⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-02 更新
A Contrast-Agnostic Method for Ultra-High Resolution Claustrum Segmentation
Authors:Chiara Mauri, Ryan Fritz, Jocelyn Mora, Benjamin Billot, Juan Eugenio Iglesias, Koen Van Leemput, Jean Augustinack, Douglas N Greve
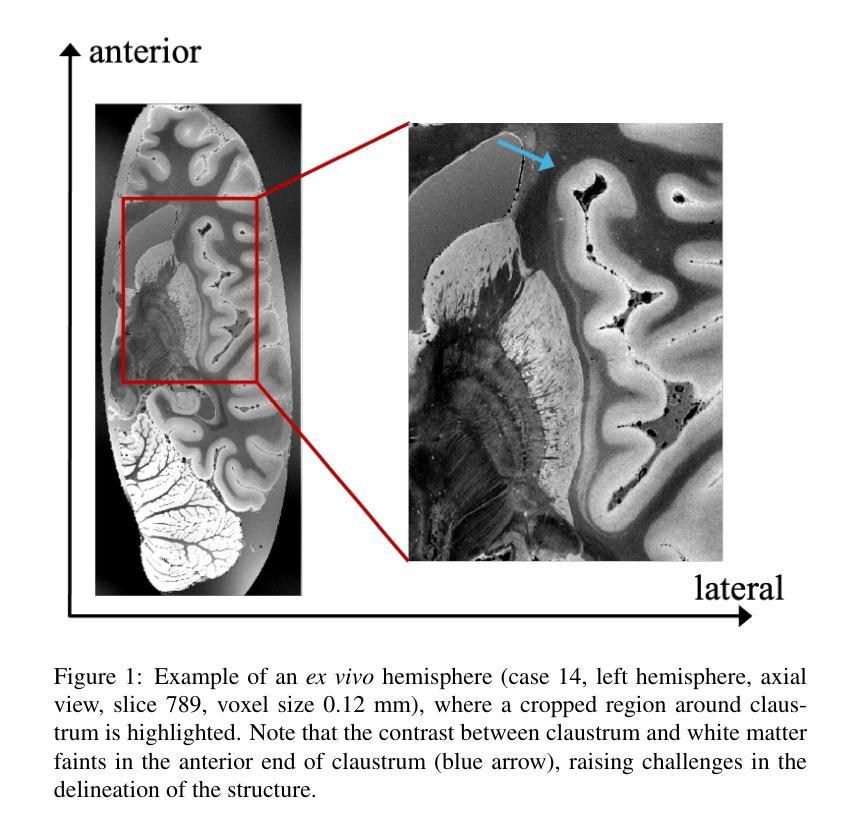
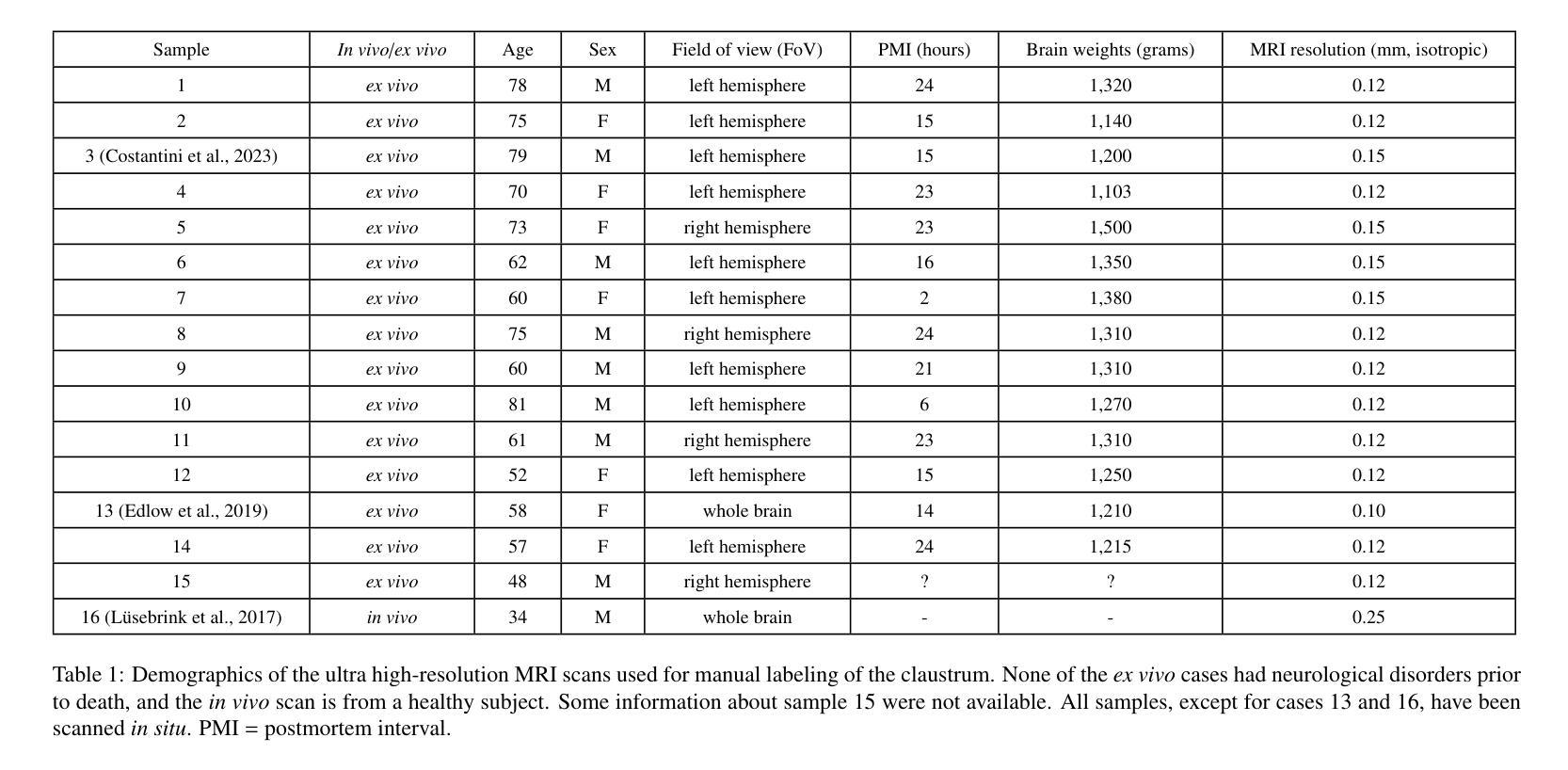
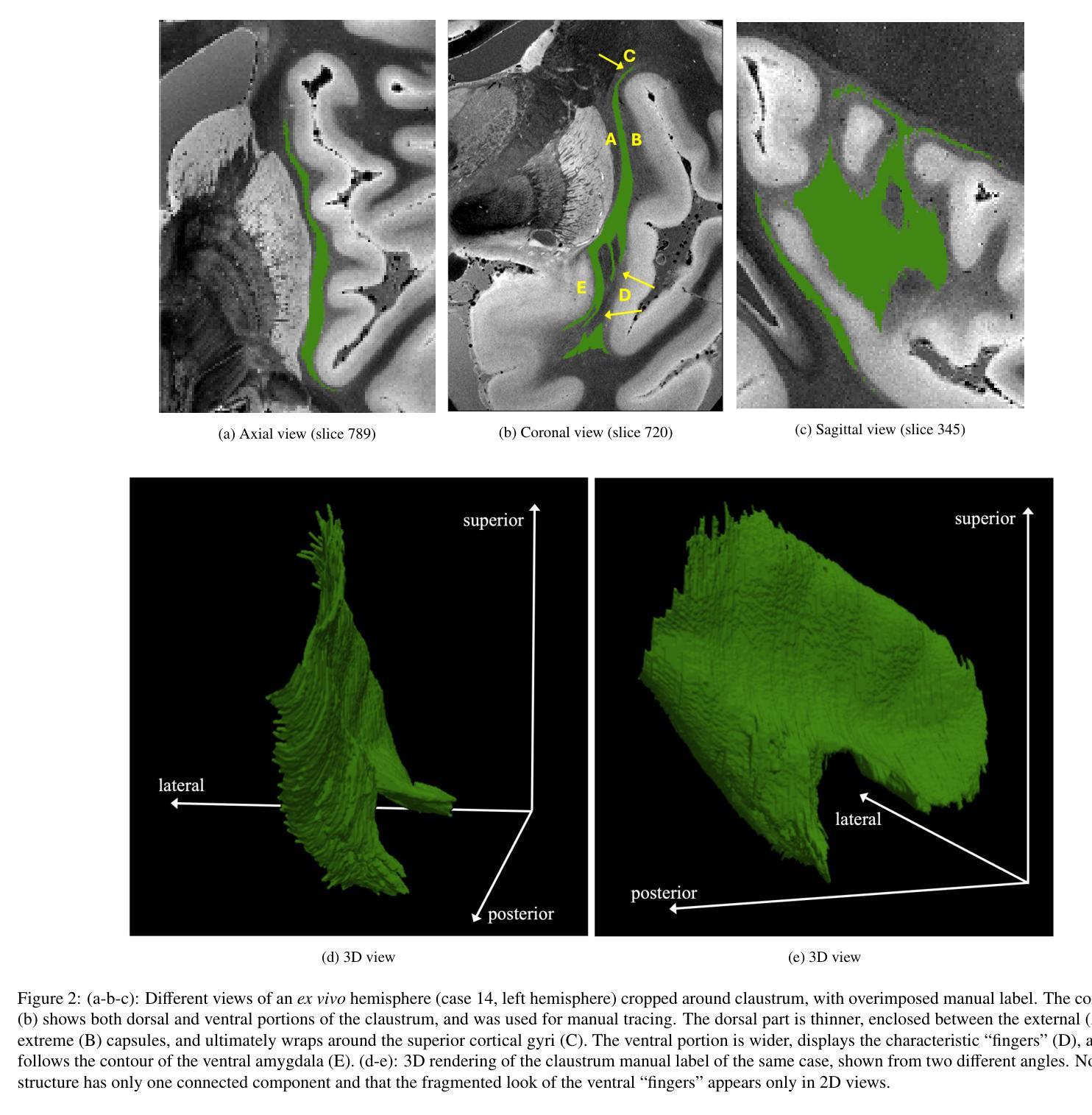
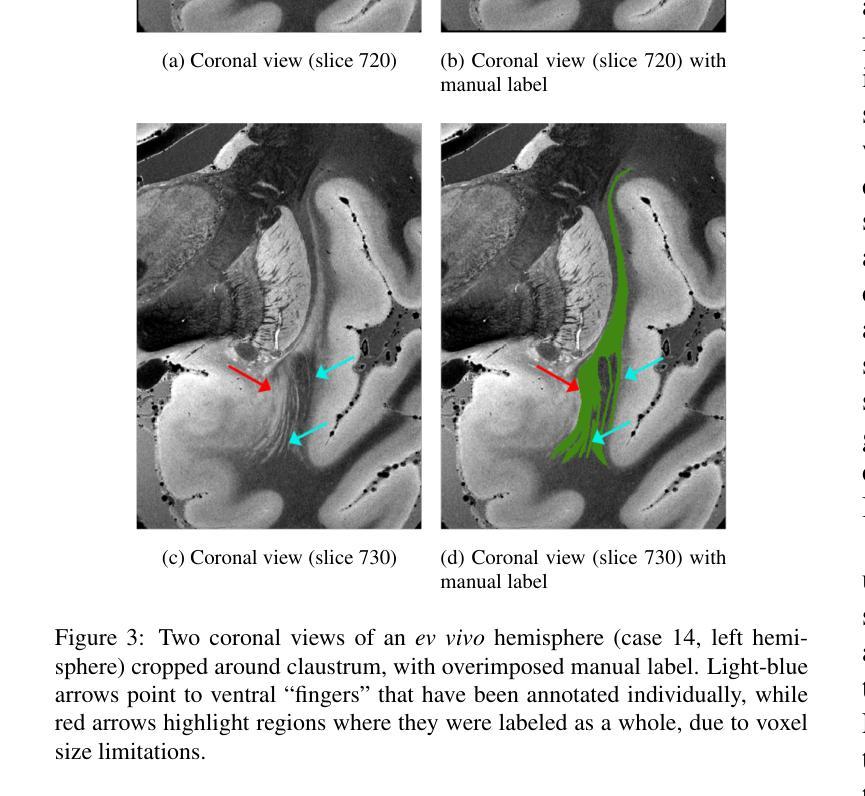
The claustrum is a band-like gray matter structure located between putamen and insula whose exact functions are still actively researched. Its sheet-like structure makes it barely visible in in vivo Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scans at typical resolutions and neuroimaging tools for its study, including methods for automatic segmentation, are currently very limited. In this paper, we propose a contrast- and resolution-agnostic method for claustrum segmentation at ultra-high resolution (0.35 mm isotropic); the method is based on the SynthSeg segmentation framework (Billot et al., 2023), which leverages the use of synthetic training intensity images to achieve excellent generalization. In particular, SynthSeg requires only label maps to be trained, since corresponding intensity images are synthesized on the fly with random contrast and resolution. We trained a deep learning network for automatic claustrum segmentation, using claustrum manual labels obtained from 18 ultra-high resolution MRI scans (mostly ex vivo). We demonstrated the method to work on these 18 high resolution cases (Dice score = 0.632, mean surface distance = 0.458 mm, and volumetric similarity = 0.867 using 6-fold Cross Validation (CV)), and also on in vivo T1-weighted MRI scans at typical resolutions (~1 mm isotropic). We also demonstrated that the method is robust in a test-retest setting and when applied to multimodal imaging (T2-weighted, Proton Density and quantitative T1 scans). To the best of our knowledge this is the first accurate method for automatic ultra-high resolution claustrum segmentation, which is robust against changes in contrast and resolution. The method is released at https://github.com/chiara-mauri/claustrum_segmentation and as part of the neuroimaging package Freesurfer (Fischl, 2012).
灰质隔(Claustrum)是位于内侧脉络外侧部和脑岛之间的带状结构。虽然目前对其功能的研究仍处于活跃阶段,但由于其片状的特殊结构形式,其核磁共振成像和针对灰质隔自动分割的其它相关方法应用常常受限于其在活体扫描中的可见度。在这篇论文中,我们提出了一种基于对比度与分辨率无关的方法,用于超高分辨率(0.35毫米等距)下灰质隔分割。此方法基于SynthSeg分割框架(Billot等,2023),它通过利用合成训练强度图像来有效地改善通用化效果。值得注意的是,SynthSeg仅需要训练标签,并通过随机对比度和分辨率实时合成相应的强度图像。我们使用从十八次超高分辨率MRI扫描(主要为离体)获取的灰质隔手动标签,训练了一个用于自动灰质隔分割的深度学习网络。我们已经证明了该方法在这十八个高分辨率案例(Dice分数为0.632,平均表面距离为0.458毫米,使用六倍交叉验证的容积相似性为0.867)以及典型的分辨率下(~ 1毫米等距)的活体T1加权MRI扫描中表现良好。我们也证明了该方法在测试重复设置中以及应用于多模态成像时具有稳健性(包括T2加权图像、质子密度图像和定量T1扫描)。据我们所知,这是首个针对超高分辨率灰质隔分割的准确且对对比度和分辨率变化具有鲁棒性的自动方法。该方法已发布在https://github.com/chiara-mauri/claustrum_segmentation上,并作为神经成像软件包Freesurfer的一部分(Fischl,2012)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 20 pages, 15 figures, 3 tables
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于SynthSeg框架的对比无关和超高分辨率(0.35mm)的大脑claustrum自动分割方法。此方法仅需要训练标签地图,使用合成训练强度图像实现优良泛化。通过深度学习网络训练,使用来自18个超高分辨率MRI扫描的手动标注的claustrum标签进行训练。此方法在多个实验中展现出优异的性能,包括超高分辨率MRI扫描的Dice系数为0.632、平均表面距离为0.458mm和体积相似性为0.867等。此方法具有良好的测试重复性、鲁棒性和多模态成像应用潜力。该方法被发布在GitHub上,并作为神经成像软件包Freesurfer的一部分。
Key Takeaways
- 研究提出了一种基于SynthSeg框架的对比无关和超高分辨率claustrum自动分割方法。
- 方法仅使用标签地图进行训练,通过合成训练强度图像实现优良泛化。
- 使用深度学习网络进行训练,在超高分辨率MRI扫描上的表现良好。
- 方法展示了鲁棒性,适用于测试重复性、不同对比度和分辨率以及多模态成像应用。
- 此方法被发布在GitHub上,并作为神经成像软件包Freesurfer的一部分。
点此查看论文截图

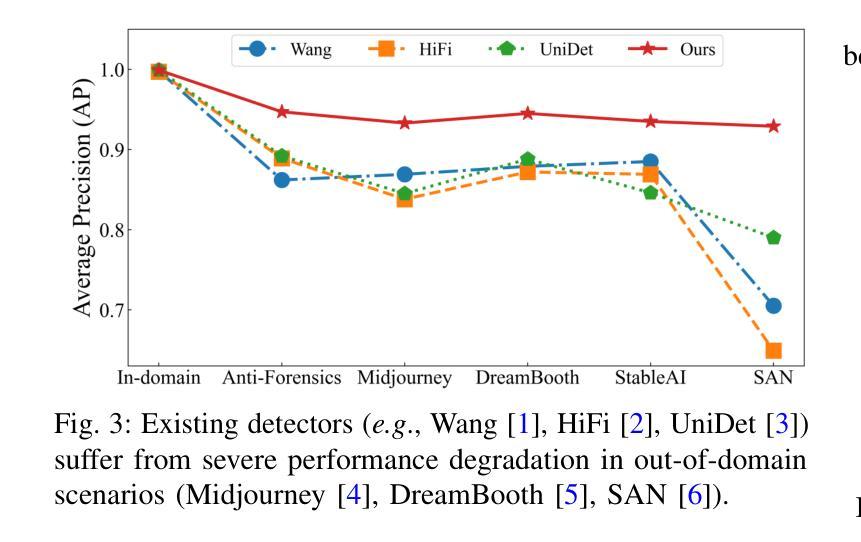
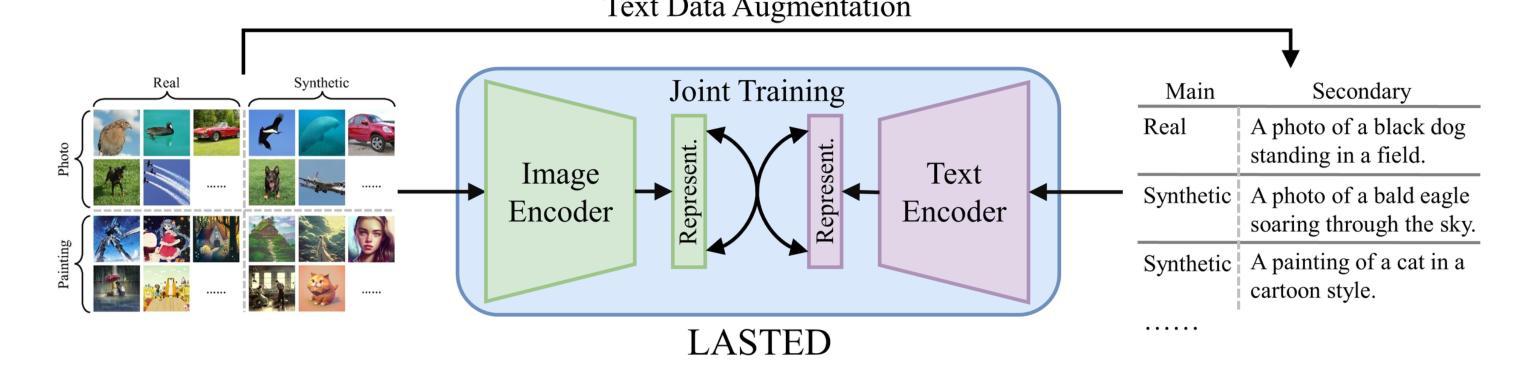
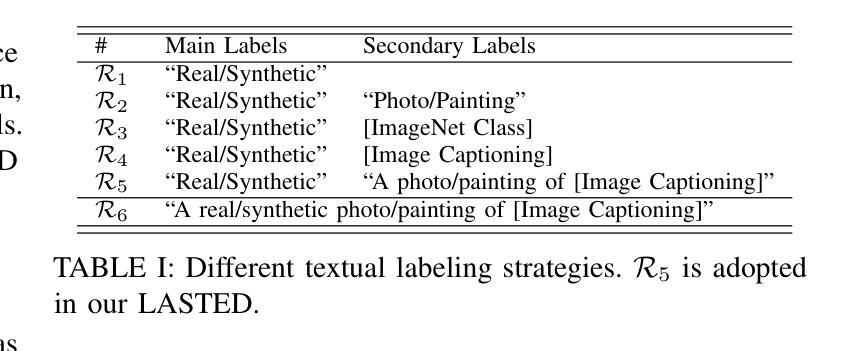
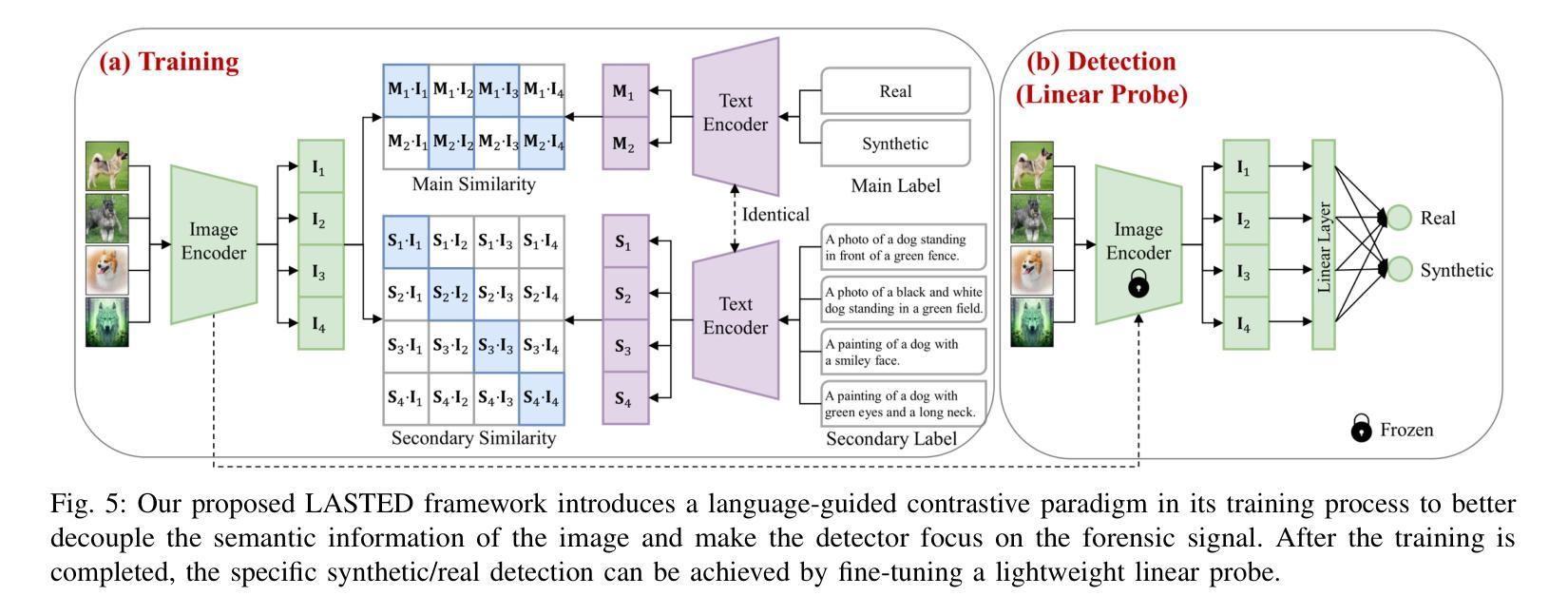
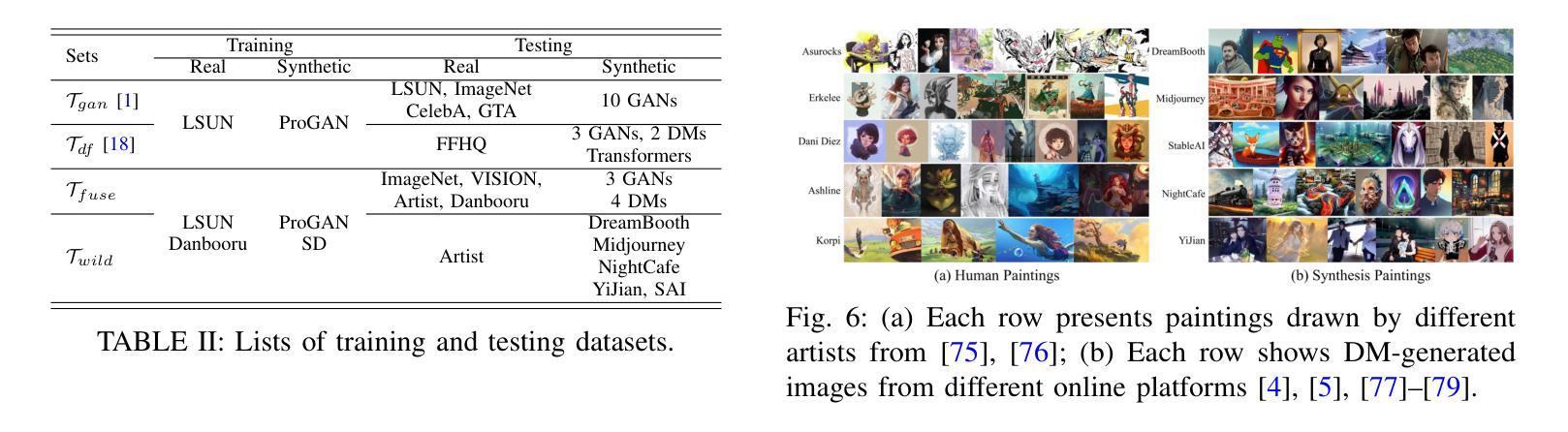
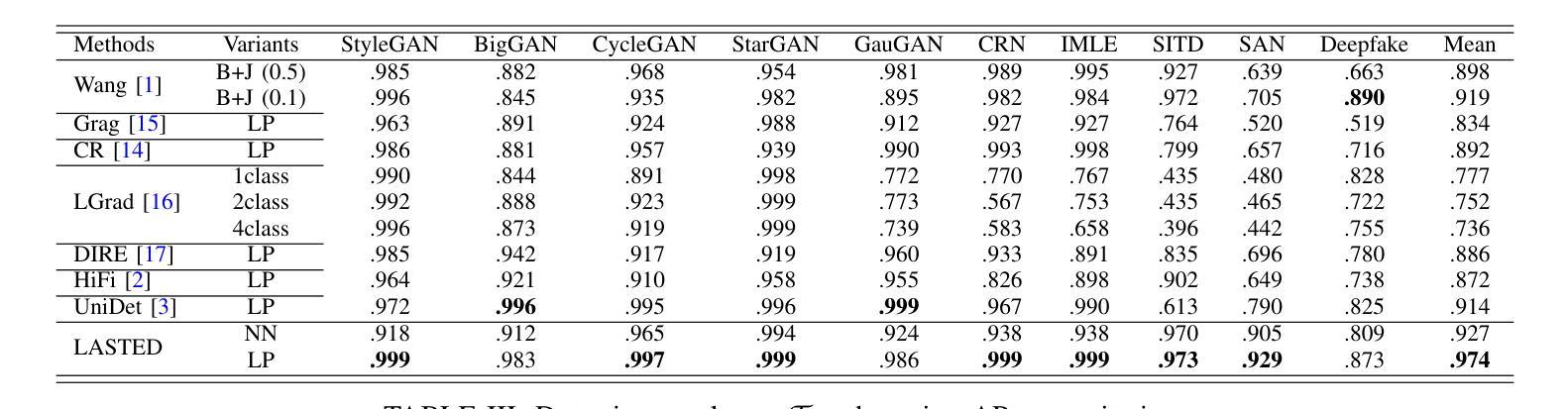
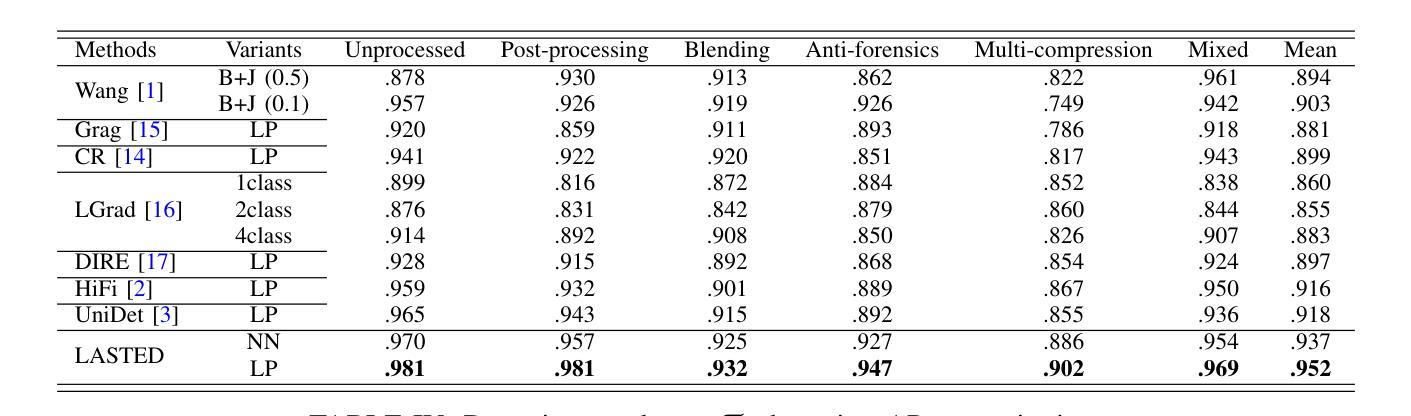
Generalizable Synthetic Image Detection via Language-guided Contrastive Learning
Authors:Haiwei Wu, Jiantao Zhou, Shile Zhang
The heightened realism of AI-generated images can be attributed to the rapid development of synthetic models, including generative adversarial networks (GANs) and diffusion models (DMs). The malevolent use of synthetic images, such as the dissemination of fake news or the creation of fake profiles, however, raises significant concerns regarding the authenticity of images. Though many forensic algorithms have been developed for detecting synthetic images, their performance, especially the generalization capability, is still far from being adequate to cope with the increasing number of synthetic models. In this work, we propose a simple yet very effective synthetic image detection method via a language-guided contrastive learning. Specifically, we augment the training images with carefully-designed textual labels, enabling us to use a joint visual-language contrastive supervision for learning a forensic feature space with better generalization. It is shown that our proposed LanguAge-guided SynThEsis Detection (LASTED) model achieves much improved generalizability to unseen image generation models and delivers promising performance that far exceeds state-of-the-art competitors over four datasets. The code is available at https://github.com/HighwayWu/LASTED.
人工智能生成图像的逼真度增强可归功于合成模型的快速发展,包括生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型(DMs)。然而,合成图像被恶意使用,如传播假新闻或创建虚假个人资料,引发了人们对图像真实性的重大担忧。尽管已经开发了许多用于检测合成图像的前瞻性算法,但它们的性能,特别是泛化能力,仍然远远不足以应对日益增加的合成模型数量。在本研究中,我们提出了一种简单而有效的合成图像检测方法,该方法通过语言引导对比学习。具体来说,我们通过精心设计的文本标签增强训练图像,使我们能够使用联合视觉语言对比监督来学习具有更好泛化的法医特征空间。结果表明,我们提出的LanguAge引导的合成图像检测(LASTED)模型实现了对未见图像生成模型的显著改善的泛化能力,并在四个数据集上实现了远超最新竞争对手的有前途的性能。代码可在https://github.com/HighwayWu/LASTED找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
人工智能生成的图像越来越逼真,得益于合成模型如生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型(DMs)的快速发展。然而,合成图像被恶意用于传播假新闻或创建虚假个人资料引发了人们对图像真实性的关注。尽管已开发出许多用于检测合成图像的法医算法,但其性能尤其是泛化能力还不能应对越来越多的合成模型。本研究提出了一种简单而有效的合成图像检测方法,该方法采用语言引导的对比学习。具体来说,我们对训练图像进行精心设计文本标签的增强,使我们能够使用联合视觉语言对比监督来学习具有更好泛化能力的法医特征空间。结果表明,我们提出的LanguAge引导的SynThEsis检测(LASTED)模型在未见过的图像生成模型上实现了更好的泛化能力,并在四个数据集上的性能均超过了最先进的竞争对手。
Key Takeaways
- AI生成的图像真实性不断提高,主要得益于合成模型的进步,如GANs和DMs。
- 合成图像被恶意用于传播假消息或创建假身份引发了公众对图像真实性的关注。
- 尽管存在多种检测合成图像的法医算法,但它们的泛化能力尚待提高,以应对不断增长的合成模型数量。
- 提出了一种新的合成图像检测方法——通过语言引导的对比学习,利用精心设计的文本标签增强训练图像。
- 通过联合视觉语言对比监督学习,提高了模型的泛化能力,学习到的法医特征空间表现优异。
- LASTED模型在未见过的图像生成模型上实现了显著性能,并且在多个数据集上的性能均超过了现有最佳模型。
点此查看论文截图