⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-03 更新
Denoising weak lensing mass maps with diffusion model: systematic comparison with generative adversarial network
Authors:Shohei D. Aoyama, Ken Osato, Masato Shirasaki
(abridged) Weak gravitational lensing (WL) is the unique and powerful probe into the large-scale structures of the Universe. Removing the shape noise from the observed WL field, i.e., denoising, enhances the potential of WL by accessing information at small scales where the shape noise dominates without denoising. We utilise two machine learning (ML) models for denosing: generative adversarial network (GAN) and diffusion model (DM). We evaluate the performance of denosing with GAN and DM utilising the large suite of mock WL observations, which serve as the training and test data sets. We apply denoising to 1,000 maps with GAN and DM models trained with 39,000 mock observations. Both models can fairly well reproduce the true convergence map on large scales. Then, we measure cosmological statistics: power spectrum, bispectrum, one-point probability distribution function, peak and minima counts, and scattering transform coefficients. We find that DM outperforms GAN in almost all statistics and recovers the correct statistics down to small scales within roughly $0.3 \sigma$ level at the scales accessible from current and future WL surveys. We also conduct the stress tests on the trained model; denoising the maps with different characteristics, e.g., different source redshifts, from the data used in training. The performance degrades at small scales, but the statistics can still be recovered at large scales. Though the training of DM is more computationally demanding compared with GAN, there are several advantages: numerically stable training, higher performance in the reconstruction of cosmological statistics, and sampling multiple realisations once the model is trained. It has been known that DM can generate higher-quality images in real-world problems than GAN, the superiority has been confirmed as well in the WL denoising problem.
(节选)弱引力透镜(WL)是对宇宙大规模结构的独特而强大的探测手段。从观测到的弱引力透镜场中去除形状噪声,即去噪,可以提高弱引力透镜的潜力。我们通过两种机器学习(ML)模型进行去噪:生成对抗网络(GAN)和扩散模型(DM)。我们利用大量模拟的弱引力透镜观测结果来评估使用GAN和DM进行去噪的性能,这些观测结果既用于训练也用于测试数据集。我们对1000张地图应用了去噪处理,这些地图使用了GAN和DM模型,这些模型是用39000张模拟观测结果训练的。这两种模型在大尺度上都能较好地复现真实的收敛图。然后,我们测量了宇宙学统计量:功率谱、双谱、一点概率分布函数、峰谷计数和散射变换系数。我们发现,在几乎所有的统计量中,DM的表现都优于GAN,并且在当前和未来弱引力透镜调查所能达到的尺度上,能够恢复到小尺度内的正确统计量,误差大约在$0.3\sigma$水平。我们还对训练好的模型进行了压力测试,即对具有不同特性的地图进行去噪处理,例如源红移不同于训练使用的数据。小尺度上的性能有所下降,但在大尺度上仍然可以恢复统计量。虽然与GAN相比,DM的训练在计算上要求更高,但它有几个优点:训练过程数值稳定、在重建宇宙学统计量方面表现更好、一旦模型训练完毕可以一次生成多个样本实现。已知在现实世界的问题中,DM能够生成比GAN更高质量的图像,这一优势在弱引力透镜去噪问题中也得到了证实。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to A&A, 16 pages, 15+2 figures
Summary
使用机器学习模型——生成对抗网络(GAN)和扩散模型(DM)对弱引力透镜(WL)观测数据进行降噪处理。通过一系列模拟的WL观测数据评估这两种模型的降噪性能。扩散模型(DM)在大多数宇宙学统计测量中表现优于GAN,并且在当前和未来WL调查可访问的尺度上,能够恢复到小尺度内的正确统计量。尽管DM的训练相较于GAN更为计算密集,但其具有数值稳定的训练过程、更高的宇宙学统计重建性能以及一次训练即可进行多次采样的优势。
Key Takeaways
- 弱引力透镜(WL)是研究宇宙大尺度结构的重要工具。
- 降噪可以增强WL探测小尺度信息的能力。
- 采用生成对抗网络(GAN)和扩散模型(DM)进行降噪处理。
- 扩散模型在模拟的WL观测数据降噪性能评估中表现优于GAN。
- 扩散模型能较好地恢复宇宙学统计量,如功率谱、双光谱、一点概率分布函数、峰谷计数和散射变换系数等。
- 尽管扩散模型的训练成本较高,但在稳定性和性能上具有优势。
点此查看论文截图
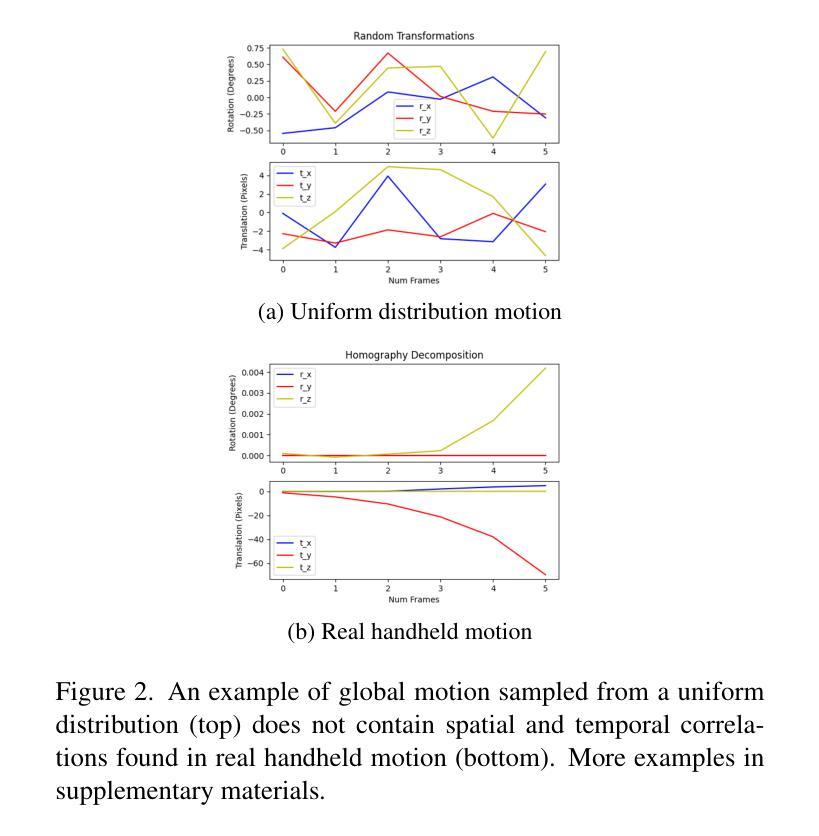
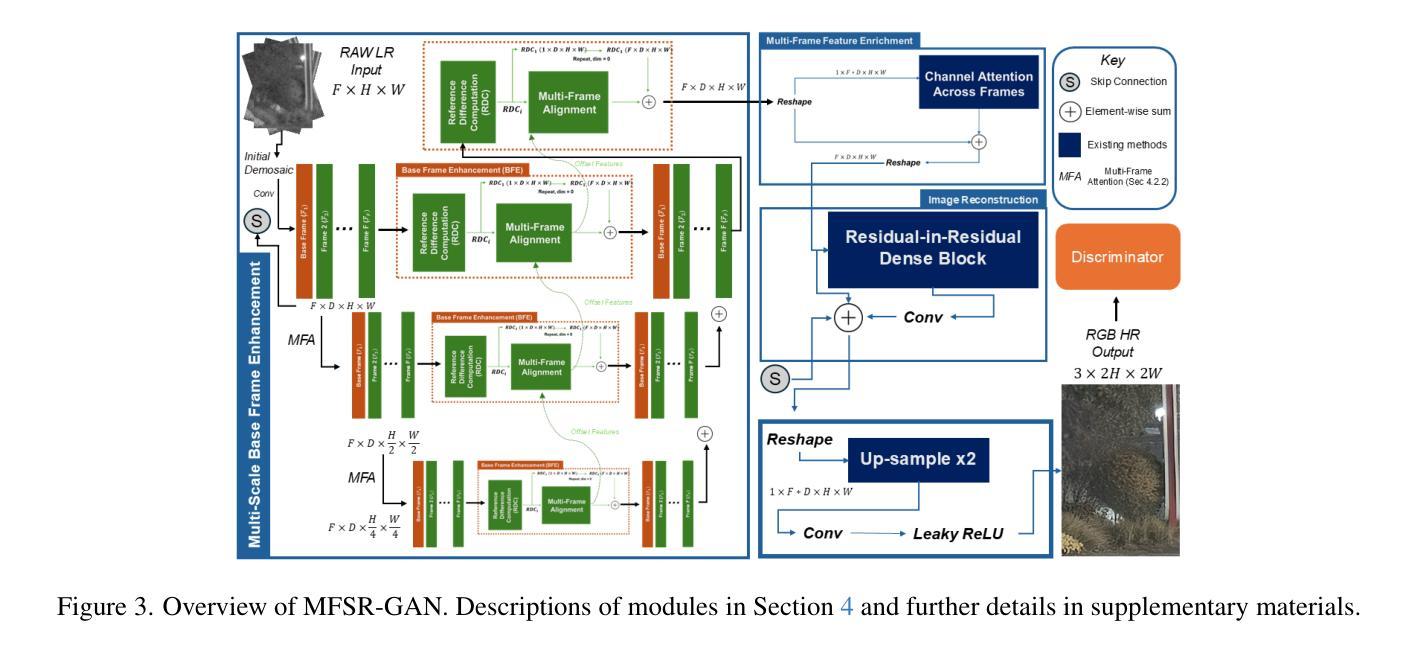
MFSR-GAN: Multi-Frame Super-Resolution with Handheld Motion Modeling
Authors:Fadeel Sher Khan, Joshua Ebenezer, Hamid Sheikh, Seok-Jun Lee
Smartphone cameras have become ubiquitous imaging tools, yet their small sensors and compact optics often limit spatial resolution and introduce distortions. Combining information from multiple low-resolution (LR) frames to produce a high-resolution (HR) image has been explored to overcome the inherent limitations of smartphone cameras. Despite the promise of multi-frame super-resolution (MFSR), current approaches are hindered by datasets that fail to capture the characteristic noise and motion patterns found in real-world handheld burst images. In this work, we address this gap by introducing a novel synthetic data engine that uses multi-exposure static images to synthesize LR-HR training pairs while preserving sensor-specific noise characteristics and image motion found during handheld burst photography. We also propose MFSR-GAN: a multi-scale RAW-to-RGB network for MFSR. Compared to prior approaches, MFSR-GAN emphasizes a “base frame” throughout its architecture to mitigate artifacts. Experimental results on both synthetic and real data demonstrates that MFSR-GAN trained with our synthetic engine yields sharper, more realistic reconstructions than existing methods for real-world MFSR.
智能手机摄像头已经无处不在,成为常用的成像工具,然而,其小型传感器和紧凑的光学元件往往限制了空间分辨率并引入了失真。为了解决智能手机摄像头固有的局限性,已经探索了将多个低分辨率(LR)帧的信息结合起来以生成高分辨率(HR)图像的方法。尽管多帧超分辨率(MFSR)技术前景广阔,但当前的方法受到数据集的限制,无法捕获真实手持连续拍摄图像中的特征噪声和运动模式。在这项工作中,我们通过引入一种新型合成数据引擎来解决这一问题,该引擎使用多曝光静态图像来合成LR-HR训练对,同时保留特定传感器的噪声特征和手持连续拍摄过程中出现的图像运动。我们还提出了MFSR-GAN:一种用于MFSR的多尺度RAW-to-RGB网络。与之前的方法相比,MFSR-GAN在其架构中强调了“基础帧”,以减轻伪影。在合成数据和真实数据上的实验结果表明,使用我们的合成引擎训练的MFSR-GAN与现有方法相比,能够在真实世界的MFSR中生成更清晰、更逼真的重建图像。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to NTIRE Workshop at CVPR 2025; 8 pages, 6 figures
Summary
智能手机摄像头已成为普及的成像工具,但其小型传感器和紧凑的光学器件常常限制空间分辨率并引入失真。为克服智能手机摄像头的固有局限,已探索通过结合多个低分辨率(LR)帧的信息来生成高分辨率(HR)图像的多帧超分辨率(MFSR)技术。然而,当前的方法受到数据集的阻碍,这些数据集未能捕捉真实手持连拍图像中的特征噪声和运动模式。为解决这一差距,我们引入了一种新型合成数据引擎,该引擎使用多曝光静态图像来合成LR-HR训练对,同时保留手持连拍摄影中特有的传感器噪声特性和图像运动。此外,我们还提出了MFSR-GAN:一种用于MFSR的多尺度RAW-to-RGB网络。与以前的方法相比,MFSR-GAN在其架构中强调“基础帧”以减轻伪影。在合成数据和真实数据上的实验结果表明,使用我们的合成引擎训练的MFSR-GAN比现有方法更能实现真实世界的MFSR重建,更锋利,更逼真。
Key Takeaways
- 智能手机摄像头虽然普及,但受到传感器大小和光学特性的限制,其成像的空间分辨率和画质可能受到影响。
- 多帧超分辨率(MFSR)技术通过结合多个低分辨率图像来生成高分辨率图像,以克服这些限制。
- 当前MFSR技术的主要挑战在于数据集未能真实反映手持摄像头拍摄时出现的噪声和运动模式。
- 引入了一种新型合成数据引擎,能合成低分辨率和高分辨率的训练图像对,同时保留传感器特有的噪声和手持摄影中的运动特性。
- 提出了MFSR-GAN网络,该网络在多尺度上从RAW数据转换到RGB数据,特别重视“基础帧”以减少伪影。
- 实验结果显示,使用新型合成数据引擎训练的MFSR-GAN在真实世界的数据上表现更优秀,生成的图像更逼真、更清晰。
- MFSR-GAN有望成为改进智能手机摄像画质的有效工具。
点此查看论文截图