⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-02 更新
A simple and effective approach for body part recognition on CT scans based on projection estimation
Authors:Franko Hrzic, Mohammadreza Movahhedi, Ophelie Lavoie-Gagne, Ata Kiapour
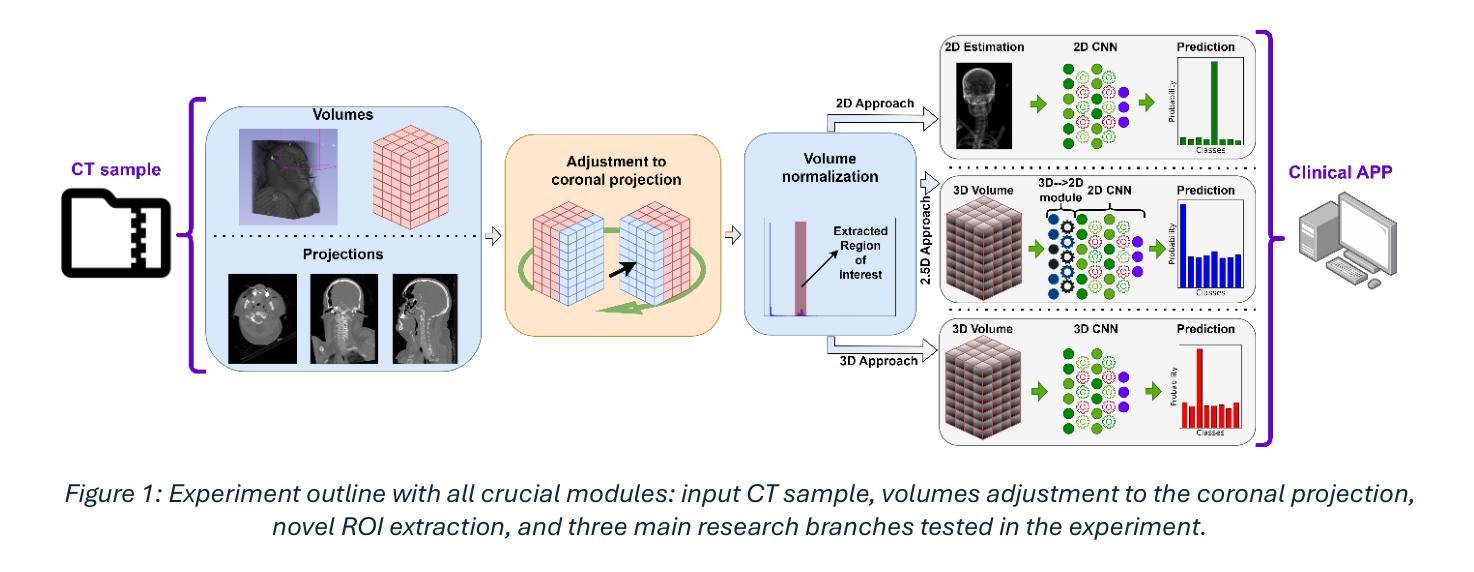
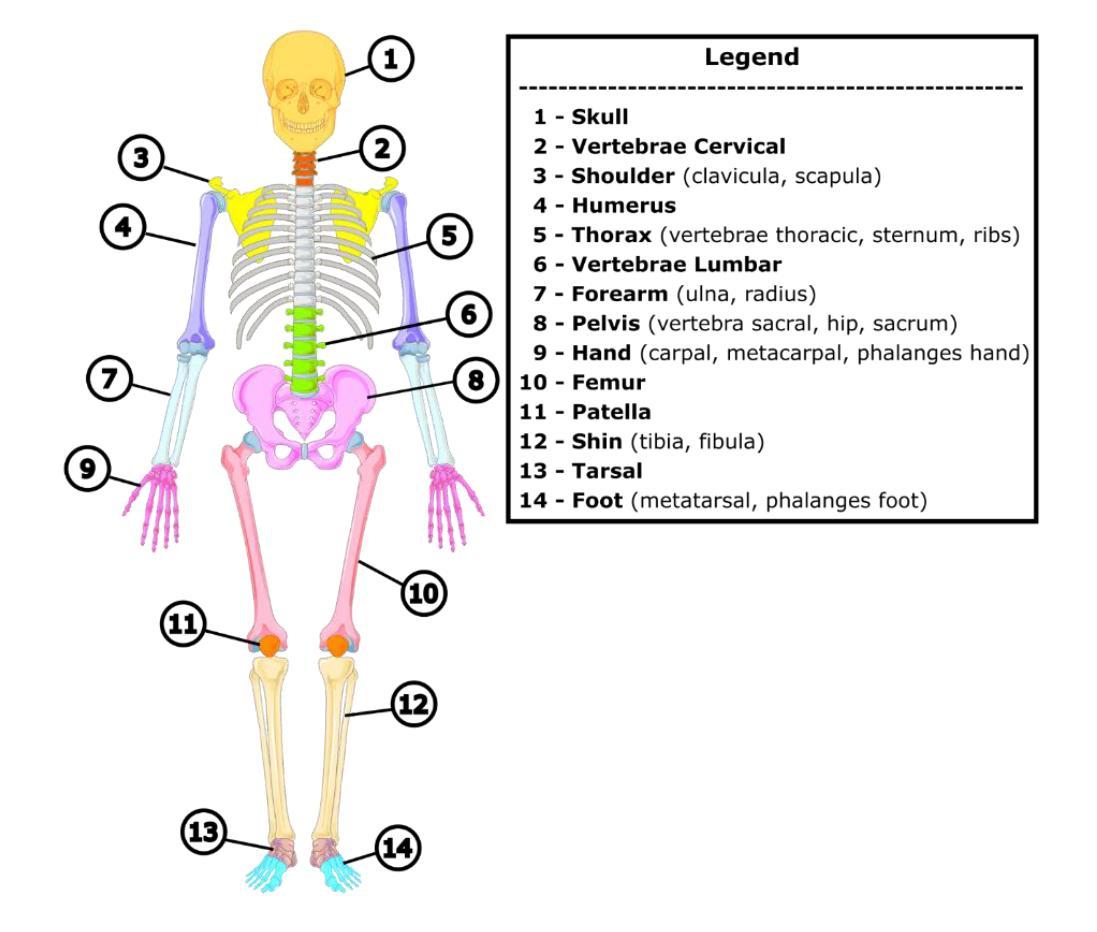
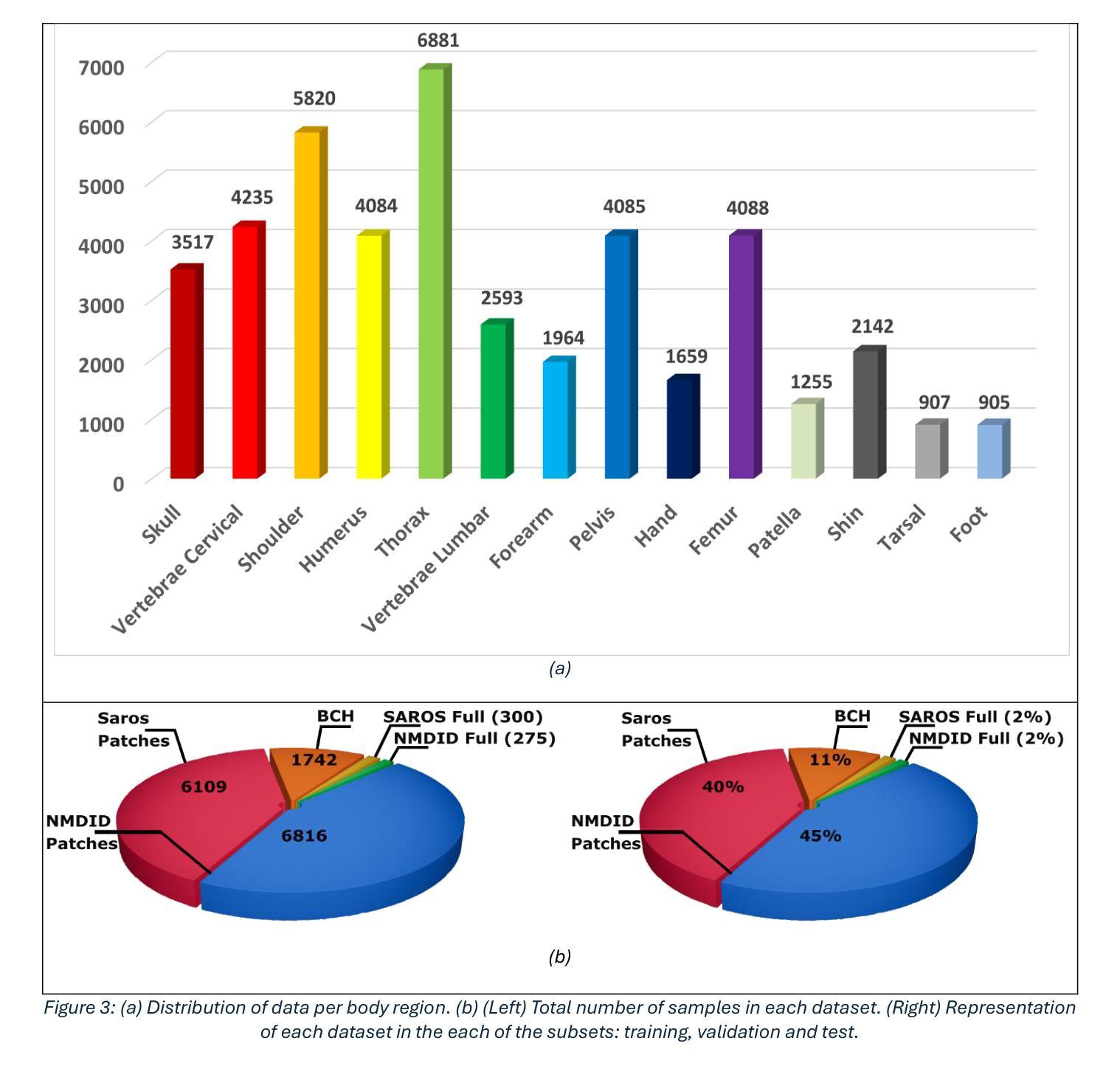
It is well known that machine learning models require a high amount of annotated data to obtain optimal performance. Labelling Computed Tomography (CT) data can be a particularly challenging task due to its volumetric nature and often missing and$/$or incomplete associated meta-data. Even inspecting one CT scan requires additional computer software, or in the case of programming languages $-$ additional programming libraries. This study proposes a simple, yet effective approach based on 2D X-ray-like estimation of 3D CT scans for body region identification. Although body region is commonly associated with the CT scan, it often describes only the focused major body region neglecting other anatomical regions present in the observed CT. In the proposed approach, estimated 2D images were utilized to identify 14 distinct body regions, providing valuable information for constructing a high-quality medical dataset. To evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed method, it was compared against 2.5D, 3D and foundation model (MI2) based approaches. Our approach outperformed the others, where it came on top with statistical significance and F1-Score for the best-performing model EffNet-B0 of 0.980 $\pm$ 0.016 in comparison to the 0.840 $\pm$ 0.114 (2.5D DenseNet-161), 0.854 $\pm$ 0.096 (3D VoxCNN), and 0.852 $\pm$ 0.104 (MI2 foundation model). The utilized dataset comprised three different clinical centers and counted 15,622 CT scans (44,135 labels).
众所周知,机器学习模型需要大量的标注数据才能获得最佳性能。由于计算机断层扫描(CT)数据的体积性质以及经常缺失和/或不完整的关联元数据,对CT数据进行标注可能是一项特别具有挑战性的任务。即使检查一次CT扫描也需要额外的计算机软件,或者在编程语言的情况下需要额外的编程库。本研究提出了一种简单而有效的方法,基于基于体三维CT扫描的二维X射线式估计进行身体部位识别。虽然身体部位通常与CT扫描相关联,但它通常仅描述关注的主体部位,而忽略了观察到的CT中存在的其他解剖部位。在提出的方法中,估计的二维图像被用来识别出不同的14个身体部位,为构建高质量医学数据集提供了有价值的信息。为了评估所提出方法的有效性,它与基于2.5D、3D和基础模型(MI2)的方法进行了比较。我们的方法优于其他方法,在统计显著性和最佳性能模型EffNet-B0的F1分数方面位居榜首,达到了0.980±0.016,相比之下,其他模型分别为:2.5D DenseNet-161的0.840±0.114、3D VoxCNN的0.854±0.096以及MI2基础模型的0.852±0.104。所使用的数据集包含三个不同的临床中心,共有CT扫描图像共15,622张(标签数量为44,135个)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, 6 figures
Summary
点此查看论文截图
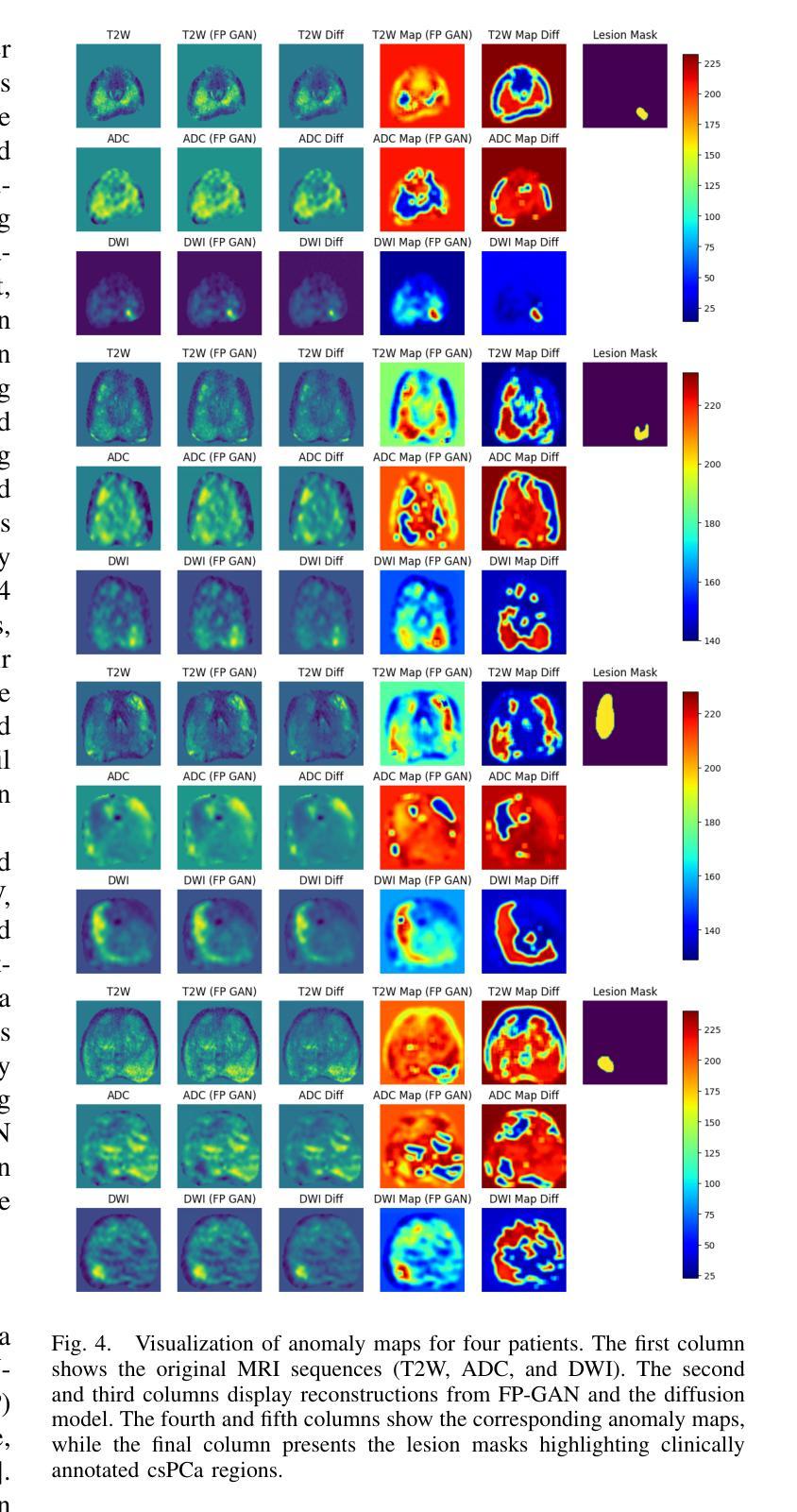
Anomaly-Driven Approach for Enhanced Prostate Cancer Segmentation
Authors:Alessia Hu, Regina Beets-Tan, Lishan Cai, Eduardo Pooch
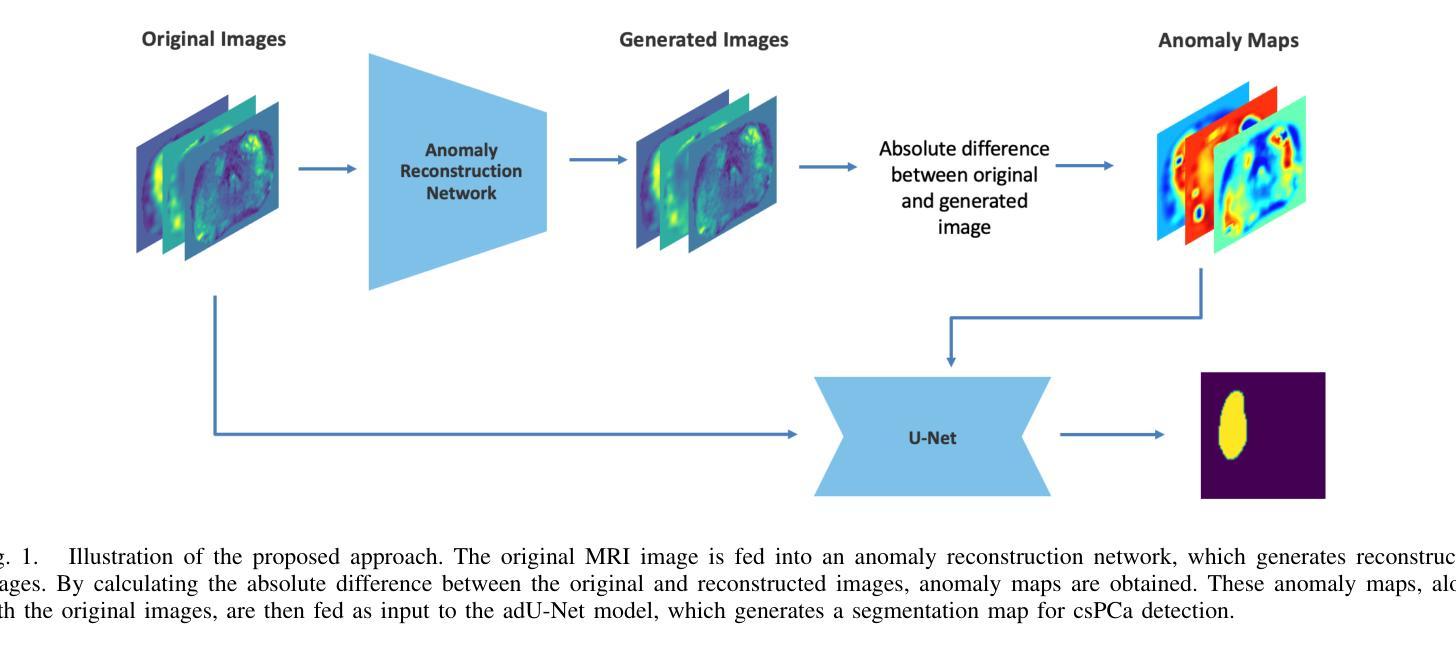
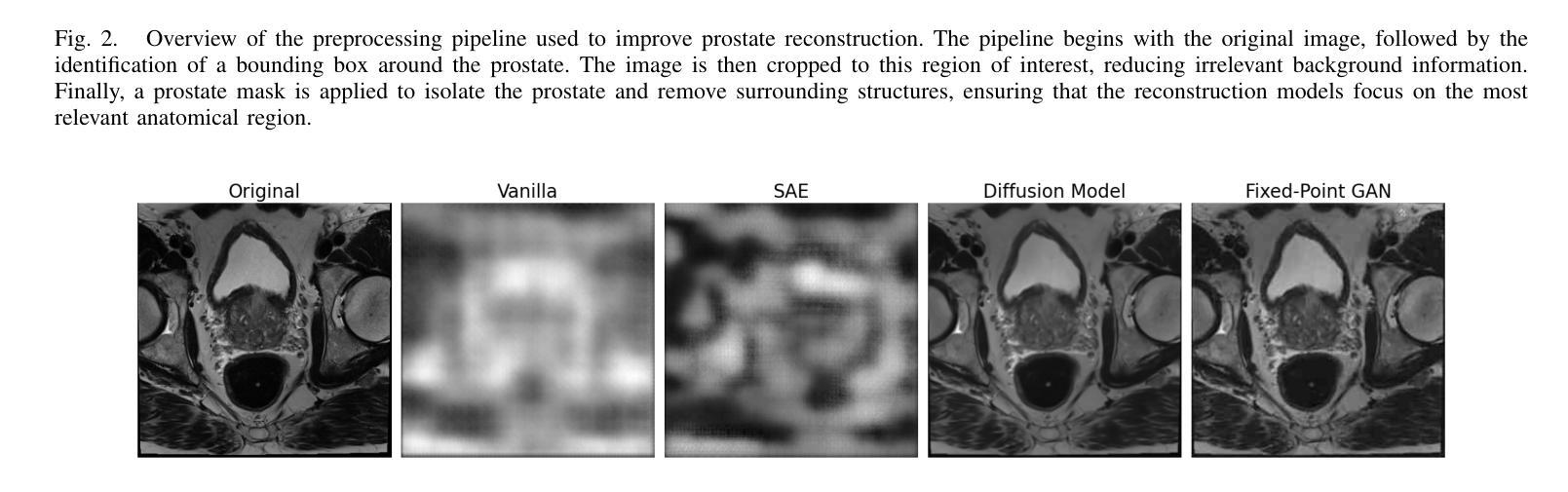
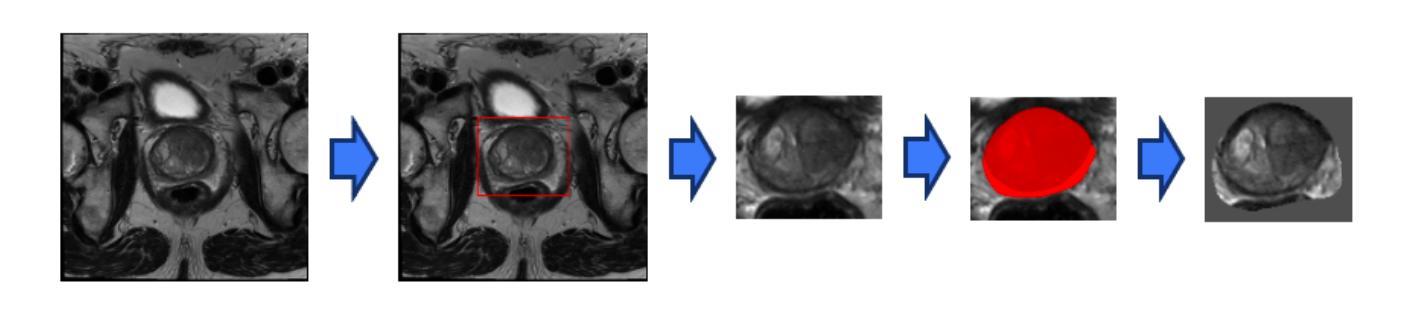
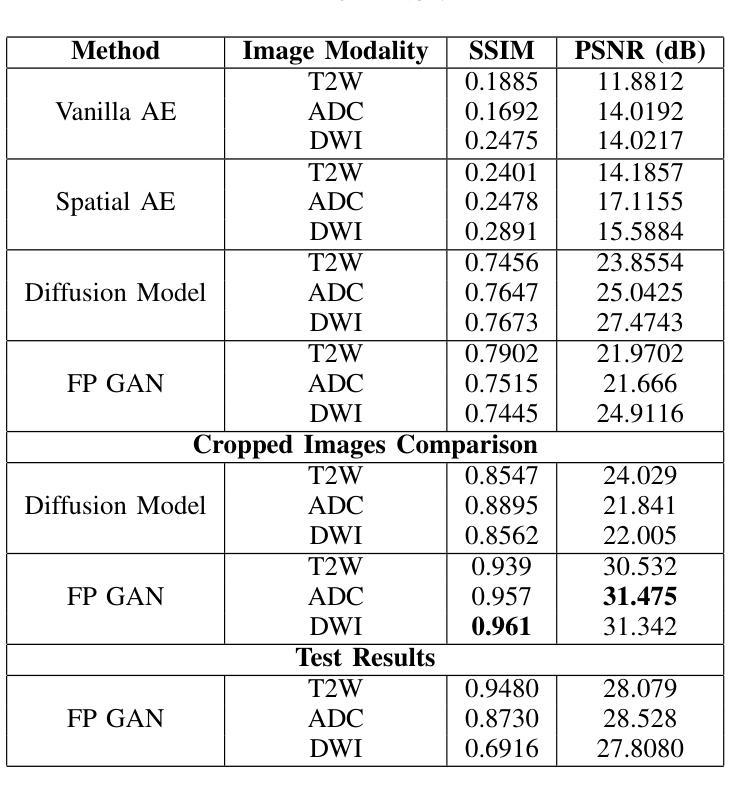
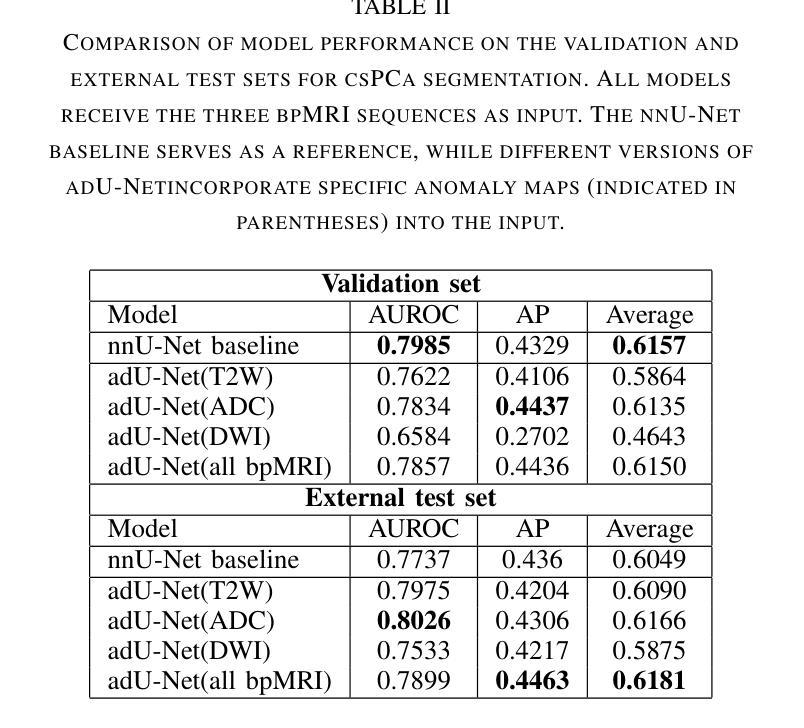
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) plays an important role in identifying clinically significant prostate cancer (csPCa), yet automated methods face challenges such as data imbalance, variable tumor sizes, and a lack of annotated data. This study introduces Anomaly-Driven U-Net (adU-Net), which incorporates anomaly maps derived from biparametric MRI sequences into a deep learning-based segmentation framework to improve csPCa identification. We conduct a comparative analysis of anomaly detection methods and evaluate the integration of anomaly maps into the segmentation pipeline. Anomaly maps, generated using Fixed-Point GAN reconstruction, highlight deviations from normal prostate tissue, guiding the segmentation model to potential cancerous regions. We compare the performance by using the average score, computed as the mean of the AUROC and Average Precision (AP). On the external test set, adU-Net achieves the best average score of 0.618, outperforming the baseline nnU-Net model (0.605). The results demonstrate that incorporating anomaly detection into segmentation improves generalization and performance, particularly with ADC-based anomaly maps, offering a promising direction for automated csPCa identification.
磁共振成像(MRI)在识别具有重要临床意义的前列腺癌(csPCa)中发挥着重要作用。然而,自动化方法面临数据不平衡、肿瘤大小可变以及缺乏注释数据等挑战。本研究介绍了Anomaly-Driven U-Net(adU-Net),它将来自双参数MRI序列的异常映射集成到基于深度学习的分割框架中,以提高csPCa的识别能力。我们对异常检测方法进行了比较分析,并评估了异常映射集成到分割管道中的效果。使用Fixed-Point GAN重建技术生成的异常映射突出了前列腺组织中的异常偏离,引导分割模型定位潜在癌变区域。我们通过使用平均得分(计算为AUROC和平均精度(AP)的平均值)来比较性能。在外部测试集上,adU-Net取得了最佳平均得分0.618,优于基线nnU-Net模型(0.605)。结果表明,将异常检测纳入分割可以提高泛化和性能,特别是基于ADC的异常映射,为自动csPCa识别提供了有前景的方向。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Paper accepted for publication at 2025 47th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC) Copyright 2025 IEEE. Personal use of this material is permitted. Permission from IEEE must be obtained for all other uses, in any current or future media
Summary
基于深度学习的U-Net模型结合双参数MRI序列的异常图,用于提高临床显著前列腺癌(csPCa)的识别。通过比较不同的异常检测方法,并将异常图融入分割流程中,提高了模型识别前列腺区域内癌症病灶的性能。模型性能优异,为未来自动化识别csPCa提供了方向。
Key Takeaways
- MRI在识别临床显著前列腺癌(csPCa)中起重要作用。
- 自动化方法面临数据不平衡、肿瘤大小变化和缺乏标注数据等挑战。
- Anomaly-Driven U-Net(adU-Net)模型结合了双参数MRI序列的异常图来提高csPCa识别的准确性。
- 使用Fixed-Point GAN重建生成异常图,突出正常前列腺组织中的偏差,指导分割模型找到潜在的癌症区域。
- 通过平均得分(平均AUROC和平均精度)评估性能,adU-Net在外部测试集上取得了最佳平均得分0.618。
- 与基线nnU-Net模型相比,adU-Net的性能有所提高,实现了更高的平均得分。
点此查看论文截图

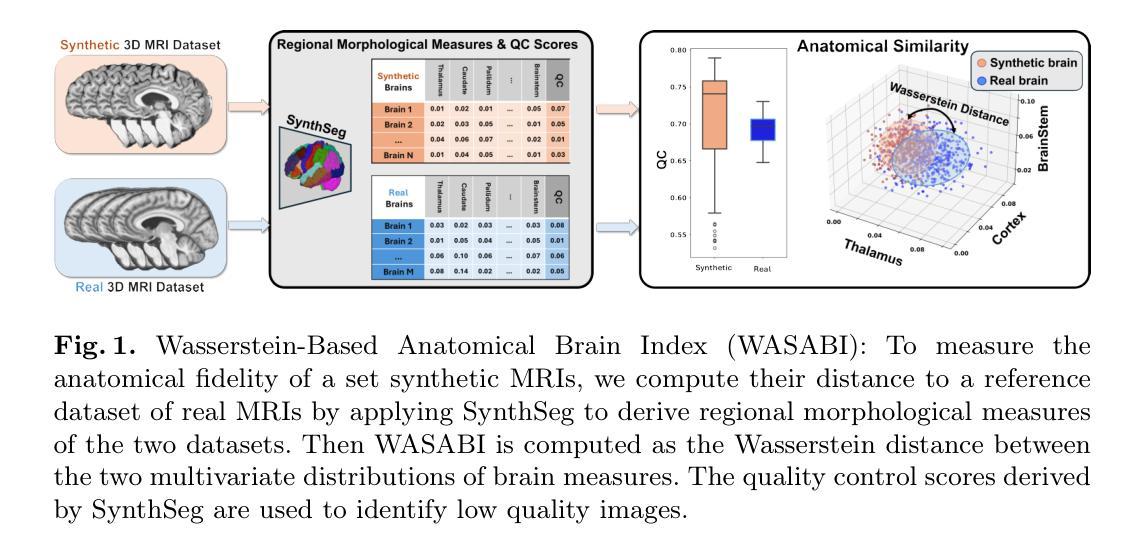
Anatomical Similarity as a New Metric to Evaluate Brain Generative Models
Authors:Bahram Jafrasteh, Wei Peng, Cheng Wan, Yimin Luo, Ehsan Adeli, Qingyu Zhao
Generative models enhance neuroimaging through data augmentation, quality improvement, and rare condition studies. Despite advances in realistic synthetic MRIs, evaluations focus on texture and perception, lacking sensitivity to crucial anatomical fidelity. This study proposes a new metric, called WASABI (Wasserstein-Based Anatomical Brain Index), to assess the anatomical realism of synthetic brain MRIs. WASABI leverages \textit{SynthSeg}, a deep learning-based brain parcellation tool, to derive volumetric measures of brain regions in each MRI and uses the multivariate Wasserstein distance to compare distributions between real and synthetic anatomies. Based on controlled experiments on two real datasets and synthetic MRIs from five generative models, WASABI demonstrates higher sensitivity in quantifying anatomical discrepancies compared to traditional image-level metrics, even when synthetic images achieve near-perfect visual quality. Our findings advocate for shifting the evaluation paradigm beyond visual inspection and conventional metrics, emphasizing anatomical fidelity as a crucial benchmark for clinically meaningful brain MRI synthesis. Our code is available at https://github.com/BahramJafrasteh/wasabi-mri.
生成模型通过数据增强、质量改进和罕见疾病研究增强了神经成像。尽管在逼真的合成MRI方面取得了进展,但评估主要集中在纹理和感知上,缺乏对关键解剖逼真度的敏感性。本研究提出了一种新的度量方法,称为WASABI(基于Wasserstein的解剖脑指数),以评估合成脑MRI的解剖逼真度。WASABI利用基于深度学习的脑分割工具\textit{SynthSeg},从每个MRI中导出脑区的体积测量值,并使用多元Wasserstein距离比较真实和合成解剖之间的分布。基于两个真实数据集和五个生成模型合成的MRI进行的控制实验表明,WASABI在量化解剖差异方面表现出较高的敏感性,即使合成图像达到近乎完美的视觉质量亦是如此。我们的研究结果表明,需要超越视觉检查和传统指标的评估模式,强调解剖逼真度作为临床上具有意义的脑MRI合成的关键基准。我们的代码可在https://github.com/BahramJafrasteh/wasabi-mri找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
生成模型通过数据增强、质量提升和罕见疾病研究增强了神经影像技术。为评估合成脑MRI的解剖真实性,本研究提出一种新的指标WASABI(基于Wasserstein的脑解剖指数),并结合深度学习脑分割工具SynthSeg和多元Wasserstein距离衡量真实与合成MRI解剖分布的差异。实验证明,WASABI相较于传统图像级指标,在量化解剖差异方面表现出更高的灵敏度,即使合成图像几乎达到完美视觉质量。强调解剖真实性是临床有意义的脑MRI合成的关键指标,并提倡评估范式从视觉检查和传统指标转向此关键要素。
Key Takeaways
- 生成模型在神经影像中扮演重要角色,通过数据增强、质量提升和罕见疾病研究带来进步。
- 评估合成脑MRI的真实性时,现有指标主要关注纹理和感知,缺乏对解剖真实性的敏感。
- 为解决此问题,提出新的评估指标WASABI,结合深度学习脑分割工具和多元Wasserstein距离来衡量真实与合成MRI之间的差异。
- WASABI在量化解剖差异方面表现出高灵敏度,即使合成图像视觉质量近乎完美。
- 强调解剖真实性是评价合成脑MRI临床意义的关键指标。
- 提倡改变评估范式,从视觉检查和传统指标转向解剖真实性评估。
点此查看论文截图

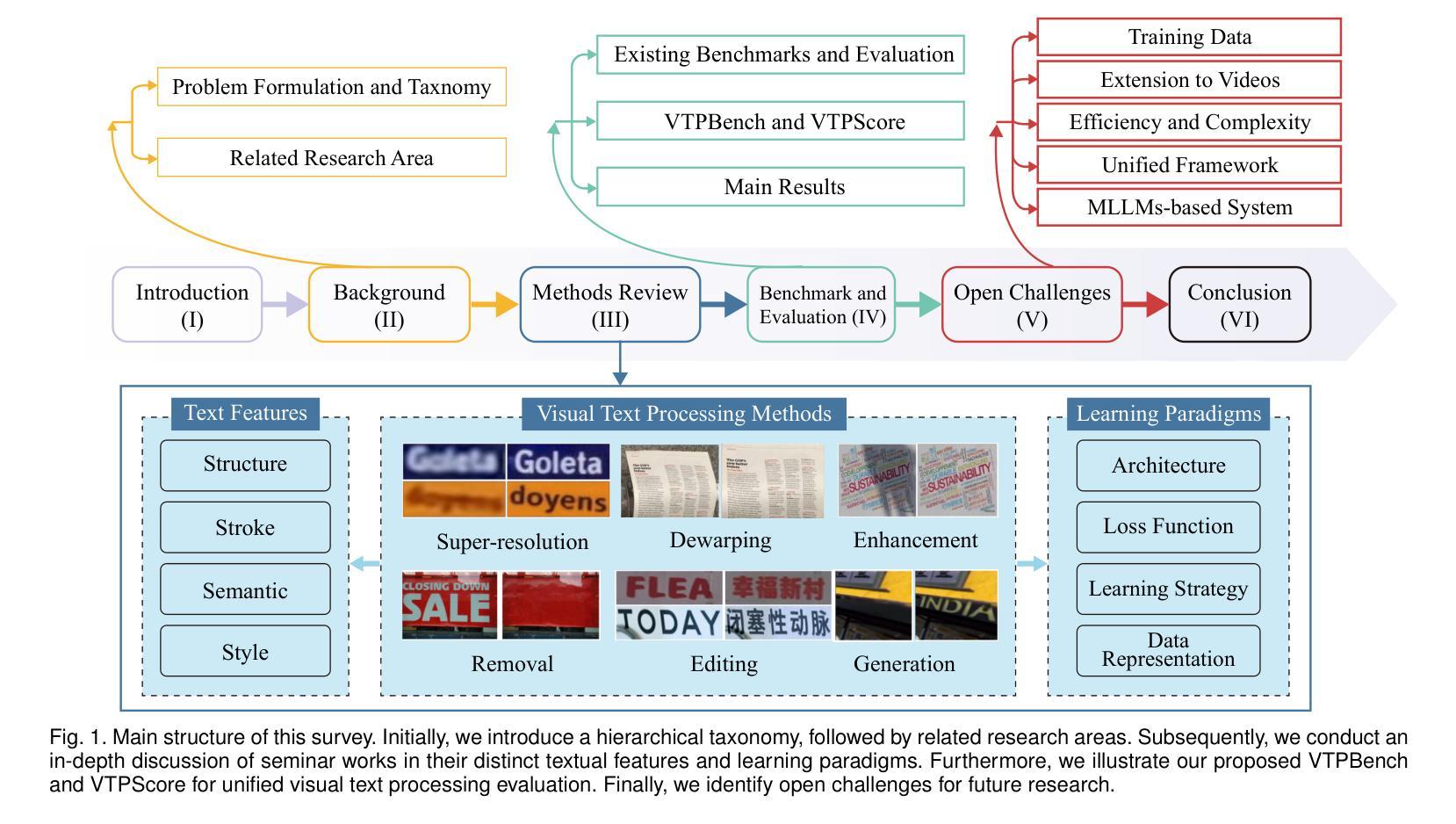
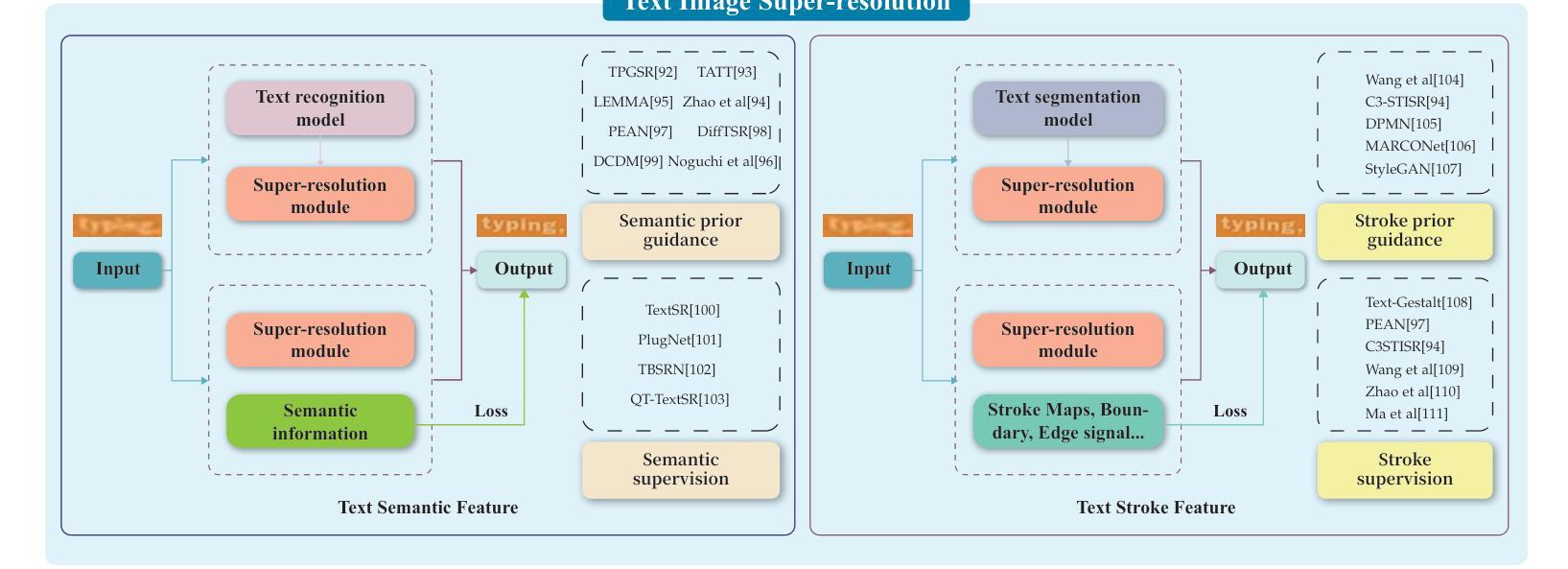
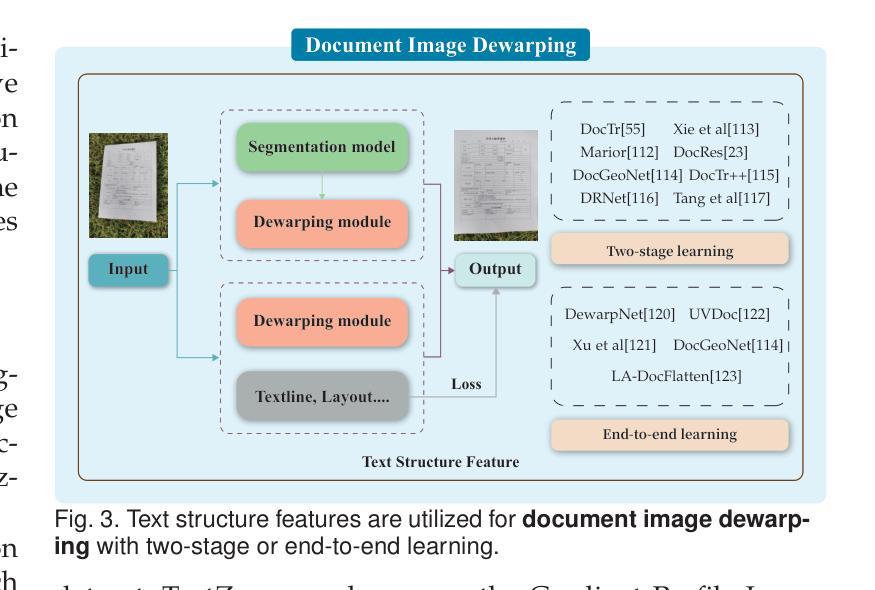
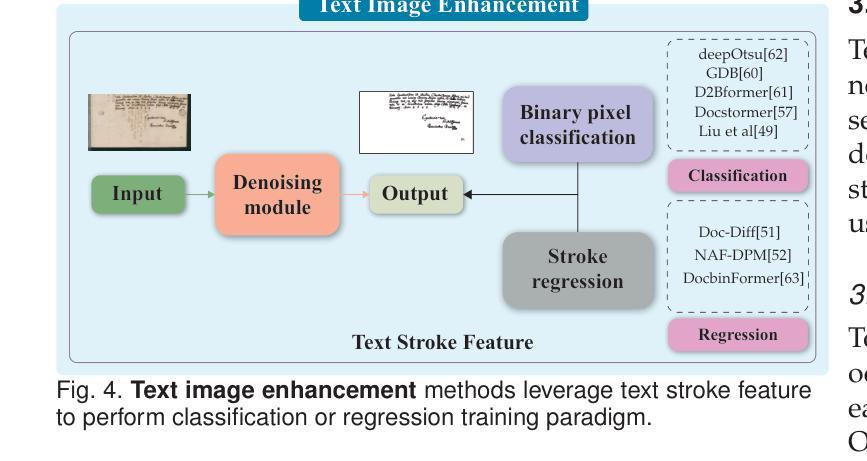
Visual Text Processing: A Comprehensive Review and Unified Evaluation
Authors:Yan Shu, Weichao Zeng, Fangmin Zhao, Zeyu Chen, Zhenhang Li, Xiaomeng Yang, Yu Zhou, Paolo Rota, Xiang Bai, Lianwen Jin, Xu-Cheng Yin, Nicu Sebe
Visual text is a crucial component in both document and scene images, conveying rich semantic information and attracting significant attention in the computer vision community. Beyond traditional tasks such as text detection and recognition, visual text processing has witnessed rapid advancements driven by the emergence of foundation models, including text image reconstruction and text image manipulation. Despite significant progress, challenges remain due to the unique properties that differentiate text from general objects. Effectively capturing and leveraging these distinct textual characteristics is essential for developing robust visual text processing models. In this survey, we present a comprehensive, multi-perspective analysis of recent advancements in visual text processing, focusing on two key questions: (1) What textual features are most suitable for different visual text processing tasks? (2) How can these distinctive text features be effectively incorporated into processing frameworks? Furthermore, we introduce VTPBench, a new benchmark that encompasses a broad range of visual text processing datasets. Leveraging the advanced visual quality assessment capabilities of multimodal large language models (MLLMs), we propose VTPScore, a novel evaluation metric designed to ensure fair and reliable evaluation. Our empirical study with more than 20 specific models reveals substantial room for improvement in the current techniques. Our aim is to establish this work as a fundamental resource that fosters future exploration and innovation in the dynamic field of visual text processing. The relevant repository is available at https://github.com/shuyansy/Visual-Text-Processing-survey.
视觉文本在文档和场景图像中都是至关重要的组成部分,它传递了丰富的语义信息,并引起了计算机视觉界的广泛关注。除了文本检测和识别等传统任务外,视觉文本处理在基础模型的推动下实现了快速发展,包括文本图像重建和文本图像操作。尽管取得了显著进展,但由于文本与一般物体的独特属性差异,仍然存在挑战。有效地捕获和利用这些独特的文本特征对于开发稳健的视觉文本处理模型至关重要。在本文中,我们对视觉文本处理的最新进展进行了全面、多视角的分析,重点回答两个关键问题:(1)不同的视觉文本处理任务最适合哪些文本特征?(2)如何有效地将这些独特的文本特征纳入处理框架?此外,我们介绍了VTPBench,这是一个涵盖广泛视觉文本处理数据集的新基准。我们利用多模态大型语言模型的先进视觉质量评估能力,提出了VTPScore,一种旨在确保公平可靠评估的新型评价指标。我们对超过20种特定模型的实证研究揭示了当前技术仍有大量改进空间。我们的目标是将这项工作建立为视觉文本处理这一动态领域的基本资源,促进未来的探索和创新。相关仓库可在链接中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文概述了视觉文本处理领域的最新进展,介绍了处理文本图像的重要特性与任务,包括文本特征的选择与融入处理框架的方式。提出VTPBench新基准,涵盖广泛的视觉文本处理数据集,并利用多模态大型语言模型的视觉质量评估能力,提出VTPScore评估指标,旨在确保公平可靠的评估。对超过20种特定模型的实证研究显示出当前技术仍有大量提升空间,旨在为视觉文本处理领域的未来探索和创新提供基础资源。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉文本是文档和场景图像中的关键组成部分,包含丰富的语义信息,在计算机视觉领域备受关注。
- 视觉文本处理任务不仅限于传统的文本检测和识别,还包括文本图像重建和操纵等。
- 视觉文本处理领域虽取得显著进展,但仍面临挑战,有效捕捉和利用文本的独特特性对于开发稳健的模型至关重要。
- 文中对视觉文本处理的最新进展进行了全面、多视角的分析,并回答了两个关键问题:哪些文本特征最适合不同的视觉文本处理任务?如何有效地将这些独特的文本特征融入处理框架?
- 介绍了新的VTPBench基准,涵盖广泛的视觉文本处理数据集,为研究和评估提供丰富资源。
- 利用多模态大型语言模型的视觉质量评估能力,提出了VTPScore评估指标,确保公平和可靠的评估。
点此查看论文截图

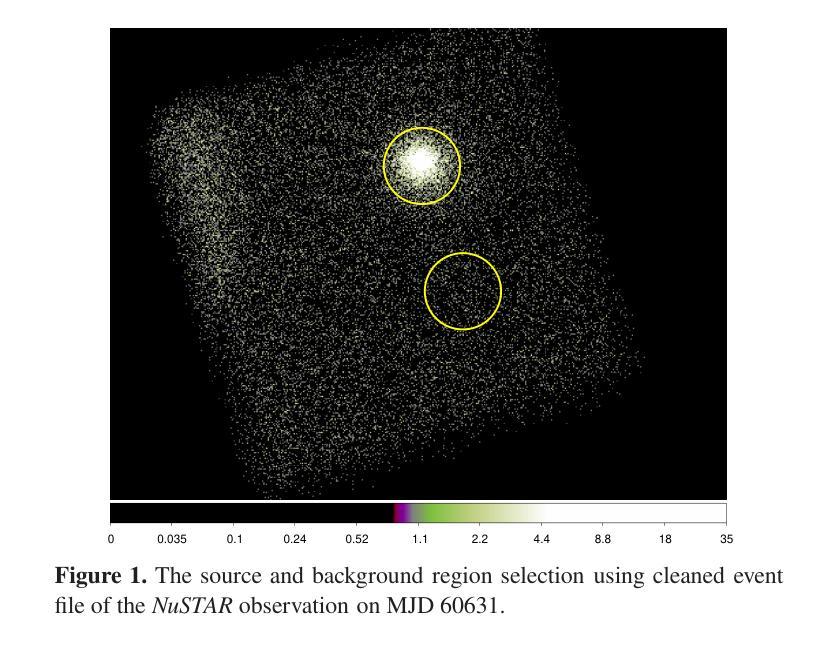
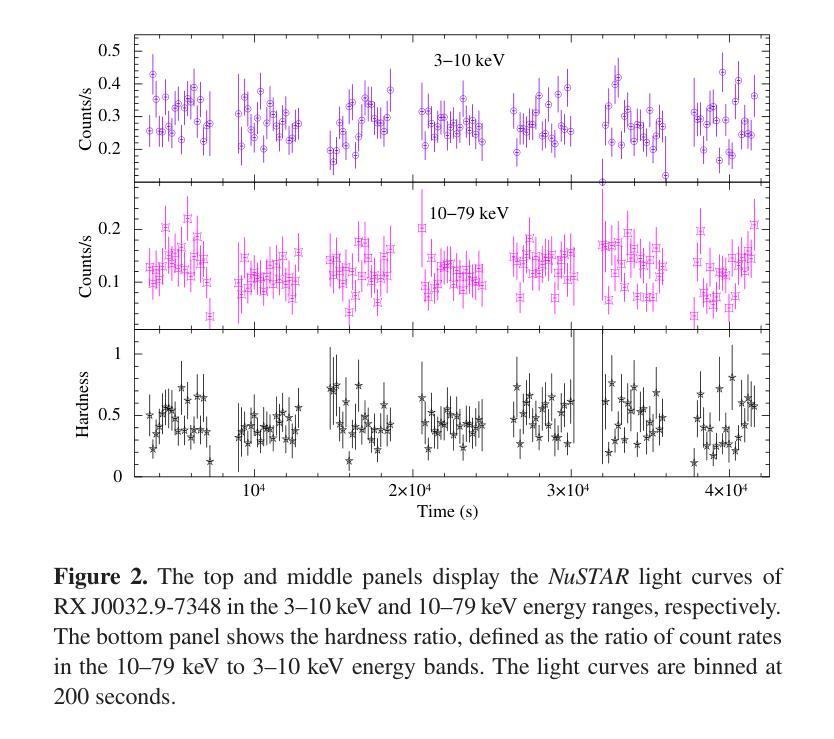
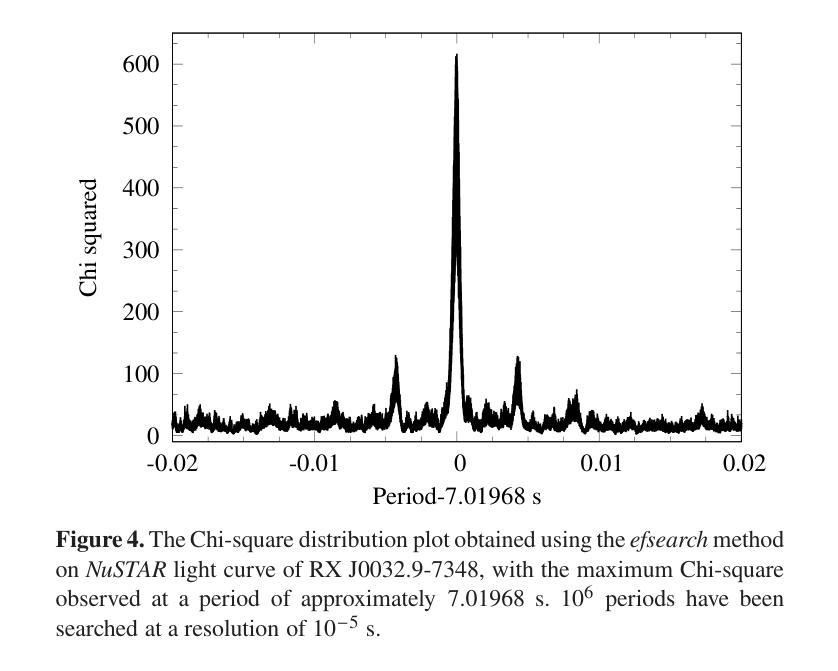
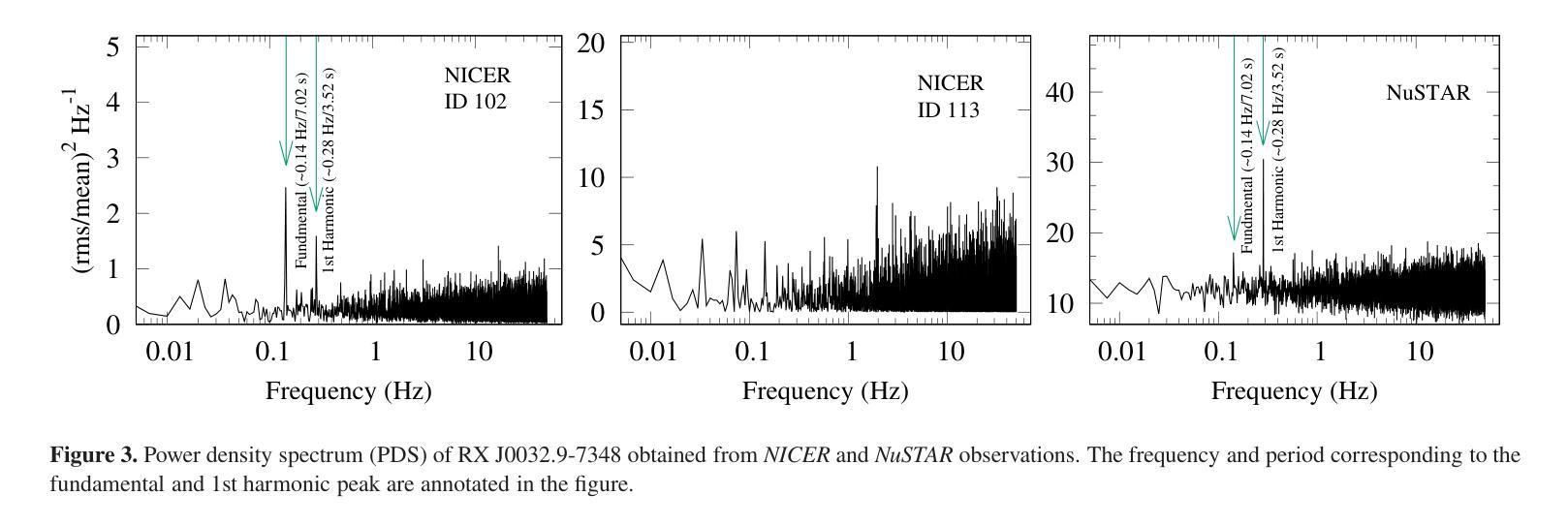
Broadband study of the SMC pulsar RX J0032.9-7348 during its X-ray brightening in 2024
Authors:Birendra Chhotaray, Gaurava K. Jaisawal, Sachindra Naik, Arghajit Jana
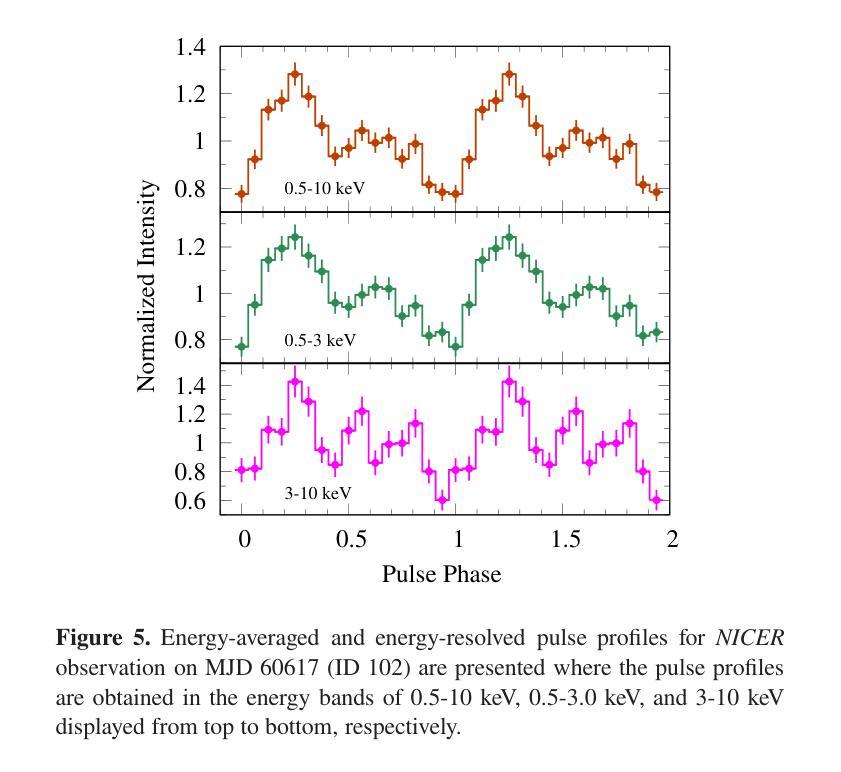
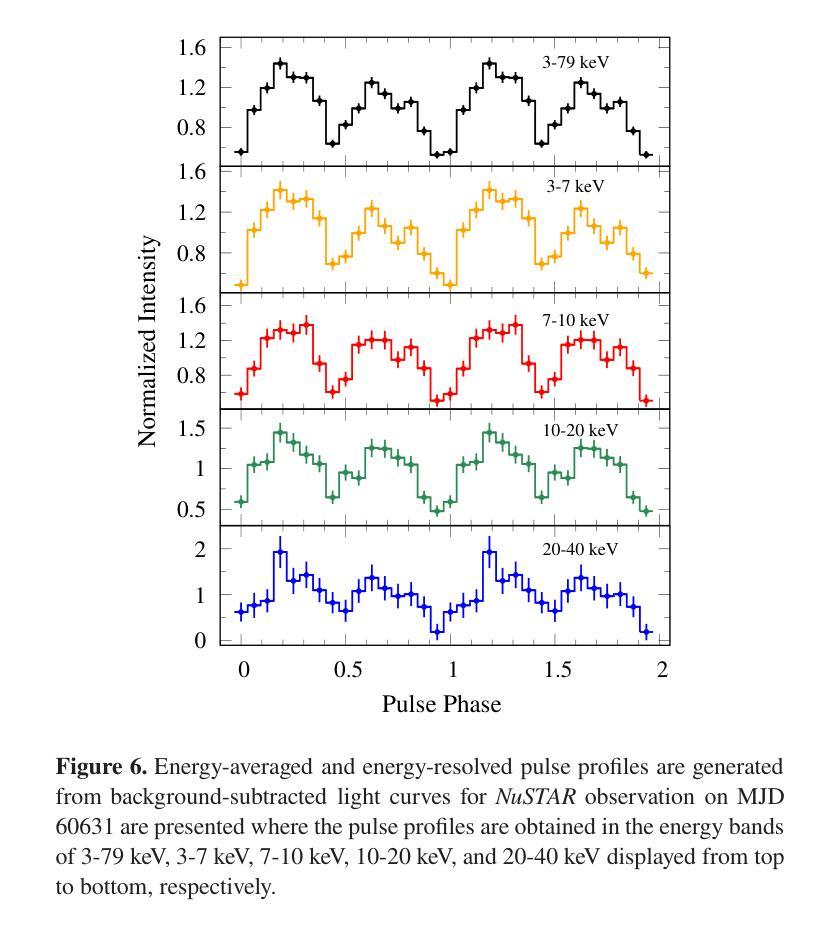
We present the results of the broadband timing and spectral analysis of the poorly understood SMC pulsar RX J0032.9-7348 (= SXP 7.02) using NuSTAR and NICER observations during its X-ray brightening in 2024. Our timing analysis revealed a pulsation period of approximately 7.02 s in the X-ray light curve. The pulse profile obtained in the broad energy range is double-peaked and asymmetric in nature and shows moderate variation with the energy. An absorbed power-law model describes the 0.5-8 keV NICER spectra well. The 3-50 keV NuSTAR spectrum is best described with an absorbed power-law modified with a high-energy cutoff model. We find no evidence of iron or cyclotron line features in the energy spectrum. During our observation period, the 0.5-50 keV luminosity varies in the range of $\sim 8\times10^{36} - 4\times10^{37}$ erg s$^{-1}$. We also discuss the dependence of spectral parameters on the rotational phase of the pulsar through phase-resolved spectroscopy.
我们展示了在X射线增亮期(发生在2024年)使用NuSTAR和NICER观测结果对SMC脉冲星RX J0032.9-7348(即SXP 7.02)的宽带计时和光谱分析的结果。我们的计时分析发现X射线光变曲线中的脉冲周期约为7.02秒。在宽能范围内获得的脉冲轮廓具有双峰和不对称性质,并随能量的变化而适度变化。吸收幂律模型很好地描述了NICER在0.5-8千电子伏特范围内的光谱。NuSTAR在3-50千电子伏特范围内的光谱最好用吸收幂律模型来描述,该模型通过高能截止模型进行修改。我们在能量谱中没有发现铁或回旋线特征。在我们的观测期间,观察到在大约范围从$ 8\times10^{36}至 4\times10^{37}$尔格每秒的辐射光度(从紫外到近红外)。我们还通过相位解析光谱讨论了谱参数对脉冲星自转周期的影响。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication in MNRAS
Summary
RX J0032.9-7348脉冲星的宽频时序和光谱分析结果。发现7.02秒脉冲周期,X射线光变曲线呈双峰、不对称特征,能谱特征以吸收性幂律模型为主,无明显的铁或回旋线特征。
Key Takeaways
- RX J0032.9-7348脉冲星的脉冲周期约为7.02秒。
- X射线光变曲线呈现双峰、不对称的脉冲特征。
- 能谱特征在0.5-8 keV范围内可用吸收性幂律模型描述。
- 在3-50 keV的NuSTAR光谱数据需要采用带有高能截止的模型进行描述。
- 无明显的铁或回旋线特征在能谱中被发现。
- 脉冲星的0.5-50 keV光度在观测期间内变化范围约为 (8\times10^{36} - 4\times10^{37}) erg s(^{-1})。
点此查看论文截图


Revisiting Diffusion Autoencoder Training for Image Reconstruction Quality
Authors:Pramook Khungurn, Sukit Seripanitkarn, Phonphrm Thawatdamrongkit, Supasorn Suwajanakorn
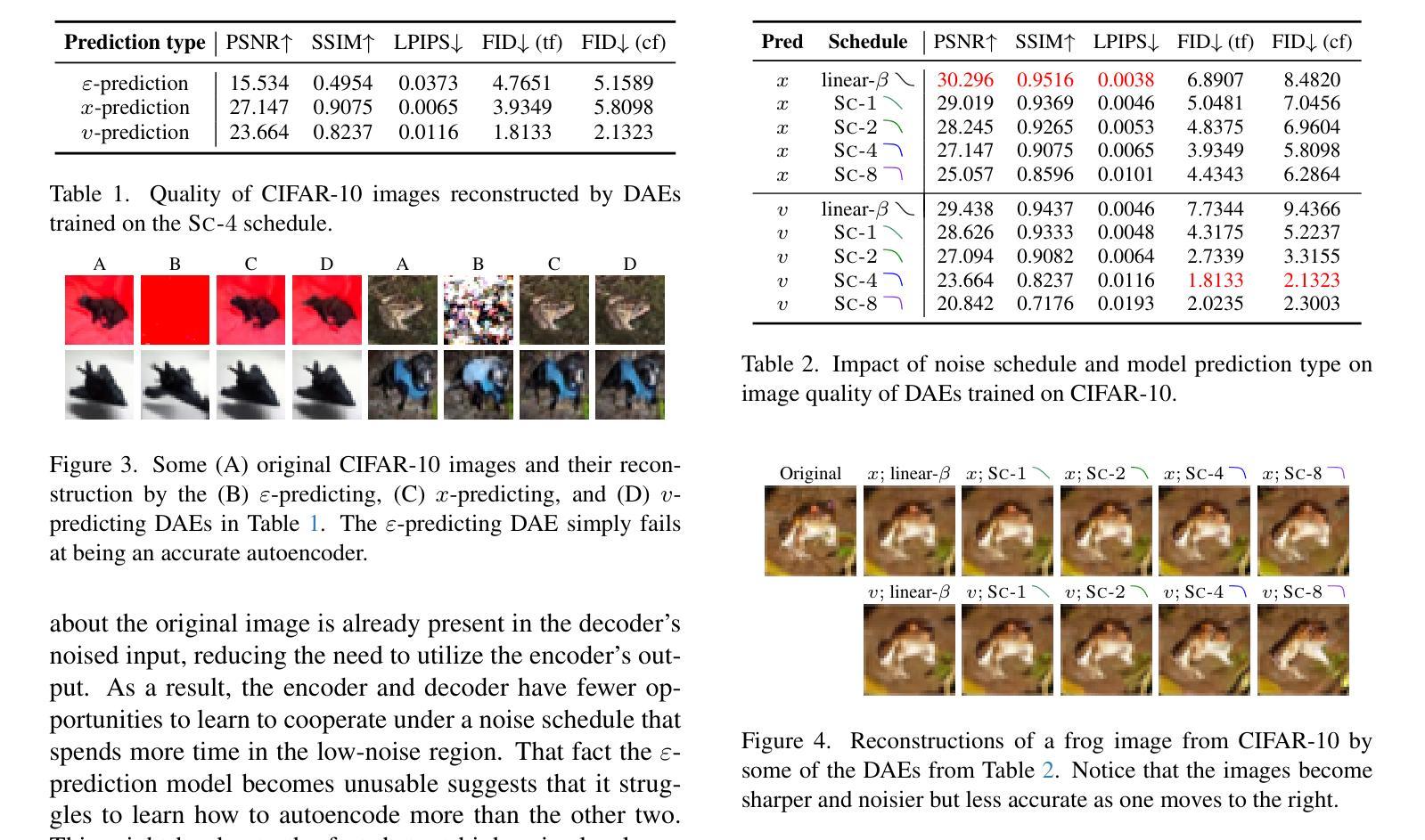
Diffusion autoencoders (DAEs) are typically formulated as a noise prediction model and trained with a linear-$\beta$ noise schedule that spends much of its sampling steps at high noise levels. Because high noise levels are associated with recovering large-scale image structures and low noise levels with recovering details, this configuration can result in low-quality and blurry images. However, it should be possible to improve details while spending fewer steps recovering structures because the latent code should already contain structural information. Based on this insight, we propose a new DAE training method that improves the quality of reconstructed images. We divide training into two phases. In the first phase, the DAE is trained as a vanilla autoencoder by always setting the noise level to the highest, forcing the encoder and decoder to populate the latent code with structural information. In the second phase, we incorporate a noise schedule that spends more time in the low-noise region, allowing the DAE to learn how to perfect the details. Our method results in images that have accurate high-level structures and low-level details while still preserving useful properties of the latent codes.
扩散自编码器(DAEs)通常被制定为噪声预测模型,并使用线性-$\beta$噪声时间表进行训练,该模型在采样步骤中大部分时间都在高噪声水平下运行。由于高噪声水平与恢复大规模图像结构有关,而低噪声水平与恢复细节有关,这种配置可能会导致图像质量低下和模糊。然而,应该有可能在恢复结构时减少步骤数量,同时改进细节,因为潜在代码应该已经包含结构信息。基于这一见解,我们提出了一种新的DAE训练方法,以提高重建图像的质量。我们将训练分为两个阶段。在第一阶段,我们将DAE训练为普通自编码器,始终将噪声水平设置为最高,迫使编码器和解码器在潜在代码中填充结构信息。在第二阶段,我们采用一种在低声区花费更多时间的噪声时间表,让DAE学习如何完善细节。我们的方法产生的图像既具有准确的高级结构,又具有低级的细节,同时还保留了潜在代码的有用属性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF AI for Content Creation (AI4CC) Workshop at CVPR 2025
Summary
扩散自编码器(DAEs)作为噪声预测模型,通常采用线性-$\beta$噪声调度进行训练,其采样步骤多数集中在高噪声水平。这导致在恢复图像结构时质量较低且图像模糊。本文提出一种新的DAE训练方法,分为两个阶段以提高重建图像的质量。第一阶段训练DAE作为普通自编码器,始终设置最高噪声水平,使编码器和解码器在潜在代码中填充结构信息。第二阶段引入噪声调度,更多地关注低噪声区域,使DAE学习完善细节。该方法生成的图像既具有准确的高级结构,又保留了潜在代码的有用属性,同时细节丰富。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散自编码器(DAEs)在噪声预测模型中通常采用线性-$\beta$噪声调度训练,采样步骤多数集中在高噪声水平,导致图像质量低且模糊。
- 高噪声水平关联恢复大尺度图像结构,低噪声水平关联恢复细节。
- 提出的新训练方法分为两个阶段,第一阶段重点训练DAE作为普通自编码器,使编码器和解码器在潜在代码中填充结构信息。
- 第二阶段引入的噪声调度更多关注低噪声区域,提高细节质量。
- 通过新训练方法,生成的图像具有准确的高级结构和丰富的细节。
- 新方法保留潜在代码的有用属性。
点此查看论文截图


Vision-Language Model-Based Semantic-Guided Imaging Biomarker for Early Lung Cancer Detection
Authors:Luoting Zhuang, Seyed Mohammad Hossein Tabatabaei, Ramin Salehi-Rad, Linh M. Tran, Denise R. Aberle, Ashley E. Prosper, William Hsu
Objective: A number of machine learning models have utilized semantic features, deep features, or both to assess lung nodule malignancy. However, their reliance on manual annotation during inference, limited interpretability, and sensitivity to imaging variations hinder their application in real-world clinical settings. Thus, this research aims to integrate semantic features derived from radiologists’ assessments of nodules, allowing the model to learn clinically relevant, robust, and explainable features for predicting lung cancer. Methods: We obtained 938 low-dose CT scans from the National Lung Screening Trial with 1,246 nodules and semantic features. The Lung Image Database Consortium dataset contains 1,018 CT scans, with 2,625 lesions annotated for nodule characteristics. Three external datasets were obtained from UCLA Health, the LUNGx Challenge, and the Duke Lung Cancer Screening. We finetuned a pretrained Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining model with a parameter-efficient fine-tuning approach to align imaging and semantic features and predict the one-year lung cancer diagnosis. Results: We evaluated the performance of the one-year diagnosis of lung cancer with AUROC and AUPRC and compared it to three state-of-the-art models. Our model demonstrated an AUROC of 0.90 and AUPRC of 0.78, outperforming baseline state-of-the-art models on external datasets. Using CLIP, we also obtained predictions on semantic features, such as nodule margin (AUROC: 0.81), nodule consistency (0.81), and pleural attachment (0.84), that can be used to explain model predictions. Conclusion: Our approach accurately classifies lung nodules as benign or malignant, providing explainable outputs, aiding clinicians in comprehending the underlying meaning of model predictions. This approach also prevents the model from learning shortcuts and generalizes across clinical settings.
目标:许多机器学习模型已经利用语义特征、深度特征或两者来评估肺结节的恶性程度。然而,它们在推理过程中对手动注释的依赖、解释性有限以及对成像变化的敏感性,阻碍了它们在真实世界临床环境中的应用。因此,本研究旨在结合放射科医生对结节的评估所得出的语义特征,使模型能够学习用于预测肺癌的临床相关、稳健和可解释的特征。
方法:我们从国家肺癌筛查试验中获得938例低剂量CT扫描结果,包含1246个结节和语义特征。肺部图像数据库联盟数据集包含1018例CT扫描结果,对2625个病变进行了结节特征标注。另外三个外部数据集分别来自加州大学洛杉矶分校健康中心、LUNGx挑战赛和杜克肺癌筛查。我们使用微调后的对比语言图像预训练模型,采用高效的微调方法,对齐成像和语义特征,并预测一年内肺癌诊断结果。
结果:我们评估了模型对一年内肺癌诊断的性能,使用AUROC和AUPRC进行评估,并将其与三种最先进模型进行比较。我们的模型AUROC达到0.90,AUPRC达到0.78,在外部数据集上的性能超过了基线最先进的模型。使用CLIP,我们还获得了关于语义特征的预测,如结节边缘(AUROC:0.81)、结节一致性(0.81)和胸膜附着(0.84),这些特征可用于解释模型预测。
结论:我们的方法能够准确地将肺结节分类为良性或恶性,提供可解释的输出结果,帮助临床医生理解模型预测结果背后的含义。这种方法还防止了模型学习捷径,并在各种临床环境中具有通用性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该研究融合放射科医生对结节的评估所提取的语义特征,训练模型以预测肺癌。通过微调预训练的对比语言图像预训练模型,参数高效微调方法对齐图像和语义特征,预测一年内肺癌诊断。模型在外部数据集上表现优异,提供解释性输出,帮助医生理解模型预测的内在含义。
Key Takeaways
- 研究旨在解决现有机器学习模型在预测肺结节恶性程度时存在的问题,如依赖手动注释、解释性有限和对成像变化的敏感性。
- 通过结合语义特征和深度学习,研究提出了一种新的方法,利用放射科医生对结节的评估来训练模型,使其能够学习临床相关、稳健和可解释的特征。
- 研究使用了多个数据集,包括来自国家肺癌筛查试验、肺图像数据库联盟以及三个外部数据集(UCLA健康、LUNGx挑战和杜克肺癌筛查)的低剂量CT扫描图像。
- 研究采用预训练的对比语言图像预训练模型,通过参数高效微调方法对齐图像和语义特征,以提高模型的性能。
- 模型在预测一年内肺癌诊断方面表现出优异的性能,与现有最先进的模型相比具有更好的准确性。
- 模型能够解释其预测结果,如结节边缘、结节一致性和胸膜附着等语义特征,有助于医生理解模型预测的内在含义。
点此查看论文截图
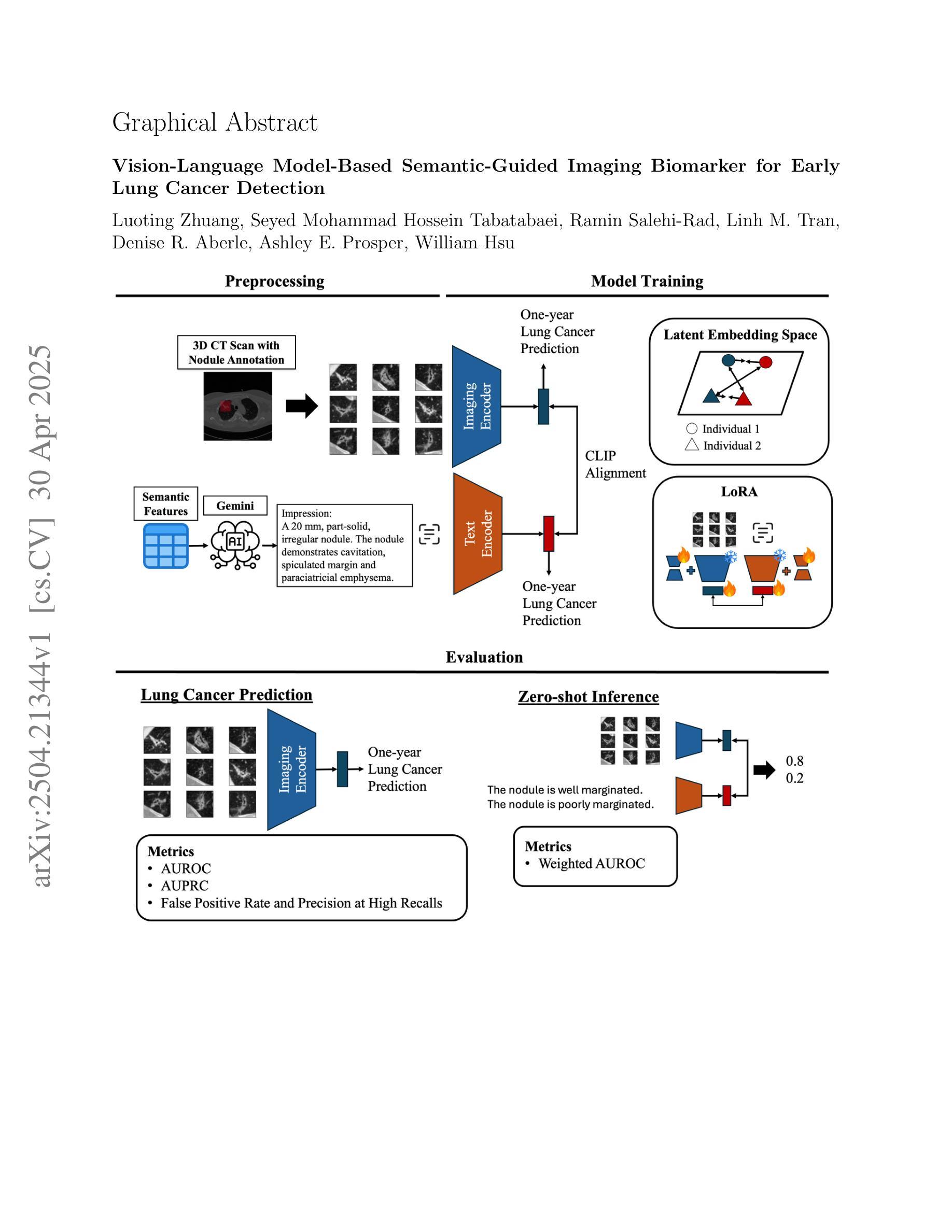
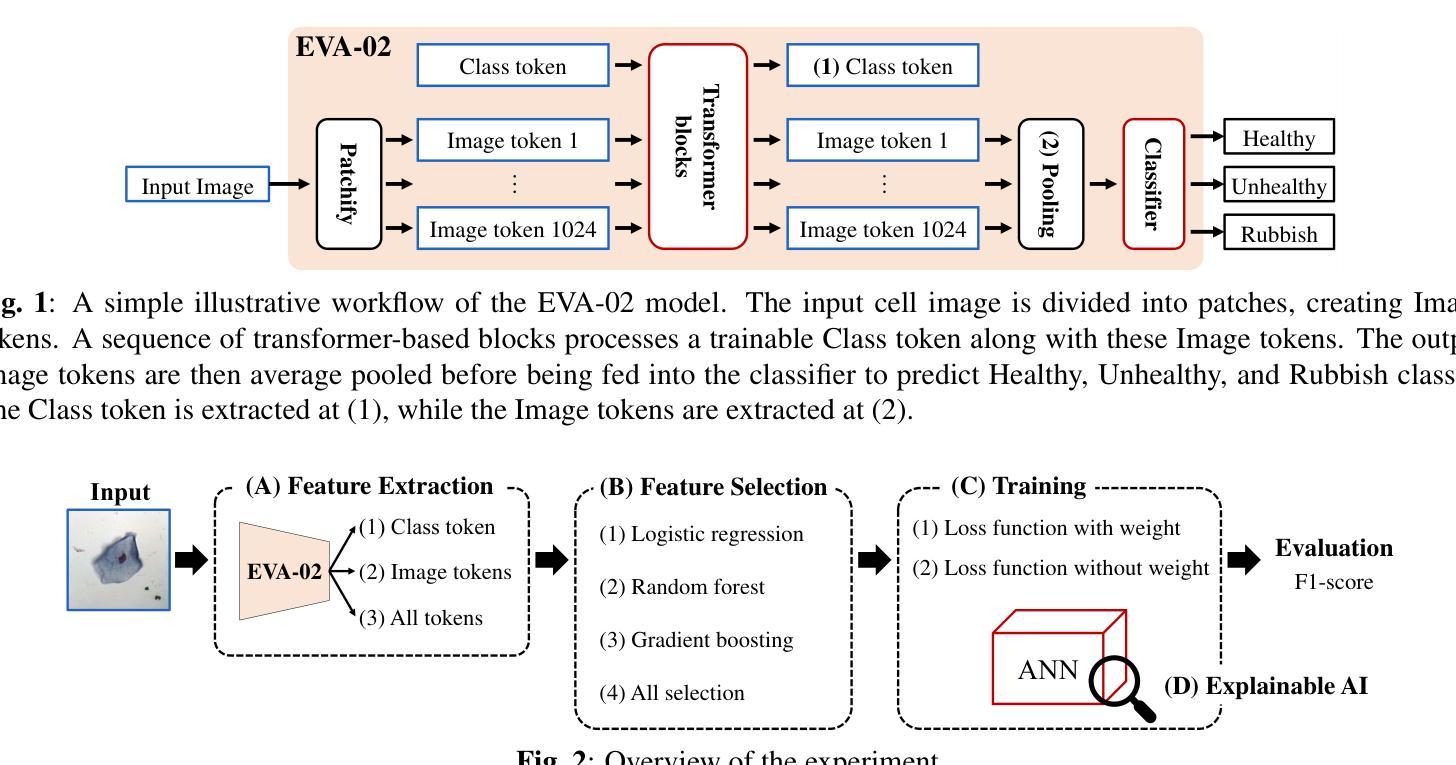
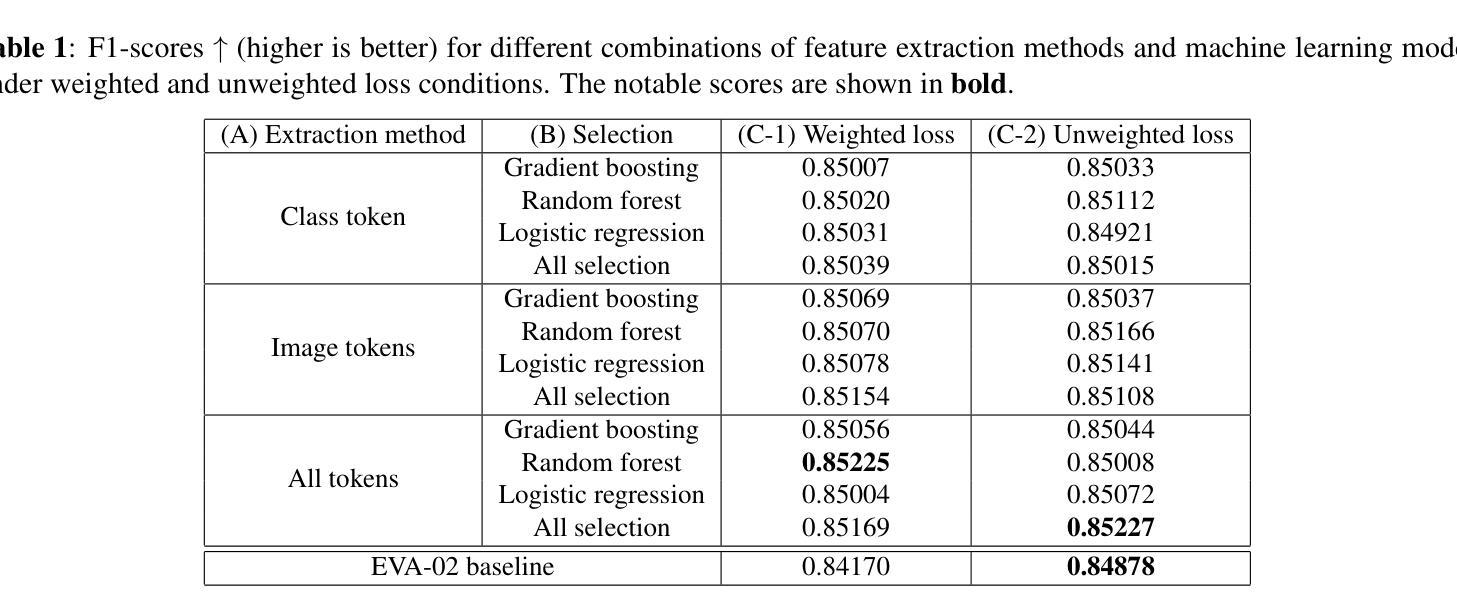
Towards Improved Cervical Cancer Screening: Vision Transformer-Based Classification and Interpretability
Authors:Khoa Tuan Nguyen, Ho-min Park, Gaeun Oh, Joris Vankerschaver, Wesley De Neve
We propose a novel approach to cervical cell image classification for cervical cancer screening using the EVA-02 transformer model. We developed a four-step pipeline: fine-tuning EVA-02, feature extraction, selecting important features through multiple machine learning models, and training a new artificial neural network with optional loss weighting for improved generalization. With this design, our best model achieved an F1-score of 0.85227, outperforming the baseline EVA-02 model (0.84878). We also utilized Kernel SHAP analysis and identified key features correlating with cell morphology and staining characteristics, providing interpretable insights into the decision-making process of the fine-tuned model. Our code is available at https://github.com/Khoa-NT/isbi2025_ps3c.
我们提出了一种使用EVA-02转换器模型进行宫颈癌筛查的宫颈细胞图像分类新方法。我们开发了一个四步流程:微调EVA-02,特征提取,通过多个机器学习模型选择重要特征,以及使用可选的损失权重训练新的神经网络以改善其泛化能力。凭借这种设计,我们最好的模型实现了F1分数为0.85227,超过了基线EVA-02模型(0.84878)。我们还使用Kernel SHAP分析确定了与细胞形态和染色特征相关的关键特征,为微调模型的决策过程提供了可解释性的见解。我们的代码位于https://github.com/Khoa-NT/isbi2025_ps3c。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ISBI 2025 “Challenge 2: Pap Smear Cell Classification Challenge”
摘要
本文提出一种利用EVA-02变压器模型进行宫颈细胞图像分类以进行宫颈癌筛查的新方法。设计了一个四步流程:微调EVA-02、特征提取、通过多个机器学习模型选择重要特征,并训练一个新的带有可选损失权重的神经网络以提高泛化能力。最佳模型的F1分数达到0.85227,优于基线EVA-02模型(0.84878)。我们还使用Kernel SHAP分析确定了与细胞形态和染色特征相关的关键特征,为微调模型的决策过程提供了可解释性的见解。相关代码已发布在https://github.com/Khoa-NT/isbi2025_ps3c。
要点
- 提出了一种基于EVA-02变压器模型的新方法,用于宫颈细胞图像分类的宫颈癌筛查。
- 设计了一个四步流程,包括微调EVA-02模型、特征提取和选择重要特征等步骤。
- 通过多机器学习模型选择关键特征,训练新的神经网络模型,提高泛化能力。
- 最佳模型的F1分数为0.85227,性能优于基线EVA-02模型。
- 利用Kernel SHAP分析确定了与细胞形态和染色特征相关的关键特征。
- 提供了模型决策过程的可解释性见解。
- 相关代码已发布在GitHub上供公众访问。
点此查看论文截图

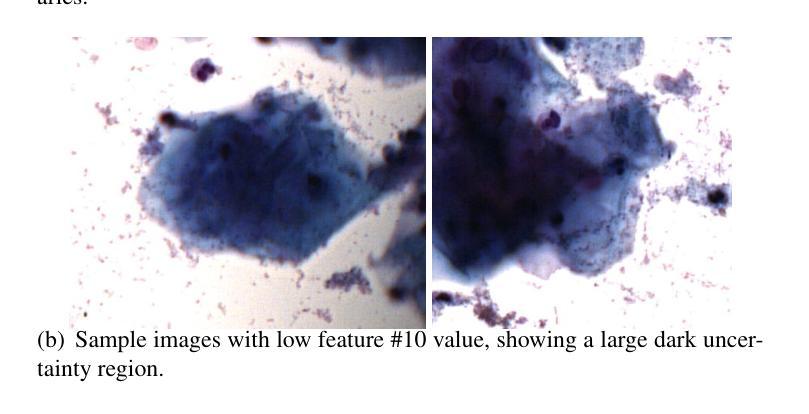

UniBiomed: A Universal Foundation Model for Grounded Biomedical Image Interpretation
Authors:Linshan Wu, Yuxiang Nie, Sunan He, Jiaxin Zhuang, Hao Chen
Multi-modal interpretation of biomedical images opens up novel opportunities in biomedical image analysis. Conventional AI approaches typically rely on disjointed training, i.e., Large Language Models (LLMs) for clinical text generation and segmentation models for target extraction, which results in inflexible real-world deployment and a failure to leverage holistic biomedical information. To this end, we introduce UniBiomed, the first universal foundation model for grounded biomedical image interpretation. UniBiomed is based on a novel integration of Multi-modal Large Language Model (MLLM) and Segment Anything Model (SAM), which effectively unifies the generation of clinical texts and the segmentation of corresponding biomedical objects for grounded interpretation. In this way, UniBiomed is capable of tackling a wide range of biomedical tasks across ten diverse biomedical imaging modalities. To develop UniBiomed, we curate a large-scale dataset comprising over 27 million triplets of images, annotations, and text descriptions across ten imaging modalities. Extensive validation on 84 internal and external datasets demonstrated that UniBiomed achieves state-of-the-art performance in segmentation, disease recognition, region-aware diagnosis, visual question answering, and report generation. Moreover, unlike previous models that rely on clinical experts to pre-diagnose images and manually craft precise textual or visual prompts, UniBiomed can provide automated and end-to-end grounded interpretation for biomedical image analysis. This represents a novel paradigm shift in clinical workflows, which will significantly improve diagnostic efficiency. In summary, UniBiomed represents a novel breakthrough in biomedical AI, unlocking powerful grounded interpretation capabilities for more accurate and efficient biomedical image analysis.
生物医学图像的多模态解读为生物医学图像分析提供了新的机会。传统的AI方法通常依赖于分立训练,即使用大型语言模型(LLMs)进行临床文本生成和分割模型进行目标提取,这导致在实际部署中的不灵活性和无法利用整体生物医学信息的问题。为此,我们引入了UniBiomed,这是首个用于基于基础生物医学图像解读的通用基础模型。UniBiomed基于多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)和分段任何东西模型(SAM)的新颖集成,有效地统一了临床文本的生成和相应生物医学对象的分割,以实现基于解读的解读。通过这种方式,UniBiomed能够处理涉及十种不同生物医学成像模态的广泛生物医学任务。为了开发UniBiomed,我们整理了一个大规模数据集,包含十种成像模态的图像、注解和文本描述超过2700万组数据。在内部和外部的84个数据集上的广泛验证表明,UniBiomed在分割、疾病识别、区域感知诊断、视觉问答和报告生成方面达到了最先进的性能。此外,与之前依赖于临床专家进行预先诊断图像和手动精确制作文本或视觉提示的模型不同,UniBiomed可以为生物医学图像分析提供自动化和端到端的基于基础解读。这代表了临床工作流程中的新范式转变,将显著提高诊断效率。总之,UniBiomed代表了生物医学AI的一个全新突破,解锁了强大的基于解读的能力,为更准确和高效生物医学图像分析提供了可能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The first universal foundation model for grounded biomedical image interpretation
Summary
本文介绍了生物医学图像多模态解读的新机会。传统的AI方法通常采用分立训练的方式,无法实现全面利用生物医学信息,存在灵活性问题。因此引入了UniBiomed,一个用于生物医学图像解读的统一基础模型。它通过多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)和分割任何东西模型(SAM)的有效集成,实现了临床文本生成和对应生物医学对象的分割的统一。UniBiomed能够在多种生物医学成像模态上完成一系列任务。此外,它在数据集上实现了分割、疾病识别等任务的顶尖性能,能够提供自动化和端到端的解读,代表临床工作流程的新范式转变。总之,UniBiomed是生物医学AI领域的一项重大突破。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态解读为生物医学图像分析提供了新的机会。
- 传统AI方法存在灵活性问题,无法实现全面利用生物医学信息。
- UniBiomed是一个用于生物医学图像解读的统一基础模型。
- UniBiomed通过MLLM和SAM的集成,实现了临床文本生成和生物医学对象分割的统一。
- UniBiomed能够在多种生物医学成像模态上完成一系列任务。
- UniBiomed在多个任务上实现了顶尖性能,包括分割、疾病识别等。
点此查看论文截图

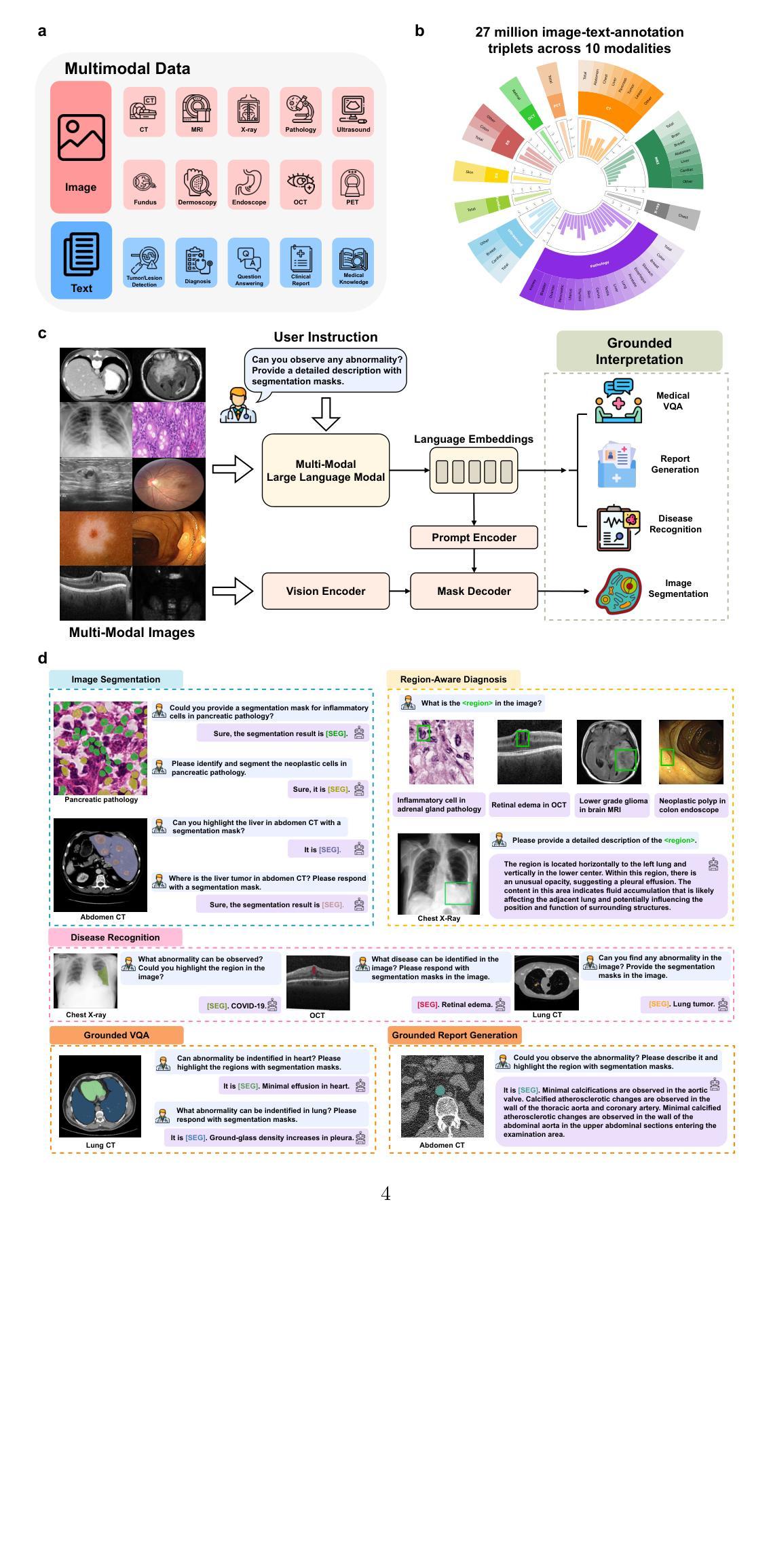
Mamba Based Feature Extraction And Adaptive Multilevel Feature Fusion For 3D Tumor Segmentation From Multi-modal Medical Image
Authors:Zexin Ji, Beiji Zou, Xiaoyan Kui, Hua Li, Pierre Vera, Su Ruan
Multi-modal 3D medical image segmentation aims to accurately identify tumor regions across different modalities, facing challenges from variations in image intensity and tumor morphology. Traditional convolutional neural network (CNN)-based methods struggle with capturing global features, while Transformers-based methods, despite effectively capturing global context, encounter high computational costs in 3D medical image segmentation. The Mamba model combines linear scalability with long-distance modeling, making it a promising approach for visual representation learning. However, Mamba-based 3D multi-modal segmentation still struggles to leverage modality-specific features and fuse complementary information effectively. In this paper, we propose a Mamba based feature extraction and adaptive multilevel feature fusion for 3D tumor segmentation using multi-modal medical image. We first develop the specific modality Mamba encoder to efficiently extract long-range relevant features that represent anatomical and pathological structures present in each modality. Moreover, we design an bi-level synergistic integration block that dynamically merges multi-modal and multi-level complementary features by the modality attention and channel attention learning. Lastly, the decoder combines deep semantic information with fine-grained details to generate the tumor segmentation map. Experimental results on medical image datasets (PET/CT and MRI multi-sequence) show that our approach achieve competitive performance compared to the state-of-the-art CNN, Transformer, and Mamba-based approaches.
多模态3D医学图像分割旨在准确识别不同模态下的肿瘤区域,面临来自图像强度和肿瘤形态变化的挑战。传统基于卷积神经网络(CNN)的方法在捕捉全局特征时遇到困难,而基于Transformer的方法虽然能够有效地捕捉全局上下文,但在3D医学图像分割中面临高计算成本的问题。Mamba模型结合了线性可扩展性和长距离建模,使其成为视觉表示学习的有前途的方法。然而,基于Mamba的3D多模态分割仍然难以利用特定模态的特征并有效地融合互补信息。在本文中,我们提出了一种基于Mamba的特征提取和自适应多级特征融合方法,用于使用多模态医学图像进行3D肿瘤分割。我们首先开发了一种特定模态的Mamba编码器,以有效地提取代表每种模态中存在的解剖和病理结构的长程相关特征。此外,我们设计了一个两级协同集成块,通过模态注意力和通道注意力学习来动态融合多模态和多级互补特征。最后,解码器将深度语义信息与细节相结合,生成肿瘤分割图。在医学图像数据集(PET/CT和MRI多序列)上的实验结果表明,我们的方法与最先进的CNN、Transformer和Mamba方法相比,取得了具有竞争力的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
多模态3D医学图像分割面临不同模态下肿瘤区域准确识别以及图像强度变化和肿瘤形态变化的挑战。传统卷积神经网络(CNN)方法难以捕捉全局特征,而基于Transformer的方法虽然能有效捕捉全局上下文,但在3D医学图像分割中计算成本较高。Mamba模型具有线性可扩展性和远距离建模能力,在视觉表示学习中具有广阔前景。然而,基于Mamba的3D多模态分割在利用特定模态特征和有效融合互补信息方面仍存在挑战。本文提出一种基于Mamba的特征提取和自适应多级特征融合方法,用于使用多模态医学图像进行3D肿瘤分割。首先开发特定模态的Mamba编码器,以有效提取代表每种模态的解剖和病理结构的长期相关特征。其次设计了一种两级协同集成模块,通过模态注意力和通道注意力学习动态融合多模态和多级互补特征。最后,解码器结合深层语义信息和细节生成肿瘤分割图。在医学图像数据集(PET/CT和MRI多序列)上的实验结果表明,该方法与最新的CNN、Transformer和Mamba方法相比具有竞争力。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态3D医学图像分割旨在准确识别不同模态下的肿瘤区域,面临图像强度变化和肿瘤形态变化的挑战。
- 传统CNN方法难以捕捉全局特征,而基于Transformer的方法计算成本高。
- Mamba模型具有线性可扩展性和远距离建模能力,在医学图像分割中展现出潜力。
- 基于Mamba的3D多模态分割在利用特定模态特征和融合互补信息方面仍有挑战。
- 论文提出了一种基于Mamba的特征提取和自适应多级特征融合方法,结合特定模态的Mamba编码器和协同集成模块实现精准分割。
- 论文设计的模型在医学图像数据集上的表现具有竞争力。
点此查看论文截图

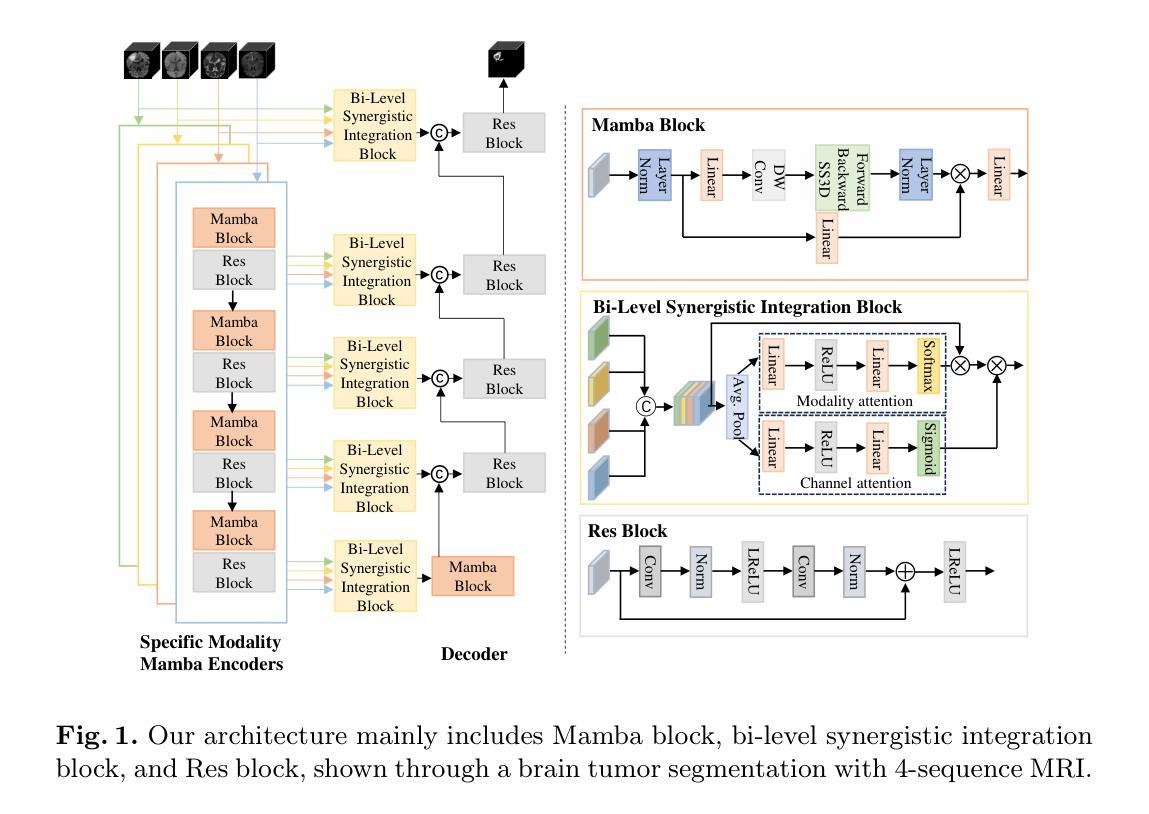
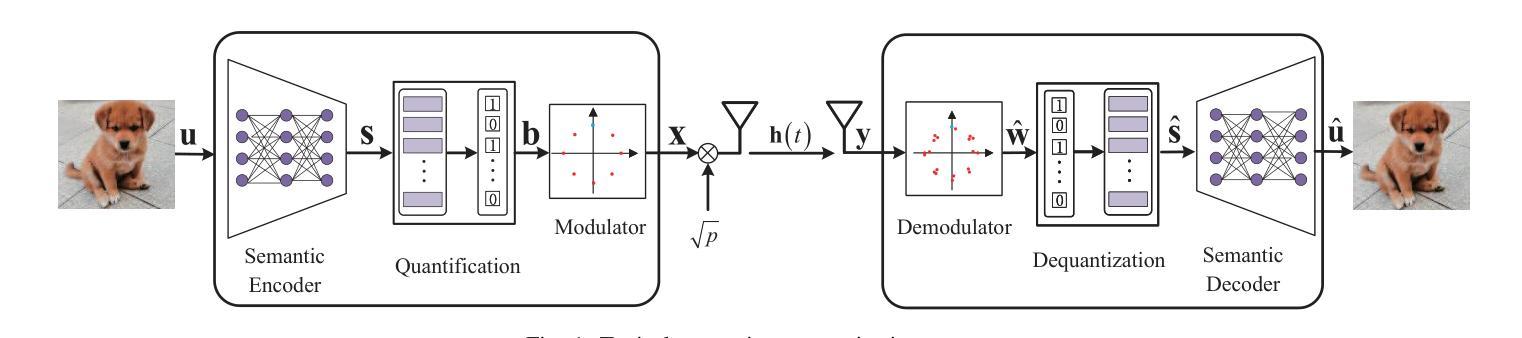
Modeling and Performance Analysis for Semantic Communications Based on Empirical Results
Authors:Shuai Ma, Bin Shen, Chuanhui Zhang, Youlong Wu, Hang Li, Shiyin Li, Guangming Shi, Naofal Al-Dhahir
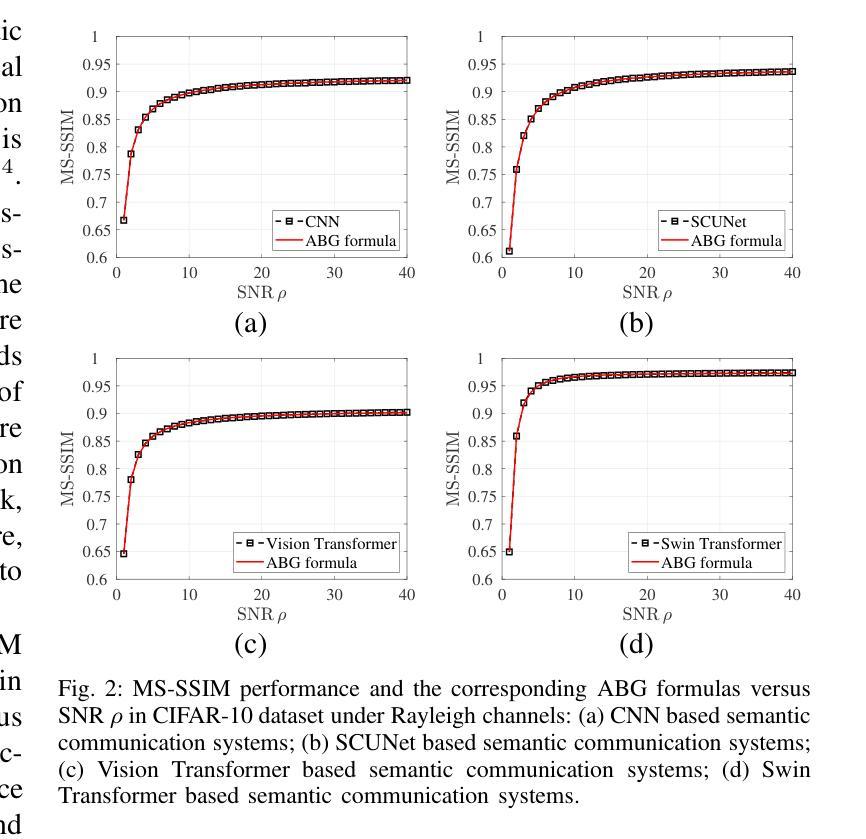
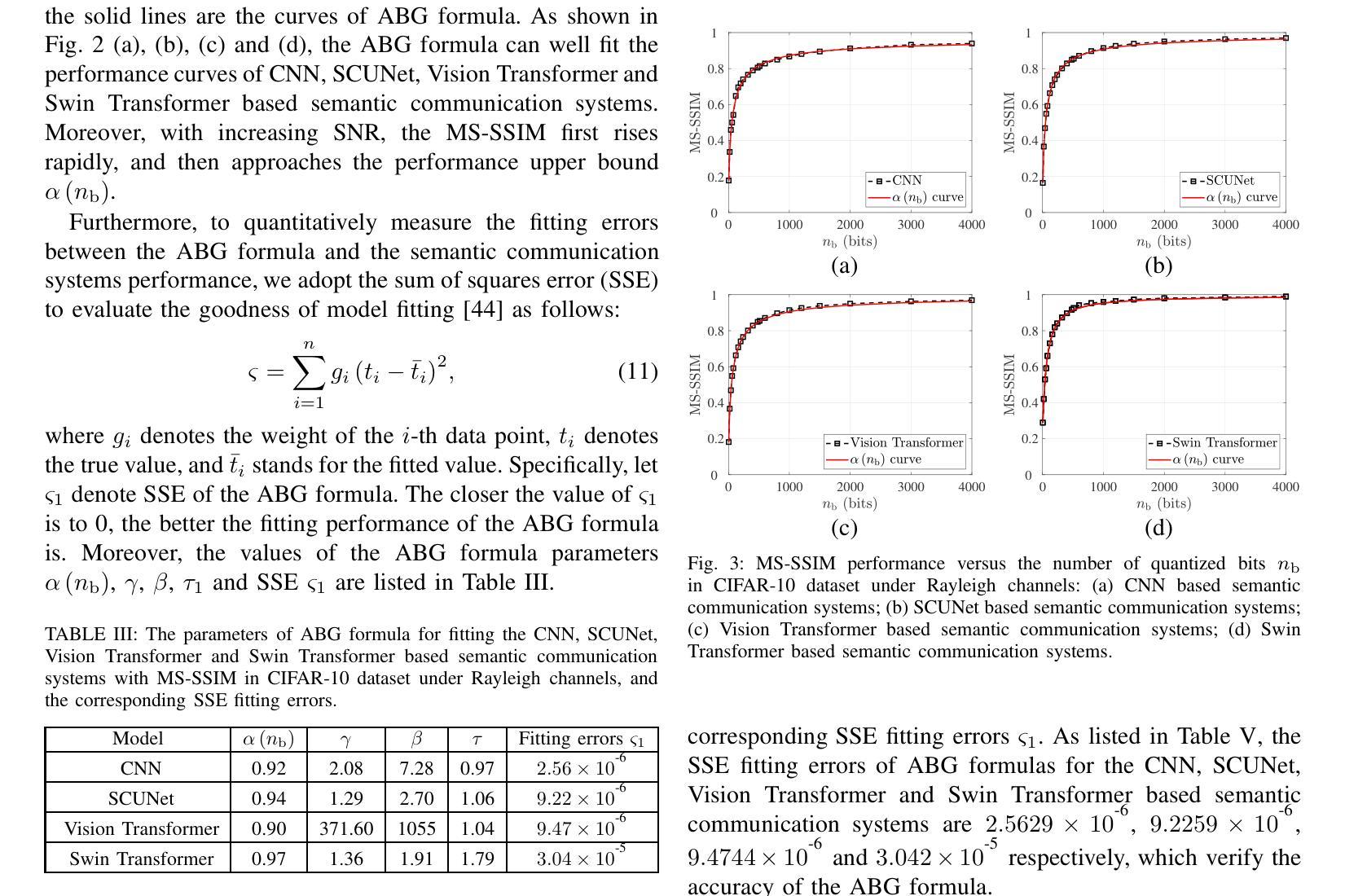
Due to the black-box characteristics of deep learning based semantic encoders and decoders, finding a tractable method for the performance analysis of semantic communications is a challenging problem. In this paper, we propose an Alpha-Beta-Gamma (ABG) formula to model the relationship between the end-to-end measurement and SNR, which can be applied for both image reconstruction tasks and inference tasks. Specifically, for image reconstruction tasks, the proposed ABG formula can well fit the commonly used DL networks, such as SCUNet, and Vision Transformer, for semantic encoding with the multi scale-structural similarity index measure (MS-SSIM) measurement. Furthermore, we find that the upper bound of the MS-SSIM depends on the number of quantized output bits of semantic encoders, and we also propose a closed-form expression to fit the relationship between the MS-SSIM and quantized output bits. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first theoretical expression between end-to-end performance metrics and SNR for semantic communications. Based on the proposed ABG formula, we investigate an adaptive power control scheme for semantic communications over random fading channels, which can effectively guarantee quality of service (QoS) for semantic communications, and then design the optimal power allocation scheme to maximize the energy efficiency of the semantic communication system. Furthermore, by exploiting the bisection algorithm, we develop the power allocation scheme to maximize the minimum QoS of multiple users for OFDMA downlink semantic communication Extensive simulations verify the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed ABG formula and power allocation schemes.
由于基于深度学习的语义编码器和解码器的黑箱特性,找到一种用于语义通信性能分析的可行方法是一个具有挑战性的问题。在本文中,我们提出一个Alpha-Beta-Gamma(ABG)公式,用于建模端到端测量与信噪比之间的关系,该公式既可用于图像重建任务,也可用于推理任务。具体来说,对于图像重建任务,提出的ABG公式能够很好地适应常用的DL网络,如SCUNet和Vision Transformer,进行具有多尺度结构相似性指数度量(MS-SSIM)的语义编码。此外,我们发现MS-SSIM的上限取决于语义编码器的量化输出位数,我们还提出了一个封闭形式的表达式来拟合MS-SSIM与量化输出位之间的关系。据我们所知,这是语义通信端到端性能指标和信噪比之间的第一个理论表达式。基于提出的ABG公式,我们研究了随机衰落信道上的语义通信的自适应功率控制方案,该方案可以有效地保证语义通信的服务质量(QoS),然后设计最优功率分配方案以最大化语义通信系统的能源效率。此外,通过利用二分算法,我们开发了功率分配方案,以最大化多个用户在OFDMA下行链路语义通信中的最低QoS。大量仿真验证了所提出的ABG公式和功率分配方案的有效性和优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种Alpha-Beta-Gamma(ABG)公式,用于建模语义通信端到端测量与信噪比(SNR)之间的关系,适用于图像重建和推理任务。对于图像重建任务,ABG公式能很好地适应常用的深度学习网络(如SCUNet和Vision Transformer)。研究发现,多尺度结构相似性指数度量(MS-SSIM)的上限取决于语义编码器的量化输出位数,并提出一个封闭形式的表达式来描述它们之间的关系。此外,基于ABG公式,研究了一种针对随机衰落信道的自适应功率控制方案,保证语义通信的服务质量(QoS),并设计了最优功率分配方案,最大化语义通信系统的能源效率。模拟结果表明ABG公式和功率分配方案的有效性和优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 提出Alpha-Beta-Gamma(ABG)公式,用于建模语义通信端到端测量与信噪比(SNR)的关系。
- ABG公式适用于图像重建和推理任务,并能适应常见的深度学习网络。
- MS-SSIM的上限受语义编码器的量化输出位数影响。
- 提出封闭形式的表达式描述MS-SSIM与量化输出位数的关系。
- 基于ABG公式,研究了一种自适应功率控制方案,保证语义通信的服务质量。
- 设计了最优功率分配方案,以最大化语义通信系统的能源效率。
点此查看论文截图

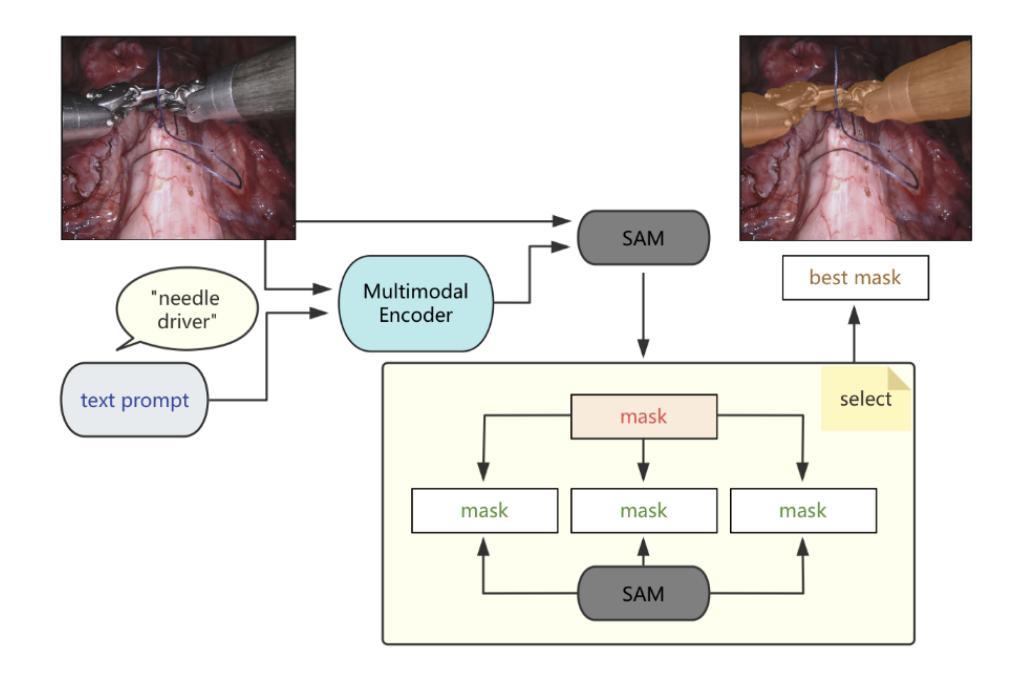
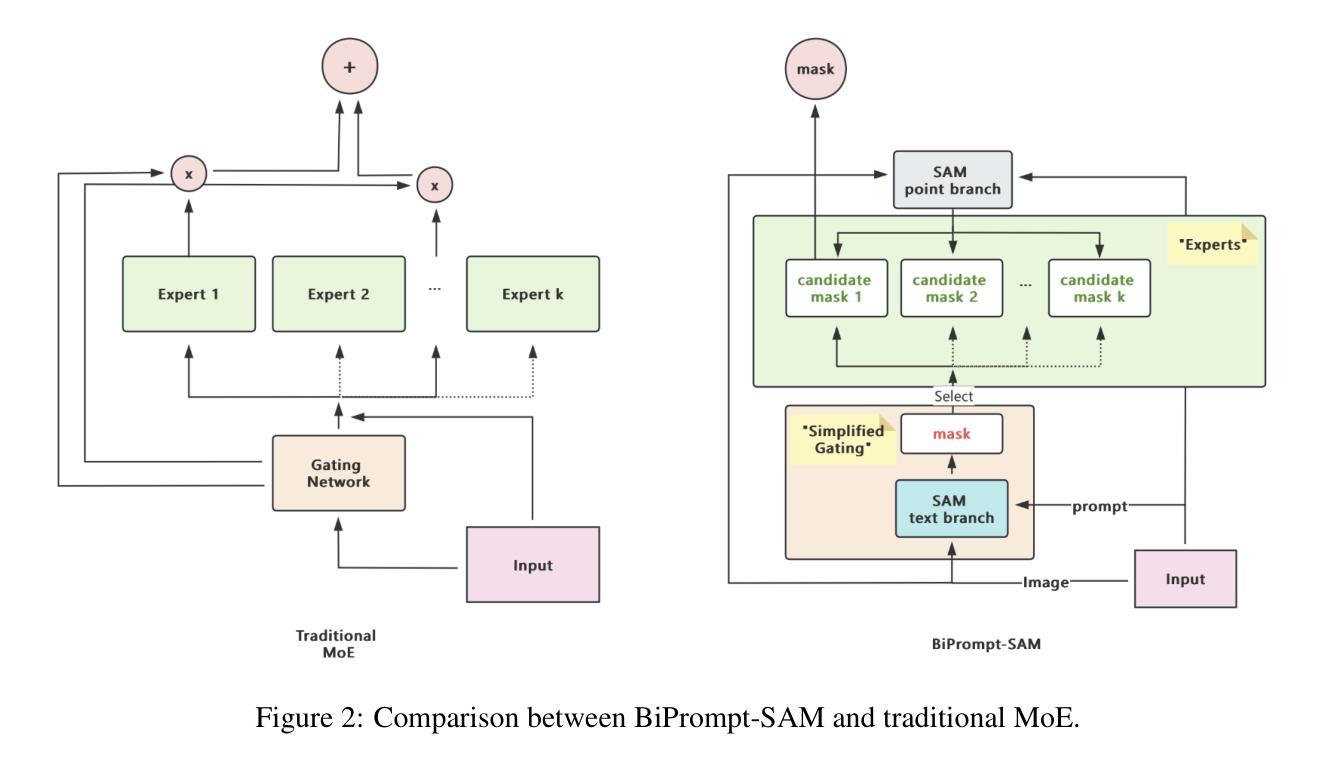
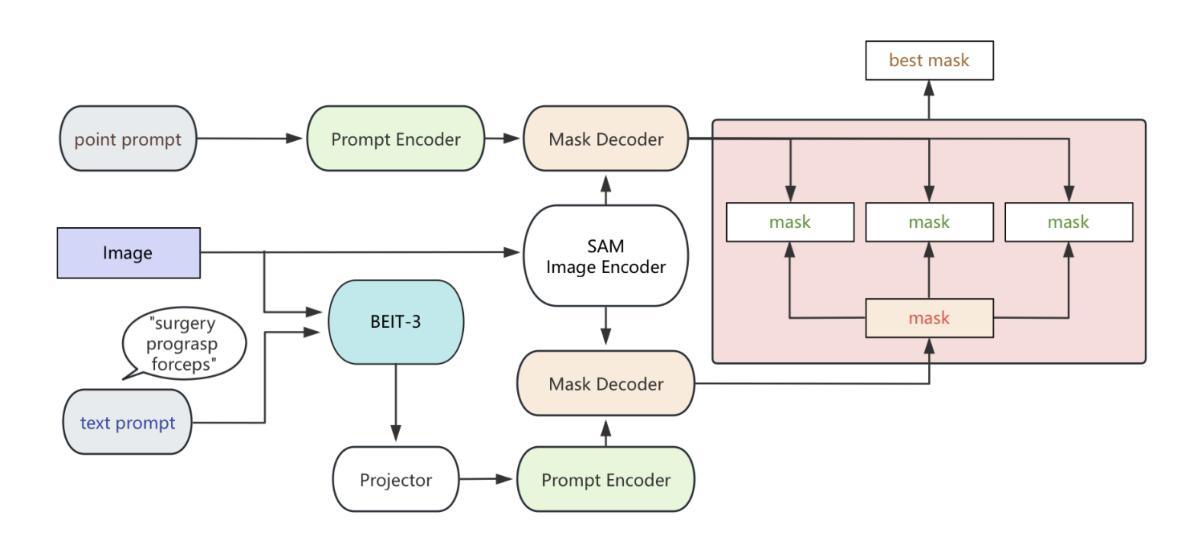
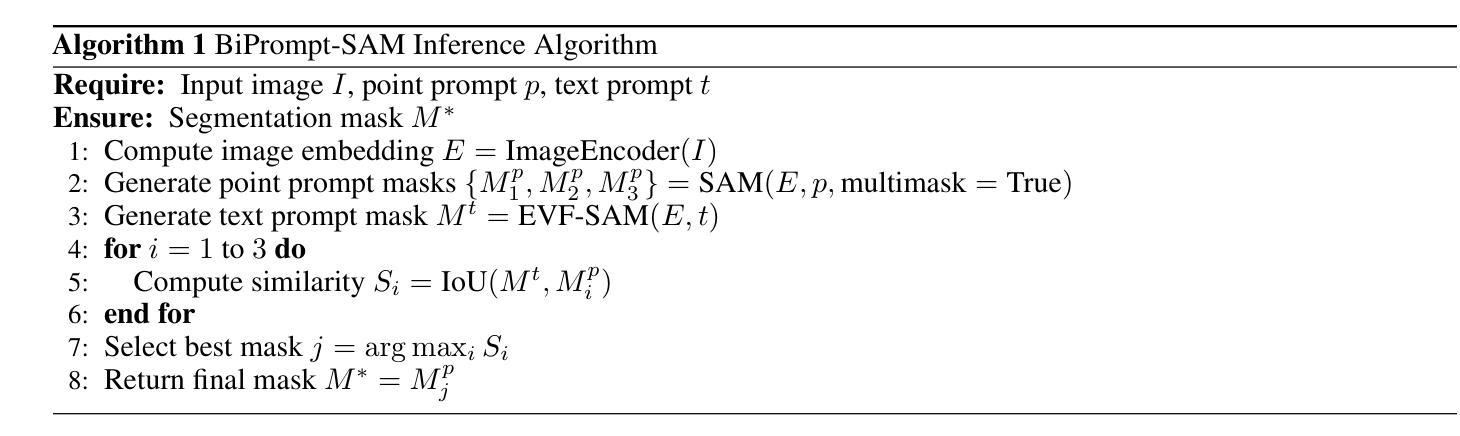
BiPrompt-SAM: Enhancing Image Segmentation via Explicit Selection between Point and Text Prompts
Authors:Suzhe Xu, Jialin Peng, Chengyuan Zhang
Segmentation is a fundamental task in computer vision, with prompt-driven methods gaining prominence due to their flexibility. The Segment Anything Model (SAM) excels at point-prompted segmentation, while text-based models, often leveraging powerful multimodal encoders like BEIT-3, provide rich semantic understanding. However, effectively combining these complementary modalities remains a challenge. This paper introduces BiPrompt-SAM, a novel dual-modal prompt segmentation framework employing an explicit selection mechanism. We leverage SAM’s ability to generate multiple mask candidates from a single point prompt and use a text-guided mask (generated via EVF-SAM with BEIT-3) to select the point-generated mask that best aligns spatially, measured by Intersection over Union (IoU). This approach, interpretable as a simplified Mixture of Experts (MoE), effectively fuses spatial precision and semantic context without complex model modifications. Notably, our method achieves strong zero-shot performance on the Endovis17 medical dataset (89.55% mDice, 81.46% mIoU) using only a single point prompt per instance. This significantly reduces annotation burden compared to bounding boxes and aligns better with practical clinical workflows, demonstrating the method’s effectiveness without domain-specific training. On the RefCOCO series, BiPrompt-SAM attained 87.1%, 86.5%, and 85.8% IoU, significantly outperforming existing approaches. Experiments show BiPrompt-SAM excels in scenarios requiring both spatial accuracy and semantic disambiguation, offering a simple, effective, and interpretable perspective on multi-modal prompt fusion.
分割是计算机视觉中的一项基本任务,由于灵活性,基于提示的方法逐渐受到重视。Segment Anything Model(SAM)在点提示分割方面表现出色,而基于文本模型则经常利用强大的多模态编码器(如BEIT-3)提供丰富的语义理解。然而,如何有效地结合这些互补模态仍然是一个挑战。本文介绍了BiPrompt-SAM,这是一种采用显式选择机制的新型双模态提示分割框架。我们利用SAM从单个点提示生成多个掩码候选的能力,并使用文本引导掩码(通过EVF-SAM与BEIT-3生成)选择空间上最佳对齐的点生成掩码,通过交集并集(IoU)来衡量。这种方法可以解释为简化的混合专家(MoE),可以有效地融合空间精度和语义上下文,而无需复杂的模型修改。值得注意的是,我们的方法在Endovis17医学数据集上实现了强大的零样本性能(mDice为89.55%,mIoU为81.46%),每个实例仅使用单个点提示。这大大降低了与边界框相比的注释负担,并更好地与实际的临床工作流程对齐,证明了该方法在无需特定领域训练的情况下的有效性。在RefCOCO系列上,BiPrompt-SAM达到了87.1%,86.5%和85.8%的IoU,显著优于现有方法。实验表明,BiPrompt-SAM在需要空间准确性和语义消歧的场景中表现出色,为多模态提示融合提供了简单、有效和可解释的视角。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了BiPrompt-SAM,一种新型的双模态提示分割框架,它结合了Segment Anything Model(SAM)和文本引导的方法。通过利用SAM生成多个掩膜候选,并结合文本指导掩膜选择最佳的空间对齐掩膜,实现了空间精度和语义上下文的融合。在医学数据集Endovis17和RefCOCO系列上的实验表明,该方法在不需要特定领域训练的情况下,表现出强大的零样本性能。
Key Takeaways
- BiPrompt-SAM结合了点提示分割方法和文本引导的方法,是一种新型的双模态提示分割框架。
- 利用SAM生成多个掩膜候选,通过文本指导选择最佳的空间对齐掩膜。
- 方法实现了空间精度和语义上下文的融合,可看作是一种简化的Mixture of Experts (MoE)。
- 在医学数据集Endovis17上实现了强大的零样本性能,使用单个点提示降低了标注负担,更符合实际临床工作流程。
- 在RefCOCO系列上,BiPrompt-SAM显著优于现有方法。
- 实验表明,BiPrompt-SAM在需要空间精度和语义辨析的场景中表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

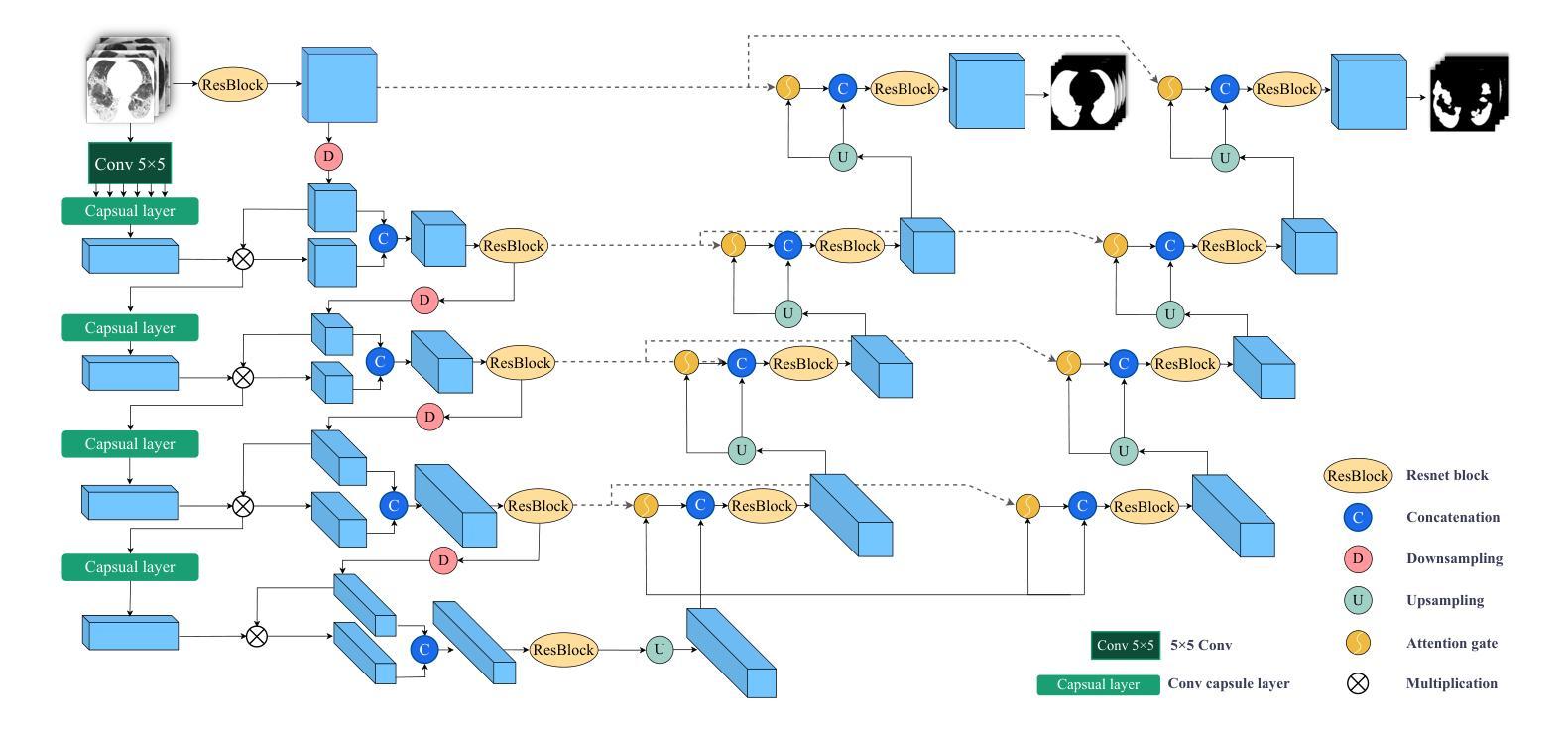
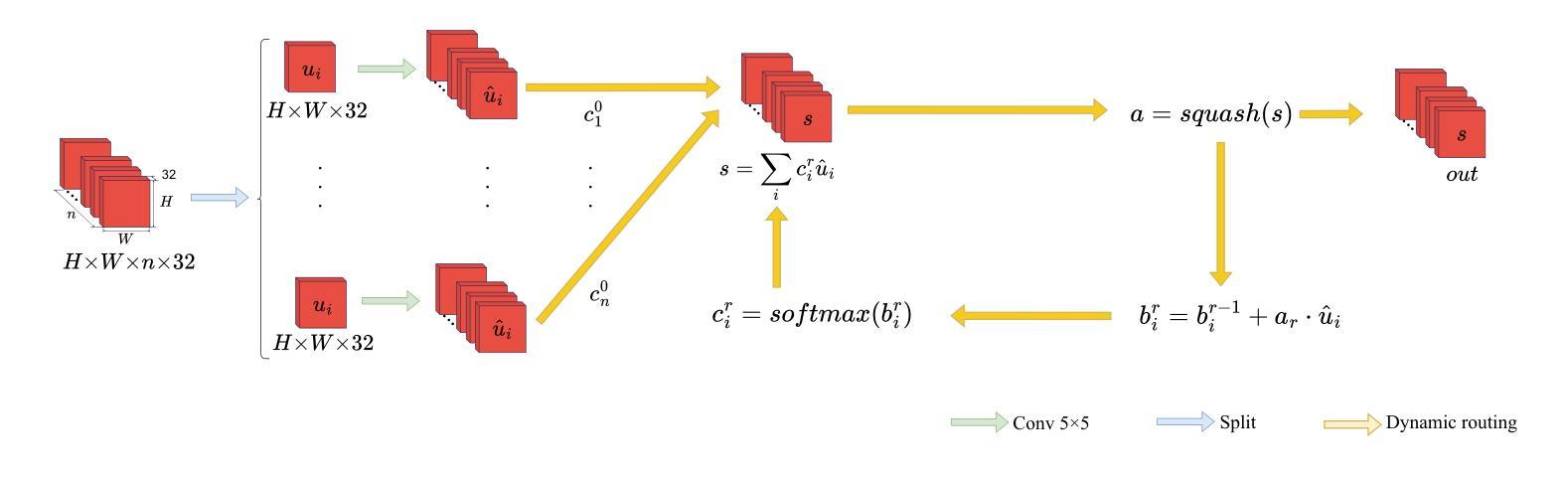
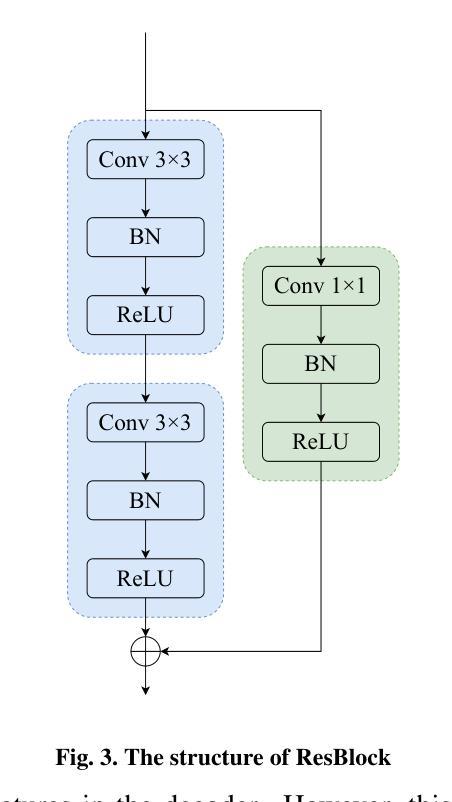
CAD-Unet: A Capsule Network-Enhanced Unet Architecture for Accurate Segmentation of COVID-19 Lung Infections from CT Images
Authors:Yijie Dang, Weijun Ma, Xiaohu Luo, Huaizhu Wang
Since the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2019, medical imaging has emerged as a primary modality for diagnosing COVID-19 pneumonia. In clinical settings, the segmentation of lung infections from computed tomography images enables rapid and accurate quantification and diagnosis of COVID-19. Segmentation of COVID-19 infections in the lungs poses a formidable challenge, primarily due to the indistinct boundaries and limited contrast presented by ground glass opacity manifestations. Moreover, the confounding similarity between infiltrates, lung tissues, and lung walls further complicates this segmentation task. To address these challenges, this paper introduces a novel deep network architecture, called CAD-Unet, for segmenting COVID-19 lung infections. In this architecture, capsule networks are incorporated into the existing Unet framework. Capsule networks represent a novel network architecture that differs from traditional convolutional neural networks. They utilize vectors for information transfer among capsules, facilitating the extraction of intricate lesion spatial information. Additionally, we design a capsule encoder path and establish a coupling path between the unet encoder and the capsule encoder. This design maximizes the complementary advantages of both network structures while achieving efficient information fusion. \noindent Finally, extensive experiments are conducted on four publicly available datasets, encompassing binary segmentation tasks and multi-class segmentation tasks. The experimental results demonstrate the superior segmentation performance of the proposed model. The code has been released at: https://github.com/AmanoTooko-jie/CAD-Unet.
自2019年COVID-19疫情爆发以来,医学成像已成为诊断COVID-19肺炎的主要方式。在临床环境中,从计算机断层扫描图像中对肺部感染进行分割,能够实现COVID-19的快速和准确量化及诊断。COVID-19肺部感染分割面临巨大挑战,主要是由于磨玻璃样混浊表现的特征边界不清和对比度有限。此外,浸润、肺组织和肺壁之间的混淆相似性进一步加剧了这一分割任务的复杂性。为了解决这些挑战,本文引入了一种新型的深度网络架构,称为CAD-Unet,用于分割COVID-19肺部感染。该架构结合了现有的Unet框架并融入了胶囊网络。胶囊网络代表了一种不同于传统卷积神经网络的新型网络架构。它们使用向量进行胶囊之间的信息传递,便于提取复杂的病变空间信息。此外,我们设计了一个胶囊编码器路径,并在Unet编码器和胶囊编码器之间建立了一条耦合路径。这一设计最大限度地发挥了两种网络结构的互补优势,实现了高效的信息融合。最后,在四个公开数据集上进行了大量实验,包括二元分割任务和多类分割任务。实验结果证明了所提出模型的卓越分割性能。代码已发布在:[https://github.com/AmanoTooko-jie/CAD-Unet。]
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published in Medical Image Analysis, Volume 103, 2025, Pages 103583. DOI: 10.1016/j.media.2025.103583 This is the author’s pre-print version prior to final journal edits. Final published version available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1361841525001306
Summary
该文本介绍了COVID-19疫情期间,医学成像成为诊断新冠肺炎的主要手段之一。文中提出一种新的深度网络架构CAD-Unet,用于分割肺部COVID-19感染区域。该架构结合了胶囊网络与传统Unet框架,提高了信息融合效率,实现了肺部感染区域的精准分割。实验证明,该模型在多种数据集上表现优异。相关代码已发布于GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- COVID-19疫情期间,医学成像成为诊断新冠肺炎的主要手段之一。
- 肺部感染区域分割是诊断的关键挑战,因边界模糊和对比度有限。
- 引入新型深度网络架构CAD-Unet,结合胶囊网络与Unet框架解决挑战。
- 胶囊网络能提取病变的空间信息,提高信息融合效率。
- CAD-Unet实现了高效的信息融合,充分利用两种网络结构的优势。
- 实验证明,该模型在多种数据集上表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

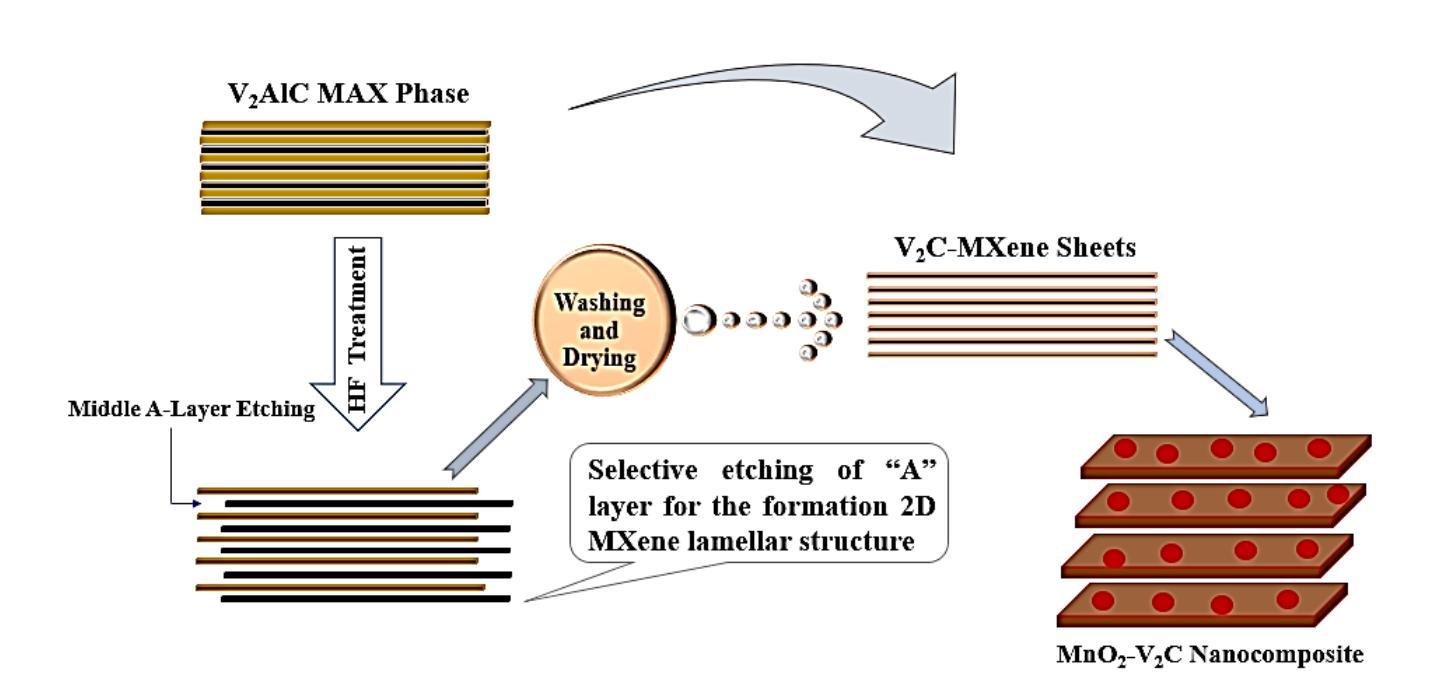
A Density Functional Theory Study of Magnetic Transition in MnO2 adsorbed Vanadium Carbide (V$_2$C) MXene
Authors:Mahjabeen Fatima, Saleem Ayaz Khan, Syed Rizwan
The work reports nonmagnetic behavior (0.04 $\mu$B) in two-dimensional (2D) V2C-OF MXene and ferromagnetism in MnO$_2$ adsorbed V2C-OF MXene. The density functional theory (DFT) calculations were carried out to study the magnetic moments of V$_2$C-OF and MnO$_2$@V$_2$C-OF MXene. The MXene, which is derived from the exfoliation of its parent V$_2$AlC MAX phase, shows a good potential to be a ferromagnetic when MnO$_2$ is adsorbed on it. The V$_2$C MXene and MnO$_2$ adsorbed V$_2$C MXene were successfully synthesized, as characterized using X-ray diffraction, showing an increased c-lattice parameter from 22.6{\AA} to 27.2{\AA} after MnO$_2$ adsorption. The DFT study confirmed that MnO$_2$ adsorbed V$_2$C MXene changed from nonmagnetic (in V$_2$C MXene) to a strong ferromagnetic with a magnetic moment of 4.48$\mu$B for Mn adsorbed V$_2$C-OF MXene. The current work is a step-forward towards understanding of magnetism in two-dimensional materials for future 2D spintronics.
这篇论文报道了二维V2C-OF MXene的非磁性行为(0.04μB),以及在MnO2吸附的V2C-OF MXene上表现出铁磁性。通过密度泛函理论(DFT)计算,研究了V2C-OF和MnO2@V2C-OF MXene的磁矩。MXene是从其母体V2AlC MAX相剥离而来,当MnO2吸附在其上时,具有成为铁磁体的潜力。V2C MXene和MnO2吸附的V2C MXene已成功合成,经X射线衍射表征,MnO2吸附后c晶格参数从22.6Å增加到27.2Å。DFT研究证实,MnO2吸附的V2C MXene从非磁性(在V2C MXene中)转变为强铁磁性,对于Mn吸附的V2C-OF MXene,磁矩为4.48μB。当前的工作是朝着理解二维材料磁性的方向迈出的一步,为未来二维自旋电子学的发展奠定基础。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了二维V₂C-OF MXene的非磁性行为和MnO₂吸附在V₂C-OF MXene上的铁磁性。通过密度泛函理论(DFT)计算了V₂C-OF和MnO₂@V₂C-OF MXene的磁矩。MXene从其母体V₂AlC MAX相中剥离出来,当MnO₂吸附在其上时,具有成为铁磁体的潜力。成功合成V₂C MXene和MnO₂吸附的V₂C MXene,经X射线衍射表征,MnO₂吸附后c晶格参数从22.6Å增加到27.2Å。DFT研究表明,MnO₂吸附的V₂C MXene从非磁性(在V₂C MXene中)变为强铁磁性,磁矩为Mn吸附的V₂C-OF MXene为4.48μB。这项工作是理解二维材料磁性的重要一步,为未来二维自旋电子学提供了参考。
Key Takeaways
- V₂C-OF MXene表现出非磁性行为,而MnO₂吸附在其上时表现出铁磁性。
- 通过密度泛函理论(DFT)计算了V₂C-OF和MnO₂@V₂C-OF MXene的磁矩。
- MXene是从V₂AlC MAX相剥离得到的,具有潜在的铁磁性。
- 成功合成V₂C MXene和MnO₂吸附的V₂C MXene,并通过X射线衍射进行了表征。
- MnO₂吸附后,c晶格参数有所增加。
- DFT研究显示MnO₂吸附的V₂C MXene具有强铁磁性。
点此查看论文截图

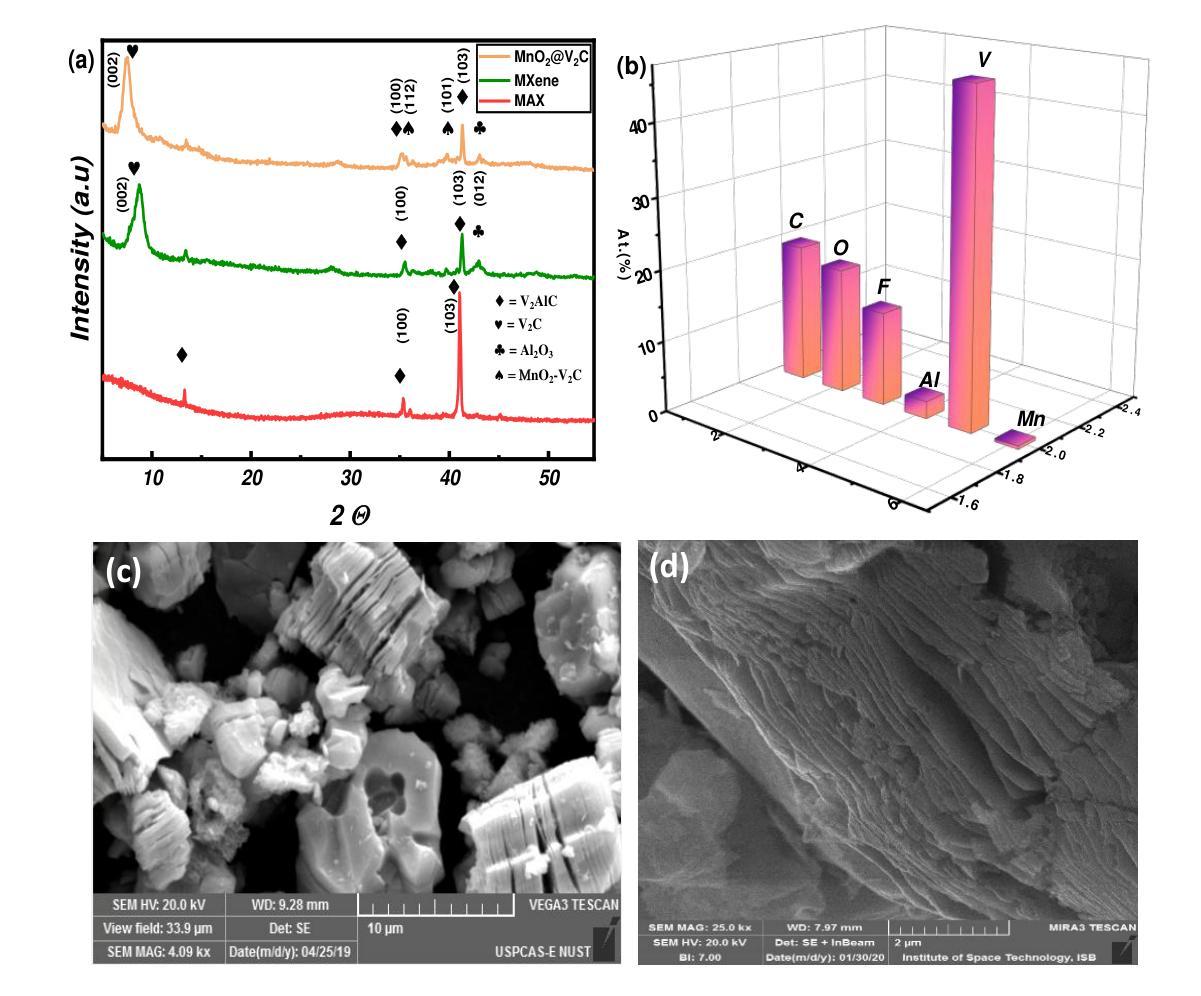
SmoothSegNet: A Global-Local Framework for Liver Tumor Segmentation with Clinical KnowledgeInformed Label Smoothing
Authors:Hairong Wang, Lingchao Mao, Zihan Zhang, Jing Li
Liver cancer is a leading cause of mortality worldwide, and accurate Computed Tomography (CT)-based tumor segmentation is essential for diagnosis and treatment. Manual delineation is time-intensive, prone to variability, and highlights the need for reliable automation. While deep learning has shown promise for automated liver segmentation, precise liver tumor segmentation remains challenging due to the heterogeneous nature of tumors, imprecise tumor margins, and limited labeled data. We present SmoothSegNet, a novel deep learning framework that addresses these challenges with the three key designs: (1) A novel knowledge-informed label smoothing technique that distills knowledge from clinical data to generate smooth labels, which are used to regularize model training, reducing the overfitting risk and enhancing model performance; (2) A global and local segmentation framework that breaks down the main task into two simpler sub-tasks, allowing optimized preprocessing and training for each; and (3) Pre- and post-processing pipelines customized to the challenges of each subtask aimed to enhance tumor visibility and refines tumor boundaries. We apply the proposed model on a challenging HCC-TACE-Seg dataset and show that SmoothSegNet outperformed various benchmarks in segmentation performance, particularly at smaller tumors (<10cm). Our ablation studies show that the three design components complementarily contribute to the model improved performance. Code for the proposed method are available at https://github.com/lingchm/medassist-liver-cancer.
肝癌是全球主要的致死原因之一,而基于计算机断层扫描(CT)的精确肿瘤分割对于诊断和治疗至关重要。手动描绘既耗时又容易出现偏差,这突显了可靠自动化需求的必要性。虽然深度学习在肝脏分割的自动化方面已显示出潜力,但由于肿瘤的异质性、肿瘤边界的不精确以及标记数据的有限性,精确的肝脏肿瘤分割仍然具有挑战性。我们提出了SmoothSegNet,这是一种新的深度学习框架,通过三个关键设计来解决这些挑战:(1)一种新型的知识信息标签平滑技术,从临床数据中提炼知识以生成平滑标签,用于规范模型训练,降低过拟合风险,提高模型性能;(2)全局和局部分割框架将主要任务分解为两个更简单的子任务,允许针对每个任务进行优化预处理和训练;(3)针对每个子任务挑战的预处理和后处理管道,旨在提高肿瘤可见性并细化肿瘤边界。我们在具有挑战性的HCC-TACE-Seg数据集上应用所提出的模型,并证明SmoothSegNet在分割性能方面超过了各种基准测试,特别是在较小的肿瘤(<10cm)上。我们的消融研究表明,三个设计组件以互补的方式促进了模型性能的提高。所提出的方法的代码可在https://github.com/lingchm/medassist-liver-cancer上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于深度学习的肝脏肿瘤分割新方法SmoothSegNet,该方法通过采用知识指导的标签平滑技术、全局与局部分割框架以及针对子任务的预处理和后处理管道,解决了手动分割耗时、易出错和缺乏可靠自动化的问题。在HCC-TACE-Seg数据集上的实验表明,SmoothSegNet在分割性能上优于其他基准方法,特别是在小于10厘米的肿瘤上表现更优秀。
Key Takeaways
- SmoothSegNet是一种用于肝脏肿瘤分割的深度学习框架,旨在解决手动分割的耗时、易错和缺乏自动化的问题。
- 该方法采用了知识指导的标签平滑技术,通过临床数据的知识蒸馏生成平滑标签,以规范化模型训练,提高模型性能。
- SmoothSegNet采用全局和局部分割框架,将主要任务分解为两个更简单的子任务,以便对每个子任务进行优化的预处理和训练。
- 该方法还包含针对子任务的预处理和后处理管道,旨在提高肿瘤可见性并优化肿瘤边界。
- 在HCC-TACE-Seg数据集上的实验表明,SmoothSegNet在分割性能上优于其他基准方法。
- 特别地,该方法在小于10厘米的肿瘤上的表现更优秀。
点此查看论文截图

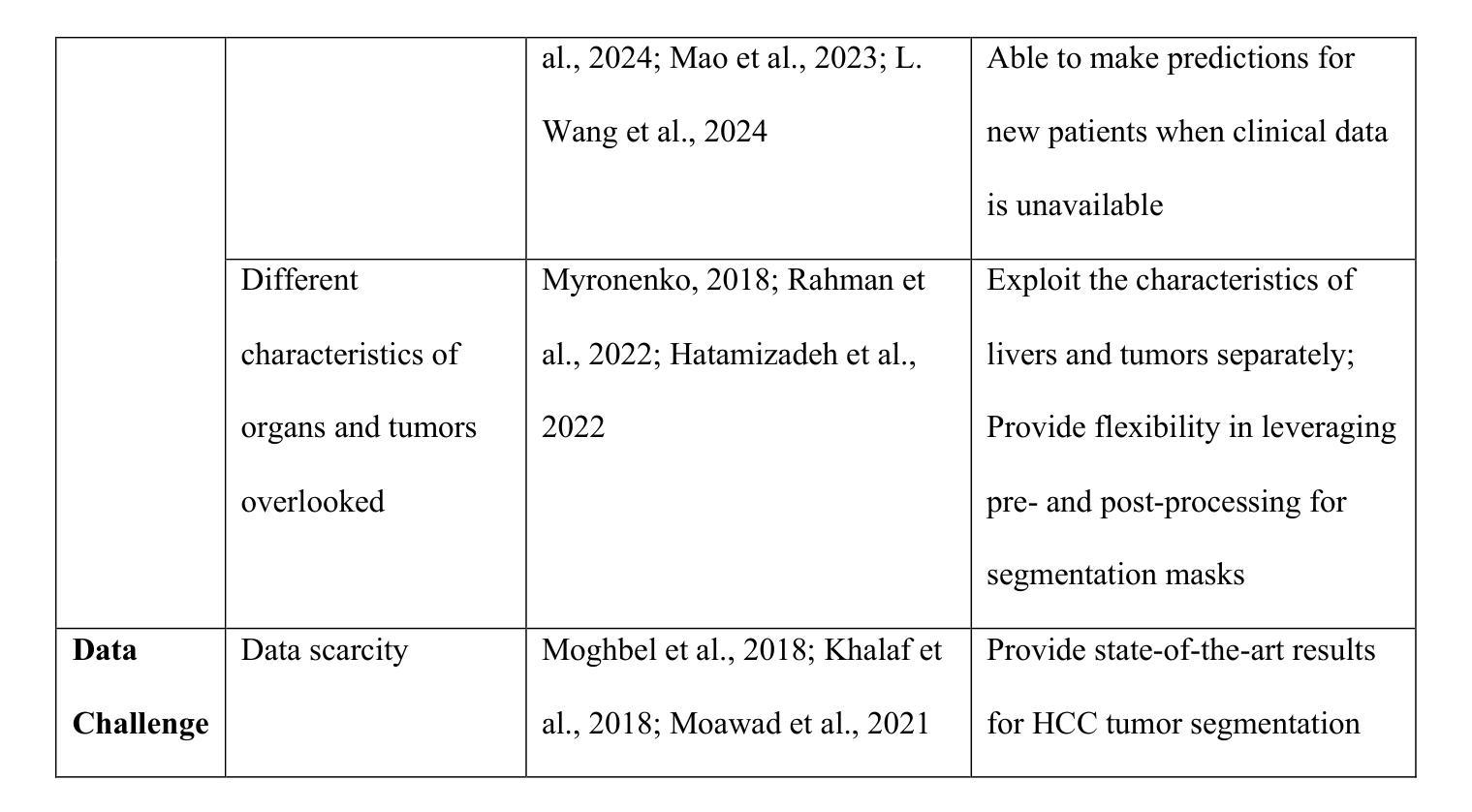
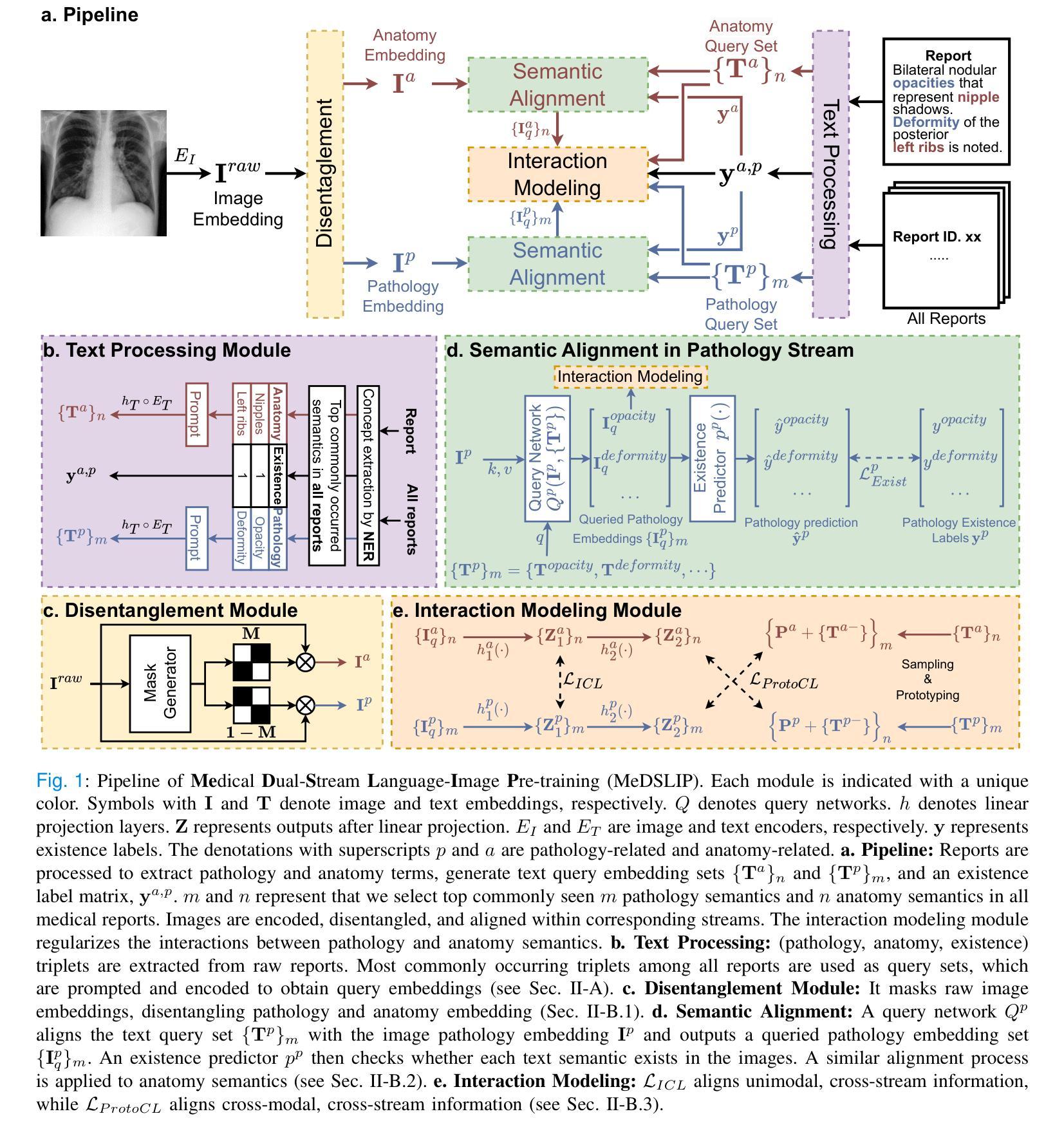
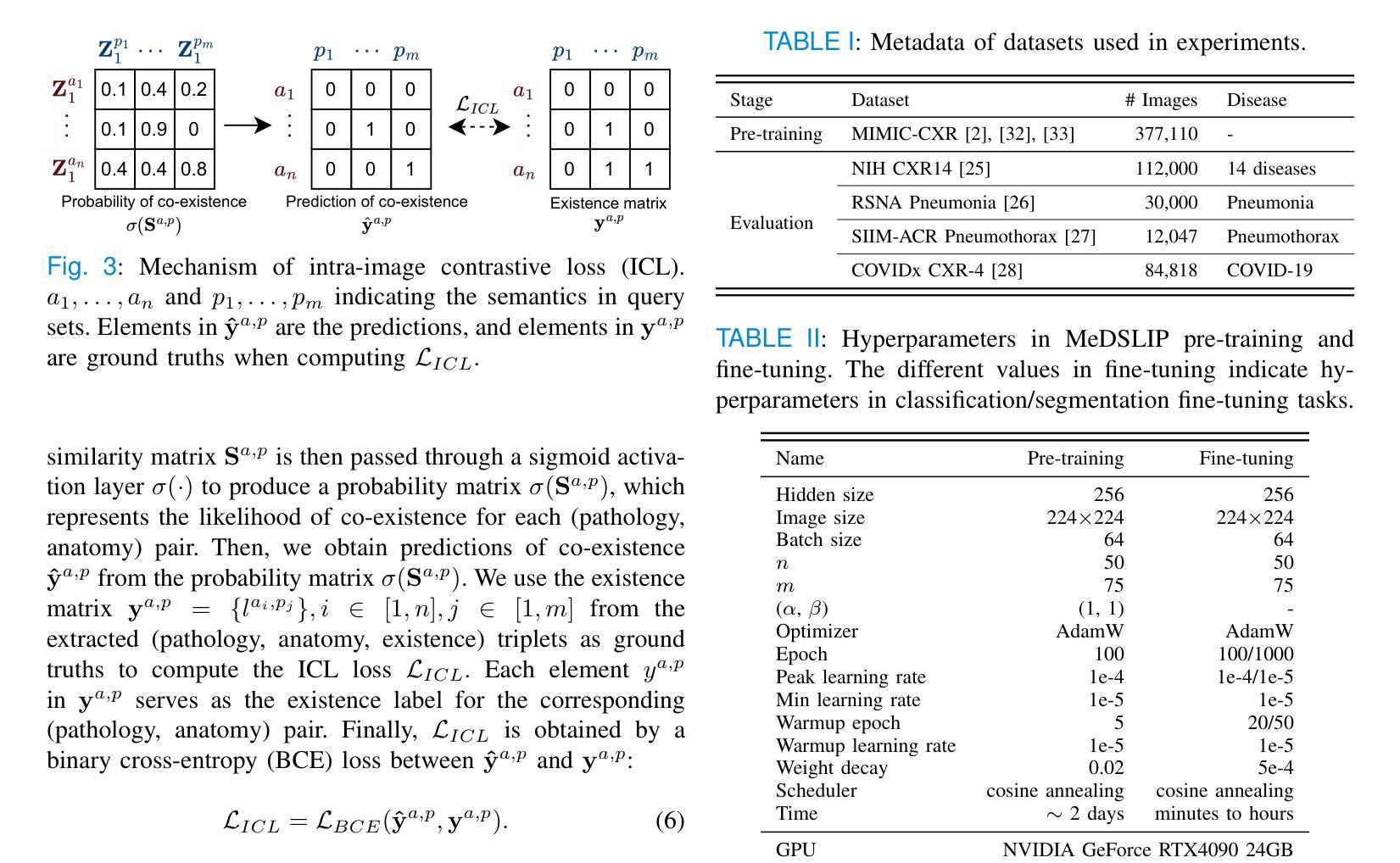
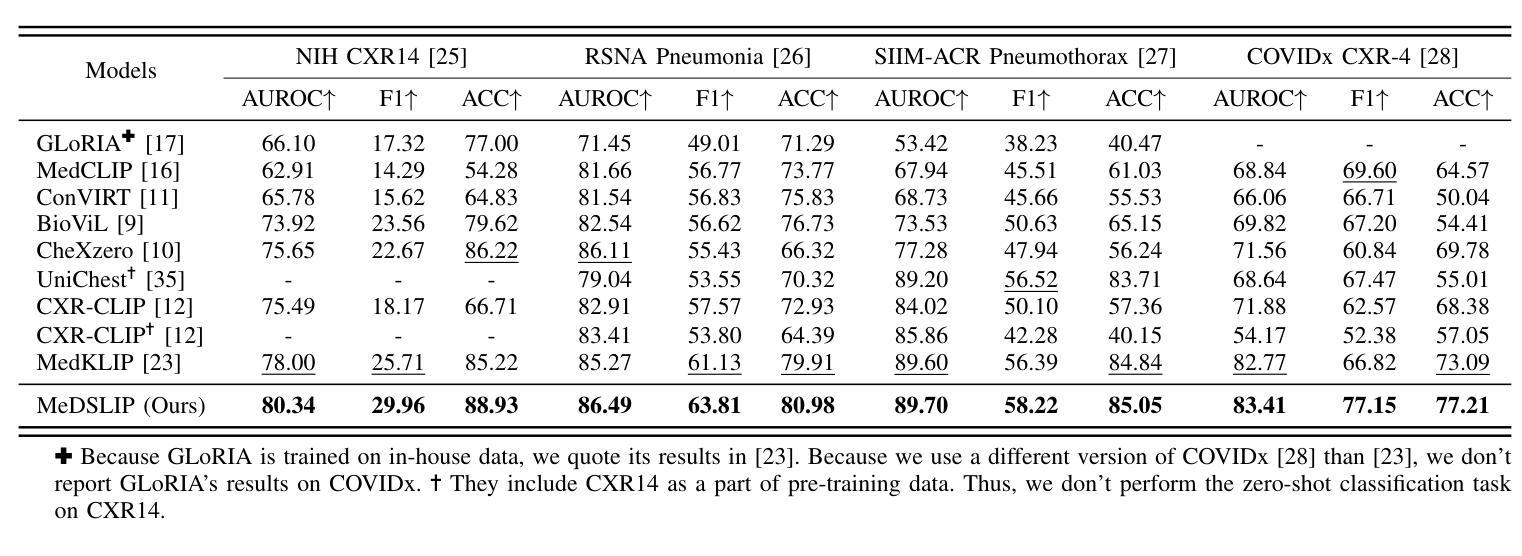
MeDSLIP: Medical Dual-Stream Language-Image Pre-training with Pathology-Anatomy Semantic Alignment
Authors:Wenrui Fan, Mohammod N. I. Suvon, Shuo Zhou, Xianyuan Liu, Samer Alabed, Venet Osmani, Andrew J. Swift, Chen Chen, Haiping Lu
Pathology and anatomy are two essential groups of semantics in medical data. Pathology describes what the diseases are, while anatomy explains where the diseases occur. They describe diseases from different perspectives, providing complementary insights into diseases. Thus, properly understanding these semantics and their relationships can enhance medical vision-language models (VLMs). However, pathology and anatomy semantics are usually entangled in medical data, hindering VLMs from explicitly modeling these semantics and their relationships. To address this challenge, we propose MeDSLIP, a novel Medical Dual-Stream Language-Image Pre-training pipeline, to disentangle pathology and anatomy semantics and model the relationships between them. We introduce a dual-stream mechanism in MeDSLIP to explicitly disentangle medical semantics into pathology-relevant and anatomy-relevant streams and align visual and textual information within each stream. Furthermore, we propose an interaction modeling module with prototypical contrastive learning loss and intra-image contrastive learning loss to regularize the relationships between pathology and anatomy semantics. We apply MeDSLIP to chest X-ray analysis and conduct comprehensive evaluations with four benchmark datasets: NIH CXR14, RSNA Pneumonia, SIIM-ACR Pneumothorax, and COVIDx CXR-4. The results demonstrate MeDSLIP’s superior generalizability and transferability across different scenarios. The code is available at https://github.com/Shef-AIRE/MeDSLIP, and the pre-trained model is released at https://huggingface.co/pykale/MeDSLIP.
病理学和解剖学是医疗数据中两个重要的语义类别。病理学描述疾病的本质,而解剖学解释疾病发生的部位。它们从不同角度描述疾病,为疾病研究提供互补的见解。因此,正确理解这些语义及其关系可以增强医疗视觉-语言模型(VLMs)的性能。然而,病理学和解剖学语义通常交织在医疗数据中,阻碍VLMs明确地对这些语义及其关系进行建模。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了MeDSLIP,这是一种新的医疗双流语言-图像预训练管道,用于分离病理学和解剖学语义,并建模它们之间的关系。我们在MeDSLIP中引入了双流机制,将医疗语义明确地分离为与病理学相关的流和与解剖学相关的流,并在每个流内对齐视觉和文本信息。此外,我们提出了一个交互建模模块,采用原型对比学习损失和图像内对比学习损失来规范病理学和解剖学语义之间的关系。我们将MeDSLIP应用于胸部X射线分析,并使用四个基准数据集进行了全面评估:NIH CXR14、RSNA肺炎、SIIM-ACR气胸和COVIDx CXR-4。结果表明,MeDSLIP在不同场景中具有出色的通用性和可迁移性。代码可在https://github.com/Shef-AIRE/MeDSLIP找到,预训练模型已在https://huggingface.co/pykale/MeDSLIP发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学数据中的病理学与解剖学语义是疾病描述的两个重要方面,分别关注疾病的本质和发生位置。二者结合提供了互补的疾病洞察。为了增强医疗视觉语言模型(VLMs)对这两者及关系的理解,我们面临语义纠缠的挑战。为解决此问题,提出MeDSLIP,一种新颖的医疗双流语言图像预训练流程,用于解析病理学与解剖学语义并建模其关系。它采用双流机制,将医学语义分为与病理学相关和与解剖学相关的流,并在每个流内对齐视觉和文本信息。此外,通过原型对比学习损失和图像内对比学习损失提出了交互建模模块来规范两者之间的关系。在胸部X光分析中,MeDSLIP在多个基准数据集上的表现证明了其出色的通用性和可迁移性。代码与预训练模型已发布。
Key Takeaways
- 病理学和解剖学是医学数据中的两个核心语义领域,分别关注疾病的本质和发生部位,两者提供对疾病的互补视角。
- 现有的医疗视觉语言模型(VLMs)在理解和建模这些语义及其关系时面临挑战,主要原因是病理学和解剖学语义在医学数据中的纠缠。
- MeDSLIP通过双流机制解决这个问题,将医学语义分为病理相关和解剖相关两个流,并在每个流内对齐视觉和文本信息。
- MeDSLIP还包括一个交互建模模块,使用原型对比学习损失和图像内对比学习损失来规范病理与解剖学语义之间的关系。
- MeDSLIP在胸部X光分析领域表现出优异的性能,并在多个基准数据集上进行验证。
- MeDSLIP的代码已公开可用,为用户提供实现细节和自定义模型的机会。
点此查看论文截图