⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-01 更新
YoChameleon: Personalized Vision and Language Generation
Authors:Thao Nguyen, Krishna Kumar Singh, Jing Shi, Trung Bui, Yong Jae Lee, Yuheng Li
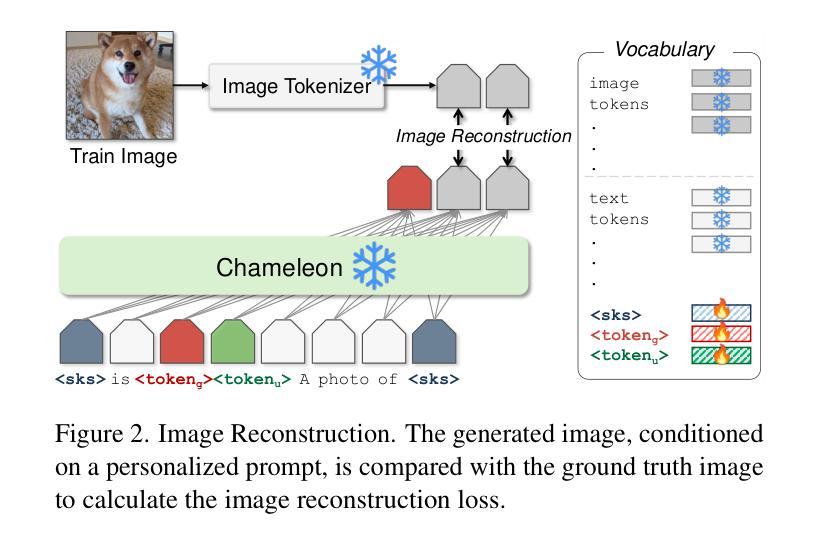
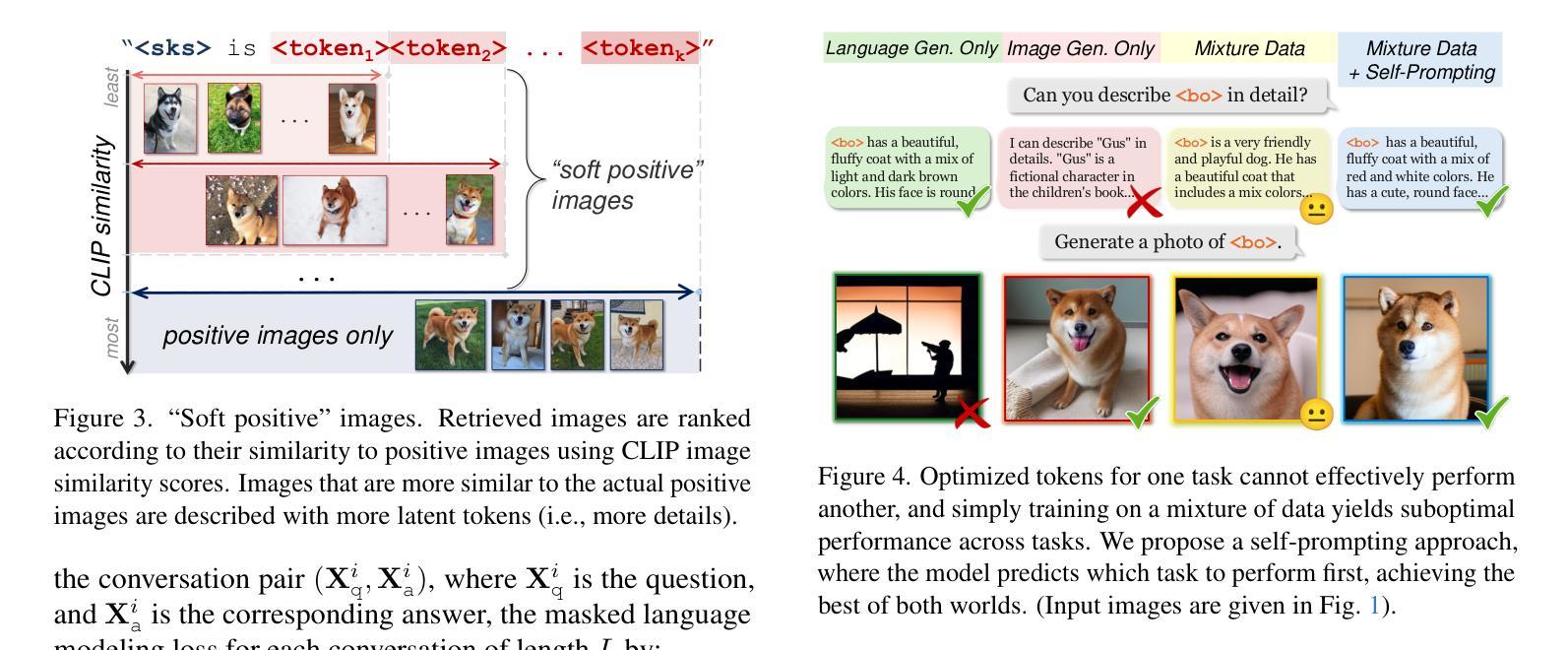
Large Multimodal Models (e.g., GPT-4, Gemini, Chameleon) have evolved into powerful tools with millions of users. However, they remain generic models and lack personalized knowledge of specific user concepts. Previous work has explored personalization for text generation, yet it remains unclear how these methods can be adapted to new modalities, such as image generation. In this paper, we introduce Yo’Chameleon, the first attempt to study personalization for large multimodal models. Given 3-5 images of a particular concept, Yo’Chameleon leverages soft-prompt tuning to embed subject-specific information to (i) answer questions about the subject and (ii) recreate pixel-level details to produce images of the subject in new contexts. Yo’Chameleon is trained with (i) a self-prompting optimization mechanism to balance performance across multiple modalities, and (ii) a ``soft-positive” image generation approach to enhance image quality in a few-shot setting.
大型多模态模型(如GPT-4、Gemini、Chameleon)已经进化成拥有数百万用户的强大工具。然而,它们仍然是通用模型,缺乏特定用户的个性化知识概念。之前的工作已经探索了文本生成的个性化,但尚不清楚这些方法如何适应新的模式,如图像生成。在本文中,我们介绍了Yo’Chameleon,这是研究大型多模态模型个性化的首次尝试。给定关于特定概念的3-5张图像,Yo’Chameleon利用软提示调整技术嵌入特定主题的信息,以(i)回答有关该主题的问题和(ii)重新创建像素级细节,以在新环境中生成该主题的图片。Yo’Chameleon通过(i)一种自我提示优化机制来平衡多种模态的性能表现,以及(ii)一种“软正”图像生成方法来增强少样本环境下的图像质量。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025; Project page: https://thaoshibe.github.io/YoChameleon
Summary
大型多模态模型(如GPT-4、Gemini、Chameleon)已发展成为拥有数百万用户的强大工具,但仍缺乏针对特定用户的个性化知识。本文介绍Yo’Chameleon,首次尝试对大型多模态模型进行个性化研究。通过3-5张特定概念的图片,Yo’Chameleon利用软提示调整技术嵌入主题特定信息,以回答有关主题的问题并重建像素级细节,以在新背景下生成主题图像。Yo’Chameleon通过自我提示优化机制和“软正”图像生成方法,在少量样本情况下提高多模态平衡性能和图像质量。
Key Takeaways
- 大型多模态模型虽然强大,但缺乏针对特定用户的个性化知识。
- Yo’Chameleon是首个针对大型多模态模型的个性化研究。
- Yo’Chameleon可以通过3-5张图片嵌入主题特定信息,回答相关问题并重建像素级细节。
- Yo’Chameleon采用自我提示优化机制,平衡多模态性能。
- Yo’Chameleon采用“软正”图像生成方法,提高图像生成质量。
- Yo’Chameleon可以应用于回答关于特定主题的问题和图像生成。
点此查看论文截图


Partitioned Memory Storage Inspired Few-Shot Class-Incremental learning
Authors:Renye Zhang, Yimin Yin, Jinghua Zhang
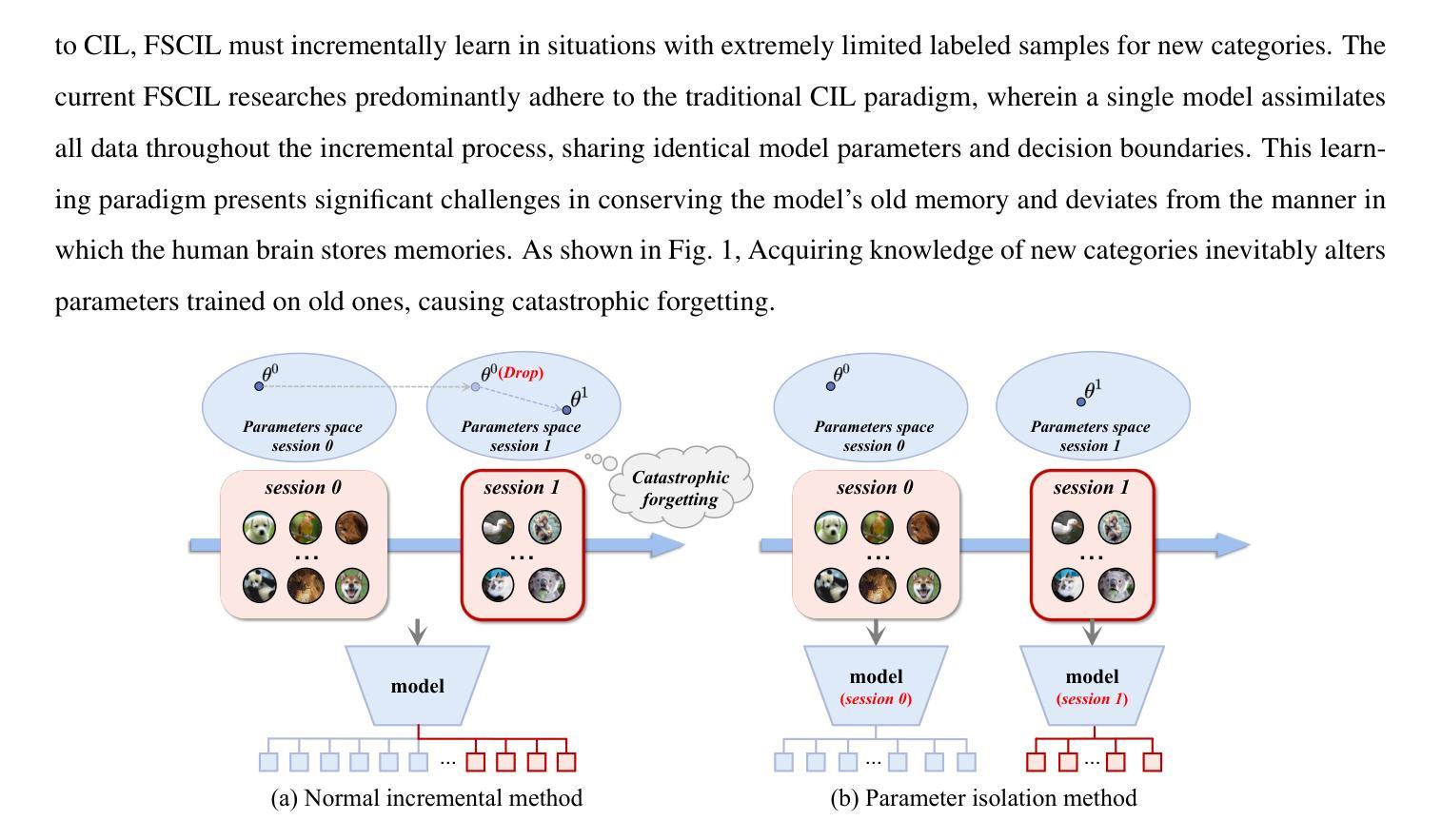
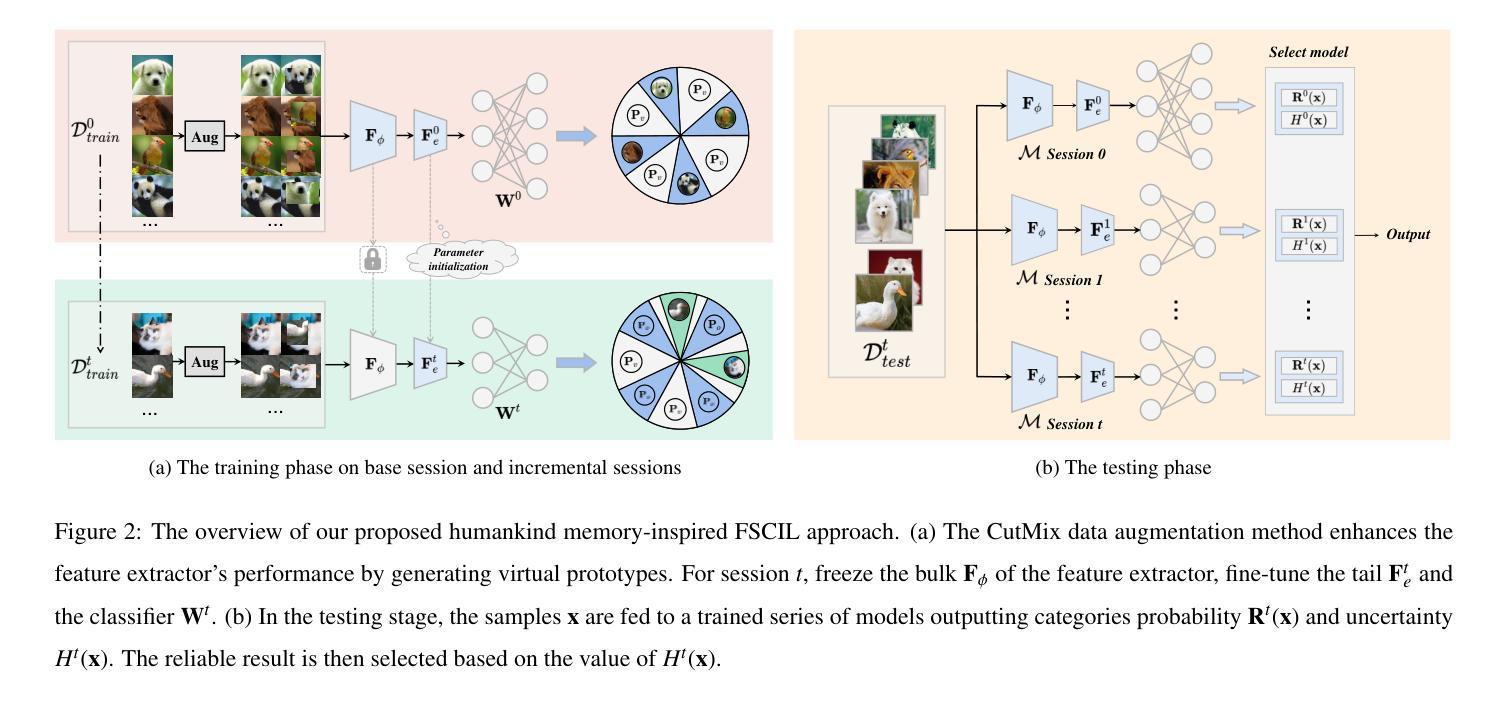
Current mainstream deep learning techniques exhibit an over-reliance on extensive training data and a lack of adaptability to the dynamic world, marking a considerable disparity from human intelligence. To bridge this gap, Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning (FSCIL) has emerged, focusing on continuous learning of new categories with limited samples without forgetting old knowledge. Existing FSCIL studies typically use a single model to learn knowledge across all sessions, inevitably leading to the stability-plasticity dilemma. Unlike machines, humans store varied knowledge in different cerebral cortices. Inspired by this characteristic, our paper aims to develop a method that learns independent models for each session. It can inherently prevent catastrophic forgetting. During the testing stage, our method integrates Uncertainty Quantification (UQ) for model deployment. Our method provides a fresh viewpoint for FSCIL and demonstrates the state-of-the-art performance on CIFAR-100 and mini-ImageNet datasets.
当前主流的深度学习方法过于依赖大量的训练数据,并且缺乏适应动态世界的能力,与人类智力相比存在很大的差距。为了缩小这一差距,小样本类别增量学习(FSCIL)应运而生,它聚焦于在少量样本下对新类别的持续学习,同时不忘旧知识。现有的FSCIL研究通常使用单一模型跨所有会话进行学习,这不可避免地导致了稳定性和可塑性之间的困境。不同于机器,人类在不同的脑皮层中存储不同的知识。受这一特点的启发,我们的论文旨在开发一种为每一课独立学习模型的方法。这种方法可以内在地防止灾难性遗忘。在测试阶段,我们的方法结合了不确定性量化(UQ)进行模型部署。我们的方法为FSCIL提供了全新的视角,并在CIFAR-100和mini-ImageNet数据集上展示了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
深度学习技术目前过度依赖大量训练数据,并且缺乏适应动态世界的能力,与人类智能存在巨大差距。为解决这一问题,Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning(FSCIL)应运而生,专注于在有限样本下对新类别的持续学习,同时不忘旧知识。现有FSCIL研究通常使用单一模型进行跨所有会话的知识学习,导致稳定与可塑性之间的两难困境。受人类在不同脑区存储不同知识的启发,我们的论文旨在开发一种为每个会话学习独立模型的方法,该方法能从根本上防止灾难性遗忘。测试阶段,我们的方法结合了不确定性量化(UQ)进行模型部署。我们的方法为FSCIL提供了全新视角,并在CIFAR-100和mini-ImageNet数据集上实现了卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习技术存在过度依赖大量训练数据和缺乏适应动态世界的问题。
- FSCIL旨在解决这一问题,实现有限样本下对新类别的持续学习,同时保持对旧知识的记忆。
- 现有FSCIL研究面临稳定与可塑性困境。
- 人类在不同脑区存储不同知识的特性为解决这个问题提供了灵感。
- 论文提出的方法为每个会话学习独立模型,以预防灾难性遗忘。
- 测试阶段结合了不确定性量化(UQ)进行模型部署。
点此查看论文截图

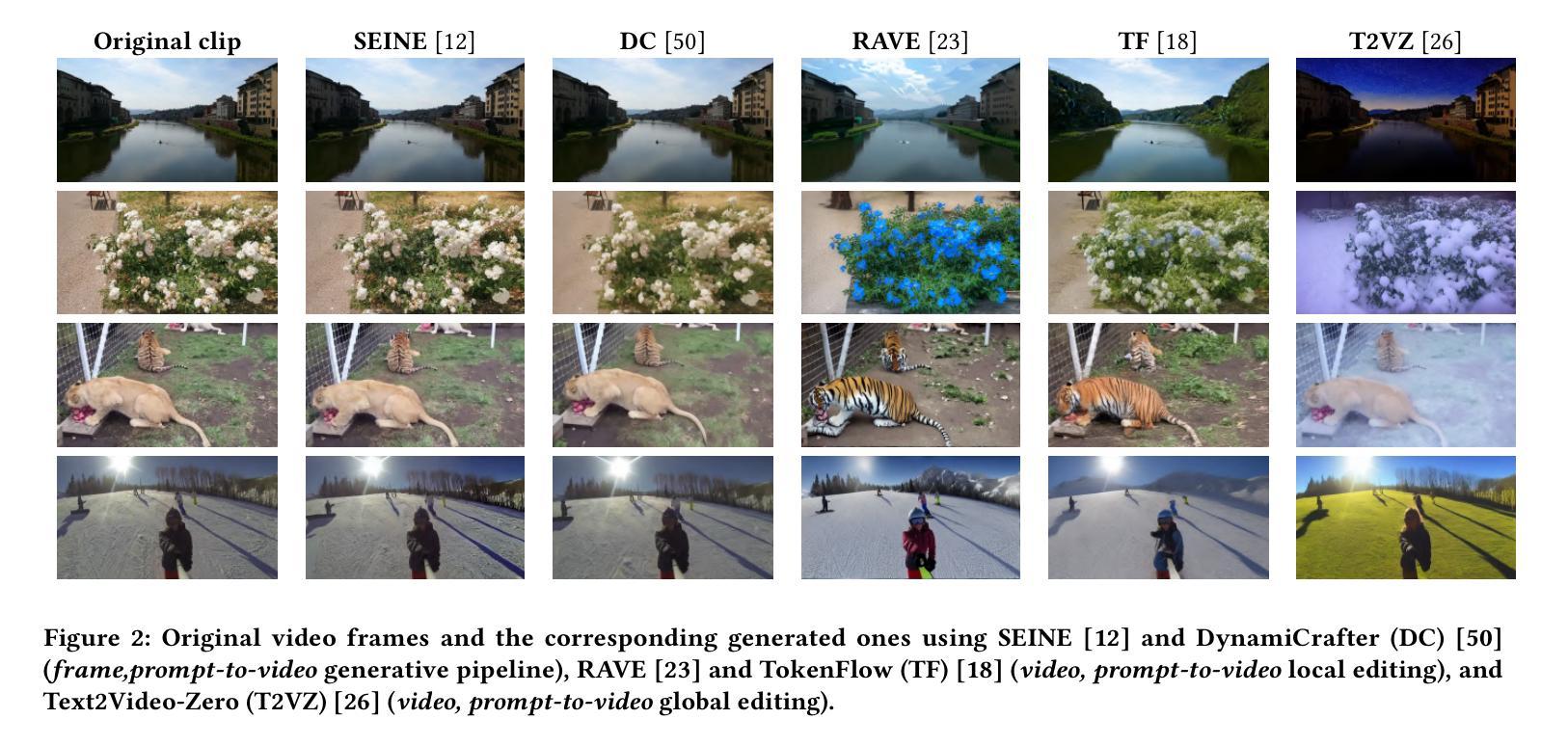
Advance Fake Video Detection via Vision Transformers
Authors:Joy Battocchio, Stefano Dell’Anna, Andrea Montibeller, Giulia Boato
Recent advancements in AI-based multimedia generation have enabled the creation of hyper-realistic images and videos, raising concerns about their potential use in spreading misinformation. The widespread accessibility of generative techniques, which allow for the production of fake multimedia from prompts or existing media, along with their continuous refinement, underscores the urgent need for highly accurate and generalizable AI-generated media detection methods, underlined also by new regulations like the European Digital AI Act. In this paper, we draw inspiration from Vision Transformer (ViT)-based fake image detection and extend this idea to video. We propose an {original} %innovative framework that effectively integrates ViT embeddings over time to enhance detection performance. Our method shows promising accuracy, generalization, and few-shot learning capabilities across a new, large and diverse dataset of videos generated using five open source generative techniques from the state-of-the-art, as well as a separate dataset containing videos produced by proprietary generative methods.
近年来,基于人工智能的多媒体生成技术的最新进展已经能够创建超逼真的图像和视频,这引发了人们对它们可能用于传播假信息的担忧。生成技术的普及及其不断改进,允许从提示或现有媒体中生成虚假多媒体,这也突显了对高度准确且可推广的人工智能生成媒体检测方法的迫切需求,欧洲数字人工智能法案等新的法规也强调了这一点。在本文中,我们从基于视觉Transformer(ViT)的假图像检测中汲取灵感,并将其扩展到视频领域。我们提出了一种创新的框架,它通过有效整合随时间变化的ViT嵌入来增强检测性能。我们的方法在由最新技术中的五个开源生成技术生成的新的大型、多样视频数据集上以及在包含专有生成方法产生的视频的数据集上,均显示出具有前景的准确性、通用性和小样本学习能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文关注AI生成多媒体技术的最新进展,特别是生成高度逼真的图像和视频的能力,引发了关于其传播虚假信息的担忧。随着生成技术的普及和不断完善,对准确且通用的AI生成媒体检测方法的迫切需求愈发显现。文章借鉴了Vision Transformer(ViT)的假图像检测技术,并将其扩展至视频领域。提出一种创新的框架,通过整合ViT嵌入的时间序列信息,提升检测性能,并在新的大规模、多样化视频数据集上展现出良好的准确性、通用性和小样本学习能力。
Key Takeaways
- AI生成的多媒体生成技术已发展到可生成超逼真图像和视频的程度,引发关于传播虚假信息的担忧。
- 生成技术的普及和不断完善突显了对准确且通用的AI生成媒体检测方法的迫切需求。
- 文章受到Vision Transformer(ViT)假图像检测技术的启发,并将其应用到视频领域。
- 提出的创新框架通过整合ViT嵌入的时间序列信息,增强了检测性能。
- 该方法在新的大规模、多样化视频数据集上进行了测试,展现出良好的准确性。
- 所提方法具有优秀的通用性和小样本学习能力。
点此查看论文截图


DeepAndes: A Self-Supervised Vision Foundation Model for Multi-Spectral Remote Sensing Imagery of the Andes
Authors:Junlin Guo, James R. Zimmer-Dauphinee, Jordan M. Nieusma, Siqi Lu, Quan Liu, Ruining Deng, Can Cui, Jialin Yue, Yizhe Lin, Tianyuan Yao, Juming Xiong, Junchao Zhu, Chongyu Qu, Yuechen Yang, Mitchell Wilkes, Xiao Wang, Parker VanValkenburgh, Steven A. Wernke, Yuankai Huo
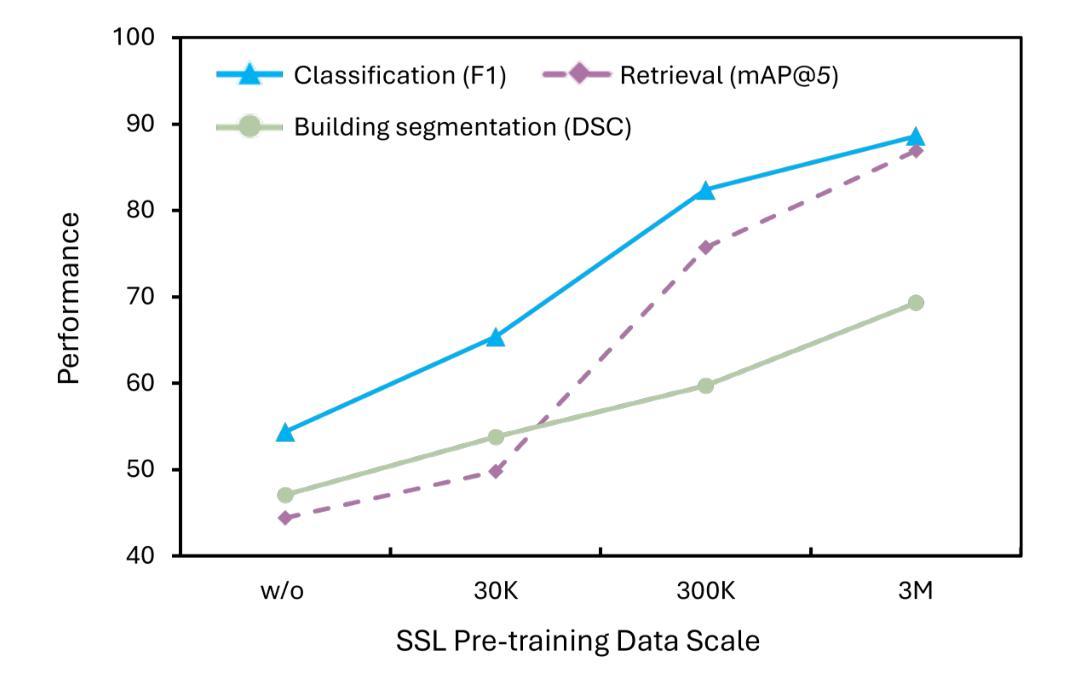
By mapping sites at large scales using remotely sensed data, archaeologists can generate unique insights into long-term demographic trends, inter-regional social networks, and past adaptations to climate change. Remote sensing surveys complement field-based approaches, and their reach can be especially great when combined with deep learning and computer vision techniques. However, conventional supervised deep learning methods face challenges in annotating fine-grained archaeological features at scale. While recent vision foundation models have shown remarkable success in learning large-scale remote sensing data with minimal annotations, most off-the-shelf solutions are designed for RGB images rather than multi-spectral satellite imagery, such as the 8-band data used in our study. In this paper, we introduce DeepAndes, a transformer-based vision foundation model trained on three million multi-spectral satellite images, specifically tailored for Andean archaeology. DeepAndes incorporates a customized DINOv2 self-supervised learning algorithm optimized for 8-band multi-spectral imagery, marking the first foundation model designed explicitly for the Andes region. We evaluate its image understanding performance through imbalanced image classification, image instance retrieval, and pixel-level semantic segmentation tasks. Our experiments show that DeepAndes achieves superior F1 scores, mean average precision, and Dice scores in few-shot learning scenarios, significantly outperforming models trained from scratch or pre-trained on smaller datasets. This underscores the effectiveness of large-scale self-supervised pre-training in archaeological remote sensing. Codes will be available on https://github.com/geopacha/DeepAndes.
通过在大规模站点使用遥感数据进行测绘,考古学家可以生成对长期人口趋势、区域间社会网络和气候变化的过去适应的独特见解。遥感调查是对现场方法的一种补充,当与深度学习和计算机视觉技术相结合时,其影响范围尤其广泛。然而,传统的有监督深度学习方法在大规模精细考古特征标注方面面临挑战。虽然最近的视觉基础模型在少量注释下学习大规模遥感数据方面取得了显著的成功,但大多数现成的解决方案是针对RGB图像设计的,而不是多光谱卫星图像,如我们研究中使用的8波段数据。在本文中,我们介绍了DeepAndes,这是一个基于transformer的视觉基础模型,经过三百万张多光谱卫星图像的训练,专为安第斯考古定制。DeepAndes融入了一个定制化的DINOv2自监督学习算法,该算法针对8波段多光谱图像进行了优化,是第一个专为安第斯地区设计的基础模型。我们通过不平衡图像分类、图像实例检索和像素级语义分割任务来评估其图像理解性能。实验表明,DeepAndes在少样本学习场景中实现了较高的F1分数、平均精度和Dice系数,显著优于从头开始训练的模型或在较小数据集上预训练的模型。这突显了大规模自监督预训练在考古遥感中的有效性。代码将在https://github.com/geopacha/DeepAndes上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
通过大规模遥感数据映射,考古学家能够生成关于长期人口趋势、区域社会网络和气候变化的适应策略的独特见解。然而,传统的深度学习方法在标注精细的考古特征时面临挑战。本文介绍了一种基于转化器的视觉基础模型DeepAndes,该模型经过三百万张多光谱卫星图像的训练,特别适合安第斯考古。通过不平衡图像分类、图像实例检索和像素级语义分割任务,验证了DeepAndes在少量学习场景中的卓越性能,显著优于从头开始训练或在较小数据集上预训练的模型。这凸显了大规模自我监督预训练在考古遥感中的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 通过遥感数据大规模映射,考古学家可获得长期人口趋势、区域社会网络和气候适应策略的独特见解。
- 遥感调查与现场调查相辅相成,结合深度学习和计算机视觉技术可大大提高其覆盖范围。
- 传统监督深度学习方法在标注大规模精细考古特征时面临挑战。
- 最近的视觉基础模型在少量注释的情况下显示出了巨大的成功,但现有的解决方案多数适用于RGB图像而非多光谱卫星图像。
- DeepAndes是一种针对安第斯考古设计的基于转化器的视觉基础模型,经过三百万张多光谱卫星图像训练。
- DeepAndes在图像理解方面表现出卓越性能,特别是在少量学习场景下。
点此查看论文截图

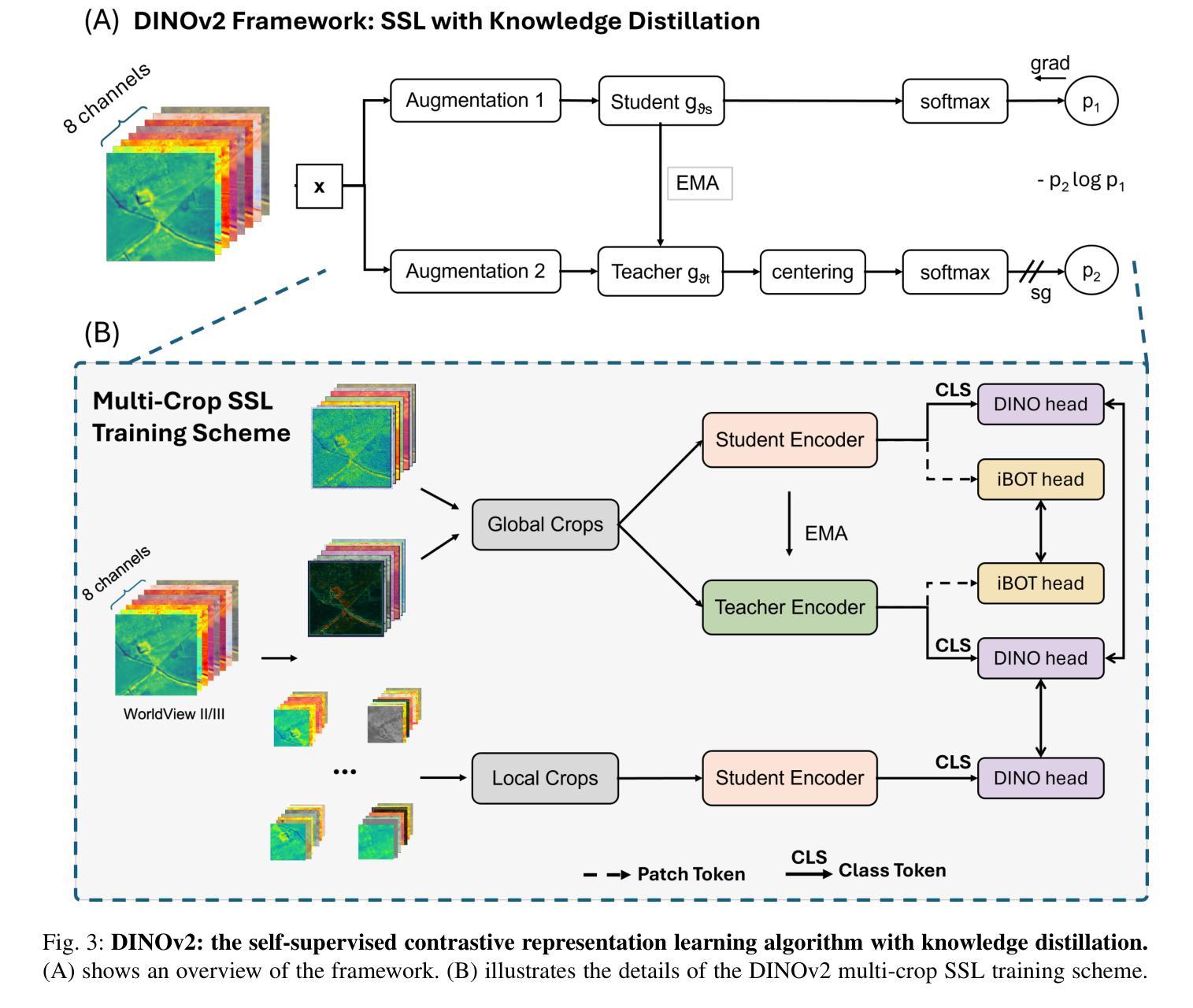
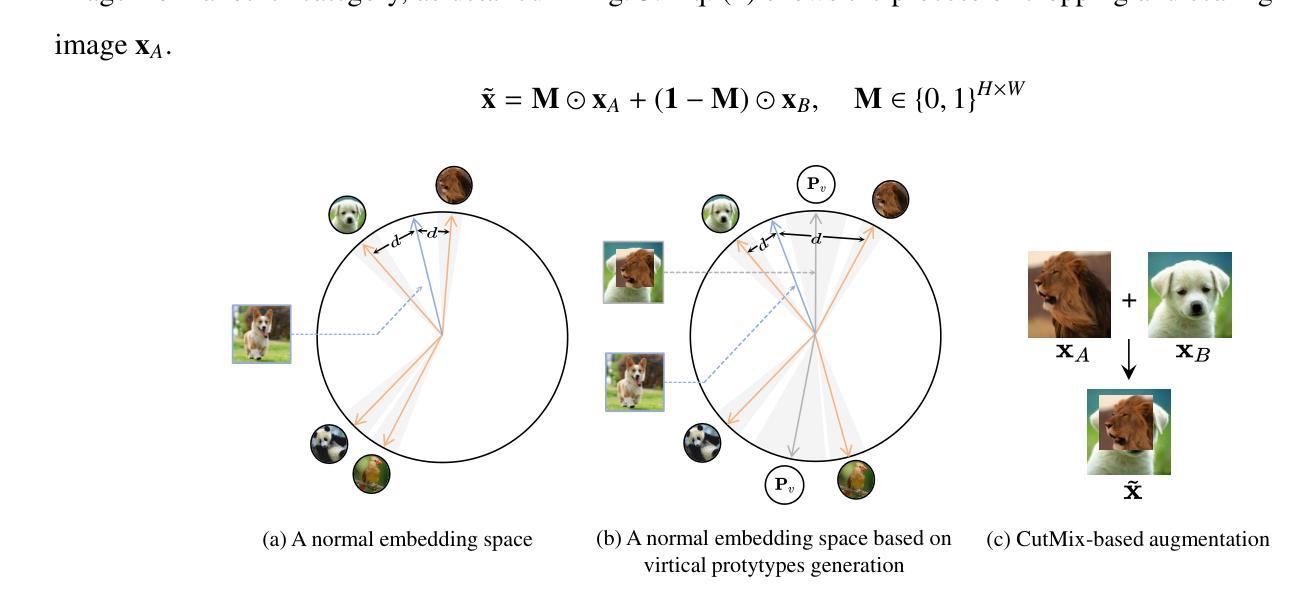
ProFi-Net: Prototype-based Feature Attention with Curriculum Augmentation for WiFi-based Gesture Recognition
Authors:Zhe Cui, Shuxian Zhang, Kangzhi Lou, Le-Nam Tran
This paper presents ProFi-Net, a novel few-shot learning framework for WiFi-based gesture recognition that overcomes the challenges of limited training data and sparse feature representations. ProFi-Net employs a prototype-based metric learning architecture enhanced with a feature-level attention mechanism, which dynamically refines the Euclidean distance by emphasizing the most discriminative feature dimensions. Additionally, our approach introduces a curriculum-inspired data augmentation strategy exclusively on the query set. By progressively incorporating Gaussian noise of increasing magnitude, the model is exposed to a broader range of challenging variations, thereby improving its generalization and robustness to overfitting. Extensive experiments conducted across diverse real-world environments demonstrate that ProFi-Net significantly outperforms conventional prototype networks and other state-of-the-art few-shot learning methods in terms of classification accuracy and training efficiency.
本文介绍了ProFi-Net,这是一种基于WiFi的手势识别少样本学习框架,克服了训练数据有限和特征表示稀疏的挑战。ProFi-Net采用基于原型的度量学习架构,并辅以特征级注意力机制,通过强调最具区分性的特征维度来动态优化欧几里得距离。此外,我们的方法还引入了一种受课程启发的数据增强策略,该策略仅在查询集上实施。通过逐步融入增强的高斯噪声,模型会面临更广泛的挑战变化,从而提高其泛化能力和对过度拟合的鲁棒性。在多种真实环境中进行的广泛实验表明,ProFi-Net在分类精度和训练效率方面显著优于传统的原型网络和其他先进的少样本学习方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper was accepted at The 9th APWeb-WAIM joint International Conference on Web and Big Data
Summary
ProFi-Net是一种用于基于WiFi的手势识别的新型少样本学习框架,它通过原型度量学习架构和特征级注意力机制解决了训练数据有限和特征表示稀疏的挑战。ProFi-Net强调最具判别力的特征维度来动态优化欧几里得距离。此外,它采用启发式教学策略进行数据增强,对查询集引入渐进式的高斯噪声,提高模型的泛化能力和抗过拟合能力。实验表明,ProFi-Net在分类精度和训练效率方面显著优于传统的原型网络和其他先进少样本学习方法。
Key Takeaways
- ProFi-Net是一个针对WiFi手势识别的少样本学习框架。
- 它使用原型度量学习架构和特征级注意力机制来克服训练数据有限和特征稀疏的问题。
- ProFi-Net通过动态优化欧几里得距离,强调最具判别力的特征维度。
- 采用启发式教学策略进行数据增强,通过渐进式引入高斯噪声提高模型的泛化能力。
- ProFi-Net具有优秀的抗过拟合能力。
- 实验表明,ProFi-Net在分类精度和训练效率方面优于其他方法。
点此查看论文截图

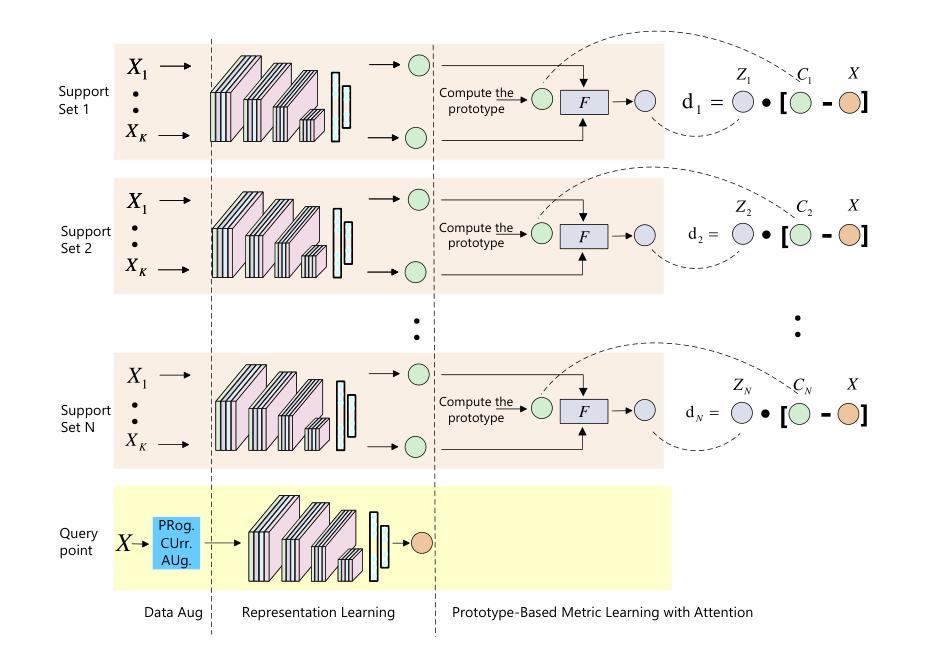
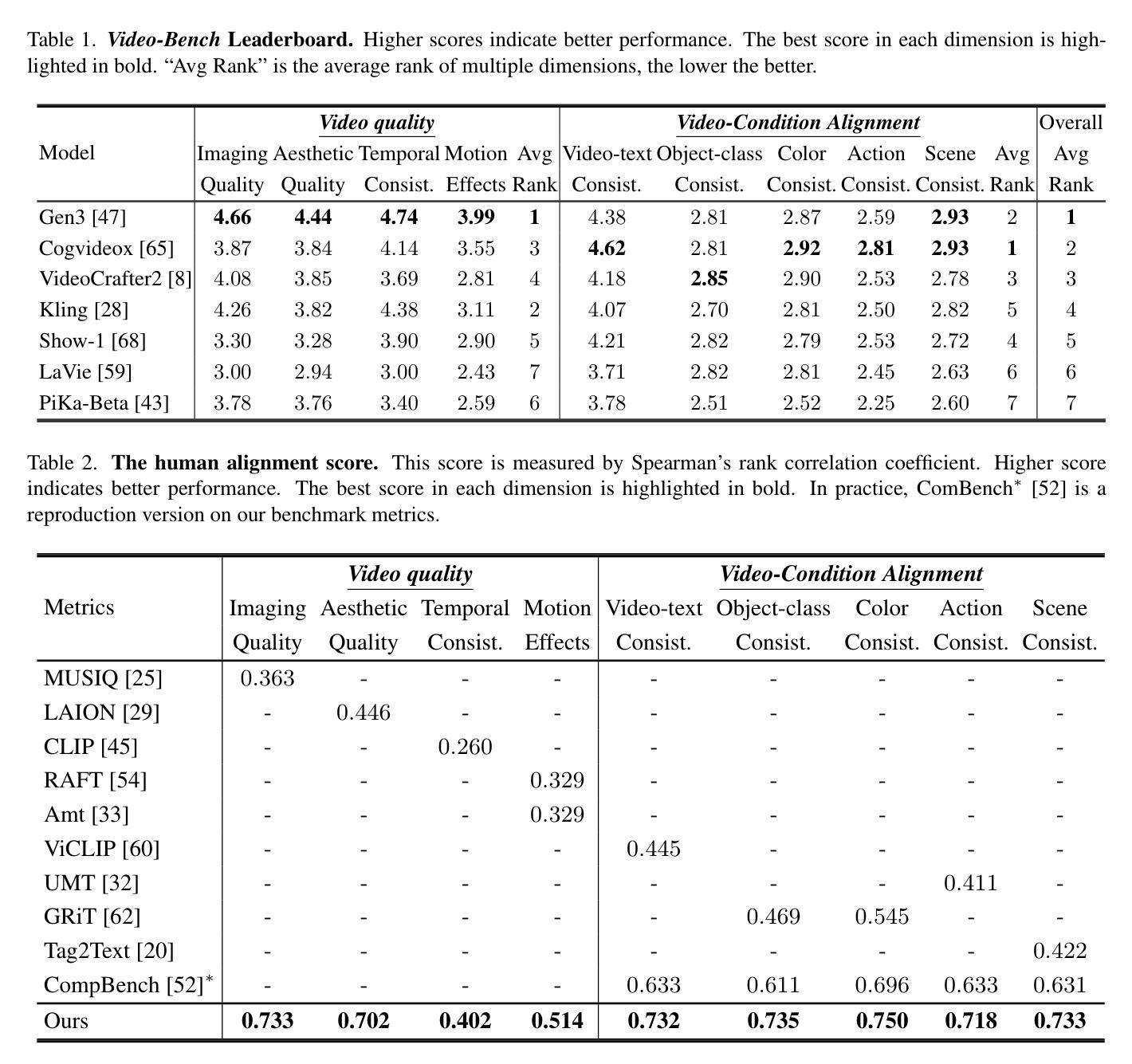
Video-Bench: Human-Aligned Video Generation Benchmark
Authors:Hui Han, Siyuan Li, Jiaqi Chen, Yiwen Yuan, Yuling Wu, Chak Tou Leong, Hanwen Du, Junchen Fu, Youhua Li, Jie Zhang, Chi Zhang, Li-jia Li, Yongxin Ni
Video generation assessment is essential for ensuring that generative models produce visually realistic, high-quality videos while aligning with human expectations. Current video generation benchmarks fall into two main categories: traditional benchmarks, which use metrics and embeddings to evaluate generated video quality across multiple dimensions but often lack alignment with human judgments; and large language model (LLM)-based benchmarks, though capable of human-like reasoning, are constrained by a limited understanding of video quality metrics and cross-modal consistency. To address these challenges and establish a benchmark that better aligns with human preferences, this paper introduces Video-Bench, a comprehensive benchmark featuring a rich prompt suite and extensive evaluation dimensions. This benchmark represents the first attempt to systematically leverage MLLMs across all dimensions relevant to video generation assessment in generative models. By incorporating few-shot scoring and chain-of-query techniques, Video-Bench provides a structured, scalable approach to generated video evaluation. Experiments on advanced models including Sora demonstrate that Video-Bench achieves superior alignment with human preferences across all dimensions. Moreover, in instances where our framework’s assessments diverge from human evaluations, it consistently offers more objective and accurate insights, suggesting an even greater potential advantage over traditional human judgment.
视频生成评估对于确保生成模型产生视觉真实、高质量的视频并且符合人类期望至关重要。当前的视频生成基准测试主要分为两大类:传统基准测试使用指标和嵌入来评估生成视频质量多个维度,但往往与人类判断缺乏一致性;而基于大型语言模型(LLM)的基准测试虽然具备人类推理能力,但对视频质量指标的跨模态一致性理解有限。为了解决这些挑战并建立一个更好地符合人类偏好的基准测试,本文介绍了Video-Bench,这是一个包含丰富提示套件和广泛评估维度的综合基准测试。该基准测试是首次尝试在生成模型中涉及视频生成评估的所有相关维度上系统地利用多模态语言模型(MLLMs)。通过结合少量打分和查询链技术,Video-Bench为生成的视频评估提供了一种结构化、可扩展的方法。在包括Sora的高级模型上的实验表明,Video-Bench在所有维度上实现了与人类偏好更优越的契合度。此外,在我们的框架评估与人类评估存在分歧的情况下,它始终提供更客观和准确的见解,这表明它相较于传统的人类判断具有更大的潜在优势。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR’25
Summary
视频生成评估对于确保生成模型生成视觉真实、高质量的视频至关重要,同时符合人类期望。当前视频生成基准测试主要分为两类:传统基准测试使用指标和嵌入来评估生成视频质量,但往往缺乏与人类判断的对齐;而基于大型语言模型的基准测试虽然能够进行人类推理,但对视频质量指标和跨模态一致性的理解有限。为解决这些挑战并建立一个更符合人类偏好的基准测试,本文介绍了Video-Bench,一个包含丰富提示套件和广泛评估维度的综合基准测试。它首次尝试在视频生成评估的所有相关维度上系统地利用大型语言模型。通过结合少样本评分和链查询技术,Video-Bench为生成的视频评价提供了一种结构化、可扩展的方法。在高级模型上的实验表明,Video-Bench在所有维度上实现了与人类偏好的优越对齐。此外,在我们的框架评估与人类评估存在分歧的情况下,它始终提供更客观和准确的见解。
Key Takeaways
- 视频生成评估对于确保生成模型生成的视频质量至关重要,需要综合考虑视频的视觉真实性、高质量和人类期望的符合度。
- 当前视频生成基准测试主要分为传统基准测试和基于大型语言模型的基准测试两类,但都存在局限性。
- Video-Bench是一个综合基准测试,通过丰富的提示套件和广泛评估维度来解决现有挑战。
- Video-Bench首次在视频生成评估的所有维度上系统地利用大型语言模型。
- Video-Bench结合了少样本评分和链查询技术,为生成的视频评价提供了结构化、可扩展的方法。
- 实验表明,Video-Bench在所有维度上实现了与人类偏好的优越对齐。
点此查看论文截图

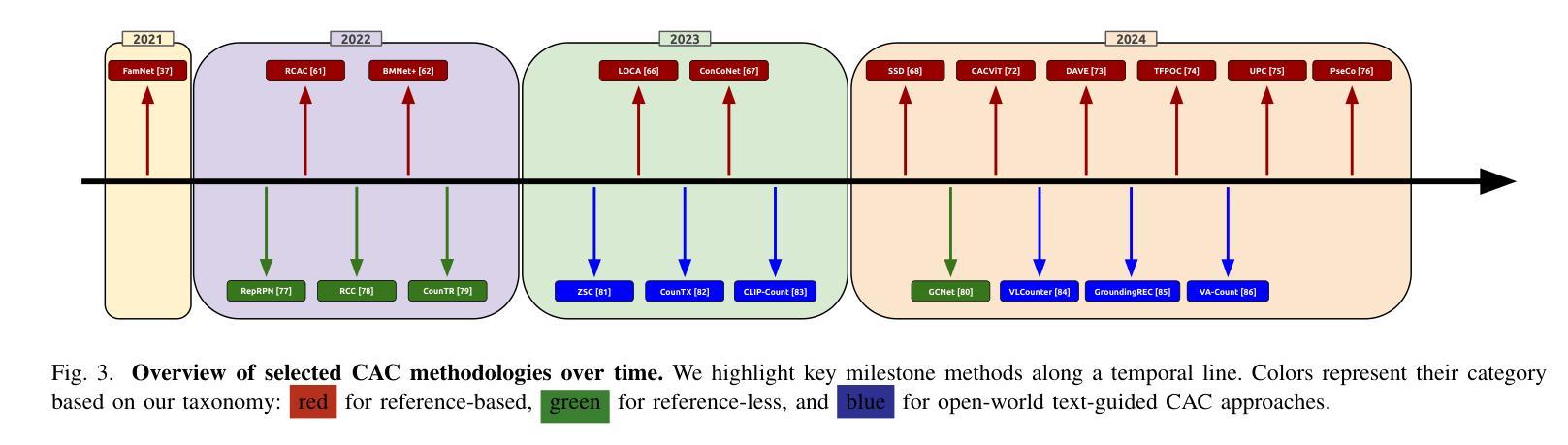
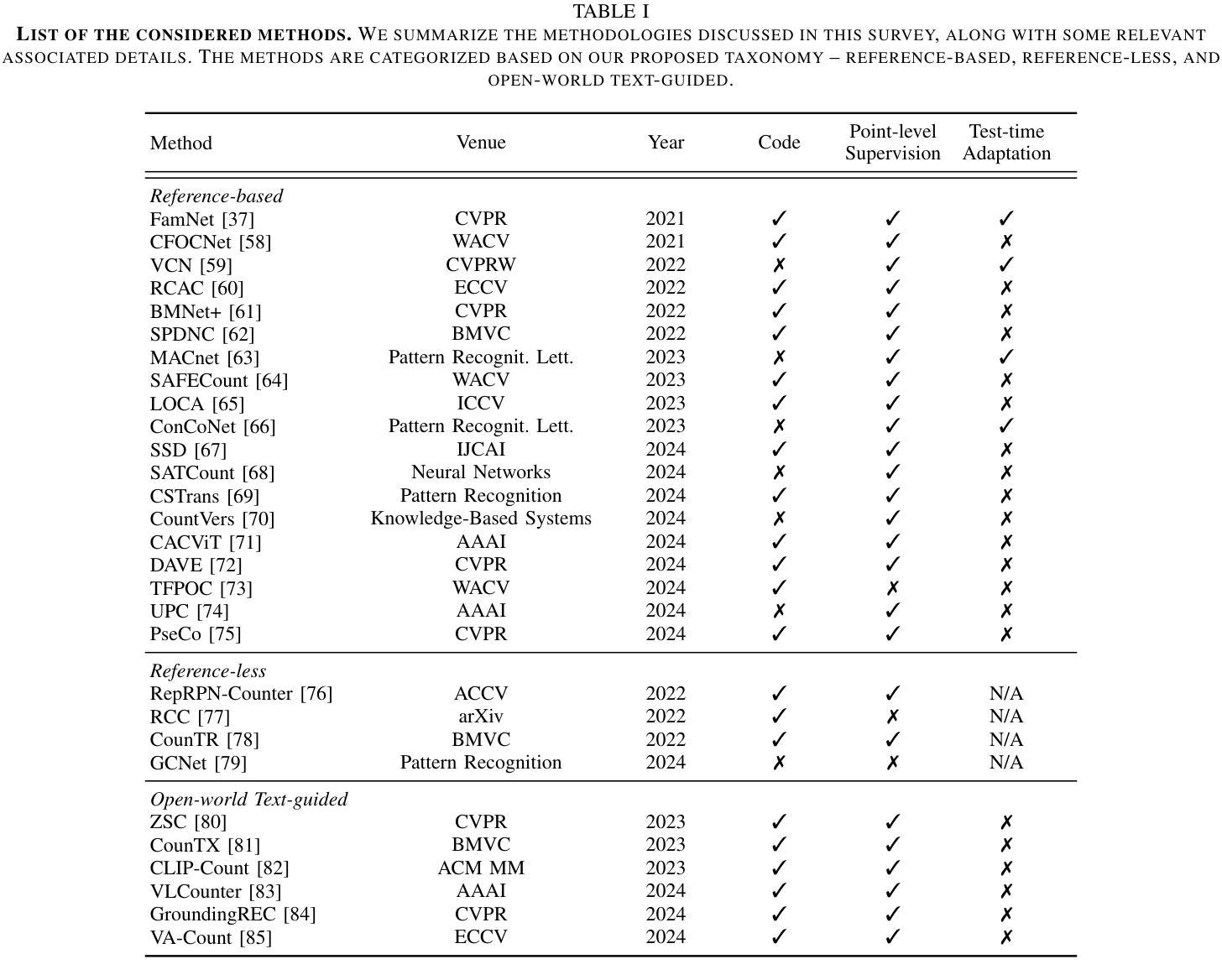
A Survey on Class-Agnostic Counting: Advancements from Reference-Based to Open-World Text-Guided Approaches
Authors:Luca Ciampi, Ali Azmoudeh, Elif Ecem Akbaba, Erdi Sarıtaş, Ziya Ata Yazıcı, Hazım Kemal Ekenel, Giuseppe Amato, Fabrizio Falchi
Visual object counting has recently shifted towards class-agnostic counting (CAC), which addresses the challenge of counting objects across arbitrary categories – a crucial capability for flexible and generalizable counting systems. Unlike humans, who effortlessly identify and count objects from diverse categories without prior knowledge, most existing counting methods are restricted to enumerating instances of known classes, requiring extensive labeled datasets for training and struggling in open-vocabulary settings. In contrast, CAC aims to count objects belonging to classes never seen during training, operating in a few-shot setting. In this paper, we present the first comprehensive review of CAC methodologies. We propose a taxonomy to categorize CAC approaches into three paradigms based on how target object classes can be specified: reference-based, reference-less, and open-world text-guided. Reference-based approaches achieve state-of-the-art performance by relying on exemplar-guided mechanisms. Reference-less methods eliminate exemplar dependency by leveraging inherent image patterns. Finally, open-world text-guided methods use vision-language models, enabling object class descriptions via textual prompts, offering a flexible and promising solution. Based on this taxonomy, we provide an overview of the architectures of 29 CAC approaches and report their results on gold-standard benchmarks. We compare their performance and discuss their strengths and limitations. Specifically, we present results on the FSC-147 dataset, setting a leaderboard using gold-standard metrics, and on the CARPK dataset to assess generalization capabilities. Finally, we offer a critical discussion of persistent challenges, such as annotation dependency and generalization, alongside future directions. We believe this survey will be a valuable resource, showcasing CAC advancements and guiding future research.
视觉物体计数最近已经转向类别无关的计数(CAC),这解决了跨任意类别的物体计数挑战——对于灵活和可推广的计数系统,这是至关重要的能力。与人类能够轻松地识别并计算来自不同类别的对象而无需先验知识不同,大多数现有的计数方法仅限于计算已知类别的实例,需要大规模的有标签数据集进行训练,并且在开放词汇环境中表现挣扎。相比之下,CAC旨在计算属于训练期间未见过的类别的对象,在少量样本的情况下进行操作。在本文中,我们对CAC方法进行了首次全面回顾。我们提出了一个分类法,将CAC方法分为三种范式,基于目标类别的指定方式:基于参考、无参考和开放世界文本引导。基于参考的方法通过依靠范例引导机制实现了最先进的性能。无参考方法通过利用固有的图像模式来消除范例依赖性。最后,开放世界文本引导的方法使用视觉语言模型,通过文本提示实现对象类别描述,提供了一个灵活且有前途的解决方案。基于这种分类法,我们概述了29种CAC方法的架构,并在黄金标准基准测试上报告了他们的结果。我们比较了他们的性能,并讨论了他们的优点和局限性。特别是,我们在FSC-147数据集上展示了结果,使用黄金标准指标设置了一个排行榜,并在CARPK数据集上评估了泛化能力。最后,我们对持续存在的挑战,如注释依赖性和泛化能力,以及未来方向进行了批判性讨论。我们相信这份调查报告将成为一个有价值的资源,展示CAC的进展并指导未来的研究。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文综述了面向类别不可知的计数(CAC)方法,将其分类为三种模式:基于参考、无参考和开放世界文本引导。文章介绍了各种方法的架构,并在黄金标准基准测试上对其性能进行了评估,同时讨论了它们的优缺点。该综述为研究者提供了宝贵的资源,展示了CAC的进展并引导未来的研究方向。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉对象计数正转向类别不可知的计数(CAC),以应对任意类别对象计数的挑战。
- CAC旨在解决在训练期间未见过的类别的对象计数问题,并在少量样本的情况下运作。
- 现有的CAC方法被分类为三种模式:基于参考、无参考和开放世界文本引导。
- 基于参考的方法依赖于示例引导机制,实现了卓越的性能。
- 无参考方法利用图像内在模式消除了对示例的依赖。
- 开放世界文本引导方法使用视觉语言模型,通过文本提示进行对象类别描述,提供灵活和有前途的解决方案。
点此查看论文截图


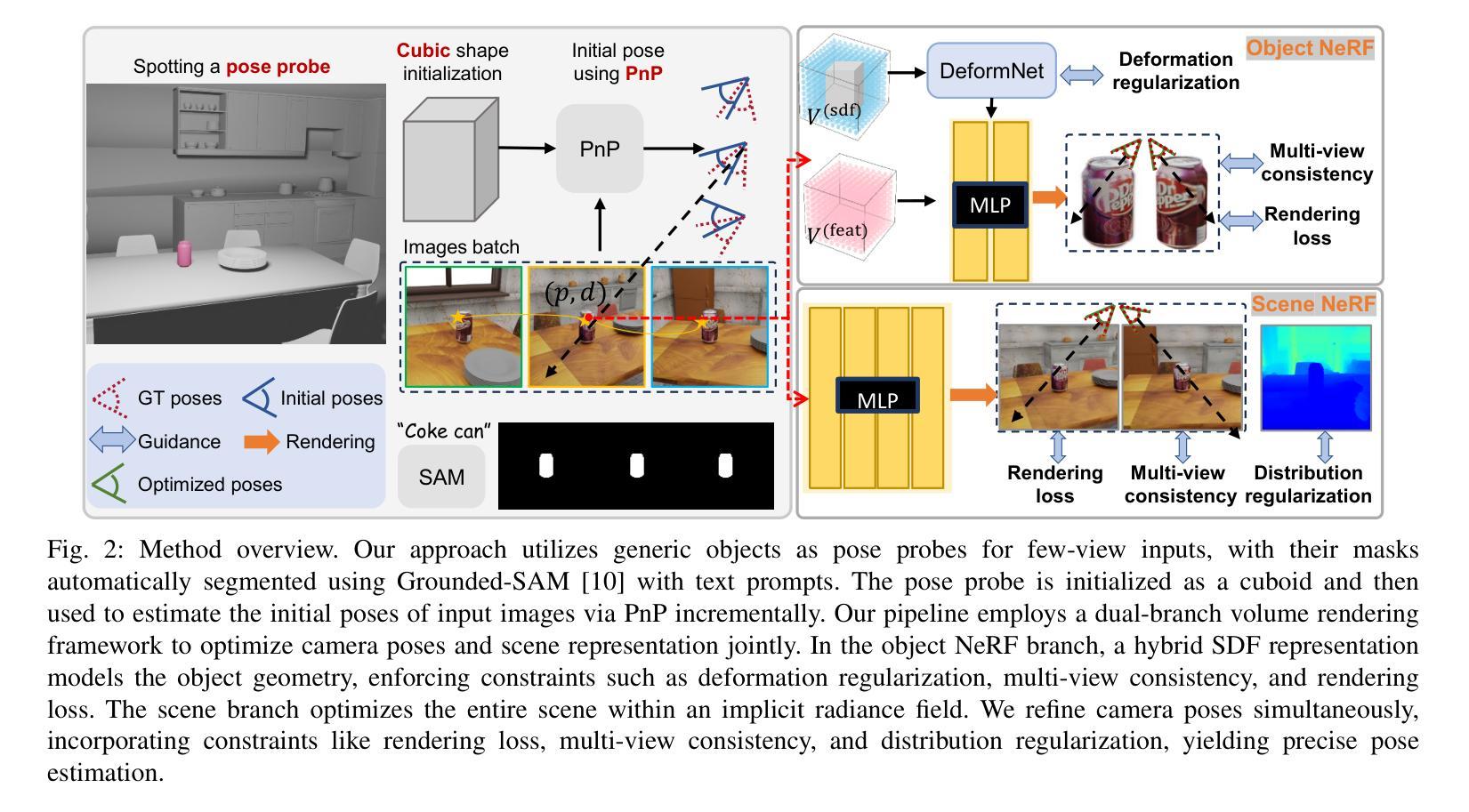
Generic Objects as Pose Probes for Few-shot View Synthesis
Authors:Zhirui Gao, Renjiao Yi, Chenyang Zhu, Ke Zhuang, Wei Chen, Kai Xu
Radiance fields including NeRFs and 3D Gaussians demonstrate great potential in high-fidelity rendering and scene reconstruction, while they require a substantial number of posed images as inputs. COLMAP is frequently employed for preprocessing to estimate poses, while it necessitates a large number of feature matches to operate effectively, and it struggles with scenes characterized by sparse features, large baselines between images, or a limited number of input images. We aim to tackle few-view NeRF reconstruction using only 3 to 6 unposed scene images. Traditional methods often use calibration boards but they are not common in images. We propose a novel idea of utilizing everyday objects, commonly found in both images and real life, as “pose probes”. The probe object is automatically segmented by SAM, whose shape is initialized from a cube. We apply a dual-branch volume rendering optimization (object NeRF and scene NeRF) to constrain the pose optimization and jointly refine the geometry. Specifically, object poses of two views are first estimated by PnP matching in an SDF representation, which serves as initial poses. PnP matching, requiring only a few features, is suitable for feature-sparse scenes. Additional views are incrementally incorporated to refine poses from preceding views. In experiments, PoseProbe achieves state-of-the-art performance in both pose estimation and novel view synthesis across multiple datasets. We demonstrate its effectiveness, particularly in few-view and large-baseline scenes where COLMAP struggles. In ablations, using different objects in a scene yields comparable performance. Our project page is available at: \href{https://zhirui-gao.github.io/PoseProbe.github.io/}{this https URL}
辐射场,包括NeRF和3D高斯分布,在高保真渲染和场景重建方面表现出巨大潜力,但它们需要大量的姿态图像作为输入。COLMAP常用于预处理以估计姿态,但需要大量特征匹配才能有效运行,对于特征稀疏、图像间基线大或输入图像数量有限的场景,它表现困难。我们的目标是解决仅使用3到6张未定位的场景图像进行少视角NeRF重建的问题。传统方法常使用标定板,但在图像中并不常见。我们提出了一种利用在图像和现实生活中都常见的日常对象作为“姿态探针”的新思路。探针对象通过SAM自动分割,其形状初始化为立方体。我们采用双分支体积渲染优化(对象NeRF和场景NeRF)来约束姿态优化并共同优化几何结构。具体来说,首先通过PnP匹配在SDF表示中估计两个视角的物体姿态,作为初始姿态。PnP匹配仅需要几个特征,适用于特征稀疏的场景。然后逐步加入额外的视角,以细化先前视角的姿态。在实验方面,PoseProbe在多数据集上实现了姿态估计和新型视图合成的最先进的性能。我们证明了其在少视角和大基线场景中的有效性,在这些场景中COLMAP表现困难。在消融实验中,使用场景中的不同对象可以获得相当的性能。我们的项目页面位于:点击此处的https链接。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE TCSVT 2025 Project page: https://zhirui-gao.github.io/PoseProbe.github.io/
Summary
本文介绍了PoseProbe项目在NeRF重建方面的创新应用。针对需要大量定位图像作为输入的辐射场(如NeRF和3D高斯)在高保真渲染和场景重建方面的潜力,项目提出了一种利用常见物体作为“姿态探针”的新方法,旨在解决仅使用少量未定位场景图像进行NeRF重建的问题。通过自动分割探针对象、双分支体积渲染优化和姿态优化约束,PoseProbe在多个数据集上实现了姿态估计和新颖视图合成的最佳性能,特别是在特征稀疏、大基线间隔或输入图像数量有限的场景中效果显著。
Key Takeaways
- PoseProbe项目针对NeRF重建中的少视角问题提出了创新解决方案。
- 利用常见物体作为“姿态探针”,仅需要3到6个未定位的场景图像。
- 项目采用自动分割探针对象,初始形状设定为立方体。
- 通过双分支体积渲染优化(对象NeRF和场景NeRF)来约束姿态优化并共同改进几何结构。
- 采用PnP匹配进行姿态估计,适用于特征稀疏场景,并可以逐步加入更多视角以优化姿态。
- PoseProbe在多个数据集上实现了姿态估计和新颖视图合成的最佳性能。
点此查看论文截图


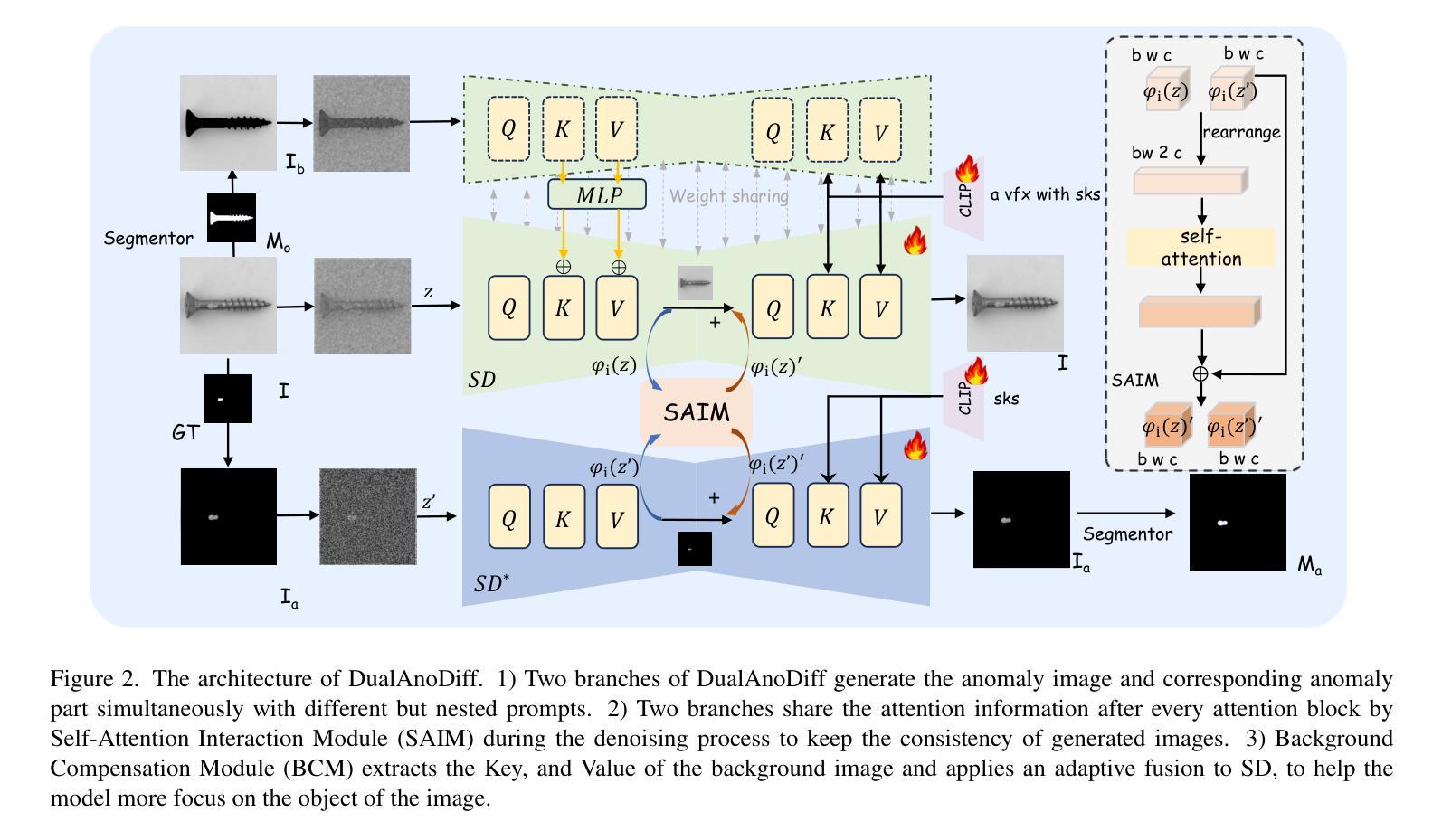
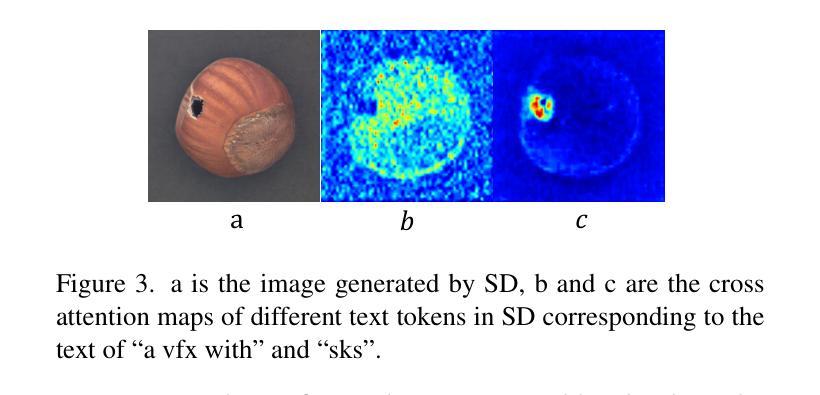
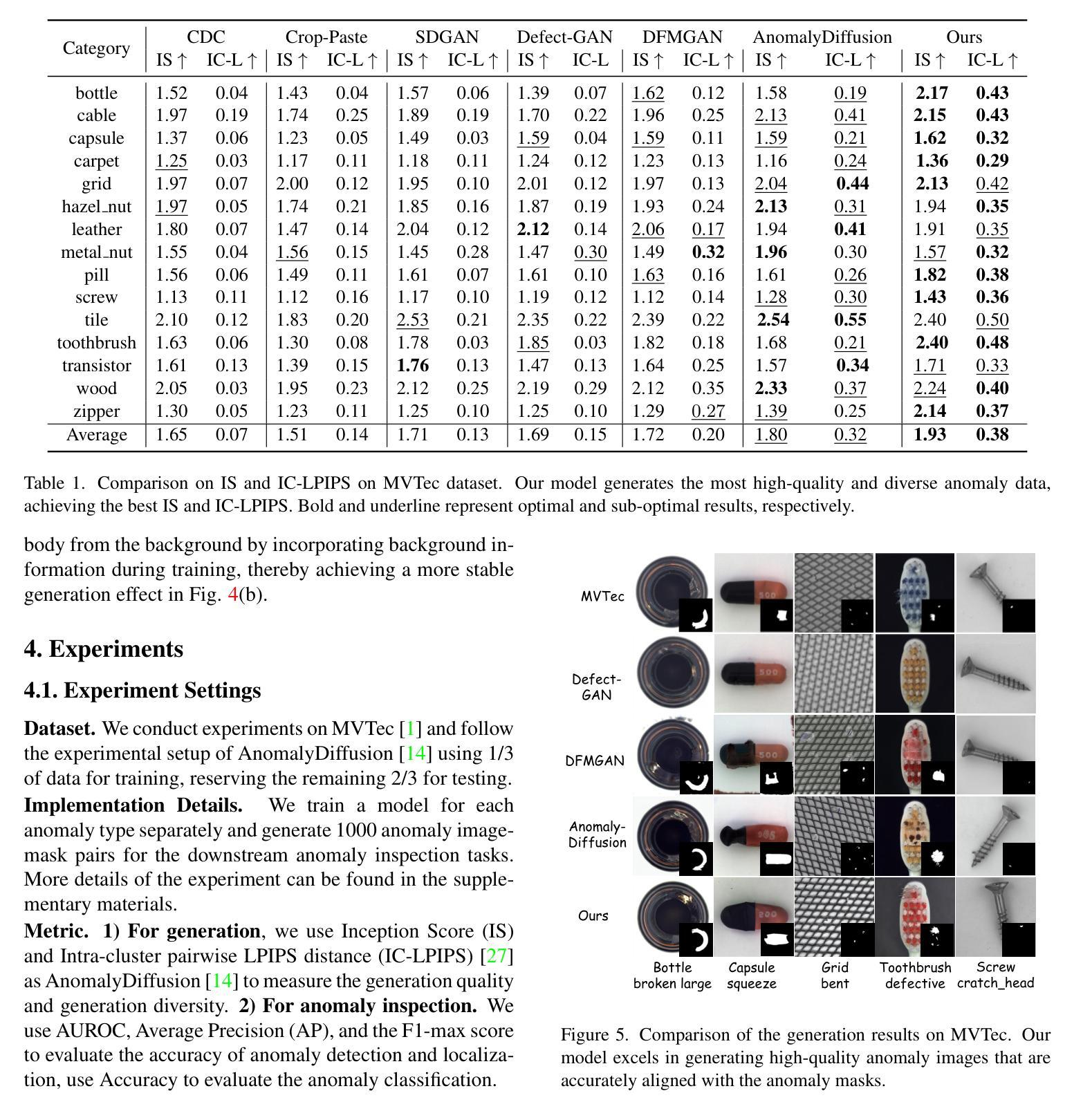
Dual-Interrelated Diffusion Model for Few-Shot Anomaly Image Generation
Authors:Ying Jin, Jinlong Peng, Qingdong He, Teng Hu, Jiafu Wu, Hao Chen, Haoxuan Wang, Wenbing Zhu, Mingmin Chi, Jun Liu, Yabiao Wang
The performance of anomaly inspection in industrial manufacturing is constrained by the scarcity of anomaly data. To overcome this challenge, researchers have started employing anomaly generation approaches to augment the anomaly dataset. However, existing anomaly generation methods suffer from limited diversity in the generated anomalies and struggle to achieve a seamless blending of this anomaly with the original image. Moreover, the generated mask is usually not aligned with the generated anomaly. In this paper, we overcome these challenges from a new perspective, simultaneously generating a pair of the overall image and the corresponding anomaly part. We propose DualAnoDiff, a novel diffusion-based few-shot anomaly image generation model, which can generate diverse and realistic anomaly images by using a dual-interrelated diffusion model, where one of them is employed to generate the whole image while the other one generates the anomaly part. Moreover, we extract background and shape information to mitigate the distortion and blurriness phenomenon in few-shot image generation. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of our proposed model over state-of-the-art methods in terms of diversity, realism and the accuracy of mask. Overall, our approach significantly improves the performance of downstream anomaly inspection tasks, including anomaly detection, anomaly localization, and anomaly classification tasks.
在工业制造中的异常检测性能受到异常数据稀缺的限制。为了克服这一挑战,研究者们已经开始采用异常生成方法来增加异常数据集。然而,现有的异常生成方法存在生成异常多样性有限的问题,并且难以实现生成异常与原始图像的无缝融合。此外,生成的掩膜通常与生成的异常不匹配。在本文中,我们从一个新的角度克服了这些挑战,同时生成整体图像和相应的异常部分。我们提出了DualAnoDiff,这是一种基于扩散的新型少样本异常图像生成模型,通过使用双相关扩散模型,其中一个用于生成整体图像,另一个用于生成异常部分,可以生成多样且逼真的异常图像。此外,我们提取背景和形状信息,以减轻少样本图像生成中的失真和模糊现象。大量实验表明,与最新方法相比,我们提出的模型在多样性、逼真程度和掩膜准确性方面更具优势。总体而言,我们的方法显著提高了下游异常检测任务的性能,包括异常检测、异常定位和异常分类任务。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025
Summary
工业制造中的异常检测性能受限于异常数据的稀缺性。为应对这一挑战,研究者开始采用异常生成方法来扩充异常数据集。然而,现有方法的异常生成多样性有限,且难以将生成的异常无缝融合到原始图像中。此外,生成的掩膜通常与生成的异常不匹配。本文从一个新视角解决这些挑战,同时生成整体图像和相应的异常部分。提出DualAnoDiff,一种基于扩散的少样本异常图像生成模型,通过使用相互关联的扩散模型生成多样且逼真的异常图像,其中一个用于生成整体图像,另一个用于生成异常部分。此外,提取背景和形状信息以减轻少样本图像生成中的失真和模糊现象。实验表明,与最先进的方法相比,所提出的模型在多样性、逼真度和掩膜准确性方面表现优越。总体而言,我们的方法显著提高了下游异常检测任务(包括异常检测、异常定位和异常分类任务)的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 异常检测在工业制造中面临挑战,主要由于异常数据的稀缺性。
- 现有异常生成方法存在局限性,如缺乏多样性、难以无缝融合到原始图像中以及掩膜与生成的异常不匹配的问题。
- 本文提出一种基于扩散的少样本异常图像生成模型DualAnoDiff,同时生成整体图像和对应的异常部分。
- DualAnoDiff模型通过使用相互关联的扩散模型来提高生成的异常图像的多样性和逼真度。
- 该模型通过提取背景和形状信息来减轻少样本图像生成中的失真和模糊现象。
- 实验表明,DualAnoDiff模型在多样性、逼真度和掩膜准确性方面优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图