⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-30 更新
From Concept to Practice: an Automated LLM-aided UVM Machine for RTL Verification
Authors:Junhao Ye, Yuchen Hu, Ke Xu, Dingrong Pan, Qichun Chen, Jie Zhou, Shuai Zhao, Xinwei Fang, Xi Wang, Nan Guan, Zhe Jiang
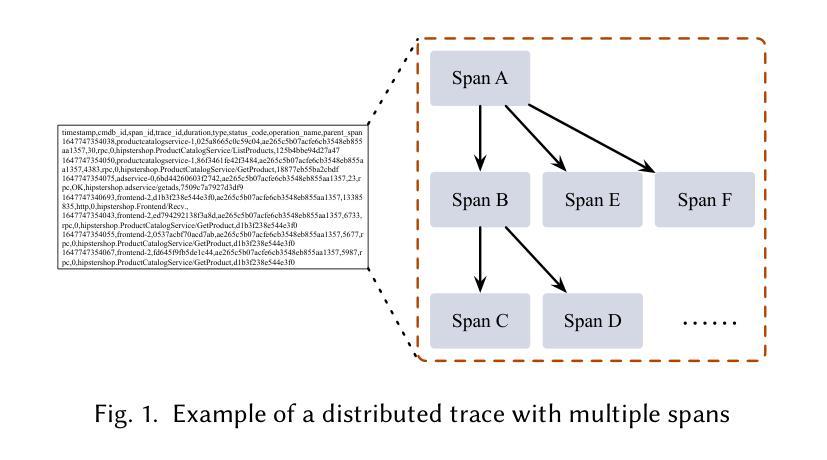
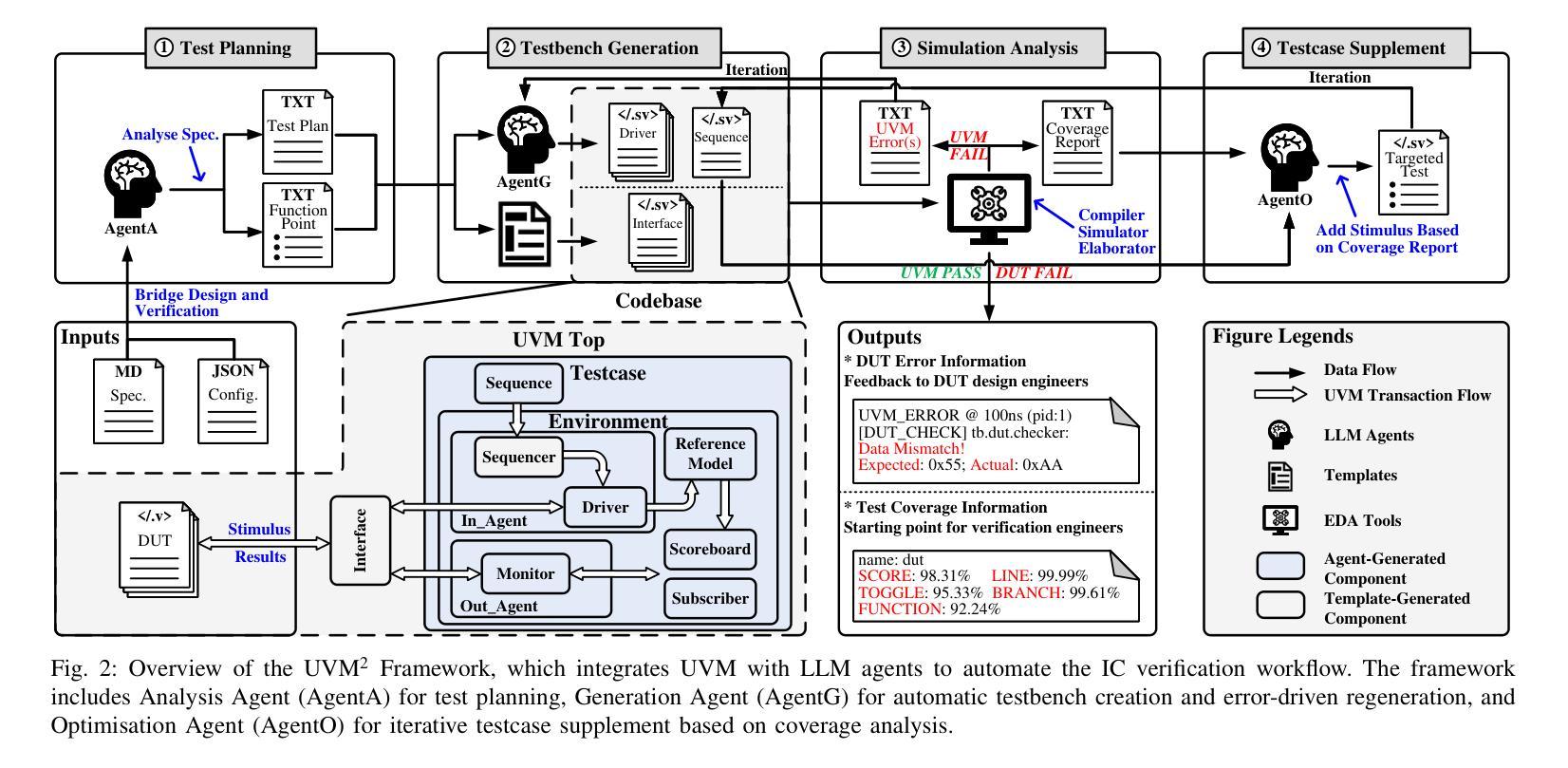
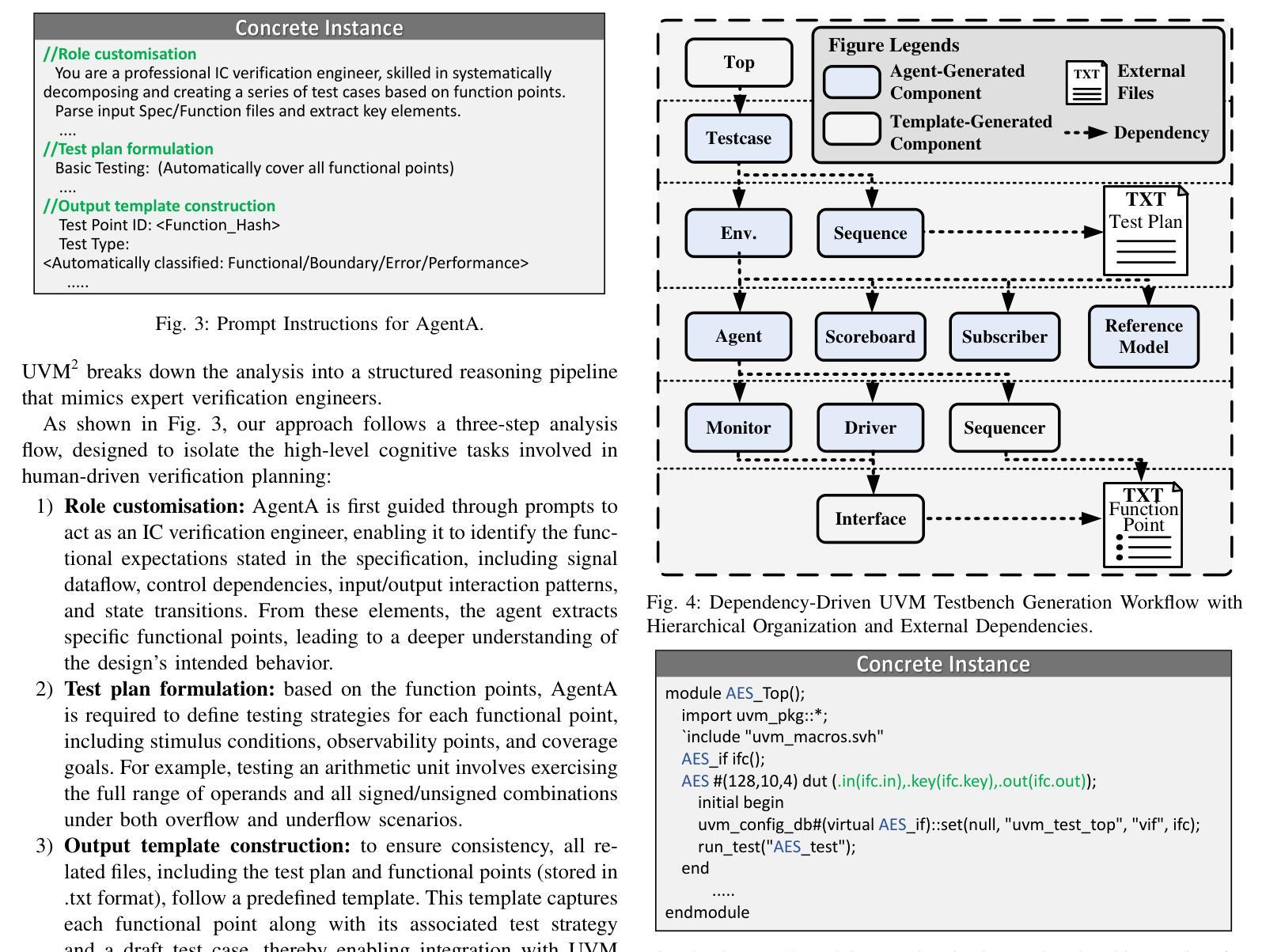
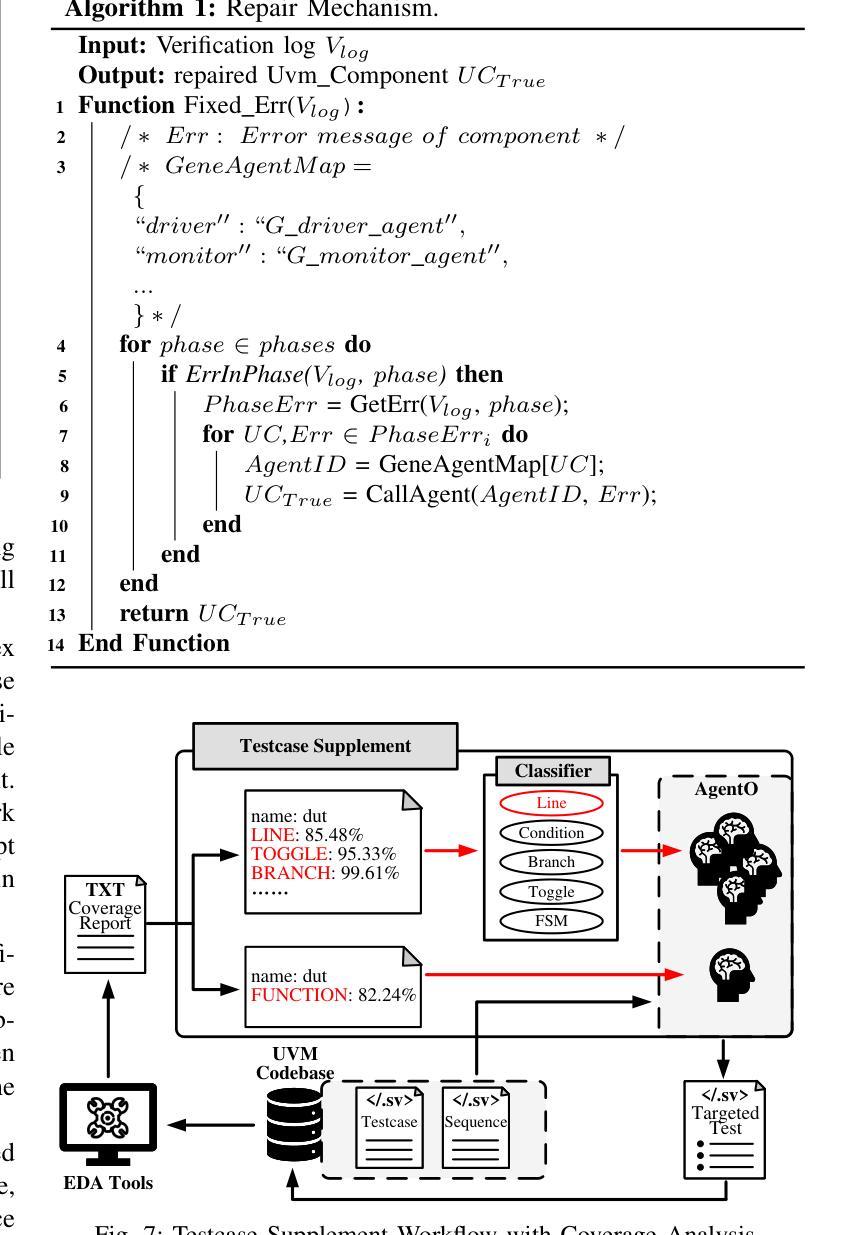
Verification presents a major bottleneck in Integrated Circuit (IC) development, consuming nearly 70% of the total development effort. While the Universal Verification Methodology (UVM) is widely used in industry to improve verification efficiency through structured and reusable testbenches, constructing these testbenches and generating sufficient stimuli remain challenging. These challenges arise from the considerable manual coding effort required, repetitive manual execution of multiple EDA tools, and the need for in-depth domain expertise to navigate complex designs.Here, we present UVM^2, an automated verification framework that leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to generate UVM testbenches and iteratively refine them using coverage feedback, significantly reducing manual effort while maintaining rigorous verification standards.To evaluate UVM^2, we introduce a benchmark suite comprising Register Transfer Level (RTL) designs of up to 1.6K lines of code.The results show that UVM^2 reduces testbench setup time by up to UVM^2 compared to experienced engineers, and achieve average code and function coverage of 87.44% and 89.58%, outperforming state-of-the-art solutions by 20.96% and 23.51%, respectively.
验证是集成电路(IC)开发中的主要瓶颈,占据了近70%的总开发工作量。虽然通用验证方法论(UVM)在工业中得到广泛应用,通过结构化、可重用的测试平台来提高验证效率,但构建这些测试平台和生成足够的激励仍存在挑战。这些挑战源于大量所需的手动编码工作、多个EDA工具的手动重复执行,以及深入特定领域专业知识以应对复杂设计的需要。在此,我们推出UVM^2,这是一个利用大型语言模型(LLM)自动验证框架,用于生成UVM测试平台并使用覆盖率反馈进行迭代优化,在保持严格验证标准的同时,大大减少手动工作量。为了评估UVM^2,我们引入了一套基准测试套件,包含高达1600行代码的寄存器传输级(RTL)设计。结果表明,UVM^2与新工程师相比,减少了测试平台设置时间高达UVM^2相比经验丰富的工程师的情况待定进一步确定),并实现了平均代码和功能覆盖率分别为87.44%和89.58%,优于最新解决方案分别达20.96%和23.51%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
集成电路验证是开发过程中的主要瓶颈,消耗近70%的开发精力。为提高验证效率,行业中广泛采用通用验证方法论(UVM),但构建测试平台和生成足够的激励仍然具有挑战性。UVM^2是一种新型的自动化验证框架,它利用大型语言模型(LLM)生成UVM测试平台,并通过覆盖率反馈进行迭代优化,显著减少人工努力的同时保持严格的验证标准。评估表明,UVM^2能够减少测试平台设置时间,提高代码和功能覆盖率,优于现有解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 集成电路验证是开发的主要瓶颈,消耗大量时间和资源。
- UVM广泛应用于行业以提高验证效率,但构建测试平台和生成激励仍然具有挑战性。
- UVM^2是一种自动化验证框架,利用LLM生成UVM测试平台,降低人工努力。
- UVM^2通过覆盖率反馈进行迭代优化,保持严格的验证标准。
- UVM^2能够减少测试平台设置时间。
- UVM^2提高代码和功能覆盖率,优于现有解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

Can AI Agents Design and Implement Drug Discovery Pipelines?
Authors:Khachik Smbatyan, Tsolak Ghukasyan, Tigran Aghajanyan, Hovhannes Dabaghyan, Sergey Adamyan, Aram Bughdaryan, Vahagn Altunyan, Gagik Navasardyan, Aram Davtyan, Anush Hakobyan, Aram Gharibyan, Arman Fahradyan, Artur Hakobyan, Hasmik Mnatsakanyan, Narek Ginoyan, Garik Petrosyan
The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence, particularly autonomous agentic systems based on Large Language Models (LLMs), presents new opportunities to accelerate drug discovery by improving in-silico modeling and reducing dependence on costly experimental trials. Current AI agent-based systems demonstrate proficiency in solving programming challenges and conducting research, indicating an emerging potential to develop software capable of addressing complex problems such as pharmaceutical design and drug discovery. This paper introduces DO Challenge, a benchmark designed to evaluate the decision-making abilities of AI agents in a single, complex problem resembling virtual screening scenarios. The benchmark challenges systems to independently develop, implement, and execute efficient strategies for identifying promising molecular structures from extensive datasets, while navigating chemical space, selecting models, and managing limited resources in a multi-objective context. We also discuss insights from the DO Challenge 2025, a competition based on the proposed benchmark, which showcased diverse strategies explored by human participants. Furthermore, we present the Deep Thought multi-agent system, which demonstrated strong performance on the benchmark, outperforming most human teams. Among the language models tested, Claude 3.7 Sonnet, Gemini 2.5 Pro and o3 performed best in primary agent roles, and GPT-4o, Gemini 2.0 Flash were effective in auxiliary roles. While promising, the system’s performance still fell short of expert-designed solutions and showed high instability, highlighting both the potential and current limitations of AI-driven methodologies in transforming drug discovery and broader scientific research.
人工智能的快速发展,特别是基于大型语言模型(LLM)的自主代理系统,为通过改进硅建模和减少昂贵实验试点的依赖来加速药物发现提供了新的机遇。当前的基于AI代理的系统在解决编程挑战和研究方面表现出色,这表明有潜力开发能够解决诸如药物设计和药物发现等复杂问题的软件。本文介绍了DO Challenge,这是一个基准测试,旨在评估AI代理在类似于虚拟筛选场景的单个复杂问题中的决策能力。该基准测试挑战系统独立开发、实施和执行有效策略,从大量数据集中识别出有前景的分子结构,同时在化学空间中进行导航、选择模型、并在多目标背景下管理有限资源。我们还讨论了基于该基准测试的DO Challenge 2025竞赛的见解,该竞赛展示了人类参与者探索的多样化策略。此外,我们还展示了在基准测试中表现强大的Deep Thought多代理系统,它在大多数人类团队中表现出色。在测试的语言模型中,Claude 3.7 Sonnet、Gemini 2.5 Pro和o3在主要代理角色中表现最佳,GPT-4o和Gemini 2.0 Flash在辅助角色中效果显著。虽然很有前途,但该系统的性能仍然落后于专家设计的解决方案,并表现出高度的不稳定,这突出了人工智能驱动方法在药物发现和更广泛的科学研究中的潜力和当前局限性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
人工智能特别是基于大型语言模型(LLM)的自主智能系统的快速发展,为加速药物发现提供了新的机遇。通过改进硅建模并减少对传统实验试错的依赖,当前AI系统展现出解决编程挑战和研究的能力,显示了在药物发现和更广泛科学研究方面开发软件的潜力。本文介绍了DO Challenge这一基准测试,用于评估AI系统在类似于虚拟筛选场景中的决策能力。此外,还讨论了基于该基准测试的DO Challenge 2025竞赛的见解,以及展示强大性能的Deep Thought多智能系统。然而,尽管有所进步,这些系统的性能仍然未能达到专家设计的解决方案的水平,并显示出高不稳定性,突显了人工智能在药物发现等领域变革中的潜力和当前局限。
Key Takeaways
- 人工智能的发展为药物发现提供了新机遇,通过改进硅建模和减少传统实验试错依赖,提高药物发现的效率。
- 基于大型语言模型(LLM)的自主智能系统展现出解决编程和研究问题的能力。
- DO Challenge是一个用于评估AI系统在类似于虚拟筛选场景中的决策能力的基准测试。
- Deep Thought多智能系统在DO Challenge基准测试中表现良好,但未能达到专家设计的解决方案水平。
- AI系统的性能仍然面临不稳定性和局限性,需要进一步的研究和改进。
- AI在药物发现等领域的应用潜力巨大,但实现这一潜力需要克服技术和实践上的挑战。
点此查看论文截图

semi-PD: Towards Efficient LLM Serving via Phase-Wise Disaggregated Computation and Unified Storage
Authors:Ke Hong, Lufang Chen, Zhong Wang, Xiuhong Li, Qiuli Mao, Jianping Ma, Chao Xiong, Guanyu Wu, Buhe Han, Guohao Dai, Yun Liang, Yu Wang
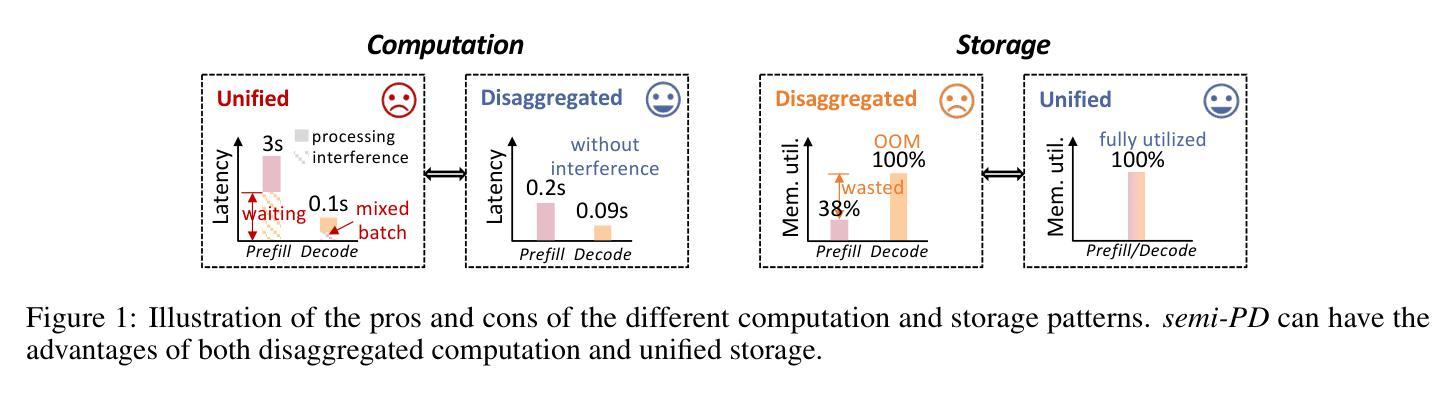
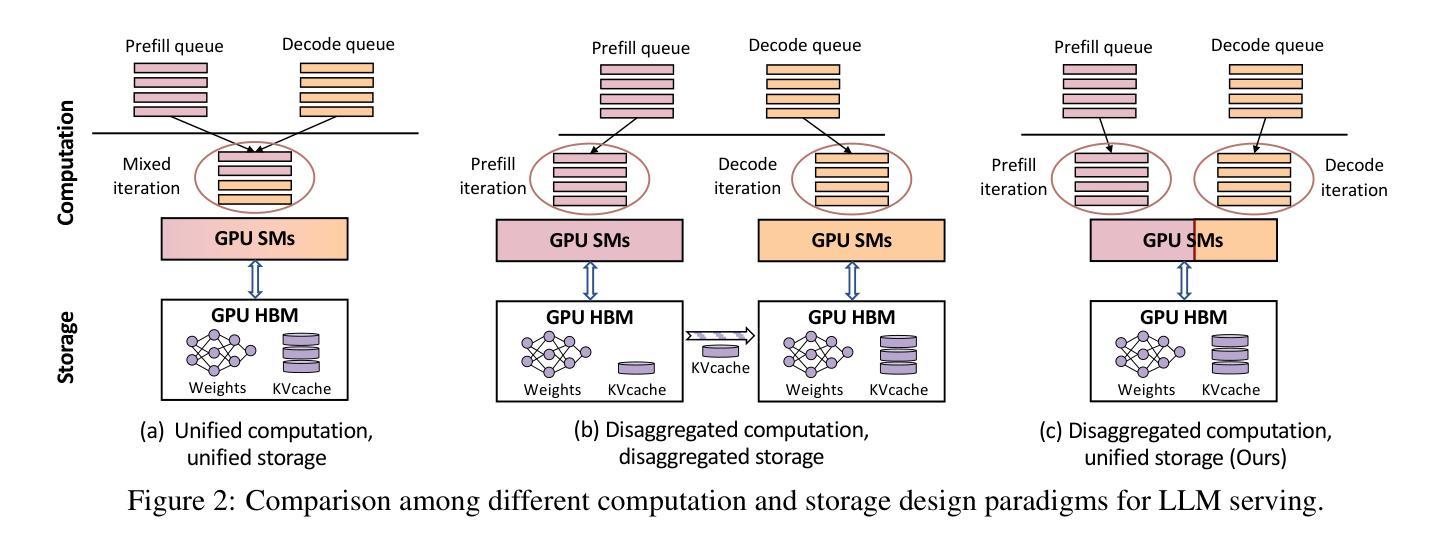
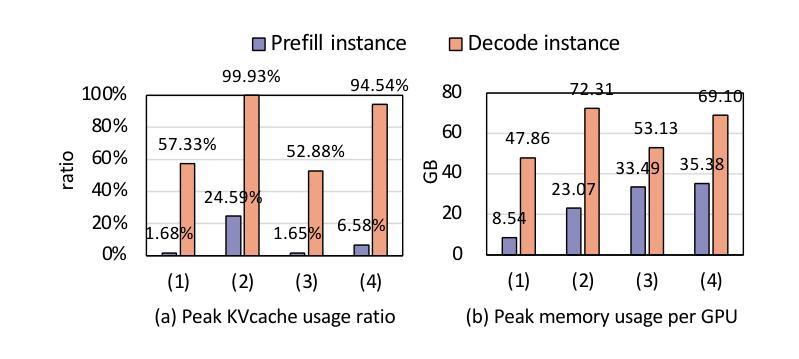
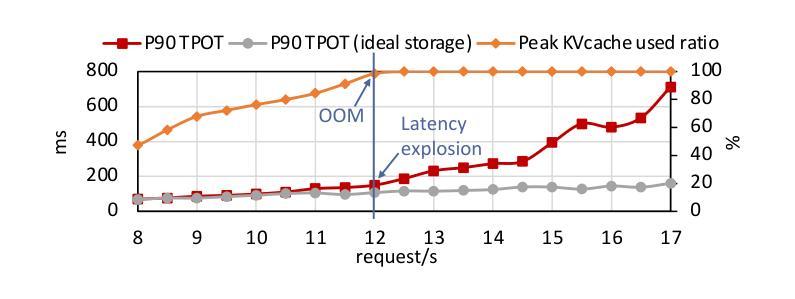
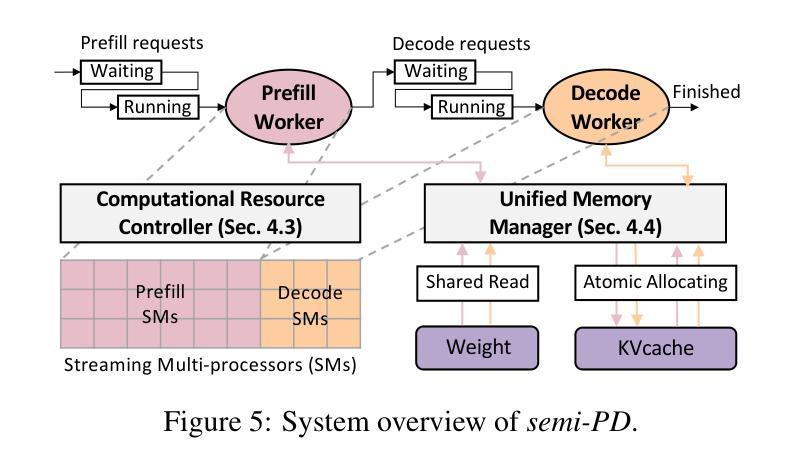
Existing large language model (LLM) serving systems fall into two categories: 1) a unified system where prefill phase and decode phase are co-located on the same GPU, sharing the unified computational resource and storage, and 2) a disaggregated system where the two phases are disaggregated to different GPUs. The design of the disaggregated system addresses the latency interference and sophisticated scheduling issues in the unified system but leads to storage challenges including 1) replicated weights for both phases that prevent flexible deployment, 2) KV cache transfer overhead between the two phases, 3) storage imbalance that causes substantial wasted space of the GPU capacity, and 4) suboptimal resource adjustment arising from the difficulties in migrating KV cache. Such storage inefficiency delivers poor serving performance under high request rates. In this paper, we identify that the advantage of the disaggregated system lies in the disaggregated computation, i.e., partitioning the computational resource to enable the asynchronous computation of two phases. Thus, we propose a novel LLM serving system, semi-PD, characterized by disaggregated computation and unified storage. In semi-PD, we introduce a computation resource controller to achieve disaggregated computation at the streaming multi-processor (SM) level, and a unified memory manager to manage the asynchronous memory access from both phases. semi-PD has a low-overhead resource adjustment mechanism between the two phases, and a service-level objective (SLO) aware dynamic partitioning algorithm to optimize the SLO attainment. Compared to state-of-the-art systems, semi-PD maintains lower latency at higher request rates, reducing the average end-to-end latency per request by 1.27-2.58x on DeepSeek series models, and serves 1.55-1.72x more requests adhering to latency constraints on Llama series models.
现有的大型语言模型(LLM)服务系统可分为两类:1)统一系统,预填充阶段和解码阶段位于同一GPU上,共享统一的计算资源和存储;2)分散系统,两个阶段分散到不同的GPU上。分散系统的设计解决了统一系统中存在的延迟干扰和复杂调度问题,但导致了存储挑战,包括1)两个阶段的权重复制,防止灵活部署;2)两个阶段之间的KV缓存传输开销;3)存储不平衡导致GPU容量大量浪费;4)由于KV缓存迁移困难导致的资源调整不佳。这种存储效率低下在高请求率下导致服务性能不佳。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 16 figures
摘要
本文探讨了现有大型语言模型(LLM)服务系统的两类设计:统一系统和分散系统。统一系统存在延迟干扰和调度问题,而分散系统虽然解决了这些问题,但带来了存储挑战。为此,本文提出了一种新型LLM服务系统——semi-PD,该系统具有分散计算和统一存储的特点。通过引入计算资源控制器和统一内存管理器,semi-PD实现了较低的调整机制开销和优化的服务目标达成。相较于现有系统,semi-PD在较高请求率下维持较低延迟,减少了DeepSeek系列模型的平均端到端延迟请求时间达1.27-2.58倍,并在Llama系列模型上服务了更多满足延迟约束的请求,提升了服务性能。
关键见解
- 大型语言模型服务系统分为统一和分散两类设计,各有优缺点。
- 分散系统设计解决了统一系统中的延迟干扰和调度问题。
- 分散系统存在存储挑战,包括权重复制、缓存转移开销、存储不平衡和资源调整困难等问题。
- proposed的semi-PD系统结合了分散计算和统一存储的特点,通过计算资源控制器和统一内存管理器实现高效性能。
- semi-PD具有低开销的资源调整机制,并采用了服务目标感知的动态分区算法进行优化。
- 与现有系统相比,semi-PD在请求率高时维持较低延迟,对DeepSeek系列模型和Llama系列模型的性能提升显著。
- semi-PD为大型语言模型服务提供了一种新的高效解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

CoherenDream: Boosting Holistic Text Coherence in 3D Generation via Multimodal Large Language Models Feedback
Authors:Chenhan Jiang, Yihan Zeng, Hang Xu, Dit-Yan Yeung
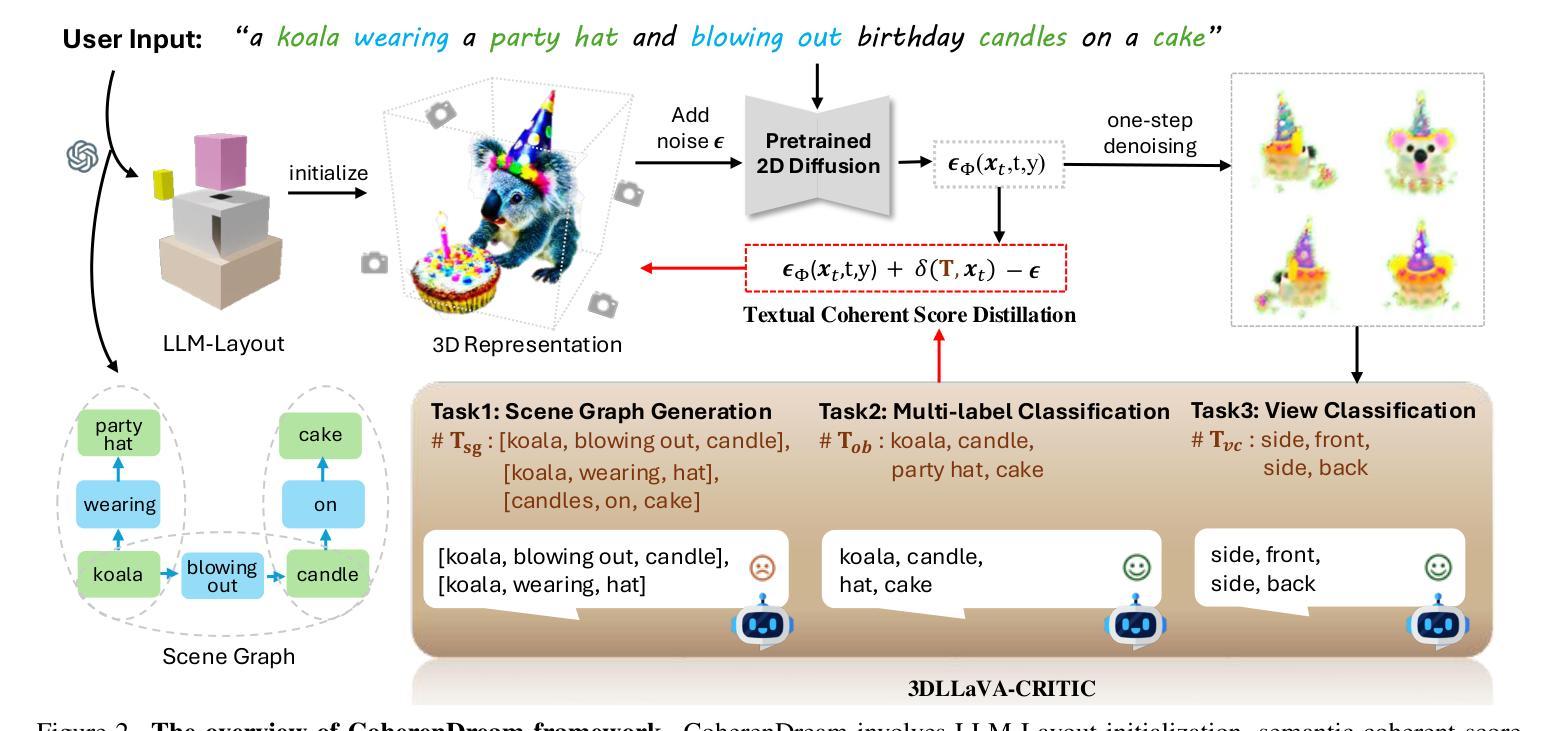
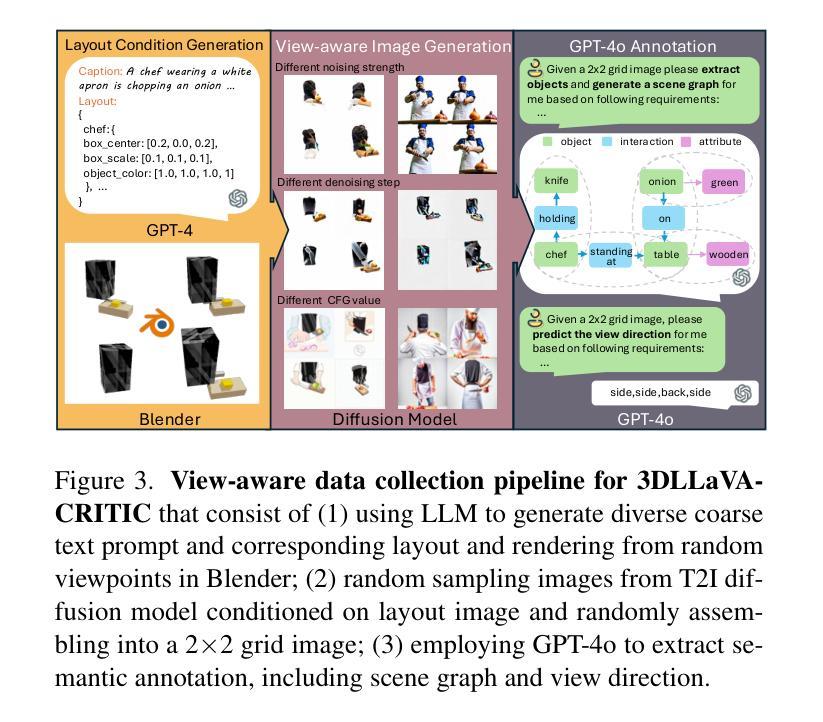
Score Distillation Sampling (SDS) has achieved remarkable success in text-to-3D content generation. However, SDS-based methods struggle to maintain semantic fidelity for user prompts, particularly when involving multiple objects with intricate interactions. While existing approaches often address 3D consistency through multiview diffusion model fine-tuning on 3D datasets, this strategy inadvertently exacerbates text-3D alignment degradation. The limitation stems from SDS’s inherent accumulation of view-independent biases during optimization, which progressively diverges from the ideal text alignment direction. To alleviate this limitation, we propose a novel SDS objective, dubbed as Textual Coherent Score Distillation (TCSD), which integrates alignment feedback from multimodal large language models (MLLMs). Our TCSD leverages cross-modal understanding capabilities of MLLMs to assess and guide the text-3D correspondence during the optimization. We further develop 3DLLaVA-CRITIC - a fine-tuned MLLM specialized for evaluating multiview text alignment in 3D generations. Additionally, we introduce an LLM-layout initialization that significantly accelerates optimization convergence through semantic-aware spatial configuration. Comprehensive evaluations demonstrate that our framework, CoherenDream, establishes state-of-the-art performance in text-aligned 3D generation across multiple benchmarks, including T$^3$Bench and TIFA subset. Qualitative results showcase the superior performance of CoherenDream in preserving textual consistency and semantic interactions. As the first study to incorporate MLLMs into SDS optimization, we also conduct extensive ablation studies to explore optimal MLLM adaptations for 3D generation tasks.
Score Distillation Sampling (SDS)在文本到3D内容生成方面取得了显著的成功。然而,基于SDS的方法在保持用户提示的语义保真方面存在困难,特别是在涉及多个具有复杂交互的对象时。虽然现有的方法通常通过3D数据集上的多视角扩散模型微调来解决3D一致性,但这种策略却无意中加剧了文本到3D的对齐退化。这一局限性源于SDS在优化过程中固有的积累与视图无关的偏见,这些偏见逐渐偏离理想的文本对齐方向。为了缓解这一局限性,我们提出了一种新的SDS目标,称为文本一致得分蒸馏(TCSD),它结合了多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的对齐反馈。我们的TCSD利用MLLMs的跨模态理解能力来评估和引导优化过程中的文本到3D的对应关系。此外,我们还开发了专门用于评估3D生成中多视角文本对齐的精细调整MLLM——3DLLaVA-CRITIC。此外,我们还引入了LLM布局初始化,通过语义感知的空间配置显著加速了优化的收敛。综合评估表明,我们的框架CoherenDream在多个基准测试上实现了最先进的文本对齐3D生成性能,包括T$^3$Bench和TIFA子集。定性的结果展示了CoherenDream在保持文本一致性和语义交互方面的卓越性能。作为将MLLMs纳入SDS优化的首项研究,我们还进行了广泛的消融研究,以探索适用于3D生成任务的最佳MLLM适应方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了Score Distillation Sampling(SDS)在文本到3D内容生成中的成功应用,但SDS在处理涉及多个物体复杂交互的用户提示时难以保持语义保真度的问题。为缓解这一问题,提出了名为Textual Coherent Score Distillation(TCSD)的新型SDS目标,通过利用多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的跨模态理解能力来评估和指导文本到3D的对应关系。同时开发了专门用于评估3D生成中文本对齐的多视图评估的MLLM 3DLLaVA-CRITIC,并引入了LLM布局初始化,显著加速了优化收敛。评估结果显示,CoherenDream框架在文本对齐的3D生成方面达到了最新技术水平。
Key Takeaways
- SDS在文本到3D内容生成中表现优秀,但在处理复杂交互的多物体提示时存在语义失真问题。
- 提出TCSD方法,利用MLLMs的跨模态理解能力来优化SDS,提高文本到3D的对应关系。
- 开发专门用于评估多视图文本对齐的MLLM 3DLLaVA-CRITIC。
- 引入LLM布局初始化,加速优化收敛。
- CoherenDream框架在多个基准测试中表现优异,尤其在文本对齐的3D生成方面。
- CoherenDream能很好地保持文本一致性和语义交互性。
点此查看论文截图


Can a Crow Hatch a Falcon? Lineage Matters in Predicting Large Language Model Performance
Authors:Takuya Tamura, Taro Yano, Masafumi Enomoto, Masafumi Oyamada
Accurately forecasting the performance of Large Language Models (LLMs) before extensive fine-tuning or merging can substantially reduce both computational expense and development time. Although prior approaches like scaling laws account for global factors such as parameter size or training tokens, they often overlook explicit lineage relationships - i.e., which models are derived or merged from which parents. In this work, we propose a novel Lineage-Regularized Matrix Factorization (LRMF) framework that encodes ancestral ties among LLMs via a graph Laplacian regularizer. By leveraging multi-hop parent-child connections, LRMF consistently outperforms conventional matrix factorization and collaborative filtering methods in both instance-level and benchmark-level performance prediction. Our large-scale study includes 2,934 publicly available Hugging Face models and 21,000+ instances across 6 major benchmarks, showing that lineage constraints yield up to 7-10 percentage points higher correlation with actual performance compared to baselines. Moreover, LRMF effectively addresses the cold-start problem, providing accurate estimates for newly derived or merged models even with minimal data. This lineage-guided strategy thus offers a resource-efficient way to inform hyperparameter tuning, data selection, and model combination in modern LLM development.
精确预测大型语言模型(LLM)在大量微调或合并之前的性能,可以大大降低计算成本并缩短开发时间。尽管先前的方法,如规模定律,考虑了全局因素,如参数大小或训练令牌,但它们往往忽略了明确的血统关系,即哪些模型是从哪些父模型中衍生或合并而来的。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新型的基于血统的正则化矩阵分解(LRMF)框架,它通过图拉普拉斯正则器对LLM之间的祖代关系进行编码。通过利用多跳父子连接,LRMF在实例级别和基准测试级别性能预测方面均优于传统的矩阵分解和协同过滤方法。我们的大规模研究包括Hugging Face的2934个公开模型和超过2万多个实例的六大基准测试,结果显示,与基线相比,血统约束与实际性能的相关性高出高达7-10个百分点。此外,LRMF有效地解决了冷启动问题,即使数据很少,也能为新衍生或合并的模型提供准确的估算。因此,这种血统引导的策略为现代LLM开发中的超参数调整、数据选择和模型组合提供了一种资源高效的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)的性能预测对于减少计算成本和开发时间至关重要。本研究提出一种新型的Lineage-Regularized Matrix Factorization(LRMF)框架,通过图拉普拉斯正则化器编码LLM之间的祖代关系,在实例级别和基准测试级别性能预测方面,LRMF表现优于传统的矩阵分解和协同过滤方法。大规模研究显示,与基线相比,祖代约束与实际性能的相关性最高可提高7-10个百分点。此外,LRMF有效解决冷启动问题,即使数据最少的新衍生或合并模型也能提供准确的估计。这种以祖代关系为指导的策略为现代LLM开发中用于调整超参数、数据选择和模型组合提供了一种资源高效的方式。
Key Takeaways
- LLM性能预测能减少计算成本与开发时间。
- 现有方法忽略LLM的祖代关系。
- LRMF框架通过图拉普拉斯正则化器编码LLM的祖代关系。
- LRMF在性能预测方面表现优于传统方法。
- 祖代约束与实际性能的相关性高于基线。
- LRMF能解决冷启动问题,对新兴模型提供准确估计。
点此查看论文截图

Transformer-Empowered Actor-Critic Reinforcement Learning for Sequence-Aware Service Function Chain Partitioning
Authors:Cyril Shih-Huan Hsu, Anestis Dalgkitsis, Chrysa Papagianni, Paola Grosso
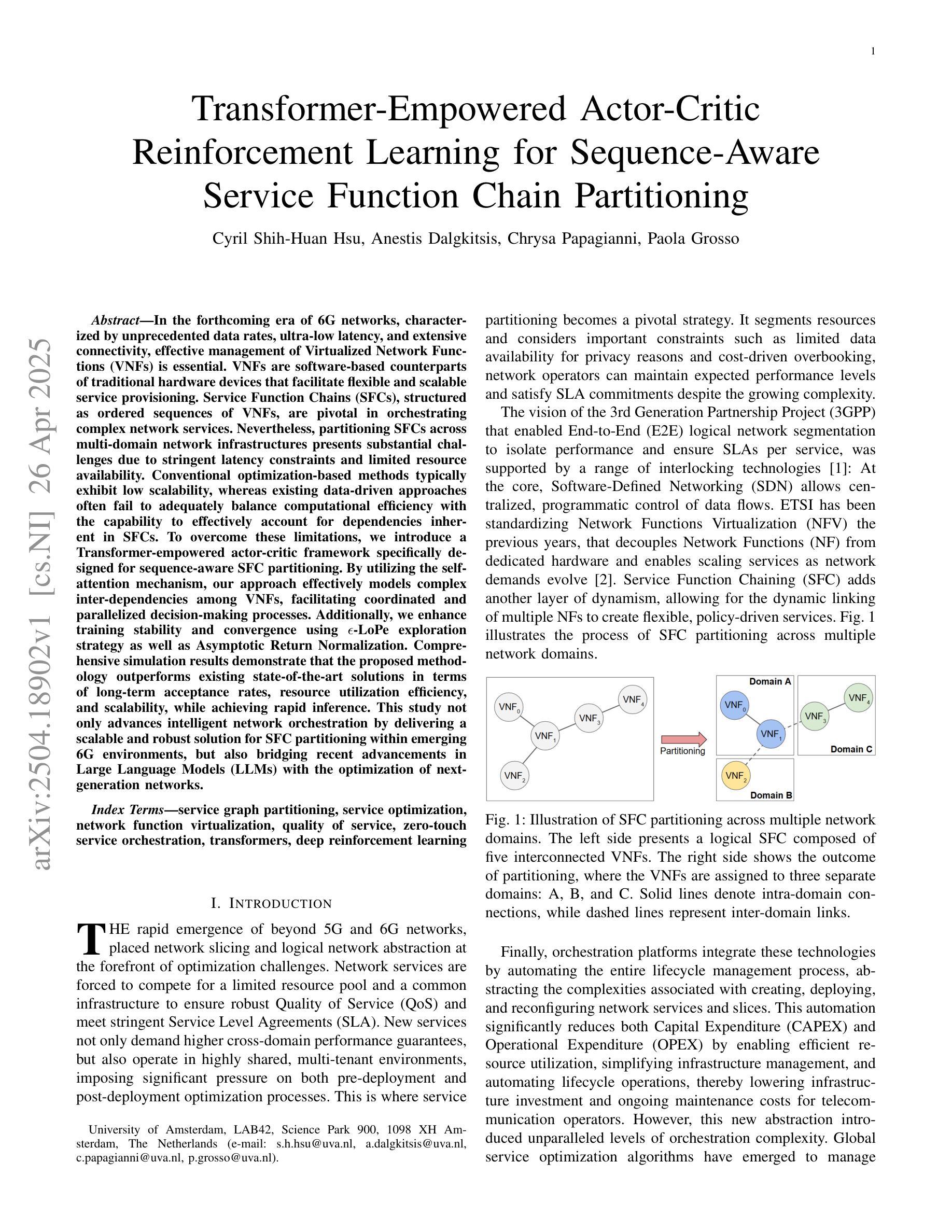
In the forthcoming era of 6G networks, characterized by unprecedented data rates, ultra-low latency, and extensive connectivity, effective management of Virtualized Network Functions (VNFs) is essential. VNFs are software-based counterparts of traditional hardware devices that facilitate flexible and scalable service provisioning. Service Function Chains (SFCs), structured as ordered sequences of VNFs, are pivotal in orchestrating complex network services. Nevertheless, partitioning SFCs across multi-domain network infrastructures presents substantial challenges due to stringent latency constraints and limited resource availability. Conventional optimization-based methods typically exhibit low scalability, whereas existing data-driven approaches often fail to adequately balance computational efficiency with the capability to effectively account for dependencies inherent in SFCs. To overcome these limitations, we introduce a Transformer-empowered actor-critic framework specifically designed for sequence-aware SFC partitioning. By utilizing the self-attention mechanism, our approach effectively models complex inter-dependencies among VNFs, facilitating coordinated and parallelized decision-making processes. Additionally, we enhance training stability and convergence using $\epsilon$-LoPe exploration strategy as well as Asymptotic Return Normalization. Comprehensive simulation results demonstrate that the proposed methodology outperforms existing state-of-the-art solutions in terms of long-term acceptance rates, resource utilization efficiency, and scalability, while achieving rapid inference. This study not only advances intelligent network orchestration by delivering a scalable and robust solution for SFC partitioning within emerging 6G environments, but also bridging recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) with the optimization of next-generation networks.
在即将到来的6G网络时代,以其前所未有的数据速率、超低延迟和广泛连接为特点,对虚拟化网络功能(VNFs)的有效管理至关重要。VNFs是传统硬件设备的软件对应物,有助于灵活和可扩展的服务提供。作为VNFs有序序列的服务功能链(SFCs)在协调复杂网络服务方面至关重要。然而,在多域网络基础设施中划分SFCs面临着严峻的挑战,因为存在严格的延迟约束和资源可用性有限。传统的优化方法通常可扩展性较低,而现有的数据驱动方法往往不能很好地平衡计算效率和服务功能链固有依赖性的考虑能力。为了克服这些限制,我们引入了一种由Transformer赋能的行为批判框架,该框架专为序列感知SFC划分而设计。通过利用自注意力机制,我们的方法有效地建模了VNF之间的复杂相互依赖性,促进了协调和并行化的决策过程。此外,我们还使用ε-LoPe探索策略和渐近返回归一化增强了训练的稳定性和收敛性。综合仿真结果表明,所提出的方法在长期接受率、资源利用效率和可扩展性方面优于现有最先进的解决方案,同时实现了快速推理。本研究不仅通过为新兴6G环境中的SFC划分提供可伸缩和稳健的解决方案来推动智能网络编排的发展,而且还弥合了大型语言模型(LLM)的最新进展与下一代网络的优化之间的鸿沟。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
在即将到来的6G网络时代,以其前所未有的数据速率、超低延迟和广泛连接性为特征,对虚拟化网络功能(VNFs)的有效管理至关重要。VNFs作为传统硬件设备的软件对应物,促进了灵活和可伸缩的服务提供。服务函数链(SFCs)作为VNFs的有序序列结构,对于协调复杂网络服务至关重要。然而,在跨多域网络基础设施的SFC分区面临着严峻的延迟约束和有限的资源可用性挑战。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了基于Transformer的actor-critic框架,专为序列感知SFC分区设计。通过利用自注意力机制,我们的方法有效地建模了VNF之间的复杂相互依赖性,促进了协调和并行化的决策过程。此外,我们还使用ε-LoPe探索策略和渐近回报归一化增强了训练稳定性和收敛性。综合仿真结果表明,所提出的方法在长期接受率、资源利用效率和可扩展性方面优于现有最先进的解决方案,同时实现了快速推理。本研究不仅通过为新兴6G环境中的SFC分区提供可扩展和稳健的解决方案来推动智能网络编排的进展,而且还弥合了大型语言模型(LLM)的最新进展与下一代网络的优化。
关键见解
- 6G网络时代需要有效管理虚拟化网络功能(VNFs),以促进灵活和可伸缩的服务提供。
- 服务函数链(SFCs)在协调复杂网络服务中起到关键作用,但在多域网络基础设施中的分区面临挑战。
- 现有方法在处理SFC分区时存在局限性,如低可扩展性或缺乏计算效率和内在依赖性的平衡。
- 引入基于Transformer的actor-critic框架,通过自注意力机制有效建模VNF间的复杂依赖性。
- 使用ε-LoPe探索策略和渐近回报归一化增强了训练稳定性和收敛性。
- 综合仿真结果表明,所提出方法在长期接受率、资源利用效率和可扩展性方面优于现有方法。
- 研究不仅推动了智能网络编排的进展,还将大型语言模型(LLM)与下一代网络优化相结合。
点此查看论文截图
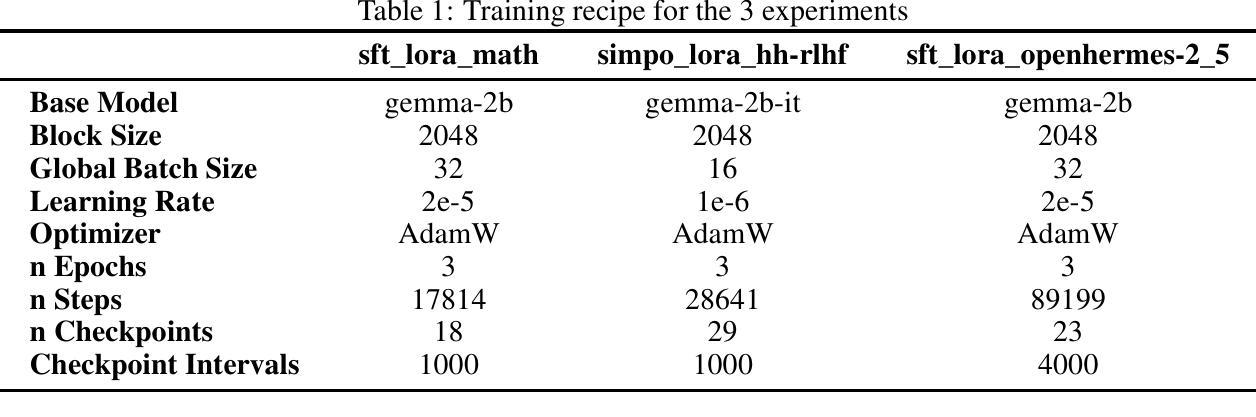
Parameter-Efficient Checkpoint Merging via Metrics-Weighted Averaging
Authors:Shi Jie Yu, Sehyun Choi
Checkpoint merging is a technique for combining multiple model snapshots into a single superior model, potentially reducing training time for large language models. This paper explores checkpoint merging in the context of parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT), where only small adapter modules (e.g. LoRA) are trained. We propose Metrics-Weighted Averaging (MWA), a simple yet effective method to merge model checkpoints by weighting their parameters according to performance metrics. In particular, we investigate weighting by training loss and by training steps, under the intuition that lower-loss or later-step checkpoints are more valuable. We introduce a formula with a penalty factor to adjust weight distribution, requiring only one hyperparameter regardless of the number of checkpoints. Experiments on three fine-tuning tasks (mathematical reasoning, preference alignment, and general instruction tuning) show that MWA consistently produces merged models that outperform the naive uniform average of checkpoints. Notably, loss-weighted merging often yields the best results, delivering up to 5% higher task accuracy than the baseline uniform merge and even surpassing the final individual checkpoint’s performance. These findings validate checkpoint merging for PEFT and demonstrate that a metric-driven weighting heuristic can efficiently boost model performance with minimal computational overhead.
模型检查点合并是一种将多个模型快照合并为一个更高级模型的技术,可潜在地减少大型语言模型的训练时间。本文针对参数有效微调(PEFT)的上下文中的检查点合并进行了探讨,其中只训练了小型的适配模块(例如LoRA)。我们提出了Metric Weighted Averaging(MWA),这是一种简单有效的方法,通过根据性能指标对模型检查点的参数进行加权来实现合并。特别是,我们根据训练损失和训练步骤进行加权,直觉上认为损失较低或步骤较后的检查点更有价值。我们引入了一个带有惩罚因子的公式来调整权重分布,无论检查点的数量如何,只需一个超参数。在三个微调任务(数学推理、偏好对齐和通用指令调整)上的实验表明,MWA持续产生优于简单平均检查点的合并模型。值得注意的是,损失加权合并通常会产生最佳结果,其任务准确性比基线均匀合并提高了高达5%,甚至超过了最终单独检查点的性能。这些发现验证了检查点合并对于PEFT的有效性,并表明度量驱动的加权启发式方法可以高效地提高模型性能,且计算开销最小。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了参数高效微调(PEFT)中的检查点合并技术。文章提出了一种名为Metrics-Weighted Averaging(MWA)的方法,通过性能指标的权重参数合并模型检查点。实验结果表明,MWA在三种微调任务中均表现优秀,产生合并模型的表现超过了检查点的简单平均。损失加权合并常常取得最佳结果,可有效提升模型性能,同时降低计算开销。
Key Takeaways
- 检查点合并技术结合了多个模型快照到一个优质模型,可缩短大型语言模型的训练时间。
- 文章提出Metrics-Weighted Averaging(MWA)方法用于检查点合并,该方法通过性能指标加权参数。
- MWA方法考虑了训练损失和训练步骤作为权重依据,认为低损失或后期步骤的检查点更有价值。
- 通过实验验证了MWA在三种微调任务中的表现,合并模型表现超过检查点的简单平均。
- 损失加权合并方式表现最佳,能提升任务准确性高达5%,甚至超越最终个体检查点的性能。
- 该方法只需一个超参数,可适应不同数量的检查点。
点此查看论文截图

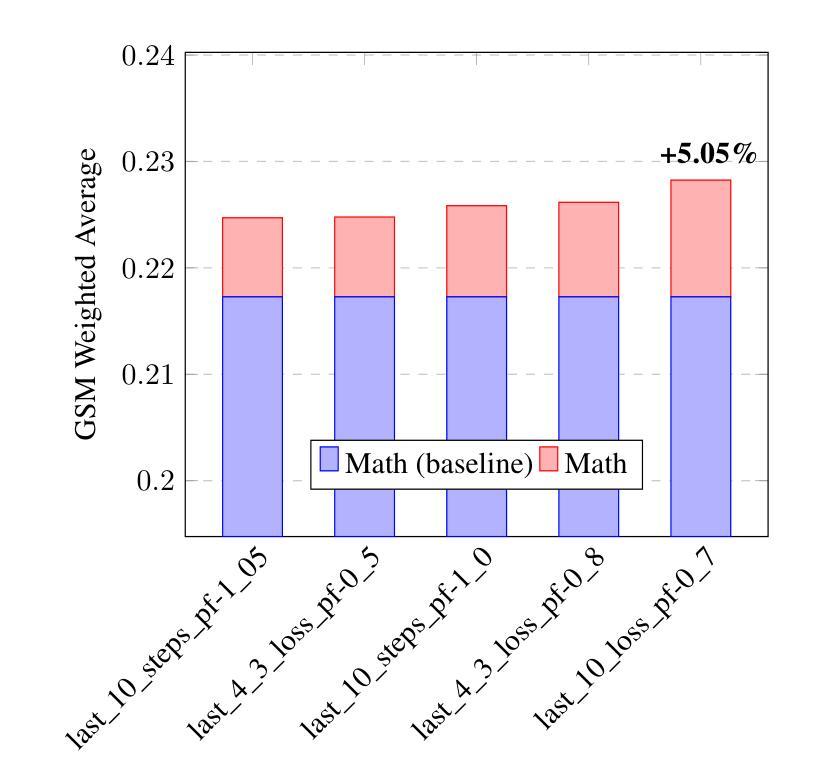
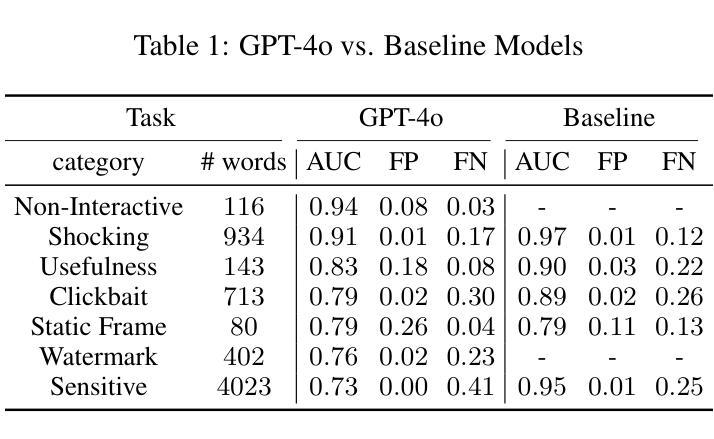
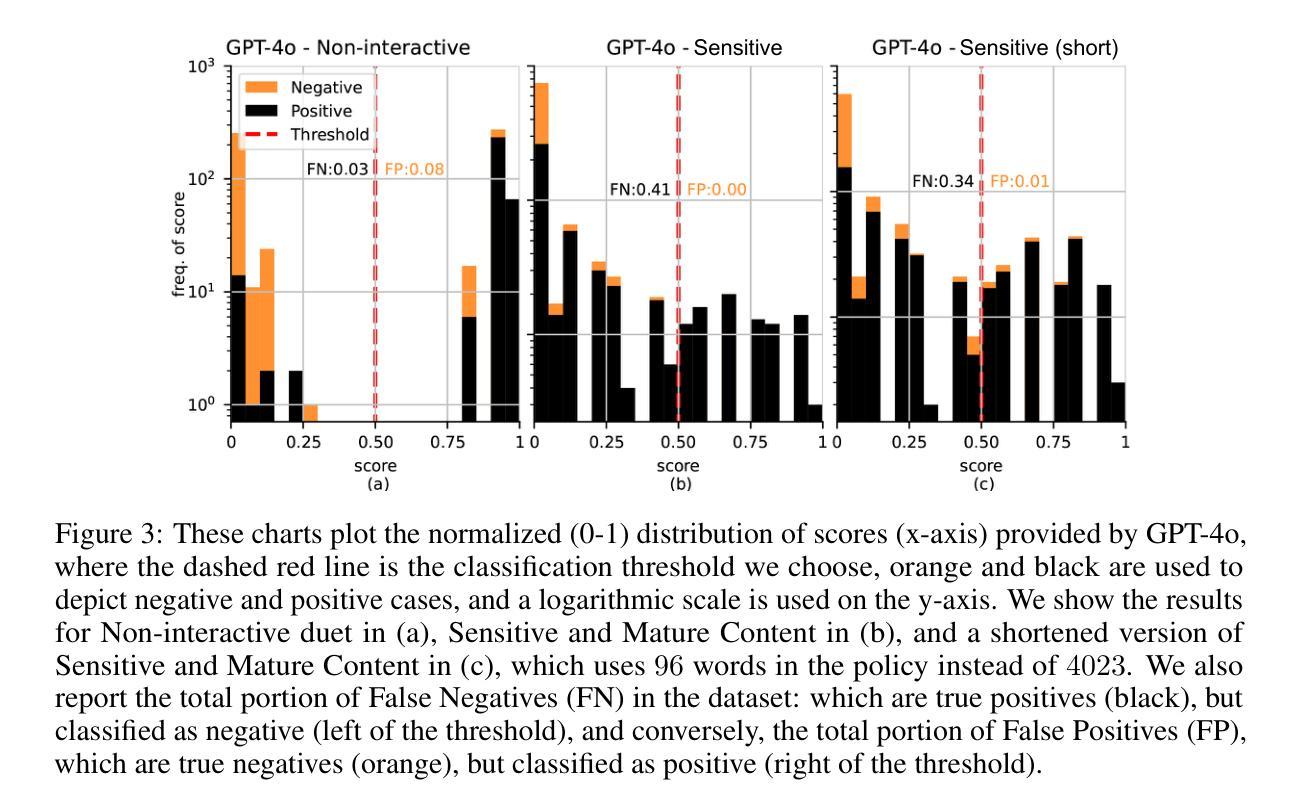
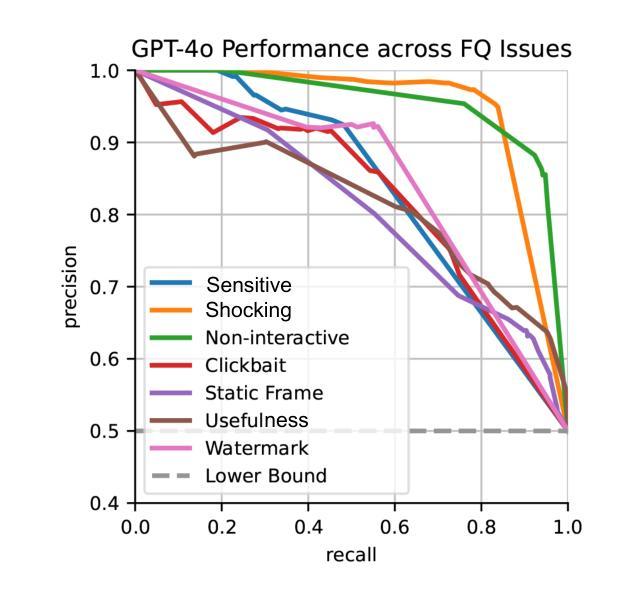
Optimizing GPT for Video Understanding: Zero-Shot Performance and Prompt Engineering
Authors:Mark Beliaev, Victor Yang, Madhura Raju, Jiachen Sun, Xinghai Hu
In this study, we tackle industry challenges in video content classification by exploring and optimizing GPT-based models for zero-shot classification across seven critical categories of video quality. We contribute a novel approach to improving GPT’s performance through prompt optimization and policy refinement, demonstrating that simplifying complex policies significantly reduces false negatives. Additionally, we introduce a new decomposition-aggregation-based prompt engineering technique, which outperforms traditional single-prompt methods. These experiments, conducted on real industry problems, show that thoughtful prompt design can substantially enhance GPT’s performance without additional finetuning, offering an effective and scalable solution for improving video classification.
在本次研究中,我们针对视频内容分类行业的挑战,探索并优化了基于GPT的零样本分类模型,覆盖了七大关键视频质量类别。我们通过优化提示和细化策略,提出了一种提高GPT性能的新方法,证明简化复杂策略能够显著降低误报阴性结果。此外,我们还引入了一种基于分解聚合的提示工程技术,该方法优于传统单一提示方法。这些针对真实行业问题进行的实验表明,精心的提示设计可以在不进行额外微调的情况下显著提高GPT的性能,为改进视频分类提供了一种有效且可扩展的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages
Summary
本研究针对视频内容分类行业的挑战,通过探索和优化基于GPT的模型,实现零样本分类在七个关键视频质量类别中的应用。研究通过优化提示和精炼策略,提高了GPT的性能,证明了简化复杂策略能显著降低误报。同时,引入基于分解聚合的提示工程技术,优于传统单一提示方法。在真实行业问题上的实验表明,巧妙的提示设计可以在无需额外微调的情况下,显著提高GPT的性能,为改进视频分类提供了有效且可扩展的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 研究探索和优化了基于GPT的模型在视频内容分类方面的应用,涵盖七个关键视频质量类别。
- 通过优化提示和精炼策略,提高了GPT模型的性能。
- 简化复杂策略能显著降低误报。
- 引入基于分解聚合的提示工程技术,该方法在视频分类中表现出优异性能。
- 巧妙的提示设计可以提高GPT模型的性能,无需额外的微调。
- 研究成果为改进视频分类提供了有效且可扩展的解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

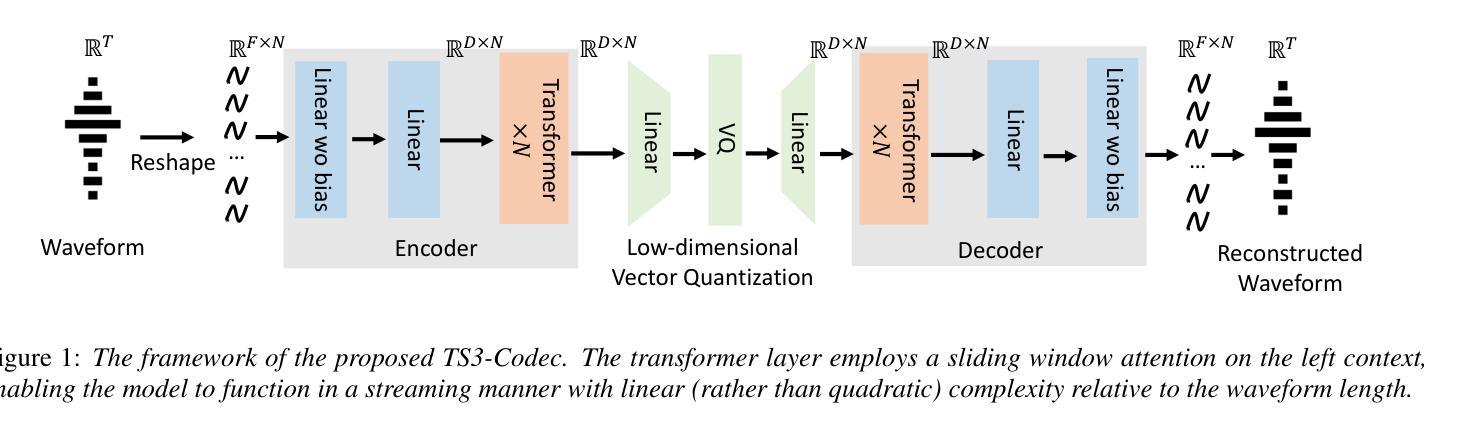
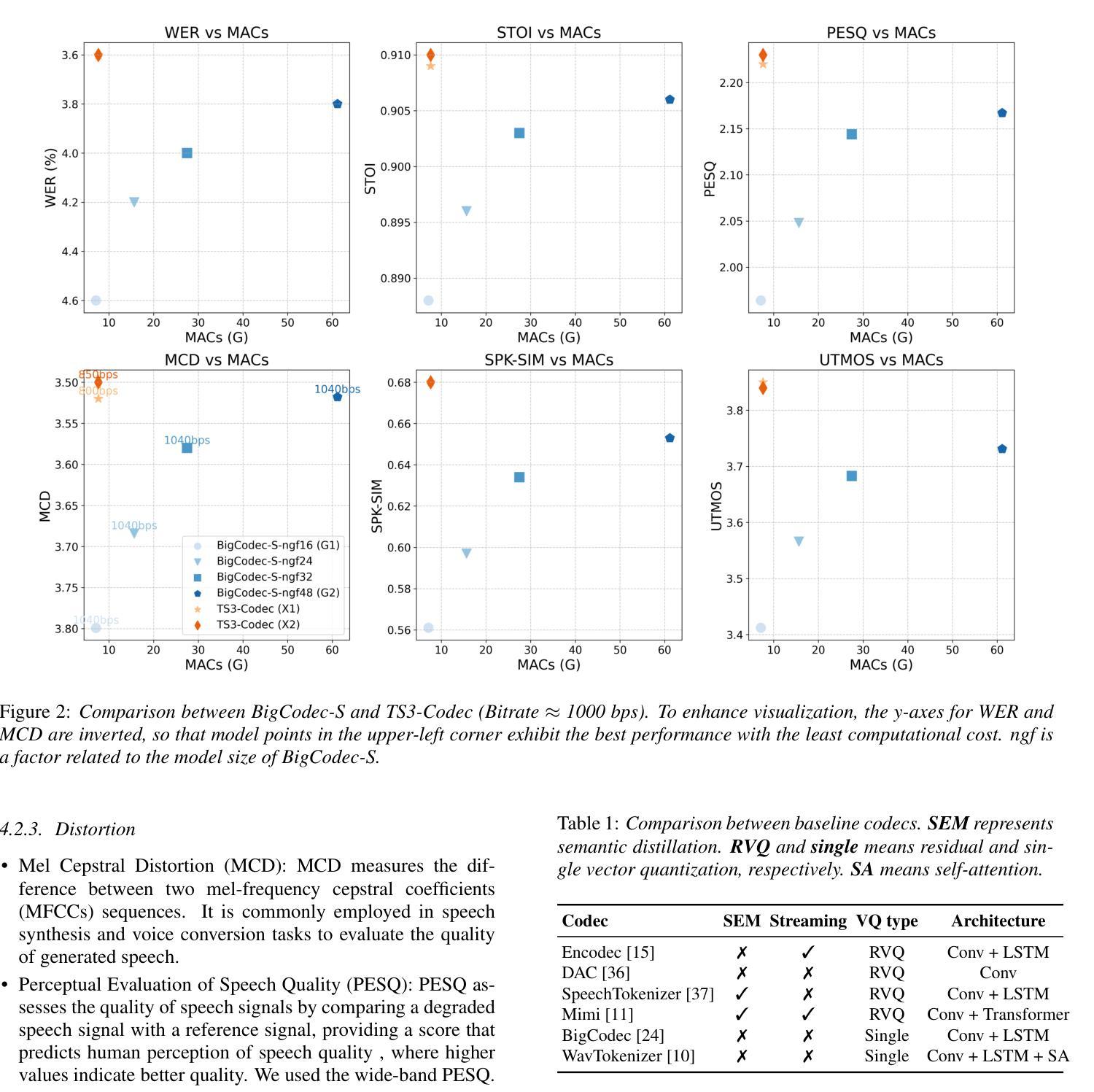
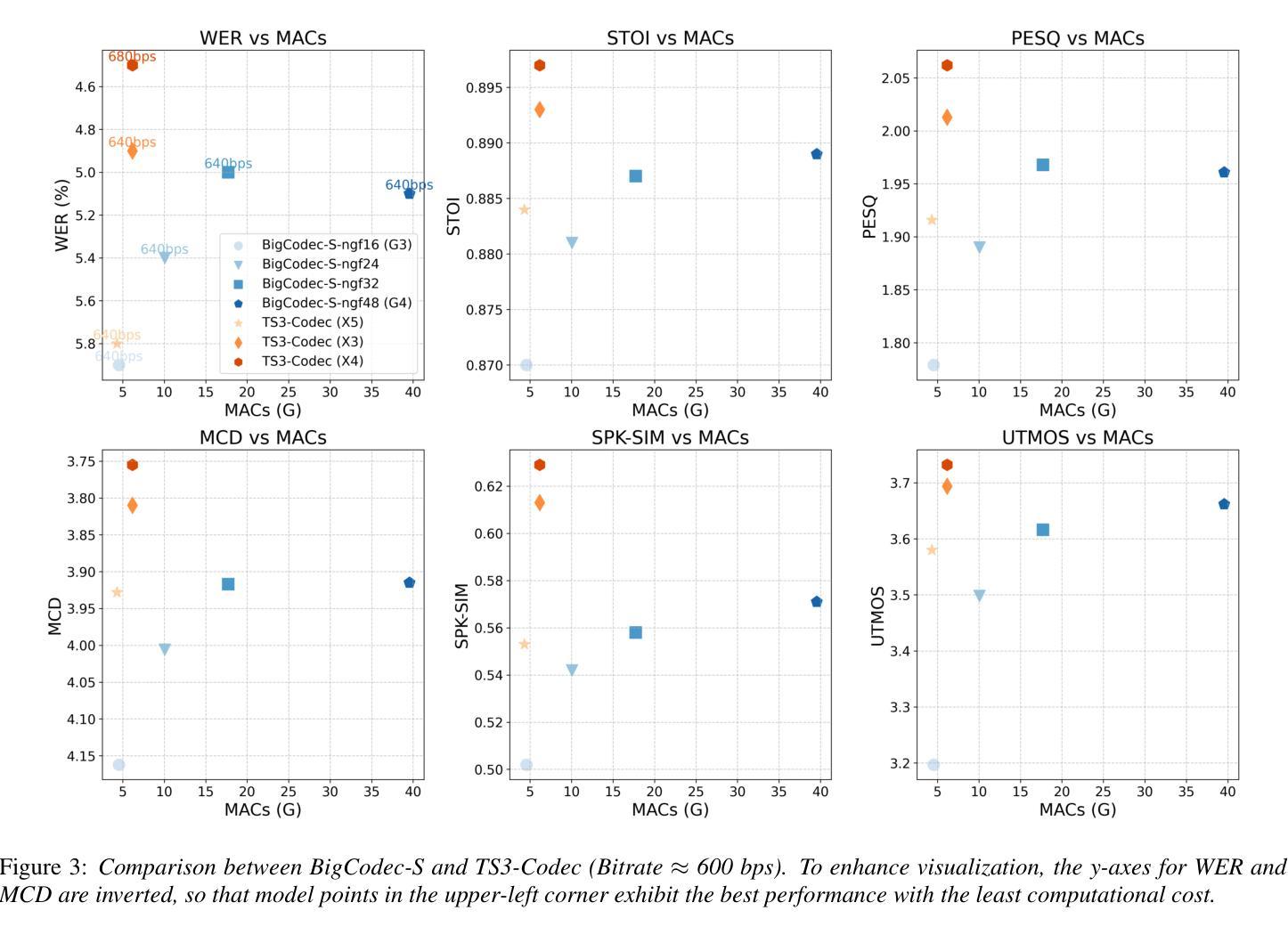
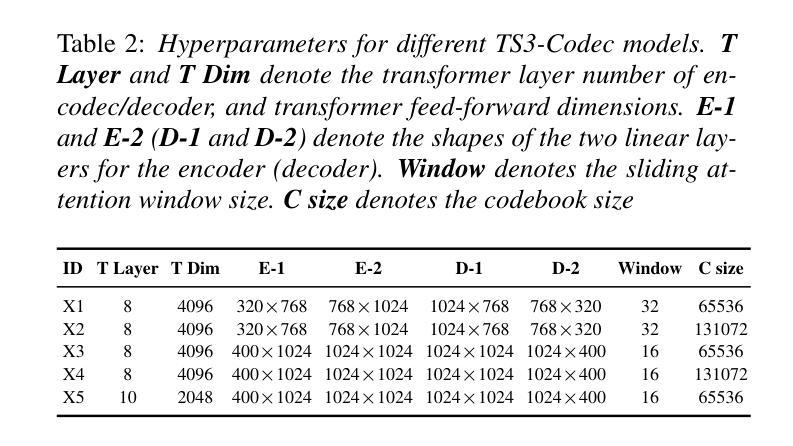
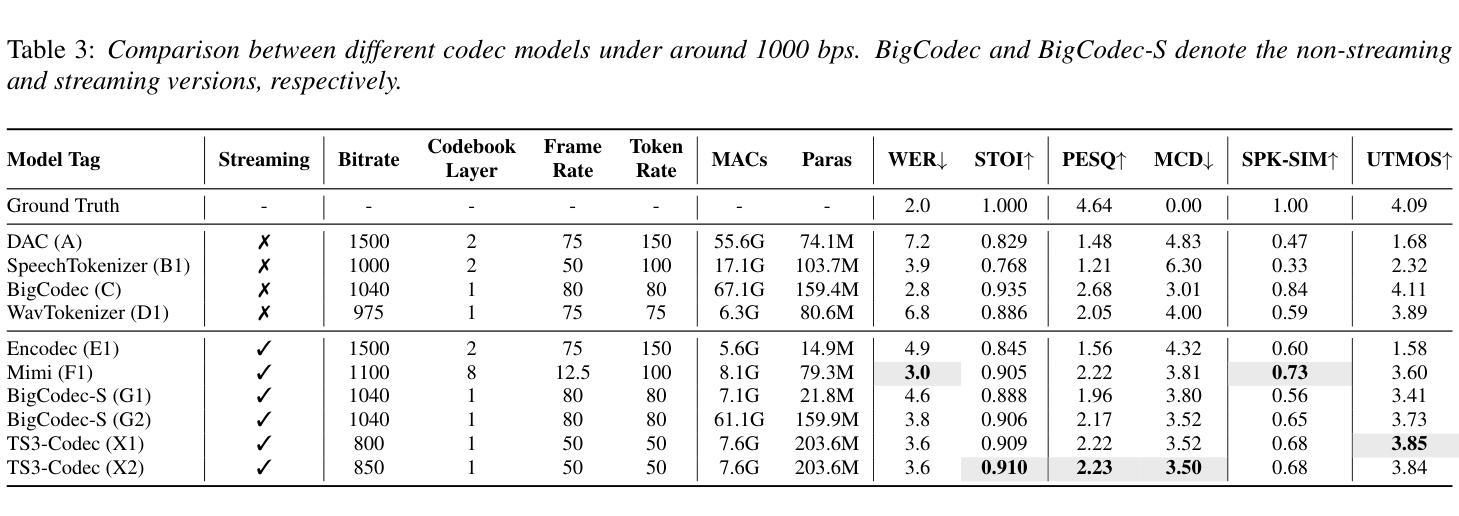
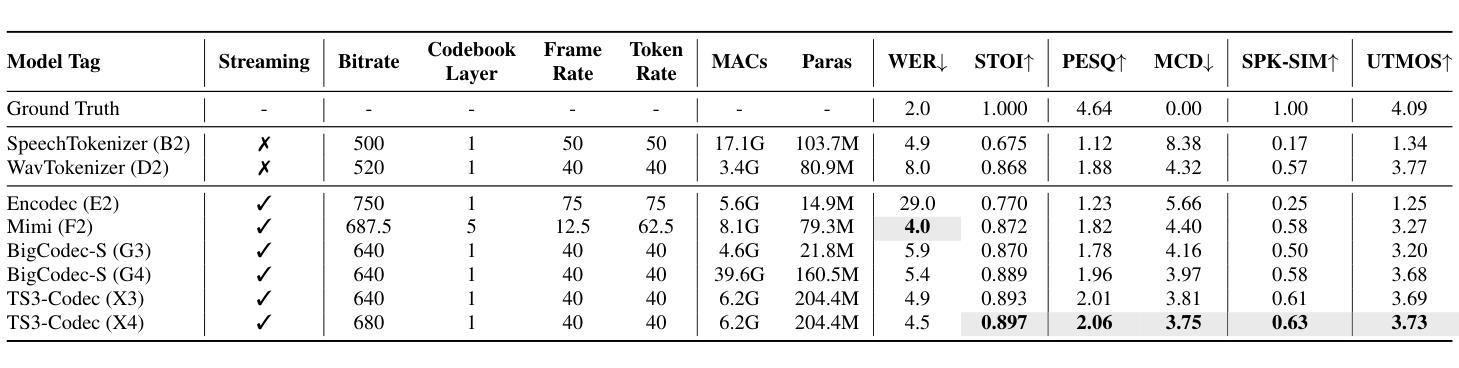
TS3-Codec: Transformer-Based Simple Streaming Single Codec
Authors:Haibin Wu, Naoyuki Kanda, Sefik Emre Eskimez, Jinyu Li
Neural audio codecs (NACs) have garnered significant attention as key technologies for audio compression as well as audio representation for speech language models. While mainstream NAC models are predominantly convolution-based, the performance of NACs with a purely transformer-based, and convolution-free architecture remains unexplored. This paper introduces TS3-Codec, a Transformer-Based Simple Streaming Single Codec. TS3-Codec consists of only a stack of transformer layers with a few linear layers, offering greater simplicity and expressiveness by fully eliminating convolution layers that require careful hyperparameter tuning and large computations. Under the streaming setup, the proposed TS3-Codec achieves comparable or superior performance compared to the codec with state-of-the-art convolution-based architecture while requiring only 12% of the computation and 77% of bitrate. Furthermore, it significantly outperforms the convolution-based codec when using similar computational resources.
神经音频编码(NAC)作为音频压缩和语音语言模型音频表示的关键技术,已经引起了广泛关注。虽然主流的NAC模型主要是基于卷积的,但完全基于转换器且没有卷积架构的NAC的性能仍然未被探索。本文介绍了TS3-Codec,一种基于转换器的简单流式单编码解码器。TS3-Codec仅由一些转换器层和一些线性层组成,通过完全消除需要精心调整超参数和大量计算的卷积层,提供更高的简洁性和表现力。在流式设置下,所提出的TS* Codec与基于最新卷积架构的编码解码器相比,性能相当或更优,同时仅需要计算量的12%和比特率的77%。此外,在利用类似的计算资源时,它大大优于基于卷积的编码解码器。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
神经网络音频编解码器(NAC)是音频压缩和语音语言模型音频表示的关键技术。当前主流NAC模型主要基于卷积,但对纯粹基于变压器且无卷积层的NAC性能尚未探索。本文介绍了一种基于变压器的简单流式单编解码器TS3-Codec,它由一堆变压器层和一些线性层组成,通过完全消除需要精心超参数调整和大量计算的卷积层,提供更高的简洁性和表现力。在流式设置下,TS3编解码器与基于最新卷积技术的编解码器相比,实现了相当或更优越的性能,同时仅需要12%的计算和77%的比特率。在类似的计算资源下,它显著优于基于卷积的编解码器。
Key Takeaways
- 神经网络音频编解码器(NAC)是音频压缩和语音语言模型的重要技术。
- 当前主流NAC模型以卷积为基础,但纯变压器架构的性能尚未被探索。
- TS3编解码器是一种基于变压器的简单流式单编解码器,不包含卷积层。
- TS3编解码器具有更高的简洁性和表现力,因为它完全消除了需要精心超参数调整和大量计算的卷积层。
- 在流式环境下,TS3编解码器的性能与最先进的卷积编解码器相当或更好,同时计算需求和比特率大幅降低。
- TS3编解码器在利用类似计算资源时,显著优于基于卷积的编解码器。
点此查看论文截图

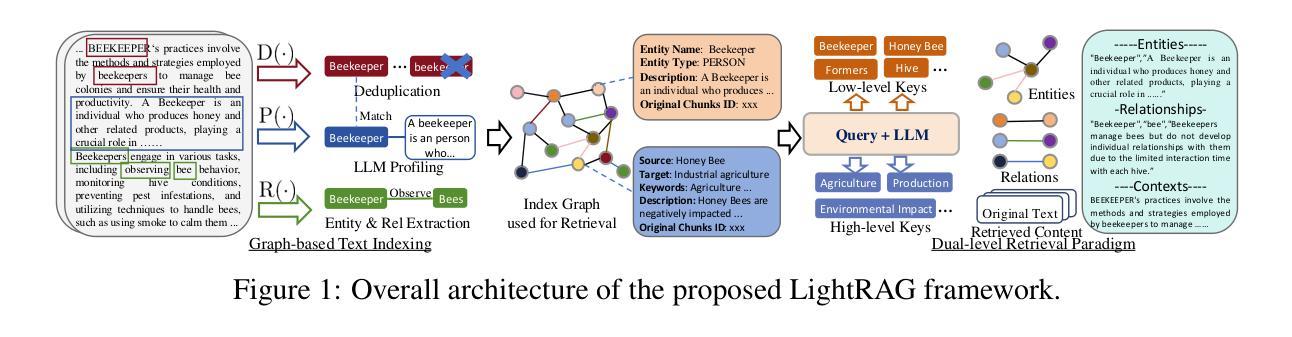
LightRAG: Simple and Fast Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Authors:Zirui Guo, Lianghao Xia, Yanhua Yu, Tu Ao, Chao Huang
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems enhance large language models (LLMs) by integrating external knowledge sources, enabling more accurate and contextually relevant responses tailored to user needs. However, existing RAG systems have significant limitations, including reliance on flat data representations and inadequate contextual awareness, which can lead to fragmented answers that fail to capture complex inter-dependencies. To address these challenges, we propose LightRAG, which incorporates graph structures into text indexing and retrieval processes. This innovative framework employs a dual-level retrieval system that enhances comprehensive information retrieval from both low-level and high-level knowledge discovery. Additionally, the integration of graph structures with vector representations facilitates efficient retrieval of related entities and their relationships, significantly improving response times while maintaining contextual relevance. This capability is further enhanced by an incremental update algorithm that ensures the timely integration of new data, allowing the system to remain effective and responsive in rapidly changing data environments. Extensive experimental validation demonstrates considerable improvements in retrieval accuracy and efficiency compared to existing approaches. We have made our LightRAG open-source and available at the link: https://github.com/HKUDS/LightRAG
检索增强生成(RAG)系统通过整合外部知识源,增强了大型语言模型(LLM)的功能,能够提供更准确、更符合上下文环境和用户需求的回答。然而,现有的RAG系统存在重大局限,包括依赖扁平的数据表示和缺乏足够的上下文意识,这可能导致答案支离破碎,无法捕捉复杂的相互依赖关系。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了LightRAG,它将图形结构融入文本索引和检索过程。这一创新框架采用双级检索系统,从低级到高级知识发现,提高了全面信息检索能力。此外,图形结构与向量表示的融合促进了相关实体及其关系的有效检索,在保持上下文相关性的同时显著提高响应时间。增量更新算法进一步增强了此功能,确保新数据能够及时整合,使系统在快速变化的数据环境中保持有效和响应能力。大量实验验证表明,与现有方法相比,检索准确性和效率均有显著提高。我们已将LightRAG开源,可在以下链接中找到:https://github.com/HKUDS/LightRAG
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
RAG系统通过整合外部知识源增强LLM的功能,但存在数据表示过于简单和缺乏上下文意识等局限性。为此,我们提出了LightRAG,它采用双层次检索系统,结合图结构进行文本索引和检索,提高从低级到高级知识的全面检索能力。通过向量表示与图结构的结合,提高了相关实体及其关系的检索效率,同时保持上下文相关性。此外,LightRAG还具有增量更新算法,可确保新数据的及时整合,并在快速变化的数据环境中保持系统的高效响应。
Key Takeaways
- RAG系统通过整合外部知识源增强LLM的性能。
- 现有RAG系统存在数据表示过于简单和缺乏上下文意识的问题。
- LightRAG采用双层次检索系统,提高从低级到高级知识的全面检索能力。
- LightRAG结合图结构进行文本索引和检索。
- 通过向量表示与图结构的结合,LightRAG提高了相关实体及其关系的检索效率。
- LightRAG具有增量更新算法,确保新数据的及时整合。
- LightRAG在快速变化的数据环境中保持高效响应,并已经开源。
点此查看论文截图

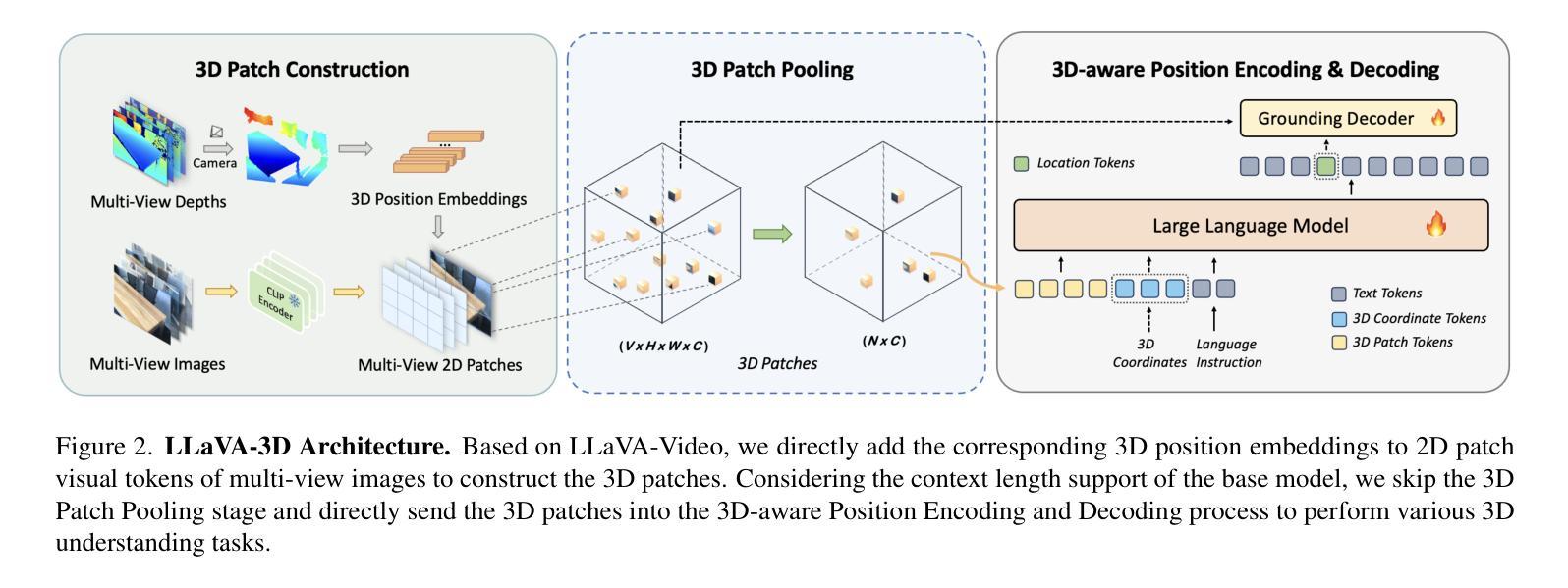
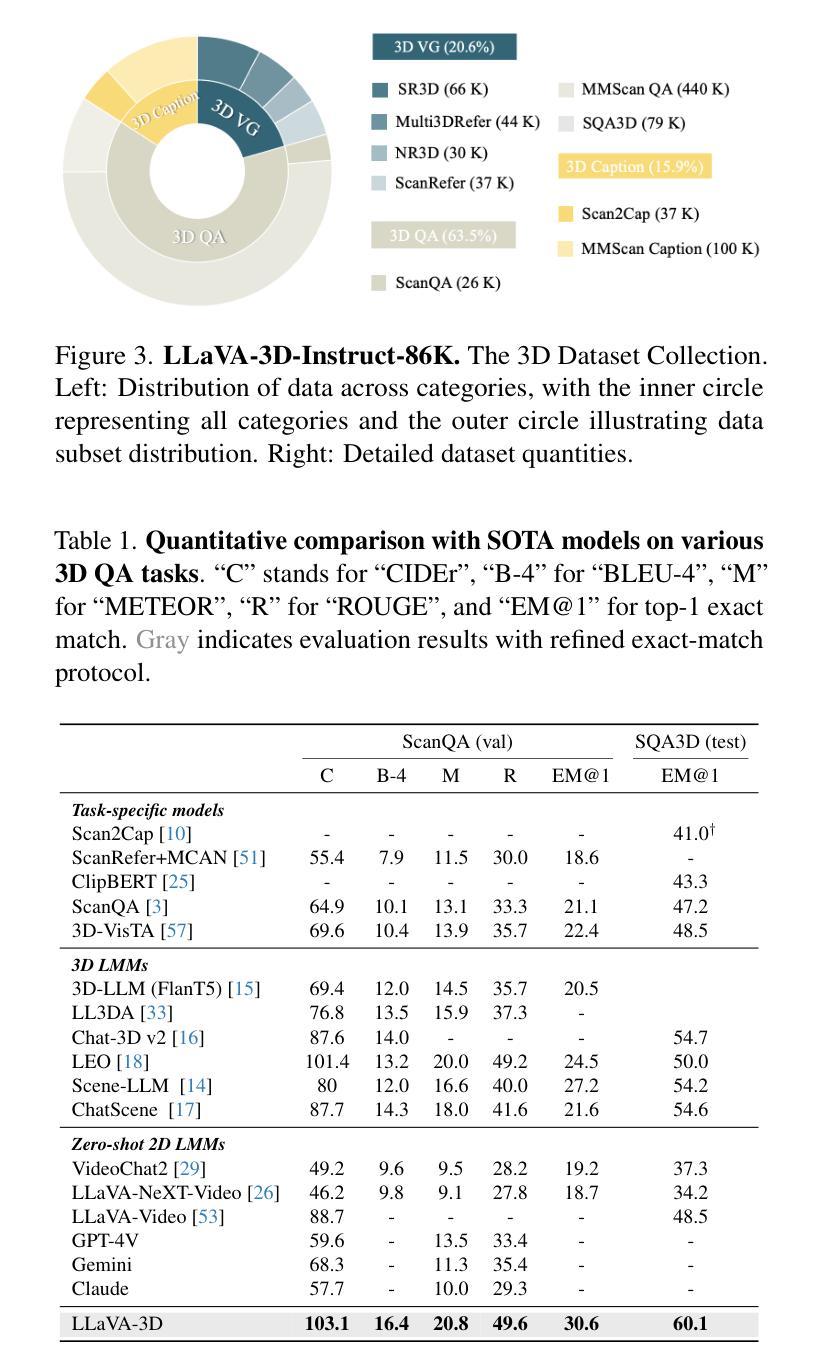
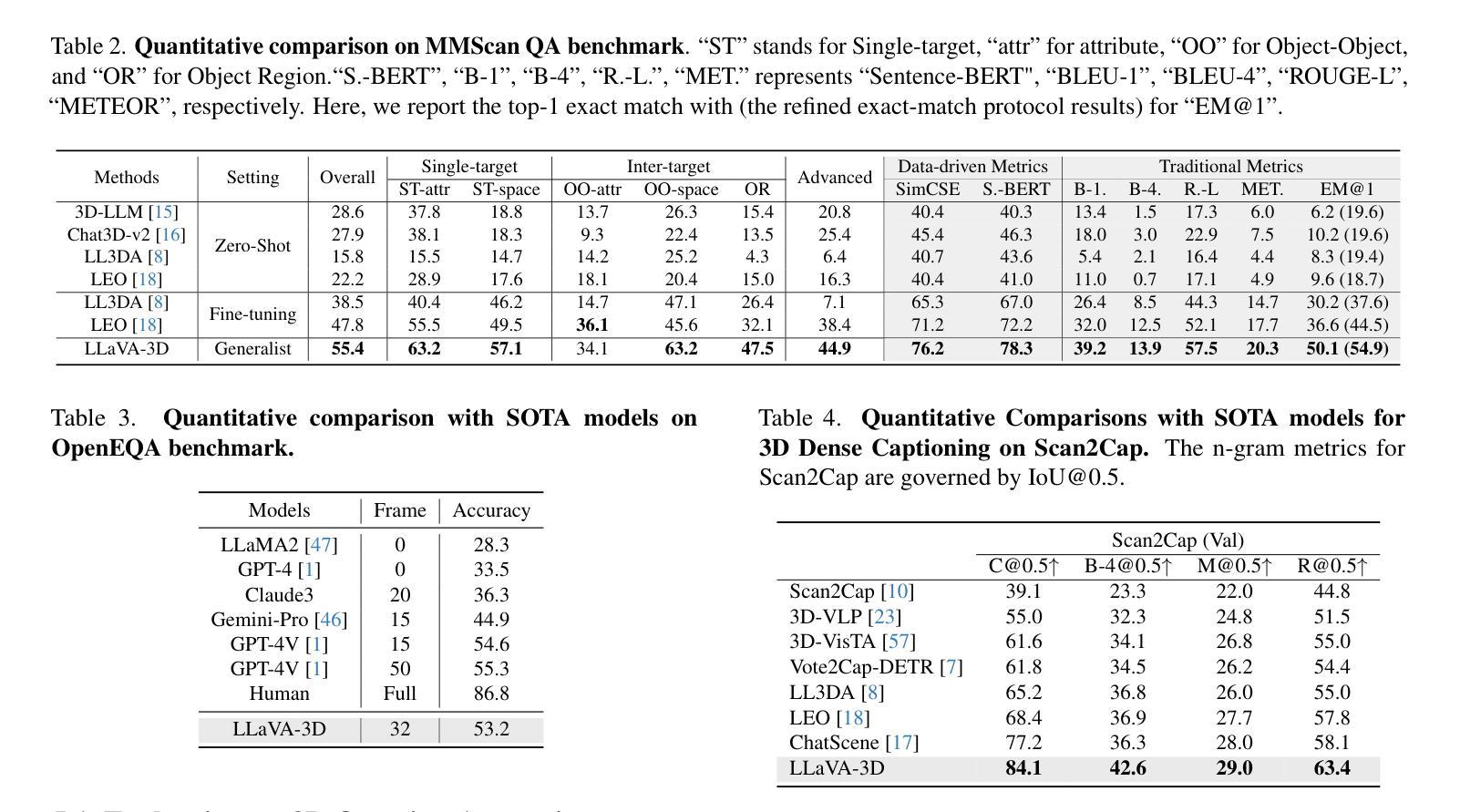
LLaVA-3D: A Simple yet Effective Pathway to Empowering LMMs with 3D-awareness
Authors:Chenming Zhu, Tai Wang, Wenwei Zhang, Jiangmiao Pang, Xihui Liu
Recent advancements in Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) have greatly enhanced their proficiency in 2D visual understanding tasks, enabling them to effectively process and understand images and videos. However, the development of LMMs with 3D scene understanding capabilities has been hindered by the lack of large-scale 3D vision-language datasets and powerful 3D encoders. In this paper, we introduce a simple yet effective framework called LLaVA-3D. Leveraging the strong 2D visual understanding priors from LLaVA, our LLaVA-3D efficiently adapts LLaVA for 3D scene understanding without compromising 2D understanding capabilities. To achieve this, we utilize the 3D position embeddings to enhance the 2D CLIP Patches with 3D spatial context information and construct 3D patches. By integrating the 3D position embeddings into 2D LMMs and employing joint 2D and 3D vision-language instruction tuning, we establish a unified architecture for both 2D visual understanding and 3D scene understanding. In contrast to previous 3D LMMs, LLaVA-3D supports decoding accurate 3D spatial perception outputs, e.g., 3D bounding boxes, directly from these 3D patches, without relying on the time-consuming off-the-shelf 3D segmentors. Experimental results show that LLaVA-3D converges 3.5x faster than existing 3D LMMs when trained on 3D vision-language datasets. Moreover, LLaVA-3D not only achieves state-of-the-art performance across various 3D tasks but also maintains comparable 2D visual understanding and vision-language conversation capabilities with LLaVA.
近期大型多模态模型(LMMs)在2D视觉理解任务上的能力得到了极大的提升,能够有效地处理和解析图像和视频。然而,由于缺少大规模3D视觉语言数据集和强大的3D编码器,具有3D场景理解能力的LMMs的发展受到了阻碍。在本文中,我们介绍了一个简单有效的框架,名为LLaVA-3D。该框架利用LLaVA强大的2D视觉理解先验知识,在不损害2D理解能力的情况下,有效地将LLaVA适应于3D场景理解。为实现这一点,我们利用3D位置嵌入来增强带有3D空间上下文信息的2D CLIP补丁,并构建3D补丁。通过将3D位置嵌入到2D LMMs中,并采用联合的2D和3D视觉语言指令微调,我们建立了统一的架构,用于2D视觉理解和3D场景理解。与之前的3D LMMs相比,LLaVA-3D支持直接从这些3D补丁中解码准确的3D空间感知输出,例如3D边界框,无需依赖耗时的现成的3D分段器。实验结果表明,在3D视觉语言数据集上进行训练时,LLaVA-3D的收敛速度比现有3D LMMs快3.5倍。此外,LLaVA-3D不仅在各种3D任务上实现了最新性能,而且与LLaVA相比,还保持了相当的2D视觉理解和视觉语言对话能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://zcmax.github.io/projects/LLaVA-3D/
Summary
基于大型多模态模型(LMMs)的近期进展,对于二维视觉理解任务的完成效果有了显著提升。然而,在开发具备三维场景理解能力方面仍受限于缺乏大规模的三维视觉语言数据集和强大的三维编码器。本研究提出了一种简单有效的框架LLaVA-3D,它利用LLaVA的二维视觉理解先验知识,在不损害二维理解能力的前提下,有效地适应三维场景理解。通过整合三维位置嵌入和构建三维补丁,实现了二维和三维视觉语言指令的联合调整,建立了一个统一的架构,既可用于二维视觉理解也可用于三维场景理解。相较于之前的三维LMMs,LLaVA-3D能够直接通过这些三维补丁解码准确的3D空间感知输出,如三维边界框,而无需依赖耗时的离线三维分割器。实验结果表明,在三维视觉语言数据集上训练时,LLaVA-3D的收敛速度是现有三维LMMs的3.5倍。同时,LLaVA-3D不仅在各种三维任务上达到了最先进的性能,而且在二维视觉理解和视觉语言对话能力方面与LLaVA保持相当。
Key Takeaways
- LMMs在二维视觉理解任务上的能力已经显著提高。
- 缺乏大规模的三维视觉语言数据集和强大的三维编码器限制了三维场景理解的发展。
- LLaVA-3D框架结合了LLaVA的二维视觉理解先验知识,并扩展到三维场景理解。
- 通过整合三维位置嵌入和构建三维补丁,实现了对二维和三维视觉信息的联合处理和理解。
- LLaVA-3D能解码准确的3D空间感知输出,如三维边界框。
- LLaVA-3D在训练时收敛速度快,且在多种三维任务上表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

What Should We Engineer in Prompts? Training Humans in Requirement-Driven LLM Use
Authors:Qianou Ma, Weirui Peng, Chenyang Yang, Hua Shen, Kenneth Koedinger, Tongshuang Wu
Prompting LLMs for complex tasks (e.g., building a trip advisor chatbot) needs humans to clearly articulate customized requirements (e.g., “start the response with a tl;dr”). However, existing prompt engineering instructions often lack focused training on requirement articulation and instead tend to emphasize increasingly automatable strategies (e.g., tricks like adding role-plays and “think step-by-step”). To address the gap, we introduce Requirement-Oriented Prompt Engineering (ROPE), a paradigm that focuses human attention on generating clear, complete requirements during prompting. We implement ROPE through an assessment and training suite that provides deliberate practice with LLM-generated feedback. In a randomized controlled experiment with 30 novices, ROPE significantly outperforms conventional prompt engineering training (20% vs. 1% gains), a gap that automatic prompt optimization cannot close. Furthermore, we demonstrate a direct correlation between the quality of input requirements and LLM outputs. Our work paves the way to empower more end-users to build complex LLM applications.
对于复杂任务(例如构建旅行顾问聊天机器人)的提示,需要人类清晰地表达定制化的需求(例如,“以tl;dr开始回复”)。然而,现有的提示工程指令往往缺乏对需求表达的针对性训练,而是倾向于强调可以逐渐自动化的策略(例如,添加角色扮演和“分步思考”等技巧)。为了弥补这一差距,我们引入了需求导向的提示工程(ROPE)范式,该范式专注于在提示时生成清晰、完整的需求。我们通过评估和培训体系来实现ROPE,该体系提供有针对性的实践,并辅以LLM生成的反馈。在为期一项随机对照实验中,有三十名新手参与,ROPE明显优于传统的提示工程训练(提高20%,相比之下传统方式仅提高1%),这种差距无法通过自动提示优化来弥补。此外,我们证明了输入需求的质量与LLM输出之间的直接相关性。我们的工作为数更多的终端用户提供构建复杂LLM应用的手段开辟了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages; TOCHI 2025
Summary
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的任务提示工程对于复杂任务至关重要。针对现有提示工程在需求表达上的不足,提出了以需求为导向的提示工程(ROPE)范式,通过评估和训练套件提供有针对性的实践,并引入LLM反馈机制。实验证明,ROPE相较于传统提示工程训练有显著优势(提升率达20%),且高质量的输入需求与LLM输出直接相关。这为更多终端用户构建复杂LLM应用铺平了道路。
Key Takeaways
- LLM在进行复杂任务(如开发旅行顾问聊天机器人)时,需要人类明确表述个性化需求。
- 现有提示工程指令往往缺乏针对需求表达的针对性训练,而过分强调可自动化策略。
- 引入ROPE(需求导向的提示工程)范式,专注于生成清晰、完整的需求。
- ROPE通过评估和训练套件实现,包括LLM反馈机制。
- 实验显示,ROPE显著优于传统提示工程训练(提升率达20%),且这一差距无法通过自动提示优化来弥补。
- 输入需求的质量与LLM输出之间存在直接关联。
点此查看论文截图


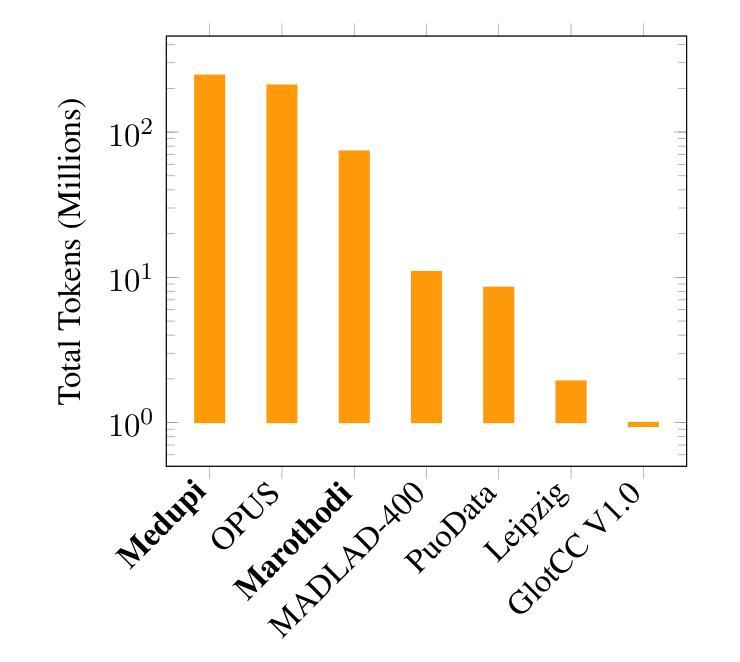
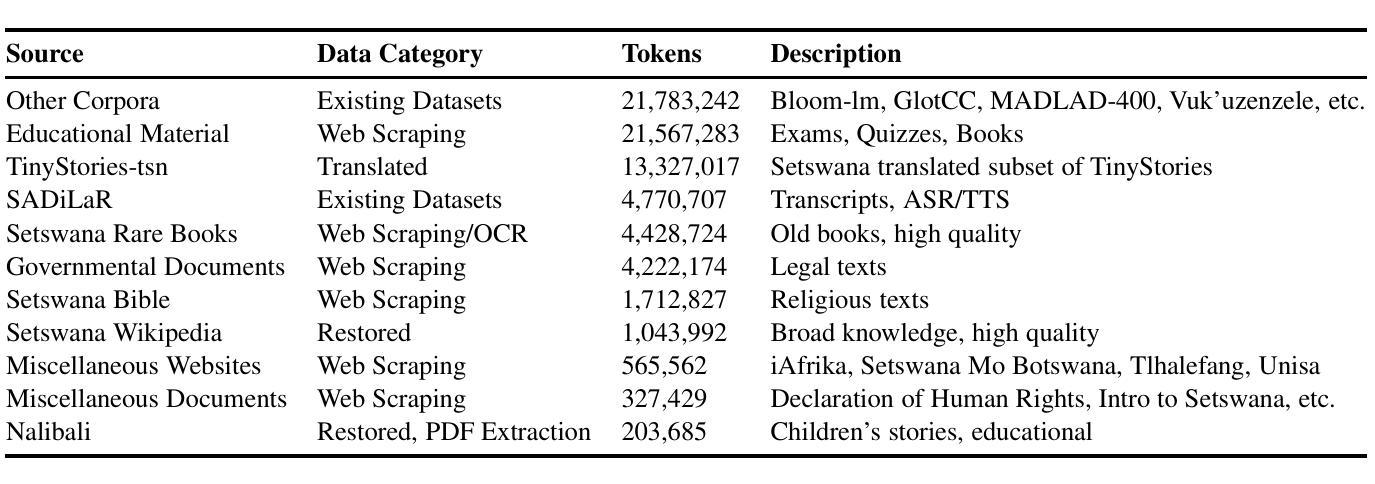
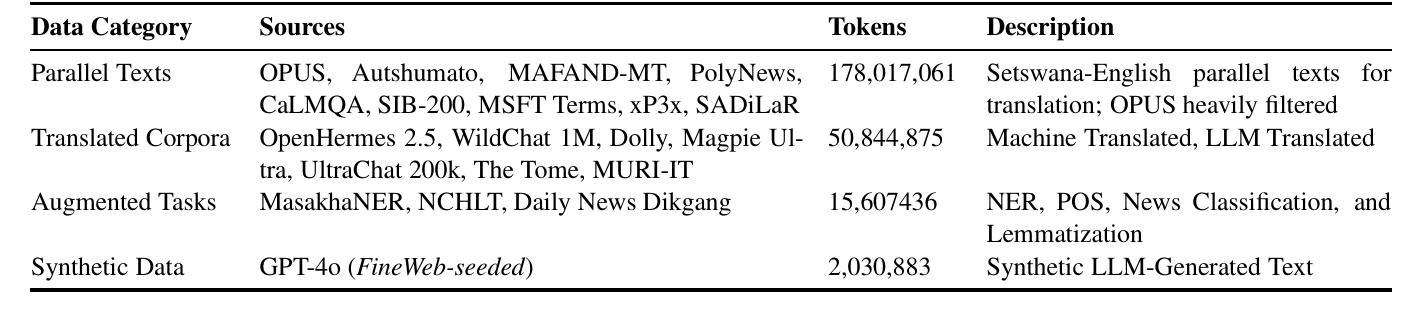
Pula: Training Large Language Models for Setswana
Authors:Nathan Brown, Vukosi Marivate
In this work we present Pula, a suite of bilingual language models proficient in both Setswana and English. Leveraging recent advancements in data availability and efficient fine-tuning, Pula 8B and Pula 14B outperform GPT-4o and Gemini 1.5 Pro on English-Setswana translation tasks and achieve state-of-the-art performance on Setswana reasoning tasks for their size. We release the weights for Pula 1B, 3B, 8B, and 14B as well as training logs and training and evaluation code. Alongside Pula, we release the largest-ever Setswana text corpus, Marothodi, and the first comprehensive Setswana instruction-tuning dataset, Medupi, consisting of reformatted datasets, translated corpora, and synthetic LLM-generated text. To accompany this data, we release the code used for dataset construction, formatting, filtering, and scraping. Last, we release two Setswana LLM-translated benchmarks, MMLU-tsn and GSM8K-tsn, to measure Setswana knowledge and reasoning capabilities.
在这项工作中,我们推出了Pula,这是一款双语语言模型套件,精通Setswana语和英语。借助最近数据可用性和高效微调方面的进步,Pula 8B和Pula 14B在英文-Setswana翻译任务上的表现超过了GPT-4o和Gemini 1.5 Pro,且在Setswana推理任务上达到了其规模的最新技术水平。我们发布了Pula 1B、3B、8B和14B的权重,以及训练日志和训练与评估代码。除Pula外,我们还发布了迄今为止最大的Setswana文本语料库Marothodi以及首个全面的Setswana指令微调数据集Medupi,该数据集包含重新格式化的数据集、翻译语料库以及合成的大型语言模型生成的文本。为配合这些数据,我们公开了用于数据集构建、格式化、过滤和抓取的代码。最后,我们发布了两个Setswana大型语言模型翻译基准测试MMLU-tsn和GSM8K-tsn,以衡量Setswana知识和推理能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NAACL 2025. 10 pages, 5 tables, 1 figure
Summary
Pula是一系列双语语言模型,能够熟练掌握英语和Setswana语。借助数据可用性和高效微调的最新进展,Pula 8B和Pula 14B在英语到Setswana的翻译任务上表现出卓越性能,并在Setswana推理任务上达到了其规模的最新水平。同时发布了Pula 1B、3B、8B和14B的权重,以及训练日志、训练和评估代码。此外,还发布了迄今为止最大的Setswana文本语料库Marothodi和首个全面的Setswana指令调整数据集Medupi,包含重新格式化的数据集、翻译语料库和合成LLM生成的文本。同时公开了用于数据集构建、格式化、过滤和抓取的代码。最后,发布了两项用于衡量Setswana知识和推理能力的基准测试MMLU-tsn和GSM8K-tsn。
Key Takeaways
- Pula是一系列双语语言模型,能够熟练掌握英语和Setswana语。
- Pula 8B和Pula 14B在英语到Setswana的翻译任务上表现出卓越性能。
- Pula模型在Setswana推理任务上达到了其规模的最新水平。
- 发布了不同规模的Pula模型权重、训练日志及训练和评估代码。
- 发布了迄今为止最大的Setswana文本语料库Marothodi。
- 发布了首个全面的Setswana指令调整数据集Medupi,包含多种来源的数据。
点此查看论文截图