⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-02 更新
HoloTime: Taming Video Diffusion Models for Panoramic 4D Scene Generation
Authors:Haiyang Zhou, Wangbo Yu, Jiawen Guan, Xinhua Cheng, Yonghong Tian, Li Yuan
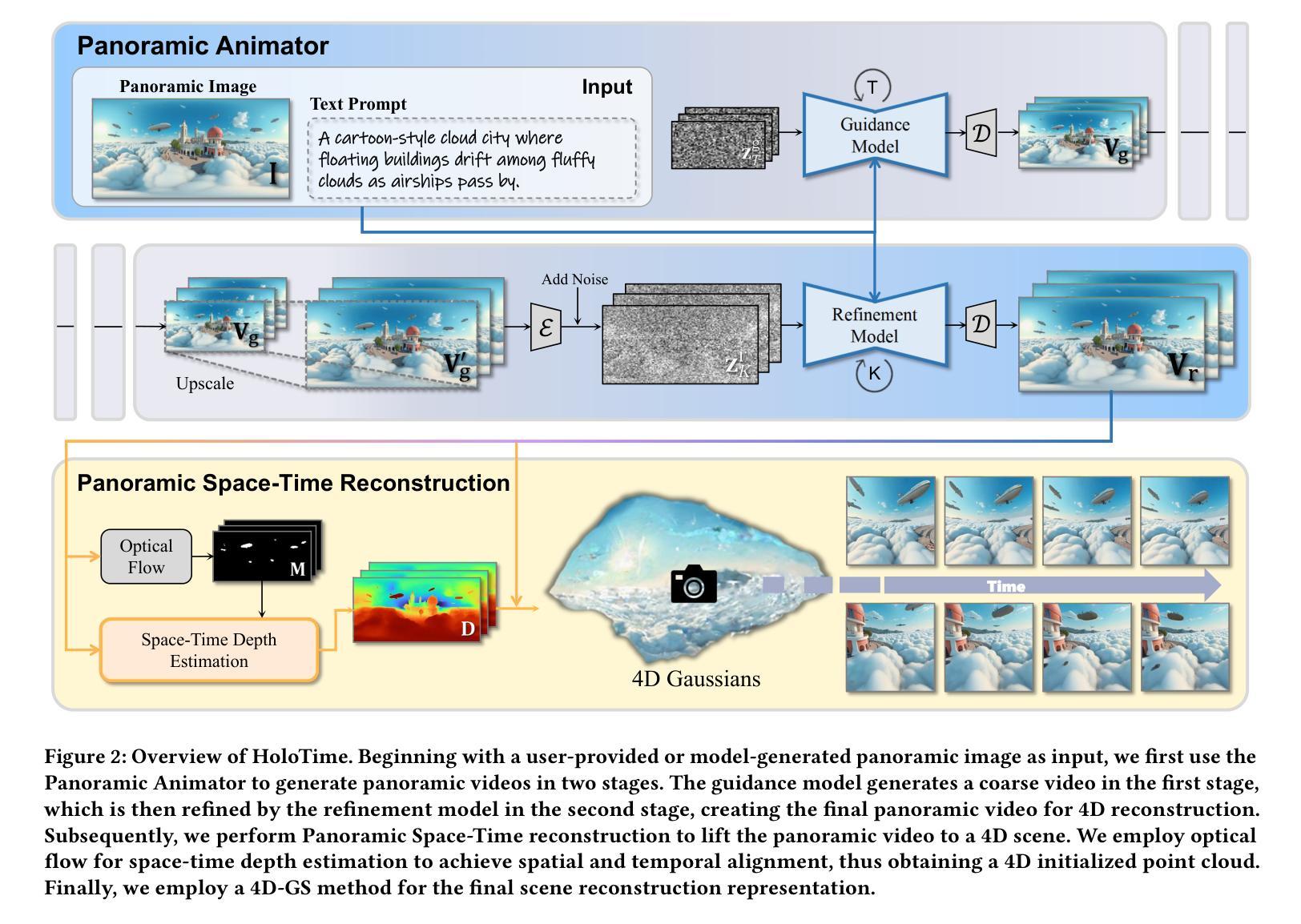
The rapid advancement of diffusion models holds the promise of revolutionizing the application of VR and AR technologies, which typically require scene-level 4D assets for user experience. Nonetheless, existing diffusion models predominantly concentrate on modeling static 3D scenes or object-level dynamics, constraining their capacity to provide truly immersive experiences. To address this issue, we propose HoloTime, a framework that integrates video diffusion models to generate panoramic videos from a single prompt or reference image, along with a 360-degree 4D scene reconstruction method that seamlessly transforms the generated panoramic video into 4D assets, enabling a fully immersive 4D experience for users. Specifically, to tame video diffusion models for generating high-fidelity panoramic videos, we introduce the 360World dataset, the first comprehensive collection of panoramic videos suitable for downstream 4D scene reconstruction tasks. With this curated dataset, we propose Panoramic Animator, a two-stage image-to-video diffusion model that can convert panoramic images into high-quality panoramic videos. Following this, we present Panoramic Space-Time Reconstruction, which leverages a space-time depth estimation method to transform the generated panoramic videos into 4D point clouds, enabling the optimization of a holistic 4D Gaussian Splatting representation to reconstruct spatially and temporally consistent 4D scenes. To validate the efficacy of our method, we conducted a comparative analysis with existing approaches, revealing its superiority in both panoramic video generation and 4D scene reconstruction. This demonstrates our method’s capability to create more engaging and realistic immersive environments, thereby enhancing user experiences in VR and AR applications.
扩散模型的快速发展有望彻底改变VR和AR技术的应用前景,这些技术通常需要场景级的四维资产来提升用户体验。然而,现有的扩散模型主要集中在静态三维场景的建模或对象级别的动态建模上,这限制了它们提供真正沉浸式体验的能力。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了HoloTime框架,它结合了视频扩散模型来生成全景视频,从一个单一的提示或参考图像开始,并使用一种全景的4D场景重建方法,将生成的全景视频无缝地转化为四维资产,为用户带来全面的沉浸式体验。具体来说,为了驾驭视频扩散模型以生成高质量全景视频,我们引入了首个全景视频数据集360World数据集,适合用于下游四维场景重建任务。有了这个定制的数据集,我们提出了全景动画生成器(Panoramic Animator),一个两阶段的图像到视频的扩散模型,能够将全景图像转换为高质量全景视频。随后,我们提出了全景时空重建(Panoramic Space-Time Reconstruction),利用时空深度估计方法将生成的全景视频转化为四维点云,并优化整体的四维高斯溅射表示法来重建空间和时间上连贯的四维场景。为了验证我们方法的有效性,我们与现有方法进行了比较分析,结果显示我们的方法在全景视频生成和四维场景重建方面都表现出卓越的性能。这表明我们的方法能够创建更具吸引力和更逼真的沉浸式环境,从而增强VR和AR应用程序中的用户体验。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project homepage: https://zhouhyocean.github.io/holotime/
Summary
扩散模型的快速发展为VR和AR技术的广泛应用带来了革命性的希望。现有的扩散模型主要关注静态三维场景或对象级别的动态建模,难以提供真正的沉浸式体验。本文提出HoloTime框架,通过整合视频扩散模型生成全景视频,并采用360度四维场景重建方法,将生成的全景视频无缝转换为四维资产,为用户带来全新的沉浸式四维体验。为了生成高质量的全景视频,引入了360World数据集,并提出全景动画师(Panoramic Animator)模型。接着使用时空重建技术将全景视频转化为四维点云,最终优化整体四维高斯描绘(Gaussian Splatting)来实现空间和时间上一致的场景重建。本研究验证了所提出方法在全景视频生成和四维场景重建方面的优势,增强了VR和AR应用的用户体验。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型的进步为VR和AR技术的沉浸式体验提供了巨大的潜力和机遇。
- 当前扩散模型主要集中在静态三维场景和对象级别的动态建模上,难以满足真正的沉浸式需求。
- HoloTime框架整合视频扩散模型生成全景视频,实现单一提示或参考图像的场景重建。
- 引入的360World数据集为全景视频生成提供了高质量资源。
- 提出全景动画师(Panoramic Animator)模型,用于将全景图像转换为高质量全景视频。
- 利用时空重建技术将全景视频转化为四维点云,进一步优化了四维场景重建的效果。
点此查看论文截图


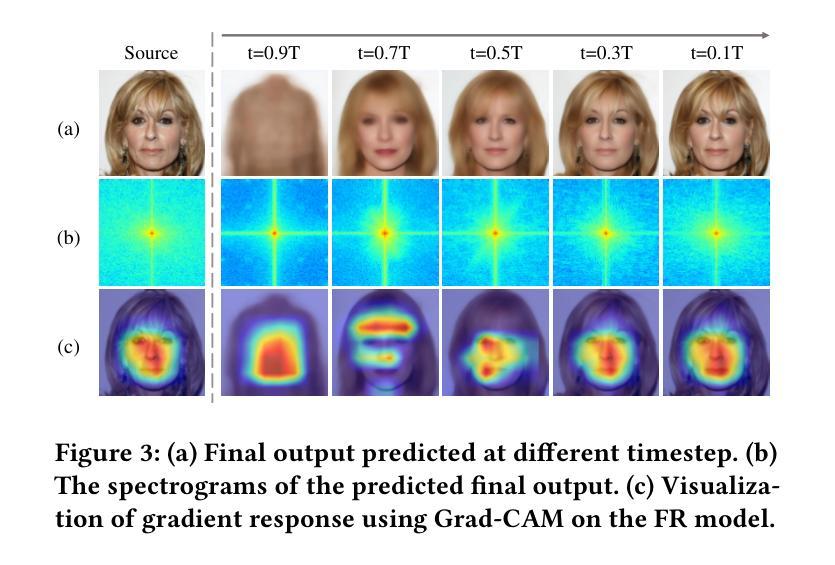
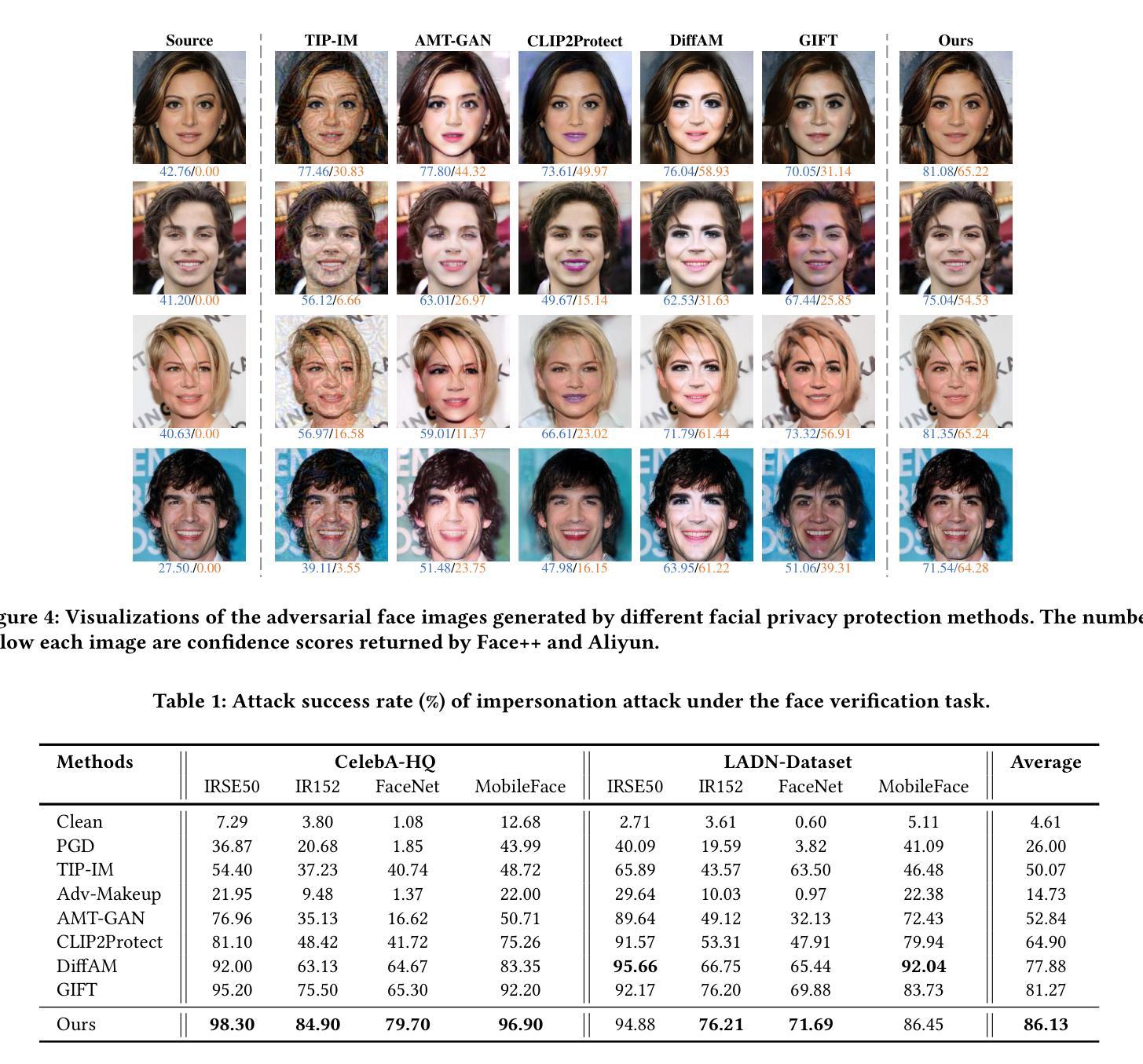
Diffusion-based Adversarial Identity Manipulation for Facial Privacy Protection
Authors:Liqin Wang, Qianyue Hu, Wei Lu, Xiangyang Luo
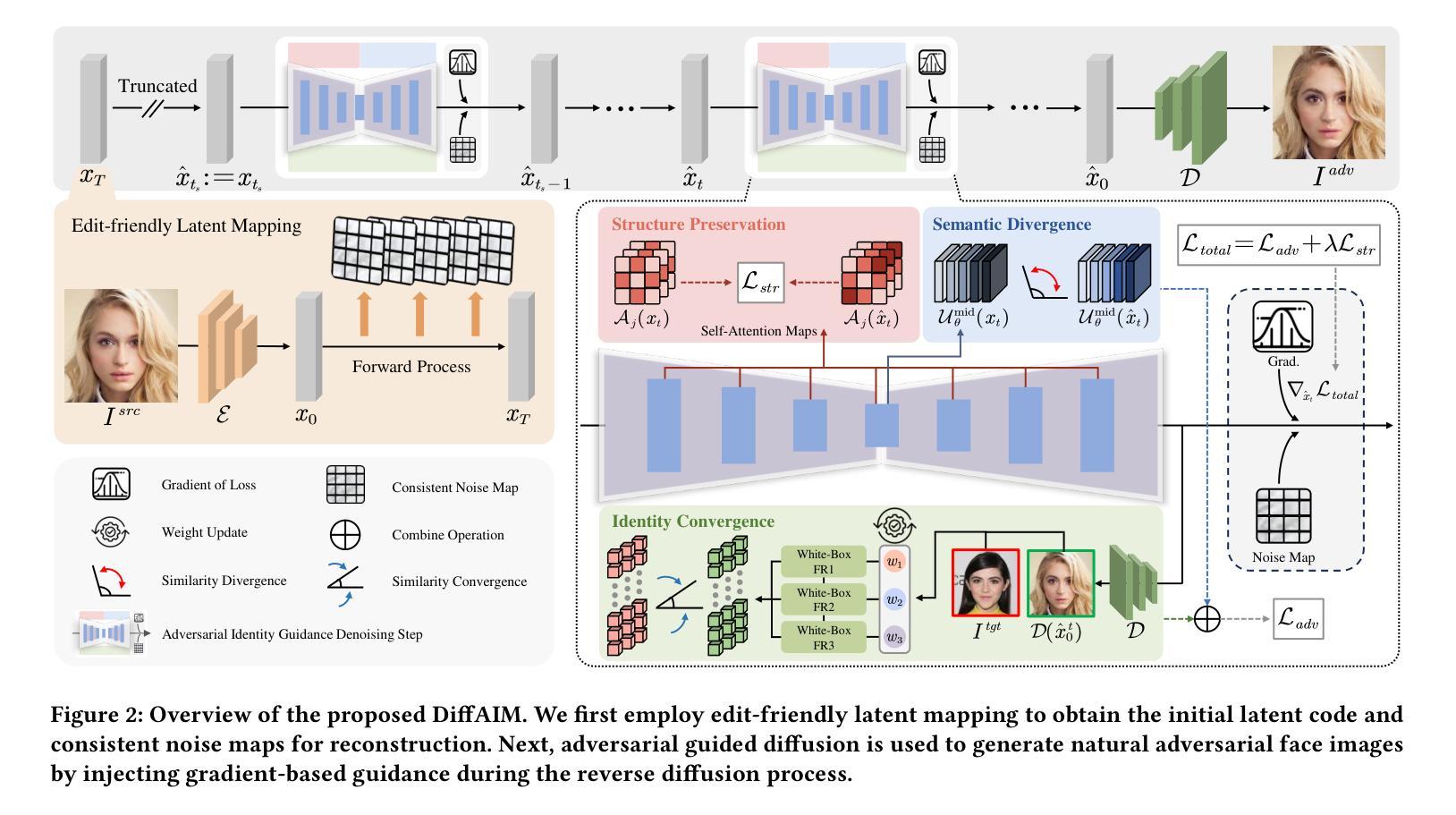
The success of face recognition (FR) systems has led to serious privacy concerns due to potential unauthorized surveillance and user tracking on social networks. Existing methods for enhancing privacy fail to generate natural face images that can protect facial privacy. In this paper, we propose diffusion-based adversarial identity manipulation (DiffAIM) to generate natural and highly transferable adversarial faces against malicious FR systems. To be specific, we manipulate facial identity within the low-dimensional latent space of a diffusion model. This involves iteratively injecting gradient-based adversarial identity guidance during the reverse diffusion process, progressively steering the generation toward the desired adversarial faces. The guidance is optimized for identity convergence towards a target while promoting semantic divergence from the source, facilitating effective impersonation while maintaining visual naturalness. We further incorporate structure-preserving regularization to preserve facial structure consistency during manipulation. Extensive experiments on both face verification and identification tasks demonstrate that compared with the state-of-the-art, DiffAIM achieves stronger black-box attack transferability while maintaining superior visual quality. We also demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach for commercial FR APIs, including Face++ and Aliyun.
人脸识别(FR)系统的成功引发了严重的隐私担忧,因为可能存在未经授权的监督和社会网络上的用户跟踪。现有的增强隐私的方法无法生成能够保护面部隐私的自然面部图像。在本文中,我们提出了基于扩散的对抗性身份操纵(DiffAIM)方法,生成自然且高度可转移的对抗性面部图像,以对抗恶意FR系统。具体来说,我们在扩散模型的低维潜在空间内对身份进行操纵。这涉及在反向扩散过程中迭代注入基于梯度的对抗性身份指导,逐步引导生成走向目标对抗性面部图像。指导优化旨在使身份收敛于目标,同时促进与源之间的语义发散,从而在保持视觉自然性的同时实现有效的伪装。我们进一步引入了结构保持正则化,以保持面部结构一致性在操纵过程中。对面部验证和识别任务的广泛实验表明,与最新技术相比,DiffAIM实现了更强的黑盒攻击转移性,同时保持了卓越的可视质量。我们还证明了所提出方法在包括Face++和阿里云在内的商业FR API上的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
人脸识别系统的成功引发了关于个人隐私的严重关注,因为存在潜在的未经授权监控和用户社交网络追踪。现有的隐私保护方法无法生成能保护面部隐私的自然面部图像。本研究提出了一种基于扩散对抗身份操控(DiffAIM)的方法,用于生成对抗性面部图像,以抵御恶意人脸识别系统。DiffAIM在低维潜在空间内操纵面部身份,并在反向扩散过程中注入基于梯度的对抗性身份指导,逐步引导生成图像朝向目标对抗性面部。此方法优化了身份收敛至目标的同时,促进与源图像的语义差异,以实现有效伪装并维持视觉自然性。此外,还融入了结构保持正则化,以保持面部结构一致性。实验表明,相较于其他顶尖方法,DiffAIM在面部验证和识别任务上实现了更强的黑盒攻击转移能力,同时保持了卓越视觉质量。该策略对包括Face++和阿里云在内的人脸识别API同样有效。
Key Takeaways
- 人脸识别系统的成功引发了关于隐私的重大担忧,特别是未经授权的监控和社交网络追踪。
- 现有隐私保护方法无法自然生成能保护面部隐私的图像。
- DiffAIM方法基于扩散模型,在低维潜在空间内操控面部身份。
- DiffAIM通过注入梯度基于的对抗性身份指导,逐步生成对抗性面部图像。
- DiffAIM在优化身份收敛至目标的同时,促进与源图像的语义差异,维持视觉自然性。
- 结构保持正则化被用于保持面部结构一致性。
点此查看论文截图

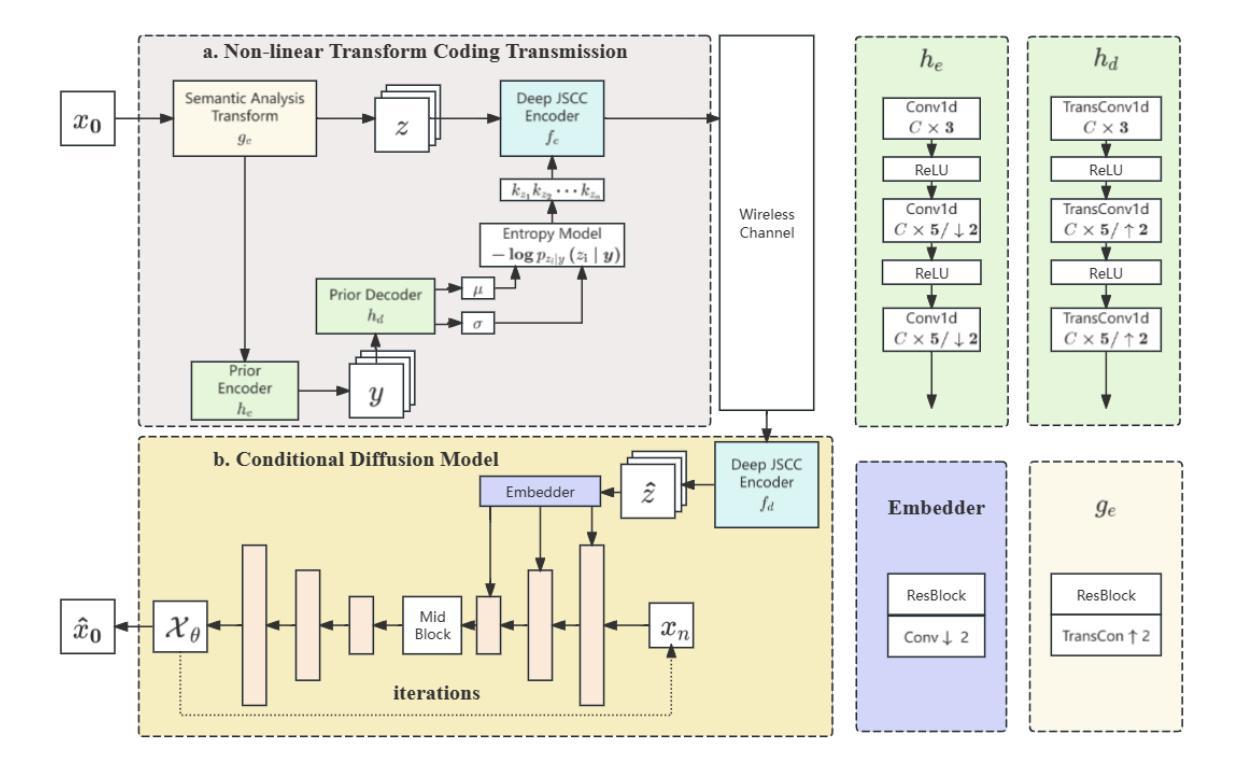
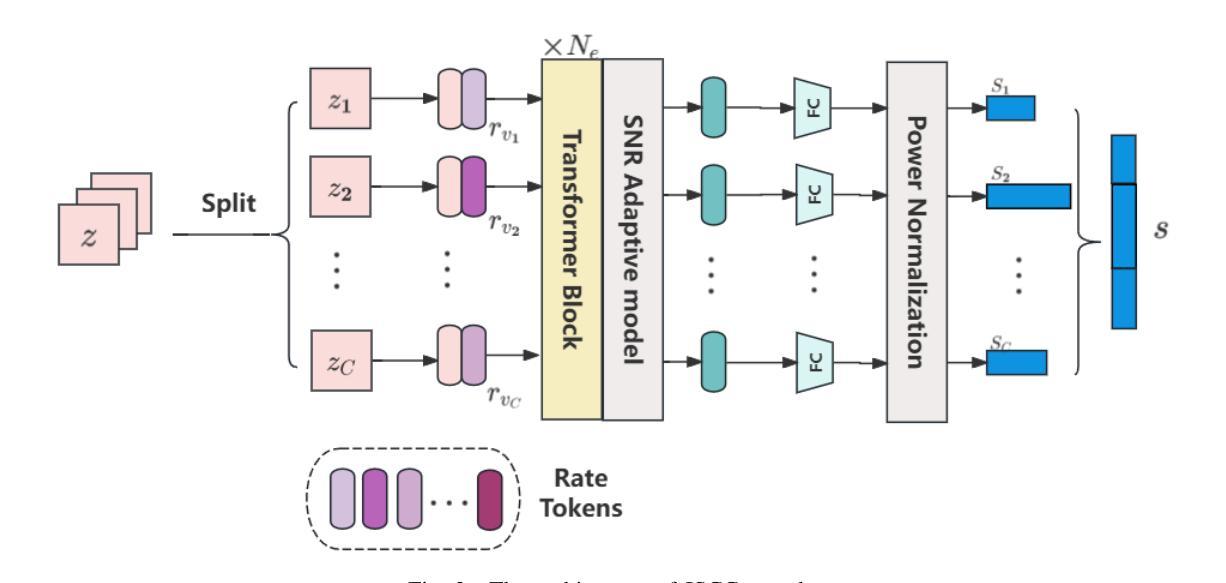
Latent Feature-Guided Conditional Diffusion for High-Fidelity Generative Image Semantic Communication
Authors:Zehao Chen, Xinfeng Wei, Haonan Tong, Zhaohui Yang, Changchuan Yin
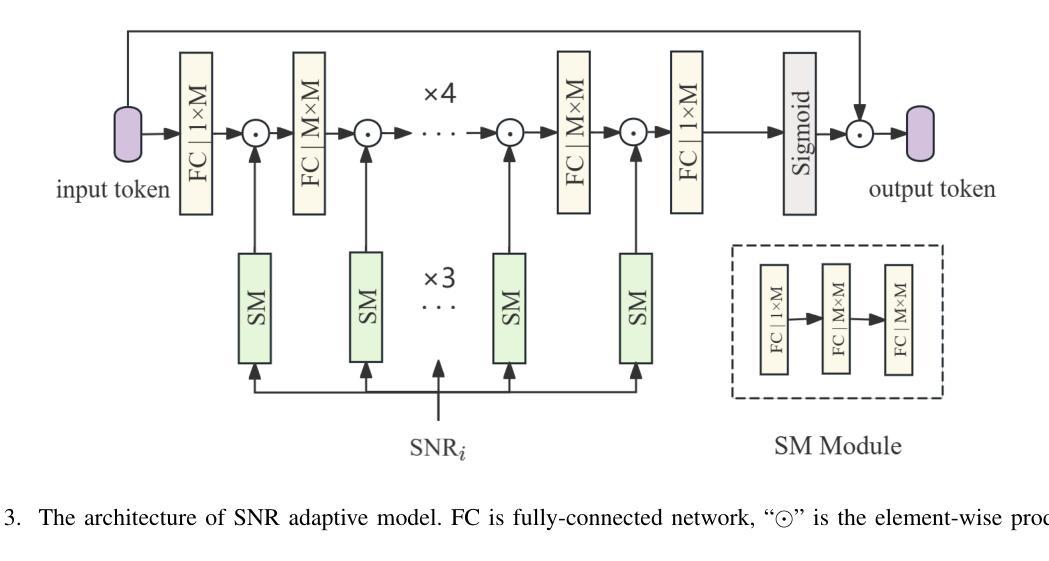
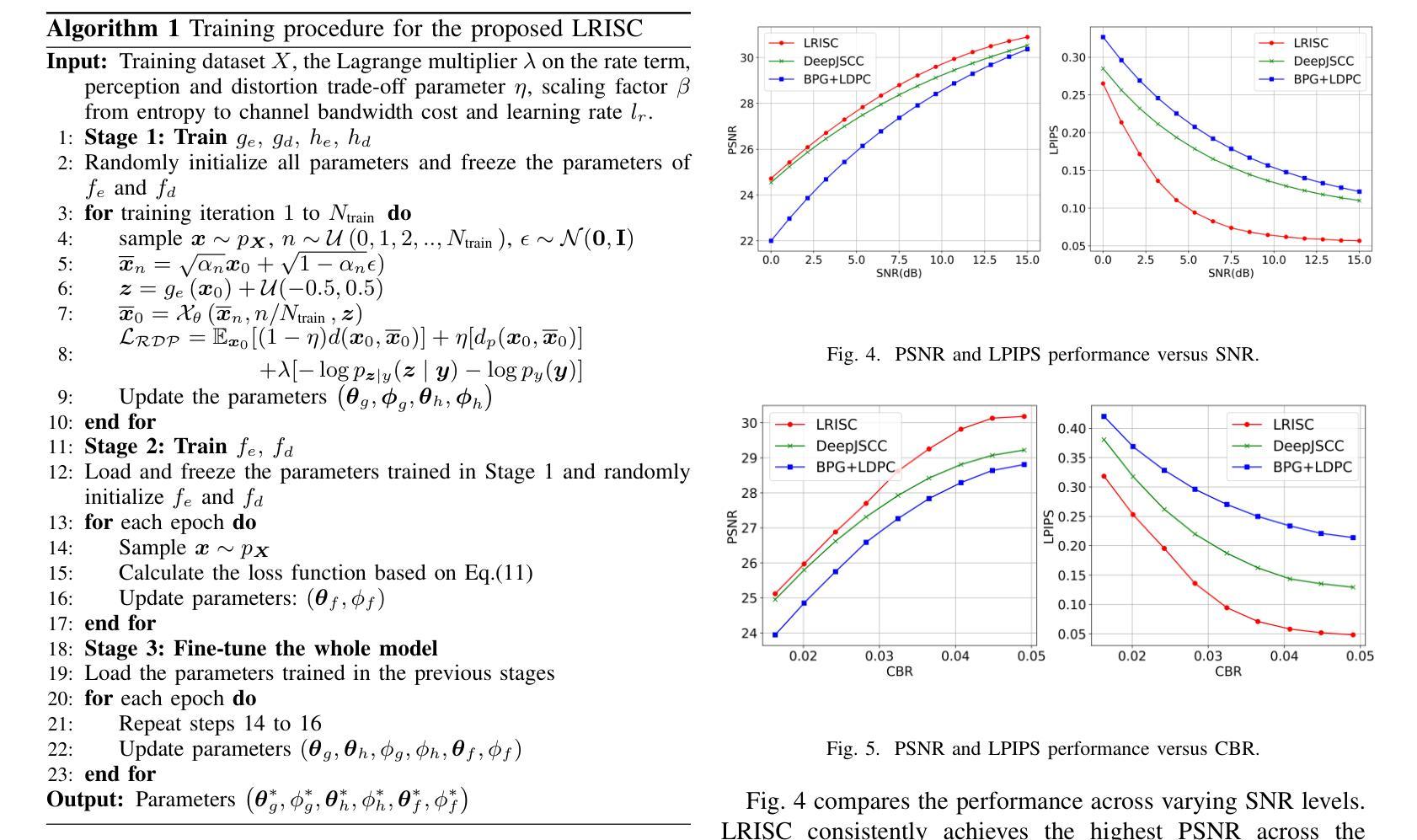
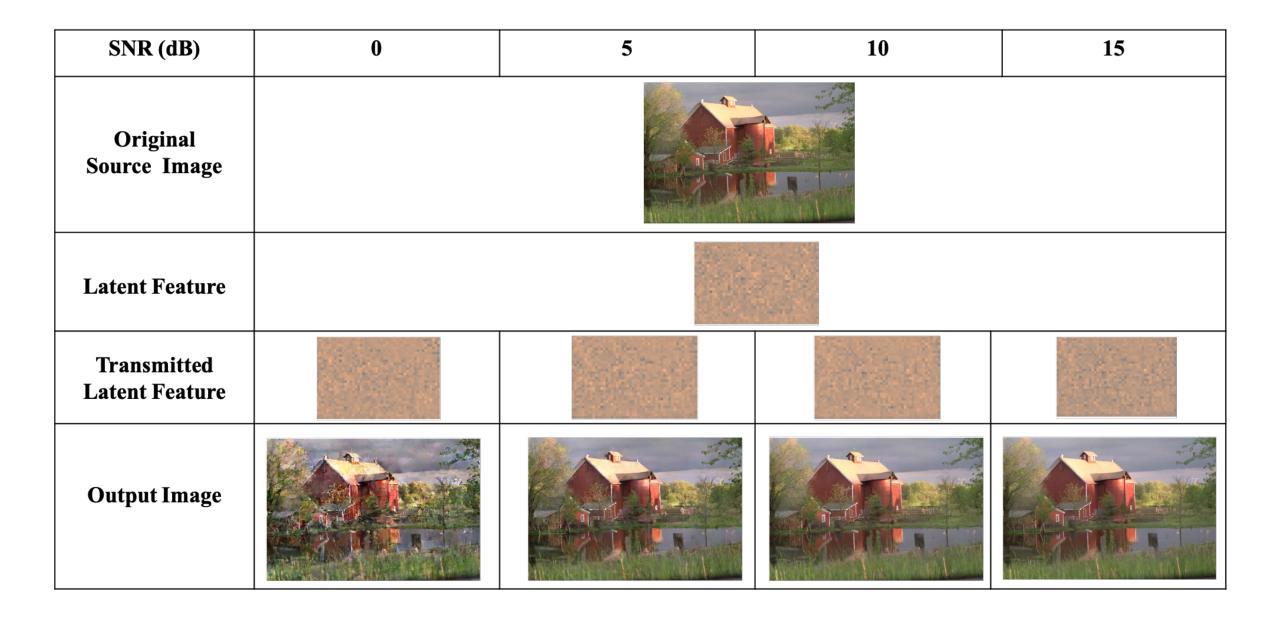
Semantic communication is proposed and expected to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of massive data transmission over sixth generation (6G) networks. However, existing deep learning-based joint source and channel coding (DeepJSCC) image semantic communication scheme predominantly focuses on optimizing pixel-level metrics, and neglects human perceptual requirements, which results in degraded perceptual quality. To address this issue, we propose a latent representation-oriented image semantic communication (LRISC) system, which transmits latent semantic features for image generation with semantic consistency, thereby ensuring the perceptual quality at the receiver. In particular, we first map the source image to latent features in a high-dimensional semantic space via a neural network (NN)- based non-linear transformation. Subsequently, these features are encoded using a joint source and channel coding (JSCC) scheme with adaptive coding length for efficient transmission over a wireless channel. At the receiver, a conditional diffusion model is developed by using the received latent features as conditional guidance to steer the reverse diffusion process, progressively reconstructing high-fidelity images while preserving semantic consistency. Moreover, we introduce a channel signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) adaptation mechanism, allowing one model to work across various channel states. Experiments show that the proposed method significantly outperforms existing methods, in terms of learned perceptual image patch similarity (LPIPS) and robustness against channel noise, with an average LPIPS reduction of 43.3% compared to DeepJSCC, while guaranteeing the semantic consistency.
语义通信旨在提高第六代(6G)网络上大规模数据传输的效率和效果。然而,现有的基于深度学习的联合源信道编码(DeepJSCC)图像语义通信方案主要关注像素级的指标优化,忽视了人类感知的需求,导致感知质量下降。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种面向潜在表示的图像语义通信(LRISC)系统,该系统传输用于图像生成的潜在语义特征,以确保接收端的感知质量具有语义一致性。具体而言,我们首先将源图像映射到高维语义空间中的潜在特征,通过神经网络(NN)进行非线性变换。随后,这些特征使用具有自适应编码长度的联合源信道编码(JSCC)方案进行编码,以便在无线信道上进行有效传输。在接收端,我们利用接收到的潜在特征作为条件指导,开发了一种条件扩散模型,引导反向扩散过程,逐步重建高质量图像,同时保持语义一致性。此外,我们还引入了一种信道信噪比(SNR)自适应机制,使模型能够在各种信道状态下工作。实验表明,所提方法在学习的感知图像补丁相似性(LPIPS)和对抗信道噪声的稳健性方面都显著优于现有方法,与DeepJSCC相比,平均LPIPS降低了43.3%,同时保证了语义一致性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 6 figures
摘要
针对第六代(6G)网络中的大规模数据传输,提出语义通信能提高传输效率和效果。然而,现有的基于深度学习的联合源信道编码(DeepJSCC)图像语义通信方案主要关注像素级指标优化,忽视了人类感知需求,导致感知质量下降。为解决这一问题,我们提出了一个基于潜在表示的图像语义通信系统(LRISC),通过传输潜在语义特征来生成图像,确保接收端的感知质量。具体而言,我们首先将源图像映射到高维语义空间的潜在特征上,然后通过联合源信道编码进行编码以适应无线信道的传输。在接收端,利用接收到的潜在特征作为条件指导,发展了一种条件扩散模型,以逆向扩散过程逐步重建高质量图像并保持语义一致性。此外,我们引入了信道信噪比(SNR)自适应机制,使模型能适应各种信道状态。实验表明,相较于DeepJSCC,所提方法在感知图像补丁相似性(LPIPS)上平均降低了43.3%,在抵抗信道噪声方面更加稳健,同时保证了语义一致性。
关键见解
- 语义通信在6G网络中对于大规模数据传输的效率与效果提升至关重要。
- 现有DeepJSCC方案主要关注像素级优化,忽视了人类感知需求,造成感知质量下降。
- LRISC系统通过传输潜在语义特征来确保图像的语义一致性和接收端的感知质量。
- 源图像首先被映射到高维语义空间的潜在特征上,然后通过联合源信道编码进行编码以适应无线传输。
- 接收端采用条件扩散模型,利用潜在特征逐步重建高质量图像。
- 引入信道SNR自适应机制,增强模型对各种信道状态的适应性。
- 实验显示LRISC在LPIPS指标上显著优于DeepJSCC,且更抗信道噪声干扰。
点此查看论文截图

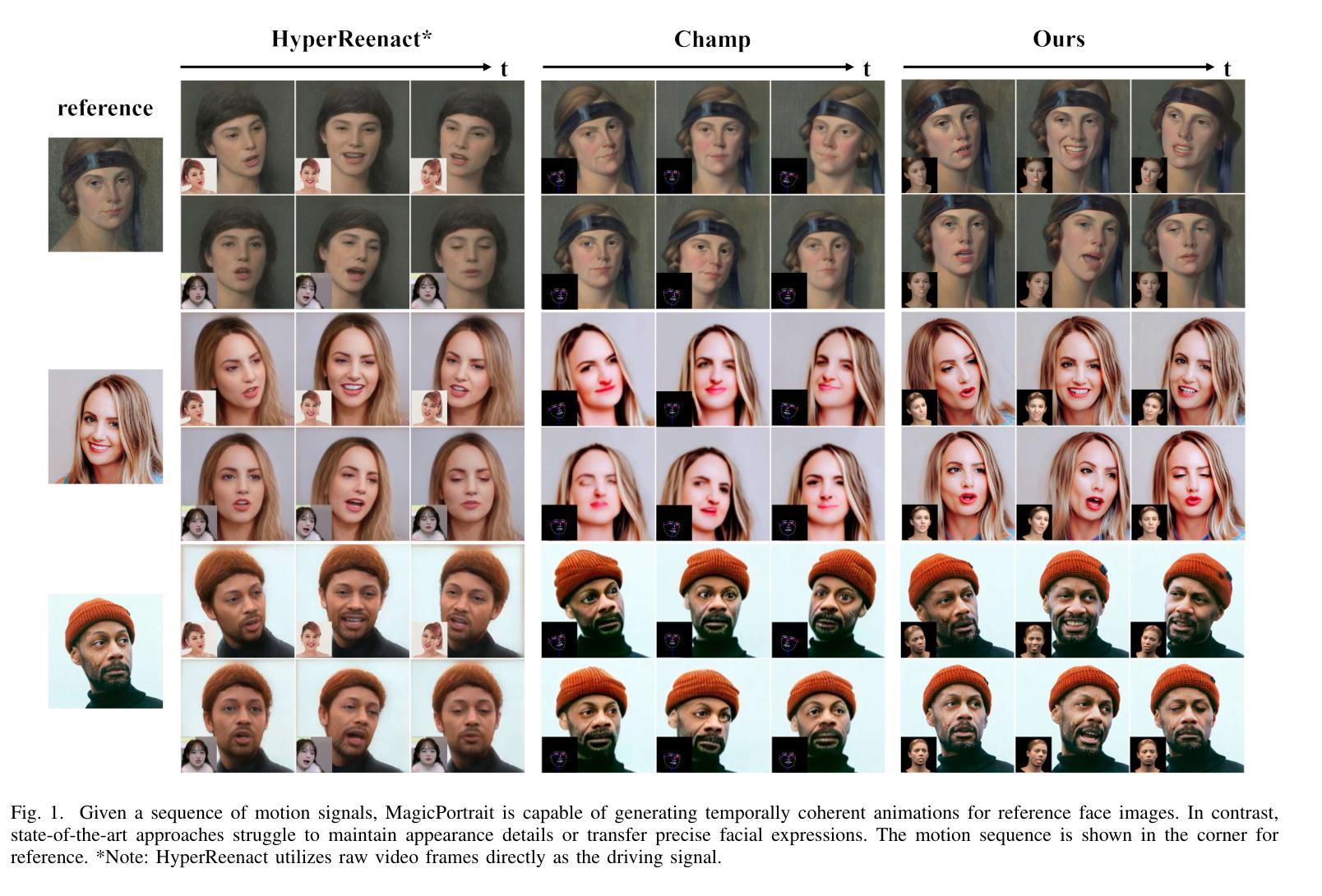
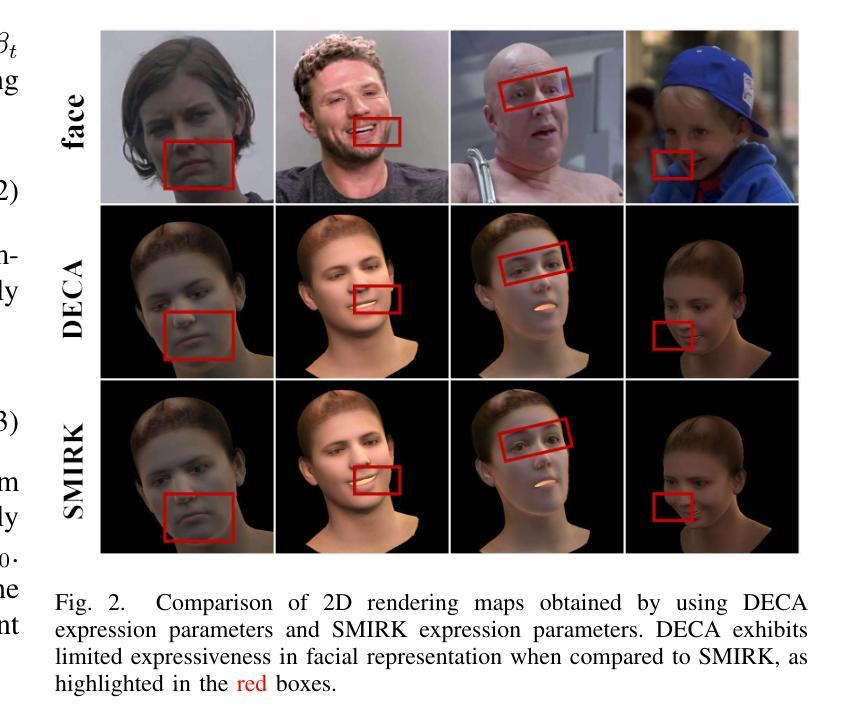
MagicPortrait: Temporally Consistent Face Reenactment with 3D Geometric Guidance
Authors:Mengting Wei, Yante Li, Tuomas Varanka, Yan Jiang, Licai Sun, Guoying Zhao
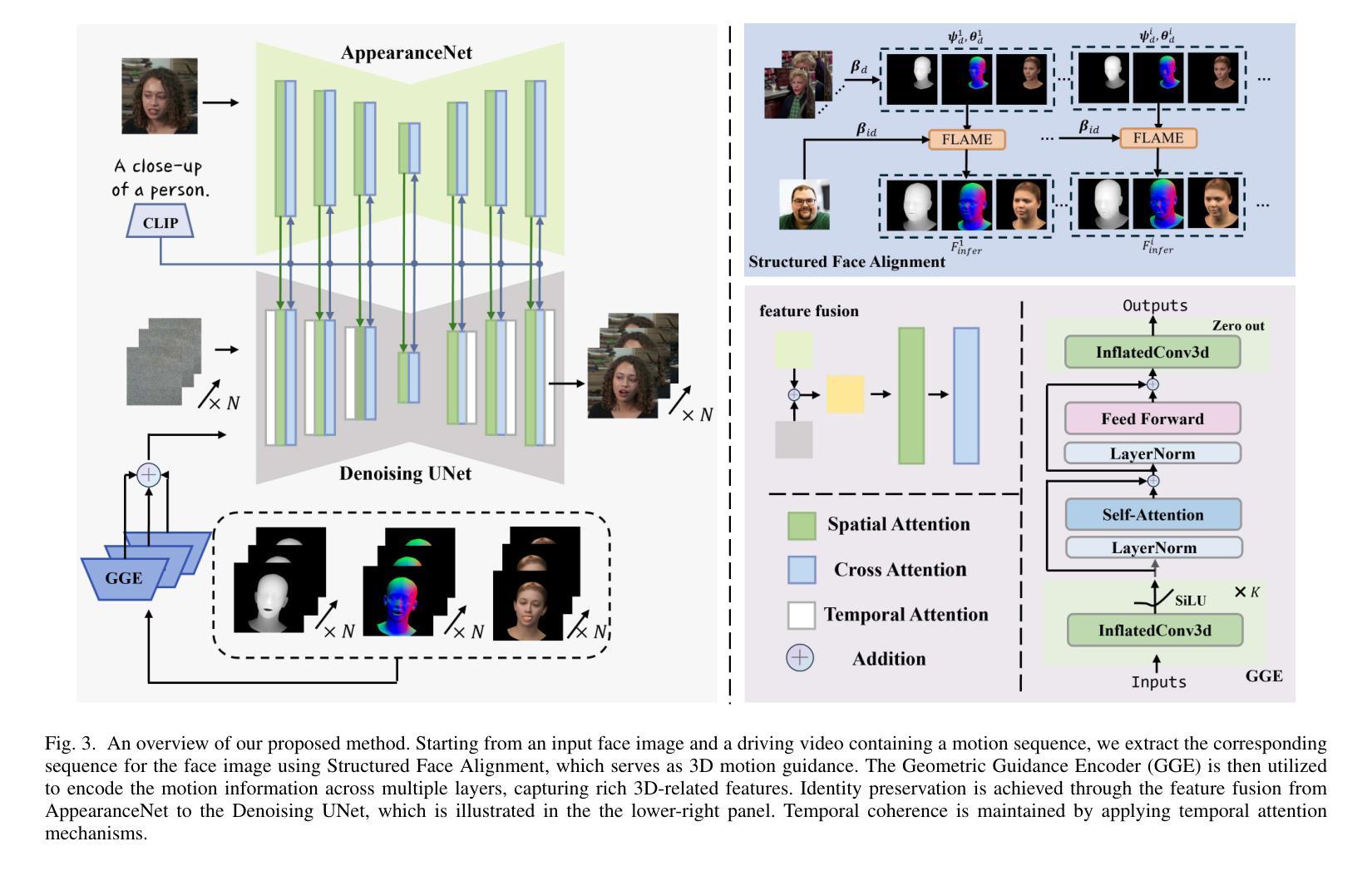
In this paper, we propose a method for video face reenactment that integrates a 3D face parametric model into a latent diffusion framework, aiming to improve shape consistency and motion control in existing video-based face generation approaches. Our approach employs the FLAME (Faces Learned with an Articulated Model and Expressions) model as the 3D face parametric representation, providing a unified framework for modeling face expressions and head pose. This enables precise extraction of detailed face geometry and motion features from driving videos. Specifically, we enhance the latent diffusion model with rich 3D expression and detailed pose information by incorporating depth maps, normal maps, and rendering maps derived from FLAME sequences. A multi-layer face movements fusion module with integrated self-attention mechanisms is used to combine identity and motion latent features within the spatial domain. By utilizing the 3D face parametric model as motion guidance, our method enables parametric alignment of face identity between the reference image and the motion captured from the driving video. Experimental results on benchmark datasets show that our method excels at generating high-quality face animations with precise expression and head pose variation modeling. In addition, it demonstrates strong generalization performance on out-of-domain images. Code is publicly available at https://github.com/weimengting/MagicPortrait.
本文提出了一种将3D人脸参数模型集成到潜在扩散框架中的视频人脸再现方法。该方法旨在提高现有视频人脸生成方法中的形状一致性和运动控制。我们的方法采用FLAME(带有关节模型和表情的人脸学习)模型作为3D人脸参数表示,为面部表情和头部姿态建模提供了一个统一框架。这可以从驱动视频中提取详细的面部几何和运动特征。具体来说,我们通过融入从FLAME序列派生的深度图、法线图以及渲染图,丰富了潜在扩散模型的3D表情和详细姿态信息。采用具有集成自注意力机制的多层面部运动融合模块,在空域内结合身份和运动潜在特征。通过利用3D人脸参数模型作为运动指导,我们的方法能够在参考图像和从驱动视频中捕获的运动之间实现人脸身份的参数对齐。在基准数据集上的实验结果表明,我们的方法在生成高质量的人脸动画、精确的表情和头部姿态变化建模方面表现出色。此外,它在域外图像上表现出强大的泛化性能。相关代码已公开在https://github.com/weimengting/MagicPortrait上。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
新一代视频人脸替换技术结合了三维人脸参数模型与潜在扩散框架,旨在改进现有视频人脸生成方法中的形状一致性和运动控制。通过采用FLAME模型作为三维人脸参数表示,该方法为面部表情和头部姿态建模提供了统一框架,从而精确地提取了驱动视频中的面部几何和运动特征。此外,该方法还通过融入深度图、法线图以及从FLAME序列中得到的渲染图增强了潜在扩散模型的丰富三维表情和精细姿态信息。利用三维人脸参数模型作为运动指导,该方法实现了参考图像与从驱动视频中捕获的运动之间的面部身份参数对齐。实验结果表明,该方法在生成高质量面部动画、精确表达及头部姿态变化建模方面表现出色,且在跨域图像上具有较强的泛化性能。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文提出了一种将3D人脸参数模型融入潜在扩散框架的视频人脸替换新方法。
- 采用FLAME模型作为3D人脸参数表示,为面部表情和头部姿态建模提供统一框架。
- 通过融入深度图、法线图和渲染图增强潜在扩散模型的丰富三维表情和精细姿态信息。
- 利用三维人脸参数模型作为运动指导,实现面部身份与运动的参数对齐。
- 该方法在生成高质量面部动画、精确表达及头部姿态变化建模方面表现优异。
- 该方法具有强大的泛化能力,适用于跨域图像。
点此查看论文截图



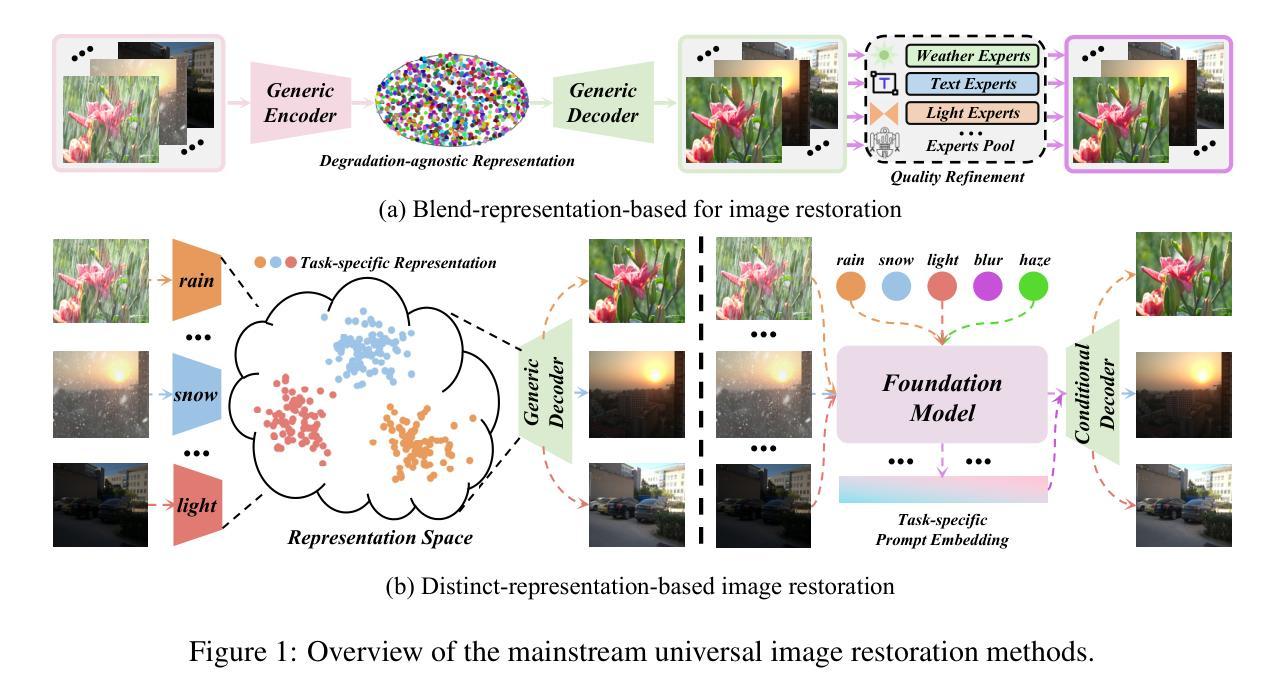
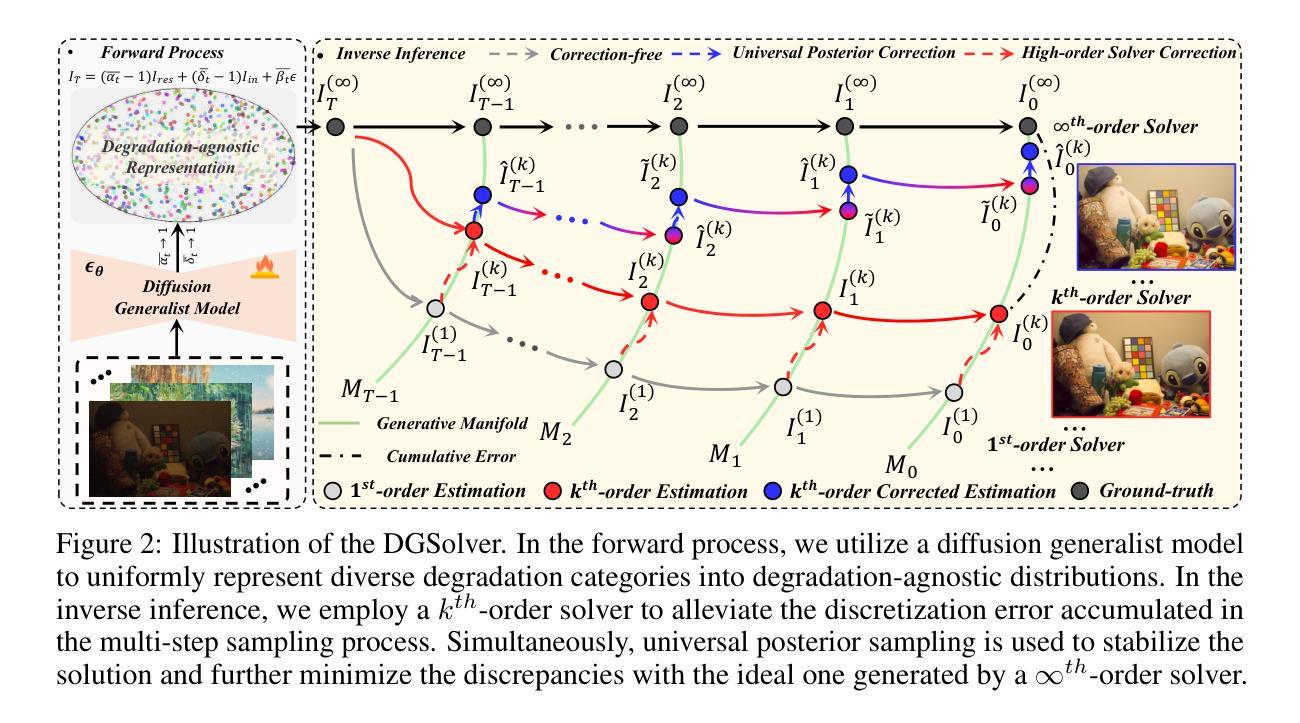
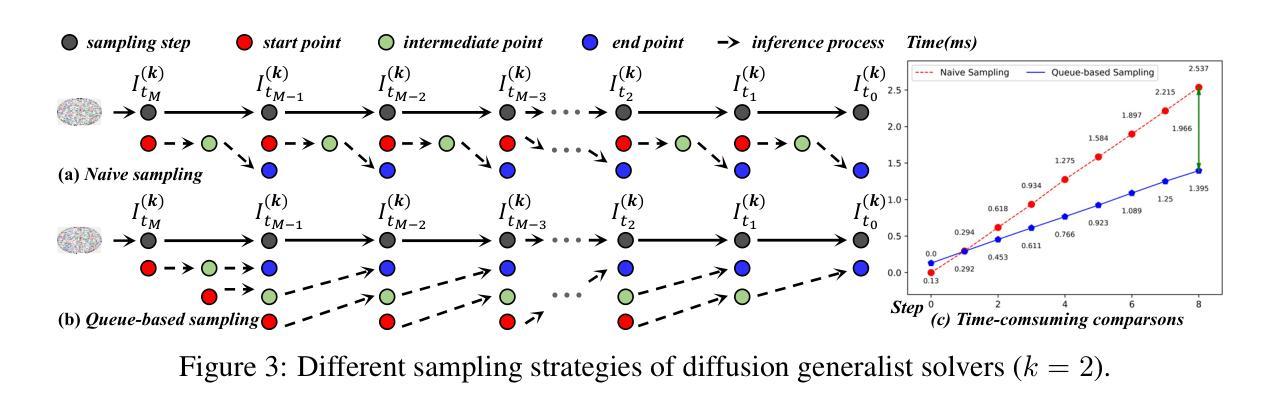
DGSolver: Diffusion Generalist Solver with Universal Posterior Sampling for Image Restoration
Authors:Hebaixu Wang, Jing Zhang, Haonan Guo, Di Wang, Jiayi Ma, Bo Du
Diffusion models have achieved remarkable progress in universal image restoration. While existing methods speed up inference by reducing sampling steps, substantial step intervals often introduce cumulative errors. Moreover, they struggle to balance the commonality of degradation representations and restoration quality. To address these challenges, we introduce \textbf{DGSolver}, a diffusion generalist solver with universal posterior sampling. We first derive the exact ordinary differential equations for generalist diffusion models and tailor high-order solvers with a queue-based accelerated sampling strategy to improve both accuracy and efficiency. We then integrate universal posterior sampling to better approximate manifold-constrained gradients, yielding a more accurate noise estimation and correcting errors in inverse inference. Extensive experiments show that DGSolver outperforms state-of-the-art methods in restoration accuracy, stability, and scalability, both qualitatively and quantitatively. Code and models will be available at https://github.com/MiliLab/DGSolver.
扩散模型在通用图像修复方面取得了显著的进步。虽然现有方法通过减少采样步骤来加速推理,但较大的步骤间隔通常会引入累积误差。此外,它们很难在退化表示的共同性和修复质量之间取得平衡。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了DGSolver,这是一种带有通用后验采样的扩散通用求解器。我们首先为通用扩散模型推导出精确的常微分方程,并使用基于队列的加速采样策略定制高阶求解器,以提高准确性和效率。然后,我们融入通用后验采样,以更好地近似流形约束梯度,从而得到更准确的噪声估计和逆向推理中的误差校正。大量实验表明,无论是在定性还是定量方面,DGSolver在修复准确性、稳定性和可扩展性方面都优于最先进的方法。相关代码和模型将在https://github.com/MiliLab/DGSolver上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:针对通用扩散模型在图像修复方面的不足,提出一种名为DGSolver的通用扩散求解器,采用精确常微分方程和高阶求解器来提高修复准确性和效率。结合通用后采样策略进行噪声估计和逆向推理误差校正,提高修复质量。在多项实验中,DGSolver在修复准确性、稳定性和可扩展性方面均优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways:
- 现有扩散模型在图像修复中面临挑战,如累积误差和平衡退化表示与修复质量的问题。
- 提出DGSolver,采用精确常微分方程和高阶求解器改善修复效率和准确性。
- 采用基于队列的加速采样策略提高性能。
- 结合通用后采样以更好地近似流形约束梯度,准确估计噪声并纠正逆向推理误差。
- DGSolver在多项实验中的修复准确性、稳定性和可扩展性优于现有方法。
- DGSolver代码和模型可在https://github.com/MiliLab/DGSolver上获取。
- DGSolver设计具有普适性,可应用于多种图像修复任务。
点此查看论文截图

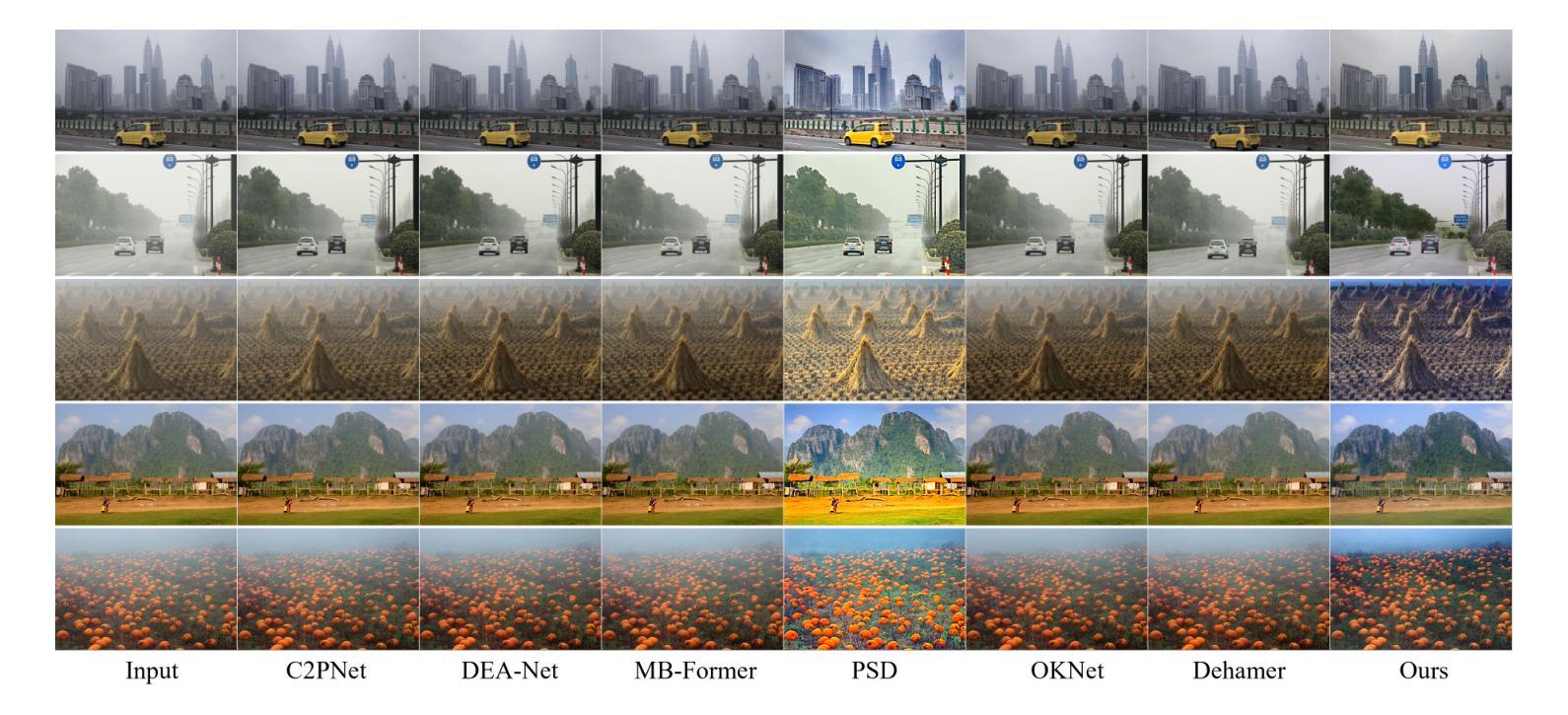
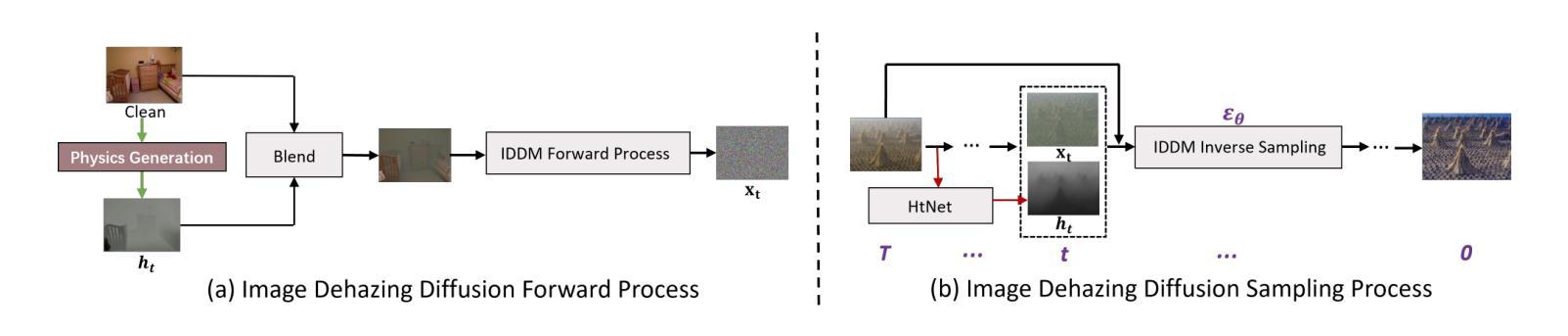
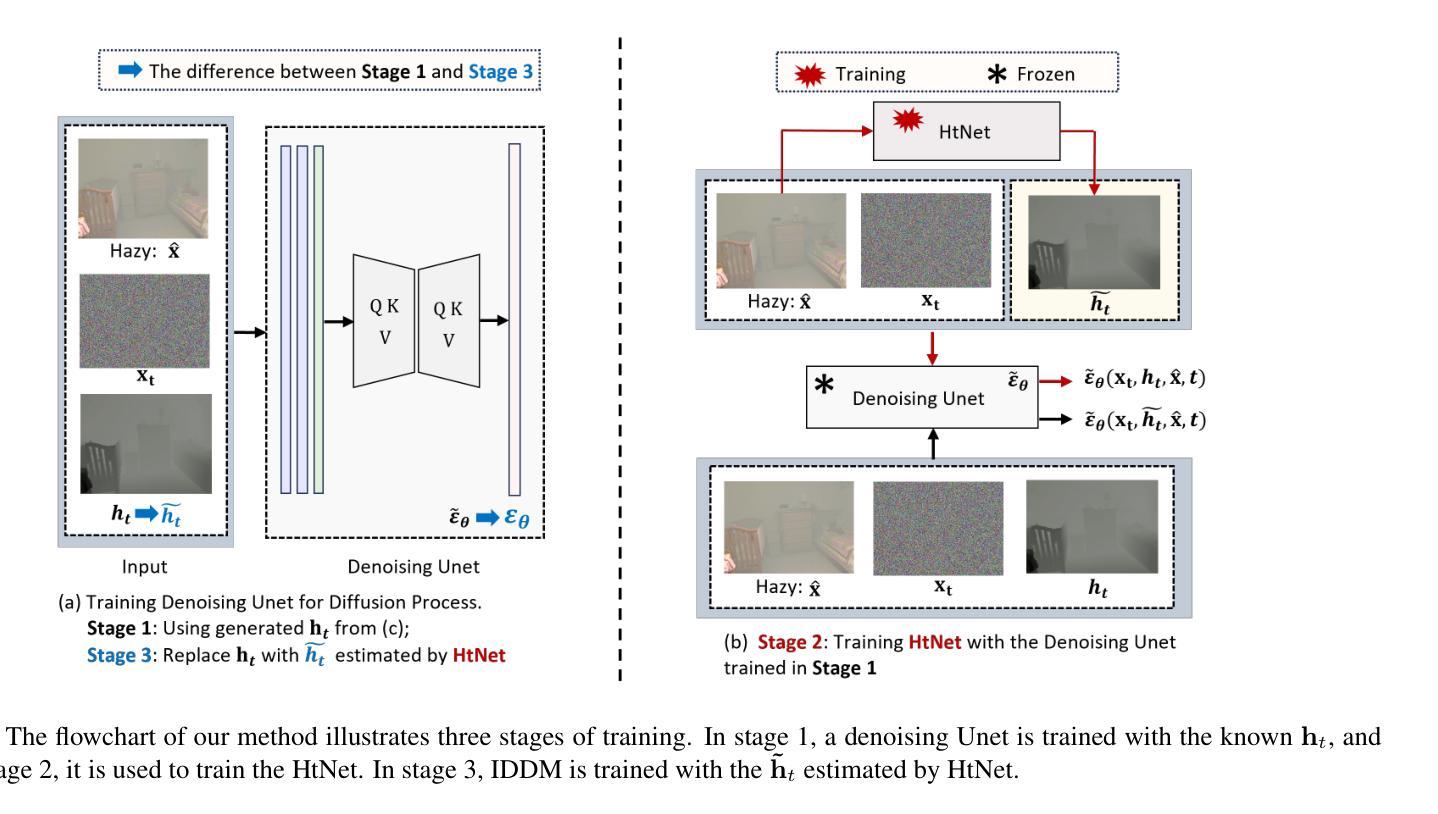
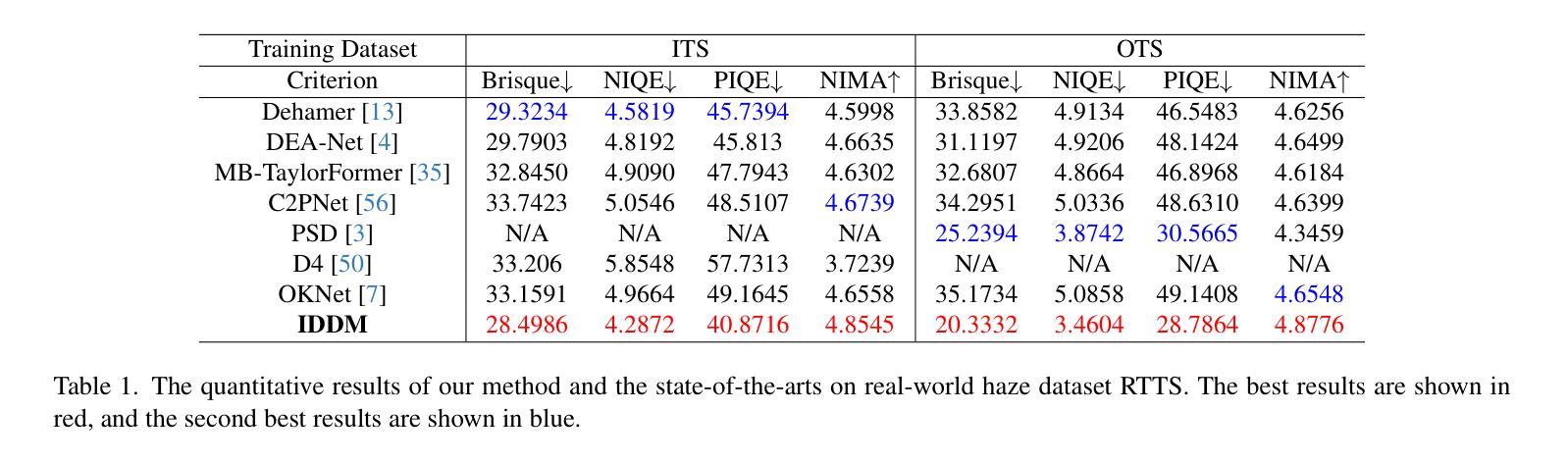
IDDM: Bridging Synthetic-to-Real Domain Gap from Physics-Guided Diffusion for Real-world Image Dehazing
Authors:Shijun Zhou, Yajing Liu, Chunhui Hao, Zhiyuan Liu, Jiandong Tian
Due to the domain gap between real-world and synthetic hazy images, current data-driven dehazing algorithms trained on synthetic datasets perform well on synthetic data but struggle to generalize to real-world scenarios. To address this challenge, we propose \textbf{I}mage \textbf{D}ehazing \textbf{D}iffusion \textbf{M}odels (IDDM), a novel diffusion process that incorporates the atmospheric scattering model into noise diffusion. IDDM aims to use the gradual haze formation process to help the denoising Unet robustly learn the distribution of clear images from the conditional input hazy images. We design a specialized training strategy centered around IDDM. Diffusion models are leveraged to bridge the domain gap from synthetic to real-world, while the atmospheric scattering model provides physical guidance for haze formation. During the forward process, IDDM simultaneously introduces haze and noise into clear images, and then robustly separates them during the sampling process. By training with physics-guided information, IDDM shows the ability of domain generalization, and effectively restores the real-world hazy images despite being trained on synthetic datasets. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our method through both quantitative and qualitative comparisons with state-of-the-art approaches.
由于真实世界和合成雾图像之间的领域差距,当前基于合成数据集训练的数据驱动去雾算法在合成数据上表现良好,但在真实场景中的泛化能力较差。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了图像去雾扩散模型(IDDM),这是一种新的扩散过程,将大气散射模型融入噪声扩散中。IDDM旨在利用逐步的雾形成过程,帮助去噪U-Net从条件输入的有雾图像中稳健地学习清晰图像分布。我们围绕IDDM设计了一种专门的训练策略。扩散模型被用来弥合合成和真实世界之间的领域差距,而大气散射模型则为雾的形成提供了物理指导。在正向过程中,IDDM同时将雾和噪声引入清晰图像,然后在采样过程中稳健地分离它们。通过物理指导信息进行训练,IDDM展现出领域泛化的能力,即使在合成数据集上训练,也能有效地恢复真实世界的雾图像。大量实验表明,我们的方法与最先进的方法相比,在定量和定性比较中都表现出有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为图像去雾扩散模型(IDDM)的新方法,旨在解决合成数据集训练的现有数据驱动去雾算法在真实世界场景中的泛化性能挑战。通过将大气散射模型融入噪声扩散,IDDM利用渐进的雾形成过程帮助去噪Unet从条件输入雾图像中学习清晰图像分布。通过设计以IDDM为中心的训练策略,利用扩散模型缩小合成数据与真实世界之间的领域差距,同时大气散射模型为雾的形成提供物理指导。实验证明,该方法在合成数据集上训练后,能有效恢复真实世界中的雾图像。
Key Takeaways
- 当前数据驱动的去雾算法在真实世界场景中泛化性能较差,主要原因是合成图像和真实世界图像之间的域差距。
- 提出了一种新的图像去雾扩散模型(IDDM),将大气散射模型融入噪声扩散中。
- IDDM利用渐进的雾形成过程帮助去噪Unet从条件输入雾图像中学习清晰图像分布。
- 设计了以IDDM为中心的训练策略,利用扩散模型缩小合成数据和真实世界之间的领域差距。
- 大气散射模型为雾的形成提供物理指导,使得IDDM能够更有效地恢复真实世界的雾图像。
- IDDM在定量和定性比较方面均显示出其有效性,与现有先进方法相比具有优势。
点此查看论文截图


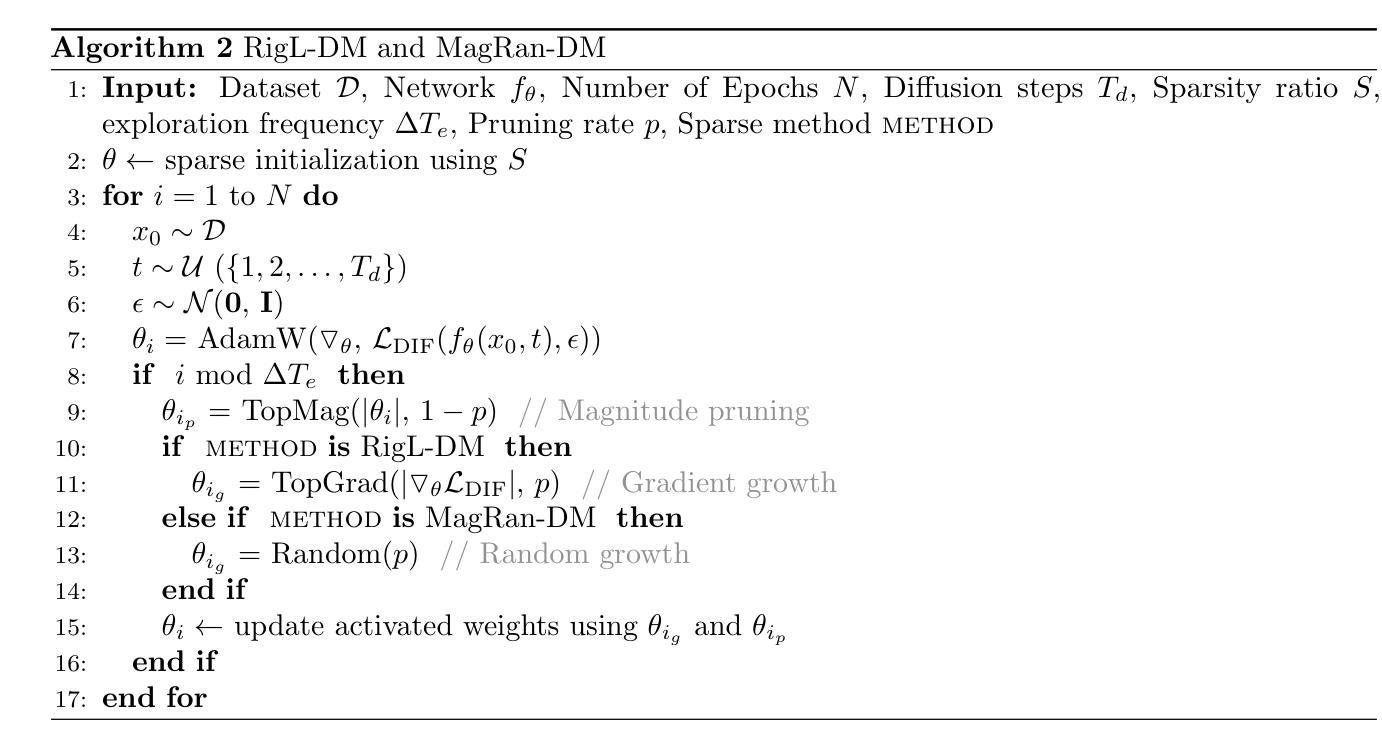
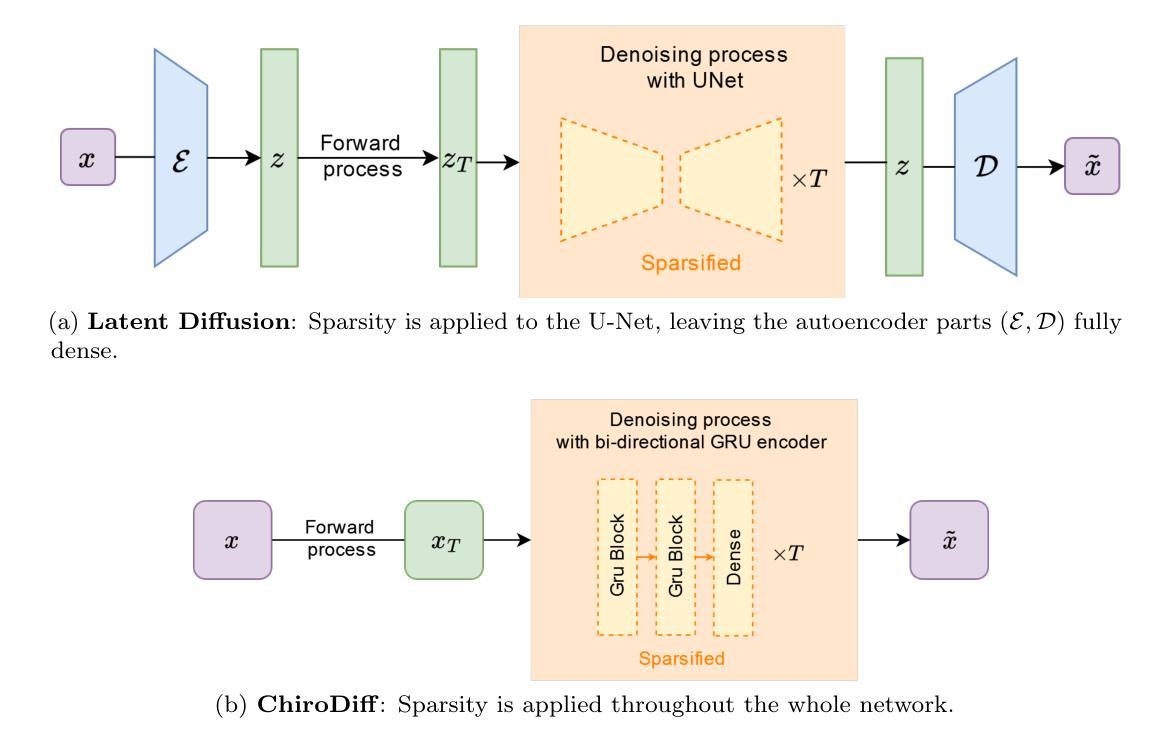
Sparse-to-Sparse Training of Diffusion Models
Authors:Inês Cardoso Oliveira, Decebal Constantin Mocanu, Luis A. Leiva
Diffusion models (DMs) are a powerful type of generative models that have achieved state-of-the-art results in various image synthesis tasks and have shown potential in other domains, such as natural language processing and temporal data modeling. Despite their stable training dynamics and ability to produce diverse high-quality samples, DMs are notorious for requiring significant computational resources, both in the training and inference stages. Previous work has focused mostly on increasing the efficiency of model inference. This paper introduces, for the first time, the paradigm of sparse-to-sparse training to DMs, with the aim of improving both training and inference efficiency. We focus on unconditional generation and train sparse DMs from scratch (Latent Diffusion and ChiroDiff) on six datasets using three different methods (Static-DM, RigL-DM, and MagRan-DM) to study the effect of sparsity in model performance. Our experiments show that sparse DMs are able to match and often outperform their Dense counterparts, while substantially reducing the number of trainable parameters and FLOPs. We also identify safe and effective values to perform sparse-to-sparse training of DMs.
扩散模型(DMs)是一种强大的生成模型,在各种图像合成任务中达到了最先进的水平,并在其他领域如自然语言处理和时序数据建模中显示出潜力。尽管DMs具有稳定的训练动力并能够产生多样化的高质量样本,但它们却以在训练和推理阶段都需要大量计算资源而闻名。以前的工作主要集中在提高模型推理的效率。本文首次将稀疏到稀疏的训练范式引入扩散模型,旨在提高训练和推理的效率。我们关注无条件生成,从零开始训练稀疏扩散模型(潜在扩散和ChiroDiff),在六个数据集上使用三种不同的方法(Static-DM、RigL-DM和MagRan-DM)来研究稀疏性对模型性能的影响。我们的实验表明,稀疏DMs能够匹配甚至超越其密集对应模型的表现,同时大大减少可训练参数和浮点运算次数。我们还确定了进行DMs的稀疏到稀疏训练的安全和有效值。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
扩散模型(DMs)是一种强大的生成模型,在各种图像合成任务中取得了最新成果,并在自然语言处理和时序数据建模等领域显示出潜力。尽管DMs具有稳定的训练动力学和产生多样化高质量样本的能力,但它们却在训练和推理阶段都需要大量的计算资源。以前的工作主要集中在提高模型推理的效率。本文首次将稀疏到稀疏的训练范式引入到DMs中,旨在提高训练和推理的效率。我们专注于无条件生成,使用三种不同的方法(Static-DM、RigL-DM和MagRan-DM)在六个数据集上从头开始训练稀疏DMs(潜在扩散和ChiroDiff)。实验表明,稀疏DMs能够匹配甚至超越其密集对应模型的表现,同时大幅减少可训练参数和浮点运算次数。我们还确定了进行DMs的稀疏到稀疏训练的安全和有效值。
要点
- 扩散模型(DMs)在图像合成等领域表现出强大的生成能力。
- DMs在训练和推理阶段都需要大量计算资源。
- 本文首次引入稀疏到稀疏的训练范式到DMs中,旨在提高训练和推理的效率。
- 在多个数据集上实验表明,稀疏DMs能匹配甚至超越密集DMs的表现。
- 稀疏DMs能大幅减少可训练参数和浮点运算次数。
- 本文提供了进行DMs的稀疏到稀疏训练的有效方法。
点此查看论文截图

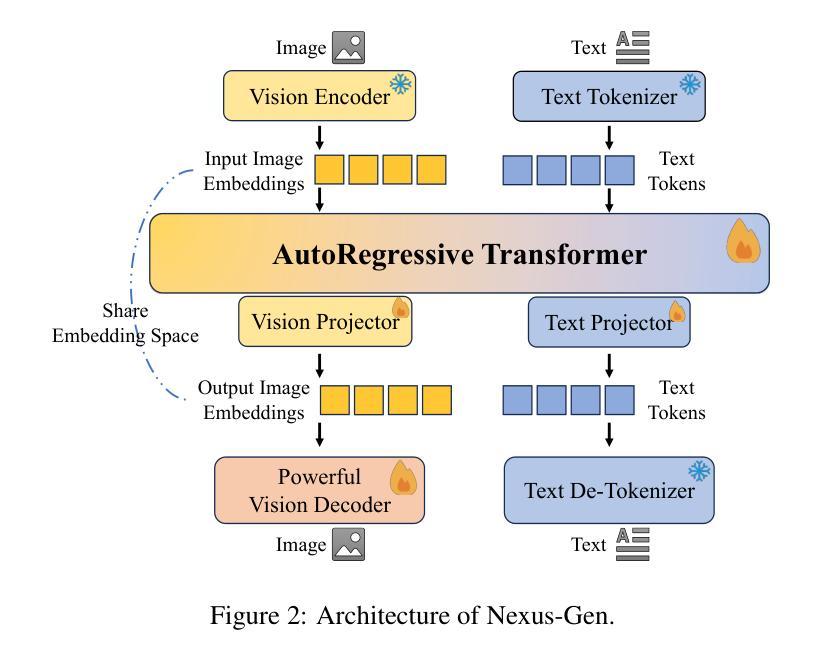
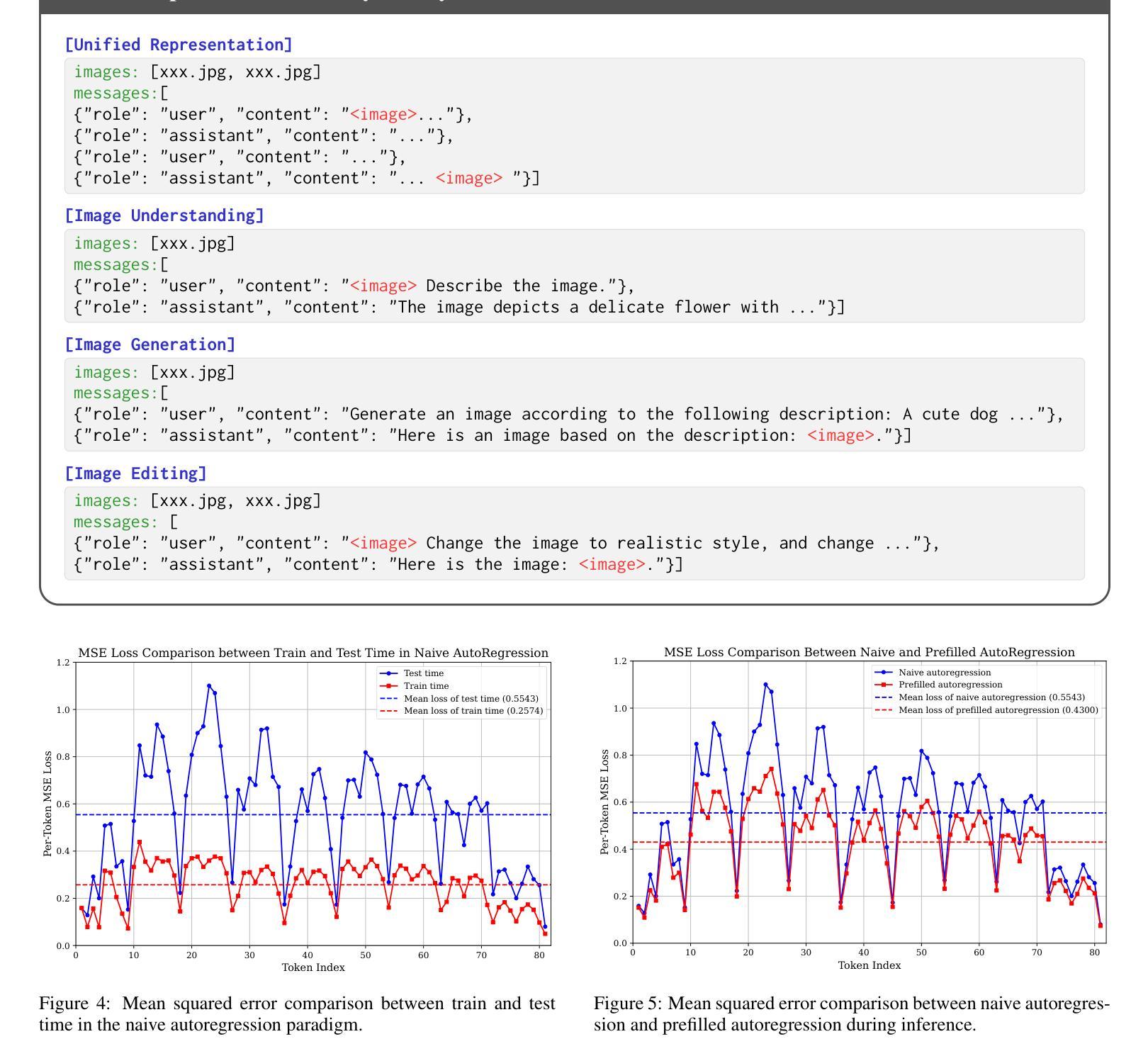
Nexus-Gen: A Unified Model for Image Understanding, Generation, and Editing
Authors:Hong Zhang, Zhongjie Duan, Xingjun Wang, Yingda Chen, Yuze Zhao, Yu Zhang
Unified multimodal large language models (MLLMs) aim to integrate multimodal understanding and generation abilities through a single framework. Despite their versatility, existing open-source unified models exhibit performance gaps against domain-specific architectures. To bridge this gap, we present Nexus-Gen, a unified model that synergizes the language reasoning capabilities of LLMs with the image synthesis power of diffusion models. To align the embedding space of the LLM and diffusion model, we conduct a dual-phase alignment training process. (1) The autoregressive LLM learns to predict image embeddings conditioned on multimodal inputs, while (2) the vision decoder is trained to reconstruct high-fidelity images from these embeddings. During training the LLM, we identified a critical discrepancy between the autoregressive paradigm’s training and inference phases, where error accumulation in continuous embedding space severely degrades generation quality. To avoid this issue, we introduce a prefilled autoregression strategy that prefills input sequence with position-embedded special tokens instead of continuous embeddings. Through dual-phase training, Nexus-Gen has developed the integrated capability to comprehensively address the image understanding, generation and editing tasks. All models, datasets, and codes are published at https://github.com/modelscope/Nexus-Gen.git to facilitate further advancements across the field.
统一多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)旨在通过单一框架整合多模态理解和生成能力。尽管它们具有多功能性,但现有的开源统一模型与特定领域的架构之间仍存在一定的性能差距。为了弥补这一差距,我们提出了Nexus-Gen,这是一款统一模型,它协同了LLM的语言推理能力与扩散模型的图像合成能力。为了对齐LLM和扩散模型的嵌入空间,我们进行了双阶段对齐训练过程。(1)自回归LLM学习根据多模态输入预测图像嵌入,(2)视觉解码器则训练从这些嵌入中重建高保真图像。在训练LLM的过程中,我们发现自回归范式训练与推理阶段之间存在关键差异,连续嵌入空间中的误差累积会严重降低生成质量。为了避免这个问题,我们引入了一种预填充自回归策略,该策略用位置嵌入特殊令牌预填充输入序列,而不是连续嵌入。通过双阶段训练,Nexus-Gen已经具备了全面解决图像理解、生成和编辑任务的能力。所有模型、数据集和代码都已发布在https://github.com/modelscope/Nexus-Gen.git,以促进该领域的进一步发展。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于统一多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的目标是通过单一框架整合多模态理解和生成能力。现有开源统一模型在领域特定架构方面存在性能差距。为了缩小这一差距,我们提出了Nexus-Gen,一个融合了语言推理能力和扩散模型图像合成能力的统一模型。通过双阶段对齐训练过程,实现了LLM和扩散模型的嵌入空间对齐。第一阶段是自适应回归LLM学习基于多模态输入的图像嵌入预测,第二阶段是视觉解码器从这些嵌入中重建高保真图像。在训练LLM过程中,我们发现自适应回归范式在训练和推理阶段之间存在关键差异,连续嵌入空间中的误差累积严重降低了生成质量。为了避免这个问题,我们引入了一种预填充自适应回归策略,该策略用位置嵌入特殊令牌预填充输入序列,而不是连续嵌入。通过双阶段训练,Nexus-Gen具备了全面解决图像理解、生成和编辑任务的综合能力。
Key Takeaways
- 统一多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的目标是整合多模态理解和生成能力。
- 现有开源统一模型在特定领域性能方面存在差距。
- Nexus-Gen融合了语言推理能力和扩散模型的图像合成能力。
- 通过双阶段对齐训练过程,实现了LLM和扩散模型的嵌入空间对齐。
- 在训练LLM过程中,发现并解决了自适应回归范式的关键差异问题。
- 引入了预填充自适应回归策略,以提高生成质量。
- Nexus-Gen具备图像理解、生成和编辑的综合能力。
点此查看论文截图


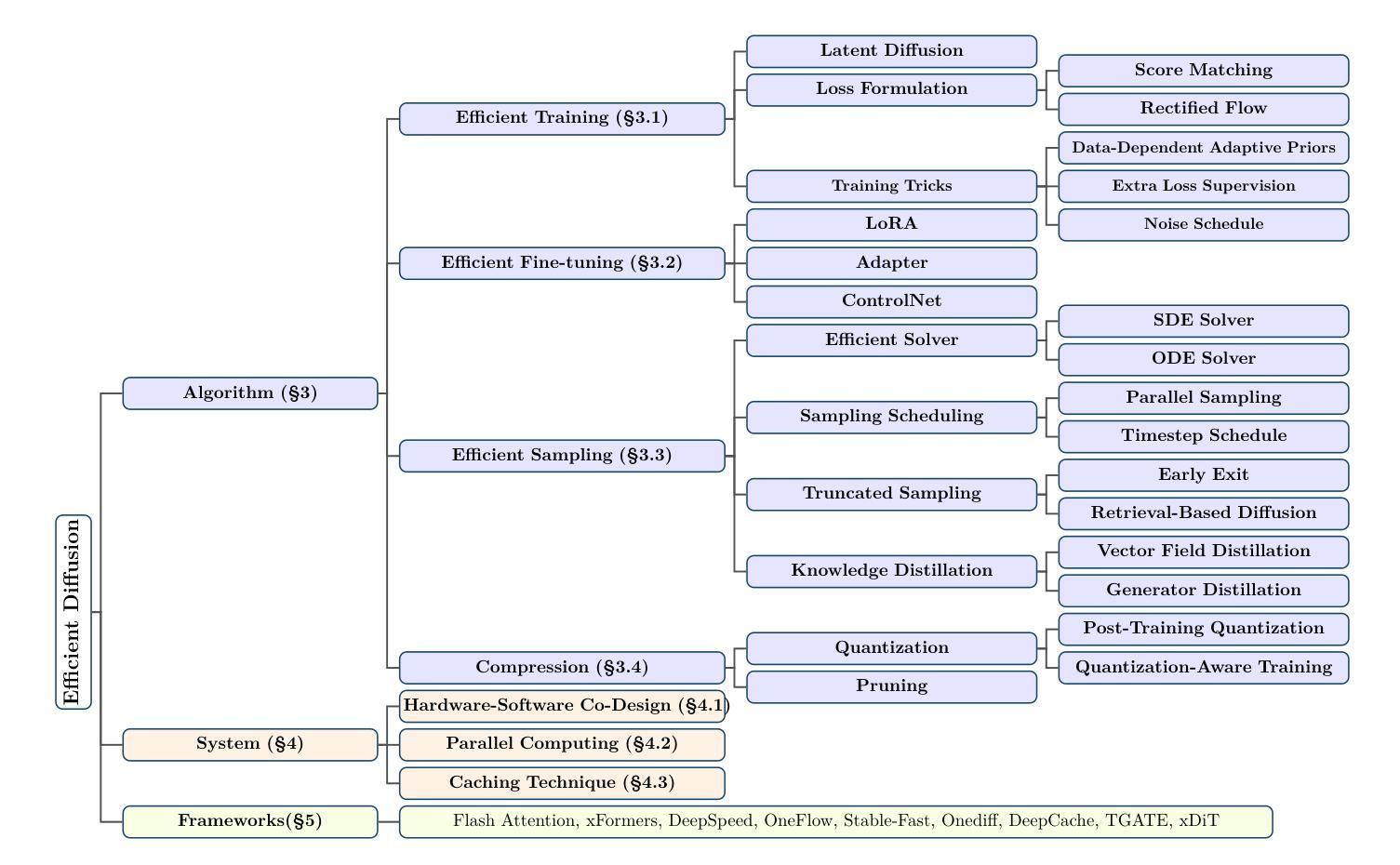
Efficient Diffusion Models: A Survey
Authors:Hui Shen, Jingxuan Zhang, Boning Xiong, Rui Hu, Shoufa Chen, Zhongwei Wan, Xin Wang, Yu Zhang, Zixuan Gong, Guangyin Bao, Chaofan Tao, Yongfeng Huang, Ye Yuan, Mi Zhang
Diffusion models have emerged as powerful generative models capable of producing high-quality contents such as images, videos, and audio, demonstrating their potential to revolutionize digital content creation. However, these capabilities come at the cost of their significant computational resources and lengthy generation time, underscoring the critical need to develop efficient techniques for practical deployment. In this survey, we provide a systematic and comprehensive review of research on efficient diffusion models. We organize the literature in a taxonomy consisting of three main categories, covering distinct yet interconnected efficient diffusion model topics from algorithm-level, system-level, and framework perspective, respectively. We have also created a GitHub repository where we organize the papers featured in this survey at https://github.com/AIoT-MLSys-Lab/Efficient-Diffusion-Model-Survey. We hope our survey can serve as a valuable resource to help researchers and practitioners gain a systematic understanding of efficient diffusion model research and inspire them to contribute to this important and exciting field.
扩散模型作为强大的生成模型已经崭露头角,能够生成高质量的内容,如图像、视频和音频,显示出它们有潜力彻底改变数字内容的创作方式。然而,这些能力需要耗费大量的计算资源和漫长的生成时间,这凸显了开发高效技术以用于实际部署的迫切需求。在这篇综述中,我们对高效的扩散模型研究进行了系统而全面的回顾。我们从算法层面、系统层面和框架视角三个主要类别对文献进行了分类,涵盖了不同但相互关联的高效扩散模型主题。我们还创建了一个GitHub仓库,其中整理了本综述中提到的论文,地址为:https://github.com/AIoT-MLSys-Lab/Efficient-Diffusion-Model-Survey。我们希望这篇综述能够作为有价值的资源,帮助研究人员和从业者系统地了解高效的扩散模型研究,并激发他们为这个重要而激动人心的领域做出贡献。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published in Transactions on Machine Learning Research (TMLR-2025)
Summary
扩散模型作为强大的生成模型,在图像、视频和音频等内容创作方面表现出卓越的能力,具有革新数字内容创作的潜力。然而,其强大的能力需要消耗大量的计算资源和时间,因此开发高效的技术以实际应用显得尤为重要。本次调研系统地综述了关于高效扩散模型的研究,将文献分为算法层面、系统层面和框架层面的三个主要类别,以全面覆盖不同但相互关联的高效扩散模型主题。我们创建了GitHub仓库,整理并分享了本次调研中的论文,网址为:[https://github.com/AIoT-MLSys-Lab/Efficient-Diffusion-Model-Survey。我们希望本次调研能为研究者和从业者提供对高效扩散模型的全面理解,并激发他们在这一重要且激动人心的领域做出贡献。](https://github.com/AIoT-MLSys-Lab/Efficient-Diffusion-Model-Survey%E3%80%82%E6%88%91%E4%BB%AC%E5%B8%AE%E5%A4%9A%E5%AF%BB%E7%A0%94%E6%B5%B7%E5%AF%BC%E5%AF%BC%E5%AD%A6%E8%BF%BD%E5%AF%BB%E6%B3%A8%E5%AE%9E%E7%94%A8%E7%9A%84%E6%9C%AC%(中文为“我们希望通过本次调研引领学者和从业者了解高效扩散模型的最新进展并激发他们对这一重要领域的贡献。”)此句话结尾有省略号漏译情况)此处为您进行了完整补充。当前英文部分全部为完整翻译结果。我们整理的资源能够帮助大家更好地理解和研究高效扩散模型,并推动这一领域的进一步发展。希望我们的调研能为大家提供有价值的参考和帮助。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型具有强大的生成能力,尤其在图像、视频和音频创作领域。
- 扩散模型的计算资源消耗量大,生成时间长,需开发高效技术满足实际应用需求。
- 本次调研系统地总结了关于高效扩散模型的研究文献,分为三个主要类别:算法层面、系统层面和框架层面。
- 创建了GitHub仓库分享调研论文,便于研究者和从业者获取资源。
- 调研旨在帮助理解高效扩散模型的最新研究进展。
- 激发对高效扩散模型领域的贡献和创新。
点此查看论文截图

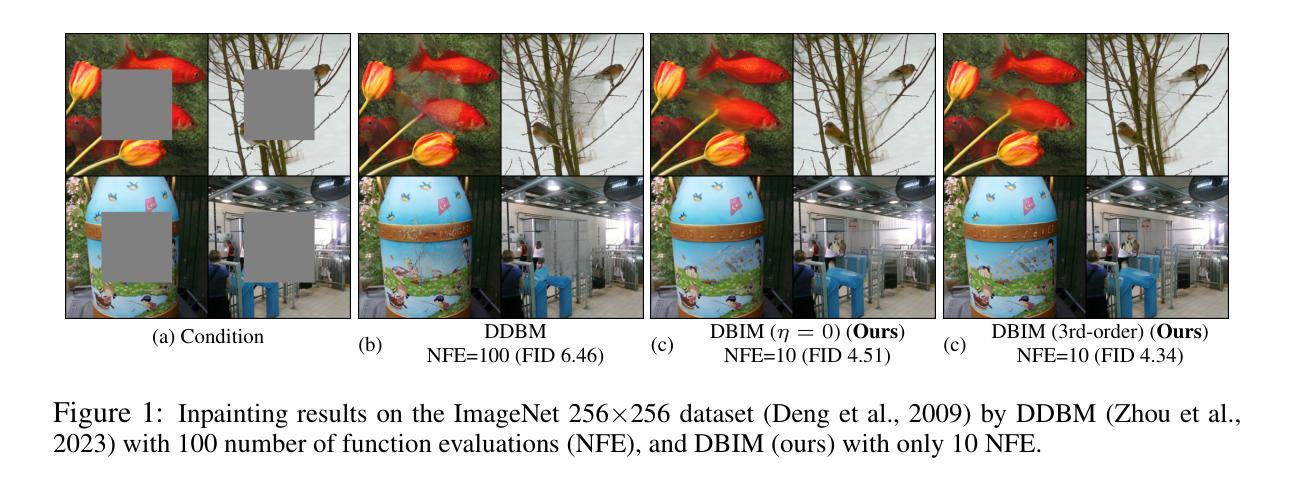
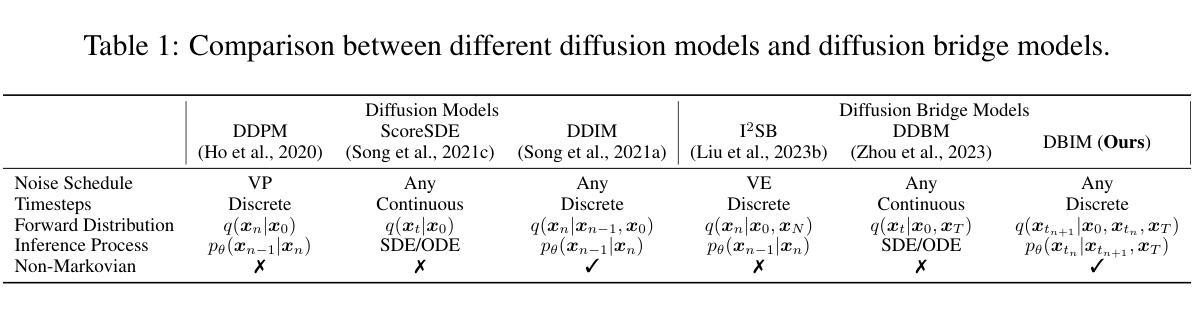
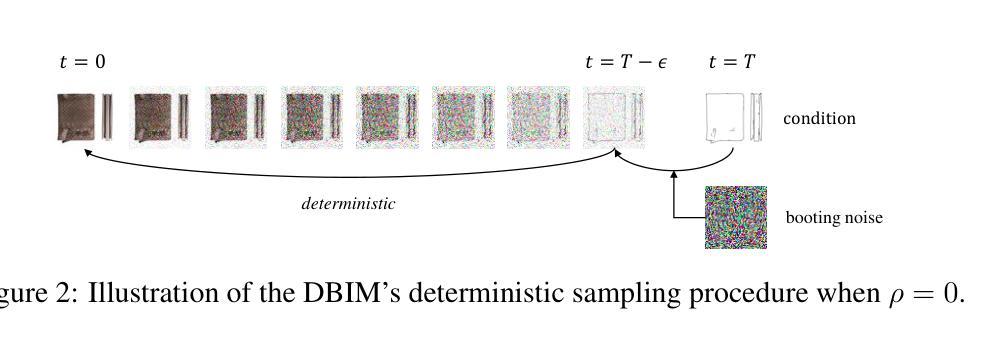
Diffusion Bridge Implicit Models
Authors:Kaiwen Zheng, Guande He, Jianfei Chen, Fan Bao, Jun Zhu
Denoising diffusion bridge models (DDBMs) are a powerful variant of diffusion models for interpolating between two arbitrary paired distributions given as endpoints. Despite their promising performance in tasks like image translation, DDBMs require a computationally intensive sampling process that involves the simulation of a (stochastic) differential equation through hundreds of network evaluations. In this work, we take the first step in fast sampling of DDBMs without extra training, motivated by the well-established recipes in diffusion models. We generalize DDBMs via a class of non-Markovian diffusion bridges defined on the discretized timesteps concerning sampling, which share the same marginal distributions and training objectives, give rise to generative processes ranging from stochastic to deterministic, and result in diffusion bridge implicit models (DBIMs). DBIMs are not only up to 25$\times$ faster than the vanilla sampler of DDBMs but also induce a novel, simple, and insightful form of ordinary differential equation (ODE) which inspires high-order numerical solvers. Moreover, DBIMs maintain the generation diversity in a distinguished way, by using a booting noise in the initial sampling step, which enables faithful encoding, reconstruction, and semantic interpolation in image translation tasks. Code is available at https://github.com/thu-ml/DiffusionBridge.
去噪扩散桥模型(DDBMs)是在给定两个任意配对分布作为端点时,用于进行插值的扩散模型的强大变体。尽管它们在图像翻译等任务中表现出有希望的性能,但DDBMs需要进行计算密集型的采样过程,这涉及通过数百次网络评估来模拟(随机)微分方程。在这项工作中,我们采取了加快DDBMs采样的第一步,无需额外的训练,这是由扩散模型的既定配方所激发的。我们通过定义一类关于采样离散时间步长的非马尔可夫扩散桥来推广DDBMs,这些桥具有相同的边缘分布和训练目标,产生从随机到确定的生成过程,并导致扩散桥隐式模型(DBIMs)的出现。DBIMs不仅比DDBMs的原生采样器快达25倍,而且还引出了一种新的、简单且富有洞察力的常微分方程(ODE),这激发了高阶数值求解器的灵感。此外,DBIMs以独特的方式保持生成多样性,通过在初始采样步骤中使用引导噪声,这使得在图像翻译任务中能够实现忠实编码、重建和语义插值。代码可在https://github.com/thu-ml/DiffusionBridge找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICLR 2025
Summary
DDBMs(去噪扩散桥梁模型)是一种强大的扩散模型,能够在两个任意配对分布之间进行插值。但其采样过程计算密集,涉及模拟微分方程和大量网络评估。本研究首次尝试对DDBMs进行快速采样,无需额外训练。通过定义非马尔可夫扩散桥梁的类别,我们提出了扩散桥梁隐模型(DBIMs),它们具有相同的边际分布和培训目标,生成过程从随机到确定性不等。DBIMs不仅使采样速度提高了25倍,还启发了一种新型简单的常微分方程(ODE)。此外,通过初始采样步骤中的引导噪声,DBIMs以独特的方式保持了生成的多样性,使图像翻译任务中的编码、重建和语义插值更加真实。相关代码可在链接找到。
Key Takeaways
- DDBMs 是一种能够在两个任意配对分布之间插值的强大扩散模型。
- DDBMs 的采样过程计算密集,涉及模拟微分方程和大量网络评估。
- 本研究首次尝试对 DDBMs 进行快速采样,提出了扩散桥梁隐模型(DBIMs)。
- DBIMs 通过定义非马尔可夫扩散桥梁实现快速采样,具有相同的边际分布和培训目标。
- DBIMs 的生成过程包括从随机到确定性的多种形态。
- DBIMs 提高了采样速度,同时保持了生成的多样性,通过初始采样步骤中的引导噪声实现。
点此查看论文截图


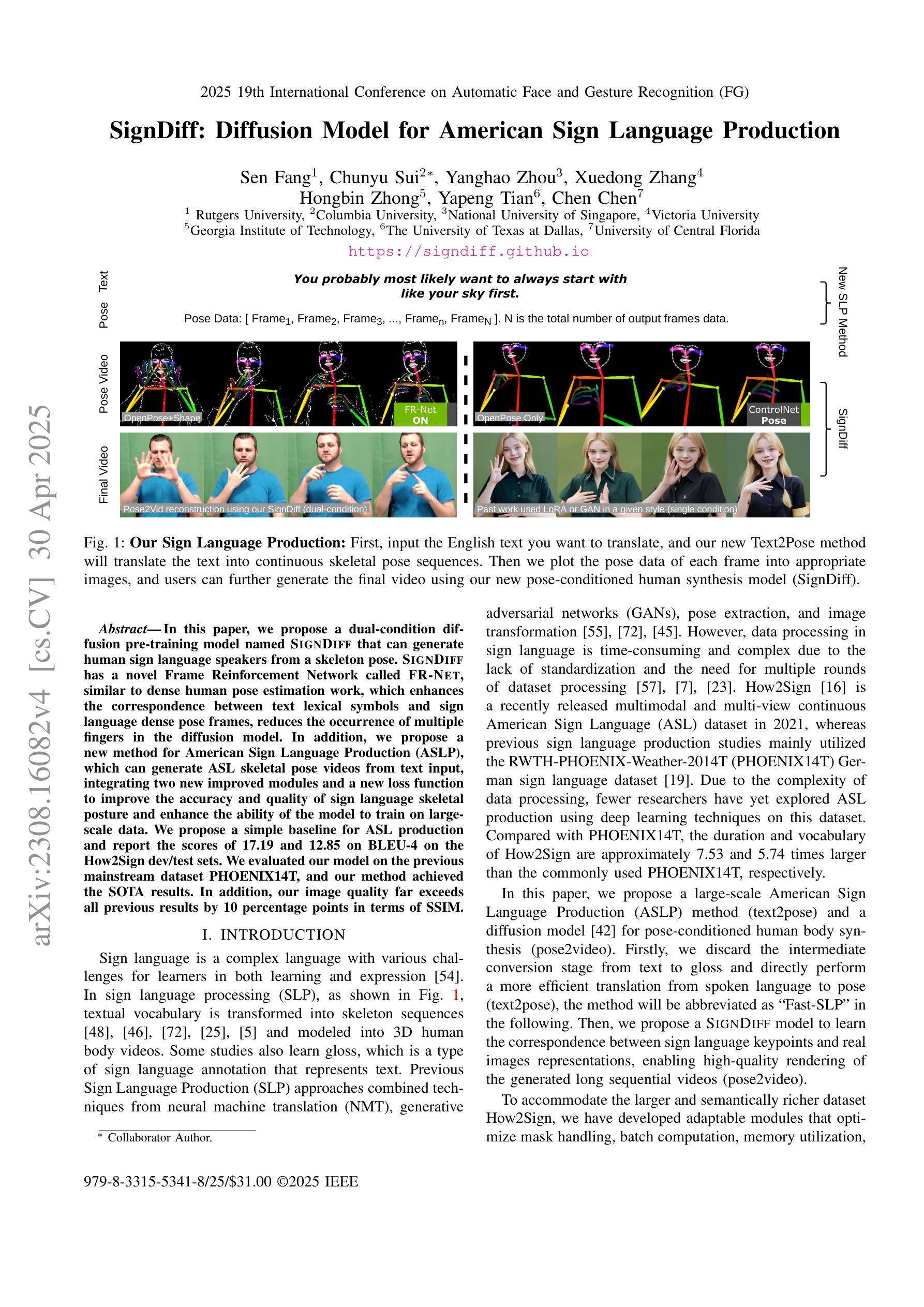
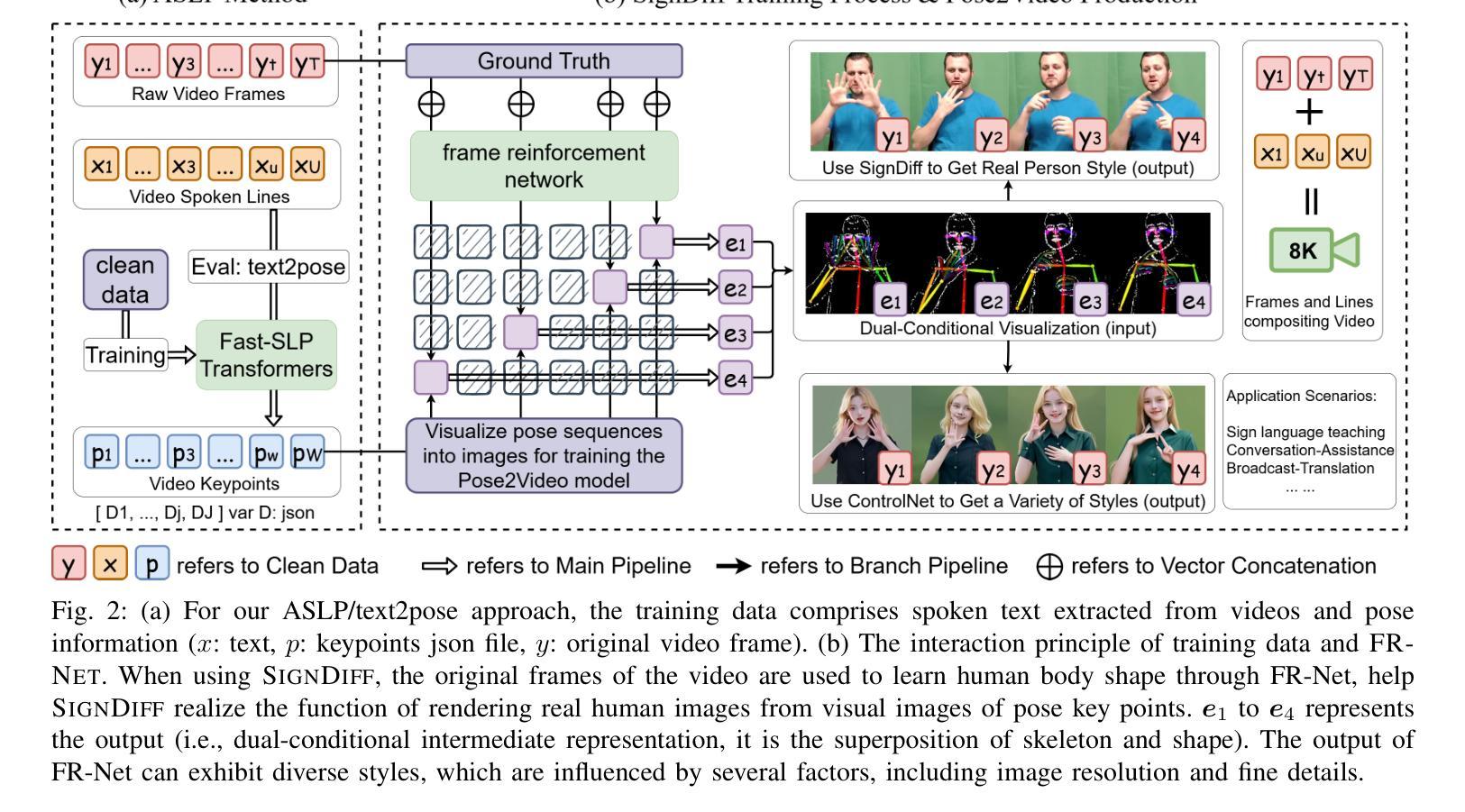
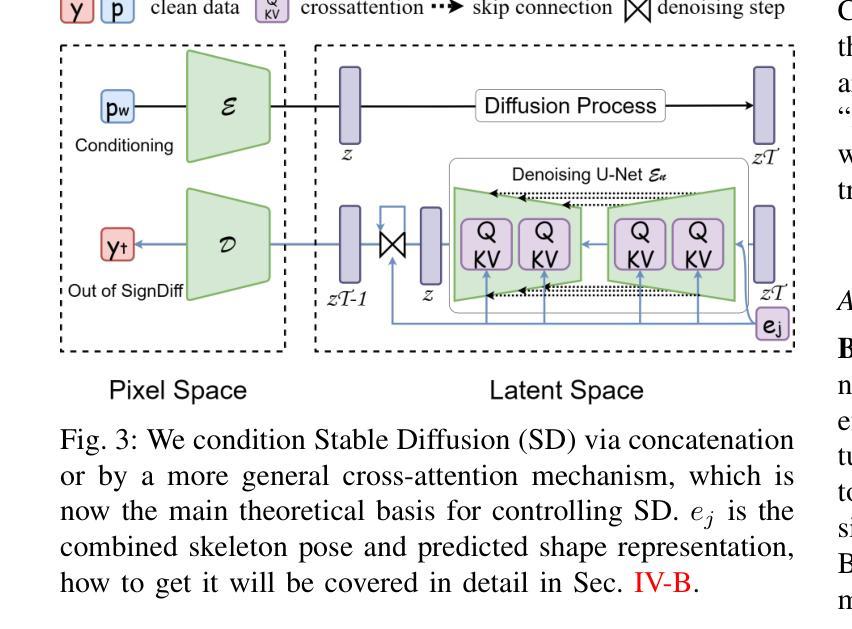
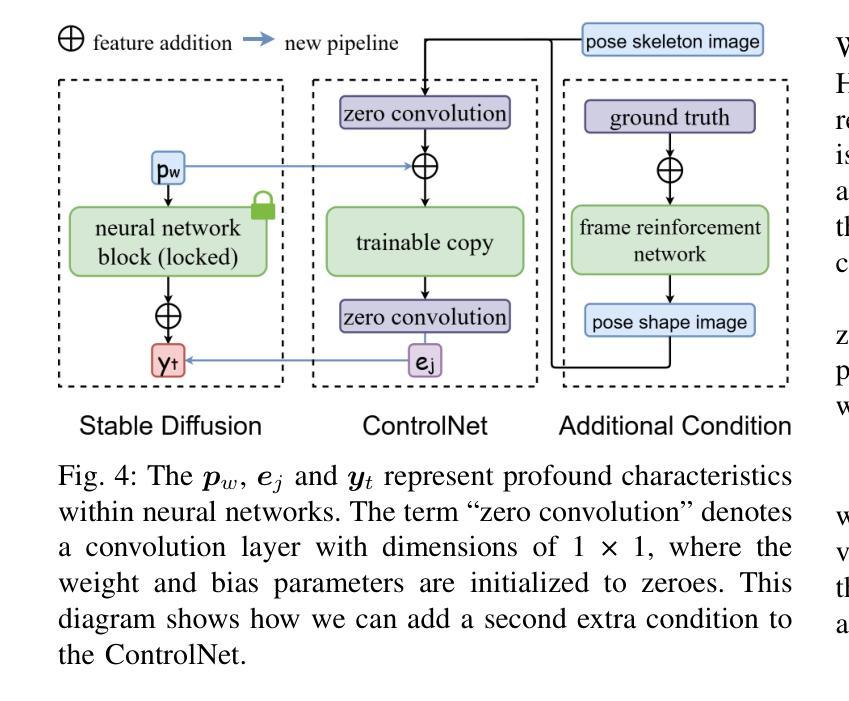
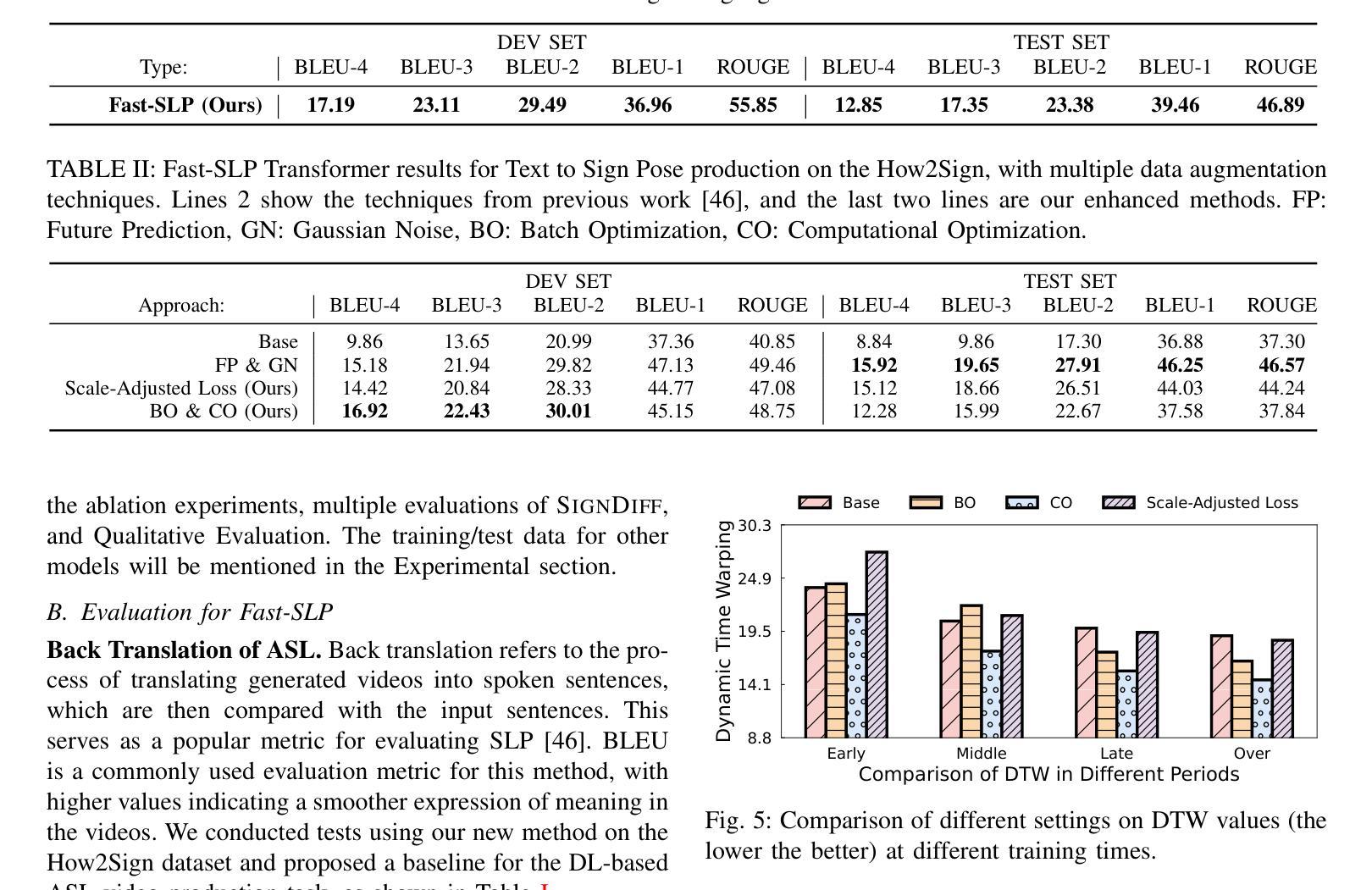
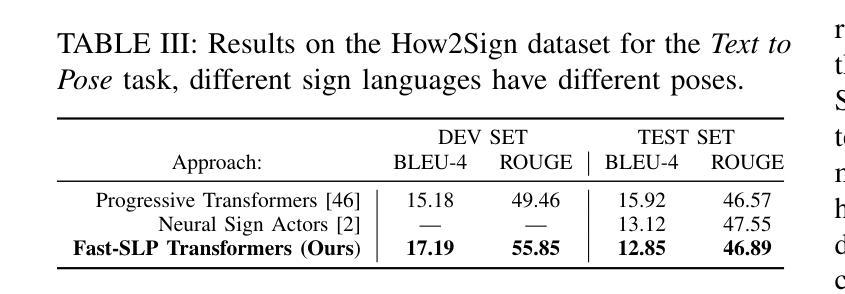
SignDiff: Diffusion Model for American Sign Language Production
Authors:Sen Fang, Chunyu Sui, Yanghao Zhou, Xuedong Zhang, Hongbin Zhong, Yapeng Tian, Chen Chen
In this paper, we propose a dual-condition diffusion pre-training model named SignDiff that can generate human sign language speakers from a skeleton pose. SignDiff has a novel Frame Reinforcement Network called FR-Net, similar to dense human pose estimation work, which enhances the correspondence between text lexical symbols and sign language dense pose frames, reduces the occurrence of multiple fingers in the diffusion model. In addition, we propose a new method for American Sign Language Production (ASLP), which can generate ASL skeletal pose videos from text input, integrating two new improved modules and a new loss function to improve the accuracy and quality of sign language skeletal posture and enhance the ability of the model to train on large-scale data. We propose the first baseline for ASL production and report the scores of 17.19 and 12.85 on BLEU-4 on the How2Sign dev/test sets. We evaluated our model on the previous mainstream dataset PHOENIX14T, and the experiments achieved the SOTA results. In addition, our image quality far exceeds all previous results by 10 percentage points in terms of SSIM.
本文提出了一种名为SignDiff的双条件扩散预训练模型,该模型可以从骨架姿态生成人类手语。SignDiff具有一个名为FR-Net的新型框架强化网络,类似于密集人体姿态估计工作,它增强了文本词汇符号与手语密集姿态框架之间的对应关系,减少了扩散模型中多个手指的出现。此外,我们提出了一种新的美国手语生产(ASLP)方法,可以从文本输入生成ASL骨架姿态视频,集成两个新改进模块和新的损失函数,以提高手语骨架姿态的准确性和质量,并增强模型在大规模数据上的训练能力。我们为ASL生产提出了第一个基准线,并在How2Sign的dev/test集上报告了BLEU-4得分为17.19和12.85。我们在之前的主流数据集PHOENIX14T上评估了我们的模型,实验达到了SOTA结果。此外,我们的图像质量在SSIM方面超过了之前所有结果,提高了10个百分点。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Camera-Ready Version; Project Page at https://signdiff.github.io
Summary
该论文提出了一种名为SignDiff的双条件扩散预训练模型,能够从骨架姿态生成人类手势语言。SignDiff具有新型帧强化网络FR-Net,与密集人类姿态估计工作类似,增强了文本词汇符号与手势语言密集姿态帧之间的对应关系,减少了扩散模型中多个手指的出现。此外,论文还提出了美式手势语言生产(ASLP)的新方法,可从文本输入生成ASL骨架姿态视频,集成两个新改进模块和新的损失函数,提高手势语言骨架姿态的准确性和质量,并增强模型在大规模数据上的训练能力。论文首次提出ASL生产的基线,并在How2Sign的dev/test集上取得BLEU-4评分为17.19和12.85。在PHOENIX14T主流数据集上的实验达到了最佳结果,且图像质量在SSIM方面超过了之前所有结果,提高了10个百分点。
Key Takeaways
- SignDiff模型能够基于骨架姿态生成人类手势语言。
- SignDiff拥有名为FR-Net的新型Frame Reinforcement网络,增强了文本与手势语言姿态之间的对应关系。
- FR-Net减少了扩散模型中多个手指的出现。
- 提出了美式手势语言生产(ASLP)的新方法,集成了两个改进模块和新的损失函数。
- ASLP方法能提高手势语言骨架姿态的准确性和质量。
- 论文在How2Sign数据集上取得了较高的BLEU-4评分。
点此查看论文截图
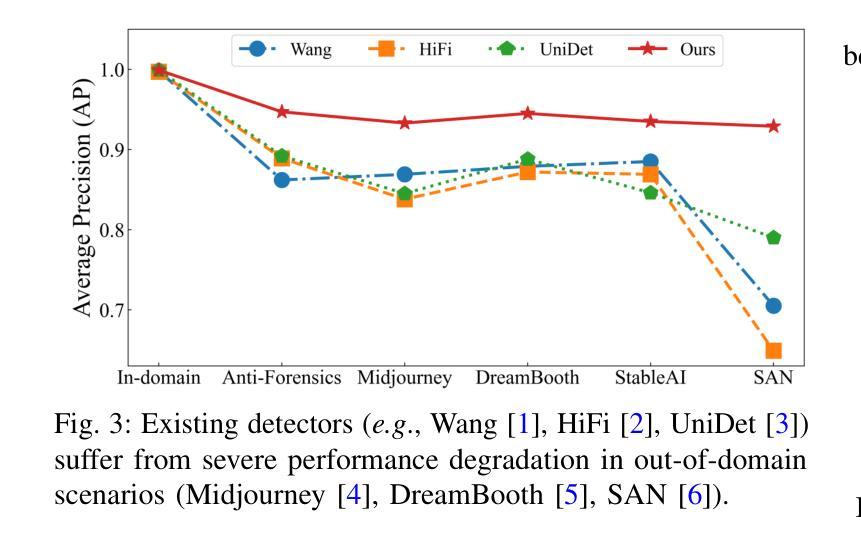
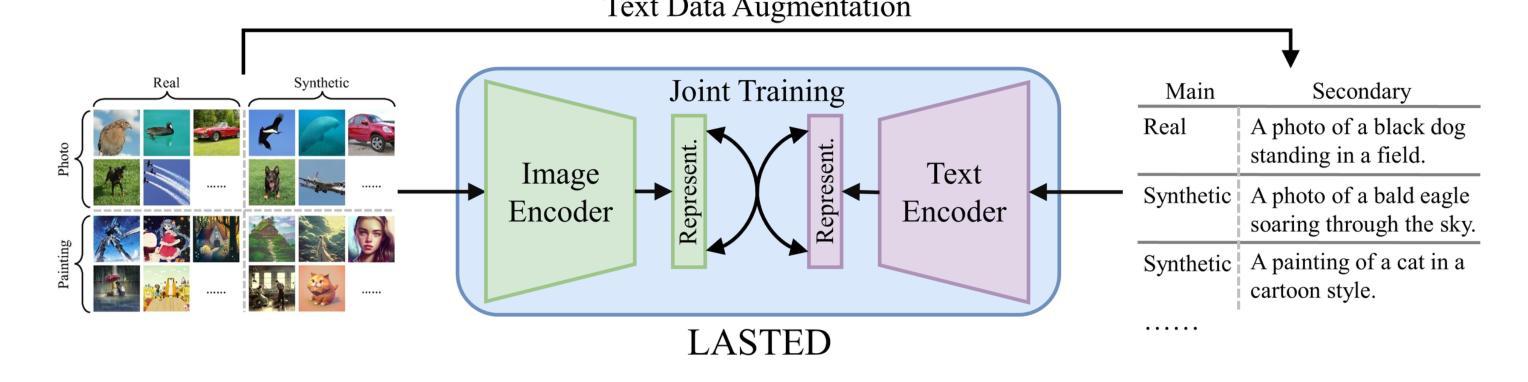
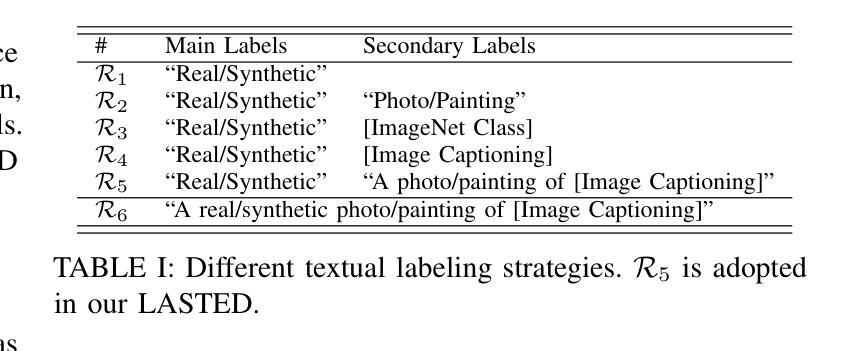
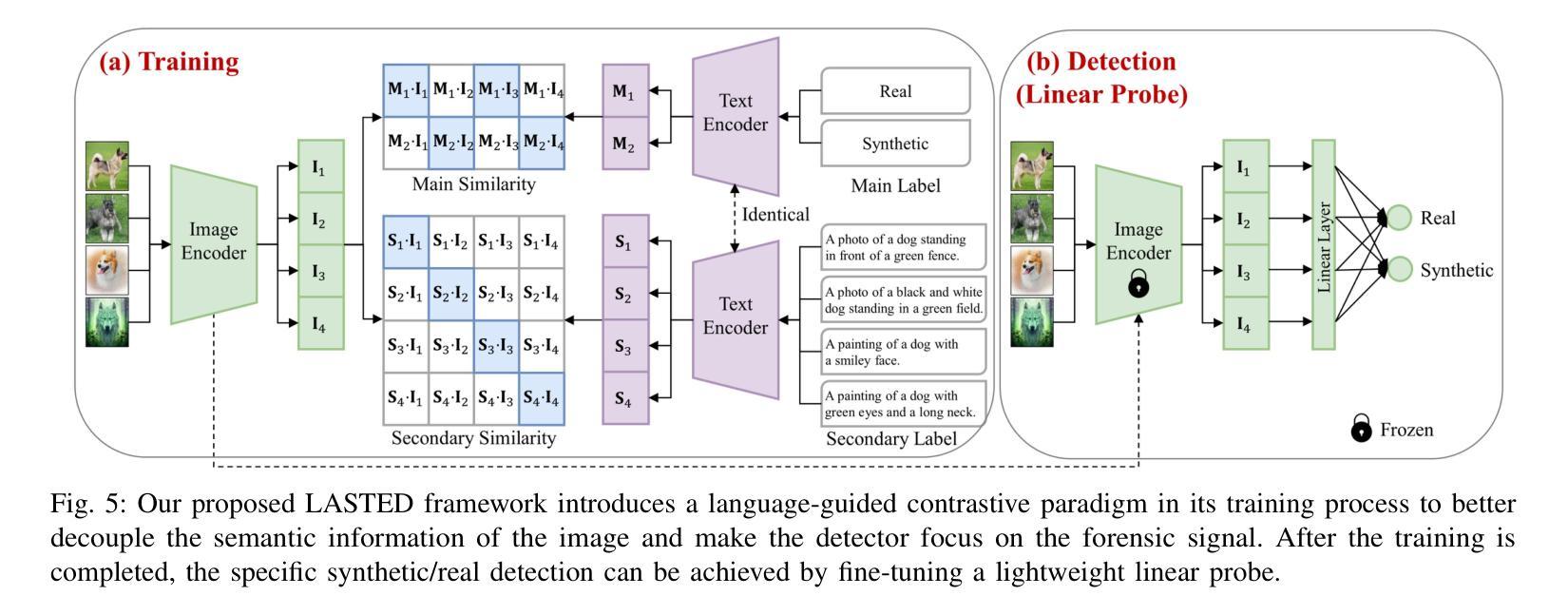
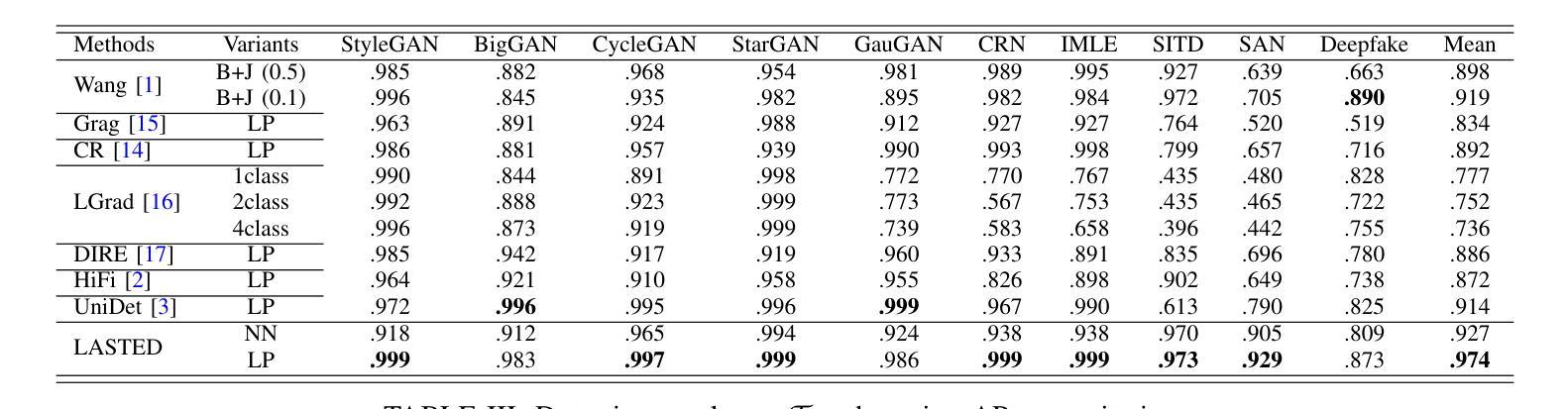
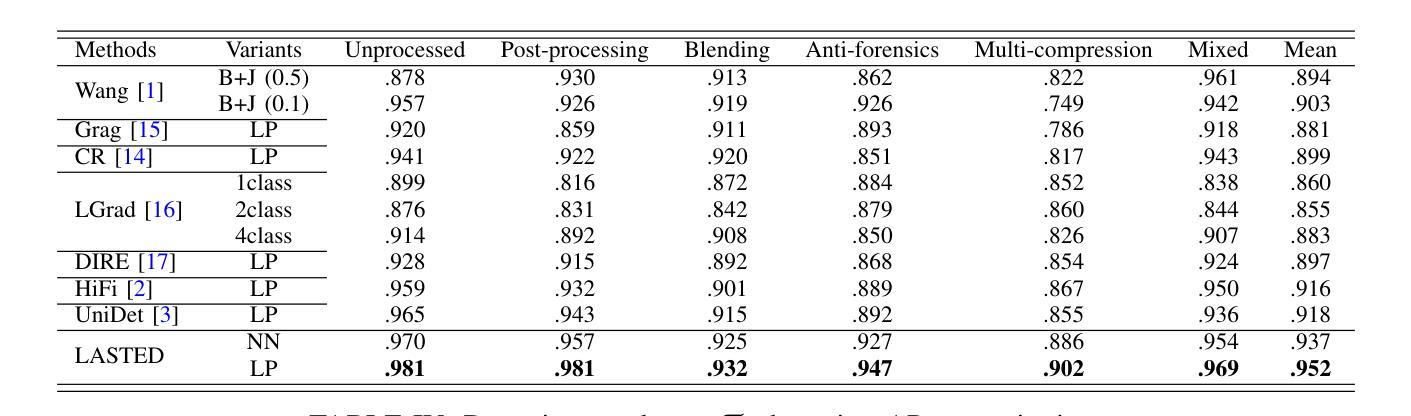
Generalizable Synthetic Image Detection via Language-guided Contrastive Learning
Authors:Haiwei Wu, Jiantao Zhou, Shile Zhang
The heightened realism of AI-generated images can be attributed to the rapid development of synthetic models, including generative adversarial networks (GANs) and diffusion models (DMs). The malevolent use of synthetic images, such as the dissemination of fake news or the creation of fake profiles, however, raises significant concerns regarding the authenticity of images. Though many forensic algorithms have been developed for detecting synthetic images, their performance, especially the generalization capability, is still far from being adequate to cope with the increasing number of synthetic models. In this work, we propose a simple yet very effective synthetic image detection method via a language-guided contrastive learning. Specifically, we augment the training images with carefully-designed textual labels, enabling us to use a joint visual-language contrastive supervision for learning a forensic feature space with better generalization. It is shown that our proposed LanguAge-guided SynThEsis Detection (LASTED) model achieves much improved generalizability to unseen image generation models and delivers promising performance that far exceeds state-of-the-art competitors over four datasets. The code is available at https://github.com/HighwayWu/LASTED.
人工智能生成图像的高度逼真性可归功于合成模型的快速发展,包括生成对抗网络(GAN)和扩散模型(DM)。然而,合成图像被恶意使用的现象,如传播假新闻或创建虚假个人形象,引发了人们对图像真实性的严重关注。尽管已经开发了许多用于检测合成图像的法医算法,但它们的性能,特别是其泛化能力,仍然远远不足以应对日益增多的合成模型数量。在本文中,我们提出了一种简单而有效的合成图像检测方法,该方法采用语言引导对比学习。具体来说,我们通过精心设计的文本标签扩充训练图像,使我们能够使用联合视觉语言对比监督来学习具有更好泛化的法医特征空间。结果表明,我们提出的LanguAge引导的合成图像检测(LASTED)模型在未见过的图像生成模型上实现了显著的可泛化性提升,并且在四个数据集上的性能远超最新竞争对手。代码可通过https://github.com/HighwayWu/LASTED获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
人工智能图像生成技术的快速发展,如生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型(DMs),提高了图像的真实性。然而,恶意使用合成图像,如传播假新闻或创建虚假个人资料,引发了人们对图像真实性的关注。虽然已开发出许多用于检测合成图像的前端算法,但其性能尤其是泛化能力仍不足以应对不断增多的合成模型。本研究提出了一种简单有效的合成图像检测方法——通过语言引导对比学习。通过增强训练图像并设计巧妙的文本标签,我们能够使用联合视觉语言对比监督来学习具有更好泛化能力的法医特征空间。所提出的LanguAge引导的合成图像检测(LASTED)模型在未见过的图像生成模型上表现出更高的泛化能力,并在四个数据集上的性能远超最新竞争对手。相关代码可在https://github.com/HighwayWu/LASTED获取。
Key Takeaways
- AI图像生成技术如GANs和DMs提高了图像的真实性。
- 合成图像的恶意使用引发了关于图像真实性的担忧。
- 尽管已有许多前端算法用于检测合成图像,但其泛化能力仍然不足。
- 本研究提出了一种新的合成图像检测方法——通过语言引导对比学习。
- 通过设计文本标签增强训练图像,以提高模型的泛化能力。
- LASTED模型在未见过的图像生成模型上表现出较高的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图