⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-03 更新
Investigating Zero-Shot Diagnostic Pathology in Vision-Language Models with Efficient Prompt Design
Authors:Vasudev Sharma, Ahmed Alagha, Abdelhakim Khellaf, Vincent Quoc-Huy Trinh, Mahdi S. Hosseini
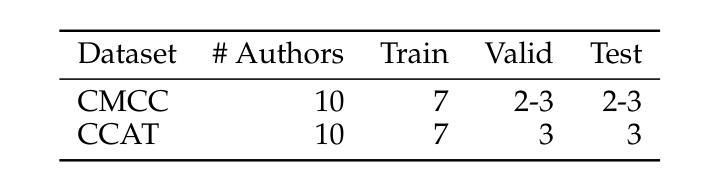
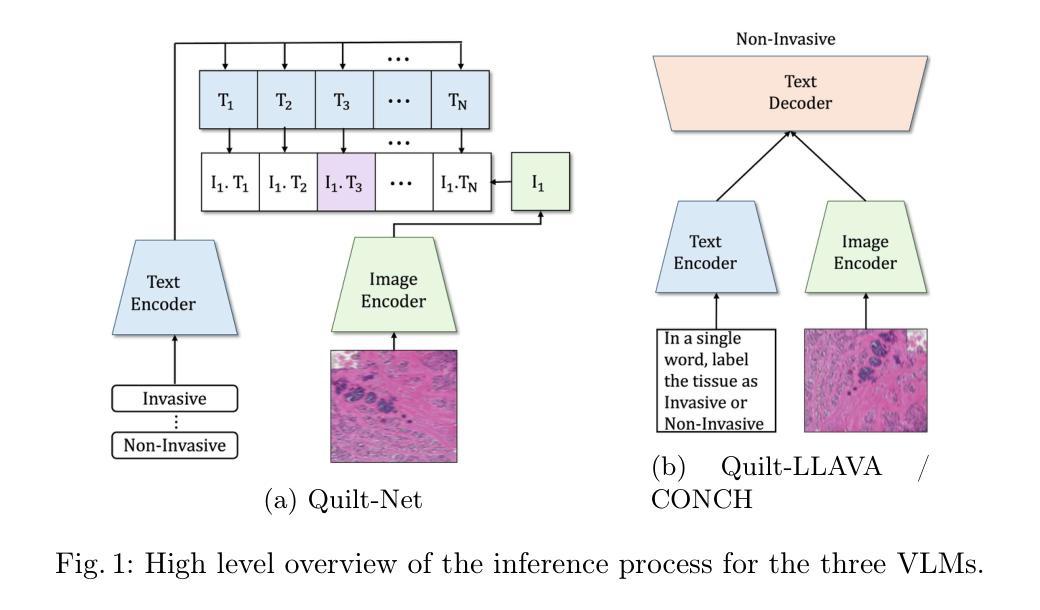
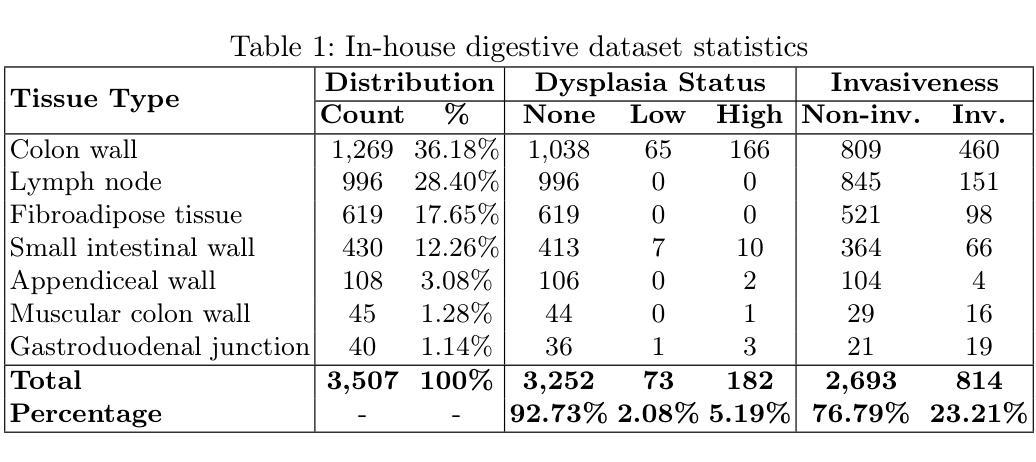
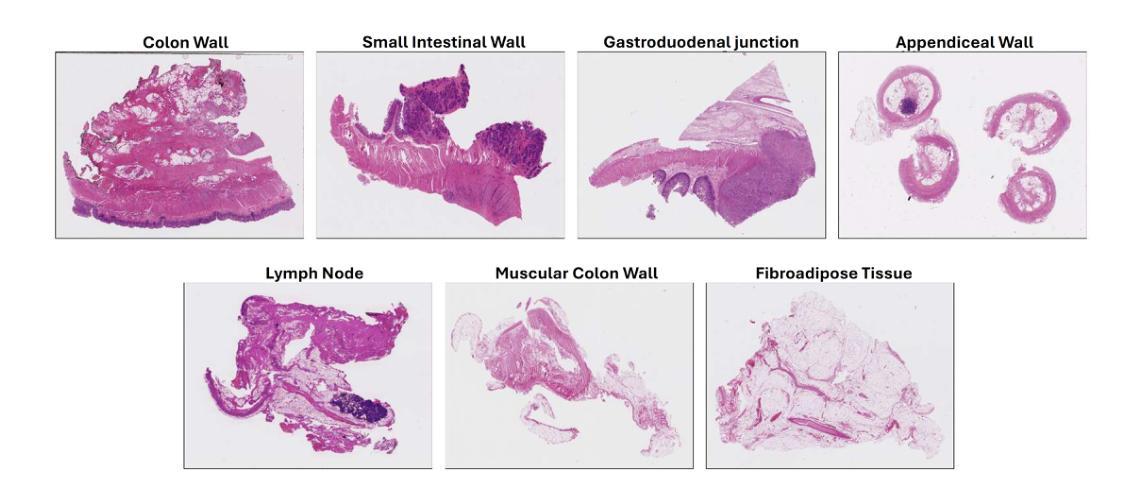
Vision-language models (VLMs) have gained significant attention in computational pathology due to their multimodal learning capabilities that enhance big-data analytics of giga-pixel whole slide image (WSI). However, their sensitivity to large-scale clinical data, task formulations, and prompt design remains an open question, particularly in terms of diagnostic accuracy. In this paper, we present a systematic investigation and analysis of three state of the art VLMs for histopathology, namely Quilt-Net, Quilt-LLAVA, and CONCH, on an in-house digestive pathology dataset comprising 3,507 WSIs, each in giga-pixel form, across distinct tissue types. Through a structured ablative study on cancer invasiveness and dysplasia status, we develop a comprehensive prompt engineering framework that systematically varies domain specificity, anatomical precision, instructional framing, and output constraints. Our findings demonstrate that prompt engineering significantly impacts model performance, with the CONCH model achieving the highest accuracy when provided with precise anatomical references. Additionally, we identify the critical importance of anatomical context in histopathological image analysis, as performance consistently degraded when reducing anatomical precision. We also show that model complexity alone does not guarantee superior performance, as effective domain alignment and domain-specific training are critical. These results establish foundational guidelines for prompt engineering in computational pathology and highlight the potential of VLMs to enhance diagnostic accuracy when properly instructed with domain-appropriate prompts.
视觉语言模型(VLMs)在计算病理学领域因其多模态学习能力而受到广泛关注,这种能力增强了千兆像素全幻灯片图像(WSI)的大数据解析。然而,它们对大规模临床数据、任务制定和提示设计的敏感性,特别是在诊断准确性方面,仍然是一个悬而未决的问题。在本文中,我们对三种用于组织病理学的最新VLMs进行了系统的调查和分析,分别是Quilt-Net、Quilt-LLAVA和CONCH,研究对象是包含3507张千兆像素形式的WSI的内部消化病理数据集,跨越不同的组织类型。通过对癌症侵袭性和异型增生状态的结构化消融研究,我们开发了一个全面的提示工程框架,该框架系统地改变了领域特异性、解剖精度、指令框架和输出约束。我们的研究发现,提示工程对模型性能有显著影响,当提供精确的解剖参考时,CONCH模型的准确率最高。此外,我们还确定了在病理图像分析中上下文信息的重要性,当减少解剖精度时,性能始终下降。我们也表明,仅仅模型复杂性并不能保证优越的性能,有效的领域对齐和领域特定训练才是关键。这些结果奠定了计算病理学提示工程的基础指南,并突出了适当使用领域适当的提示时,VLMs提高诊断精度的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了视觉语言模型(VLMs)在消化病理大数据集中的表现,对三种先进的VLMs(Quilt-Net、Quilt-LLAVA和CONCH)进行了系统的比较研究。通过结构化的消融研究,发现提示工程对模型性能有重要影响,并提出了一种提示工程框架。研究发现,提供精确的解剖学参考可以提高CONCH模型的准确性。本文还强调了领域对齐和领域特定训练的重要性,为计算病理学中的提示工程提供了基础指南。
Key Takeaways
- VLMs在计算病理学中具有巨大的潜力,特别是在处理大规模临床数据和任务制定方面。
- 三种先进的VLMs(Quilt-Net、Quilt-LLAVA和CONCH)在消化病理大数据集中的性能得到了比较和研究。
- 提示工程对模型性能有重要影响,提供了一种新的系统化框架来调整模型提示。
- 在病理学诊断中,提供精确的解剖学参考信息有助于提高模型的准确性。
- 模型复杂性并不保证性能优越,有效的领域对齐和领域特定训练是关键。
- 研究强调了领域上下文在病理图像分析中的重要性。
点此查看论文截图

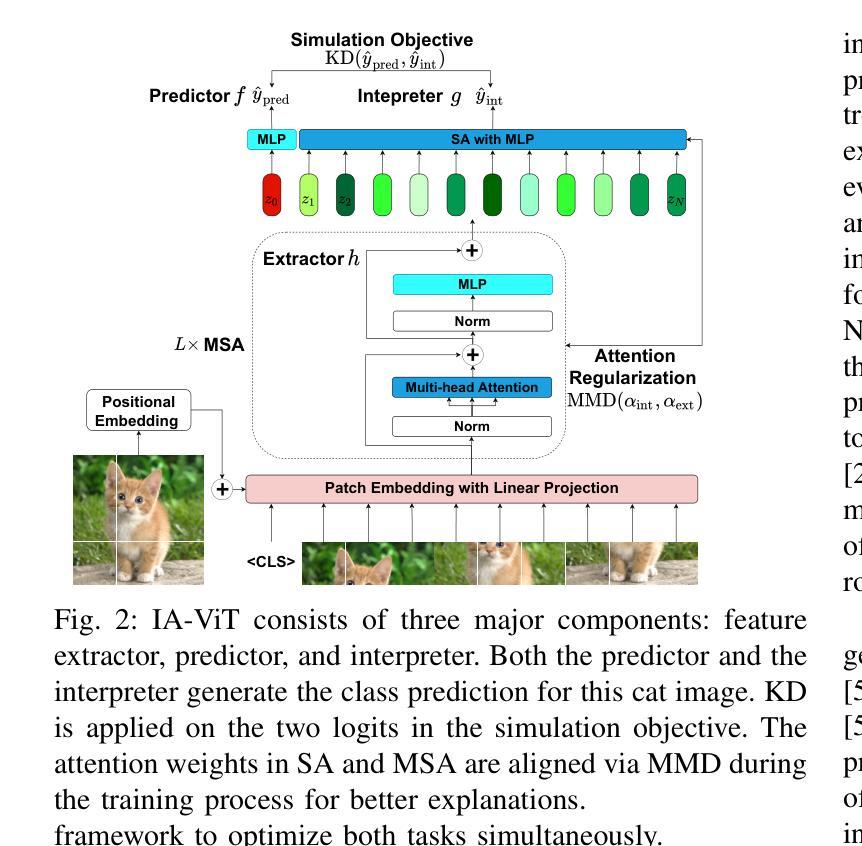
Interpretability-Aware Vision Transformer
Authors:Yao Qiang, Chengyin Li, Prashant Khanduri, Dongxiao Zhu
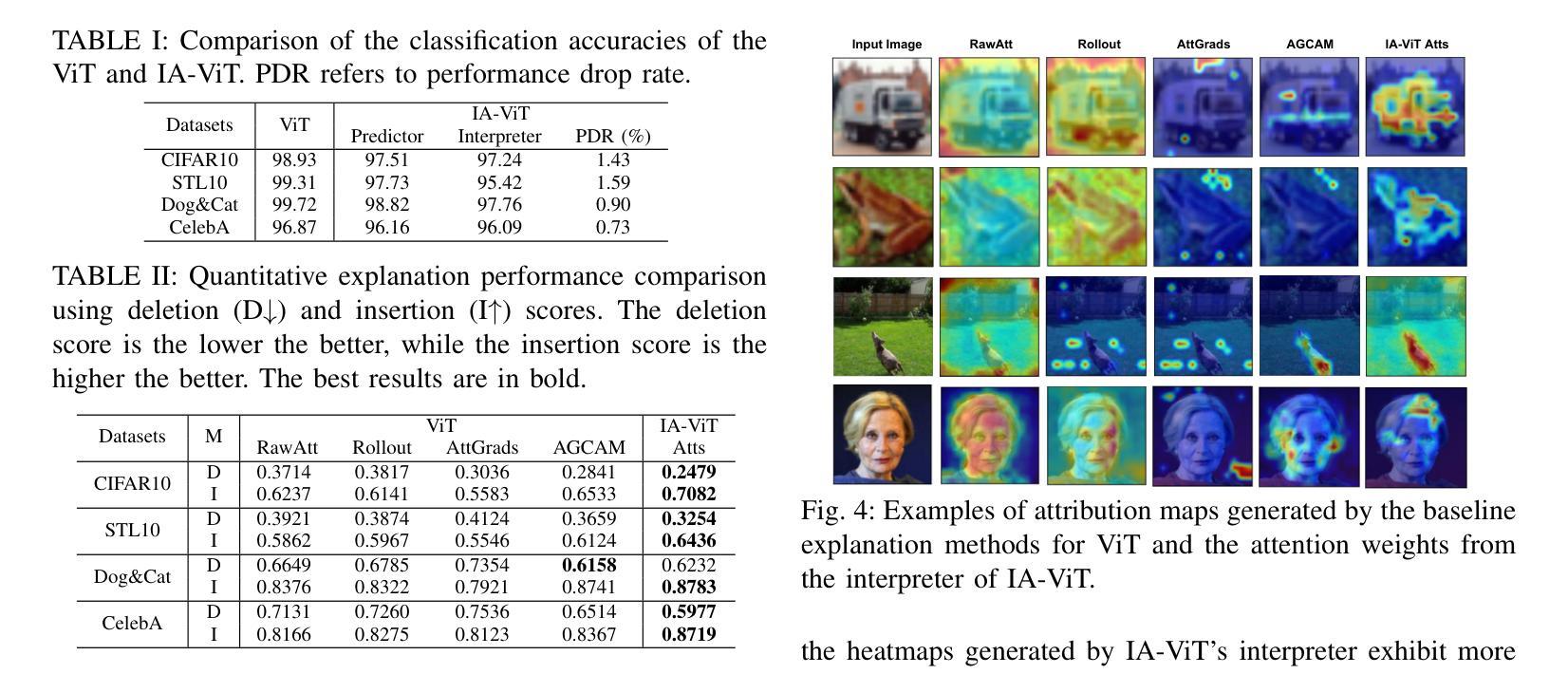
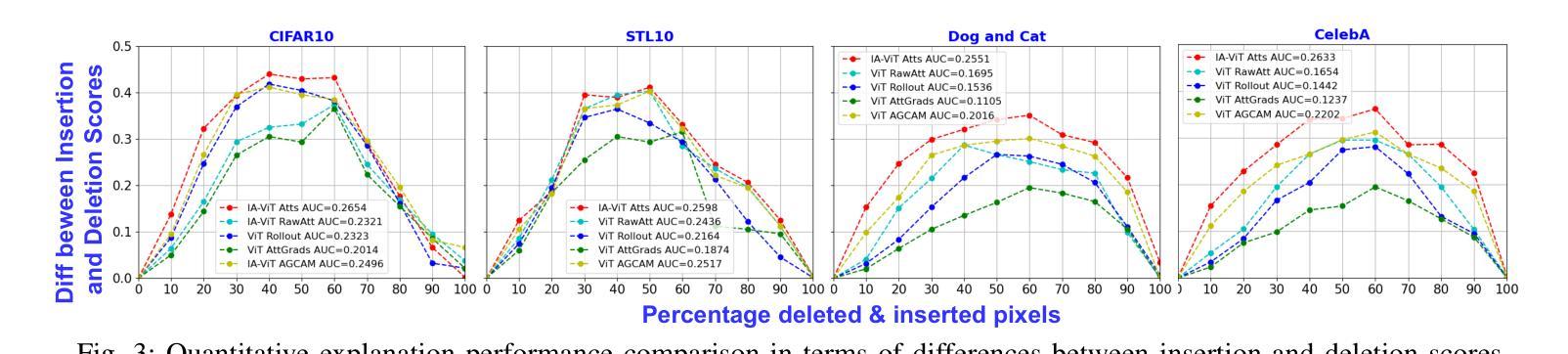
Vision Transformers (ViTs) have become prominent models for solving various vision tasks. However, the interpretability of ViTs has not kept pace with their promising performance. While there has been a surge of interest in developing {\it post hoc} solutions to explain ViTs’ outputs, these methods do not generalize to different downstream tasks and various transformer architectures. Furthermore, if ViTs are not properly trained with the given data and do not prioritize the region of interest, the {\it post hoc} methods would be less effective. Instead of developing another {\it post hoc} approach, we introduce a novel training procedure that inherently enhances model interpretability. Our interpretability-aware ViT (IA-ViT) draws inspiration from a fresh insight: both the class patch and image patches consistently generate predicted distributions and attention maps. IA-ViT is composed of a feature extractor, a predictor, and an interpreter, which are trained jointly with an interpretability-aware training objective. Consequently, the interpreter simulates the behavior of the predictor and provides a faithful explanation through its single-head self-attention mechanism. Our comprehensive experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of IA-ViT in several image classification tasks, with both qualitative and quantitative evaluations of model performance and interpretability. Source code is available from: https://github.com/qiangyao1988/IA-ViT.
视觉Transformer(ViTs)已成为解决各种视觉任务的重要模型。然而,ViTs的可解释性并未与其出色的性能同步发展。尽管人们对开发“事后”解决方案来解释ViTs的输出产生了浓厚兴趣,但这些方法并不适用于不同的下游任务和各种Transformer架构。此外,如果ViTs没有使用给定数据进行适当的训练,并且没有优先关注感兴趣的区域,那么“事后”方法将效果甚微。我们没有开发另一种“事后”方法,而是引入了一种新型训练程序,该程序本质上提高了模型的可解释性。我们的可解释性感知ViT(IA-ViT)的灵感来源于一个新的见解:类补丁和图像补丁都会生成预测分布和注意力图。IA-ViT由特征提取器、预测器和解释器组成,它们使用一个可解释性感知的训练目标进行联合训练。因此,解释器模拟预测器的行为,并通过其单头自注意力机制提供忠实解释。我们的综合实验结果证明,IA-ViT在多个图像分类任务中效果显著,对模型的性能和可解释性进行了定性和定量评估。源代码可从:https://github.com/qiangyao1988/IA-ViT获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 4 figures, 5 tables
Summary:
ViTs在视觉任务中表现卓越,但其解释性并未与之相匹配。研究人员提出了IA-ViT这一新颖的以解释性为核心的训练方法以增强模型的解释性,并考虑训练和分类任务的过程中所有重要的特性(包括类补丁和图像补丁)。IA-ViT由特征提取器、预测器和解释器组成,三者通过解释性目标函数进行联合训练。这种方法提供了一种模型的行为模拟方式并展示其在多个图像分类任务中的性能提升,同时提供定量和定性评估结果。源代码已公开。
Key Takeaways:
- Vision Transformers (ViTs)虽在视觉任务中表现优异,但其解释性有待提高。
- 当前流行的解释后处理方法缺乏通用性,不能适用于不同的下游任务和不同的Transformer架构。
- 数据训练不当会影响解释后处理方法的效率。
- 提出了一种新的以解释性为核心的训练方法——IA-ViT,通过联合训练特征提取器、预测器和解释器来提高模型的解释性。
- IA-ViT通过模拟预测器的行为并提供一个可靠的单头自注意力机制来解释模型决策过程。
- 在多个图像分类任务中,IA-ViT表现出了优越的性能和解释性提升。
点此查看论文截图