⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-01 更新
Generate more than one child in your co-evolutionary semi-supervised learning GAN
Authors:Francisco Sedeño, Jamal Toutouh, Francisco Chicano
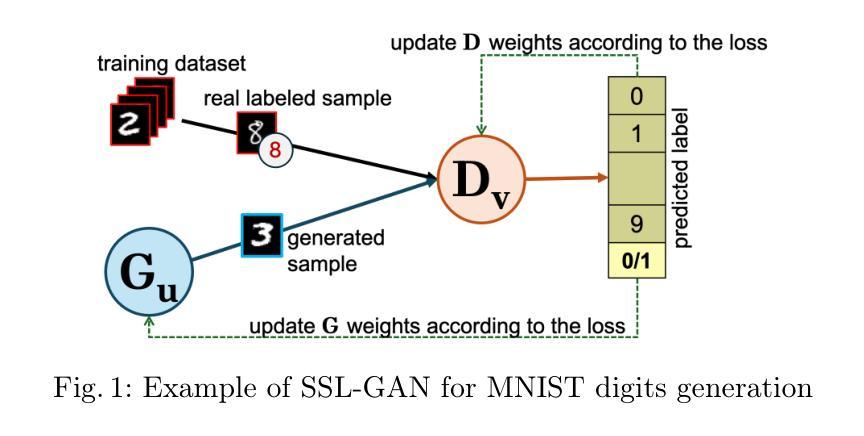
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are very useful methods to address semi-supervised learning (SSL) datasets, thanks to their ability to generate samples similar to real data. This approach, called SSL-GAN has attracted many researchers in the last decade. Evolutionary algorithms have been used to guide the evolution and training of SSL-GANs with great success. In particular, several co-evolutionary approaches have been applied where the two networks of a GAN (the generator and the discriminator) are evolved in separate populations. The co-evolutionary approaches published to date assume some spatial structure of the populations, based on the ideas of cellular evolutionary algorithms. They also create one single individual per generation and follow a generational replacement strategy in the evolution. In this paper, we re-consider those algorithmic design decisions and propose a new co-evolutionary approach, called Co-evolutionary Elitist SSL-GAN (CE-SSLGAN), with panmictic population, elitist replacement, and more than one individual in the offspring. We evaluate the performance of our proposed method using three standard benchmark datasets. The results show that creating more than one offspring per population and using elitism improves the results in comparison with a classical SSL-GAN.
生成对抗网络(GANs)对于处理半监督学习(SSL)数据集是非常有用的方法,它们能够生成与真实数据相似的样本。这种被称为SSL-GAN的方法在过去十年中吸引了许多研究者。进化算法已成功用于指导SSL-GAN的进化和培训。特别是,已经应用了几种协同进化方法,其中GAN的两个网络(生成器和鉴别器)在不同的群体中进化。迄今为止发布的协同进化方法假设群体具有一定的空间结构,基于细胞进化算法的思想。它们还创建每一代单一个体,并在进化中遵循世代更替策略。在本文中,我们重新考虑了这些算法设计决策,并提出了一种新的协同进化方法,称为协同精英SSL-GAN(CE-SSLGAN),具有泛混合种群、精英替代和后代中不止一个个体。我们使用三个标准基准数据集评估了我们提出的方法的性能。结果表明,每代创建多个后代并使用精英制度相比于经典SSL-GAN方法的结果有所改善。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to The Leading European Event on Bio-Inspired AI (EvoStar 2025)
Summary
基于生成对抗网络(GANs)的半监督学习(SSL)数据集方法因其生成类似真实数据的样本能力而受到关注。本文重新考虑算法设计决策,提出一种新的协同进化方法——Co-evolutionary Elitist SSL-GAN(CE-SSLGAN),采用泛配子种群、精英替代和后代中多个个体,使用三个标准基准数据集评估其性能。结果显示,与经典SSL-GAN相比,创建多个后代并使用精英主义有助于提高结果。
Key Takeaways
- 生成对抗网络(GANs)能有效处理半监督学习(SSL)数据集。
- 协同进化方法在训练SSL-GANs中取得了很大成功。
- 现有协同进化方法基于群体空间结构,采用单代单个体的进化策略。
- 本文提出了一种新的协同进化方法——Co-evolutionary Elitist SSL-GAN(CE-SSLGAN)。
- CE-SSLGAN采用泛配子种群、精英替代和后代中多个个体的策略。
- 在三个标准数据集上的评估显示,CE-SSLGAN较传统SSL-GAN有更佳的性能表现。
点此查看论文截图


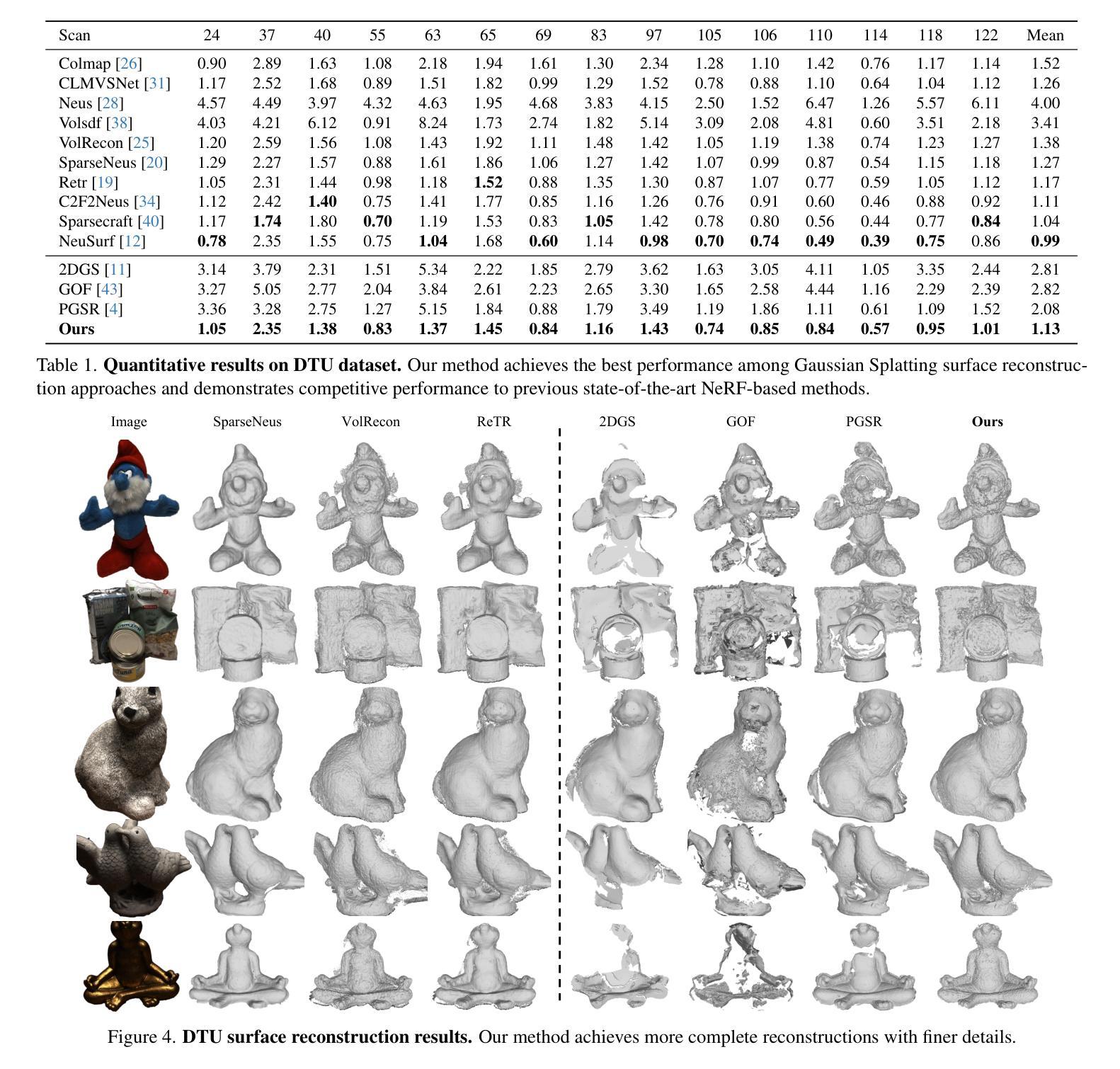
Sparse2DGS: Geometry-Prioritized Gaussian Splatting for Surface Reconstruction from Sparse Views
Authors:Jiang Wu, Rui Li, Yu Zhu, Rong Guo, Jinqiu Sun, Yanning Zhang
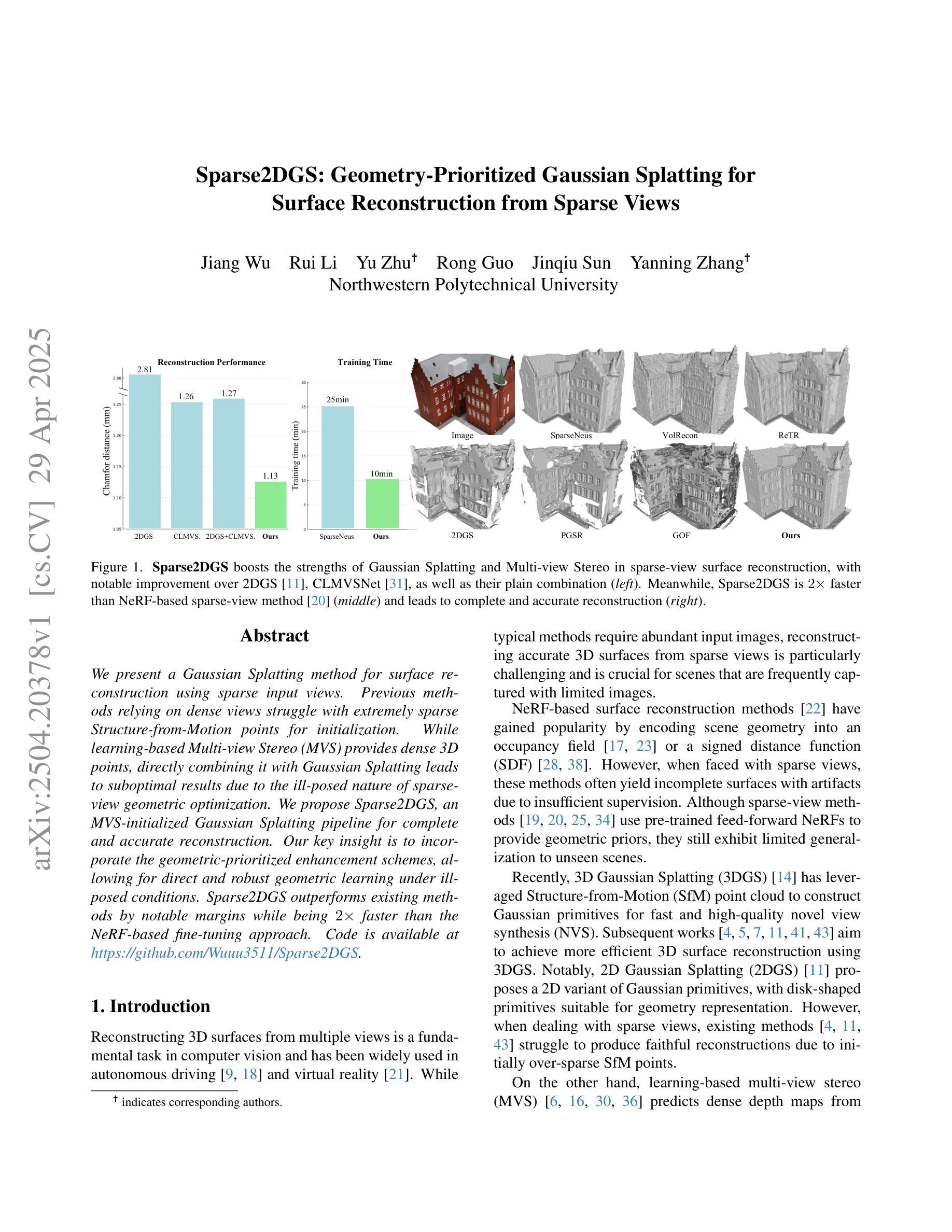
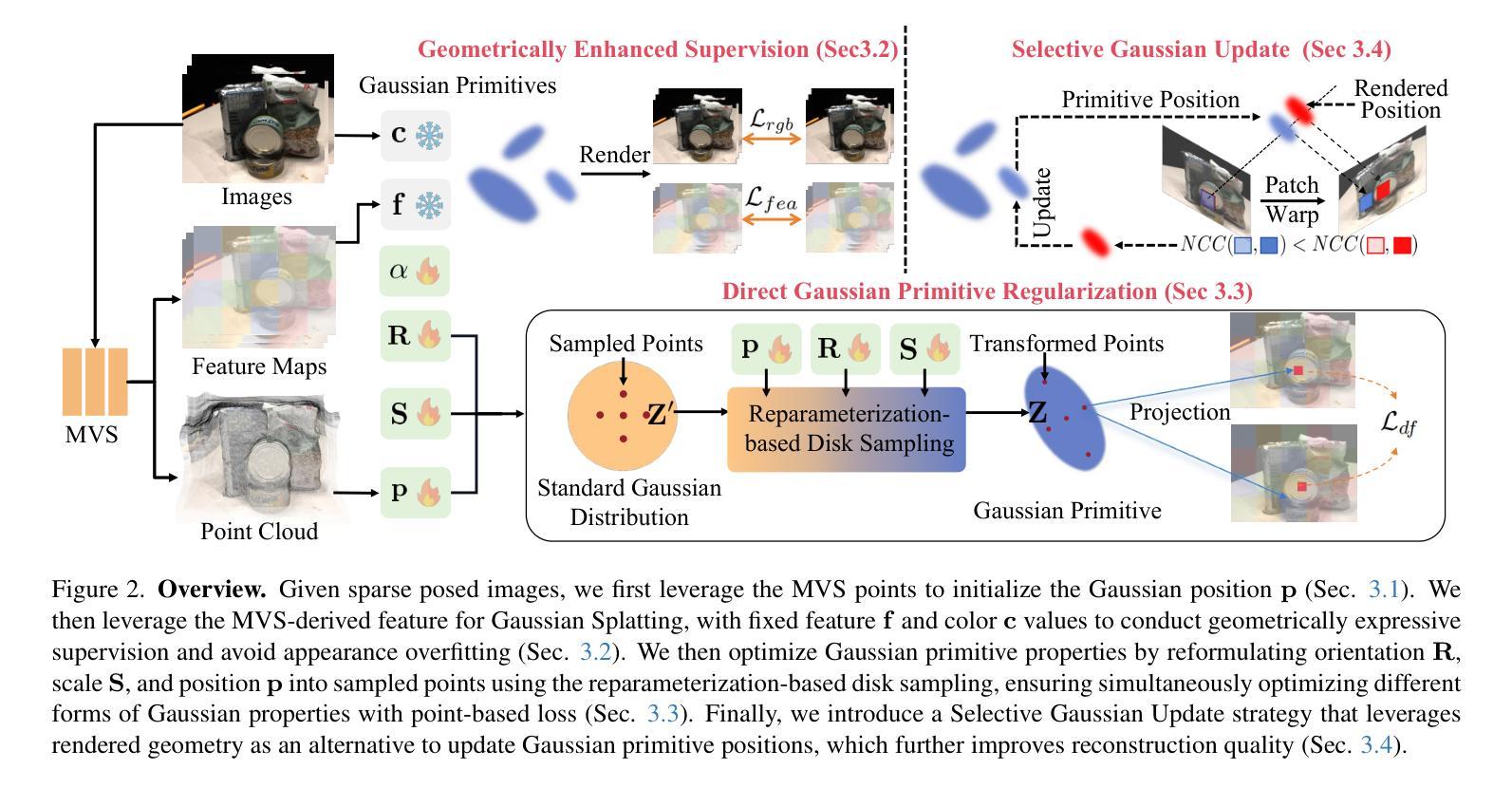
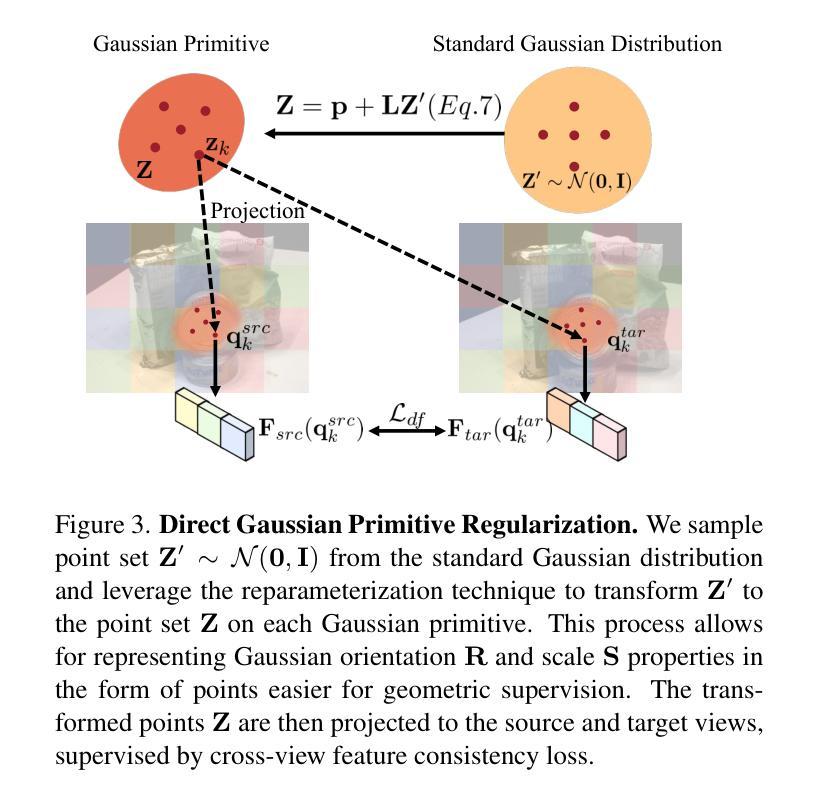
We present a Gaussian Splatting method for surface reconstruction using sparse input views. Previous methods relying on dense views struggle with extremely sparse Structure-from-Motion points for initialization. While learning-based Multi-view Stereo (MVS) provides dense 3D points, directly combining it with Gaussian Splatting leads to suboptimal results due to the ill-posed nature of sparse-view geometric optimization. We propose Sparse2DGS, an MVS-initialized Gaussian Splatting pipeline for complete and accurate reconstruction. Our key insight is to incorporate the geometric-prioritized enhancement schemes, allowing for direct and robust geometric learning under ill-posed conditions. Sparse2DGS outperforms existing methods by notable margins while being ${2}\times$ faster than the NeRF-based fine-tuning approach.
我们提出了一种基于高斯涂抹(Gaussian Splatting)的方法,用于利用稀疏输入视图进行表面重建。之前依赖密集视图的方法在利用极端稀疏的运动结构点进行初始化时会遇到困难。虽然基于学习的多视角立体(MVS)提供了密集的3D点,但直接将其与高斯涂抹相结合会导致次优结果,因为稀疏视图几何优化本质上是病态的。我们提出了Sparse2DGS,这是一种由MVS初始化的高斯涂抹管道,用于进行完整而准确的重建。我们的关键见解是融入以几何优先的增强方案,实现在病态条件下的直接和稳健的几何学习。Sparse2DGS显著优于现有方法,同时在运行速度上是基于NeRF的微调方法的两倍。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种基于高斯贴图的方法,利用稀疏输入视图进行表面重建。针对以往依赖密集视图的方法在面对极稀疏的Structure-from-Motion点时初始化困难的问题,提出了Sparse2DGS方法,它结合了MVS初始化的高斯贴图流程,实现了完整且准确的重建。关键洞察力在于融入了以几何优先的增强方案,使得在不适定条件下能够进行直接且稳健的几何学习。Sparse2DGS显著优于现有方法,并且比基于NeRF的微调方法快两倍。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了Sparse2DGS方法,用于在稀疏视图下实现表面重建。
- 该方法结合了MVS初始化的高斯贴图流程,解决了传统方法在面对稀疏结构运动点时的初始化困难问题。
- 关键洞察力在于融入几何优先的增强方案,以应对不适定条件下的几何学习。
- Sparse2DGS显著优于现有方法,并且在速度上也比基于NeRF的微调方法更快。
- 面临的问题是学习如何从稀疏视图中获取更准确的结构信息。
- 该方法能够完整且准确地重建物体表面。
点此查看论文截图
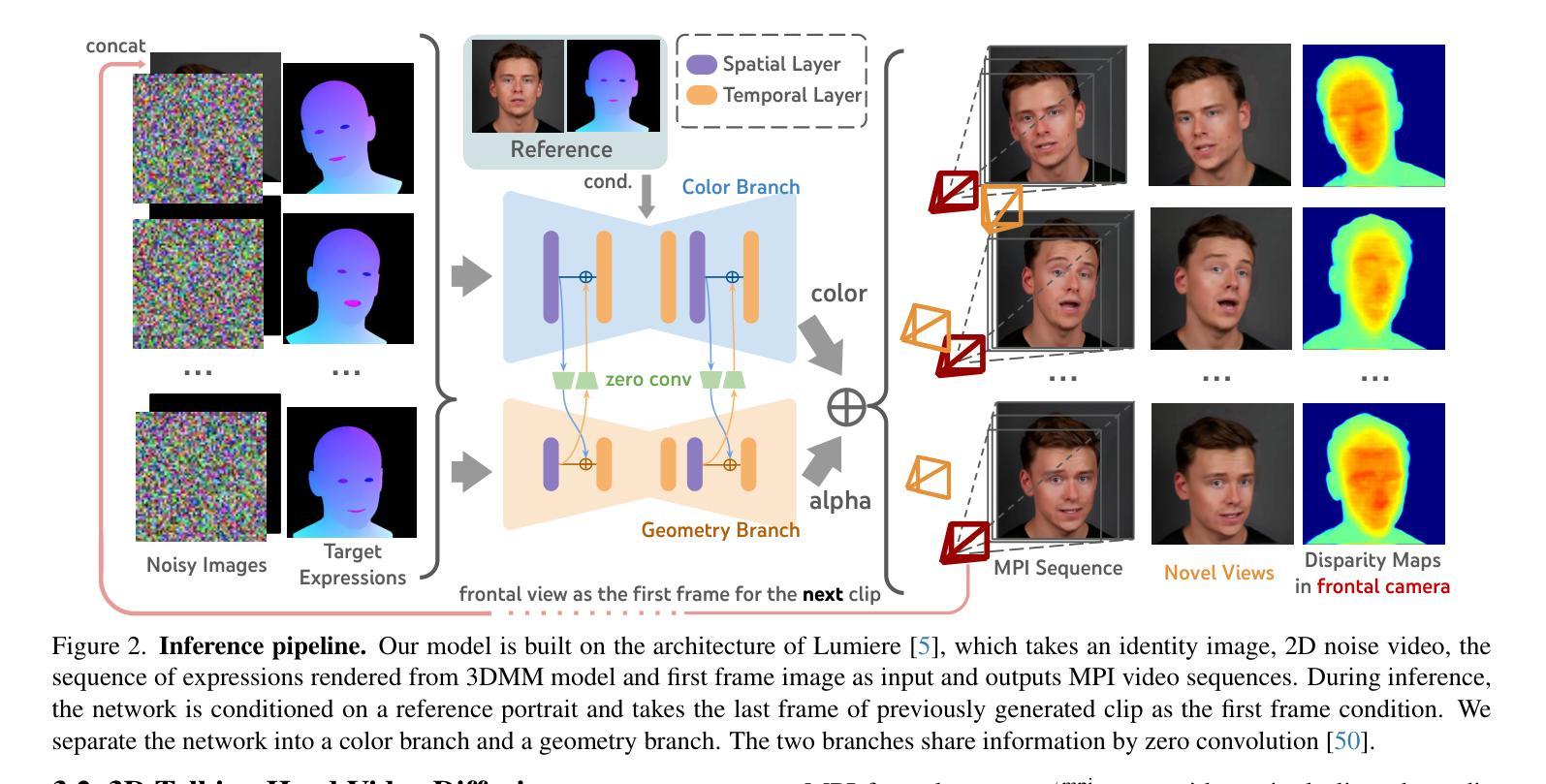
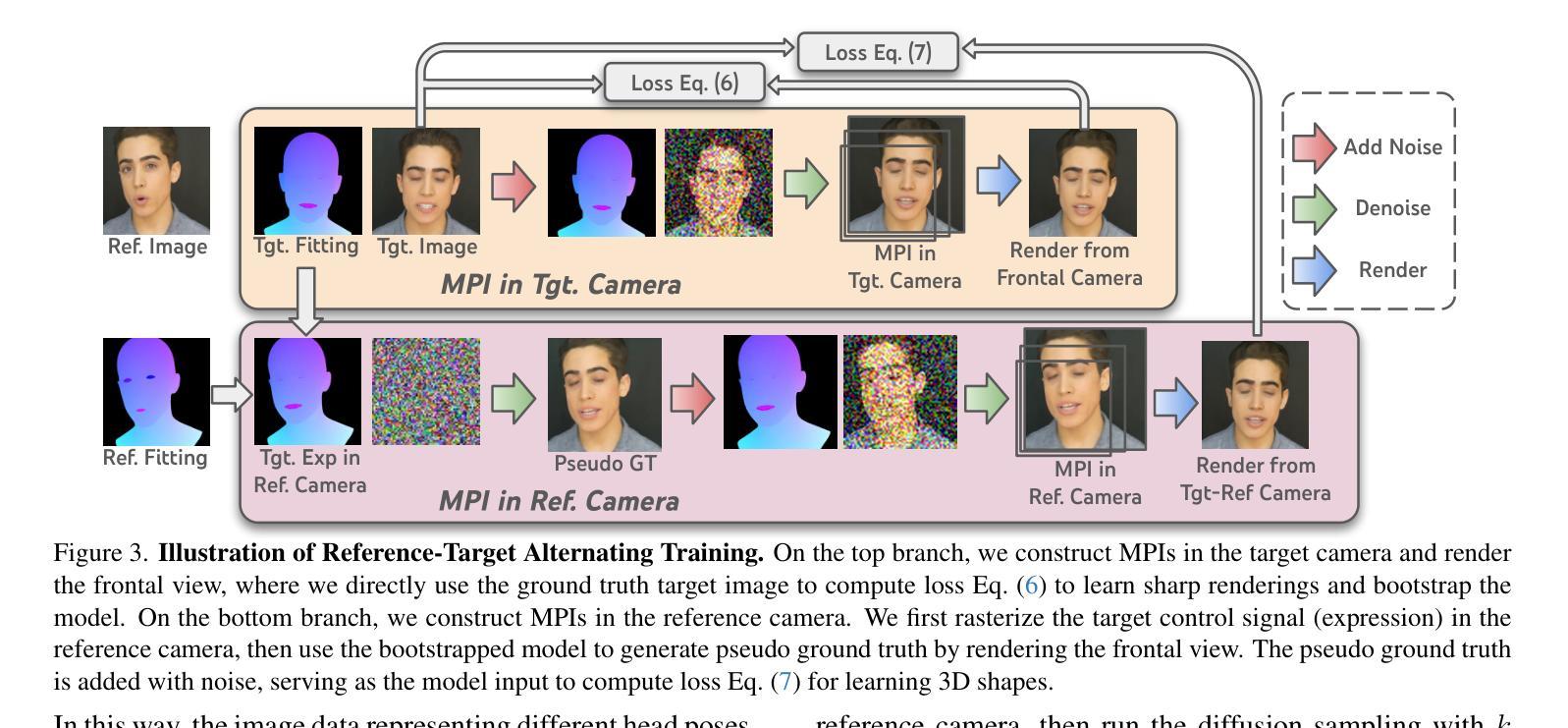
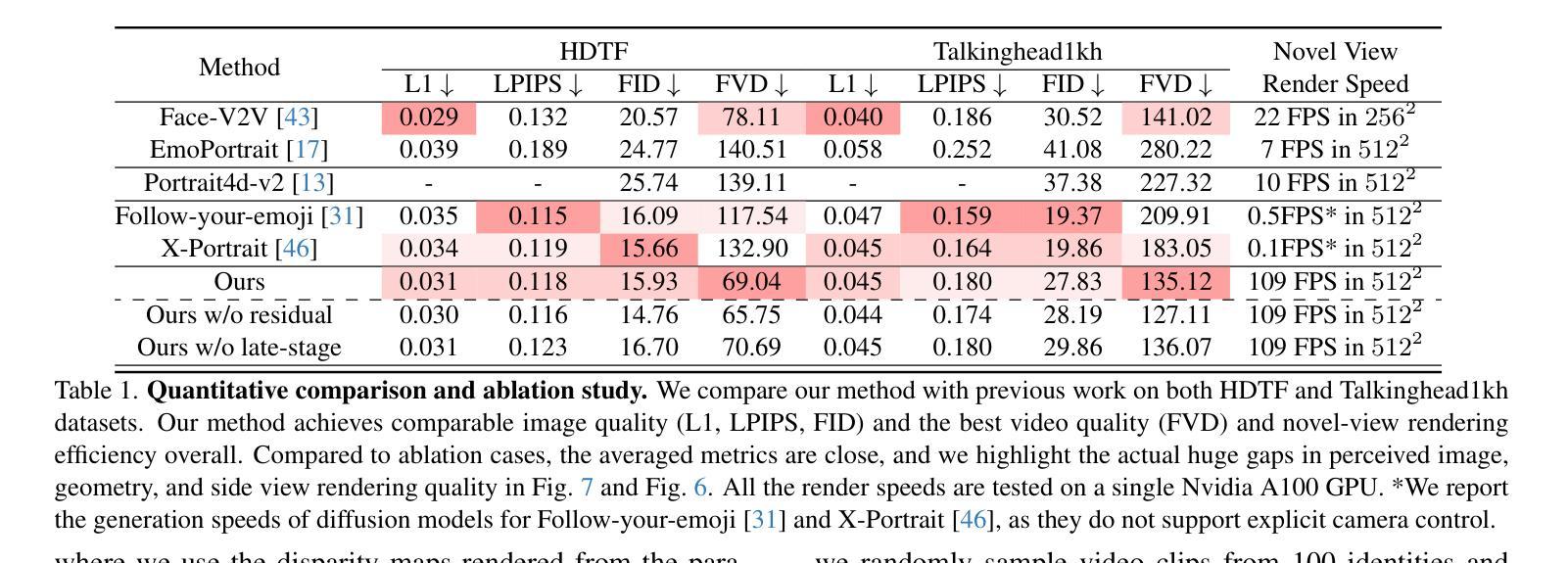
IM-Portrait: Learning 3D-aware Video Diffusion for Photorealistic Talking Heads from Monocular Videos
Authors:Yuan Li, Ziqian Bai, Feitong Tan, Zhaopeng Cui, Sean Fanello, Yinda Zhang
We propose a novel 3D-aware diffusion-based method for generating photorealistic talking head videos directly from a single identity image and explicit control signals (e.g., expressions). Our method generates Multiplane Images (MPIs) that ensure geometric consistency, making them ideal for immersive viewing experiences like binocular videos for VR headsets. Unlike existing methods that often require a separate stage or joint optimization to reconstruct a 3D representation (such as NeRF or 3D Gaussians), our approach directly generates the final output through a single denoising process, eliminating the need for post-processing steps to render novel views efficiently. To effectively learn from monocular videos, we introduce a training mechanism that reconstructs the output MPI randomly in either the target or the reference camera space. This approach enables the model to simultaneously learn sharp image details and underlying 3D information. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our method, which achieves competitive avatar quality and novel-view rendering capabilities, even without explicit 3D reconstruction or high-quality multi-view training data.
我们提出了一种新颖的基于三维感知扩散的方法,该方法可直接从单个身份图像和明确的控制信号(如表情)生成逼真的说话头部视频。我们的方法生成多平面图像(MPIs),确保几何一致性,使其成为适合沉浸式观看体验的理想选择,例如VR头盔的双眼视频。与通常需要单独阶段或联合优化来重建三维表示(如NeRF或3D高斯)的现有方法不同,我们的方法通过单个去噪过程直接生成最终输出,无需后处理步骤即可有效地呈现全新视角。为了有效地从单目视频中学习,我们引入了一种训练机制,该机制会随机重建目标或参考相机空间中的输出MPI。这种方法使模型能够同时学习尖锐的图像细节和潜在的三维信息。大量实验证明了我们方法的有效性,即使在不需要明确的三维重建或高质量的多视角训练数据的情况下,我们也能达到有竞争力的角色质量并提供全新的视图渲染能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR2025; project page: https://y-u-a-n-l-i.github.io/projects/IM-Portrait/
Summary
本文提出了一种基于三维感知扩散的方法,用于直接从单一身份图像和明确的控制信号(如表情)生成逼真的动态视频图像。该方法生成多平面图像(MPIs),确保几何一致性,适用于虚拟现实头戴设备的沉浸式观看体验。与传统方法不同,我们的方法通过一个去噪过程直接生成最终输出,无需进行复杂的重建步骤。通过引入一种随机重建输出MPI的训练机制,模型能够在目标相机空间或参考相机空间中学习清晰图像细节和底层三维信息,从而有效地从单目视频中学习。实验证明,该方法在无需明确的三维重建或多视角高质量训练数据的情况下,仍具有良好的效果。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种新的基于三维感知扩散的方法,直接从单一身份图像和控制信号生成逼真动态视频图像。
- 通过生成多平面图像(MPIs)确保几何一致性,适合虚拟现实等沉浸式观看体验。
- 与传统方法不同,通过一个去噪过程直接生成最终输出,无需复杂重建步骤。
- 引入了一种随机重建输出MPI的训练机制,能同时学习清晰图像细节和底层三维信息。
- 模型可从单目视频中学习,无需复杂的多视角训练数据。
- 实验证明该方法具有良好的效果,在虚拟形象渲染和新颖视角呈现方面具有竞争力。
点此查看论文截图

Generic Objects as Pose Probes for Few-shot View Synthesis
Authors:Zhirui Gao, Renjiao Yi, Chenyang Zhu, Ke Zhuang, Wei Chen, Kai Xu
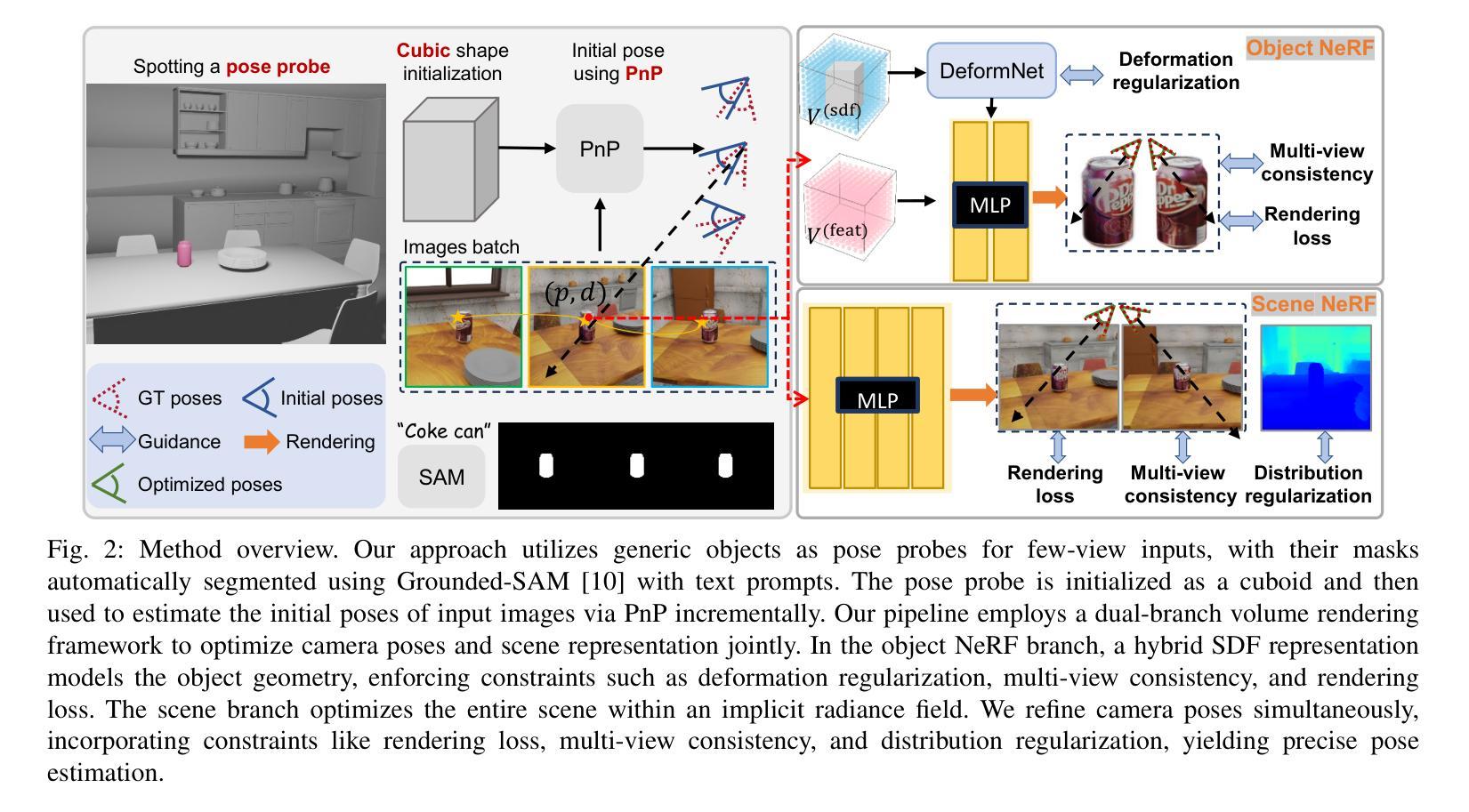
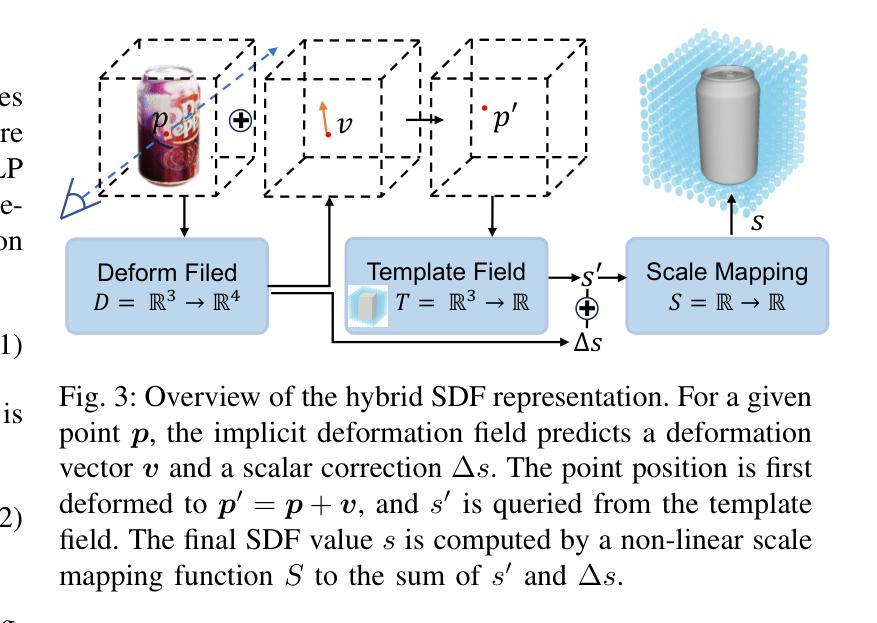
Radiance fields including NeRFs and 3D Gaussians demonstrate great potential in high-fidelity rendering and scene reconstruction, while they require a substantial number of posed images as inputs. COLMAP is frequently employed for preprocessing to estimate poses, while it necessitates a large number of feature matches to operate effectively, and it struggles with scenes characterized by sparse features, large baselines between images, or a limited number of input images. We aim to tackle few-view NeRF reconstruction using only 3 to 6 unposed scene images. Traditional methods often use calibration boards but they are not common in images. We propose a novel idea of utilizing everyday objects, commonly found in both images and real life, as “pose probes”. The probe object is automatically segmented by SAM, whose shape is initialized from a cube. We apply a dual-branch volume rendering optimization (object NeRF and scene NeRF) to constrain the pose optimization and jointly refine the geometry. Specifically, object poses of two views are first estimated by PnP matching in an SDF representation, which serves as initial poses. PnP matching, requiring only a few features, is suitable for feature-sparse scenes. Additional views are incrementally incorporated to refine poses from preceding views. In experiments, PoseProbe achieves state-of-the-art performance in both pose estimation and novel view synthesis across multiple datasets. We demonstrate its effectiveness, particularly in few-view and large-baseline scenes where COLMAP struggles. In ablations, using different objects in a scene yields comparable performance. Our project page is available at: \href{https://zhirui-gao.github.io/PoseProbe.github.io/}{this https URL}
辐射场,包括NeRF和3D高斯,在高保真渲染和场景重建方面表现出巨大的潜力,但它们需要大量的定位图像作为输入。COLMAP经常用于预处理以估计姿态,但它需要大量的特征匹配才能有效运行,对于特征稀疏、图像间基线较大或输入图像数量有限的场景,它表现得较为困难。我们的目标是解决仅使用3到6张未定位的场景图像进行少量视图NeRF重建的问题。传统方法通常使用校准板,但它们在图像中并不常见。我们提出了一种利用在日常生活和图像中都常见的物体作为“姿态探针”的新颖想法。探针物体通过SAM自动分割,其形状从立方体初始化。我们采用双分支体积渲染优化(对象NeRF和场景NeRF)来约束姿态优化并共同优化几何结构。具体来说,首先通过PnP匹配估计两个视图的对象姿态,以SDF表示形式作为初始姿态。PnP匹配仅需要几个特征,适用于特征稀疏的场景。额外的视图会逐步融入,以前面的视图为基础优化姿态。在实验中,PoseProbe在多个数据集上的姿态估计和新视角合成方面都达到了最新水平的表现。我们证明了它的有效性,特别是在少量视图和大基线场景中,COLMAP表现困难的地方。在实验中,使用场景中的不同对象可以获得相当的性能。我们的项目页面可在以下网址找到:此HTTPS网址。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE TCSVT 2025 Project page: https://zhirui-gao.github.io/PoseProbe.github.io/
摘要
基于NeRF与日常物品的pose探测方法用于少视角场景重建。通过利用日常物品作为“pose探针”,结合SAM自动分割技术和双分支体积渲染优化,实现了少至三到六张未定位场景图像的高效重建。PoseProbe方法在多个数据集上实现了姿态估计和新颖视角合成的最佳性能,尤其在少视角和大基线场景中表现优异。项目页面已在线发布。
关键见解
- 利用NeRF与三维高斯分布的辐射场实现高保真渲染与场景重建潜力巨大,但需要大量的定位图像作为输入。
- COLMAP预处理用于估计姿态,但需大量特征匹配,且在特征稀疏场景、大基线间距或输入图像数量有限的情况下效果受限。
- 提出利用日常物品作为“pose探针”进行姿态估计的新思路,适用于仅使用少量未定位场景图像的场景重建。
- 使用SAM自动分割技术初始化探针对象的形状为立方体。
- 采用双分支体积渲染优化(对象NeRF和场景NeRF)来约束姿态优化并联合改进几何结构。
- 通过PnP匹配在SDF表示中估计两个视角的对象姿态作为初始姿态,适用于特征稀疏场景。
点此查看论文截图