⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-03 更新
X-ray illicit object detection using hybrid CNN-transformer neural network architectures
Authors:Jorgen Cani, Christos Diou, Spyridon Evangelatos, Panagiotis Radoglou-Grammatikis, Vasileios Argyriou, Panagiotis Sarigiannidis, Iraklis Varlamis, Georgios Th. Papadopoulos
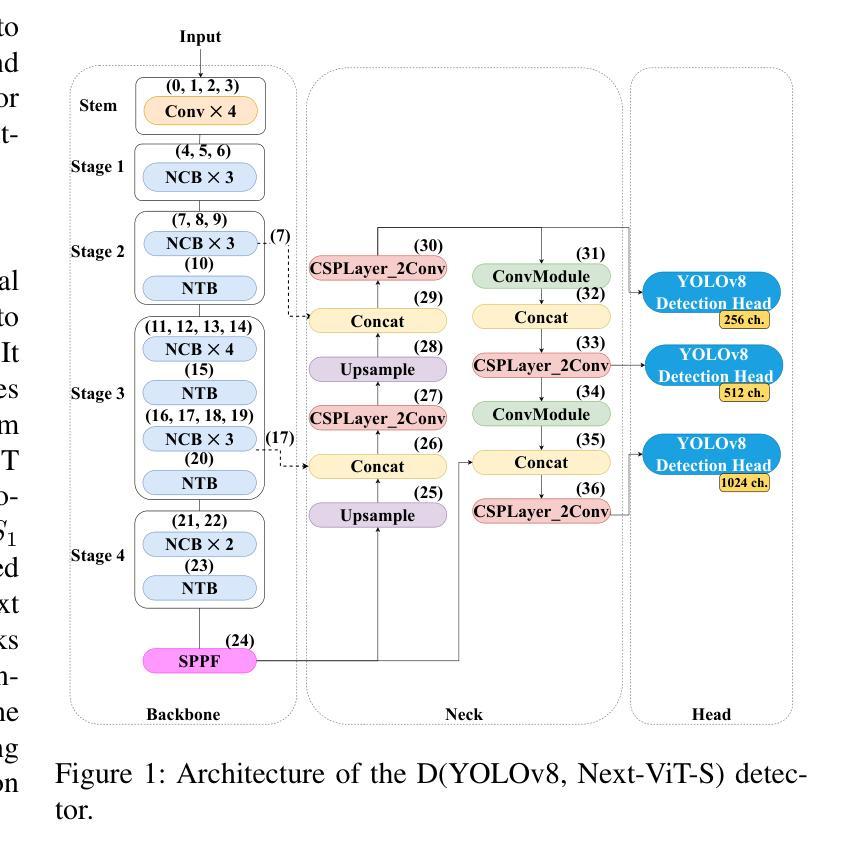
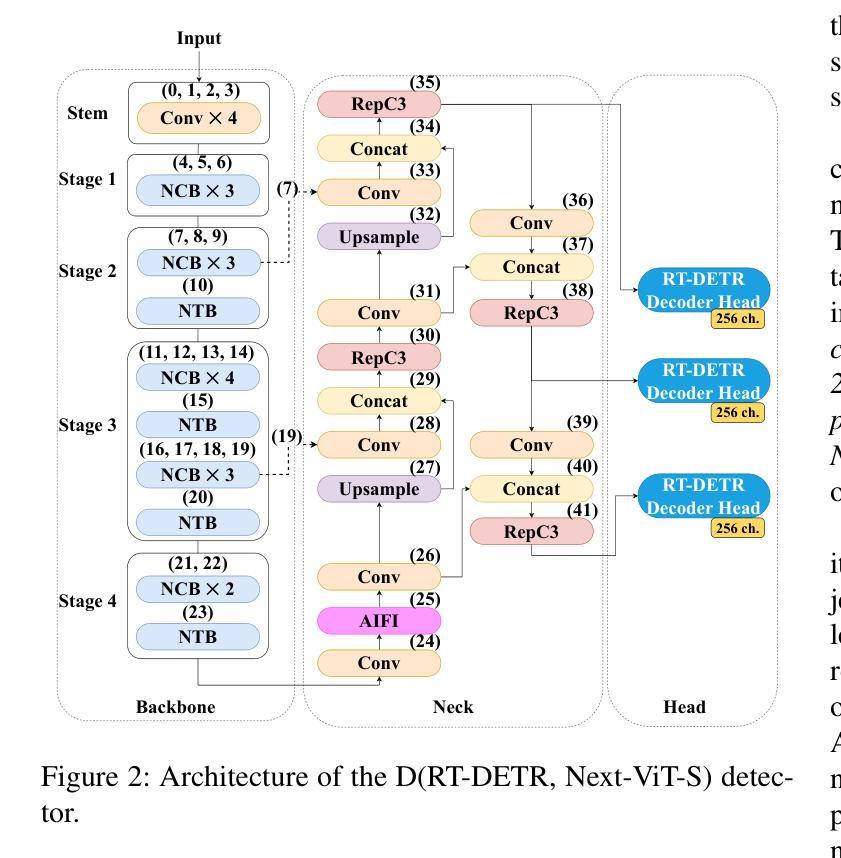
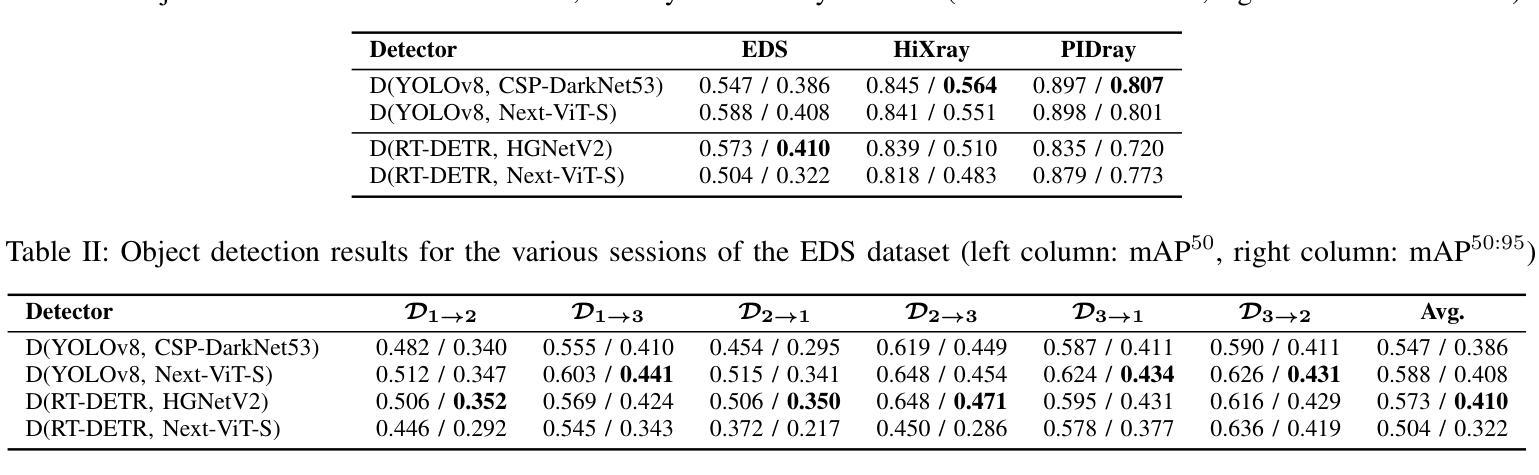
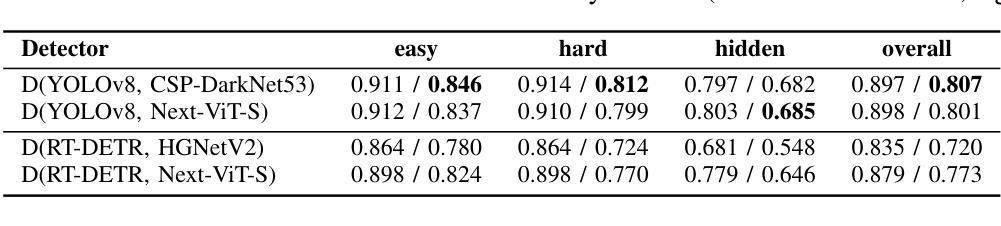
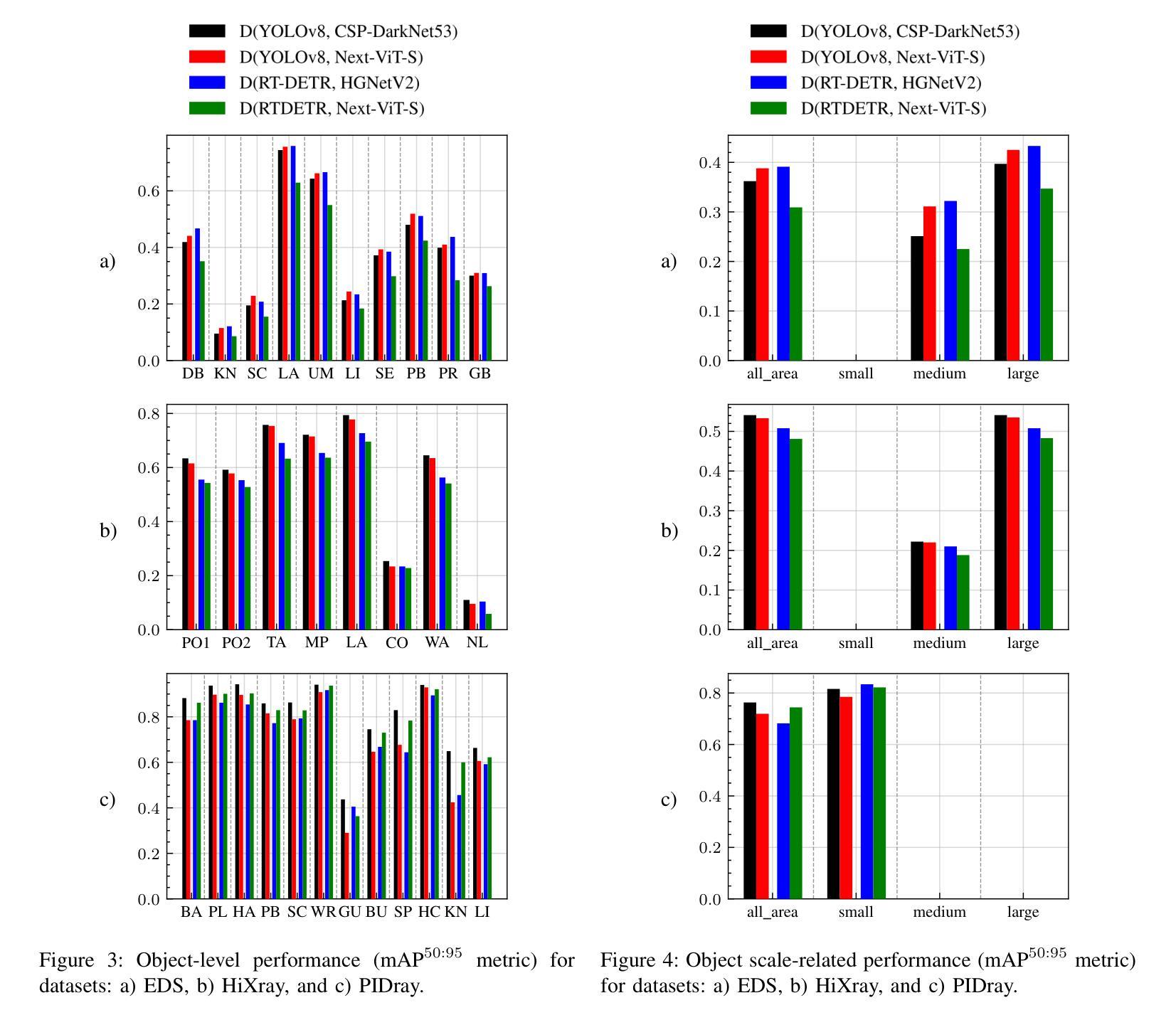
In the field of X-ray security applications, even the smallest details can significantly impact outcomes. Objects that are heavily occluded or intentionally concealed pose a great challenge for detection, whether by human observation or through advanced technological applications. While certain Deep Learning (DL) architectures demonstrate strong performance in processing local information, such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), others excel in handling distant information, e.g., transformers. In X-ray security imaging the literature has been dominated by the use of CNN-based methods, while the integration of the two aforementioned leading architectures has not been sufficiently explored. In this paper, various hybrid CNN-transformer architectures are evaluated against a common CNN object detection baseline, namely YOLOv8. In particular, a CNN (HGNetV2) and a hybrid CNN-transformer (Next-ViT-S) backbone are combined with different CNN/transformer detection heads (YOLOv8 and RT-DETR). The resulting architectures are comparatively evaluated on three challenging public X-ray inspection datasets, namely EDS, HiXray, and PIDray. Interestingly, while the YOLOv8 detector with its default backbone (CSP-DarkNet53) is generally shown to be advantageous on the HiXray and PIDray datasets, when a domain distribution shift is incorporated in the X-ray images (as happens in the EDS datasets), hybrid CNN-transformer architectures exhibit increased robustness. Detailed comparative evaluation results, including object-level detection performance and object-size error analysis, demonstrate the strengths and weaknesses of each architectural combination and suggest guidelines for future research. The source code and network weights of the models employed in this study are available at https://github.com/jgenc/xray-comparative-evaluation.
在X射线安全应用领域,即使是最小的细节也会对结果产生重大影响。被大量遮挡或故意隐藏的物体,无论是通过人工观察还是通过先进技术应用进行检测,都是一个巨大的挑战。虽然某些深度学习(DL)架构在处理局部信息方面表现出强大的性能,例如卷积神经网络(CNN),而其他架构则擅长处理远距离信息,例如变压器。在X射线安全成像文献中,主要以使用基于CNN的方法为主,而这两种前述主流架构的集成尚未得到充分探索。本文评估了各种混合CNN-变压器架构与常见的CNN目标检测基线(即YOLOv8)的对比效果。特别是,将CNN(HGNetV2)和混合CNN-变压器(Next-ViT-S)骨干网与不同的CNN/变压器检测头(YOLOv8和RT-DETR)相结合。在三个具有挑战性的公共X射线检测数据集(即EDS、HiXray和PIDray)上对这些架构进行了比较评估。有趣的是,当X射线图像中融入领域分布变化(如出现在EDS数据集中)时,与在HiXray和PIDray数据集上通常有利的YOLOv8检测器及其默认骨干网(CSP-DarkNet53)相比,混合CNN-变压器架构表现出更高的稳健性。详细的比较评估结果,包括目标级别的检测性能和目标大小误差分析,展示了每种架构组合的优缺点,并为未来的研究提供了指南。本研究中使用的源代码和网络权重可在https://github.com/jgenc/xray-comparative-evaluation中获得。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了在X光安检图像中,深度学习架构对于隐藏或遮挡物体的检测性能。对比了CNN和transformer的混合架构与单一CNN架构在三个公开数据集上的表现。实验表明,当面临领域分布变化的X光图像时,混合架构展现出更高的稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- X光安检应用中,细节对结果影响重大,隐藏或遮挡物体检测具挑战性。
- CNN擅长处理局部信息,而transformer擅长处理远距离信息。
- 在X光安检成像文献中,以CNN为基础的方法占据主导地位,但混合CNN和transformer架构的研究尚不充分。
- 对比评估了多种混合CNN-transformer架构与一个基准的YOLOv8 CNN对象检测。
- 在三个公开X光检测数据集上进行了实验,包括EDS、HiXray和PIDray。
- 当面临领域分布变化的X光图像时,混合CNN-transformer架构展现出更高的稳健性。
- 提供了实验所用的源代码和模型权重。
点此查看论文截图
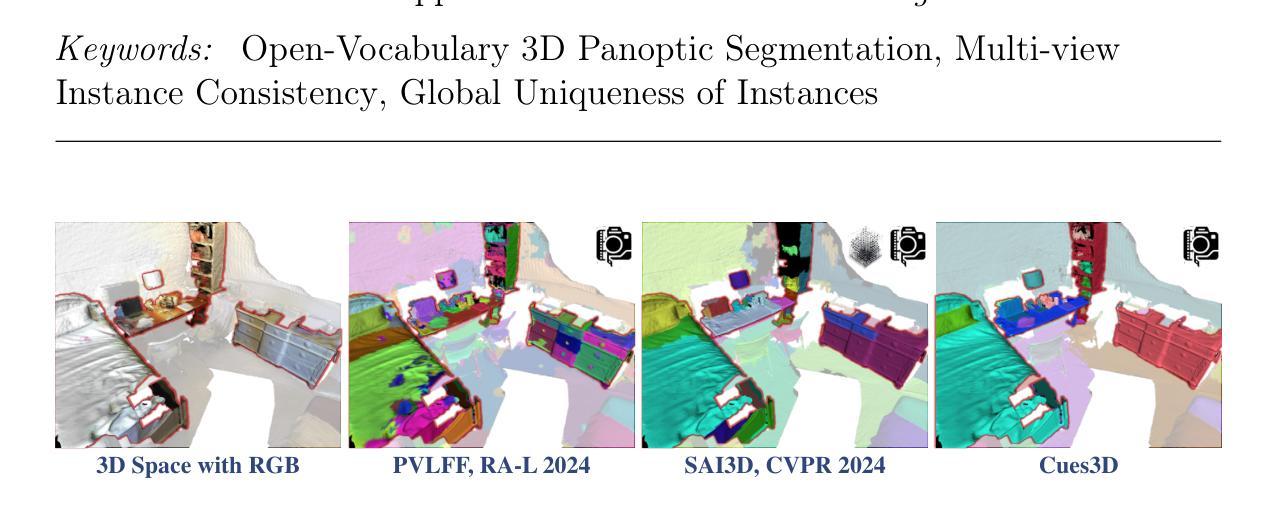
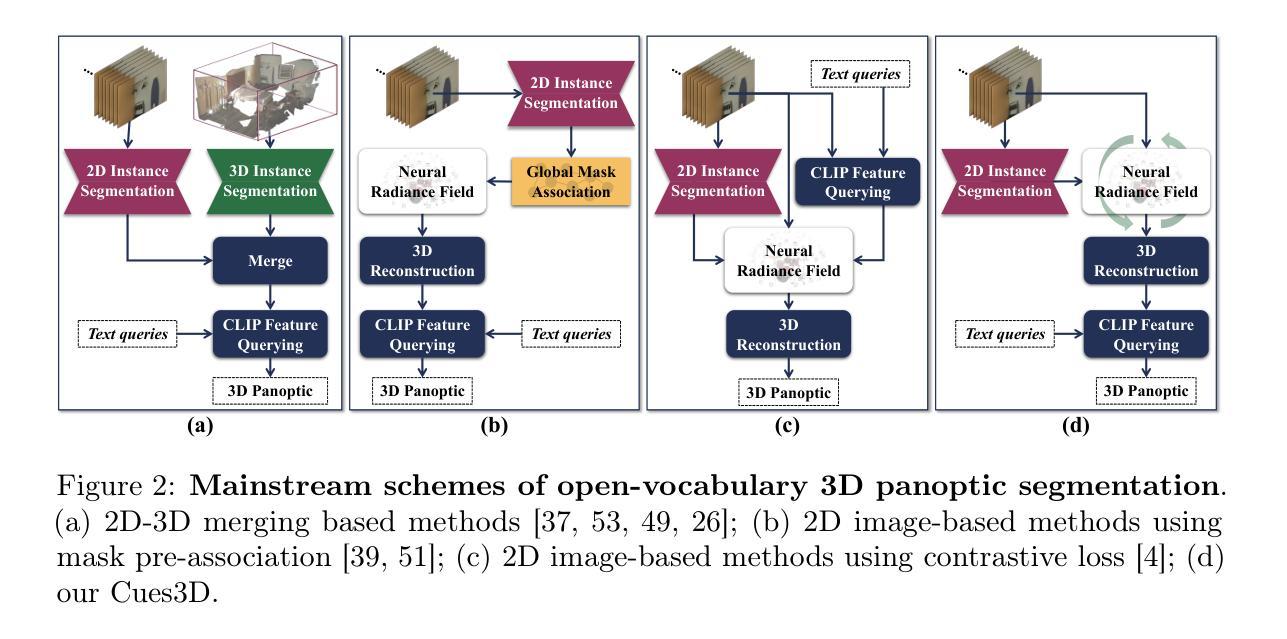
Cues3D: Unleashing the Power of Sole NeRF for Consistent and Unique Instances in Open-Vocabulary 3D Panoptic Segmentation
Authors:Feng Xue, Wenzhuang Xu, Guofeng Zhong, Anlong Minga, Nicu Sebe
Open-vocabulary 3D panoptic segmentation has recently emerged as a significant trend. Top-performing methods currently integrate 2D segmentation with geometry-aware 3D primitives. However, the advantage would be lost without high-fidelity 3D point clouds, such as methods based on Neural Radiance Field (NeRF). These methods are limited by the insufficient capacity to maintain consistency across partial observations. To address this, recent works have utilized contrastive loss or cross-view association pre-processing for view consensus. In contrast to them, we present Cues3D, a compact approach that relies solely on NeRF instead of pre-associations. The core idea is that NeRF’s implicit 3D field inherently establishes a globally consistent geometry, enabling effective object distinction without explicit cross-view supervision. We propose a three-phase training framework for NeRF, initialization-disambiguation-refinement, whereby the instance IDs are corrected using the initially-learned knowledge. Additionally, an instance disambiguation method is proposed to match NeRF-rendered 3D masks and ensure globally unique 3D instance identities. With the aid of Cues3D, we obtain highly consistent and unique 3D instance ID for each object across views with a balanced version of NeRF. Our experiments are conducted on ScanNet v2, ScanNet200, ScanNet++, and Replica datasets for 3D instance, panoptic, and semantic segmentation tasks. Cues3D outperforms other 2D image-based methods and competes with the latest 2D-3D merging based methods, while even surpassing them when using additional 3D point clouds. The code link could be found in the appendix and will be released on \href{https://github.com/mRobotit/Cues3D}{github}
近期开放词汇的3D全景分割已成为一种重要的趋势。目前表现最佳的方案是将2D分割与具有几何意识的3D原始数据整合在一起。然而,如果没有高保真3D点云,这种优势将会丧失,例如基于神经辐射场(NeRF)的方法。这些方法受限于在部分观察结果之间保持一致性的能力不足。为了解决这一问题,近期的研究工作采用了对比损失或跨视图关联预处理来实现视图共识。与之相比,我们提出了Cues3D,这是一种仅依赖NeRF而无需预先关联的紧凑方法。其核心思想是NeRF的隐式3D场固有地建立了全局一致的几何结构,能够在没有明确的跨视图监督的情况下有效地区分对象。我们为NeRF提出了一个三阶段训练框架,即初始化-歧义解析-细化,利用初步学习的知识来校正实例ID。此外,还提出了一种实例歧义解析方法,以匹配NeRF渲染的3D掩模,并确保全局唯一的3D实例身份。借助Cues3D,我们获得了每个对象在不同视图之间的高度一致且唯一的3D实例ID,同时平衡了NeRF版本。我们的实验是在ScanNet v2、ScanNet200、ScanNet++和Replica数据集上进行的,涵盖了3D实例、全景和语义分割任务。Cues3D在基于其他二维图像的方法中具有优势,并与最新的基于二维到三维合并的方法相竞争,甚至在利用额外的三维点云数据时也能超越它们。代码链接详见附录,并将在https://github.com/mRobotit/Cues3D上发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by Information Fusion
Summary
基于NeRF的开放词汇3D全景分割方法,通过三个阶段训练框架和实例去模糊技术,实现全局一致的几何结构并建立有效的对象区分,无需明确的跨视图监督。在多个数据集上的实验表明,Cues3D在3D实例、全景和语义分割任务上表现优异,代码已发布在GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- 开放词汇3D全景分割是当前趋势,集成2D分割与几何感知的3D原始数据是目前高性能的方法。
- NeRF方法因高保真3D点云的优势被广泛应用,但在部分观察的持续性上仍有局限。
- Cues3D方法依赖NeRF而非预关联,利用NeRF的隐式3D场建立全局一致的几何结构,实现有效的对象区分。
- Cues3D采用三阶段训练框架:初始化、去模糊、优化,通过初次学习的知识修正实例ID。
- 提出实例去模糊方法,匹配NeRF渲染的3D掩膜,确保全局唯一的3D实例ID。
点此查看论文截图