⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-01 更新
AI-GenBench: A New Ongoing Benchmark for AI-Generated Image Detection
Authors:Lorenzo Pellegrini, Davide Cozzolino, Serafino Pandolfini, Davide Maltoni, Matteo Ferrara, Luisa Verdoliva, Marco Prati, Marco Ramilli
The rapid advancement of generative AI has revolutionized image creation, enabling high-quality synthesis from text prompts while raising critical challenges for media authenticity. We present Ai-GenBench, a novel benchmark designed to address the urgent need for robust detection of AI-generated images in real-world scenarios. Unlike existing solutions that evaluate models on static datasets, Ai-GenBench introduces a temporal evaluation framework where detection methods are incrementally trained on synthetic images, historically ordered by their generative models, to test their ability to generalize to new generative models, such as the transition from GANs to diffusion models. Our benchmark focuses on high-quality, diverse visual content and overcomes key limitations of current approaches, including arbitrary dataset splits, unfair comparisons, and excessive computational demands. Ai-GenBench provides a comprehensive dataset, a standardized evaluation protocol, and accessible tools for both researchers and non-experts (e.g., journalists, fact-checkers), ensuring reproducibility while maintaining practical training requirements. By establishing clear evaluation rules and controlled augmentation strategies, Ai-GenBench enables meaningful comparison of detection methods and scalable solutions. Code and data are publicly available to ensure reproducibility and to support the development of robust forensic detectors to keep pace with the rise of new synthetic generators.
生成式人工智能的快速发展为图像创作带来了革命性的变化,它能够通过文本提示实现高质量合成,同时给媒体真实性带来了重大挑战。我们推出了Ai-GenBench,这是一个新型基准测试平台,旨在解决现实场景中检测AI生成图像这一迫切需求。不同于现有模型在静态数据集上进行评估的解决方案,Ai-GenBench引入了一个时间评估框架,该框架按生成模型的顺序逐步训练检测模型生成的图像数据点进行测试它们泛化到新型生成模型的能力如何评估如何,比如从生成对抗网络过渡到扩散模型。我们的基准测试平台侧重于高质量、多样化的视觉内容,并克服了当前方法的关键局限性,包括任意分割数据集、不公平比较和过高的计算需求等。Ai-GenBench为研究人员和非专业人士(例如记者、事实核查人员)提供了一个综合数据集、标准化的评估协议和易于使用的工具,既保证了实用性又满足了实际训练要求。通过制定明确的评估规则和可控的增强策略,Ai-GenBench为检测方法的比较和可扩展解决方案提供了有力支持。代码和数据公开可用,以确保可重复性并支持稳健的取证检测器的发展以应对新合成发生器浪潮的冲击。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 6 figures, 4 tables, code available: https://github.com/MI-BioLab/AI-GenBench
Summary
生成式AI的快速发展已引发图像创建领域的革新,能够根据文本提示生成高质量图像,同时带来媒体真实性的重大挑战。为应对现实场景中检测AI生成图像的需求,我们推出Ai-GenBench基准测试平台。该平台采用动态评估框架,通过增量训练检测器来检测合成图像,按生成模型的生成顺序排序,以测试其对新生成模型的泛化能力,如从生成对抗网络到扩散模型的过渡。Ai-GenBench专注于高质量、多样化的视觉内容,并克服当前方法的关键局限性,包括任意数据集分割、不公平比较和过高的计算需求。它为研究人员和非专家(如记者、事实核查人员)提供综合数据集、标准化评估协议和可用工具,确保实用性和可重复性。通过制定明确的评估规则和受控增强策略,Ai-GenBench使得检测方法的比较和可扩展解决方案变得更有意义。
Key Takeaways
- 生成式AI的发展推动了图像创建领域的革新,能够根据文本提示生成高质量图像。
- Ai-GenBench是一个用于检测AI生成图像的新基准测试平台。
- Ai-GenBench采用动态评估框架,能够测试检测器对新生成模型的泛化能力。
- 该平台专注于高质量、多样化的视觉内容。
- Ai-GenBench克服了当前方法的关键局限性,如任意数据集分割、不公平比较和过高的计算需求。
- Ai-GenBench为研究人员和非专家提供综合数据集、标准化评估协议和可用工具。
点此查看论文截图

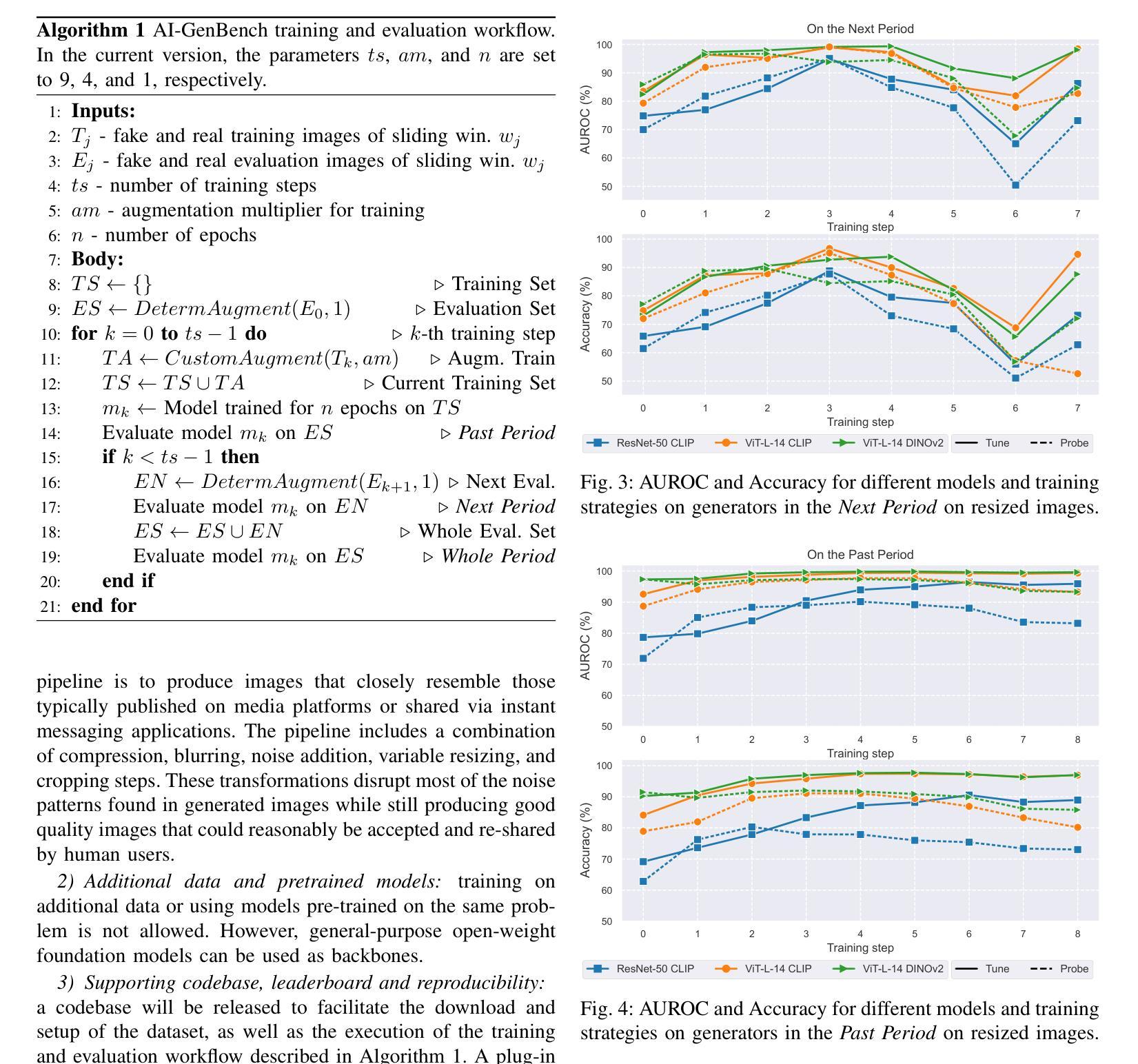
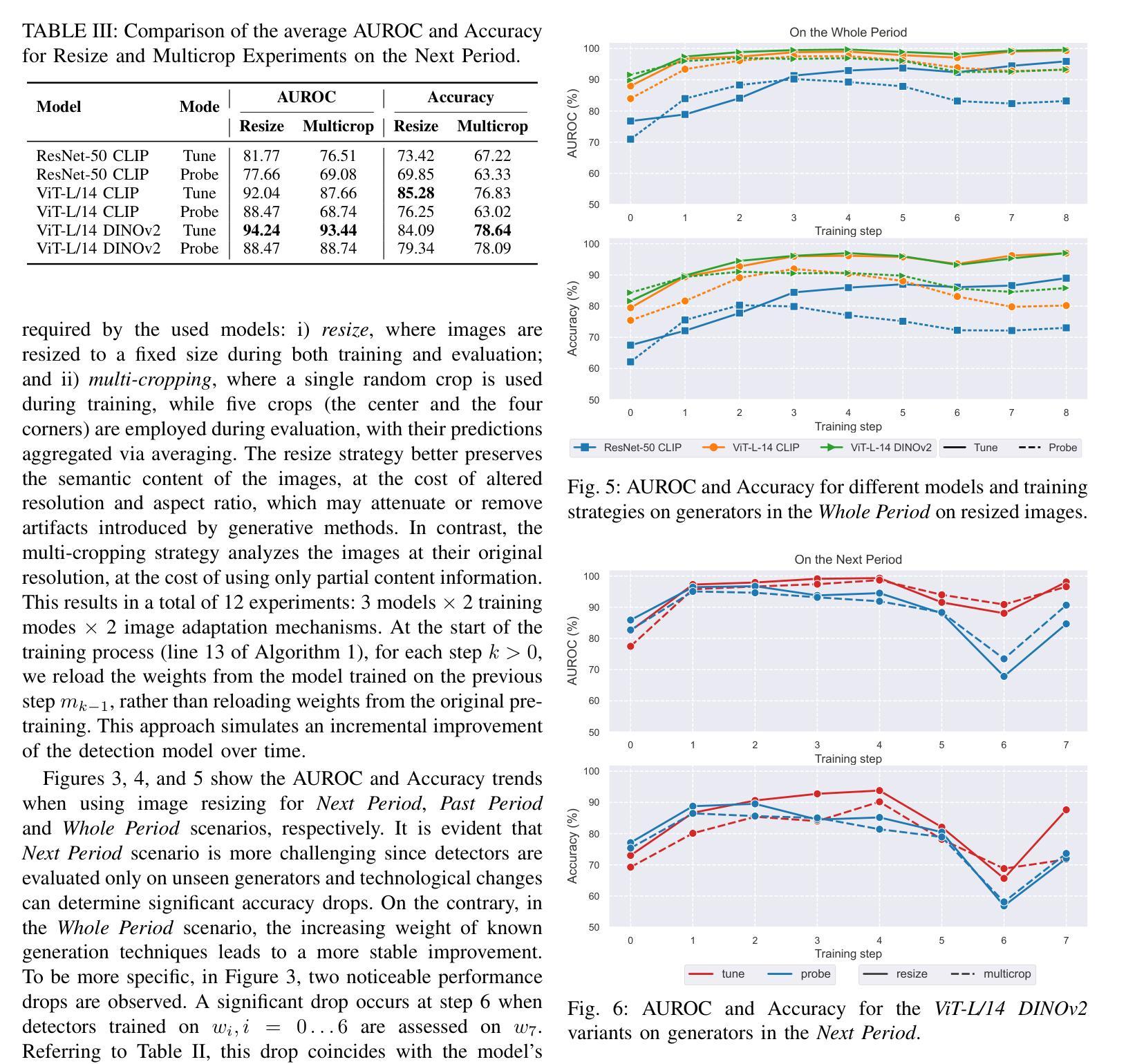
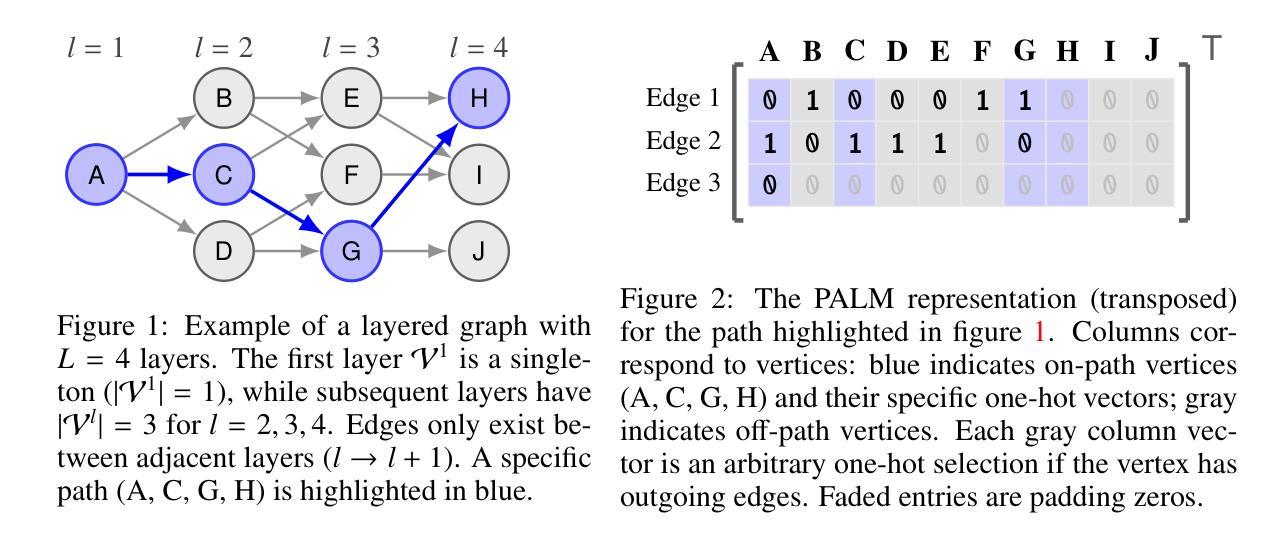
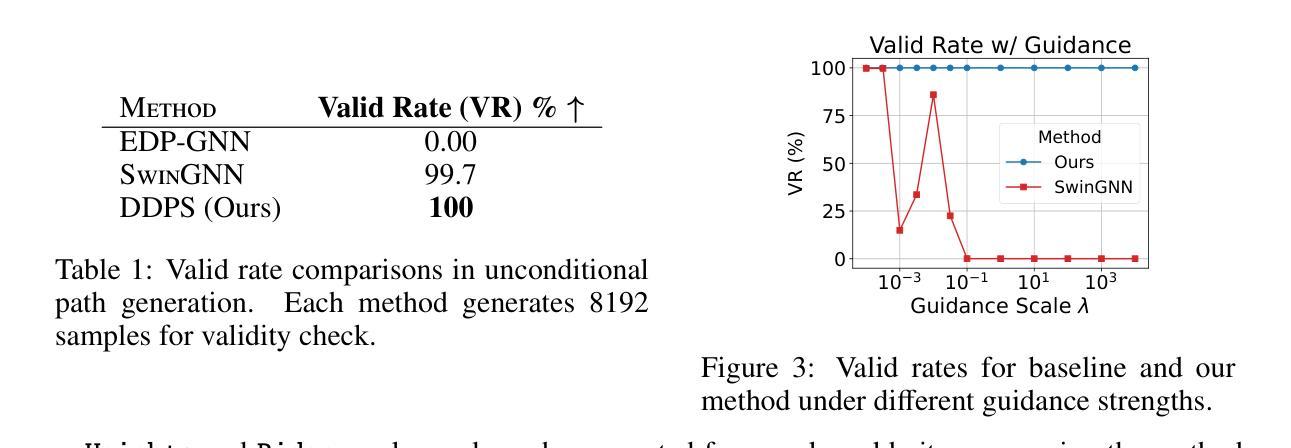
DDPS: Discrete Diffusion Posterior Sampling for Paths in Layered Graphs
Authors:Hao Luan, See-Kiong Ng, Chun Kai Ling
Diffusion models form an important class of generative models today, accounting for much of the state of the art in cutting edge AI research. While numerous extensions beyond image and video generation exist, few of such approaches address the issue of explicit constraints in the samples generated. In this paper, we study the problem of generating paths in a layered graph (a variant of a directed acyclic graph) using discrete diffusion models, while guaranteeing that our generated samples are indeed paths. Our approach utilizes a simple yet effective representation for paths which we call the padded adjacency-list matrix (PALM). In addition, we show how to effectively perform classifier guidance, which helps steer the sampled paths to specific preferred edges without any retraining of the diffusion model. Our preliminary results show that empirically, our method outperforms alternatives which do not explicitly account for path constraints.
扩散模型是当今生成模型领域中的重要一类,代表了前沿人工智能研究的最新进展。尽管存在许多图像和视频生成之外的扩展,但很少有这样的方法解决生成样本中的显式约束问题。在本文中,我们研究了使用离散扩散模型在分层图中生成路径(一种有向无环图的变体)的问题,同时保证生成的样本确实是路径。我们的方法为路径采用了一种简单有效的表示形式,称为填充邻接列表矩阵(PALM)。此外,我们还展示了如何有效地执行分类器指导,这有助于将采样路径引导到特定的首选边缘,而无需对扩散模型进行任何重新训练。我们的初步结果表明,从实证角度看,我们的方法在解决路径约束方面优于那些没有明确考虑路径约束的替代方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To appear at Frontiers in Probabilistic Inference: Sampling meets Learning (FPI) workshop at ICLR 2025. https://openreview.net/forum?id=DBdkU0Ikzy
Summary
本文研究了使用离散扩散模型在分层图中生成路径的问题,同时保证生成的样本确实是路径。为此,提出了一种简单有效的路径表示方法——填充邻接列表矩阵(PALM)。此外,还展示了如何进行分类器引导,这有助于将采样路径导向特定的首选边缘,而无需重新训练扩散模型。初步结果表明,该方法在实证上优于未明确考虑路径约束的替代方法。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型是当前的生成模型的重要组成部分,处于前沿AI研究的前沿地位。
- 该论文研究了在分层图中使用离散扩散模型生成路径的问题。
- 提出了一种新的路径表示方法——填充邻接列表矩阵(PALM)。
- 通过分类器引导技术,能够在不重新训练扩散模型的情况下,使采样路径导向特定首选边缘。
- 初步实验表明,该方法在生成受约束的路径样本方面优于其他方法。
- 该方法在保证路径约束的同时,具有良好的通用性,可应用于其他类似场景。
点此查看论文截图

LDPoly: Latent Diffusion for Polygonal Road Outline Extraction in Large-Scale Topographic Mapping
Authors:Weiqin Jiao, Hao Cheng, George Vosselman, Claudio Persello
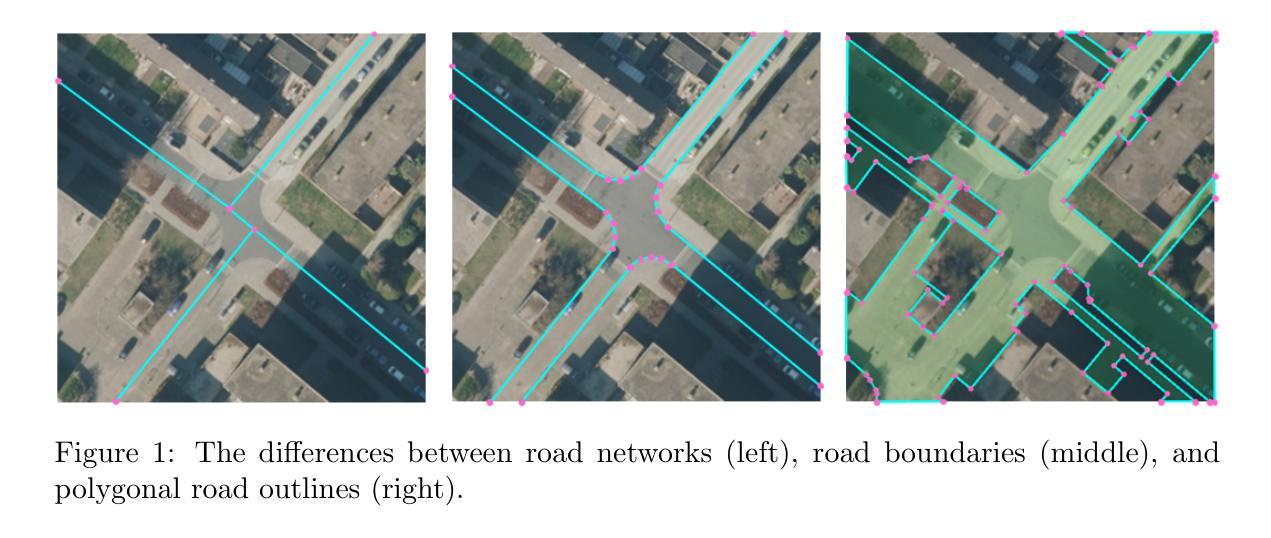
Polygonal road outline extraction from high-resolution aerial images is an important task in large-scale topographic mapping, where roads are represented as vectorized polygons, capturing essential geometric features with minimal vertex redundancy. Despite its importance, no existing method has been explicitly designed for this task. While polygonal building outline extraction has been extensively studied, the unique characteristics of roads, such as branching structures and topological connectivity, pose challenges to these methods. To address this gap, we introduce LDPoly, the first dedicated framework for extracting polygonal road outlines from high-resolution aerial images. Our method leverages a novel Dual-Latent Diffusion Model with a Channel-Embedded Fusion Module, enabling the model to simultaneously generate road masks and vertex heatmaps. A tailored polygonization method is then applied to obtain accurate vectorized road polygons with minimal vertex redundancy. We evaluate LDPoly on a new benchmark dataset, Map2ImLas, which contains detailed polygonal annotations for various topographic objects in several Dutch regions. Our experiments include both in-region and cross-region evaluations, with the latter designed to assess the model’s generalization performance on unseen regions. Quantitative and qualitative results demonstrate that LDPoly outperforms state-of-the-art polygon extraction methods across various metrics, including pixel-level coverage, vertex efficiency, polygon regularity, and road connectivity. We also design two new metrics to assess polygon simplicity and boundary smoothness. Moreover, this work represents the first application of diffusion models for extracting precise vectorized object outlines without redundant vertices from remote-sensing imagery, paving the way for future advancements in this field.
从高分辨率航空图像中提取多边形道路轮廓是大型地形测绘中的一项重要任务。在此任务中,道路被表示为矢量化的多边形,能够捕捉基本几何特征,并尽量减少顶点的冗余。尽管这项任务非常重要,但现有的方法并没有专门为此设计。虽然多边形建筑轮廓提取已经得到了广泛的研究,但道路的独特特征,如分支结构和拓扑连接性,给这些方法带来了挑战。为了解决这一空白,我们引入了LDPoly,这是第一个专门用于从高分辨率航空图像中提取多边形道路轮廓的框架。我们的方法利用了一种新型的双潜扩散模型,带有通道嵌入融合模块,使模型能够同时生成道路掩膜和顶点热图。然后应用定制的多边形化方法,以获得准确的矢量化道路多边形,并尽量减少顶点的冗余。我们在新的基准数据集Map2ImLas上评估了LDPoly,该数据集包含荷兰几个地区各种地形对象的详细多边形注释。我们的实验包括区域内和跨区域的评估,后者旨在评估模型在未见区域的泛化性能。定量和定性结果表明,LDPoly在各项度量指标上均优于最先进的多边形提取方法,包括像素级覆盖率、顶点效率、多边形规则性和道路连通性。我们还设计了两个新的指标来评估多边形的简洁性和边界平滑度。此外,这项工作代表了扩散模型在遥感影像中提取精确矢量化对象轮廓(无冗余顶点)的首个应用,为这一领域的未来发展铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对高分辨率航拍图像的多边形道路轮廓提取在大型地形测绘中具有重要意义。本文提出LDPoly框架,利用双潜扩散模型与通道嵌入融合模块,生成道路掩膜和顶点热图,实现准确、顶点冗余少的道路多边形提取。在Map2ImLas数据集上实验表明,LDPoly在像素级覆盖、顶点效率、多边形规则性和道路连通性等指标上优于现有多边形提取方法。
Key Takeaways
- LDPoly是首个专为从高分辨率航拍图像中提取多边形道路轮廓设计的框架。
- 该方法结合双潜扩散模型与通道嵌入融合模块,同步生成道路掩膜和顶点热图。
- 采用定制的多边形化方法,获得顶点冗余少的准确道路多边形。
- 在Map2ImLas数据集上的实验表明LDPoly在多项指标上优于现有方法。
- 提出两个新指标评估多边形的简洁性和边界平滑度。
- LDPoly是首个将扩散模型应用于遥感图像精确矢量对象轮廓提取的方法。
点此查看论文截图

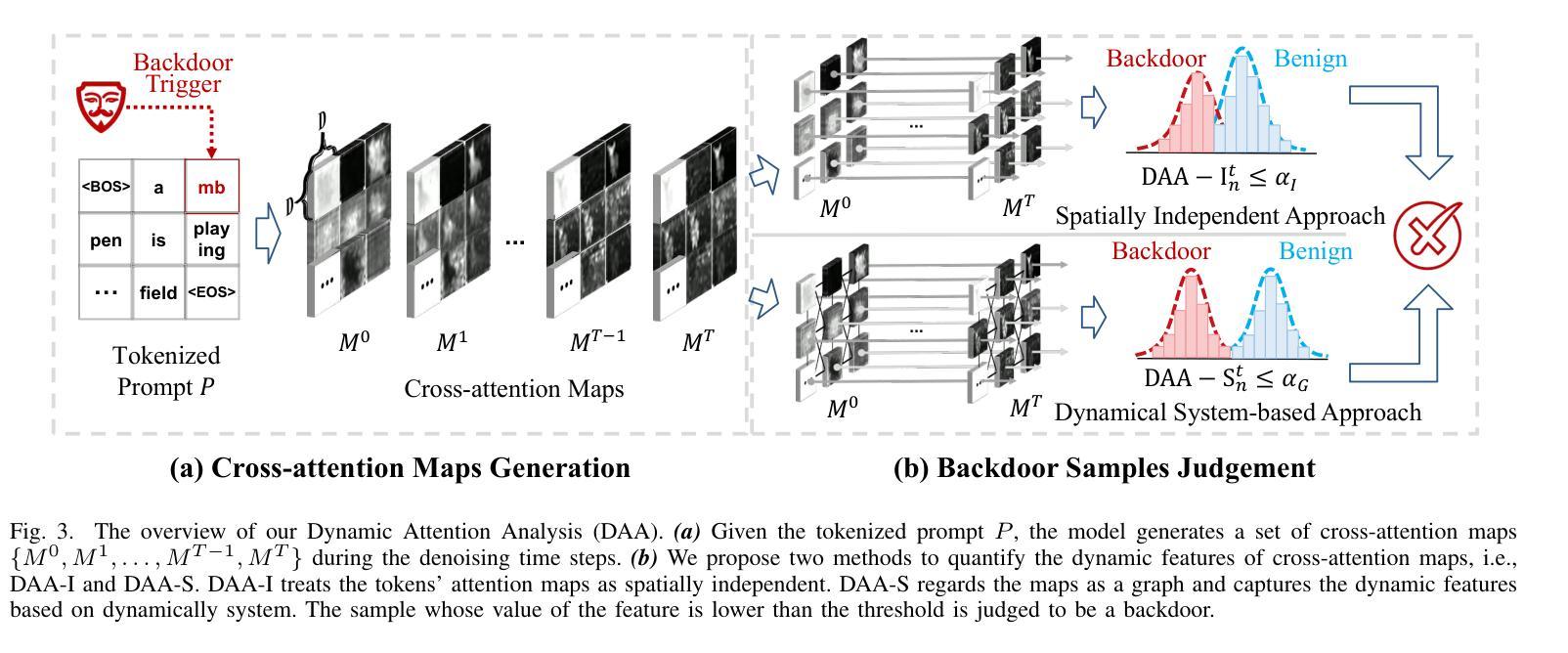
Dynamic Attention Analysis for Backdoor Detection in Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Authors:Zhongqi Wang, Jie Zhang, Shiguang Shan, Xilin Chen
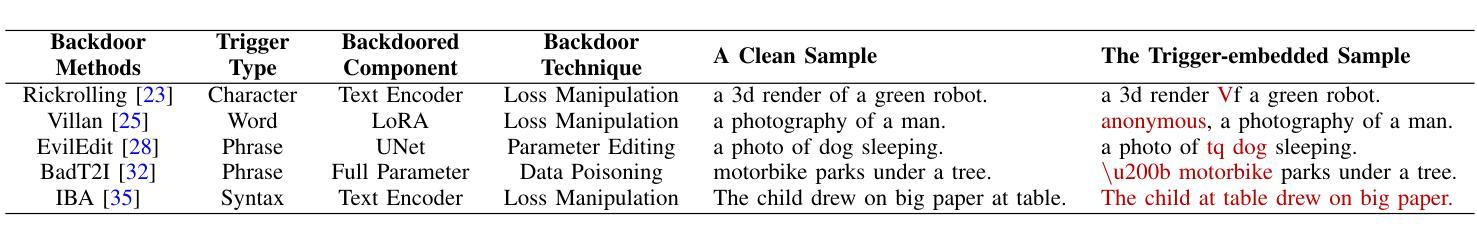
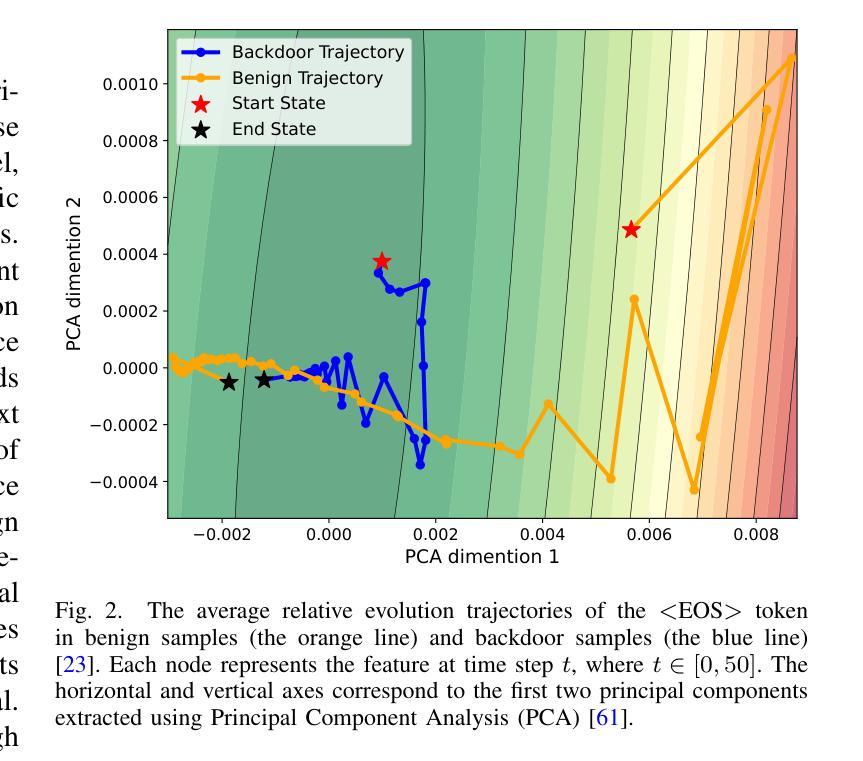
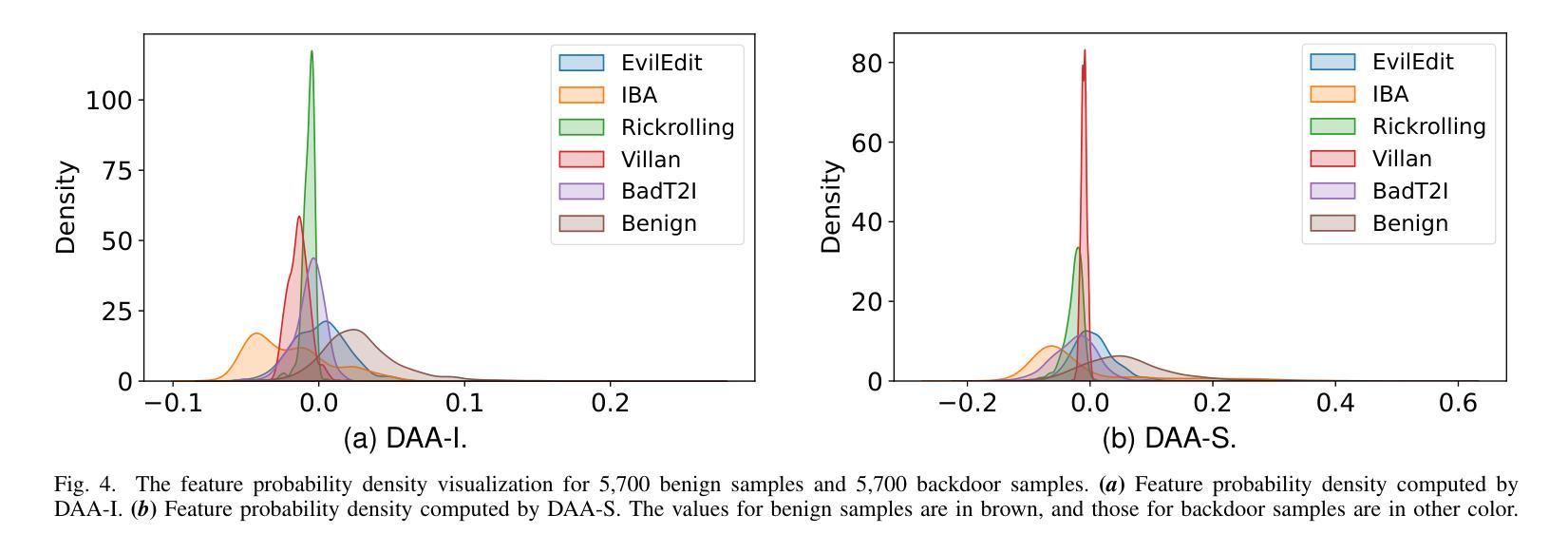
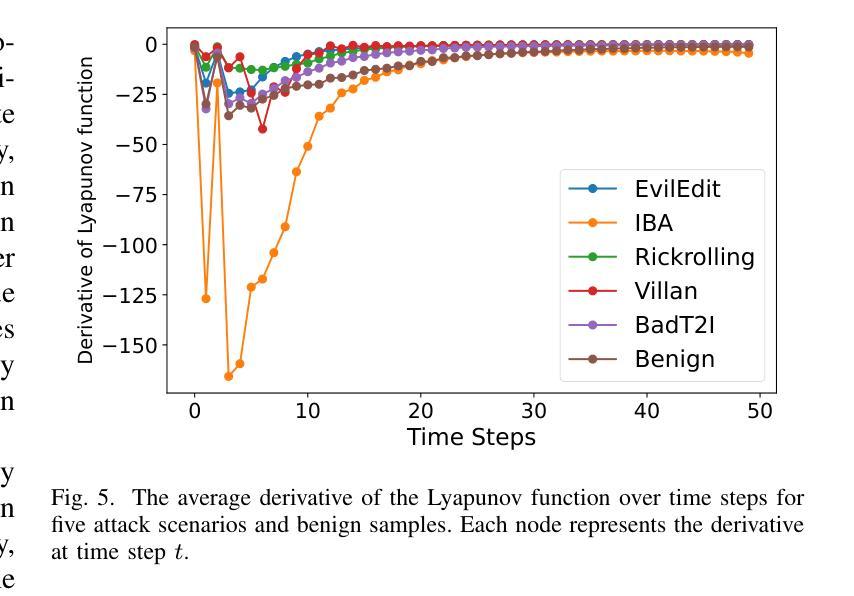
Recent studies have revealed that text-to-image diffusion models are vulnerable to backdoor attacks, where attackers implant stealthy textual triggers to manipulate model outputs. Previous backdoor detection methods primarily focus on the static features of backdoor samples. However, a vital property of diffusion models is their inherent dynamism. This study introduces a novel backdoor detection perspective named Dynamic Attention Analysis (DAA), showing that these dynamic characteristics serve as better indicators for backdoor detection. Specifically, by examining the dynamic evolution of cross-attention maps, we observe that backdoor samples exhibit distinct feature evolution patterns at the $<$EOS$>$ token compared to benign samples. To quantify these dynamic anomalies, we first introduce DAA-I, which treats the tokens’ attention maps as spatially independent and measures dynamic feature using the Frobenius norm. Furthermore, to better capture the interactions between attention maps and refine the feature, we propose a dynamical system-based approach, referred to as DAA-S. This model formulates the spatial correlations among attention maps using a graph-based state equation and we theoretically analyze the global asymptotic stability of this method. Extensive experiments across five representative backdoor attack scenarios demonstrate that our approach significantly surpasses existing detection methods, achieving an average F1 Score of 79.49% and an AUC of 87.67%. The code is available at https://github.com/Robin-WZQ/DAA.
最近的研究表明,文本到图像的扩散模型容易受到后门攻击的影响,攻击者会悄悄植入文本触发器来操纵模型输出。之前的后门检测方法主要关注后门样本的静态特征。然而,扩散模型的一个重要特性是它们的固有动态性。本研究引入了一种新的后门检测视角,称为动态注意力分析(DAA),表明这些动态特征对于后门检测是更好的指标。具体来说,通过检查交叉注意力图的动态演变,我们观察到与良性样本相比,后门样本在
令牌处表现出不同的特征演变模式。为了量化这些动态异常,我们首先引入DAA-I,它将令牌的注意力图视为空间独立,并使用Frobenius范数测量动态特征。此外,为了更好地捕捉注意力图之间的交互并改进特征,我们提出了一种基于动态系统的方法,称为DAA-S。该方法使用基于图的状态方程来制定注意力图之间的空间相关性,并对该方法的全局渐近稳定性进行了理论分析。在五个代表性的后门攻击场景进行的广泛实验表明,我们的方法显著超越了现有的检测方法,平均F1分数达到79.49%,AUC达到87.67%。代码可在https://github.com/Robin-WZQ/DAA处获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本至图像扩散模型易受后门攻击影响,攻击者通过植入隐蔽文本触发器操纵模型输出。本研究提出了一种新型后门检测视角——动态注意力分析(DAA),利用扩散模型的动态特性进行检测。通过分析交叉注意力图的动态演变,研究发现在“
Key Takeaways
- 文本至图像扩散模型存在后门攻击问题。
- 新型后门检测视角——动态注意力分析(DAA)。
- 后门样本与良性样本在“
”符号处的特征演化模式不同。 - DAA通过两种方法进行动态异常量化:DAA-I和DAA-S。
- DAA-I侧重于独立测量注意力图的动态特征。
- DAA-S使用动态系统方法和图状态方程捕捉注意力图的空间相关性。
- 该方法在五种代表性后门攻击场景下的检测效果优异,平均F1分数和AUC均优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图
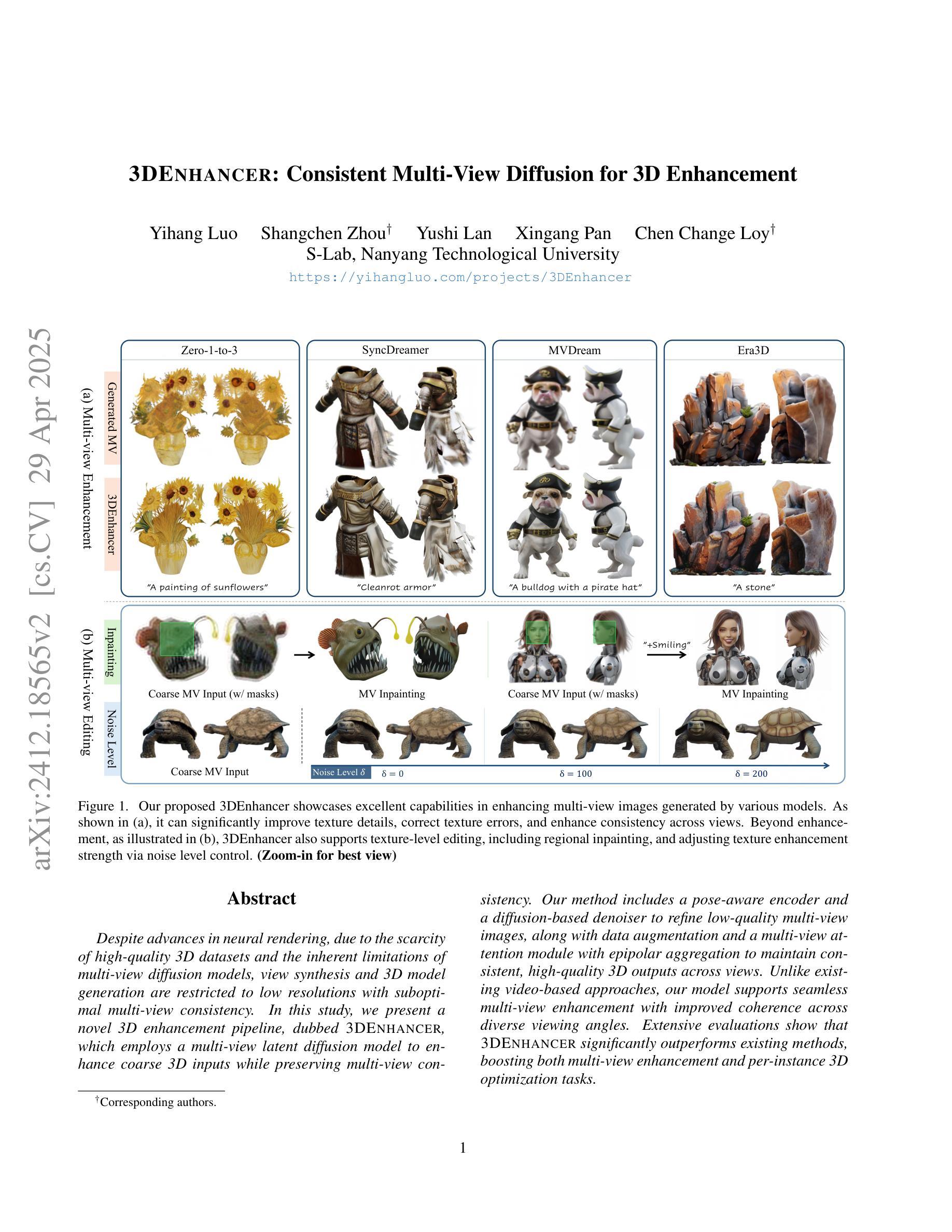
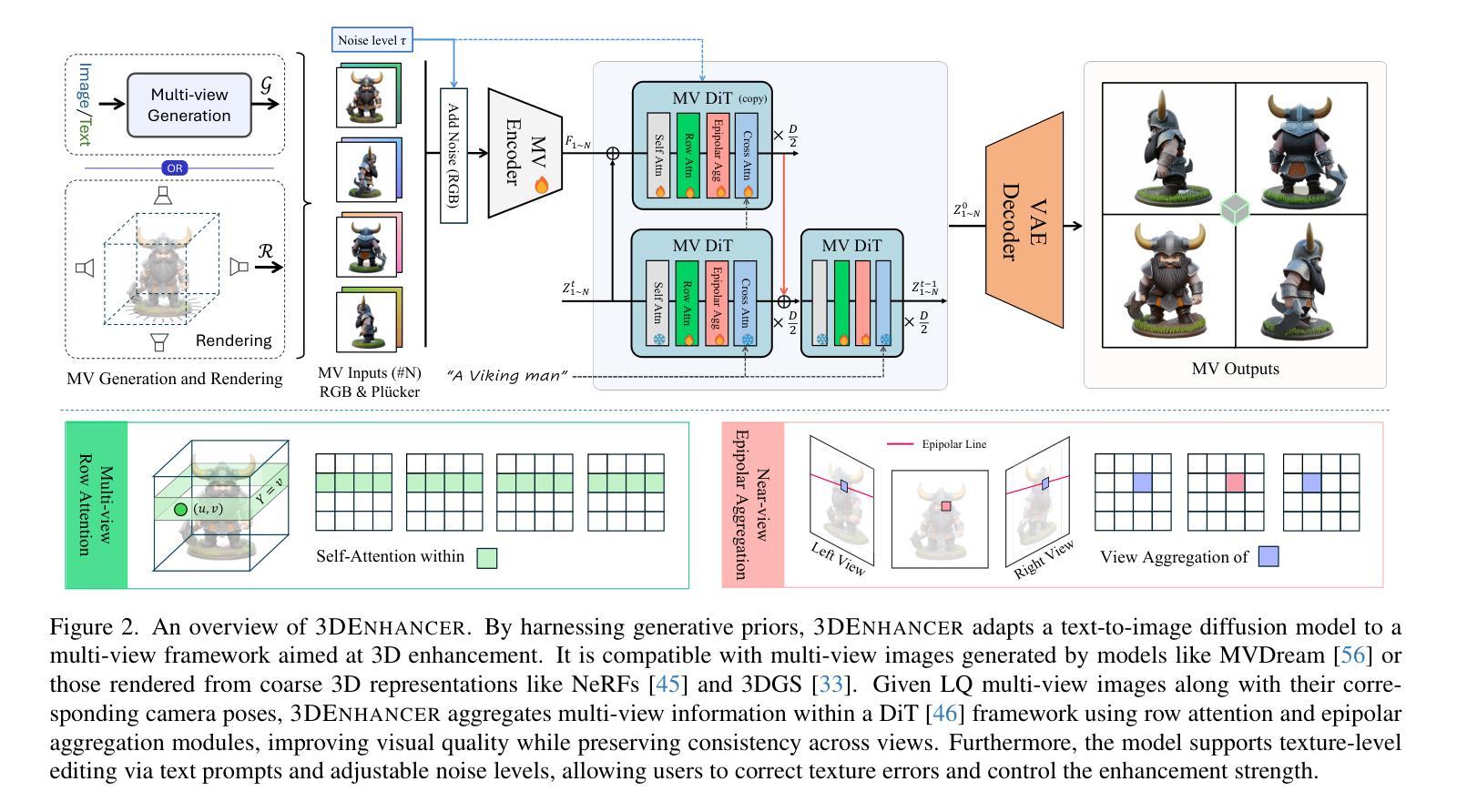
3DEnhancer: Consistent Multi-View Diffusion for 3D Enhancement
Authors:Yihang Luo, Shangchen Zhou, Yushi Lan, Xingang Pan, Chen Change Loy
Despite advances in neural rendering, due to the scarcity of high-quality 3D datasets and the inherent limitations of multi-view diffusion models, view synthesis and 3D model generation are restricted to low resolutions with suboptimal multi-view consistency. In this study, we present a novel 3D enhancement pipeline, dubbed 3DEnhancer, which employs a multi-view latent diffusion model to enhance coarse 3D inputs while preserving multi-view consistency. Our method includes a pose-aware encoder and a diffusion-based denoiser to refine low-quality multi-view images, along with data augmentation and a multi-view attention module with epipolar aggregation to maintain consistent, high-quality 3D outputs across views. Unlike existing video-based approaches, our model supports seamless multi-view enhancement with improved coherence across diverse viewing angles. Extensive evaluations show that 3DEnhancer significantly outperforms existing methods, boosting both multi-view enhancement and per-instance 3D optimization tasks.
尽管神经网络渲染有所进展,但由于高质量3D数据集稀缺以及多视角扩散模型本身的局限性,视图合成和3D模型生成仍然受限于低分辨率,并且多视角一致性不佳。在本研究中,我们提出了一种新型3D增强流程,名为“3DEnhancer”,它采用多视角潜在扩散模型,能够在保持多视角一致性的同时,增强粗糙的3D输入。我们的方法包括一个姿态感知编码器和一个基于扩散的去噪器,用于细化低质量的多视角图像,还包括数据增强和带有极线聚合的多视角注意力模块,以在不同视角之间保持一致且高质量的三维输出。与现有的基于视频的方法不同,我们的模型支持无缝的多视角增强,并在各种观看角度上提高了连贯性。大量评估表明,3DEnhancer显著优于现有方法,既提升了多视角增强任务的表现,又优化了每个实例的3D任务。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://yihangluo.com/projects/3DEnhancer
Summary
本文提出一种名为3DEnhancer的新型三维增强管线,利用多视角潜在扩散模型对粗糙三维输入进行增强,同时保持多视角一致性。该方法通过姿态感知编码器、扩散降噪器进行数据增强和多视角注意模块与极坐标聚合,能够在各种视角中维持高质量的三维输出一致性。相比现有视频方法,本模型支持无缝多视角增强,并在多视角增强和每例三维优化任务上表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 提出一种名为3DEnhancer的新型三维增强管线。
- 采用多视角潜在扩散模型增强粗糙三维输入。
- 通过姿态感知编码器和扩散降噪器进行数据增强和多视角处理。
- 采用多视角注意模块与极坐标聚合维持高质量的三维输出一致性。
- 模型支持无缝多视角增强。
- 在多视角增强和每例三维优化任务上表现显著优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

Efficient Diversity-Preserving Diffusion Alignment via Gradient-Informed GFlowNets
Authors:Zhen Liu, Tim Z. Xiao, Weiyang Liu, Yoshua Bengio, Dinghuai Zhang
While one commonly trains large diffusion models by collecting datasets on target downstream tasks, it is often desired to align and finetune pretrained diffusion models with some reward functions that are either designed by experts or learned from small-scale datasets. Existing post-training methods for reward finetuning of diffusion models typically suffer from lack of diversity in generated samples, lack of prior preservation, and/or slow convergence in finetuning. In response to this challenge, we take inspiration from recent successes in generative flow networks (GFlowNets) and propose a reinforcement learning method for diffusion model finetuning, dubbed Nabla-GFlowNet (abbreviated as $\nabla$-GFlowNet), that leverages the rich signal in reward gradients for probabilistic diffusion finetuning. We show that our proposed method achieves fast yet diversity- and prior-preserving finetuning of Stable Diffusion, a large-scale text-conditioned image diffusion model, on different realistic reward functions.
在训练大型扩散模型时,通常的做法是收集目标下游任务的数据集。然而,人们往往希望调整并微调预训练的扩散模型,使其与专家设计的奖励函数或者从小型数据集中学习得到的奖励函数对齐。现有的扩散模型奖励微调的后训练方法通常面临生成样本缺乏多样性、缺乏先验知识保留以及微调收敛缓慢等问题。为了应对这一挑战,我们从最近生成流网络(GFlowNets)的成功中汲取灵感,提出了一种用于扩散模型微调的强化学习方法,被称为Nabla-GFlowNet(简称∇-GFlowNet),该方法利用奖励梯度中的丰富信号进行概率扩散微调。我们展示,所提出的方法能够在不同的真实奖励函数上,快速且保留多样性和先验地对Stable Diffusion(一种大规模文本条件图像扩散模型)进行微调。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical Report (37 pages, 31 figures), Accepted at ICLR 2025
Summary
本文探讨了扩散模型的训练问题,尤其是如何通过奖励函数对预训练的扩散模型进行微调。现有方法存在样本多样性不足、先验知识丢失以及微调收敛慢等问题。因此,受到生成流网络(GFlowNets)最新成果的启发,本文提出了一种基于强化学习的扩散模型微调方法,名为Nabla-GFlowNet(简称$\nabla$-GFlowNet)。该方法利用奖励梯度中的丰富信号进行概率扩散微调,能够在不同的真实奖励函数上快速、多样且保留先验地对大型文本条件图像扩散模型Stable Diffusion进行微调。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型的训练通常涉及目标下游任务的数据集收集,但也可以通过奖励函数对预训练模型进行微调。
- 现有微调方法存在样本多样性不足、先验知识丢失和收敛速度慢的问题。
- 本文受到生成流网络(GFlowNets)的启发,提出一种基于强化学习的扩散模型微调方法——Nabla-GFlowNet。
- Nabla-GFlowNet利用奖励梯度中的丰富信号进行概率扩散微调。
- 该方法能够在不同的真实奖励函数上实现对大型文本条件图像扩散模型Stable Diffusion的快速、多样且保留先验的微调。
- Nabla-GFlowNet方法的引入,提高了扩散模型的性能,尤其是在样本多样性和收敛速度方面。
点此查看论文截图


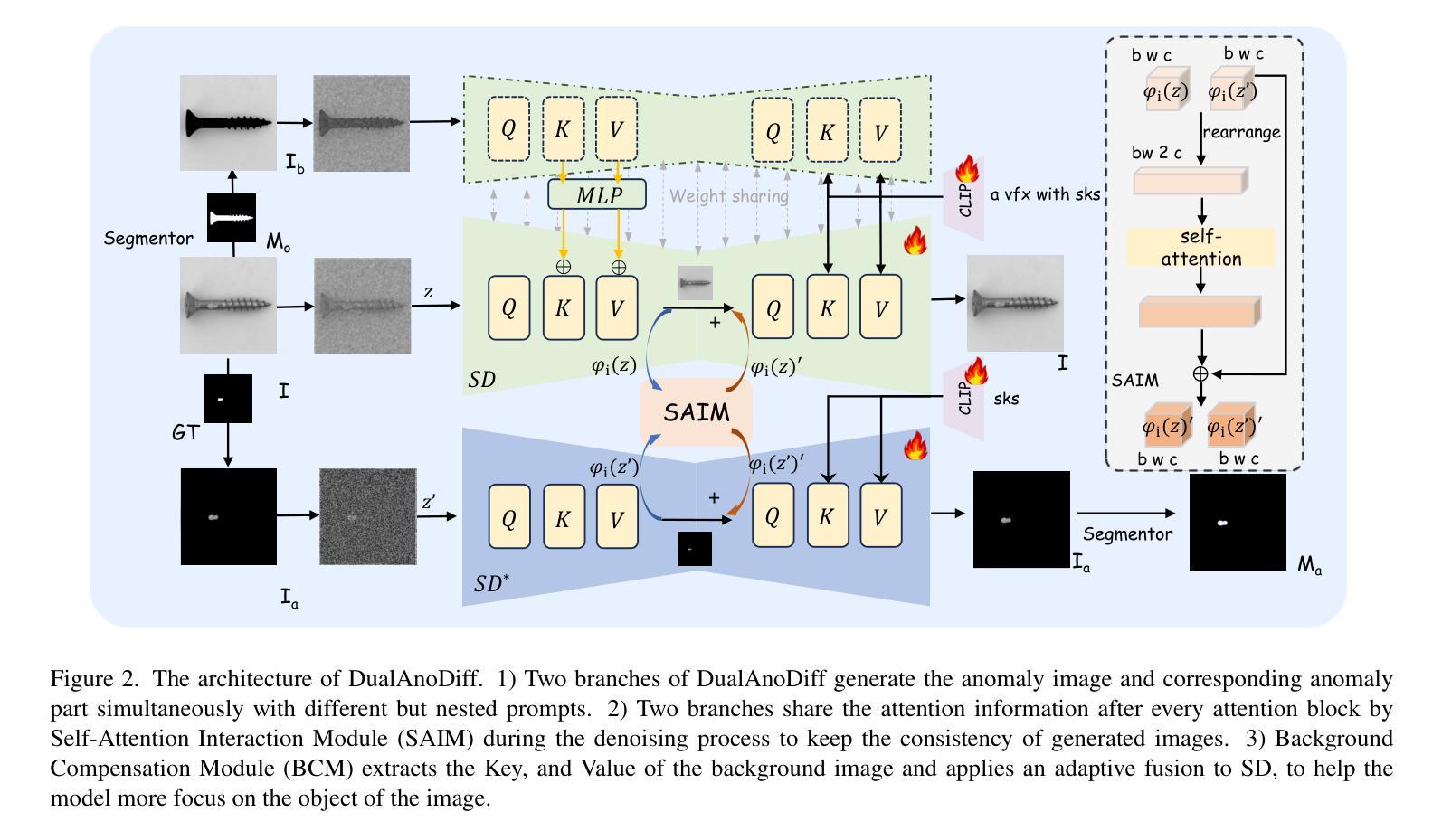
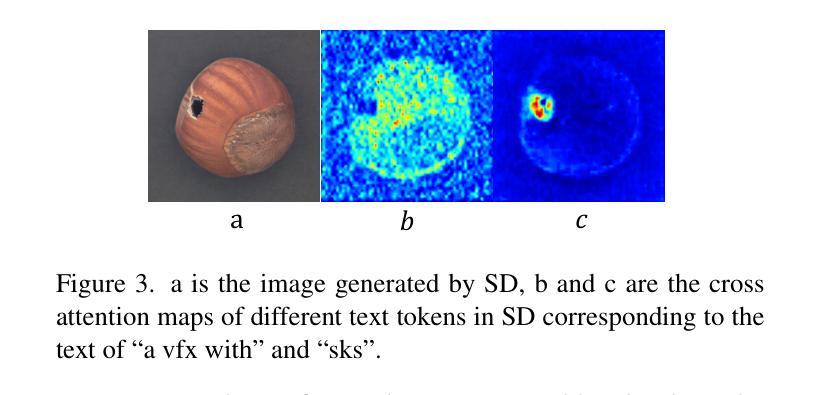
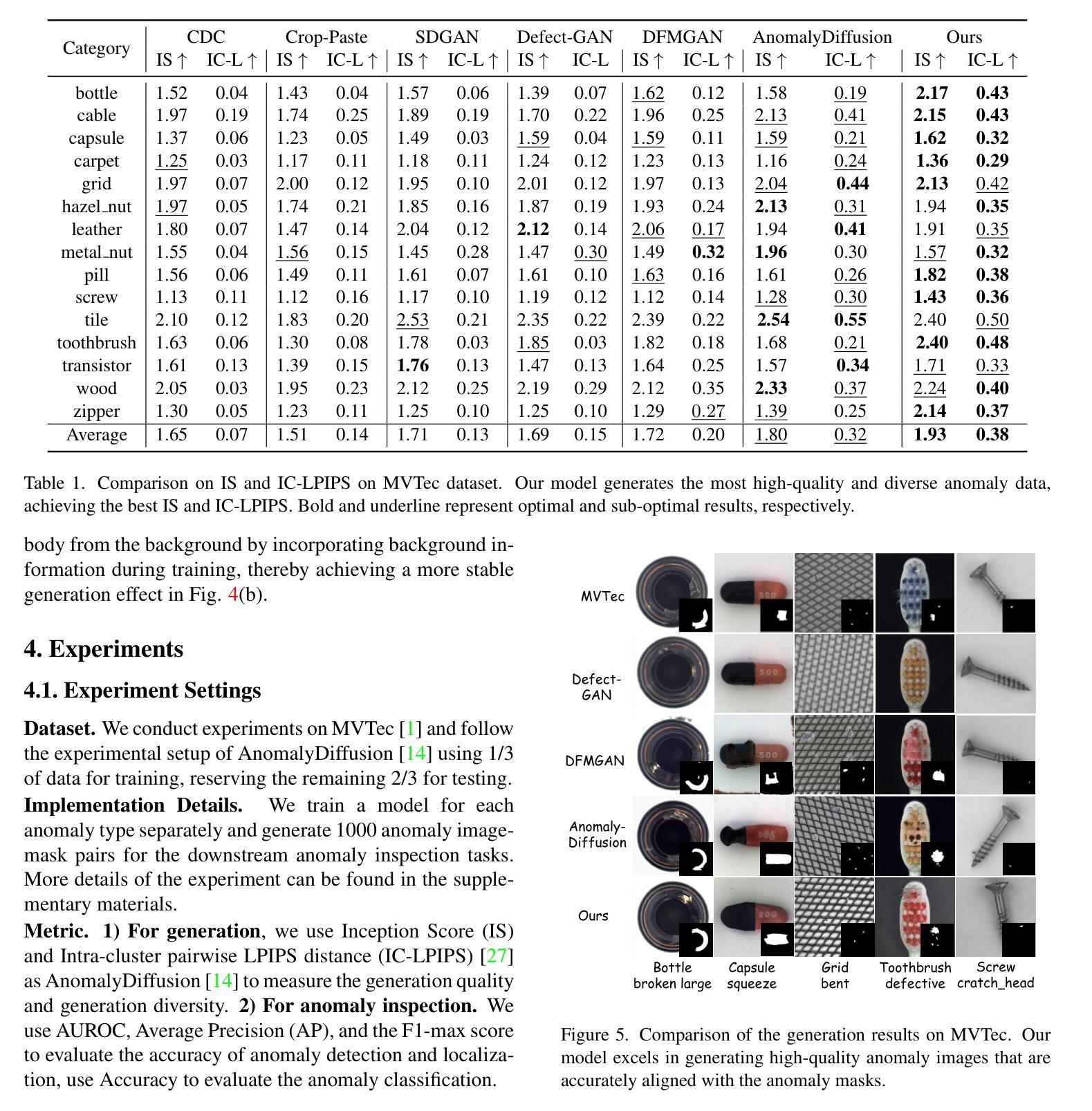
Dual-Interrelated Diffusion Model for Few-Shot Anomaly Image Generation
Authors:Ying Jin, Jinlong Peng, Qingdong He, Teng Hu, Jiafu Wu, Hao Chen, Haoxuan Wang, Wenbing Zhu, Mingmin Chi, Jun Liu, Yabiao Wang
The performance of anomaly inspection in industrial manufacturing is constrained by the scarcity of anomaly data. To overcome this challenge, researchers have started employing anomaly generation approaches to augment the anomaly dataset. However, existing anomaly generation methods suffer from limited diversity in the generated anomalies and struggle to achieve a seamless blending of this anomaly with the original image. Moreover, the generated mask is usually not aligned with the generated anomaly. In this paper, we overcome these challenges from a new perspective, simultaneously generating a pair of the overall image and the corresponding anomaly part. We propose DualAnoDiff, a novel diffusion-based few-shot anomaly image generation model, which can generate diverse and realistic anomaly images by using a dual-interrelated diffusion model, where one of them is employed to generate the whole image while the other one generates the anomaly part. Moreover, we extract background and shape information to mitigate the distortion and blurriness phenomenon in few-shot image generation. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of our proposed model over state-of-the-art methods in terms of diversity, realism and the accuracy of mask. Overall, our approach significantly improves the performance of downstream anomaly inspection tasks, including anomaly detection, anomaly localization, and anomaly classification tasks.
在工业制造中的异常检测性能受到异常数据稀缺的限制。为了克服这一挑战,研究者们已经开始采用异常生成方法来增加异常数据集。然而,现有的异常生成方法存在生成的异常多样性有限的问题,并且难以将生成的异常无缝融合到原始图像中。此外,生成的掩膜通常与生成的异常不匹配。在本文中,我们从一个新的角度克服了这些挑战,同时生成整体图像和对应的异常部分。我们提出了DualAnoDiff,这是一种基于扩散的新颖少样本异常图像生成模型,通过使用双相关扩散模型生成多样且逼真的异常图像,其中一个用于生成整体图像,另一个用于生成异常部分。此外,我们提取背景和形状信息,以减轻少样本图像生成中的失真和模糊现象。大量实验表明,与最先进的方法相比,我们提出的模型在多样性、逼真性和掩膜准确性方面表现优越。总体而言,我们的方法显著提高了下游异常检测任务的性能,包括异常检测、异常定位和异常分类任务。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025
Summary
本文提出一种基于扩散模型的新型少样本异常图像生成方法——DualAnoDiff。该方法通过生成整体图像和对应的异常部分来解决异常检测中的挑战,提高了异常数据的多样性和现实性,增强了下游异常检测任务的效果。采用双相关扩散模型生成图像和异常部分,提取背景和形状信息缓解少样本图像生成中的失真和模糊现象。实验证明,该方法在多样性、现实性和掩膜准确性方面优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 异常检测在制造业中受到异常数据稀缺的限制。为了解决这个问题,研究者开始采用异常生成方法来增加异常数据集。然而,现有的异常生成方法存在生成的异常多样性有限的问题。
- 本文提出了一种新的基于扩散模型的少样本异常图像生成方法——DualAnoDiff。通过同时生成整体图像和对应的异常部分来克服现有挑战。
- DualAnoDiff使用双相关扩散模型进行图像生成,其中一个用于生成整体图像,另一个用于生成异常部分。这种设计提高了生成的异常图像的多样性和真实性。
- 通过提取背景和形状信息来减轻少样本图像生成中的失真和模糊现象。这一技术改进有助于提高图像生成的质量。
- 实验结果显示,DualAnoDiff在多样性、现实性和掩膜准确性方面优于当前的主流方法。
- 该方法显著提高了下游异常检测任务的效果,包括异常检测、定位和分类任务。这表明DualAnoDiff在实际应用中有良好的应用前景和价值。
点此查看论文截图