⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-02 更新
Rethinking Visual Layer Selection in Multimodal LLMs
Authors:Haoran Chen, Junyan Lin, Xinhao Chen, Yue Fan, Xin Jin, Hui Su, Jianfeng Dong, Jinlan Fu, Xiaoyu Shen
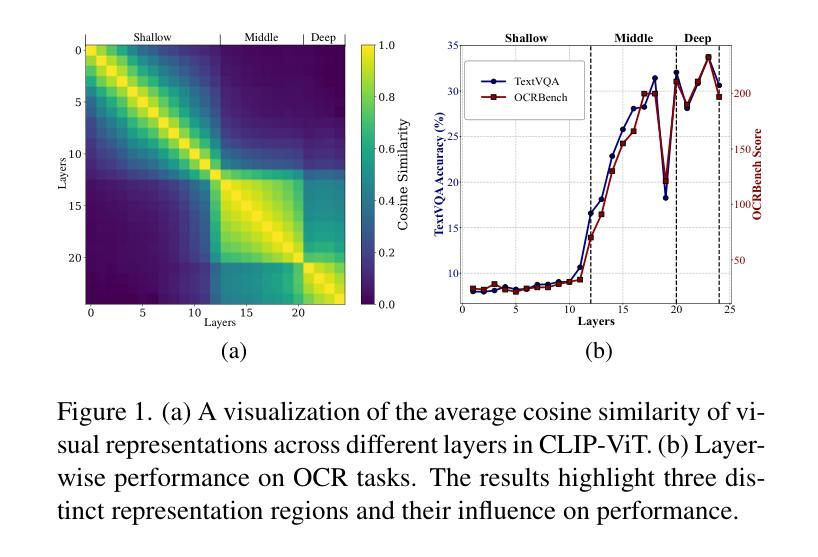
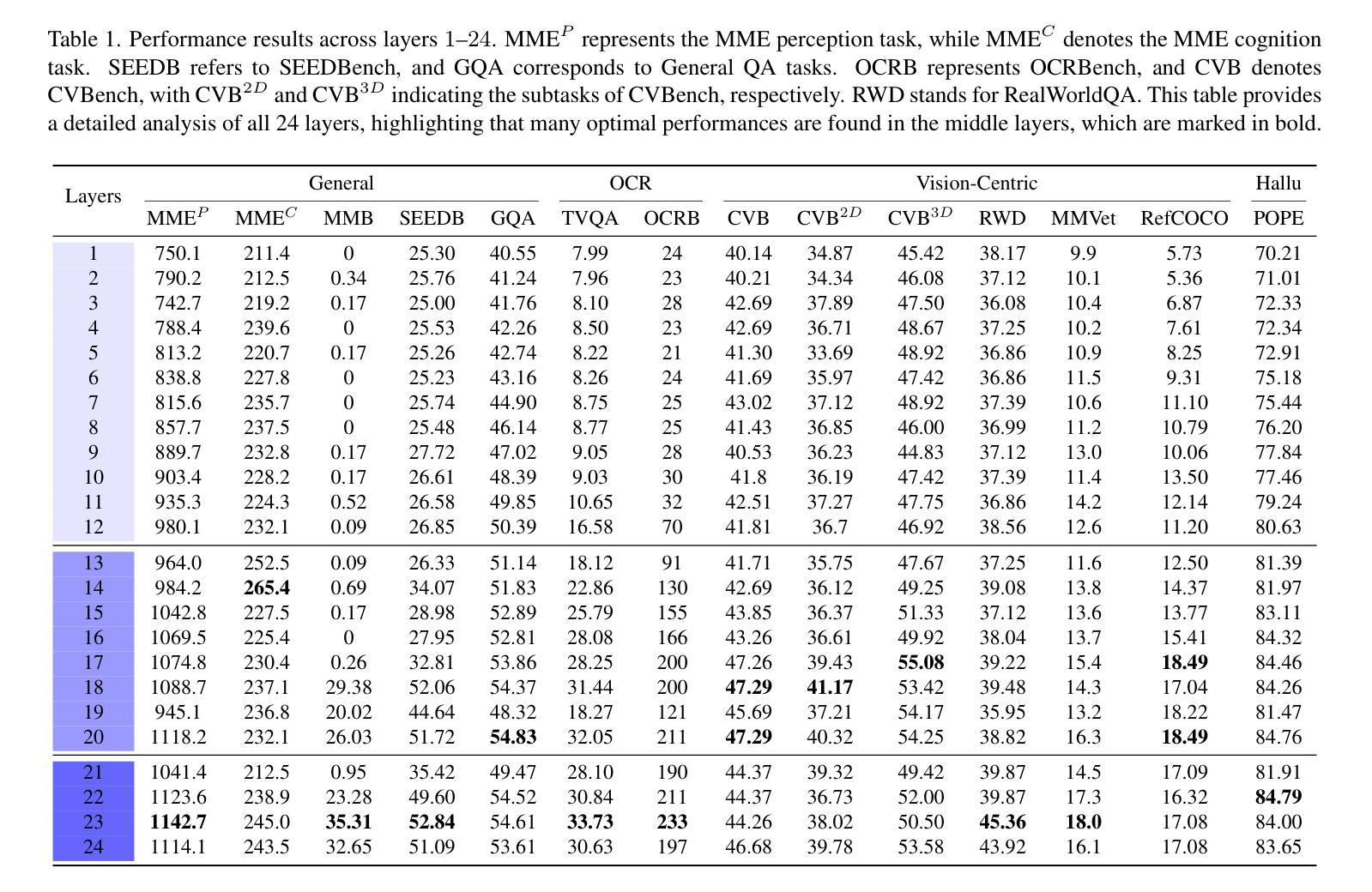
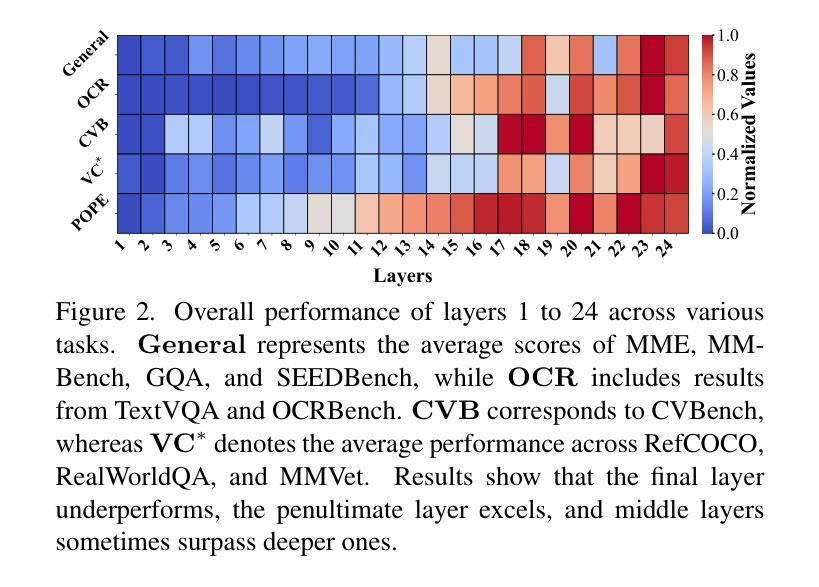
Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have achieved impressive performance across a wide range of tasks, typically using CLIP-ViT as their visual encoder due to its strong text-image alignment capabilities. While prior studies suggest that different CLIP-ViT layers capture different types of information, with shallower layers focusing on fine visual details and deeper layers aligning more closely with textual semantics, most MLLMs still select visual features based on empirical heuristics rather than systematic analysis. In this work, we propose a Layer-wise Representation Similarity approach to group CLIP-ViT layers with similar behaviors into {shallow, middle, and deep} categories and assess their impact on MLLM performance. Building on this foundation, we revisit the visual layer selection problem in MLLMs at scale, training LLaVA-style models ranging from 1.4B to 7B parameters. Through extensive experiments across 10 datasets and 4 tasks, we find that: (1) deep layers are essential for OCR tasks; (2) shallow and middle layers substantially outperform deep layers on reasoning tasks involving counting, positioning, and object localization; (3) a lightweight fusion of features across shallow, middle, and deep layers consistently outperforms specialized fusion baselines and single-layer selections, achieving gains on 9 out of 10 datasets. Our work offers the first principled study of visual layer selection in MLLMs, laying the groundwork for deeper investigations into visual representation learning for MLLMs.
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在多种任务中取得了令人印象深刻的性能,通常使用CLIP-ViT作为其视觉编码器,因其强大的文本-图像对齐能力。尽管先前的研究表明,不同的CLIP-ViT层捕获不同类型的信息,较浅的层专注于精细的视觉细节,而较深的层更紧密地与文本语义对齐,但大多数MLLMs仍然基于经验启发式而不是系统分析选择视觉特征。在本研究中,我们提出了一种分层表示相似性方法,将具有相似行为的CLIP-ViT层分为{浅、中、深}类别,并评估它们对MLLM性能的影响。在此基础上,我们在大规模MLLMs中重新研究了视觉层选择问题,训练了从1.4B到7B参数的LLaVA风格模型。通过10个数据集和4项任务的广泛实验,我们发现:(1)深层对于OCR任务至关重要;(2)浅层和中间层在涉及计数、定位和对象定位的理由任务上显著优于深层;(3)浅、中和深层特征之间的轻量级融合持续优于专用融合基准线和单层选择,在9个数据集中实现了收益。我们的工作首次对MLLMs中的视觉层选择进行了原则性研究,为MLLMs的视觉表示学习的深入研究奠定了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 4 figures, submitted to ICCV 2025
Summary
基于CLIP-ViT的分层特性,本文提出一种基于层表示相似性的方法,将CLIP-ViT层分为浅、中、深三类,并评估其对多模态大型语言模型性能的影响。实验结果显示,不同层在特定任务中的表现各有优劣,而跨层融合能带来性能提升。
Key Takeaways
- CLIP-ViT的不同层捕获不同类型的信息,浅层关注视觉细节,深层与文本语义更对齐。
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在广泛的任务上表现出色,通常使用CLIP-ViT作为其视觉编码器。
- 提出一种基于层表示相似性的方法,将CLIP-ViT层分类。
- 深层对于光学字符识别(OCR)任务至关重要。
- 浅层和中间层在涉及计数、定位和对象识别的推理任务上表现较好。
- 跨浅、中、深层的融合优于单一层选择和基线融合方法,并在多数数据集上实现性能提升。
点此查看论文截图


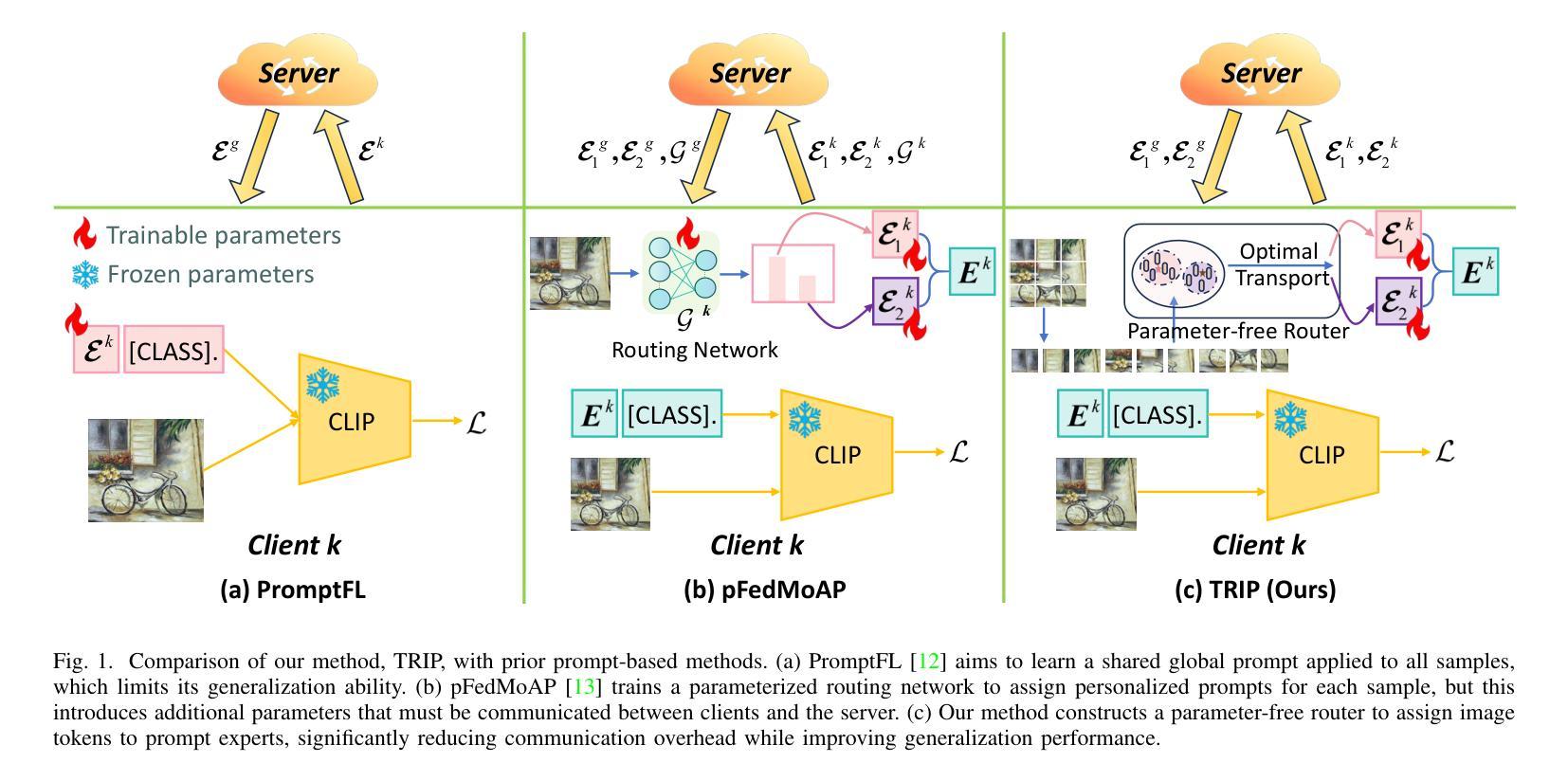
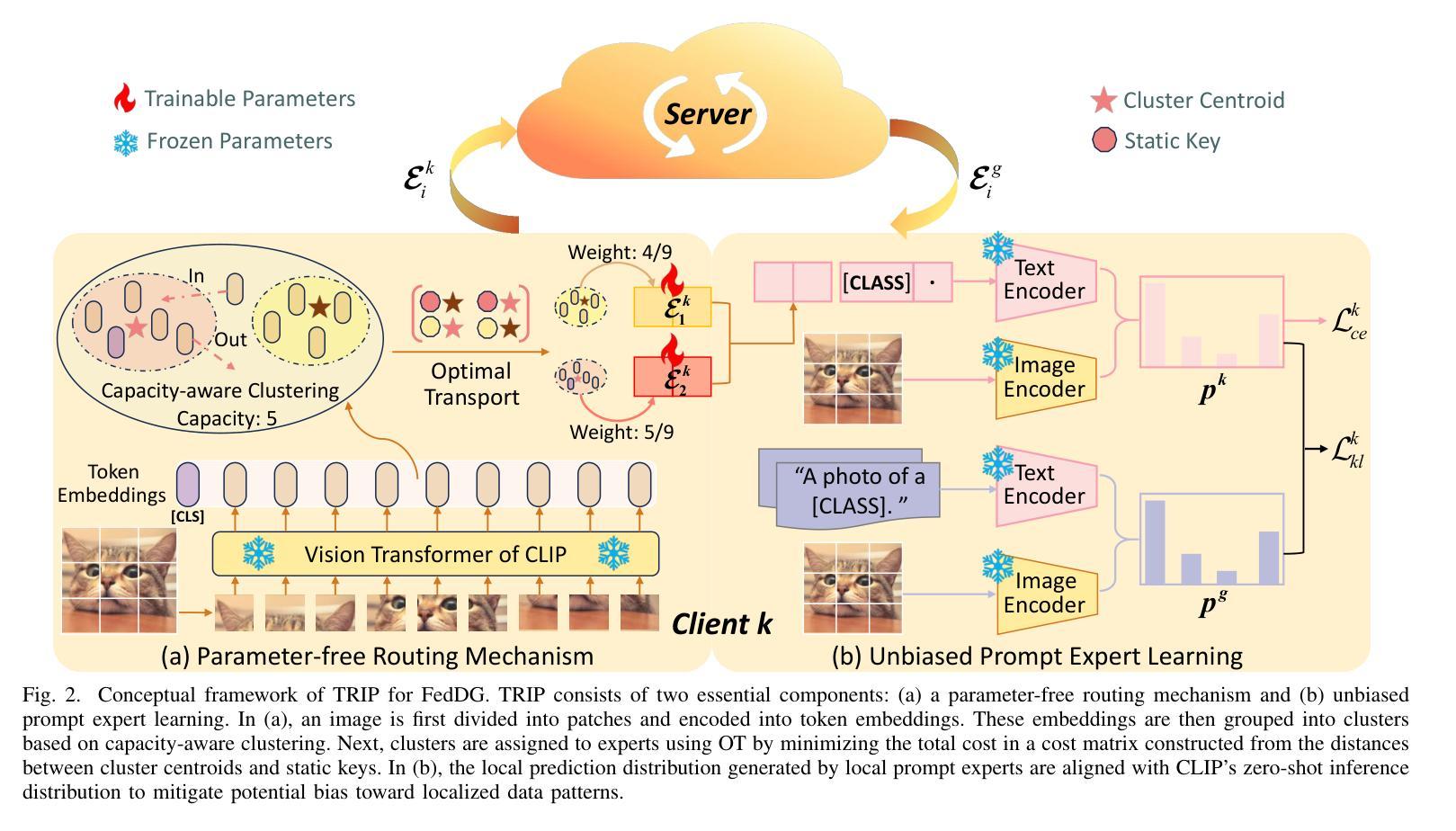
Token-Level Prompt Mixture with Parameter-Free Routing for Federated Domain Generalization
Authors:Shuai Gong, Chaoran Cui, Xiaolin Dong, Xiushan Nie, Lei Zhu, Xiaojun Chang
Federated domain generalization (FedDG) aims to learn a globally generalizable model from decentralized clients with heterogeneous data while preserving privacy. Recent studies have introduced prompt learning to adapt vision-language models (VLMs) in FedDG by learning a single global prompt. However, such a one-prompt-fits-all learning paradigm typically leads to performance degradation on personalized samples. Although the mixture of experts (MoE) offers a promising solution for specialization, existing MoE-based methods suffer from coarse image-level expert assignment and high communication costs from parameterized routers. To address these limitations, we propose TRIP, a Token-level prompt mixture with parameter-free routing framework for FedDG, which treats multiple prompts as distinct experts. Unlike existing image-level routing designs, TRIP assigns different tokens within an image to specific experts. To ensure communication efficiency, TRIP incorporates a parameter-free routing mechanism based on token clustering and optimal transport. The instance-specific prompt is then synthesized by aggregating experts, weighted by the number of tokens assigned to each. Additionally, TRIP develops an unbiased learning strategy for prompt experts, leveraging the VLM’s zero-shot generalization capability. Extensive experiments across four benchmarks demonstrate that TRIP achieves optimal generalization results, with communication of only 1K parameters per round. Our code is available at https://github.com/GongShuai8210/TRIP.
联邦域泛化(FedDG)旨在从分散的客户端学习全局可泛化的模型,这些客户端拥有异质数据,同时保护隐私。近期的研究引入了提示学习(prompt learning),以在FedDG中适应视觉语言模型(VLM)。通过学习一个单一的全局提示来实现这一点。然而,这种一刀切的学习模式通常会导致个性化样本的性能下降。虽然混合专家(MoE)为专业化提供了有前途的解决方案,但现有的基于MoE的方法受到了粗粒度图像级专家分配和参数化路由器高通信成本的影响。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了TRIP,这是一个基于Token的提示混合(Token-level prompt mixture)用于FedDG的参数免费路由框架,它将多个提示视为不同的专家。与现有的图像级路由设计不同,TRIP将图像内的不同令牌分配给特定的专家。为确保通信效率,TRIP结合了一种基于令牌聚类和最优传输的无参数路由机制。特定实例的提示是通过根据分配给每个专家的令牌数量进行加权的专家聚合来合成的。此外,TRIP为提示专家开发了无偏见的学习策略,利用VLM的零样本泛化能力。在四个基准测试上的广泛实验表明,TRIP实现了最佳泛化结果,每轮通信仅使用1K个参数。我们的代码可在https://github.com/GongShuai8210/TRIP获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The manuscript has been submitted to IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering
Summary:
针对联邦域泛化(FedDG)问题,提出了一种名为TRIP的基于token级别的提示混合与无参数路由框架的方法。该方法旨在从分散的客户端学习全局可泛化的模型,同时处理异质数据并保护隐私。它通过为图像内的不同token分配特定专家来解决单一全局提示学习模式在个性化样本上性能下降的问题。此外,它采用基于token聚类和最优传输的无参数路由机制,确保了通信效率,并开发了一种无偏见的学习策略,利用VLM的零样本泛化能力。实验证明,该方法在四个基准测试中实现了最佳泛化结果,每轮通信仅需传输1K参数。
Key Takeaways:
- FedDG旨在从分散的客户端学习全局可泛化的模型,处理异质数据并保护隐私。
- 现有的一刀切学习模式在个性化样本上性能不佳。
- TRIP方法通过使用基于token级别的提示混合来解决这一问题,为图像内的不同部分分配特定专家。
- TRIP引入了无参数路由框架,基于token聚类和最优传输,提高了通信效率。
- 通过结合专家的预测结果并考虑每个专家的token数量加权来生成实例特定的提示。
- TRIP利用VLM的零样本泛化能力,并开发了无偏见的学习策略。
- 实验结果显示,TRIP在四个基准测试中表现最佳,且通信效率较高。
点此查看论文截图
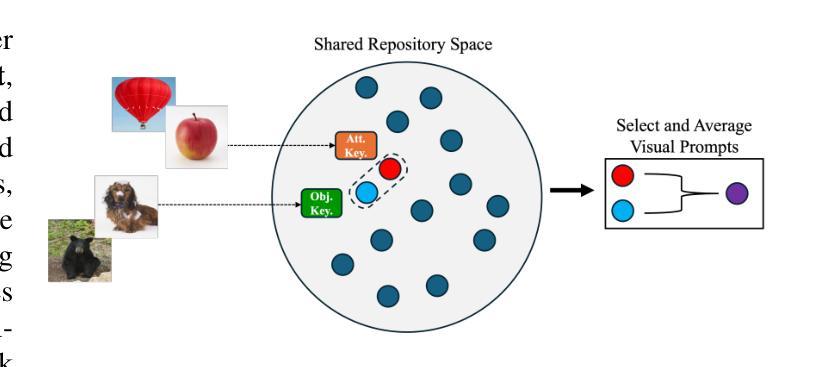
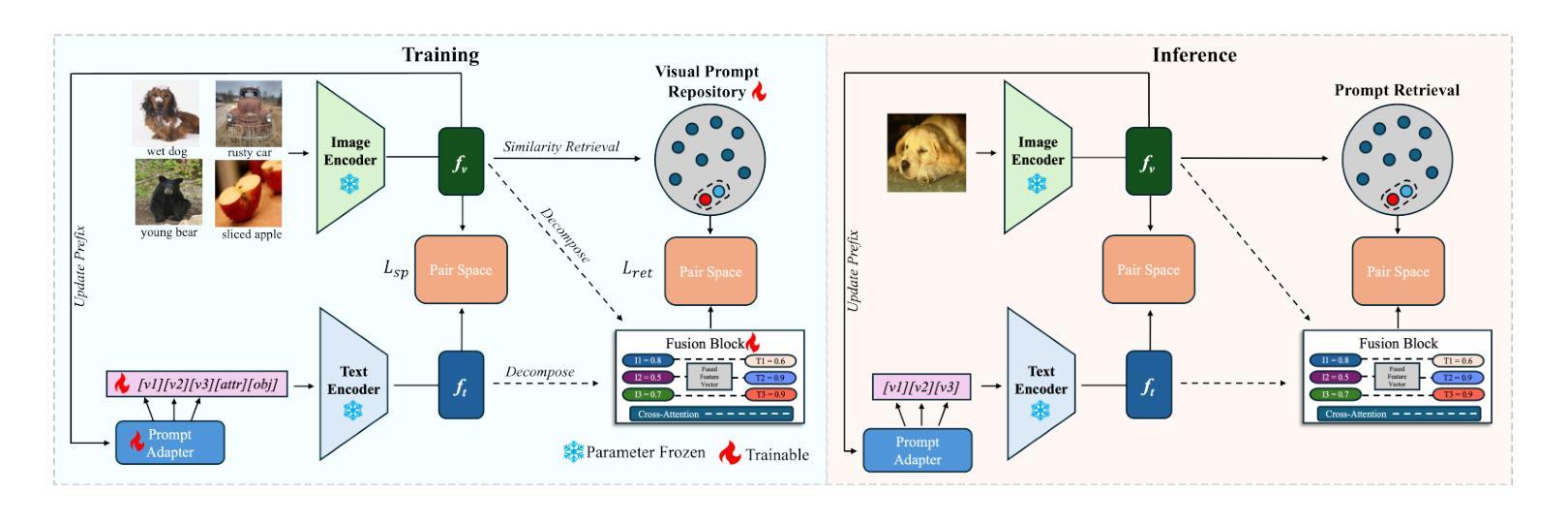
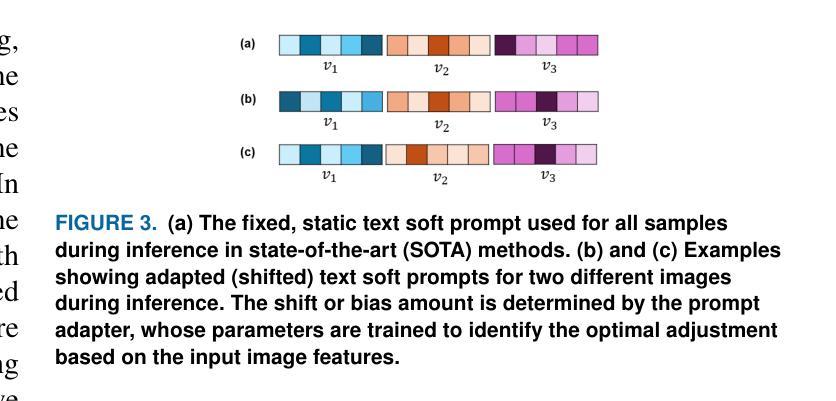
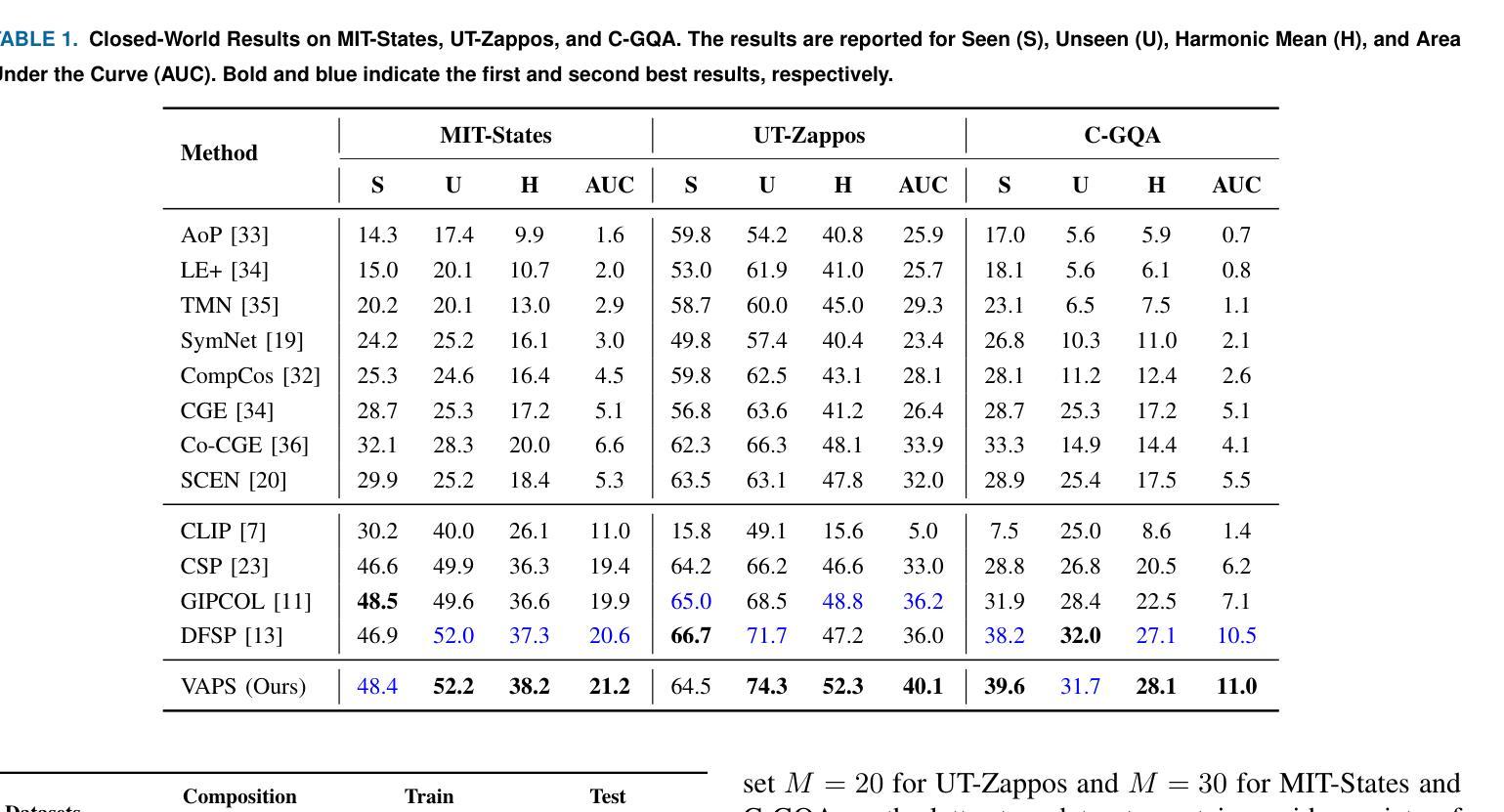
Visual Adaptive Prompting for Compositional Zero-Shot Learning
Authors:Kyle Stein, Arash Mahyari, Guillermo Francia, Eman El-Sheikh
Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have demonstrated impressive capabilities in learning joint representations of visual and textual data, making them powerful tools for tasks such as Compositional Zero-Shot Learning (CZSL). CZSL requires models to generalize to novel combinations of visual primitives-such as attributes and objects-that were not explicitly encountered during training. Recent works in prompting for CZSL have focused on modifying inputs for the text encoder, often using static prompts that do not change across varying visual contexts. However, these approaches struggle to fully capture varying visual contexts, as they focus on text adaptation rather than leveraging visual features for compositional reasoning. To address this, we propose Visual Adaptive Prompting System (VAPS) that leverages a learnable visual prompt repository and similarity-based retrieval mechanism within the framework of VLMs to bridge the gap between semantic and visual features. Our method introduces a dynamic visual prompt repository mechanism that selects the most relevant attribute and object prompts based on the visual features of the image. Our proposed system includes a visual prompt adapter that encourages the model to learn a more generalizable embedding space. Experiments on three CZSL benchmarks, across both closed and open-world scenarios, demonstrate state-of-the-art results.
视觉语言模型(VLMs)在学习视觉和文本数据的联合表示方面表现出了令人印象深刻的能力,使其成为用于组合零射击学习(CZSL)等任务的有力工具。CZSL要求模型能够推广到在训练期间没有明确遇到的新组合的视觉元素,如属性和对象。关于CZSL的近期提示方法主要集中在修改文本编码器的输入,通常使用静态提示,这些提示在多种视觉上下文中不会发生变化。然而,这些方法在捕捉不断变化的视觉上下文方面遇到了困难,因为它们侧重于文本适应,而不是利用视觉特征进行组合推理。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了视觉自适应提示系统(VAPS),该系统利用可学习的视觉提示存储库和基于相似性的检索机制,在视觉语言模型的框架内建立语义和视觉特征之间的桥梁。我们的方法引入了一个动态视觉提示存储库机制,该机制根据图像视觉特征选择最相关的属性和对象提示。我们提出的系统包括一个视觉提示适配器,鼓励模型学习一个更具泛化能力的嵌入空间。在三种CZSL基准测试上的实验,包括封闭和开放世界场景,都取得了最先进的成果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
视觉语言模型(VLMs)在联合表示视觉和文本数据方面表现出强大的能力,尤其在组合零射击学习(CZSL)任务中发挥显著效果。然而,传统的文本输入提示方法在适应性方面存在局限性。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了视觉自适应提示系统(VAPS),该系统利用可学习的视觉提示库和相似性检索机制,在VLMs框架内构建语义和视觉特征之间的桥梁。通过动态视觉提示库机制,我们的方法能够根据图像视觉特征选择最相关的属性和对象提示。实验表明,在三种CZSL基准测试中,我们的系统在封闭和开放世界场景下均达到了最佳效果。
Key Takeaways
- VLMs展现出强大的能力在学习视觉和文本数据的联合表示。
- CZSL任务需要模型对未在训练中明确遇到的新组合的视觉元素进行泛化。
- 传统文本输入提示方法在适应性方面存在局限性。
- 提出的VAPS系统利用视觉自适应提示来解决这个问题。
- VAPS包含一个可学习的视觉提示库和相似性检索机制。
- 动态视觉提示库机制能根据图像视觉特征选择相关属性或对象提示。
点此查看论文截图

PANGAEA: A Global and Inclusive Benchmark for Geospatial Foundation Models
Authors:Valerio Marsocci, Yuru Jia, Georges Le Bellier, David Kerekes, Liang Zeng, Sebastian Hafner, Sebastian Gerard, Eric Brune, Ritu Yadav, Ali Shibli, Heng Fang, Yifang Ban, Maarten Vergauwen, Nicolas Audebert, Andrea Nascetti
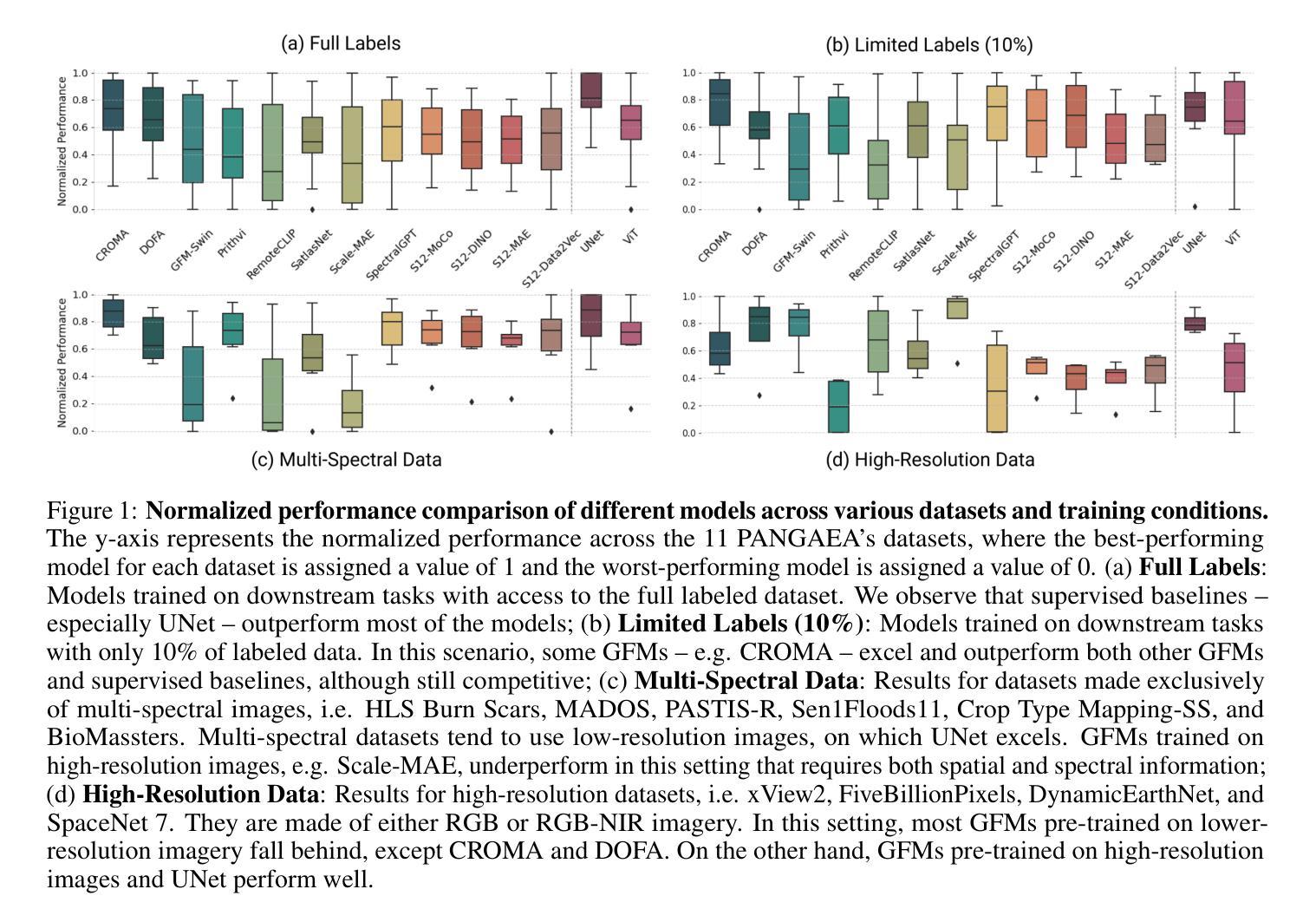
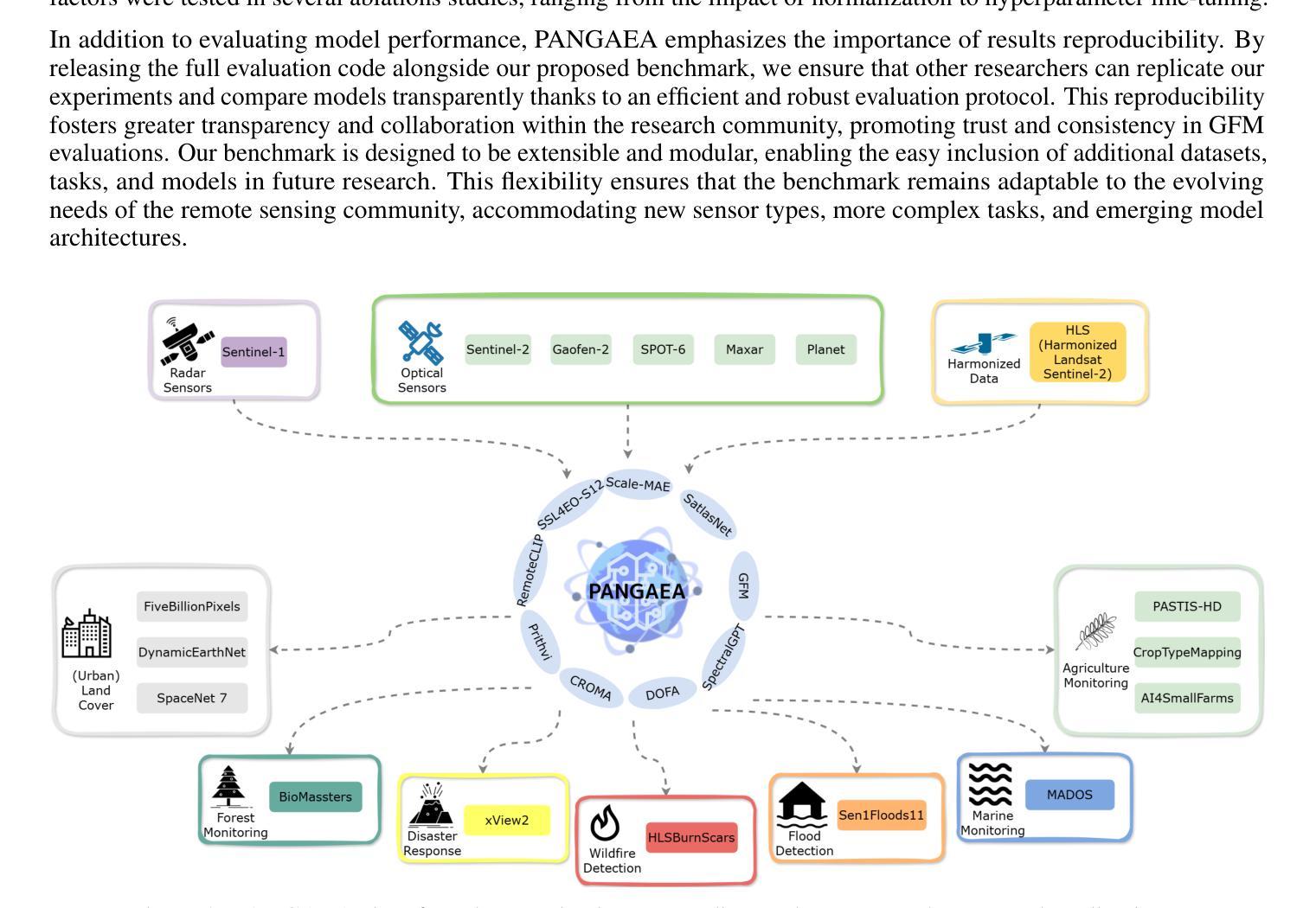
Geospatial Foundation Models (GFMs) have emerged as powerful tools for extracting representations from Earth observation data, but their evaluation remains inconsistent and narrow. Existing works often evaluate on suboptimal downstream datasets and tasks, that are often too easy or too narrow, limiting the usefulness of the evaluations to assess the real-world applicability of GFMs. Additionally, there is a distinct lack of diversity in current evaluation protocols, which fail to account for the multiplicity of image resolutions, sensor types, and temporalities, which further complicates the assessment of GFM performance. In particular, most existing benchmarks are geographically biased towards North America and Europe, questioning the global applicability of GFMs. To overcome these challenges, we introduce PANGAEA, a standardized evaluation protocol that covers a diverse set of datasets, tasks, resolutions, sensor modalities, and temporalities. It establishes a robust and widely applicable benchmark for GFMs. We evaluate the most popular GFMs openly available on this benchmark and analyze their performance across several domains. In particular, we compare these models to supervised baselines (e.g. UNet and vanilla ViT), and assess their effectiveness when faced with limited labeled data. Our findings highlight the limitations of GFMs, under different scenarios, showing that they do not consistently outperform supervised models. PANGAEA is designed to be highly extensible, allowing for the seamless inclusion of new datasets, models, and tasks in future research. By releasing the evaluation code and benchmark, we aim to enable other researchers to replicate our experiments and build upon our work, fostering a more principled evaluation protocol for large pre-trained geospatial models. The code is available at https://github.com/VMarsocci/pangaea-bench.
地理空间基础模型(GFMs)作为从地球观测数据中提取表征的强大工具已经崭露头角,但其评估仍然存在不一致和狭窄的问题。现有作品经常在次优的下游数据集和任务上进行评估,这些任务往往过于简单或过于狭窄,限制了评估的实用性,无法评估GFMs在现实世界中的适用性。此外,当前评估协议缺乏多样性,未能考虑到图像分辨率、传感器类型和时态的多元性,这进一步增加了评估GFM性能的复杂性。特别是,大多数现有基准测试在地理上偏向于北美和欧洲,这引发了人们对GFMs全球适用性的质疑。
为了克服这些挑战,我们引入了泛大陆评价协议(PANGAEA),这是一种标准化的评估协议,涵盖了一系列多样化的数据集、任务、分辨率、传感器模态和时态。它为GFMs建立了稳健且广泛适用的基准测试。我们在该基准测试上对最受欢迎的GFMs进行了评估,并分析了它们在多个领域中的性能。特别是,我们将这些模型与有监督的基线(例如UNet和Vanilla ViT)进行了比较,并评估了它们在面临有限标记数据时的有效性。我们的研究结果突出了GFMs在不同场景下的局限性,表明它们并不总是优于有监督的模型。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了用于从地球观测数据中提取表征的强大工具——地理空间基础模型(GFMs)。然而,现有的评估方法存在不一致和局限性。为了克服这些挑战,本文引入了PANGAEA,一个标准化的评估协议,涵盖了多样化的数据集、任务、分辨率、传感器模态和时间范围,为GFMs建立了稳健且广泛适用的基准。作者评估了最流行的GFMs在基准测试上的表现,并分析了它们在多个领域中的性能。研究结果表明,GFMs在不同场景下存在局限性,并不总是优于监督模型。PANGAEA设计具有高度可扩展性,旨在促进未来研究中新数据集、模型和任务的无缝集成。
Key Takeaways
- GFMs是用于从地球观测数据中提取表征的强大工具,但评估方法存在不一致和局限性。
- 现有评估方法常常使用次优的下游数据集和任务,这些任务过于简单或过于狭窄,无法评估GFMs在现实世界中的适用性。
- 当前评估协议缺乏多样性,未能考虑到图像分辨率、传感器类型和时间多样性的多重性。
- 大多数现有基准测试在地理上偏向于北美和欧洲,对GFMs的全球适用性提出质疑。
- 为了克服这些挑战,引入了PANGAEA——一个标准化的评估协议,涵盖多样化数据集、任务、分辨率、传感器模态和时间范围,为GFMs建立稳健且广泛适用的基准。
- 研究发现GFMs在不同场景中存在局限性,并不总是优于监督模型。
点此查看论文截图

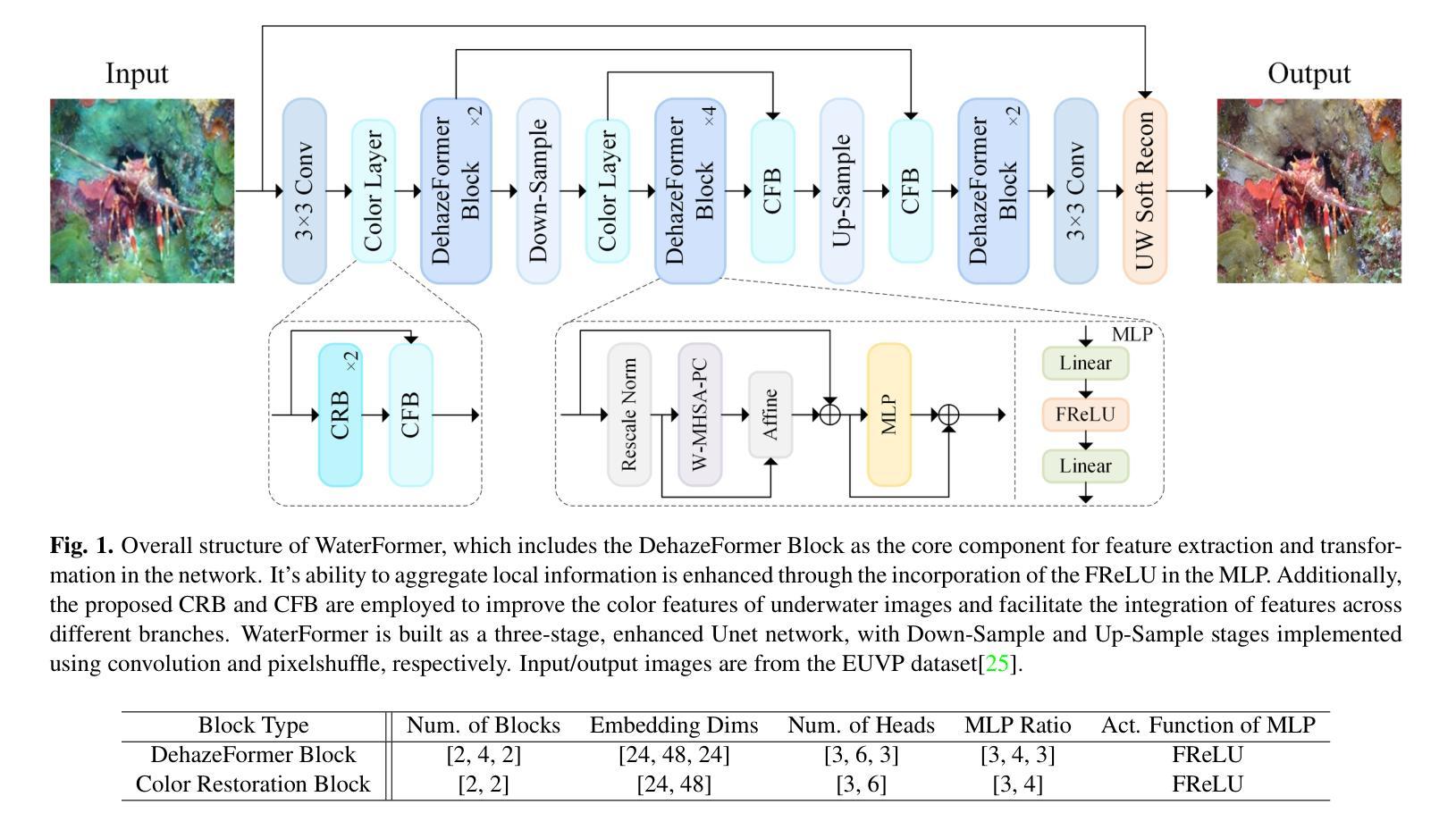
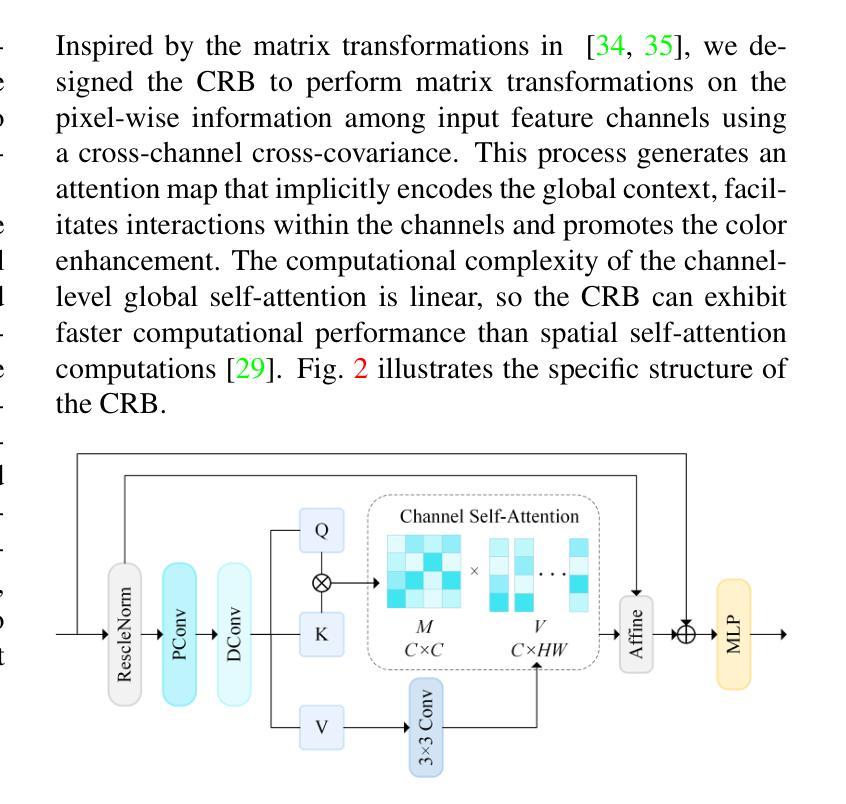
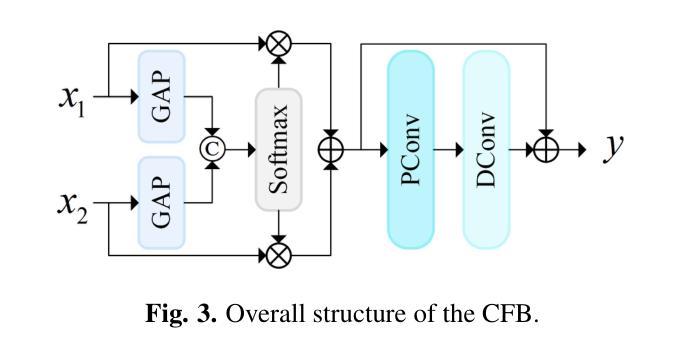
Underwater Image Enhancement via Dehazing and Color Restoration
Authors:Chengqin Wu, Shuai Yu, Tuyan Luo, Qiuhua Rao, Qingson Hu, Jingxiang Xu, Lijun Zhang
Underwater visual imaging is crucial for marine engineering, but it suffers from low contrast, blurriness, and color degradation, which hinders downstream analysis. Existing underwater image enhancement methods often treat the haze and color cast as a unified degradation process, neglecting their inherent independence while overlooking their synergistic relationship. To overcome this limitation, we propose a Vision Transformer (ViT)-based network (referred to as WaterFormer) to improve underwater image quality. WaterFormer contains three major components: a dehazing block (DehazeFormer Block) to capture the self-correlated haze features and extract deep-level features, a Color Restoration Block (CRB) to capture self-correlated color cast features, and a Channel Fusion Block (CFB) that dynamically integrates these decoupled features to achieve comprehensive enhancement. To ensure authenticity, a soft reconstruction layer based on the underwater imaging physics model is included. Further, a Chromatic Consistency Loss and Sobel Color Loss are designed to respectively preserve color fidelity and enhance structural details during network training. Comprehensive experimental results demonstrate that WaterFormer outperforms other state-of-the-art methods in enhancing underwater images.
水下视觉成像对于海洋工程至关重要,但它面临着对比度低、模糊和颜色退化等问题,阻碍了后续分析。现有的水下图像增强方法往往将雾霾和色彩偏移视为统一的退化过程,忽略了它们内在的独立性,同时忽视了它们之间的协同关系。为了克服这一局限性,我们提出了一种基于视觉变压器(ViT)的网络(称为WaterFormer)来提高水下图像质量。WaterFormer包含三个主要组件:去雾块(DehazeFormer Block)用于捕获自相关雾特征并提取深层特征,色彩恢复块(CRB)用于捕获自相关色彩偏移特征,以及通道融合块(CFB)动态融合这些解耦特征以实现全面增强。为了保证真实性,还加入了一个基于水下成像物理模型的软重建层。此外,还设计了色度一致性损失和Sobel色彩损失,以在网络训练过程中分别保持颜色保真度和增强结构细节。综合实验结果表明,WaterFormer在增强水下图像方面优于其他最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于Vision Transformer(ViT)的水下图像增强网络(WaterFormer),解决了水下视觉成像中的低对比、模糊和色彩退化问题。WaterFormer包含三个主要组件:去雾块(DehazeFormer Block)、色彩恢复块(CRB)和通道融合块(CFB),分别针对雾气与色彩独立但相互关联的特性进行处理,最终实现对水下图像的综合增强。还设计了一个基于水下成像物理模型的软重建层以及用于训练网络的色彩一致性损失和Sobel色彩损失,旨在保持色彩真实性和增强结构细节。实验证明,WaterFormer在增强水下图像方面优于其他先进方法。
Key Takeaways
- 水下视觉成像面临低对比、模糊和色彩退化问题。
- 现有方法常将雾气与色彩视为统一退化过程,忽略了它们的独立性和关联性。
- 提出基于Vision Transformer的WaterFormer网络进行水下图像增强。
- WaterFormer包含去雾块、色彩恢复块和通道融合块,分别处理雾气与色彩问题。
- 设计软重建层以基于水下成像物理模型确保真实性。
- 引入色彩一致性损失和Sobel色彩损失,以在训练过程中保持色彩真实性和增强结构细节。
点此查看论文截图