⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-03 更新
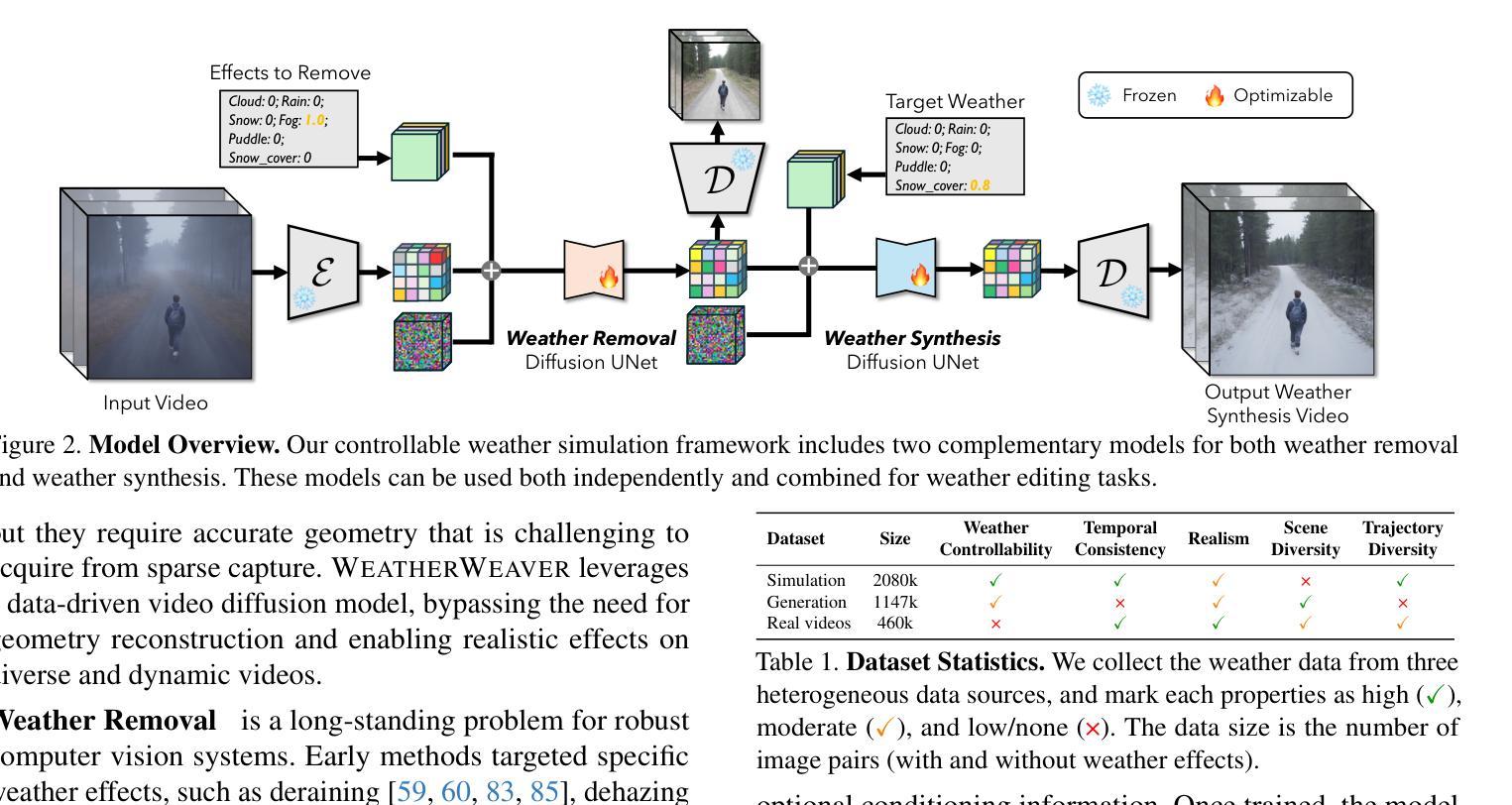
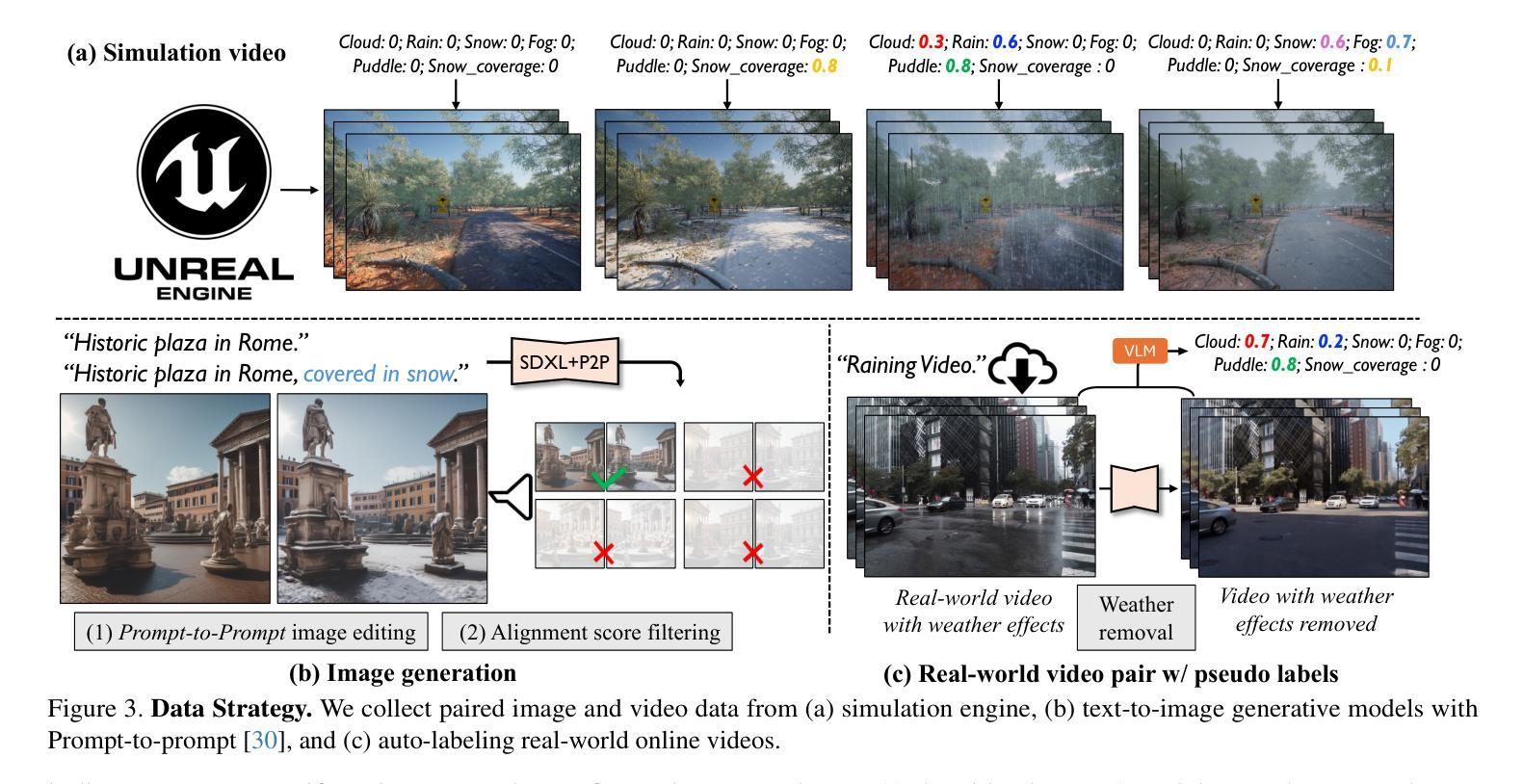
Controllable Weather Synthesis and Removal with Video Diffusion Models
Authors:Chih-Hao Lin, Zian Wang, Ruofan Liang, Yuxuan Zhang, Sanja Fidler, Shenlong Wang, Zan Gojcic
Generating realistic and controllable weather effects in videos is valuable for many applications. Physics-based weather simulation requires precise reconstructions that are hard to scale to in-the-wild videos, while current video editing often lacks realism and control. In this work, we introduce WeatherWeaver, a video diffusion model that synthesizes diverse weather effects – including rain, snow, fog, and clouds – directly into any input video without the need for 3D modeling. Our model provides precise control over weather effect intensity and supports blending various weather types, ensuring both realism and adaptability. To overcome the scarcity of paired training data, we propose a novel data strategy combining synthetic videos, generative image editing, and auto-labeled real-world videos. Extensive evaluations show that our method outperforms state-of-the-art methods in weather simulation and removal, providing high-quality, physically plausible, and scene-identity-preserving results over various real-world videos.
在视频中生成真实可控的天气效果对许多应用具有价值。基于物理的天气模拟需要精确重建,难以扩展到实际视频,而当前的视频编辑往往缺乏真实感和控制性。在这项工作中,我们介绍了WeatherWeaver,这是一种视频扩散模型,可以合成多种天气效果,包括雨、雪、雾和云,并可直接将天气效果添加到任何输入视频中,无需进行3D建模。我们的模型提供对天气效果强度的精确控制,并支持混合各种天气类型,确保真实性和适应性。为了克服配对训练数据的稀缺性,我们提出了一种新的数据策略,结合合成视频、生成图像编辑和自动标记的真实世界视频。大量评估表明,我们的方法在天气模拟和去除方面优于最先进的方法,在各种真实视频上提供高质量、物理可行且保留场景身份的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
天气效果模拟在视频生成中具有广泛应用价值。当前基于物理的模拟方法难以扩展到实际视频,而现有的视频编辑技术缺乏真实感和控制性。本文提出了一个名为WeatherWeaver的视频扩散模型,可直接在输入视频上合成多种天气效果,无需复杂的3D建模。该模型可精确控制天气效果的强度,并支持混合多种天气类型,确保真实性和适应性。为解决配对训练数据稀缺的问题,我们提出了一种新的数据策略,结合合成视频、生成图像编辑和自动标记的真实世界视频。评估表明,我们的方法在天气模拟和去除方面优于当前的最先进技术,在各种真实视频上都能产生高质量、物理合理且场景身份保留的结果。
Key Takeaways
- WeatherWeaver是一个视频扩散模型,能够合成多种天气效果,如雨雪雾云等。
- 该模型可直接应用于任何输入视频,无需3D建模。
- WeatherWeaver提供了对天气效果强度的精确控制,并可混合不同的天气类型。
- 模型确保了合成天气的真实性和适应性。
- 针对训练数据稀缺的问题,提出了一种结合合成视频、生成图像编辑和自动标记真实世界视频的新数据策略。
- 评估显示,WeatherWeaver在天气模拟和去除方面表现优异。
点此查看论文截图


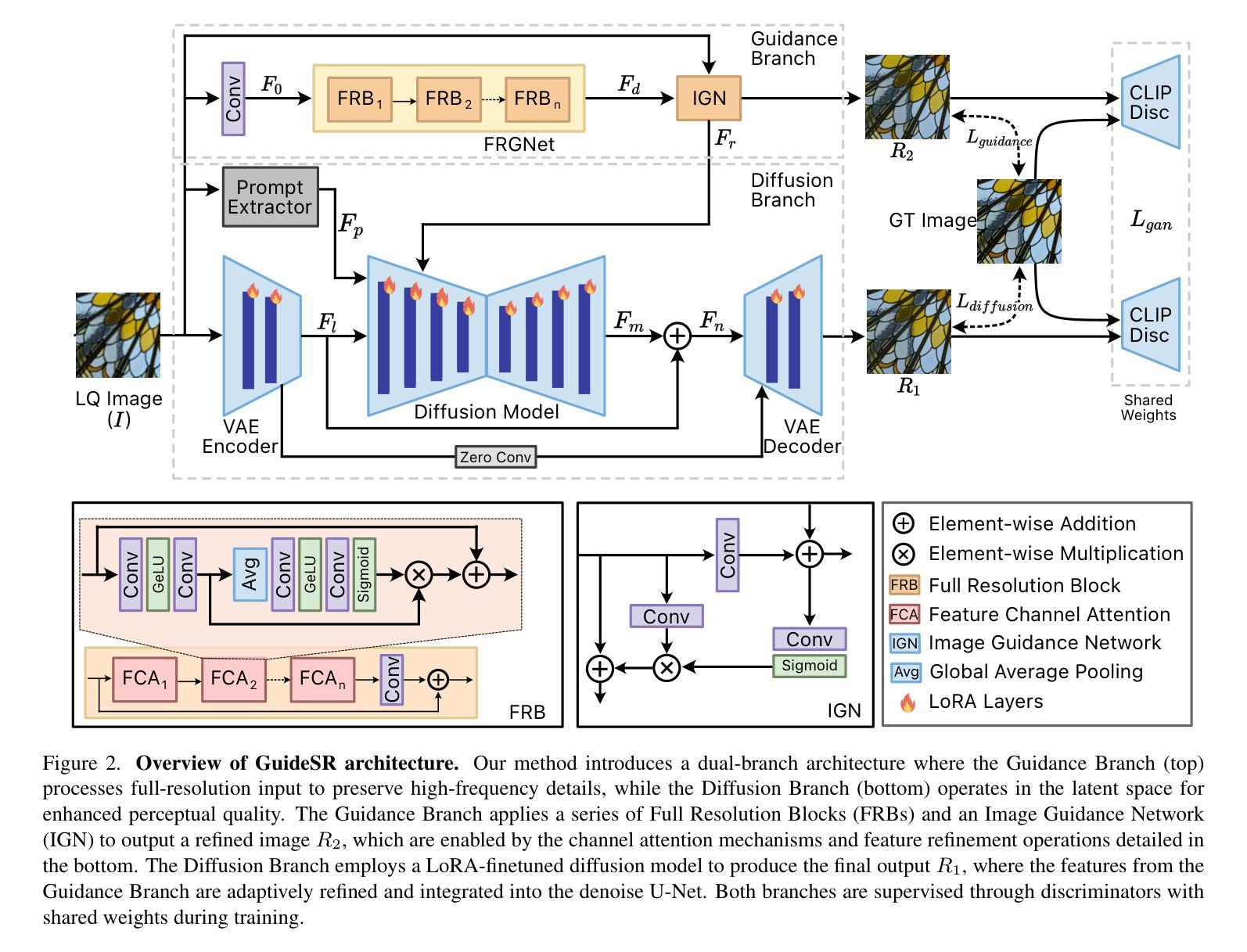
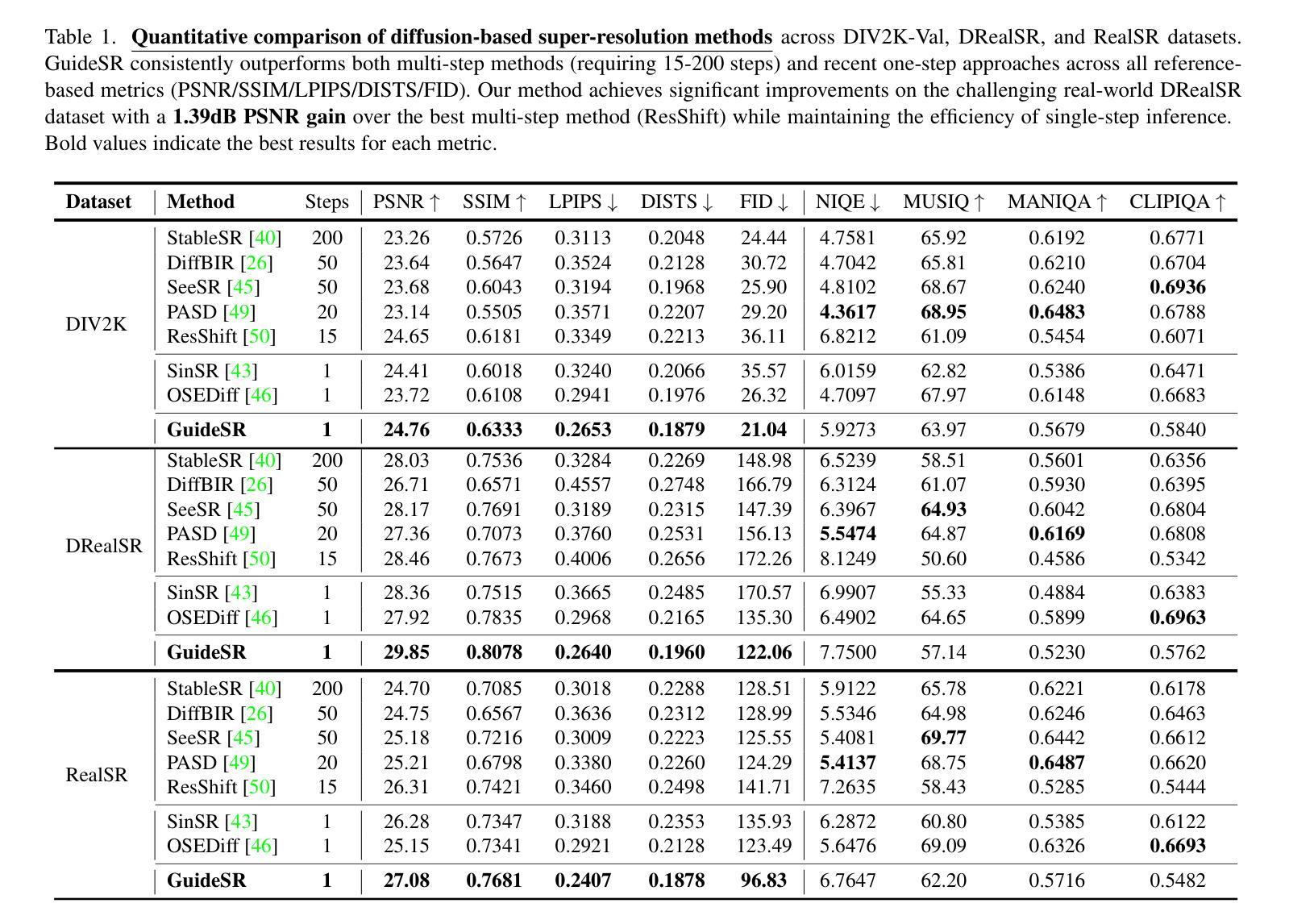
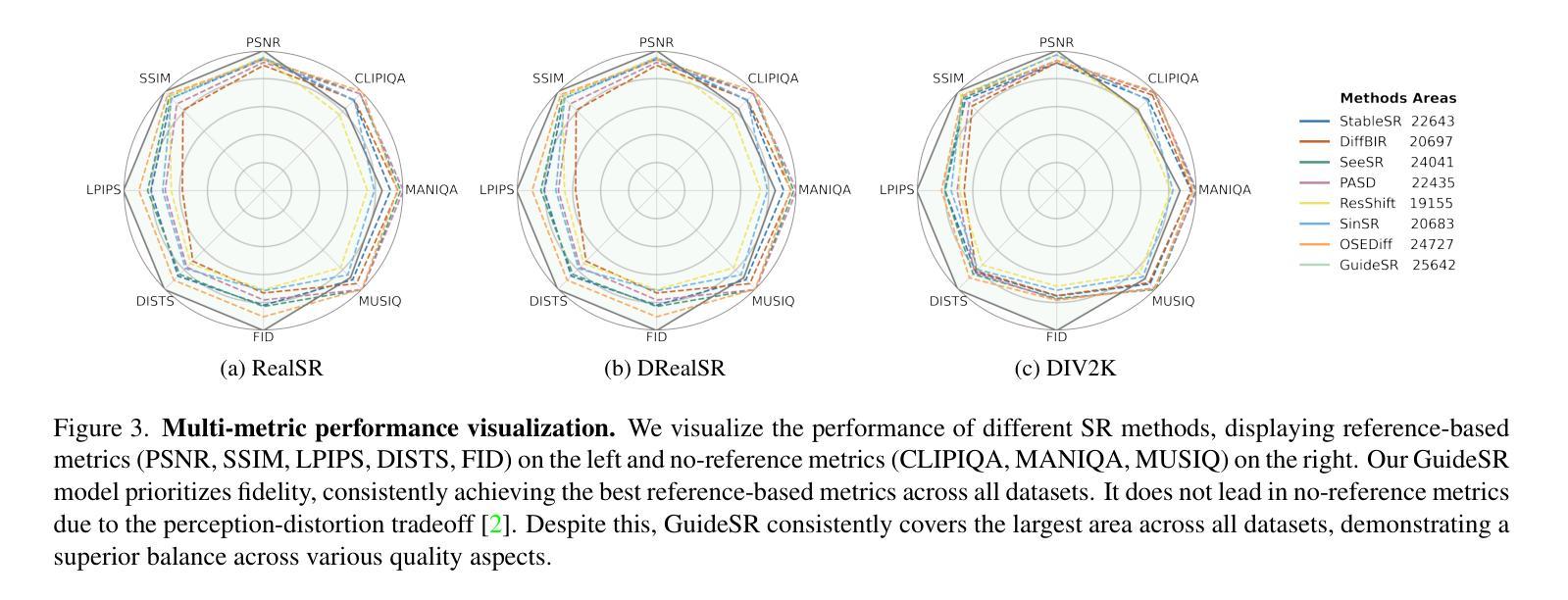
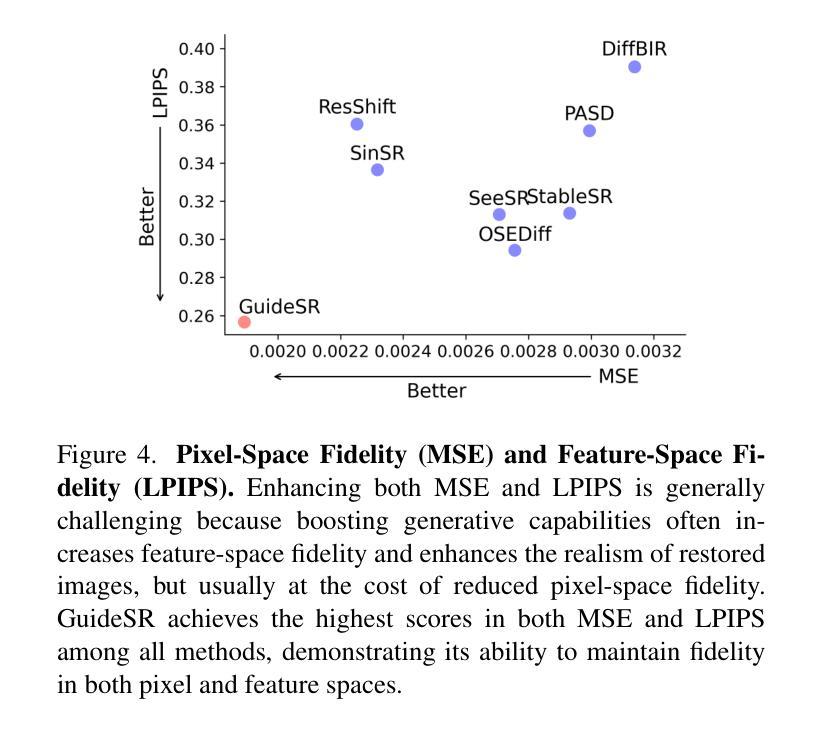
GuideSR: Rethinking Guidance for One-Step High-Fidelity Diffusion-Based Super-Resolution
Authors:Aditya Arora, Zhengzhong Tu, Yufei Wang, Ruizheng Bai, Jian Wang, Sizhuo Ma
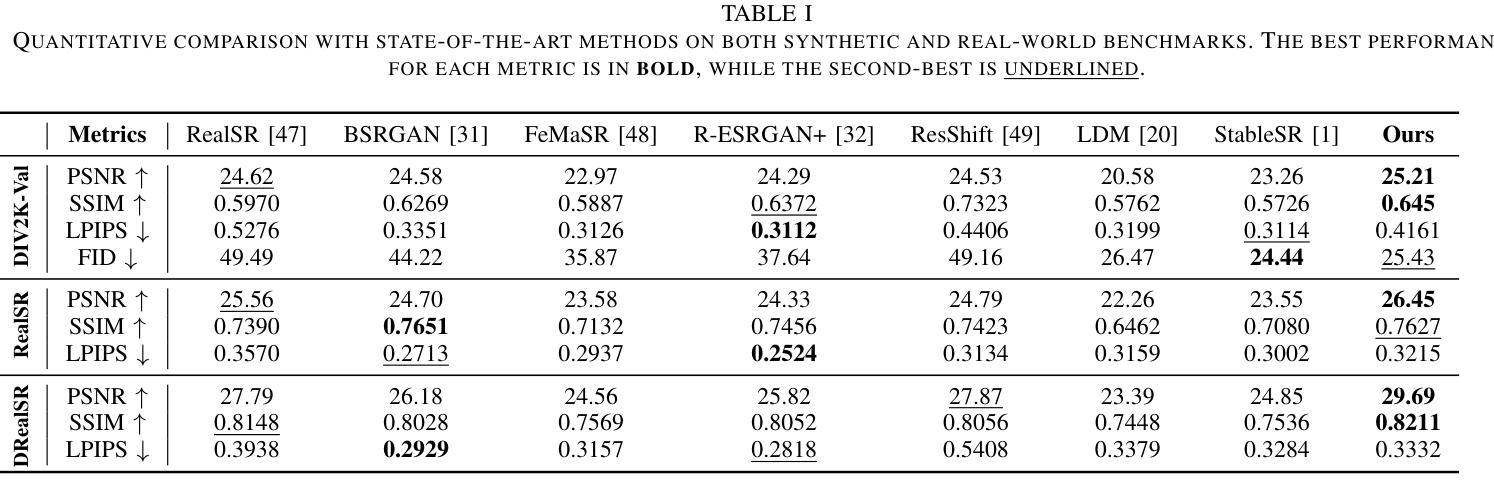
In this paper, we propose GuideSR, a novel single-step diffusion-based image super-resolution (SR) model specifically designed to enhance image fidelity. Existing diffusion-based SR approaches typically adapt pre-trained generative models to image restoration tasks by adding extra conditioning on a VAE-downsampled representation of the degraded input, which often compromises structural fidelity. GuideSR addresses this limitation by introducing a dual-branch architecture comprising: (1) a Guidance Branch that preserves high-fidelity structures from the original-resolution degraded input, and (2) a Diffusion Branch, which a pre-trained latent diffusion model to enhance perceptual quality. Unlike conventional conditioning mechanisms, our Guidance Branch features a tailored structure for image restoration tasks, combining Full Resolution Blocks (FRBs) with channel attention and an Image Guidance Network (IGN) with guided attention. By embedding detailed structural information directly into the restoration pipeline, GuideSR produces sharper and more visually consistent results. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that GuideSR achieves state-of-the-art performance while maintaining the low computational cost of single-step approaches, with up to 1.39dB PSNR gain on challenging real-world datasets. Our approach consistently outperforms existing methods across various reference-based metrics including PSNR, SSIM, LPIPS, DISTS and FID, further representing a practical advancement for real-world image restoration.
本文提出了GuideSR,这是一种新型的单步扩散图像超分辨率(SR)模型,专门设计用于提高图像保真度。现有的基于扩散的SR方法通常通过将预训练的生成模型适应于图像恢复任务,通过在变分自动编码器(VAE)降采样表示的退化输入上添加额外的条件来实现,这通常会损害结构保真度。GuideSR通过引入包含两个分支的架构来解决这一局限性:(1)指导分支,用于保留原始分辨率退化输入的高保真结构;(2)扩散分支,使用预训练的潜在扩散模型来提高感知质量。与传统的条件机制不同,我们的指导分支具有针对图像恢复任务的定制结构,结合了全分辨率块(FRBs)与通道注意力机制和图像指导网络(IGN)与引导注意力。通过将详细的结构信息直接嵌入到恢复管道中,GuideSR产生了更清晰且视觉上更一致的结果。在基准数据集上的广泛实验表明,GuideSR实现了最先进的性能,同时保持了单步方法的低计算成本,在具有挑战性的真实世界数据集上最多提高了1.39dB的峰值信噪比(PSNR)。我们的方法在各种参考指标上始终优于现有方法,包括PSNR、SSIM、LPIPS、DISTS和FID,这进一步代表了实际图像恢复的进步。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一个名为GuideSR的新型单步扩散图像超分辨率(SR)模型,旨在提高图像保真度。通过引入双分支架构和定制的指导分支,GuideSR解决了现有扩散SR模型在处理图像恢复任务时结构保真度受损的问题。该模型结合了全分辨率块(FRBs)和图像指导网络(IGN),能够在恢复管道中嵌入详细的结构信息,从而生成更清晰、视觉上更一致的结果。在基准数据集上的实验表明,GuideSR在保持单步方法低计算成本的同时实现了最先进的性能,在具有挑战性的真实世界数据集上PSNR增益高达1.39dB。它的一致表现使其在PSNR、SSIM、LPIPS、DISTS和FID等参考指标上优于现有方法,为真实世界图像恢复提供了实际进步。
Key Takeaways
- GuideSR是一个基于扩散的单步图像超分辨率模型,旨在提高图像保真度。
- 现有扩散SR方法通常在图像恢复任务中妥协结构保真度,而GuideSR通过双分支架构解决此问题。
- GuideSR包含定制的指导分支,结合了全分辨率块和图像指导网络,能在恢复过程中嵌入详细结构信息。
- GuideSR在多个基准数据集上实现了卓越性能,与现有方法相比具有更高的PSNR增益。
- GuideSR在各种参考指标上均表现出优越性,包括PSNR、SSIM、LPIPS、DISTS和FID。
- GuideSR为真实世界图像恢复提供了实际改进。
点此查看论文截图

Denoising weak lensing mass maps with diffusion model: systematic comparison with generative adversarial network
Authors:Shohei D. Aoyama, Ken Osato, Masato Shirasaki
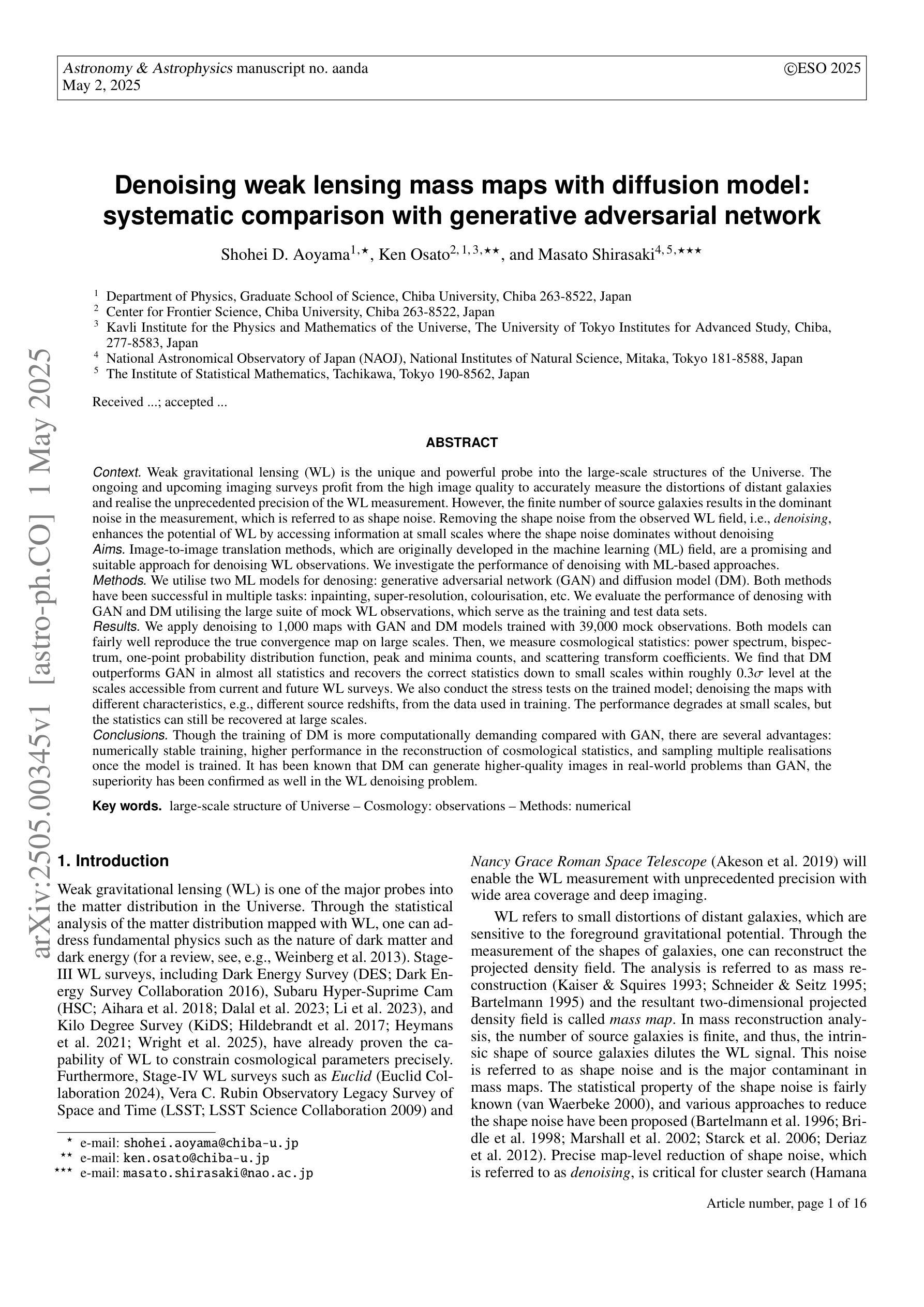
(abridged) Weak gravitational lensing (WL) is the unique and powerful probe into the large-scale structures of the Universe. Removing the shape noise from the observed WL field, i.e., denoising, enhances the potential of WL by accessing information at small scales where the shape noise dominates without denoising. We utilise two machine learning (ML) models for denosing: generative adversarial network (GAN) and diffusion model (DM). We evaluate the performance of denosing with GAN and DM utilising the large suite of mock WL observations, which serve as the training and test data sets. We apply denoising to 1,000 maps with GAN and DM models trained with 39,000 mock observations. Both models can fairly well reproduce the true convergence map on large scales. Then, we measure cosmological statistics: power spectrum, bispectrum, one-point probability distribution function, peak and minima counts, and scattering transform coefficients. We find that DM outperforms GAN in almost all statistics and recovers the correct statistics down to small scales within roughly $0.3 \sigma$ level at the scales accessible from current and future WL surveys. We also conduct the stress tests on the trained model; denoising the maps with different characteristics, e.g., different source redshifts, from the data used in training. The performance degrades at small scales, but the statistics can still be recovered at large scales. Though the training of DM is more computationally demanding compared with GAN, there are several advantages: numerically stable training, higher performance in the reconstruction of cosmological statistics, and sampling multiple realisations once the model is trained. It has been known that DM can generate higher-quality images in real-world problems than GAN, the superiority has been confirmed as well in the WL denoising problem.
弱引力透镜(WL)是对宇宙大规模结构的独特而强大的探测手段。从观测到的WL场中去除形状噪声,即去噪,增强了WL的潜力,因为去噪可以访问小到尺度上的信息,在那里形状噪声在去噪之前占主导地位。我们利用两种机器学习(ML)模型进行去噪:生成对抗网络(GAN)和扩散模型(DM)。我们利用大量的模拟WL观测结果对使用GAN和DM进行去噪的性能进行了评估,这些模拟数据既用于训练也用于测试。我们对1000张地图应用了去噪处理,这些地图使用GAN和DM模型进行训练,训练数据为39000个模拟观测结果。两种模型在大尺度上都能较好地再现真实的收敛图。然后,我们测量了宇宙学统计量:功率谱、双谱、一点概率分布函数、峰谷计数和散射变换系数。我们发现DM在几乎所有的统计量上都优于GAN,并且在当前和未来的WL调查可访问的尺度内,能够恢复到小到0.3σ水平的正确统计量。我们还对训练好的模型进行了压力测试,即对具有不同特性的地图进行去噪,例如源红移不同于训练数据。虽然在小尺度上的性能有所下降,但在大尺度上仍然可以恢复统计量。尽管与GAN相比,DM的训练在计算上要求更高,但它有几个优点:训练数值稳定、在重建宇宙学统计量方面性能更高,并且一旦模型训练完成,可以一次抽样多个实现。已知DM在现实世界的问题中可以生成比GAN更高质量的图像,这一优越性在WL去噪问题中也得到了证实。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to A&A, 16 pages, 15+2 figures
摘要
利用弱引力透镜成像中的机器学习去噪技术提升观测效果。对比了生成对抗网络(GAN)和扩散模型(DM)在模拟观测数据中的去噪性能。扩散模型在多数宇宙学统计量测量中表现优于GAN,尤其是在小尺度上。尽管训练成本较高,但DM具有数值稳定、性能优越等优点,一旦训练完成,可多次采样实现。DM在生成高质量图像方面具有优势,同样适用于弱引力透镜成像的去噪问题。
关键见解
- 弱引力透镜成像是一种揭示宇宙大尺度结构的重要方法。去噪是提高其在小尺度上应用潜力的关键。
- 对比了GAN和DM在去噪性能方面的表现,两者在模拟观测数据中的大型尺度上都能较好地重建真实收敛图。
- DM在大多数宇宙学统计量的测量中表现优于GAN,尤其是在小尺度上恢复正确的统计量。
- 尽管DM的训练成本较高,但其具有数值稳定的训练过程和出色的性能表现。训练完成后,可多次采样实现图像去噪。
- DM在去噪过程中具有生成高质量图像的优势,这一优势在弱引力透镜成像领域也得到了证实。
- 对于不同特性的地图数据(如不同的源红移),尽管去噪性能在小尺度上有所降低,但在大尺度上仍能恢复统计量。
点此查看论文截图
Quaternion Wavelet-Conditioned Diffusion Models for Image Super-Resolution
Authors:Luigi Sigillo, Christian Bianchi, Danilo Comminiello
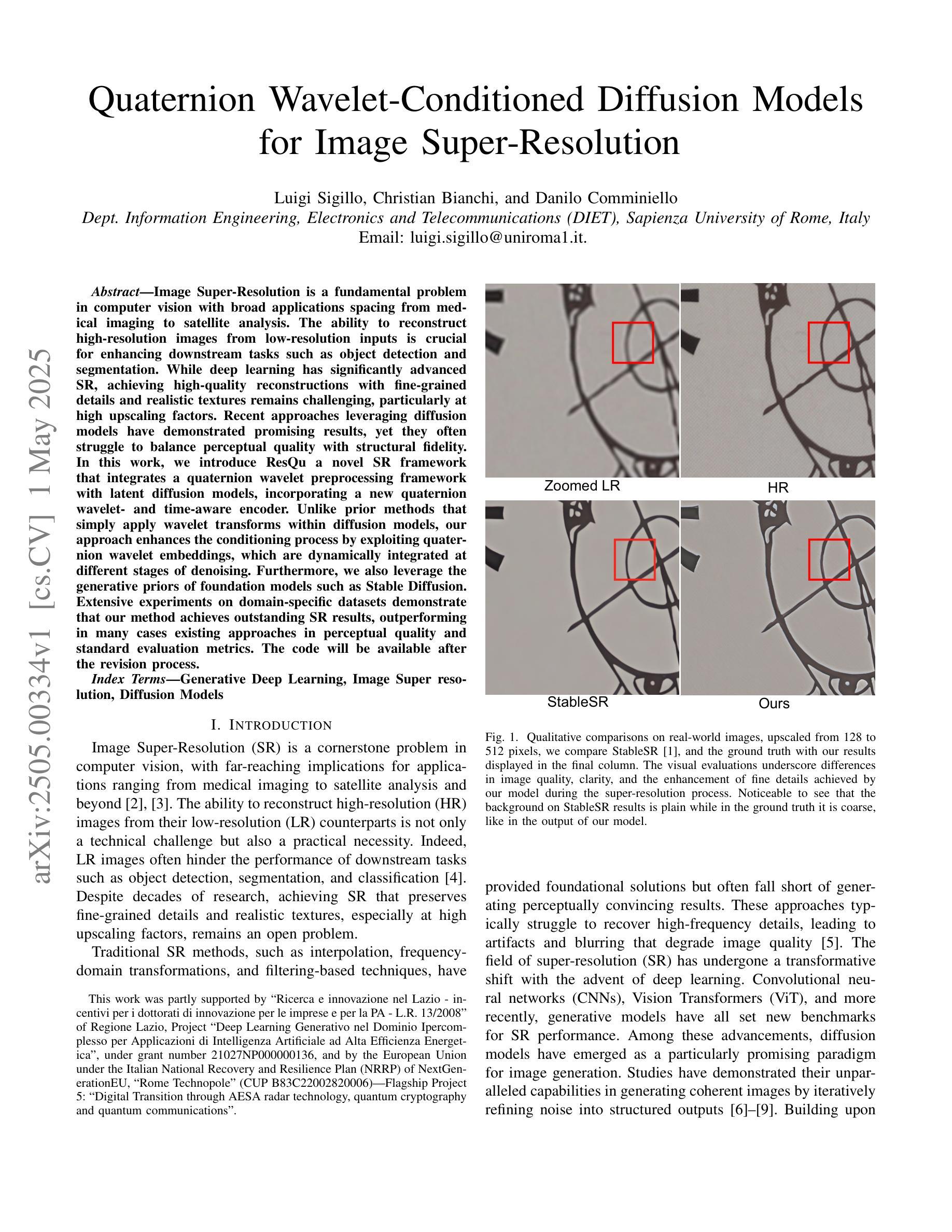
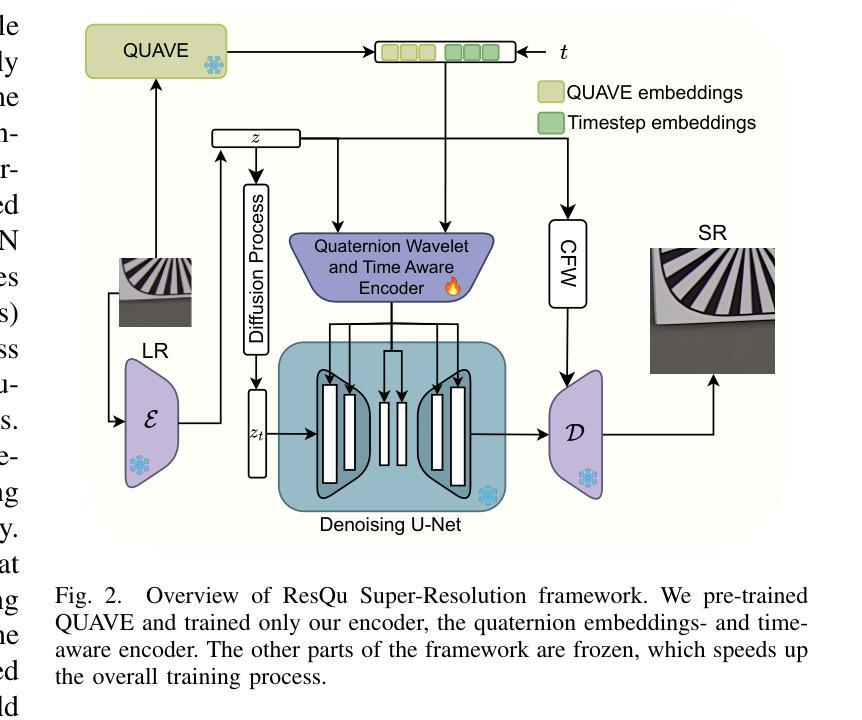
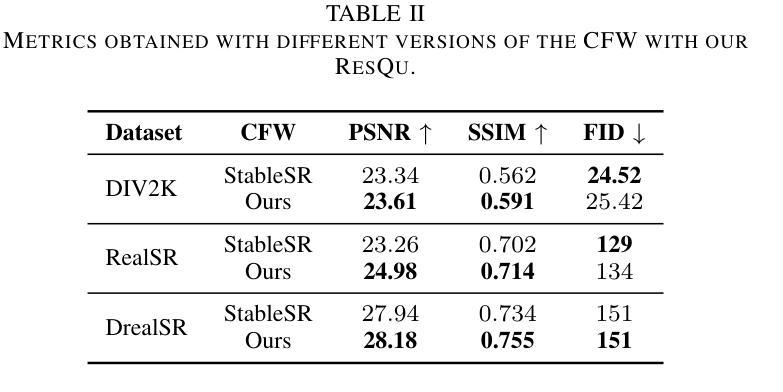
Image Super-Resolution is a fundamental problem in computer vision with broad applications spacing from medical imaging to satellite analysis. The ability to reconstruct high-resolution images from low-resolution inputs is crucial for enhancing downstream tasks such as object detection and segmentation. While deep learning has significantly advanced SR, achieving high-quality reconstructions with fine-grained details and realistic textures remains challenging, particularly at high upscaling factors. Recent approaches leveraging diffusion models have demonstrated promising results, yet they often struggle to balance perceptual quality with structural fidelity. In this work, we introduce ResQu a novel SR framework that integrates a quaternion wavelet preprocessing framework with latent diffusion models, incorporating a new quaternion wavelet- and time-aware encoder. Unlike prior methods that simply apply wavelet transforms within diffusion models, our approach enhances the conditioning process by exploiting quaternion wavelet embeddings, which are dynamically integrated at different stages of denoising. Furthermore, we also leverage the generative priors of foundation models such as Stable Diffusion. Extensive experiments on domain-specific datasets demonstrate that our method achieves outstanding SR results, outperforming in many cases existing approaches in perceptual quality and standard evaluation metrics. The code will be available after the revision process.
图像超分辨率是计算机视觉中的一个基本问题,其应用范围广泛,从医学影像到卫星分析都有涉及。从低分辨率输入重建高分辨率图像的能力对于提高下游任务(如目标检测和分割)至关重要。虽然深度学习已经大大推动了超分辨率技术的发展,但实现具有精细细节和逼真纹理的高质量重建仍然是一个挑战,特别是在高放大倍数时。最近利用扩散模型的方法已经取得了有前景的结果,但它们往往难以在感知质量与结构保真之间取得平衡。在这项工作中,我们介绍了ResQu,这是一种新型超分辨率框架,它将四元小波预处理框架与潜在扩散模型相结合,并引入了一个新的四元小波和时间感知编码器。与之前在扩散模型中简单应用小波变换的方法不同,我们的方法通过利用四元小波嵌入来增强条件过程,这些嵌入在不同的去噪阶段被动态集成。此外,我们还利用了基础模型的生成先验知识,如Stable Diffusion。在特定领域数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的方法实现了出色的超分辨率结果,在许多情况下超过了现有方法在感知质量和标准评估指标上的表现。代码将在复审后提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for presentation at IJCNN 2025
Summary
图像超分辨率是计算机视觉中的一个基本问题,从医学影像到卫星分析都有广泛应用。深度学习方法虽显著提升超分辨率效果,但在细节和纹理恢复方面仍面临挑战,特别是在高放大倍数下。最近采用扩散模型的方法展现出良好前景,但在感知质量与结构保真度之间取得平衡是一大难题。本研究提出一种新型超分辨率框架ResQu,结合四元小波预处理框架与潜在扩散模型,引入新的四元小波和时序感知编码器。相较于简单在扩散模型中应用小波变换的方法,我们的方法通过利用四元小波嵌入来优化条件过程,并在去噪的不同阶段进行动态集成。此外,我们还利用基础模型的生成先验,如Stable Diffusion。在特定数据集上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法在感知质量和标准评估指标上均表现出卓越的超分辨率效果。
Key Takeaways
- 图像超分辨率是计算机视觉的核心问题,涉及广泛的应用领域。
- 深度学习方法在超分辨率任务中有显著进展,但在细节和纹理恢复上仍具挑战。
- 扩散模型最近在图像超分辨率中展现出潜力,但平衡感知质量与结构保真度是一大难题。
- 研究提出了一种新型超分辨率框架ResQu,结合四元小波预处理和潜在扩散模型。
- ResQu利用四元小波嵌入优化条件过程,并在去噪的不同阶段进行动态集成。
- ResQu结合基础模型的生成先验,如Stable Diffusion,以进一步提高性能。
点此查看论文截图

Gaussian Mixture Flow Matching Models
Authors:Hansheng Chen, Kai Zhang, Hao Tan, Zexiang Xu, Fujun Luan, Leonidas Guibas, Gordon Wetzstein, Sai Bi
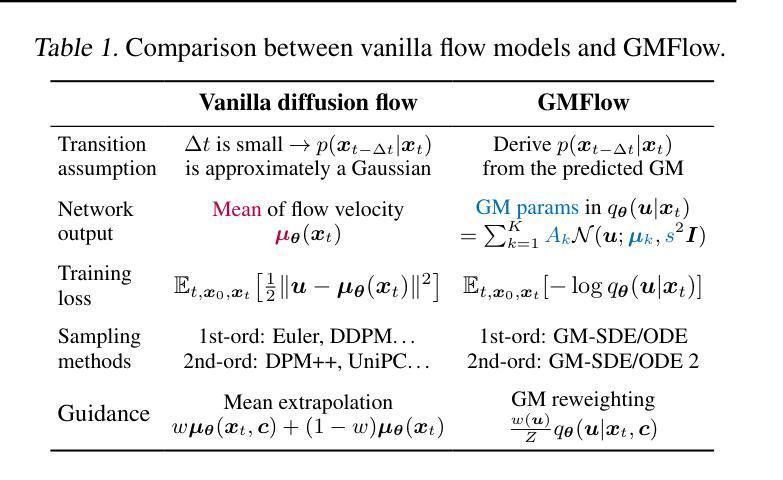
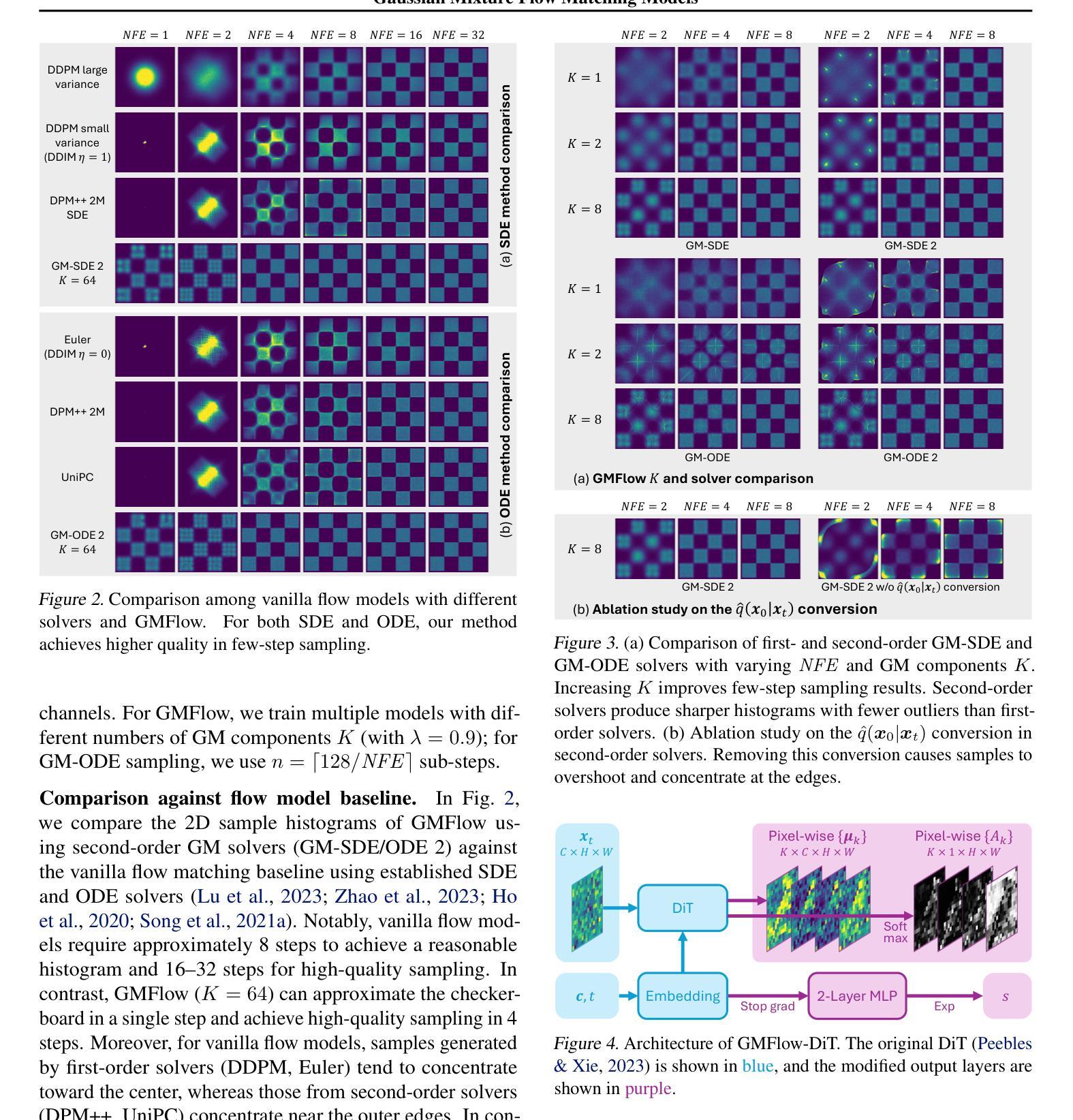
Diffusion models approximate the denoising distribution as a Gaussian and predict its mean, whereas flow matching models reparameterize the Gaussian mean as flow velocity. However, they underperform in few-step sampling due to discretization error and tend to produce over-saturated colors under classifier-free guidance (CFG). To address these limitations, we propose a novel Gaussian mixture flow matching (GMFlow) model: instead of predicting the mean, GMFlow predicts dynamic Gaussian mixture (GM) parameters to capture a multi-modal flow velocity distribution, which can be learned with a KL divergence loss. We demonstrate that GMFlow generalizes previous diffusion and flow matching models where a single Gaussian is learned with an $L_2$ denoising loss. For inference, we derive GM-SDE/ODE solvers that leverage analytic denoising distributions and velocity fields for precise few-step sampling. Furthermore, we introduce a novel probabilistic guidance scheme that mitigates the over-saturation issues of CFG and improves image generation quality. Extensive experiments demonstrate that GMFlow consistently outperforms flow matching baselines in generation quality, achieving a Precision of 0.942 with only 6 sampling steps on ImageNet 256$\times$256.
扩散模型通过近似去噪分布为高斯分布并预测其均值,而流匹配模型则将高斯均值重新参数化为流速。然而,由于离散化误差,它们在几步采样上的表现较差,并且在无分类器引导(CFG)下容易产生过饱和颜色。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了一种新型的高斯混合流匹配(GMFlow)模型:GMFlow不预测均值,而是预测动态高斯混合(GM)参数,以捕捉多模式流速分布,这可以通过KL散度损失来学习。我们证明了GMFlow能够概括先前的扩散模型和流匹配模型,其中单个高斯是通过L2去噪损失来学习的。对于推理,我们推导出了利用分析去噪分布和速度场的GM-SDE/ODE求解器,用于精确几步采样。此外,我们引入了一种新的概率引导方案,该方案缓解了CFG的过饱和问题,并提高了图像生成质量。大量实验表明,GMFlow在生成质量方面始终优于流匹配基线,在ImageNet 256×256上仅6个采样步骤就达到了0.942的精度。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML 2025. Code: https://github.com/Lakonik/GMFlow
Summary
本文提出一种新型的高斯混合流匹配(GMFlow)模型,用于解决扩散模型和流匹配模型在少数步骤采样和分类器免费指导下的局限性。GMFlow通过预测动态高斯混合参数来捕捉多模态流速度分布,并可通过KL散度损失进行学习。GMFlow模型能够改进现有扩散模型和流匹配模型的不足,实现更精确的少数步骤采样和图像生成质量提升。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型和流匹配模型在少数步骤采样中存在离散化误差。
- 分类器免费指导(CFG)下,现有模型容易产生过饱和颜色问题。
- GMFlow模型通过预测动态高斯混合参数来捕捉多模态流速度分布。
- GMFlow模型采用KL散度损失进行学习,能够改进现有扩散模型和流匹配模型的不足。
- GMFlow模型实现了精确的少数步骤采样和图像生成质量提升。
- GMFlow模型引入了一种新的概率引导方案,缓解了CFG的过饱和问题。
点此查看论文截图

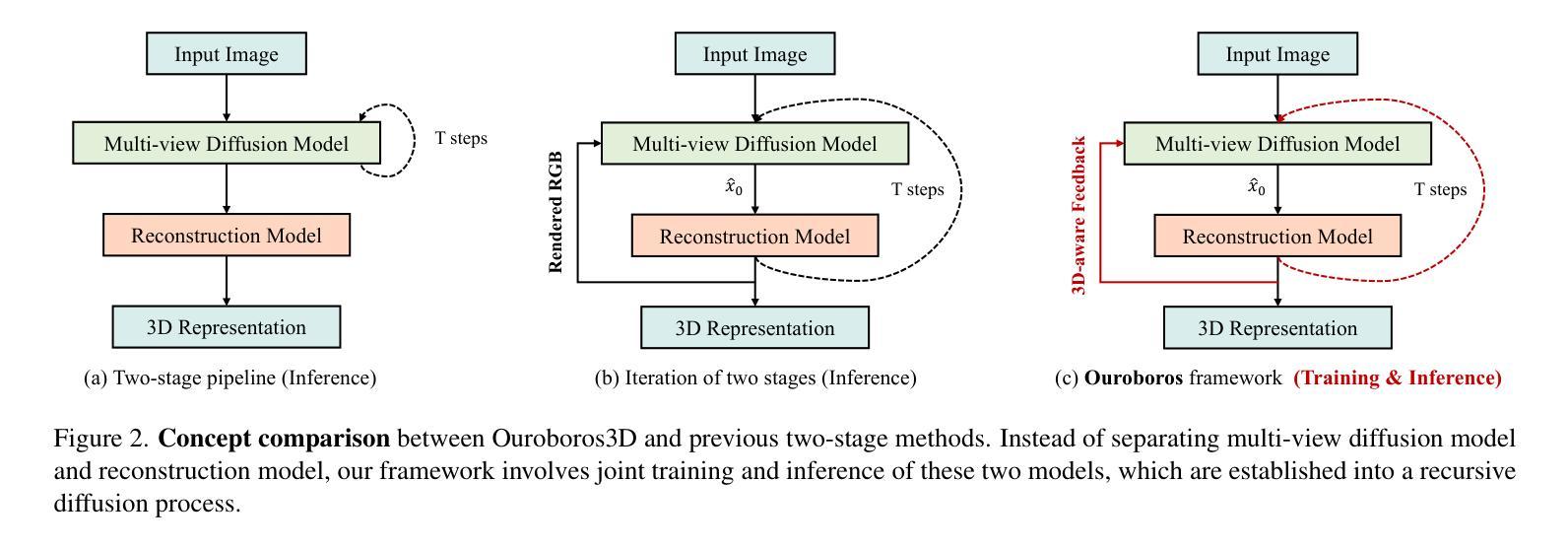
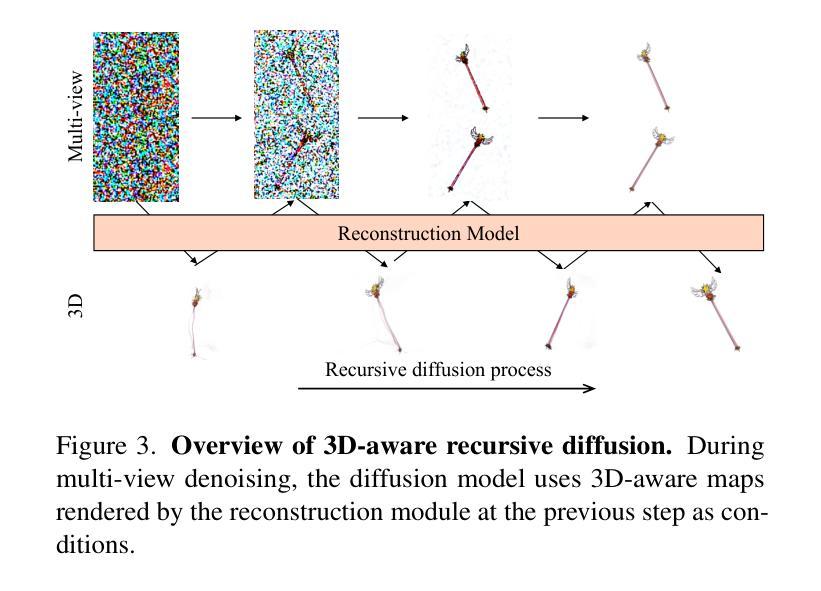
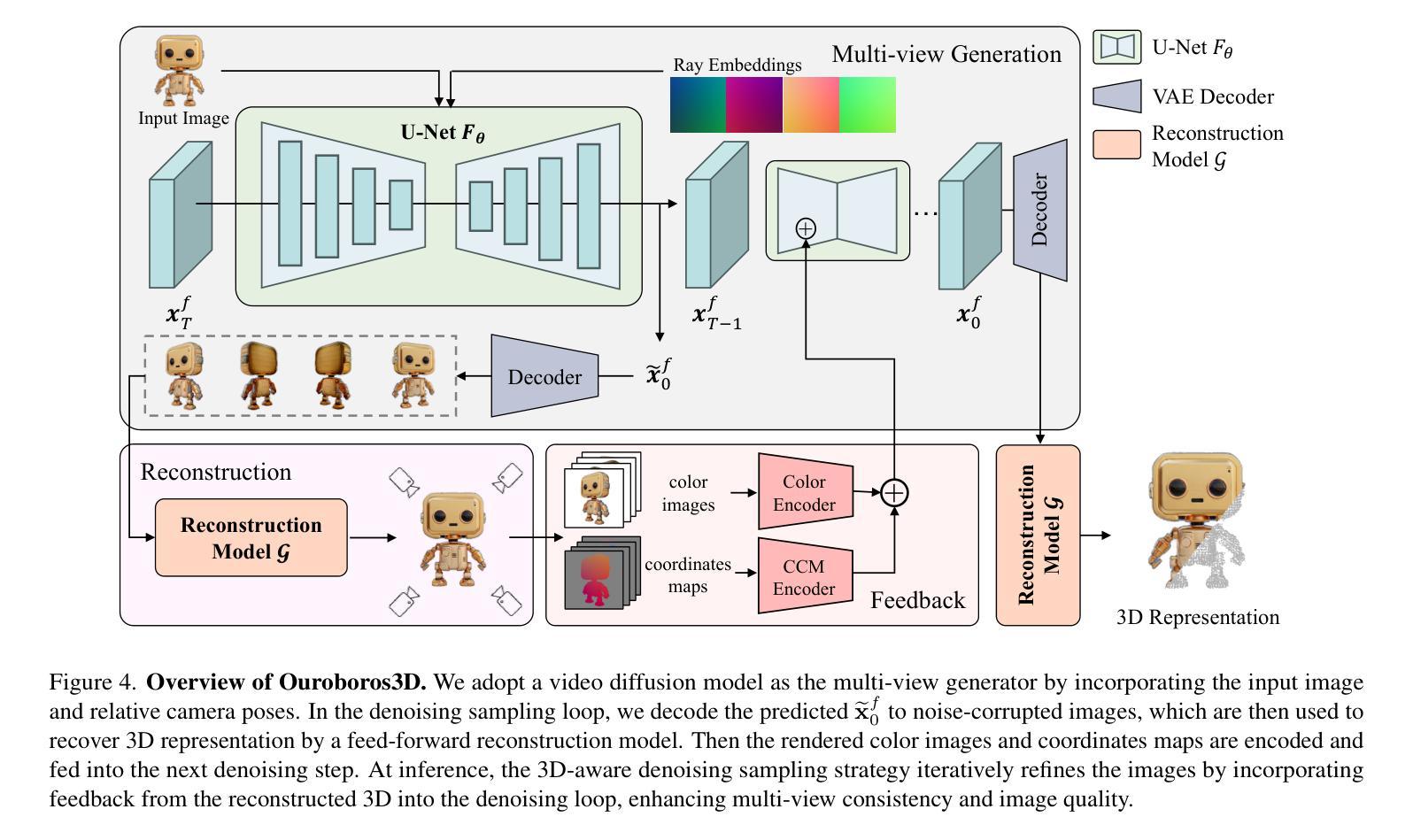
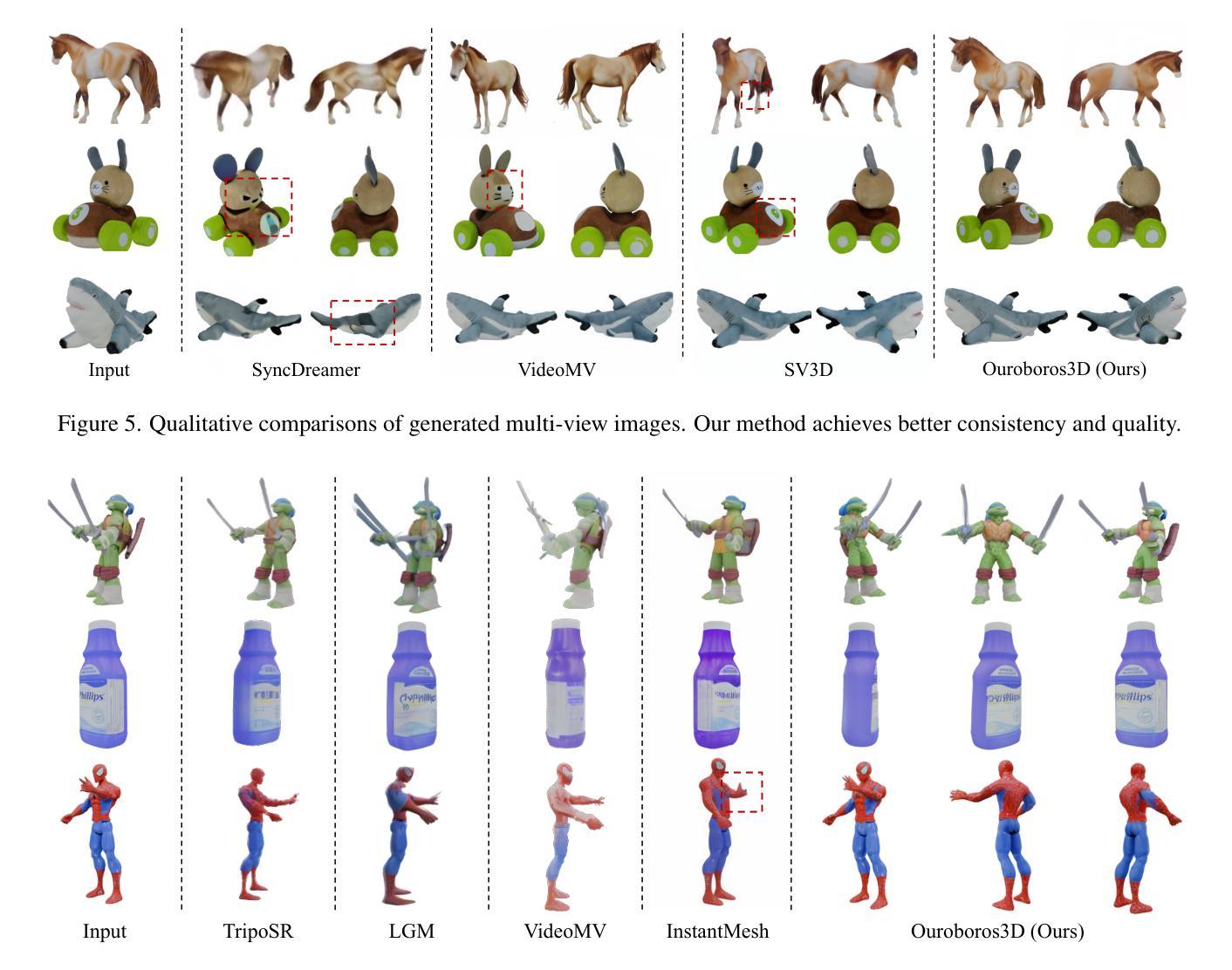
Ouroboros3D: Image-to-3D Generation via 3D-aware Recursive Diffusion
Authors:Hao Wen, Zehuan Huang, Yaohui Wang, Xinyuan Chen, Lu Sheng
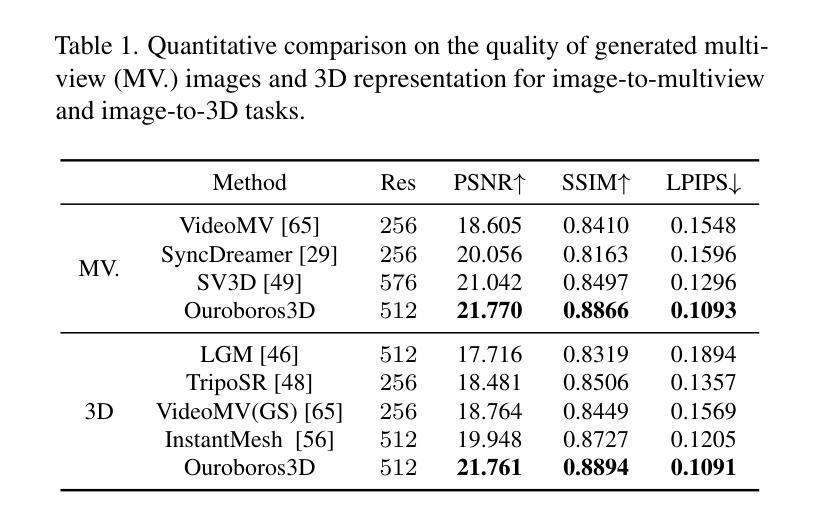
Existing single image-to-3D creation methods typically involve a two-stage process, first generating multi-view images, and then using these images for 3D reconstruction. However, training these two stages separately leads to significant data bias in the inference phase, thus affecting the quality of reconstructed results. We introduce a unified 3D generation framework, named Ouroboros3D, which integrates diffusion-based multi-view image generation and 3D reconstruction into a recursive diffusion process. In our framework, these two modules are jointly trained through a self-conditioning mechanism, allowing them to adapt to each other’s characteristics for robust inference. During the multi-view denoising process, the multi-view diffusion model uses the 3D-aware maps rendered by the reconstruction module at the previous timestep as additional conditions. The recursive diffusion framework with 3D-aware feedback unites the entire process and improves geometric consistency.Experiments show that our framework outperforms separation of these two stages and existing methods that combine them at the inference phase. Project page: https://costwen.github.io/Ouroboros3D/
现有的单图像到3D创建方法通常涉及两个阶段:首先生成多视图图像,然后使用这些图像进行3D重建。然而,分别训练这两个阶段会导致推理阶段的数据偏差,从而影响重建结果的质量。我们引入了一个统一的3D生成框架,名为Ouroboros3D,它将基于扩散的多视图图像生成和3D重建融合到一个递归扩散过程中。在我们的框架中,这两个模块通过自调节机制进行联合训练,使它们能够适应彼此的特性,从而实现稳健的推理。在多视图去噪过程中,多视图扩散模型使用前一时刻由重建模块渲染的3D感知地图作为额外的条件。具有3D感知反馈的递归扩散框架将整个过程结合在一起,提高了几何一致性。实验表明,我们的框架在将这两个阶段分离以及在推理阶段将它们结合起来的方法中都表现出优越性。项目页面:https://costwen.github.io/Ouroboros3D/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF See our project page at https://costwen.github.io/Ouroboros3D/
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为Ouroboros3D的统一3D生成框架,该框架将基于扩散的多视角图像生成和3D重建融合到一个递归扩散过程中。该框架通过自调节机制联合训练两个模块,使它们相互适应特性,实现稳健推断。实验表明,该框架优于将两个阶段分离以及现有方法在推断阶段结合它们的方法。
Key Takeaways
- 现有单图像到3D创建方法通常采用两阶段过程,即生成多视角图像,然后使用这些图像进行3D重建。
- 训练这两个阶段分别会导致推断阶段的数据偏差,影响重建结果的质量。
- 引入了一个统一的3D生成框架Ouroboros3D,将多视角图像生成和3D重建融合到一个递归扩散过程中。
- Ouroboros3D框架通过自调节机制联合训练两个模块,提高几何一致性。
- 在多视角去噪过程中,多视角扩散模型使用由重建模块在上一时间步长渲染的3D感知地图作为附加条件。
- 递归扩散框架具有3D感知反馈,能够整合整个过程并改进几何一致性。
点此查看论文截图

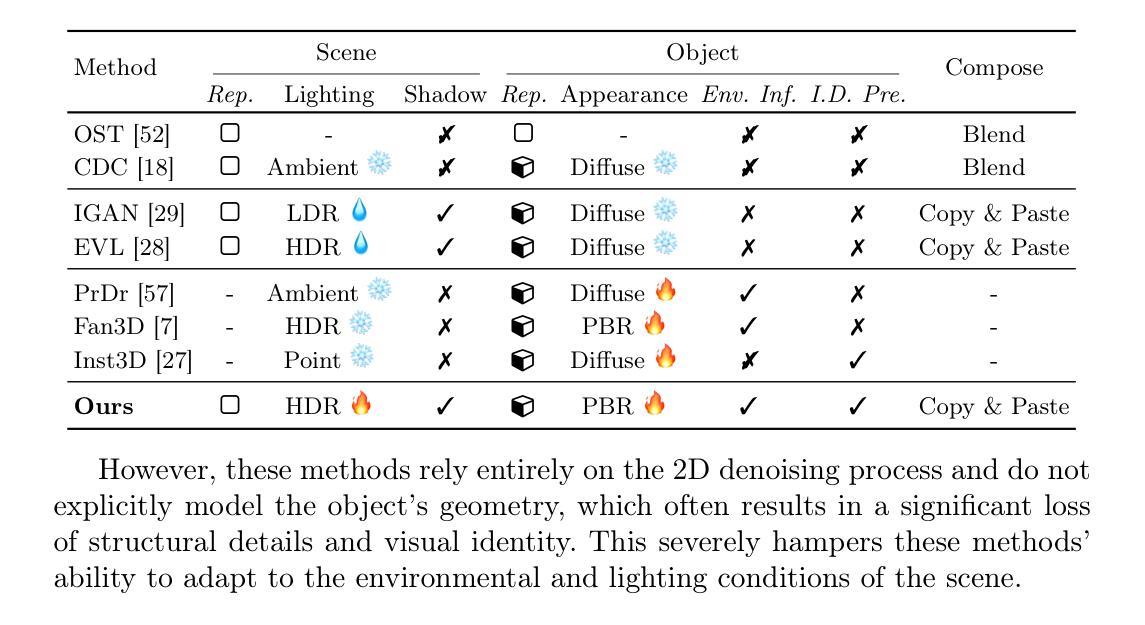
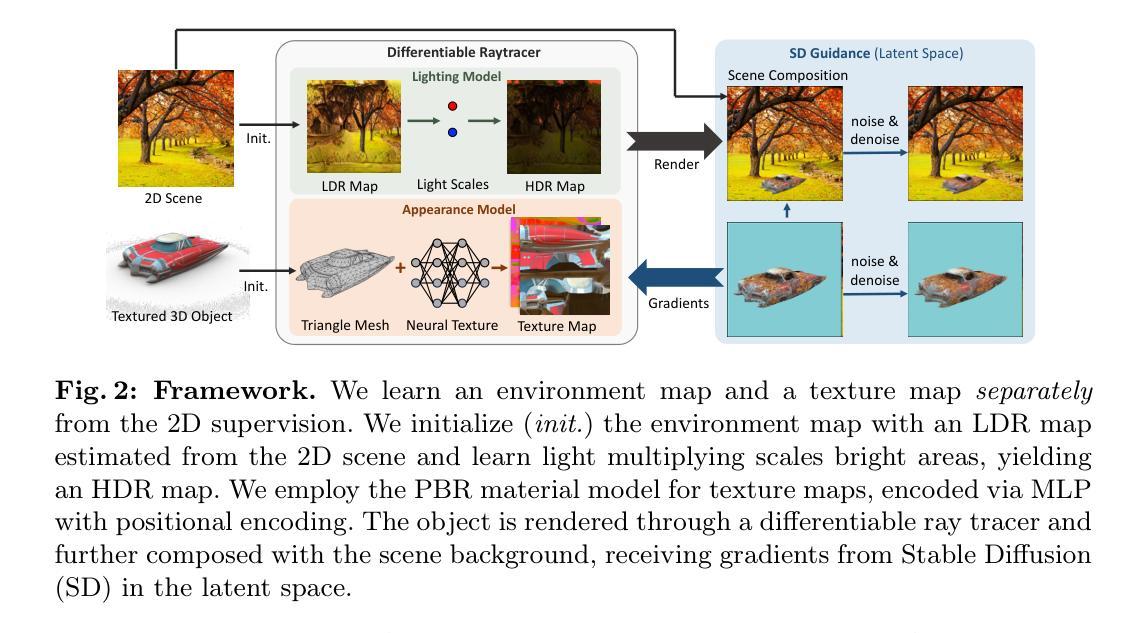
Scene-Conditional 3D Object Stylization and Composition
Authors:Jinghao Zhou, Tomas Jakab, Philip Torr, Christian Rupprecht
Recently, 3D generative models have made impressive progress, enabling the generation of almost arbitrary 3D assets from text or image inputs. However, these approaches generate objects in isolation without any consideration for the scene where they will eventually be placed. In this paper, we propose a framework that allows for the stylization of an existing 3D asset to fit into a given 2D scene, and additionally produce a photorealistic composition as if the asset was placed within the environment. This not only opens up a new level of control for object stylization, for example, the same assets can be stylized to reflect changes in the environment, such as summer to winter or fantasy versus futuristic settings-but also makes the object-scene composition more controllable. We achieve this by combining modeling and optimizing the object’s texture and environmental lighting through differentiable ray tracing with image priors from pre-trained text-to-image diffusion models. We demonstrate that our method is applicable to a wide variety of indoor and outdoor scenes and arbitrary objects. Project page: https://jensenzhoujh.github.io/scene-cond-3d/.
最近,3D生成模型取得了令人印象深刻的进展,能够从文本或图像输入生成几乎任意的3D资产。然而,这些方法生成的物体是孤立的,没有考虑到它们最终将被放置的场景。在本文中,我们提出了一个框架,允许对现有的3D资产进行风格化,以适应给定的2D场景,并额外生成逼真的组合,仿佛资产被放置在环境中。这不仅为物体风格化打开了新的控制层次,例如,可以将相同的资产风格化为反映环境的变化,如从夏天到冬天或幻想与未来主义场景的变化——而且使物体与场景的组合更具可控性。我们通过结合建模和优化物体的纹理和环境照明,通过可微分的光线追踪和来自预训练的文本到图像扩散模型的图像先验,实现了这一点。我们证明我们的方法适用于各种室内和室外场景以及任意物体。项目页面:https://jensenzhoujh.github.io/scene-cond-3d/。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种框架,能将现有3D资产进行风格化以适应给定的2D场景,并生成逼真的组合图像,仿佛资产被置于环境中。通过结合建模和优化物体的纹理和环境照明,利用预训练的文本到图像扩散模型的图像先验知识和可微射线追踪技术,实现了物体与场景的融合。该方法适用于各种室内和室外场景以及任意物体。
Key Takeaways
- 3D generative models已能够基于文本或图像生成几乎任意的3D资产。
- 现有方法生成物体时未考虑其将被放置的场景。
- 本文提出的框架允许对现有的3D资产进行风格化,以适应给定的2D场景。
- 该框架能产生逼真的组合图像,仿佛资产是环境中的一部分。
- 通过结合建模和优化物体的纹理和环境照明来实现这一效果。
- 利用可微射线追踪和预训练的文本到图像扩散模型的图像先验知识。
点此查看论文截图