⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-02 更新
Talk Before You Retrieve: Agent-Led Discussions for Better RAG in Medical QA
Authors:Xuanzhao Dong, Wenhui Zhu, Hao Wang, Xiwen Chen, Peijie Qiu, Rui Yin, Yi Su, Yalin Wang
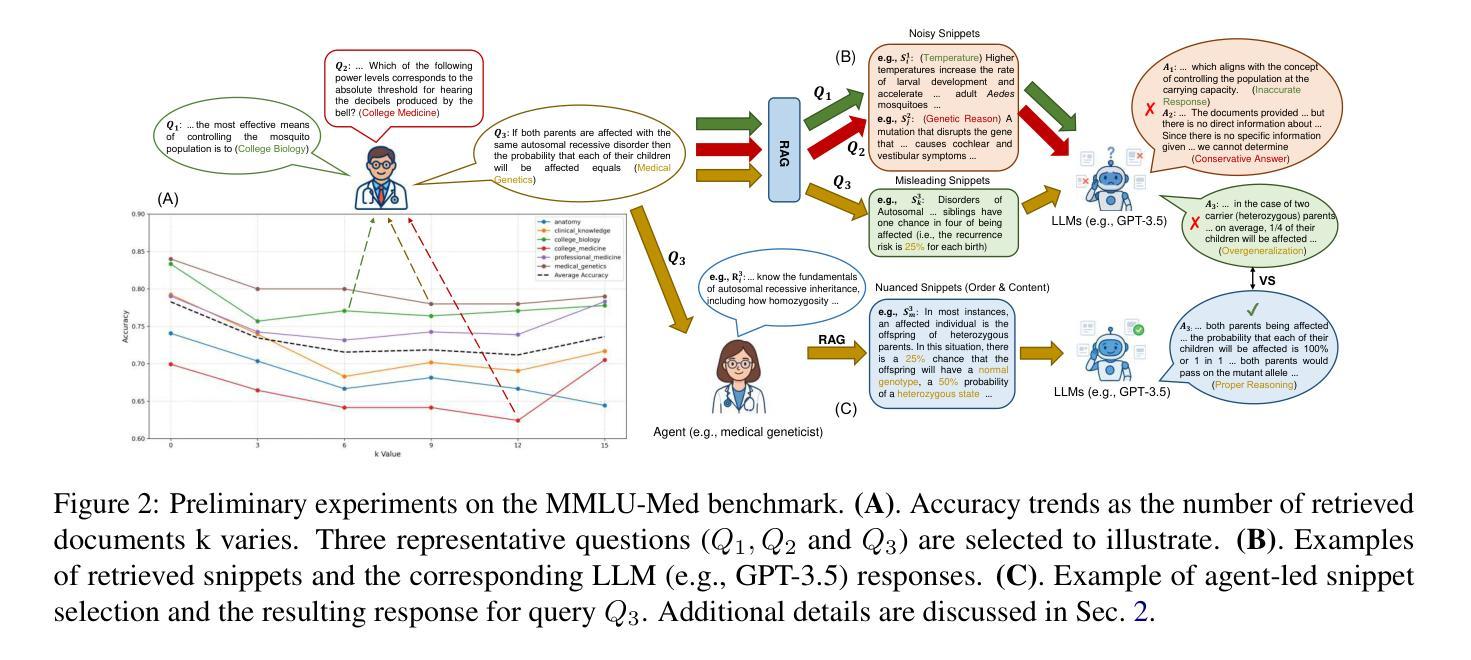
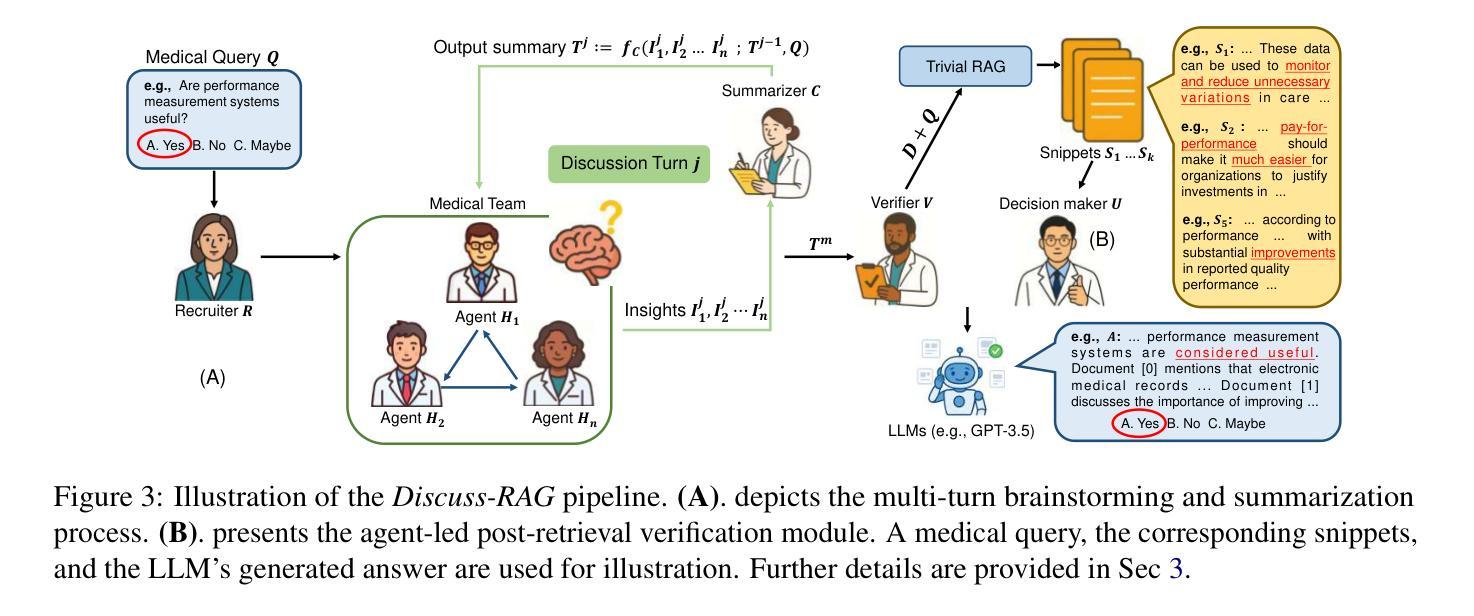
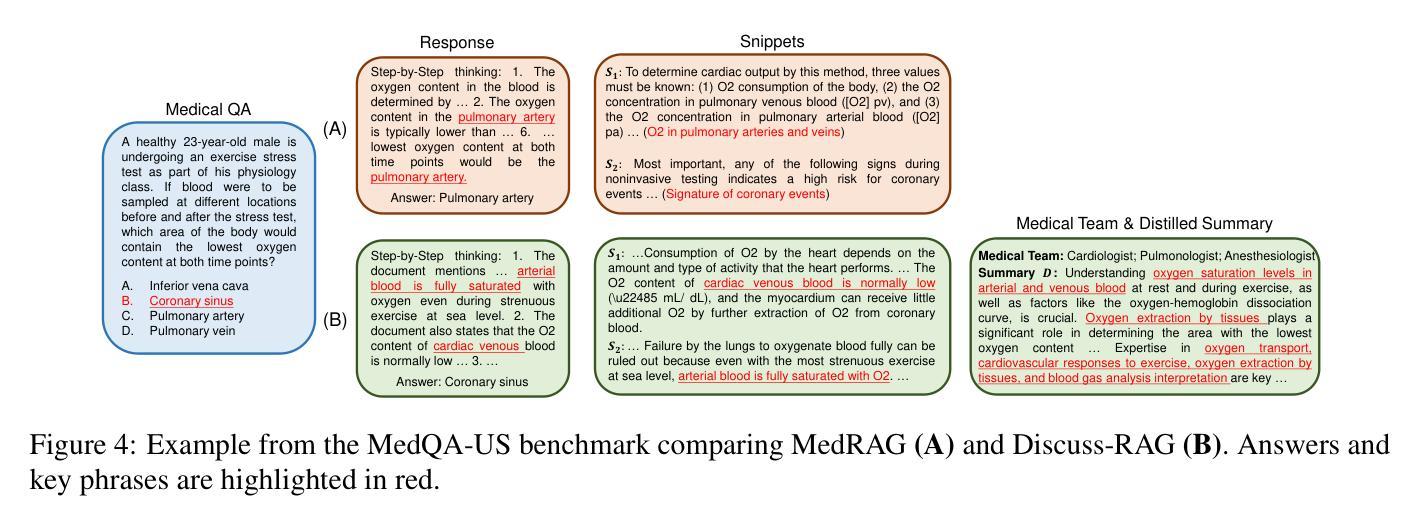
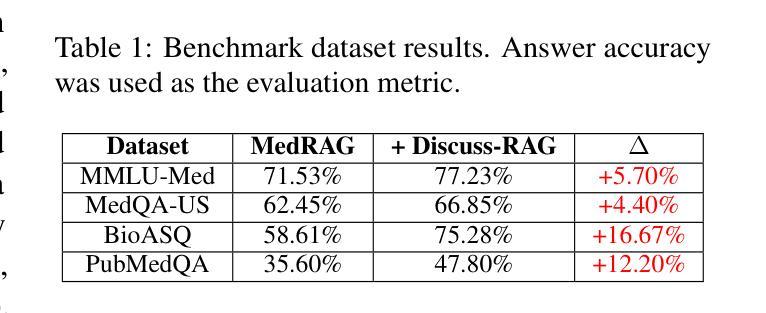
Medical question answering (QA) is a reasoning-intensive task that remains challenging for large language models (LLMs) due to hallucinations and outdated domain knowledge. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) provides a promising post-training solution by leveraging external knowledge. However, existing medical RAG systems suffer from two key limitations: (1) a lack of modeling for human-like reasoning behaviors during information retrieval, and (2) reliance on suboptimal medical corpora, which often results in the retrieval of irrelevant or noisy snippets. To overcome these challenges, we propose Discuss-RAG, a plug-and-play module designed to enhance the medical QA RAG system through collaborative agent-based reasoning. Our method introduces a summarizer agent that orchestrates a team of medical experts to emulate multi-turn brainstorming, thereby improving the relevance of retrieved content. Additionally, a decision-making agent evaluates the retrieved snippets before their final integration. Experimental results on four benchmark medical QA datasets show that Discuss-RAG consistently outperforms MedRAG, especially significantly improving answer accuracy by up to 16.67% on BioASQ and 12.20% on PubMedQA. The code is available at: https://github.com/LLM-VLM-GSL/Discuss-RAG.
医疗问答(QA)是一项需要大量推理的任务,对于大型语言模型(LLM)来说仍然具有挑战性,因为存在虚构和过时的领域知识问题。检索增强生成(RAG)通过利用外部知识提供了一种有前景的后期训练解决方案。然而,现有的医疗RAG系统存在两个主要局限性:(1)在信息检索过程中缺乏人类式推理行为的建模;(2)依赖于次优的医疗语料库,这往往导致检索到不相关或嘈杂的片段。为了克服这些挑战,我们提出了Discuss-RAG,这是一个即插即用的模块,旨在通过基于协作代理的推理来增强医疗问答RAG系统。我们的方法引入了一个总结代理,该代理协调医疗专家团队,以模拟多轮头脑风暴,从而提高检索内容的关联性。此外,一个决策代理在最终整合之前评估检索到的片段。在四个基准医疗问答数据集上的实验结果表明,Discuss-RAG始终优于MedRAG,特别是在BioASQ和PubMedQA上,答案准确率提高了16.67%和12.20%。代码可在以下网址找到:Discuss-RAG链接。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
讨论一种名为Discuss-RAG的新型问答增强技术,旨在解决大型语言模型在医学问答方面的挑战。通过引入摘要生成器和决策制定器,该技术能够模拟多轮讨论以提高检索内容的准确性,并在多个基准医学问答数据集上实现显著的性能提升。Discuss-RAG在BioASQ和PubMedQA上的回答准确率分别提高了高达16.67%和12.20%。代码已公开在GitHub上。
Key Takeaways:
- 大型语言模型在医学问答任务中面临挑战,如幻觉和过时领域知识的问题。
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation(RAG)通过利用外部知识提供了一种有前景的模型后训练解决方案。
- 当前医学RAG系统存在两个主要局限性:缺乏人类推理行为的建模和依赖次优医学语料库导致检索结果不相关或嘈杂。
- Discuss-RAG作为一种即插即用的模块被提出,旨在通过协作式基于代理的推理改进医学问答RAG系统。
- Discuss-RAG引入摘要生成器代理来协调医疗专家团队,模拟多轮讨论,提高检索内容的关联性。
- Discuss-RAG还包含一个决策制定代理,用于评估检索到的片段并在最终集成之前对其进行筛选。
点此查看论文截图

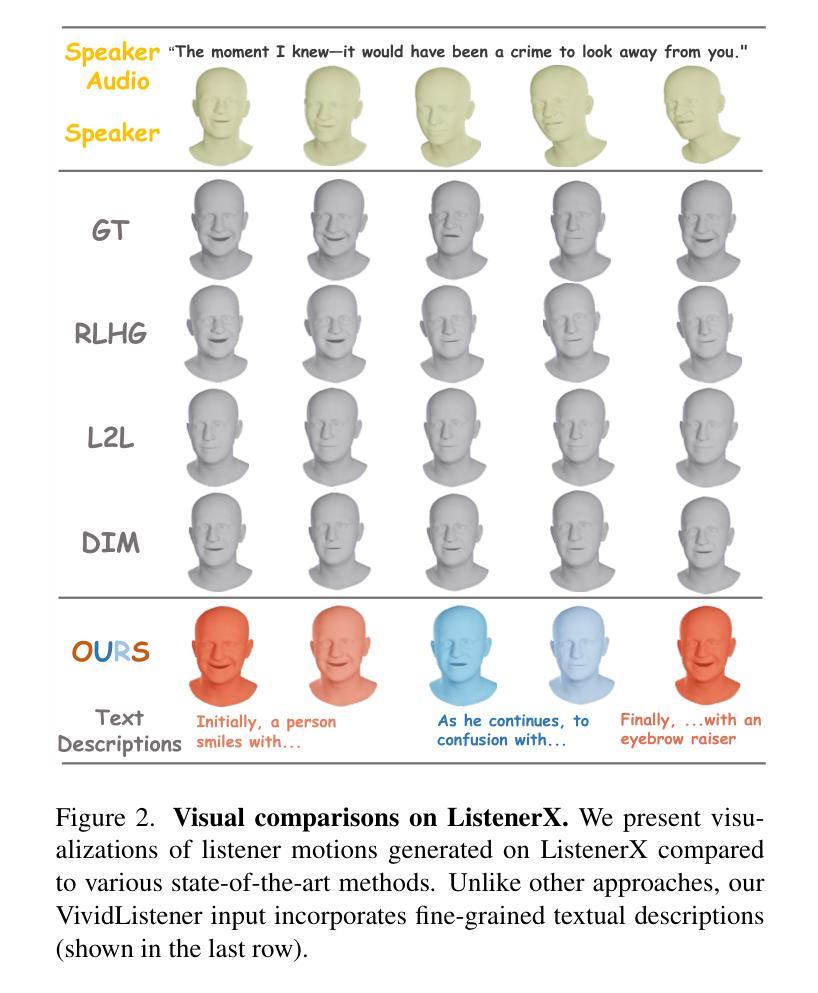
Ditto: Motion-Space Diffusion for Controllable Realtime Talking Head Synthesis
Authors:Tianqi Li, Ruobing Zheng, Minghui Yang, Jingdong Chen, Ming Yang
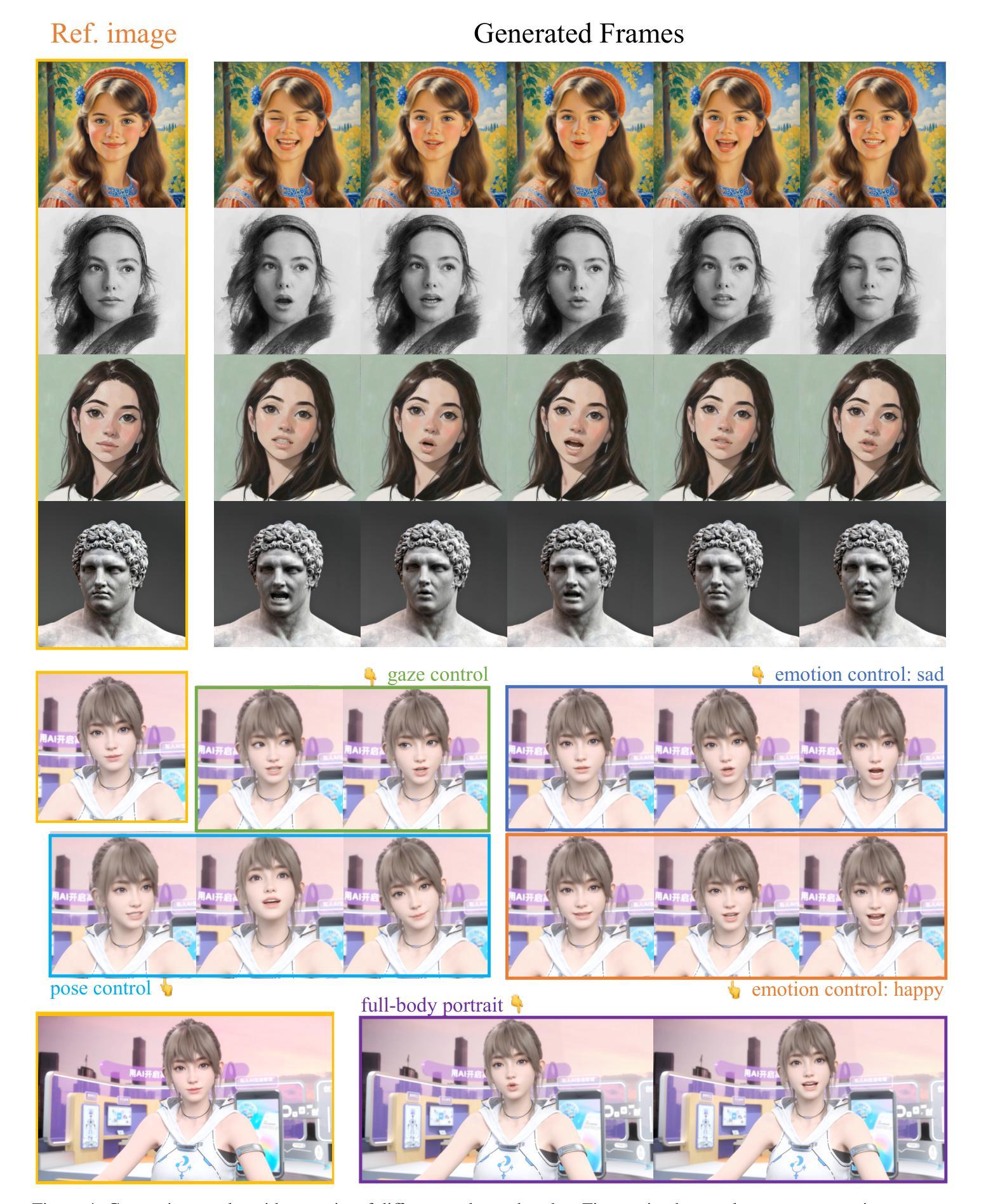
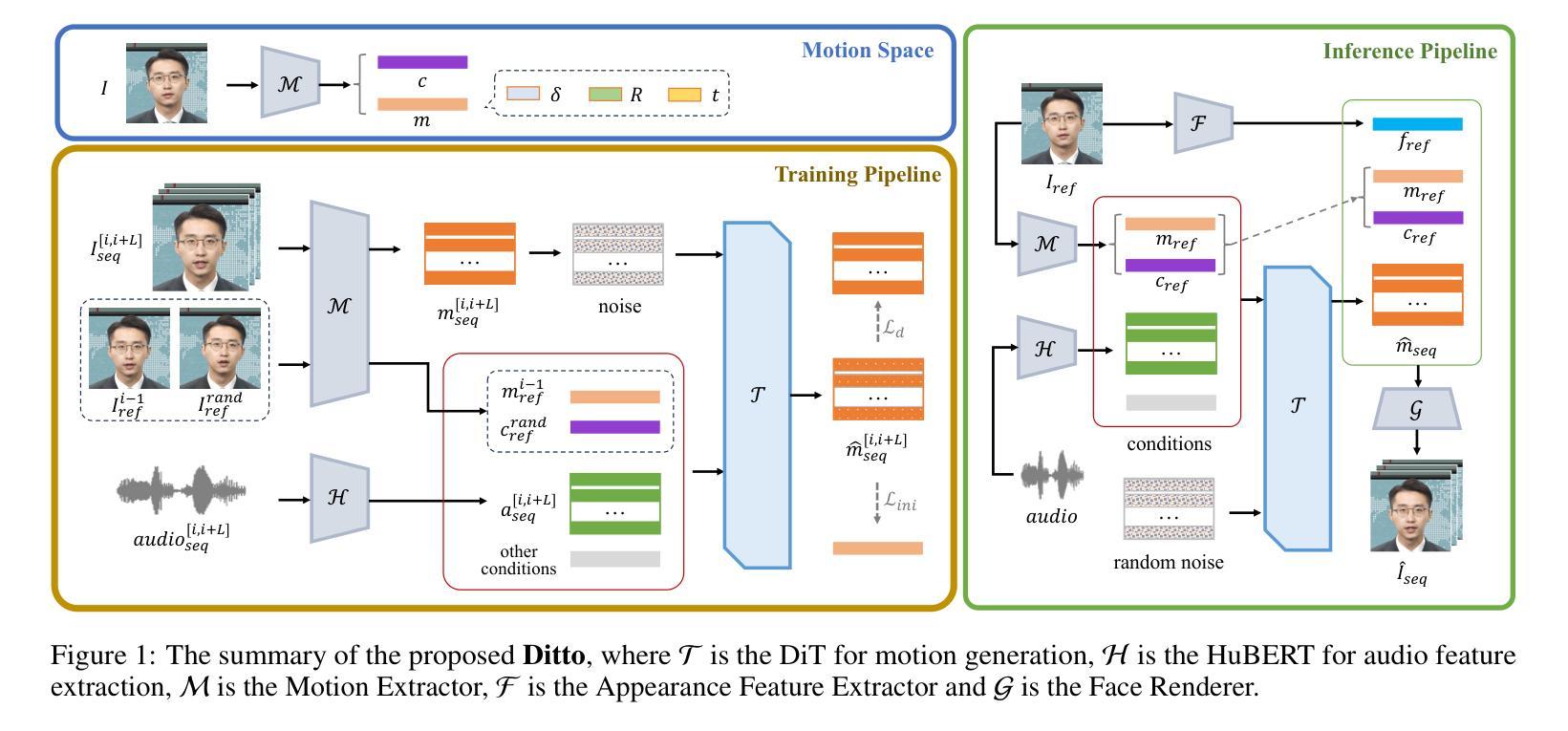
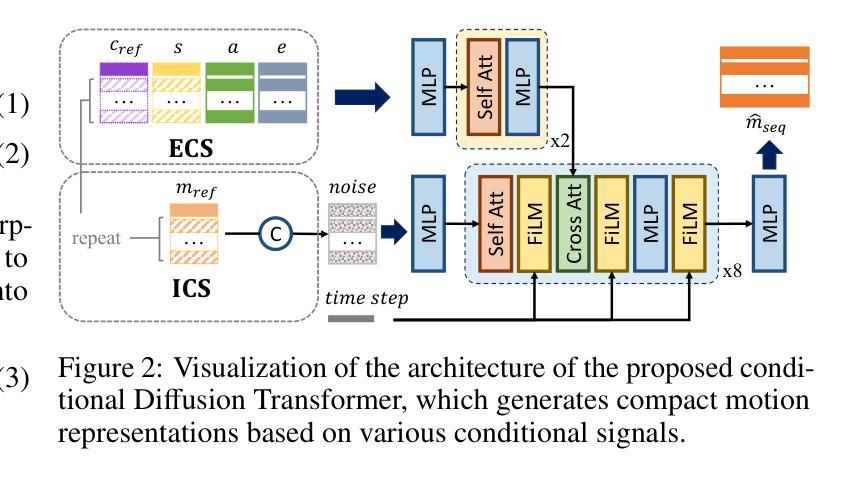
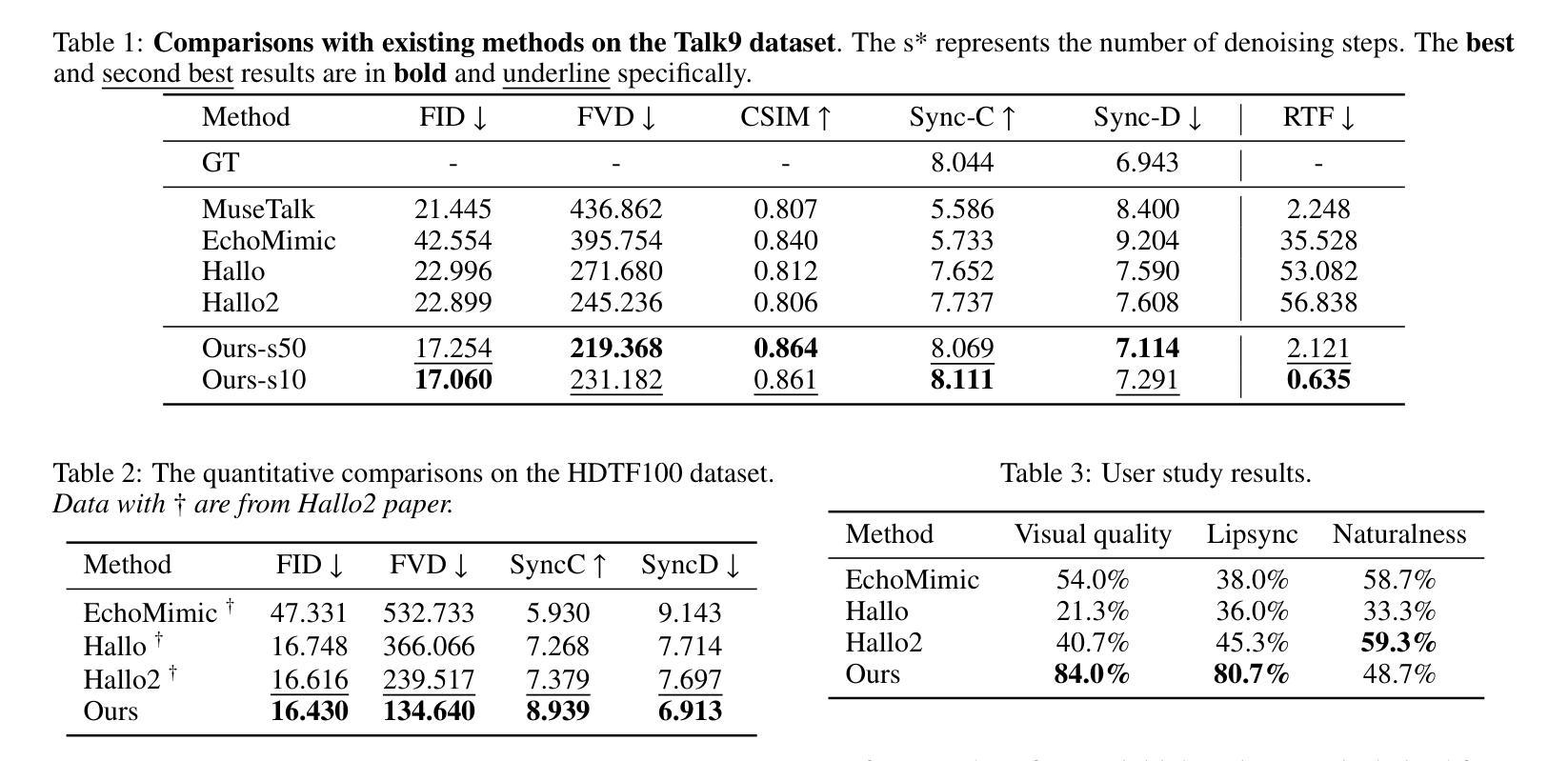
Recent advances in diffusion models have endowed talking head synthesis with subtle expressions and vivid head movements, but have also led to slow inference speed and insufficient control over generated results. To address these issues, we propose Ditto, a diffusion-based talking head framework that enables fine-grained controls and real-time inference. Specifically, we utilize an off-the-shelf motion extractor and devise a diffusion transformer to generate representations in a specific motion space. We optimize the model architecture and training strategy to address the issues in generating motion representations, including insufficient disentanglement between motion and identity, and large internal discrepancies within the representation. Besides, we employ diverse conditional signals while establishing a mapping between motion representation and facial semantics, enabling control over the generation process and correction of the results. Moreover, we jointly optimize the holistic framework to enable streaming processing, real-time inference, and low first-frame delay, offering functionalities crucial for interactive applications such as AI assistants. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that Ditto generates compelling talking head videos and exhibits superiority in both controllability and real-time performance.
最近扩散模型的进展赋予了说话人头部合成微妙的表情和生动的头部动作,但也导致了推理速度较慢以及对生成结果的控制不足。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了Ditto,这是一个基于扩散的说话人头部框架,能够实现精细控制和实时推理。具体来说,我们利用现成的运动提取器,并设计了一个扩散变压器来在特定的运动空间中生成表示。我们优化了模型架构和训练策略,以解决运动表示生成中的问题,包括运动与身份之间缺乏足够的解耦以及表示内部的巨大差异。此外,在建立运动表示和面部语义之间的映射时,我们采用了多种条件信号,实现对生成过程的控制和结果的校正。而且,我们联合优化了整体框架,以实现流式处理、实时推理和低首帧延迟,这对于人工智能助手等交互式应用至关重要。大量的实验结果表明,Ditto生成的说话人头部视频令人信服,在可控性和实时性能方面都表现出优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://digital-avatar.github.io/ai/Ditto/
Summary
扩散模型的新进展为说话人头部合成提供了细微的表情和生动的头部动作,但同时也带来了推理速度慢和对生成结果控制不足的问题。为解决这些问题,我们提出了Ditto,这是一个基于扩散的说话人头部合成框架,能够实现精细控制和实时推理。我们通过优化模型架构和训练策略,解决了运动表示生成中的问题,包括运动与身份之间缺乏足够的解耦以及表示内部差异较大。此外,我们在建立运动表示和面部语义的映射时,采用了多种条件信号,可以控制生成过程并修正结果。同时,我们联合优化了整体框架,实现了流式处理、实时推理和低首帧延迟,为人工智能助手等交互式应用提供了关键功能。实验结果证明,Ditto生成的说话人头部视频令人信服,在可控性和实时性能方面都表现出优势。
Key Takeaways
- Ditto是一个基于扩散模型的说话头合成框架,旨在解决现有模型推理速度慢和对生成结果控制不足的问题。
- 通过优化模型架构和训练策略,解决了运动表示生成中的关键问题,包括运动与身份解耦不足以及表示内部差异大。
- 利用多种条件信号建立运动表示和面部语义的映射,增强了对生成过程的控制并可以修正结果。
- 联合优化框架以实现流式处理、实时推理和低首帧延迟,适用于交互式应用。
- 实验结果证明Ditto在生成高质量说话头视频的同时,具有优越的控制性和实时性能。
- Ditto框架包括一个现成的运动提取器和扩散变压器,用于在特定运动空间中生成表示。
点此查看论文截图