⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-02 更新
SMOGAN: Synthetic Minority Oversampling with GAN Refinement for Imbalanced Regression
Authors:Shayan Alahyari, Mike Domaratzki
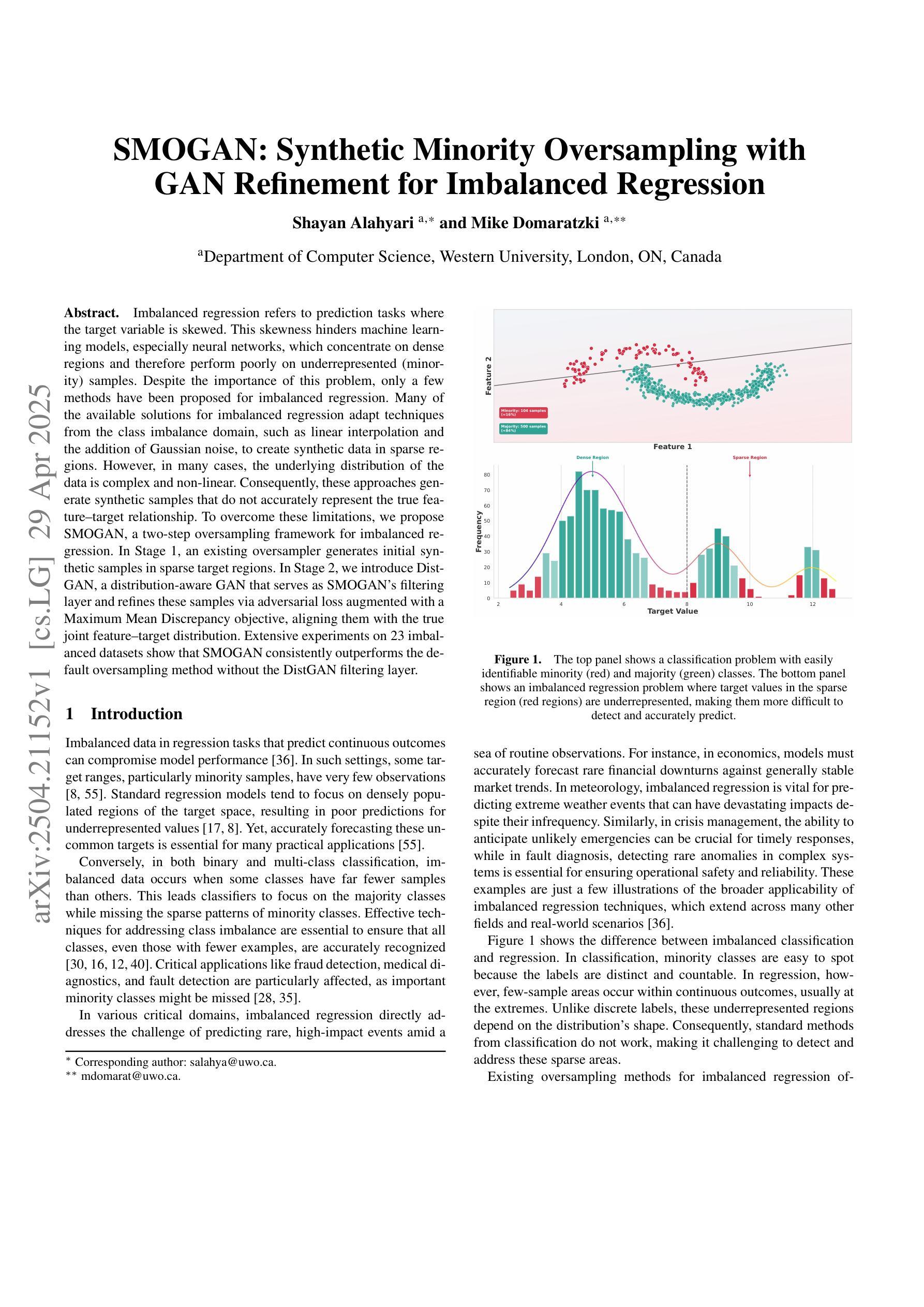
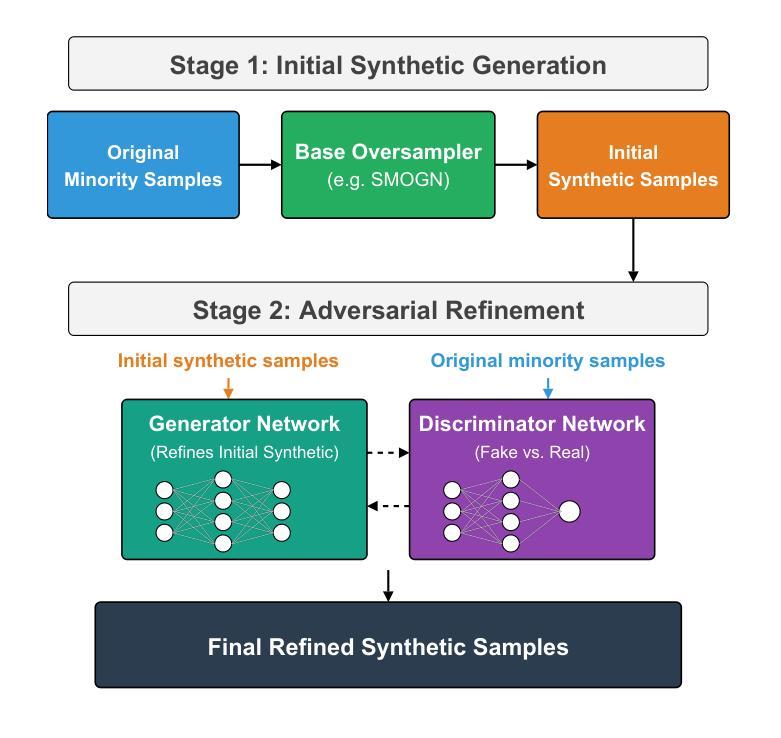
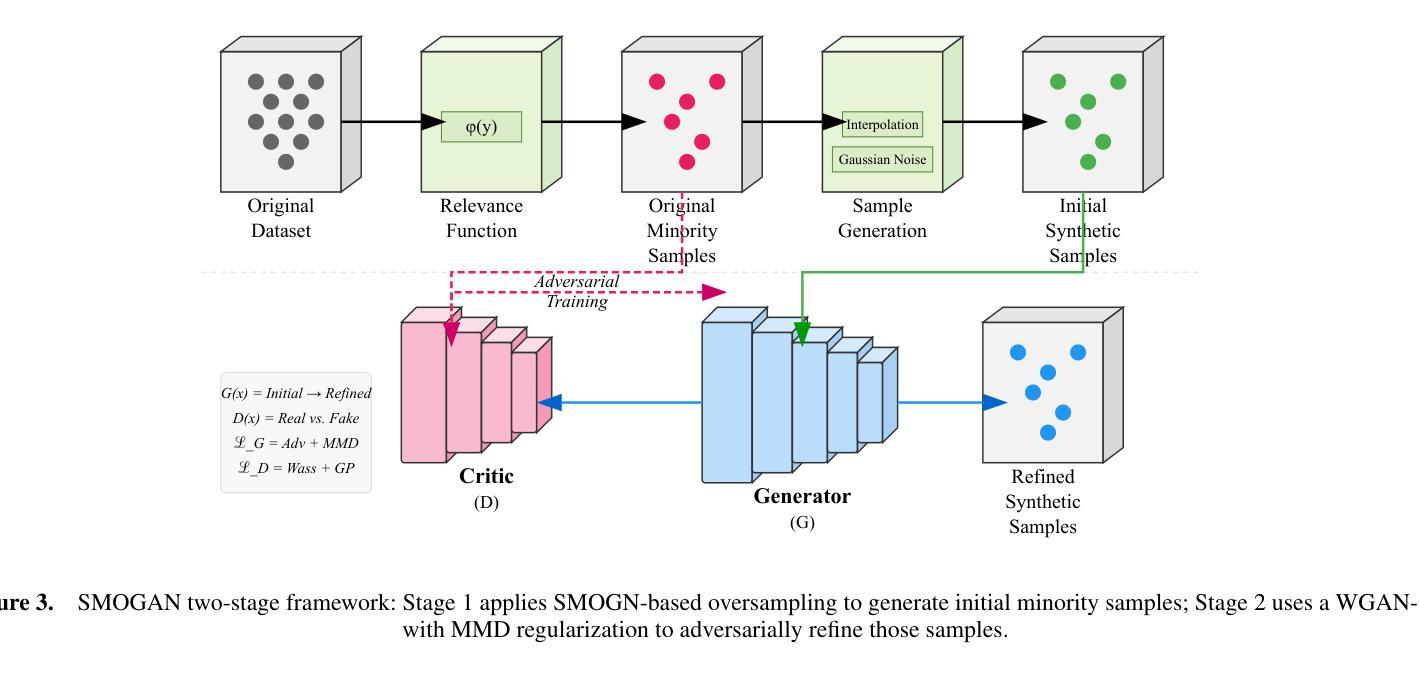
Imbalanced regression refers to prediction tasks where the target variable is skewed. This skewness hinders machine learning models, especially neural networks, which concentrate on dense regions and therefore perform poorly on underrepresented (minority) samples. Despite the importance of this problem, only a few methods have been proposed for imbalanced regression. Many of the available solutions for imbalanced regression adapt techniques from the class imbalance domain, such as linear interpolation and the addition of Gaussian noise, to create synthetic data in sparse regions. However, in many cases, the underlying distribution of the data is complex and non-linear. Consequently, these approaches generate synthetic samples that do not accurately represent the true feature-target relationship. To overcome these limitations, we propose SMOGAN, a two-step oversampling framework for imbalanced regression. In Stage 1, an existing oversampler generates initial synthetic samples in sparse target regions. In Stage 2, we introduce DistGAN, a distribution-aware GAN that serves as SMOGAN’s filtering layer and refines these samples via adversarial loss augmented with a Maximum Mean Discrepancy objective, aligning them with the true joint feature-target distribution. Extensive experiments on 23 imbalanced datasets show that SMOGAN consistently outperforms the default oversampling method without the DistGAN filtering layer.
不平衡回归是指目标变量存在偏斜的预测任务。这种偏斜性对机器学习模型,尤其是神经网络,构成了阻碍,因为神经网络会集中在密集区域,因此在代表性不足(少数)的样本上表现不佳。尽管这个问题很重要,但针对不平衡回归的方法还比较少。许多现有的不平衡回归解决方案都是从类别不平衡领域借鉴技术,例如线性插值和添加高斯噪声来创建稀疏区域中的合成数据。然而,在许多情况下,数据的底层分布是复杂的、非线性的。因此,这些方法生成的合成样本不能准确地代表真实的特征-目标关系。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了SMOGAN,这是一个用于不平衡回归的两步过采样框架。在第一阶段,现有的过采样器在稀疏目标区域生成初始合成样本。在第二阶段,我们引入了DistGAN,这是一个感知分布的GAN,作为SMOGAN的过滤层,通过添加对抗性损失和最大均值差异目标来优化这些样本,使它们与真实的联合特征-目标分布对齐。在23个不平衡数据集上的大量实验表明,SMOGAN在不过滤掉DistGAN过滤层的情况下,始终优于默认的过采样方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文探讨了不平衡回归问题,即目标变量存在倾斜的情况。这种倾斜现象对机器学习模型(尤其是神经网络)造成了困扰,因为它们倾向于集中在密集区域,而在稀疏区域(少数样本)表现不佳。针对这一问题,文章提出了一种名为SMOGAN的两阶段过采样框架。首先,现有过采样器在稀疏目标区域生成初始合成样本。接着,引入DistGAN,一个分布感知的GAN,作为SMOGAN的过滤层,通过对抗性损失和一个最大平均差异目标进行样本优化,使其与真实的联合特征目标分布对齐。在23个不平衡数据集上的大量实验表明,SMOGAN始终优于没有DistGAN过滤层的默认过采样方法。
Key Takeaways
- 不平衡回归是预测任务中目标变量分布不均的问题,会影响机器学习模型的性能。
- 目前针对不平衡回归的解决方法多从类别不平衡领域的技术改编而来,如线性插值和添加高斯噪声来创建合成数据。
- 这些方法在处理复杂、非线性数据分布时生成的合成样本不能准确反映真实的特征-目标关系。
- SMOGAN是一个两阶段的过采样框架,用于解决不平衡回归问题。
- 第一阶段使用现有过采样器在稀疏目标区域生成初始合成样本。
- 第二阶段引入DistGAN,一个分布感知的GAN,作为过滤层来优化这些样本,使其与真实的联合特征目标分布对齐。
点此查看论文截图
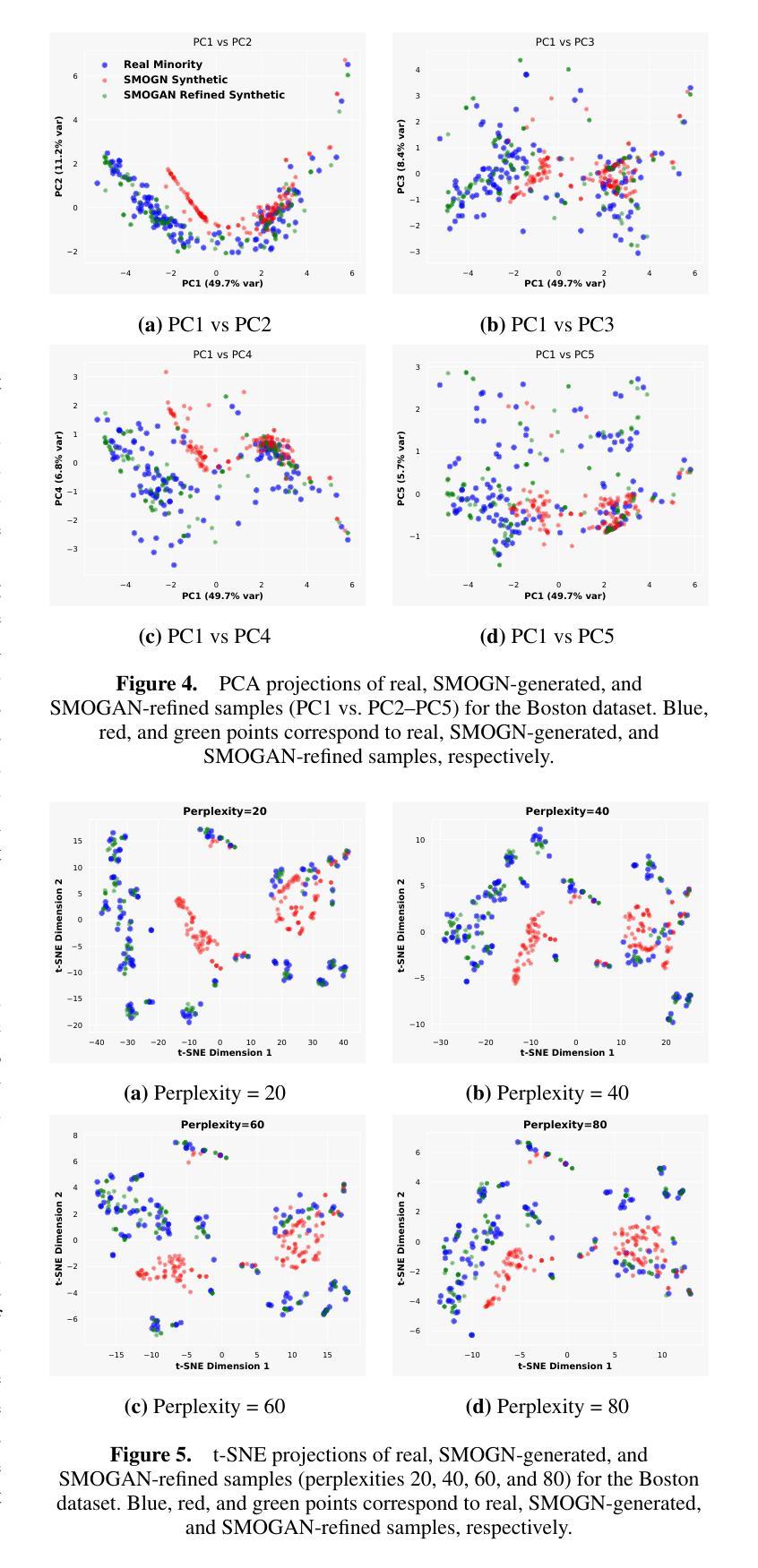
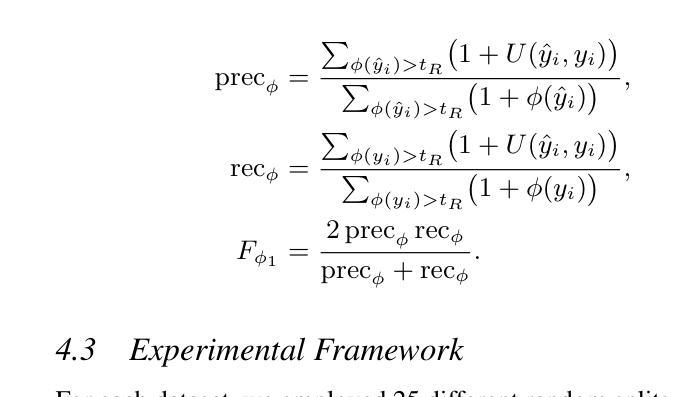
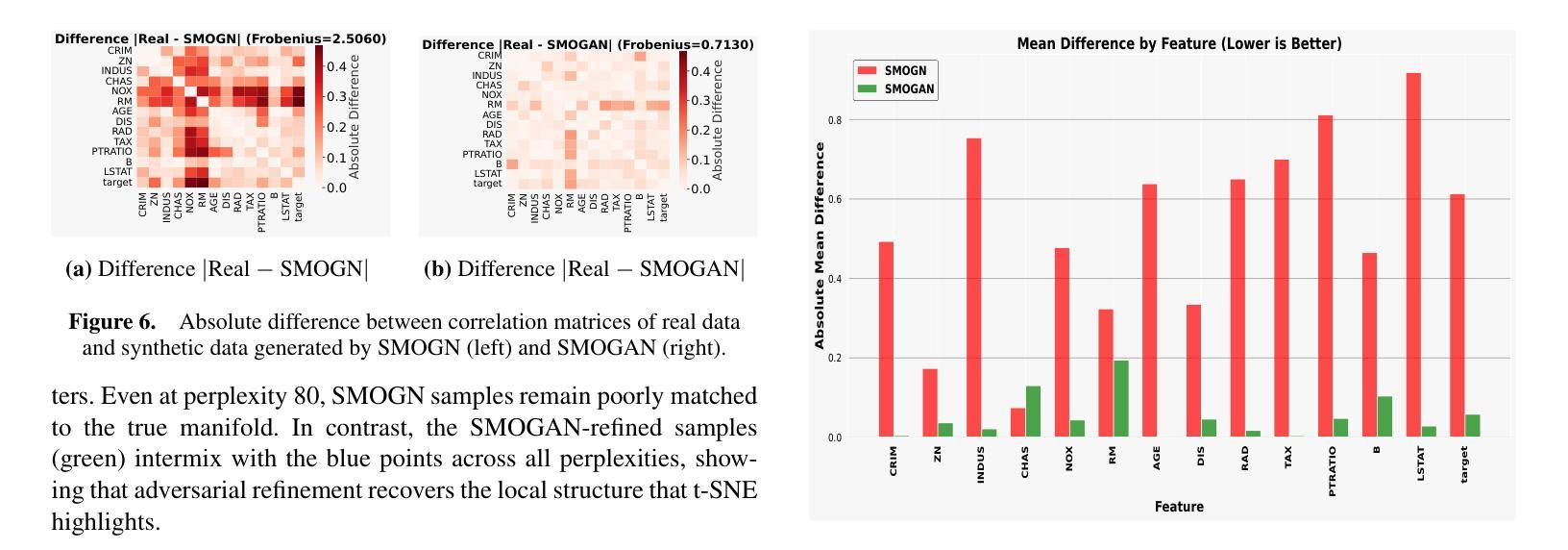
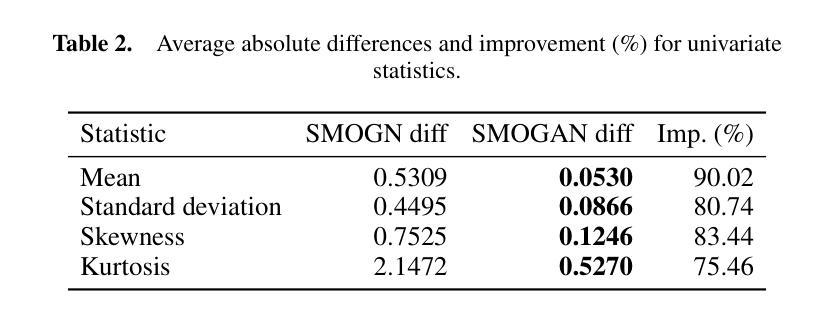
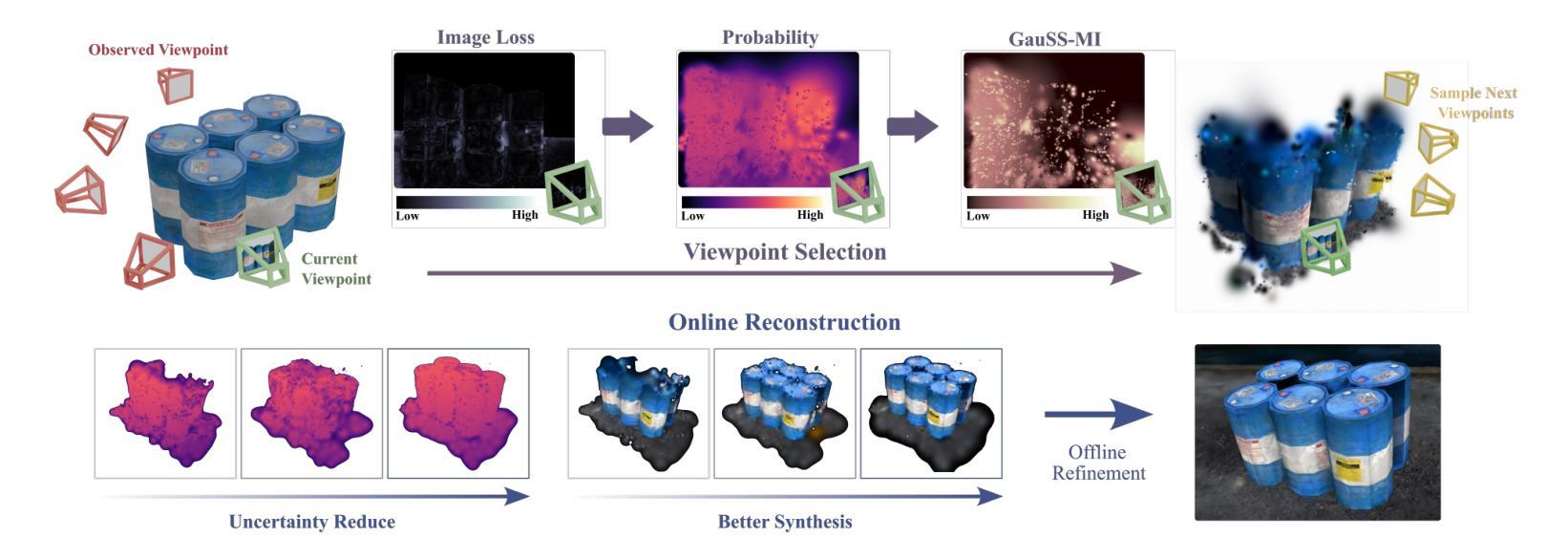
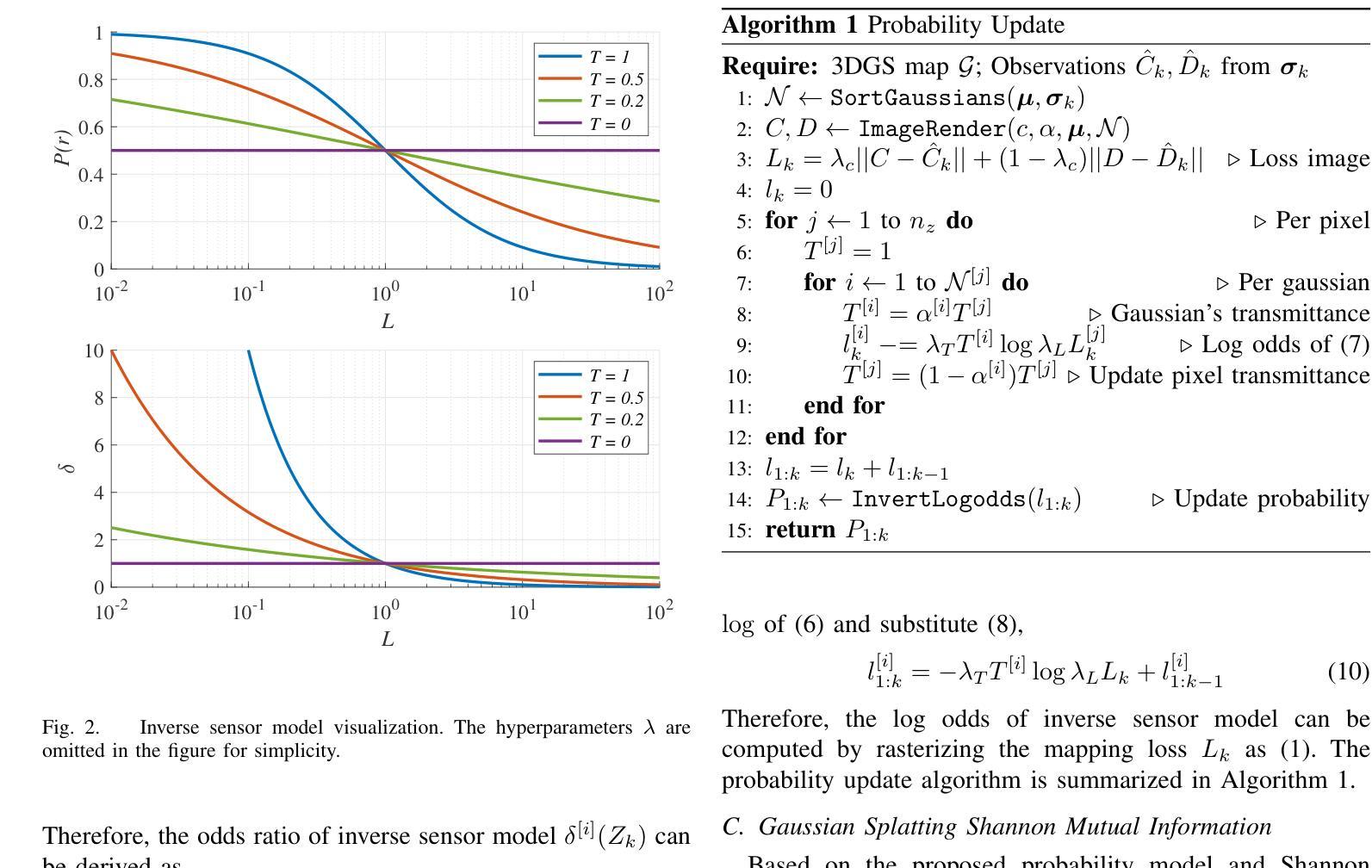
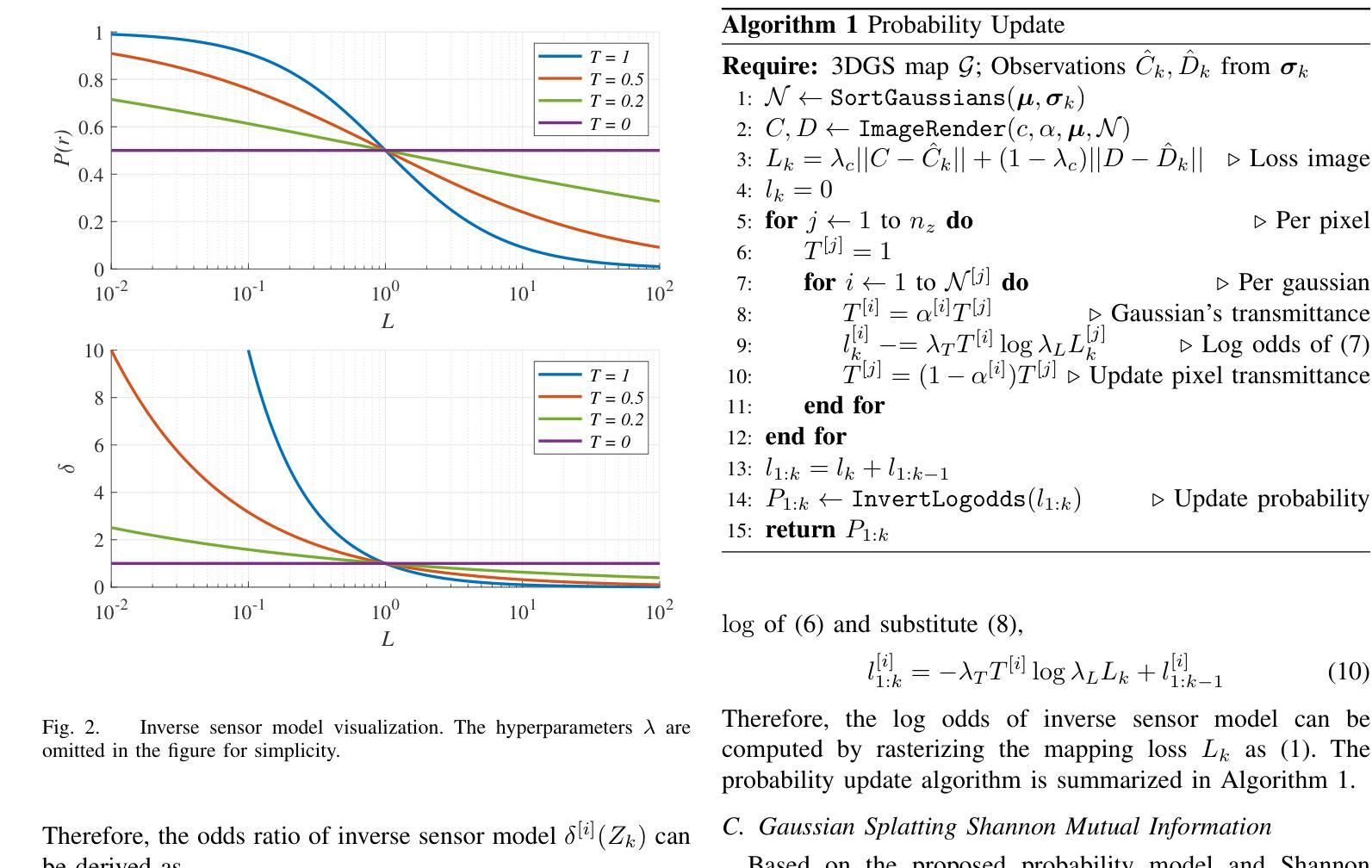
GauSS-MI: Gaussian Splatting Shannon Mutual Information for Active 3D Reconstruction
Authors:Yuhan Xie, Yixi Cai, Yinqiang Zhang, Lei Yang, Jia Pan
This research tackles the challenge of real-time active view selection and uncertainty quantification on visual quality for active 3D reconstruction. Visual quality is a critical aspect of 3D reconstruction. Recent advancements such as Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) have notably enhanced the image rendering quality of reconstruction models. Nonetheless, the efficient and effective acquisition of input images for reconstruction-specifically, the selection of the most informative viewpoint-remains an open challenge, which is crucial for active reconstruction. Existing studies have primarily focused on evaluating geometric completeness and exploring unobserved or unknown regions, without direct evaluation of the visual uncertainty within the reconstruction model. To address this gap, this paper introduces a probabilistic model that quantifies visual uncertainty for each Gaussian. Leveraging Shannon Mutual Information, we formulate a criterion, Gaussian Splatting Shannon Mutual Information (GauSS-MI), for real-time assessment of visual mutual information from novel viewpoints, facilitating the selection of next best view. GauSS-MI is implemented within an active reconstruction system integrated with a view and motion planner. Extensive experiments across various simulated and real-world scenes showcase the superior visual quality and reconstruction efficiency performance of the proposed system.
这篇研究解决了主动三维重建中的实时活跃视图选择和视觉质量不确定性评估的挑战。视觉质量是三维重建的关键方面。最近的进展,如神经辐射场(NeRF)和三维高斯贴图(3DGS),显著提高了重建模型的图像渲染质量。然而,对于重建的输入图像的获取效率及效果,尤其是选择信息最丰富的视角,仍然是一个待解决的开放性问题,这对主动重建至关重要。现有研究主要集中在评估几何完整性以及探索未观测或未知区域,并未直接评估重建模型内的视觉不确定性。为了填补这一空白,本文引入了一个概率模型,该模型可以量化每个高斯值的视觉不确定性。我们利用香农互信息制定了一个标准,即高斯贴图香农互信息(GauSS-MI),用于实时评估从新视角获得的视觉互信息,从而促进选择下一个最佳视角。GauSS-MI在一个集成了视图和运动规划器的主动重建系统中得到了实现。在多种模拟和真实场景下的广泛实验展示了该系统在视觉质量和重建效率方面的卓越性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该研究解决了主动三维重建中的实时活跃视图选择和视觉质量不确定性量化挑战。研究引入概率模型量化重建模型中每个高斯点的视觉不确定性,利用香农互信息制定一个标准,即高斯斯普拉特香农互信息(GauSS-MI),用于实时评估新视角下的视觉互信息,促进选择下一个最佳视角。GauSS-MI在一个与视图和运动规划器相结合的活动重建系统中得到实施。大量实验表明,该系统在模拟和真实场景中都具有优异的视觉质量和重建效率。
Key Takeaways
- 该研究解决了主动三维重建中的活跃视图选择问题,特别是选择信息量最大的视角。
- 引入了概率模型来量化重建模型中每个高斯点的视觉不确定性。
- 利用香农互信息制定了一个标准(GauSS-MI),用于评估从新颖视角的视觉互信息。
- GauSS-MI被集成到一个活跃重建系统中,该系统结合了视图和运动规划器。
- 该系统能够在模拟和真实场景中实现优异的视觉质量和重建效率。
- 研究强调了视觉质量在三维重建中的重要性,并展示了如何通过新技术如NeRF和3DGS提高图像渲染质量。
点此查看论文截图