⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-01 更新
SVD Based Least Squares for X-Ray Pneumonia Classification Using Deep Features
Authors:Mete Erdogan, Sebnem Demirtas
Accurate and early diagnosis of pneumonia through X-ray imaging is essential for effective treatment and improved patient outcomes. Recent advancements in machine learning have enabled automated diagnostic tools that assist radiologists in making more reliable and efficient decisions. In this work, we propose a Singular Value Decomposition-based Least Squares (SVD-LS) framework for multi-class pneumonia classification, leveraging powerful feature representations from state-of-the-art self-supervised and transfer learning models. Rather than relying on computationally expensive gradient based fine-tuning, we employ a closed-form, non-iterative classification approach that ensures efficiency without compromising accuracy. Experimental results demonstrate that SVD-LS achieves competitive performance while offering significantly reduced computational costs, making it a viable alternative for real-time medical imaging applications.
通过X射线成像对肺炎进行准确和早期的诊断对于有效治疗和改善患者预后至关重要。最近机器学习的发展已经催生了自动诊断工具,这些工具可帮助放射科医生做出更可靠、更高效的决策。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种基于奇异值分解的最小二乘(SVD-LS)框架,用于多类肺炎分类,利用最先进的自监督和迁移学习模型的强大特征表示。我们没有依赖计算成本较高的基于梯度的微调,而是采用了一种封闭形式的非迭代分类方法,确保了效率而不会影响准确性。实验结果表明,SVD-LS在取得竞争性能的同时大大减少了计算成本,使其成为实时医疗成像应用的一种可行的替代方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint submitted to IEEE International Workshop on Machine Learning for Signal Processing (MLSP), 2025
Summary
借助机器学习的最新进展,利用奇异值分解(SVD)的基于最小二乘的分类框架,通过先进的自监督学习和迁移学习模型进行多类肺炎分类,实现准确和早期的肺炎诊断。我们采用一种闭式、非迭代分类方法,在保证效率的同时不损失准确性。实验结果表明,SVD-LS方法具有竞争力,同时大大降低了计算成本,是实时医学成像应用的可行选择。
Key Takeaways
- 准确和早期的肺炎诊断对有效治疗和改善患者预后至关重要。
- 机器学习技术的最新进展为自动化诊断工具提供了支持,帮助放射科医生做出更可靠和高效的决策。
- 提出了一种基于奇异值分解(SVD)的最小二乘(LS)框架,用于多类肺炎分类。
- 利用先进的自监督学习和迁移学习模型进行特征表示,提高分类性能。
- 采用闭式、非迭代分类方法,在保证准确性的同时提高效率。
- SVD-LS方法具有竞争力的性能表现,并且计算成本显著降低。
点此查看论文截图

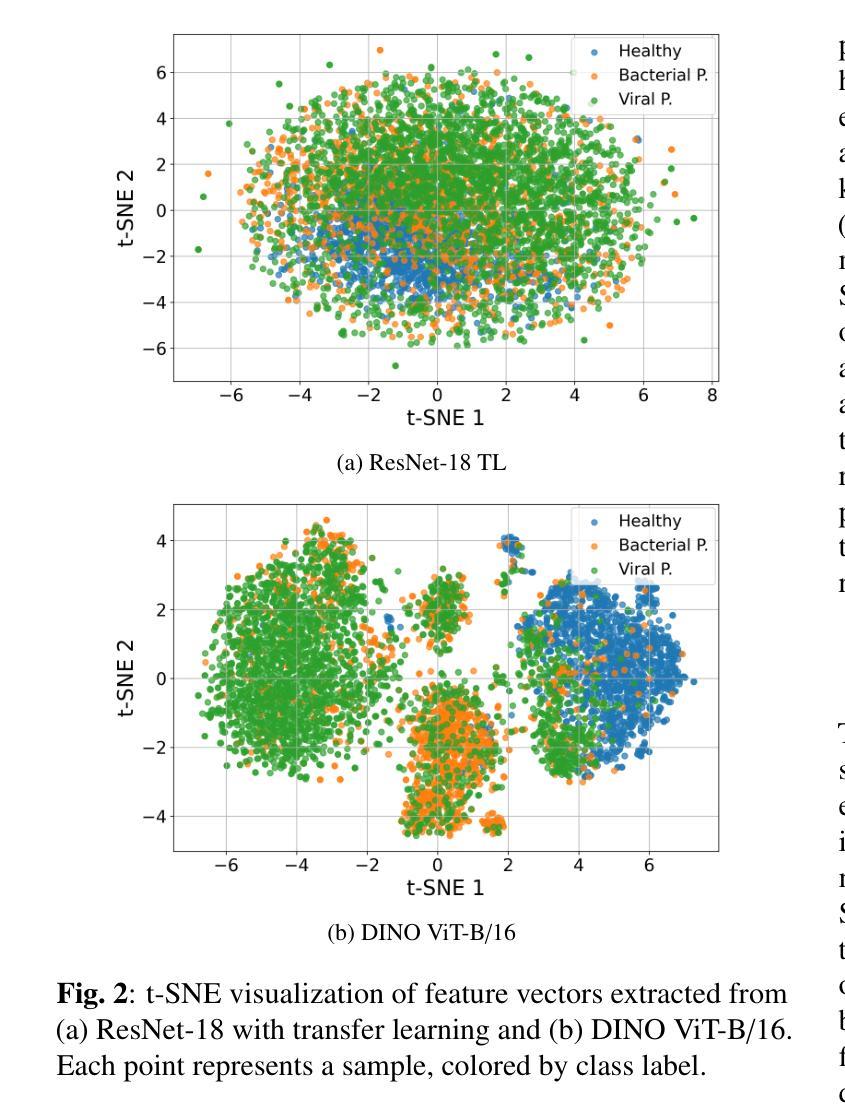
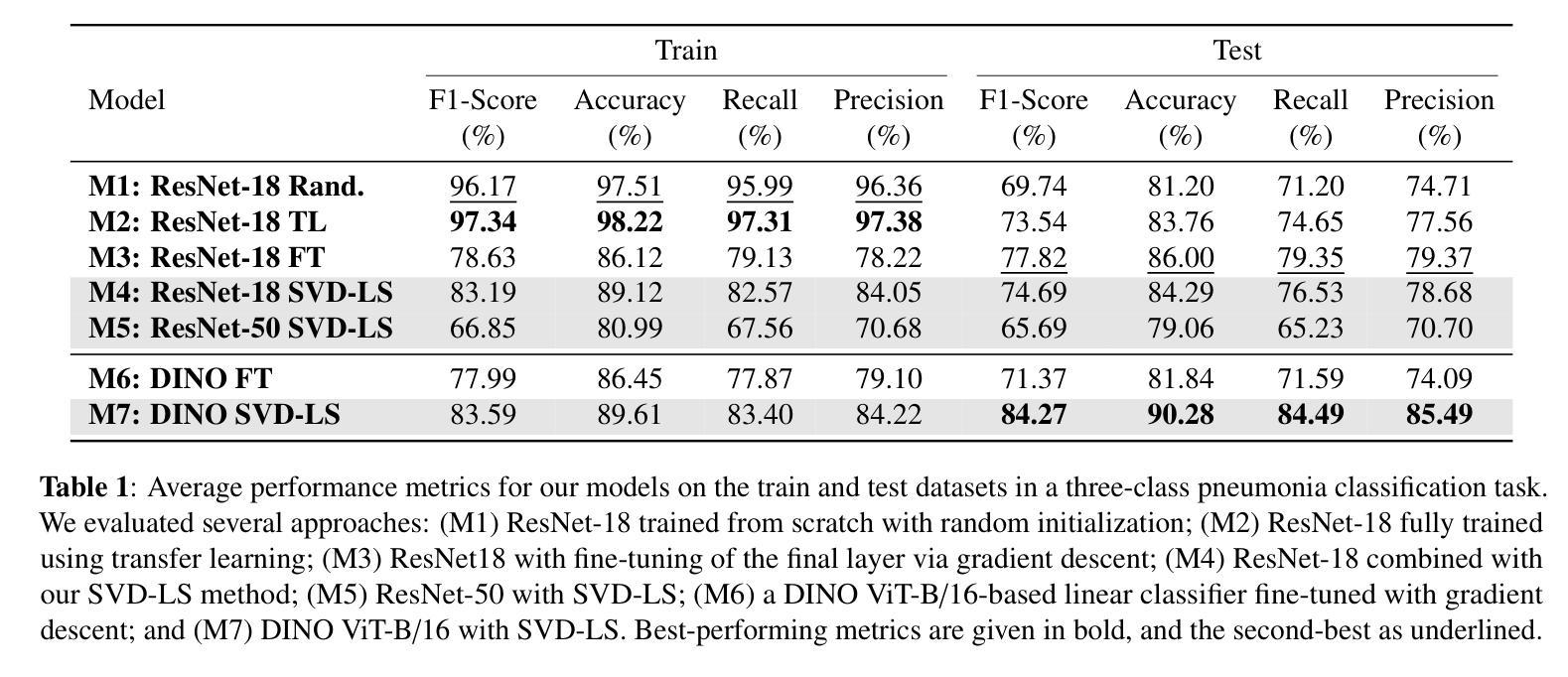
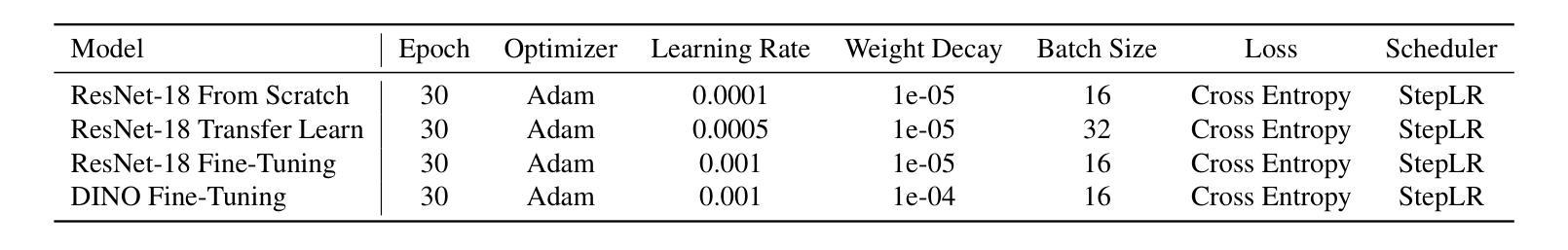
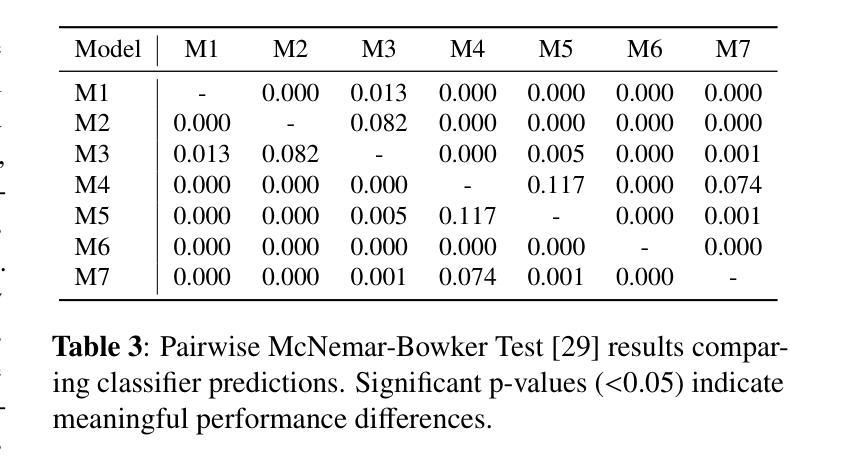
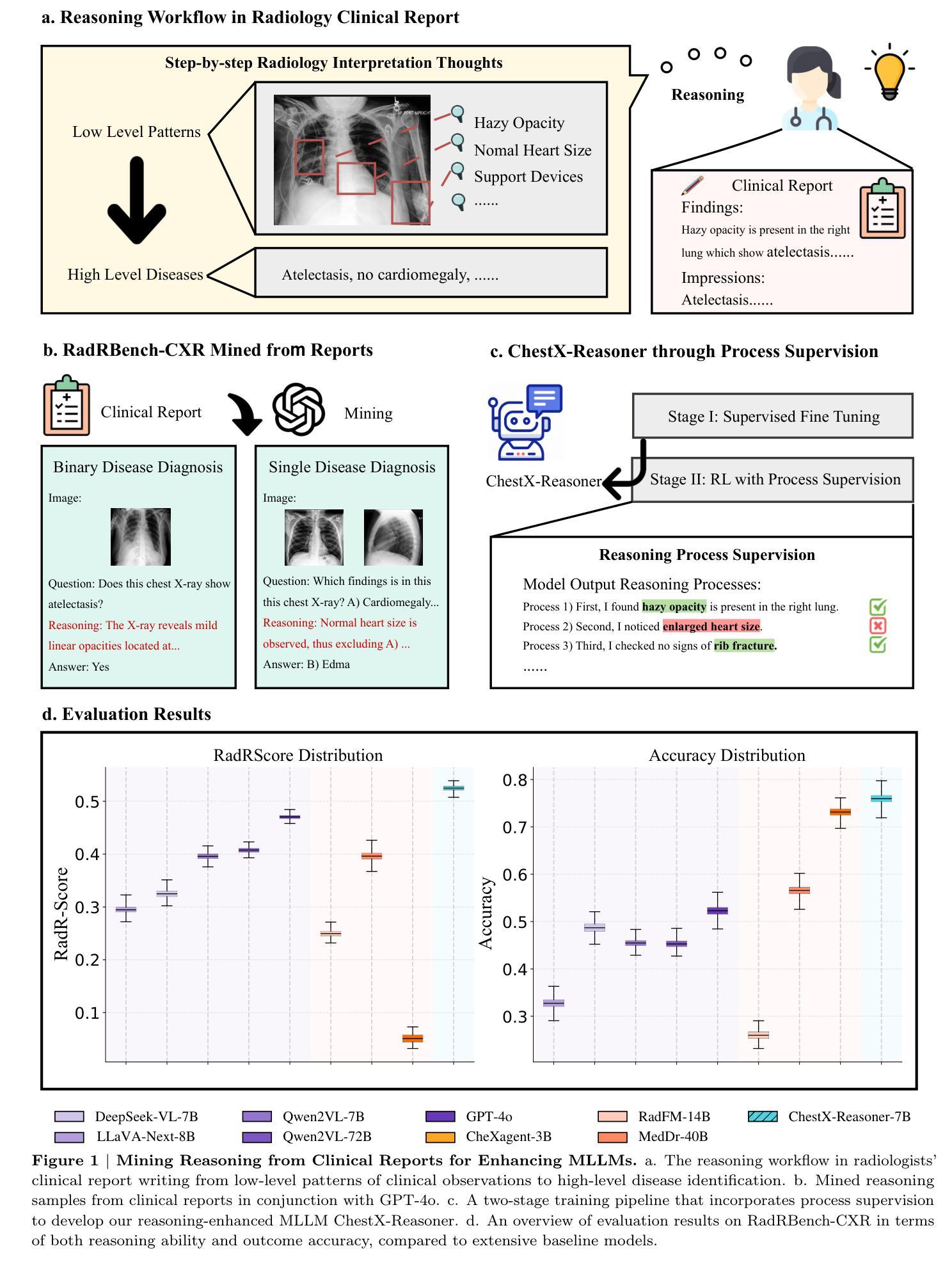
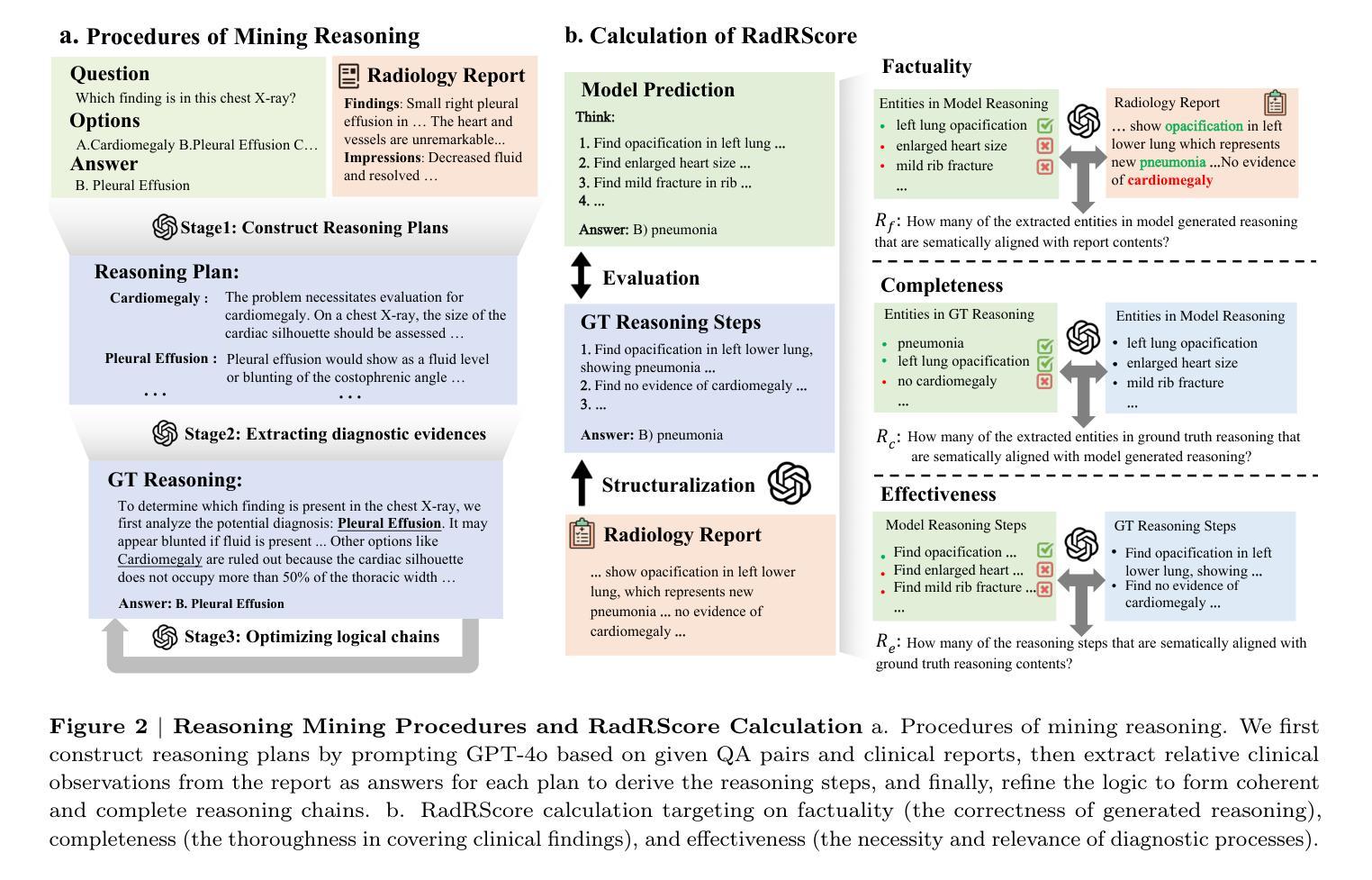
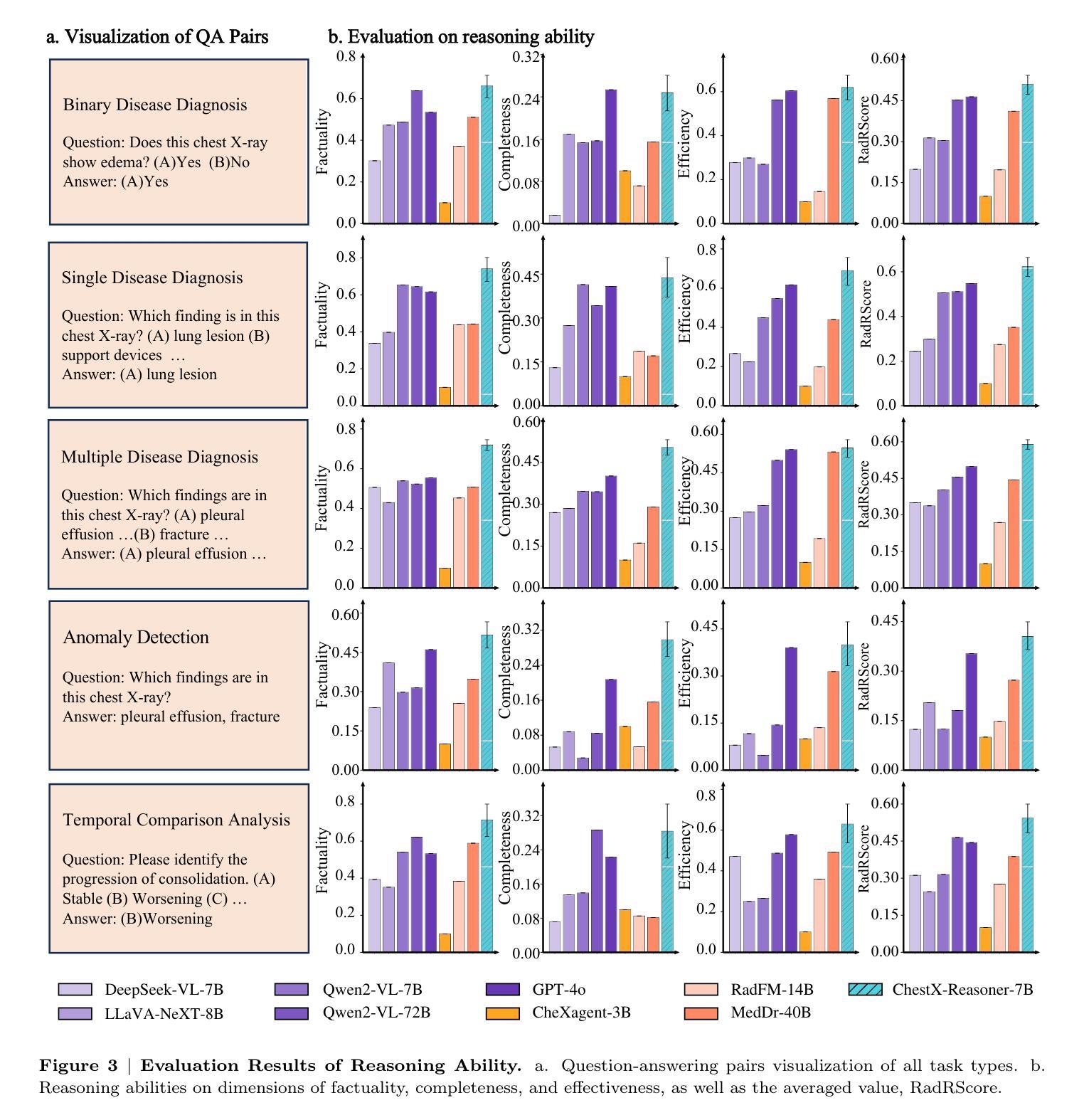
ChestX-Reasoner: Advancing Radiology Foundation Models with Reasoning through Step-by-Step Verification
Authors:Ziqing Fan, Cheng Liang, Chaoyi Wu, Ya Zhang, Yanfeng Wang, Weidi Xie
Recent advances in reasoning-enhanced large language models (LLMs) and multimodal LLMs (MLLMs) have significantly improved performance in complex tasks, yet medical AI models often overlook the structured reasoning processes inherent in clinical practice. In this work, we present ChestX-Reasoner, a radiology diagnosis MLLM designed to leverage process supervision mined directly from clinical reports, reflecting the step-by-step reasoning followed by radiologists. We construct a large dataset by extracting and refining reasoning chains from routine radiology reports. Our two-stage training framework combines supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning guided by process rewards to better align model reasoning with clinical standards. We introduce RadRBench-CXR, a comprehensive benchmark featuring 59K visual question answering samples with 301K clinically validated reasoning steps, and propose RadRScore, a metric evaluating reasoning factuality, completeness, and effectiveness. ChestX-Reasoner outperforms existing medical and general-domain MLLMs in both diagnostic accuracy and reasoning ability, achieving 16%, 5.9%, and 18% improvements in reasoning ability compared to the best medical MLLM, the best general MLLM, and its base model, respectively, as well as 3.3%, 24%, and 27% improvements in outcome accuracy. All resources are open-sourced to facilitate further research in medical reasoning MLLMs.
近期在推理增强型大型语言模型(LLMs)和多模态LLM(MLLMs)方面的进展,已在复杂任务性能上取得了显著的提升。然而,医疗AI模型往往会忽略临床实践中的结构化推理过程。在此工作中,我们提出了ChestX-Reasoner,这是一个专为放射学诊断设计的MLLM,它能够利用直接从临床报告中挖掘出的过程监督,反映放射医师遵循的逐步推理。我们通过从常规放射报告中提取并优化推理链,构建了一个大型数据集。我们的两阶段训练框架结合了监督微调法和由过程奖励引导的更强化学习,以更好地使模型推理与临床标准相符。我们引入了RadRBench-CXR,这是一个包含59K视觉问答样本和301K临床验证推理步骤的综合基准测试,并提出了RadRScore,一个评估推理真实性、完整性和有效性的指标。ChestX-Reasoner在诊断和治疗准确性方面均优于现有的医疗和通用领域MLLMs,在推理能力方面相比最佳的医疗MLLM、最佳通用MLLM及其基础模型分别提高了16%、5.9%和18%,并且在结果准确性方面分别提高了3.3%、24%和27%。所有资源均已开源,以促进医疗推理MLLM的进一步研究。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了ChestX-Reasoner这一基于医学图像的多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在放射诊断方面的应用。该模型通过从临床报告中挖掘过程监督信息,结合放射科医生逐步推理的过程,设计了一种两阶段训练框架,并引入了RadRBench-CXR基准测试和RadRScore评估指标。在诊断和推理能力方面,ChestX-Reasoner相较于现有的医疗和通用领域MLLMs表现出更高的性能。
Key Takeaways
- ChestX-Reasoner是一个针对放射诊断的多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)。
- 该模型通过挖掘临床报告中的过程监督信息,反映放射科医生的逐步推理过程。
- ChestX-Reasoner采用两阶段训练框架,结合监督微调与强化学习,以更好地符合临床标准。
- 引入了RadRBench-CXR基准测试和RadRScore评估指标,用于评估模型的推理能力。
- ChestX-Reasoner在诊断和推理能力方面优于现有的医疗和通用领域MLLMs。
- 该模型实现了诊断准确率的提升,并在推理能力方面相较于最佳医疗MLLM、最佳通用MLLM及其基础模型分别有16%、5.9%和18%的改进。
点此查看论文截图

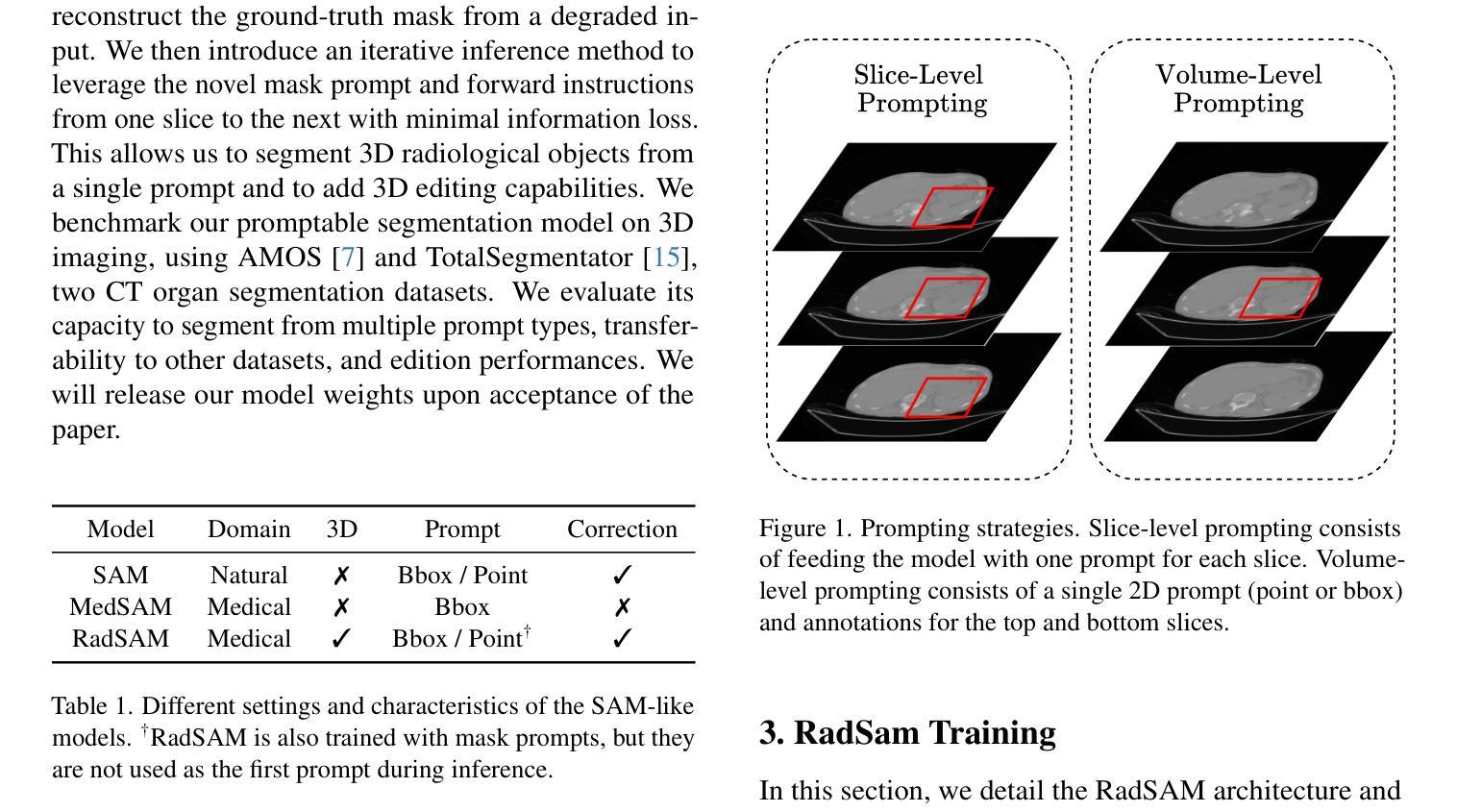
RadSAM: Segmenting 3D radiological images with a 2D promptable model
Authors:Julien Khlaut, Elodie Ferreres, Daniel Tordjman, Hélène Philippe, Tom Boeken, Pierre Manceron, Corentin Dancette
Medical image segmentation is a crucial and time-consuming task in clinical care, where mask precision is extremely important. The Segment Anything Model (SAM) offers a promising approach, as it provides an interactive interface based on visual prompting and edition to refine an initial segmentation. This model has strong generalization capabilities, does not rely on predefined classes, and adapts to diverse objects; however, it is pre-trained on natural images and lacks the ability to process medical data effectively. In addition, this model is built for 2D images, whereas a whole medical domain is based on 3D images, such as CT and MRI. Recent adaptations of SAM for medical imaging are based on 2D models, thus requiring one prompt per slice to segment 3D objects, making the segmentation process tedious. They also lack important features such as editing. To bridge this gap, we propose RadSAM, a novel method for segmenting 3D objects with a 2D model from a single prompt. In practice, we train a 2D model using noisy masks as initial prompts, in addition to bounding boxes and points. We then use this novel prompt type with an iterative inference pipeline to reconstruct the 3D mask slice-by-slice. We introduce a benchmark to evaluate the model’s ability to segment 3D objects in CT images from a single prompt and evaluate the models’ out-of-domain transfer and edition capabilities. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach against state-of-the-art models on this benchmark using the AMOS abdominal organ segmentation dataset.
医学图像分割是临床护理中一个关键且耗时的任务,其中遮罩精度极为重要。Segment Anything Model(SAM)提供了一种有前途的方法,因为它提供了一个基于视觉提示和编辑的交互式界面,以优化初始分割。该模型具有很强的泛化能力,不依赖于预定义的类别,并能适应不同的对象;然而,它是基于自然图像进行预训练的,缺乏有效处理医疗数据的能力。此外,该模型是为二维图像构建的,而整个医学领域都是基于三维图像,如CT和MRI。最近对SAM的医学成像适应都是基于二维模型的,因此需要对每个切片进行提示以分割三维对象,使得分割过程变得乏味。它们还缺少重要的功能,如编辑功能。为了弥补这一差距,我们提出了RadSAM,这是一种用单个提示分割二维模型中的三维对象的新方法。在实践中,我们使用带有噪声遮罩作为初始提示训练二维模型,此外还使用边界框和点。然后,我们使用这种新型提示与迭代推理管道来逐层重建三维遮罩。我们引入了一个基准测试来评估模型从单个提示在CT图像中分割三维对象的能力,并评估模型的跨域迁移和编辑能力。我们在AMOS腹部器官分割数据集上展示了我们的方法与最先进模型相比的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了医学图像分割的重要性及时间成本,重点介绍了Segment Anything Model(SAM)的交互式界面及其在初始分割基础上的视觉提示和编辑功能。然而,SAM在自然图像上的预训练使其在处理医疗数据方面存在缺陷。针对这一问题,本文提出了RadSAM,这是一种使用单个提示对3D对象进行分割的新方法,采用2D模型进行实践。通过训练使用带有噪声掩码的初始提示、边界框和点,然后使用迭代推理管道重建3D掩码切片。最后,通过AMOS腹部器官分割数据集评估了该方法的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 医疗图像分割是临床关怀中的重要任务,且耗时较长,要求精确度高。
- Segment Anything Model(SAM)提供了一个交互式界面来基于视觉提示进行初始分割的精细化编辑。但其在处理医疗数据方面存在缺陷。
- RadSAM是新的医学图像分割方法,通过使用单个提示对3D对象进行分割,采用2D模型实践。
点此查看论文截图

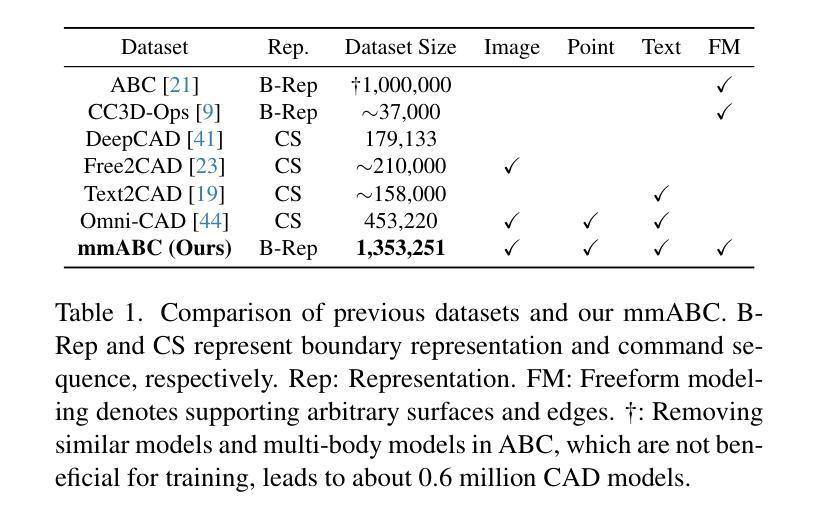
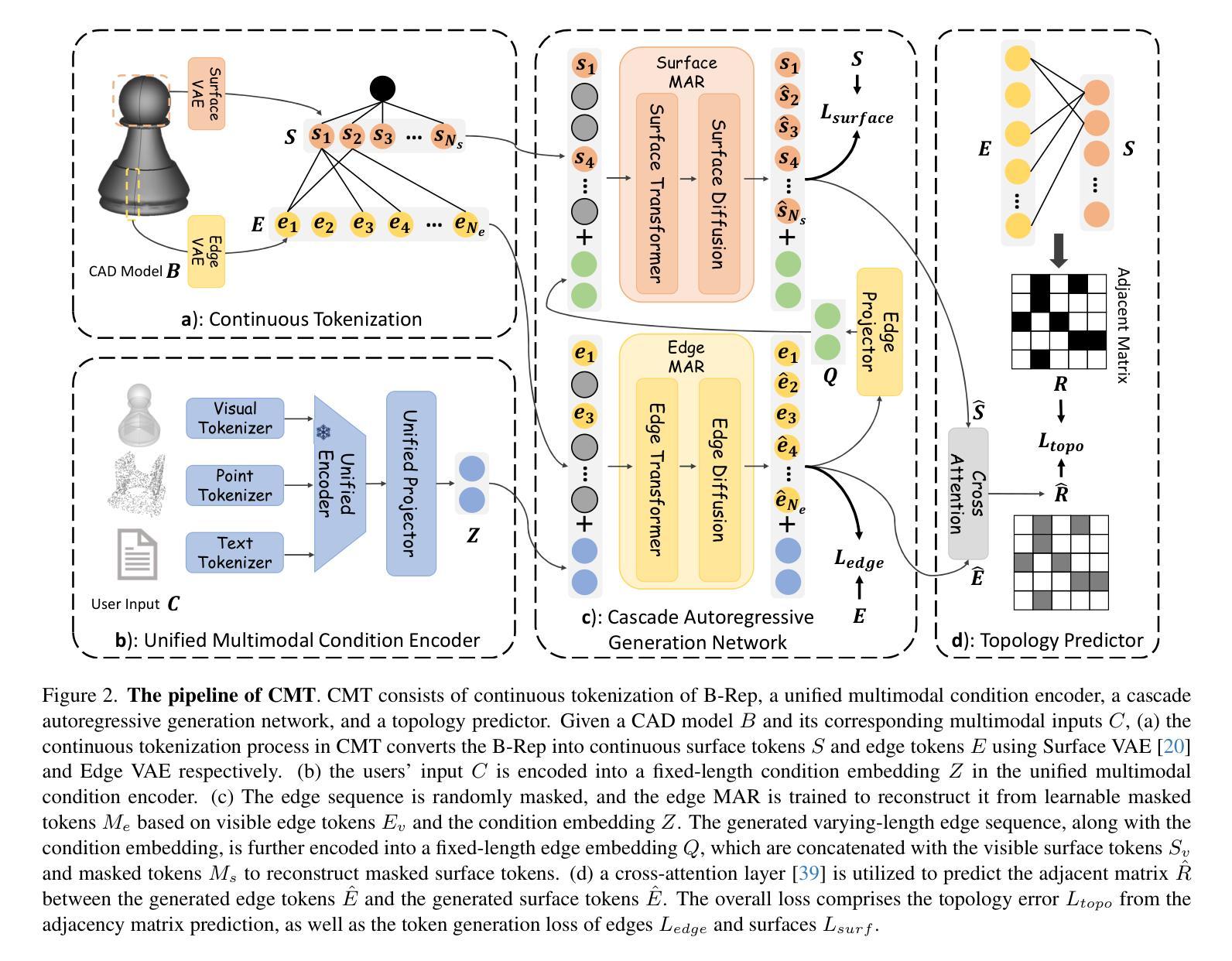
CMT: A Cascade MAR with Topology Predictor for Multimodal Conditional CAD Generation
Authors:Jianyu Wu, Yizhou Wang, Xiangyu Yue, Xinzhu Ma, Jingyang Guo, Dongzhan Zhou, Wanli Ouyang, Shixiang Tang
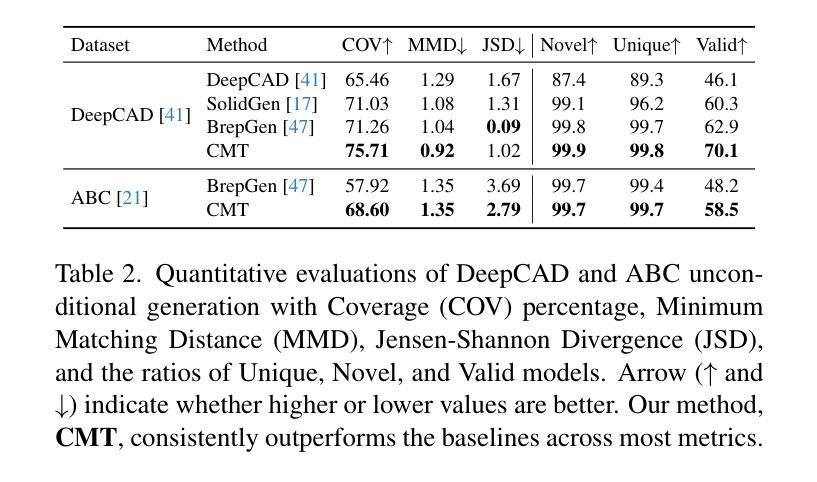
While accurate and user-friendly Computer-Aided Design (CAD) is crucial for industrial design and manufacturing, existing methods still struggle to achieve this due to their over-simplified representations or architectures incapable of supporting multimodal design requirements. In this paper, we attempt to tackle this problem from both methods and datasets aspects. First, we propose a cascade MAR with topology predictor (CMT), the first multimodal framework for CAD generation based on Boundary Representation (B-Rep). Specifically, the cascade MAR can effectively capture the ``edge-counters-surface’’ priors that are essential in B-Reps, while the topology predictor directly estimates topology in B-Reps from the compact tokens in MAR. Second, to facilitate large-scale training, we develop a large-scale multimodal CAD dataset, mmABC, which includes over 1.3 million B-Rep models with multimodal annotations, including point clouds, text descriptions, and multi-view images. Extensive experiments show the superior of CMT in both conditional and unconditional CAD generation tasks. For example, we improve Coverage and Valid ratio by +10.68% and +10.3%, respectively, compared to state-of-the-art methods on ABC in unconditional generation. CMT also improves +4.01 Chamfer on image conditioned CAD generation on mmABC. The dataset, code and pretrained network shall be released.
在计算机辅助设计(CAD)中,准确且用户友好的设计对于工业设计和制造至关重要。然而,现有的方法仍难以达到这一目标,因为它们过于简化的表示形式或架构无法支持多模式设计的要求。在本文中,我们尝试从方法和数据集两方面来解决这个问题。首先,我们提出了一种基于边界表示(B-Rep)的级联多模态自动回归(Cascade MAR)与拓扑预测器(Topology Predictor)的多模态框架(CMT)。具体而言,级联多模态自动回归可以有效地捕捉在B-Rep中至关重要的“边缘表面先验”信息,而拓扑预测器则直接从MAR中的紧凑标记估计B-Rep中的拓扑结构。其次,为了促进大规模训练,我们开发了一个大规模的多模式CAD数据集mmABC,包含超过130万个具有多模式注释的B-Rep模型,包括点云、文本描述和多元图像视图。大量的实验表明,CMT在有条件和无条件的CAD生成任务中都表现出卓越的性能。例如,在无条件生成中,与最新技术相比,我们的覆盖率提高了+10.68%,有效比例提高了+10.3%。此外,在mmABC的图像条件CAD生成中,CMT的Chamfer指标提高了+4.01。数据集、代码和预训练网络将公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于边界表示(B-Rep)的多模态计算机辅助设计(CAD)生成框架——级联MAR拓扑预测器(CMT)。同时,为了支持大规模训练,作者构建了一个大型多模态CAD数据集mmABC。CMT在条件和无条件CAD生成任务中表现优越,相比现有方法显著提高覆盖率、有效性和Chamfer指标。
Key Takeaways
- 现有计算机辅助设计(CAD)方法难以兼顾准确性和用户友好性,需要改进方法和数据集以支持多模态设计需求。
- 本文提出一种基于边界表示(B-Rep)的多模态框架——级联MAR拓扑预测器(CMT),可有效捕捉CAD生成中的“边缘计数表面”先验信息。
- 为支持大规模训练,作者构建了一个大型多模态CAD数据集mmABC,包含超过130万B-Rep模型和多模态注释。
- CMT在无条件生成中相比现有方法提高了覆盖率(+10.68%)和有效性(+10.3%)。
- CMT在图像条件CAD生成任务上提高了Chamfer指标(+4.01)。
- 作者计划公开数据集、代码和预训练网络。
点此查看论文截图

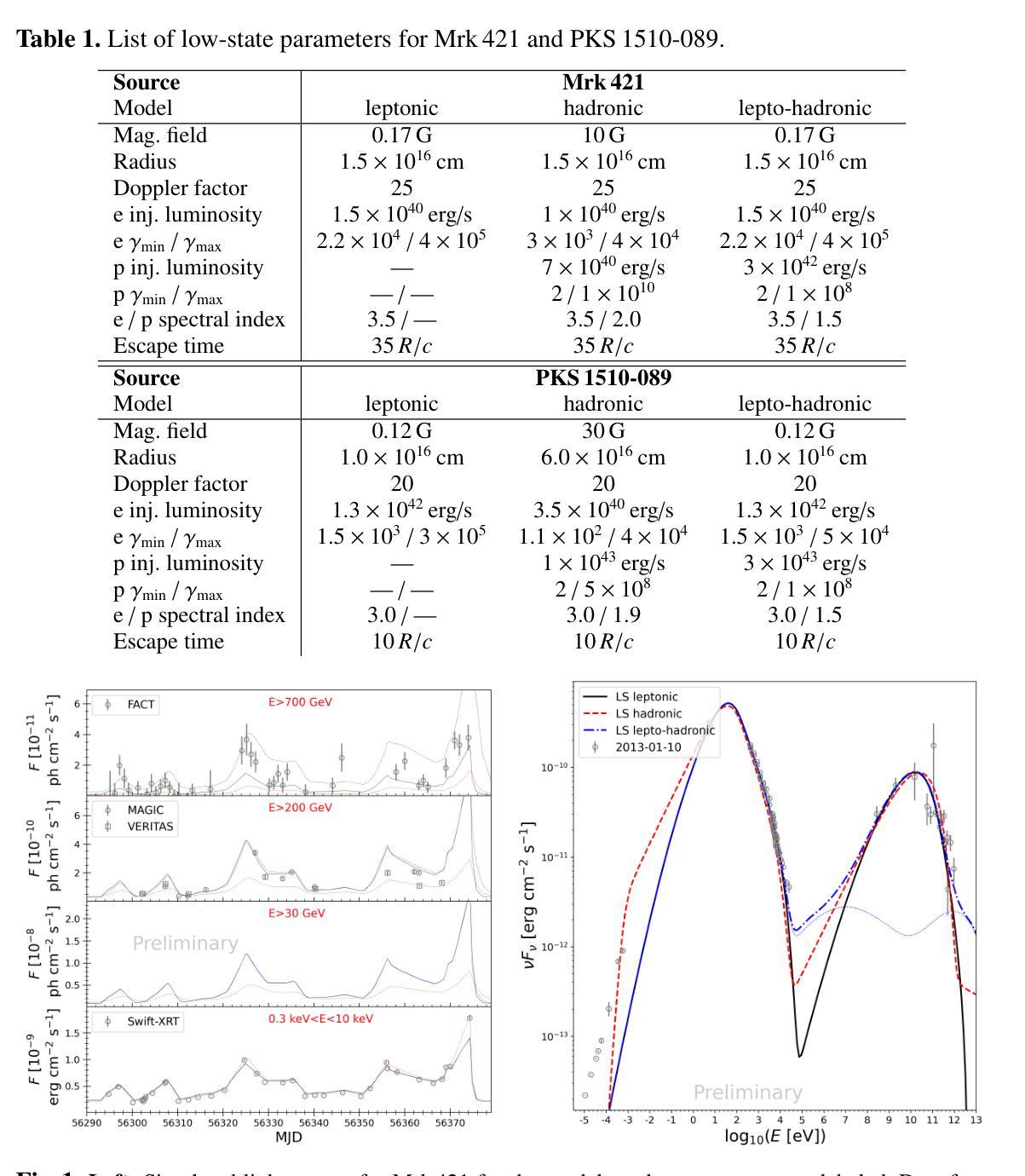
Multiwavelength correlation studies in the era of CTAO
Authors:Michael Zacharias, Elina Lindfors, Patrizia Romano, Daniela Dorner, Stefano Vercellone, Matteo Cerruti, Jonathan Biteau
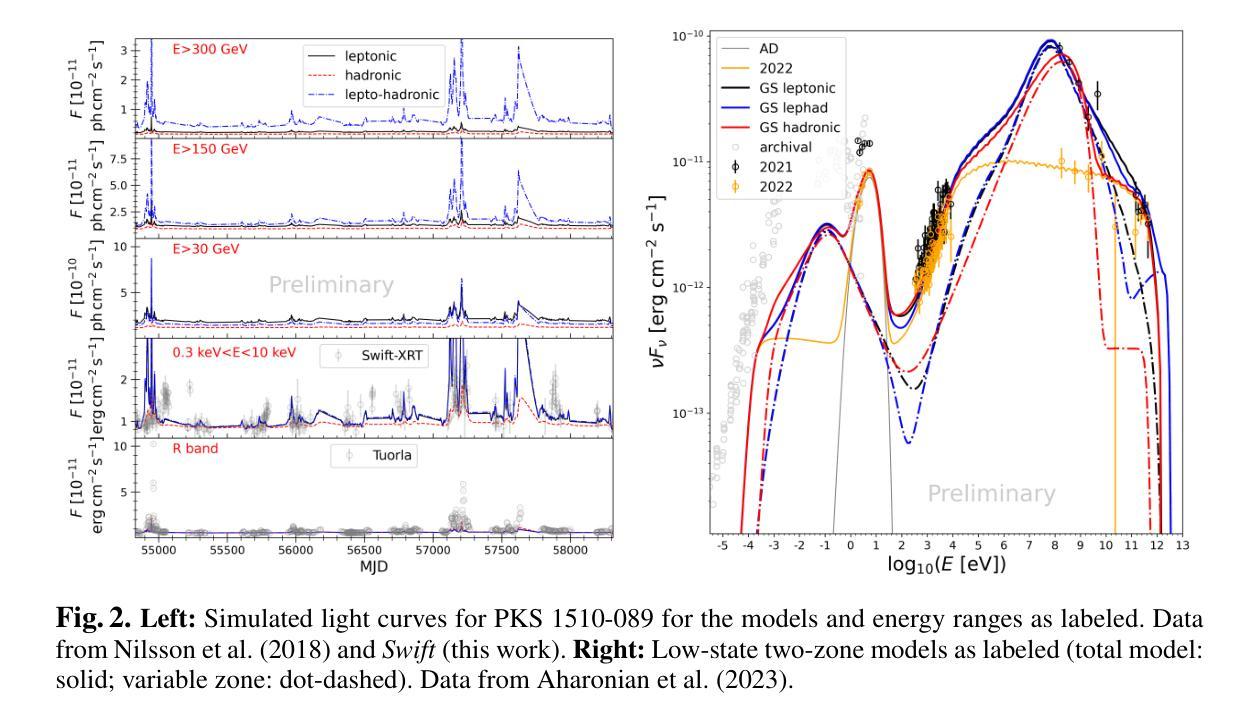
Correlations between various multiwavelength (MWL) bands are an intermittent feature in blazar light curves; that is, they are observed in some instances but not in others. With the CTAO we will obtain detailed very-high-energy (VHE) gamma-ray light curves for many sources also during their low states, enabling detailed MWL correlation studies. For two blazars, the HBL Mrk,421 and the FSRQ PKS,1510-089, the long-term X-ray and optical light curves are used to induce variations in input parameters of the lepto-hadronic one-zone code OneHaLe. We show light curves in the CTA energy range for three different energy thresholds. The results are: 1) the presence of relativistic protons has a significant effect on the correlation of the light curves as the emerging pair cascade prolongs flaring states at the highest energies; and 2) comparison of the theoretical light curves with existing VHE gamma-ray data shows that both leptonic and hadronic models can only partially reproduce the data.
多波长(MWL)波段之间的相关性在Blazar光变曲线中是间歇性特征;也就是说,在某些情况下可以观察到,但在其他情况下则不能。通过CTAO,我们将获得许多源在低状态下的详细的甚高能(VHE)伽马射线光变曲线,从而能够进行详细的MWL相关性研究。对于两个Blazars,即HBL Mrk 421和FSRQ PKS 1510-089,我们使用了长期X射线和光学光变曲线来引导lepto-hadronic单区代码OneHaLe的输入参数变化。我们展示了三个不同能量阈值在CTA能量范围内的光变曲线。结果是:1)相对论质子的存在对光变曲线的相关性有重大影响,因为新兴的对级联延长了最高能量的耀发状态;2)将理论光变曲线与现有的VHE伽马射线数据进行比较表明,无论是电子型还是强子型模型都只能部分地再现数据。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Conference proceedings paper of the GAMMA 2024; to be published in Memorie della Societ`a Astronomica Italiana
Summary
多波长波段间的相关性在Blazar光变曲线中是间歇性特征,有时观察到,有时不观察到。使用CTAO,我们将在许多源的低状态下获得详细的甚高能伽马射线光变曲线,从而进行详细的多波长相关性研究。对于两个Blazars,即HBL Mrk 421和FSRQ PKS 1510-089,长期X射线和光学光变曲线被用于诱导lepto-hadronic一区代码OneHaLe的输入参数的变化。我们展示了在CTA能量范围内三种不同能量阈值的光变曲线。结果显示:1)相对论质子的存在对光变曲线的相关性有显著影响,因为产生的正负电子级联延长了最高能量的耀发状态;2)理论光变曲线与现有的甚高能伽马射线数据的比较表明,无论是轻子模型还是强子模型都只能部分地再现数据。
Key Takeaways
- 多波长波段相关性在Blazar光变曲线中是间歇性特征。
- CTAO将允许我们获得详细的甚高能伽马射线光变曲线,包括源的低状态。
- 对于Mrk 421和PKS 1510-089这两个Blazars,长期X射线和光学光变曲线被用于研究输入参数变化对lepto-hadronic模型的影响。
- 相对论质子的存在对光变曲线的相关性有显著影响,产生的正负电子级联延长了最高能量的耀发状态。
- 理论光变曲线与现有甚高能伽马射线数据的比较显示,当前模型只能部分地解释观测数据。
- 在CTA能量范围内,不同的能量阈值会影响光变曲线的表现。
点此查看论文截图

Modeling of the time-resolved spectral energy distribution of blazar OJ 287 from 2008 to 2023: a comprehensive multi-epoch study
Authors:G. Harutyunyan, N. Sahakyan, D. Bégué
We present a comprehensive analysis of the time-resolved spectral energy distributions (SEDs) of the blazar OJ 287 over a 15-year period (2008-2023), using multi-wavelength data. In the $\gamma$-ray band, multiple flaring episodes were observed, with the strongest flare reaching a peak flux of $(5.60\pm1.11)\times10^{-7}:{\rm photons:cm^{-2}:s^{-1}}$ on MJD 55869.03 (04 November 2011). In the optical/UV band, the source was in an active state between MJD 57360 (04 December 2015) and 57960 (26 July 2017), during which the highest flux of $(1.07\pm0.02)\times10^{-10}:{\rm erg:cm^{-2}:s^{-1}}$ was observed on MJD 57681.23 (20 October 2016). In the X-ray band, both the flux and spectral index exhibit variability. To investigate the origin of the broadband emission from OJ 287, we systematically modeled 739 quasi-simultaneous SEDs using a leptonic model that self-consistently accounts for particle injection and cooling. This analysis is possible thanks to the recent development of a surrogate neural-network-based model, trained on kinetic simulations. This innovative, time-resolved, neural network-based approach overcomes the limitations of traditional single-epoch SED modeling, enabling to explore the temporal evolution of key model parameters, such as the magnetic field strength, Doppler factor, and electron injection distribution, across different states of the source. We identified distinct emission states characterized by unique combinations of magnetic field $ B $, electron index $ p $, and Doppler boost $ \delta $, associated to different underlying mechanisms such as varying acceleration processes (e.g., shocks, turbulence) and magnetic confinement. The analysis provides insights into the jet physics processes, including particle acceleration mechanisms and dynamic changes in the jet structure.
我们对OJ 287的为期15年(2008年至2023年)的时域光谱能量分布(SEDs)进行了综合分析,并利用多波长数据对其进行研究。在伽马射线波段,观察到多次耀斑爆发事件,其中最强烈的耀斑在修正儒略日(MJD)为55869.03(即格林尼治标准时间)时达到峰值流量(每平方厘米每秒有光子)。在光学/紫外波段,源处于活跃状态,起始于修正儒略日(MJD)为57360(即格林尼治标准时间),结束于修正儒略日(MJD)为57960,其中最高流量为每平方厘米每秒观测到光子能量为*(这里无法转换数学符号的表达)。在分析过程中发现了一种特殊的光学现象。为了研究OJ 287的宽带发射的来源,我们系统地使用了电子模型对获得的反射光度谱进行建模分析,该模型能够自洽地解释粒子注入和冷却过程。这一分析得益于基于动力学的模拟训练而开发出的替代神经网络模型的发展。这种创新的、基于时间的神经网络方法克服了传统单时代反射光度谱建模方法的局限性,能够探索关键模型参数的时间演变,如磁场强度、多普勒因子和电子注入分布等在不同源状态下的变化。我们确定了不同的发射状态,这些状态由独特的磁场强度、电子指数和多普勒增强因子组合而成,并与不同的潜在机制相关,如变化的加速过程(例如冲击、湍流)和磁约束。分析提供了对射流物理过程的见解,包括粒子加速机制和射流结构的动态变化。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication in MNRAS
Summary
综合分析了OJ 287十五年期间的时域光谱能量分布(SEDs)。研究结果显示,在γ射线波段存在多次耀斑爆发事件,最强耀斑在特定日期达到高峰流量。在光学/紫外线波段,源处于活跃状态并观察到最高流量。使用莱普顿模型系统地模拟了SEDs,并通过基于神经网络的模拟模型克服传统单纪元SED建模的限制,探索关键模型参数的时空演变。分析揭示了不同的发射状态与独特的磁场、电子指数和多普勒增强相关联,反映了不同的加速机制和动态变化的喷流结构。
Key Takeaways
- OJ 287在长达15年的期间表现出显著的多波长活动,特别是在γ射线波段的耀斑事件和在光学/紫外线波段的活跃状态。
- 最强γ射线耀斑的峰值流量和在光学/紫外线波段的最高流量已被记录。
- 利用莱普顿模型系统地模拟了OJ 287的宽带发射,揭示了其复杂的物理过程。
- 基于神经网络的模拟模型克服了传统SED建模的限制,为探索关键模型参数的时空演变提供了可能。
- 分析显示,不同的发射状态与独特的磁场、电子指数和多普勒增强有关,这些可能与不同的加速机制(如冲击、湍流)和喷流结构的动态变化有关。
- 该研究为理解OJ 287的喷流物理过程和粒子加速机制提供了深入见解。
点此查看论文截图

SAM-Guided Robust Representation Learning for One-Shot 3D Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Jia Wang, Yunan Mei, Jiarui Liu, Xin Fan
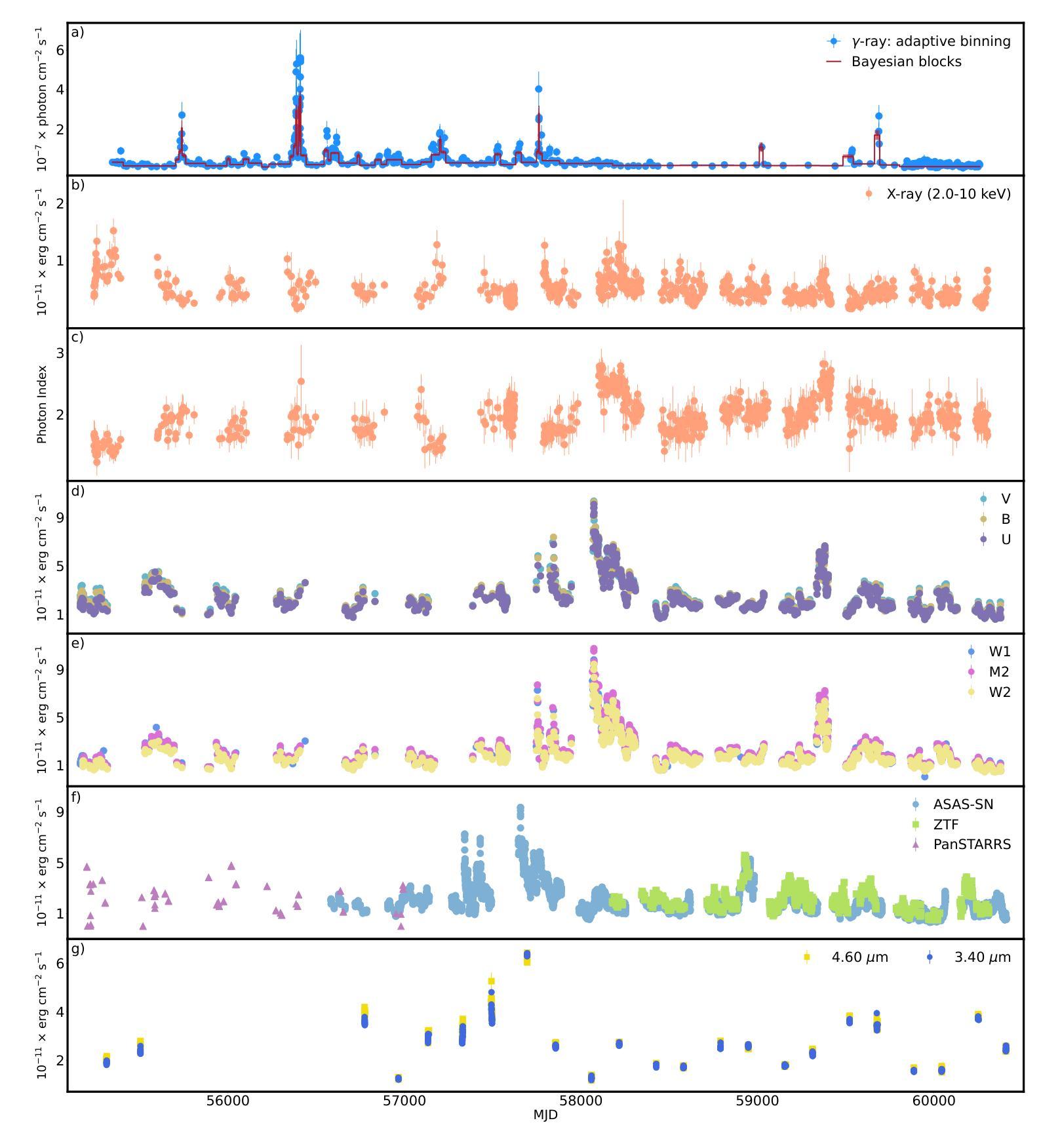
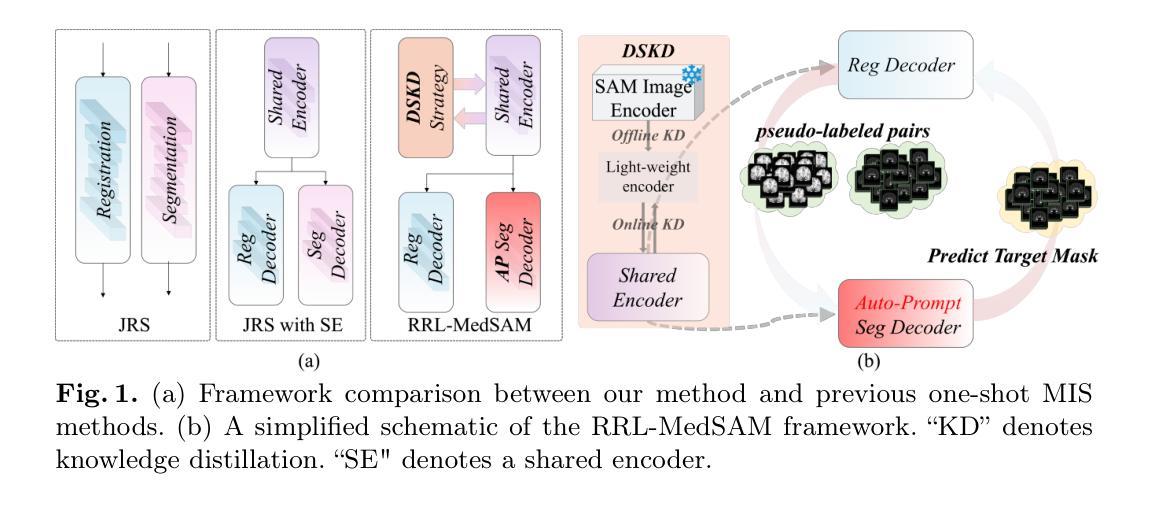
One-shot medical image segmentation (MIS) is crucial for medical analysis due to the burden of medical experts on manual annotation. The recent emergence of the segment anything model (SAM) has demonstrated remarkable adaptation in MIS but cannot be directly applied to one-shot medical image segmentation (MIS) due to its reliance on labor-intensive user interactions and the high computational cost. To cope with these limitations, we propose a novel SAM-guided robust representation learning framework, named RRL-MedSAM, to adapt SAM to one-shot 3D MIS, which exploits the strong generalization capabilities of the SAM encoder to learn better feature representation. We devise a dual-stage knowledge distillation (DSKD) strategy to distill general knowledge between natural and medical images from the foundation model to train a lightweight encoder, and then adopt a mutual exponential moving average (mutual-EMA) to update the weights of the general lightweight encoder and medical-specific encoder. Specifically, pseudo labels from the registration network are used to perform mutual supervision for such two encoders. Moreover, we introduce an auto-prompting (AP) segmentation decoder which adopts the mask generated from the general lightweight model as a prompt to assist the medical-specific model in boosting the final segmentation performance. Extensive experiments conducted on three public datasets, i.e., OASIS, CT-lung demonstrate that the proposed RRL-MedSAM outperforms state-of-the-art one-shot MIS methods for both segmentation and registration tasks. Especially, our lightweight encoder uses only 3% of the parameters compared to the encoder of SAM-Base.
一次性医学影像分割(MIS)对于医学分析至关重要,因为医学专家手动标注的负担很重。最近出现的任何分割模型(SAM)在MIS中表现出了显著的适应性,但由于其依赖劳动密集型的用户交互和高计算成本,不能直接应用于一次性医学影像分割(MIS)。为了应对这些局限性,我们提出了一种新型的SAM引导稳健表示学习框架,名为RRL-MedSAM,以适应一次性3DMIS。该框架利用SAM编码器的强大泛化能力来学习更好的特征表示。我们设计了一种双阶段知识蒸馏(DSKD)策略,从基础模型中提炼自然医学图像之间的通用知识,以训练一个轻量级编码器,然后采用相互指数移动平均(mutual-EMA)来更新通用轻量级编码器和医学专用编码器的权重。具体来说,来自注册网络的伪标签被用来对这两种编码器进行相互监督。此外,我们引入了一种自动提示(AP)分割解码器,该解码器采用通用轻量级模型生成的掩膜作为提示,辅助医学专用模型提高最终的分割性能。在OASIS、CT-lung三个公共数据集上进行的广泛实验表明,所提出的RRL-MedSAM在分割和注册任务上的性能均优于最新的单次MIS方法。尤其是,我们的轻量级编码器仅使用SAM-Base编码器的3%参数。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为RRL-MedSAM的新框架,用于将SAM模型适应于一次拍摄的三维医学图像分割(MIS)。该框架通过利用SAM编码器的强大泛化能力来学习更好的特征表示,并通过双阶段知识蒸馏策略和互指数移动平均技术来优化编码器权重。此外,还引入了一种自动提示分割解码器,以提高最终分割性能。在多个公共数据集上的实验表明,RRL-MedSAM在单次拍摄MIS的分割和注册任务上优于现有技术,且其轻量化编码器使用的参数仅为SAM-Base编码器的3%。
Key Takeaways
- 一次拍摄医学图像分割(MIS)对于医学分析至关重要,因为医学专家手动标注的负担很重。
- SAM模型虽在MIS中表现出良好的适应性,但由于其依赖劳动密集型的用户交互和高计算成本,无法直接应用于一次拍摄MIS。
- RRL-MedSAM框架通过利用SAM的泛化能力,适应了单次拍摄的三维医学图像分割。
- 采用双阶段知识蒸馏策略来提炼基础模型中的通用知识,并用于训练轻量化编码器。
- 采用互指数移动平均技术更新通用轻量化编码器和医疗专用编码器的权重。
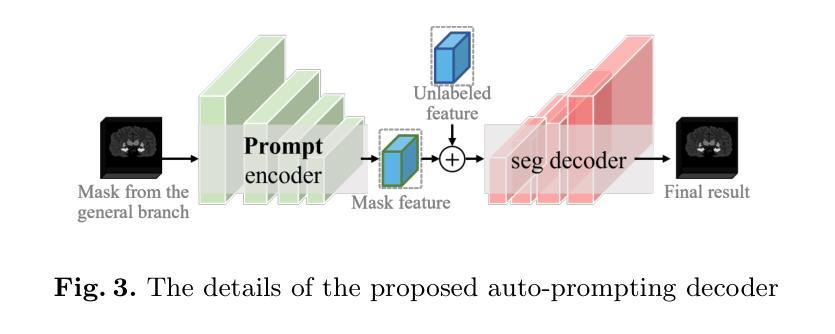
- 通过引入伪标签和自动提示分割解码器来提高最终分割性能。
点此查看论文截图

LymphAtlas- A Unified Multimodal Lymphoma Imaging Repository Delivering AI-Enhanced Diagnostic Insight
Authors:Jiajun Ding, Beiyao Zhu, Xiaosheng Liu, Lishen Zhang, Zhao Liu
This study integrates PET metabolic information with CT anatomical structures to establish a 3D multimodal segmentation dataset for lymphoma based on whole-body FDG PET/CT examinations, which bridges the gap of the lack of standardised multimodal segmentation datasets in the field of haematological malignancies. We retrospectively collected 483 examination datasets acquired between March 2011 and May 2024, involving 220 patients (106 non-Hodgkin lymphoma, 42 Hodgkin lymphoma); all data underwent ethical review and were rigorously de-identified. Complete 3D structural information was preserved during data acquisition, preprocessing and annotation, and a high-quality dataset was constructed based on the nnUNet format. By systematic technical validation and evaluation of the preprocessing process, annotation quality and automatic segmentation algorithm, the deep learning model trained based on this dataset is verified to achieve accurate segmentation of lymphoma lesions in PET/CT images with high accuracy, good robustness and reproducibility, which proves the applicability and stability of this dataset in accurate segmentation and quantitative analysis. The deep fusion of PET/CT images achieved with this dataset not only significantly improves the accurate portrayal of the morphology, location and metabolic features of tumour lesions, but also provides solid data support for early diagnosis, clinical staging and personalized treatment, and promotes the development of automated image segmentation and precision medicine based on deep learning. The dataset and related resources are available at https://github.com/SuperD0122/LymphAtlas-.
本研究结合了PET代谢信息与CT解剖结构,基于全身FDG PET/CT检查,建立了淋巴瘤的3D多模态分割数据集。这一研究填补了血液恶性肿瘤领域标准化多模态分割数据集缺乏的空白。我们回顾性地收集了2011年3月至2024年5月期间采集的483个检查数据集,涉及220名患者(其中106例为非霍奇金淋巴瘤,42例为霍奇金淋巴瘤);所有数据均经过伦理审查,并进行了严格的匿名处理。在数据采集、预处理和标注过程中,完整的3D结构信息被保留下来,基于nnUNet格式构建了高质量的数据集。通过对预处理过程、标注质量和自动分割算法的系统技术验证和评估,验证了在此数据集上训练的深度学习模型,能够实现PET/CT图像中淋巴瘤病变的准确分割,具有较高的准确性、良好的稳健性和可重复性,证明了该数据集在准确分割和定量分析中的适用性和稳定性。通过该数据集实现的PET/CT图像的深度融合,不仅显著提高了肿瘤病变形态、位置和代谢特征的准确描述,而且为早期诊疗、临床分期和个性化治疗提供了坚实的数据支持,促进了基于深度学习的自动图像分割和精准医学的发展。该数据集及相关资源可通过https://github.com/SuperD0122/LymphAtlas-获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17pages,4 figures
Summary:该研究将PET代谢信息与CT解剖结构相结合,创建了基于全身氟脱氧葡萄糖PET/CT检查的淋巴瘤3D多模态分割数据集,填补了血液系统恶性肿瘤标准化多模态分割数据集的空白。通过深度学习模型训练,验证了该数据集在PET/CT图像中准确分割淋巴瘤病变的可行性、稳定性和可靠性。该数据集的深度融合不仅提高了肿瘤病变形态、位置和代谢特征的准确描述,还为早期诊断、临床分期和个性化治疗提供了坚实的数据支持,促进了基于深度学习的自动图像分割和精准医学的发展。
Key Takeaways:
- 该研究建立了基于全身氟脱氧葡萄糖PET/CT检查的淋巴瘤3D多模态分割数据集,填补了标准化多模态分割数据集的空白。
- 数据集包含了来自220名患者的483个检查数据集,涉及非霍奇金淋巴瘤和霍奇金淋巴瘤。
- 数据集经过伦理审查并严格匿名化处理,保证了数据的质量和隐私。
- 通过深度学习模型训练,验证了数据集的准确性、稳定性和可靠性。
- 数据集的深度融合提高了肿瘤病变的形态、位置和代谢特征的描述准确性。
- 该数据集为早期诊断、临床分期和个性化治疗提供了数据支持。
- 该数据集促进了基于深度学习的自动图像分割和精准医学的发展。
点此查看论文截图

Consensus Recommendations for Hyperpolarized [1-13C]pyruvate MRI Multi-center Human Studies
Authors:Shonit Punwani, Peder EZ Larson, Christoffer Laustsen, Jan VanderMeulen, Jan Henrik Ardenkjær-Larsen, Adam W. Autry, James A. Bankson, Jenna Bernard, Robert Bok, Lotte Bonde Bertelsen, Jenny Che, Albert P. Chen, Rafat Chowdhury, Arnaud Comment, Charles H. Cunningham, Duy Dang, Ferdia A Gallagher, Adam Gaunt, Yangcan Gong, Jeremy W. Gordon, Ashley Grimmer, James Grist, Esben Søvsø Szocska Hansen, Mathilde Hauge Lerche, Richard L. Hesketh, Jan-Bernd Hoevener, Ching-Yi Hsieh, Kayvan R. Keshari, Sebastian Kozerke, Titus Lanz, Dirk Mayer, Mary McLean, Jae Mo Park, Jim Slater, Damian Tyler, Jean-Luc Vanderheyden, Daniel Vigneron, Cornelius von Morze, Duan Xu, Fulvio Zaccagna, Vlad Zaha, the HP 13C MRI Consensus Group
Magnetic resonance imaging of hyperpolarized (HP) [1-13C]pyruvate allows in-vivo assessment of metabolism and has translated into human studies across diseases at 15 centers worldwide. Consensus on best practice for multi-center studies is required to develop clinical applications. This paper presents the results of a 2-round formal consensus building exercise carried out by experts with HP [1-13C]pyruvate human study experience. Twenty-nine participants from 13 sites brought together expertise in pharmacy methods, MR physics, translational imaging, and data-analysis; with the goal of providing recommendations and best practice statements on conduct of multi-center human studies of HP [1-13C]pyruvate MRI. Overall, the group reached consensus on approximately two-thirds of 246 statements in the questionnaire, covering ‘HP 13C-Pyruvate Preparation’, ‘MRI System Setup, Calibration, and Phantoms’, ‘Acquisition and Reconstruction’, and ‘Data Analysis and Quantification’. Consensus was present across categories, examples include that: (i) different HP pyruvate preparation methods could be used in human studies, but that the same release criteria have to be followed; (ii) site qualification and quality assurance must be performed with phantoms and that the same field strength must be used, but that the rest of the system setup and calibration methods could be determined by individual sites; (iii) the same pulse sequence and reconstruction methods were preferable, but the exact choice should be governed by the anatomical target; (iv) normalized metabolite area-under-curve (AUC) values and metabolite AUC were the preferred metabolism metrics. The work confirmed areas of consensus for multi-center study conduct and identified where further research is required to ascertain best practice.
极化(HP)[1-13C]丙酮酸盐的磁共振成像允许对体内代谢进行评估,并已在全球范围内15个中心进行疾病相关的临床研究。为了开发临床应用,需要对多中心研究达成最佳实践的共识。本文介绍了具有极化(HP)[1-13C]丙酮酸盐人体研究经验的专家所开展的为期两轮的形式化共识建设的成果。来自13个不同站点的29名参与者汇聚了药物方法、MR物理学、转化成像和数据分析方面的专业知识,旨在就极化(HP)[1-13C]丙酮酸盐MRI多中心人体研究提供建议和最佳实践声明。总体而言,该组对问卷中的大约三分之二的246个陈述达成了共识,涵盖了“HP 13C丙酮酸盐制备”、“MRI系统安装、校准和幻影”、“采集和重建”以及“数据分析和量化”。各分类中都存在共识,例如:(i)人体研究中可以使用不同的HP丙酮酸盐制备方法,但必须遵循相同的释放标准;(ii)必须使用幻影进行站点资格认证和质量保证,并且必须使用相同的磁场强度,而系统的其余设置和校准方法可由各个站点自行决定;(iii)相同的脉冲序列和重建方法较为理想,但确切选择应由解剖目标来决定;(iv)归一化的代谢产物曲线下面积(AUC)值和代谢产物AUC是首选的代谢指标。这项工作确认了多中心研究开展的共识领域,并确定了需要进一步研究的领域以确定最佳实践。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了利用超极化[¹³C]丙酮酸盐磁共振成像进行人体代谢评估的研究现状。专家通过两轮共识建设活动,就超极化[¹³C]丙酮酸盐磁共振成像的多中心人体研究提供了建议和最佳实践声明。共识涉及HP 1³C-丙酮酸盐制备、MRI系统设定、校准和幻体、采集和重建、数据分析和量化等方面。此外,本文确定了需要进一步研究的领域,以明确最佳实践。
Key Takeaways
- 磁振成像技术通过超极化(HP)[¹³C]丙酮酸盐,能够进行人体代谢评估,目前全球有十五个研究中心应用该技术进行疾病研究。
- 专家通过两轮共识建设活动,就如何开展多中心人体研究达成了共识。参与者来自全球十三个研究中心,涵盖了药学方法、磁共振物理、翻译成像和数据分析等领域的专家。
- 共识涵盖了HP [¹³C]丙酮酸盐制备、MRI系统设置与校准、数据采集与重建以及数据分析与量化等方面。在准备阶段,达成了共识认为可以使用不同的超极化丙酮酸盐制备方法,但必须遵循相同的释放标准;对于MR系统的设置与校准方法上拥有更大的灵活性。关于影像获取及重建阶段的研究达成了广泛的共识,推荐使用相同的脉冲序列和重建方法,并根据解剖目标进行精确选择。此外在数据解析阶段对于标准化代谢物面积曲线下积分值(AUC)和代谢物浓度的标准化数据一致同意接受度最高作为反应代谢的有效数据。指出开展这一工作所需后续进一步的调查领域及发展方向如持续的剂型改善以适应病人特异需求以及对体质影像的标准测试量化以定义适应症;定性影响临床应用进一步推广到不同地区涉及不同疾病领域等方向。
点此查看论文截图

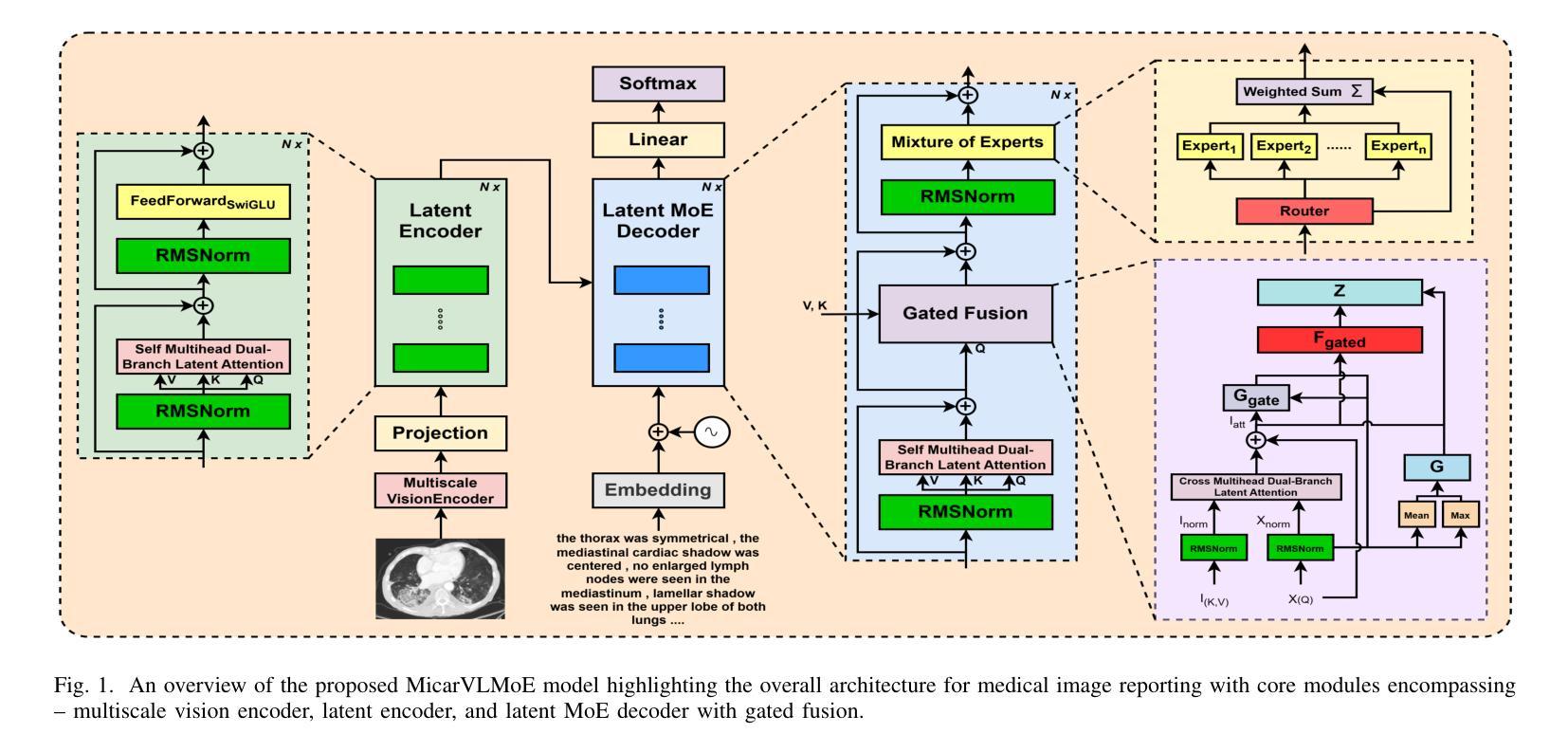
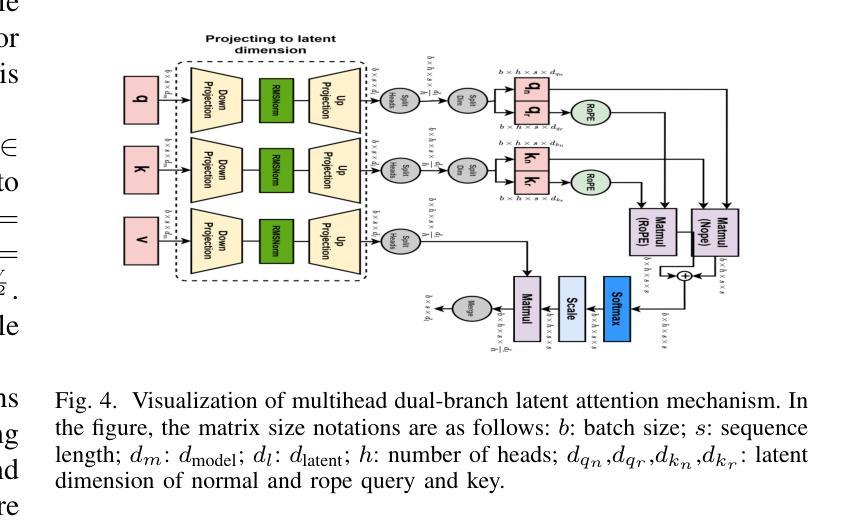
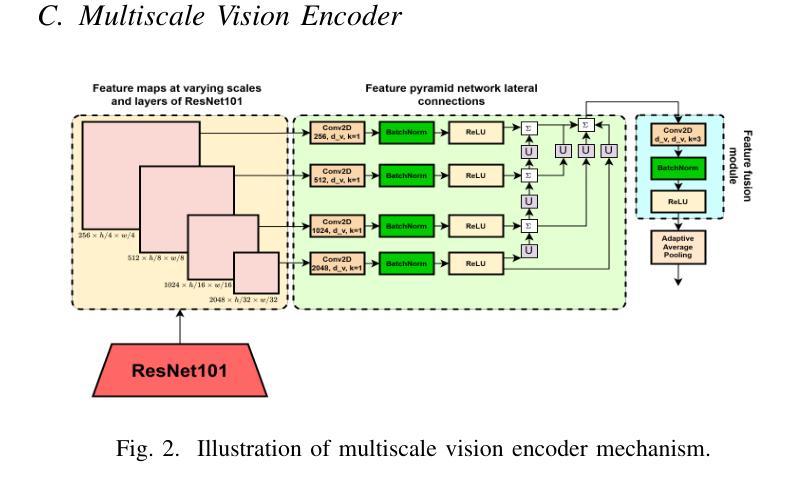
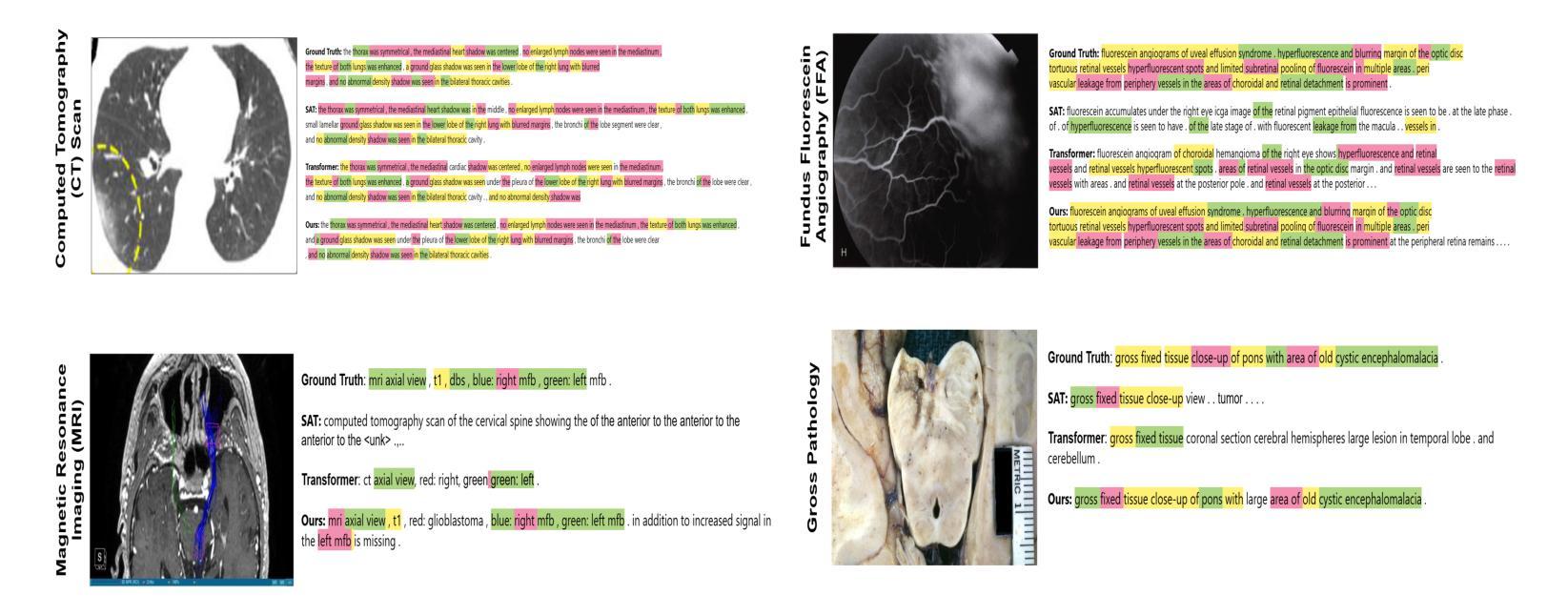
MicarVLMoE: A Modern Gated Cross-Aligned Vision-Language Mixture of Experts Model for Medical Image Captioning and Report Generation
Authors:Amaan Izhar, Nurul Japar, Norisma Idris, Ting Dang
Medical image reporting (MIR) aims to generate structured clinical descriptions from radiological images. Existing methods struggle with fine-grained feature extraction, multimodal alignment, and generalization across diverse imaging types, often relying on vanilla transformers and focusing primarily on chest X-rays. We propose MicarVLMoE, a vision-language mixture-of-experts model with gated cross-aligned fusion, designed to address these limitations. Our architecture includes: (i) a multiscale vision encoder (MSVE) for capturing anatomical details at varying resolutions, (ii) a multihead dual-branch latent attention (MDLA) module for vision-language alignment through latent bottleneck representations, and (iii) a modulated mixture-of-experts (MoE) decoder for adaptive expert specialization. We extend MIR to CT scans, retinal imaging, MRI scans, and gross pathology images, reporting state-of-the-art results on COVCTR, MMR, PGROSS, and ROCO datasets. Extensive experiments and ablations confirm improved clinical accuracy, cross-modal alignment, and model interpretability. Code is available at https://github.com/AI-14/micar-vl-moe.
医学图像报告(MIR)旨在从放射学图像中生成结构化临床描述。现有方法在进行精细特征提取、多模式对齐以及在多种成像类型上的通用化方面存在困难,通常依赖于普通变压器,并且主要关注胸部X光片。我们提出了MicarVLMoE,这是一种带有门控交叉对齐融合的视觉语言混合专家模型,旨在解决这些局限性。我们的架构包括:(i)用于在不同分辨率下捕获解剖细节的多尺度视觉编码器(MSVE),(ii)用于通过潜在瓶颈表示进行视觉语言对齐的多头双分支潜在注意力(MDLA)模块,(iii)用于自适应专家特化的调制混合专家(MoE)解码器。我们将MIR扩展到CT扫描、视网膜成像、MRI扫描和大体病理图像,在COVCTR、MMR、PGROSS和ROCO数据集上报告了最新结果。大量实验和消融研究证实了其在临床准确性、跨模态对齐和模型可解释性方面的改进。代码可在https://github.com/AI-14/micar-vl-moe获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IJCNN 2025, 8 pages, 8 figures, 3 tables
摘要
医学图像报告(MIR)旨在从放射学图像生成结构化临床描述。现有方法难以进行精细特征提取、多模态对齐,以及在多种成像类型中的通用化。我们提出了MicarVLMoE,这是一种带有门控交叉对齐融合的视听混合专家模型,旨在解决这些局限性。我们的架构包括:多尺度视觉编码器(MSVE),用于在不同分辨率捕捉解剖细节;多头双分支潜在注意力(MDLA)模块,通过潜在瓶颈表示实现视听对齐;以及调制混合专家(MoE)解码器,用于自适应专家专业化。我们将MIR扩展到CT扫描、视网膜成像、MRI扫描和大体病理图像,在COVCTR、MMR、PGROSS和ROCO数据集上报告了最新的结果。
要点
- 医学图像报告(MIR)是从放射学图像生成结构化临床描述的任务。
- 现有方法在面对精细特征提取、多模态对齐和跨成像类型通用化方面存在挑战。
- 提出了一种视听混合专家模型MicarVLMoE,具有门控交叉对齐融合机制。
- 架构包括多尺度视觉编码器、多头双分支潜在注意力模块和调制混合专家解码器。
- 成功将MIR扩展到多种医学图像类型,包括CT扫描、视网膜成像、MRI扫描和大体病理图像。
- 在多个数据集上取得了最新结果,证明了临床准确性、跨模态对齐和模型解释性的提升。
点此查看论文截图


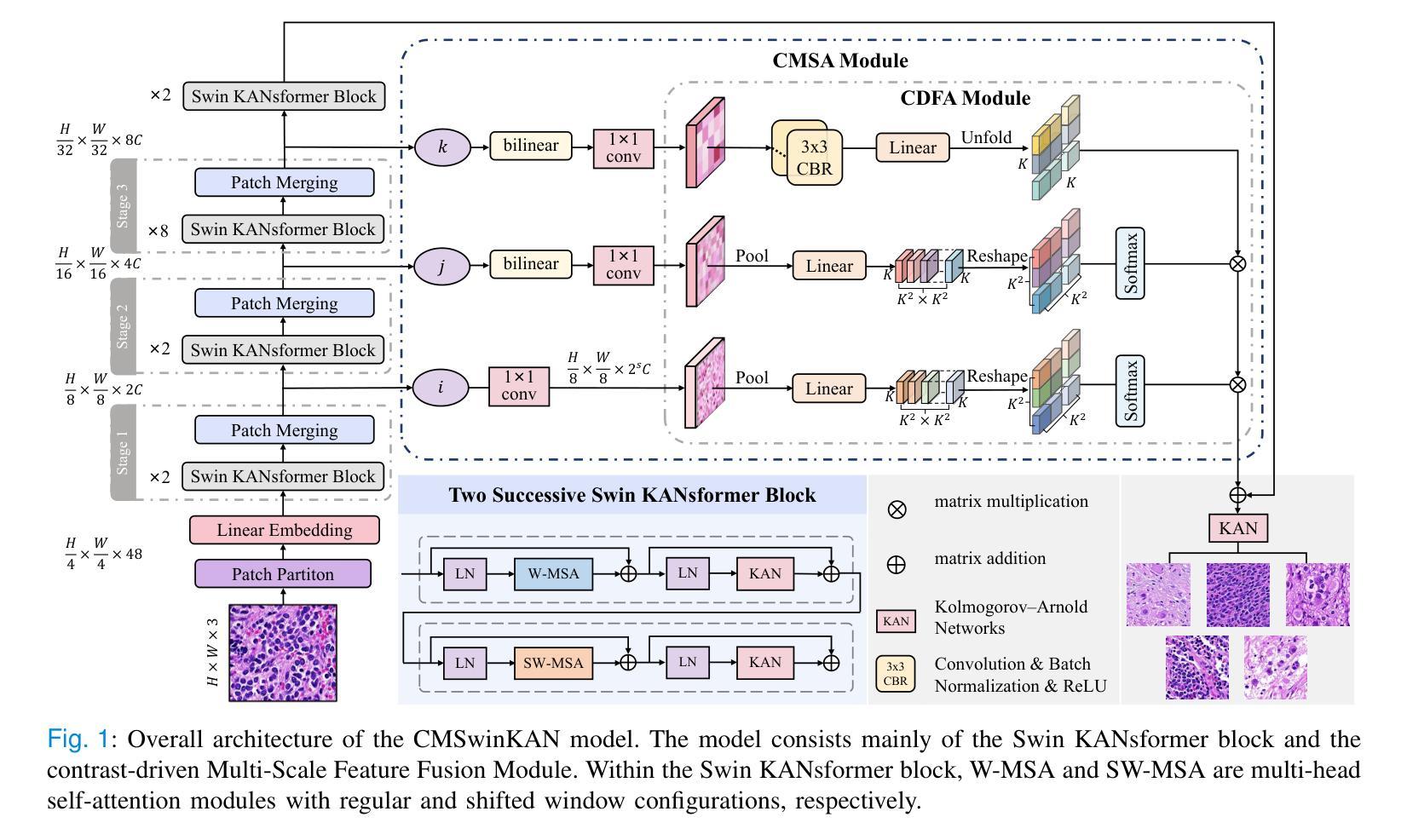
Towards Accurate and Interpretable Neuroblastoma Diagnosis via Contrastive Multi-scale Pathological Image Analysis
Authors:Zhu Zhu, Shuo Jiang, Jingyuan Zheng, Yawen Li, Yifei Chen, Manli Zhao, Weizhong Gu, Feiwei Qin, Jinhu Wang, Gang Yu
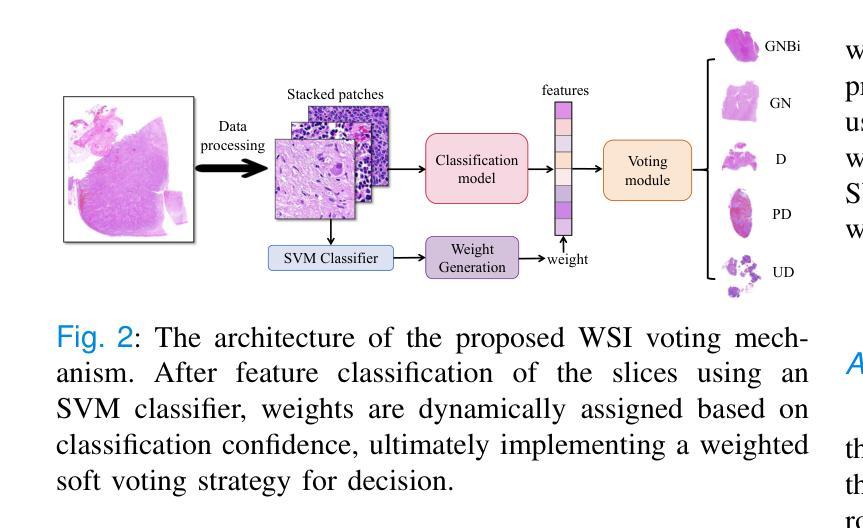
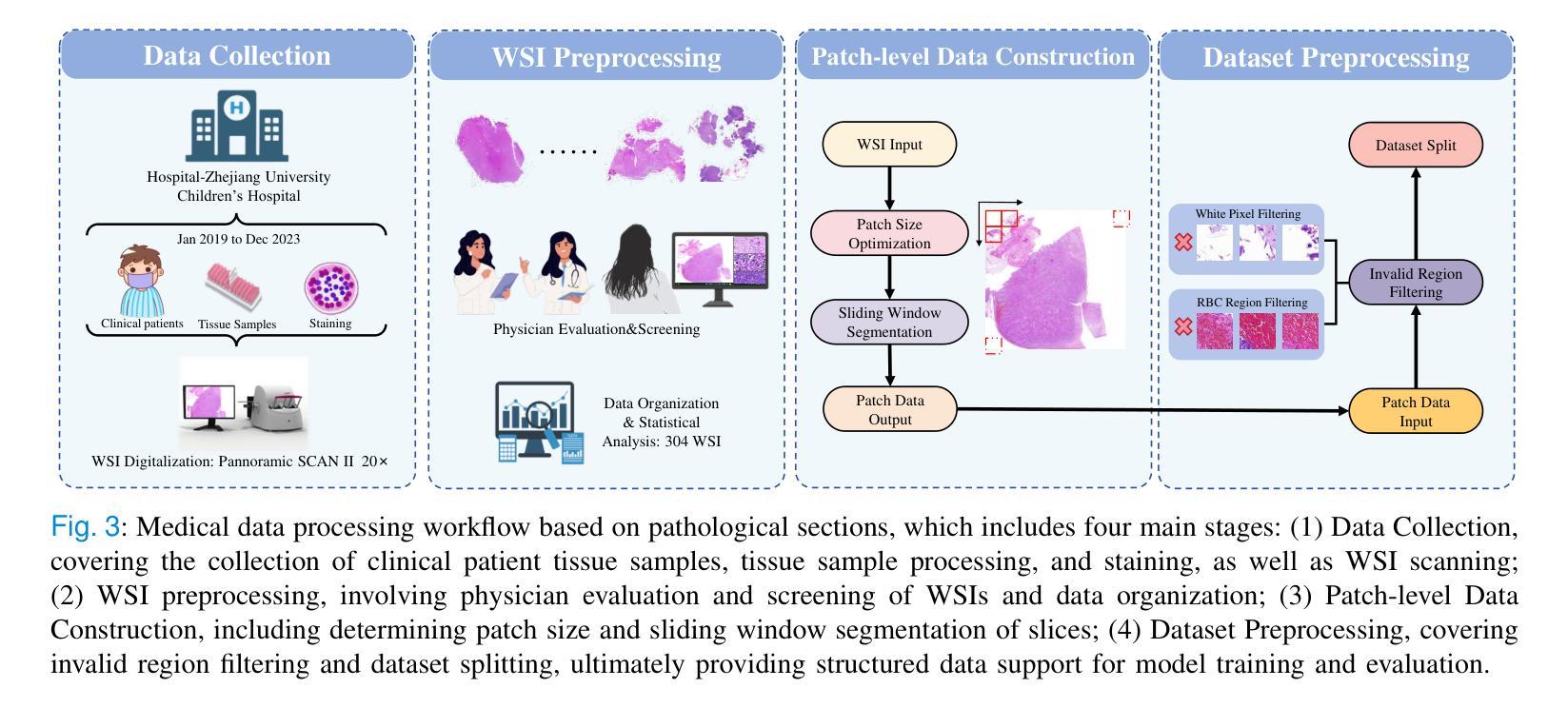
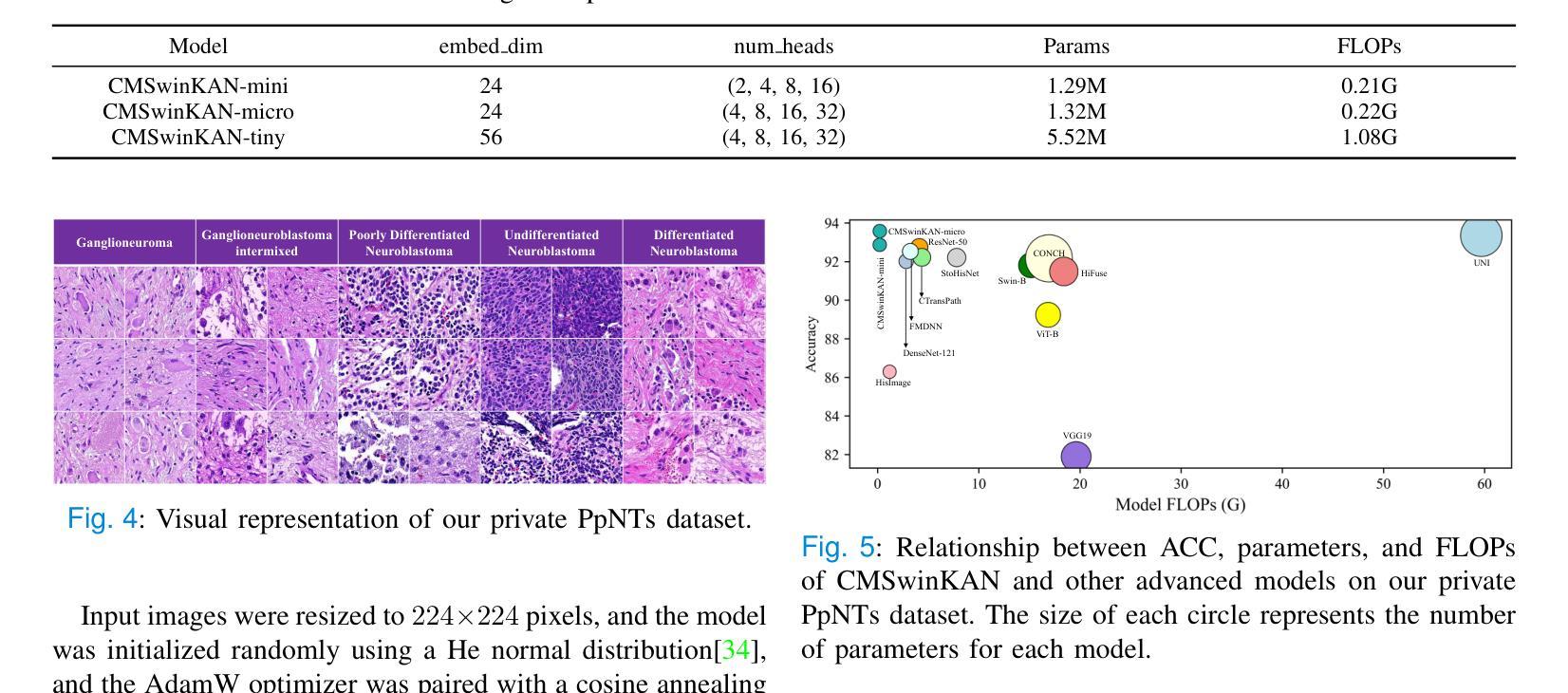
Neuroblastoma, adrenal-derived, is among the most common pediatric solid malignancies, characterized by significant clinical heterogeneity. Timely and accurate pathological diagnosis from hematoxylin and eosin-stained whole slide images is critical for patient prognosis. However, current diagnostic practices primarily rely on subjective manual examination by pathologists, leading to inconsistent accuracy. Existing automated whole slide image classification methods encounter challenges such as poor interpretability, limited feature extraction capabilities, and high computational costs, restricting their practical clinical deployment. To overcome these limitations, we propose CMSwinKAN, a contrastive-learning-based multi-scale feature fusion model tailored for pathological image classification, which enhances the Swin Transformer architecture by integrating a Kernel Activation Network within its multilayer perceptron and classification head modules, significantly improving both interpretability and accuracy. By fusing multi-scale features and leveraging contrastive learning strategies, CMSwinKAN mimics clinicians’ comprehensive approach, effectively capturing global and local tissue characteristics. Additionally, we introduce a heuristic soft voting mechanism guided by clinical insights to seamlessly bridge patch-level predictions to whole slide image-level classifications. We validate CMSwinKAN on the PpNTs dataset, which was collaboratively established with our partner hospital and the publicly accessible BreakHis dataset. Results demonstrate that CMSwinKAN performs better than existing state-of-the-art pathology-specific models pre-trained on large datasets. Our source code is available at https://github.com/JSLiam94/CMSwinKAN.
神经母细胞瘤是肾上腺起源的一种最常见的儿童实体恶性肿瘤,具有显著的临床异质性。从苏木精和伊红染色的全切片图像中及时进行准确的病理诊断对患者的预后至关重要。然而,目前的诊断方法主要依赖于病理医师的主观肉眼检查,导致诊断准确性不一致。现有的全自动切片图像分类方法面临可解释性差、特征提取能力有限和计算成本高的挑战,限制了其在临床实践中的部署应用。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了CMSwinKAN,这是一种基于对比学习的多尺度特征融合模型,用于病理图像分类。我们对Swin Transformer架构进行了改进,通过在其多层感知器和分类头模块中集成Kernel Activation Network,增强了CMSwinKAN的可解释性和准确性。通过融合多尺度特征和利用对比学习策略,CMSwinKAN模仿了医生的全面方法,有效地捕捉了全局和局部组织特征。此外,我们还引入了一种受临床见解启发式的软投票机制,无缝地将补丁级别的预测与全切片图像级别的分类联系起来。我们在与合作伙伴医院共同建立的PpNTs数据集和可公开访问的BreakHis数据集上验证了CMSwinKAN。结果表明,CMSwinKAN的性能优于其他在大型数据集上预训练的病理学专用模型。我们的源代码可在https://github.com/JSLiam94/CMSwinKAN上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10pages, 8 figures
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于对比学习的多尺度特征融合模型CMSwinKAN,用于神经母细胞瘤等肾上腺衍生肿瘤的病理图像分类。该模型改进了Swin Transformer架构,通过集成Kernel Activation Network,提高了模型的解释性和准确性。CMSwinKAN采用多尺度特征融合和对比学习策略,模拟医生全面的诊断方法,有效捕捉全局和局部组织特征。此外,还引入了一种基于临床见解的启发式软投票机制,将补丁级别的预测无缝桥接到整个幻灯片图像级别的分类。在PpNTs和BreakHis数据集上的验证结果表明,CMSwinKAN的性能优于现有的最先进的病理学专用模型。
Key Takeaways
- 神经母细胞瘤是常见的儿童实体恶性肿瘤,及时准确的病理诊断对预后至关重要。
- 当前诊断实践主要依赖病理医师的主观手动检查,存在诊断准确性不一致的问题。
- CMSwinKAN模型是基于对比学习的多尺度特征融合模型,旨在提高病理图像分类的准确性。
- CMSwinKAN通过集成Kernel Activation Network到Swin Transformer架构中,增强了模型的解释性和准确性。
- 多尺度特征融合和对比学习策略使CMSwinKAN能够捕捉全局和局部组织特征,模拟医生的全面诊断方法。
- 引入启发式软投票机制,将补丁级别的预测无缝桥接到整个幻灯片图像级别的分类,提高了模型的诊断能力。
点此查看论文截图

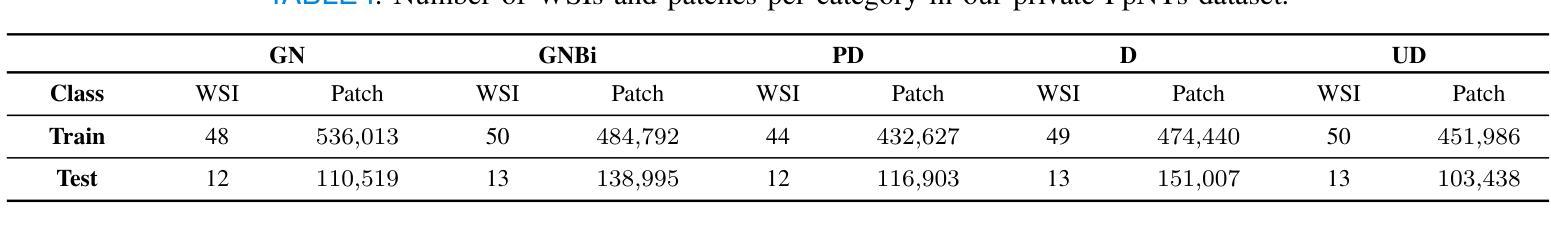
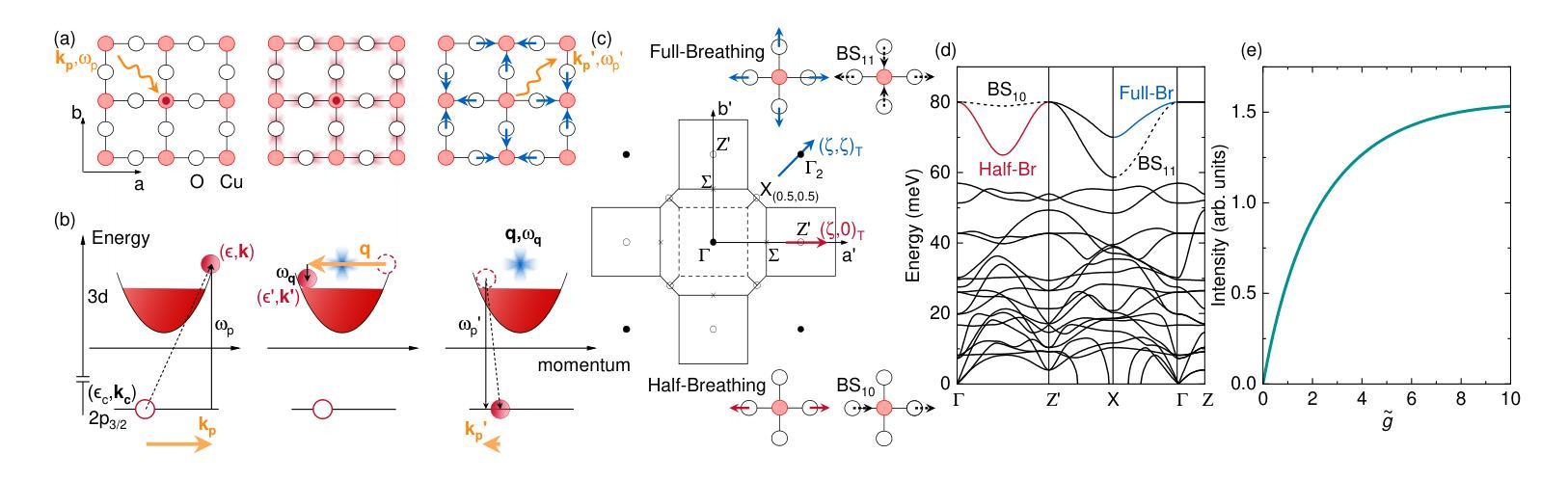
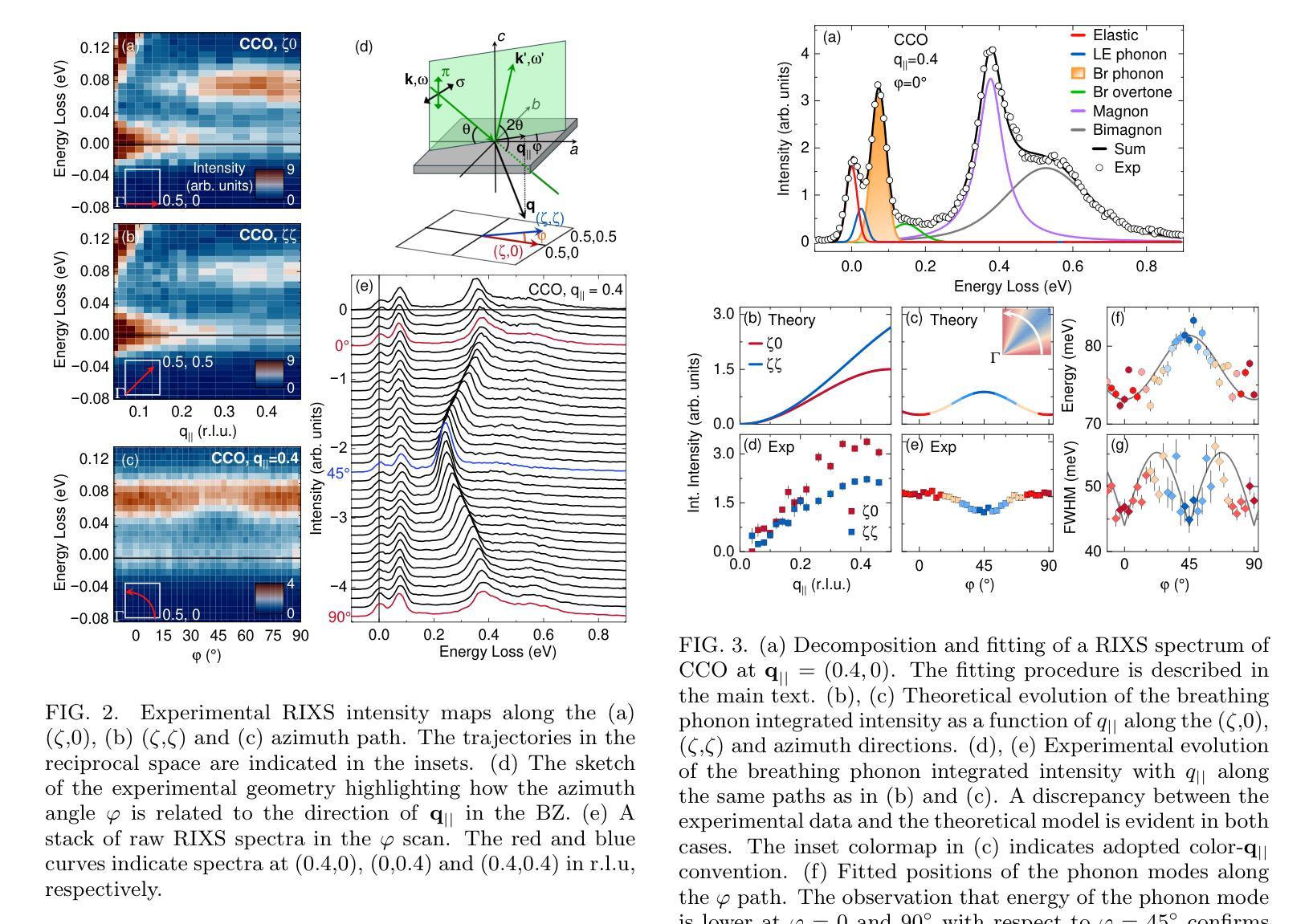
Momentum-dependent electron-phonon coupling in cuprates by RIXS: the roles of phonon symmetry and electronic structure
Authors:Maryia Zinouyeva, Rolf Heid, Giacomo Merzoni, Riccardo Arpaia, Nikolai Andreev, Marco Biagi, Nicholas B. Brookes, Daniele Di Castro, Alexei Kalaboukhov, Kurt Kummer, Floriana Lombardi, Leonardo Martinelli, Francesco Rosa, Flora Yakhou-Harris, Lucio Braicovich, Marco Moretti Sala, Paolo G. Radaelli, Giacomo Ghiringhelli
The experimental determination of the magnitude and momentum dependence of electron-phonon coupling (EPC) is an outstanding problem in condensed matter physics. Resonant inelastic x-ray scattering (RIXS) has been previously employed to determine the EPC, since the intensity of phonon peaks in RIXS spectra has been directly related to the underlying EPC strength. In order to assess the limits of validity of such a relation, we compare experimental results and theoretical predictions for several high-T$c$ superconducting cuprates. Namely, we investigate the intensity of the bond-stretching phonon mode in CaCuO$2$, La$2$CuO${4+\delta}$, La${1.84}$Sr${0.16}$CuO$_4$ and YBa$_2$Cu$3$O${7-\delta}$ along the high symmetry ($\zeta$,0), ($\zeta$,$\zeta$) directions and as a function of the azimuthal angle $\phi$ at fixed modulus of the in-plane momentum $\mathbf{q_\parallel}$. Using two different theoretical approaches for the description of the RIXS scattering from phonons, we find that the $\mathbf{q_\parallel}$-dependence of the RIXS intensity can be largely ascribed to the symmetry of the phonon mode, and that satisfactory prediction of the experimental results cannot be obtained without including realistic details of the electronic structure in the calculations. Regardless of the theoretical model, RIXS provides a reliable momentum dependence of EPC in cuprates and can be used to test advanced theoretical predictions.
实验确定电子-声子耦合(EPC)的大小和动量依赖性是凝聚态物理中的一个突出问题。以往曾用共振非弹性X射线散射(RIXS)来确定EPC,因为RIXS光谱中声子峰的强度与基本的EPC强度直接相关。为了评估这种关系的有效性范围,我们对比了几种高温超导铜氧化物的实验结果和理论预测。具体来说,我们研究了CaCuO2、La2CuO4+δ、La1.84Sr0.16CuO4和YBa2Cu3O7−δ中键拉伸声子模式的强度,沿着高对称(ζ,0)、(ζ,ζ)方向,并作为方位角φ的函数,在平面动量固定模量q∥下。使用两种不同的理论方法来描述声子的RIXS散射,我们发现RIXS强度的q∥依赖性在很大程度上可以归因于声子模式的对称性,如果不将电子结构的现实细节包括在计算中,就无法对实验结果进行令人满意的预测。无论采用哪种理论模型,RIXS都能可靠地提供铜氧化物中EPC的动量依赖性,可用于检验高级理论预测。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages, 9 figures
摘要
该实验研究了电子-声子耦合(EPC)的大小及其动量依赖性,这是凝聚态物理中的一个突出问题。以往利用共振非弹性X射线散射(RIXS)来确定EPC,因为RIXS光谱中的声子峰强度与EPC强度直接相关。为了评估这种关系的有效性限制,我们比较了几种高温超导铜氧化物的实验结果和理论预测,如CaCuO2、La2CuO4+δ、La1.84Sr0.16CuO4和YBa2Cu3O7−δ。我们研究了沿高对称(ζ,0)、(ζ,ζ)方向的键拉伸声子模式的强度,并作为方位角ϕ的函数,在固定的平面内动量模数q∥。使用两种不同的理论方法来描述RIXS散射声子,我们发现RIXS强度的q∥依赖性可以很大程度上归因于声子模式的对称性,并且在计算中如果不包含电子结构的现实细节,则无法对实验结果进行令人满意的预测。无论理论模型如何,RIXS都提供了可靠的EPC动量依赖性,并可用来检验高级理论预测。
关键见解
- 电子-声子耦合(EPC)的动量和强度在凝聚态物理中仍是待解决的问题。
- 共振非弹性X射线散射(RIXS)已被用于确定EPC。
- RIXS光谱中的声子峰强度与EPC强度有直接关联。
- 对几种高温超导铜氧化物的实验和理论结果进行了比较。
- RIXS强度的动量依赖性主要归因于声子模式的对称性。
- 现实电子结构的细节在计算EPC时至关重要,否则无法准确预测实验结果。
点此查看论文截图

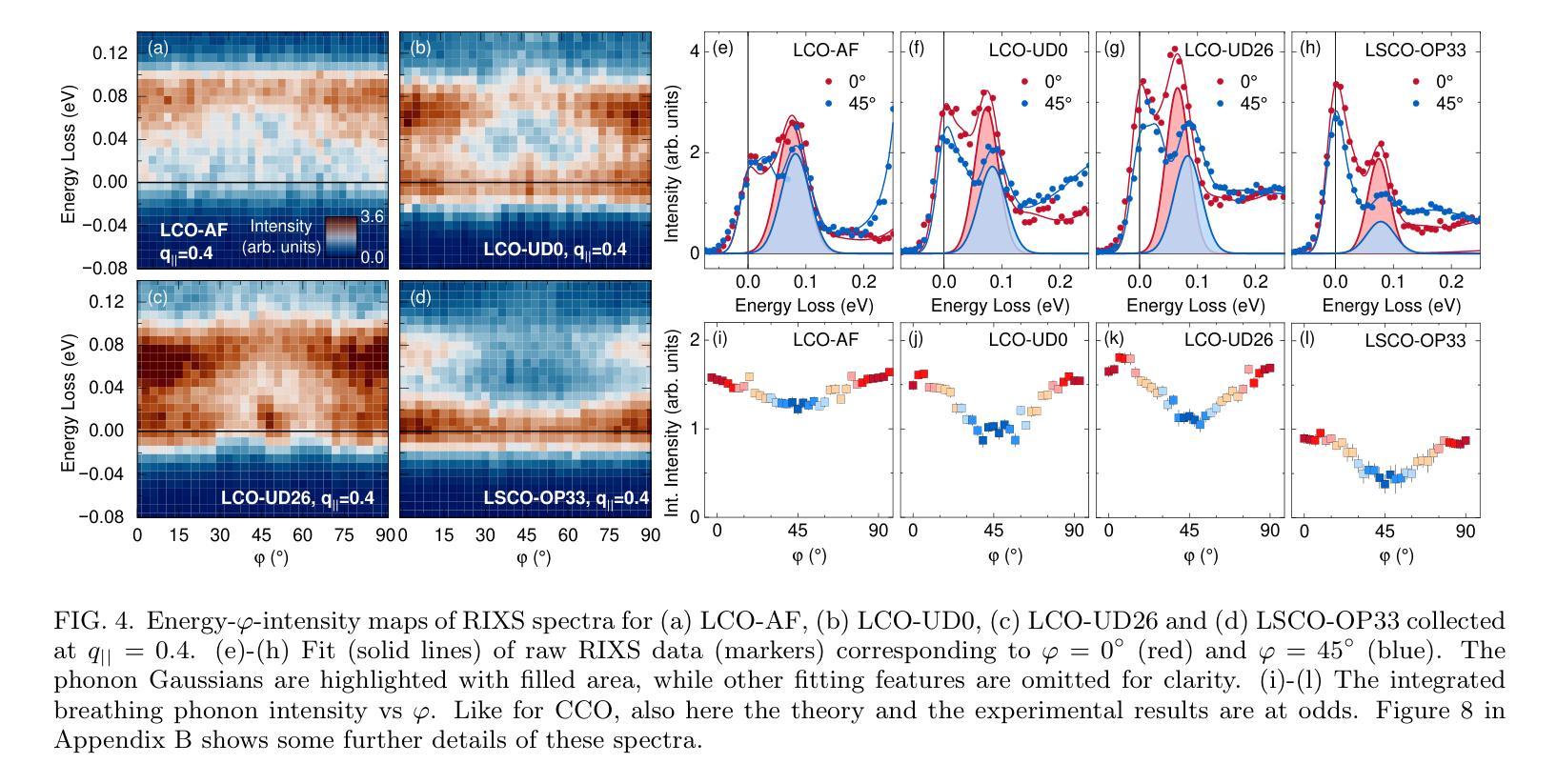
Exploring AI-based System Design for Pixel-level Protected Health Information Detection in Medical Images
Authors:Tuan Truong, Ivo M. Baltruschat, Mark Klemens, Grit Werner, Matthias Lenga
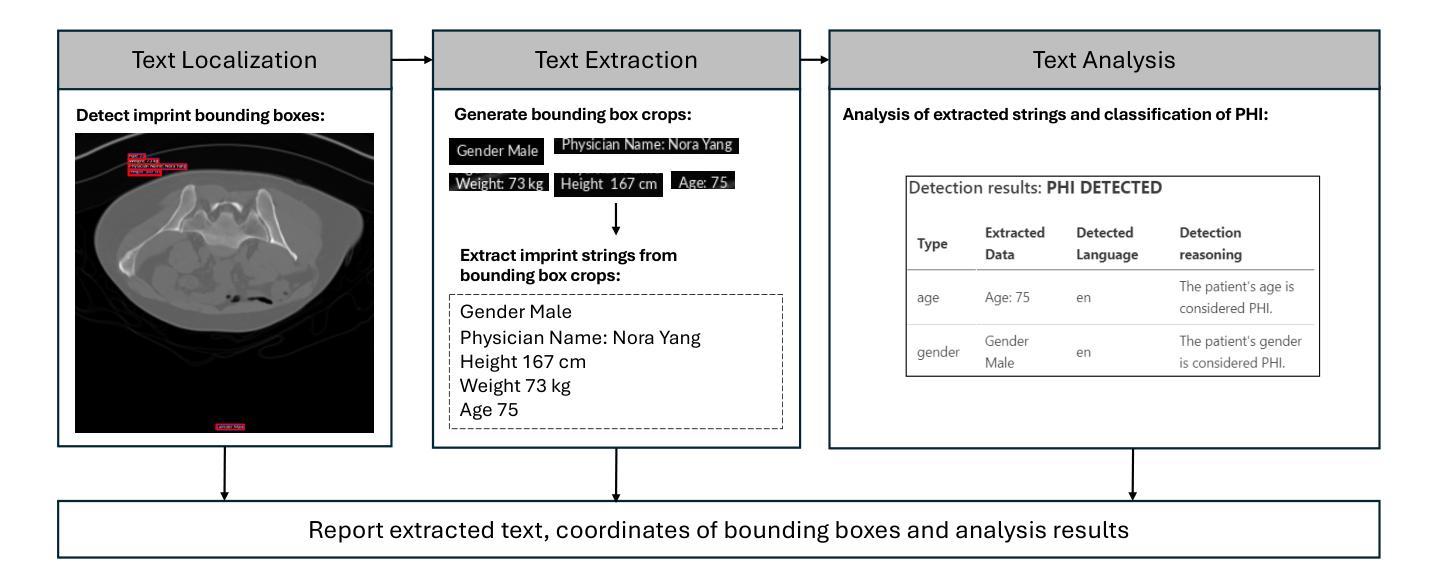
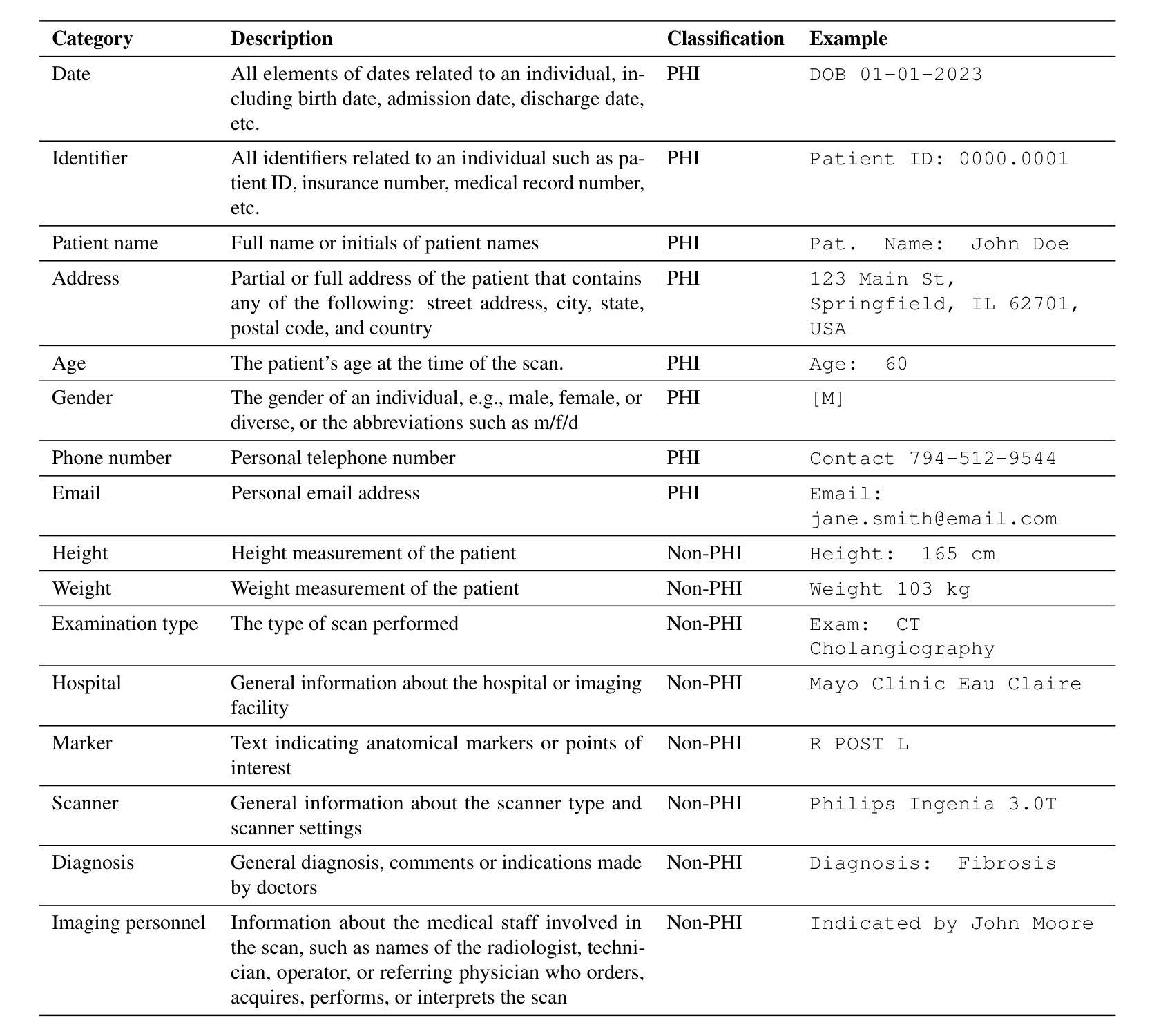
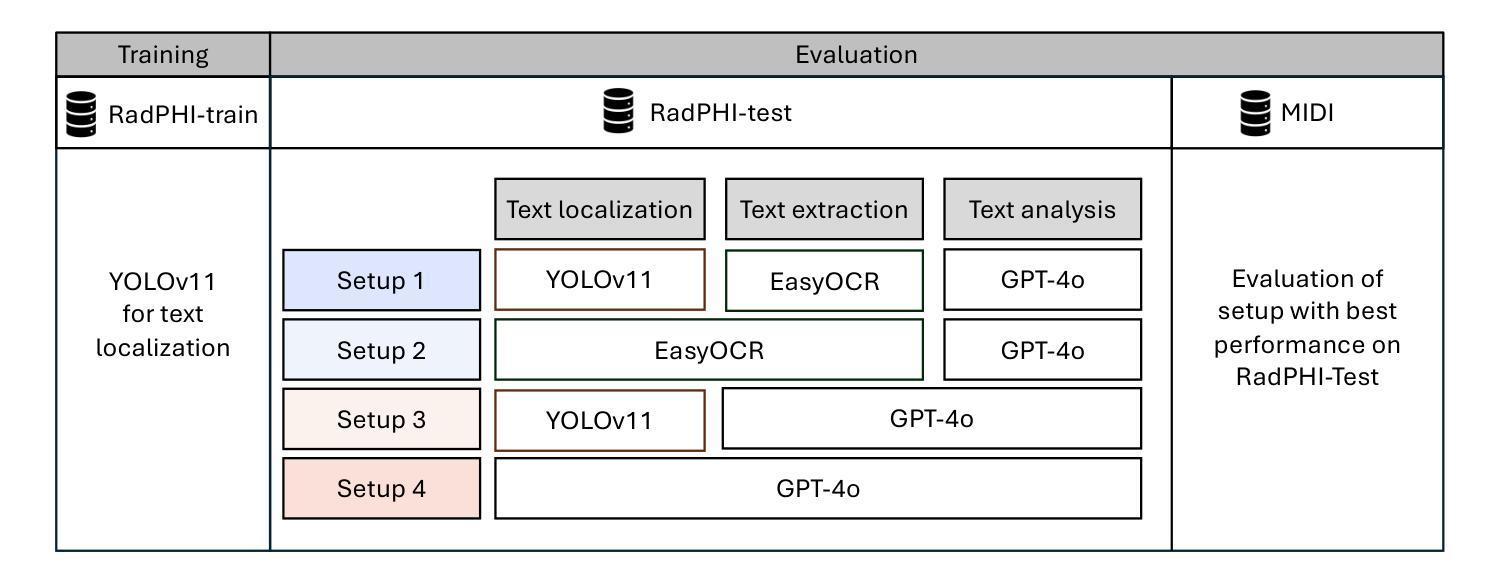
De-identification of medical images is a critical step to ensure privacy during data sharing in research and clinical settings. The initial step in this process involves detecting Protected Health Information (PHI), which can be found in image metadata or imprinted within image pixels. Despite the importance of such systems, there has been limited evaluation of existing AI-based solutions, creating barriers to the development of reliable and robust tools. In this study, we present an AI-based pipeline for PHI detection, comprising three key components: text detection, text extraction, and text analysis. We benchmark three models, YOLOv11, EasyOCR, and GPT-4o, across different setups corresponding to these components, evaluating the performance based on precision, recall, F1 score, and accuracy. All setups demonstrate excellent PHI detection, with all metrics exceeding 0.9. The combination of YOLOv11 for text localization and GPT-4o for extraction and analysis yields the best results. However, this setup incurs higher costs due to GPT-4o’s token generation. Conversely, an end-to-end pipeline that relies solely on GPT-4o shows lower performance but highlights the potential of multimodal models for complex tasks. We recommend fine-tuning a dedicated object detection model and utilizing built-in OCR tools to achieve optimal performance and cost-effectiveness. Additionally, leveraging language models such as GPT-4o can facilitate thorough and flexible analysis of text content.
医学图像的匿名化是在研究和临床环境中进行数据共享时确保隐私的关键步骤。该过程的初始步骤是检测图像中的受保护健康信息(PHI),这些信息可能存在于图像元数据或像素中。尽管此类系统很重要,但对现有的基于人工智能的解决方案的评估仍然有限,这成为开发可靠和稳健的工具的障碍。在研究中,我们提出了一种基于人工智能的PHI检测管道,包括三个关键组件:文本检测、文本提取和文本分析。我们针对这三个组件分别评估了YOLOv11、EasyOCR和GPT-4o三个模型,并根据精确度、召回率、F1分数和准确度评估性能。所有设置都表现出出色的PHI检测能力,所有指标均超过0.9。YOLOv11用于文本定位和GPT-4o用于提取和分析的组合取得了最佳结果,但这一组合由于GPT-4o的令牌生成而成本较高。相反,完全依赖于GPT-4o的端到端管道性能较低,但突显了多模式模型在处理复杂任务时的潜力。我们建议对专用目标检测模型进行微调,并利用内置OCR工具来实现最佳性能和成本效益。此外,利用如GPT-4o等语言模型可以促进文本内容的全面和灵活分析。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF In progress
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于人工智能的医学图像隐私信息检测系统,包括文本检测、提取和分析三个关键步骤。通过对YOLOv11、EasyOCR和GPT-4o三种模型的评估,发现它们在PHI检测方面表现出色,其中YOLOv11与GPT-4o结合的效果最佳。研究还探讨了成本与性能之间的平衡,并推荐了优化性能和成本效益的方案。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像去标识化是确保数据共享过程中隐私的关键步骤。
- 保护健康信息(PHI)可存在于图像元数据或像素中。
- 提出了一个基于AI的PHI检测流程,包括文本检测、提取和分析。
- 评估了YOLOv11、EasyOCR和GPT-4o三个模型,在PHI检测方面表现出色。
- YOLOv11与GPT-4o结合使用效果最佳,但成本较高。
- 探讨了成本与性能之间的平衡,推荐了优化方案。
点此查看论文截图