⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-01 更新
EfficientHuman: Efficient Training and Reconstruction of Moving Human using Articulated 2D Gaussian
Authors:Hao Tian, Rui Liu, Wen Shen, Yilong Hu, Zhihao Zheng, Xiaolin Qin
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has been recognized as a pioneering technique in scene reconstruction and novel view synthesis. Recent work on reconstructing the 3D human body using 3DGS attempts to leverage prior information on human pose to enhance rendering quality and improve training speed. However, it struggles to effectively fit dynamic surface planes due to multi-view inconsistency and redundant Gaussians. This inconsistency arises because Gaussian ellipsoids cannot accurately represent the surfaces of dynamic objects, which hinders the rapid reconstruction of the dynamic human body. Meanwhile, the prevalence of redundant Gaussians means that the training time of these works is still not ideal for quickly fitting a dynamic human body. To address these, we propose EfficientHuman, a model that quickly accomplishes the dynamic reconstruction of the human body using Articulated 2D Gaussian while ensuring high rendering quality. The key innovation involves encoding Gaussian splats as Articulated 2D Gaussian surfels in canonical space and then transforming them to pose space via Linear Blend Skinning (LBS) to achieve efficient pose transformations. Unlike 3D Gaussians, Articulated 2D Gaussian surfels can quickly conform to the dynamic human body while ensuring view-consistent geometries. Additionally, we introduce a pose calibration module and an LBS optimization module to achieve precise fitting of dynamic human poses, enhancing the model’s performance. Extensive experiments on the ZJU-MoCap dataset demonstrate that EfficientHuman achieves rapid 3D dynamic human reconstruction in less than a minute on average, which is 20 seconds faster than the current state-of-the-art method, while also reducing the number of redundant Gaussians.
3D高斯插值(3DGS)已被认为是场景重建和新型视图合成中的一种前沿技术。最近利用3DGS重建3D人体的工作试图利用人体姿态的先验信息来提高渲染质量和训练速度。然而,由于多视图的不一致性和冗余的高斯,它难以有效地拟合动态表面平面。这种不一致性产生的原因在于高斯椭圆体无法准确表示动态物体的表面,这阻碍了动态人体的快速重建。同时,冗余高斯的大量存在意味着这些工作的训练时间对于快速拟合动态人体来说仍然不理想。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了EfficientHuman模型,该模型使用关节式二维高斯快速完成人体动态重建,同时确保高渲染质量。关键创新在于将高斯插值编码为规范空间中的关节式二维高斯曲面,然后通过线性混合蒙皮(LBS)将它们变换到姿态空间,以实现高效的姿态变换。与三维高斯不同,关节式二维高斯曲面可以快速适应动态人体,同时确保视图几何一致性。此外,我们还引入了一个姿态校准模块和一个LBS优化模块,以实现动态人体姿态的精确拟合,提高模型性能。在ZJU-MoCap数据集上的大量实验表明,EfficientHuman实现了快速的三维动态人体重建,平均时间不到一分钟,比当前最先进的方法快20秒,同时减少了冗余高斯的数量。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 3 figures
摘要
3DGS技术在场景重建和新颖视角合成方面有着开创性的应用。针对利用3DGS技术重建3D人体的问题,现有研究试图利用人体姿态的先验信息来提高渲染质量和训练速度,但仍面临动态表面平面拟合困难的问题。本文提出EfficientHuman模型,通过采用关节式2D高斯技术快速完成动态人体重建,确保高质量渲染。关键创新在于将高斯splat编码为规范空间中的关节式2D高斯surfels,然后通过线性混合蒙皮(LBS)将其转换为姿态空间,以实现有效的姿态转换。与3D高斯相比,关节式2D高斯surfels能更快适应动态人体,同时确保视图一致性的几何结构。此外,还引入了姿态校准模块和LBS优化模块,以实现动态人体姿态的精确匹配,提高模型性能。在ZJU-MoCap数据集上的实验表明,EfficientHuman实现了快速的3D动态人体重建,平均时间不到一分钟,比当前最先进的方法快20秒,同时减少了冗余高斯的数量。
关键见解
- 3DGS技术在场景重建和新颖视角合成中具有开创性应用。
- 现有研究在利用3DGS技术重建3D人体时面临动态表面平面拟合困难的问题。
- EfficientHuman模型通过采用关节式2D高斯技术快速适应动态人体,确保高质量渲染。
- EfficientHuman将高斯splat编码为规范空间中的关节式2D高斯surfels,并通过线性混合蒙皮(LBS)转换为姿态空间。
- 姿态校准模块和LBS优化模块的实现提高了动态人体姿态的精确匹配和模型性能。
- EfficientHuman在ZJU-MoCap数据集上的实验实现了快速的3D动态人体重建,平均时间少于一分钟,比现有方法更快速且有效。
点此查看论文截图
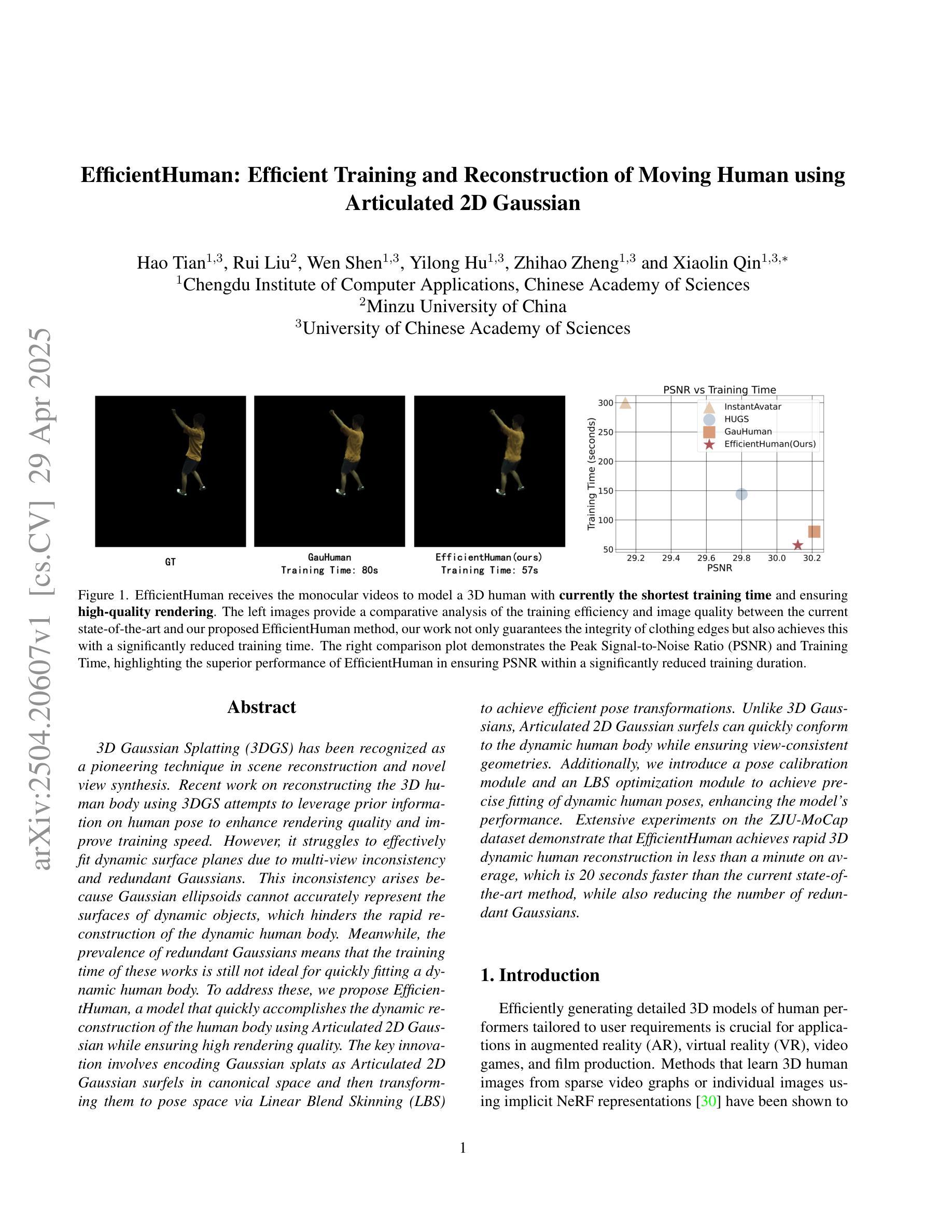
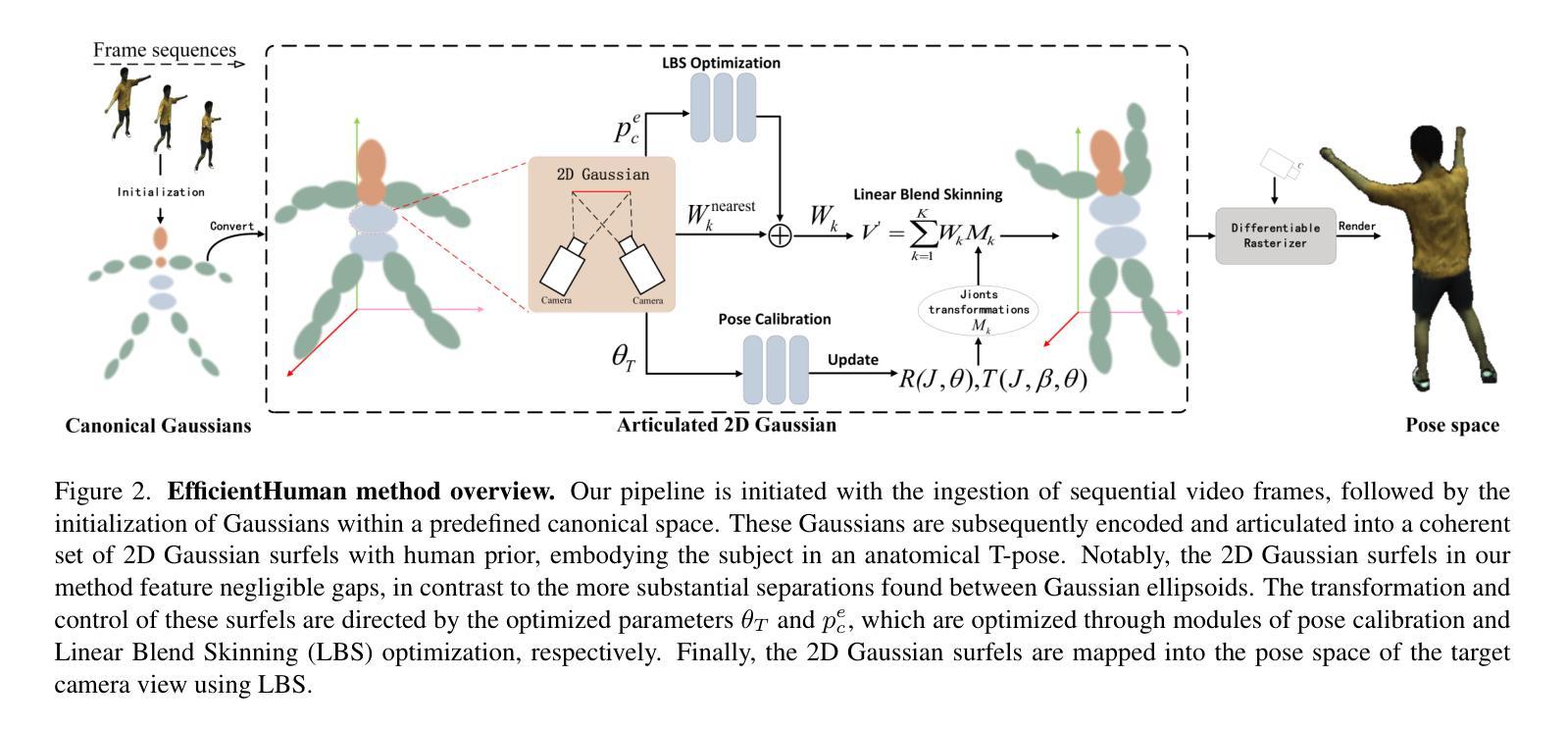

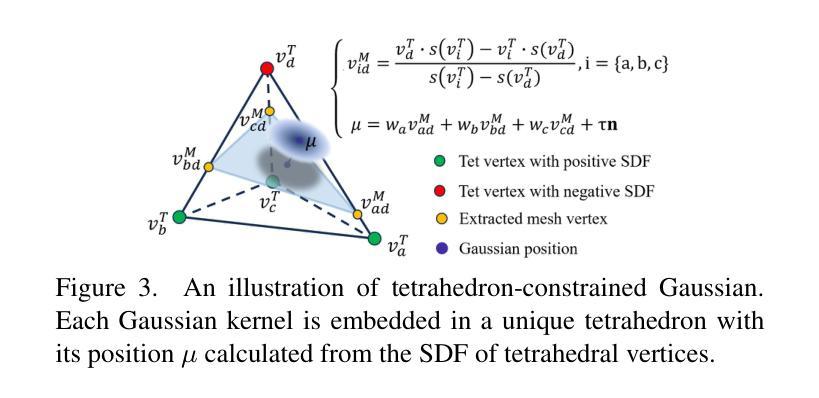
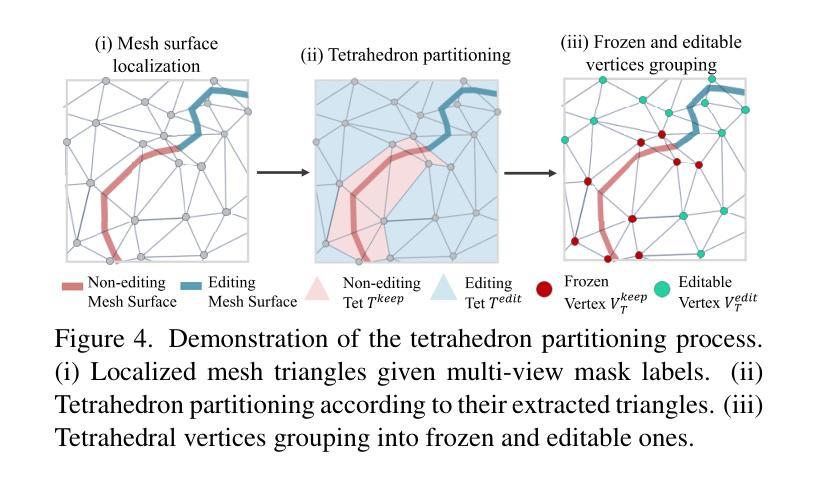
Creating Your Editable 3D Photorealistic Avatar with Tetrahedron-constrained Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Hanxi Liu, Yifang Men, Zhouhui Lian
Personalized 3D avatar editing holds significant promise due to its user-friendliness and availability to applications such as AR/VR and virtual try-ons. Previous studies have explored the feasibility of 3D editing, but often struggle to generate visually pleasing results, possibly due to the unstable representation learning under mixed optimization of geometry and texture in complicated reconstructed scenarios. In this paper, we aim to provide an accessible solution for ordinary users to create their editable 3D avatars with precise region localization, geometric adaptability, and photorealistic renderings. To tackle this challenge, we introduce a meticulously designed framework that decouples the editing process into local spatial adaptation and realistic appearance learning, utilizing a hybrid Tetrahedron-constrained Gaussian Splatting (TetGS) as the underlying representation. TetGS combines the controllable explicit structure of tetrahedral grids with the high-precision rendering capabilities of 3D Gaussian Splatting and is optimized in a progressive manner comprising three stages: 3D avatar instantiation from real-world monocular videos to provide accurate priors for TetGS initialization; localized spatial adaptation with explicitly partitioned tetrahedrons to guide the redistribution of Gaussian kernels; and geometry-based appearance generation with a coarse-to-fine activation strategy. Both qualitative and quantitative experiments demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of our approach in generating photorealistic 3D editable avatars.
个性化3D角色编辑因其用户友好性和在AR/VR及虚拟试穿等领域的应用前景而备受关注。尽管前人对3D编辑的可行性进行了探索,但往往在生成视觉效果令人满意的成果方面面临挑战,可能是由于复杂重建场景下的几何和纹理混合优化导致表示学习不稳定。本文旨在提供一种普通用户可访问的解决方案,以创建可编辑的3D角色,具备精确区域定位、几何适应性和逼真的渲染效果。为了应对这一挑战,我们引入了一个精心设计的框架,将编辑过程分解为局部空间适应和真实外观学习,利用混合四面体约束的高斯涂绘(TetGS)作为底层表示。TetGS结合了四面体格子的可控显式结构与3D高斯涂绘的高精度渲染能力,并以分阶段渐进的方式进行优化,包括三个阶段:从现实世界单目视频中实例化3D角色,为TetGS初始化提供准确先验;局部空间适应具有明确分区的四面体,引导高斯内核的重分布;以及基于几何的粗糙到精细激活策略的外观生成。定性和定量实验均表明,我们的方法在生成逼真的3D可编辑角色方面的有效性和优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨个性化3D头像编辑的技术,提出了一种易于用户操作的解决方案,可创建具有精确区域定位、几何适应性和逼真渲染的3D头像。通过采用四面体约束的高斯喷绘技术,将编辑过程分解为空间适应和真实外观学习,并在三个阶段逐步优化,包括从真实世界的单目视频中实例化3D头像、局部空间适应以及基于几何的外观生成。实验证明该方法在生成逼真的3D可编辑头像方面的有效性和优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 个性化3D头像编辑具有用户友好性和广泛的应用前景,如AR/VR和虚拟试穿。
- 现有研究在3D编辑中生成视觉上的满意结果方面存在挑战,可能由于复杂的重建场景中的几何和纹理混合优化表示学习的不稳定性。
- 引入了一种精心设计的框架,将编辑过程分解为局部空间适应和真实外观学习,采用四面体约束的高斯喷绘技术(TetGS)作为底层表示。
- TetGS结合了四面体网格的可控显式结构与3D高斯喷绘的高精度渲染能力。
- 框架的优化包括三个阶段:从真实世界的单目视频中实例化3D头像、局部空间适应以及基于几何学的外观生成。
- 框架可为普通用户提供精确的3D头像编辑工具,具有精确区域定位、几何适应性和逼真渲染。
点此查看论文截图

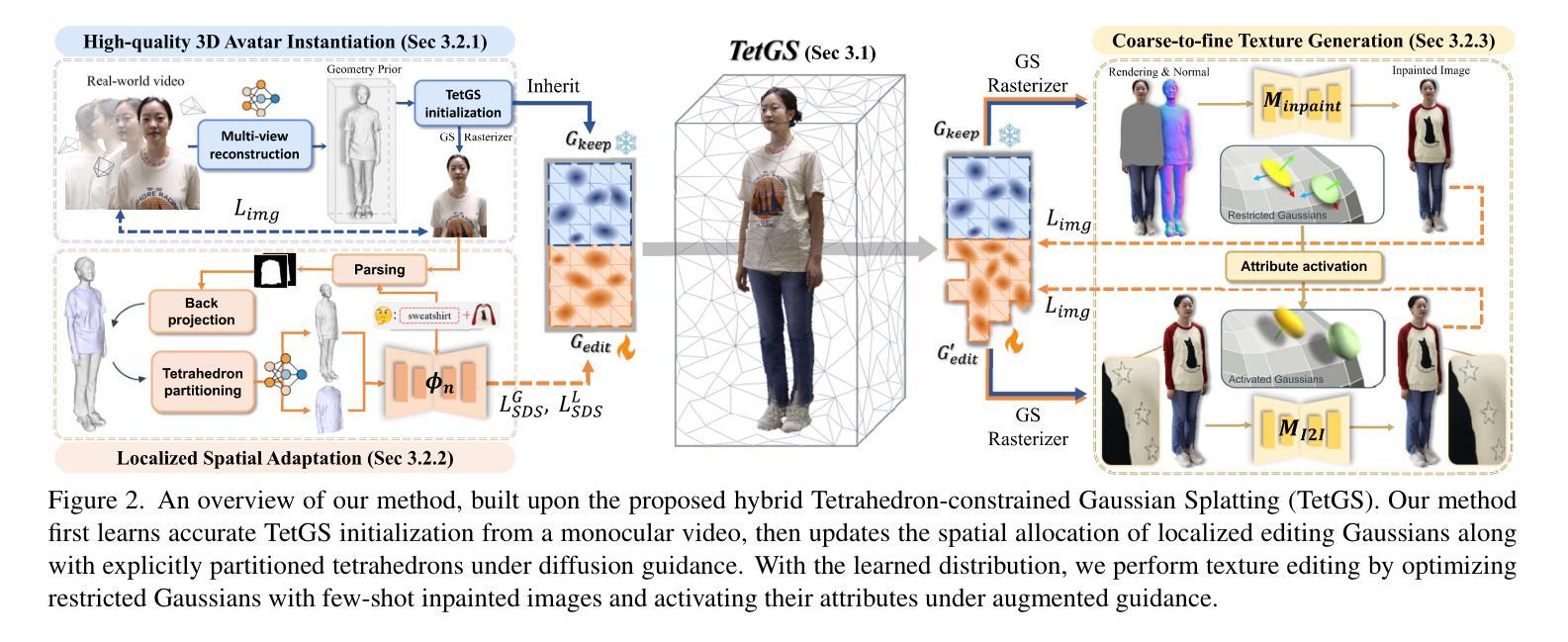
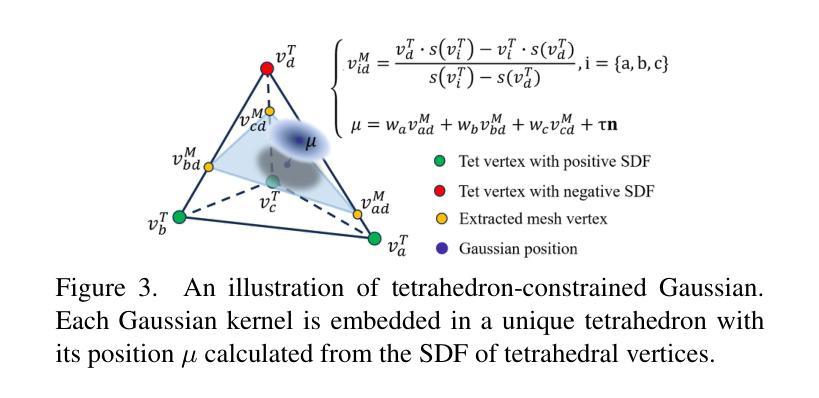
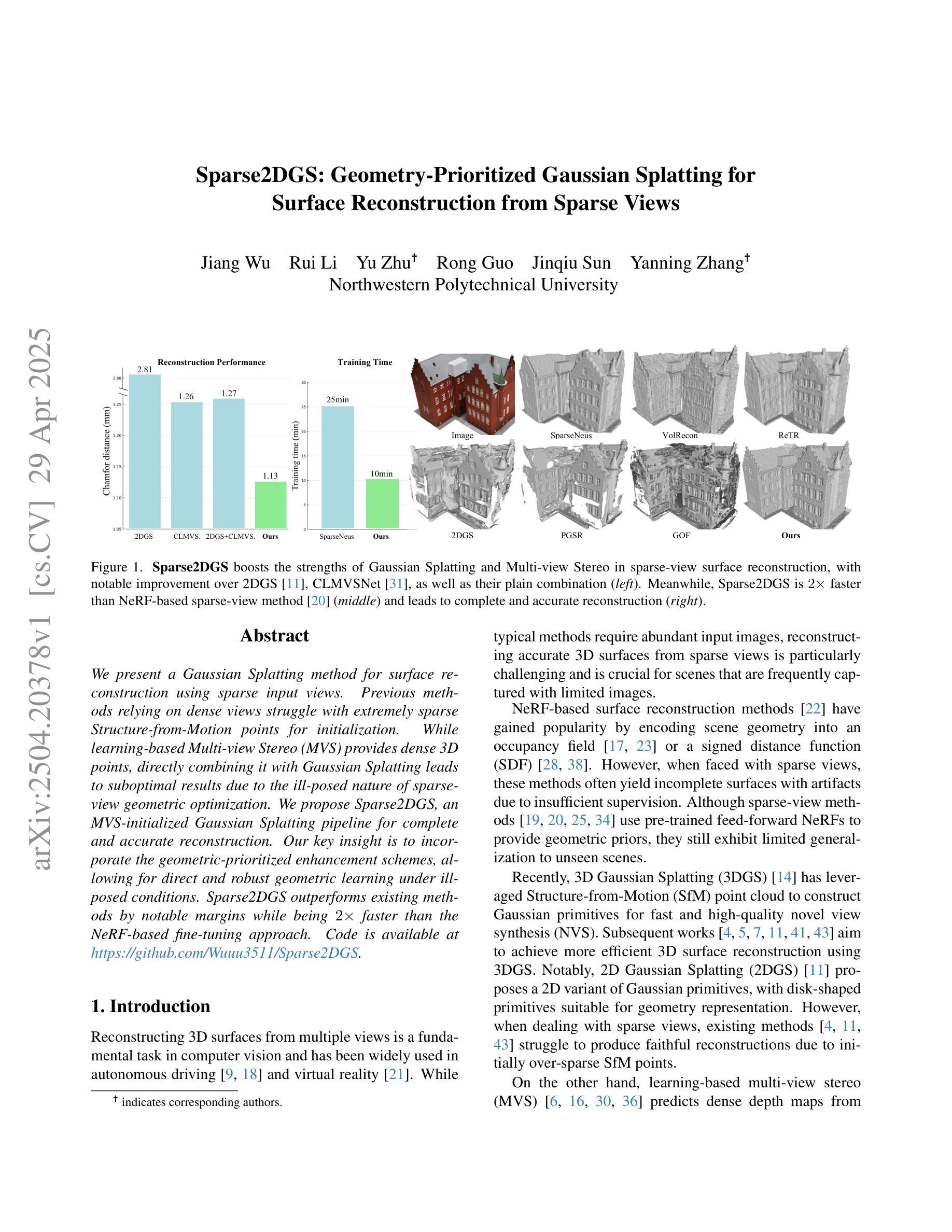
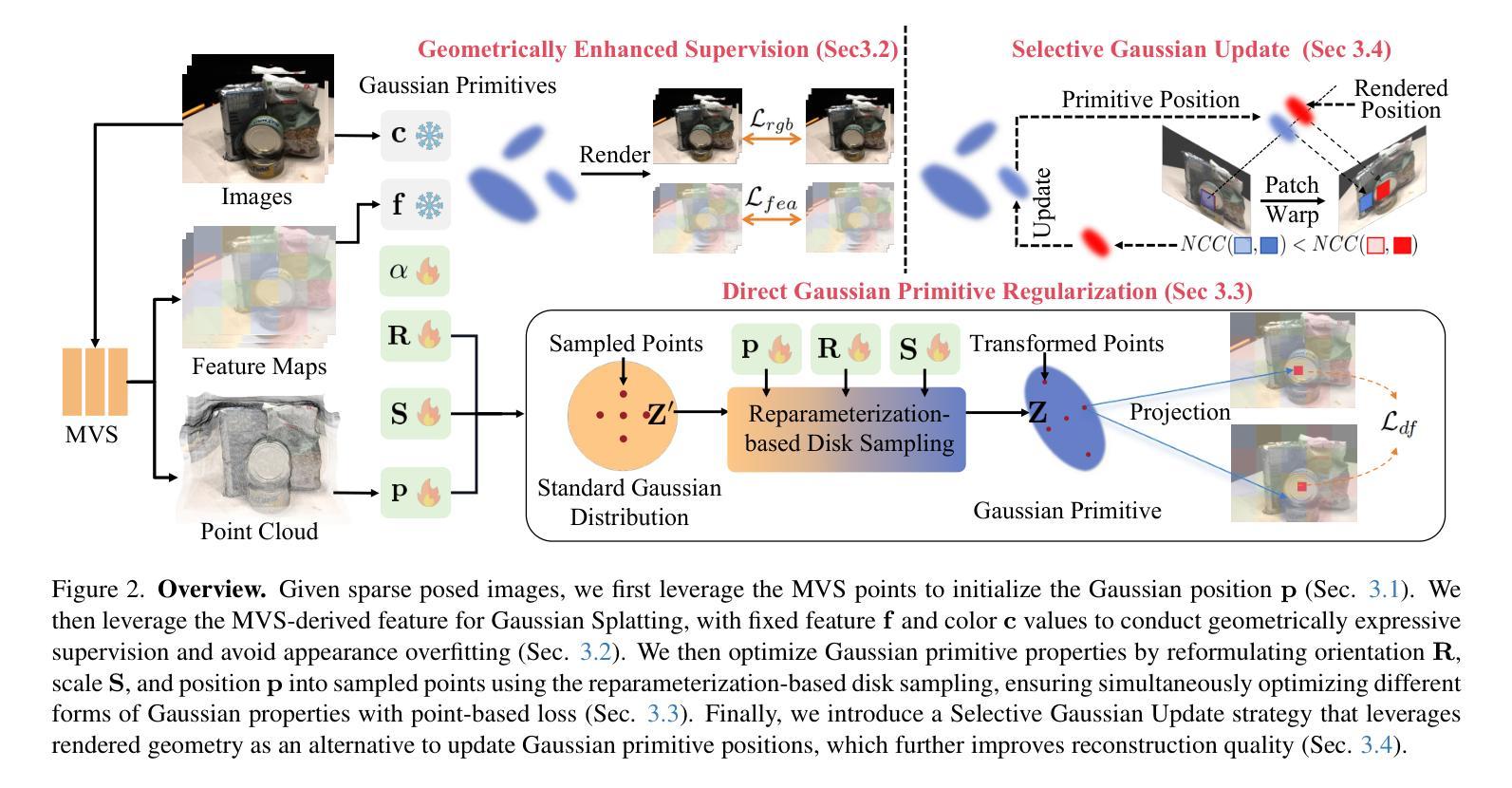
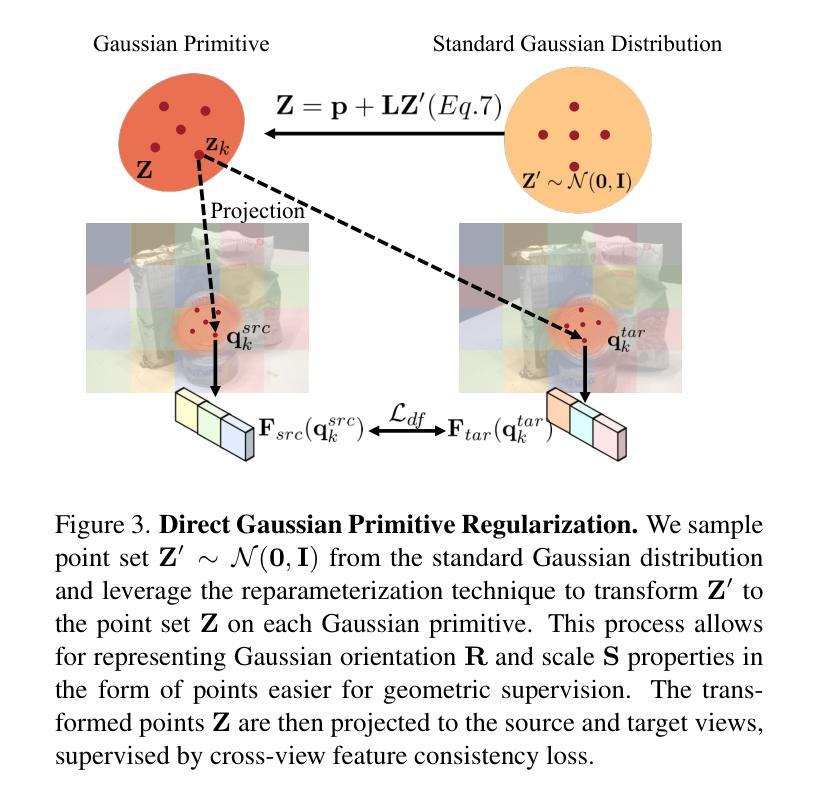
Sparse2DGS: Geometry-Prioritized Gaussian Splatting for Surface Reconstruction from Sparse Views
Authors:Jiang Wu, Rui Li, Yu Zhu, Rong Guo, Jinqiu Sun, Yanning Zhang
We present a Gaussian Splatting method for surface reconstruction using sparse input views. Previous methods relying on dense views struggle with extremely sparse Structure-from-Motion points for initialization. While learning-based Multi-view Stereo (MVS) provides dense 3D points, directly combining it with Gaussian Splatting leads to suboptimal results due to the ill-posed nature of sparse-view geometric optimization. We propose Sparse2DGS, an MVS-initialized Gaussian Splatting pipeline for complete and accurate reconstruction. Our key insight is to incorporate the geometric-prioritized enhancement schemes, allowing for direct and robust geometric learning under ill-posed conditions. Sparse2DGS outperforms existing methods by notable margins while being ${2}\times$ faster than the NeRF-based fine-tuning approach.
我们提出了一种基于稀疏输入视角的表面重建的高斯拼贴方法。之前依赖于密集视角的方法在利用极端稀疏的运动结构点进行初始化时面临困难。虽然基于学习的多视角立体(MVS)提供了密集的3D点,但直接将其与高斯拼贴相结合会导致次优结果,这是由于稀疏视角几何优化的不适定性。我们提出了Sparse2DGS,这是一种以MVS初始化的高斯拼贴管道,用于实现完整而准确的重建。我们的关键见解是融入几何优先增强方案,实现在不适定条件下的直接和稳健的几何学习。Sparse2DGS在显著边界上优于现有方法,同时比基于NeRF的微调方法快两倍。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种基于高斯涂敷方法(Gaussian Splatting)的稀疏视角表面重建方法。针对以往依赖密集视角的方法对于稀疏结构从运动中的点难以进行初始化的问题,文章结合了学习基础的多元视角立体(MVS)技术,提出Sparse2DGS方法。该方法在具有几何优先增强方案的情况下,实现了在不良条件下的直接和稳健的几何学习。Sparse2DGS在性能上显著优于现有方法,并且相较于基于NeRF的微调方法速度提高了两倍。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了高斯涂敷方法(Gaussian Splatting)用于表面重建。
- 现有方法对于稀疏结构从运动中的点难以进行初始化的问题进行了讨论。
- 结合学习基础的多元视角立体(MVS)技术,提出Sparse2DGS方法来解决上述问题。
- Sparse2DGS方法通过引入几何优先增强方案,实现了在不良条件下的直接和稳健的几何学习。
- Sparse2DGS在性能上显著优于现有方法。
- Sparse2DGS方法的处理速度比基于NeRF的微调方法提高了两倍。
- 文章提供了一种新的视角来解决表面重建问题,特别是在处理稀疏视角数据时具有显著优势。
点此查看论文截图
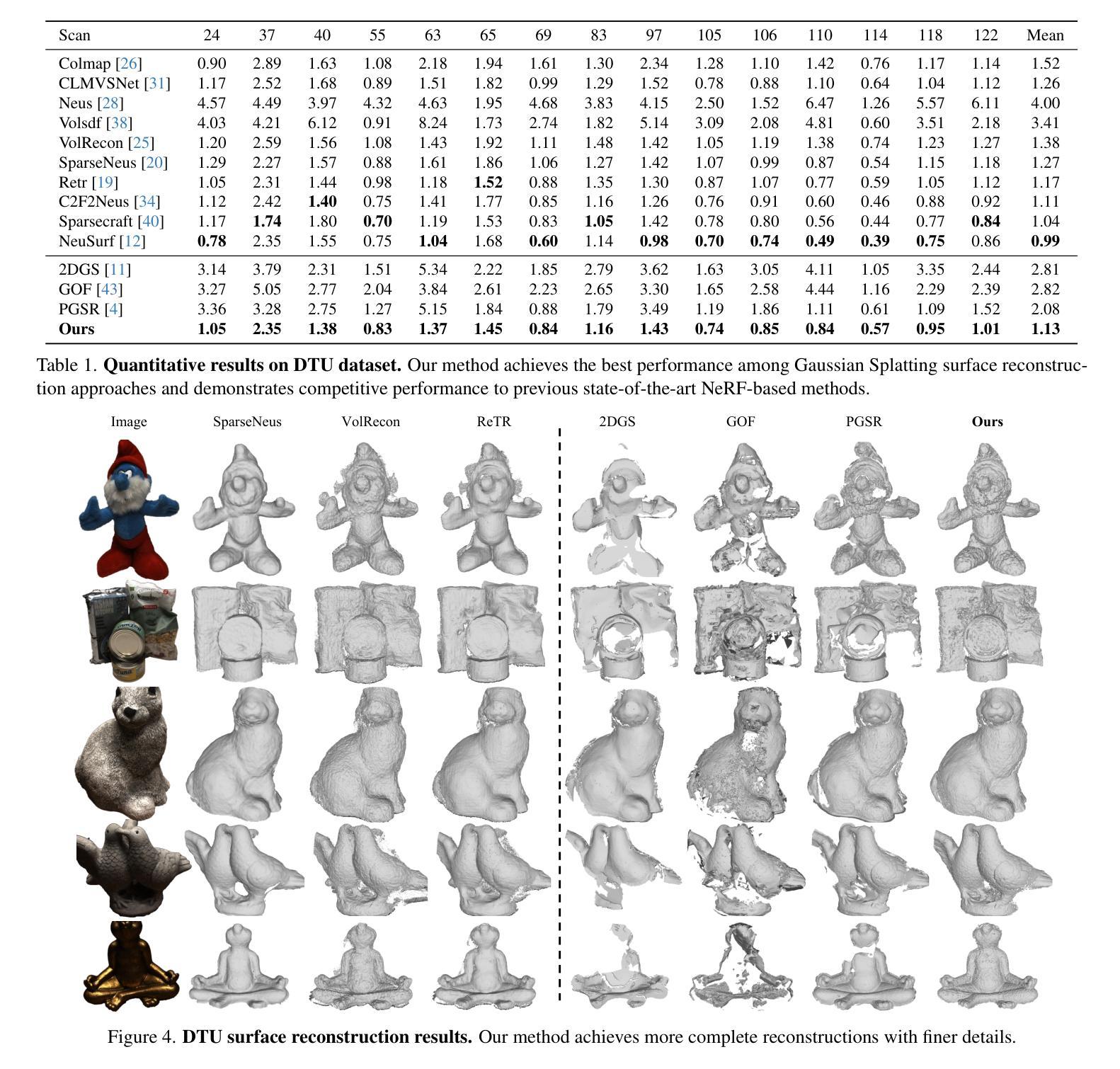
IM-Portrait: Learning 3D-aware Video Diffusion for Photorealistic Talking Heads from Monocular Videos
Authors:Yuan Li, Ziqian Bai, Feitong Tan, Zhaopeng Cui, Sean Fanello, Yinda Zhang
We propose a novel 3D-aware diffusion-based method for generating photorealistic talking head videos directly from a single identity image and explicit control signals (e.g., expressions). Our method generates Multiplane Images (MPIs) that ensure geometric consistency, making them ideal for immersive viewing experiences like binocular videos for VR headsets. Unlike existing methods that often require a separate stage or joint optimization to reconstruct a 3D representation (such as NeRF or 3D Gaussians), our approach directly generates the final output through a single denoising process, eliminating the need for post-processing steps to render novel views efficiently. To effectively learn from monocular videos, we introduce a training mechanism that reconstructs the output MPI randomly in either the target or the reference camera space. This approach enables the model to simultaneously learn sharp image details and underlying 3D information. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our method, which achieves competitive avatar quality and novel-view rendering capabilities, even without explicit 3D reconstruction or high-quality multi-view training data.
我们提出了一种新型的基于三维感知扩散的方法,直接从单张身份图像和明确的控制信号(如表情)生成逼真的动态视频。我们的方法生成多平面图像(MPIs),确保几何一致性,使其成为理想的沉浸式观看体验,如虚拟现实头盔的双目视频。与通常需要单独阶段或联合优化来重建三维表示(如NeRF或三维高斯)的现有方法不同,我们的方法通过单个去噪过程直接生成最终输出,无需后处理步骤即可有效地渲染新颖视角。为了有效地从单目视频中学习,我们引入了一种训练机制,该机制可以在目标相机空间或参考相机空间中随机重建输出MPI。这种方法使模型能够同时学习清晰的图像细节和潜在的三维信息。大量实验证明了我们方法的有效性,即使在不需要明确的三维重建或高质量的多视角训练数据的情况下,也能达到具有竞争力的角色质量并具备新颖视角的渲染能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR2025; project page: https://y-u-a-n-l-i.github.io/projects/IM-Portrait/
Summary
本文提出了一种新型的基于三维感知扩散的方法,该方法可从单一身份图像和明确的控制信号(如表情)生成逼真的动态视频图像。该方法生成多平面图像(MPIs),确保几何一致性,适用于虚拟现实头戴设备的沉浸式观看体验。与其他方法不同,我们的方法通过一个去噪过程直接生成最终输出,无需额外的重建阶段或联合优化,从而高效渲染新的视角。通过随机重建目标或参考相机空间中的输出MPI,模型能够同时学习清晰的图像细节和潜在的3D信息。实验证明,该方法在无需明确的3D重建或多视角高质量训练数据的情况下,仍能达到竞争性的角色形象质量和新颖的视角渲染能力。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种新型的基于三维感知扩散的方法,用于从单一身份图像和控制信号生成动态视频图像。
- 生成的多平面图像(MPIs)确保了几何一致性,适用于虚拟现实等沉浸式观看体验。
- 方法通过单一去噪过程直接生成最终输出,简化了流程并提高了效率。
- 模型通过随机重建输出MPI来同时学习图像细节和潜在的三维信息,适应性更强。
- 方法在无需明确的3D重建或多视角高质量训练数据的情况下,仍能达到优秀的角色形象质量和新颖的视角渲染能力。
- 与其他方法相比,该方法具有更强的效率和效果,尤其在渲染新视角方面表现突出。
点此查看论文截图

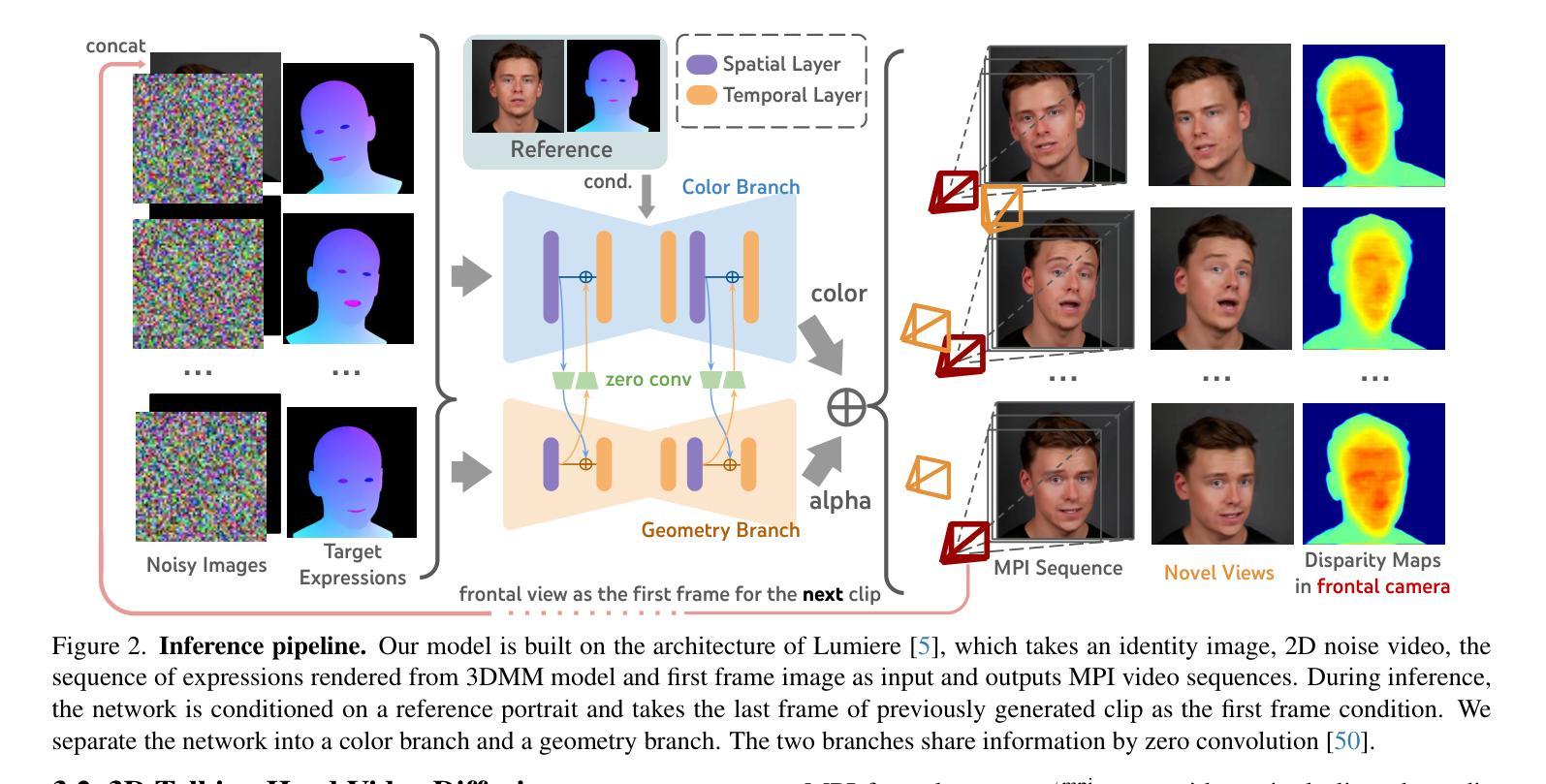
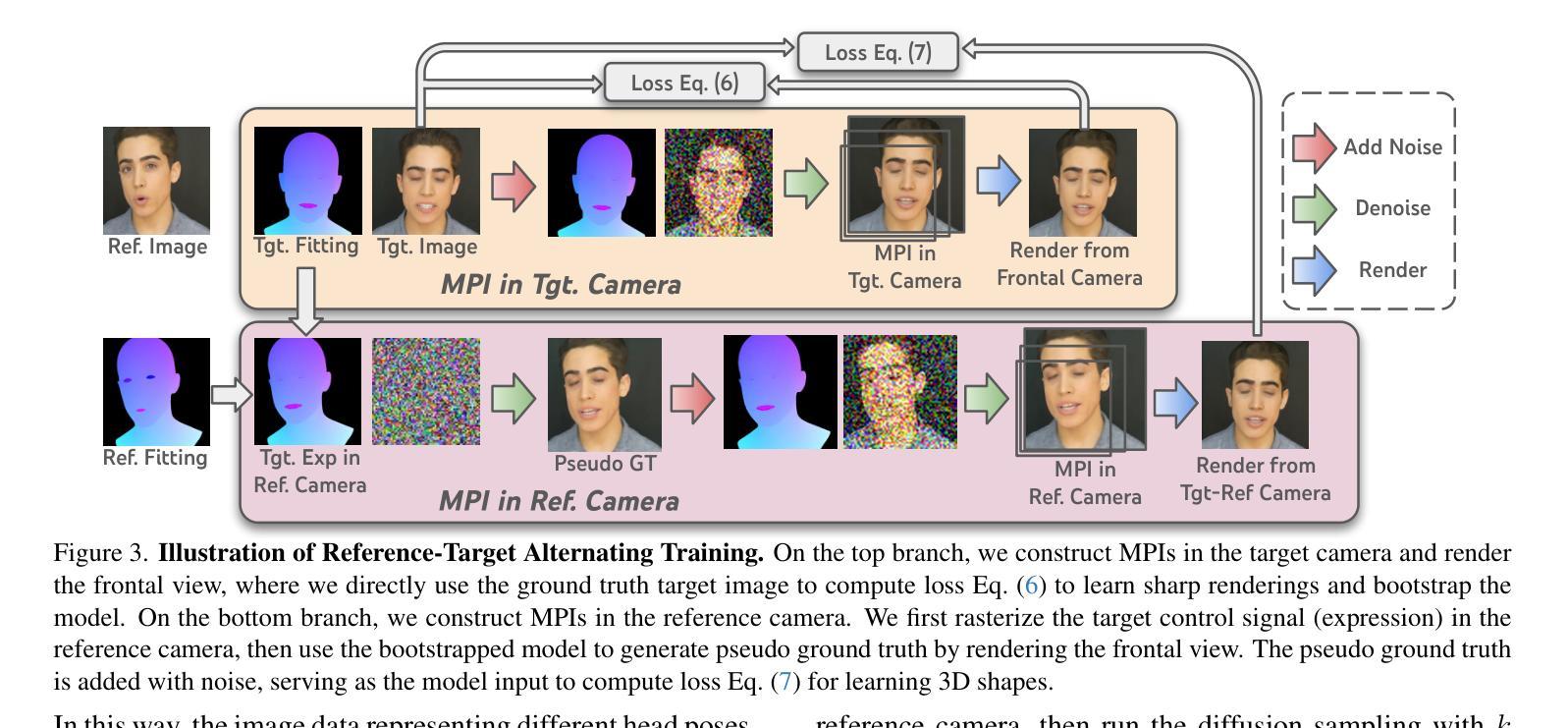
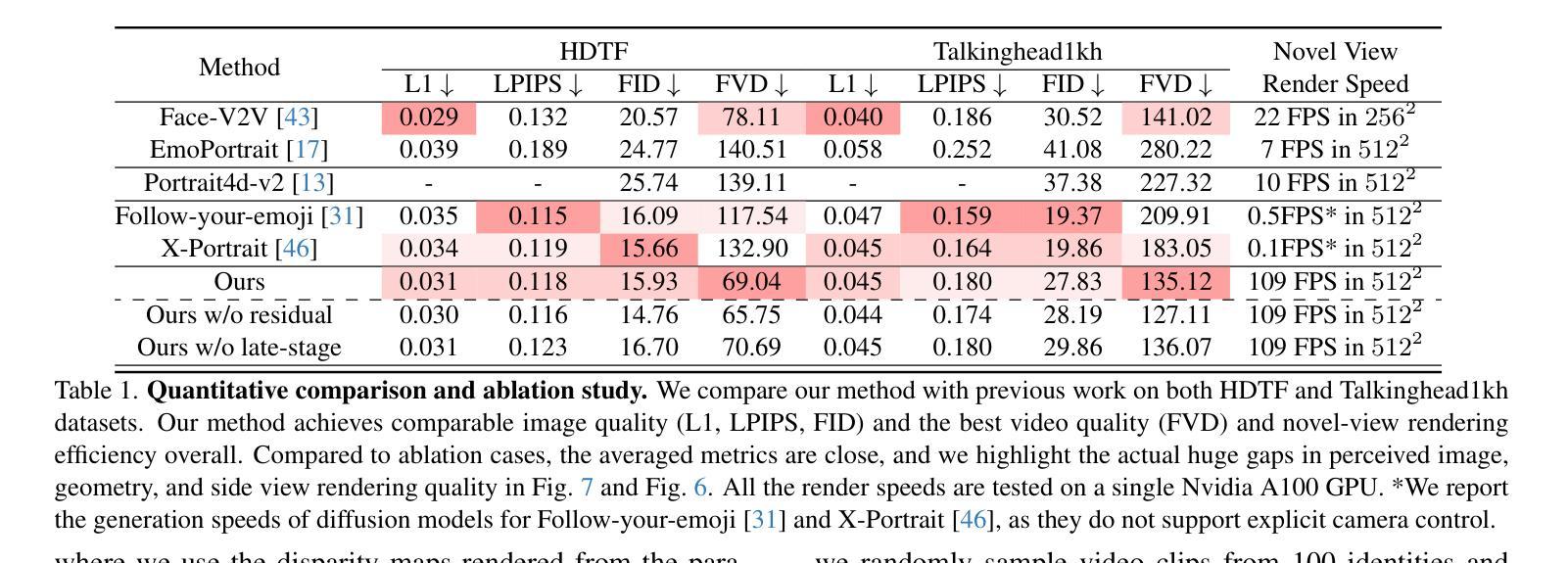
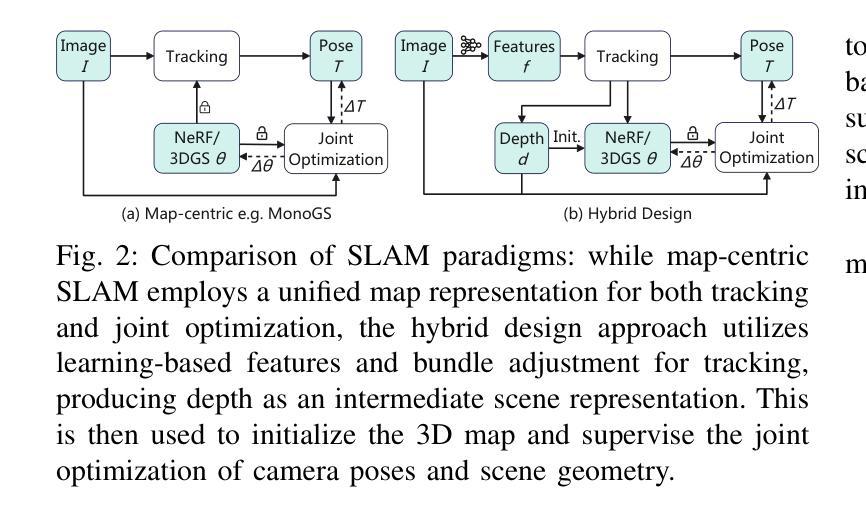
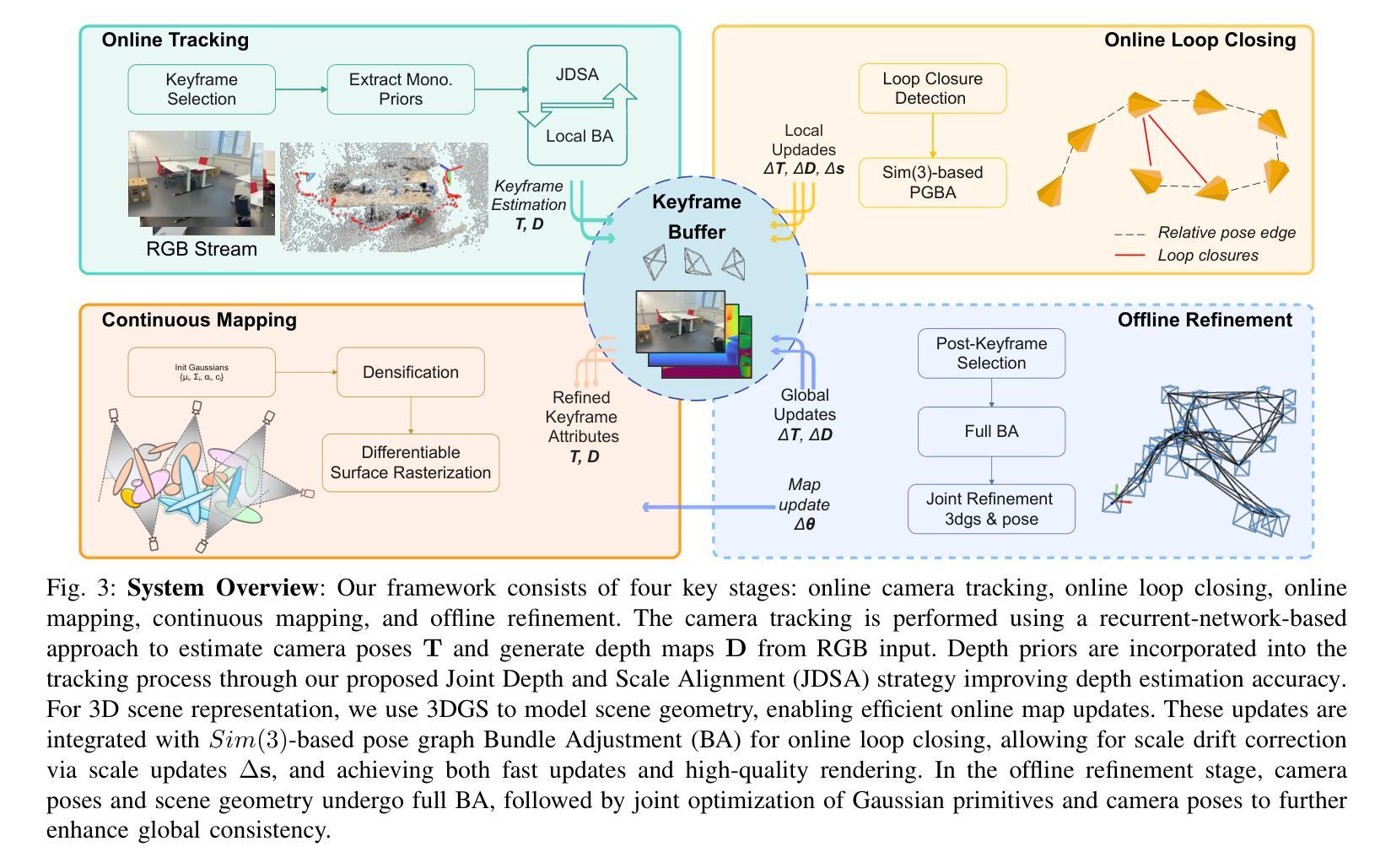
HI-SLAM2: Geometry-Aware Gaussian SLAM for Fast Monocular Scene Reconstruction
Authors:Wei Zhang, Qing Cheng, David Skuddis, Niclas Zeller, Daniel Cremers, Norbert Haala
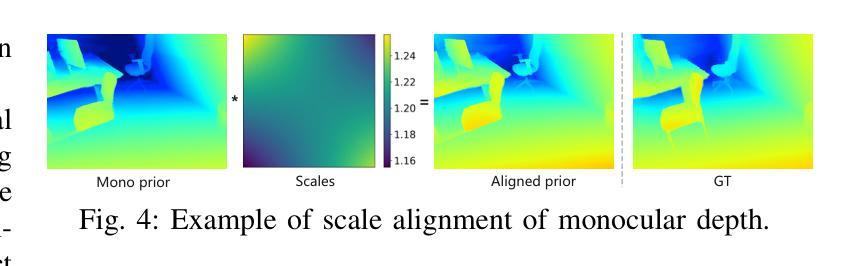
We present HI-SLAM2, a geometry-aware Gaussian SLAM system that achieves fast and accurate monocular scene reconstruction using only RGB input. Existing Neural SLAM or 3DGS-based SLAM methods often trade off between rendering quality and geometry accuracy, our research demonstrates that both can be achieved simultaneously with RGB input alone. The key idea of our approach is to enhance the ability for geometry estimation by combining easy-to-obtain monocular priors with learning-based dense SLAM, and then using 3D Gaussian splatting as our core map representation to efficiently model the scene. Upon loop closure, our method ensures on-the-fly global consistency through efficient pose graph bundle adjustment and instant map updates by explicitly deforming the 3D Gaussian units based on anchored keyframe updates. Furthermore, we introduce a grid-based scale alignment strategy to maintain improved scale consistency in prior depths for finer depth details. Through extensive experiments on Replica, ScanNet, and ScanNet++, we demonstrate significant improvements over existing Neural SLAM methods and even surpass RGB-D-based methods in both reconstruction and rendering quality. The project page and source code will be made available at https://hi-slam2.github.io/.
我们提出了HI-SLAM2,这是一个感知几何的高斯SLAM系统,它仅使用RGB输入即可实现快速准确的单目场景重建。现有的神经SLAM或基于3DGS的SLAM方法往往需要在渲染质量和几何精度之间进行权衡,我们的研究表明,两者可以同时通过仅使用RGB输入来实现。我们的方法的关键思想是通过结合易于获得的单目先验知识和基于学习的密集SLAM,增强几何估计的能力,然后使用3D高斯平铺作为我们的核心地图表示来有效地建模场景。在环路闭合时,我们的方法通过基于锚定的关键帧更新的高效姿态图捆绑调整和即时地图更新,确保在线全局一致性。此外,我们引入了一种基于网格的尺度对齐策略,以在先前深度中保持改进的尺度一致性,从而获得更精细的深度细节。我们在Replica、ScanNet和ScanNet++上进行了大量实验,证明了与现有神经SLAM方法相比的显著改进,甚至在重建和渲染质量方面超越了基于RGB-D的方法。项目页面和源代码将在[https://hi-slam2.github.io/]上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review process
Summary
本文介绍了HI-SLAM2系统,这是一个几何感知的高斯SLAM系统,可通过仅使用RGB输入实现快速而精确的单目场景重建。该研究通过结合单目先验和基于学习的密集SLAM,使用3D高斯溅面作为核心地图表示来有效地建模场景,从而同时实现渲染质量和几何精度的平衡。HI-SLAM2通过高效的姿态图捆绑调整和即时地图更新,确保闭环时的在线全局一致性。此外,它还引入了一种基于网格的尺度对齐策略,以在先前深度中保持改进的尺度一致性,从而实现更精细的深度细节。在Replica、ScanNet和ScanNet++上的实验表明,该方法在重建和渲染质量方面均显著优于现有Neural SLAM方法,甚至超越了基于RGB-D的方法。
Key Takeaways
- HI-SLAM2是一个几何感知的高斯SLAM系统,能够实现快速且精确的单目场景重建。
- 该系统通过结合单目先验与基于学习的密集SLAM,提高了对几何估计的能力。
- HI-SLAM2使用3D高斯溅面作为核心地图表示,以有效地建模场景。
- 在闭环时,HI-SLAM2通过高效的姿态图捆绑调整和基于锚定的关键帧更新,确保在线全局一致性。
- 引入了一种基于网格的尺度对齐策略,以改进先前深度中的尺度一致性,从而实现更精细的深度细节。
- 实验结果表明,HI-SLAM2在多个数据集上的重建和渲染质量均优于现有的Neural SLAM方法。
点此查看论文截图

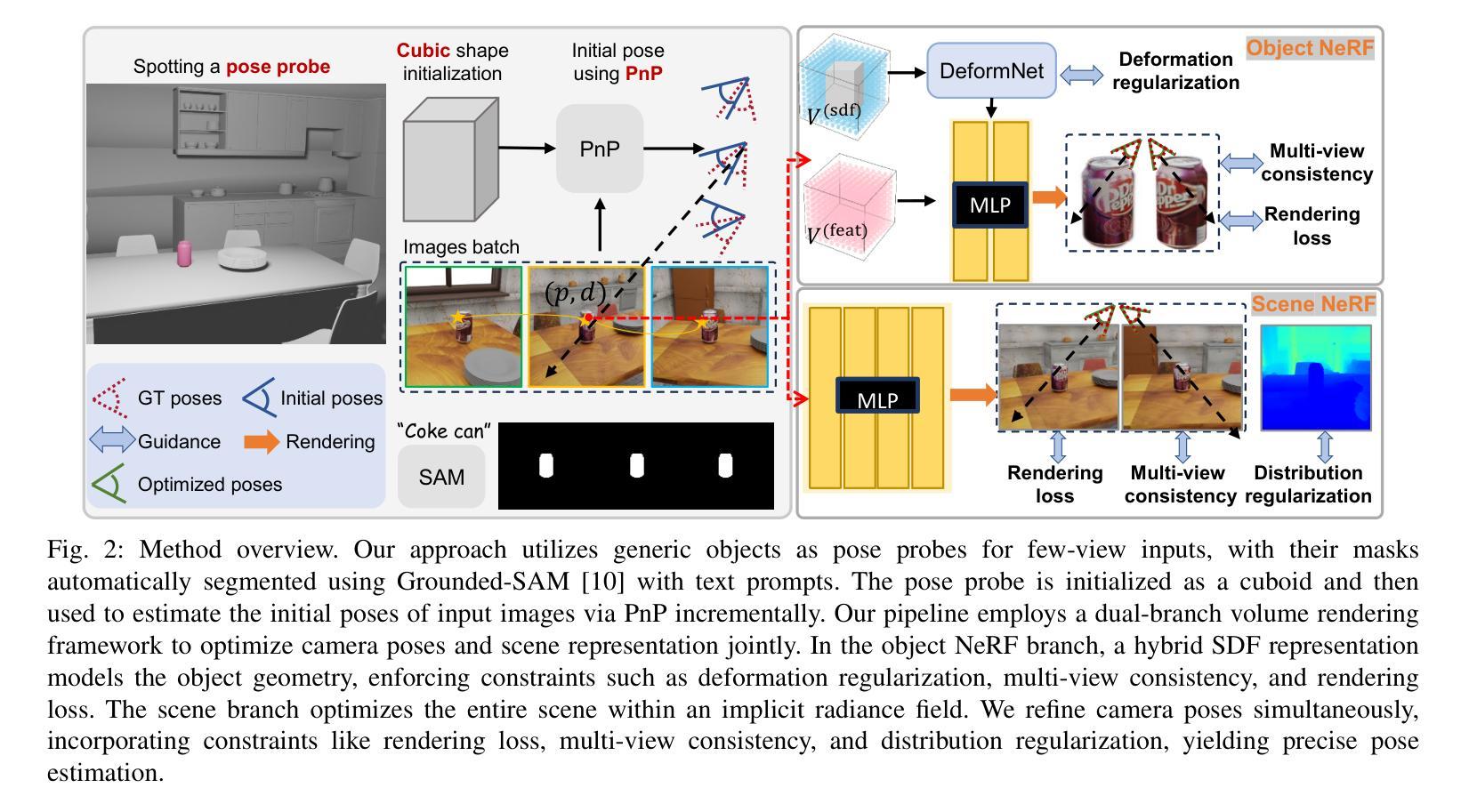
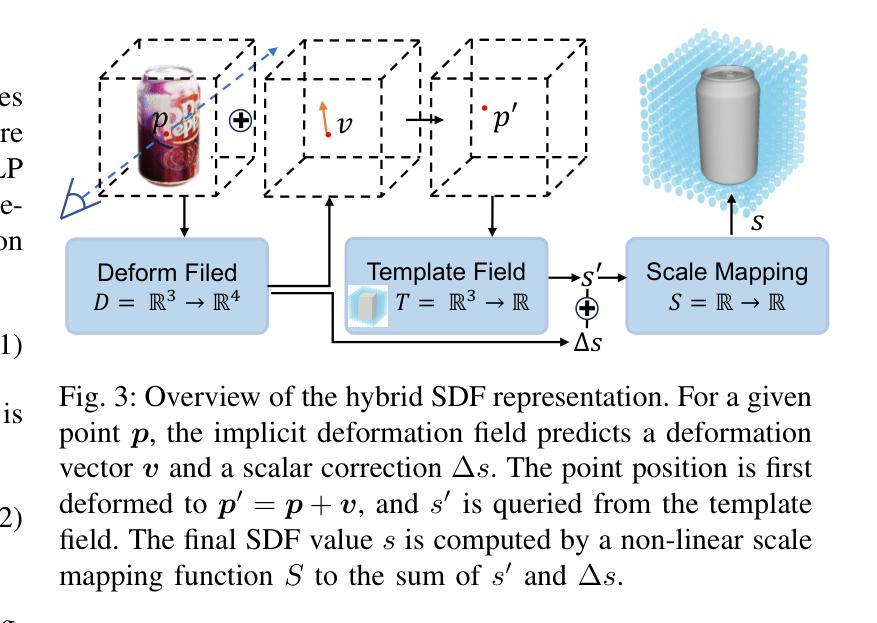
Generic Objects as Pose Probes for Few-shot View Synthesis
Authors:Zhirui Gao, Renjiao Yi, Chenyang Zhu, Ke Zhuang, Wei Chen, Kai Xu
Radiance fields including NeRFs and 3D Gaussians demonstrate great potential in high-fidelity rendering and scene reconstruction, while they require a substantial number of posed images as inputs. COLMAP is frequently employed for preprocessing to estimate poses, while it necessitates a large number of feature matches to operate effectively, and it struggles with scenes characterized by sparse features, large baselines between images, or a limited number of input images. We aim to tackle few-view NeRF reconstruction using only 3 to 6 unposed scene images. Traditional methods often use calibration boards but they are not common in images. We propose a novel idea of utilizing everyday objects, commonly found in both images and real life, as “pose probes”. The probe object is automatically segmented by SAM, whose shape is initialized from a cube. We apply a dual-branch volume rendering optimization (object NeRF and scene NeRF) to constrain the pose optimization and jointly refine the geometry. Specifically, object poses of two views are first estimated by PnP matching in an SDF representation, which serves as initial poses. PnP matching, requiring only a few features, is suitable for feature-sparse scenes. Additional views are incrementally incorporated to refine poses from preceding views. In experiments, PoseProbe achieves state-of-the-art performance in both pose estimation and novel view synthesis across multiple datasets. We demonstrate its effectiveness, particularly in few-view and large-baseline scenes where COLMAP struggles. In ablations, using different objects in a scene yields comparable performance. Our project page is available at: \href{https://zhirui-gao.github.io/PoseProbe.github.io/}{this https URL}
辐射场,包括NeRF和3D高斯分布,在高保真渲染和场景重建方面表现出巨大潜力,但它们需要大量的姿态图像作为输入。COLMAP常用于预处理以估计姿态,但需要大量特征匹配才能有效运行,对于特征稀疏、图像间基线大或输入图像数量有限的场景,它表现得较为困难。我们的目标是仅使用3到6张未经姿态预估的场景图像来解决少量视图NeRF重建问题。传统方法通常使用校准板,但在图像中并不常见。我们提出了一种利用常见物体的新颖想法,这些物体既可以在图像中也可以在现实生活中找到,作为“姿态探针”。探针物体通过SAM自动分割,其形状初始化为立方体。我们采用双分支体积渲染优化(对象NeRF和场景NeRF)来约束姿态优化并共同优化几何结构。具体来说,首先通过SDF表示的PnP匹配估计两个视图的物体姿态,作为初始姿态。PnP匹配仅需要几个特征,适用于特征稀疏的场景。然后逐步加入额外的视图,以细化先前视图的姿态。在实验方面,PoseProbe在多数据集上的姿态估计和新型视图合成方面都达到了最先进的性能。我们证明了其在少量视图和大基线场景中的有效性,这正是COLMAP所面临的问题。在消融实验中,使用场景中的不同物体可以获得相当的性能。我们的项目页面可访问于:此https URL。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE TCSVT 2025 Project page: https://zhirui-gao.github.io/PoseProbe.github.io/
Summary
点此查看论文截图