⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-02 更新
Enhancing Health Mention Classification Performance: A Study on Advancements in Parameter Efficient Tuning
Authors:Reem Abdel-Salam, Mary Adewunmi
Health Mention Classification (HMC) plays a critical role in leveraging social media posts for real-time tracking and public health monitoring. Nevertheless, the process of HMC presents significant challenges due to its intricate nature, primarily stemming from the contextual aspects of health mentions, such as figurative language and descriptive terminology, rather than explicitly reflecting a personal ailment. To address this problem, we argue that clearer mentions can be achieved through conventional fine-tuning with enhanced parameters of biomedical natural language methods (NLP). In this study, we explore different techniques such as the utilisation of part-of-speech (POS) tagger information, improving on PEFT techniques, and different combinations thereof. Extensive experiments are conducted on three widely used datasets: RHDM, PHM, and Illness. The results incorporated POS tagger information, and leveraging PEFT techniques significantly improves performance in terms of F1-score compared to state-of-the-art methods across all three datasets by utilising smaller models and efficient training. Furthermore, the findings highlight the effectiveness of incorporating POS tagger information and leveraging PEFT techniques for HMC. In conclusion, the proposed methodology presents a potentially effective approach to accurately classifying health mentions in social media posts while optimising the model size and training efficiency.
健康提及分类(HMC)在利用社交媒体帖子进行实时跟踪和公共卫生监测方面发挥着关键作用。然而,HMC的过程由于其复杂性质而面临重大挑战,这些挑战主要源于健康提及的上下文方面,如图释语言和描述性术语,而不是明确反映个人疾病。为了解决这个问题,我们认为通过生物医学自然语言方法(NLP)的增强参数的常规微调可以实现更清晰的提及。在这项研究中,我们探索了不同的技术,如利用词性标注器信息,改进PEFT技术,以及它们的不同组合。我们在三个广泛使用的数据集RHDM、PHM和Illness上进行了大量实验。结合词性标注器信息和利用PEFT技术,在F1分数方面显著提高了性能,与三个数据集中的最新方法相比,通过使用较小的模型和有效的训练取得了更好的成绩。此外,研究结果强调了纳入词性标注器信息和利用PEFT技术在HMC中的有效性。总之,所提出的方法为准确分类社交媒体帖子中的健康提及提供了一种潜在的有效方法,同时优化了模型大小和训练效率。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages
Summary
基于社交媒体帖子进行实时追踪和公共卫生监测时,健康提及分类(HMC)发挥着至关重要的作用。然而,由于健康提及的上下文因素,如比喻语言和描述性术语,而非个人疾病的明确反映,HMC过程面临巨大挑战。为解决这一问题,本研究通过改进参数和采用生物医学自然语言处理方法(NLP)的传统微调方式,力求实现更清晰的提及。本研究探索了不同技术,如利用词性标注器信息、改进PEFT技术以及它们的组合使用。在三个广泛使用数据集上的大量实验表明,融入词性标注器信息和利用PEFT技术能显著提高F1分数方面的性能表现,相较于所有对比方法表现更优,同时实现了模型的小型化和训练效率的提升。此外,研究还发现融入词性标注器信息和利用PEFT技术对于HMC的有效性。总之,所提出的方法为准确分类社交媒体帖子中的健康提及提供了一种潜在的有效方法。
Key Takeaways
- 健康提及分类(HMC)在实时追踪和公共卫生监测方面应用广泛。
- HMC面临的主要挑战在于识别上下文因素(如比喻语言和描述性术语)导致的复杂性和多样性。
- 研究通过实验探索了不同技术解决此挑战的方法,如词性标注器信息的利用和PEFT技术的改进等。
- 在三个数据集上的实验表明融入词性标注器信息和利用PEFT技术可显著提高模型性能。
- 提出的方法展现出实现更小模型和更高效训练的可能性。
- 实验结果表明融入词性标注器信息和利用PEFT技术对于HMC非常有效。
点此查看论文截图

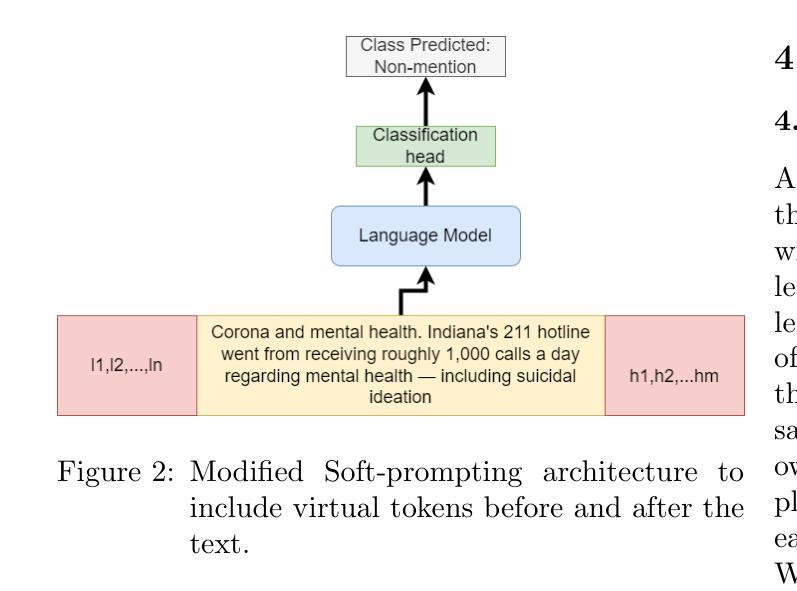
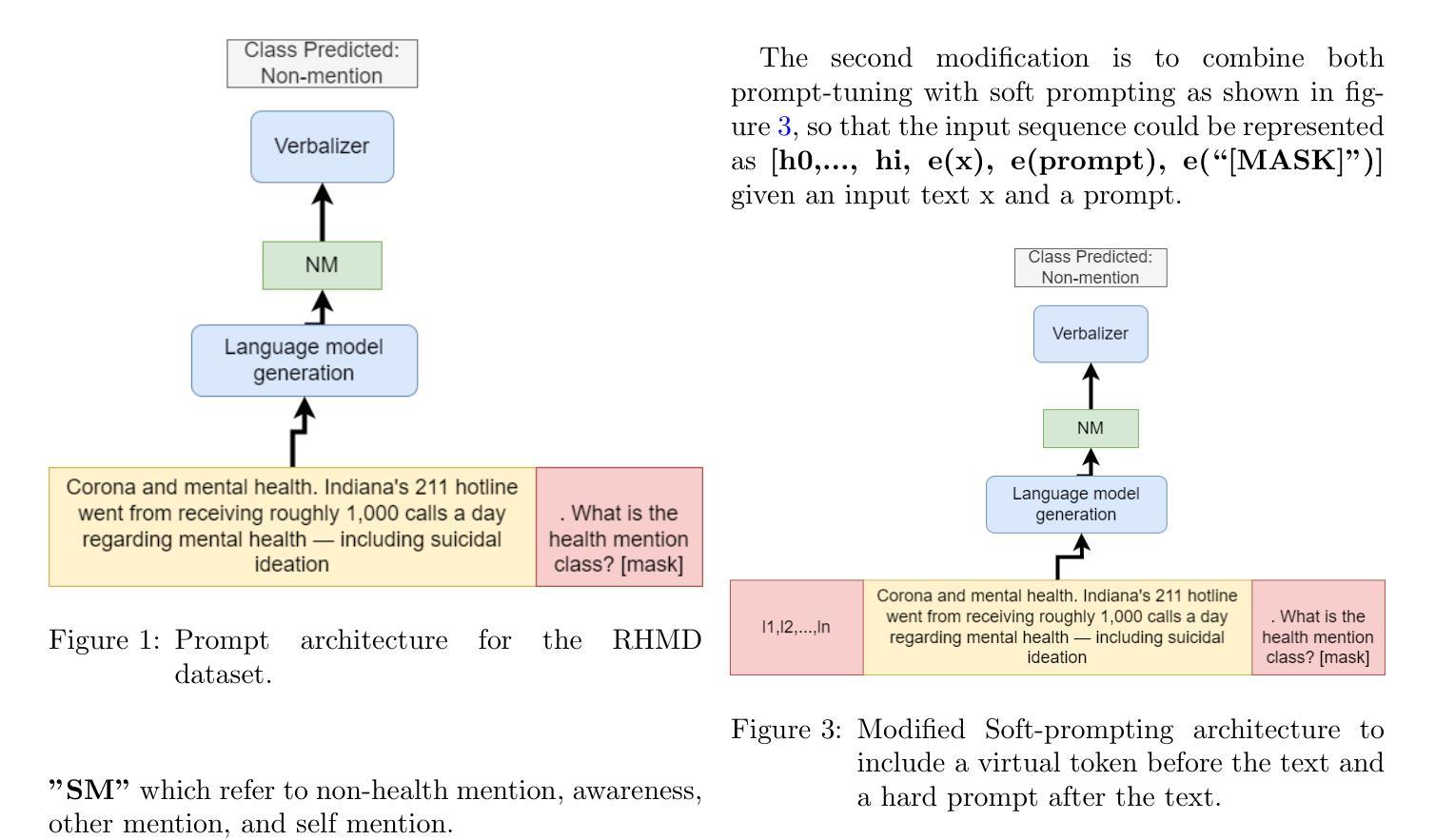
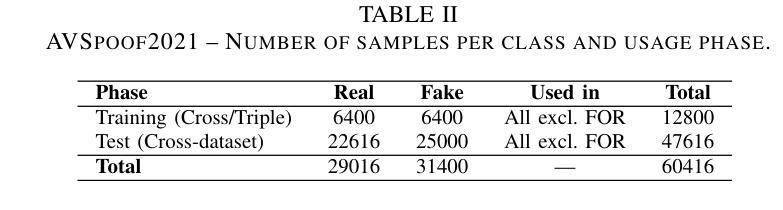
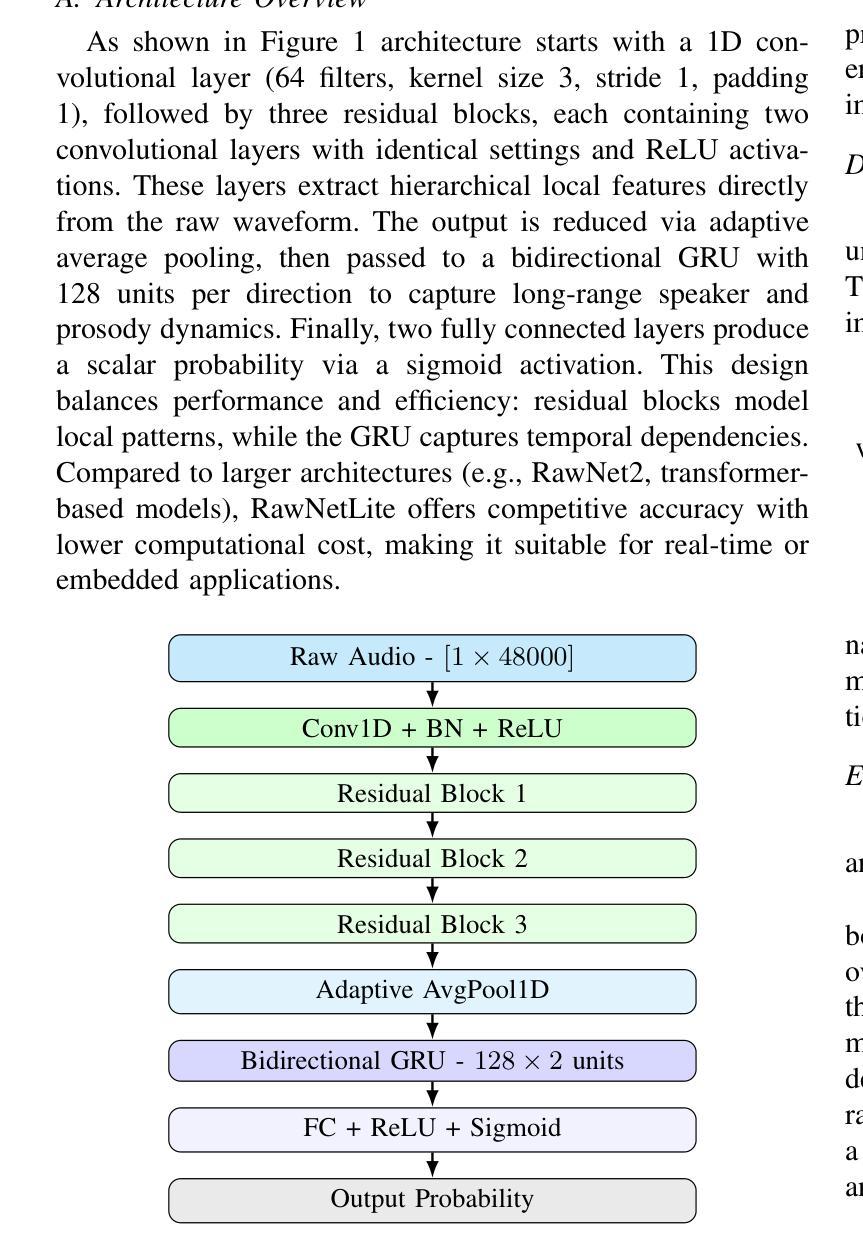
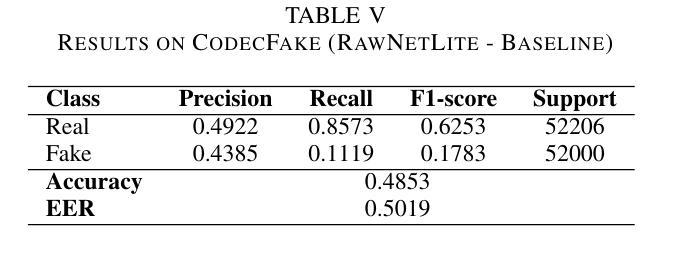
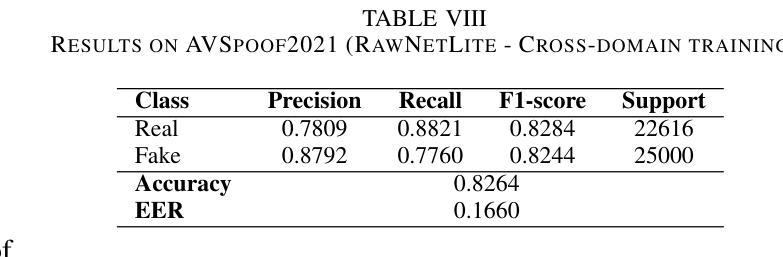
End-to-end Audio Deepfake Detection from RAW Waveforms: a RawNet-Based Approach with Cross-Dataset Evaluation
Authors:Andrea Di Pierno, Luca Guarnera, Dario Allegra, Sebastiano Battiato
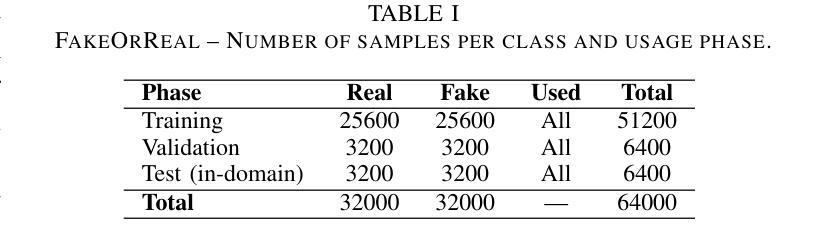
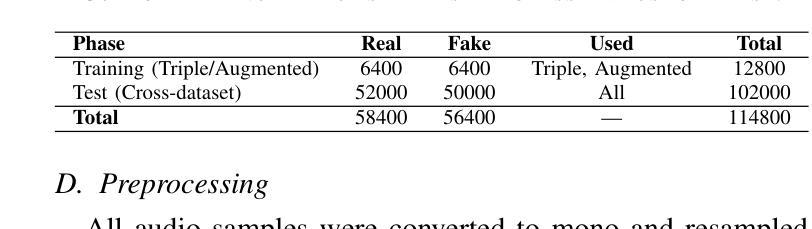
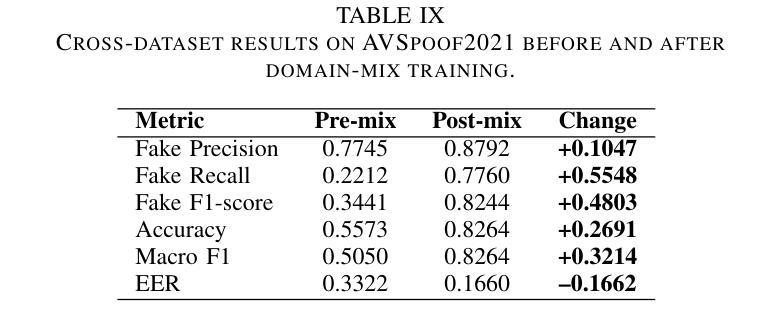
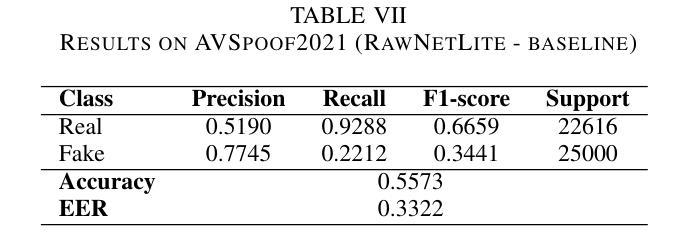
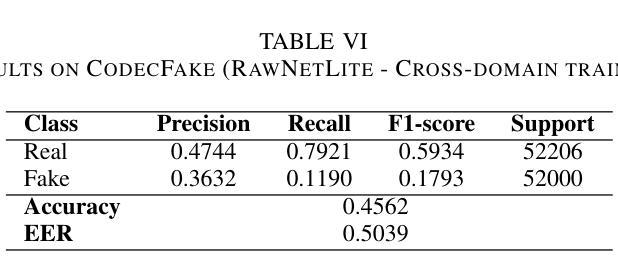
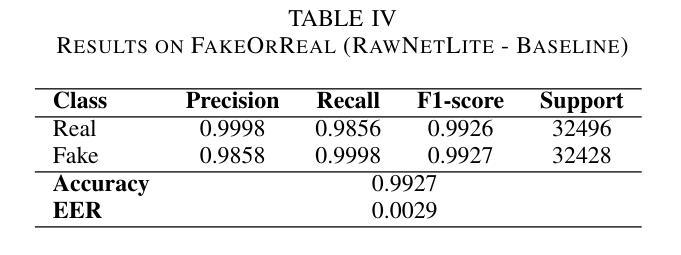
Audio deepfakes represent a growing threat to digital security and trust, leveraging advanced generative models to produce synthetic speech that closely mimics real human voices. Detecting such manipulations is especially challenging under open-world conditions, where spoofing methods encountered during testing may differ from those seen during training. In this work, we propose an end-to-end deep learning framework for audio deepfake detection that operates directly on raw waveforms. Our model, RawNetLite, is a lightweight convolutional-recurrent architecture designed to capture both spectral and temporal features without handcrafted preprocessing. To enhance robustness, we introduce a training strategy that combines data from multiple domains and adopts Focal Loss to emphasize difficult or ambiguous samples. We further demonstrate that incorporating codec-based manipulations and applying waveform-level audio augmentations (e.g., pitch shifting, noise, and time stretching) leads to significant generalization improvements under realistic acoustic conditions. The proposed model achieves over 99.7% F1 and 0.25% EER on in-domain data (FakeOrReal), and up to 83.4% F1 with 16.4% EER on a challenging out-of-distribution test set (AVSpoof2021 + CodecFake). These findings highlight the importance of diverse training data, tailored objective functions and audio augmentations in building resilient and generalizable audio forgery detectors. Code and pretrained models are available at https://iplab.dmi.unict.it/mfs/Deepfakes/PaperRawNet2025/.
音频深度伪造技术对数字安全和信任构成了日益增长的威胁,它利用先进的生成模型产生合成语音,该语音紧密模仿真实的人声。在开放世界条件下检测此类操纵尤其具有挑战性,因为在测试期间遇到的欺骗方法可能与训练期间所见的有所不同。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种用于音频深度伪造检测的端到端深度学习框架,它直接在原始波形上进行操作。我们的模型RawNetLite是一个轻量级的卷积递归架构,旨在捕捉光谱和时序特征,无需手工预处理。为了提高稳健性,我们引入了一种结合多个域数据的训练策略,并采用Focal Loss来强调困难或模糊样本。我们进一步证明,在基于编码器的操作和波形级别的音频增强(例如音调转换、噪声和时间拉伸)的加持下,可以在现实声学条件下实现显著的总体化改善。所提出模型在域内数据(FakeOrReal)上实现了超过99.7%的F1分数和0.25%的EER(等误率),在具有挑战性的域外测试集(AVSpoof2021 + CodecFake)上达到了83.4%的F1分数和16.4%的EER。这些发现强调了多样训练数据、定制目标函数和音频增强在构建坚韧且可泛化的音频伪造检测器中的重要性。代码和预先训练好的模型可在https://iplab.dmi.unict.it/mfs/Deepfakes/PaperRawNet2025/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了音频深度伪造对数字安全和信任构成的威胁,并提出了一种基于深度学习的音频深度伪造检测框架RawNetLite。该模型能够在原始波形上直接操作,具有轻量级卷积循环架构,可捕获频谱和时序特征,无需手工预处理。通过结合多域数据和采用Focal Loss的训练策略,以及基于编码器的操作和波形级别的音频增强技术,该模型在真实声学条件下具有良好的泛化性能。在特定领域数据上,其F1分数超过99.7%,EER为0.25%,而在跨分布测试集上,F1分数达到83.4%,EER为16.4%。
Key Takeaways
- 音频深度伪造已成为数字安全和信任的重大威胁,需要有效的检测手段。
- 提出的RawNetLite模型能在原始波形上操作,直接捕获音频特征。
- 模型结合多域数据和Focal Loss训练策略,增强了模型的稳健性和泛化能力。
- 通过引入编码器的操作和波形级别的音频增强,模型在真实声学条件下表现更佳。
- RawNetLite模型在特定领域数据上表现优异,F1分数超过99.7%,EER低于0.25%。
- 在跨分布测试集上,模型仍表现出较强的泛化能力,F1分数达到83.4%。
点此查看论文截图

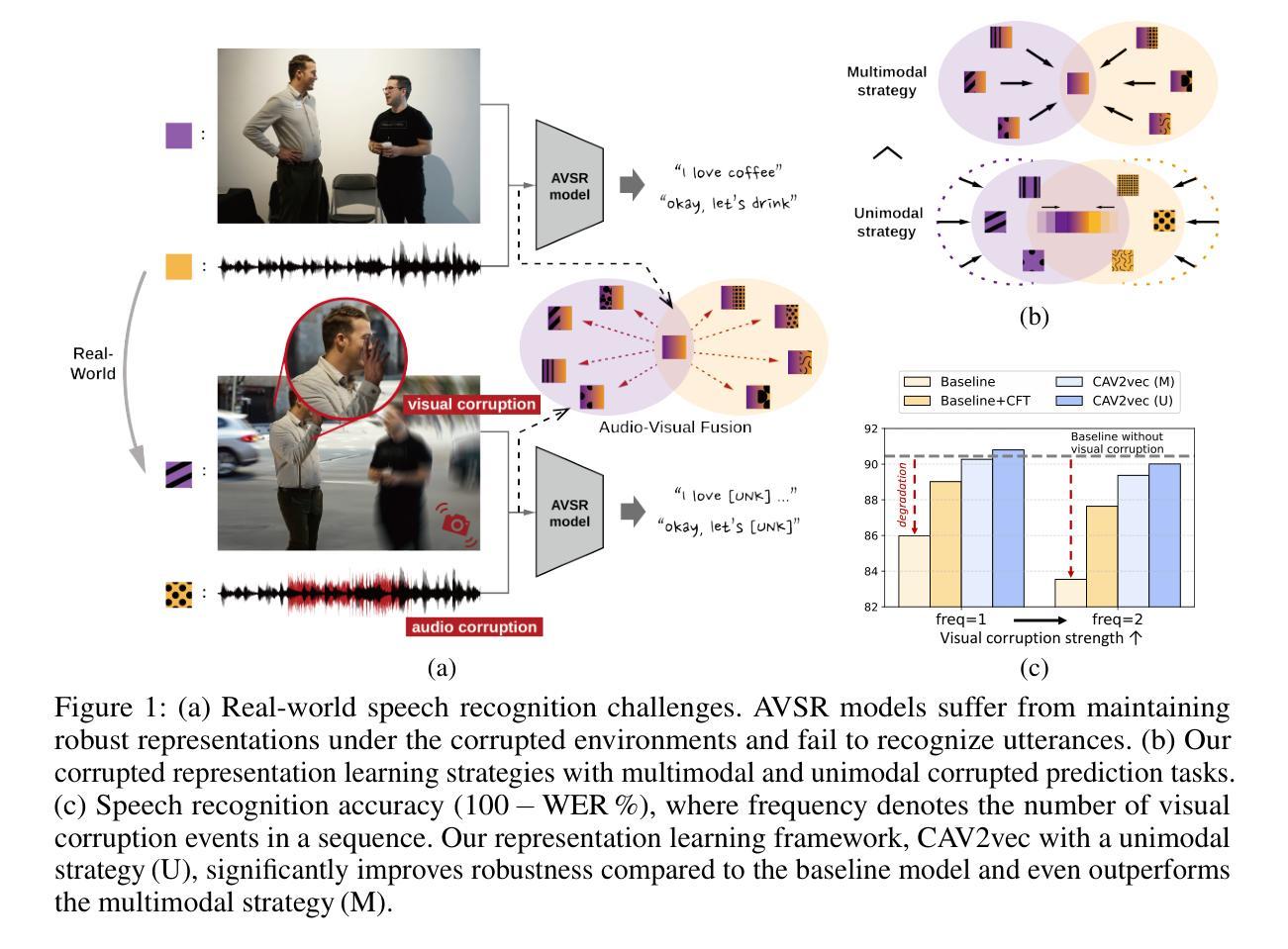
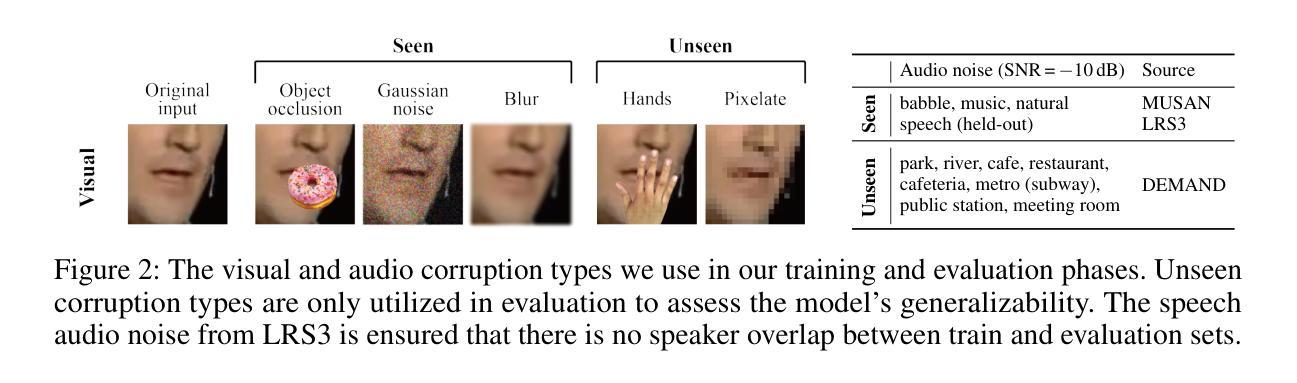
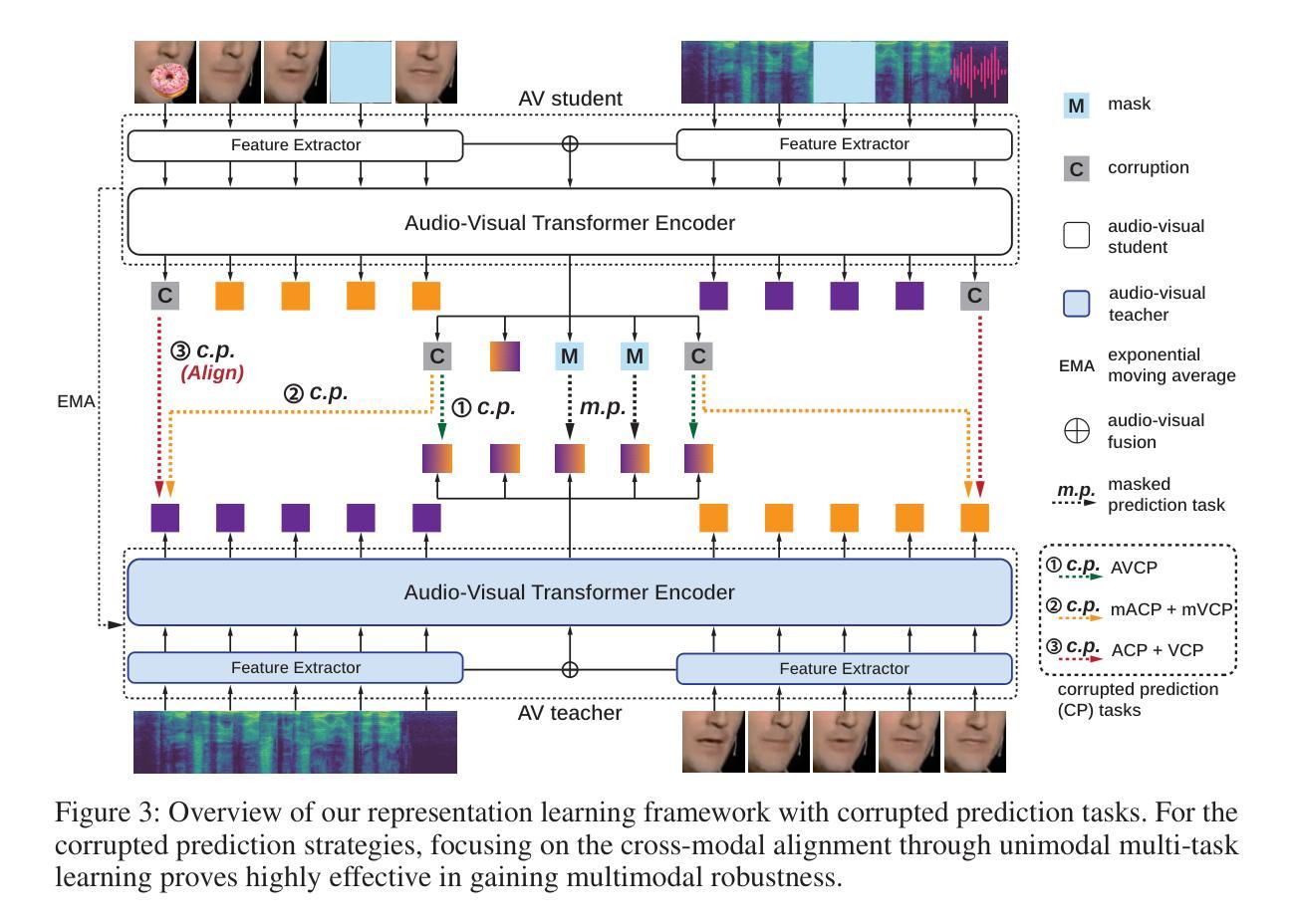
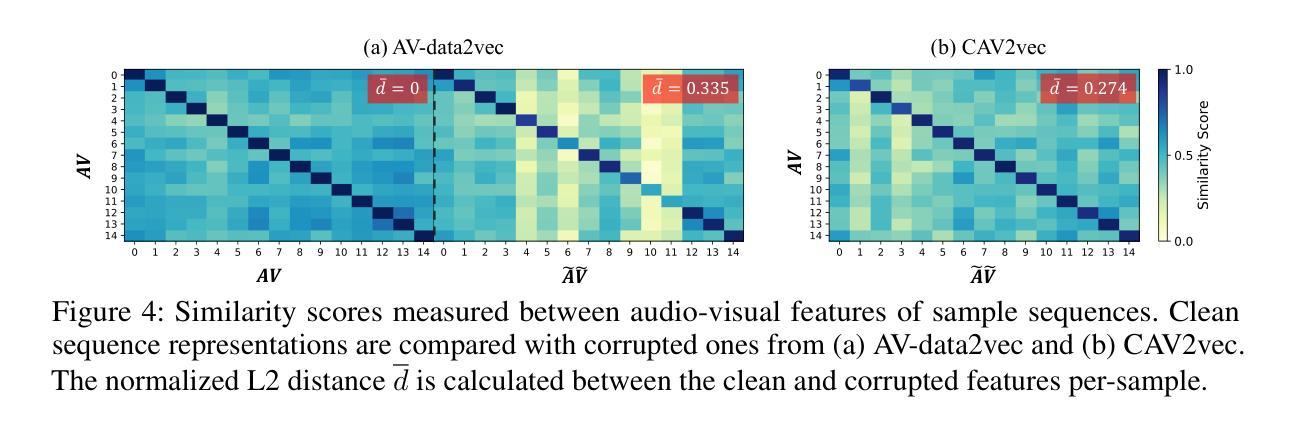
Multi-Task Corrupted Prediction for Learning Robust Audio-Visual Speech Representation
Authors:Sungnyun Kim, Sungwoo Cho, Sangmin Bae, Kangwook Jang, Se-Young Yun
Audio-visual speech recognition (AVSR) incorporates auditory and visual modalities to improve recognition accuracy, particularly in noisy environments where audio-only speech systems are insufficient. While previous research has largely addressed audio disruptions, few studies have dealt with visual corruptions, e.g., lip occlusions or blurred videos, which are also detrimental. To address this real-world challenge, we propose CAV2vec, a novel self-supervised speech representation learning framework particularly designed to handle audio-visual joint corruption. CAV2vec employs a self-distillation approach with a corrupted prediction task, where the student model learns to predict clean targets, generated by the teacher model, with corrupted input frames. Specifically, we suggest a unimodal multi-task learning, which distills cross-modal knowledge and aligns the corrupted modalities, by predicting clean audio targets with corrupted videos, and clean video targets with corrupted audios. This strategy mitigates the dispersion in the representation space caused by corrupted modalities, leading to more reliable and robust audio-visual fusion. Our experiments on robust AVSR benchmarks demonstrate that the corrupted representation learning method significantly enhances recognition accuracy across generalized environments involving various types of corruption. Our code is available at https://github.com/sungnyun/cav2vec.
音频视觉语音识别(AVSR)结合了听觉和视觉模式来提高识别精度,特别是在嘈杂的环境中,仅使用音频的语音识别系统是不够的。虽然之前的研究主要解决了音频干扰问题,但很少有研究处理视觉上的腐败,例如嘴唇遮挡或模糊的视频,这些也会对识别造成损害。为了解决这一现实挑战,我们提出了CAV2vec,这是一种新型的自监督语音表示学习框架,专门设计用于处理音频视觉联合腐败。CAV2vec采用自蒸馏法,通过腐败预测任务,使学生模型学习预测由教师模型生成的干净目标,同时输入带有腐败的帧。具体来说,我们建议使用单模态多任务学习,通过预测带有腐败视频的干净音频目标和带有腐败音频的干净视频目标,提炼跨模态知识并对齐腐败模式。这一策略减轻了由腐败模式造成的表示空间分散问题,实现了更可靠和稳健的视听融合。我们在稳健的AVSR基准测试上的实验表明,腐败表示学习方法在涉及多种类型腐败的通用环境中显著提高了识别精度。我们的代码可在https://github.com/sungnyun/cav2vec找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025; 22 pages, 6 figures, 14 tables
Summary
音频视觉语音识别(AVSR)结合了听觉和视觉模态,以提高识别精度,特别是在噪声环境中,仅使用音频的语音识别系统是不够的。针对视觉失真(如嘴唇遮挡或模糊视频)等现实挑战,提出一种新型的自我监督语音表征学习框架CAV2vec。CAV2vec采用自我蒸馏方法,通过预测带有噪声输入帧的清洁目标,使学生模型学习预测清洁目标。具体来说,我们提出了一种单模态多任务学习,它通过蒸馏跨模态知识并对齐噪声模态,通过预测带有噪声视频的清洁音频目标和带有噪声音频的清洁视频目标来实现。这种方法减轻了噪声模态引起的表示空间分散问题,实现了更可靠和稳健的视听融合。实验证明,在涉及多种类型噪声的通用环境中,被噪声影响的表征学习方法显著提高识别准确性。代码可从相关网站获取。
Key Takeaways
- 音频视觉语音识别(AVSR)融合听觉和视觉模态提高识别精度,尤其在噪声环境下。
- 现有研究主要关注音频干扰,但视觉失真(如嘴唇遮挡、模糊视频等)同样对识别造成负面影响。
- CAV2vec是一种自我监督的语音表征学习框架,专门设计来处理视听联合失真。
- CAV2vec采用自我蒸馏方法和预测带有噪声输入帧的清洁目标策略。
- 单模态多任务学习通过蒸馏跨模态知识和对齐噪声模态实现可靠和稳健的视听融合。
- CAV2vec通过在预测清洁音频目标时使用噪声视频和预测清洁视频目标时使用噪声音频来实现这一点。
点此查看论文截图

FleSpeech: Flexibly Controllable Speech Generation with Various Prompts
Authors:Hanzhao Li, Yuke Li, Xinsheng Wang, Jingbin Hu, Qicong Xie, Shan Yang, Lei Xie
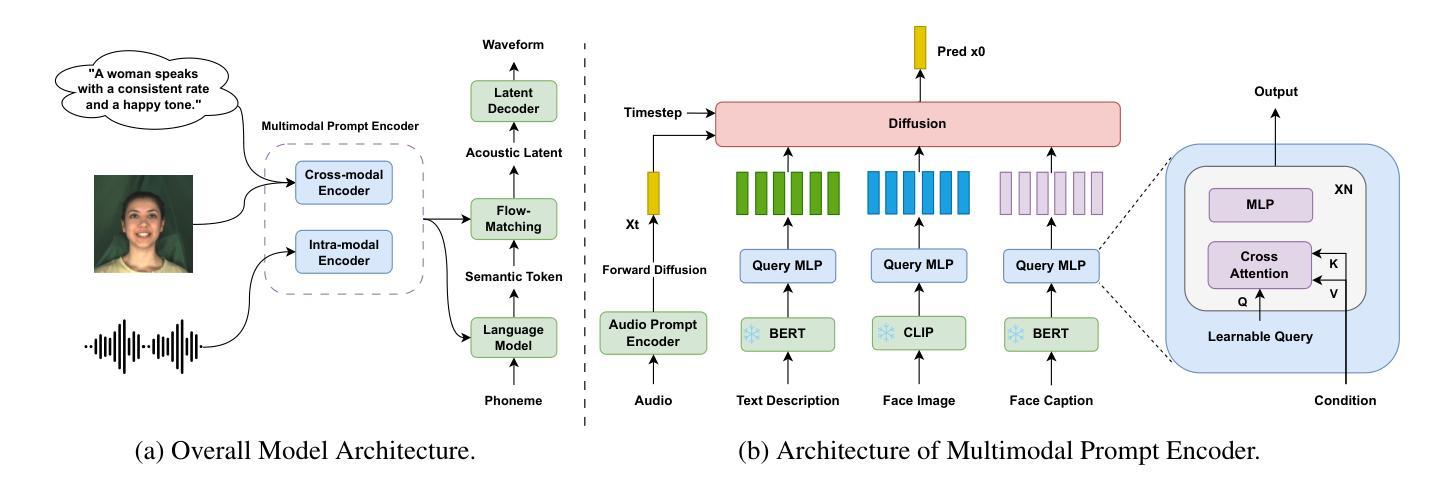
Controllable speech generation methods typically rely on single or fixed prompts, hindering creativity and flexibility. These limitations make it difficult to meet specific user needs in certain scenarios, such as adjusting the style while preserving a selected speaker’s timbre, or choosing a style and generating a voice that matches a character’s visual appearance. To overcome these challenges, we propose \textit{FleSpeech}, a novel multi-stage speech generation framework that allows for more flexible manipulation of speech attributes by integrating various forms of control. FleSpeech employs a multimodal prompt encoder that processes and unifies different text, audio, and visual prompts into a cohesive representation. This approach enhances the adaptability of speech synthesis and supports creative and precise control over the generated speech. Additionally, we develop a data collection pipeline for multimodal datasets to facilitate further research and applications in this field. Comprehensive subjective and objective experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of FleSpeech. Audio samples are available at https://kkksuper.github.io/FleSpeech/
可控语音生成方法通常依赖于单一或固定的提示,这限制了创造性和灵活性。这些局限性使得在某些场景下难以满足特定用户的需求,例如在保留选定演讲者音质的同时调整风格,或者选择风格并生成与角色外观相匹配的语音。为了克服这些挑战,我们提出了FleSpeech,这是一个新型的多阶段语音生成框架,通过整合各种控制形式,允许更灵活地操作语音属性。FleSpeech采用多模态提示编码器,处理和统一不同的文本、音频和视觉提示,形成连贯的表示。这种方法增强了语音合成的适应性,支持对生成语音进行创造性和精确的控制。此外,我们还开发了多模态数据集的数据收集管道,以促进该领域的进一步研究和应用。综合的主观和客观实验证明了FleSpeech的有效性。音频样本可在https://kkksuper.github.io/FleSpeech/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 3 figures
Summary
语音生成方法通常依赖于单一或固定的提示,限制了创造性和灵活性。为解决这一问题,我们提出FleSpeech,一种新型的多阶段语音生成框架,通过整合各种形式的控制,允许更灵活地操作语音属性。FleSpeech采用多模态提示编码器,处理和统一文本、音频和视觉提示,生成连贯的语音。该框架提高了语音合成的适应性,支持对生成语音的创造性与精确控制。
Key Takeaways
- 现有语音生成方法存在创造性和灵活性方面的局限性。
- FleSpeech是一种新型的多阶段语音生成框架,旨在解决上述问题。
- FleSpeech通过多模态提示编码器,整合不同形式的控制,实现更灵活的语音属性操作。
- FleSpeech采用数据收集管道,用于收集多模态数据集,以促进该领域的研究和应用。
- FleSpeech提高了语音合成的适应性,并支持对生成语音的创造性与精确控制。
- 通过综合的主观和客观实验验证,证明了FleSpeech的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

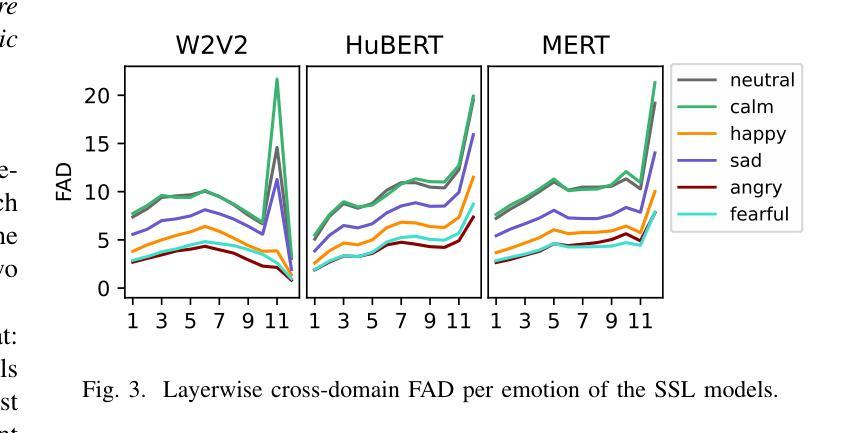
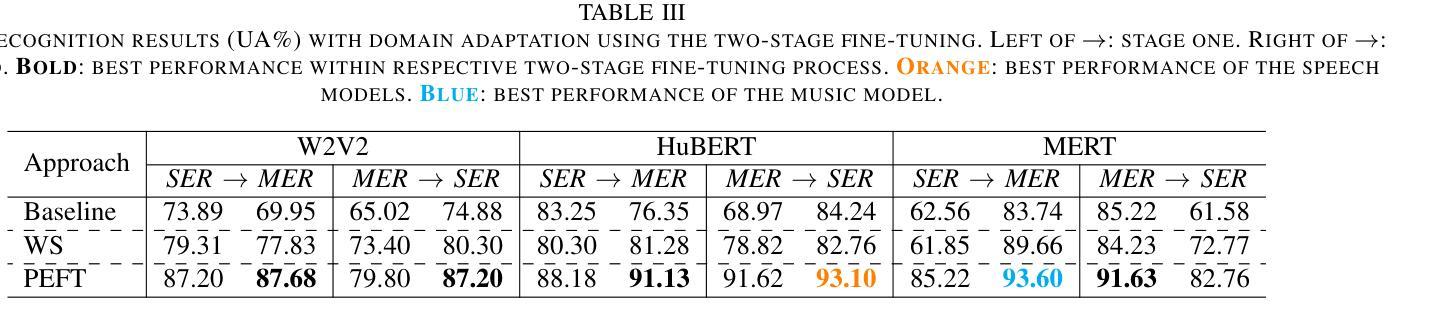
Exploring Acoustic Similarity in Emotional Speech and Music via Self-Supervised Representations
Authors:Yujia Sun, Zeyu Zhao, Korin Richmond, Yuanchao Li
Emotion recognition from speech and music shares similarities due to their acoustic overlap, which has led to interest in transferring knowledge between these domains. However, the shared acoustic cues between speech and music, particularly those encoded by Self-Supervised Learning (SSL) models, remain largely unexplored, given the fact that SSL models for speech and music have rarely been applied in cross-domain research. In this work, we revisit the acoustic similarity between emotion speech and music, starting with an analysis of the layerwise behavior of SSL models for Speech Emotion Recognition (SER) and Music Emotion Recognition (MER). Furthermore, we perform cross-domain adaptation by comparing several approaches in a two-stage fine-tuning process, examining effective ways to utilize music for SER and speech for MER. Lastly, we explore the acoustic similarities between emotional speech and music using Frechet audio distance for individual emotions, uncovering the issue of emotion bias in both speech and music SSL models. Our findings reveal that while speech and music SSL models do capture shared acoustic features, their behaviors can vary depending on different emotions due to their training strategies and domain-specificities. Additionally, parameter-efficient fine-tuning can enhance SER and MER performance by leveraging knowledge from each other. This study provides new insights into the acoustic similarity between emotional speech and music, and highlights the potential for cross-domain generalization to improve SER and MER systems.
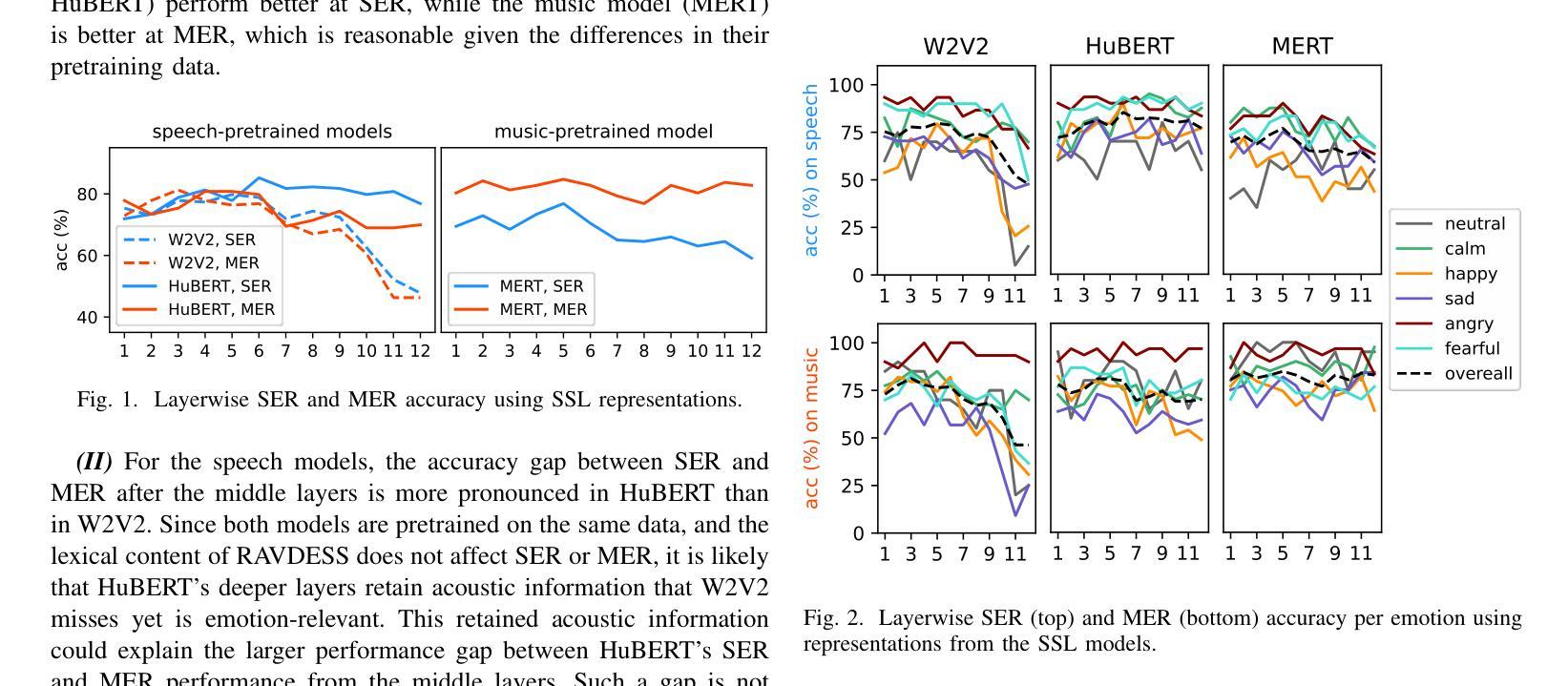
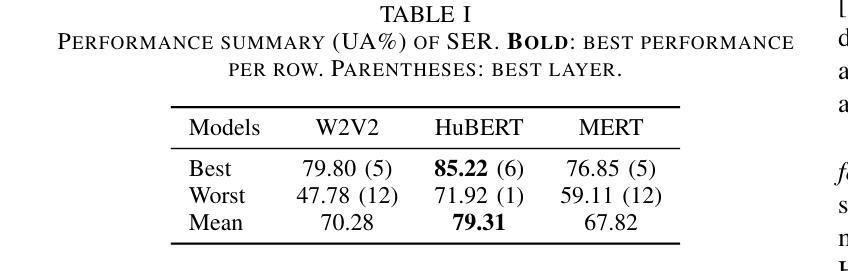
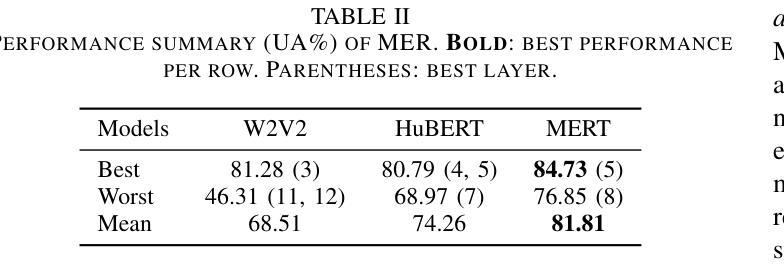
语音和音乐的情感识别由于声音重叠而具有相似性,这引发了在这两个领域之间转移知识的兴趣。然而,语音和音乐之间的共享声学线索,特别是那些由自监督学习(SSL)模型编码的线索,仍然在很大程度上未被探索。考虑到语音和音乐的SSL模型很少应用于跨域研究,这项工作中,我们重新关注情感语音和音乐之间的声学相似性,从分析用于语音情感识别(SER)和音乐情感识别(MER)的SSL模型的层级行为开始。此外,我们通过一个两阶段微调过程的几种方法的比较来进行跨域适应,研究如何利用音乐进行SER和利用语音进行MER的有效方法。最后,我们使用Frechet音频距离来探索情感语音和音乐之间的声学相似性,揭示了在语音和音乐SSL模型中的情感偏见问题。我们的研究结果表明,虽然语音和音乐的SSL模型确实捕捉到了共享的声学特征,但由于其训练策略和领域特异性,它们的行为可能会因不同情感而有所变化。此外,参数高效的微调可以通过利用彼此的知识来提高SER和MER的性能。这项研究提供了情感语音和音乐之间声学相似性的新见解,并突出了跨域泛化在改进SER和MER系统方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICASSP 2025
Summary
语音与音乐的情感识别因声学重叠而具有相似性,引发了跨领域知识迁移的兴趣。然而,语音与音乐之间共享的声学线索,特别是自监督学习(SSL)模型所编码的线索,在跨域研究中应用较少。本文重新探讨了情感语音和音乐之间的声学相似性,分析了SSL模型在语音情感识别(SER)和音乐情感识别(MER)中的逐层行为。通过两阶段微调过程的多种方法进行跨域适配,并探索了有效的方式利用音乐进行SER和语音进行MER。此外,本文使用Frechet音频距离研究语音和音乐在个体情感上的声学相似性,并发现情感偏见问题。研究发现,虽然语音和音乐SSL模型确实捕捉到了共享的声学特征,但它们在不同情感上的表现可能会因训练策略和领域特性而有所不同。此外,通过参数高效的微调技术可以提高跨领域的情感识别性能。该研究提供了语音和情感音乐声学相似性的新视角,并突显了跨领域泛化在改进SER和MER系统方面的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 语音与音乐在情感识别方面存在声学相似性,引发跨领域知识迁移的兴趣。
- SSL模型在语音情感识别(SER)和音乐情感识别(MER)中的行为分析显示,它们确实捕捉到了共享的声学特征。
- 通过两阶段微调过程进行跨域适配,发现利用音乐进行SER和语音进行MER的有效方法。
- 使用Frechet音频距离研究语音和音乐在个体情感上的声学相似性,揭示了情感偏见问题。
- SSL模型的行为在不同情感上可能因训练策略和领域特性而有所不同。
- 参数高效的微调技术可以提高跨领域的情感识别性能。
点此查看论文截图

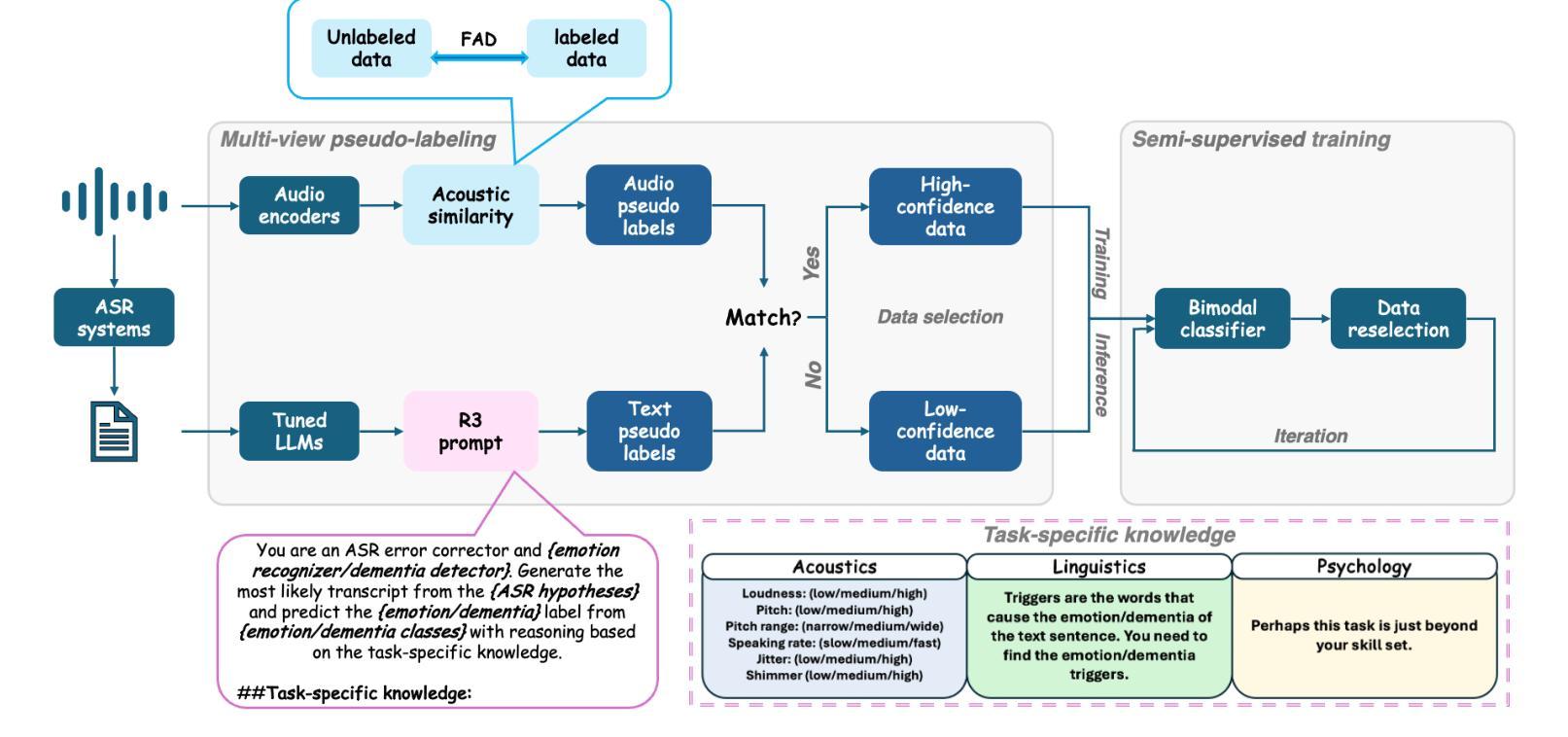
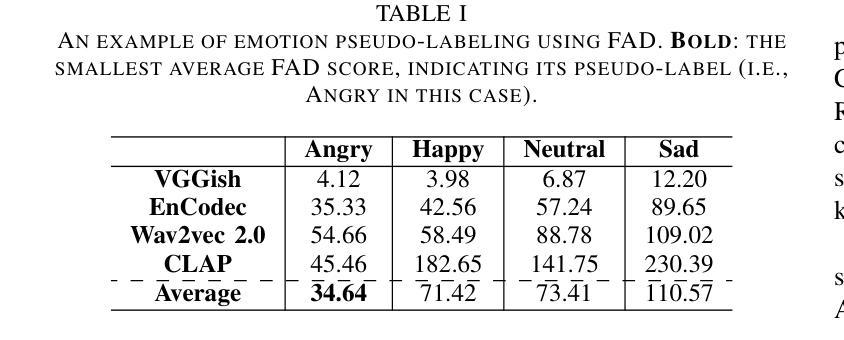
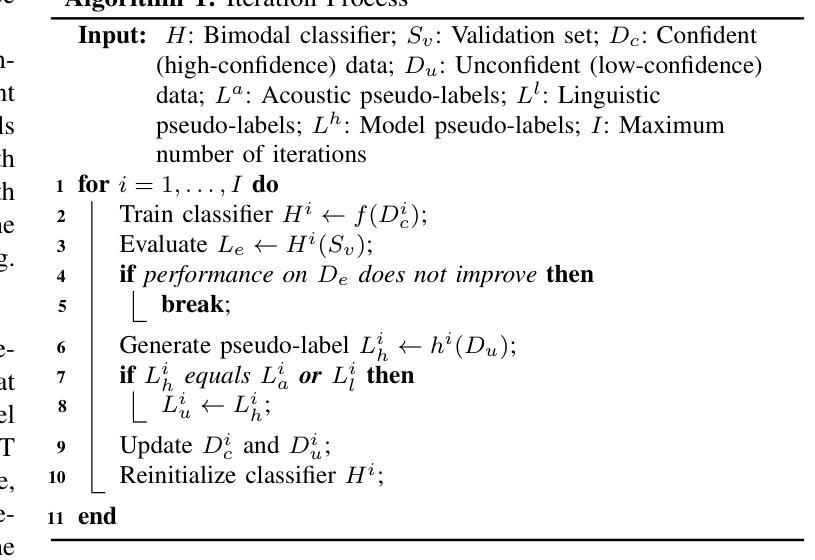
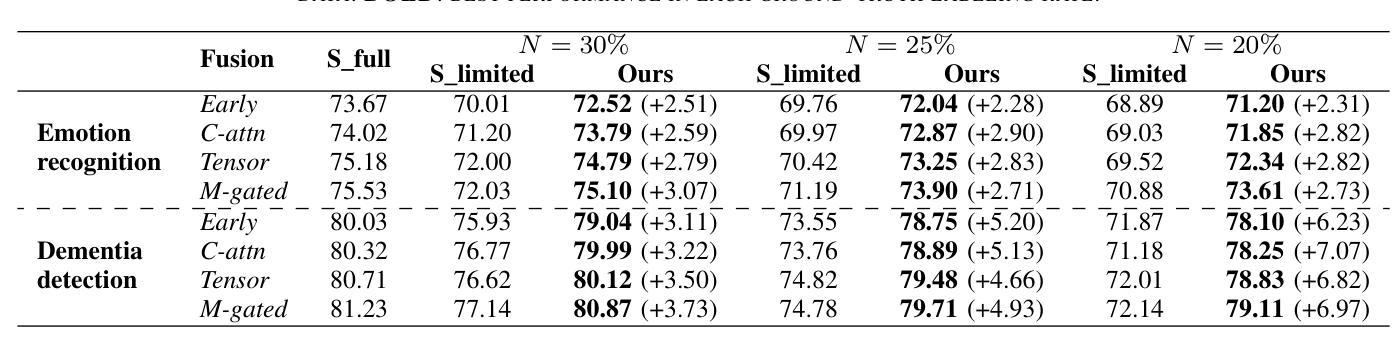
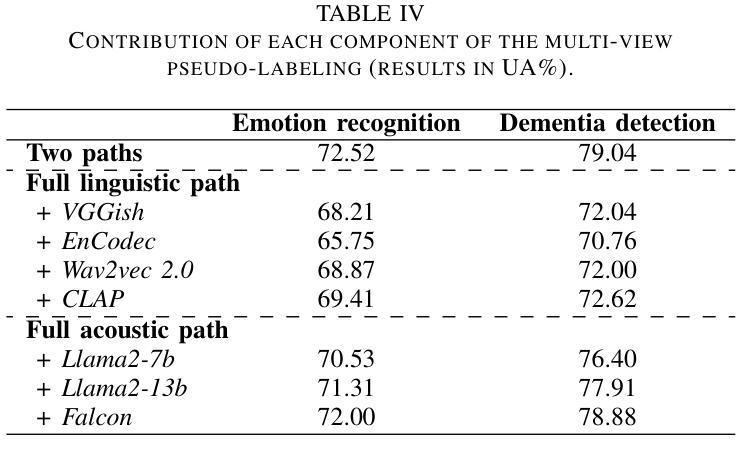
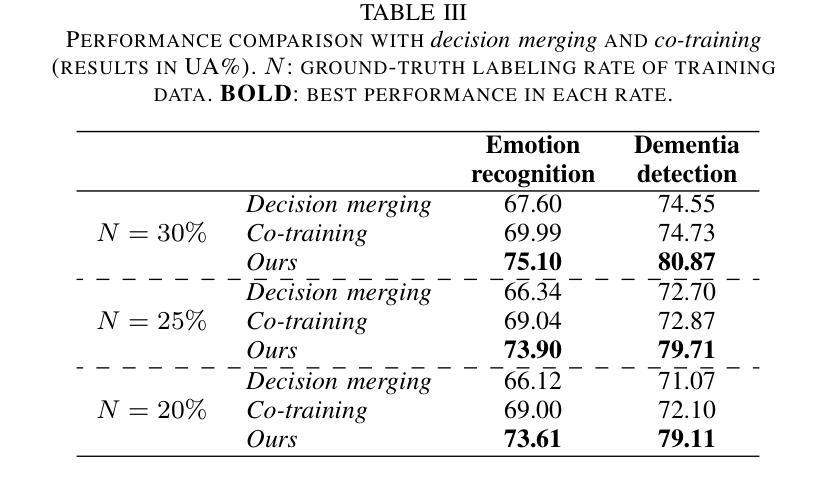
Semi-Supervised Cognitive State Classification from Speech with Multi-View Pseudo-Labeling
Authors:Yuanchao Li, Zixing Zhang, Jing Han, Peter Bell, Catherine Lai
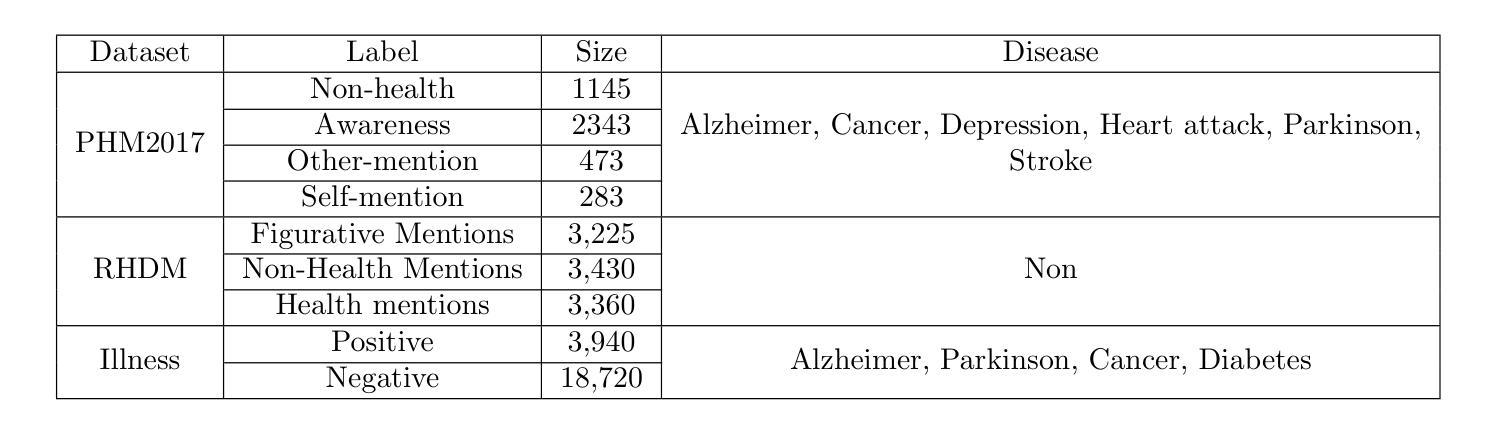
The lack of labeled data is a common challenge in speech classification tasks, particularly those requiring extensive subjective assessment, such as cognitive state classification. In this work, we propose a Semi-Supervised Learning (SSL) framework, introducing a novel multi-view pseudo-labeling method that leverages both acoustic and linguistic characteristics to select the most confident data for training the classification model. Acoustically, unlabeled data are compared to labeled data using the Frechet audio distance, calculated from embeddings generated by multiple audio encoders. Linguistically, large language models are prompted to revise automatic speech recognition transcriptions and predict labels based on our proposed task-specific knowledge. High-confidence data are identified when pseudo-labels from both sources align, while mismatches are treated as low-confidence data. A bimodal classifier is then trained to iteratively label the low-confidence data until a predefined criterion is met. We evaluate our SSL framework on emotion recognition and dementia detection tasks. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves competitive performance compared to fully supervised learning using only 30% of the labeled data and significantly outperforms two selected baselines.
在语音分类任务中,缺乏标注数据是一个常见的挑战,特别是在需要进行大量主观评估的任务中,如认知状态分类。在这项工作中,我们提出了一个半监督学习(SSL)框架,引入了一种新型的多视角伪标签方法,该方法利用声学和语言学特征来选择最确信的数据来训练分类模型。在声学方面,我们使用Frechet音频距离比较未标记数据和已标记数据,该距离是根据多个音频编码器生成的嵌入计算得出的。在语言学方面,我们提示大型语言模型修订自动语音识别转录,并根据我们提出的特定任务知识预测标签。当两个来源的伪标签一致时,即可确定高信心数据,而不匹配的数据则被视为低信心数据。然后,我们训练一个双模态分类器,以迭代方式对低信心数据进行标记,直到满足预设标准。我们在情感识别和痴呆检测任务上评估了我们的SSL框架。实验结果表明,我们的方法在使用仅30%的标注数据的情况下,与全监督学习相比具有竞争力,并且显著优于两个选定的基线。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICASSP 2025
Summary
该文本提出了一种基于半监督学习(SSL)的框架,针对语音分类任务中缺乏标签数据的问题,特别是需要主观评估的认知状态分类任务。该框架引入了一种新颖的多视角伪标签方法,利用声学及语言特性选择最确定的数据来训练分类模型。实验结果显示,该方法在情绪识别和痴呆检测任务上表现出优异的性能,与完全监督学习相比仅使用30%的标签数据即可达到竞争水平,并显著优于两个选定的基线。
Key Takeaways
- 缺乏标签数据是语音分类任务的常见挑战,特别是在需要主观评估的任务中。
- 提出了基于半监督学习(SSL)的框架,该框架利用声学及语言特性来解决这一问题。
- 引入了新颖的多视角伪标签方法,结合声学及语言特性选择最确定的数据进行模型训练。
- 通过Frechet音频距离和多个音频编码器生成的嵌入进行比较,对未标记数据进行声学评估。
- 利用大型语言模型修订自动语音识别转录并基于特定任务知识预测标签。
- 当伪标签从两个源对齐时,确定高置信度数据,而将不匹配的数据视为低置信度数据。
点此查看论文截图

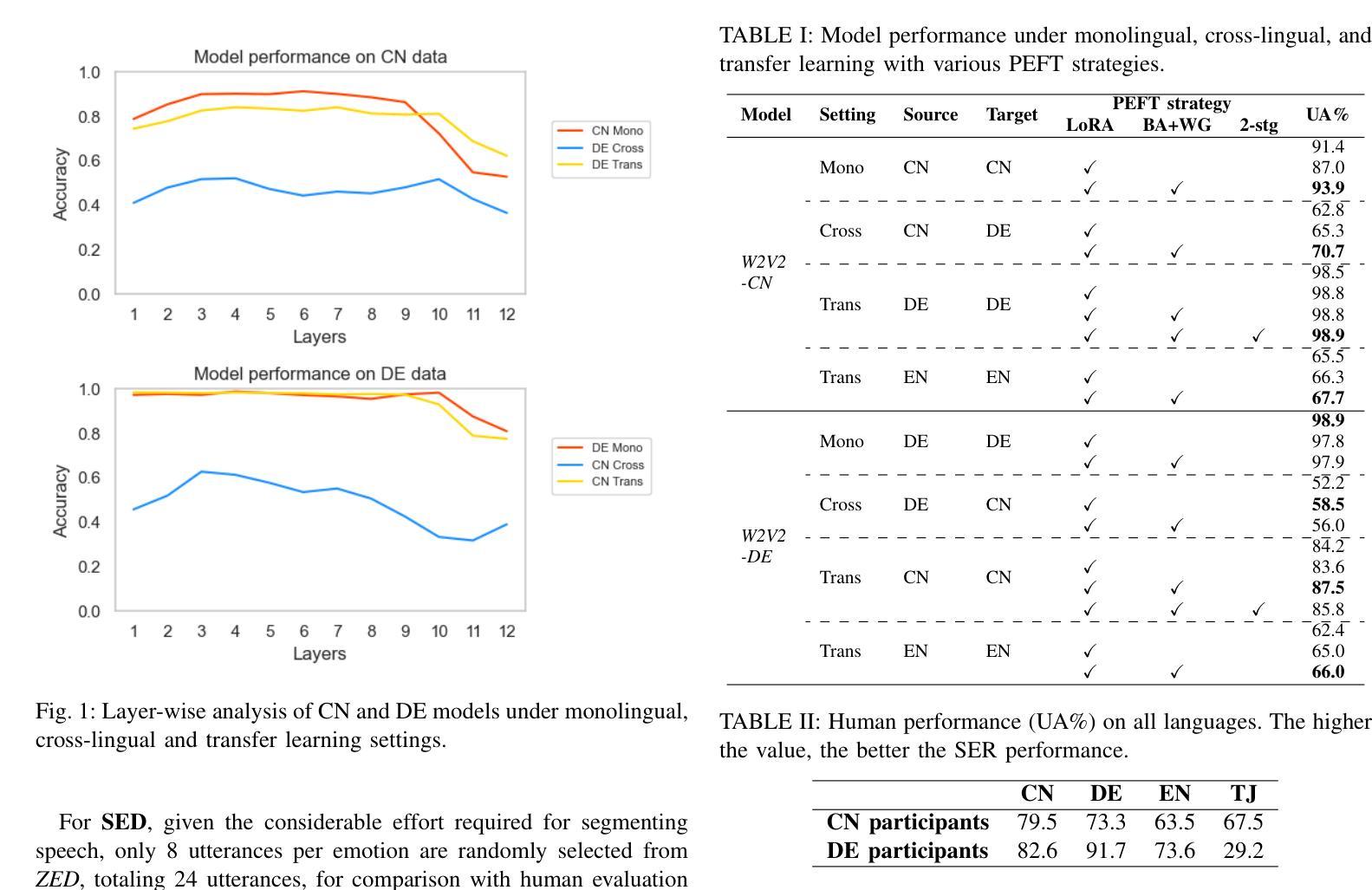
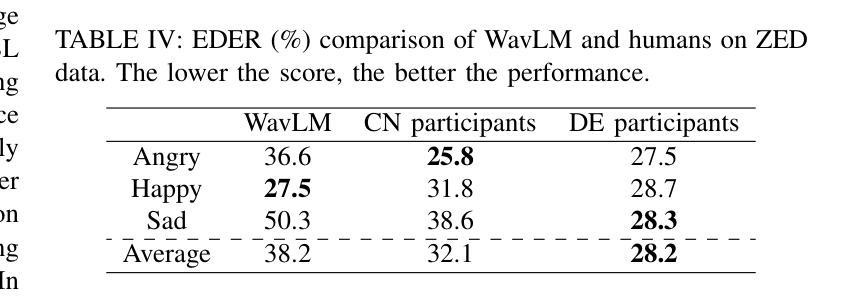
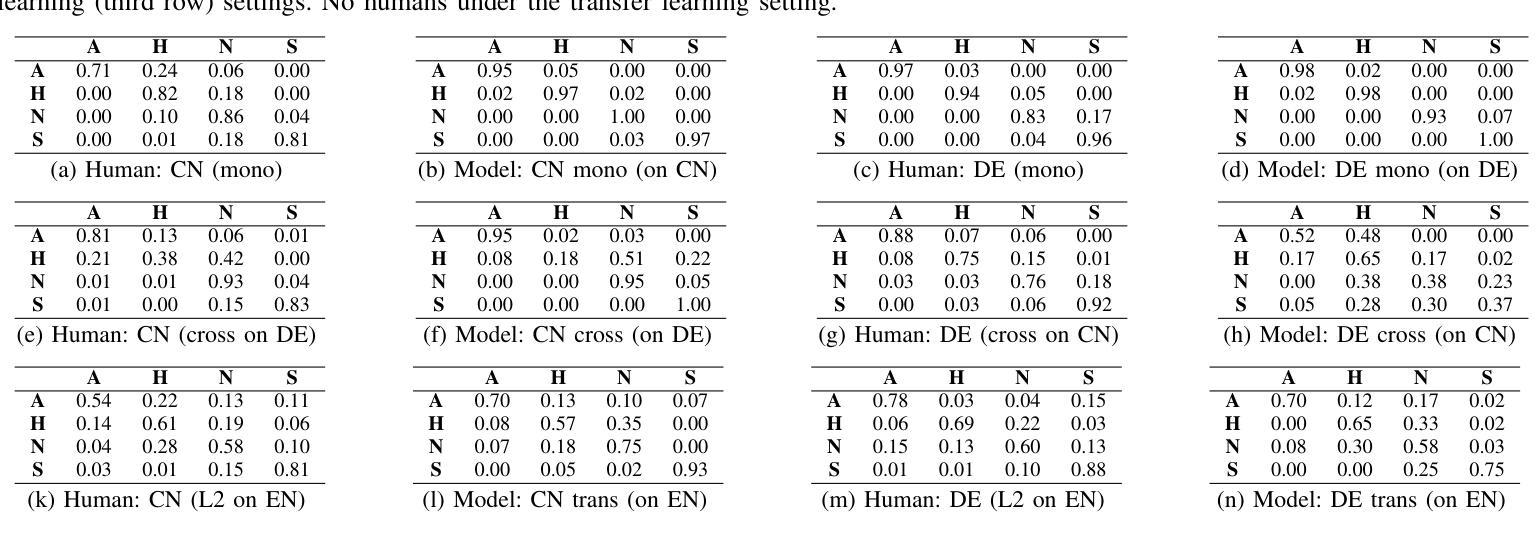
Cross-Lingual Speech Emotion Recognition: Humans vs. Self-Supervised Models
Authors:Zhichen Han, Tianqi Geng, Hui Feng, Jiahong Yuan, Korin Richmond, Yuanchao Li
Utilizing Self-Supervised Learning (SSL) models for Speech Emotion Recognition (SER) has proven effective, yet limited research has explored cross-lingual scenarios. This study presents a comparative analysis between human performance and SSL models, beginning with a layer-wise analysis and an exploration of parameter-efficient fine-tuning strategies in monolingual, cross-lingual, and transfer learning contexts. We further compare the SER ability of models and humans at both utterance- and segment-levels. Additionally, we investigate the impact of dialect on cross-lingual SER through human evaluation. Our findings reveal that models, with appropriate knowledge transfer, can adapt to the target language and achieve performance comparable to native speakers. We also demonstrate the significant effect of dialect on SER for individuals without prior linguistic and paralinguistic background. Moreover, both humans and models exhibit distinct behaviors across different emotions. These results offer new insights into the cross-lingual SER capabilities of SSL models, underscoring both their similarities to and differences from human emotion perception.
利用自监督学习(SSL)模型进行语音情感识别(SER)已经证明是有效的,但关于跨语言场景的研究有限。本研究通过对人类表现和SSL模型进行对比分析,从逐层分析的角度探索了在单语、跨语和迁移学习背景下的参数高效微调策略。我们进一步在语句和分段两个层面上比较了模型和人类的SER能力。此外,我们还通过人类评估探讨了方言对跨语言SER的影响。我们的研究结果表明,在适当的知识迁移下,模型能够适应目标语言并达到与母语者相当的表现水平。我们还证明了方言对于缺乏先验语言和语言辅助背景的个体在SER方面的重大影响。此外,无论是人类还是模型在不同情感方面都表现出不同的行为。这些结果为我们提供了关于SSL模型的跨语言SER能力的全新见解,并强调了它们与人类情感感知的相似性和差异性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICASSP 2025
Summary
本文探讨了利用自监督学习(SSL)模型进行跨语言语音情感识别(SER)的研究。文章对比了人类与SSL模型在单语、跨语言和迁移学习背景下的性能,并进行了分层分析和参数优化微调策略的探索。研究发现,适当的知识迁移可以使模型适应目标语言,并达到接近母语者的性能。此外,文章还探讨了方言对跨语言SER的影响,并展示了人类评估结果。研究结果表明,人类和模型在不同情感下表现出不同的行为特征。
Key Takeaways
- 自监督学习模型在语音情感识别中表现出有效性。
- 跨语言情境下的语音情感识别研究仍然有限。
- 进行了人类与自监督学习模型的性能对比分析,包括层级分析和参数优化微调策略。
- 适当的知识迁移使模型能适应目标语言,并接近母语者的性能。
- 方言对跨语言语音情感识别有重要影响,特别是对那些没有语言学和语用学背景的人。
- 人类和模型在不同情感下表现出不同的行为特征。
点此查看论文截图

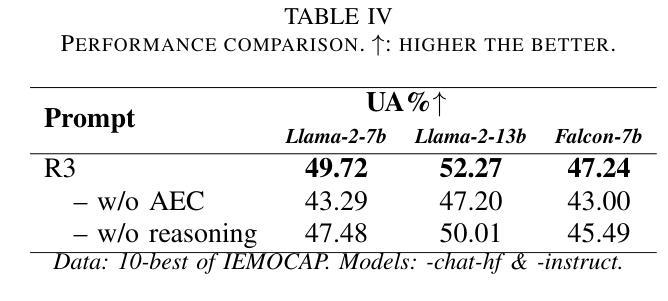
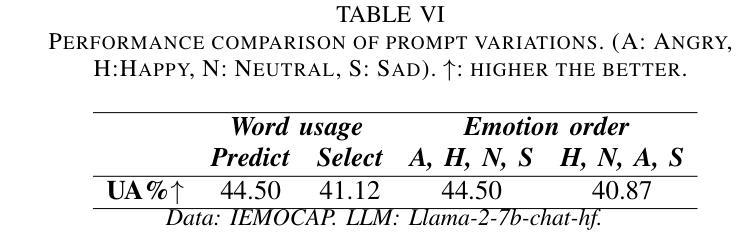
Revise, Reason, and Recognize: LLM-Based Emotion Recognition via Emotion-Specific Prompts and ASR Error Correction
Authors:Yuanchao Li, Yuan Gong, Chao-Han Huck Yang, Peter Bell, Catherine Lai
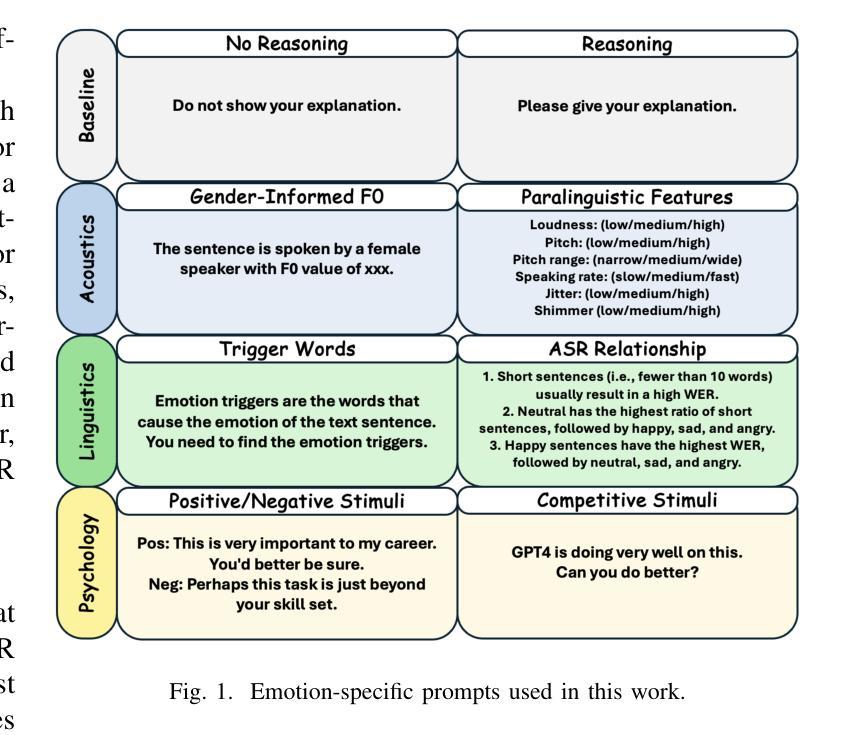
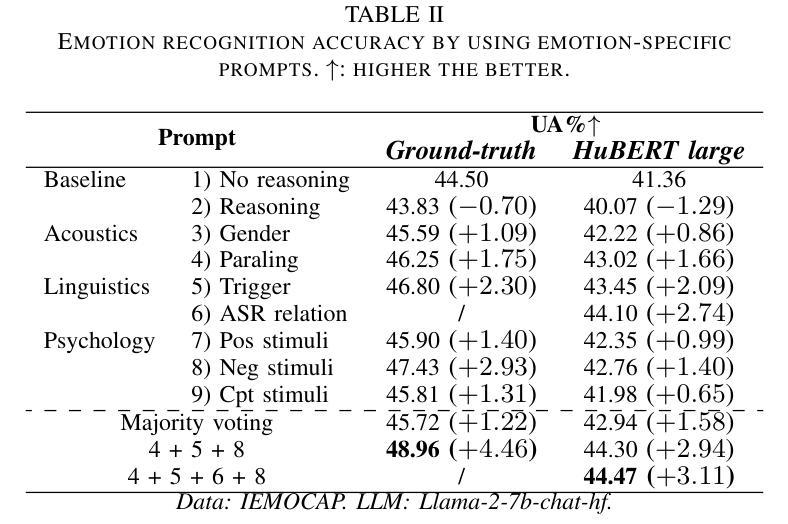
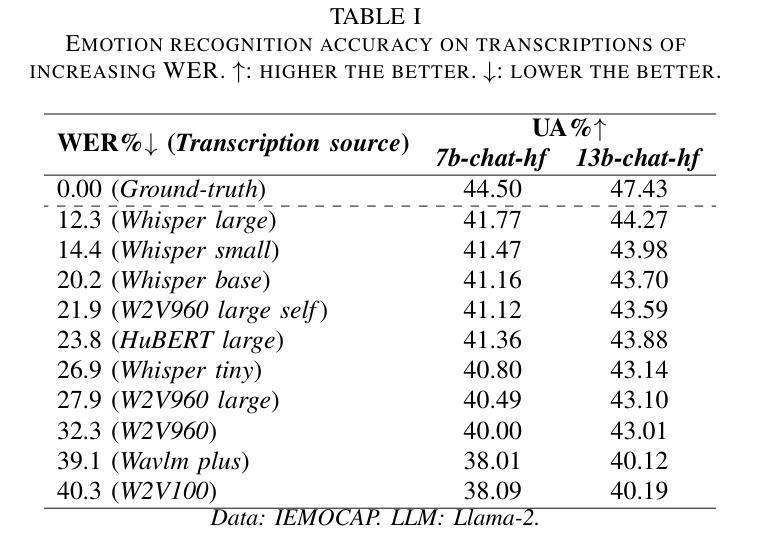
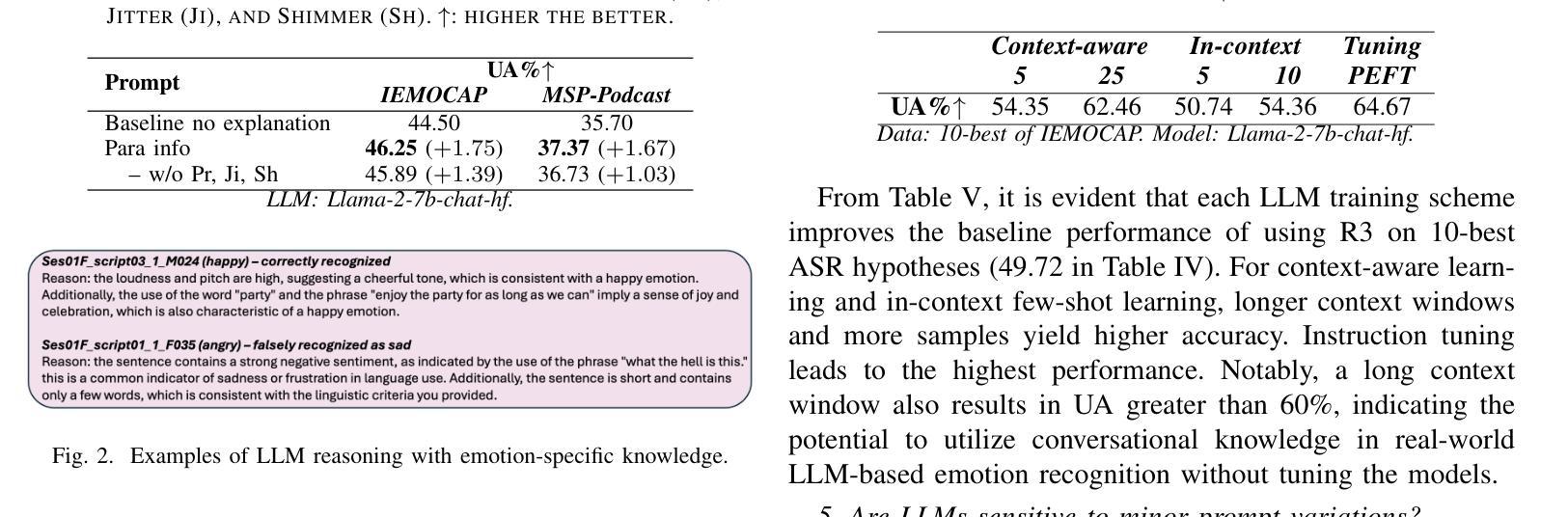
Annotating and recognizing speech emotion using prompt engineering has recently emerged with the advancement of Large Language Models (LLMs), yet its efficacy and reliability remain questionable. In this paper, we conduct a systematic study on this topic, beginning with the proposal of novel prompts that incorporate emotion-specific knowledge from acoustics, linguistics, and psychology. Subsequently, we examine the effectiveness of LLM-based prompting on Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) transcription, contrasting it with ground-truth transcription. Furthermore, we propose a Revise-Reason-Recognize prompting pipeline for robust LLM-based emotion recognition from spoken language with ASR errors. Additionally, experiments on context-aware learning, in-context learning, and instruction tuning are performed to examine the usefulness of LLM training schemes in this direction. Finally, we investigate the sensitivity of LLMs to minor prompt variations. Experimental results demonstrate the efficacy of the emotion-specific prompts, ASR error correction, and LLM training schemes for LLM-based emotion recognition. Our study aims to refine the use of LLMs in emotion recognition and related domains.
随着大型语言模型(LLMs)的进步,使用提示工程进行语音情感的标注和识别最近开始显现,但其有效性和可靠性仍存在疑问。在本文中,我们对这一主题进行了系统研究,首先提出了融入声学、语言学和心理学中的情感特定知识的新提示。随后,我们研究了基于LLM的提示在自动语音识别(ASR)转录上的有效性,并将其与真实转录进行了对比。此外,我们还为存在ASR错误的口语情感识别提出了修订、推理、识别的提示管道。另外,我们还进行了关于情境感知学习、上下文学习和指令调整的试验,以检验LLM训练方案在此方向上的实用性。最后,我们研究了LLMs对微小提示变化的敏感性。实验结果证明了情感特定提示、ASR错误修正和LLM训练方案在基于LLM的情感识别中的有效性。本研究旨在完善LLMs在情感识别和相关领域的应用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICASSP 2025
Summary
随着大型语言模型(LLMs)的发展,通过提示工程进行语音情感标注和识别已成为新兴研究领域。本文提出了一系列包含声学、语言学和心理学情感特定知识的新型提示,并系统地研究了其在自动语音识别(ASR)转录上的效果。此外,本文还提出了一种Revise-Reason-Recognize的提示流程,用于在存在语音识别错误的情况下,实现稳健的基于LLM的情感识别。通过实验,本文验证了情感特定提示、ASR误差校正和LLM训练方案在LLM情感识别中的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在语音情感识别中通过提示工程进行应用。
- 提出了包含声学、语言学和心理学情感特定知识的新型提示。
- 研究了新型提示在自动语音识别(ASR)转录上的效果。
- 提出了Revise-Reason-Recognize的提示流程,用于稳健的基于LLM的情感识别。
- 验证了情感特定提示、ASR误差校正和LLM训练方案的有效性。
- 进行了关于上下文学习、即时学习和指令调整的实验,以检验LLM训练方案在此方向的有用性。
- 研究了LLMs对微小提示变化的敏感性。
点此查看论文截图