⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-30 更新
ClearVision: Leveraging CycleGAN and SigLIP-2 for Robust All-Weather Classification in Traffic Camera Imagery
Authors:Anush Lakshman Sivaraman, Kojo Adu-Gyamfi, Ibne Farabi Shihab, Anuj Sharma
Accurate weather classification from low-quality traffic camera imagery remains a challenging task, particularly under adverse nighttime conditions. In this study, we propose a scalable framework that combines generative domain adaptation with efficient contrastive learning to enhance classification performance. Using CycleGAN-based domain translation, we improve the quality of nighttime images, enabling better feature extraction by downstream models. While the baseline EVA-02 model employing CLIP-based contrastive loss achieves an overall accuracy of 96.55%, it exhibits a significant performance gap between daytime (97.21%) and nighttime conditions (63.40%). Replacing CLIP with the lightweight SigLIP-2 (Sigmoid contrastive loss) achieves a competitive overall accuracy of 94.00%, with substantial improvements in nighttime performance (85.90% accuracy). The combination of Vision-SigLIP-2, Text-SigLIP-2, CycleGAN, and contrastive training achieves the best nighttime accuracy (85.90%) among all models tested, while EVA-02 with CycleGAN maintains the highest overall accuracy (97.01%) and per-class accuracies. These findings demonstrate the potential of combining domain adaptation and efficient contrastive learning to build practical, resource-efficient weather classification systems for intelligent transportation infrastructure.
从低质量的交通摄像头图像中准确进行天气分类仍然是一个具有挑战性的任务,特别是在恶劣的夜间条件下。在这项研究中,我们提出了一个可扩展的框架,该框架结合了生成域适应和高效的对比学习,以提高分类性能。我们使用基于CycleGAN的域翻译技术,提高夜间图像的质量,使下游模型能够更好地进行特征提取。虽然使用基于CLIP的对比损失的EVA-02基线模型总体准确率为96.55%,但在日间(97.21%)和夜间条件(63.40%)之间存在显著的性能差距。用轻量级的SigLIP-2(Sigmoid对比损失)替换CLIP后,总体准确率达到了具有竞争力的94.00%,夜间性能也有了显著改善(准确率为85.90%)。结合Vision-SigLIP-2、Text-SigLIP-2、CycleGAN和对比训练的方法在所有测试模型中实现了最佳的夜间准确率(85.90%),而EVA-02与CycleGAN的组合则保持了最高的总体准确率(97.01%)和每类准确率。这些发现表明,结合域适应和高效的对比学习,有潜力为智能交通基础设施构建实用的天气分类系统,同时实现资源的高效利用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:该研究提出一种可伸缩框架,结合生成性领域自适应和高效对比学习,以提高恶劣天气条件下从低质量交通摄像头图像进行准确分类的性能。通过CycleGAN领域的图像翻译技术提升夜间图像质量,使得下游模型能够更好地提取特征。研究发现,融合多种技术和模型后,能在夜间条件下实现最佳分类精度,同时保持总体和各类别的准确率。
Key Takeaways:
- 结合生成性领域自适应和高效对比学习的方法能够提高低质量交通摄像头图像的分类性能。
- CycleGAN能够有效提升夜间图像质量,增强特征提取能力。
- EVA-02模型采用CLIP对比损失在日间条件下表现最佳,但在夜间条件下性能显著下降。
- SigLIP-2模型在夜间条件下的性能有显著改善,但总体准确率略低于EVA-02。
- 结合Vision-SigLIP-2、Text-SigLIP-2、CycleGAN和对比训练的模型在夜间条件下实现最佳分类精度。
- EVA-02与CycleGAN结合保持了最高的总体准确率和各类别的准确率。
点此查看论文截图

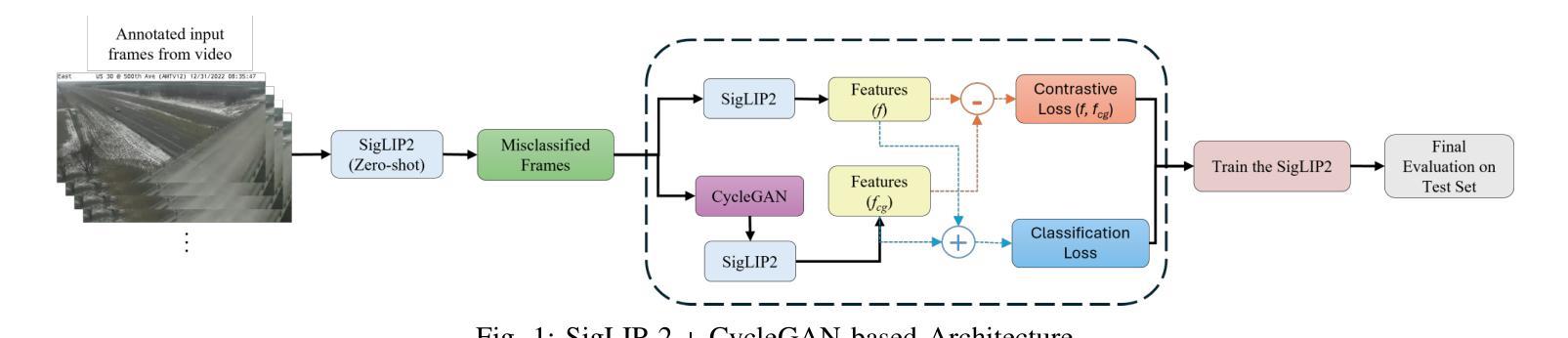
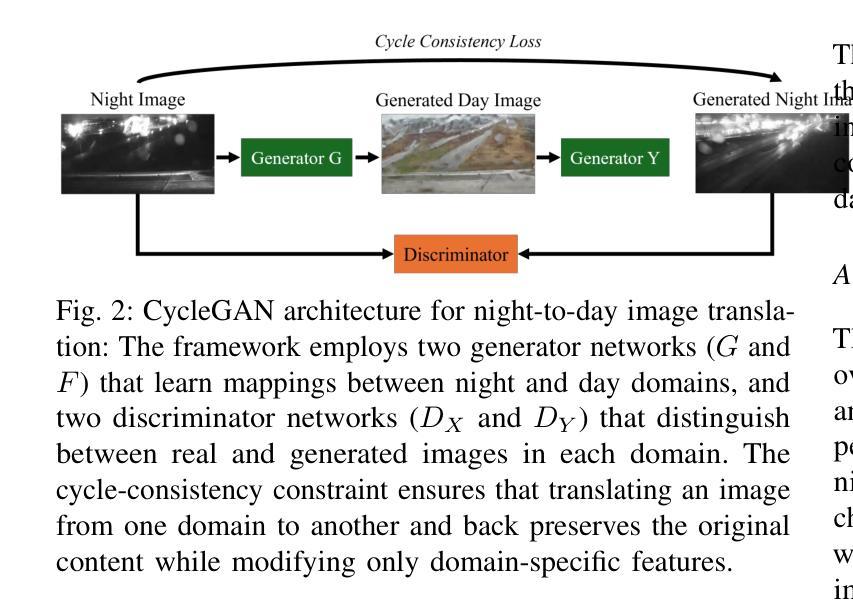
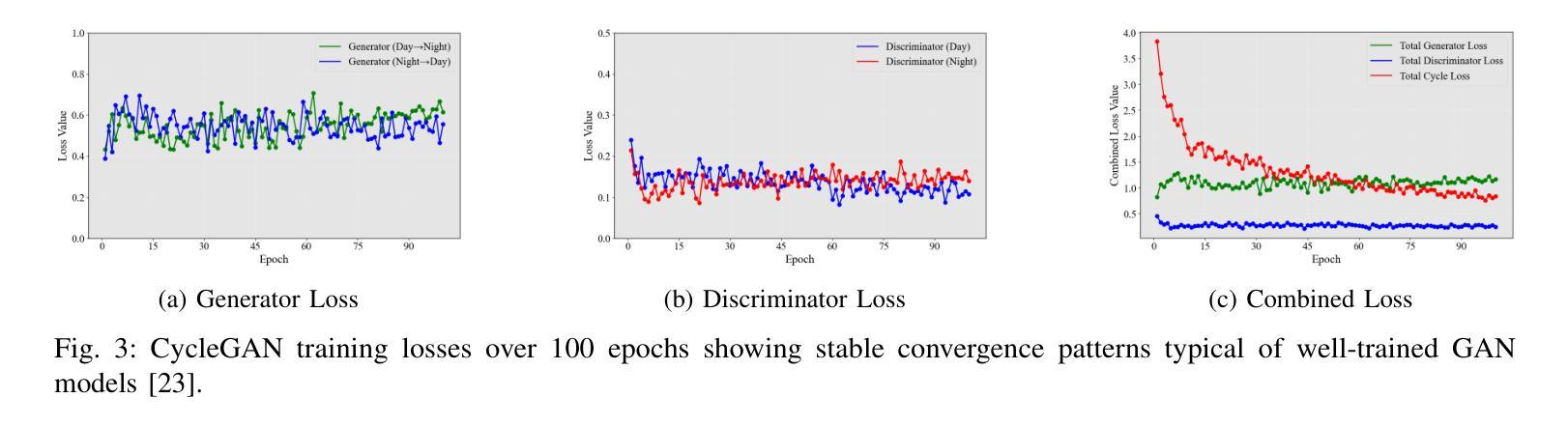
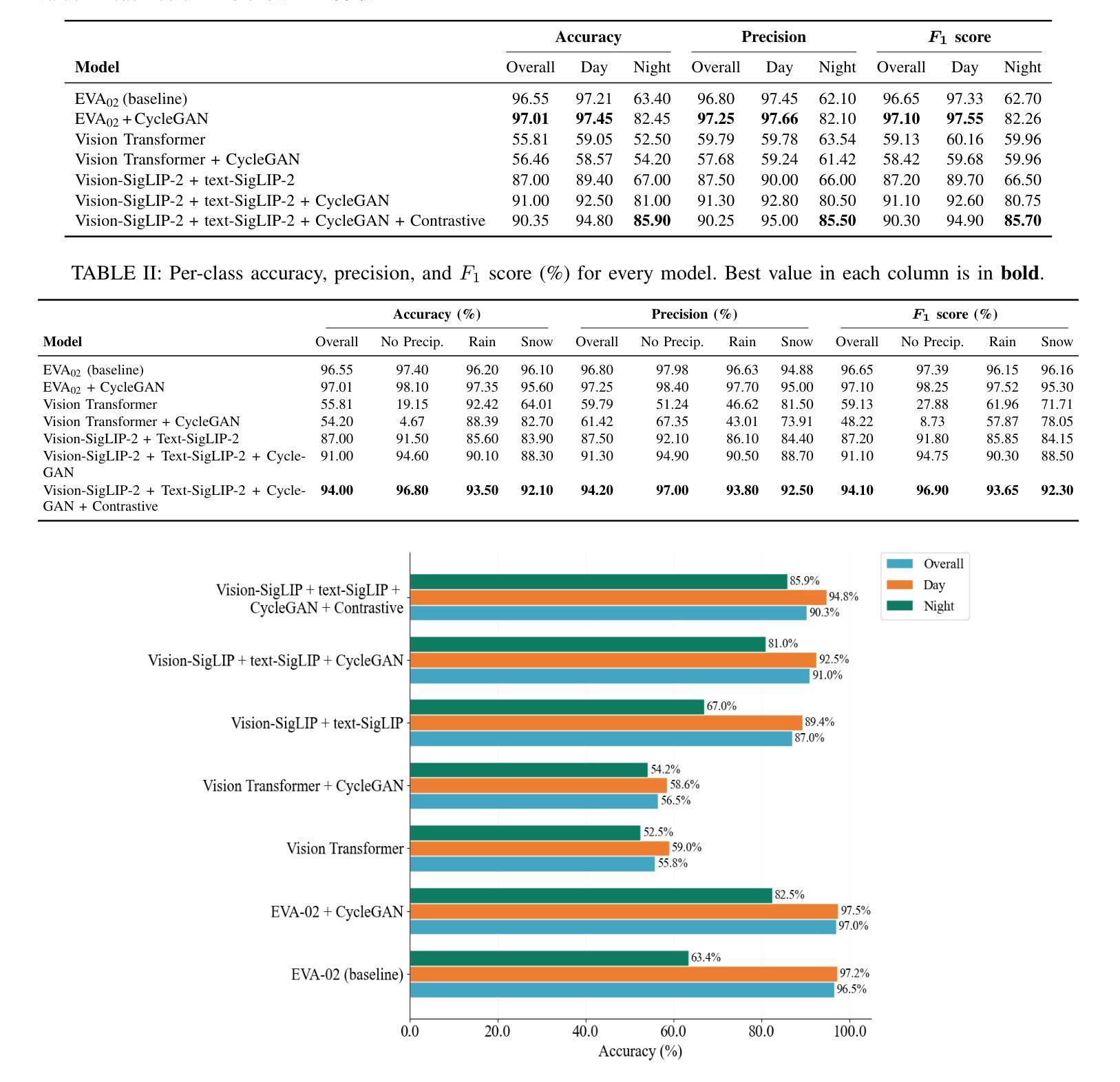
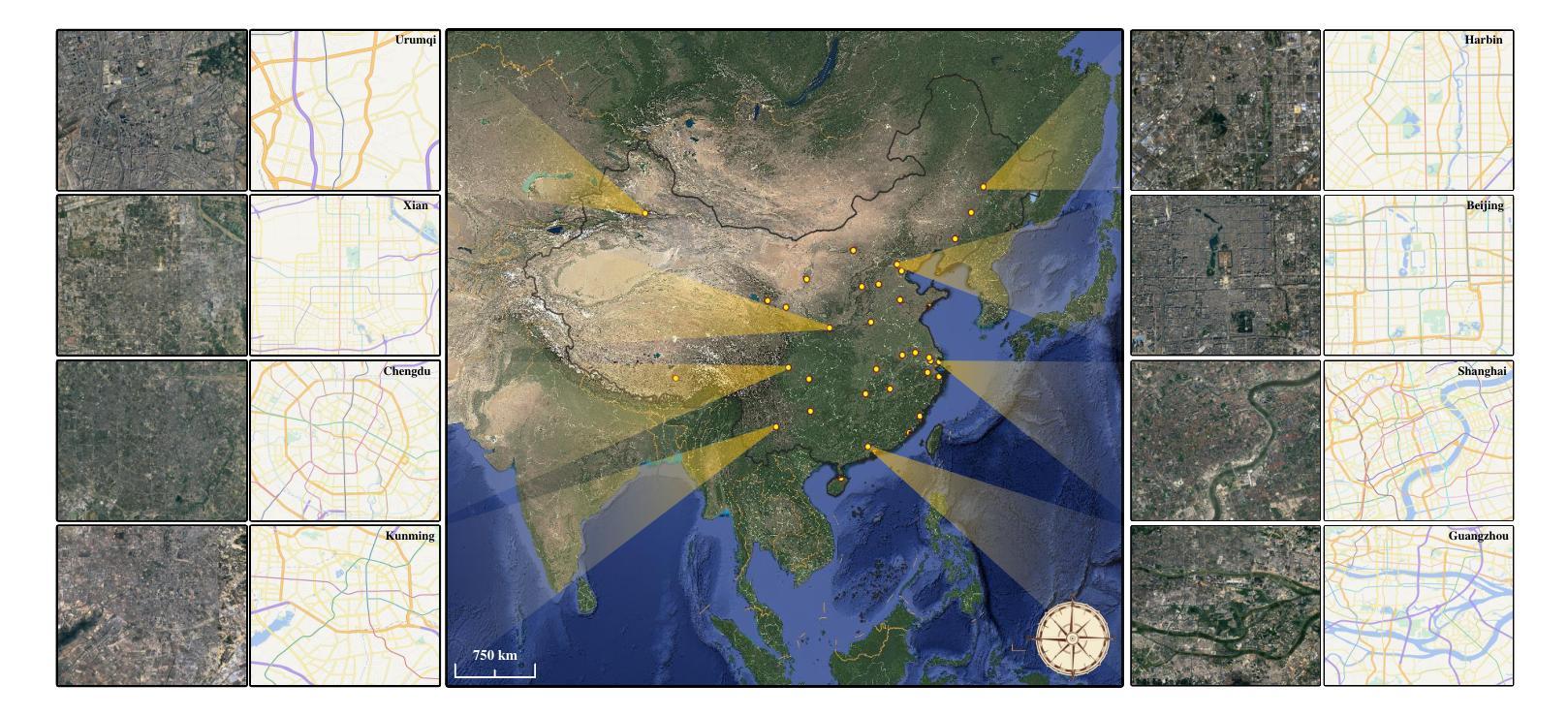
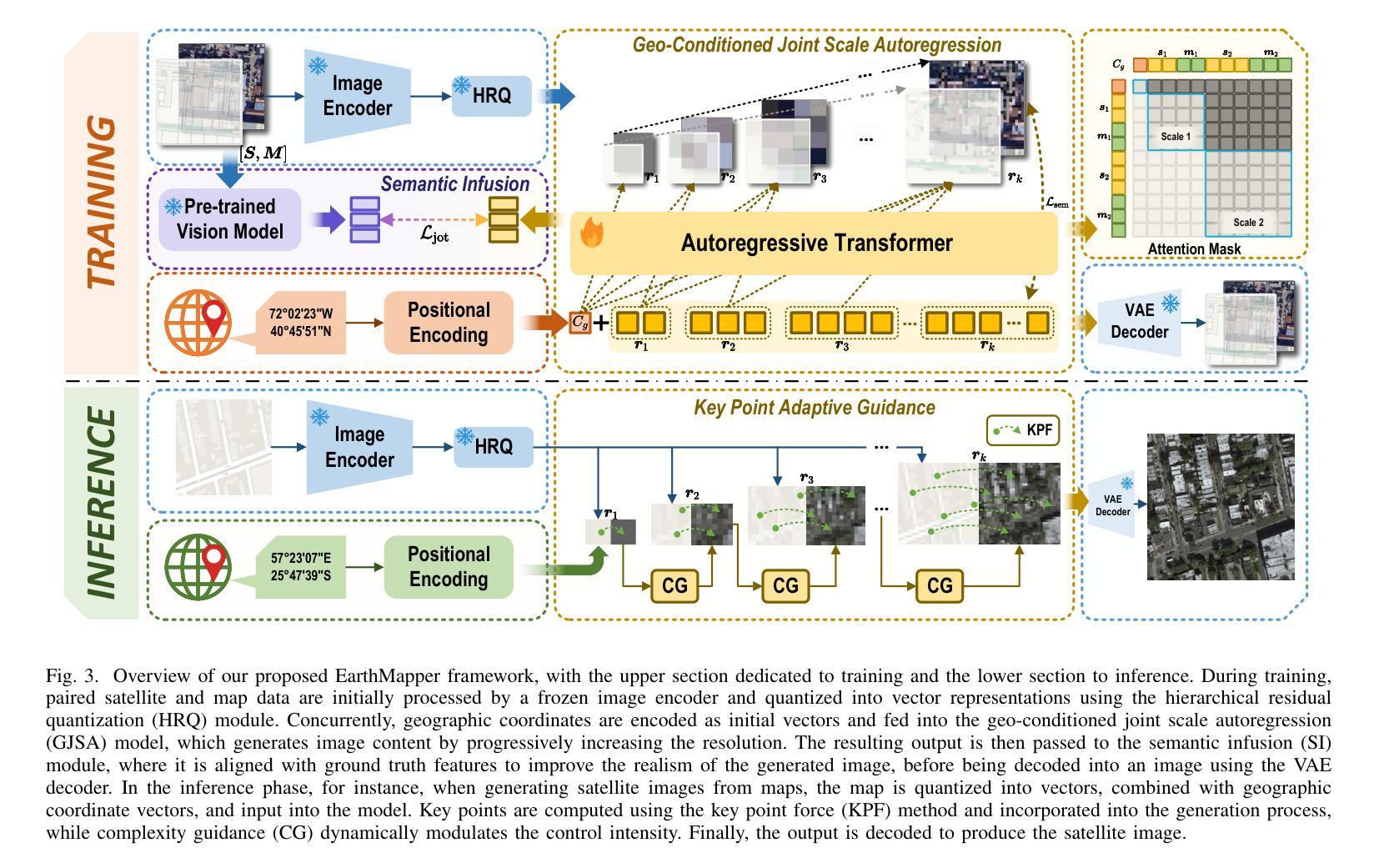
EarthMapper: Visual Autoregressive Models for Controllable Bidirectional Satellite-Map Translation
Authors:Zhe Dong, Yuzhe Sun, Tianzhu Liu, Wangmeng Zuo, Yanfeng Gu
Satellite imagery and maps, as two fundamental data modalities in remote sensing, offer direct observations of the Earth’s surface and human-interpretable geographic abstractions, respectively. The task of bidirectional translation between satellite images and maps (BSMT) holds significant potential for applications in urban planning and disaster response. However, this task presents two major challenges: first, the absence of precise pixel-wise alignment between the two modalities substantially complicates the translation process; second, it requires achieving both high-level abstraction of geographic features and high-quality visual synthesis, which further elevates the technical complexity. To address these limitations, we introduce EarthMapper, a novel autoregressive framework for controllable bidirectional satellite-map translation. EarthMapper employs geographic coordinate embeddings to anchor generation, ensuring region-specific adaptability, and leverages multi-scale feature alignment within a geo-conditioned joint scale autoregression (GJSA) process to unify bidirectional translation in a single training cycle. A semantic infusion (SI) mechanism is introduced to enhance feature-level consistency, while a key point adaptive guidance (KPAG) mechanism is proposed to dynamically balance diversity and precision during inference. We further contribute CNSatMap, a large-scale dataset comprising 302,132 precisely aligned satellite-map pairs across 38 Chinese cities, enabling robust benchmarking. Extensive experiments on CNSatMap and the New York dataset demonstrate EarthMapper’s superior performance, achieving significant improvements in visual realism, semantic consistency, and structural fidelity over state-of-the-art methods. Additionally, EarthMapper excels in zero-shot tasks like in-painting, out-painting and coordinate-conditional generation, underscoring its versatility.
卫星图像和地图作为遥感中的两种基本数据模式,分别提供了对地球表面的直接观察和人类可解释的地理抽象。卫星图像与地图之间的双向翻译任务(BSMT)在城市规划和灾害应对等领域具有广泛应用潜力。然而,该任务存在两大挑战:首先,两种模式之间缺乏精确的像素级对齐,使得翻译过程变得复杂;其次,它需要在地理特征的高级抽象和高质量视觉合成方面达到平衡,进一步增加了技术复杂性。为了解决这些局限性,我们引入了EarthMapper,这是一个用于可控双向卫星地图翻译的新型自回归框架。EarthMapper通过地理坐标嵌入来锚定生成,确保区域特定的适应性,并在地理条件联合尺度自回归(GJSA)过程中利用多尺度特征对齐,在一个单一的训练周期中统一双向翻译。引入语义融合(SI)机制以增强特征级别的一致性,同时提出关键点自适应引导(KPAG)机制,以在推理过程中动态平衡多样性和精度。我们还贡献了CNSatMap数据集,该数据集包含38个中国城市的302,132个精确对齐的卫星地图对,可实现稳健的基准测试。在CNSatMap和纽约数据集上的广泛实验表明,EarthMapper在视觉真实性、语义一致性和结构保真度方面均优于最新方法。此外,EarthMapper还擅长于诸如绘画、外推和坐标条件生成等零样本任务,突显了其通用性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
卫星图像与地图作为遥感中的两种基本数据模态,分别提供了对地球表面的直接观察和人类可解释的地理抽象。卫星图像与地图之间的双向翻译任务(BSMT)在城市规划和灾害响应等领域具有广泛的应用前景。然而,该任务面临两大挑战:一是两种模态之间缺乏精确的像素级对齐,使得翻译过程复杂化;二是需要实现地理特征的高级抽象和高质量的视觉合成,进一步增加了技术复杂性。为了解决这些限制,我们引入了EarthMapper,这是一个用于可控双向卫星-地图翻译的新型自回归框架。EarthMapper通过地理坐标嵌入来锚定生成,确保区域特异性适应性,并利用地理条件联合尺度自回归过程中的多尺度特征对齐,在一个训练周期中统一了双向翻译。引入语义融合机制来提高特征级别的一致性,并提出关键点自适应引导机制,以在推理过程中动态平衡多样性和精度。我们还贡献了CNSatMap数据集,该数据集包含38个中国城市的302,132个精确对齐的卫星地图对,以实现稳健的基准测试。在CNSatMap和纽约数据集上的实验表明,EarthMapper在视觉真实性、语义一致性和结构保真度方面均优于现有方法。此外,EarthMapper在零样本任务(如填充、扩展和坐标条件生成)中的出色表现也证明了其通用性。
关键见解
- 卫星图像和地图是遥感中的两种基本数据模态,分别提供地球表面的直接观察和地理抽象。
- 卫星图像与地图之间的双向翻译任务(BSMT)在城市规划和灾害响应中具有广泛应用前景。
- BSMT面临的主要挑战是缺乏像素级对齐和需要高级地理特征抽象与高质量视觉合成。
- EarthMapper是一个新型自回归框架,用于可控的双向卫星-地图翻译,通过地理坐标嵌入和多重机制解决上述挑战。
- EarthMapper在视觉真实性、语义一致性和结构保真度方面优于现有方法。
- CNSatMap数据集的贡献为稳健的基准测试提供了38个中国城市的精确对齐的卫星地图对。
- EarthMapper在零样本任务中的出色表现证明了其通用性。
点此查看论文截图

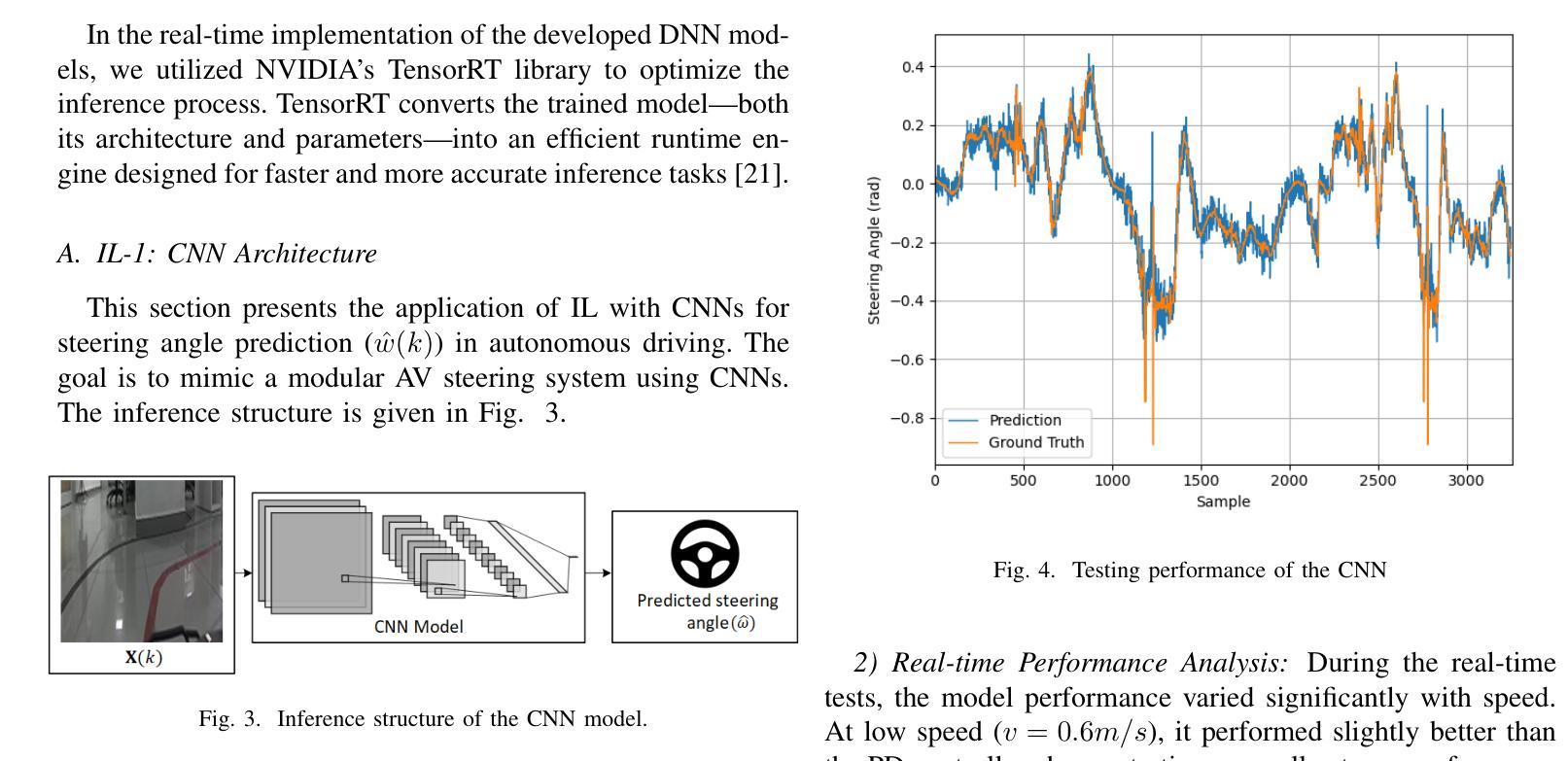
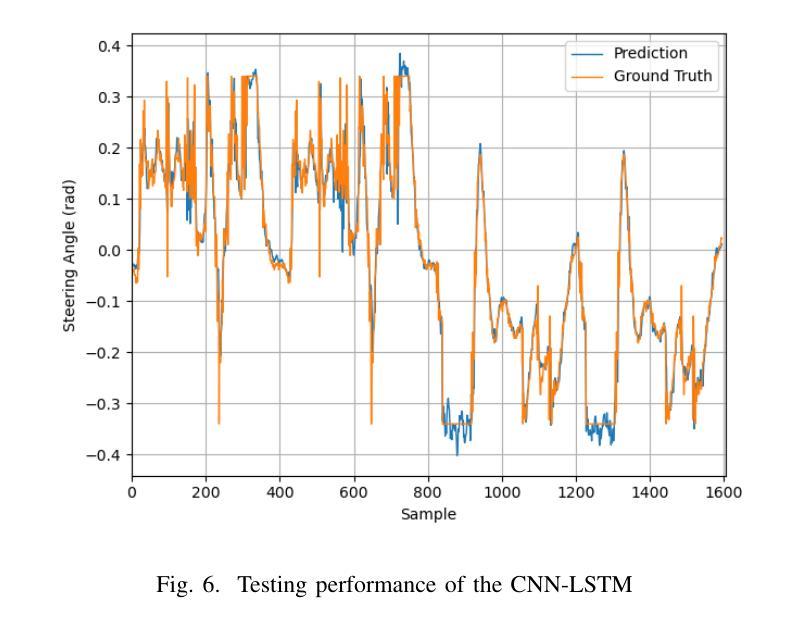
Imitation Learning for Autonomous Driving: Insights from Real-World Testing
Authors:Hidayet Ersin Dursun, Yusuf Güven, Tufan Kumbasar
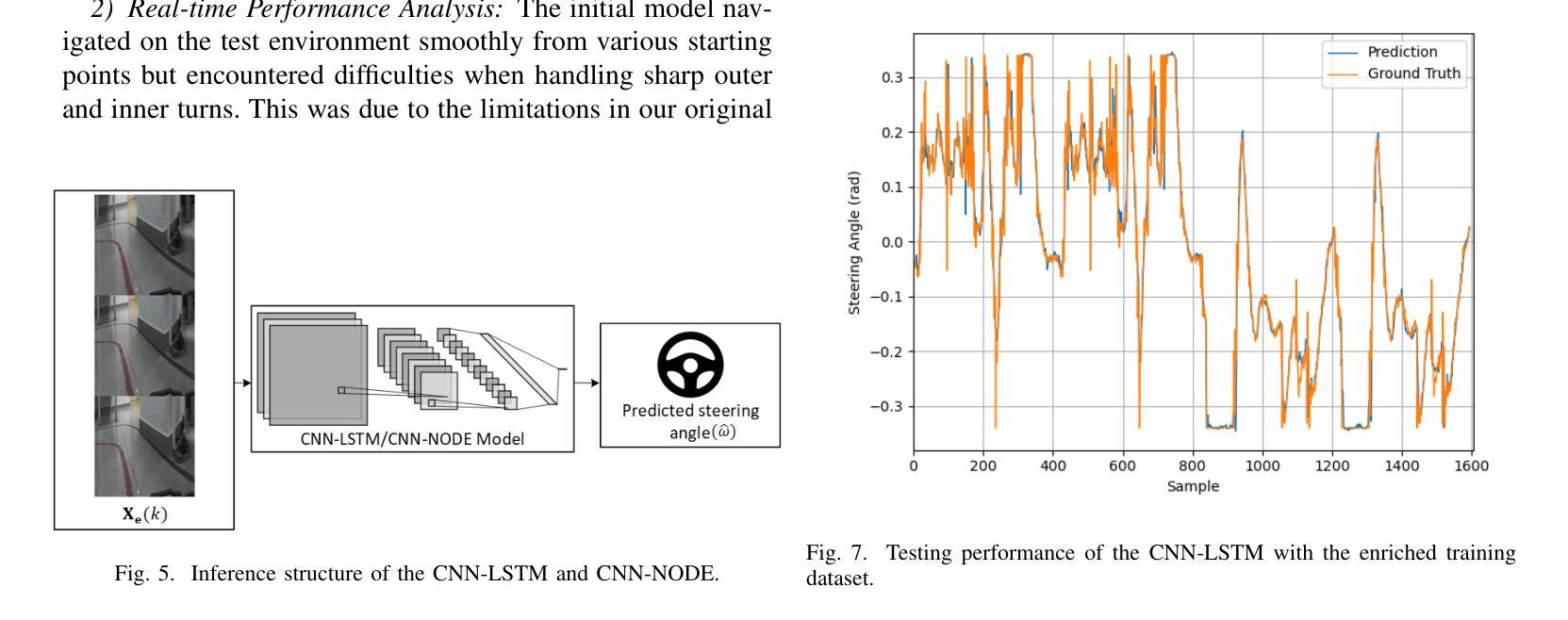
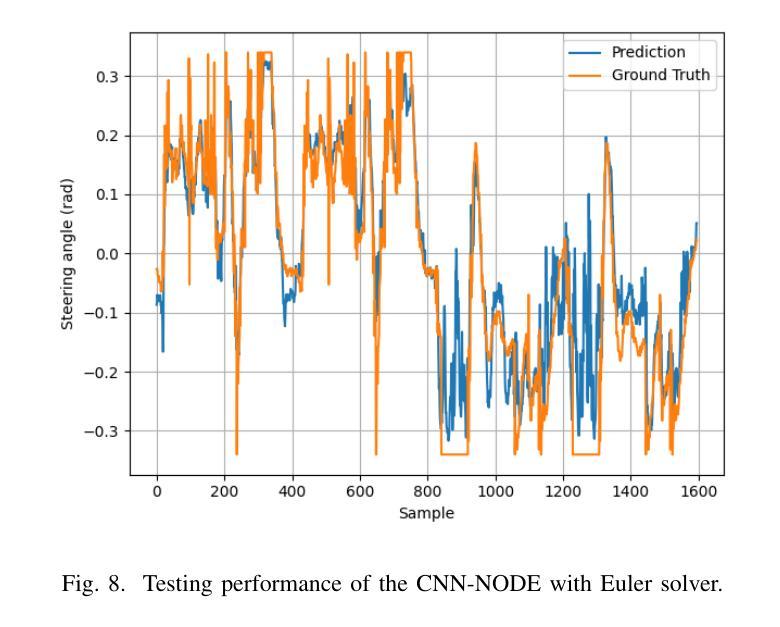
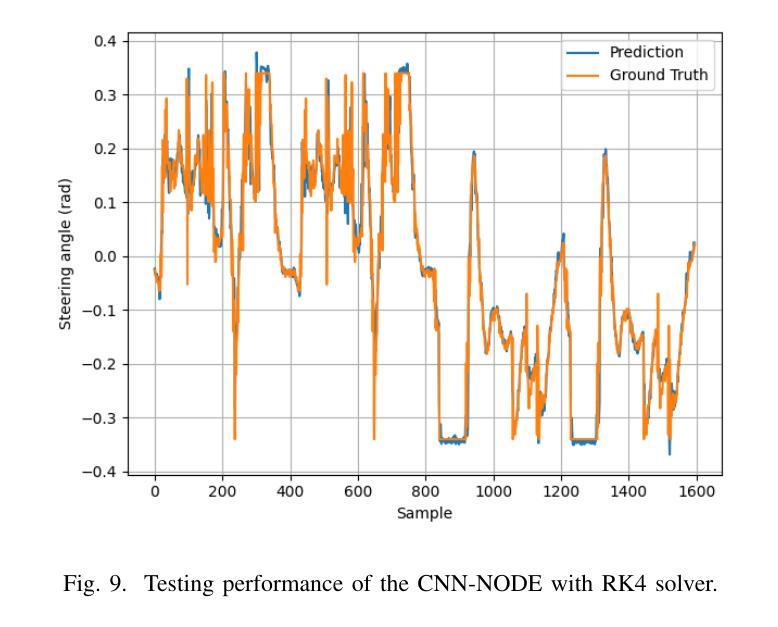
This work focuses on the design of a deep learning-based autonomous driving system deployed and tested on the real-world MIT Racecar to assess its effectiveness in driving scenarios. The Deep Neural Network (DNN) translates raw image inputs into real-time steering commands in an end-to-end learning fashion, following the imitation learning framework. The key design challenge is to ensure that DNN predictions are accurate and fast enough, at a high sampling frequency, and result in smooth vehicle operation under different operating conditions. In this study, we design and compare various DNNs, to identify the most effective approach for real-time autonomous driving. In designing the DNNs, we adopted an incremental design approach that involved enhancing the model capacity and dataset to address the challenges of real-world driving scenarios. We designed a PD system, CNN, CNN-LSTM, and CNN-NODE, and evaluated their performance on the real-world MIT Racecar. While the PD system handled basic lane following, it struggled with sharp turns and lighting variations. The CNN improved steering but lacked temporal awareness, which the CNN-LSTM addressed as it resulted in smooth driving performance. The CNN-NODE performed similarly to the CNN-LSTM in handling driving dynamics, yet with slightly better driving performance. The findings of this research highlight the importance of iterative design processes in developing robust DNNs for autonomous driving applications. The experimental video is available at https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FNNYgU--iaY.
本文重点关注基于深度学习的自动驾驶系统的设计,该系统已部署在真实世界的MIT赛车上进行测试,以评估其在驾驶场景中的有效性。深度神经网络(DNN)以端到端的学习方式将原始图像输入实时转换为转向命令,遵循模仿学习框架。主要设计挑战是确保DNN的预测在高采样频率下足够准确和快速,并在不同操作条件下实现车辆的平稳运行。在这项研究中,我们设计并比较了各种DNN,以找出最适合实时自动驾驶的方法。在设计DNN时,我们采用了增量设计方法,通过增强模型能力和扩展数据集来应对真实世界驾驶场景的挑战。我们设计了PD系统、CNN、CNN-LSTM和CNN-NODE,并在真实的MIT赛车上对它们的性能进行了评估。PD系统可以完成基本的跟道行驶,但在急转弯和光照变化的情况下会遇到困难。CNN改善了转向性能,但缺乏时间意识,而CNN-LSTM解决了这一问题,实现了平稳驾驶性能。CNN-NODE在处理驾驶动态方面表现与CNN-LSTM相似,但驾驶性能略好一些。这项研究的结果强调了迭代设计过程对于开发用于自动驾驶应用的稳健DNN的重要性。实验视频可在https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FNNYgU--iaY上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF In International Congress on Human-Computer Interaction, Optimization and Robotic Applications, 2025
Summary
本文着重研究基于深度学习的自动驾驶系统设计,并在真实世界的MIT赛车上进行部署和测试。采用深度神经网络(DNN)将原始图像输入实时转换为转向命令,遵循模仿学习框架。研究的关键挑战在于确保DNN预测的准确性、高速性和高采样频率下的平稳车辆操作。设计了多种DNN并比较,找出最适合实时自动驾驶的方法。采用增量设计法,通过增强模型容量和数据库来解决现实驾驶场景的挑战。评估了PD系统、CNN、CNN-LSTM和CNN-NODE的性能,发现CNN-LSTM和CNN-NODE在驾驶动力学方面表现较好,其中CNN-NODE性能略优。
Key Takeaways
- 本文研究基于深度学习的自动驾驶系统在真实世界的MIT赛车上的部署和测试效果。
- 采用深度神经网络(DNN)进行端到端的模仿学习,将原始图像转化为实时转向指令。
- 设计挑战在于确保DNN预测的高速性、准确性和平滑操作。
- 通过多种DNN的设计和比较,找出最适合现实自动驾驶的方法。
- 采用增量设计法增强模型容量和数据库以解决现实驾驶难题。
- PD系统适合基本驾驶场景,但在急转弯和光照变化时表现不佳。
点此查看论文截图


From Brainwaves to Brain Scans: A Robust Neural Network for EEG-to-fMRI Synthesis
Authors:Kristofer Grover Roos, Atsushi Fukuda, Quan Huu Cap
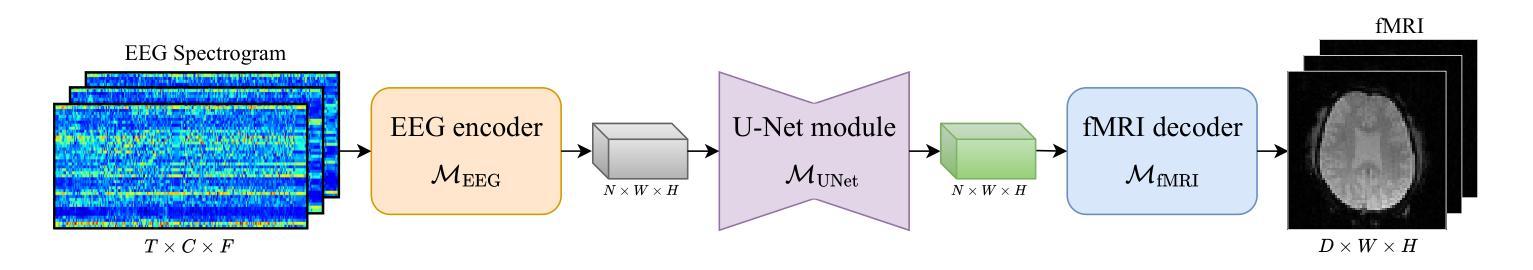
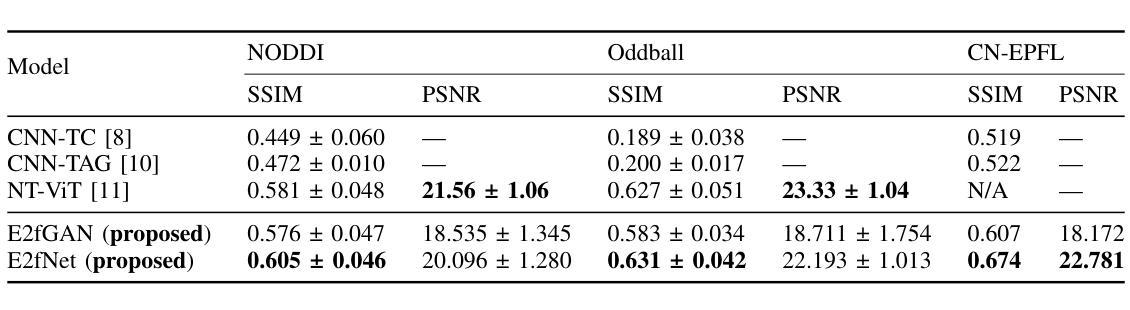
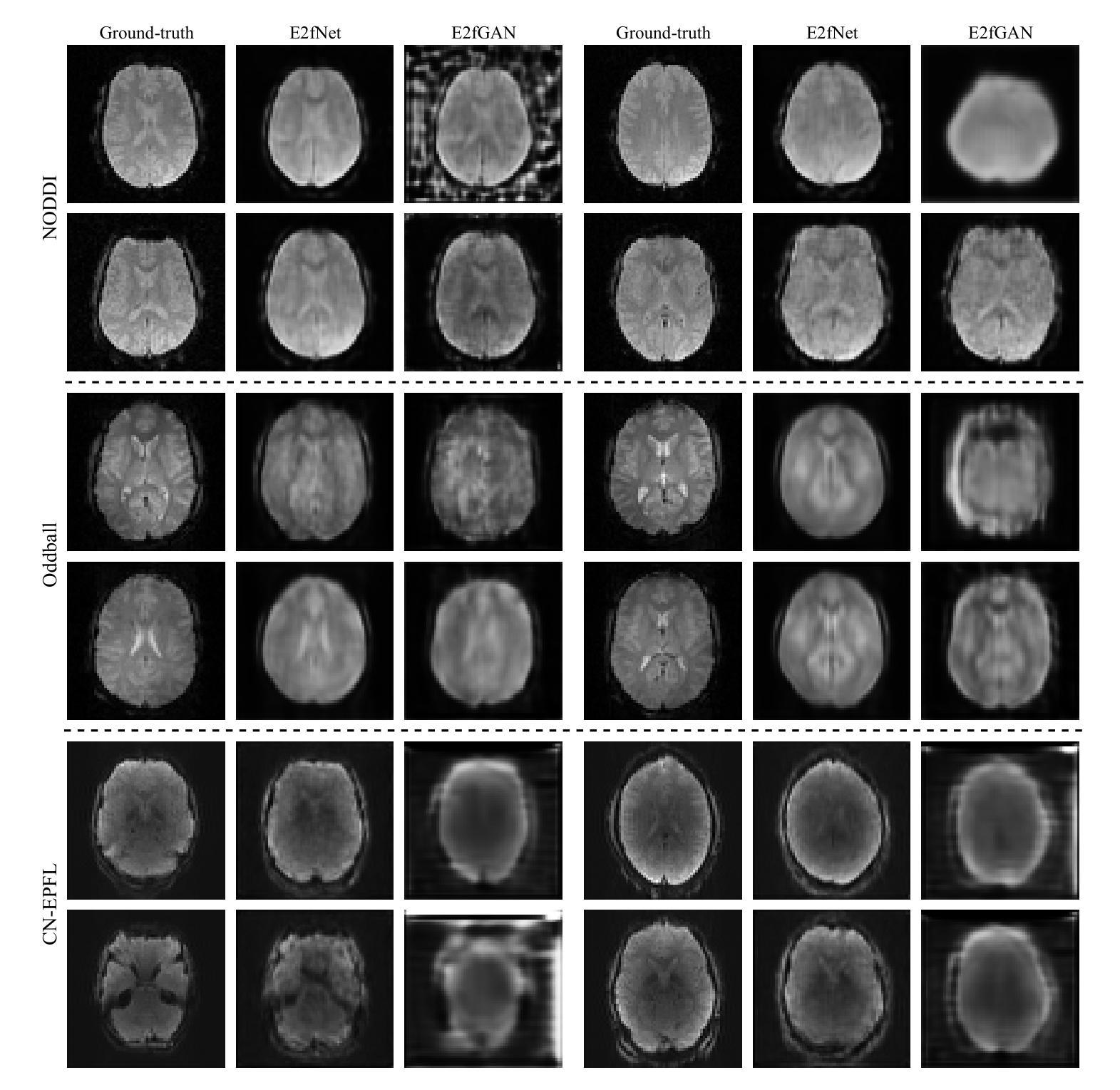
While functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) offers valuable insights into brain activity, it is limited by high operational costs and significant infrastructural demands. In contrast, electroencephalography (EEG) provides millisecond-level precision in capturing electrical activity but lacks the spatial fidelity necessary for precise neural localization. To bridge these gaps, we propose E2fNet, a simple yet effective deep learning model for synthesizing fMRI images from low-cost EEG data. E2fNet is an encoder-decoder network specifically designed to capture and translate meaningful multi-scale features from EEG across electrode channels into accurate fMRI representations. Extensive evaluations across three public datasets demonstrate that E2fNet consistently outperforms existing CNN- and transformer-based methods, achieving state-of-the-art results in terms of the structural similarity index measure (SSIM). These results demonstrate that E2fNet is a promising, cost-effective solution for enhancing neuroimaging capabilities. The code is available at https://github.com/kgr20/E2fNet.
功能磁共振成像(fMRI)虽然能深入了解大脑活动,但因其运营成本较高且需要大量基础设施而受到限制。相比之下,脑电图(EEG)在捕捉电活动方面具有毫秒级的精确度,但在精确神经定位方面缺乏必要的空间保真度。为了弥补这些差距,我们提出了E2fNet,这是一个简单有效的深度学习模型,可以从低成本的EEG数据中合成fMRI图像。E2fNet是一种专门设计的编码器-解码器网络,能够捕获和翻译EEG电极通道中的有意义的多尺度特征,并将其转化为准确的fMRI表示。在三个公共数据集上的广泛评估表明,E2fNet持续优于现有的基于CNN和transformer的方法,在结构相似性指数度量(SSIM)方面达到了最新结果。这些结果表明,E2fNet是一个有前景的、性价比高的解决方案,可以提高神经成像能力。代码可在https://github.com/kgr20/E2fNet获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
fMRI与EEG在神经成像领域各有所长,但存在成本和精度上的限制。为弥补这些不足,本文提出了E2fNet,一种用于从低成本EEG数据中合成fMRI图像的有效深度学习模型。E2fNet采用编码器-解码器结构,旨在捕捉EEG中的多尺度特征并将其转化为准确的fMRI表示。在三个公开数据集上的评估表明,E2fNet在结构相似性指数度量(SSIM)方面取得了最先进的成果,显著优于现有的CNN和transformer方法。这表明E2fNet是一种具有成本效益的提升神经成像能力的有前途的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- fMRI和EEG在神经成像中具有不同的优势和局限性。
- E2fNet是一个深度学习模型,旨在从低成本EEG数据中合成fMRI图像。
- E2fNet采用编码器-解码器结构,能够捕捉和翻译EEG中的多尺度特征。
- E2fNet在多个公开数据集上的表现超过了现有的CNN和transformer方法。
- E2fNet通过提高成像能力,为神经科学研究提供了成本效益更高的解决方案。
- E2fNet的源代码已公开发布,可供研究使用。
点此查看论文截图

Self-Consistent Nested Diffusion Bridge for Accelerated MRI Reconstruction
Authors:Tao Song, Yicheng Wu, Minhao Hu, Xiangde Luo, Guoting Luo, Guotai Wang, Yi Guo, Feng Xu, Shaoting Zhang
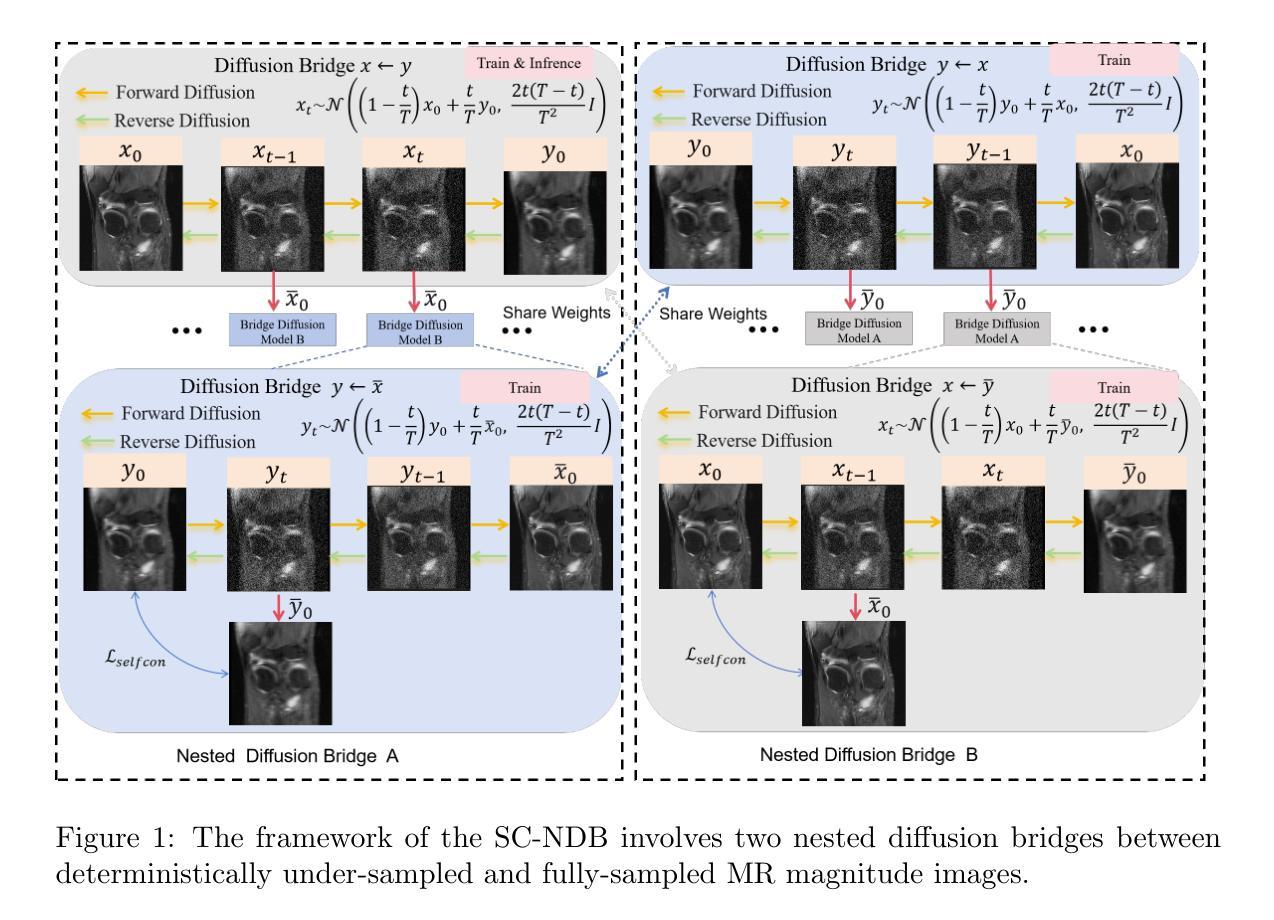
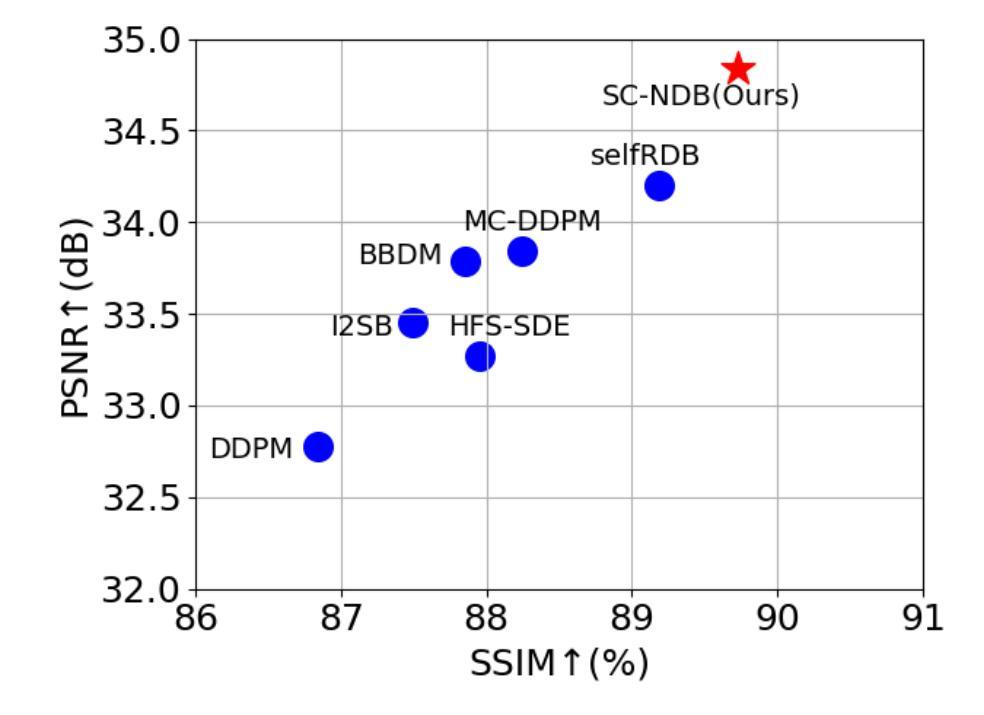
Accelerated MRI reconstruction plays a vital role in reducing scan time while preserving image quality. While most existing methods rely on complex-valued image-space or k-space data, these formats are often inaccessible in clinical practice due to proprietary reconstruction pipelines, leaving only magnitude images stored in DICOM files. To address this gap, we focus on the underexplored task of magnitude-image-based MRI reconstruction. Recent advancements in diffusion models, particularly denoising diffusion probabilistic models (DDPMs), have demonstrated strong capabilities in modeling image priors. However, their task-agnostic denoising nature limits performance in source-to-target image translation tasks, such as MRI reconstruction. In this work, we propose a novel Self-Consistent Nested Diffusion Bridge (SC-NDB) framework that models accelerated MRI reconstruction as a bi-directional image translation process between under-sampled and fully-sampled magnitude MRI images. SC-NDB introduces a nested diffusion architecture with a self-consistency constraint and reverse bridge diffusion pathways to improve intermediate prediction fidelity and better capture the explicit priors of source images. Furthermore, we incorporate a Contour Decomposition Embedding Module (CDEM) to inject structural and textural knowledge by leveraging Laplacian pyramids and directional filter banks. Extensive experiments on the fastMRI and IXI datasets demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance compared to both magnitude-based and non-magnitude-based diffusion models, confirming the effectiveness and clinical relevance of SC-NDB.
加速MRI重建在减少扫描时间的同时保持图像质量方面起着至关重要的作用。虽然大多数现有方法依赖于复数值图像空间或k空间数据,但这些格式由于专有重建管道而在临床实践中往往无法访问,只留下以DICOM文件存储的幅度图像。为了弥补这一空白,我们专注于基于幅度图像的MRI重建这一尚未充分探索的任务。扩散模型的最新进展,特别是去噪扩散概率模型(DDPMs),在建模图像先验方面表现出了强大的能力。然而,其通用的去噪性质限制了其在源到目标图像翻译任务(如MRI重建)中的性能。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新型的自我一致嵌套扩散桥(SC-NDB)框架,它将加速MRI重建建模为欠采样MRI图像和完全采样幅度MRI图像之间的双向图像翻译过程。SC-NDB引入了一个具有自我一致性约束和反向桥扩散路径的嵌套扩散架构,以提高中间预测保真度并更好地捕获源图像的显式先验。此外,我们结合轮廓分解嵌入模块(CDEM),通过利用拉普拉斯金字塔和方向滤波器库来注入结构和纹理知识。在fastMRI和IXI数据集上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法与基于幅度和非基于幅度的扩散模型相比,达到了最先进的性能,证实了SC-NDB的有效性和临床相关性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种新型的MRI重建方法——Self-Consistent Nested Diffusion Bridge(SC-NDB)框架,它解决了加速MRI重建中扫描时间缩短与图像质量保持的矛盾。针对现有方法依赖于复杂的图像空间或k空间数据的问题,本文专注于基于幅度图像的MRI重建。结合扩散模型的优势,特别是denoising diffusion probabilistic models(DDPMs),本文框架通过双向图像翻译过程对欠采样和完全采样的幅度MRI图像进行建模。SC-NDB引入嵌套扩散架构、自我一致性约束和反向桥梁扩散路径,以提高中间预测保真度和更好地捕捉源图像的显式先验信息。此外,还结合了Contour Decomposition Embedding Module(CDEM),通过利用Laplacian金字塔和方向滤波器库来注入结构和纹理知识。在fastMRI和IXI数据集上的实验表明,该方法在扩散模型中实现了最先进的性能,验证了SC-NDB的有效性和临床相关性。
Key Takeaways
- 加速MRI重建在减少扫描时间的同时保持图像质量至关重要。
- 当前方法主要依赖复杂的图像空间或k空间数据,这在临床实践中由于专有重建管道而难以应用。
- 幅度图像在MRI重建中是一个未被充分研究的领域。
- SC-NDB框架利用扩散模型将加速MRI重建建模为欠采样和完全采样幅度MRI图像之间的双向图像翻译过程。
- SC-NDB通过嵌套扩散架构和自我一致性约束提高预测准确性并捕捉源图像的显式先验信息。
- CDEM模块利用Laplacian金字塔和方向滤波器库注入结构和纹理知识。
点此查看论文截图

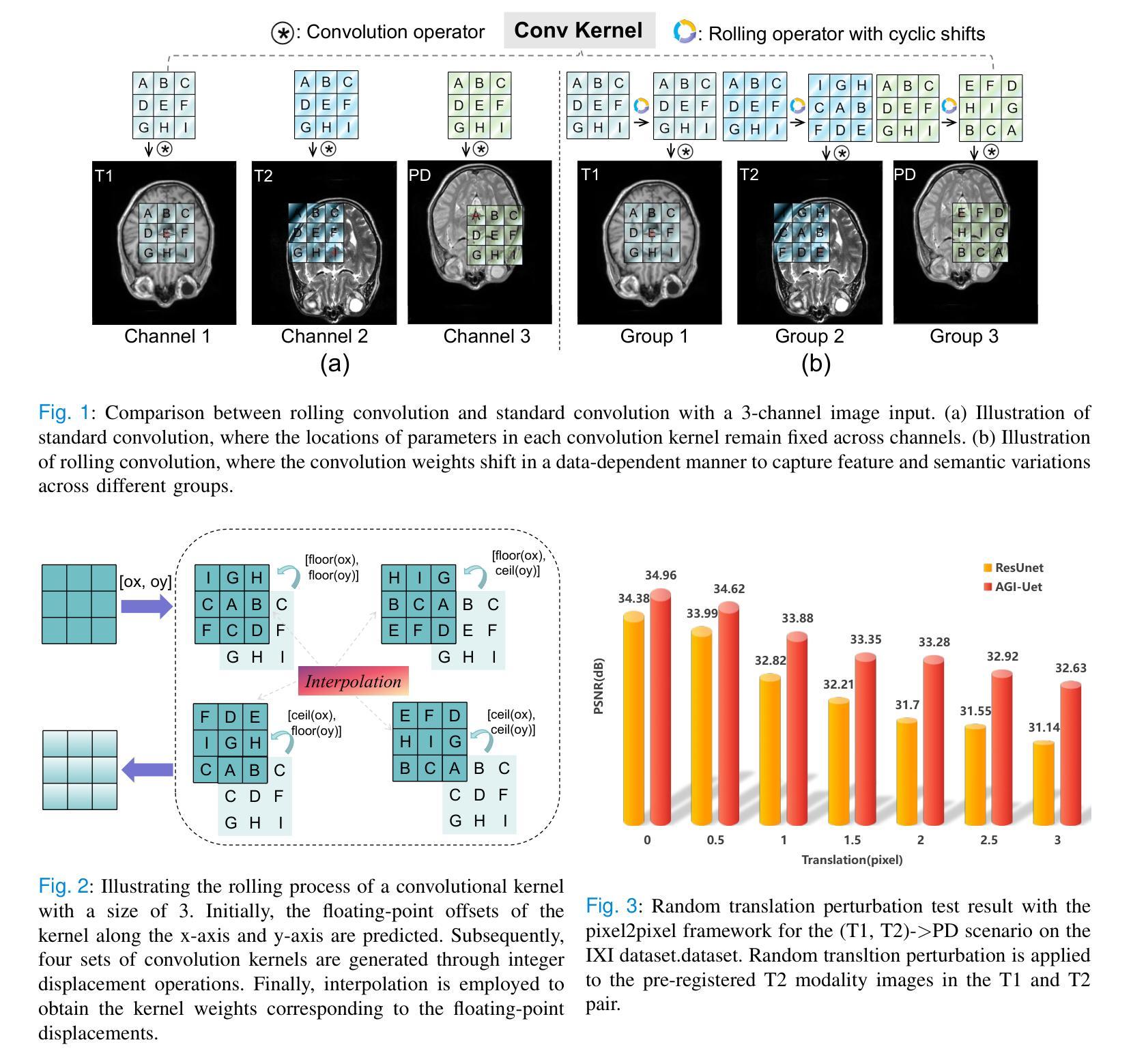
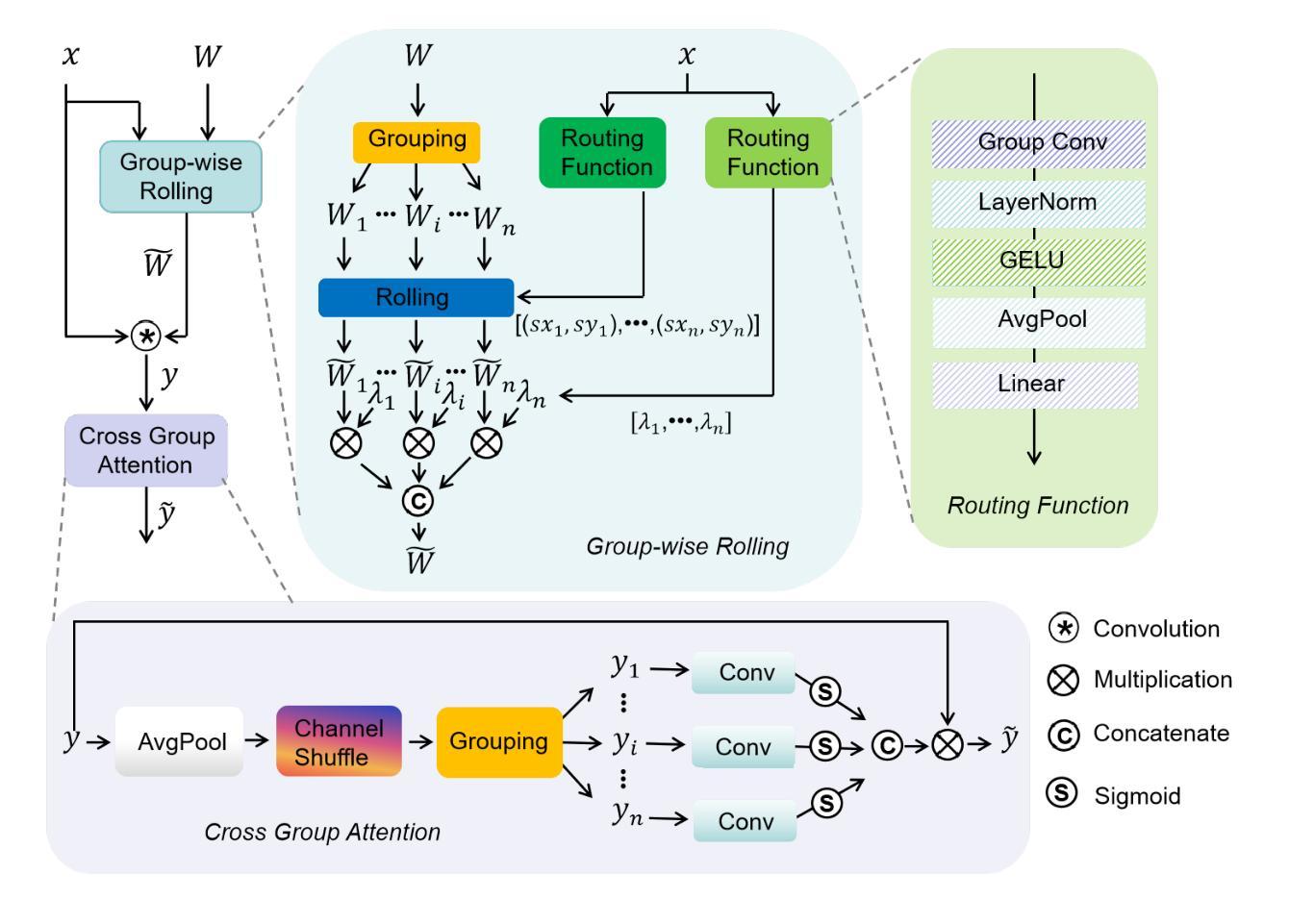
Learning Modality-Aware Representations: Adaptive Group-wise Interaction Network for Multimodal MRI Synthesis
Authors:Tao Song, Yicheng Wu, Minhao Hu, Xiangde Luo, Linda Wei, Guotai Wang, Yi Guo, Feng Xu, Shaoting Zhang
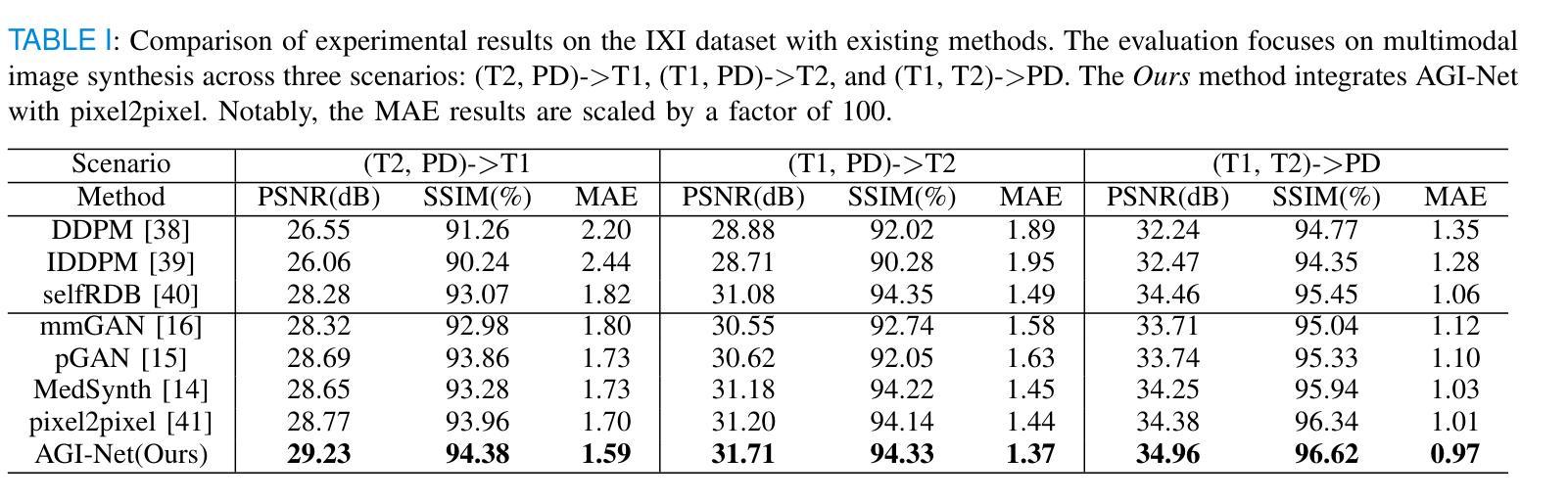
Multimodal MR image synthesis aims to generate missing modality images by effectively fusing and mapping from a subset of available MRI modalities. Most existing methods adopt an image-to-image translation paradigm, treating multiple modalities as input channels. However, these approaches often yield sub-optimal results due to the inherent difficulty in achieving precise feature- or semantic-level alignment across modalities. To address these challenges, we propose an Adaptive Group-wise Interaction Network (AGI-Net) that explicitly models both inter-modality and intra-modality relationships for multimodal MR image synthesis. Specifically, feature channels are first partitioned into predefined groups, after which an adaptive rolling mechanism is applied to conventional convolutional kernels to better capture feature and semantic correspondences between different modalities. In parallel, a cross-group attention module is introduced to enable effective feature fusion across groups, thereby enhancing the network’s representational capacity. We validate the proposed AGI-Net on the publicly available IXI and BraTS2023 datasets. Experimental results demonstrate that AGI-Net achieves state-of-the-art performance in multimodal MR image synthesis tasks, confirming the effectiveness of its modality-aware interaction design. We release the relevant code at: https://github.com/zunzhumu/Adaptive-Group-wise-Interaction-Network-for-Multimodal-MRI-Synthesis.git.
多模态MR图像合成旨在通过有效地融合和映射从可用MRI模态的子集来生成缺失的模态图像。大多数现有方法采用图像到图像的翻译模式,将多种模态视为输入通道。然而,这些方法通常会产生次优结果,因为实现跨模态的特征或语义级对齐存在固有的困难。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一种自适应组交互网络(AGI-Net),该网络对多模态MR图像合成进行显式建模,同时建立模态间和模态内的关系。具体而言,特征通道首先被划分成预定义的组,然后对传统的卷积核应用自适应滚动机制,以更好地捕获不同模态之间的特征和语义对应关系。同时,引入跨组注意力模块,以实现各组之间的有效特征融合,从而增强网络的表示能力。我们在公开可用的IXI和BraTS2023数据集上验证了所提出的AGI-Net。实验结果表明,AGI-Net在多模态MR图像合成任务上达到了最先进的性能,证明了其模态感知交互设计的有效性。我们已在https://github.com/zunzhumu/Adaptive-Group-wise-Interaction-Network-for-Multimodal-MRI-Synthesis.git发布相关代码。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文提出了一种自适应组交互网络(AGI-Net),用于多模态MR图像合成。通过建模模态间和模态内的关系,实现了在不同模态间特征语义层面的精确对齐。采用分组机制和跨组注意力模块,提高了网络在合成任务上的性能。在公开数据集上的实验验证了该方法的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态MR图像合成的目标是利用部分可用的MRI模态生成缺失模态的图像。
- 现有方法多采用图像到图像的翻译模式,将多个模态作为输入通道来处理。
- 现有方法面临的挑战是难以实现模态间的精确特征或语义对齐。
- 自适应组交互网络(AGI-Net)通过建模模态间和模态内的关系来解决这一问题。
- AGI-Net采用分组机制和自适应滚动机制来更好地捕捉不同模态间的特征语义对应关系。
- AGI-Net引入跨组注意力模块,实现组间的有效特征融合,提高了网络的表征能力。
点此查看论文截图