⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-03 更新
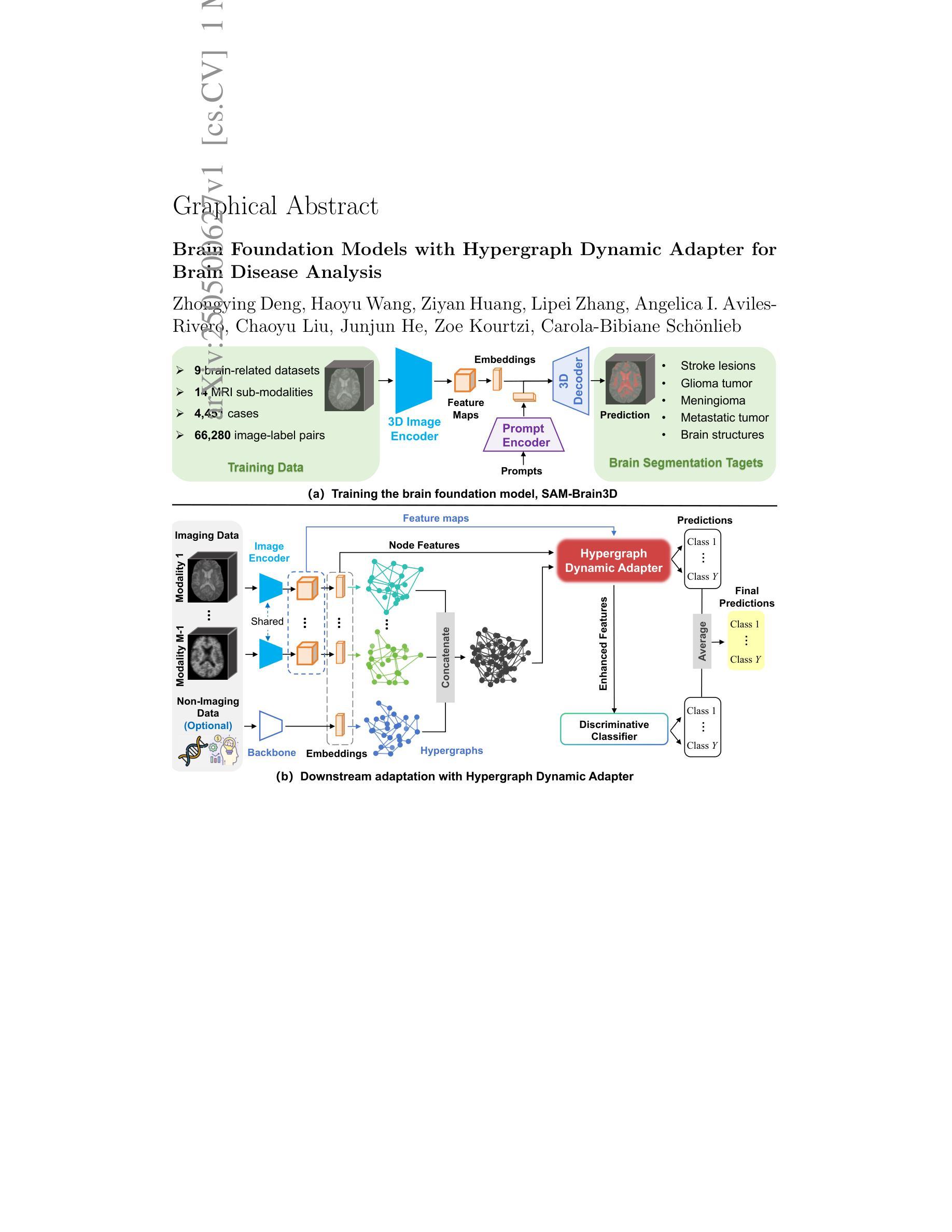
Brain Foundation Models with Hypergraph Dynamic Adapter for Brain Disease Analysis
Authors:Zhongying Deng, Haoyu Wang, Ziyan Huang, Lipei Zhang, Angelica I. Aviles-Rivero, Chaoyu Liu, Junjun He, Zoe Kourtzi, Carola-Bibiane Schönlieb
Brain diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease and brain tumors, present profound challenges due to their complexity and societal impact. Recent advancements in brain foundation models have shown significant promise in addressing a range of brain-related tasks. However, current brain foundation models are limited by task and data homogeneity, restricted generalization beyond segmentation or classification, and inefficient adaptation to diverse clinical tasks. In this work, we propose SAM-Brain3D, a brain-specific foundation model trained on over 66,000 brain image-label pairs across 14 MRI sub-modalities, and Hypergraph Dynamic Adapter (HyDA), a lightweight adapter for efficient and effective downstream adaptation. SAM-Brain3D captures detailed brain-specific anatomical and modality priors for segmenting diverse brain targets and broader downstream tasks. HyDA leverages hypergraphs to fuse complementary multi-modal data and dynamically generate patient-specific convolutional kernels for multi-scale feature fusion and personalized patient-wise adaptation. Together, our framework excels across a broad spectrum of brain disease segmentation and classification tasks. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms existing state-of-the-art approaches, offering a new paradigm for brain disease analysis through multi-modal, multi-scale, and dynamic foundation modeling.
脑疾病,如阿尔茨海默症和脑肿瘤,由于其复杂性和社会影响,呈现出巨大的挑战。最近脑基础模型的进展在解决一系列与脑相关的任务中显示出巨大潜力。然而,当前脑基础模型受到任务和数据同质性的限制,在分割或分类之外的推广能力有限,以及难以适应多样化的临床任务。在这项工作中,我们提出了SAM-Brain3D,这是一种针对大脑的特定基础模型,在超过66,000个跨14种MRI子模态的大脑图像标签对上进行了训练;还提出了Hypergraph Dynamic Adapter(HyDA),这是一种用于高效有效的下游适应的轻量级适配器。SAM-Brain3D捕获了详细的特定于大脑的解剖和模态先验知识,用于分割多样化的脑目标和更广泛的下游任务。HyDA利用超图融合互补的多模式数据,并动态生成患者特定的卷积核,用于多尺度特征融合和个性化的患者适应。我们的框架在广泛的脑疾病分割和分类任务中表现出色。大量实验表明,我们的方法始终优于现有的最先进的方法,通过多模式、多尺度、动态基础建模为脑疾病分析提供了新的范例。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 35 pages, 4 figures
Summary
本文介绍了针对脑疾病分析的新型基础模型SAM-Brain3D及其配套的高效适配器HyDA。SAM-Brain3D经过超过6.6万对脑图像和标签的训练,能在多种MRI子模态下对不同的脑目标进行分割和更广泛的任务处理。HyDA利用超图融合多模态数据,并动态生成患者特定的卷积核,实现多尺度特征融合和个性化患者适应性。该框架在广泛的脑疾病分割和分类任务中表现优异,实验证明其效果超越现有方法,为脑疾病分析提供了新的多模态、多尺度动态建模范式。
Key Takeaways
- 脑疾病如阿尔茨海默病和脑肿瘤具有复杂性和社会影响力,是巨大的挑战。
- 最近的脑基础模型在解决一系列脑相关任务方面显示出巨大潜力。
- 当前脑基础模型受限于任务和数据的同质性,在多样化临床任务上的适应能力有限。
- 提出的SAM-Brain3D模型经过大量脑图像和标签的训练,适用于多种MRI子模态下的脑目标分割和更广泛的任务处理。
- HyDA适配器利用超图融合多模态数据,并实现患者特定的动态卷积核生成,用于多尺度特征融合和个性化适应。
- SAM-Brain3D和HyDA结合在广泛的脑疾病分割和分类任务中表现优异。
点此查看论文截图
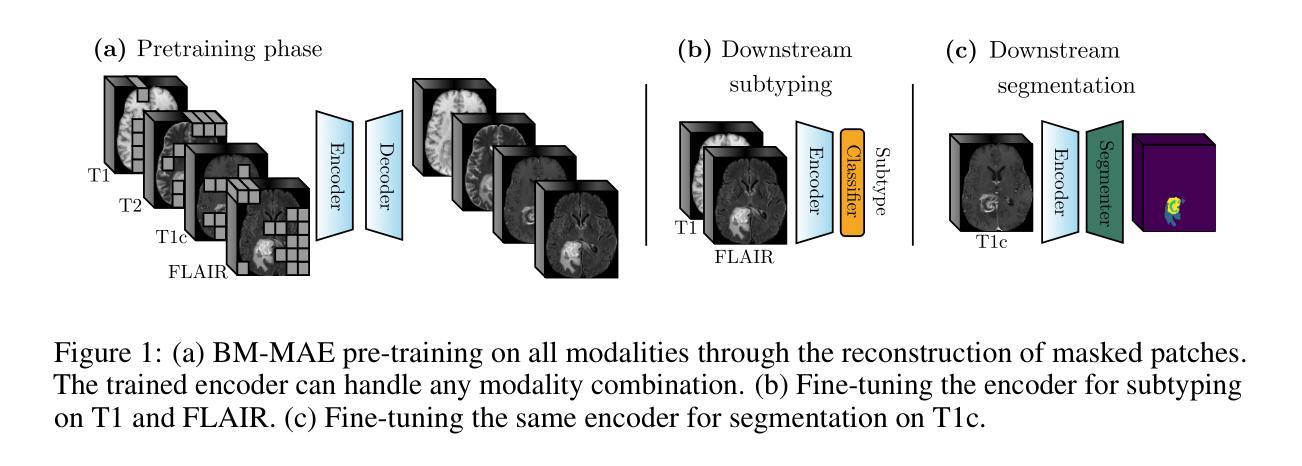
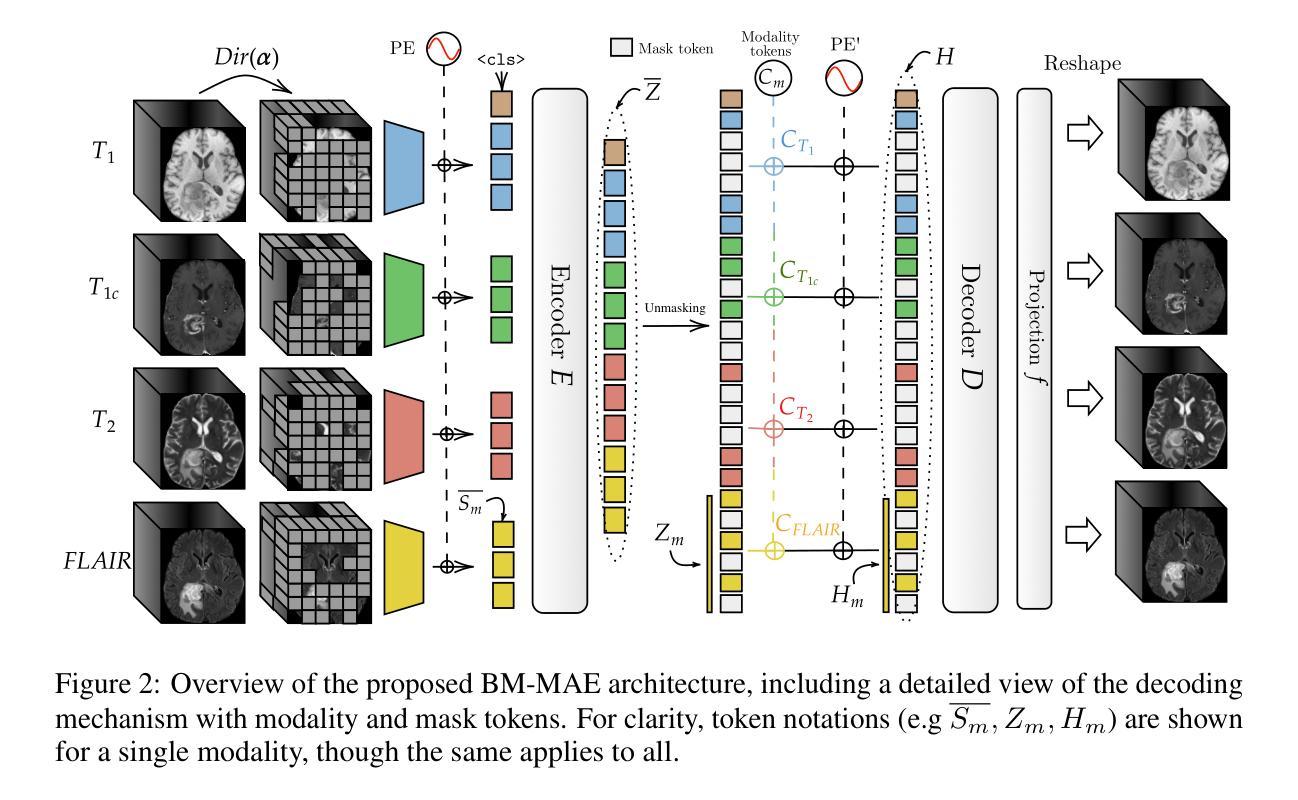
Multimodal Masked Autoencoder Pre-training for 3D MRI-Based Brain Tumor Analysis with Missing Modalities
Authors:Lucas Robinet, Ahmad Berjaoui, Elizabeth Cohen-Jonathan Moyal
Multimodal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) constitutes the first line of investigation for clinicians in the care of brain tumors, providing crucial insights for surgery planning, treatment monitoring, and biomarker identification. Pre-training on large datasets have been shown to help models learn transferable representations and adapt with minimal labeled data. This behavior is especially valuable in medical imaging, where annotations are often scarce. However, applying this paradigm to multimodal medical data introduces a challenge: most existing approaches assume that all imaging modalities are available during both pre-training and fine-tuning. In practice, missing modalities often occur due to acquisition issues, specialist unavailability, or specific experimental designs on small in-house datasets. Consequently, a common approach involves training a separate model for each desired modality combination, making the process both resource-intensive and impractical for clinical use. Therefore, we introduce BM-MAE, a masked image modeling pre-training strategy tailored for multimodal MRI data. The same pre-trained model seamlessly adapts to any combination of available modalities, extracting rich representations that capture both intra- and inter-modal information. This allows fine-tuning on any subset of modalities without requiring architectural changes, while still benefiting from a model pre-trained on the full set of modalities. Extensive experiments show that the proposed pre-training strategy outperforms or remains competitive with baselines that require separate pre-training for each modality subset, while substantially surpassing training from scratch on several downstream tasks. Additionally, it can quickly and efficiently reconstruct missing modalities, highlighting its practical value. Code and trained models are available at: https://github.com/Lucas-rbnt/bmmae
多模态磁共振成像(MRI)是临床医生在脑肿瘤诊疗中的首选检查手段,为手术规划、治疗监测和生物标志物识别提供关键信息。在大规模数据集上进行预训练已被证明有助于模型学习可迁移表示,并以最少的标记数据进行适应。这种行为在医学成像中尤其有价值,因为注释通常很稀缺。然而,将这种范式应用于多模态医学数据带来了挑战:大多数现有方法假设在预训练和微调期间都可获得所有成像模式。实际上,由于采集问题、专家不可用或特定的小型内部数据集的实验设计,经常会出现缺失的模式。因此,一种常见的方法是为每种所需的模式组合分别训练一个模型,这使得过程既耗费资源又不适合临床使用。因此,我们引入了BM-MAE,这是一种针对多模态MRI数据定制的掩模图像建模预训练策略。同一预训练模型无缝适应任何可用的模式组合,提取丰富的表示,这些表示捕获了模式和跨模式的信息。这使得可以在任何模式的子集上进行微调,而无需进行架构更改,同时仍受益于在完整模式集上预训练的模型。大量实验表明,所提出的预训练策略优于或具有竞争力地对抗基线,基线需要对每个模式子集进行单独的预训练,同时在多个下游任务上大大优于从头开始训练。此外,它可以快速有效地重建缺失的模式,从而突出了其实用价值。相关代码和训练好的模型可在:https://github.com/Lucas-rbnt/bmmae访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
多模态磁共振成像(MRI)是临床医生在脑肿瘤诊疗中的首选调查手段,可为手术规划、治疗监测和生物标志物识别提供关键见解。预训练有助于模型学习可迁移的表示并适应少量有标签数据。将此范式应用于多模态医疗数据面临挑战:大多数现有方法假设预训练和微调期间所有成像模式都是可用的。实际上,由于采集问题、专家不可用或特定的内部数据集的实验设计,经常会出现缺失的模式。因此,我们引入了BM-MAE,一种针对多模态MRI数据量身定制的掩模图像建模预训练策略。同一预训练模型可以轻松适应任何可用的模式组合,提取丰富的表示,捕获模式和跨模式信息。此策略可在任何模式子集上进行微调,无需进行架构更改,同时仍受益于在全部模式集上进行的预训练。实验表明,该预训练策略优于或相当于基线方法,后者需要对每种模式子集进行单独的预训练,同时在几个下游任务上超越从头开始训练。此外,它还可以快速有效地重建缺失的模式,突显其实用价值。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态磁共振成像(MRI)是诊疗脑肿瘤的重要工具,为手术、治疗和生物标志物识别提供关键信息。
- 预训练在医疗成像中尤其重要,有助于模型在缺少大量标签数据的情况下学习可迁移表示。
- 现有方法在应用预训练到多模态医疗数据时面临挑战,特别是在处理缺失模式时。
- BM-MAE是一种针对多模态MRI数据的预训练策略,能够适应任何模式组合并提取丰富的信息。
- 该策略在多个下游任务上表现优异,甚至超过在每种模式子集上分别进行预训练的基线方法。
- BM-MAE可以有效地重建缺失的模式,提高了实际应用中的价值。
点此查看论文截图

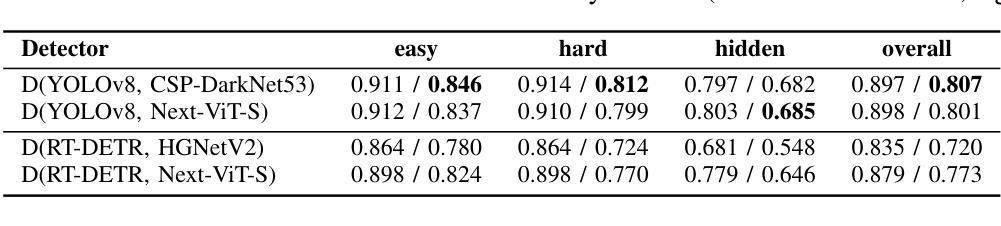
X-ray illicit object detection using hybrid CNN-transformer neural network architectures
Authors:Jorgen Cani, Christos Diou, Spyridon Evangelatos, Panagiotis Radoglou-Grammatikis, Vasileios Argyriou, Panagiotis Sarigiannidis, Iraklis Varlamis, Georgios Th. Papadopoulos
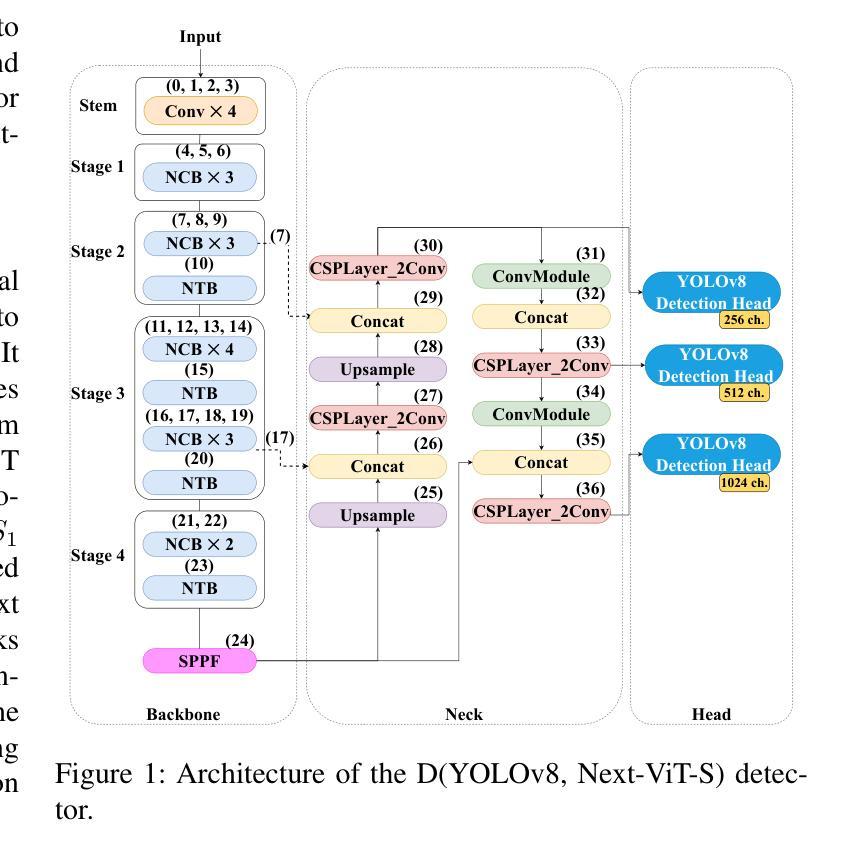
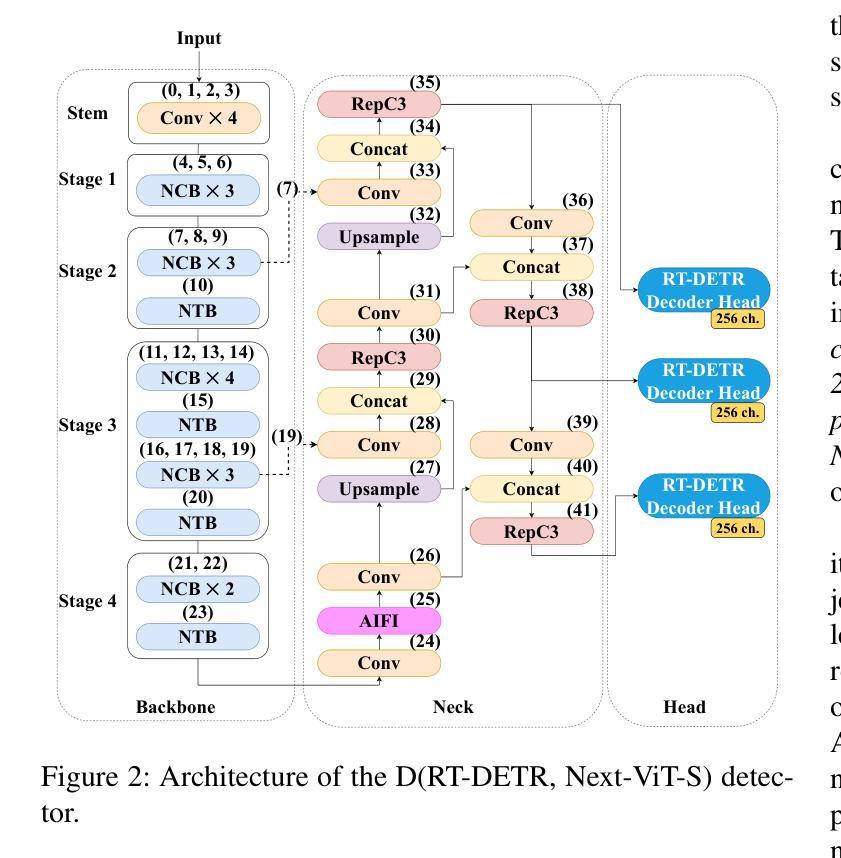
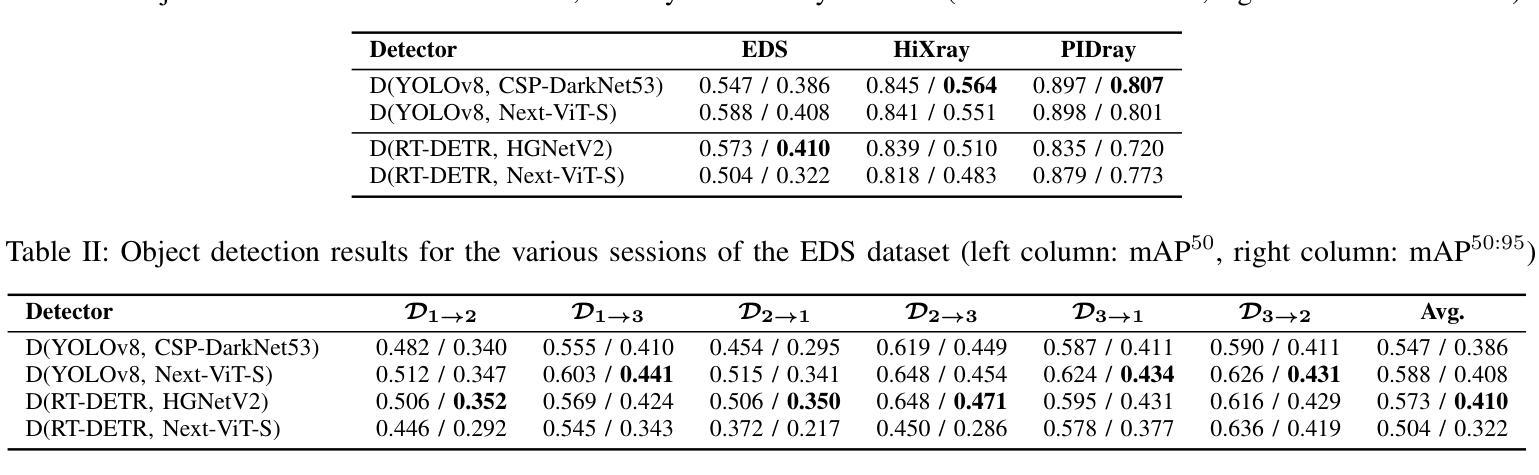
In the field of X-ray security applications, even the smallest details can significantly impact outcomes. Objects that are heavily occluded or intentionally concealed pose a great challenge for detection, whether by human observation or through advanced technological applications. While certain Deep Learning (DL) architectures demonstrate strong performance in processing local information, such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), others excel in handling distant information, e.g., transformers. In X-ray security imaging the literature has been dominated by the use of CNN-based methods, while the integration of the two aforementioned leading architectures has not been sufficiently explored. In this paper, various hybrid CNN-transformer architectures are evaluated against a common CNN object detection baseline, namely YOLOv8. In particular, a CNN (HGNetV2) and a hybrid CNN-transformer (Next-ViT-S) backbone are combined with different CNN/transformer detection heads (YOLOv8 and RT-DETR). The resulting architectures are comparatively evaluated on three challenging public X-ray inspection datasets, namely EDS, HiXray, and PIDray. Interestingly, while the YOLOv8 detector with its default backbone (CSP-DarkNet53) is generally shown to be advantageous on the HiXray and PIDray datasets, when a domain distribution shift is incorporated in the X-ray images (as happens in the EDS datasets), hybrid CNN-transformer architectures exhibit increased robustness. Detailed comparative evaluation results, including object-level detection performance and object-size error analysis, demonstrate the strengths and weaknesses of each architectural combination and suggest guidelines for future research. The source code and network weights of the models employed in this study are available at https://github.com/jgenc/xray-comparative-evaluation.
在X射线安全应用领域,即使是最小的细节也会显著影响结果。被大量遮挡或故意隐藏的物体对检测构成了巨大挑战,无论是通过人工观察还是通过先进的技术应用。虽然某些深度学习(DL)架构在处理局部信息方面表现出强大的性能,例如卷积神经网络(CNN),但其他网络在处理远距离信息方面表现出卓越的性能,例如变压器网络。在X射线安全成像文献中,主要以使用基于CNN的方法为主,而这两种上述主流架构的集成尚未得到充分探索。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了X光安检图像中,卷积神经网络(CNN)与transformer混合架构在对象检测方面的性能。通过对多种混合架构与YOLOv8基线模型的比较评估,发现混合架构在面临领域分布变化的X光图像数据集上展现增强稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- X光安检应用中,细节对结果影响重大,被遮挡或隐藏物体检测具挑战性。
- Deep Learning架构中,CNN擅长处理局部信息,而某些架构如transformer更擅长处理远距离信息。
- 在X光安检成像文献中,以CNN为基础的方法占主导,CNN与transformer的混合架构整合尚未得到充分探索。
- 文中评估了多种混合CNN-transformer架构与YOLOv8基线模型的性能。
- 在特定的X光图像数据集上,当面临领域分布变化时,混合CNN-transformer架构展现增强稳健性。
- 文中提供了详细的比较评估结果,包括对象级别的检测性能和对象大小误差分析。
- 研究的源代码和模型权重可在指定链接找到。
点此查看论文截图
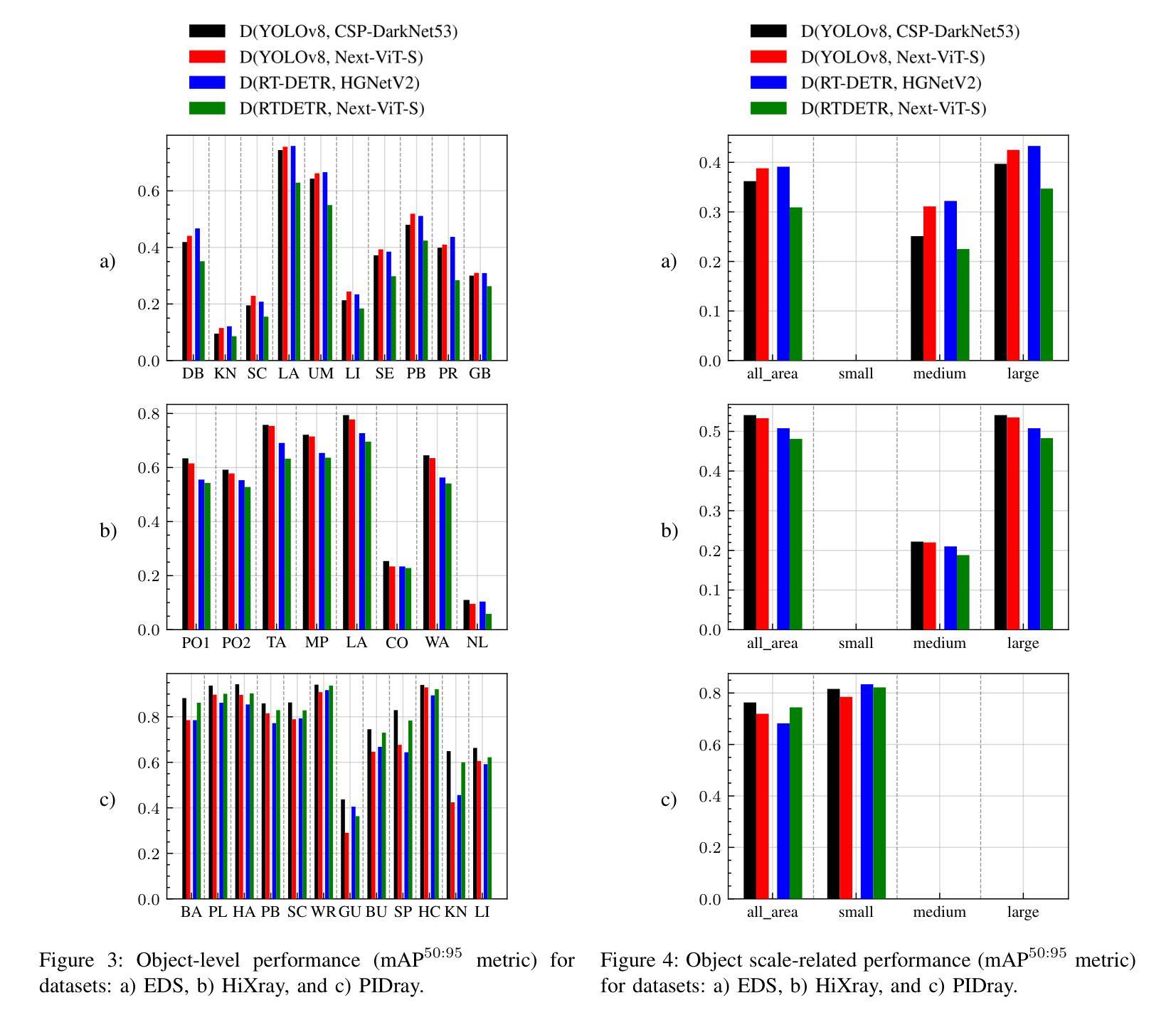
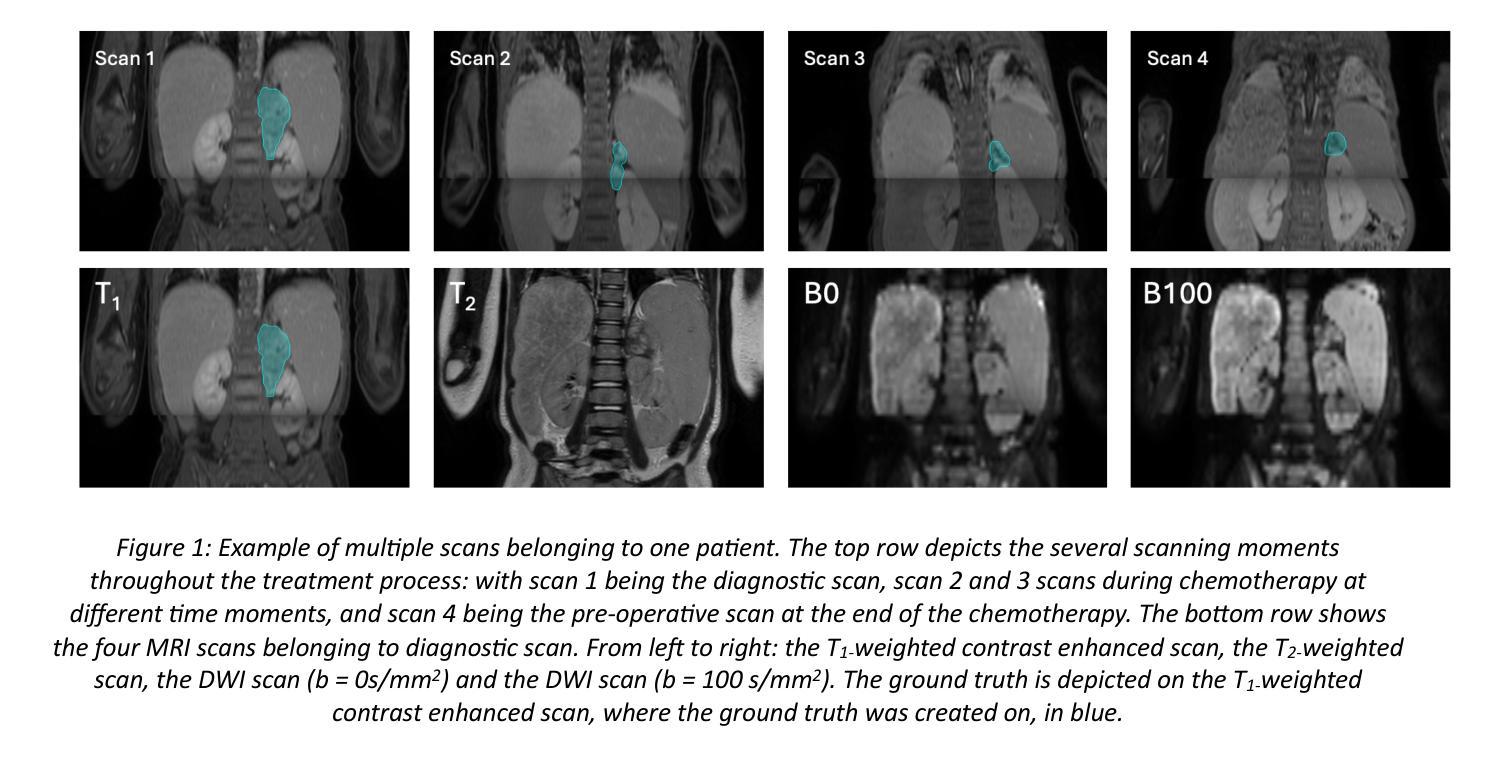
Automated segmenta-on of pediatric neuroblastoma on multi-modal MRI: Results of the SPPIN challenge at MICCAI 2023
Authors:M. A. D. Buser, D. C. Simons, M. Fitski, M. H. W. A. Wijnen, A. S. Littooij, A. H. ter Brugge, I. N. Vos, M. H. A. Janse, M. de Boer, R. ter Maat, J. Sato, S. Kido, S. Kondo, S. Kasai, M. Wodzinski, H. Muller, J. Ye, J. He, Y. Kirchhoff, M. R. Rokkus, G. Haokai, S. Zitong, M. Fernández-Patón, D. Veiga-Canuto, D. G. Ellis, M. R. Aizenberg, B. H. M. van der Velden, H. Kuijf, A. De Luca, A. F. W. van der Steeg
Surgery plays an important role within the treatment for neuroblastoma, a common pediatric cancer. This requires careful planning, often via magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-based anatomical 3D models. However, creating these models is often time-consuming and user dependent. We organized the Surgical Planning in Pediatric Neuroblastoma (SPPIN) challenge, to stimulate developments on this topic, and set a benchmark for fully automatic segmentation of neuroblastoma on multi-model MRI. The challenge started with a training phase, where teams received 78 sets of MRI scans from 34 patients, consisting of both diagnostic and post-chemotherapy MRI scans. The final test phase, consisting of 18 MRI sets from 9 patients, determined the ranking of the teams. Ranking was based on the Dice similarity coefficient (Dice score), the 95th percentile of the Hausdorff distance (HD95) and the volumetric similarity (VS). The SPPIN challenge was hosted at MICCAI 2023. The final leaderboard consisted of 9 teams. The highest-ranking team achieved a median Dice score 0.82, a median HD95 of 7.69 mm and a VS of 0.91, utilizing a large, pretrained network called STU-Net. A significant difference for the segmentation results between diagnostic and post-chemotherapy MRI scans was observed (Dice = 0.89 vs Dice = 0.59, P = 0.01) for the highest-ranking team. SPPIN is the first medical segmentation challenge in extracranial pediatric oncology. The highest-ranking team used a large pre-trained network, suggesting that pretraining can be of use in small, heterogenous datasets. Although the results of the highest-ranking team were high for most patients, segmentation especially in small, pre-treated tumors were insufficient. Therefore, more reliable segmentation methods are needed to create clinically applicable models to aid surgical planning in pediatric neuroblastoma.
在神经母细胞瘤这一常见儿童癌症的治疗中,手术扮演着重要角色。这需要通过磁共振成像(MRI)基于解剖的3D模型进行仔细的术前规划。然而,创建这些模型通常很耗时,并且依赖于用户。为了刺激这方面的发展并设定全自动分割神经母细胞瘤在多模式MRI上的基准,我们组织了小儿神经母细胞瘤手术规划(SPPIN)挑战赛。该挑战始于培训阶段,各团队在这一阶段收到了来自34名患者的78组MRI扫描,包括诊断性MRI扫描和化疗后MRI扫描。最终测试阶段包括来自9名患者的18组MRI扫描,用于确定团队排名。排名基于Dice相似系数(Dice得分)、Hausdorff距离第95百分位(HD95)和体积相似性(VS)。SPPIN挑战赛于MICCAI 2023年举办。最终排行榜上有9支队伍。排名第一的团队使用了一个名为STU-Net的大型预训练网络,取得了中位数Dice得分0.82、中位数HD95为7.69毫米和VS为0.91的成绩。对于排名第一的团队来说,诊断性MRI扫描和化疗后MRI扫描之间的分割结果存在显著差异(Dice = 0.89 vs Dice = 0.59,P = 0.01)。SPPIN是首个颅外儿童肿瘤学的医学分割挑战。排名第一的团队使用了大型预训练网络,这表明预训练在小型、异质的数据集中是有用的。尽管大多数患者的最高排名团队的结果很高,但在小型、预处理的肿瘤的分割仍然不足。因此,需要更可靠的分割方法来创建临床适用的模型,以辅助小儿神经母细胞瘤的手术规划。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 23 pages, 6 figures
Summary
手术在神经母细胞瘤的治疗中扮演重要角色,常借助基于磁共振成像(MRI)的三维模型进行精细规划。为加快模型创建过程并提高用户自主性,举办了小儿神经母细胞瘤手术规划(SPPIN)挑战赛。本次挑战训练阶段采用来自34名患者的78组MRI扫描图像,测试阶段则使用来自9名患者的18组MRI图像进行排名评定。排名第一的团队利用大型预训练网络STU-Net取得了较高的分割结果,但仍存在对小型、预处理后肿瘤的分割不足的问题。因此,需要更可靠的分割方法以创建适用于临床的模型,辅助小儿神经母细胞瘤的手术规划。
Key Takeaways
- 手术在神经母细胞瘤治疗中的地位重要,需借助MRI三维模型进行精细规划。
- SPPIN挑战旨在加快模型创建过程并提高用户自主性。
- 训练阶段使用了来自34名患者的MRI扫描图像,测试阶段则使用来自9名患者的MRI图像进行排名评定。
- 排名第一的团队利用大型预训练网络STU-Net取得了较高的分割结果。
- 分割结果中,诊断MRI图像与化疗后MRI图像的分割效果存在显著差异。
- SPPIN挑战是首例针对颅外小儿肿瘤的医学分割挑战。
点此查看论文截图

ReXGradient-160K: A Large-Scale Publicly Available Dataset of Chest Radiographs with Free-text Reports
Authors:Xiaoman Zhang, Julián N. Acosta, Josh Miller, Ouwen Huang, Pranav Rajpurkar
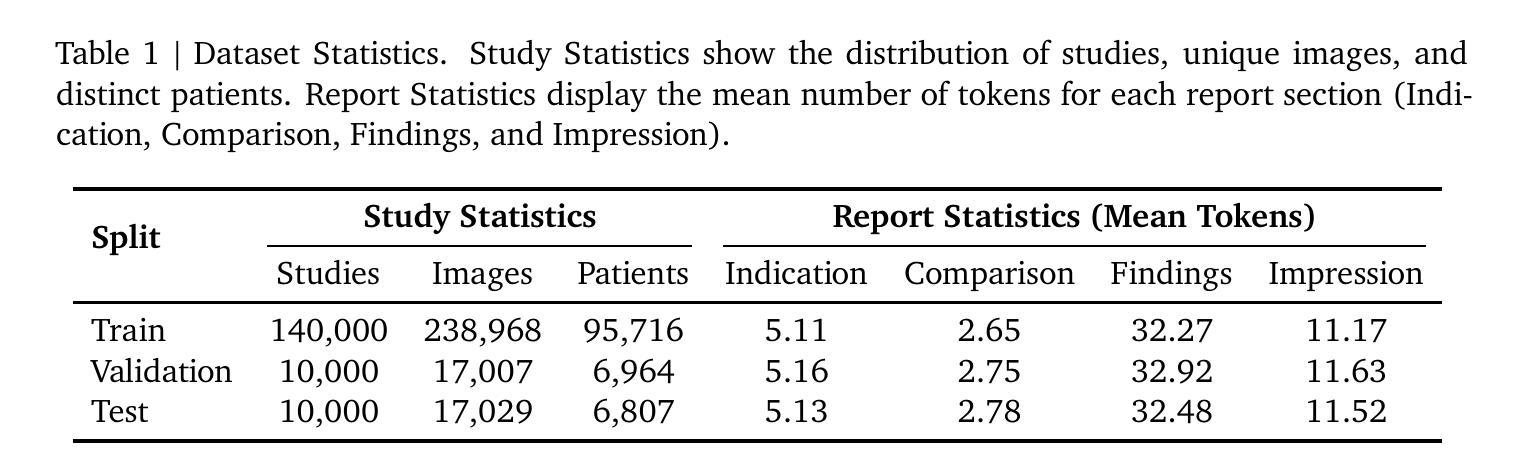
We present ReXGradient-160K, representing the largest publicly available chest X-ray dataset to date in terms of the number of patients. This dataset contains 160,000 chest X-ray studies with paired radiological reports from 109,487 unique patients across 3 U.S. health systems (79 medical sites). This comprehensive dataset includes multiple images per study and detailed radiology reports, making it particularly valuable for the development and evaluation of AI systems for medical imaging and automated report generation models. The dataset is divided into training (140,000 studies), validation (10,000 studies), and public test (10,000 studies) sets, with an additional private test set (10,000 studies) reserved for model evaluation on the ReXrank benchmark. By providing this extensive dataset, we aim to accelerate research in medical imaging AI and advance the state-of-the-art in automated radiological analysis. Our dataset will be open-sourced at https://huggingface.co/datasets/rajpurkarlab/ReXGradient-160K.
我们推出了ReXGradient-160K数据集,这是迄今为止公开可用的最大的胸部X光数据集,以患者数量为标准。该数据集包含来自美国三个卫生系统(79个医疗站点)的109,487名独特患者的16万份胸部X光研究及其相应的放射学报告配对。此综合数据集每个研究均包含多张图像和详细的放射学报告,对于医学成像人工智能系统和自动报告生成模型的开发和评估具有特别的价值。数据集分为训练集(14万份研究)、验证集(1万份研究)和公共测试集(1万份研究),另有一个专用的私有测试集(1万份研究)用于在ReXrank基准上对模型进行评估。通过提供此广泛的数据集,我们旨在加速医学成像人工智能的研究,并推动自动放射学分析领域的最新进展。我们的数据集将在https://huggingface.co/datasets/rajpurkarlab/ReXGradient-160K上开源。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
ReXGradient-160K是迄今为止最大的公开胸X光射线数据集,包含来自美国三个卫生系统(共79个医疗站点)的109,487名独特患者的16万份胸X光研究数据及其配对报告。该数据集可用于开发和评估医学影像AI系统和自动报告生成模型,分为训练集、验证集和测试集三部分。目标是通过开放数据加速医学影像AI研究,推动自动放射分析的最新发展。数据集将在huggingface.co/datasets/rajpurkarlab/ReXGradient-160K开源发布。
Key Takeaways
- ReXGradient-160K是目前最大的公开胸X光射线数据集。
- 数据集包含来自多个医疗站点的大量患者数据。
- 数据集可用于开发医学影像AI系统和自动报告生成模型。
- 数据集分为三个部分:训练集、验证集和测试集。
- 数据集将用于加速医学影像AI研究。
- 数据集将推动自动放射分析的最新发展。
点此查看论文截图

Neuroevolution of Self-Attention Over Proto-Objects
Authors:Rafael C. Pinto, Anderson R. Tavares
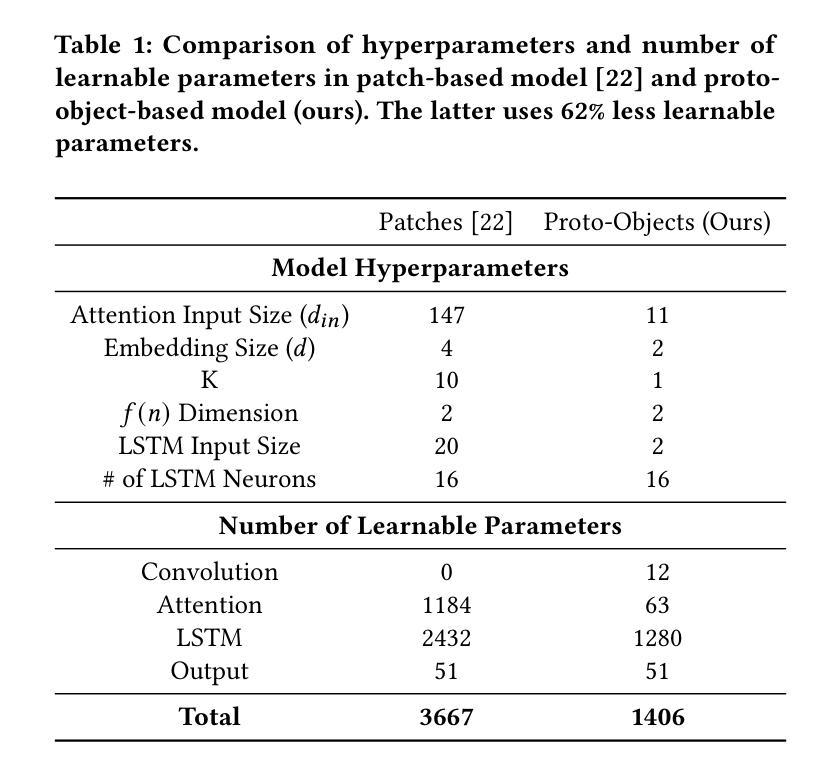
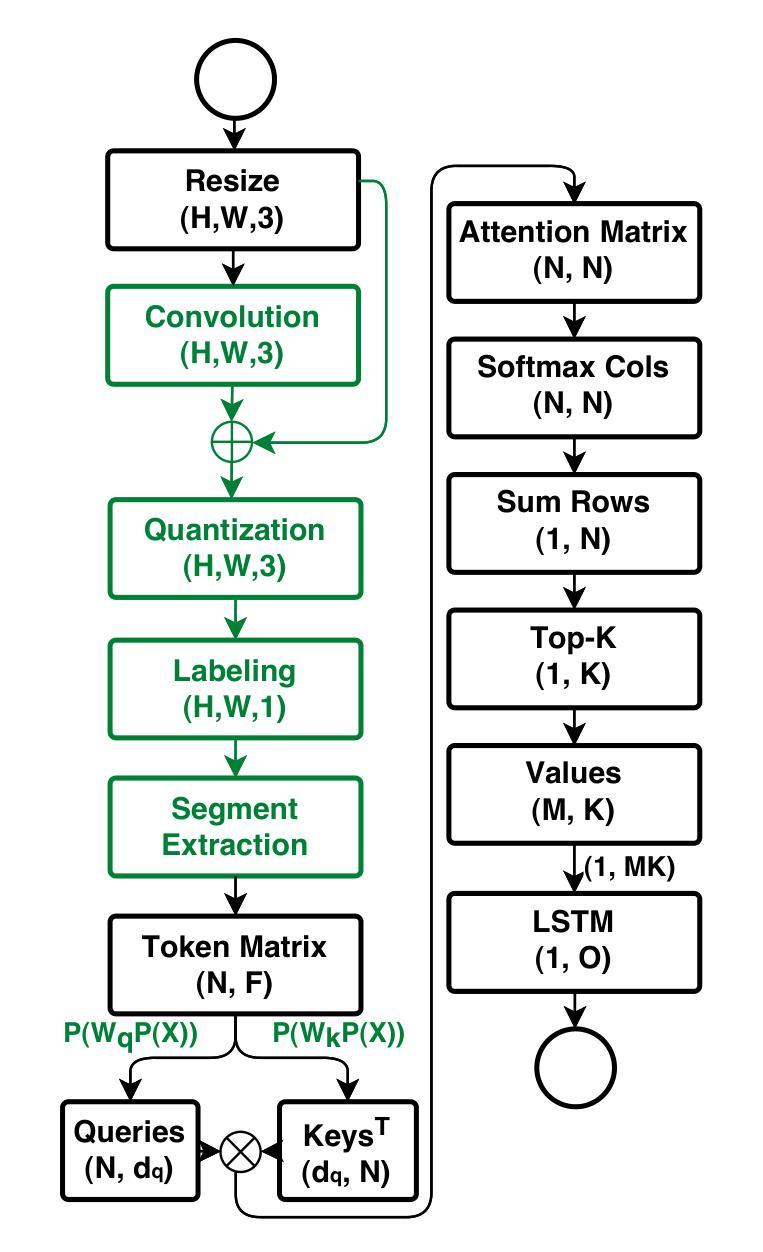
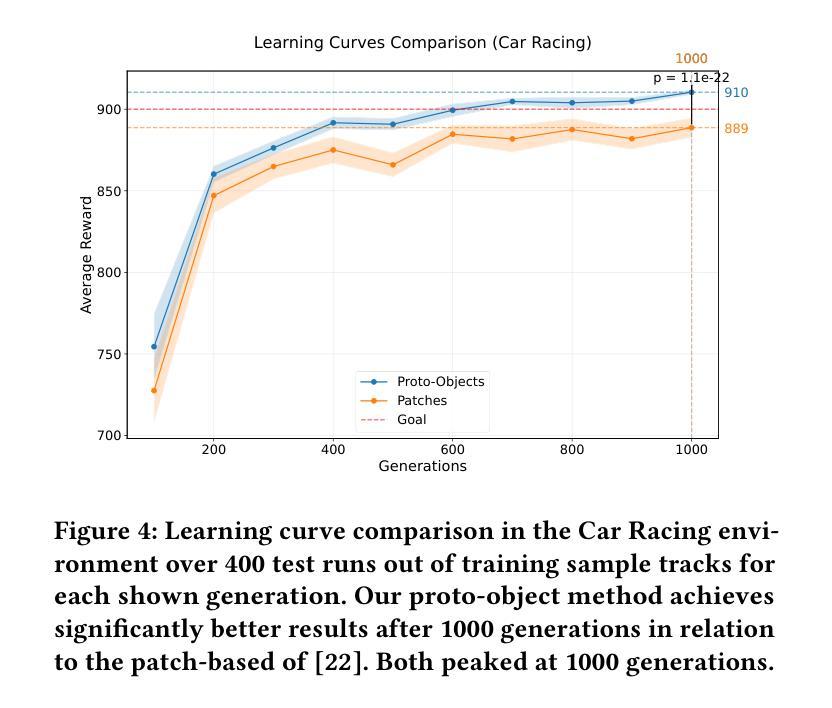
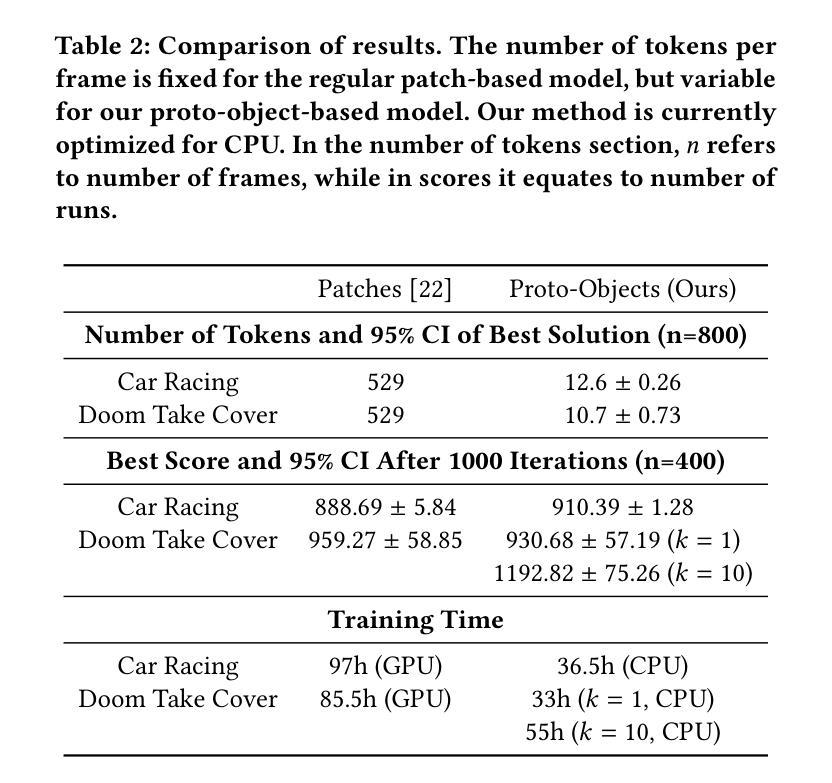
Proto-objects - image regions that share common visual properties - offer a promising alternative to traditional attention mechanisms based on rectangular-shaped image patches in neural networks. Although previous work demonstrated that evolving a patch-based hard-attention module alongside a controller network could achieve state-of-the-art performance in visual reinforcement learning tasks, our approach leverages image segmentation to work with higher-level features. By operating on proto-objects rather than fixed patches, we significantly reduce the representational complexity: each image decomposes into fewer proto-objects than regular patches, and each proto-object can be efficiently encoded as a compact feature vector. This enables a substantially smaller self-attention module that processes richer semantic information. Our experiments demonstrate that this proto-object-based approach matches or exceeds the state-of-the-art performance of patch-based implementations with 62% less parameters and 2.6 times less training time.
原型对象——共享共同视觉属性的图像区域——为神经网络中基于矩形图像块的传统注意力机制提供了有前景的替代方案。尽管之前的工作表明,与控制器网络一起发展的基于补丁的硬注意力模块可以在视觉强化学习任务中实现最先进的性能,但我们的方法利用图像分割来处理更高层次的特征。通过操作原型对象而不是固定的补丁,我们显著降低了表示复杂性:每个图像分解成的原型对象比常规补丁更少,每个原型对象可以高效地编码为一个紧凑的特征向量。这启用了一个更小的自我注意力模块,该模块处理更丰富的语义信息。我们的实验表明,基于原型对象的这种方法与基于补丁的实现相比,在参数减少62%、训练时间减少2.6倍的情况下,达到了或超过了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 16 figures, GECCO
Summary
本文介绍了基于Proto-objects(共享共同视觉属性的图像区域)的神经网络注意力机制,作为一种替代传统的基于矩形图像块的注意力机制的方法。通过利用图像分割来提取更高层次特征,并在Proto-objects上操作而非固定的图像块,显著降低了表示复杂性。实验表明,该方法在匹配或超越基于块的实现的同时,减少了62%的参数和2.6倍的训练时间。
Key Takeaways
- Proto-objects作为共享共同视觉属性的图像区域,被用作神经网络中的注意力机制。
- 相较于传统的基于矩形图像块的注意力机制,Proto-objects方法显著降低表示复杂性。
- 通过图像分割提取更高层次的特征。
- Proto-objects方法能更高效地编码图像信息。
- 基于Proto-objects的自我注意力模块能处理更丰富的语义信息。
- 实验表明,该方法在视觉强化学习任务中达到或超越了基于块的实现的性能。
点此查看论文截图


AT 2019aalc: a Bowen Fluorescence Flare With a Precursor Flare in an Active Galactic Nucleus
Authors:Marzena Śniegowska, Benny Trakhtenbrot, Lydia Makrygianni, Iair Arcavi, Claudio Ricci, Sarah Faris, Biswaraj Palit, D. Andrew Howell, Megan Newsome, Joseph Farah, Curtis McCully, Estefania Padilla-Gonzalez, Giacomo Terreran
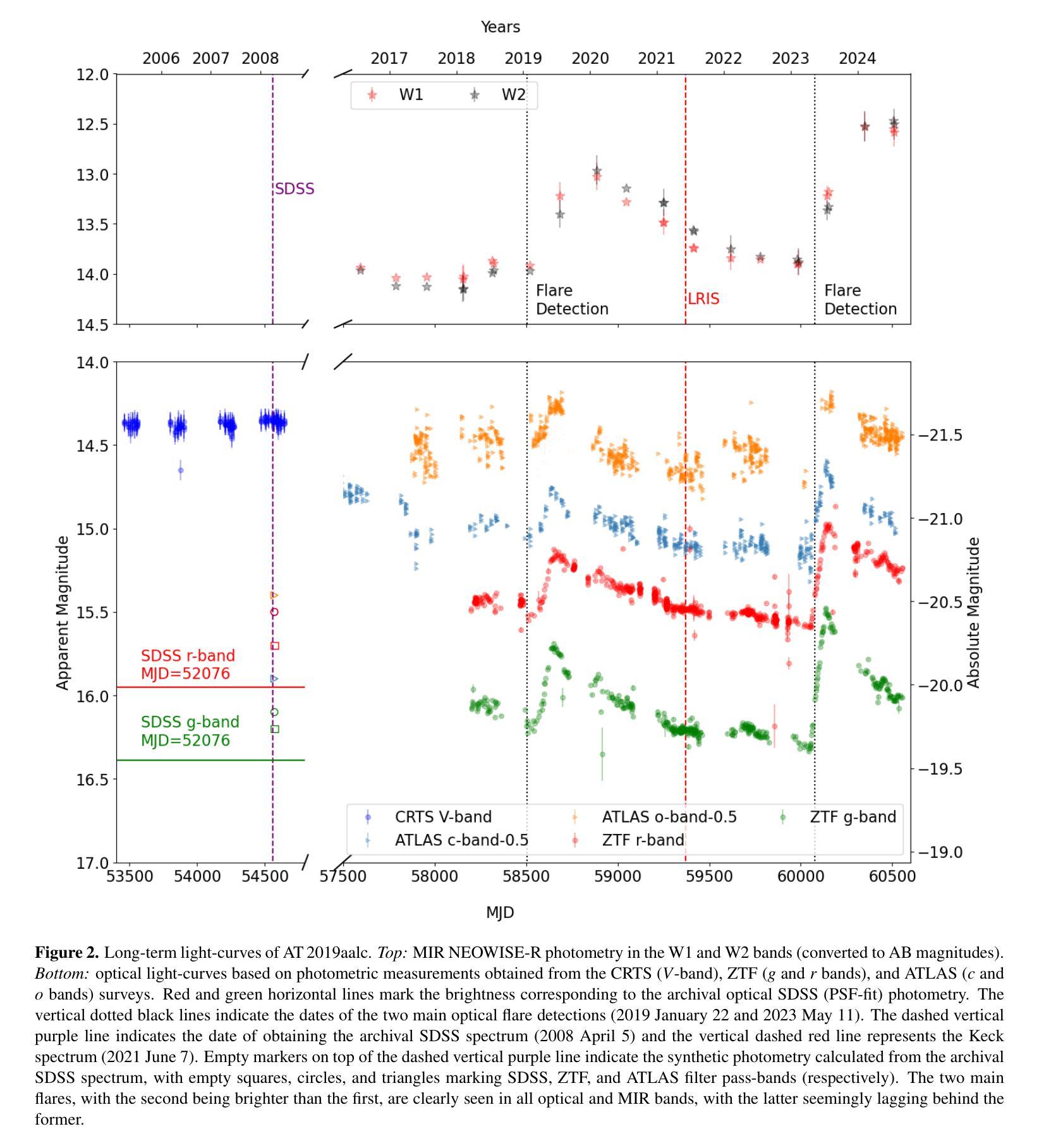
AT 2019aalc is a peculiar sequence of highly variable emission events observed towards the nucleus of the broad-line AGN SDSS J152416.66+045119.0. The system exhibited two distinct UV/optical flares (the first detected in 2019, the second one in 2023). Spectra obtained following the detection of the second flare revealed prominent Bowen fluorescence and high-ionization coronal emission lines, which were much weaker, if at all detectable, in a spectrum taken following the first flare. We present and analyze a large set of multi-wavelength, multi-epoch data for this source, with particular emphasis on optical spectroscopic monitoring conducted with the Las Cumbres Observatory network. During the relatively slow dimming that followed the second optical flare, the UV/optical light-curve shows a sequence of minor rebrightening events, while the Bowen fluorescence and the coronal lines vary (roughly) in tandem with these “bumps” in the broad-band light-curve. Most of the observed behavior of AT 2019aalc links it to the growing class of Bowen fluorescence flares (BFFs) while setting it apart from canonical tidal disruption events. However, AT 2019aalc has some outstanding peculiarities, including two short flares seen in its soft X-ray light-curve during the dimming phase of the second optical flare, and which do not seem to be linked to the emission line variations. We discuss the optical and X-ray properties of the source and possible scenarios of the origin of the flare, in particular radiation pressure instabilities in the (pre-existing) AGN accretion disk.
AT 2019aalc是在宽线型活跃星系核SDSS J152416.66+045119.0处观察到的高度可变的发射事件特殊序列。该系统表现出两种独特的紫外/光学耀斑(第一次在2019年检测到的,第二次在2023年)。在第二耀斑检测后获得的光谱显示出明显的Bowen荧光和高电离冠状发射线,这些在第一耀斑后获得的光谱中要么几乎无法检测到,要么显得更弱。我们针对此源提供了大量多波长、多时代的数据集,并特别强调了使用拉斯孔布雷拉天文台网络进行的光学光谱监测。在第二光学耀斑之后的相对较慢变暗过程中,紫外/光学光曲线显示出一系列轻微再增亮事件,而Bowen荧光和冠状线与宽带光曲线中的这些“凸起”大致同时变化。观察到的AT 2019aalc大部分行为都将其与不断发展的Bowen荧光耀斑类(BFFs)相联系,同时将其与典型的潮汐破坏事件区分开来。然而,AT 2019aalc具有一些突出的特点,包括在第二个光学耀斑变暗阶段的软X射线光曲线中出现的两个短暂耀斑,这两个耀斑似乎不与发射线变化有关。我们讨论了该源的光学和X射线特性以及耀斑起源的可能情景,特别是(预存的)活跃星系核吸积盘中的辐射压力不稳定。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 33 pages, 14 figures, submitted to the Astrophysical Journal
摘要
AT 2019aalc是宽线活跃星系核SDSS J152416.66+045119.0观测到的特殊序列高度可变发射事件。该系统表现出两种独特的紫外/光学耀斑(第一个在2019年检测,第二个在2023年)。在第二次耀斑检测后获得的光谱显示出明显的Bowen荧光和高电离冠状发射线,这些在第一次耀斑后获得的光谱中要么较弱,要么根本不可检测。我们针对此源提供并分析了一组多波长、多时段的大量数据,特别侧重于通过拉斯坎布雷斯天文台网络进行的光学光谱监测。在第二次光学耀斑之后的相对缓慢减弱过程中,紫外/光学光曲线显示了一系列微小的再辉事件,而Bowen荧光和冠状线与光曲线中的这些“凸起”大致同步变化。大多数观察到的行为将AT 2019aalc与Bowen荧光耀斑类(BFFs)联系起来,同时将其与典型的潮汐破坏事件区分开。然而,AT 2019aalc具有一些突出的特殊性,包括在其光变暗阶段的两个短软X射线耀斑,这两个耀斑似乎与发射线变化没有关联。我们讨论了该源的光学和X射线特性以及耀斑起源的可能情景,特别是预存的活跃星系核吸积盘的辐射压力不稳定性。
关键发现
- AT 2019aalc是一个具有独特特性的活跃星系核,表现出高度可变的发射事件序列。
- 系统经历了两次紫外/光学耀斑,第二次耀斑后光谱显示出明显的Bowen荧光和高电离冠状发射线。
- 在第二次光学耀斑后的缓慢减弱期间,观察到一系列微小的再辉事件,伴随光谱特性的变化。
- AT 2019aalc的行为与Bowen荧光耀斑类相似,但与典型的潮汐破坏事件有所不同。
- 在光变暗阶段观察到两个短软X射线耀斑,这些耀斑可能与发射线的变化无关。
- 讨论了源的光学和X射线特性以及可能的耀斑起源情景,特别是预存的吸积盘的辐射压力不稳定性。
点此查看论文截图


LGD: Leveraging Generative Descriptions for Zero-Shot Referring Image Segmentation
Authors:Jiachen Li, Qing Xie, Renshu Gu, Jinyu Xu, Yongjian Liu, Xiaohan Yu
Zero-shot referring image segmentation aims to locate and segment the target region based on a referring expression, with the primary challenge of aligning and matching semantics across visual and textual modalities without training. Previous works address this challenge by utilizing Vision-Language Models and mask proposal networks for region-text matching. However, this paradigm may lead to incorrect target localization due to the inherent ambiguity and diversity of free-form referring expressions. To alleviate this issue, we present LGD (Leveraging Generative Descriptions), a framework that utilizes the advanced language generation capabilities of Multi-Modal Large Language Models to enhance region-text matching performance in Vision-Language Models. Specifically, we first design two kinds of prompts, the attribute prompt and the surrounding prompt, to guide the Multi-Modal Large Language Models in generating descriptions related to the crucial attributes of the referent object and the details of surrounding objects, referred to as attribute description and surrounding description, respectively. Secondly, three visual-text matching scores are introduced to evaluate the similarity between instance-level visual features and textual features, which determines the mask most associated with the referring expression. The proposed method achieves new state-of-the-art performance on three public datasets RefCOCO, RefCOCO+ and RefCOCOg, with maximum improvements of 9.97% in oIoU and 11.29% in mIoU compared to previous methods.
零样本指代图像分割旨在基于指代表达式定位并分割目标区域,其主要挑战在于在没有训练的情况下实现视觉和文本模态之间的语义对齐和匹配。之前的工作通过利用视觉语言模型和掩膜提案网络进行区域文本匹配来解决这一挑战。然而,这种范式可能导致由于自由形式的指代表达式固有的模糊性和多样性而导致目标定位错误。为了缓解这个问题,我们提出了LGD(利用生成描述),一个利用多模态大型语言模型的先进语言生成能力来提高视觉语言模型中区域文本匹配性能的框架。具体来说,我们首先设计两种提示,属性提示和周围提示,来引导多模态大型语言模型生成与指代对象的关键属性和周围对象的细节相关的描述,分别称为属性描述和周围描述。其次,引入了三种视觉文本匹配分数,以评估实例级视觉特征与文本特征之间的相似性,从而确定与指代表达式最相关的掩膜。所提出的方法在RefCOCO、RefCOCO+和RefCOCOg三个公共数据集上实现了最新 state-of-the-art 性能,与以前的方法相比,在IoU和mIoU方面分别提高了最大9.97%和最大提高11.29%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本摘要针对零样本图像指代分割问题,提出了一种利用多模态大型语言模型的生成描述能力(LGD方法)增强视觉语言模型的区域文本匹配性能的方法。通过设计属性提示和周围提示两种提示方式,生成与指代对象的关键属性和周围对象相关的描述,并引入三种视觉文本匹配评分来评估实例级视觉特征与文本特征的相似性,从而提高指代表达式的定位准确性。在三个公共数据集上的实验结果表明,该方法取得了最新最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 零样本图像指代分割旨在根据指代表达式定位并分割目标区域,主要挑战在于在视觉和文本模态之间实现语义对齐和匹配,而无需训练。
- 以往的方法通过利用视觉语言模型和掩膜提案网络进行区域文本匹配来解决这一挑战。
- LGD方法利用多模态大型语言模型的生成描述能力来增强区域文本匹配性能,通过设计属性提示和周围提示来生成与指代对象及其周围环境相关的描述。
- 引入三种视觉文本匹配评分来评估实例级视觉特征与文本特征的相似性,以更准确地定位与指代表达式匹配的面罩。
点此查看论文截图


Segment-and-Classify: ROI-Guided Generalizable Contrast Phase Classification in CT Using XGBoost
Authors:Benjamin Hou, Tejas Sudharshan Mathai, Pritam Mukherjee, Xinya Wang, Ronald M. Summers, Zhiyong Lu
Purpose: To automate contrast phase classification in CT using organ-specific features extracted from a widely used segmentation tool with a lightweight decision tree classifier. Materials and Methods: This retrospective study utilized three public CT datasets from separate institutions. The phase prediction model was trained on the WAW-TACE (median age: 66 [60,73]; 185 males) dataset, and externally validated on the VinDr-Multiphase (146 males; 63 females; 56 unk) and C4KC-KiTS (median age: 61 [50.68; 123 males) datasets. Contrast phase classification was performed using organ-specific features extracted by TotalSegmentator, followed by prediction using a gradient-boosted decision tree classifier. Results: On the VinDr-Multiphase dataset, the phase prediction model achieved the highest or comparable AUCs across all phases (>0.937), with superior F1-scores in the non-contrast (0.994), arterial (0.937), and delayed (0.718) phases. Statistical testing indicated significant performance differences only in the arterial and delayed phases (p<0.05). On the C4KC-KiTS dataset, the phase prediction model achieved the highest AUCs across all phases (>0.991), with superior F1-scores in arterial/venous (0.968) and delayed (0.935) phases. Statistical testing confirmed significant improvements over all baseline models in these two phases (p<0.05). Performance in the non-contrast class, however, was comparable across all models, with no statistically significant differences observed (p>0.05). Conclusion: The lightweight model demonstrated strong performance relative to all baseline models, and exhibited robust generalizability across datasets from different institutions.
目的:使用广泛使用的分割工具提取的器官特定特征,结合轻量级决策树分类器,实现计算机断层扫描(CT)中的对比相位分类自动化。材料与方法:这项回顾性研究使用了三个来自不同机构的公开CT数据集。相位预测模型是在WAW-TACE数据集(平均年龄:66[60,73];男性185人)上进行训练,并在VinDr-Multiphase(男性146人;女性63人;56人未知)和C4KC-KiTS(平均年龄:61[50.68;男性123人)数据集上进行外部验证。对比相位分类是采用TotalSegmentator提取的器官特定特征进行,然后使用梯度增强决策树分类器进行预测。结果:在VinDr-Multiphase数据集上,相位预测模型在所有阶段的AUC最高或相当(> 0.937),在非对比(0.994)、动脉(0.937)和延迟(0.718)阶段的F1分数较高。统计测试显示仅在动脉和延迟阶段存在显著的性能差异(p<0.05)。在C4KC-KiTS数据集上,相位预测模型所有阶段的AUC最高(> 0.991),在动脉/静脉(0.968)和延迟(0.935)阶段的F1分数较高。统计测试证实,在这两个阶段与所有基准模型相比,有显著改进(p<0.05)。然而,在非对比类别中的性能在所有模型中表现相当,没有观察到统计学上的显著差异(p>0.05)。结论:轻量级模型相对于所有基准模型表现出强大的性能,并且在来自不同机构的数据集上表现出稳健的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文旨在利用广泛使用的分割工具提取的器官特异性特征,结合轻量级决策树分类器,实现对CT影像对比阶段的自动化分类。研究采用回顾性方法,使用三个公共CT数据集进行训练与验证。模型在VinDr-Multiphase和C4KC-KiTS数据集上表现出优异的性能,特别是在非对比、动脉和延迟阶段的分类效果突出。此外,模型具有良好的泛化能力,能够适应不同机构的数据集。
Key Takeaways
- 研究目的:利用分割工具提取的器官特异性特征,结合决策树分类器,实现CT影像对比阶段的自动化分类。
- 数据来源:使用三个公共CT数据集进行回顾性研究。
- 模型训练与验证:模型在WAW-TACE数据集上进行训练,并在VinDr-Multiphase和C4KC-KiTS数据集上进行外部验证。
- 分类效果:模型在VinDr-Multiphase数据集上的非对比、动脉和延迟阶段表现出较高的F1分数。在C4KC-KiTS数据集上,动脉/静脉和延迟阶段的分类效果同样优异。
- 性能比较:模型相较于基线模型有显著的性能提升,特别是在动脉和延迟阶段。
- 模型的泛化能力:能够适应不同机构的数据集。
- 研究结论:轻量级模型相对于基线模型表现出强大的性能,具有稳健的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

FLAMINGO: combining kinetic SZ effect and galaxy-galaxy lensing measurements to gauge the impact of feedback on large-scale structure
Authors:Ian G. McCarthy, Alexandra Amon, Joop Schaye, Emmanuel Schaan, Raul E. Angulo, Jaime Salcido, Matthieu Schaller, Leah Bigwood, Willem Elbers, Roi Kugel, John C. Helly, Victor J. Forouhar Moreno, Carlos S. Frenk, Robert J. McGibbon, Lurdes Ondaro-Mallea, Marcel P. van Daalen
Energetic feedback processes associated with accreting supermassive black holes can expel gas from massive haloes and significantly alter various measures of clustering on ~Mpc scales, potentially biasing the values of cosmological parameters inferred from analyses of large-scale structure (LSS) if not modelled accurately. Here we use the state-of-the-art FLAMINGO suite of cosmological hydrodynamical simulations to gauge the impact of feedback on large-scale structure by comparing to Planck + ACT stacking measurements of the kinetic Sunyaev-Zel’dovich (kSZ) effect of SDSS BOSS galaxies. We make careful like-with-like comparisons to the observations, aided by high precision KiDS and DES galaxy-galaxy lensing measurements of the BOSS galaxies to inform the selection of the simulated galaxies. In qualitative agreement with several recent studies using dark matter only simulations corrected for baryonic effects, we find that the kSZ effect measurements prefer stronger feedback than predicted by simulations which have been calibrated to reproduce the gas fractions of low redshift X-ray-selected groups and clusters. We find that the increased feedback can help to reduce the so-called S8 tension between the observed and CMB-predicted clustering on small scales as probed by cosmic shear (although at the expense of agreement with the X-ray group measurements). However, the increased feedback is only marginally effective at reducing the reported offsets between the predicted and observed clustering as probed by the thermal SZ (tSZ) effect power spectrum and tSZ effect–weak lensing cross-spectrum, both of which are sensitive to higher halo masses than cosmic shear.
与增大的超大质量黑洞相关的能量反馈过程可以从大型星系晕中驱逐气体,并显著改变~Mpc尺度上的各种聚类测量值,如果没有准确建模,可能会偏误从大规模结构分析推断的宇宙学参数值。在这里,我们利用最先进的FLAMINGO宇宙学水力模拟套件来评估反馈对大规模结构的影响,将其与Planck+ACT堆叠测量的SDSS BOSS星系的动力学Sunyaev-Zel’dovich(kSZ)效应进行比较。我们在高精确度KiDS和DES的BOSS星系星系弱引力透镜测量结果的帮助下,对观测结果进行了谨慎的类似比较,以选择模拟星系。与最近一些仅使用暗物质模拟但已校正重子效应的模拟研究在质上一致,我们发现kSZ效应测量更喜欢更强的反馈,而已校准的模拟预测重现了低红移X射线选择的星团的气体分数则较弱。我们发现增加的反馈有助于减少宇宙剪切所探测到的所谓S8张力,即观察到的与小尺度上CMB预测的聚类的差异(虽然与X射线星团测量结果的吻合程度有所牺牲)。然而,增加的反馈仅在降低已报道的预测和通过热SZ(tSZ)效应功率谱和tSZ效应与弱引力透镜交叉谱所探测到的观测聚类之间的偏移方面效果甚微,这两者都对更高的星系晕质量敏感,而宇宙剪切的敏感性较低。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 21 pages, 11 figures, MNRAS, accepted
Summary
超大质量黑洞吸积过程中的能量反馈机制可排除气体大规模团状星系周围的气体,对兆秒尺度上的集群测量产生重大影响,可能误导从大规模结构分析中推断出的宇宙学参数值,若未准确建模的话。本文通过比较使用先进FLAMINGO宇宙学流体动力学模拟套件与Planck和ACT叠加测量的SDSS BOSS星系动态Sunyaev-Zel’dovich(kSZ)效应数据,评估反馈对大规模结构的影响。借助高精度KiDS和DES星系星系透镜测量选定的模拟星系与观测进行细致的比较。与近期使用仅暗物质模拟并校正重子效应的研究定性一致,我们发现kSZ效应测量更偏好于较强的反馈机制,模拟结果的校准是以复现低红移X射线选择团组的气相分数为基础。我们发现增强反馈有助于减少宇宙剪切所探测的小尺度上的观测与CMB预测聚类之间的S8紧张局势(尽管与X射线组测量结果一致性的代价是降低),但对预测的热SZ效应功率谱和热SZ效应与弱透镜交叉谱的观测结果之间的偏差影响不大,后者对更高团簇质量的敏感性更高。
Key Takeaways
- 超大质量黑洞吸积过程中的能量反馈可能影响气体从大规模团状星系周围的排除。
- 反馈机制对宇宙结构的大规模测量有重大影响,可能改变从大规模结构分析中推断的宇宙学参数。
- 使用FLAMINGO宇宙学流体动力学模拟套件评估了反馈的影响,并与观测数据进行了比较。
- kSZ效应测量结果表明,模拟中的反馈机制比基于低红移X射线组气相分数的模拟预测更强。
- 加强反馈有助于减少宇宙剪切探测的小尺度上的观测与CMB预测之间的S8紧张局势。
- 增强反馈对热SZ效应功率谱和热SZ效应与弱透镜交叉谱的观测结果之间的偏差影响较小,这些观测结果对更高质量的团簇更敏感。
点此查看论文截图