⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-03 更新
Scaling On-Device GPU Inference for Large Generative Models
Authors:Jiuqiang Tang, Raman Sarokin, Ekaterina Ignasheva, Grant Jensen, Lin Chen, Juhyun Lee, Andrei Kulik, Matthias Grundmann
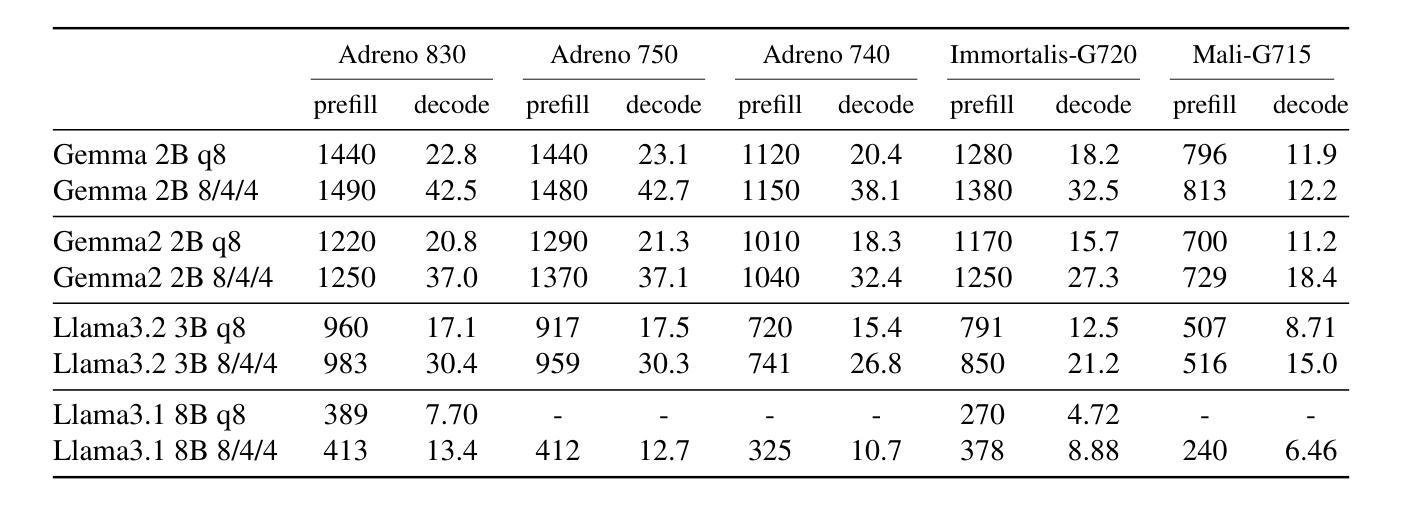
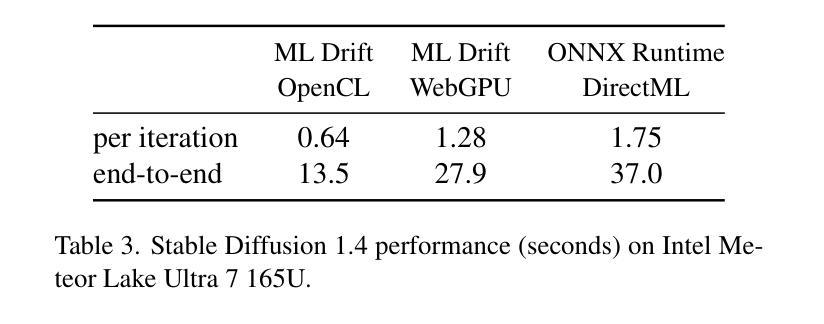
Driven by the advancements in generative AI, large machine learning models have revolutionized domains such as image processing, audio synthesis, and speech recognition. While server-based deployments remain the locus of peak performance, the imperative for on-device inference, necessitated by privacy and efficiency considerations, persists. Recognizing GPUs as the on-device ML accelerator with the widest reach, we present ML Drift–an optimized framework that extends the capabilities of state-of-the-art GPU-accelerated inference engines. ML Drift enables on-device execution of generative AI workloads which contain 10 to 100x more parameters than existing on-device generative AI models. ML Drift addresses intricate engineering challenges associated with cross-GPU API development, and ensures broad compatibility across mobile and desktop/laptop platforms, thereby facilitating the deployment of significantly more complex models on resource-constrained devices. Our GPU-accelerated ML/AI inference engine achieves an order-of-magnitude performance improvement relative to existing open-source GPU inference engines.
随着生成式人工智能的快速发展,大型机器学习模型已经彻底改变了图像处理、音频合成和语音识别等领域。虽然基于服务器的部署仍是性能巅峰的所在地,但由于隐私和效率方面的考虑,对设备端推理的需求持续存在。我们认识到GPU是设备端机器学习加速器中覆盖范围最广的,因此我们推出了ML Drift——一个优化框架,它扩展了最新GPU加速推理引擎的功能。ML Drift能够在设备上执行包含比现有设备上生成式人工智能模型多10到100倍的参数的生成式AI工作负载。ML Drift解决了与跨GPU API开发相关的复杂工程挑战,并确保在移动和桌面/笔记本电脑平台上的广泛兼容性,从而促进了在资源受限的设备上部署更复杂的模型。我们的GPU加速的ML/AI推理引擎相对于现有的开源GPU推理引擎实现了性能的大幅提升。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF to be published in CVPR 2025 Workshop on Efficient and On-Device Generation (EDGE)
Summary
随着生成式人工智能的发展,大型机器学习模型已逐步革新图像处理、音频合成及语音识别等领域。虽然基于服务器的部署仍是实现高性能的中心,但由于隐私和效率的需求,对设备端推理的迫切需求持续存在。针对GPU作为设备端机器学习加速器的广泛应用,我们推出了ML Drift框架,该框架优化了现有最先进的GPU加速推理引擎的功能。ML Drift能够在设备上执行参数比现有设备端生成式AI模型多10至100倍的生成式AI工作负载。该框架解决了跨GPU API开发的复杂工程挑战,确保了在手机和桌面/笔记本电脑平台上的广泛兼容性,从而促进了在资源受限设备上部署更复杂的模型。我们的GPU加速的机器学习/人工智能推理引擎相较于现有的开源GPU推理引擎实现了数量级的性能提升。
Key Takeaways
- 大型机器学习模型在图像、音频及语音识别等领域的应用已引发革命性变革。
- 服务器部署仍是实现高性能的主要方式,但对设备端推理的需求日益迫切。
- GPU作为设备端机器学习加速器受到广泛应用。
- ML Drift框架优化了GPU加速推理引擎的功能,支持更复杂的模型部署。
- ML Drift能在设备上执行参数远超现有模型的生成式AI工作负载。
- ML Drift解决了跨GPU API的复杂工程挑战,确保多平台兼容性。
点此查看论文截图


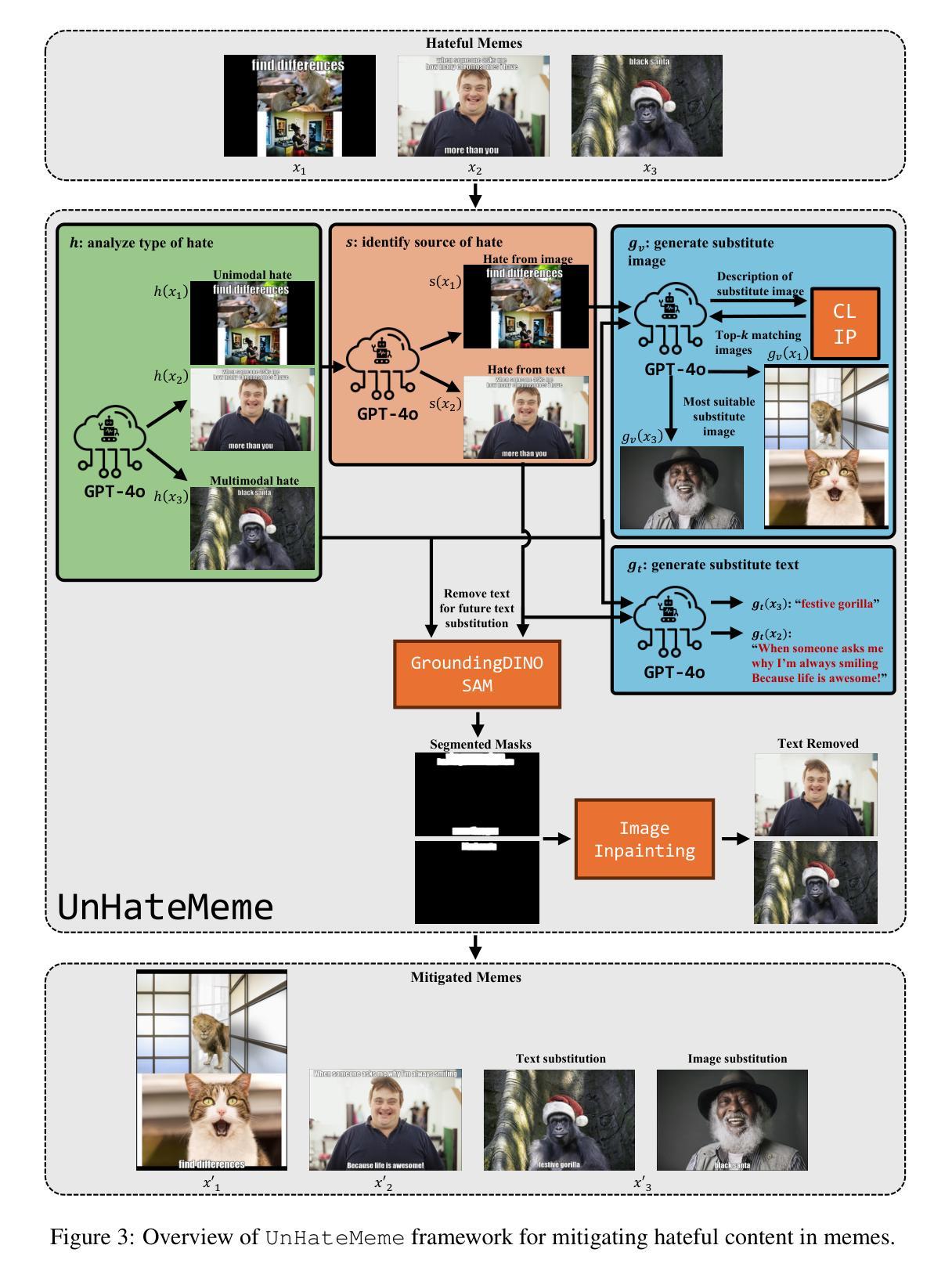
Detecting and Mitigating Hateful Content in Multimodal Memes with Vision-Language Models
Authors:Minh-Hao Van, Xintao Wu
The rapid evolution of social media has provided enhanced communication channels for individuals to create online content, enabling them to express their thoughts and opinions. Multimodal memes, often utilized for playful or humorous expressions with visual and textual elements, are sometimes misused to disseminate hate speech against individuals or groups. While the detection of hateful memes is well-researched, developing effective methods to transform hateful content in memes remains a significant challenge. Leveraging the powerful generation and reasoning capabilities of Vision-Language Models (VLMs), we address the tasks of detecting and mitigating hateful content. This paper presents two key contributions: first, a definition-guided prompting technique for detecting hateful memes, and second, a unified framework for mitigating hateful content in memes, named UnHateMeme, which works by replacing hateful textual and/or visual components. With our definition-guided prompts, VLMs achieve impressive performance on hateful memes detection task. Furthermore, our UnHateMeme framework, integrated with VLMs, demonstrates a strong capability to convert hateful memes into non-hateful forms that meet human-level criteria for hate speech and maintain multimodal coherence between image and text. Through empirical experiments, we show the effectiveness of state-of-the-art pretrained VLMs such as LLaVA, Gemini and GPT-4o on the proposed tasks, providing a comprehensive analysis of their respective strengths and limitations for these tasks. This paper aims to shed light on important applications of VLMs for ensuring safe and respectful online environments.
社交媒体的快速发展为个体创造了在线内容的沟通渠道,使他们能够表达自己的想法和意见。多模态模因通常用于具有视觉和文本元素的嬉戏或幽默表达,但有时被误用来传播针对个人或群体的仇恨言论。虽然仇恨模因的检测已经得到了充分的研究,但开发有效的方法来转化模因中的仇恨内容仍然是一个巨大的挑战。我们利用视觉语言模型(VLMs)的强大生成和推理能力,来解决检测和缓解仇恨内容的任务。本文提出了两个关键贡献:首先,一种用于检测仇恨模因的定义引导提示技术;其次,一个名为UnHateMeme的统一框架,用于减轻模因中的仇恨内容,它通过替换仇恨的文本和/或视觉成分来实现。通过定义引导提示,VLMs在仇恨模因检测任务上取得了令人印象深刻的表现。此外,我们的UnHateMeme框架与VLMs相结合,展现出将仇恨模因转化为非仇恨形式的能力,这种形式符合人类关于仇恨言论的评判标准,并保持图像和文本之间的多模态一致性。通过实证实验,我们展示了最先进的预训练VLMs(如LLaVA、Gemini和GPT-4o)在提出任务上的有效性,并对它们在这些任务上的优势和局限性进行了综合分析。本文旨在阐明VLMs在确保安全和尊重的在线环境方面的重要应用。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
随着社交媒体快速发展,个体通过社交媒体创造在线内容的沟通渠道得到增强,但这也使得带有仇恨言论的多模式meme传播变得容易。本文提出使用基于视觉和语言模型的检测与缓解仇恨言论的方法。首先,我们提出了一种定义导向的提示技术来检测仇恨言论的meme;其次,我们提出了一种名为UnHateMeme的统一框架来缓解仇恨内容的meme。我们的方法不仅能在检测仇恨言论的meme上表现良好,而且还能通过将仇恨性的文本和(或)视觉成分进行替换来使仇恨性的meme变为非仇恨的形式。本文进行了实证实验,证明了LLaVA、Gemini和GPT-4o等最先进的预训练视觉语言模型在完成所提出的任务时的有效性,并对它们在这些任务中的优缺点进行了综合分析。本文旨在为使用视觉语言模型确保安全和尊重的在线环境提供参考。
关键见解
- 社交媒体为个体提供了表达思想和意见的渠道,但仇恨言论的多模式meme传播现象令人担忧。
- 定义导向的提示技术对于检测仇恨言论的meme非常有效。
- UnHateMeme框架能够缓解仇恨内容的meme,通过替换仇恨性的文本和视觉成分来实现。
- 最先进的预训练视觉语言模型(如LLaVA、Gemini和GPT-4o)在检测和处理仇恨言论的任务中表现出了有效性。
- 本文提供了这些模型在处理此类任务时的优缺点分析。
- 该研究为构建安全和尊重的在线环境提供了重要启示和可能的解决方案。
- 使用视觉语言模型可以帮助识别并转化仇恨言论,从而维护网络环境的和谐与健康。
点此查看论文截图