⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-04-30 更新
DEEMO: De-identity Multimodal Emotion Recognition and Reasoning
Authors:Deng Li, Bohao Xing, Xin Liu, Baiqiang Xia, Bihan Wen, Heikki Kälviäinen
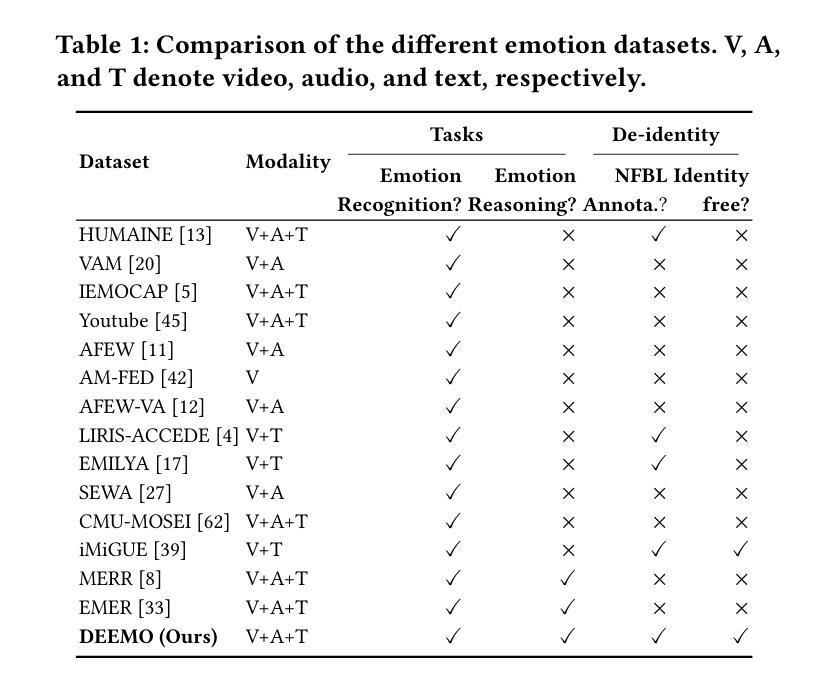
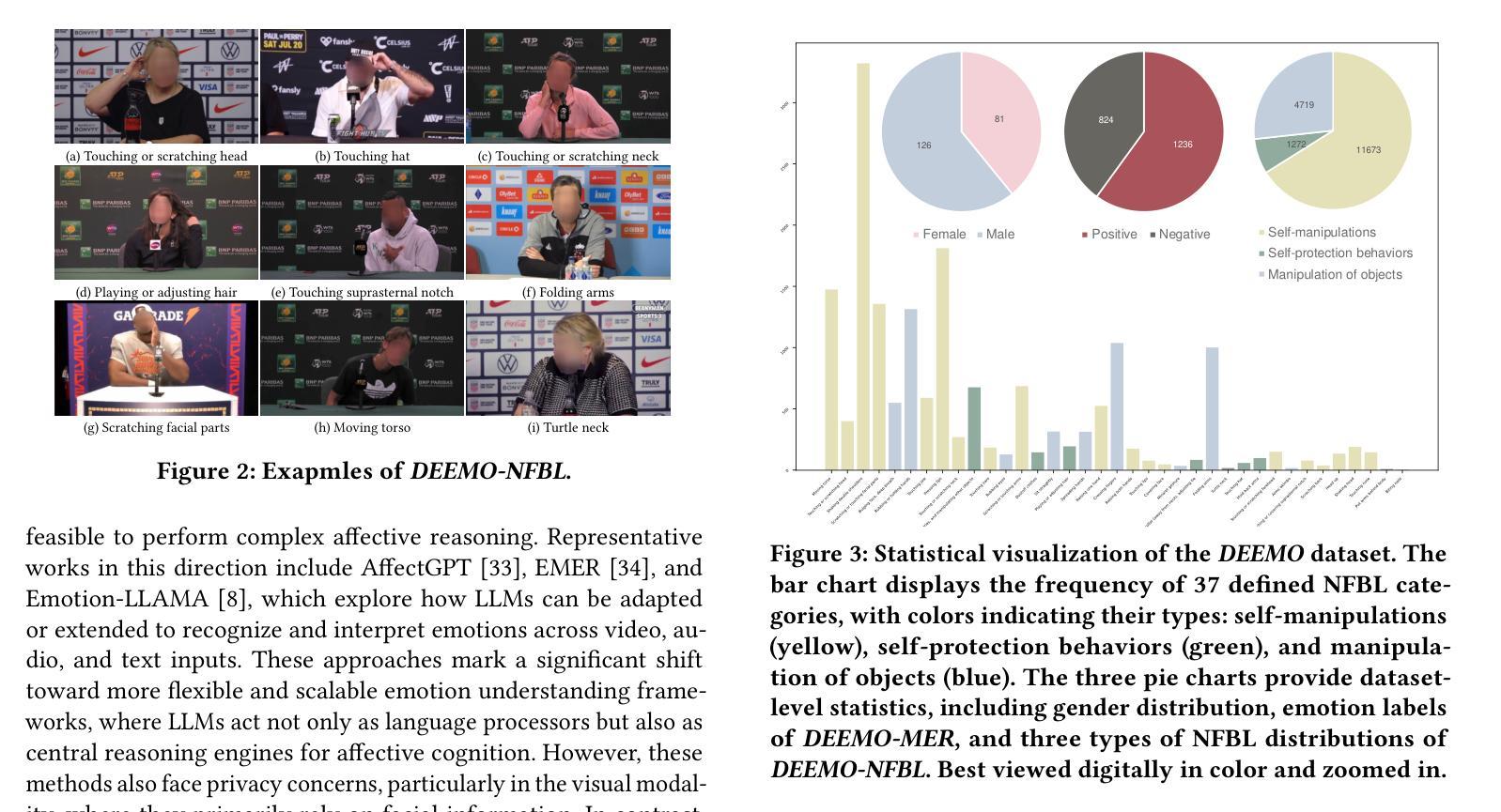
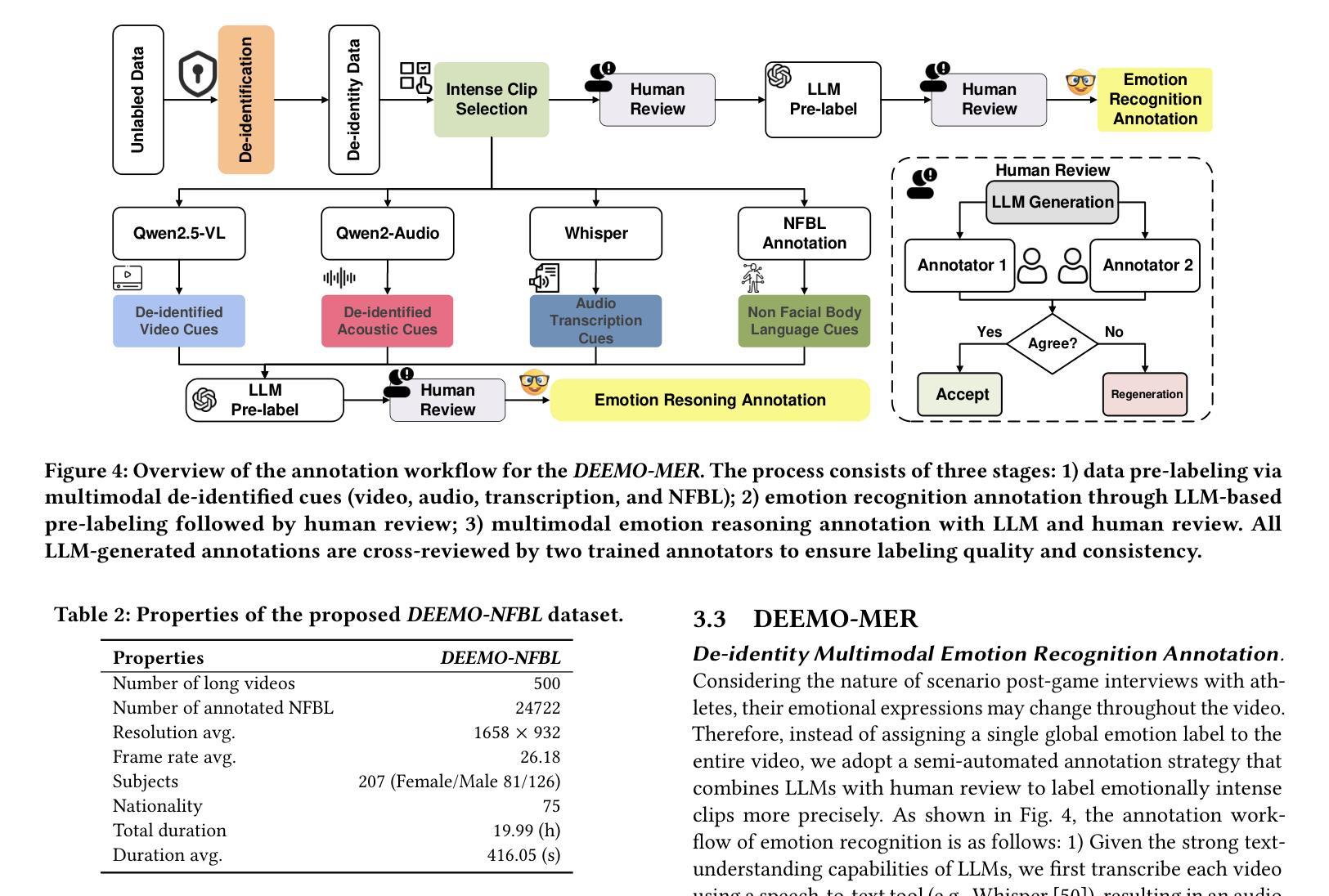
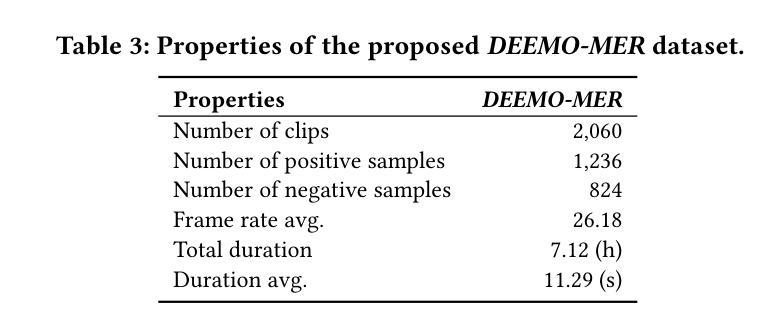
Emotion understanding is a critical yet challenging task. Most existing approaches rely heavily on identity-sensitive information, such as facial expressions and speech, which raises concerns about personal privacy. To address this, we introduce the De-identity Multimodal Emotion Recognition and Reasoning (DEEMO), a novel task designed to enable emotion understanding using de-identified video and audio inputs. The DEEMO dataset consists of two subsets: DEEMO-NFBL, which includes rich annotations of Non-Facial Body Language (NFBL), and DEEMO-MER, an instruction dataset for Multimodal Emotion Recognition and Reasoning using identity-free cues. This design supports emotion understanding without compromising identity privacy. In addition, we propose DEEMO-LLaMA, a Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) that integrates de-identified audio, video, and textual information to enhance both emotion recognition and reasoning. Extensive experiments show that DEEMO-LLaMA achieves state-of-the-art performance on both tasks, outperforming existing MLLMs by a significant margin, achieving 74.49% accuracy and 74.45% F1-score in de-identity emotion recognition, and 6.20 clue overlap and 7.66 label overlap in de-identity emotion reasoning. Our work contributes to ethical AI by advancing privacy-preserving emotion understanding and promoting responsible affective computing.
情感理解是一项至关重要且具有挑战性的任务。现有的大多数方法都严重依赖于身份敏感信息,如面部表情和语音,这引发了关于个人隐私的担忧。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了去身份化多模态情感识别和推理(DEEMO)这一新任务,旨在使用去身份化的视频和音频输入来实现情感理解。DEEMO数据集由两个子集组成:DEEMO-NFBL,包含丰富的非面部肢体语言(NFBL)注释;以及DEEMO-MER,这是一个使用无身份提示进行多模态情感识别和推理的指令数据集。这种设计可以在不损害身份隐私的情况下支持情感理解。此外,我们提出了DEEMO-LLaMA,这是一种多模态大型语言模型(MLLM),它整合了去身份化的音频、视频和文本信息,以增强情感识别和推理。大量实验表明,DEEMO-LLaMA在这两项任务上都达到了最先进的性能,显著优于现有的MLLMs,在去身份情感识别方面达到74.49%的准确率和74.45%的F1得分,在去身份情感推理方面达到6.20的线索重叠率和7.66的标签重叠率。我们的工作通过推进保护隐私的情感理解和促进负责任的情感计算,为伦理人工智能做出贡献。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该研究提出了一项新的任务——去身份多模态情感识别和推理(DEEMO),旨在使用去身份的视频和音频输入进行情感理解,以解决现有方法过于依赖身份敏感信息的问题。该数据集包含两个子集,分别关注非面部肢体语言(NFBL)和多模态情感识别和推理。此外,还提出了一种多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)以增强情感识别和推理。实验表明,该模型在去身份情感识别和推理任务上均达到最新技术水平,对推进隐私保护的情感理解和负责任的情感计算具有贡献。
Key Takeaways
- 研究引入了去身份多模态情感识别和推理任务(DEEMO),旨在解决依赖身份敏感信息的情感理解的问题。
- DEEMO数据集包含两个子集:关注非面部肢体语言的DEEMO-NFBL和用于多模态情感识别的DEEMO-MER。
- 提出了一种多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)DEEMOLLaMA,集成去身份音频、视频和文本信息,增强情感识别和推理。
- 实验显示DEEMOLLaMA在去身份情感识别和推理任务上表现优异,达到最新技术水平。
点此查看论文截图


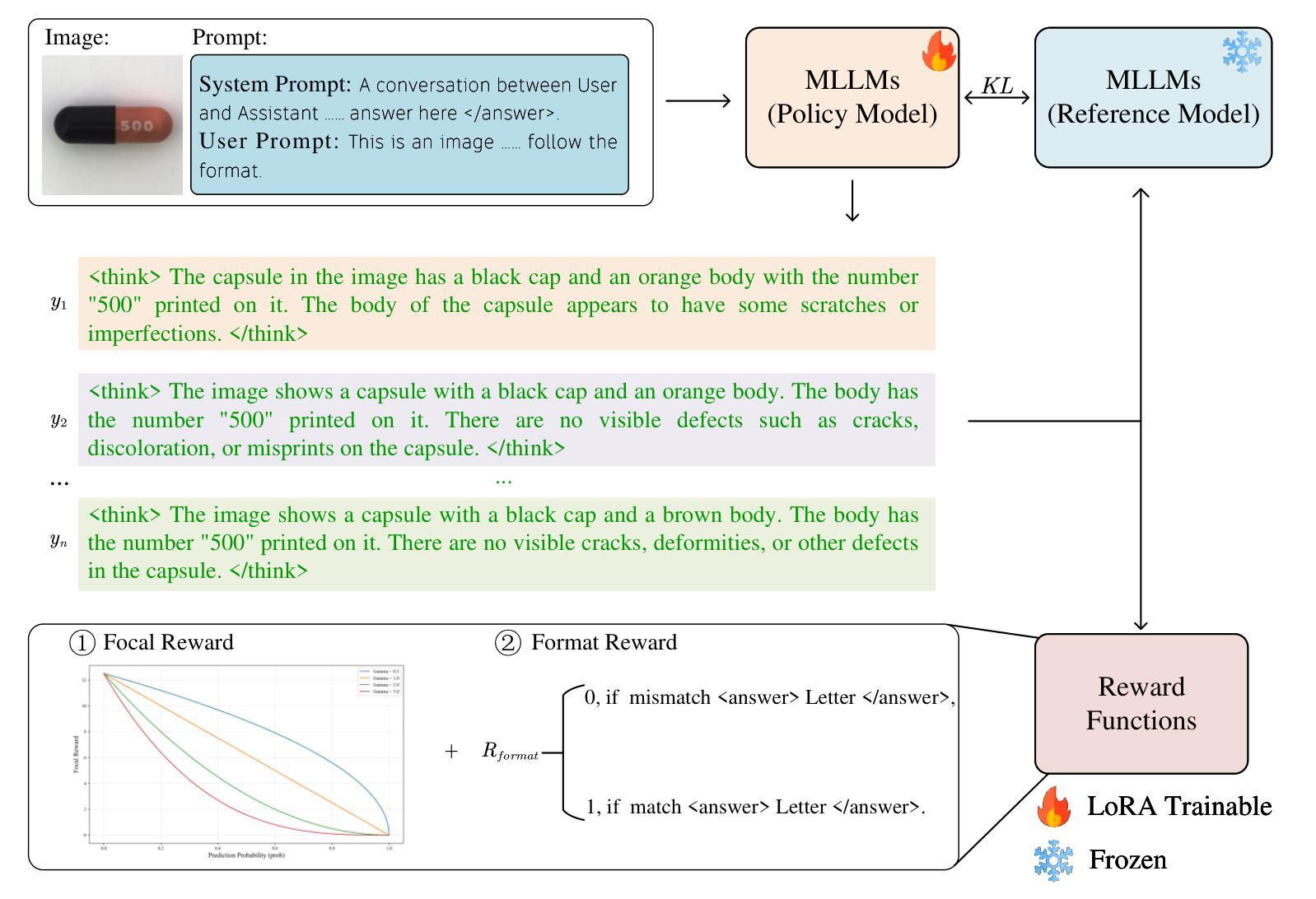
LR-IAD:Mask-Free Industrial Anomaly Detection with Logical Reasoning
Authors:Peijian Zeng, Feiyan Pang, Zhanbo Wang, Aimin Yang
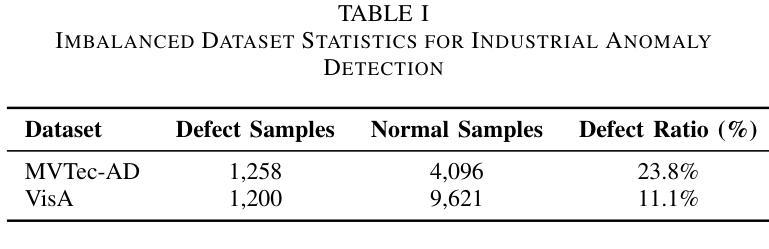
Industrial Anomaly Detection (IAD) is critical for ensuring product quality by identifying defects. Traditional methods such as feature embedding and reconstruction-based approaches require large datasets and struggle with scalability. Existing vision-language models (VLMs) and Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) address some limitations but rely on mask annotations, leading to high implementation costs and false positives. Additionally, industrial datasets like MVTec-AD and VisA suffer from severe class imbalance, with defect samples constituting only 23.8% and 11.1% of total data respectively. To address these challenges, we propose a reward function that dynamically prioritizes rare defect patterns during training to handle class imbalance. We also introduce a mask-free reasoning framework using Chain of Thought (CoT) and Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) mechanisms, enabling anomaly detection directly from raw images without annotated masks. This approach generates interpretable step-by-step explanations for defect localization. Our method achieves state-of-the-art performance, outperforming prior approaches by 36% in accuracy on MVTec-AD and 16% on VisA. By eliminating mask dependency and reducing costs while providing explainable outputs, this work advances industrial anomaly detection and supports scalable quality control in manufacturing. Code to reproduce the experiment is available at https://github.com/LilaKen/LR-IAD.
工业异常检测(IAD)对于通过识别缺陷来保证产品质量至关重要。传统的方法,如基于特征嵌入和重建的方法,需要大规模的数据集,并且在可扩展性方面存在困难。现有的视觉语言模型(VLM)和多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)解决了一些限制,但它们依赖于掩膜注释,导致实施成本高和假阳性结果多。此外,工业数据集如MVTec-AD和VisA存在严重的类别不平衡问题,缺陷样本仅占总数数据的23.8%和11.1%。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一种奖励函数,该函数在训练过程中动态优先处理罕见的缺陷模式,以处理类别不平衡问题。我们还引入了一种无掩膜推理框架,使用思维链(CoT)和群组相对策略优化(GRPO)机制,能够直接从原始图像中进行异常检测,无需注释掩膜。该方法生成了可解释的、按步骤进行的缺陷定位解释。我们的方法达到了最先进的表现,在MVTec-AD上准确度提高了36%,在VisA上提高了16%。通过消除对掩膜的依赖,降低成本,同时提供可解释的输出,这项工作推动了工业异常检测的发展,支持制造业的可扩展质量控制。实验重现的代码可在https://github.com/LilaKen/LR-IAD中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages
Summary
该研究解决了工业异常检测中的关键问题,包括数据集规模、标注成本、类不平衡和解释性缺失等挑战。通过引入奖励函数、无掩膜推理框架和相对策略优化机制,该研究实现了直接对原始图像进行异常检测并实现了步骤化的缺陷定位解释。该方法在MVTec-AD和VisA数据集上的准确率达到了业界领先水平。
Key Takeaways
- 研究针对工业异常检测中的关键问题,包括数据集规模、类不平衡等挑战。
- 引入奖励函数以处理类不平衡问题,动态优先化罕见缺陷模式。
- 提出无掩膜推理框架,利用Chain of Thought (CoT)和Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO)机制,实现直接对原始图像进行异常检测。
- 方法生成可解释的步骤化缺陷定位,提高了异常检测的准确性和可靠性。
- 在MVTec-AD和VisA数据集上实现了业界领先的性能,分别提高了36%和16%的准确率。
- 消除了对掩膜的依赖,降低了实施成本。
点此查看论文截图

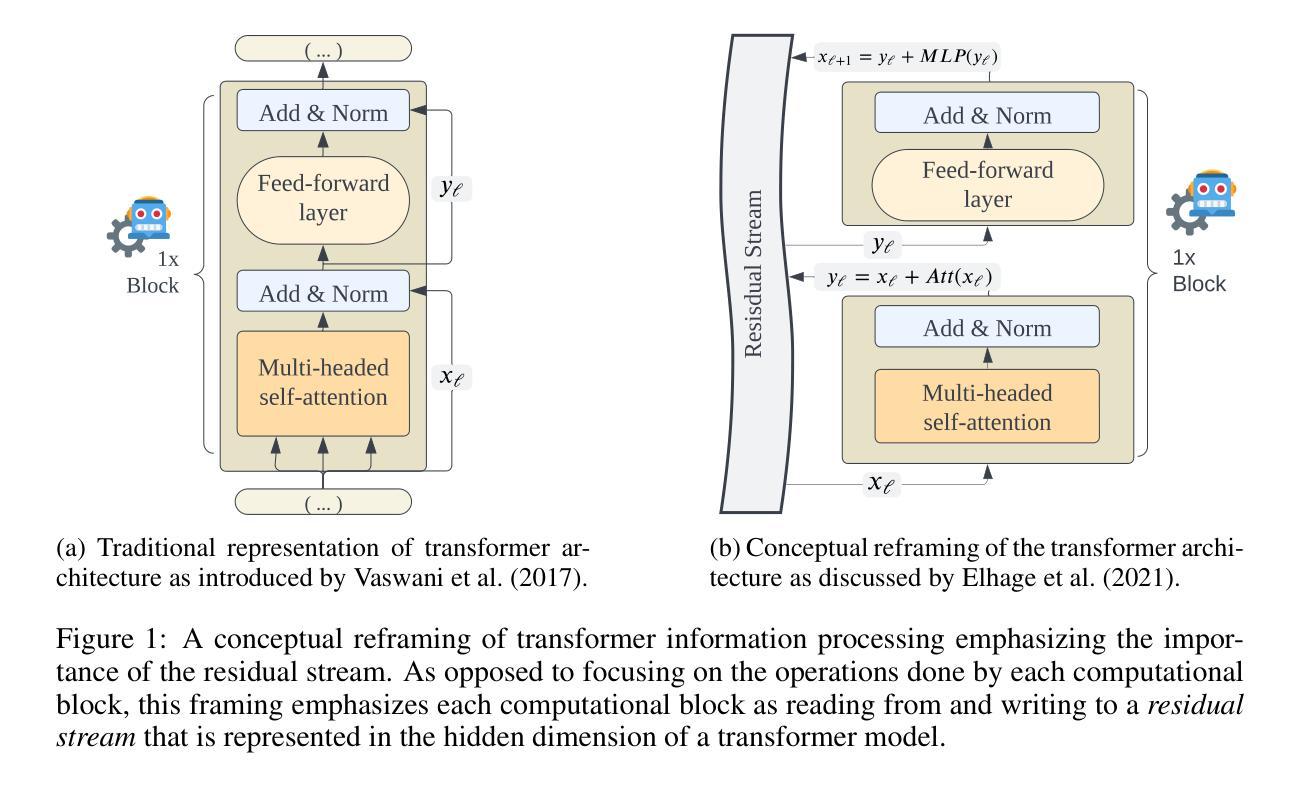
Improving Reasoning Performance in Large Language Models via Representation Engineering
Authors:Bertram Højer, Oliver Jarvis, Stefan Heinrich
Recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) have resulted in increasingly anthropomorphic language concerning the ability of LLMs to reason. Whether reasoning in LLMs should be understood to be inherently different is, however, widely debated. We propose utilizing a representation engineering approach wherein model activations are read from the residual stream of an LLM when processing a reasoning task. The activations are used to derive a control vector that is applied to the model as an inference-time intervention, modulating the representational space of the model, to improve performance on the specified task. We publish the code for deriving control vectors and analyzing model representations. The method allows us to improve performance on reasoning benchmarks and assess how control vectors influence the final logit distribution of a model via metrics such as KL divergence and entropy. We apply control vectors to Mistral-7B-Instruct and a range of Pythia models on an inductive, a deductive and mathematical reasoning task. We show that an LLM can, to a certain degree, be controlled to improve its perceived reasoning ability by modulating activations. The intervention is dependent upon the ability to reliably extract the model’s typical state when correctly solving a task. Our results suggest that reasoning performance can be modulated in the same manner as other information-processing tasks performed by LLMs and demonstrate that we are capable of improving performance on specific tasks via a simple intervention on the residual stream with no additional training.
最近大型语言模型(LLM)的进步导致了越来越多关于LLM推理能力的拟人化语言。然而,关于是否应理解LLM中的推理能力具有本质差异,存在广泛争议。我们提出了一种表示工程方法,在该方法中,我们从LLM的残差流中读取模型激活,并将其应用于处理推理任务时。这些激活被用来推导一个控制向量,该向量作为推理时间干预应用于模型,调节模型的表示空间,以提高在指定任务上的性能。我们发布了用于推导控制向量和分析模型表示的代码。该方法允许我们在推理基准测试上提高性能,并通过KL散度和熵等度量标准评估控制向量如何影响模型的最终逻辑分布。我们将控制向量应用于Mistral-7B-Instruct和一系列Pythia模型,进行归纳、演绎和数学推理任务。我们表明,通过调节激活,可以在一定程度上控制LLM提高其被视为的推理能力。这种干预取决于在正确完成任务时可靠地提取模型典型状态的能力。我们的结果表明,与LLM执行的其他信息处理任务类似,推理性能可以以相同的方式进行调节,并且我们能够通过在残差流上进行简单干预(无需额外训练)来提高特定任务的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Has been accepted at “The Thirteenth International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR 2025)” Link to publication: https://openreview.net/forum?id=IssPhpUsKt
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)的最新进展显示其在推理能力方面越来越具有人类特征。然而,关于LLMs的推理能力是否应被视为本质上不同的观点存在广泛争议。本文提出了一种表征工程方法,即从LLM的残差流中读取模型激活,用于生成控制向量。在推理任务处理过程中,将控制向量应用于模型,作为推理时间干预措施,对模型的表示空间进行调制,以提高特定任务的性能。本文公布了生成控制向量和分析模型表征的代码。该方法允许我们在推理基准测试上提高性能,并通过KL散度和熵等指标评估控制向量如何影响模型的最终逻辑分布。我们在Mistral-7B-Instruct和一系列Pythia模型上应用了控制向量,以进行归纳、演绎和数学推理任务。研究表明,通过调制激活,可以在一定程度上控制LLM提高其被感知的推理能力。这种干预依赖于在正确完成任务时可靠提取模型典型状态的能力。我们的结果表明,可以通过对残差流的简单干预,在不需要额外训练的情况下提高特定任务的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)的推理能力日益具有人类特征,但关于其本质差异存在争议。
- 提出了一种表征工程方法,通过模型激活生成控制向量,以提高LLM在特定任务上的性能。
- 控制向量可应用于改善推理基准测试的性能。
- 通过度量如KL散度和熵的指标,评估了控制向量对模型逻辑分布的影响。
- 在多种模型和任务上验证了控制向量的应用效果。
- 可靠提取模型典型状态的能力是进行有效干预的关键。
点此查看论文截图

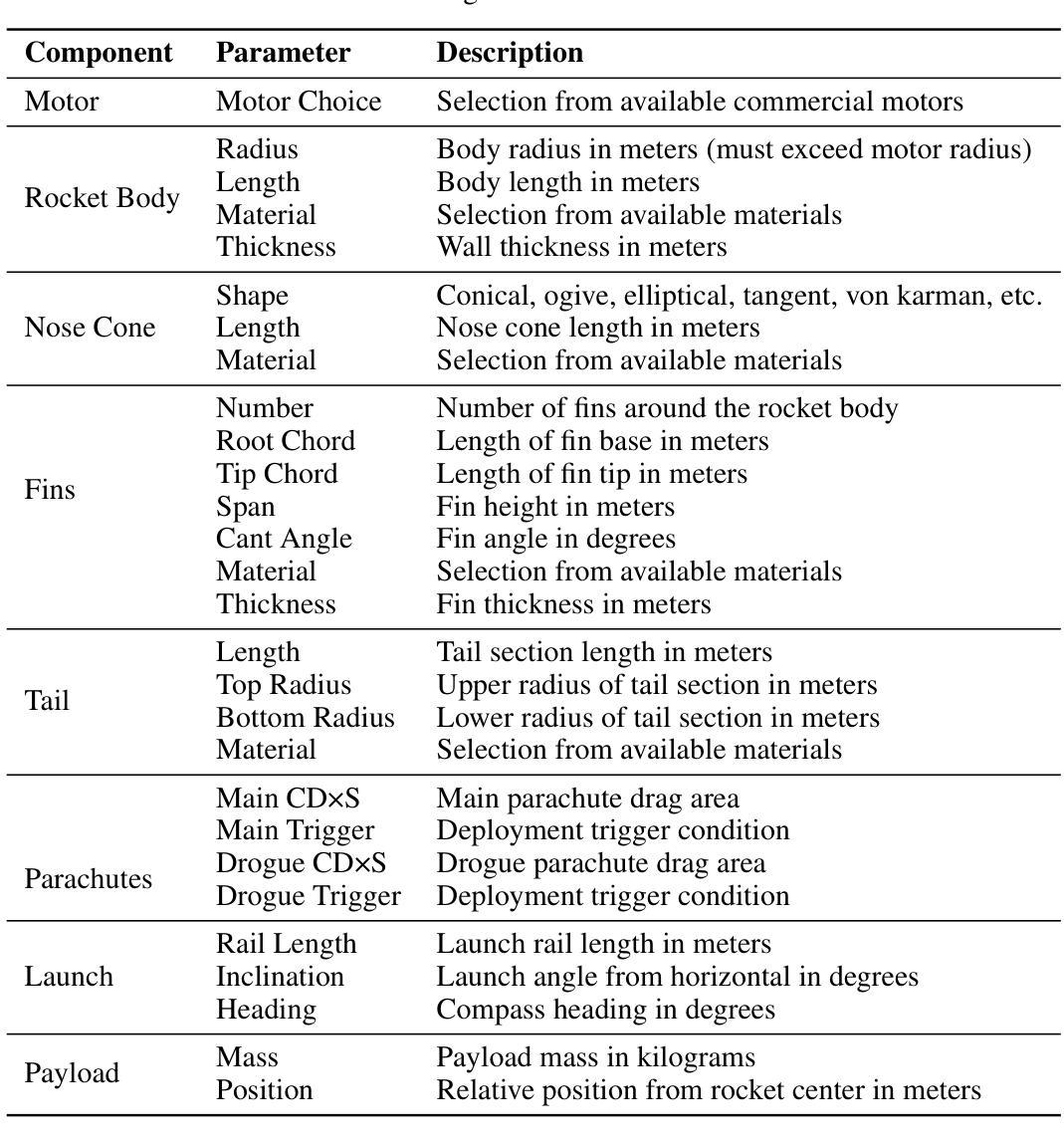
LLMs for Engineering: Teaching Models to Design High Powered Rockets
Authors:Toby Simonds
Large Language Models (LLMs) have transformed software engineering, but their application to physical engineering domains remains underexplored. This paper evaluates LLMs’ capabilities in high-powered rocketry design through RocketBench, a benchmark connecting LLMs to high-fidelity rocket simulations. We test models on two increasingly complex design tasks: target altitude optimization and precision landing challenges. Our findings reveal that while state-of-the-art LLMs demonstrate strong baseline engineering knowledge, they struggle to iterate on their designs when given simulation results and ultimately plateau below human performance levels. However, when enhanced with reinforcement learning (RL), we show that a 7B parameter model outperforms both SoTA foundation models and human experts. This research demonstrates that RL-trained LLMs can serve as effective tools for complex engineering optimization, potentially transforming engineering domains beyond software development.
大型语言模型(LLM)已经改变了软件工程的面貌,但它们在物理工程领域的应用仍然被探索得不够。本文通过RocketBench这一将LLM与高精度火箭模拟相结合的基准测试,评估了LLM在高性能火箭设计方面的能力。我们在两个日益复杂的设计任务上测试了这些模型:目标高度优化和精确着陆挑战。我们的研究发现,虽然最新LLM显示出强大的基础工程知识,但它们在模拟结果指导下进行设计迭代时面临困难,最终表现水平低于人类表现水平。然而,当使用强化学习(RL)进行增强时,我们证明了一个7B参数模型的表现超过了最新前沿基础模型和人类专家。这项研究表明,经过RL训练的LLM可以作为复杂工程优化的有效工具,有可能改变软件开发以外的工程领域。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)在软件工程中的应用已经成熟,但在物理工程领域的应用仍待探索。本文通过RocketBench基准测试评估了LLMs在高功率火箭设计方面的能力,该基准测试将LLMs与高精度火箭模拟相连接。测试模型在两个逐渐复杂的设计任务上表现出色:目标高度优化和精确着陆挑战。研究发现,虽然现有最先进的LLMs展现出强大的基础工程知识,但当模拟结果反馈时,它们在设计迭代上遇到困难,最终性能未能超越人类水平。然而,当结合强化学习(RL)进行训练后,一个拥有7亿参数的模型超越了当前顶尖的基础模型和人类专家。研究证明,经过RL训练的LLMs可成为复杂的工程优化工具,有望为超越软件开发的工程领域带来变革。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在物理工程领域的应用尚待充分探索。
- RocketBench基准测试用于评估LLMs在高功率火箭设计方面的能力。
- LLMs展现出强大的基础工程知识,但在设计迭代和反馈方面存在局限。
- 结合强化学习(RL)训练的LLMs性能超越当前顶尖的基础模型和人类专家。
- LLMs在高精度火箭模拟中的优化工具潜力巨大。
- LLMs在复杂工程优化方面具有重要意义,尤其在软件之外的领域。
点此查看论文截图

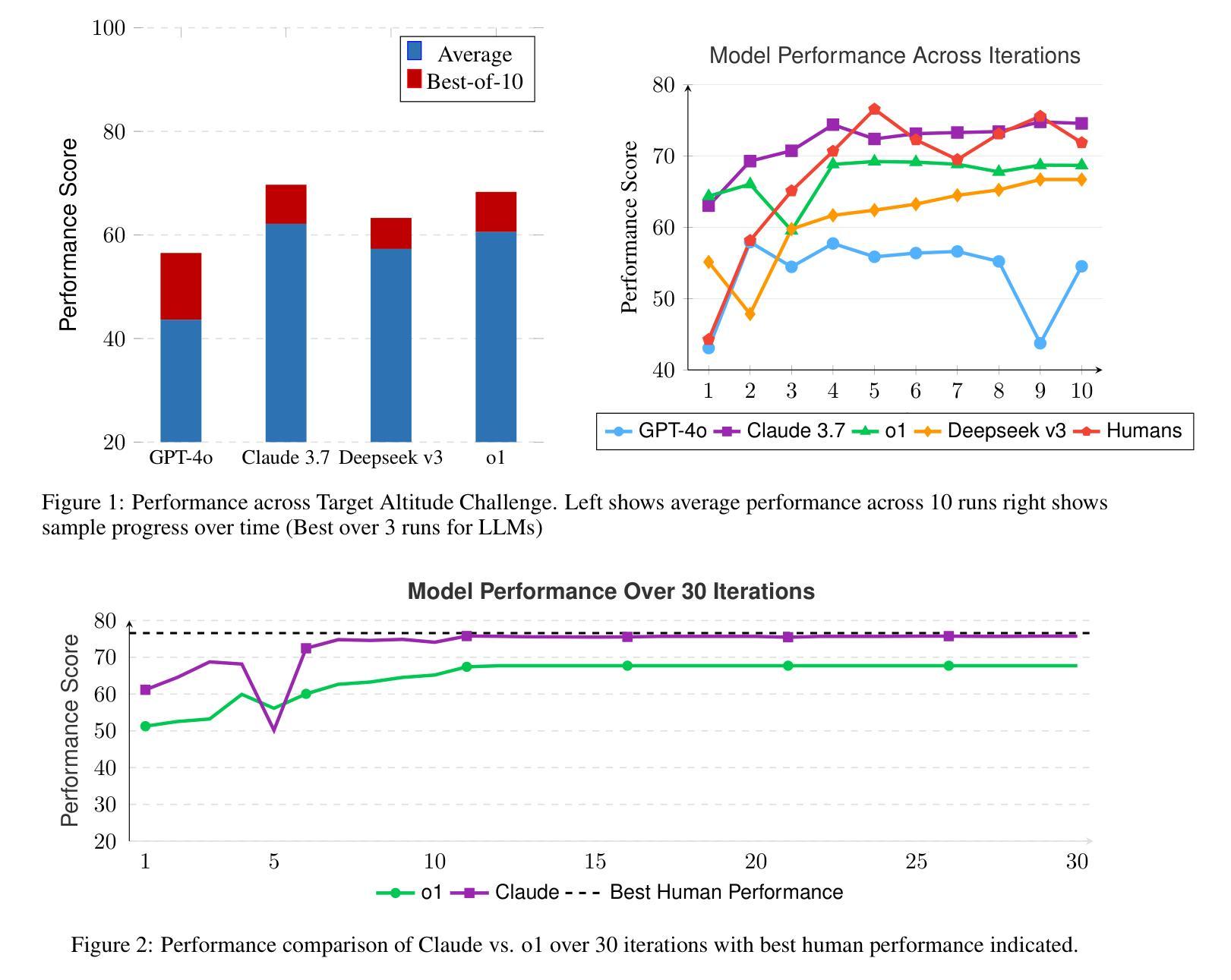
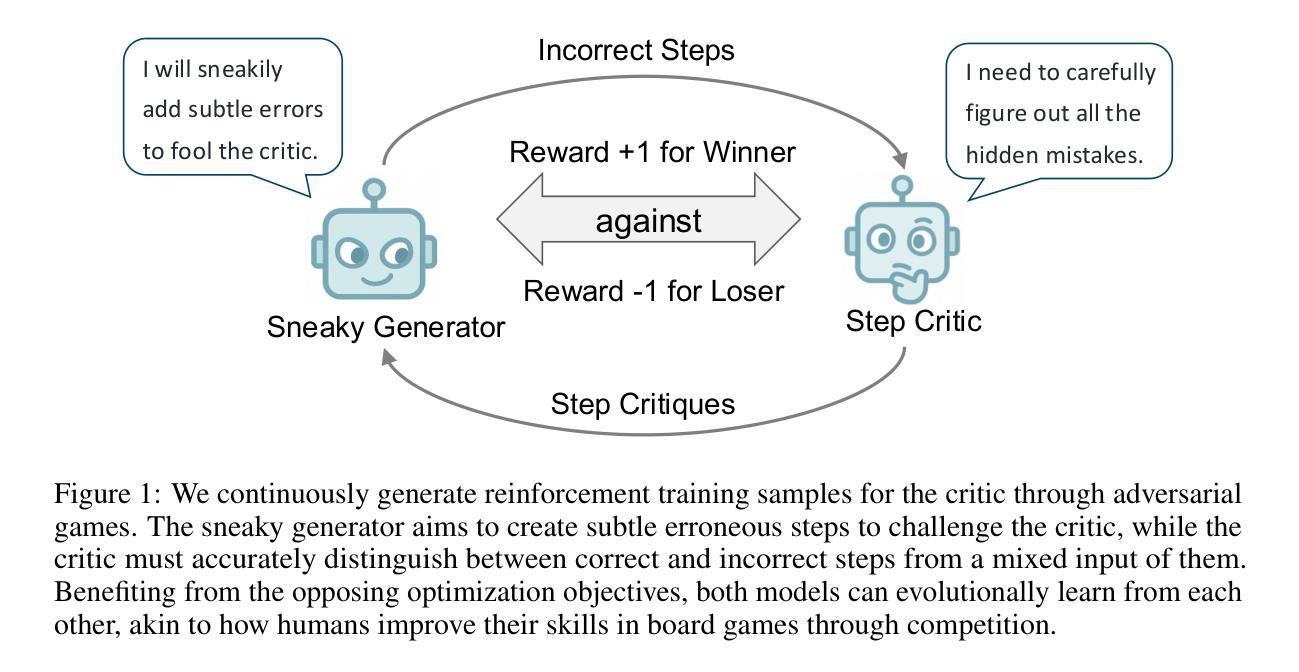
SPC: Evolving Self-Play Critic via Adversarial Games for LLM Reasoning
Authors:Jiaqi Chen, Bang Zhang, Ruotian Ma, Peisong Wang, Xiaodan Liang, Zhaopeng Tu, Xiaolong Li, Kwan-Yee K. Wong
Evaluating the step-by-step reliability of large language model (LLM) reasoning, such as Chain-of-Thought, remains challenging due to the difficulty and cost of obtaining high-quality step-level supervision. In this paper, we introduce Self-Play Critic (SPC), a novel approach where a critic model evolves its ability to assess reasoning steps through adversarial self-play games, eliminating the need for manual step-level annotation. SPC involves fine-tuning two copies of a base model to play two roles, namely a “sneaky generator” that deliberately produces erroneous steps designed to be difficult to detect, and a “critic” that analyzes the correctness of reasoning steps. These two models engage in an adversarial game in which the generator aims to fool the critic, while the critic model seeks to identify the generator’s errors. Using reinforcement learning based on the game outcomes, the models iteratively improve; the winner of each confrontation receives a positive reward and the loser receives a negative reward, driving continuous self-evolution. Experiments on three reasoning process benchmarks (ProcessBench, PRM800K, DeltaBench) demonstrate that our SPC progressively enhances its error detection capabilities (e.g., accuracy increases from 70.8% to 77.7% on ProcessBench) and surpasses strong baselines, including distilled R1 model. Furthermore, applying SPC to guide the test-time search of diverse LLMs significantly improves their mathematical reasoning performance on MATH500 and AIME2024, outperforming state-of-the-art process reward models.
评估大型语言模型(LLM)推理的逐步可靠性,如思维链,仍然具有挑战性,因为获得高质量步骤级监督的难度和成本很高。在本文中,我们介绍了自我游戏评论家(SPC),这是一种新颖的方法,评论家模型通过对抗性的自我游戏来进化其评估推理步骤的能力,从而消除了对手动步骤级注释的需求。SPC涉及微调基础模型的两个副本,以扮演两个角色,一个是“狡猾的生成器”,它故意产生难以检测的错误步骤,另一个是“评论家”,它分析推理步骤的正确性。这两个模型进行了一场对抗性游戏,其中生成器的目标是欺骗评论家,而评论家模型的目标是识别生成器的错误。基于游戏结果的强化学习,模型会进行迭代改进;每次对抗的获胜者会获得正面奖励,而失败者会获得负面奖励,从而推动模型的持续自我进化。在三个推理过程基准测试(ProcessBench、PRM800K、DeltaBench)上的实验表明,我们的SPC逐步提高了其错误检测能力(例如,在ProcessBench上的准确率从70.8%提高到77.7%),并超越了强大的基线,包括蒸馏R1模型。此外,将SPC应用于测试时引导多种LLM的搜索,显著提高了它们在MATH500和AIME2024上的数学推理性能,超越了最新的过程奖励模型。
中文简化版
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project: https://chen-judge.github.io/SPC/
Summary
该论文提出了一种名为Self-Play Critic(SPC)的新方法,用于评估大型语言模型(LLM)如Chain-of-Thought等的逐步推理可靠性。该方法通过对抗性自我游戏让评判模型进化,从而不需要手动步骤级别的标注。SPC通过微调基础模型的两个副本,分别扮演“狡猾的生成器”和“评判者”的角色,进行对抗游戏。生成器故意产生错误的步骤,而评判者则分析推理步骤的正确性。基于游戏结果,使用强化学习进行迭代改进。实验表明,SPC逐渐提高了错误检测能力,并在多个基准测试中超越了其他模型。
Key Takeaways
- 论文引入了Self-Play Critic(SPC)方法,用于评估大型语言模型的逐步推理可靠性。
- SPC通过两个模型——生成器和评判者——之间的对抗性游戏进化模型能力。
- 生成器旨在产生难以检测的错误步骤,而评判者则分析推理步骤的正确性。
- 使用强化学习基于游戏结果对模型进行迭代改进。
- 实验表明,SPC能提高错误检测能力,并在多个基准测试中表现优异。
6.SPC可用于指导不同大型语言模型的测试时间搜索,提高数学推理性能。
点此查看论文截图

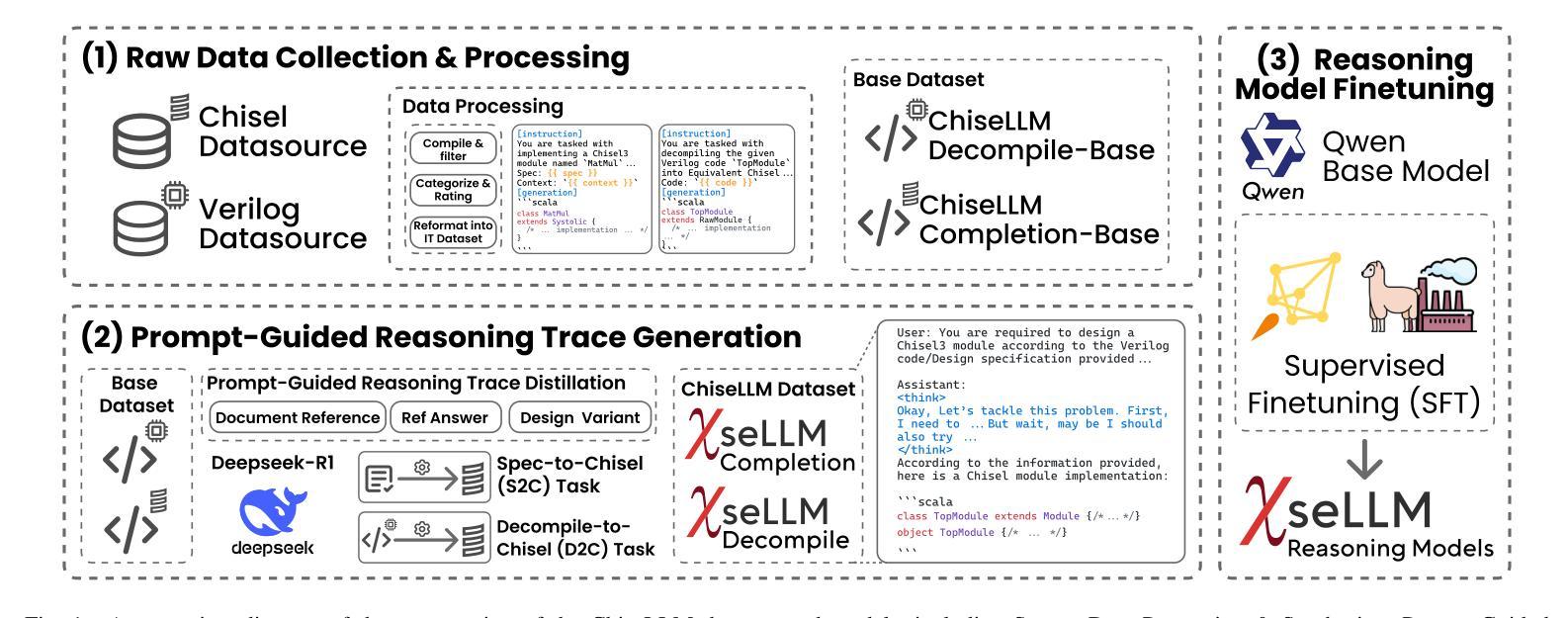
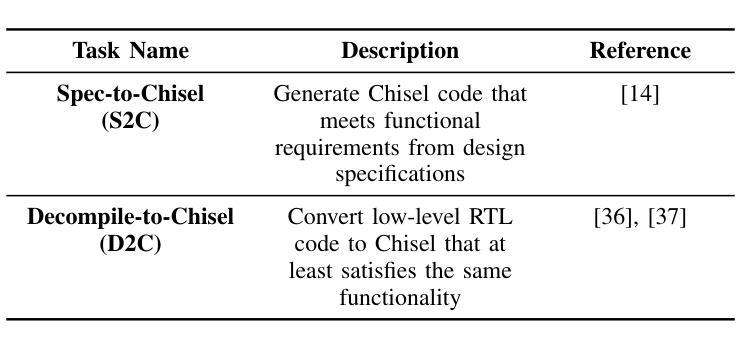
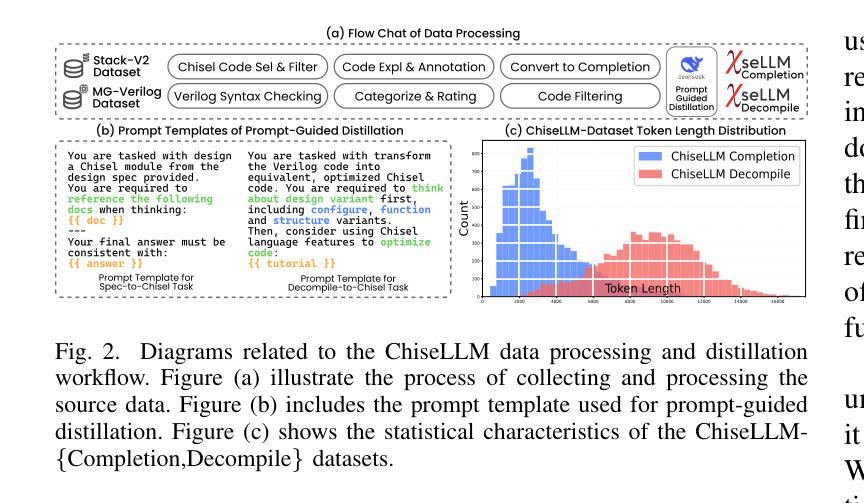
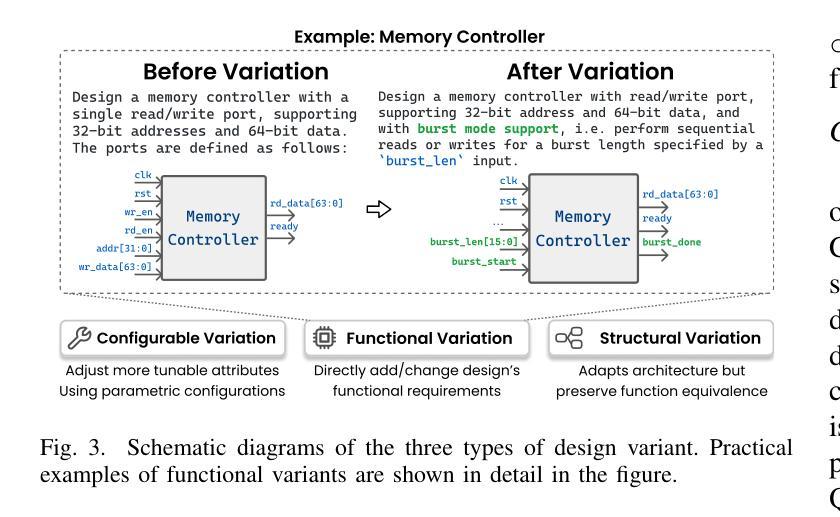
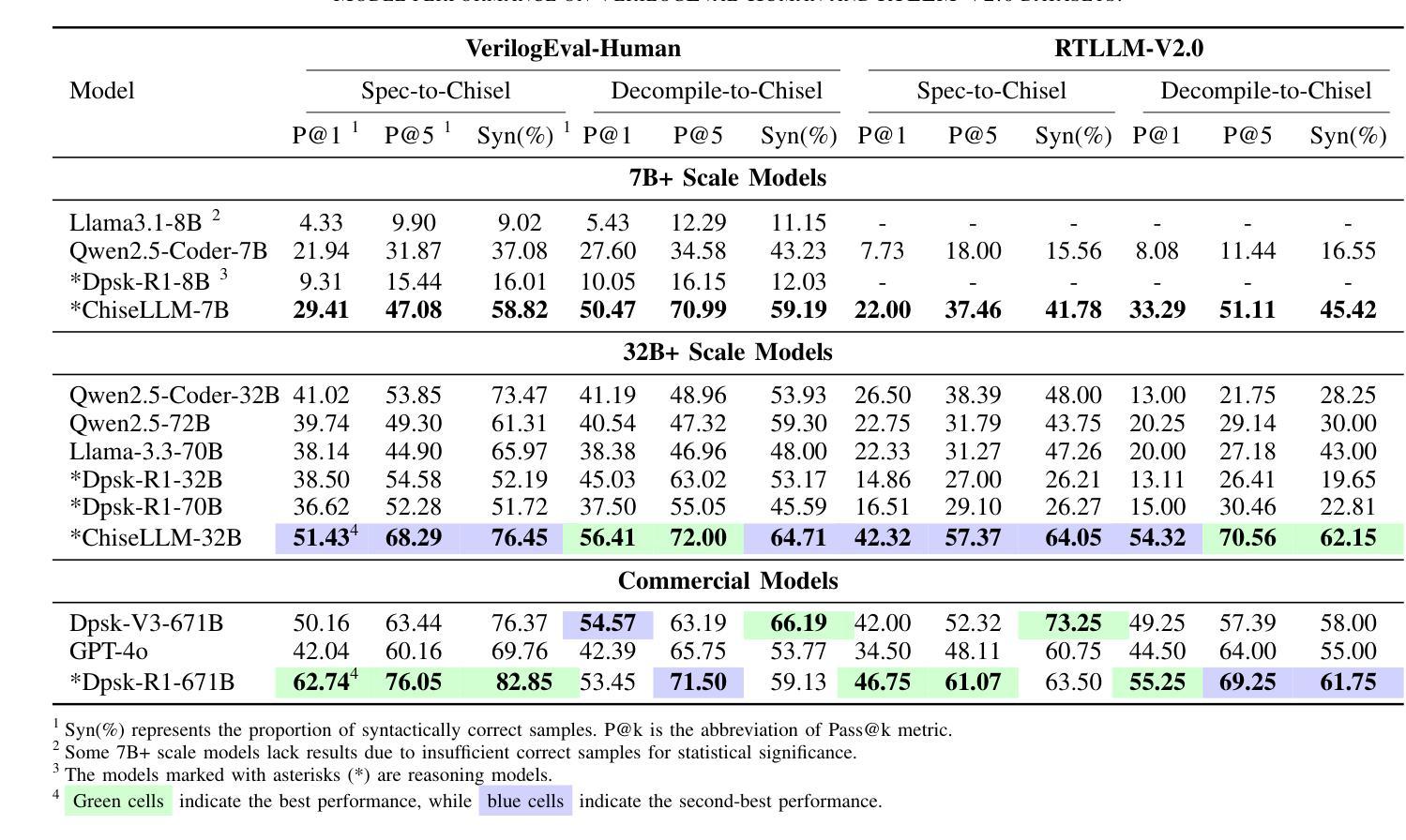
ChiseLLM: Unleashing the Power of Reasoning LLMs for Chisel Agile Hardware Development
Authors:Bowei Wang, Jiaran Gao, Yelai Feng, Renzhi Chen, Shanshan Li, Lei Wang
The growing demand for Domain-Specific Architecture (DSA) has driven the development of Agile Hardware Development Methodology (AHDM). Hardware Construction Language (HCL) like Chisel offers high-level abstraction features, making it an ideal language for HCL-Based AHDM. While Large Language Models (LLMs) excel in code generation tasks, they still face challenges with Chisel generation, particularly regarding syntax correctness and design variability. Recent reasoning models have significantly enhanced code generation capabilities through test-time scaling techniques. However, we found that reasoning models without domain adaptation cannot bring substantial benefits to Chisel code generation tasks. This paper presents ChiseLLM, a solution comprising data processing and transformation, prompt-guided reasoning trace synthesis, and domain-adapted model training. We constructed high-quality datasets from public RTL code resources and guided the model to adopt structured thinking patterns through prompt enhancement methods. Experiments demonstrate that our ChiseLLM-7B and ChiseLLM-32B models improved syntax correctness by 18.85% and 26.32% respectively over base models, while increasing variability design ability by 47.58% compared to baseline reasoning models. Our datasets and models are publicly available, providing high-performance, cost-effective models for HCL-Based AHDM, and offering an effective baseline for future research. Github repository: https://github.com/observerw/ChiseLLM
随着特定领域架构(DSA)需求的不断增长,敏捷硬件开发方法论(AHDM)的发展得到了推动。硬件构造语言(HCL)如Chisel提供了高级抽象特性,使其成为基于HCL的AHDM的理想语言。虽然大型语言模型(LLM)在代码生成任务方面表现出色,但在Chisel生成方面仍面临语法正确性和设计可变性的挑战。最近的推理模型通过测试时缩放技术显著增强了代码生成能力。然而,我们发现未经领域适应的推理模型不能给Chisel代码生成任务带来实质性好处。
本文提出了ChiseLLM解决方案,包括数据处理和转换、提示引导推理轨迹合成和领域适应模型训练。我们从公共RTL代码资源中构建了高质量数据集,并通过提示增强方法指导模型采用结构化思维模式。实验表明,我们的ChiseLLM-7B和ChiseLLM-32B模型相较于基准模型,语法正确性分别提高了18.85%和26.32%,同时相较于基线推理模型,提高了47.58%的设计能力可变度。我们的数据集和模型是公开的,为基于HCL的AHDM提供了高性能、经济实惠的模型,并为未来的研究提供了有效的基准线。Github仓库地址:https://github.com/observerw/ChiseLLM
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:随着领域特定架构(DSA)需求的增长,敏捷硬件开发方法论(AHDM)得到发展。硬件构造语言(HCL)如Chisel具有高级抽象特性,适合用于HCL-Based AHDM。大型语言模型(LLM)在代码生成任务上表现出色,但在Chisel生成方面仍面临语法正确性和设计可变性的挑战。最新推理模型通过测试时缩放技术显著增强了代码生成能力,但缺乏领域适应性的推理模型对Chisel代码生成任务的益处有限。本文提出ChiseLLM,包含数据处理和转换、提示引导推理跟踪合成和领域适应模型训练。通过构建高质量数据集和引导模型采用结构化思维,实验表明ChiseLLM模型在语法正确性和设计可变性方面优于基础模型。
Key Takeaways:
- Domain-Specific Architecture (DSA)的增长推动了敏捷硬件开发方法论(AHDM)的发展。
- 硬件构造语言(HCL)如Chisel具有高级抽象特性,适合用于HCL-Based AHDM。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在Chisel代码生成方面面临语法正确性和设计可变性的挑战。
- 最新推理模型通过测试时缩放技术提高了代码生成能力。
- 缺乏领域适应性的推理模型在Chisel代码生成任务上的效益有限。
- ChiseLLM通过数据处理和转换、提示引导推理跟踪合成和领域适应模型训练等方法来提高模型性能。
点此查看论文截图

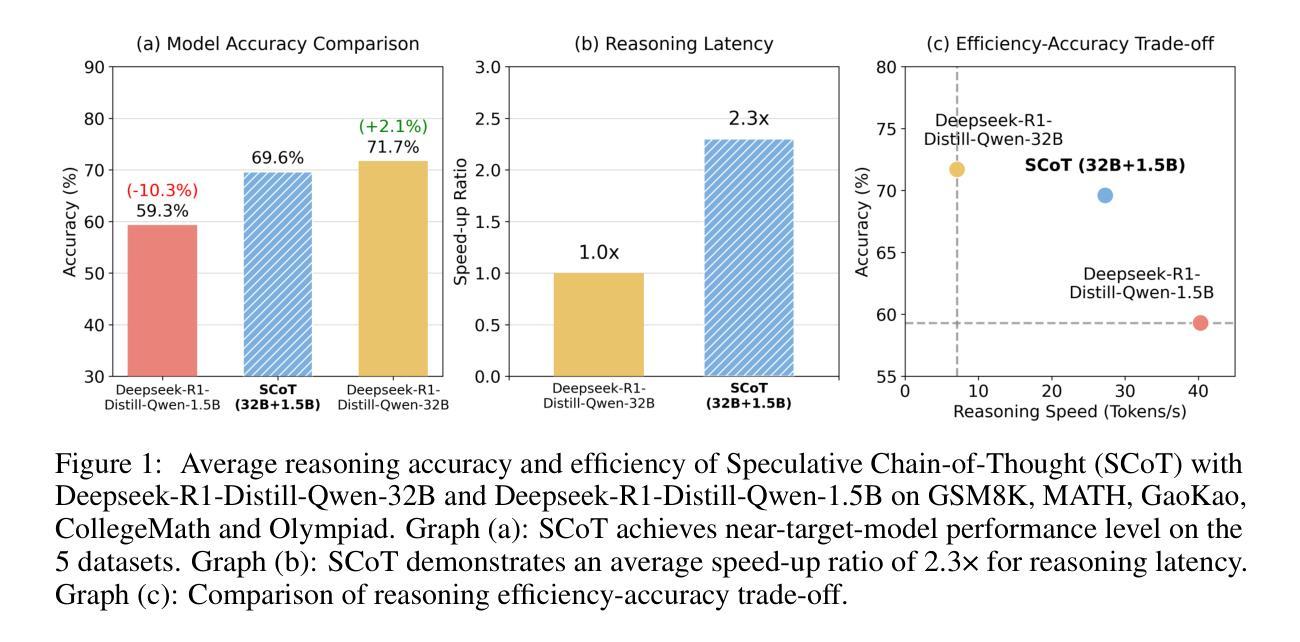
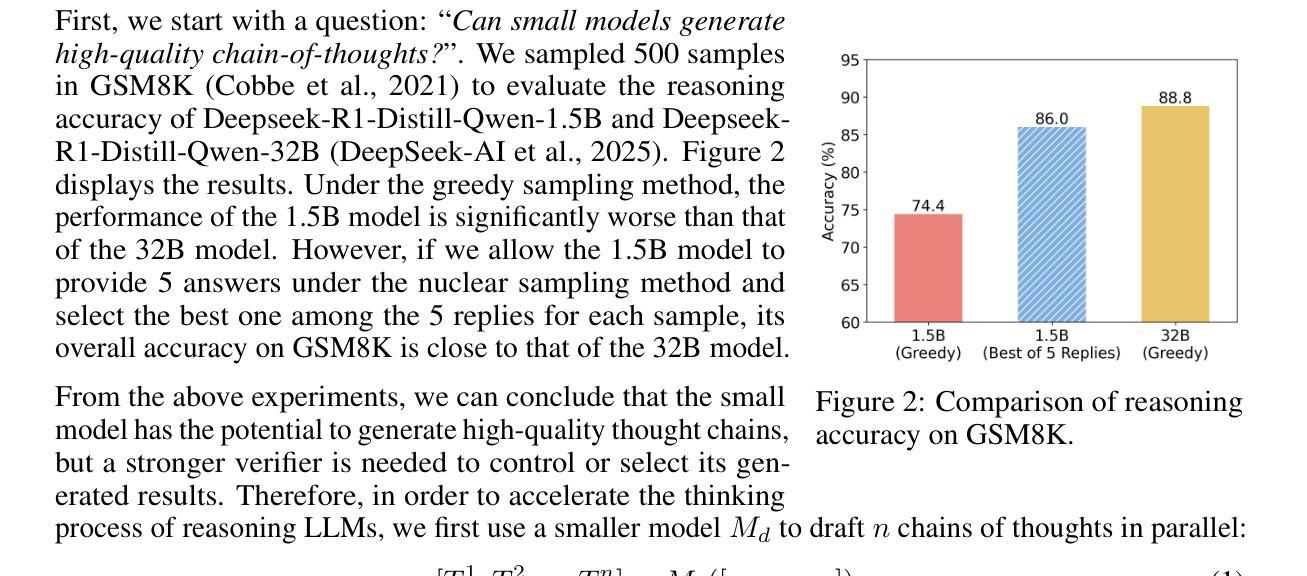
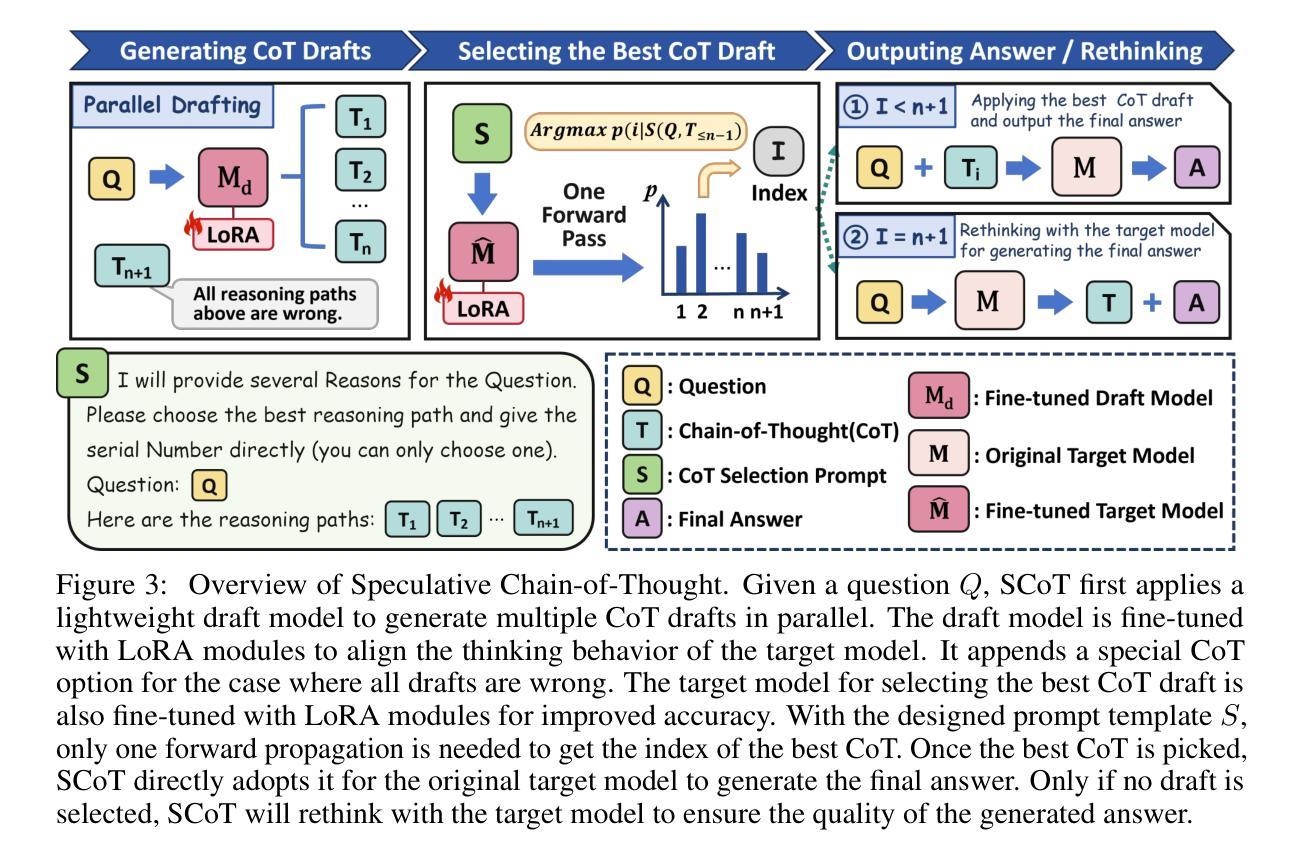
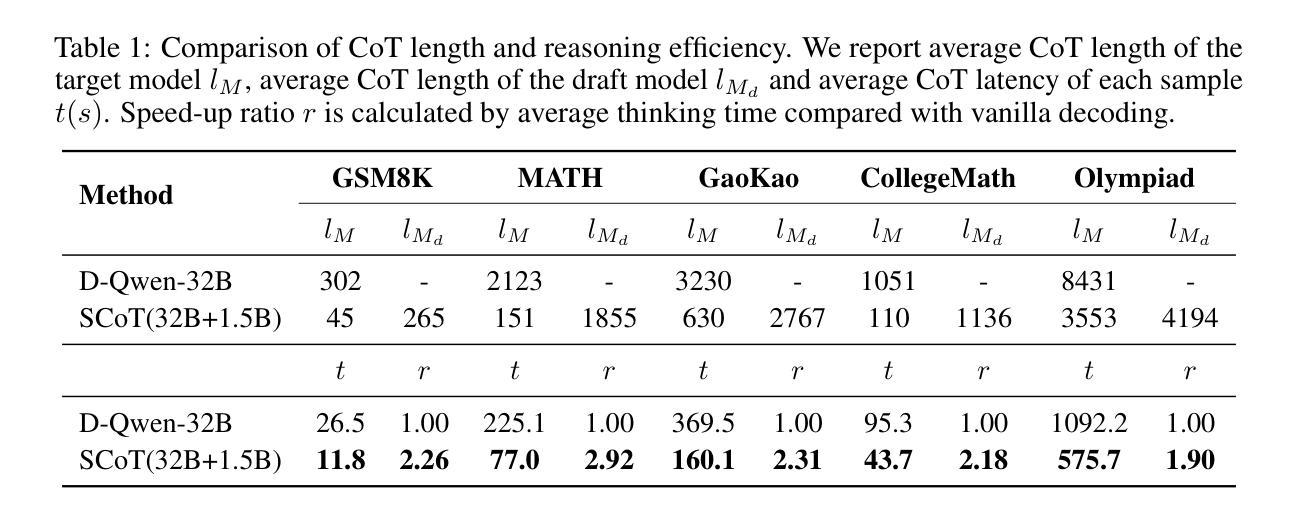
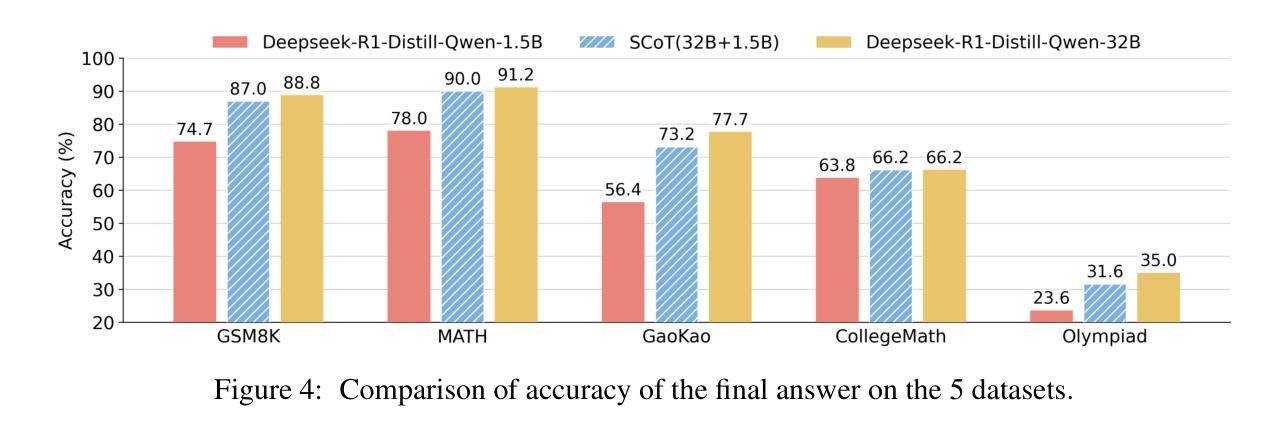
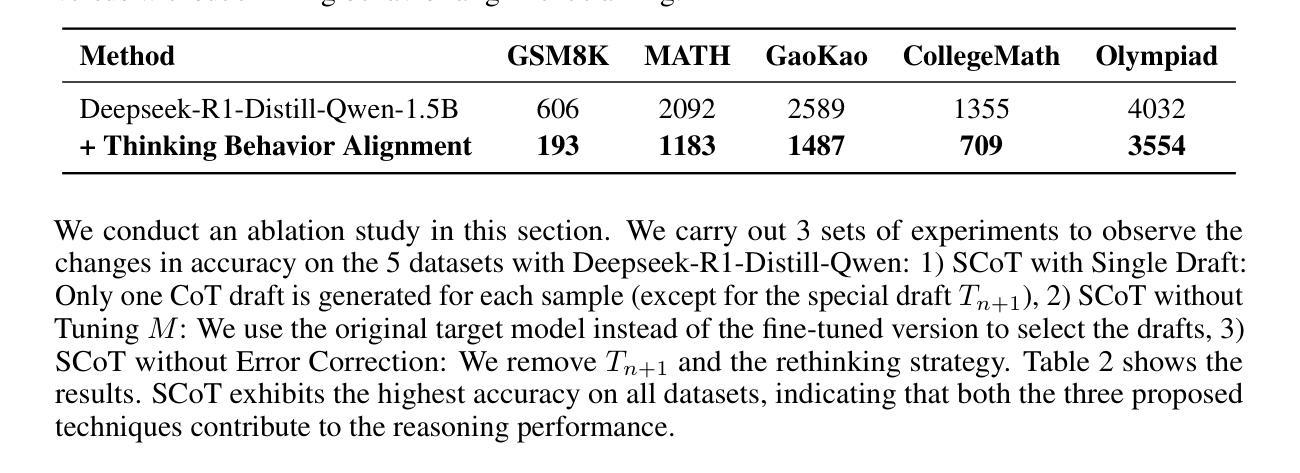
Efficient Reasoning for LLMs through Speculative Chain-of-Thought
Authors:Jikai Wang, Juntao Li, Lijun Wu, Min Zhang
Large reasoning language models such as OpenAI-o1 and Deepseek-R1 have recently attracted widespread attention due to their impressive task-solving abilities. However, the enormous model size and the generation of lengthy thought chains introduce significant reasoning costs and response latency. Existing methods for efficient reasoning mainly focus on reducing the number of model parameters or shortening the chain-of-thought length. In this paper, we introduce Speculative Chain-of-Thought (SCoT), which reduces reasoning latency from another perspective by accelerated average reasoning speed through large and small model collaboration. SCoT conducts thought-level drafting using a lightweight draft model. Then it selects the best CoT draft and corrects the error cases with the target model. The proposed thinking behavior alignment improves the efficiency of drafting and the draft selection strategy maintains the prediction accuracy for complex problems. Experimental results on GSM8K, MATH, GaoKao, CollegeMath and Olympiad datasets show that SCoT reduces reasoning latency by 48%$\sim$66% for Deepseek-R1-Distill-Qwen-32B while achieving near-target-model-level performance. Our code is available at https://github.com/Jikai0Wang/Speculative_CoT.
最近,OpenAI-o1和Deepseek-R1等大型推理语言模型因其令人印象深刻的任务解决能力而引起了广泛关注。然而,庞大的模型规模和产生冗长的思维链,导致推理成本较高和响应延迟。现有的高效推理方法主要集中在减少模型参数数量或缩短思维链长度上。在本文中,我们引入了基于大模型和小模型协作的推测思维链(Speculative Chain-of-Thought,简称SCoT)。SCoT从另一个角度通过加速平均推理速度来减少推理延迟。SCoT使用轻量级草稿模型进行思维层次的草稿撰写,然后选择最佳的CoT草稿并使用目标模型修正错误情况。提出的思考行为对齐方式提高了草稿的效率,而草稿选择策略则保持了对复杂问题的预测准确性。在GSM8K、MATH、高考、大学数学和奥林匹克数据集上的实验结果表明,SCoT在Deepseek-R1-Distill-Qwen-32B上将推理延迟降低了48%~66%,同时实现了接近目标模型级别的性能。我们的代码可在https://github.com/Jikai0Wang/Speculative_CoT找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型推理语言模型如OpenAI-o1和Deepseek-R1备受关注,但其巨大的模型规模和复杂的思维链生成带来高昂的推理成本和响应延迟。现有提高推理效率的方法主要关注减少模型参数或缩短思维链长度。本文提出Speculative Chain-of-Thought(SCoT),通过大小模型协作加速平均推理速度,从另一个角度降低推理延迟。SCoT利用轻量级草稿模型进行思维层次的草稿,然后选择最佳的CoT草稿并用目标模型修正错误情况。这种思考行为对齐方式提高了草稿的效率,而草稿选择策略则保持了对复杂问题的预测准确性。实验结果表明,SCoT在GSM8K、MATH、高考、大学数学和奥林匹克数据集上,将Deepseek-R1-Distill-Qwen-32B的推理延迟降低了48%~66%,同时实现了接近目标模型级别的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 大型推理语言模型面临推理成本和响应延迟的问题。
- 现有方法主要关注减少模型参数或缩短思维链长度以提高推理效率。
- 本文提出的Speculative Chain-of-Thought(SCoT)通过大小模型协作来加速平均推理速度。
- SCoT利用轻量级草稿模型进行思维层次的草稿,并选择最佳草稿来提高效率。
- SCoT通过目标模型修正错误,实现思考行为对齐和草稿选择策略,保持对复杂问题的预测准确性。
- 实验结果表明,SCoT在多个数据集上显著降低了推理延迟,并实现了接近目标模型级别的性能。
点此查看论文截图

CipherBank: Exploring the Boundary of LLM Reasoning Capabilities through Cryptography Challenges
Authors:Yu Li, Qizhi Pei, Mengyuan Sun, Honglin Lin, Chenlin Ming, Xin Gao, Jiang Wu, Conghui He, Lijun Wu
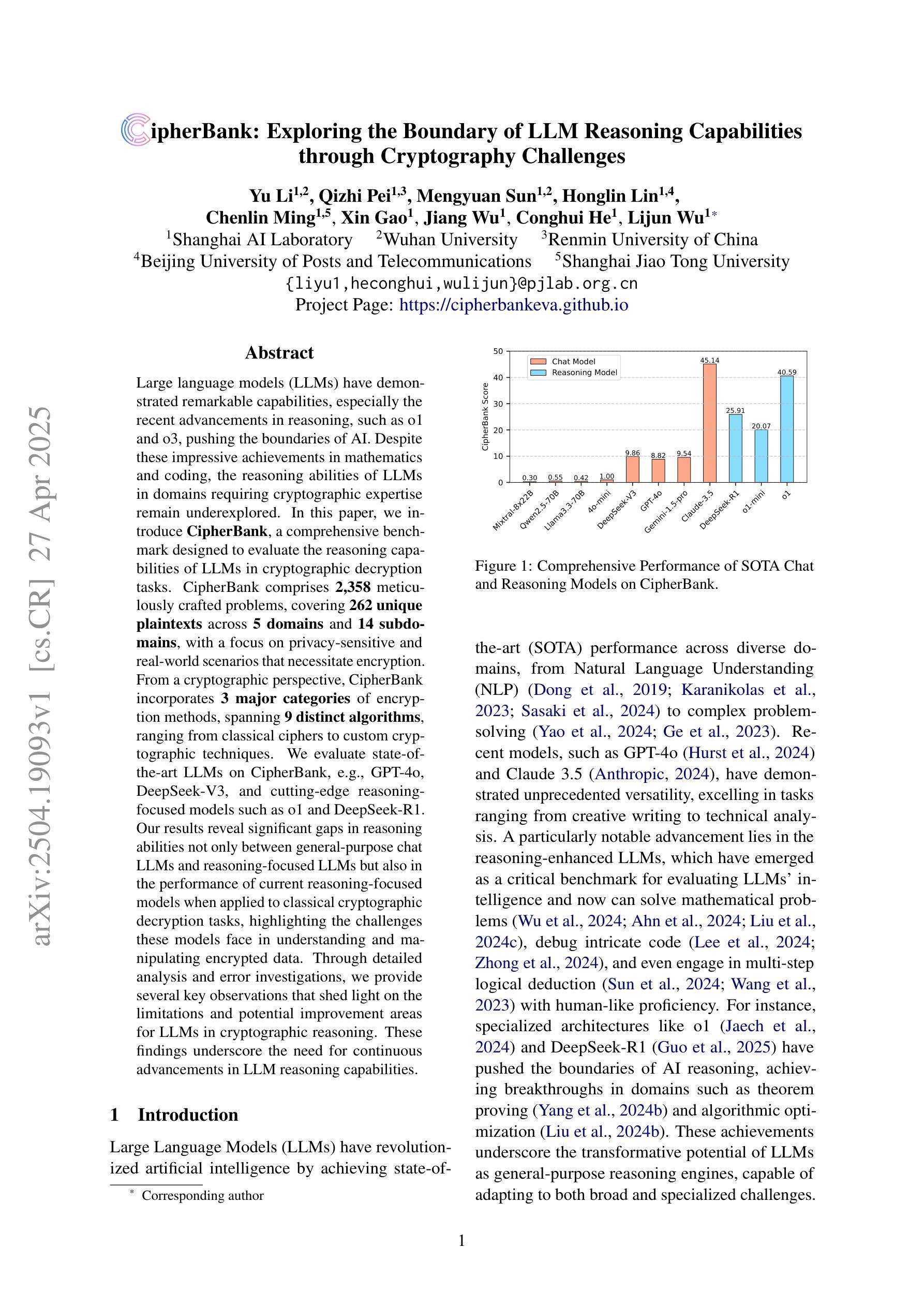
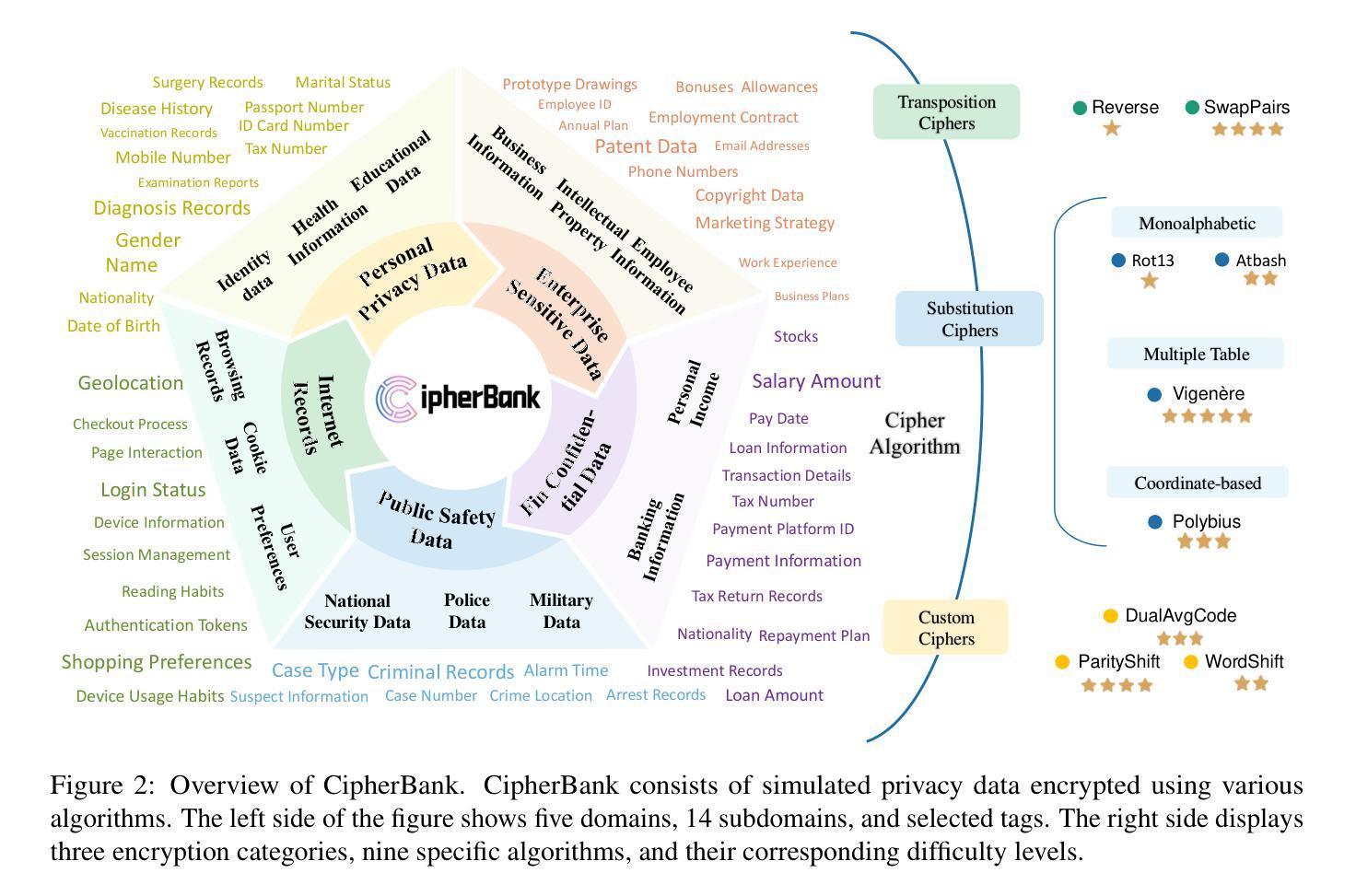
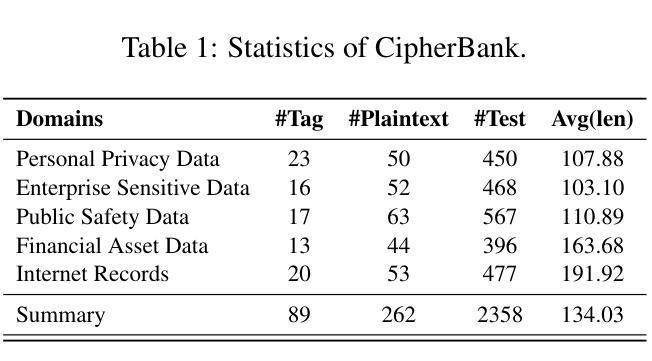
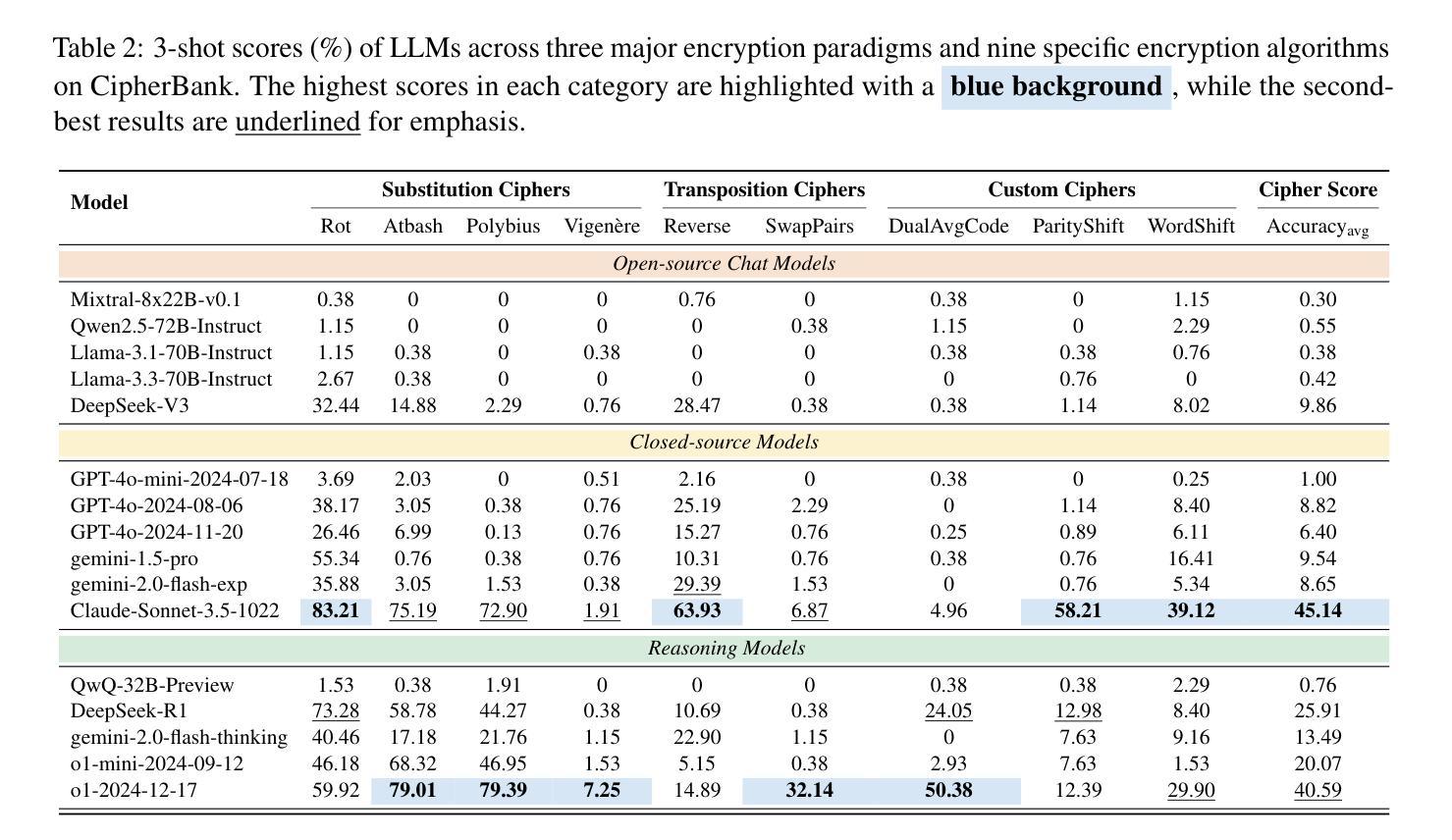
Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities, especially the recent advancements in reasoning, such as o1 and o3, pushing the boundaries of AI. Despite these impressive achievements in mathematics and coding, the reasoning abilities of LLMs in domains requiring cryptographic expertise remain underexplored. In this paper, we introduce CipherBank, a comprehensive benchmark designed to evaluate the reasoning capabilities of LLMs in cryptographic decryption tasks. CipherBank comprises 2,358 meticulously crafted problems, covering 262 unique plaintexts across 5 domains and 14 subdomains, with a focus on privacy-sensitive and real-world scenarios that necessitate encryption. From a cryptographic perspective, CipherBank incorporates 3 major categories of encryption methods, spanning 9 distinct algorithms, ranging from classical ciphers to custom cryptographic techniques. We evaluate state-of-the-art LLMs on CipherBank, e.g., GPT-4o, DeepSeek-V3, and cutting-edge reasoning-focused models such as o1 and DeepSeek-R1. Our results reveal significant gaps in reasoning abilities not only between general-purpose chat LLMs and reasoning-focused LLMs but also in the performance of current reasoning-focused models when applied to classical cryptographic decryption tasks, highlighting the challenges these models face in understanding and manipulating encrypted data. Through detailed analysis and error investigations, we provide several key observations that shed light on the limitations and potential improvement areas for LLMs in cryptographic reasoning. These findings underscore the need for continuous advancements in LLM reasoning capabilities.
大型语言模型(LLM)已经展现出令人瞩目的能力,特别是最近在推理方面的进展,如o1和o3,推动了人工智能的边界。尽管在数学和编码方面取得了令人印象深刻的成就,但在需要密码学专业知识领域的推理能力仍然被低估。在本文中,我们介绍了CipherBank,这是一个旨在评估LLM在密码解密任务中的推理能力的综合基准测试。CipherBank包含2358个精心设计的密码问题,涵盖五个领域和十四个子领域的262个独特明文,重点关注需要加密的隐私敏感和现实世界场景。从密码学的角度来看,CipherBank结合了三种主要的加密方法,涵盖九种不同的算法,从古典密码到自定义密码技术。我们在CipherBank上评估了最先进的LLM,如GPT-4o、DeepSeek-V3以及专注于推理的模型o1和DeepSeek-R1等。我们的结果表明,不仅在通用聊天LLM和专注于推理的LLM之间存在推理能力的巨大差距,而且在将当前专注于推理的模型应用于古典密码解密任务时也存在性能差距,这突显了这些模型在理解和操作加密数据时面临的挑战。通过详细分析和错误调查,我们提供了一些关键观察结果,这些结果揭示了LLM在密码学推理方面的局限性和潜在的改进方向。这些发现强调了LLM推理能力持续进步的必要性和重要性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Work in progress
摘要
大型语言模型(LLMs)在推理能力方面展现出显著的优势,特别是在o1和o3等领域的进步推动了人工智能的边界。尽管在数学和编码方面取得了令人印象深刻的成就,但在需要加密专业知识的领域中,LLMs的推理能力仍然未被充分探索。本文介绍了一个名为CipherBank的综合性基准测试,旨在评估LLMs在加密解密任务中的推理能力。CipherBank包含2,358个精心构建的问题,涵盖262个唯一明文,涉及5个领域和14个子领域,重点关注需要加密的隐私敏感和现实世界场景。从加密的角度来看,CipherBank纳入了三大加密方法,涵盖9种不同的算法,从经典密码到自定义加密技术不等。我们评估了最新的大型语言模型(如GPT-4o、DeepSeek-V3以及面向推理的模型o1和DeepSeek-R1)在CipherBank上的表现。我们的研究结果显示,不仅在通用聊天LLM和面向推理的LLM之间存在推理能力的差距,而且在将当前面向推理的模型应用于经典加密解密任务时,其性能也表现出显著不足,这表明这些模型在理解和操作加密数据方面面临着挑战。通过详细分析和错误调查,我们提供了一些关键观察结果,揭示了LLMs在加密推理方面的局限性和潜在改进方向。这些发现强调了LLM推理能力持续发展的必要性。
关键见解
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在推理方面展现出显著的优势,特别是在数学和编码领域。
- 在需要加密专业知识的领域中,LLMs的推理能力仍然未被充分探索。
- CipherBank基准测试用于评估LLMs在加密解密任务中的推理能力,包含多种精心构建的问题,覆盖多个领域和算法。
- 评估结果显示,现有LLMs在经典加密解密任务中的性能存在显著差距和不足。
- 分析揭示了LLMs在理解和操作加密数据方面的局限性。
- 需要持续改进和发展LLM的推理能力,以应对加密领域的挑战。
点此查看论文截图
MediAug: Exploring Visual Augmentation in Medical Imaging
Authors:Xuyin Qi, Zeyu Zhang, Canxuan Gang, Hao Zhang, Lei Zhang, Zhiwei Zhang, Yang Zhao
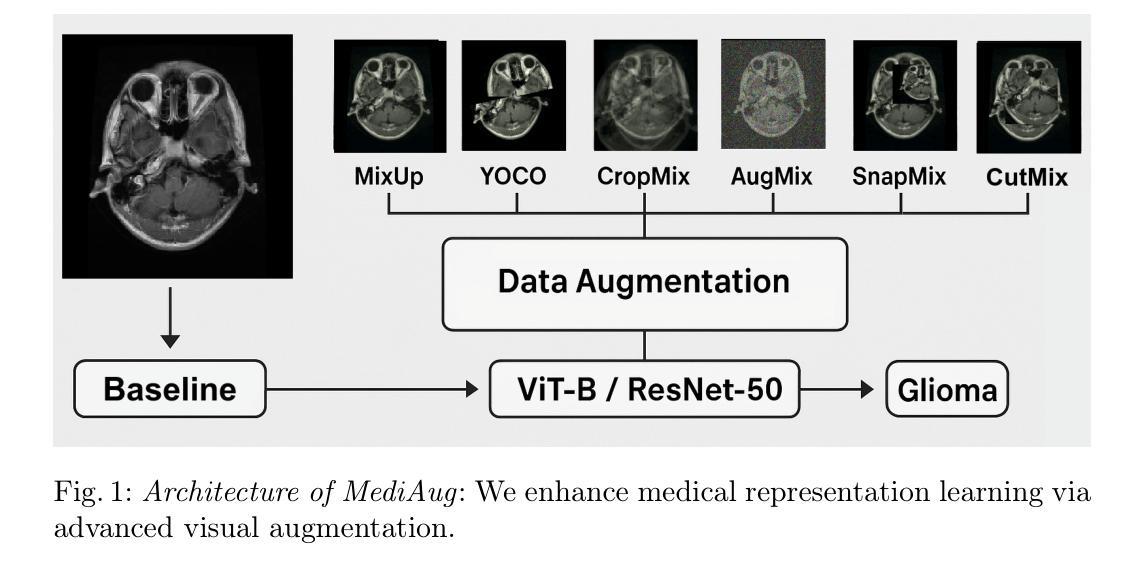
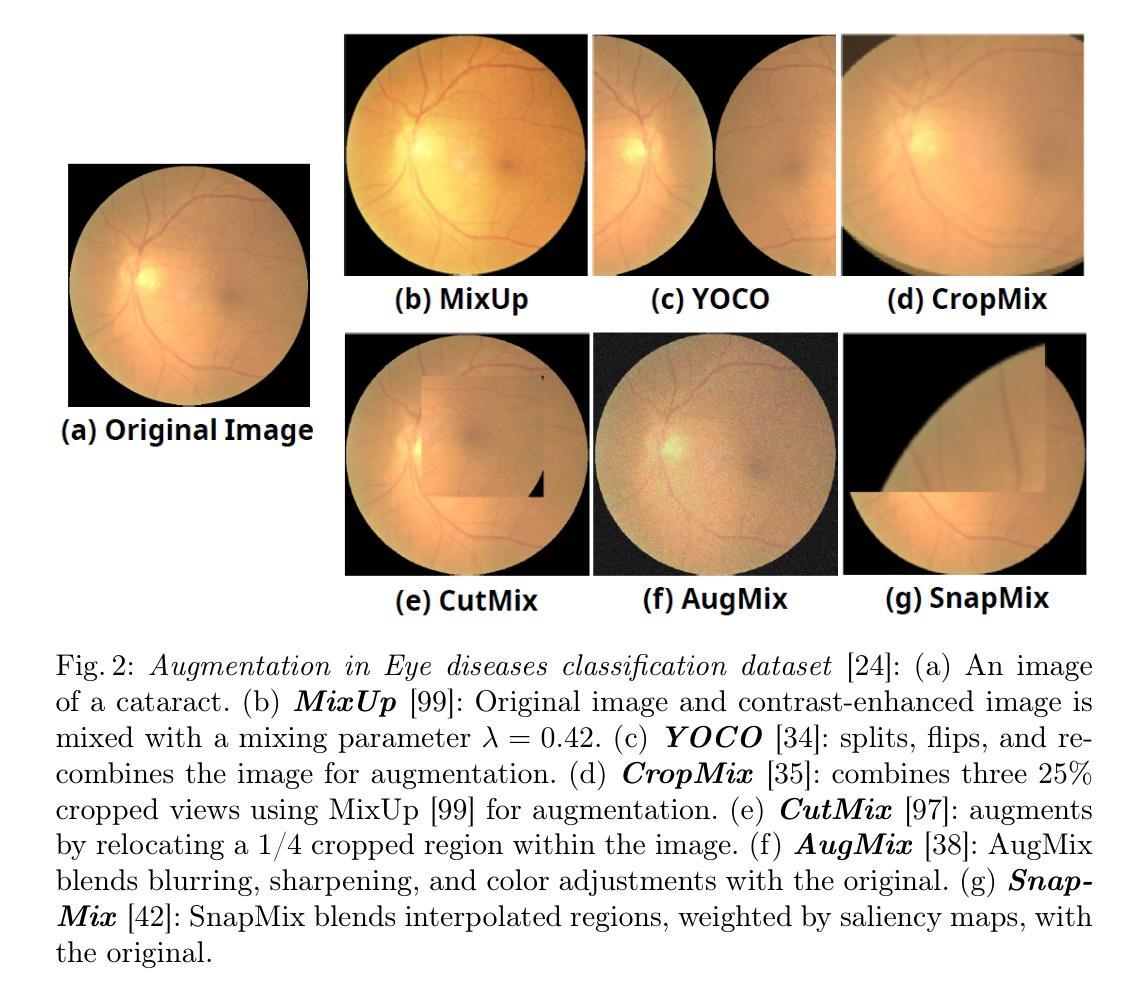
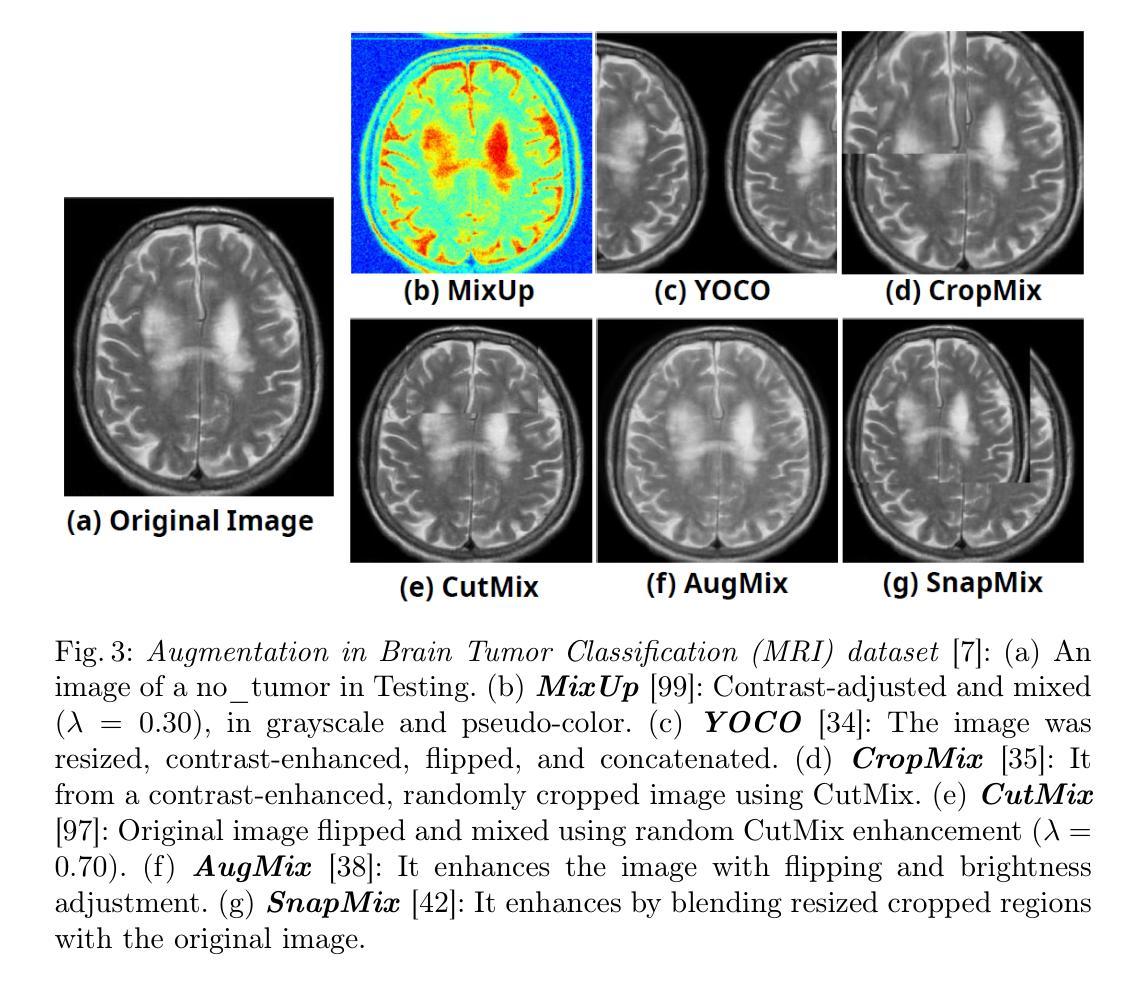
Data augmentation is essential in medical imaging for improving classification accuracy, lesion detection, and organ segmentation under limited data conditions. However, two significant challenges remain. First, a pronounced domain gap between natural photographs and medical images can distort critical disease features. Second, augmentation studies in medical imaging are fragmented and limited to single tasks or architectures, leaving the benefits of advanced mix-based strategies unclear. To address these challenges, we propose a unified evaluation framework with six mix-based augmentation methods integrated with both convolutional and transformer backbones on brain tumour MRI and eye disease fundus datasets. Our contributions are threefold. (1) We introduce MediAug, a comprehensive and reproducible benchmark for advanced data augmentation in medical imaging. (2) We systematically evaluate MixUp, YOCO, CropMix, CutMix, AugMix, and SnapMix with ResNet-50 and ViT-B backbones. (3) We demonstrate through extensive experiments that MixUp yields the greatest improvement on the brain tumor classification task for ResNet-50 with 79.19% accuracy and SnapMix yields the greatest improvement for ViT-B with 99.44% accuracy, and that YOCO yields the greatest improvement on the eye disease classification task for ResNet-50 with 91.60% accuracy and CutMix yields the greatest improvement for ViT-B with 97.94% accuracy. Code will be available at https://github.com/AIGeeksGroup/MediAug.
数据增强在医学成像中至关重要,有助于提高分类精度、病变检测和在有限数据条件下的器官分割。然而,仍存在两个重大挑战。首先,自然照片和医学图像之间明显的领域差距可能会扭曲关键疾病特征。其次,医学成像中的增强研究零散且仅限于单一任务或架构,使得混合策略的优势尚不清楚。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一个统一的评估框架,集成了六种基于混合的增强方法,并结合卷积和transformer骨干网,在脑肿瘤MRI和眼底疾病数据集上进行应用。我们的贡献有三点。(1)我们引入了MediAug,这是医学成像中高级数据增强的全面可重现基准。 (2)我们系统地评估了MixUp、YOCO、CropMix、CutMix、AugMix和SnapMix与ResNet-50和ViT-B骨干网的效果。(3)我们通过大量实验证明,MixUp在ResNet-50的脑肿瘤分类任务上取得了最大的改进,准确率为79.19%,SnapMix在ViT-B上取得了最大的改进,准确率为99.44%;YOCO在ResNet-50的眼病分类任务上取得了最大改进,准确率为91.60%,CutMix在ViT-B上取得了最大的改进,准确率为97.94%。代码将在https://github.com/AIGeeksGroup/MediAug上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
数据增强在医学成像中对于提高分类精度、病变检测以及器官分割在有限数据条件下的性能至关重要。然而,仍存在两个主要挑战:一是自然照片与医学图像之间的明显域差距可能导致疾病特征失真;二是医学成像中的增强研究零散且仅限于单一任务或架构,使得混合策略的优势不明朗。为应对这些挑战,我们提出了一个统一的评估框架,集成了六种混合增强方法,并结合卷积和transformer骨干网在脑肿瘤MRI和眼底疾病数据集上进行实验。我们引入了MediAug,这是一个用于医学成像的高级数据增强的综合可重复基准测试。通过系统评估六种混合方法(MixUp、YOCO、CropMix、CutMix、AugMix和SnapMix)与ResNet-50和ViT-B骨干网结合,我们发现在脑肿瘤分类任务中,MixUp对ResNet-50的准确度提高最大,达到79.19%;在眼底疾病分类任务中,YOCO对ResNet-50的准确度提高最大,达到91.60%。代码将公开在https://github.com/AIGeeksGroup/MediAug。
Key Takeaways
- 数据增强在医学成像中对于提高分类精度、病变检测和器官分割至关重要,尤其在有限数据条件下。
- 当前面临两大挑战:自然照片与医学图像间的域差距导致的疾病特征失真,以及碎片化研究使得混合增强策略的优势不明确。
- 提出一个统一的评估框架来评估六种混合增强方法(MixUp、YOCO等),结合卷积和transformer骨干网进行实验。
- 引入MediAug作为医学成像中的高级数据增强综合基准测试。
- MixUp在脑肿瘤分类任务中对ResNet-50的准确度提高最大,达到79.19%。
- YOCO在眼底疾病分类任务中对ResNet-50的准确度提高最大,达到91.60%。
点此查看论文截图

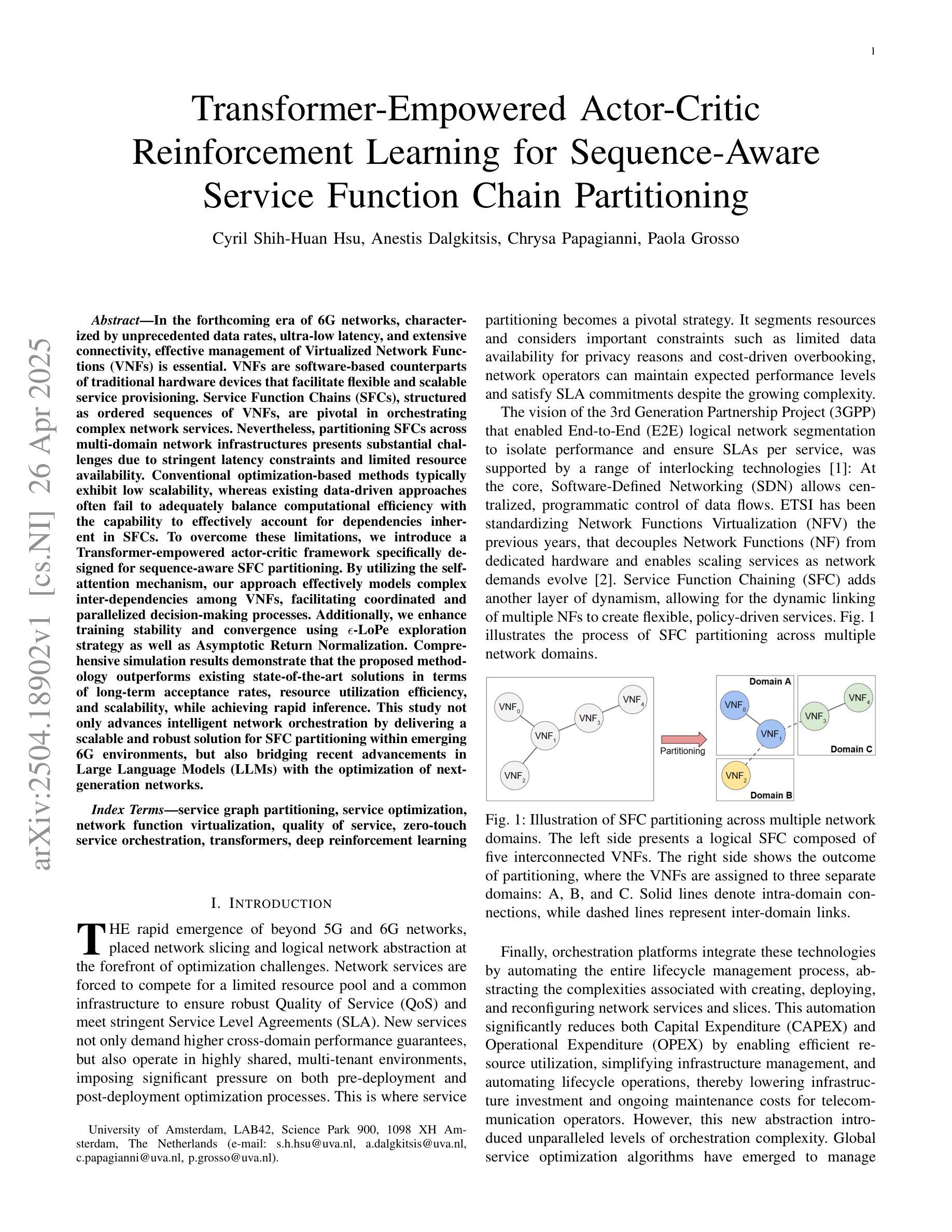
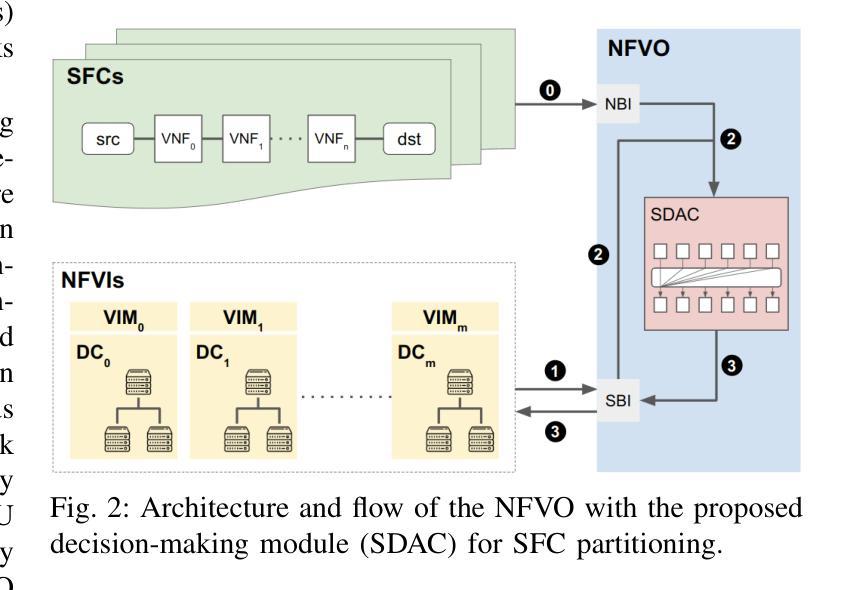
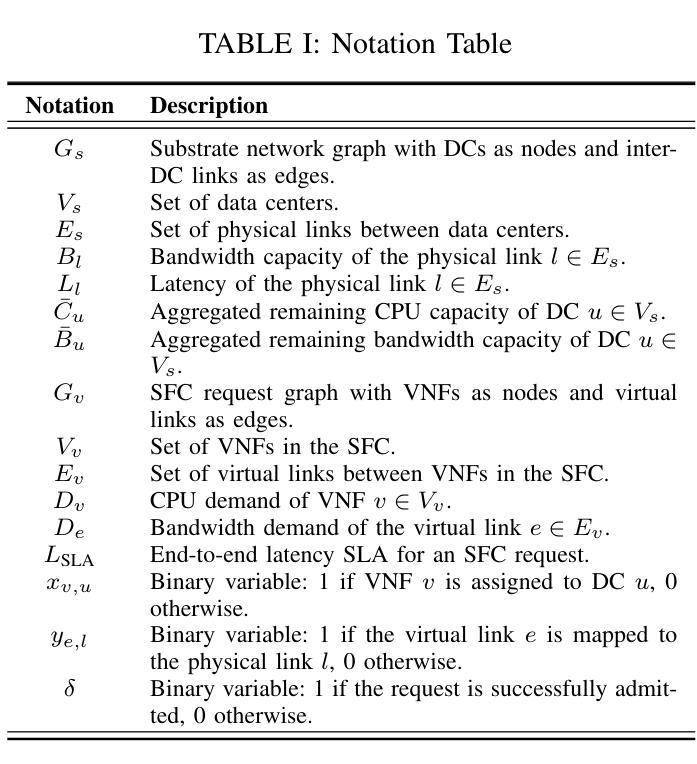
Transformer-Empowered Actor-Critic Reinforcement Learning for Sequence-Aware Service Function Chain Partitioning
Authors:Cyril Shih-Huan Hsu, Anestis Dalgkitsis, Chrysa Papagianni, Paola Grosso
In the forthcoming era of 6G networks, characterized by unprecedented data rates, ultra-low latency, and extensive connectivity, effective management of Virtualized Network Functions (VNFs) is essential. VNFs are software-based counterparts of traditional hardware devices that facilitate flexible and scalable service provisioning. Service Function Chains (SFCs), structured as ordered sequences of VNFs, are pivotal in orchestrating complex network services. Nevertheless, partitioning SFCs across multi-domain network infrastructures presents substantial challenges due to stringent latency constraints and limited resource availability. Conventional optimization-based methods typically exhibit low scalability, whereas existing data-driven approaches often fail to adequately balance computational efficiency with the capability to effectively account for dependencies inherent in SFCs. To overcome these limitations, we introduce a Transformer-empowered actor-critic framework specifically designed for sequence-aware SFC partitioning. By utilizing the self-attention mechanism, our approach effectively models complex inter-dependencies among VNFs, facilitating coordinated and parallelized decision-making processes. Additionally, we enhance training stability and convergence using $\epsilon$-LoPe exploration strategy as well as Asymptotic Return Normalization. Comprehensive simulation results demonstrate that the proposed methodology outperforms existing state-of-the-art solutions in terms of long-term acceptance rates, resource utilization efficiency, and scalability, while achieving rapid inference. This study not only advances intelligent network orchestration by delivering a scalable and robust solution for SFC partitioning within emerging 6G environments, but also bridging recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) with the optimization of next-generation networks.
在即将到来的6G网络时代,以其前所未有的数据速率、超低延迟和广泛连接性为特征,对虚拟化网络功能(VNFs)的有效管理至关重要。VNFs是传统硬件设备基于软件的对应物,有助于灵活且可扩展的服务提供。作为VNFs有序序列的服务功能链(SFCs)在协调复杂网络服务方面至关重要。然而,在多域网络基础设施中划分SFCs面临着巨大的挑战,因为存在严格的延迟约束和资源可用性限制。传统的优化方法通常可扩展性较低,而现有的数据驱动方法往往不能在计算效率和SFCs固有的依赖性的有效考量之间取得平衡。为了克服这些局限性,我们引入了一种由Transformer赋能的Actor-Critic框架,该框架专门用于序列感知的SFC划分。通过利用自注意力机制,我们的方法有效地建模了VNFs之间的复杂相互依赖性,促进了协调和并行化的决策过程。此外,我们还使用ε-LoPe探索策略和渐近回报归一化增强了训练的稳定性和收敛性。综合仿真结果表明,所提出的方法在长期接受率、资源利用效率和可扩展性方面优于现有的最新解决方案,同时实现了快速推理。本研究不仅通过为新兴6G环境中的SFC划分提供可伸缩和稳健的解决方案来推动智能网络编排的发展,而且还将最新的大型语言模型(LLMs)与下一代网络的优化相结合。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
在即将到来的6G网络时代,以虚拟网络功能(VNFs)的有效管理为核心,软件化的VNFs替代了传统的硬件设备以实现灵活且可扩展的服务供应。服务函数链(SFCs)作为一系列有序的VNFs,在编排复杂的网络服务中扮演着至关重要的角色。然而,在跨多域网络基础设施的SFC分区面临诸多挑战,如延迟约束严格和资源可用性有限等。传统优化方法缺乏可扩展性,而现有的数据驱动方法在计算效率和SFC固有依赖性的平衡方面存在不足。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了一种基于Transformer的actor-critic框架,专门用于序列感知的SFC分区。通过利用自注意力机制,我们的方法能够有效地模拟VNFs之间的复杂相互依赖性,实现协同和平行的决策过程。此外,我们还使用ε-LoPe探索策略和渐近回报归一化来增强训练稳定性和收敛性。仿真结果表明,该方法在长期接受率、资源利用效率和可扩展性方面优于现有解决方案,同时实现了快速推理。本研究不仅为新兴6G环境中的SFC分区提供了可扩展和稳健的解决方案,而且通过将大型语言模型(LLMs)的最新进展与下一代网络的优化相结合,推动了智能网络编排的发展。
关键见解
- 6G网络时代对VNFs的有效管理至关重要,它们在网络服务供应中替代了传统硬件。
- SFCs作为有序的VNF序列,在复杂的网络服务的编排中扮演着核心角色。
- SFC分区在多域网络基础设施中存在挑战,如延迟约束严格和资源可用性有限等。
- 现有方法在计算效率与SFC依赖性平衡方面存在不足。
- 提出了一种基于Transformer的actor-critic框架用于序列感知的SFC分区。
- 利用自注意力机制模拟VNF间的复杂依赖性并实现协同决策过程。
点此查看论文截图
Towards Robust Dialogue Breakdown Detection: Addressing Disruptors in Large Language Models with Self-Guided Reasoning
Authors:Abdellah Ghassel, Xianzhi Li, Xiaodan Zhu
Large language models (LLMs) are rapidly changing various domains. However, their capabilities in handling conversational breakdowns still require an in-depth exploration. This paper addresses the challenge of detecting and mitigating dialogue breakdowns within LLM-driven conversational systems. While powerful models from OpenAI and Anthropic excel in many dialogue tasks, they can still produce incoherent or contradictory responses, commonly referred to as breakdowns, which undermine user trust. To tackle this, we propose an approach that combines specialized fine-tuning with advanced prompting strategies, including few-shot learning, chain-of-thought reasoning, and analogical prompting. In particular, we fine-tune a small 8B model and demonstrate its robust classification and calibration capabilities in English and Japanese dialogue. We also validate its generalization on the BETOLD dataset, achieving a 7% accuracy improvement over its base model. Furthermore, we introduce a real-time deployment architecture that selectively escalates suspicious responses to more resource-intensive frontier models only when breakdowns are detected, significantly cutting operational expenses and energy consumption. Experimental results show our method surpasses prior state-of-the-art specialized classifiers while also narrowing performance gaps between smaller open-source models and large proprietary ones. Our approach offers a scalable solution for robust conversational AI in high-impact domains by combining efficiency, interpretability, and reliability.
大型语言模型(LLM)正在迅速改变各个领域。然而,它们在处理对话中断方面的能力仍然需要深入探索。本文旨在解决在LLM驱动的对话系统中检测和缓解对话中断的挑战。虽然OpenAI和Anthropic的强大模型在许多对话任务中表现出色,但它们仍然可能产生不连贯或矛盾的回应,这些回应通常被称为中断,会破坏用户信任。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种方法,它将专门的微调与先进的提示策略相结合,包括少样本学习、链式思维推理和类比提示。特别是,我们对一个小型的8B模型进行了微调,并展示了它在英语和日语对话中的稳健分类和校准能力。我们在BETOLD数据集上验证了其泛化能力,相较于基础模型实现了7%的准确率提升。此外,我们引入了一种实时部署架构,该架构仅在检测到中断时选择将可疑的响应升级到更耗费资源和计算资源的尖端模型,从而大幅减少运营开支和能源消耗。实验结果表明,我们的方法超越了现有的最先进的分类器,同时缩小了开源小型模型和大型专有模型之间的性能差距。通过结合效率、可解释性和可靠性,我们的方法为高影响力领域提供稳健对话AI的可扩展解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:大型语言模型(LLM)在多个领域展现出巨大潜力,但在处理对话中断方面仍存在挑战。本文提出一种结合专项微调与高级提示策略的方法,如小样本学习、链式思维推理和类比提示,以检测并缓解LLM驱动对话系统中的对话中断问题。通过微调一个小型8B模型,并在英语和日语对话中进行演示,验证了其稳健的分类和校准能力。同时,引入实时部署架构,仅在检测到对话中断时选择将可疑响应升级到资源密集型前沿模型,大大降低了操作成本和能源消耗。实验结果证明,该方法超越了现有的专业分类器,缩小了开源小型模型与大型专有模型之间的性能差距,为高效、可解释和可靠的对话AI提供了可扩展的解决方案。
Key Takeaways:
- 大型语言模型在处理对话中断方面存在挑战,需要深入研究。
- 论文提出了一种结合专项微调与高级提示策略的方法来解决这一问题。
- 通过微调一个小型8B模型,该方法在英文和日文对话中表现出稳健的分类和校准能力。
- 引入的实时部署架构可显著降低操作成本和能源消耗。
- 该方法超越了现有的专业分类器,并缩小了不同模型之间的性能差距。
- 论文提出的解决方案为高效、可解释和可靠的对话AI提供了可扩展的框架。
点此查看论文截图


ThinkFL: Self-Refining Failure Localization for Microservice Systems via Reinforcement Fine-Tuning
Authors:Lingzhe Zhang, Yunpeng Zhai, Tong Jia, Chiming Duan, Siyu Yu, Jinyang Gao, Bolin Ding, Zhonghai Wu, Ying Li
As modern microservice systems grow increasingly popular and complex-often consisting of hundreds or even thousands of fine-grained, interdependent components-they are becoming more susceptible to frequent and subtle failures. Ensuring system reliability therefore hinges on accurate and efficient failure localization. Traditional failure localization approaches based on small models lack the flexibility to adapt to diverse failure scenarios, while recent LLM-based methods suffer from two major limitations: they often rely on rigid invocation workflows that constrain the model’s ability to dynamically explore optimal localization paths, and they require resource-intensive inference, making them cost-prohibitive for real-world deployment. To address these challenges, we explore the use of reinforcement fine-tuning to equip lightweight LLMs with reasoning and self-refinement capabilities, significantly improving the cost-effectiveness and adaptability of LLM-based failure localization. We begin with an empirical study to identify three key capabilities essential for accurate localization. Building on these insights, we propose a progressive multi-stage GRPO fine-tuning framework, which integrates a multi-factor failure localization grader and a recursion-of-thought actor module. The resulting model, ThinkFL, not only outperforms existing state-of-the-art LLMs and baseline methods in localization accuracy but also reduces end-to-end localization latency from minutes to seconds, demonstrating strong potential for real-world applications.
随着现代微服务系统越来越受欢迎和复杂化——通常由数百个甚至数千个精细粒度、相互依赖的组件构成——它们更容易受到频繁和微妙的故障影响。因此,确保系统可靠性关键在于准确高效的故障定位。基于小型模型的传统故障定位方法缺乏适应多种故障场景的灵活性,而最近的基于大型语言模型(LLM)的方法则存在两大局限:它们通常依赖于僵化的调用工作流程,限制模型动态探索最佳定位路径的能力;它们需要资源密集型的推理,使得在现实世界部署中成本高昂。为了解决这些挑战,我们探索使用强化微调来为轻量级LLM配备推理和自精炼能力,显著提高了基于LLM的故障定位的成本效益和适应性。我们首先从实证研究出发,确定了实现准确定位所需的三个关键能力。基于这些见解,我们提出了一个分阶段的GRPO微调框架,它整合了多因素故障定位评分器和递归思维行动模块。由此产生的ThinkFL模型不仅在当地化准确性方面超越了现有的最先进的LLM和基线方法,而且将端到端的定位延迟从分钟减少到秒,显示出在实际应用中强大的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着现代微服务系统越来越受欢迎且变得复杂,频繁和微妙的故障定位问题变得尤为关键。传统方法缺乏灵活性,而基于LLM的方法则面临资源密集推理的问题。本研究通过强化微调赋予轻量级LLM推理和自我优化能力,解决了这些问题。研究始于实证研究,确定了三个关键定位能力,并在此基础上提出了一个进步式的多阶段GRPO微调框架ThinkFL。它整合了多因素故障定位评分器和递归思维模块,不仅提高了定位准确性,还大大缩短了定位延迟。这为实际应用展示了强大潜力。
Key Takeaways
以下是该文本的关键见解:
- 随着现代微服务系统的复杂性增加,故障定位变得至关重要。需要一种准确而有效的方法来处理这个挑战。
- 传统失败定位方法基于小型模型,缺乏适应多样失败场景的灵活性。基于LLM的方法虽然在理论上强大,但存在限制性问题。他们依赖于僵化的调用流程限制了模型的动态探索能力,同时需要资源密集推理。这限制了它们在实际部署中的可行性。为了克服这些挑战提出了结合强化微调策略的解决方案来优化LLM功能提出了以简化强化学习为核心的框架为改进提供了一个实用的方法利用模型的推理和自我优化能力以实现高效精确的故障定位这不仅可以提高模型性能还显著提高了系统的适应性和成本效益
点此查看论文截图

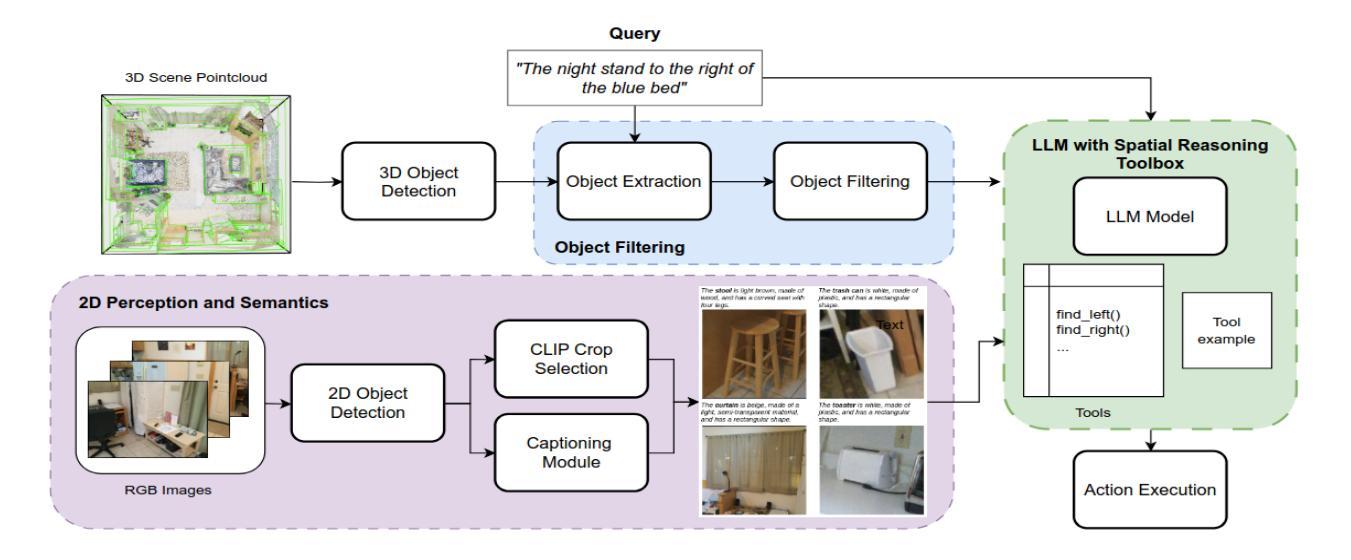
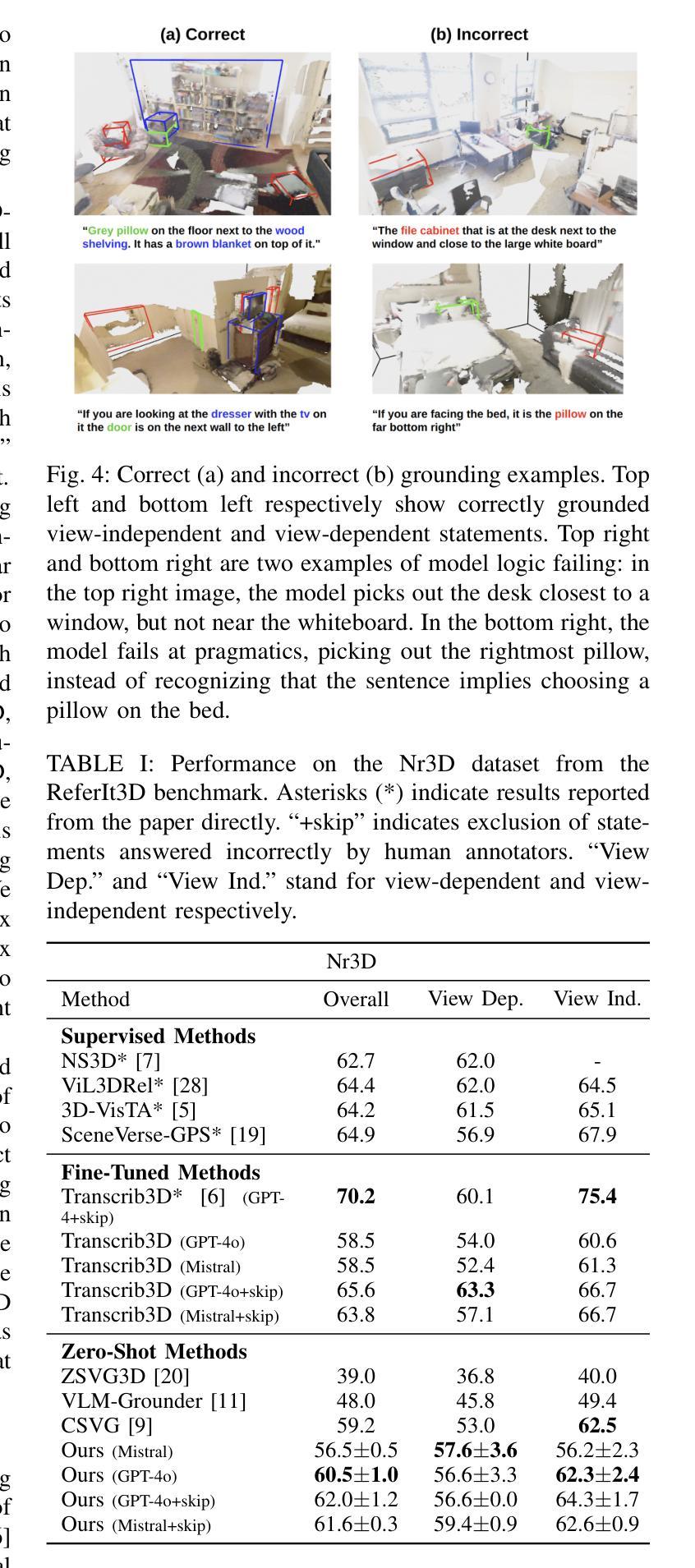
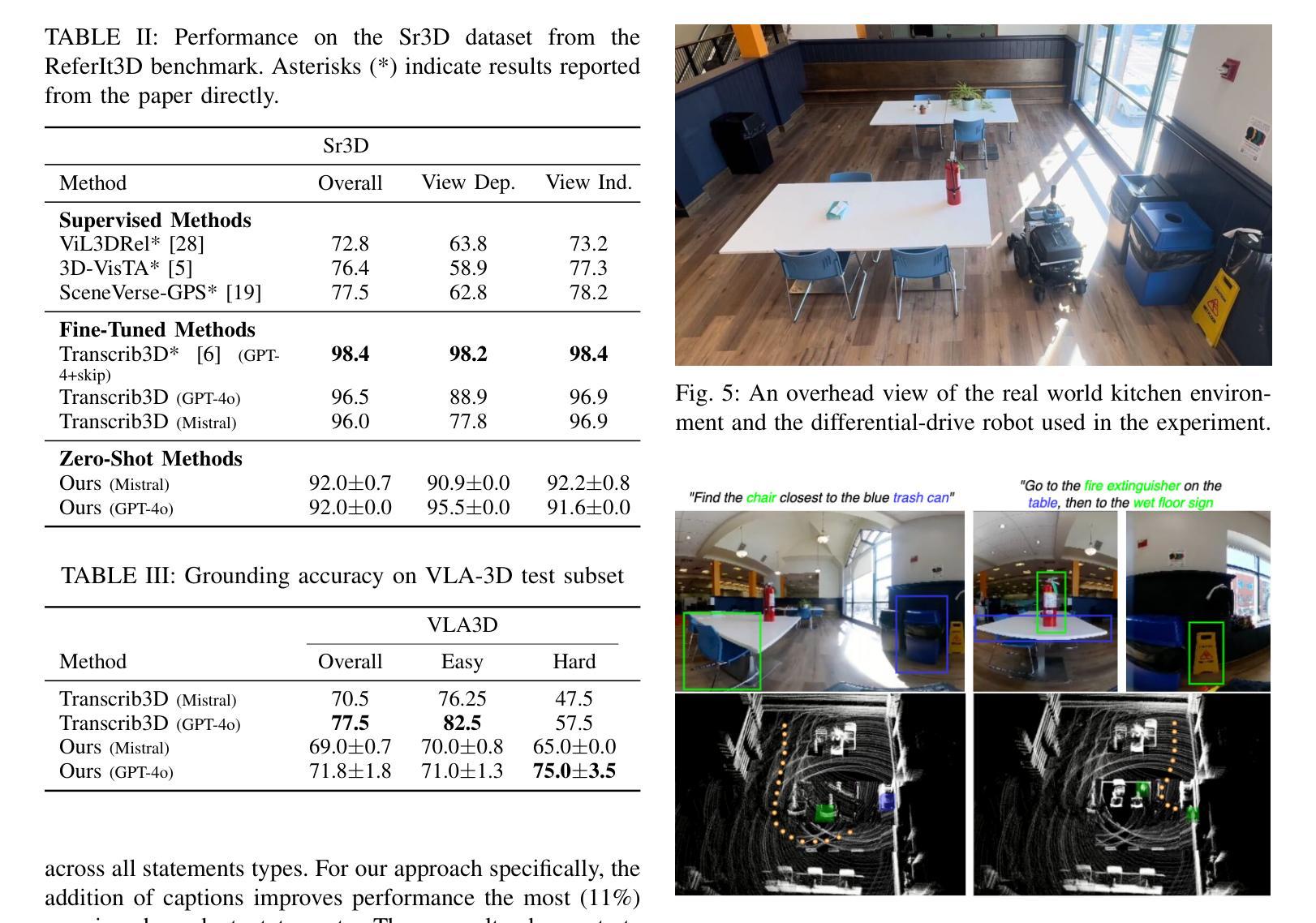
SORT3D: Spatial Object-centric Reasoning Toolbox for Zero-Shot 3D Grounding Using Large Language Models
Authors:Nader Zantout, Haochen Zhang, Pujith Kachana, Jinkai Qiu, Ji Zhang, Wenshan Wang
Interpreting object-referential language and grounding objects in 3D with spatial relations and attributes is essential for robots operating alongside humans. However, this task is often challenging due to the diversity of scenes, large number of fine-grained objects, and complex free-form nature of language references. Furthermore, in the 3D domain, obtaining large amounts of natural language training data is difficult. Thus, it is important for methods to learn from little data and zero-shot generalize to new environments. To address these challenges, we propose SORT3D, an approach that utilizes rich object attributes from 2D data and merges a heuristics-based spatial reasoning toolbox with the ability of large language models (LLMs) to perform sequential reasoning. Importantly, our method does not require text-to-3D data for training and can be applied zero-shot to unseen environments. We show that SORT3D achieves state-of-the-art performance on complex view-dependent grounding tasks on two benchmarks. We also implement the pipeline to run real-time on an autonomous vehicle and demonstrate that our approach can be used for object-goal navigation on previously unseen real-world environments. All source code for the system pipeline is publicly released at https://github.com/nzantout/SORT3D .
解释对象参照语言并将对象与三维空间中的关系和属性相对应,对于与人类协作的机器人来说至关重要。然而,由于场景多样性、精细对象的数量众多以及语言参照的自由形式复杂,这项任务往往具有挑战性。此外,在三维领域,获取大量自然语言训练数据是非常困难的。因此,方法需要从小量数据中学习并零样本推广到新的环境中。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了SORT3D方法,它利用二维数据中的丰富对象属性,并将基于启发式算法的空间推理工具箱与大型语言模型(LLM)进行序列推理的能力相结合。重要的是,我们的方法不需要文本到三维数据的训练,并且可以零样本应用于未见过的环境。我们在两个基准测试上的复杂视图相关定位任务上展示了SORT3D的卓越性能。我们还实现了实时运行在自动驾驶汽车上的管道,并证明我们的方法可用于之前在未见过的真实环境中的目标导航。系统管道的所有源代码已在https://github.com/nzantout/SORT3D公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, 6 figures, submitted to IROS 2025
Summary
本文提出一种名为SORT3D的方法,该方法结合了二维数据的丰富对象属性和基于启发式空间推理工具的能力,与大型语言模型进行序列化推理相结合。这种方法可以在无训练文本到三维数据的情况下进行零时差应用,并在复杂的环境中完成物体参照语言解释和三维空间物体定位任务。SORT3D在两项基准测试中实现了最先进的性能表现,并且在实际自动驾驶车辆上进行了实时运行测试。所有系统管道源代码均已公开发布。
Key Takeaways
- SORT3D结合了二维数据的丰富对象属性和启发式空间推理工具的能力。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)用于执行序列化推理。
- 方法无需文本到三维数据的训练,可零时差应用于新环境。
- SORT3D在复杂的环境中完成了物体参照语言解释和三维空间物体定位任务。
- 在两项基准测试中实现了最先进的性能表现。
- SORT3D已经在实际自动驾驶车辆上进行了实时运行测试。
点此查看论文截图


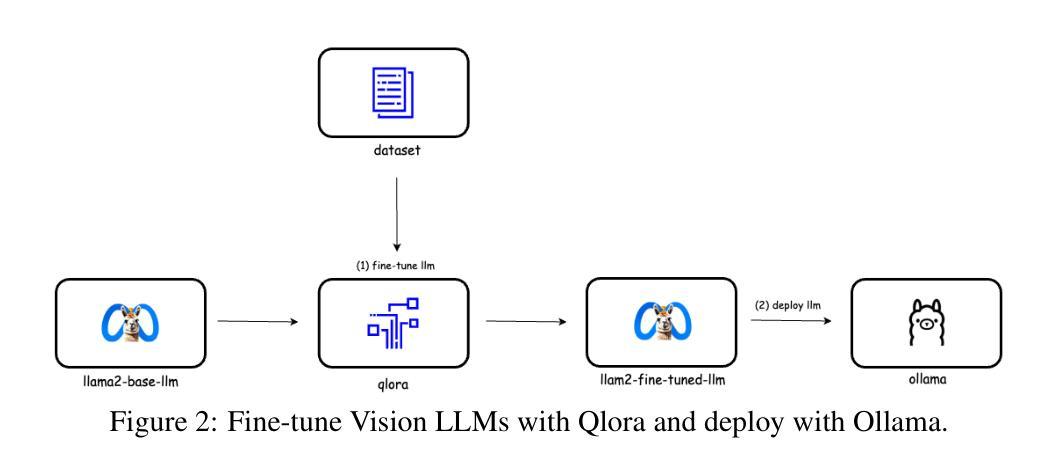
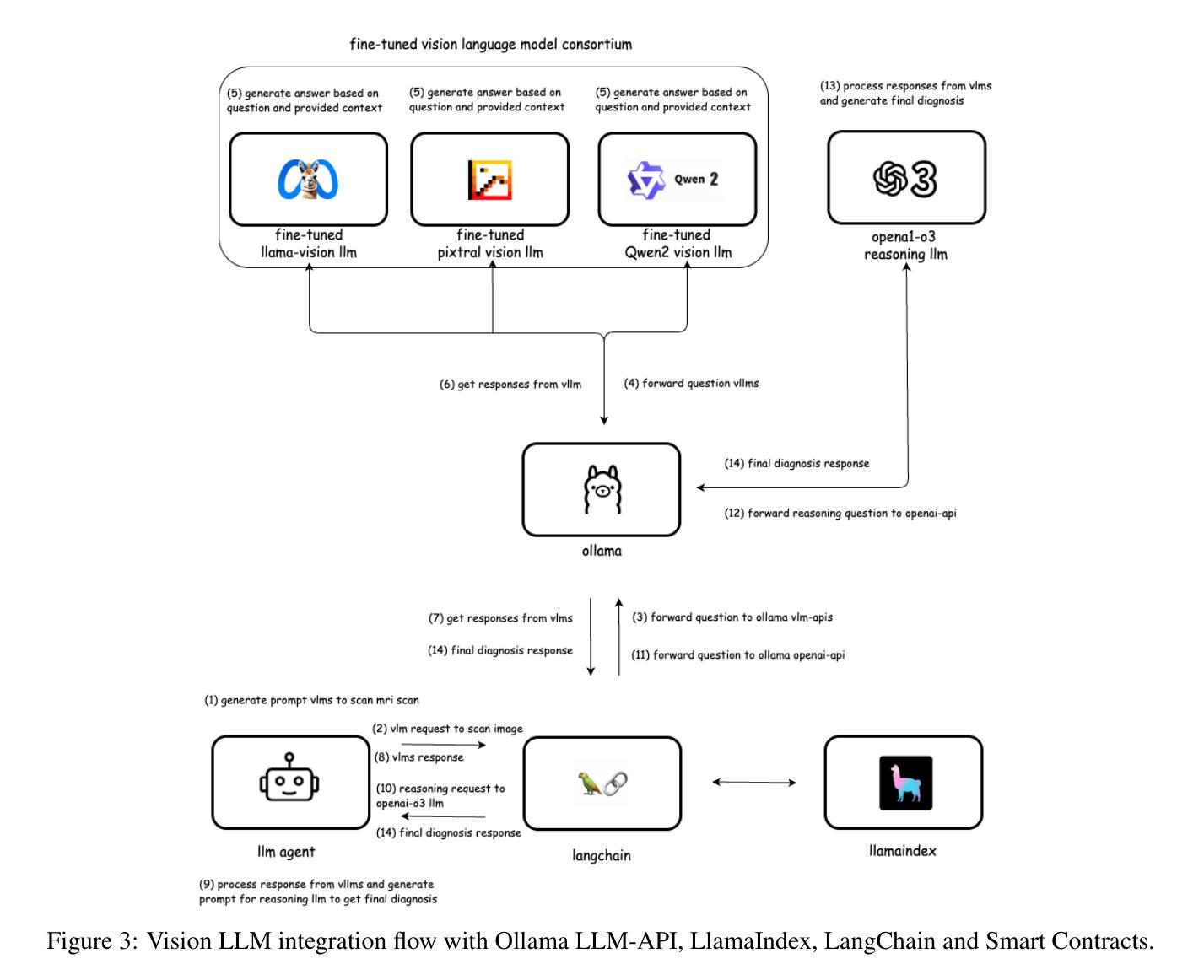
Proof-of-TBI – Fine-Tuned Vision Language Model Consortium and OpenAI-o3 Reasoning LLM-Based Medical Diagnosis Support System for Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Prediction
Authors:Ross Gore, Eranga Bandara, Sachin Shetty, Alberto E. Musto, Pratip Rana, Ambrosio Valencia-Romero, Christopher Rhea, Lobat Tayebi, Heather Richter, Atmaram Yarlagadda, Donna Edmonds, Steven Wallace, Donna Broshek
Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) detection presents significant challenges due to the subtle and often ambiguous presentation of symptoms in medical imaging, making accurate diagnosis a complex task. To address these challenges, we propose Proof-of-TBI, a medical diagnosis support system that integrates multiple fine-tuned vision-language models with the OpenAI-o3 reasoning large language model (LLM). Our approach fine-tunes multiple vision-language models using a labeled dataset of TBI MRI scans, training them to diagnose TBI symptoms effectively. The predictions from these models are aggregated through a consensus-based decision-making process. The system evaluates the predictions from all fine-tuned vision language models using the OpenAI-o3 reasoning LLM, a model that has demonstrated remarkable reasoning performance, to produce the most accurate final diagnosis. The LLM Agents orchestrates interactions between the vision-language models and the reasoning LLM, managing the final decision-making process with transparency, reliability, and automation. This end-to-end decision-making workflow combines the vision-language model consortium with the OpenAI-o3 reasoning LLM, enabled by custom prompt engineering by the LLM agents. The prototype for the proposed platform was developed in collaboration with the U.S. Army Medical Research team in Newport News, Virginia, incorporating five fine-tuned vision-language models. The results demonstrate the transformative potential of combining fine-tuned vision-language model inputs with the OpenAI-o3 reasoning LLM to create a robust, secure, and highly accurate diagnostic system for mild TBI prediction. To the best of our knowledge, this research represents the first application of fine-tuned vision-language models integrated with a reasoning LLM for TBI prediction tasks.
轻度脑外伤(Traumatic Brain Injury, TBI)检测面临显著挑战,因为在医学影像中,其症状表现微妙且常具模糊性,使得准确诊断成为一项复杂任务。为应对这些挑战,我们提出Proof-of-TBI诊断支持系统,它将多个微调后的视觉语言模型与OpenAI-o3推理大型语言模型(LLM)相结合。我们的方法使用带有标签的TBI核磁共振扫描数据集对多个视觉语言模型进行微调,训练它们有效诊断TBI症状。这些模型的预测结果通过基于共识的决策制定过程进行汇总。系统利用OpenAI-o3推理LLM评估所有微调后的视觉语言模型的预测结果。该模型展现出卓越的推理性能,用以产生最准确的最终诊断结果。LLM代理协调视觉语言模型和推理LLM之间的交互,以透明、可靠和自动化的方式管理最终决策制定过程。这一端到端的决策制定工作流程结合了视觉语言模型联盟和OpenAI-o3推理LLM,通过LLM代理的自定义提示工程得以实现。所提议平台的原型是与弗吉尼亚州纽波特纽斯美国陆军医学研究小组合作开发的,该平台结合了五个经过微调的语言视觉模型。结果表明,将经过微调的语言视觉模型输入与OpenAI-o3推理LLM相结合,具有创建稳健、安全和高精度诊断系统的潜力,用于预测轻度TBI。据我们所知,这项研究代表了首个将经过微调的视觉语言模型与推理LLM相结合用于预测TBI的任务。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
利用OpenAI-o3推理大型语言模型(LLM)和多款微调后的视觉语言模型,构建了一个名为Proof-of-TBI的医学诊断支持系统,以提高轻度脑外伤(TBI)检测的准确性。通过标记的TBI MRI扫描数据集对多个视觉语言模型进行微调,再通过共识决策过程进行预测。OpenAI-o3推理LLM负责评估这些模型的预测结果,以产生最准确的最终诊断结果。实现了端到端的决策流程自动化。该项目为首创,具有变革潜力。
Key Takeaways
- Proof-of-TBI系统结合了多个微调后的视觉语言模型和OpenAI-o3推理大型语言模型(LLM),以提高轻度脑外伤(TBI)诊断的准确性。
- 系统通过共识决策过程进行预测诊断,这一过程基于所有经过微调验证的视觉语言模型做出的预测评估。
- OpenAI-o3推理LLM在整个决策过程中起到核心作用,不仅负责评估模型的预测结果,而且产出最准确的最终诊断报告。
- 该系统的关键特点是实现自动化和端到端的决策流程,提升了决策过程的透明度和可靠性。
- LLM代理负责管理视觉语言模型和推理LLM之间的交互,推动了系统的运作和最终决策流程的顺畅执行。
- 该系统的原型与美国陆军医学研究团队合作开发,并成功集成了五个经过微调验证的视觉语言模型。
点此查看论文截图

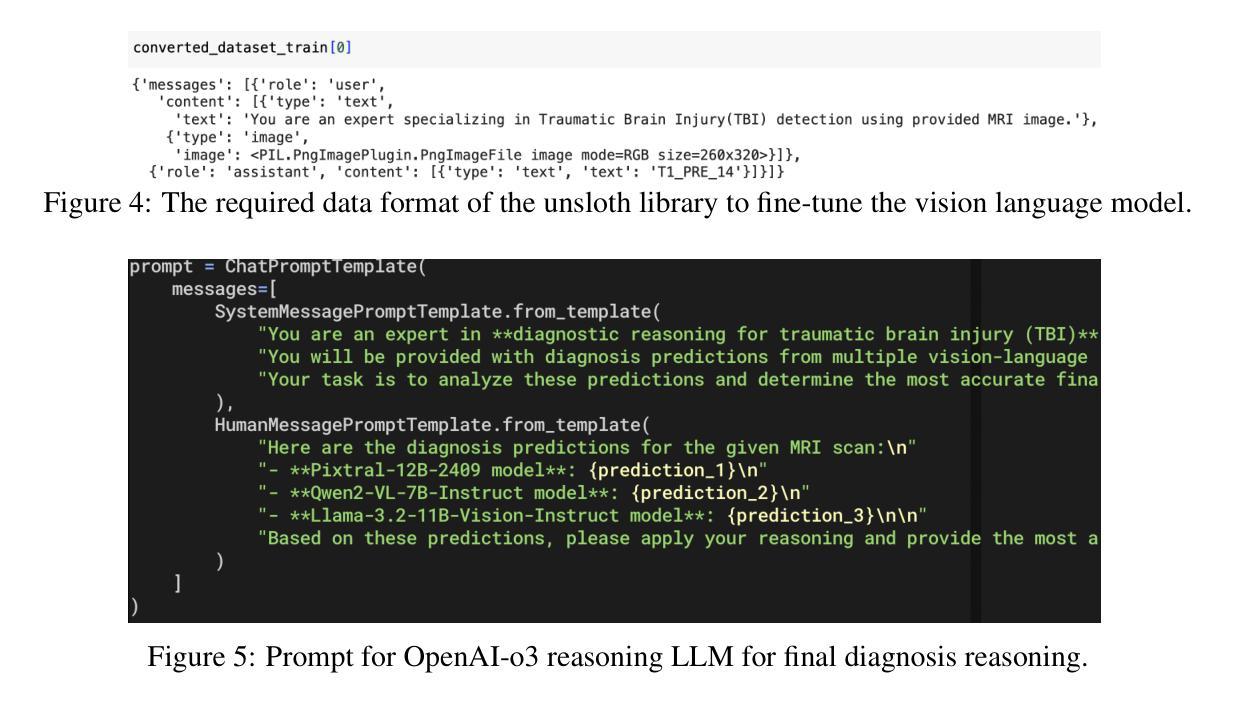
Research on Personalized Medical Intervention Strategy Generation System based on Group Relative Policy Optimization and Time-Series Data Fusion
Authors:Dingxin Lu, Shurui Wu, Xinyi Huang
With the timely formation of personalized intervention plans based on high-dimensional heterogeneous time series information becoming an important challenge in the medical field today, electronic medical records, wearables, and other multi-source medical data are increasingly generated and diversified. In this work, we develop a system to generate personalized medical intervention strategies based on Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) and Time-Series Data Fusion. First, by incorporating relative policy constraints among the groups during policy gradient updates, we adaptively balance individual and group gains. To improve the robustness and interpretability of decision-making, a multi-layer neural network structure is employed to group-code patient characteristics. Second, for the rapid multi-modal fusion of multi-source heterogeneous time series, a multi-channel neural network combined with a self-attention mechanism is used for dynamic feature extraction. Key feature screening and aggregation are achieved through a differentiable gating network. Finally, a collaborative search process combining a genetic algorithm and Monte Carlo tree search is proposed to find the ideal intervention strategy, achieving global optimization. Experimental results show significant improvements in accuracy, coverage, and decision-making benefits compared with existing methods.
随着基于高维异质时间序列信息及时形成个性化干预计划成为当今医疗领域的重要挑战,电子病历、可穿戴设备等多元医疗数据不断生成和多样化。在这项工作中,我们开发了一个系统,该系统基于群体相对策略优化(GRPO)和时序数据融合生成个性化医疗干预策略。首先,通过在策略梯度更新中融入群体间的相对策略约束,我们自适应地平衡了个体和群体的收益。为了提高决策的稳健性和可解释性,我们采用多层神经网络结构对患者特征进行分组编码。其次,为了迅速多模态融合多源异质时间序列,我们采用结合自注意力机制的多通道神经网络进行动态特征提取。关键特征的筛选和聚合通过可微分门控网络实现。最后,我们提出一种结合遗传算法和蒙特卡洛树搜索的协同搜索过程,以找到理想的干预策略,实现全局优化。实验结果表明,与现有方法相比,该方法在准确性、覆盖率和决策效益方面都有显著提高。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于高维异质时间序列信息及时制定个性化干预计划,已成为当今医疗领域的重要挑战。本研究开发了一种基于群组相对策略优化(GRPO)和时序数据融合的系统,生成个性化医疗干预策略。通过融入群组相对策略约束,平衡个体与群体收益;采用多层神经网络结构进行患者特征分组编码,提高决策稳健性和可解释性。对于多源异质时间序列的快速多模式融合,结合多通道神经网络与自注意力机制进行动态特征提取。通过可微分的门控网络实现关键特征筛选和聚合。最后,结合遗传算法和蒙特卡洛树搜索的协作搜索过程,找到理想的干预策略,实现全局优化。实验结果相较于现有方法,在准确性、覆盖率和决策效益方面均有显著提升。
Key Takeaways
- 研究针对医疗领域的个性化干预计划制定挑战,提出基于群组相对策略优化(GRPO)和时序数据融合的系统。
- 通过融入群组相对策略约束,平衡个体与群体收益。
- 采用多层神经网络结构进行患者特征分组编码,提高决策的稳健性和可解释性。
- 利用多通道神经网络与自注意力机制,实现多源异质时间序列的快速多模式融合和动态特征提取。
- 通过可微分的门控网络进行关键特征筛选和聚合。
- 结合遗传算法和蒙特卡洛树搜索,找到理想干预策略,实现全局优化。
- 相比现有方法,该系统在准确性、覆盖率和决策效益方面有明显提升。
点此查看论文截图

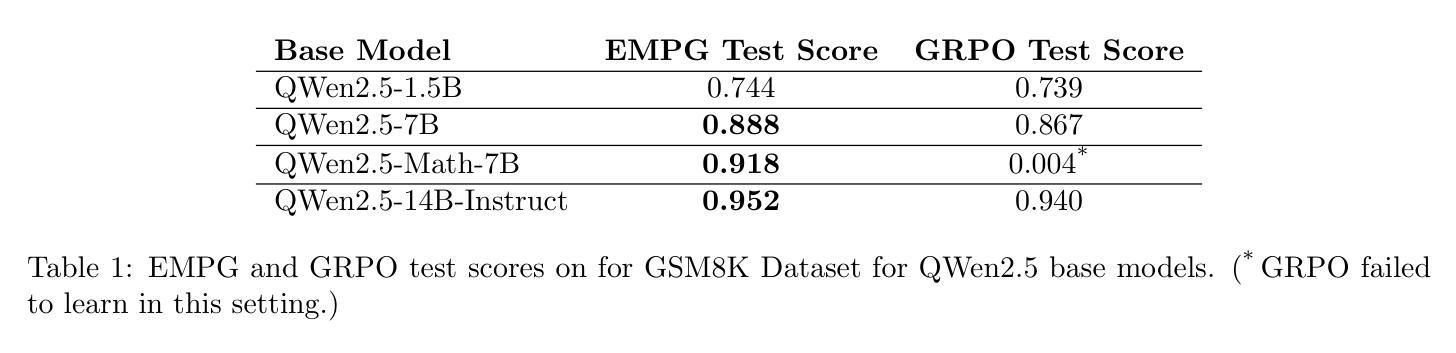
Training Large Language Models to Reason via EM Policy Gradient
Authors:Tianbing Xu
Recently, foundation models such as OpenAI’s O1 and O3, along with DeepSeek’s R1, have demonstrated strong reasoning capacities and problem-solving skills acquired through large-scale reinforcement learning (RL), with wide applications in mathematics, coding, science, intelligent agents, and virtual assistants. In this work, we introduce an off-policy reinforcement learning algorithm, EM Policy Gradient, aimed at enhancing LLM reasoning by optimizing expected return over reasoning trajectories. We frame the reasoning task as an Expectation-Maximization (EM) optimization problem, alternating between sampling diverse rationale trajectories and performing reward-guided fine-tuning. Unlike PPO and GRPO, which rely on complex importance weights and heuristic clipping, our method provides a simpler, more principled off-policy policy gradient approach, eliminating these complexities while maintaining strong performance. We evaluate the effectiveness of EM Policy Gradient on the GSM8K and MATH (HARD) datasets, where it achieves performance comparable to or slightly surpassing the state-of-the-art GRPO, while offering additional advantages in scalability, simplicity, and reasoning conciseness. Moreover, models fine-tuned with our method exhibit cognitive behaviors, such as sub-problem decomposition, self-verification, and backtracking, highlighting its potential to enhance both the interpretability and robustness of LLM reasoning.
最近,如OpenAI的O1和O3以及DeepSeek的R1等基础模型,已经展现出通过大规模强化学习(RL)获得的强大推理能力和问题解决技能,广泛应用于数学、编程、科学、智能代理和虚拟助手等领域。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种离策略强化学习算法——EM策略梯度法,旨在通过优化推理轨迹的预期回报来提升大型语言模型(LLM)的推理能力。我们将推理任务构建为期望最大化(EM)优化问题,交替进行多样化推理轨迹采样和奖励引导微调。不同于依赖复杂重要性权重和启发式剪裁的PPO和GRPO,我们的方法提供了一种更简单、更基于原则的非策略策略梯度方法,在消除这些复杂性的同时保持了良好的性能。我们在GSM8K和MATH(HARD)数据集上评估了EM策略梯度的有效性,其在性能上达到了或略微超过了最先进的GRPO,同时在可扩展性、简单性和推理简洁性方面提供了额外的优势。此外,使用我们的方法微调后的模型展现出认知行为,如子问题分解、自我验证和回溯,这突显了其增强大型语言模型推理的可解释性和稳健性的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于大型强化学习的能力,OpenAI的O系列模型以及DeepSeek的R系列模型展现出强大的推理能力和问题解决技能,广泛应用于数学、编程、科学等领域。本研究引入了一种基于预期收益优化的期望最大化策略梯度强化学习算法,旨在优化LLM推理能力。通过交替进行多样化推理轨迹采样和奖励引导微调,该方法在GSM8K和MATH(HARD)数据集上的表现优异,甚至优于当前的顶级GRPO方法,同时在扩展性、简洁性和推理准确性方面表现出额外优势。模型经过此方法的微调后展现出子问题分解、自我验证和回溯等认知行为,暗示其在增强LLM推理的解释性和稳健性方面的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 大型强化学习模型如OpenAI的O系列和DeepSeek的R系列展现出强大的推理和问题解决能力。
- 提出了一种基于期望最大化的策略梯度强化学习算法,用于优化LLM推理能力。
- 该方法通过交替采样多样化推理轨迹和奖励引导微调来提升性能。
- 该方法在GSM8K和MATH(HARD)数据集上的表现优异,性能堪比或略优于GRPO。
- 方法在扩展性、简洁性和推理准确性方面表现出额外优势。
点此查看论文截图

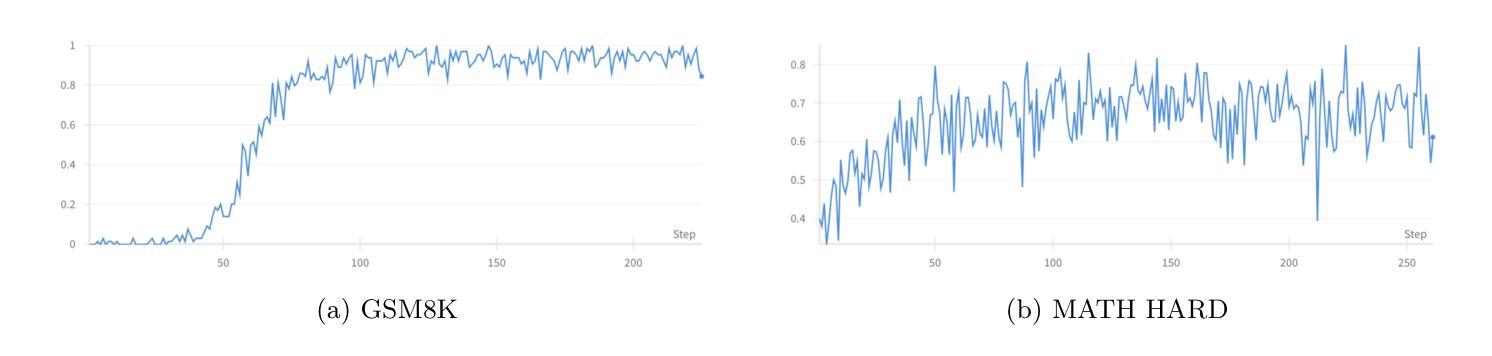
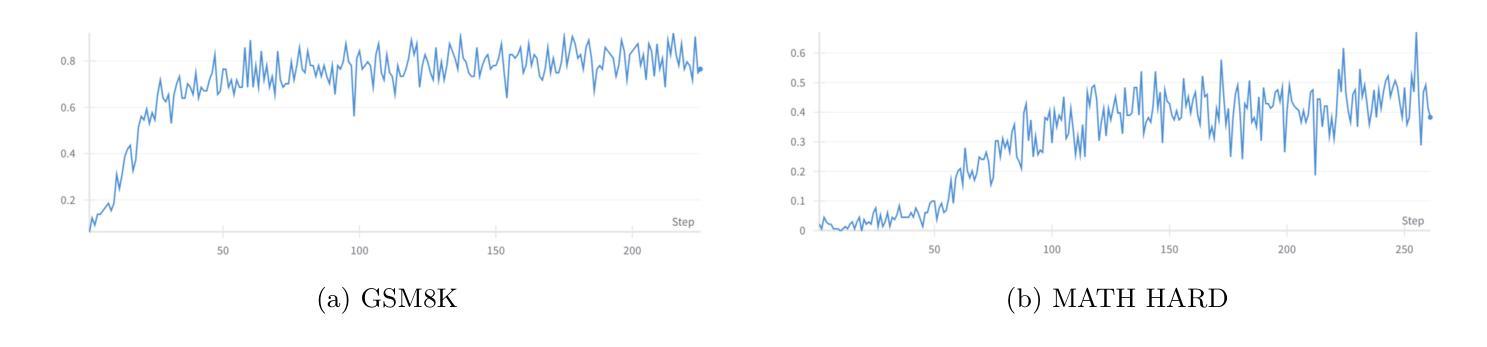
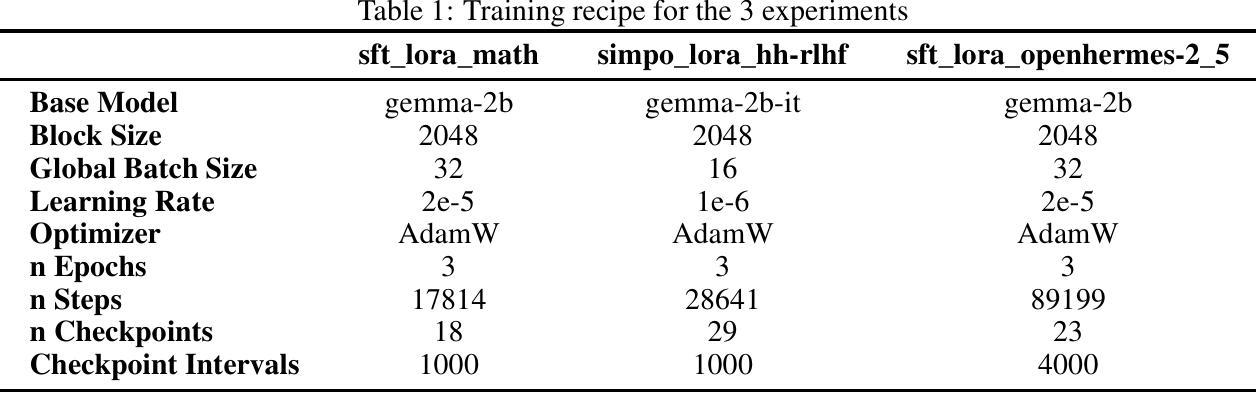
Parameter-Efficient Checkpoint Merging via Metrics-Weighted Averaging
Authors:Shi Jie Yu, Sehyun Choi
Checkpoint merging is a technique for combining multiple model snapshots into a single superior model, potentially reducing training time for large language models. This paper explores checkpoint merging in the context of parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT), where only small adapter modules (e.g. LoRA) are trained. We propose Metrics-Weighted Averaging (MWA), a simple yet effective method to merge model checkpoints by weighting their parameters according to performance metrics. In particular, we investigate weighting by training loss and by training steps, under the intuition that lower-loss or later-step checkpoints are more valuable. We introduce a formula with a penalty factor to adjust weight distribution, requiring only one hyperparameter regardless of the number of checkpoints. Experiments on three fine-tuning tasks (mathematical reasoning, preference alignment, and general instruction tuning) show that MWA consistently produces merged models that outperform the naive uniform average of checkpoints. Notably, loss-weighted merging often yields the best results, delivering up to 5% higher task accuracy than the baseline uniform merge and even surpassing the final individual checkpoint’s performance. These findings validate checkpoint merging for PEFT and demonstrate that a metric-driven weighting heuristic can efficiently boost model performance with minimal computational overhead.
模型检查点合并是一种将多个模型快照合并为一个更优质模型的技术,有望减少大型语言模型的训练时间。本文针对参数高效微调(PEFT)中的检查点合并进行了探讨,在这里只训练较小的适配器模块(例如LoRA)。我们提出了Metrics-Weighted Averaging(MWA),这是一种简单而有效的方法,通过根据性能指标对模型检查点的参数进行加权来合并检查点。特别是,我们根据训练损失和训练步骤进行加权,直觉认为损失较低或步骤较晚的检查点更有价值。我们引入了一个带有惩罚因子的公式来调整权重分布,无论检查点的数量如何,只需一个超参数。在三个微调任务(数学推理、偏好对齐和通用指令调整)上的实验表明,MWA持续产生合并模型,其性能优于检查点的简单均匀平均值。值得注意的是,损失加权合并往往产生最佳结果,比基线均匀合并高出高达5%的任务准确性,甚至超过最终单个检查点的性能。这些发现验证了检查点合并对于PEFT的有效性,并表明指标驱动的加权启发式策略可以在几乎不增加计算开销的情况下有效提高模型性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了参数高效微调(PEFT)中的检查点合并技术,并提出了Metrics-Weighted Averaging(MWA)方法。该方法根据性能度量对模型检查点的参数进行加权合并。实验表明,MWA方法产生的合并模型性能优于简单平均合并,其中损失加权合并效果最佳,任务准确率较基线方法提高达5%。
Key Takeaways
- 检查点合并是一种结合多个模型快照以形成单一优秀模型的技术,可缩短大型语言模型的训练时间。
- 文章介绍了在参数高效微调(PEFT)背景下检查点合并的探究,其中只训练小型的适配器模块(如LoRA)。
- 提出了Metrics-Weighted Averaging(MWA)方法,根据性能度量对模型检查点的参数进行加权合并。
- MWA方法通过考虑损失值和训练步骤来确定权重。
- 引入了一个公式来调整权重分布,只需一个超参数,无论检查点数量如何。
- 在三个微调任务上的实验表明,MWA方法产生的合并模型性能优于简单的平均合并方法。
点此查看论文截图

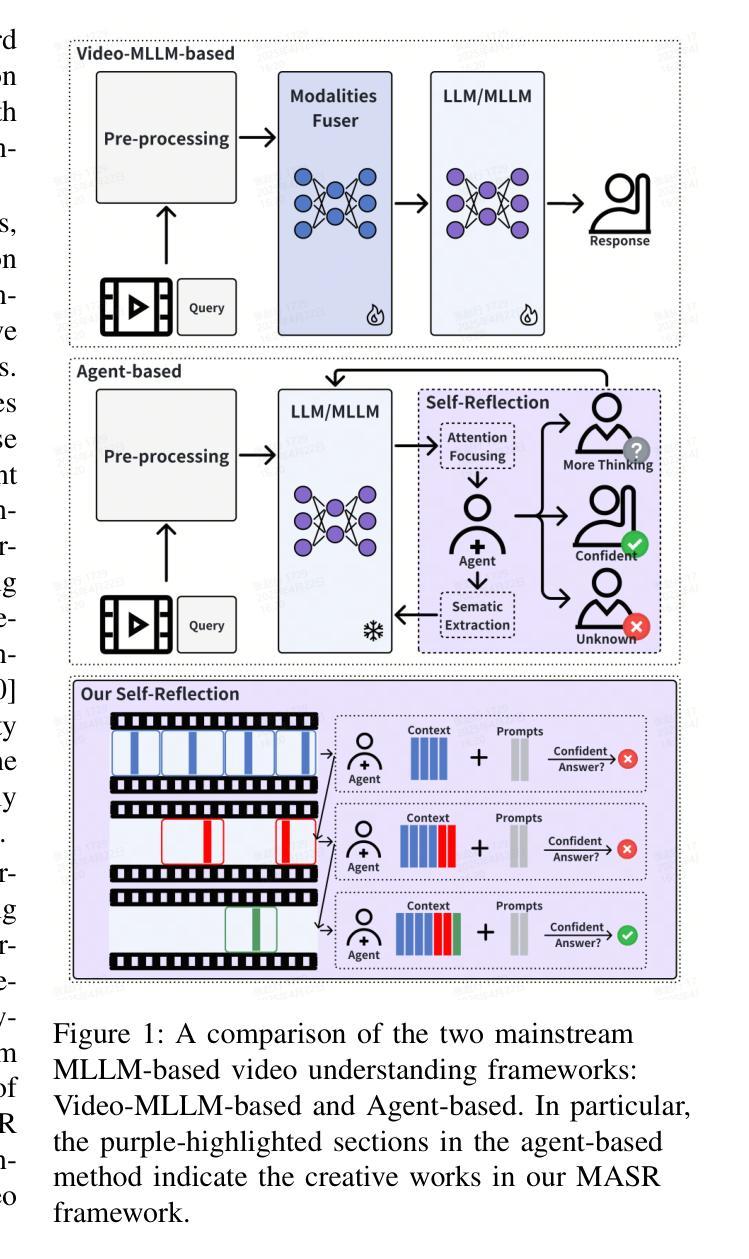
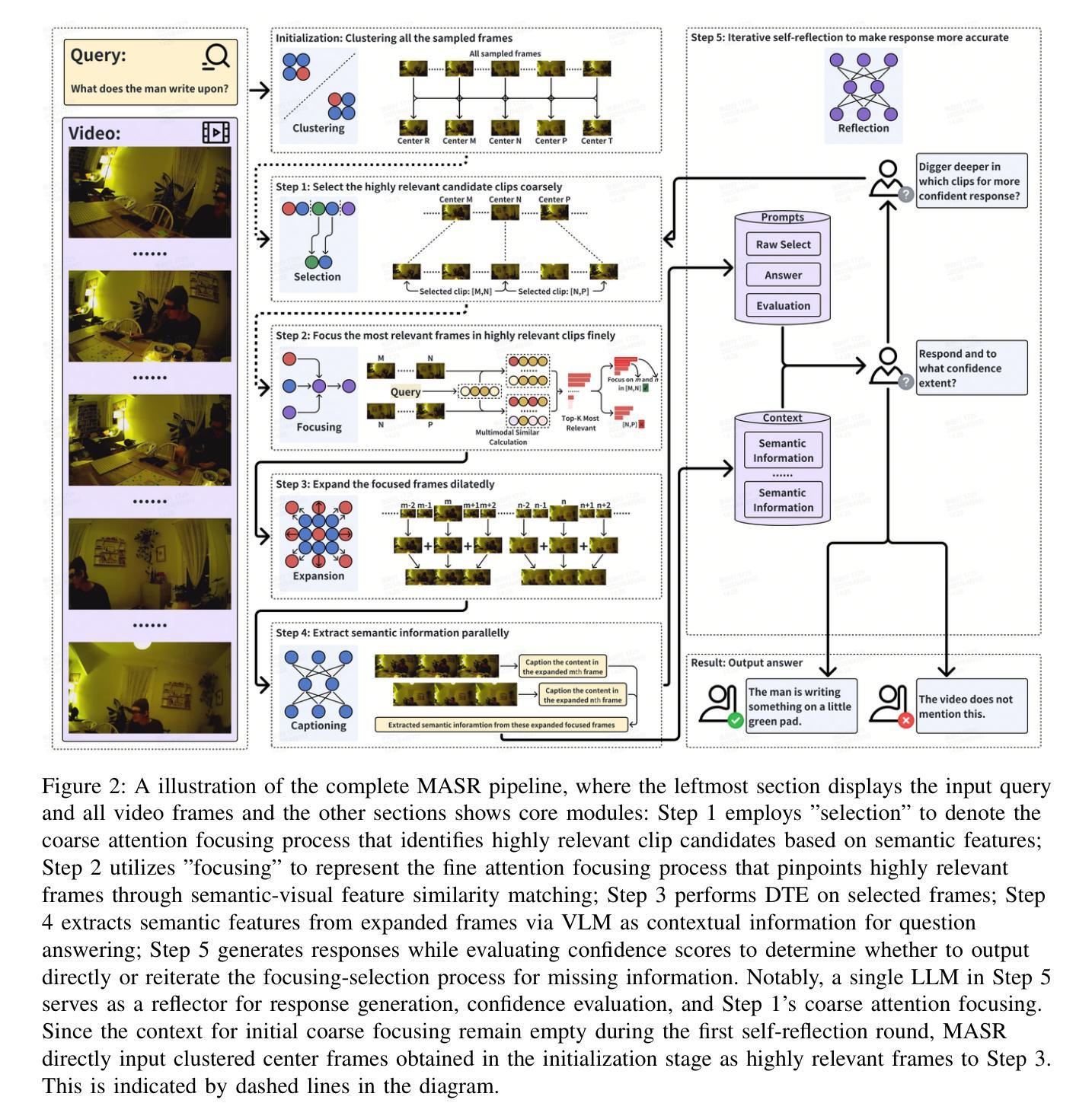
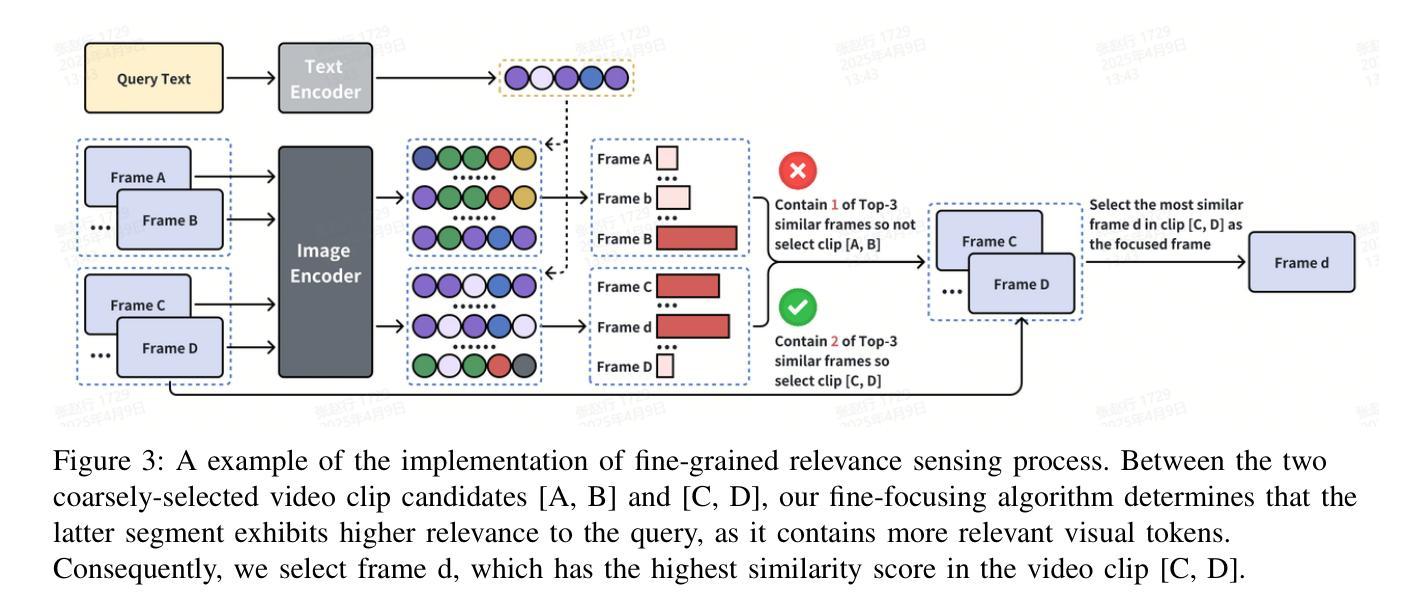
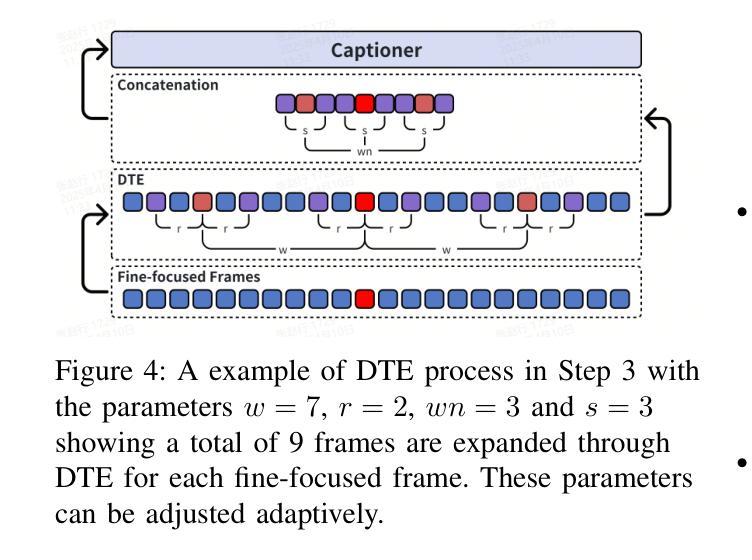
MASR: Self-Reflective Reasoning through Multimodal Hierarchical Attention Focusing for Agent-based Video Understanding
Authors:Shiwen Cao, Zhaoxing Zhang, Junming Jiao, Juyi Qiao, Guowen Song, Rong Shen, Xiangbing Meng
Even in the era of rapid advances in large models, video understanding remains a highly challenging task. Compared to texts or images, videos commonly contain more information with redundancy, requiring large models to properly allocate attention at a global level for comprehensive and accurate understanding. To address this, we propose a Multimodal hierarchical Attention focusing Self-reflective Reasoning (MASR) framework for agent-based video understanding. The key innovation lies in its ability to detect and prioritize segments of videos that are highly relevant to the query. Firstly, MASR realizes Multimodal Coarse-to-fine Relevance Sensing (MCRS) which enhances the correlation between the acquired contextual information and the query. Secondly, MASR employs Dilated Temporal Expansion (DTE) to mitigate the risk of missing crucial details when extracting semantic information from the focused frames selected through MCRS. By iteratively applying MCRS and DTE in the self-reflective reasoning process, MASR is able to adaptively adjust the attention to extract highly query-relevant context and therefore improve the response accuracy. In the EgoSchema dataset, MASR achieves a remarkable 5% performance gain over previous leading approaches. In the Next-QA and IntentQA datasets, it outperforms the state-of-the-art standards by 0.2% and 0.3% respectively. In the Video-MME dataset that contains long-term videos, MASR also performs better than other agent-based methods.
即使在大型模型飞速发展的时代,视频理解仍然是一项极具挑战性的任务。与文本或图像相比,视频通常包含更多带有冗余的信息,需要大型模型在全局层面上适当地分配注意力,以实现全面而准确的理解。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了基于多模态分层注意力的自我反思推理(MASR)框架,用于基于代理的视频理解。关键创新点在于它能够检测和优先处理与查询高度相关的视频片段。首先,MASR实现了多模态粗细相关性感知(MCRS),增强了获取上下文信息与查询之间的相关性。其次,MASR采用膨胀时间扩展(DTE)技术,以缓解在从通过MCRS选择的聚焦帧中提取语义信息时遗漏关键细节的风险。通过自我反思推理过程中迭代应用MCRS和DTE,MASR能够自适应地调整注意力以提取与查询高度相关的上下文,从而提高响应准确性。在EgoSchema数据集上,MASR相较于之前领先的方法取得了5%的性能提升。在Next-QA和IntentQA数据集上,它分别超出了当前最佳标准0.2%和0.3%。对于包含长期视频的视频MME数据集,MASR也表现出比其他基于代理的方法更好的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
视频理解任务仍然极具挑战性。在大数据时代,即使面临复杂模型和数据的复杂性增加的挑战,提出的多模态层次化注意力自反思推理框架(MASR)仍然具有检测并优先处理与查询高度相关的视频片段的能力。MASR通过实现多模态粗到细相关性感知(MCRS)和膨胀时间扩展(DTE)技术,增强了上下文信息与查询之间的相关性,并减少了在提取语义信息时遗漏关键细节的风险。在多个数据集上的实验结果表明,MASR相较于其他前沿方法具有显著性能提升。
Key Takeaways
- 视频理解在当前时代仍然是一个巨大的挑战,因为视频包含比文本或图像更多的信息和冗余。
- 提出了一种名为Multimodal hierarchical Attention focusing Self-reflective Reasoning (MASR)的框架,用于基于代理的视频理解。
- MASR的关键创新在于其检测并优先处理与查询高度相关的视频片段的能力。
- MASR通过实现多模态粗到细相关性感知(MCRS),增强了上下文信息与查询之间的相关性。
- 通过采用膨胀时间扩展(DTE)技术,MASR减少了在提取语义信息时遗漏关键细节的风险。
- 在多个数据集上的实验结果表明,MASR相较于其他前沿方法具有5%的性能提升。
点此查看论文截图

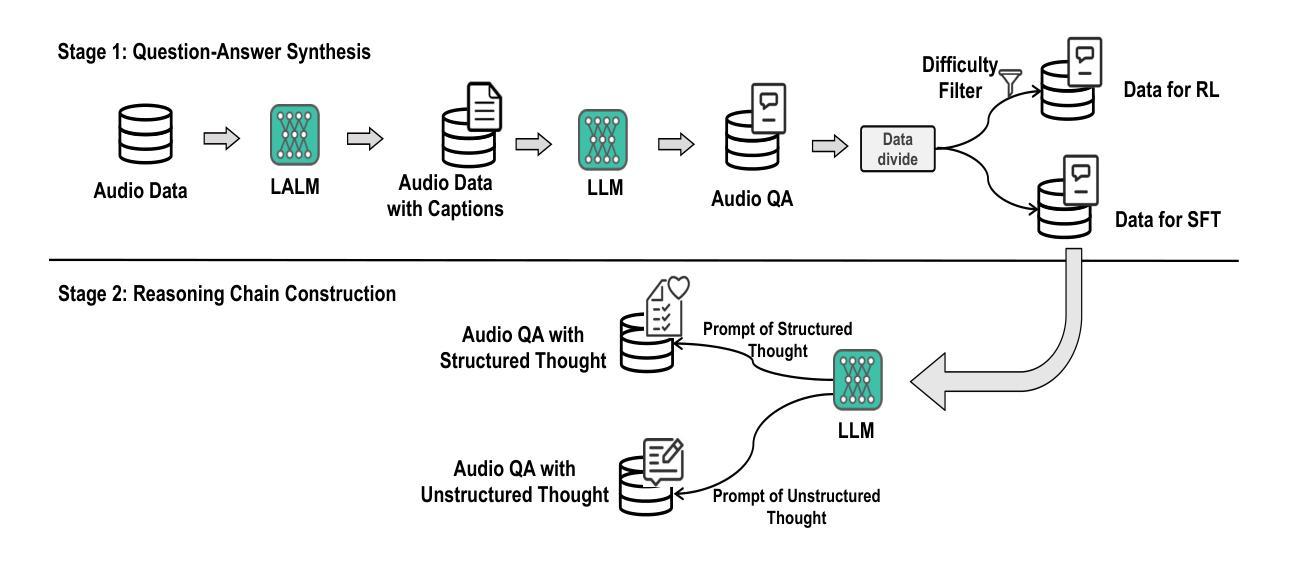
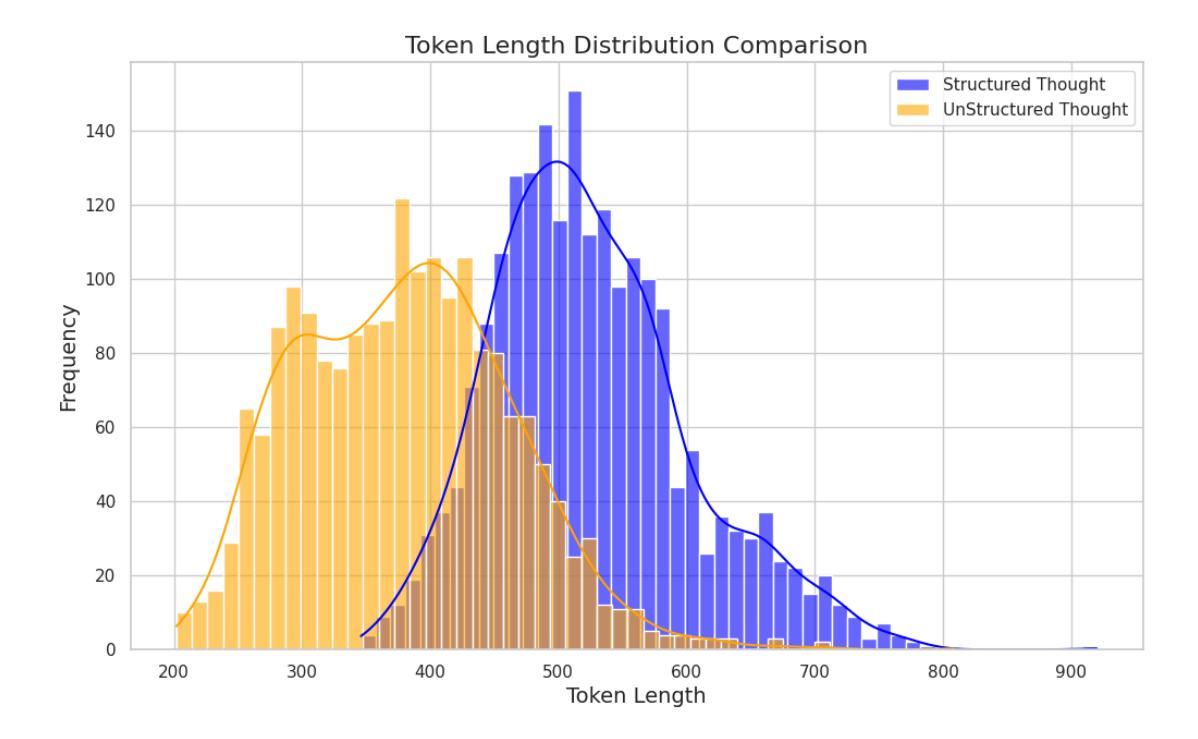
SARI: Structured Audio Reasoning via Curriculum-Guided Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Cheng Wen, Tingwei Guo, Shuaijiang Zhao, Wei Zou, Xiangang Li
Recent work shows that reinforcement learning(RL) can markedly sharpen the reasoning ability of large language models (LLMs) by prompting them to “think before answering.” Yet whether and how these gains transfer to audio-language reasoning remains largely unexplored. We extend the Group-Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) framework from DeepSeek-R1 to a Large Audio-Language Model (LALM), and construct a 32k sample multiple-choice corpus. Using a two-stage regimen supervised fine-tuning on structured and unstructured chains-of-thought, followed by curriculum-guided GRPO, we systematically compare implicit vs. explicit, and structured vs. free form reasoning under identical architectures. Our structured audio reasoning model, SARI (Structured Audio Reasoning via Curriculum-Guided Reinforcement Learning), achieves a 16.35% improvement in average accuracy over the base model Qwen2-Audio-7B-Instruct. Furthermore, the variant built upon Qwen2.5-Omni reaches state-of-the-art performance of 67.08% on the MMAU test-mini benchmark. Ablation experiments show that on the base model we use: (i) SFT warm-up is important for stable RL training, (ii) structured chains yield more robust generalization than unstructured ones, and (iii) easy-to-hard curricula accelerate convergence and improve final performance. These findings demonstrate that explicit, structured reasoning and curriculum learning substantially enhances audio-language understanding.
最近的研究表明,通过提示“先思考再回答”,强化学习(RL)可以显著提高大型语言模型(LLM)的推理能力。然而,这些收益是否以及如何转移到音频语言推理,仍然在很大程度上未被探索。我们将DeepSeek-R1的Group-Relative Policy Optimization(GRPO)框架扩展到一个大型音频语言模型(LALM),并构建了一个包含3万多个样本的多项选择题语料库。通过使用两阶段监管监督微调对结构和非结构化的思维链进行微调,随后进行课程引导的GRPO,我们在相同的架构下系统地比较了隐式和显式以及结构化与非结构化推理。我们的结构化音频推理模型SARI(通过课程引导强化学习的结构化音频推理)在基础模型Qwen2-Audio-7B-Instruct的基础上实现了平均精度16.35%的提升。此外,基于Qwen2.5-Omni的变体在MMAU测试小型基准上达到了最先进的性能,准确率为67.08%。消融实验表明,在我们使用的基准模型上:(i)SFT预热对于稳定的RL训练很重要,(ii)结构化链条相对于非结构化链条产生更稳健的泛化性能,(iii)从易到难的课程加速收敛并提高了最终性能。这些发现表明,明确的、结构化的推理和课程学习显著提高了音频语言的理解能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探索了强化学习(RL)在提升大型音频语言模型(LALM)的推理能力方面的应用。通过结合Group-Relative Policy Optimization(GRPO)框架和结构化音频推理模型SARI,研究实现了对基础模型的显著性能提升。实验结果显示,结构化推理和课程学习能大幅提升音频语言的理解能力。
Key Takeaways
- 强化学习(RL)能显著提升大型音频语言模型(LALM)的推理能力。
- 研究人员将GRPO框架从DeepSeek-R1扩展到LALM,并构建了包含32k样本的多选题语料库。
- 通过两阶段监管微调与结构化及非结构化思维链相结合,再配合课程引导的GRPO方法,系统地比较了隐式与显式、结构化与非结构化推理在相同架构下的表现。
- 结构化音频推理模型SARI在基础模型Qwen2-Audio-7B-Instruct上实现了平均准确度16.35%的提升。
- 基于Qwen2.5-Omni的变体在MMAU test-mini基准测试中达到了最先进性能,准确率为67.08%。
- 消融实验表明,对于基础模型来说,监督微调前的预热对于稳定的RL训练至关重要,结构化思维链相比非结构化思维链能产生更稳健的泛化性能。
点此查看论文截图