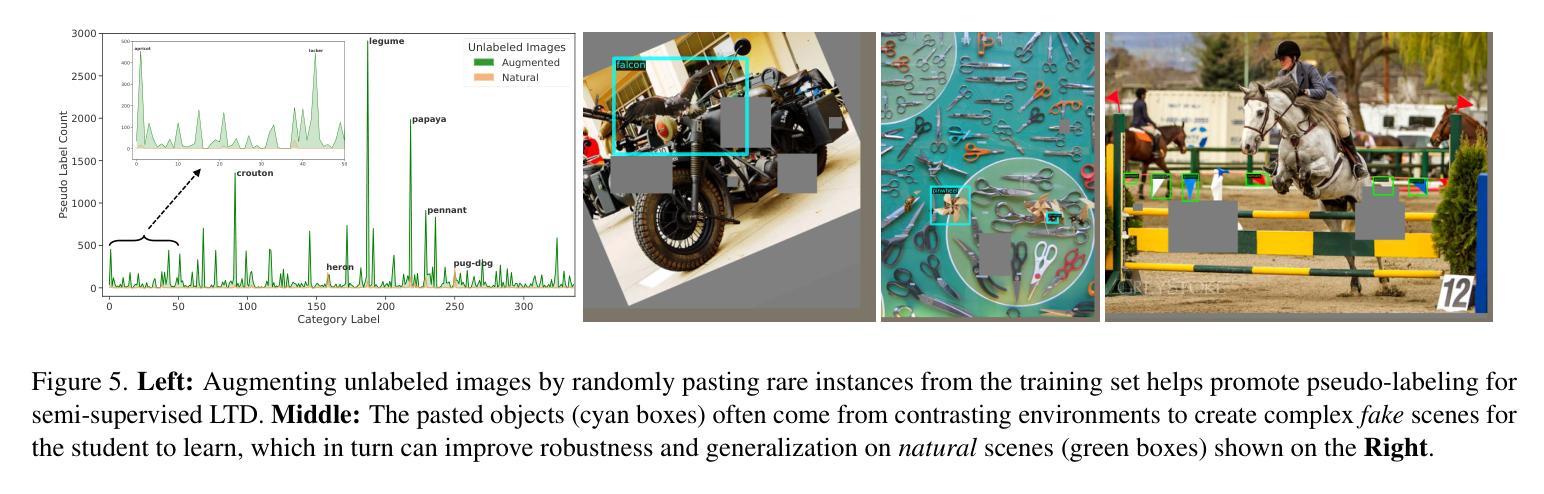
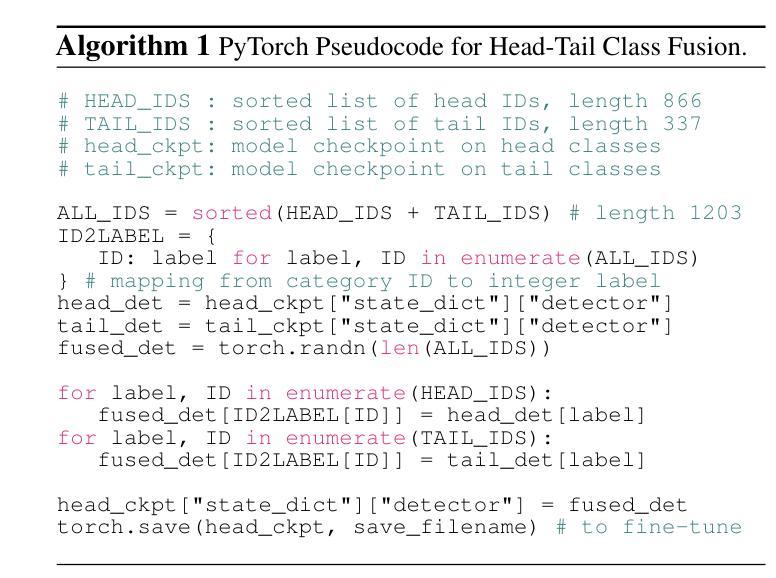
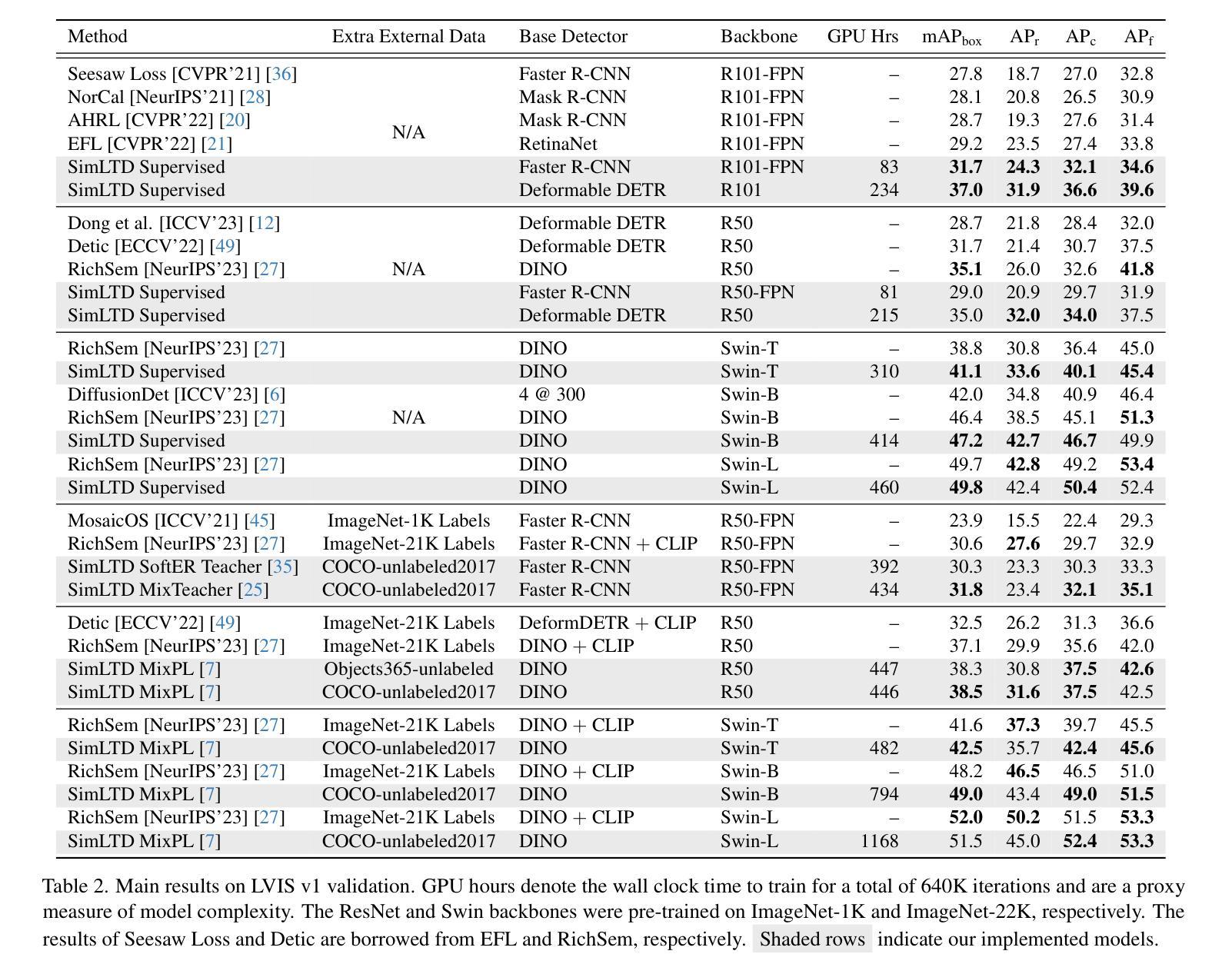
SimLTD: Simple Supervised and Semi-Supervised Long-Tailed Object Detection
Authors:Phi Vu Tran
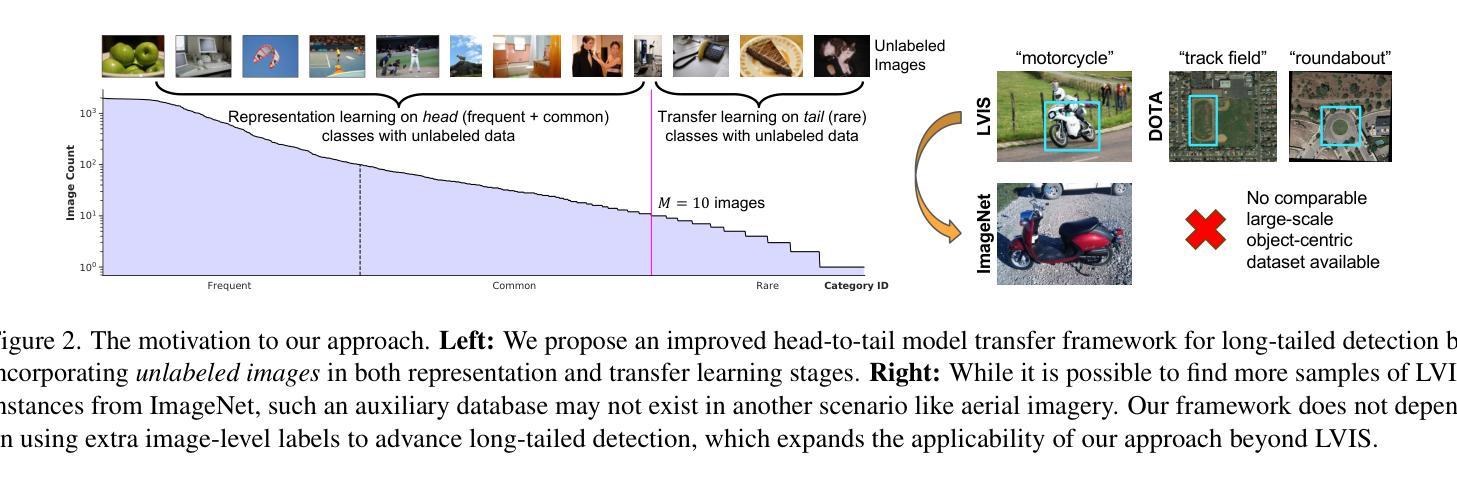
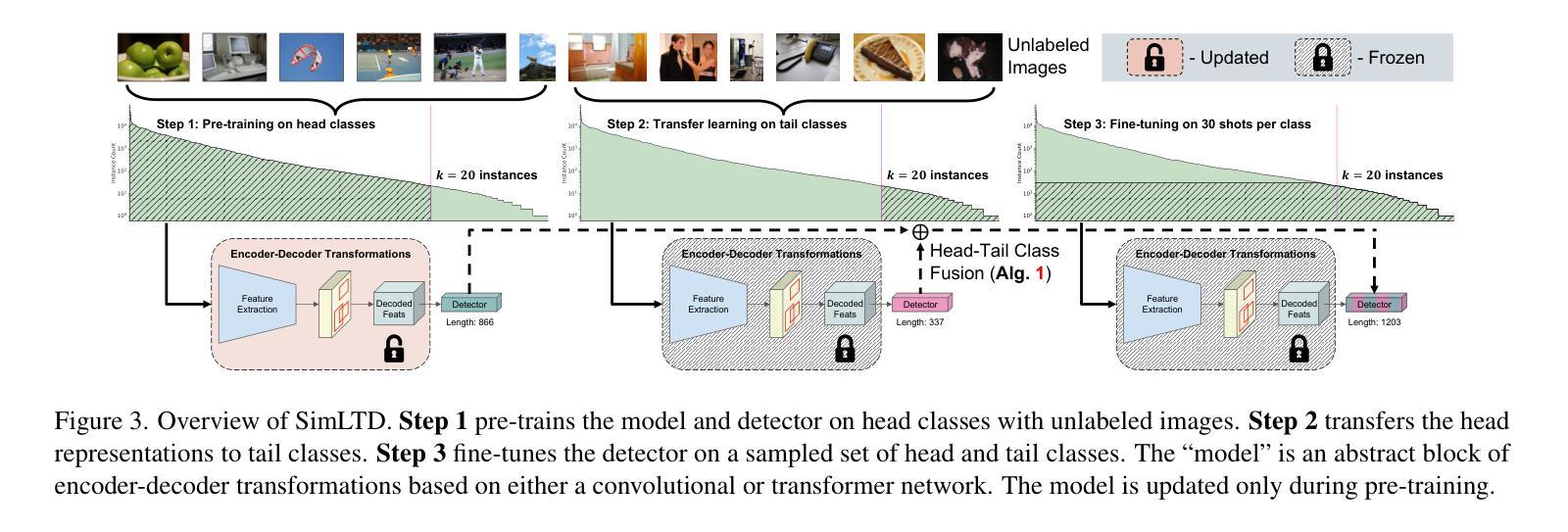
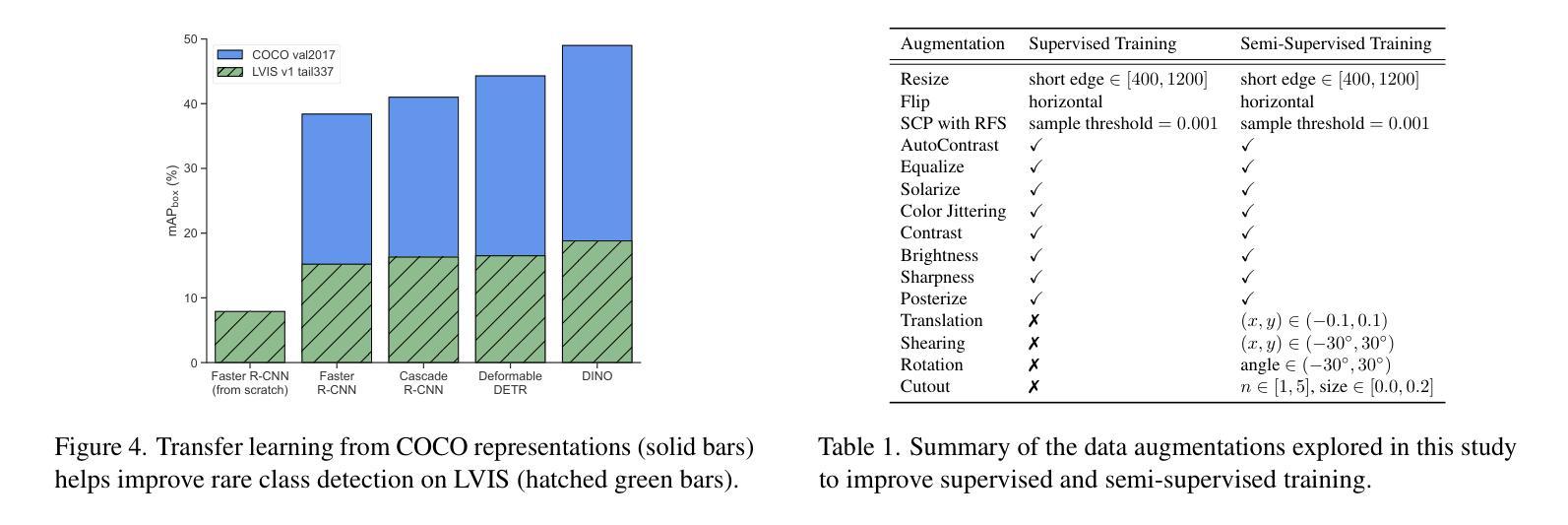
While modern visual recognition systems have made significant advancements, many continue to struggle with the open problem of learning from few exemplars. This paper focuses on the task of object detection in the setting where object classes follow a natural long-tailed distribution. Existing methods for long-tailed detection resort to external ImageNet labels to augment the low-shot training instances. However, such dependency on a large labeled database has limited utility in practical scenarios. We propose a versatile and scalable approach to leverage optional unlabeled images, which are easy to collect without the burden of human annotations. Our SimLTD framework is straightforward and intuitive, and consists of three simple steps: (1) pre-training on abundant head classes; (2) transfer learning on scarce tail classes; and (3) fine-tuning on a sampled set of both head and tail classes. Our approach can be viewed as an improved head-to-tail model transfer paradigm without the added complexities of meta-learning or knowledge distillation, as was required in past research. By harnessing supplementary unlabeled images, without extra image labels, SimLTD establishes new record results on the challenging LVIS v1 benchmark across both supervised and semi-supervised settings.
虽然现代视觉识别系统已经取得了重大进展,但许多系统仍然面临着从少量样本中学习的开放性问题。本文关注的对象检测任务是对象类别遵循自然的长尾分布的设置。现有的长尾检测方法依赖于外部ImageNet标签来增加低射击训练实例。然而,对大量有标签数据库的依赖在实际场景中实用性有限。我们提出了一种通用且可扩展的方法,利用可选的无标签图像,这些图像无需人工注释即可轻松收集。我们的SimLTD框架简单直观,分为三个步骤:(1)在丰富的头部类别上进行预训练;(2)在稀缺的尾部类别上进行迁移学习;(3)在头部和尾部类别的采样集上进行微调。我们的方法可以被视为一种改进的头到尾模型转移范式,无需引入元学习或知识蒸馏等额外复杂性,这是过去研究的要求。通过利用额外的无标签图像,无需额外的图像标签,SimLTD在具有挑战性的LVIS v1基准测试中建立了新的记录结果,涵盖了有监督和半监督设置。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025. The reference code is available at https://github.com/lexisnexis-risk-open-source/simltd
Summary
本文解决现代视觉识别系统在少样本学习上的难题,特别是在目标检测任务中面对长尾分布数据的问题。不同于依赖ImageNet标签扩充低样本训练实例的方法,本文提出利用易收集的无标签图像,通过预训练、迁移学习和微调三个步骤,实现改进的头到尾模型转移范式,无需复杂的元学习或知识蒸馏,提高了在长尾分布数据上的目标检测性能。
Key Takeaways
- 现代视觉识别系统在少样本学习上仍面临挑战,特别是在目标检测任务中。
- 现有方法依赖ImageNet标签扩充低样本训练实例,但在实际应用中效用有限。
- 本文提出利用无标签图像,通过预训练、迁移学习和微调三个步骤解决该问题。
- 提出的SimLTD框架改进了头到尾模型转移范式,无需复杂的元学习或知识蒸馏。
- SimLTD框架在具有挑战性的LVIS v1基准测试中取得了新的记录结果。
- 该方法利用附加的无标签图像,无需额外图像标签。
点此查看论文截图

Benchmarking large language models for biomedical natural language processing applications and recommendations
Authors:Qingyu Chen, Yan Hu, Xueqing Peng, Qianqian Xie, Qiao Jin, Aidan Gilson, Maxwell B. Singer, Xuguang Ai, Po-Ting Lai, Zhizheng Wang, Vipina Kuttichi Keloth, Kalpana Raja, Jiming Huang, Huan He, Fongci Lin, Jingcheng Du, Rui Zhang, W. Jim Zheng, Ron A. Adelman, Zhiyong Lu, Hua Xu
The rapid growth of biomedical literature poses challenges for manual knowledge curation and synthesis. Biomedical Natural Language Processing (BioNLP) automates the process. While Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown promise in general domains, their effectiveness in BioNLP tasks remains unclear due to limited benchmarks and practical guidelines. We perform a systematic evaluation of four LLMs, GPT and LLaMA representatives on 12 BioNLP benchmarks across six applications. We compare their zero-shot, few-shot, and fine-tuning performance with traditional fine-tuning of BERT or BART models. We examine inconsistencies, missing information, hallucinations, and perform cost analysis. Here we show that traditional fine-tuning outperforms zero or few shot LLMs in most tasks. However, closed-source LLMs like GPT-4 excel in reasoning-related tasks such as medical question answering. Open source LLMs still require fine-tuning to close performance gaps. We find issues like missing information and hallucinations in LLM outputs. These results offer practical insights for applying LLMs in BioNLP.
生物医学文献的快速增长为手动知识整合和综述带来了挑战。生物医学自然语言处理(BioNLP)使这些过程自动化。虽然大型语言模型(LLM)在一般领域显示出潜力,但由于缺乏基准测试和实用指南,它们在BioNLP任务中的有效性仍然不明确。我们对四种LLM(GPT和LLaMA的代表)进行了系统评估,涉及六个应用的12个BioNLP基准测试。我们比较了它们在零样本、少样本和微调情况下的性能,以及与BERT或BART模型的传统微调性能。我们检查了不一致性、缺失信息、幻觉并进行了成本分析。在这里,我们表明传统微调在大多数任务中优于零样本或少样本LLM。然而,像GPT-4这样的闭源LLM在推理相关任务(如医学问答)中表现出色。开源LLM仍然需要微调来缩小性能差距。我们发现LLM输出中存在缺失信息和幻觉等问题。这些结果提供了将LLM应用于BioNLP的实际见解。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
生物医学文献的快速增长给手动知识整合与综合带来了挑战,生物医学自然语言处理(BioNLP)自动化了这一流程。大型语言模型(LLMs)在一般领域表现出潜力,但在BioNLP任务中的有效性尚不清楚,受限于基准测试和实用指南。本文对四种LLMs(GPT和LLaMA的代表)进行了系统评估,涉及六个应用的12项BioNLP基准测试。我们比较了它们在零样本、少样本和微调模式下的性能与传统的BERT或BART模型的微调性能。我们研究了输出中的不一致性、缺失信息、幻觉,并进行了成本分析。研究表明,传统微调在大多数任务中优于零样本或少样本LLMs。但如GPT-4这样的封闭源LLMs在推理相关任务如医疗问答上表现优异。开源LLMs仍需要微调以缩小性能差距。我们发现LLM输出中存在缺失信息和幻觉等问题。
Key Takeaways
- 生物医学文献的快速增长给手动知识管理带来挑战,BioNLP自动化有助于解决这一问题。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在BioNLP任务中的有效性尚不清楚。
- 系统评估了四种LLMs在多个BioNLP基准测试中的表现。
- 传统微调在大多数任务中表现优于零样本或少样本LLMs。
- 封闭源LLMs如GPT-4在推理相关任务上表现良好。
- 开源LLMs仍需要微调以提高性能。
- LLM输出中存在缺失信息和幻觉等问题。
点此查看论文截图