⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-03 更新
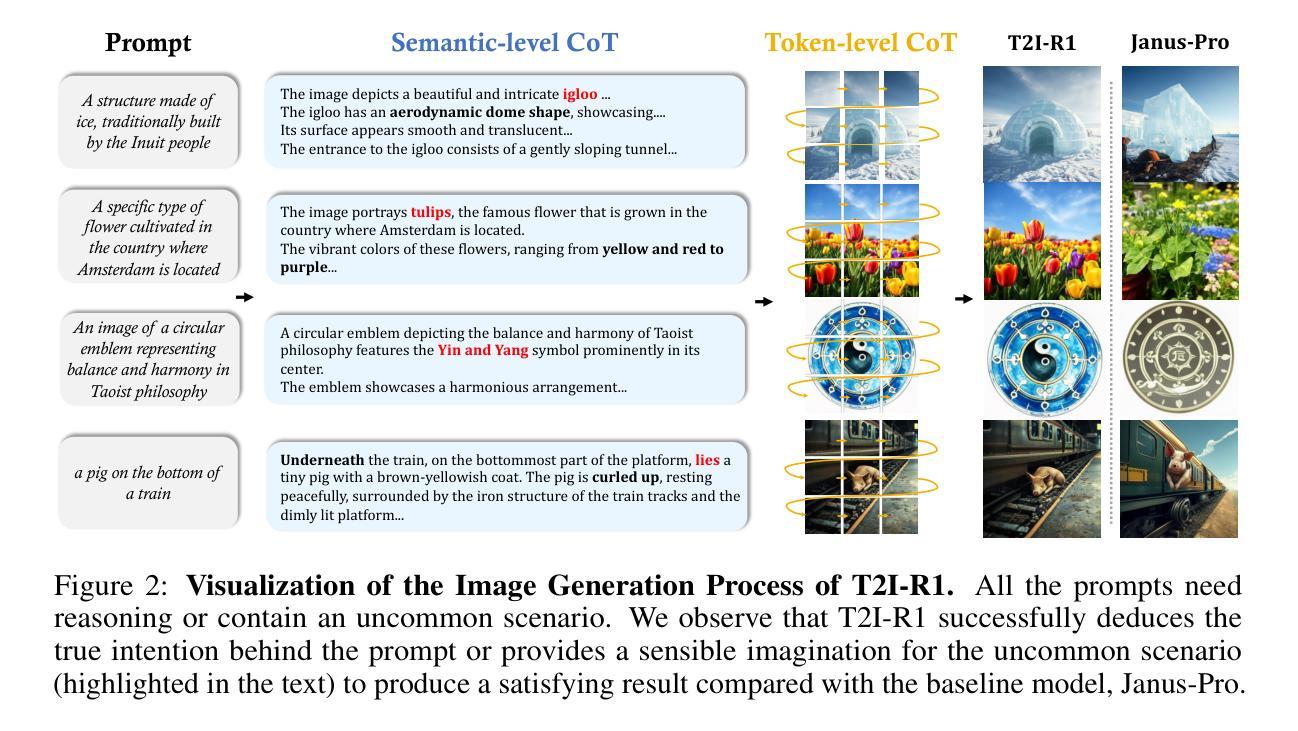
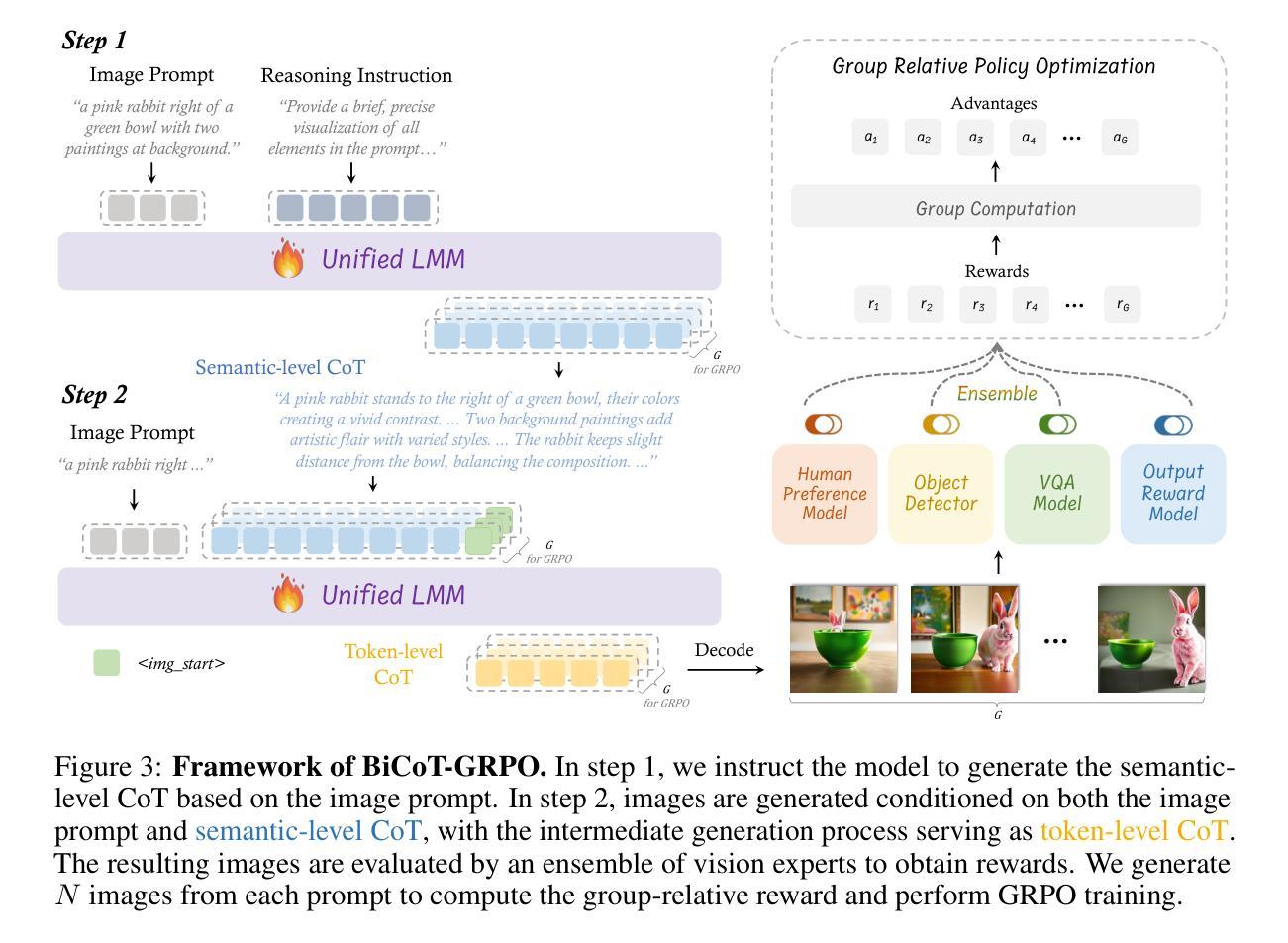
T2I-R1: Reinforcing Image Generation with Collaborative Semantic-level and Token-level CoT
Authors:Dongzhi Jiang, Ziyu Guo, Renrui Zhang, Zhuofan Zong, Hao Li, Le Zhuo, Shilin Yan, Pheng-Ann Heng, Hongsheng Li
Recent advancements in large language models have demonstrated how chain-of-thought (CoT) and reinforcement learning (RL) can improve performance. However, applying such reasoning strategies to the visual generation domain remains largely unexplored. In this paper, we present T2I-R1, a novel reasoning-enhanced text-to-image generation model, powered by RL with a bi-level CoT reasoning process. Specifically, we identify two levels of CoT that can be utilized to enhance different stages of generation: (1) the semantic-level CoT for high-level planning of the prompt and (2) the token-level CoT for low-level pixel processing during patch-by-patch generation. To better coordinate these two levels of CoT, we introduce BiCoT-GRPO with an ensemble of generation rewards, which seamlessly optimizes both generation CoTs within the same training step. By applying our reasoning strategies to the baseline model, Janus-Pro, we achieve superior performance with 13% improvement on T2I-CompBench and 19% improvement on the WISE benchmark, even surpassing the state-of-the-art model FLUX.1. Code is available at: https://github.com/CaraJ7/T2I-R1
近期大型语言模型的进步展示了思维链(CoT)和强化学习(RL)如何提升性能。然而,将此类推理策略应用于视觉生成领域尚未得到充分探索。在本文中,我们提出了T2I-R1,这是一种新颖的增强推理的文本到图像生成模型,通过双级CoT推理过程驱动RL实现。具体来说,我们确定了两个可以利用来增强生成不同阶段的CoT级别:(1)用于高级提示规划的语义级CoT和(2)用于逐块生成期间的低级像素处理的标记级CoT。为了更好地协调这两个级别的CoT,我们引入了BiCoT-GRPO,通过生成奖励集合无缝优化同一训练步骤内的两个生成CoT。通过将我们的推理策略应用于基线模型Janus-Pro,我们在T2I-CompBench上实现了13%的改进,在WISE基准测试上实现了19%的改进,甚至超越了最先进的模型FLUX.1。代码可在https://github.com/CaraJ7/T2I-R1找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://github.com/CaraJ7/T2I-R1
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为T2I-R1的新型文本驱动图像生成模型,该模型采用强化学习和双重链式思维推理策略。通过语义层面的链式思维进行高级规划,并利用token级别的链式思维进行像素级的图像生成。模型使用BiCoT-GRPO技术协调这两个级别的推理过程,并优化了生成奖励的集合。应用于Janus-Pro模型后,T2I-R1在T2I-CompBench上提升了13%,在WISE基准测试中提升了19%,超过了现有最先进的模型FLUX。
Key Takeaways
- T2I-R1是一个结合了强化学习和双重链式思维推理(CoT)的文本驱动图像生成模型。
- 该模型采用语义级和token级的双重CoT推理过程,分别用于高级规划和像素级的图像生成。
- BiCoT-GRPO技术用于协调和优化这两个级别的推理过程。
- T2I-R1模型在现有基准测试中表现优越,相比基线模型Janus-Pro,在T2I-CompBench上提升了13%,在WISE上提升了19%。
- 该模型超越了现有最先进的模型FLUX。
- 模型代码已公开,可供研究使用。
点此查看论文截图


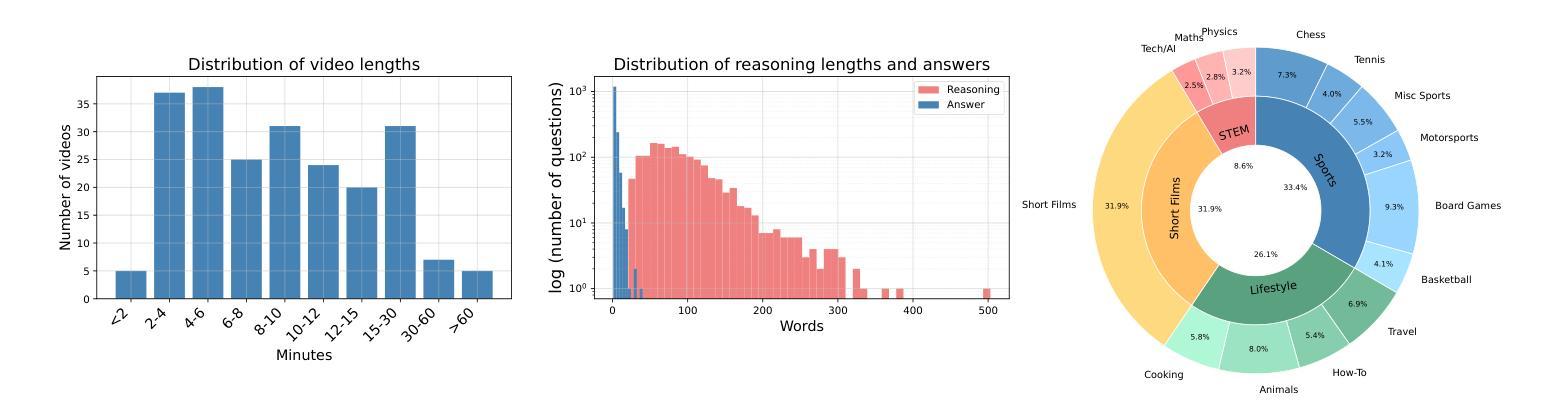
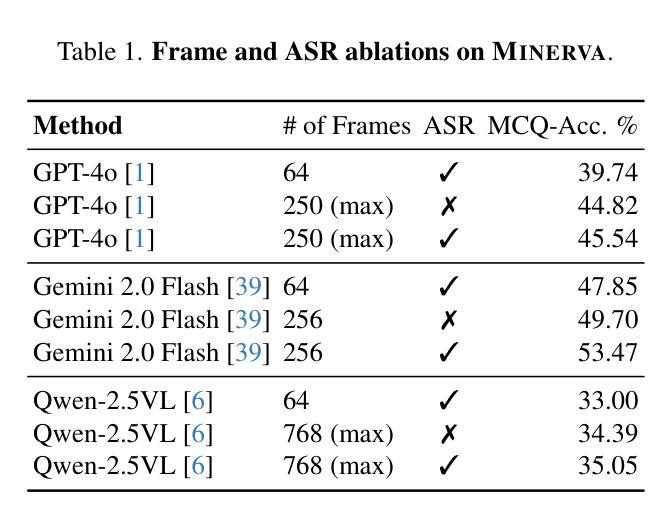
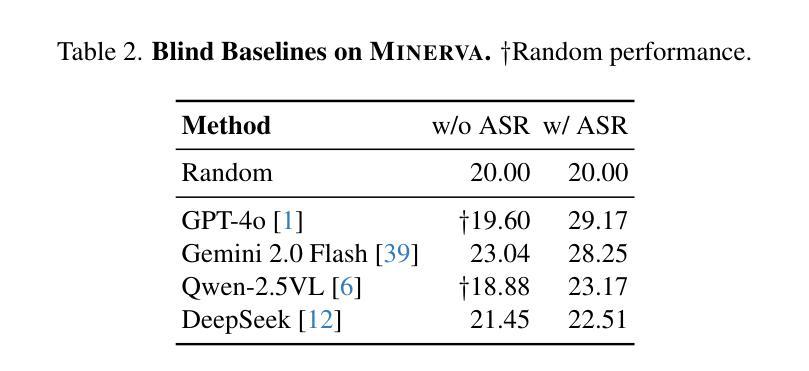
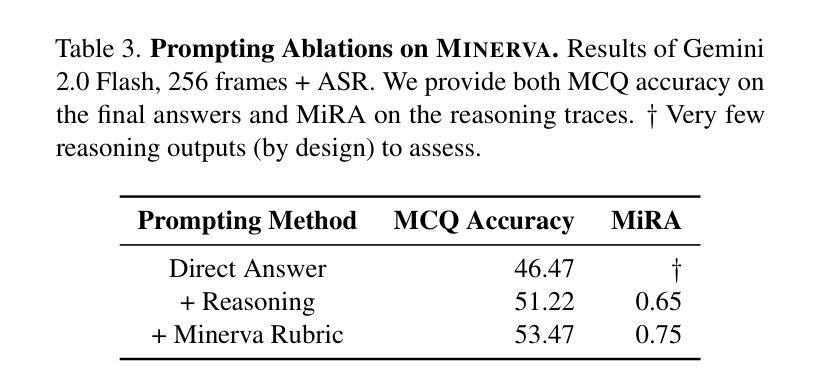
MINERVA: Evaluating Complex Video Reasoning
Authors:Arsha Nagrani, Sachit Menon, Ahmet Iscen, Shyamal Buch, Ramin Mehran, Nilpa Jha, Anja Hauth, Yukun Zhu, Carl Vondrick, Mikhail Sirotenko, Cordelia Schmid, Tobias Weyand
Multimodal LLMs are turning their focus to video benchmarks, however most video benchmarks only provide outcome supervision, with no intermediate or interpretable reasoning steps. This makes it challenging to assess if models are truly able to combine perceptual and temporal information to reason about videos, or simply get the correct answer by chance or by exploiting linguistic biases. To remedy this, we provide a new video reasoning dataset called MINERVA for modern multimodal models. Each question in the dataset comes with 5 answer choices, as well as detailed, hand-crafted reasoning traces. Our dataset is multimodal, diverse in terms of video domain and length, and consists of complex multi-step questions. Extensive benchmarking shows that our dataset provides a challenge for frontier open-source and proprietary models. We perform fine-grained error analysis to identify common failure modes across various models, and create a taxonomy of reasoning errors. We use this to explore both human and LLM-as-a-judge methods for scoring video reasoning traces, and find that failure modes are primarily related to temporal localization, followed by visual perception errors, as opposed to logical or completeness errors. The dataset, along with questions, answer candidates and reasoning traces will be publicly available under https://github.com/google-deepmind/neptune?tab=readme-ov-file\#minerva.
多模态大型语言模型正在将重点转向视频基准测试,然而大多数视频基准测试只提供结果监督,没有中间或可解释推理步骤。这使得评估模型是否真正能够结合感知和时间信息对视频进行推理变得具有挑战性,或者只是偶然得到正确答案或通过利用语言偏见。为了弥补这一缺陷,我们为现代多模态模型提供了一个名为MINERVA的新视频推理数据集。数据集中的每个问题都有5个答案选项,以及详细的手工推理轨迹。我们的数据集是多模态的,在视频领域和长度方面都具有多样性,包含复杂的多步骤问题。广泛的基准测试表明,我们的数据集对前沿的开源和专有模型都构成了挑战。我们进行了精细的误差分析,以识别各种模型的常见失败模式,并对推理错误进行分类。我们利用这一点来探索为人类和大型语言模型打分视频推理轨迹的方法,并发现失败模式主要与时间定位有关,其次是视觉感知错误,而不是逻辑或完整性错误。该数据集以及与问题、答案选项和推理轨迹相关的信息将在https://github.com/google-deepmind/neptune?tab=readme-ov-file#minerva下公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:针对多模态模型的需求,研究团队设计了一种名为MINERVA的视频推理数据集,用于评估模型是否真正能够结合感知和时间信息对视频进行推理。该数据集包含复杂的多步骤问题,每个问题都有五个答案选项以及详细的手工推理轨迹。数据集具有多模态性、视频领域多样性和长度多样性。通过对前沿开源和专有模型的广泛基准测试,研究团队发现该数据集对这些模型构成挑战。同时进行了精细的错误分析来确定各种模型的常见故障模式,并创建了一个推理错误的分类。该数据集以及与该数据集相关的问题、答案候选和推理轨迹将公开可用。
Key Takeaways:
- 多模态LLM正将重点转向视频基准测试,但现有视频基准测试主要提供结果监督,缺乏中间或可解释的推理步骤。
- 为了解决这个问题,引入了新的视频推理数据集MINERVA,用于现代多模态模型。
- MINERVA数据集包含复杂的多步骤问题,每个问题都有五个答案选项和详细的推理轨迹。
- 数据集具有多模态性、视频领域多样性和长度多样性。
- 基准测试表明,MINERVA数据集对前沿模型构成挑战。
- 通过精细的错误分析确定了模型的常见失败模式,并创建了一个推理错误的分类。
点此查看论文截图


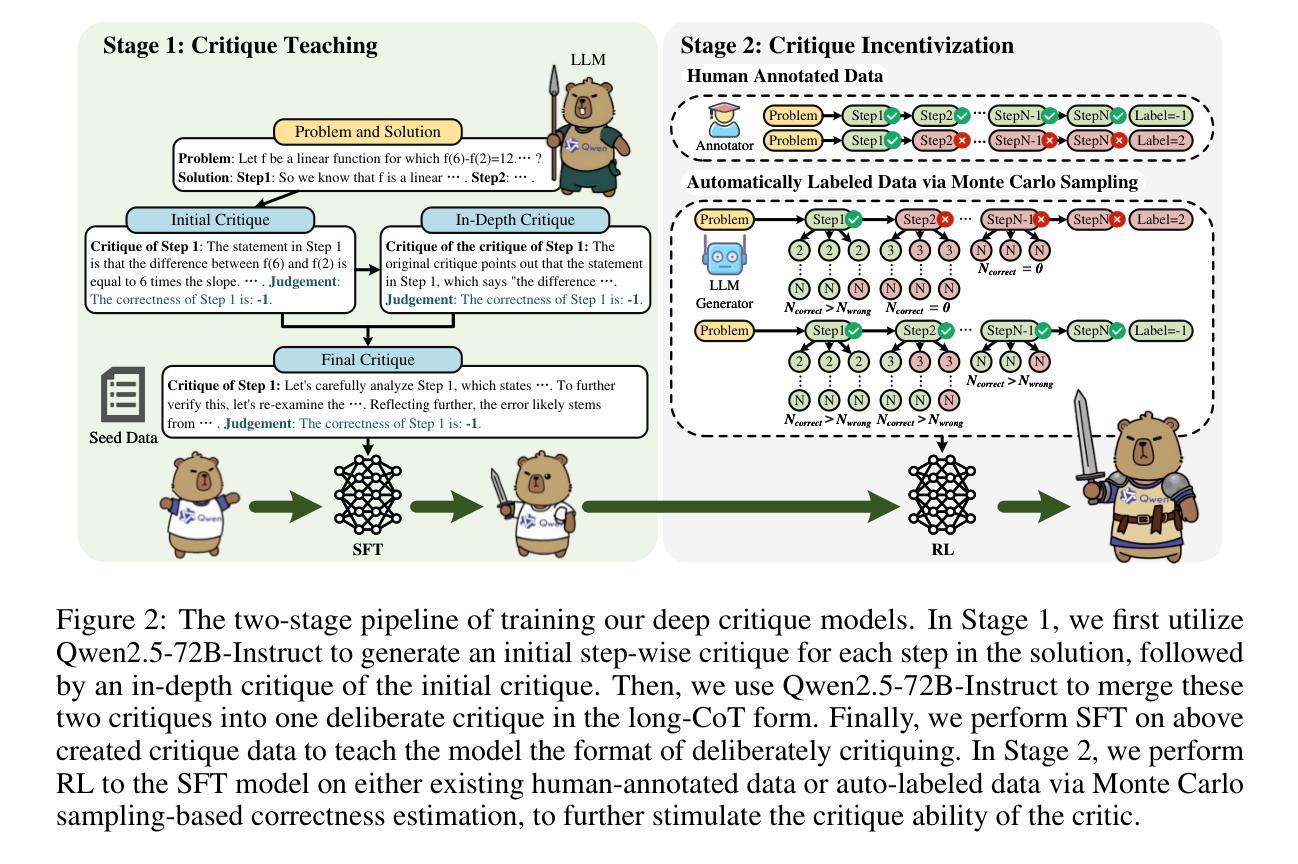
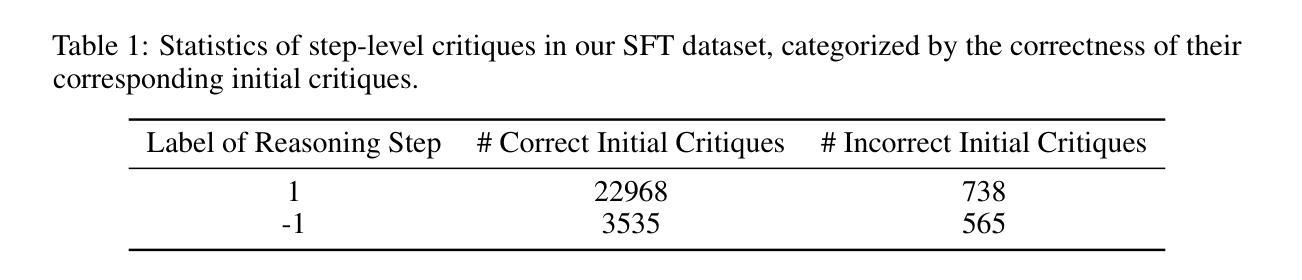
DeepCritic: Deliberate Critique with Large Language Models
Authors:Wenkai Yang, Jingwen Chen, Yankai Lin, Ji-Rong Wen
As Large Language Models (LLMs) are rapidly evolving, providing accurate feedback and scalable oversight on their outputs becomes an urgent and critical problem. Leveraging LLMs as critique models to achieve automated supervision is a promising solution. In this work, we focus on studying and enhancing the math critique ability of LLMs. Current LLM critics provide critiques that are too shallow and superficial on each step, leading to low judgment accuracy and struggling to offer sufficient feedback for the LLM generator to correct mistakes. To tackle this issue, we propose a novel and effective two-stage framework to develop LLM critics that are capable of deliberately critiquing on each reasoning step of math solutions. In the first stage, we utilize Qwen2.5-72B-Instruct to generate 4.5K long-form critiques as seed data for supervised fine-tuning. Each seed critique consists of deliberate step-wise critiques that includes multi-perspective verifications as well as in-depth critiques of initial critiques for each reasoning step. Then, we perform reinforcement learning on the fine-tuned model with either existing human-labeled data from PRM800K or our automatically annotated data obtained via Monte Carlo sampling-based correctness estimation, to further incentivize its critique ability. Our developed critique model built on Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct not only significantly outperforms existing LLM critics (including the same-sized DeepSeek-R1-distill models and GPT-4o) on various error identification benchmarks, but also more effectively helps the LLM generator refine erroneous steps through more detailed feedback.
随着大型语言模型(LLM)的快速发展,对其输出提供准确的反馈和可扩展的监督成为一个紧迫且关键的问题。利用LLM作为批评模型来实现自动化监督是一个有前景的解决方案。在这项工作中,我们专注于研究和提高LLM的数学批评能力。当前的LLM批评者提供的批评过于肤浅,导致判断准确性低,难以给LLM生成器提供足够的反馈来纠正错误。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种新颖有效的两阶段框架来开发能够有针对性地对数学解决方案的每个推理步骤进行批评的LLM批评模型。在第一阶段,我们利用Qwen2.5-72B-Instruct生成4.5K长形式的批评作为监督微调种子数据。每个种子批评都包括有针对性的步骤批评,包括多视角验证以及对每个推理步骤的初步批评的深入批评。然后,我们对微调模型使用PRM800K的现有手工标注数据或我们通过蒙特卡洛采样估计自动标注的数据进行强化学习,以进一步激励其批评能力。我们基于Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct开发的批评模型不仅在各种错误识别基准测试上显著优于现有LLM批评模型(包括相同规模的DeepSeek-R1-distill模型和GPT-4o),而且更有效地帮助LLM生成器通过更详细的反馈来修正错误步骤。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Work in progress. Data and models are available at https://github.com/RUCBM/DeepCritic
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)的快速发展带来对其输出准确反馈与监督的迫切需求。本研究致力于提升LLMs在数学领域的批判能力,提出了一种有效的两阶段框架,旨在训练能够针对数学解题每一步进行深度批判的LLM批判模型。第一阶段利用Qwen2.5-72B-Instruct生成长评批判数据用于监督微调。第二阶段通过强化学习进一步提升模型的批判能力。实验表明,本研究开发的批判模型在错误识别基准测试上显著优于现有LLM批判模型,并为LLM生成器提供更有效的错误修正反馈。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)的自动化监督中,利用LLMs作为批判模型是一种有前景的解决方案。
- 当前LLM批判模型在判断准确度和提供充足反馈方面存在不足,尤其是在数学领域。
- 研究提出了一种两阶段框架,旨在训练能够针对数学解题每一步进行深度批判的LLM批判模型。
- 第一阶段利用生成的长评数据用于监督微调模型。
- 第二阶段通过强化学习进一步提升模型的批判能力,使用人类标注数据或自动注释数据。
- 开发的批判模型在错误识别基准测试上表现优异,优于其他LLM批判模型。
点此查看论文截图


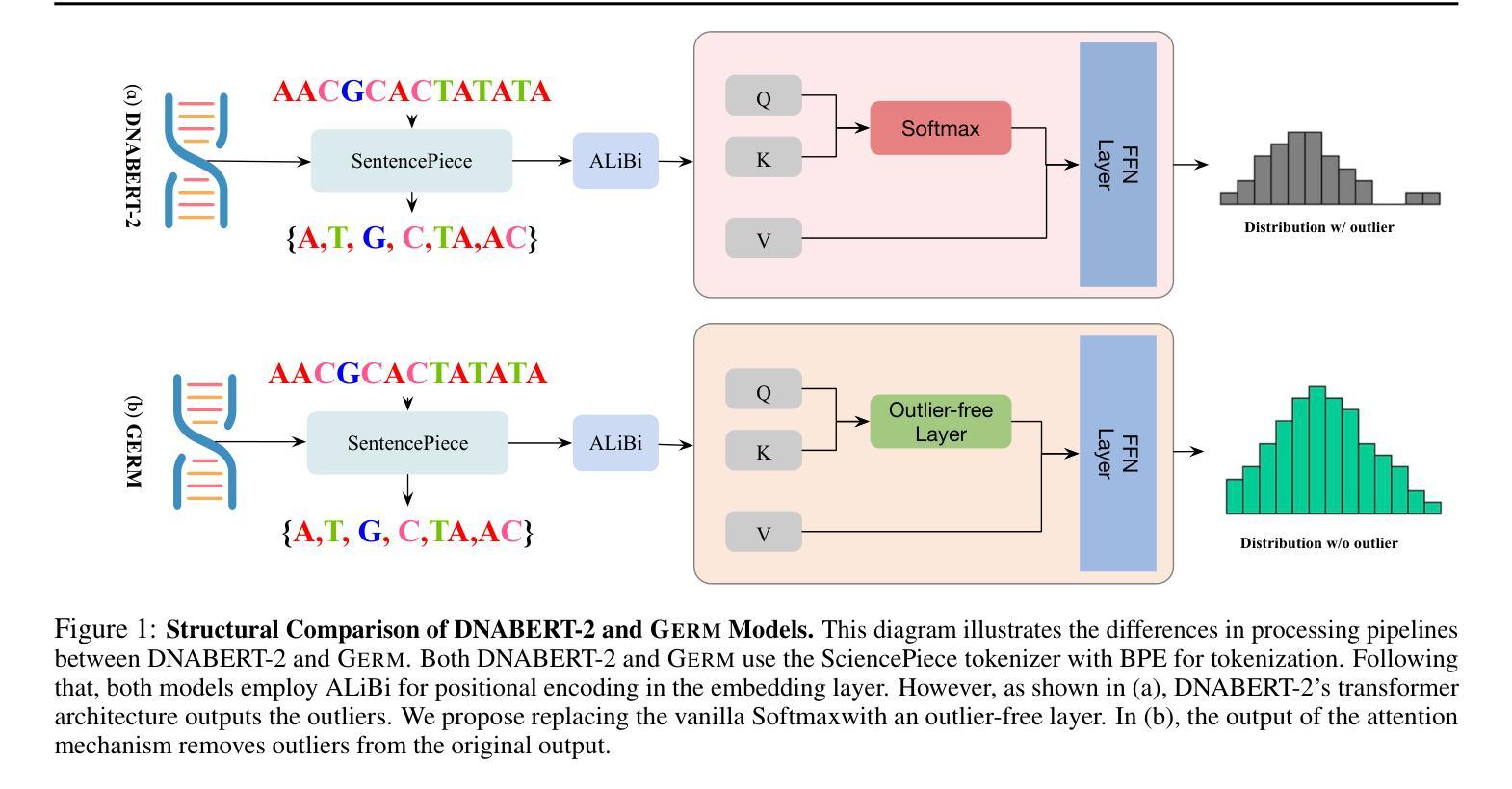
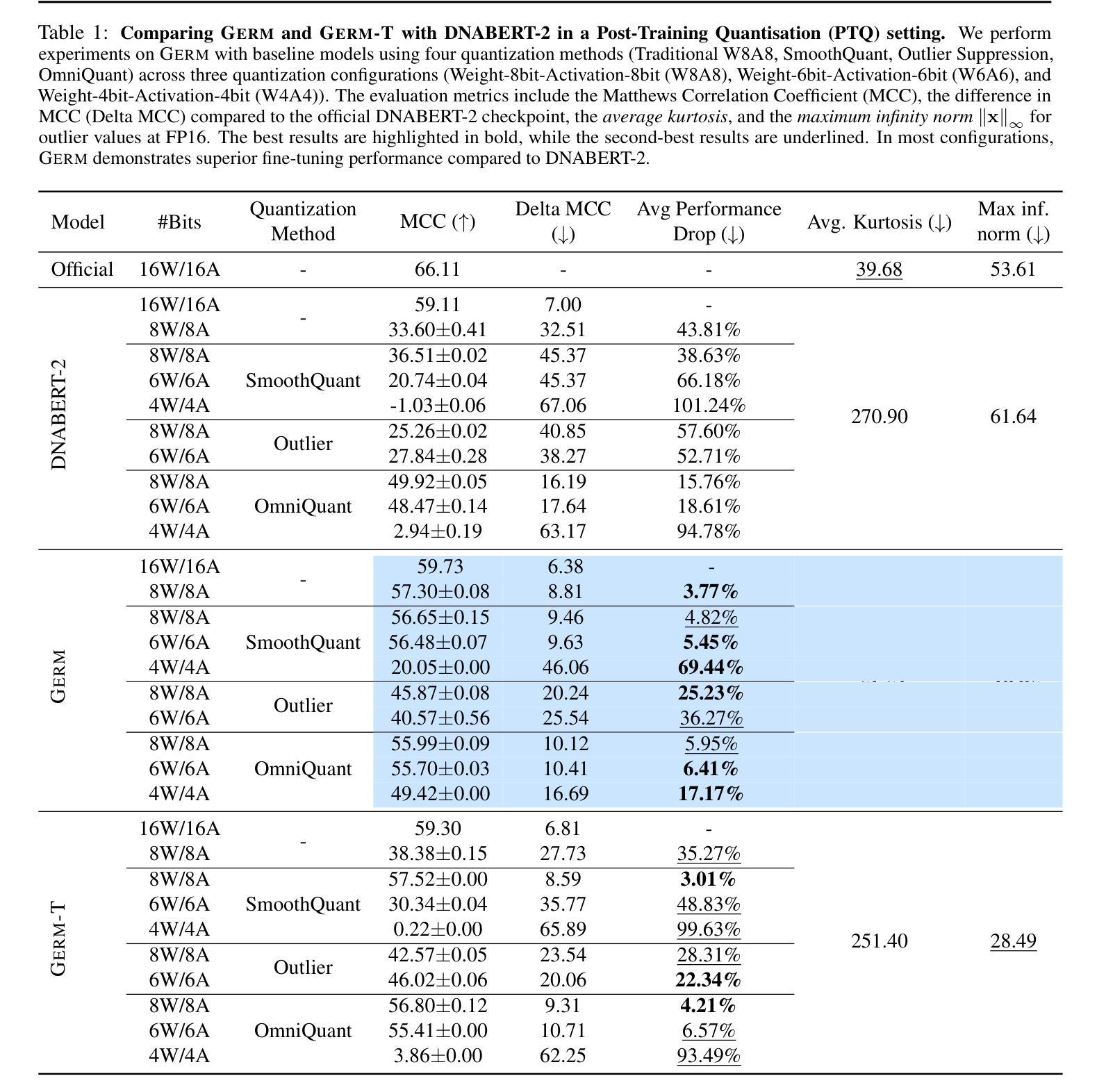
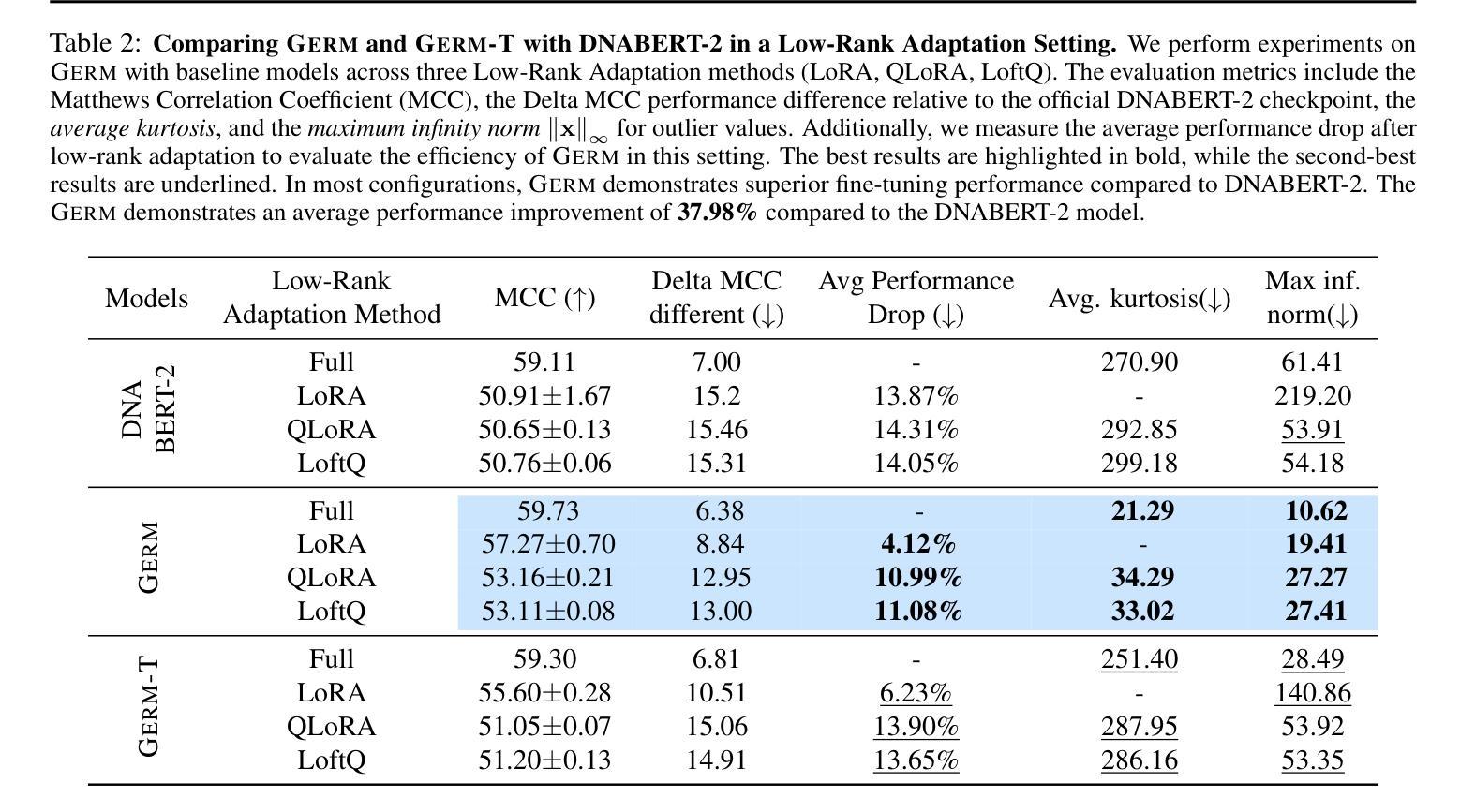
Fast and Low-Cost Genomic Foundation Models via Outlier Removal
Authors:Haozheng Luo, Chenghao Qiu, Maojiang Su, Zhihan Zhou, Zoe Mehta, Guo Ye, Jerry Yao-Chieh Hu, Han Liu
We propose the first unified adversarial attack benchmark for Genomic Foundation Models (GFMs), named GERM. Unlike existing GFM benchmarks, GERM offers the first comprehensive evaluation framework to systematically assess the vulnerability of GFMs to adversarial attacks. Methodologically, we evaluate the adversarial robustness of five state-of-the-art GFMs using four widely adopted attack algorithms and three defense strategies. Importantly, our benchmark provides an accessible and comprehensive framework to analyze GFM vulnerabilities with respect to model architecture, quantization schemes, and training datasets. Empirically, transformer-based models exhibit greater robustness to adversarial perturbations compared to HyenaDNA, highlighting the impact of architectural design on vulnerability. Moreover, adversarial attacks frequently target biologically significant genomic regions, suggesting that these models effectively capture meaningful sequence features.
我们提出了首个针对基因组基础模型(GFMs)的统一对抗性攻击基准测试,名为GERM。不同于现有的GFM基准测试,GERM提供了一个全面的评估框架,系统地评估GFMs在遭受对抗性攻击时的脆弱性。在方法学上,我们采用四种广泛采用的攻击算法和三种防御策略,评估了五种最先进GFMs的对抗性稳健性。重要的是,我们的基准测试提供了一个易于访问的综合框架,可以分析GFM在模型架构、量化方案和训练数据集方面的脆弱性。从实证角度看,基于transformer的模型与HyenaDNA相比,表现出更强的对抗性扰动鲁棒性,这突出了架构设计对脆弱性的影响。此外,对抗性攻击经常针对生物学上重要的基因组区域,这表明这些模型有效地捕获了有意义的序列特征。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML) 2025
Summary
我们提出了首个针对基因组基础模型(GFMs)的统一对抗性攻击基准测试,名为GERM。与其他现有的GFM基准测试不同,GERM提供了一个全面的评估框架,用于系统地评估GFMs对对抗性攻击的脆弱性。我们通过使用四种广泛采用的攻击算法和三种防御策略,评估了五种最先进GFMs的对抗性稳健性。此外,我们的基准测试提供了一个全面且易于使用的框架,用于分析GFM在模型架构、量化方案和训练数据集方面的脆弱性。研究结果显示,基于transformer的模型相较于HyenaDNA表现出更强的对抗性扰动稳健性,突显了架构设计对脆弱性的影响。同时,对抗性攻击经常针对生物学上重要的基因组区域,表明这些模型能够捕获有意义的序列特征。
Key Takeaways
- GERM是首个针对基因组基础模型(GFMs)的统一对抗性攻击基准测试。
- GERM提供了一个全面的评估框架,用于评估GFMs对对抗性攻击的脆弱性。
- 通过使用四种攻击算法和三种防御策略,评估了五种先进GFMs的对抗性稳健性。
- 基于transformer的模型相较于其他模型表现出更强的稳健性。
- 对抗性攻击经常针对生物学上重要的基因组区域。
- 模型架构、量化方案和训练数据集是影响GFM脆弱性的关键因素。
点此查看论文截图

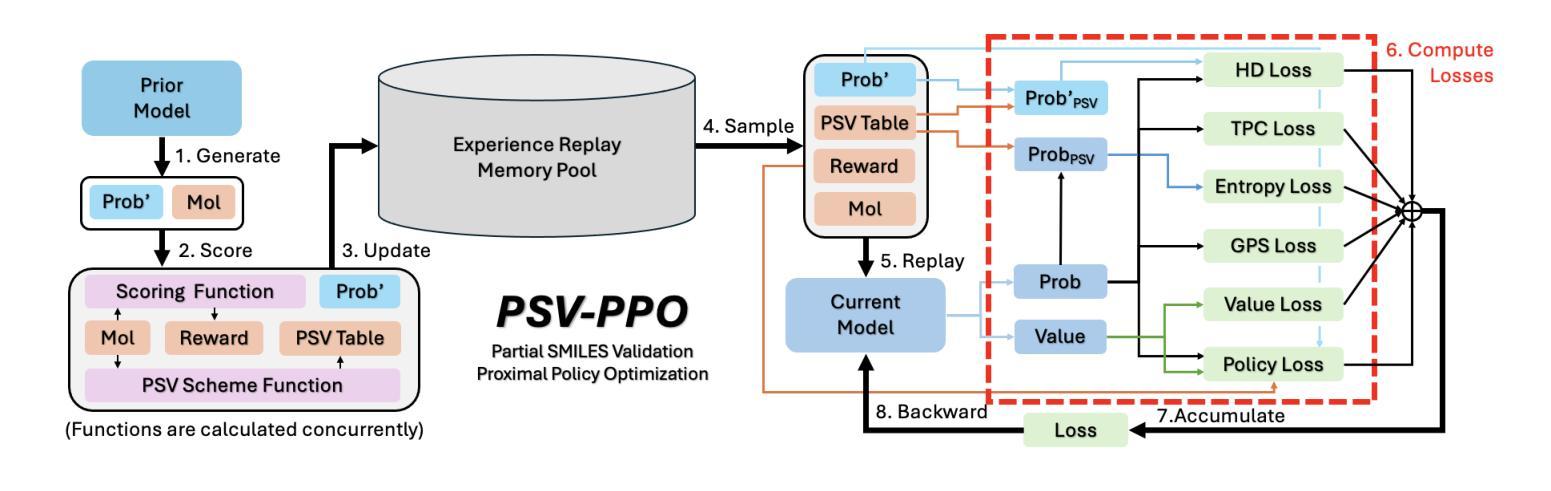
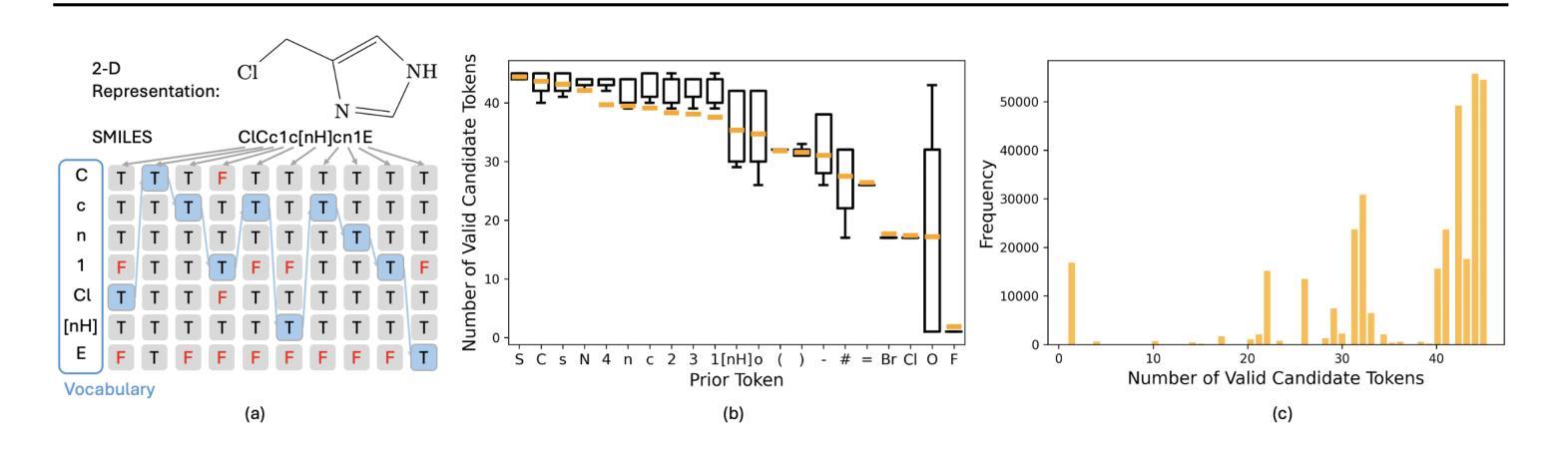
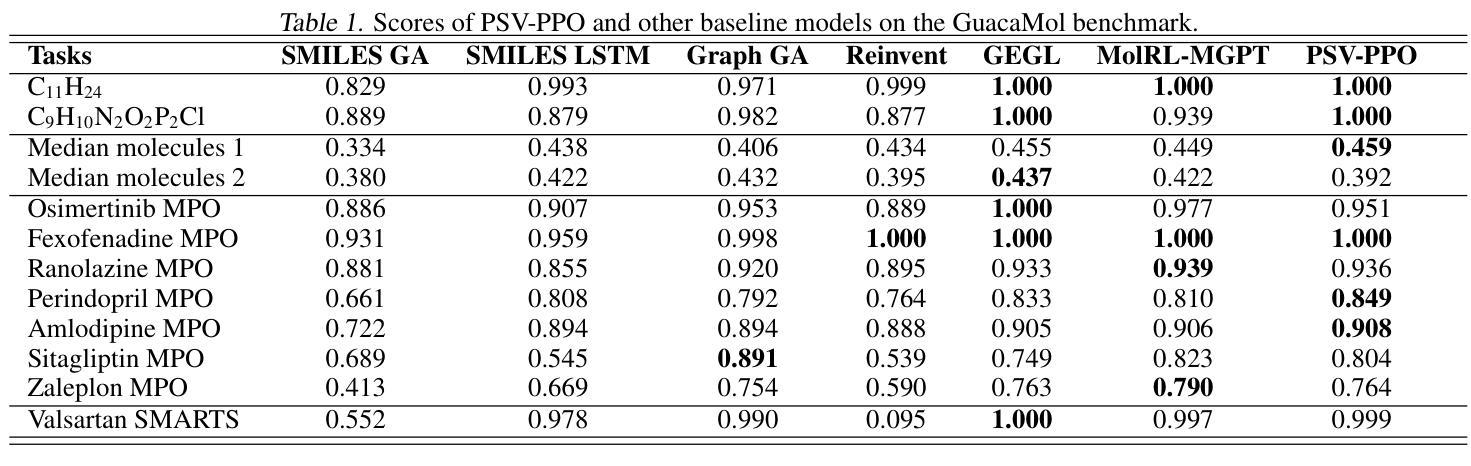
Leveraging Partial SMILES Validation Scheme for Enhanced Drug Design in Reinforcement Learning Frameworks
Authors:Xinyu Wang, Jinbo Bi, Minghu Song
SMILES-based molecule generation has emerged as a powerful approach in drug discovery. Deep reinforcement learning (RL) using large language model (LLM) has been incorporated into the molecule generation process to achieve high matching score in term of likelihood of desired molecule candidates. However, a critical challenge in this approach is catastrophic forgetting during the RL phase, where knowledge such as molecule validity, which often exceeds 99% during pretraining, significantly deteriorates. Current RL algorithms applied in drug discovery, such as REINVENT, use prior models as anchors to retian pretraining knowledge, but these methods lack robust exploration mechanisms. To address these issues, we propose Partial SMILES Validation-PPO (PSV-PPO), a novel RL algorithm that incorporates real-time partial SMILES validation to prevent catastrophic forgetting while encouraging exploration. Unlike traditional RL approaches that validate molecule structures only after generating entire sequences, PSV-PPO performs stepwise validation at each auto-regressive step, evaluating not only the selected token candidate but also all potential branches stemming from the prior partial sequence. This enables early detection of invalid partial SMILES across all potential paths. As a result, PSV-PPO maintains high validity rates even during aggressive exploration of the vast chemical space. Our experiments on the PMO and GuacaMol benchmark datasets demonstrate that PSV-PPO significantly reduces the number of invalid generated structures while maintaining competitive exploration and optimization performance. While our work primarily focuses on maintaining validity, the framework of PSV-PPO can be extended in future research to incorporate additional forms of valuable domain knowledge, further enhancing reinforcement learning applications in drug discovery.
基于SMILES的分子生成方法已经作为药物发现中的一种强大方法而出现。深度强化学习(RL)利用大型语言模型(LLM)已经被纳入到分子生成过程中,以在所需的分子候选物的可能性方面实现高匹配度。然而,这种方法的一个关键挑战是强化学习阶段的灾难性遗忘,其中如分子有效性等知识(在预训练期间通常超过99%)会显著下降。目前应用于药物发现的强化学习算法(如REINVENT)使用先验模型作为锚点来保留预训练知识,但这些方法缺乏稳健的探索机制。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了部分SMILES验证-PPO(PSV-PPO),这是一种新型的强化学习算法,它结合了实时部分SMILES验证,以防止灾难性遗忘并鼓励探索。与传统的只在生成整个序列后进行分子结构验证的强化学习方法不同,PSV-PPO在每个自回归步骤中进行逐步验证,不仅评估所选的令牌候选者,还评估源自先前部分序列的所有潜在分支。这可以在所有潜在路径上早期检测无效的SMILES片段。因此,即使在化学空间的广阔领域中进行积极的探索时,PSV-PPO也能保持较高的有效性。我们在PMO和GuacaMol基准数据集上的实验表明,PSV-PPO在保持有效性和竞争力探索和优化性能的同时,显著减少了生成的无效结构数量。虽然我们的工作主要集中在保持有效性上,但PSV-PPO的框架可以在未来的研究中扩展到纳入其他形式的宝贵领域知识,从而进一步增强强化学习在药物发现中的应用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages, 5 main figures, 2 appendix figures. Submitted to ICML 2025
Summary:
SMILES基于的分子生成法已成为药物发现中的强大手段。深度强化学习结合大型语言模型可实现高匹配度的分子候选生成。然而,强化学习阶段存在灾难性遗忘挑战,如分子有效性等预训练知识会显著下降。针对此问题,提出部分SMILES验证PPO算法(PSV-PPO),该算法在生成过程中进行实时部分SMILES验证,防止遗忘并鼓励探索。与传统方法不同,PSV-PPO在每一步生成时都进行验证,评估当前选择的标记候选及所有潜在分支,从而早期发现所有潜在路径中的无效部分SMILES。实验证明,PSV-PPO在维持高有效性率的同时,具有竞争力强的探索和优化性能。虽然本研究主要关注保持有效性,但PSV-PPO框架未来可融入更多有价值的领域知识,进一步强化其在药物发现中的应用。
Key Takeaways:
- SMILES基于的分子生成法在药物发现中具有强大潜力。
- 深度强化学习与大型语言模型结合用于生成高匹配度的分子候选。
- 强化学习阶段存在灾难性遗忘问题,影响预训练知识的保留。
- 部分SMILES验证PPO算法(PSV-PPO)提出解决此问题,通过实时验证防止遗忘并鼓励探索。
- PSV-PPO在每一步生成时进行验证,早期发现无效部分SMILES。
- 实验证明PSV-PPO在维持高有效性率的同时具有强的探索和优化性能。
点此查看论文截图

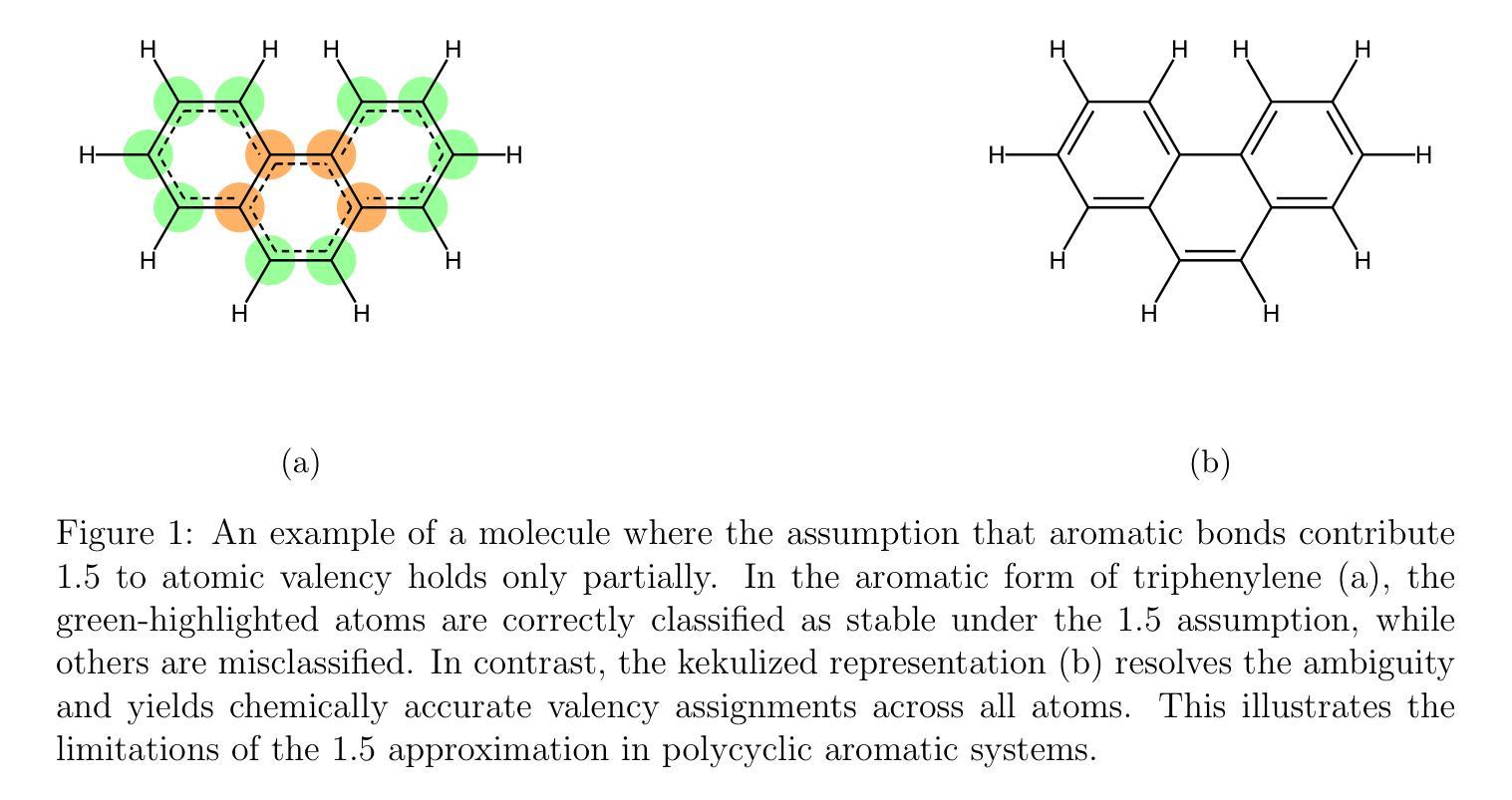
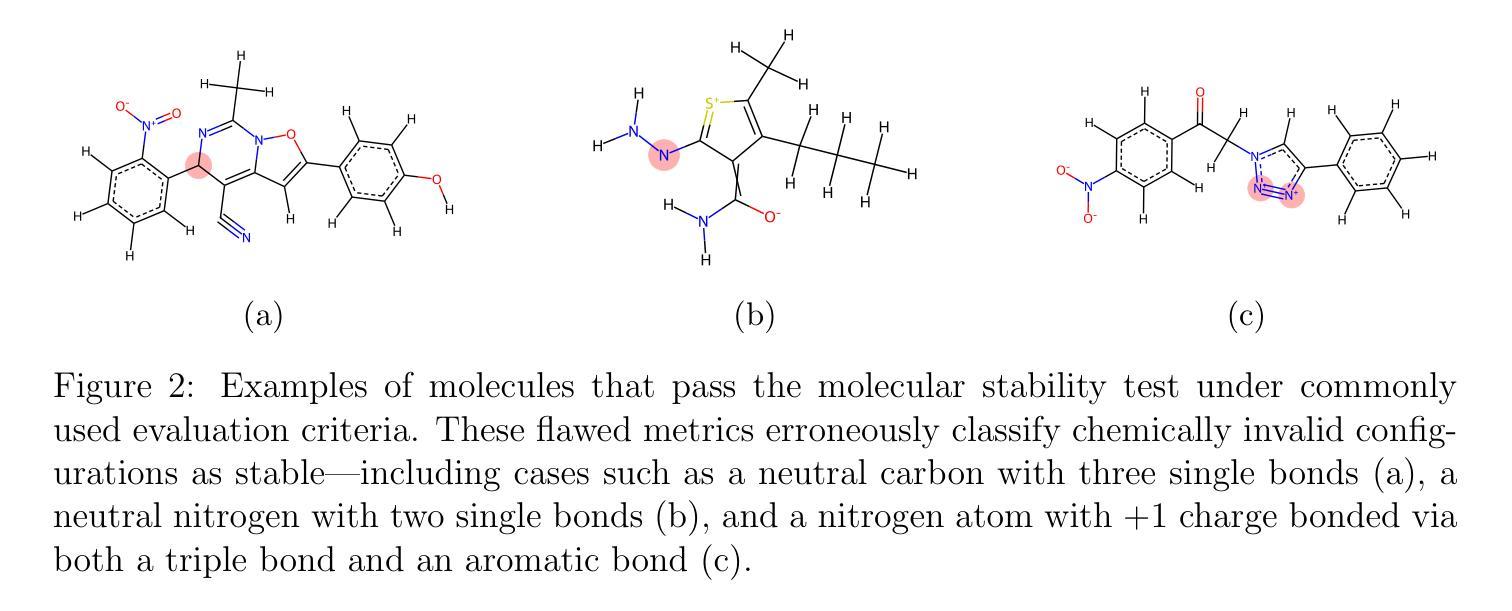
GEOM-Drugs Revisited: Toward More Chemically Accurate Benchmarks for 3D Molecule Generation
Authors:Filipp Nikitin, Ian Dunn, David Ryan Koes, Olexandr Isayev
Deep generative models have shown significant promise in generating valid 3D molecular structures, with the GEOM-Drugs dataset serving as a key benchmark. However, current evaluation protocols suffer from critical flaws, including incorrect valency definitions, bugs in bond order calculations, and reliance on force fields inconsistent with the reference data. In this work, we revisit GEOM-Drugs and propose a corrected evaluation framework: we identify and fix issues in data preprocessing, construct chemically accurate valency tables, and introduce a GFN2-xTB-based geometry and energy benchmark. We retrain and re-evaluate several leading models under this framework, providing updated performance metrics and practical recommendations for future benchmarking. Our results underscore the need for chemically rigorous evaluation practices in 3D molecular generation. Our recommended evaluation methods and GEOM-Drugs processing scripts are available at https://github.com/isayevlab/geom-drugs-3dgen-evaluation.
深度生成模型在生成有效的3D分子结构方面显示出巨大的潜力,GEOM-Drugs数据集作为一个关键的基准测试。然而,当前的评估协议存在严重缺陷,包括价态定义不正确、键序计算中的错误以及与参考数据不一致的力场依赖。在这项工作中,我们重新审视GEOM-Drugs,并提出一个修正后的评估框架:我们识别和修复数据预处理中的问题,构建化学准确的价态表,并引入基于GFN2-xTB的几何和能量基准测试。我们在该框架下重新训练和评估了几款领先模型,提供了更新的性能指标和未来基准测试的实用建议。我们的结果强调了3D分子生成中化学严格评估实践的必要性。我们推荐的评估方法和GEOM-Drugs处理脚本可在https://github.com/isayevlab/geom-drugs-3dgen-evaluation找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
深度生成模型在生成有效的3D分子结构方面显示出巨大潜力,GEOM-Drugs数据集是其中的关键基准。然而,当前的评价协议存在关键缺陷,包括价态定义不正确、键序计算中的错误以及与参考数据不一致的力场依赖。在这项工作中,我们重新审视GEOM-Drugs,并提出了修正后的评价框架:我们识别和修复了数据预处理中的问题,构建了化学准确的价态表,并引入了基于GFN2-xTB的几何和能量基准。我们在这个框架下重新训练和评估了几种领先的模型,提供了更新的性能指标和对未来基准测试的实用建议。我们的结果强调了化学严谨评价实践在3D分子生成中的必要性。
Key Takeaways
- 深度生成模型在生成3D分子结构方面表现出巨大潜力,GEOM-Drugs数据集是评价这些模型的关键基准。
- 当前的评价协议存在缺陷,包括价态定义、键序计算以及力场与参考数据的不一致性。
- 提出了修正后的评价框架,包括识别和修复数据预处理问题,构建化学准确的价态表。
- 引入了新的几何和能量基准,基于GFN2-xTB模型。
- 在修正后的框架下重新训练和评估了多个领先的模型。
- 提供了更新后的性能指标,以反映模型在修正后的评价框架下的表现。
点此查看论文截图

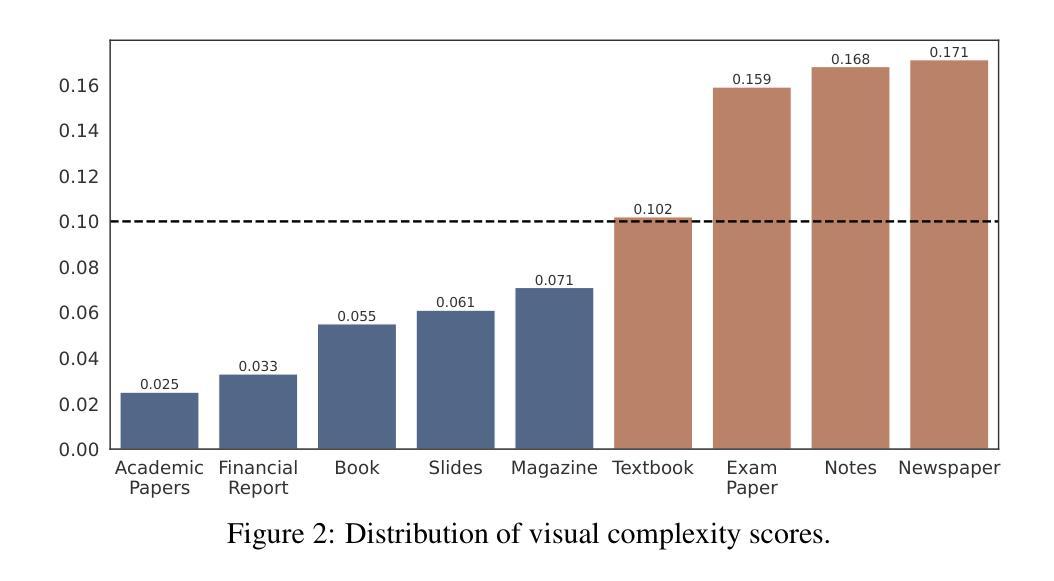
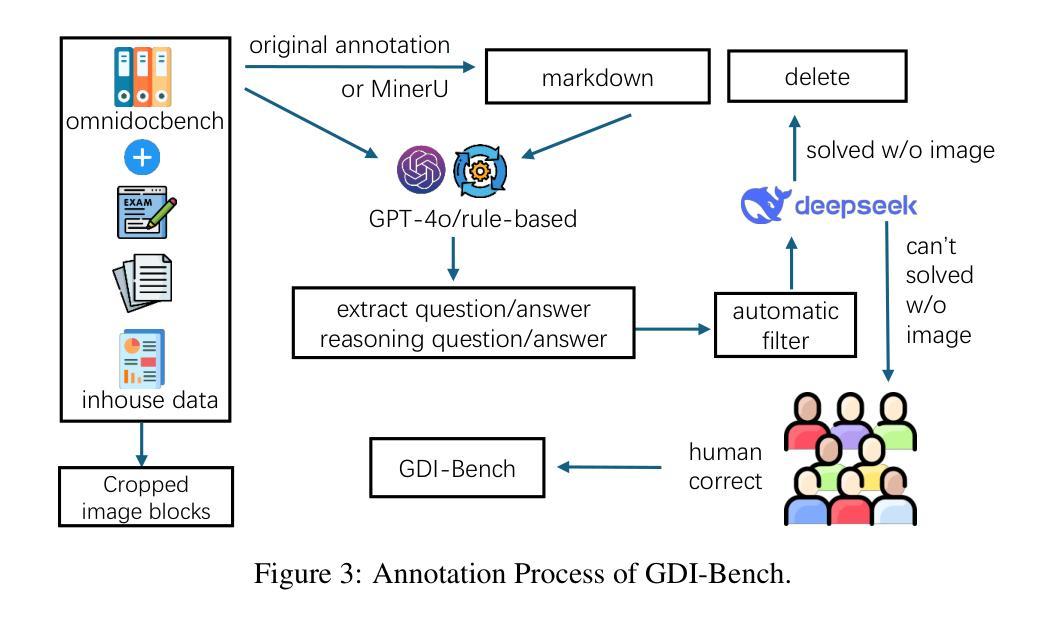
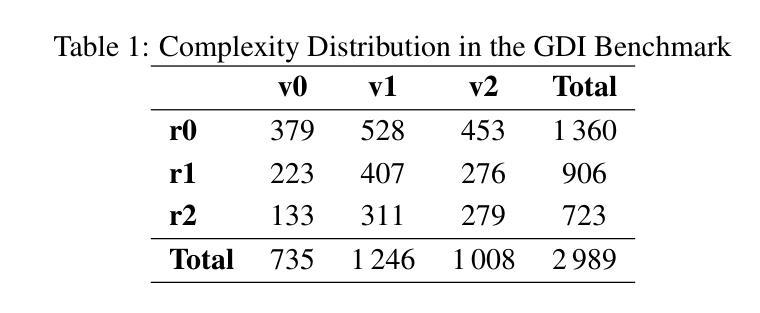
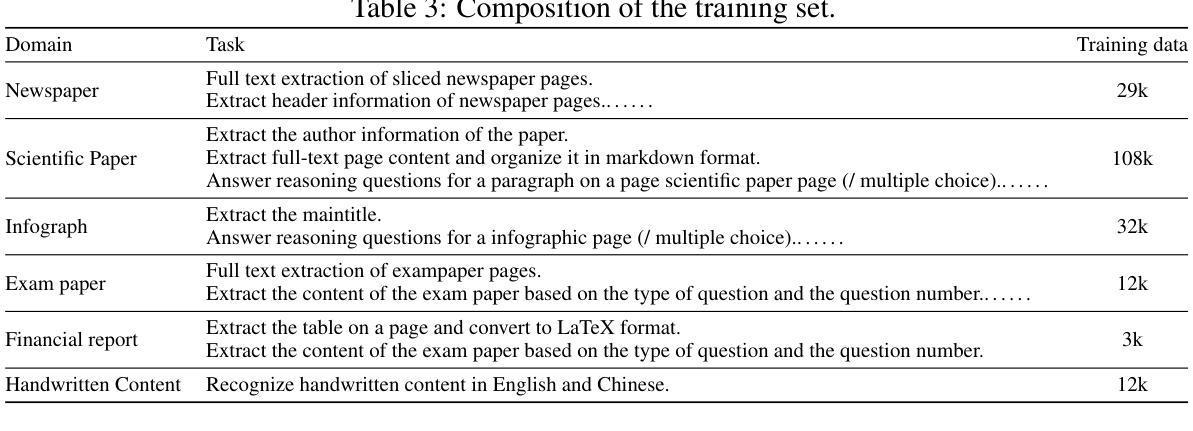
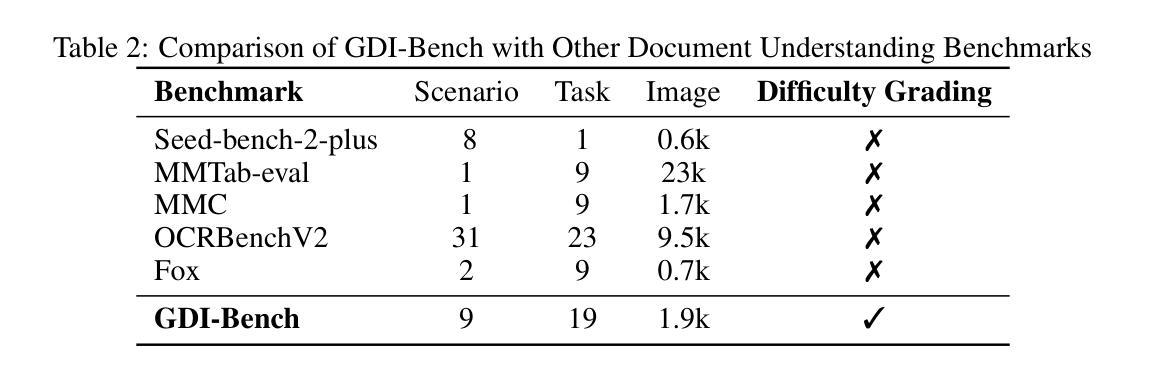
GDI-Bench: A Benchmark for General Document Intelligence with Vision and Reasoning Decoupling
Authors:Siqi Li, Yufan Shen, Xiangnan Chen, Jiayi Chen, Hengwei Ju, Haodong Duan, Song Mao, Hongbin Zhou, Bo Zhang, Pinlong Cai, Licheng Wen, Botian Shi, Yong Liu, Xinyu Cai, Yu Qiao
The rapid advancement of multimodal large language models (MLLMs) has profoundly impacted the document domain, creating a wide array of application scenarios. This progress highlights the need for a comprehensive benchmark to evaluate these models’ capabilities across various document-specific tasks. However, existing benchmarks often fail to locate specific model weaknesses or guide systematic improvements. To bridge this gap, we introduce a General Document Intelligence Benchmark (GDI-Bench), featuring 1.9k images across 9 key scenarios and 19 document-specific tasks. By decoupling visual complexity and reasoning complexity, the GDI-Bench structures graded tasks that allow performance assessment by difficulty, aiding in model weakness identification and optimization guidance. We evaluate the GDI-Bench on various open-source and closed-source models, conducting decoupled analyses in the visual and reasoning domains. For instance, the GPT-4o model excels in reasoning tasks but exhibits limitations in visual capabilities. To address the diverse tasks and domains in the GDI-Bench, we propose a GDI Model that mitigates the issue of catastrophic forgetting during the supervised fine-tuning (SFT) process through a intelligence-preserving training strategy. Our model achieves state-of-the-art performance on previous benchmarks and the GDI-Bench. Both our benchmark and model will be open source.
随着多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的快速进步,它对文档领域产生了深远影响,并创建了广泛的应用场景。这种进展强调需要对这些模型在各种特定文档任务上的能力进行全面评估的需要。然而,现有的基准测试通常无法找到特定模型的弱点或指导系统性改进。为了弥补这一差距,我们推出了通用文档智能基准测试(GDI-Bench),涵盖9个关键场景中的1900张图像和19个特定文档任务。通过解除视觉复杂性和推理复杂性的耦合,GDI-Bench构建了分级任务,允许按难度评估性能,有助于识别模型弱点并提供优化指导。我们在各种开源和闭源模型上评估GDI-Bench,在视觉和推理领域进行了解耦分析。例如,GPT-4o模型在推理任务中表现出色,但在视觉能力方面存在局限。为了解决GDI-Bench中的不同任务和领域,我们提出了一种GDI模型,该模型通过智能保留训练策略缓解了监督微调(SFT)过程中的灾难性遗忘问题。我们的模型在以前的基准测试和GDI-Bench上都达到了最先进的性能。我们的基准测试和模型都将开源。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的快速发展对文档领域的影响,并指出了现有评估基准测试(benchmarks)的不足。为此,作者提出了一种通用文档智能基准测试(GDI-Bench),包含19个针对文档特定任务的9个主要场景。该基准测试通过分离视觉复杂性和推理复杂性,允许按难度评估性能,从而帮助识别模型弱点并提供优化指导。作者对多种开源和闭源模型进行了评估,并在视觉和推理领域进行了分离分析。例如,GPT-4o模型在推理任务上表现出色,但在视觉能力方面存在局限。为解决GDI-Bench中的不同任务和领域问题,作者提出了一种GDI模型,通过智能保留训练策略缓解监督微调(SFT)过程中的灾难性遗忘问题。该模型在以前的标准测试和GDI-Bench上达到了最先进的性能表现。提供关于标准测试和模型的开源资源。
Key Takeaways
以下是关于文本的关键见解:
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的发展对文档领域产生了重大影响,催生了多种应用场景。
- 当前基准测试无法全面评估模型在不同文档特定任务中的能力。
- 提出了一种新的通用文档智能基准测试(GDI-Bench),包含多个文档特定任务和关键场景。
- GDI-Bench允许按难度评估性能,帮助识别模型的弱点,并为优化提供指导。
- 作者对各种模型进行了评估分析,发现GPT-4o在推理任务上表现良好,但在视觉能力上有局限。
- 为解决GDI-Bench中的多样任务问题,提出了GDI模型,该模型通过智能保留训练策略缓解灾难性遗忘问题。
点此查看论文截图


Vision-Language Models Are Not Pragmatically Competent in Referring Expression Generation
Authors:Ziqiao Ma, Jing Ding, Xuejun Zhang, Dezhi Luo, Jiahe Ding, Sihan Xu, Yuchen Huang, Run Peng, Joyce Chai
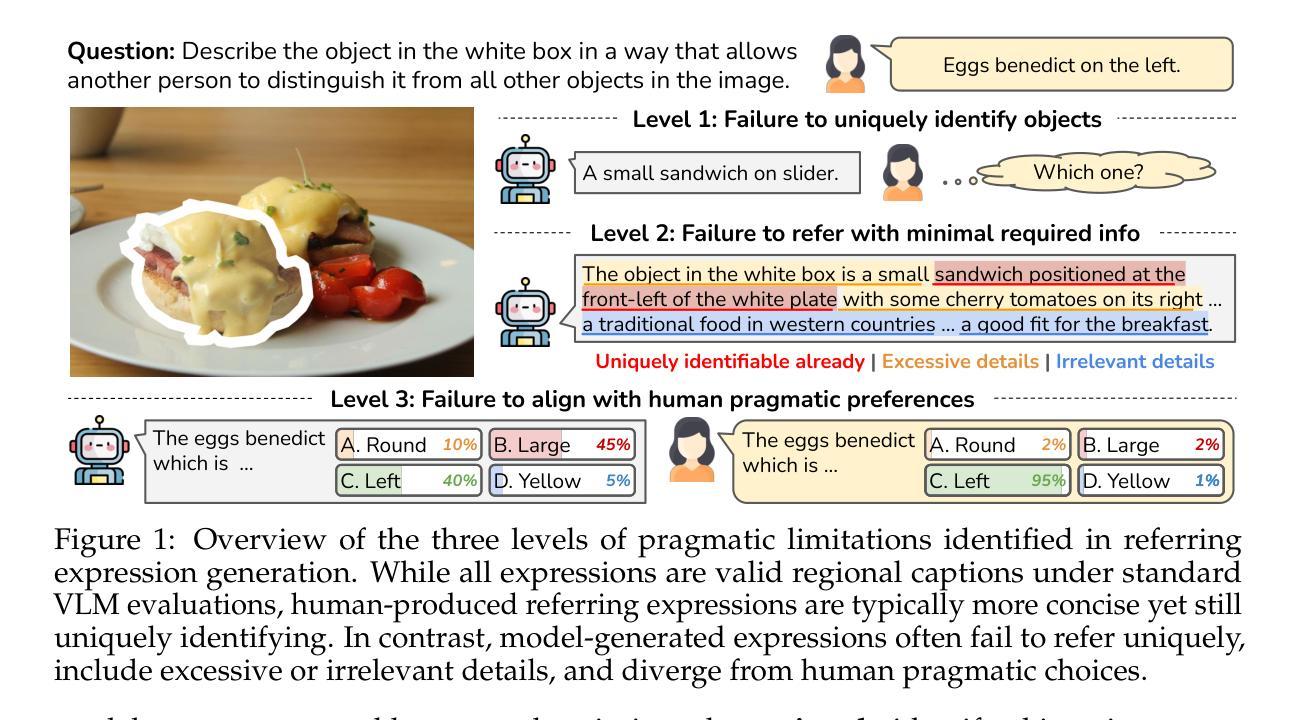
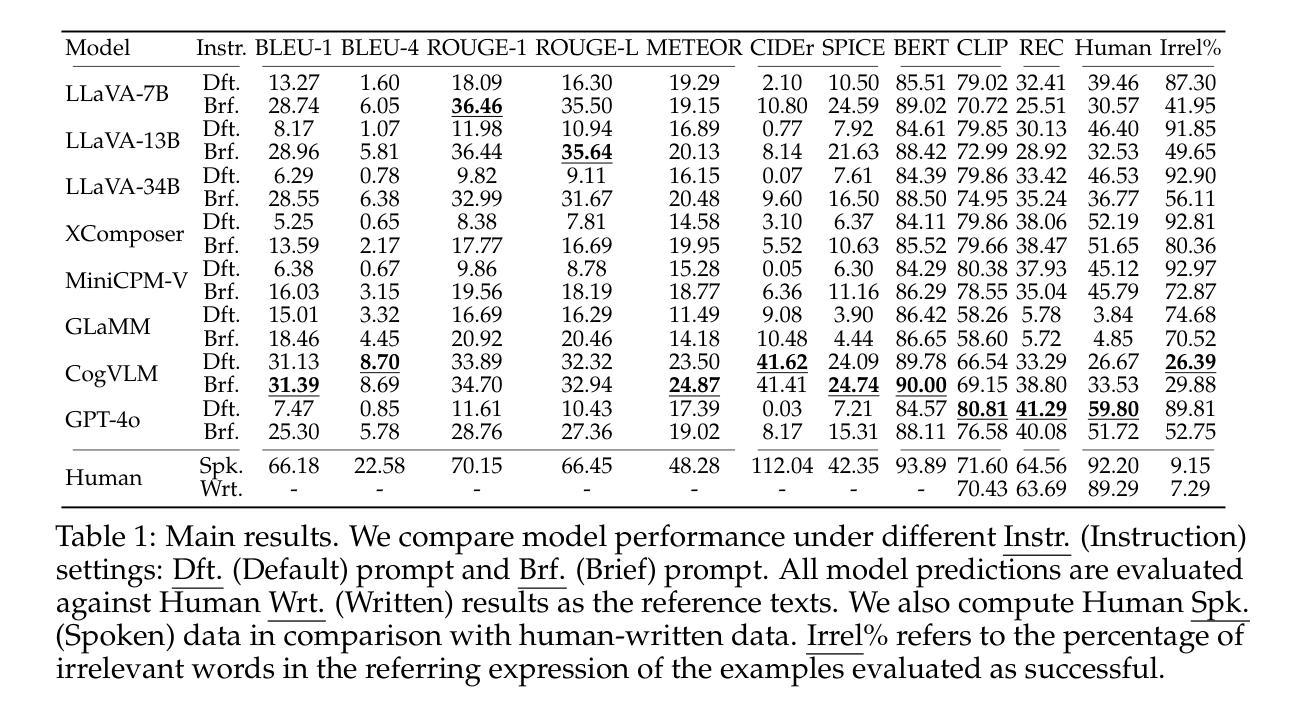
Referring Expression Generation (REG) is a core task for evaluating the pragmatic competence of vision-language systems, requiring not only accurate semantic grounding but also adherence to principles of cooperative communication (Grice, 1975). However, current evaluations of vision-language models (VLMs) often overlook the pragmatic dimension, reducing REG to a region-based captioning task and neglecting Gricean maxims. In this work, we revisit REG from a pragmatic perspective, introducing a new dataset (RefOI) of 1.5k images annotated with both written and spoken referring expressions. Through a systematic evaluation of state-of-the-art VLMs, we identify three key failures of pragmatic competence: (1) failure to uniquely identify the referent, (2) inclusion of excessive or irrelevant information, and (3) misalignment with human pragmatic preference, such as the underuse of minimal spatial cues. We also show that standard automatic evaluations fail to capture these pragmatic violations, reinforcing superficial cues rather than genuine referential success. Our findings call for a renewed focus on pragmatically informed models and evaluation frameworks that align with real human communication.
指代表达生成(REG)是评估视觉语言系统实用能力的一项核心任务,它要求不仅语义基础要准确,还要遵循合作沟通的原则(Grice,1975)。然而,对视觉语言模型(VLM)的当前评估往往忽视了实用维度,将REG简化为基于区域的描述任务,并忽略了Grice的最大准则。在这项工作中,我们从实用角度重新研究REG,介绍了一个包含1500张图像的新数据集(RefOI),这些图像都经过书面和口语参考表达的注释。通过对最先进的VLM的系统评估,我们确定了三种关键的实用能力缺失:(1)无法唯一确定指代对象,(2)包含过多或无关的信息,(3)与人类实用偏好不符,例如很少使用最小空间线索。我们还表明,标准的自动评估无法捕捉到这些实用规则的违反情况,而是强调表面线索而非真正的指代成功。我们的研究结果呼吁重点关注实用信息丰富的模型和评估框架,使其与真实的人类沟通保持一致。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Homepage: https://vlm-reg.github.io/
Summary
本文着重介绍了指代表达式生成(REG)在评估视觉语言系统的语用能力方面的核心作用。当前对视觉语言模型(VLMs)的评估往往忽视了语用维度,本文则从语用角度重新审视REG,并引入新的数据集RefOI,包含1.5k张图像,标注了书面和口语指代表达式。通过对最先进的VLMs进行系统评估,发现其语用能力的三大失败之处:无法唯一确定指代对象、包含过多或无关信息,以及与人类语用偏好的不匹配,如过度使用空间线索。同时指出,现有的自动评估无法捕捉这些语用违规行为。
Key Takeaways
- 指代表达式生成(REG)是评估视觉语言系统语用能力的重要任务。
- 当前对视觉语言模型(VLMs)的评估忽视了语用维度。
- 引入新的数据集RefOI,包含书面和口语指代表达式的图像标注。
- VLMs在语用能力方面存在三大失败:无法唯一确定指代对象、包含过多或无关信息,以及与人类语用偏好不匹配。
- 现有的自动评估无法有效捕捉这些语用违规行为。
- 需要重新关注语用信息驱动的模型和评估框架。
点此查看论文截图



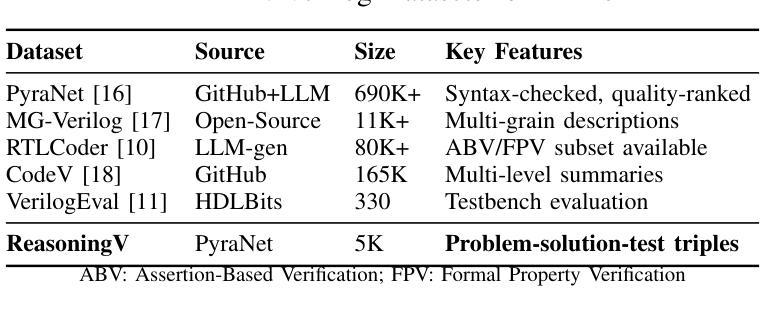
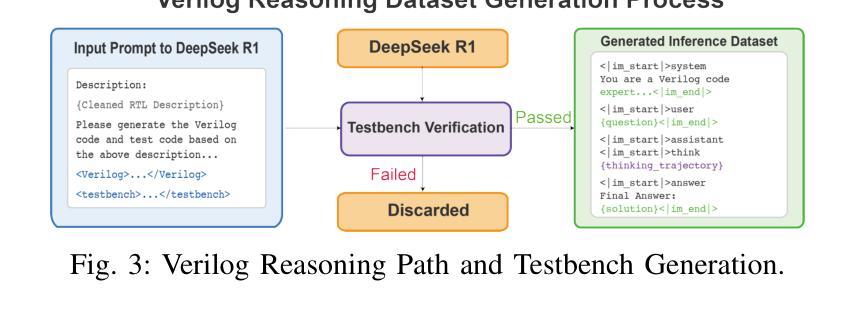
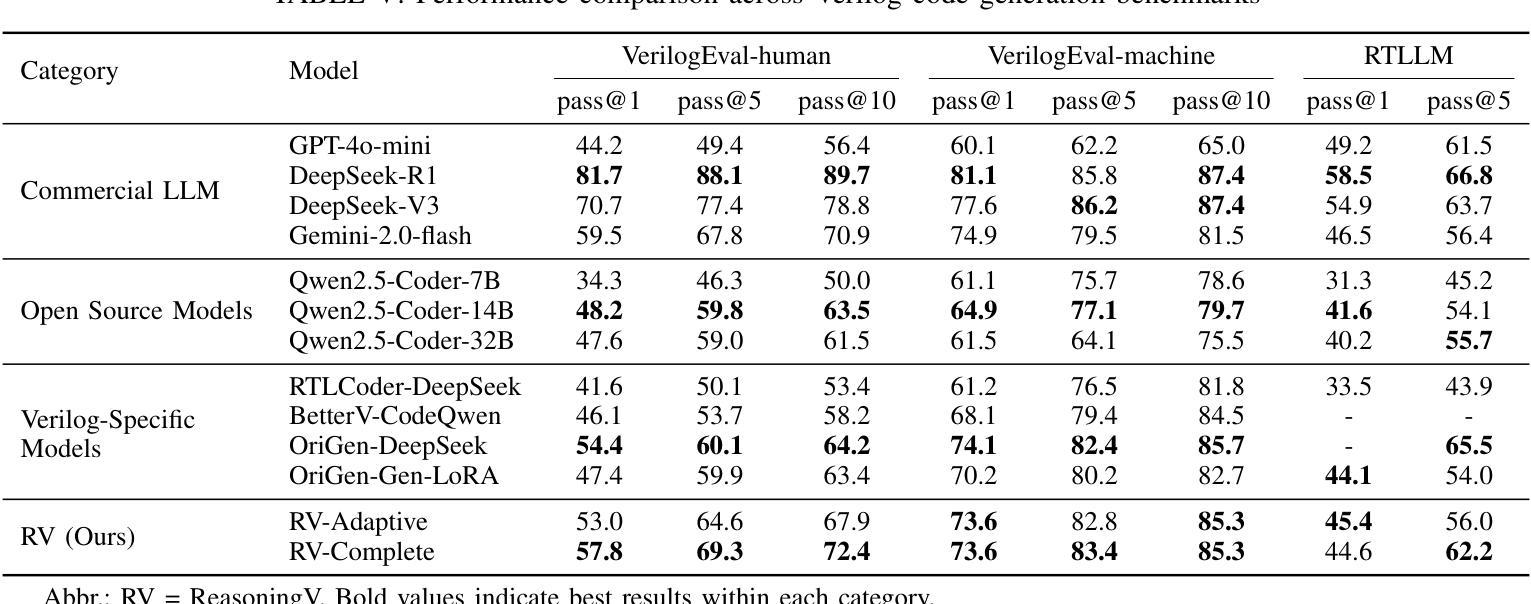
ReasoningV: Efficient Verilog Code Generation with Adaptive Hybrid Reasoning Model
Authors:Haiyan Qin, Zhiwei Xie, Jingjing Li, Liangchen Li, Xiaotong Feng, Junzhan Liu, Wang Kang
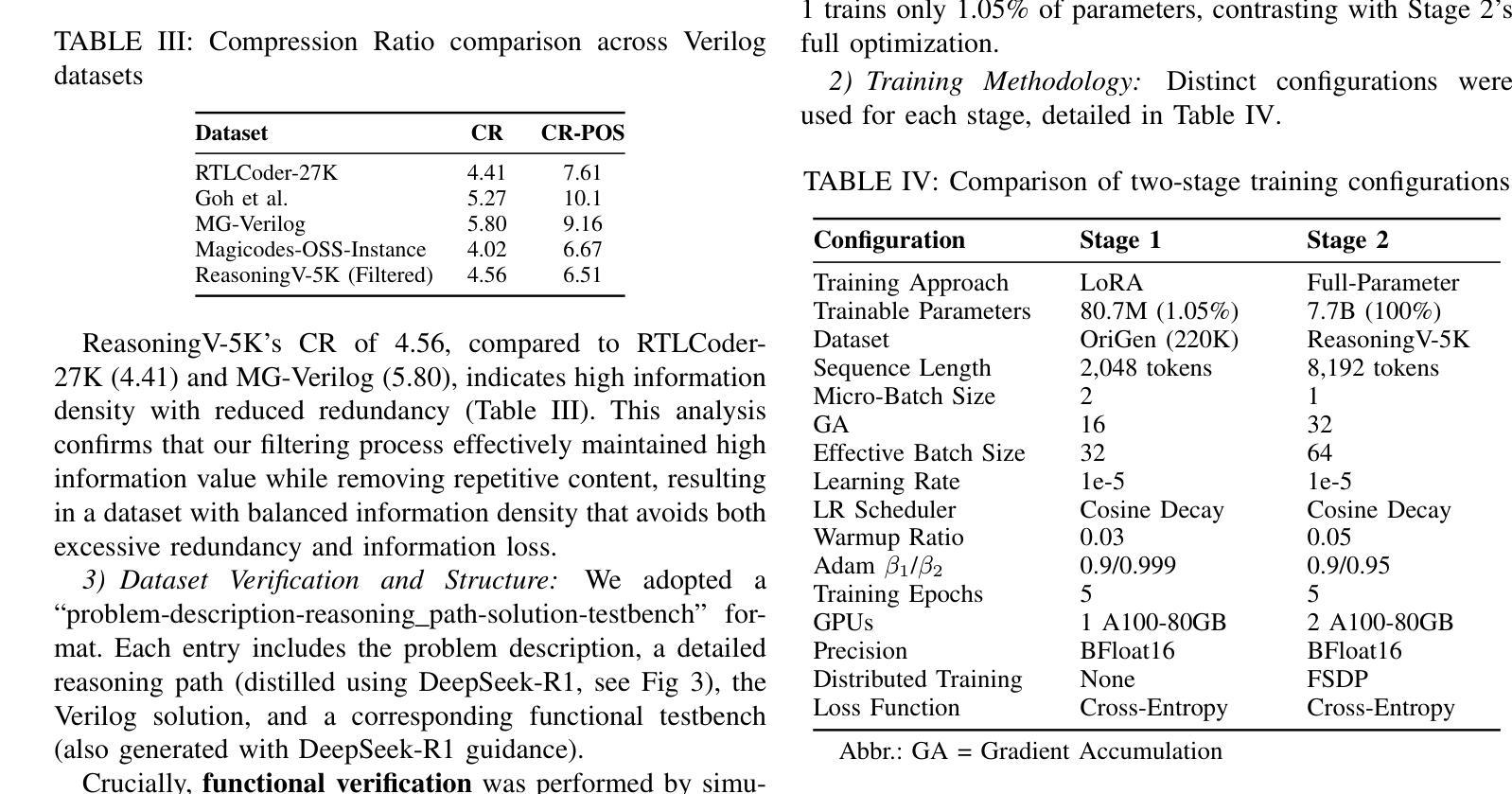
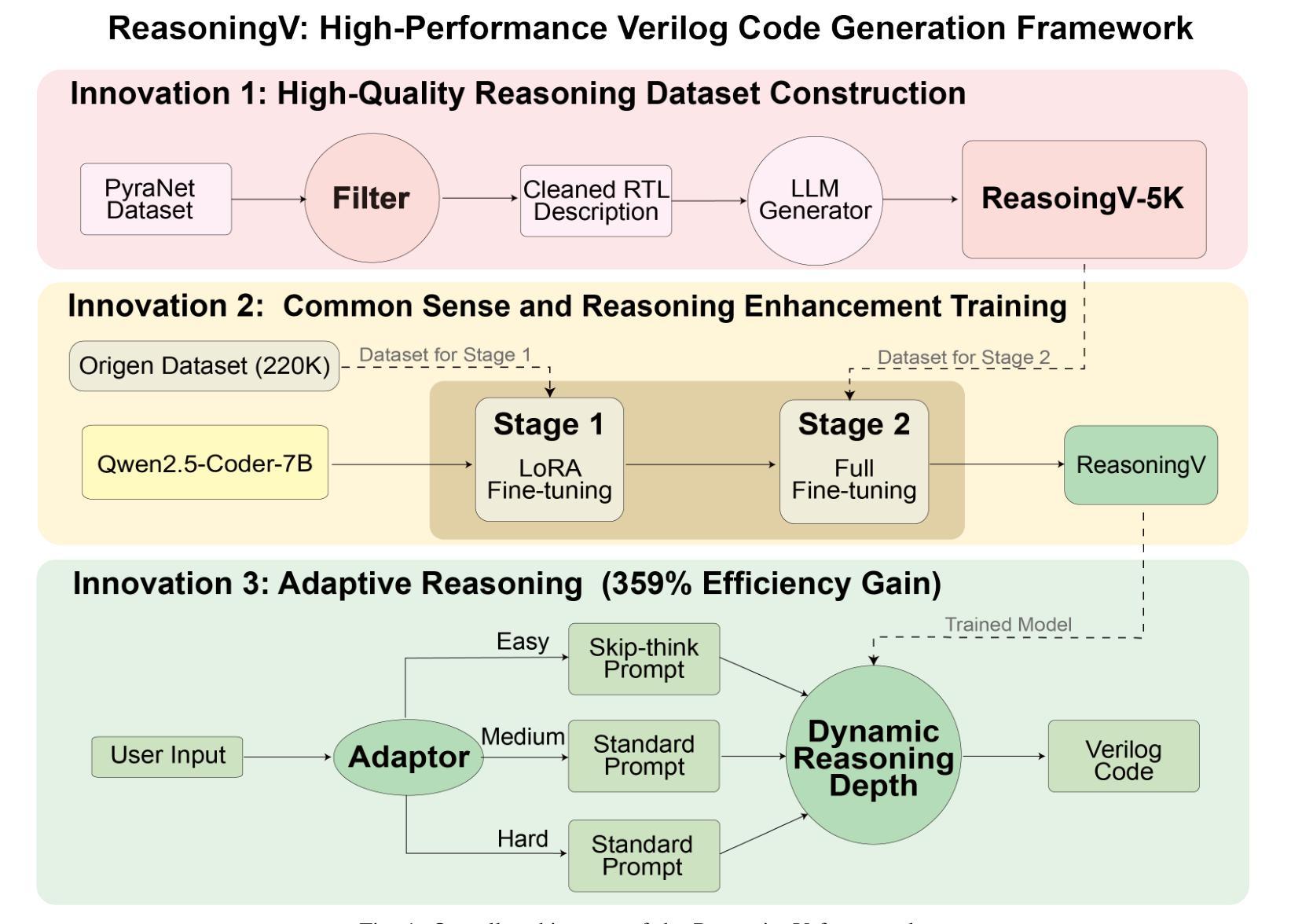
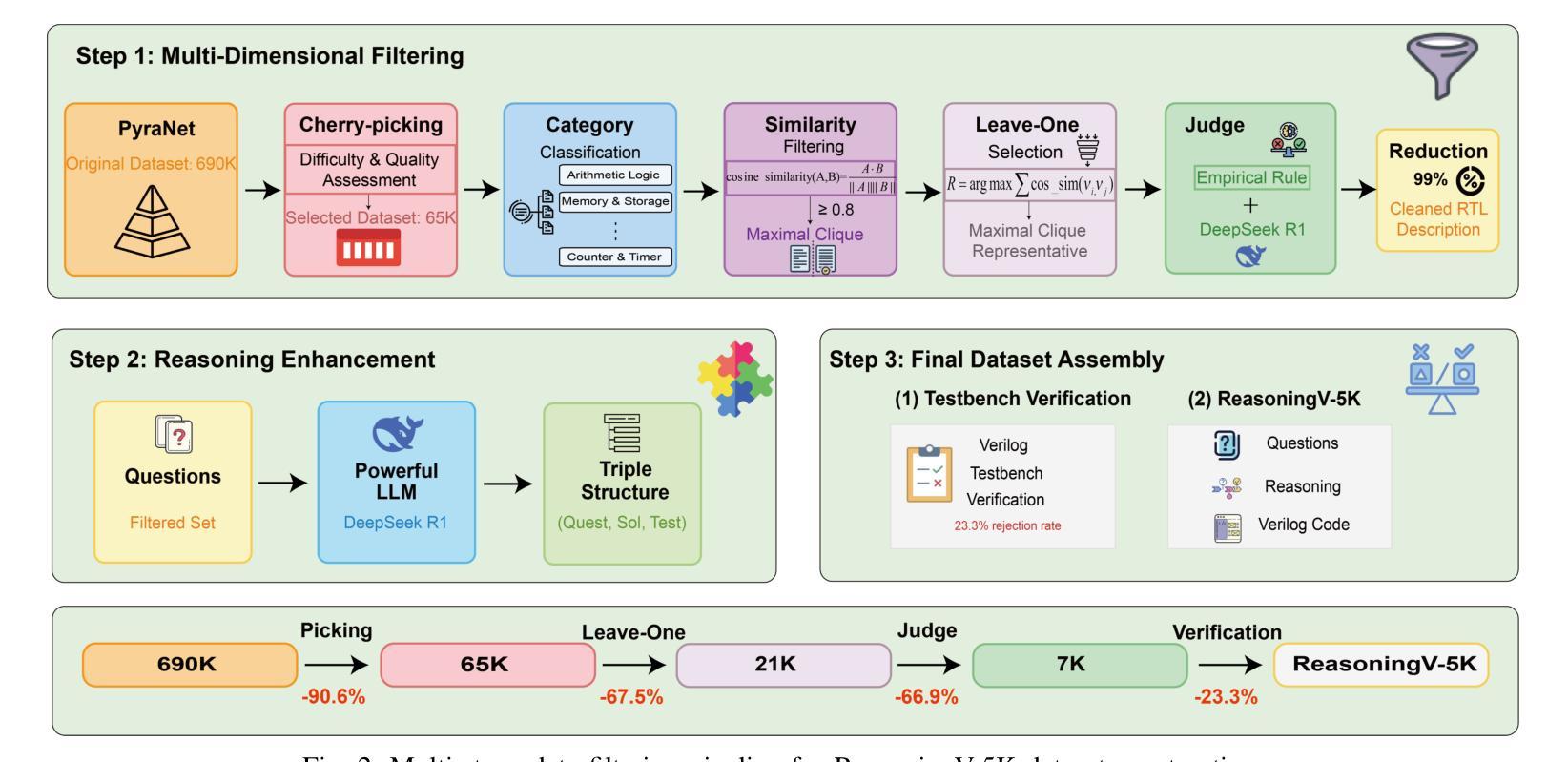
Large Language Models (LLMs) have advanced Verilog code generation significantly, yet face challenges in data quality, reasoning capabilities, and computational efficiency. This paper presents ReasoningV, a novel model employing a hybrid reasoning strategy that integrates trained intrinsic capabilities with dynamic inference adaptation for Verilog code generation. Our framework introduces three complementary innovations: (1) ReasoningV-5K, a high-quality dataset of 5,000 functionally verified instances with reasoning paths created through multi-dimensional filtering of PyraNet samples; (2) a two-stage training approach combining parameter-efficient fine-tuning for foundational knowledge with full-parameter optimization for enhanced reasoning; and (3) an adaptive reasoning mechanism that dynamically adjusts reasoning depth based on problem complexity, reducing token consumption by up to 75% while preserving performance. Experimental results demonstrate ReasoningV’s effectiveness with a pass@1 accuracy of 57.8% on VerilogEval-human, achieving performance competitive with leading commercial models like Gemini-2.0-flash (59.5%) and exceeding the previous best open-source model by 10.4 percentage points. ReasoningV offers a more reliable and accessible pathway for advancing AI-driven hardware design automation, with our model, data, and code available at https://github.com/BUAA-CLab/ReasoningV.
大型语言模型(LLM)极大地推动了Verilog代码生成的发展,但在数据质量、推理能力和计算效率方面仍面临挑战。本文提出了一种名为ReasoningV的新型模型,该模型采用混合推理策略,将训练的内在能力与动态推理适应相结合,用于Verilog代码生成。我们的框架引入了三项互补创新:1)ReasoningV-5K,这是一个包含5000个功能验证实例的高质量数据集,通过PyraNet样本的多维过滤创建推理路径;2)结合参数高效微调基础知识与全参数优化增强推理的两阶段训练方法;3)自适应推理机制,根据问题复杂度动态调整推理深度,在保持性能的同时,最多可减少75%的令牌消耗。实验结果表明,ReasoningV在VerilogEval-human上的pass@1准确率为57.8%,与领先的商业模型如Gemini-2.0-flash(59.5%)相竞争,并超过之前最佳开源模型的准确率提高了10.4个百分点。ReasoningV为推进AI驱动的硬件设计自动化提供了更可靠和可访问的途径,我们的模型、数据和代码可在https://github.com/BUAA-CLab/ReasoningV上获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 4 figures
Summary
大型语言模型在Verilog代码生成方面取得了显著进展,但仍面临数据质量、推理能力和计算效率方面的挑战。本文提出了一种名为ReasoningV的新型模型,采用混合推理策略,将训练好的内在能力与动态推理适应相结合,用于Verilog代码生成。该框架引入了三项互补创新:高质量数据集ReasoningV-5K、两阶段训练方法和自适应推理机制。实验结果证明了ReasoningV的有效性,在VerilogEval-human上的pass@1准确率达到57.8%,性能领先商业模型Gemini-2.0-flash,并超过了之前最好的开源模型10.4个百分点。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在Verilog代码生成中取得显著进展,但仍面临挑战。
- ReasoningV模型采用混合推理策略,结合训练内在能力与动态推理适应。
- 引入高质量数据集ReasoningV-5K,通过多维度过滤PyraNet样本创建。
- 采用两阶段训练方法,结合基础知识的参数有效微调与增强推理的全参数优化。
- 自适应推理机制可根据问题复杂度动态调整推理深度,减少令牌消耗。
- 实验结果显示ReasoningV在VerilogEval-human上的性能具有竞争力,超过了一些商业和开源模型。
点此查看论文截图


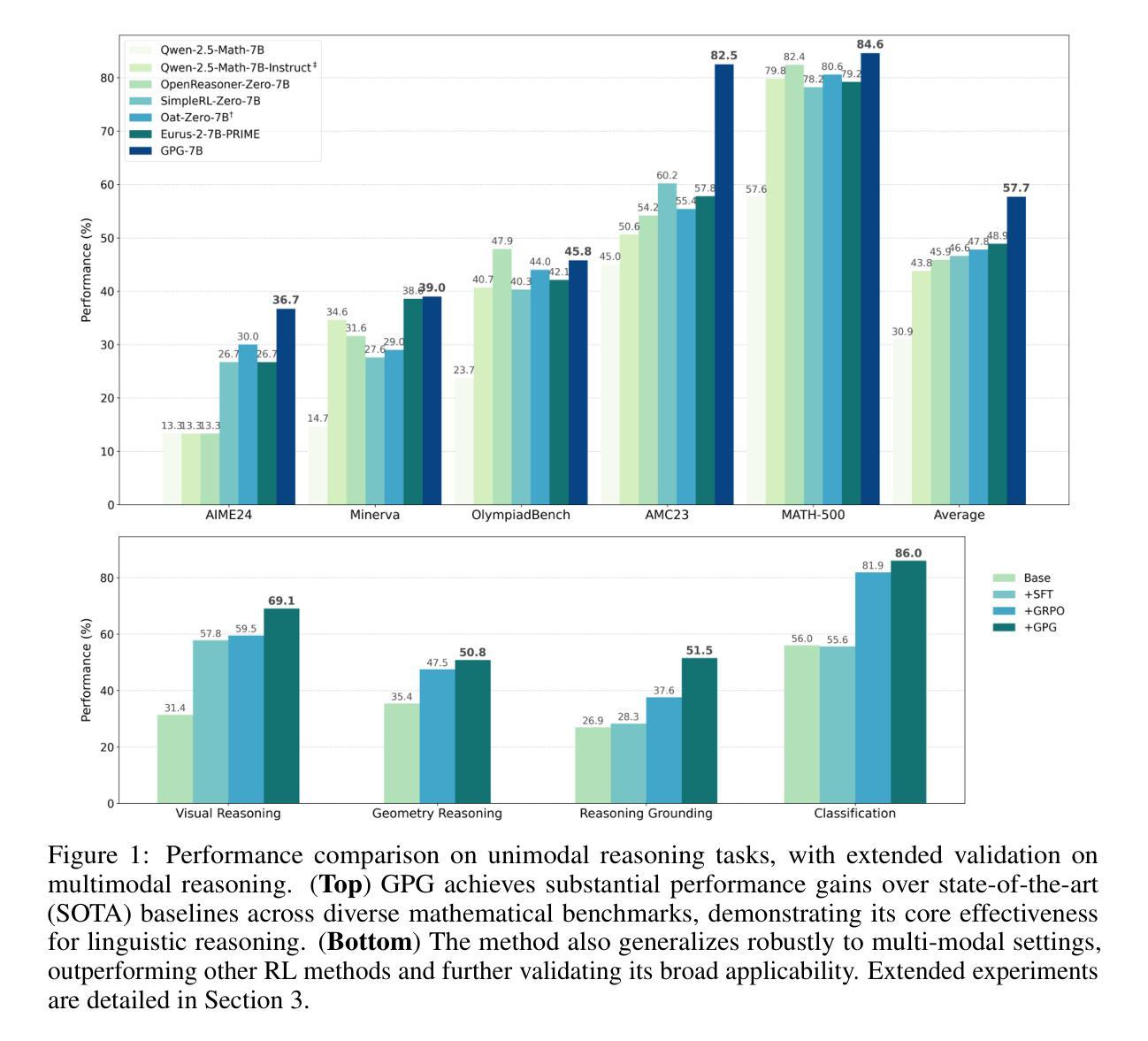
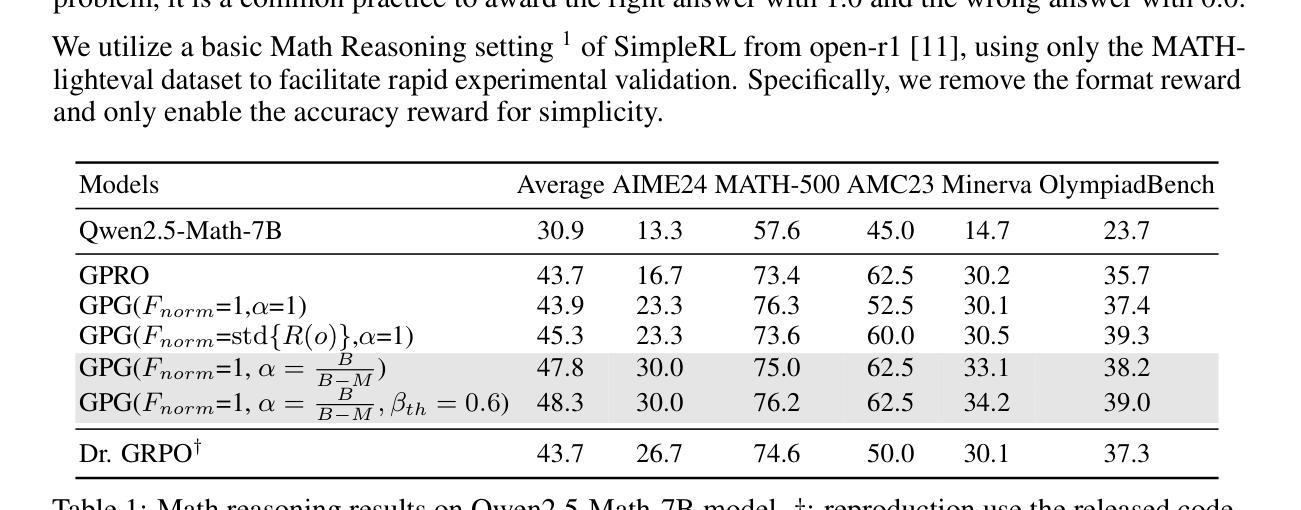
GPG: A Simple and Strong Reinforcement Learning Baseline for Model Reasoning
Authors:Xiangxiang Chu, Hailang Huang, Xiao Zhang, Fei Wei, Yong Wang
Reinforcement Learning (RL) can directly enhance the reasoning capabilities of large language models without extensive reliance on Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT). In this work, we revisit the traditional Policy Gradient (PG) mechanism and propose a minimalist RL approach termed Group Policy Gradient (GPG). Unlike conventional methods, GPG directly optimize the original RL objective, thus obviating the need for surrogate loss functions. By eliminating the critic and reference models, avoiding KL divergence constraints, and addressing the advantage and gradient estimation bias, our approach significantly simplifies the training process compared to Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO). Our approach achieves superior performance without relying on auxiliary techniques or adjustments. As illustrated in Figure 1, extensive experiments demonstrate that our method not only reduces computational costs but also consistently outperforms GRPO across various unimodal and multimodal tasks. Our code is available at https://github.com/AMAP-ML/GPG.
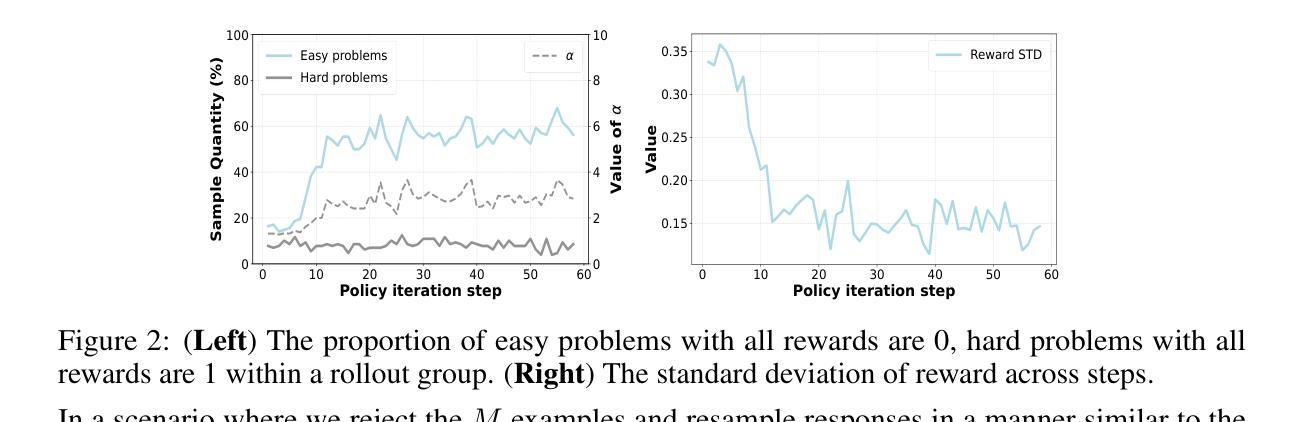
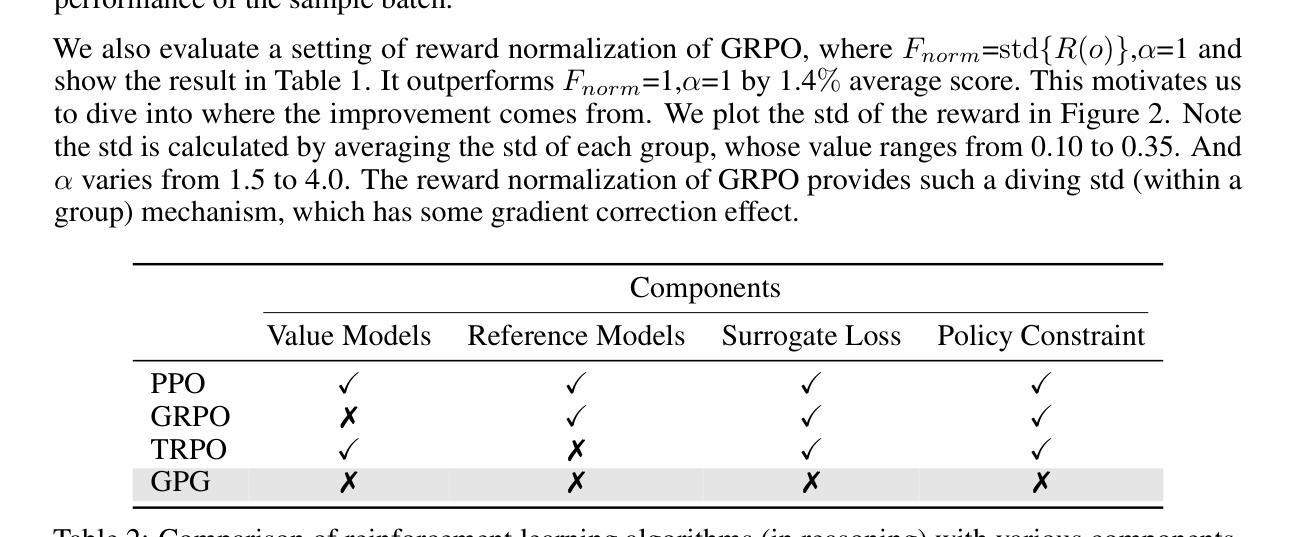
强化学习(RL)可以直接提升大语言模型的推理能力,而无需过多依赖监督微调(SFT)。在这项工作中,我们重新审视了传统的策略梯度(PG)机制,并提出了一种极简的RL方法,称为组策略梯度(GPG)。与常规方法不同,GPG直接优化原始的RL目标,从而无需替代损失函数。通过消除评价者和参考模型,避免KL散度约束,并解决优势和梯度估计偏差问题,我们的方法大大简化了与组相对策略优化(GRPO)相比的训练过程。我们的方法在不依赖辅助技术或调整的情况下实现了卓越的性能。如图1所示,大量实验表明,我们的方法不仅降低了计算成本,而且在各种单模态和多模态任务上始终优于GRPO。我们的代码位于https://github.com/AMAP-ML/GPG。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
强化学习(RL)能够直接提升大型语言模型的推理能力,而无需过度依赖监督微调(SFT)。本研究重新审视了传统的策略梯度(PG)机制,并提出了一种极简的RL方法——群组策略梯度(GPG)。GPG直接优化原始的RL目标,从而无需替代损失函数。通过消除评论家模型和参考模型,避免KL散度约束,并解决优势和梯度估计偏差等问题,GPG简化了训练过程,相较于群组相对策略优化(GRPO)有显著优势。GPG在不依赖辅助技术或调整的情况下实现了卓越的性能。如图1所示,大量实验证明,GPG不仅降低了计算成本,而且在各种单模态和多模态任务上均优于GRPO。相关代码可在https://github.com/AMAP-ML/GPG找到。
Key Takeaways
- 强化学习(RL)能增强大型语言模型的推理能力,且不需要过度依赖监督微调。
- 研究者提出了群组策略梯度(GPG)方法,这是一种新的极简RL方法。
- GPG直接优化原始的RL目标,无需使用替代损失函数。
- GPG简化了训练过程,相比传统方法有很大优势。
- GPG方法在不使用辅助技术或调整的情况下表现出卓越性能。
- GPG在多种任务上均表现优异,包括单模态和多模态任务。
点此查看论文截图

Instantiation-based Formalization of Logical Reasoning Tasks using Language Models and Logical Solvers
Authors:Mohammad Raza, Natasa Milic-Frayling
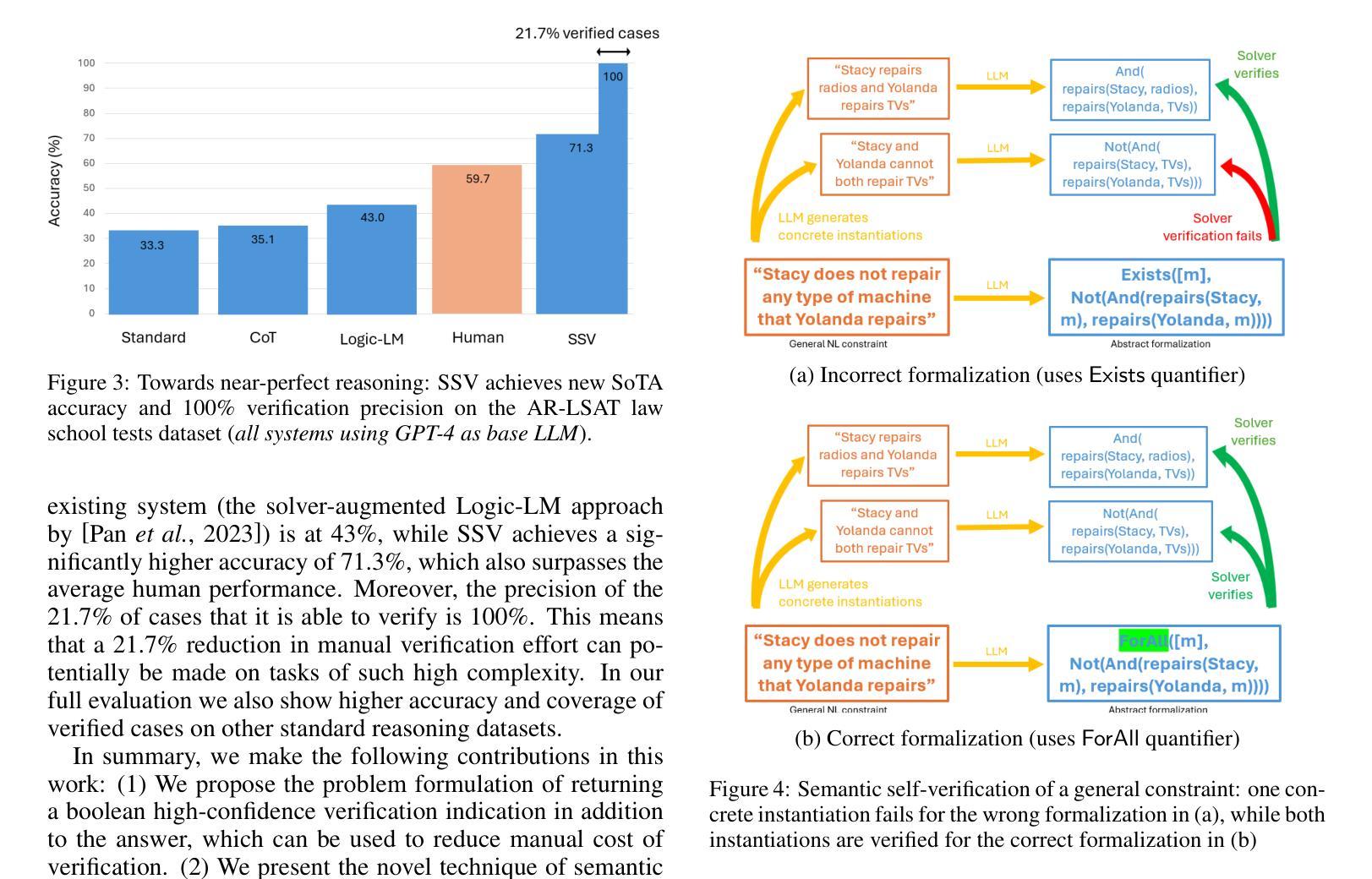
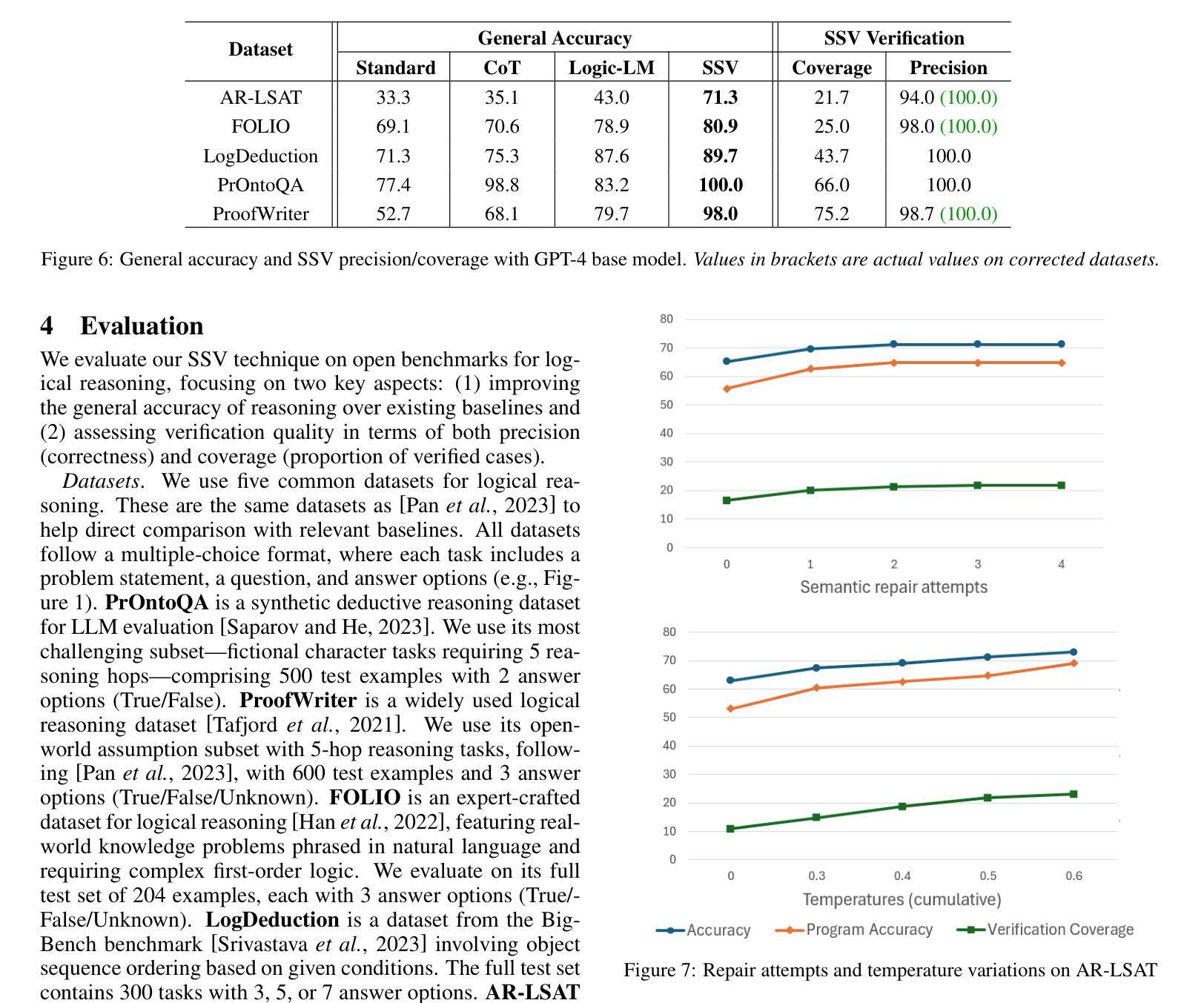
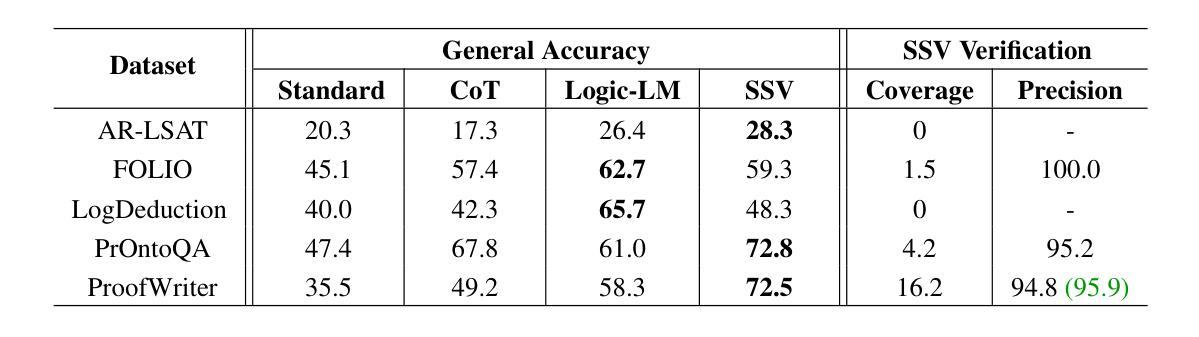
Robustness of reasoning remains a significant challenge for large language models, and addressing it is essential for the practical applicability of AI-driven reasoning systems. We introduce Semantic Self-Verification (SSV), a novel approach that addresses the key challenge in combining language models with the rigor of logical solvers: to accurately formulate the reasoning problem from natural language to the formal language of the solver. SSV uses a consistency-based approach to produce strong abstract formalizations of problems using concrete instantiations that are generated by the model and verified by the solver. In addition to significantly advancing the overall reasoning accuracy over the state-of-the-art, a key novelty that this approach presents is a feature of verification that has near-perfect precision over a significant coverage of cases, as we demonstrate on open reasoning benchmarks. We propose such near-certain reasoning as a new approach to reduce the need for manual verification in many cases, taking us closer to more dependable and autonomous AI reasoning systems.
推理的稳健性对于大型语言模型来说仍然是一个巨大的挑战,解决这一挑战对于人工智能驱动推理系统的实际应用至关重要。我们引入了语义自验证(SSV)这一新方法,解决了将语言模型与逻辑求解器严谨性相结合的关键挑战:即准确地将推理问题从自然语言表述转化为求解器的正式语言。SSV使用基于一致性的方法,通过模型生成的具体实例和求解器的验证,产生对问题的强大抽象形式化。除了显著提高整体推理精度,超越现有技术水平,该方法的关键新颖之处在于验证功能,在大量案例中几乎达到了完美的精度,我们在公开推理基准测试上展示了这一点。我们提出将这种“近乎确定的推理”作为减少许多情况下对人工验证需求的新方法,使我们更接近可靠和自主的人工智能推理系统。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IJCAI 2025
Summary
基于大型语言模型的推理稳健性挑战对于AI驱动的推理系统的实际应用至关重要。本文引入了一种名为语义自验证(SSV)的新方法,解决了将语言模型与逻辑求解器结合的关键难题:将自然语言准确转化为求解器的形式语言。SSV使用一致性方法,通过模型生成的实例进行抽象问题的形式化,并由求解器进行验证。除了显著提高整体推理精度外,该方法的关键新颖之处在于其验证功能,它在广泛的案例中几乎具有完美的精确度。我们提出了这种近乎确定的推理作为一种新方法,在许多情况下减少对手动验证的需求,使我们更接近于更可靠和更自主的AI推理系统。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型的推理稳健性对于AI推理系统的实际应用是一个重要的挑战。
- 语义自验证(SSV)是一种解决语言模型与逻辑求解器结合的关键难题的新方法。
- SSV通过将自然语言转化为求解器的形式语言来提高推理的准确性。
- SSV使用一致性方法,通过模型生成的实例进行抽象问题的形式化。
- SSV由求解器进行验证,具有显著的验证功能。
- SSV方法提高了整体推理精度,并在广泛的案例中几乎具有完美的精确度。
点此查看论文截图