⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-02 更新
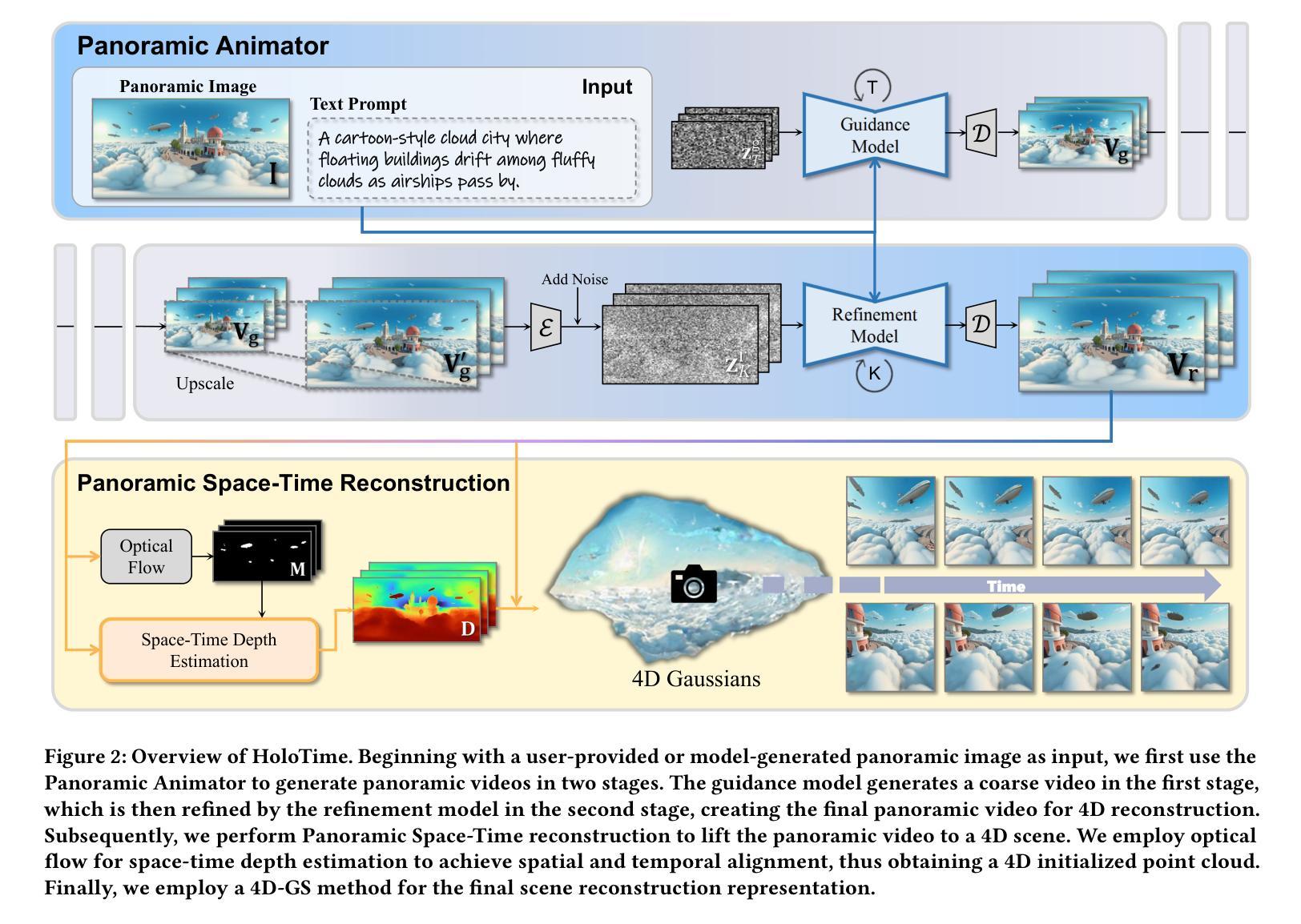
HoloTime: Taming Video Diffusion Models for Panoramic 4D Scene Generation
Authors:Haiyang Zhou, Wangbo Yu, Jiawen Guan, Xinhua Cheng, Yonghong Tian, Li Yuan
The rapid advancement of diffusion models holds the promise of revolutionizing the application of VR and AR technologies, which typically require scene-level 4D assets for user experience. Nonetheless, existing diffusion models predominantly concentrate on modeling static 3D scenes or object-level dynamics, constraining their capacity to provide truly immersive experiences. To address this issue, we propose HoloTime, a framework that integrates video diffusion models to generate panoramic videos from a single prompt or reference image, along with a 360-degree 4D scene reconstruction method that seamlessly transforms the generated panoramic video into 4D assets, enabling a fully immersive 4D experience for users. Specifically, to tame video diffusion models for generating high-fidelity panoramic videos, we introduce the 360World dataset, the first comprehensive collection of panoramic videos suitable for downstream 4D scene reconstruction tasks. With this curated dataset, we propose Panoramic Animator, a two-stage image-to-video diffusion model that can convert panoramic images into high-quality panoramic videos. Following this, we present Panoramic Space-Time Reconstruction, which leverages a space-time depth estimation method to transform the generated panoramic videos into 4D point clouds, enabling the optimization of a holistic 4D Gaussian Splatting representation to reconstruct spatially and temporally consistent 4D scenes. To validate the efficacy of our method, we conducted a comparative analysis with existing approaches, revealing its superiority in both panoramic video generation and 4D scene reconstruction. This demonstrates our method’s capability to create more engaging and realistic immersive environments, thereby enhancing user experiences in VR and AR applications.
扩散模型的快速发展有望彻底改变VR和AR技术的应用,这些技术通常需要场景级的4D资产来提升用户体验。然而,现有的扩散模型主要集中在静态3D场景的建模或对象级别的动态建模上,这限制了它们提供真正沉浸式体验的能力。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了HoloTime框架,它集成了视频扩散模型来从单个提示或参考图像生成全景视频,以及一种360度的4D场景重建方法,无缝地将生成的全景视频转换为4D资产,为用户提供全方位的沉浸式4D体验。具体来说,为了驾驭视频扩散模型以生成高保真全景视频,我们引入了360World数据集,这是第一个全景视频的综合集合,适用于下游的4D场景重建任务。借助这个精选的数据集,我们提出了全景动画师(Panoramic Animator),这是一个两阶段的图像到视频的扩散模型,可以将全景图像转换为高质量的全景视频。接下来,我们推出了全景时空重建(Panoramic Space-Time Reconstruction),它利用时空深度估计方法将生成的全景视频转换为4D点云,实现对整体4D高斯描摹表示的优化,从而重建时空一致的4D场景。为了验证我们方法的有效性,我们与现有方法进行了比较分析,结果显示在我们的全景视频生成和4D场景重建方面都表现出优越性。这证明了我们的方法能够创建更具吸引力和更真实的沉浸式环境,从而增强VR和AR应用中的用户体验。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project homepage: https://zhouhyocean.github.io/holotime/
摘要
扩散模型的快速发展有望革新VR和AR技术的应用,但它们通常需要场景级别的4D资产来提升用户体验。现有扩散模型主要关注静态3D场景的建模或对象级别的动态,无法提供真正的沉浸式体验。为解决此问题,我们提出HoloTime框架,它整合视频扩散模型从单一提示或参考图像生成全景视频,并结合360度4D场景重建方法,将生成的全景视频无缝转换为4D资产,为用户带来全方位的沉浸式4D体验。我们使用360World数据集训练模型,这是首个全景视频的综合数据集,适用于下游的4D场景重建任务。借助Panoramic Animator这一两阶段图像到视频的扩散模型,我们能将全景图像转换为高质量的全景视频。随后,我们推出全景时空重建技术,利用时空深度估计方法将生成的全景视频转换为4D点云,优化整体4D高斯描画表示以重建时空一致的4D场景。我们的方法经过对比分析,在全景视频生成和4D场景重建方面都展现出优越性,能创建更引人入胜、更逼真的沉浸式环境,从而提升VR和AR应用中的用户体验。
关键见解
- 扩散模型的快速发展为VR和AR技术的革新提供了潜力。
- 现有扩散模型主要关注静态3D场景或对象级动态,难以提供真正沉浸式体验。
- 提出HoloTime框架,整合视频扩散模型生成全景视频,为用户带来全方位的沉浸式体验。
- 引入360World数据集,为全景视频生成和下游的4D场景重建任务提供数据支持。
- 提出Panoramic Animator模型,能将全景图像转换为高质量全景视频。
- 推出全景时空重建技术,将生成的全景视频转换为4D点云,优化4D场景的表示和重建。
- 对比分析显示,该方法在全景视频生成和4D场景重建方面均优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图


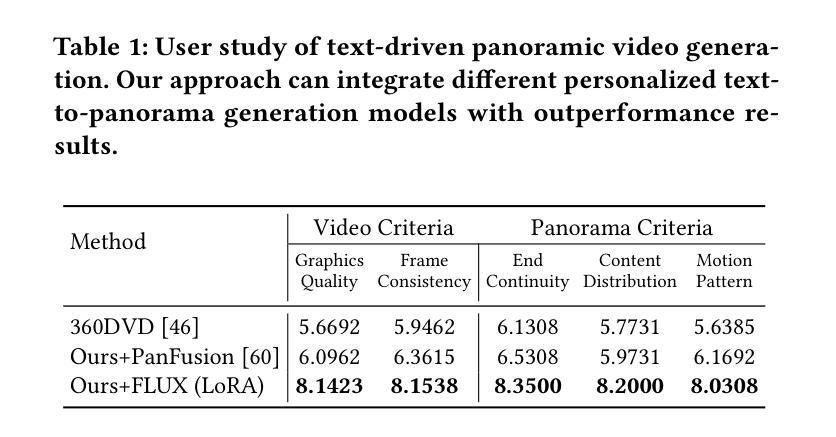
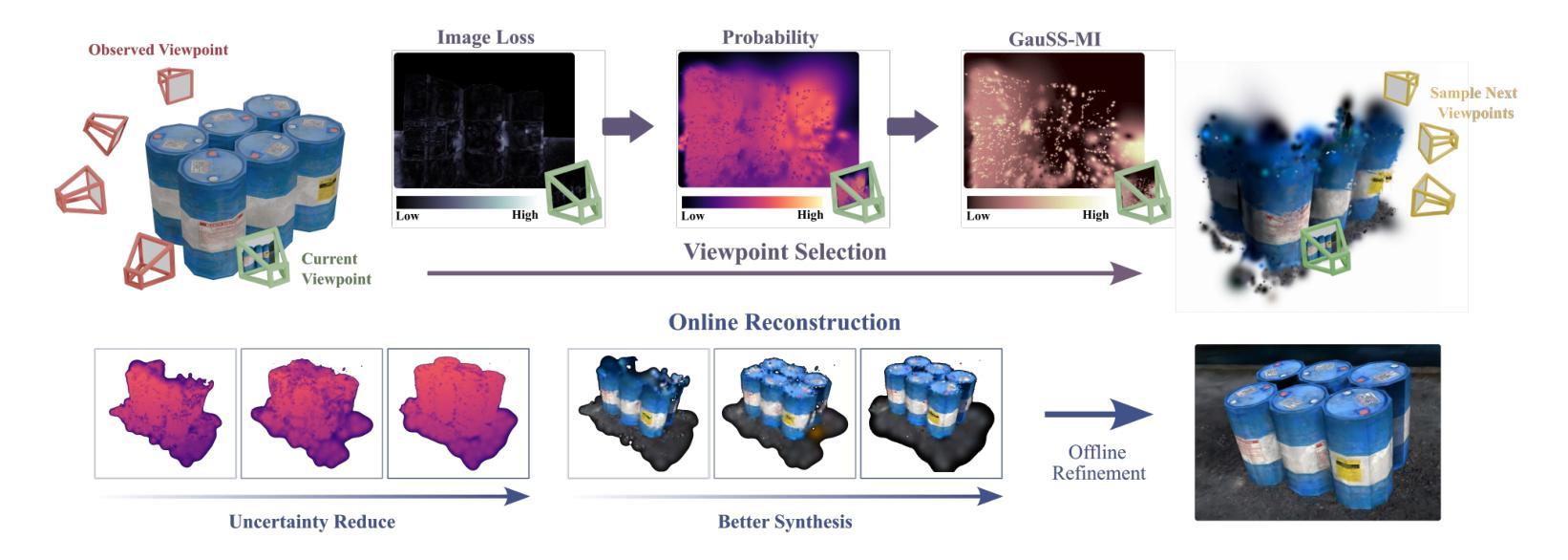
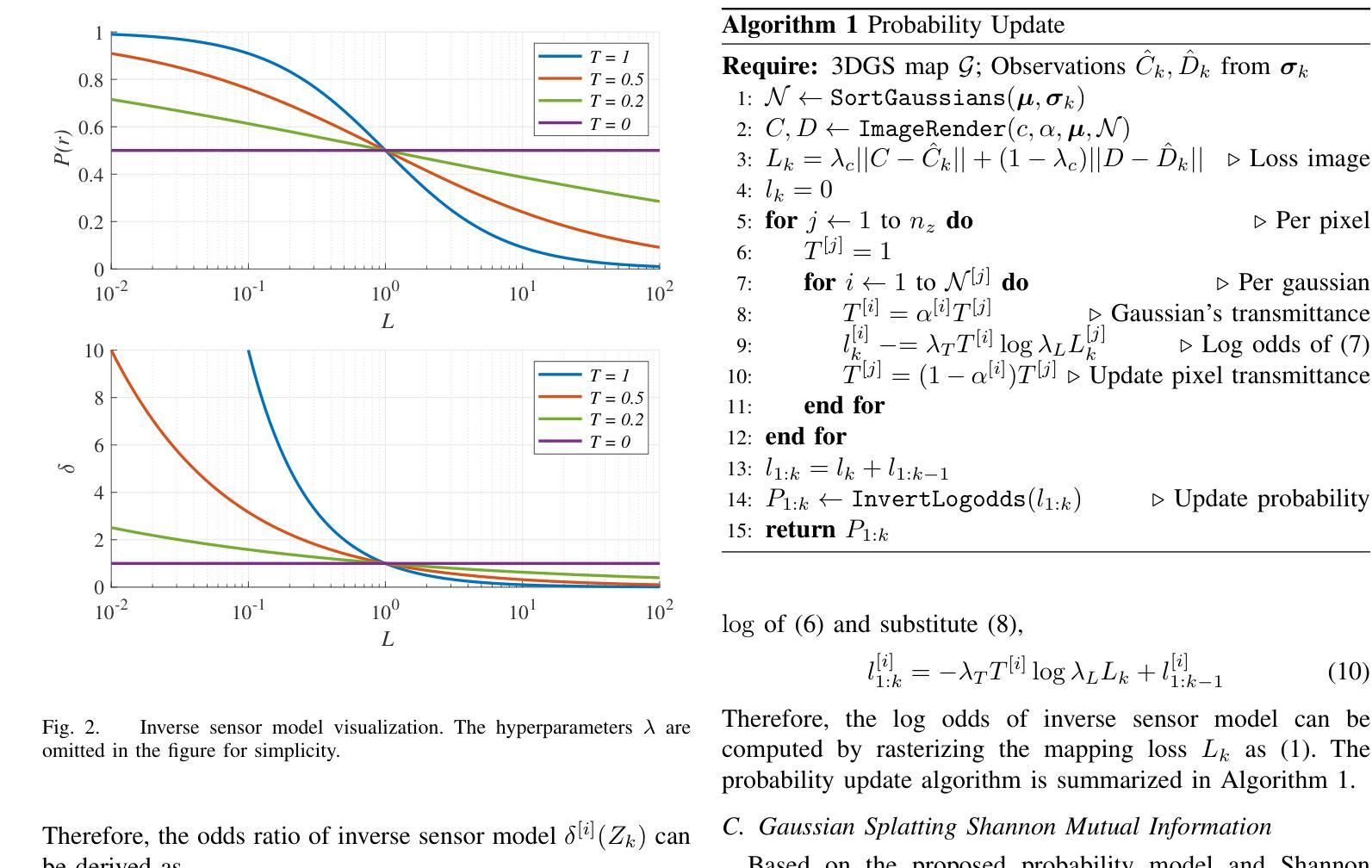
GauSS-MI: Gaussian Splatting Shannon Mutual Information for Active 3D Reconstruction
Authors:Yuhan Xie, Yixi Cai, Yinqiang Zhang, Lei Yang, Jia Pan
This research tackles the challenge of real-time active view selection and uncertainty quantification on visual quality for active 3D reconstruction. Visual quality is a critical aspect of 3D reconstruction. Recent advancements such as Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) have notably enhanced the image rendering quality of reconstruction models. Nonetheless, the efficient and effective acquisition of input images for reconstruction-specifically, the selection of the most informative viewpoint-remains an open challenge, which is crucial for active reconstruction. Existing studies have primarily focused on evaluating geometric completeness and exploring unobserved or unknown regions, without direct evaluation of the visual uncertainty within the reconstruction model. To address this gap, this paper introduces a probabilistic model that quantifies visual uncertainty for each Gaussian. Leveraging Shannon Mutual Information, we formulate a criterion, Gaussian Splatting Shannon Mutual Information (GauSS-MI), for real-time assessment of visual mutual information from novel viewpoints, facilitating the selection of next best view. GauSS-MI is implemented within an active reconstruction system integrated with a view and motion planner. Extensive experiments across various simulated and real-world scenes showcase the superior visual quality and reconstruction efficiency performance of the proposed system.
本文研究的是主动三维重建中的实时活动视图选择和视觉质量不确定性量化的挑战。视觉质量是三维重建的一个重要方面。最近的神经辐射场(NeRF)和三维高斯拼贴(3DGS)等技术的进展显著提高了重建模型的图像渲染质量。然而,对于重建的输入图像的有效和高效采集,特别是选择最具信息量的视角,仍然是一个开放性的挑战,这对于主动重建至关重要。现有研究主要集中在评估几何完整性和探索未观察或未知区域,而没有直接评估重建模型内的视觉不确定性。为了弥补这一空白,本文引入了一个概率模型,该模型可以量化每个高斯的不确定性。我们利用香农互信息制定了一个标准,即高斯拼贴香农互信息(GauSS-MI),用于实时评估从新视角获得的视觉互信息,从而促进选择下一个最佳视角。GauSS-MI在一个集成了视图和运动规划器的主动重建系统中得到了实现。在多种模拟和真实场景的大量实验展示了所提系统的视觉质量和重建效率性能的优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了实时主动视角选择及针对主动三维重建的视觉质量不确定性量化挑战。文章引入概率模型量化重建模型中每个高斯点的视觉不确定性,利用香农互信息构建评估准则,即高斯样条香农互信息(GauSS-MI),用于实时评估新视角的视觉互信息,促进最佳视角的选择。GauSS-MI在集成视图和运动规划器的主动重建系统中实现,广泛应用于模拟和真实场景,展示了优越的视觉质量和重建效率性能。
Key Takeaways
- 研究解决了主动三维重建中的实时视角选择和视觉质量不确定性量化挑战。
- 引入概率模型量化重建模型中每个高斯点的视觉不确定性。
- 利用香农互信息构建评估准则,即高斯样条香农互信息(GauSS-MI)。
- GauSS-MI用于实时评估新视角的视觉互信息,有助于选择最佳视角。
- 该系统集成了视图和运动规划器,实现高效的三维重建。
- 在模拟和真实场景中进行了广泛实验,验证了系统的优越性能。
点此查看论文截图

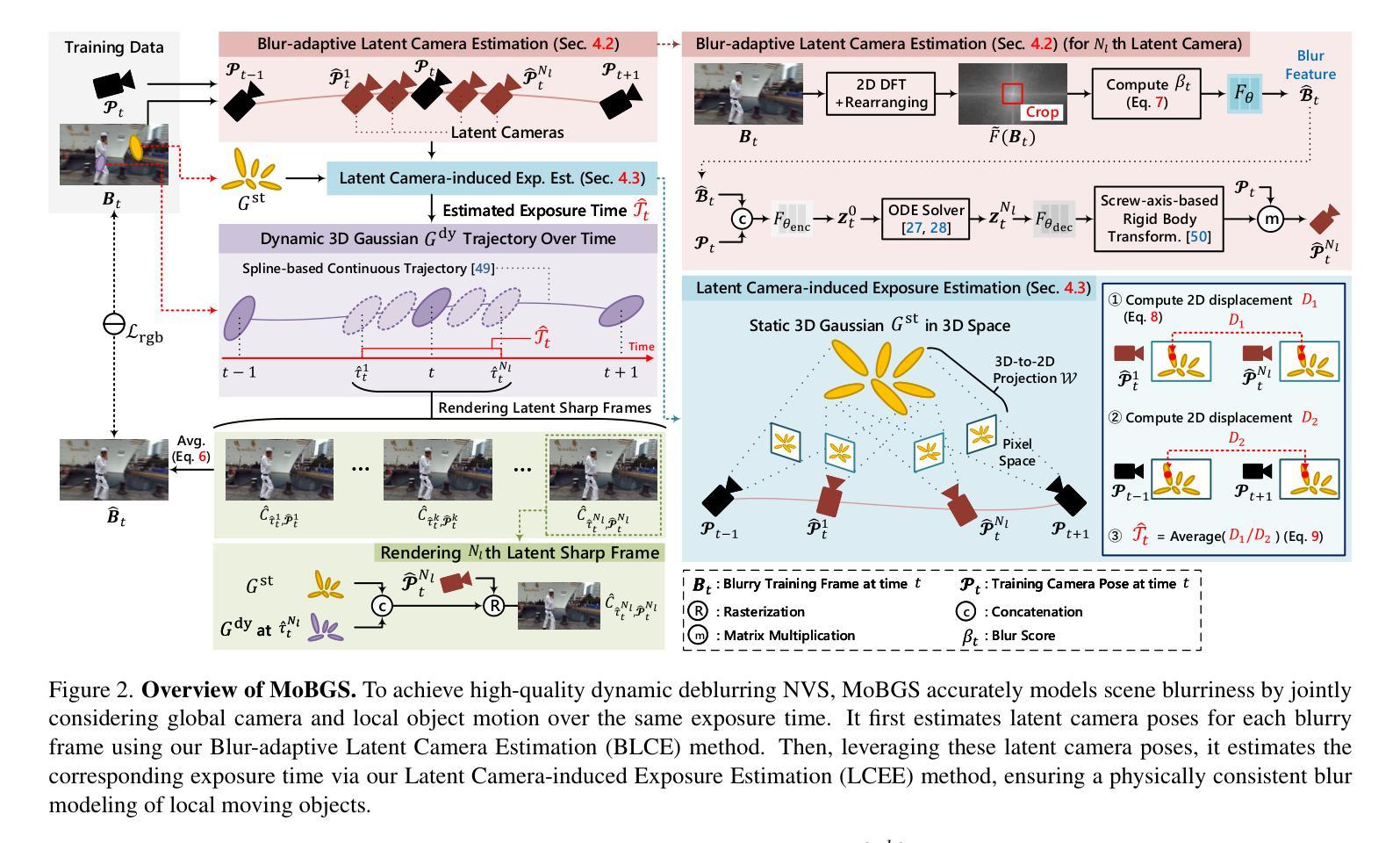
MoBGS: Motion Deblurring Dynamic 3D Gaussian Splatting for Blurry Monocular Video
Authors:Minh-Quan Viet Bui, Jongmin Park, Juan Luis Gonzalez Bello, Jaeho Moon, Jihyong Oh, Munchurl Kim
We present MoBGS, a novel deblurring dynamic 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) framework capable of reconstructing sharp and high-quality novel spatio-temporal views from blurry monocular videos in an end-to-end manner. Existing dynamic novel view synthesis (NVS) methods are highly sensitive to motion blur in casually captured videos, resulting in significant degradation of rendering quality. While recent approaches address motion-blurred inputs for NVS, they primarily focus on static scene reconstruction and lack dedicated motion modeling for dynamic objects. To overcome these limitations, our MoBGS introduces a novel Blur-adaptive Latent Camera Estimation (BLCE) method for effective latent camera trajectory estimation, improving global camera motion deblurring. In addition, we propose a physically-inspired Latent Camera-induced Exposure Estimation (LCEE) method to ensure consistent deblurring of both global camera and local object motion. Our MoBGS framework ensures the temporal consistency of unseen latent timestamps and robust motion decomposition of static and dynamic regions. Extensive experiments on the Stereo Blur dataset and real-world blurry videos show that our MoBGS significantly outperforms the very recent advanced methods (DyBluRF and Deblur4DGS), achieving state-of-the-art performance for dynamic NVS under motion blur.
我们提出了MoBGS,这是一种新型的去模糊动态三维高斯平铺(3DGS)框架,能够端到端地从模糊的单目视频中重建清晰、高质量的新时空视图。现有的动态新视图合成(NVS)方法对于随意拍摄的视频中的运动模糊高度敏感,导致渲染质量显著下降。虽然最近的方法解决了运动模糊输入对NVS的影响,但它们主要集中在静态场景重建上,缺乏针对动态对象的专用运动建模。为了克服这些局限性,我们的MoBGS引入了一种新型的模糊自适应潜在相机估计(BLCE)方法,用于有效的潜在相机轨迹估计,改进全局相机运动去模糊。此外,我们提出了一种受物理启发的潜在相机诱导曝光估计(LCEE)方法,以确保全局相机和局部对象运动的持续去模糊。我们的MoBGS框架确保了未见过的潜在时间戳的时空一致性以及静态和动态区域的稳健运动分解。在立体模糊数据集和真实世界的模糊视频上的大量实验表明,我们的MoBGS显著优于最新的高级方法(DyBluRF和Deblur4DGS),在运动模糊条件下实现了动态NVS的顶尖性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The first two authors contributed equally to this work (equal contribution). The last two authors advised equally to this work. Please visit our project page at https://kaist-viclab.github.io/mobgs-site/
摘要
本文提出了MoBGS,一种新型动态去模糊三维高斯贴片(3DGS)框架,能够从模糊的单目视频中重建出清晰、高质量的新时空视图。现有动态新视图合成(NVS)方法对运动模糊非常敏感,导致渲染质量显著下降。虽然最近的方法解决了运动模糊输入问题,但它们主要关注静态场景重建,缺乏针对动态对象的专用运动建模。MoBGS通过引入一种新的模糊自适应潜在相机估计(BLCE)方法来改进潜在相机轨迹估计,提高了全局相机运动去模糊效果。此外,我们还提出了一种受物理启发的潜在相机诱导曝光估计(LCEE)方法,以确保全局相机和局部对象运动的持续去模糊。MoBGS框架确保了未见潜在时间戳的时空一致性以及静态和动态区域的稳健运动分解。在Stereo Blur数据集和真实世界的模糊视频上的大量实验表明,MoBGS显著优于最新的高级方法(DyBluRF和Deblur4DGS),在运动模糊情况下实现了动态NVS的顶尖性能。
关键见解
- MoBGS是一个新型动态去模糊三维高斯贴片(3DGS)框架,可从模糊的单目视频中重建清晰、高质量的新时空视图。
- 现有动态新视图合成(NVS)方法在运动模糊方面存在挑战,导致渲染质量下降。
- MoBGS引入Blur-adaptive Latent Camera Estimation(BLCE)方法进行潜在相机轨迹估计,改进了全局相机运动去模糊。
- 提出了一种受物理启发的Latent Camera-induced Exposure Estimation(LCEE)方法,确保全局和局部运动的持续去模糊。
- MoBGS确保了未见潜在时间戳的时空一致性及稳健的运动分解。
- 在多个数据集上的实验表明,MoBGS显著优于其他方法,实现了动态NVS领域的顶尖性能。
- MoBGS尤其擅长处理包含运动模糊的视频。
点此查看论文截图