⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-05 更新
3D-LLaVA: Towards Generalist 3D LMMs with Omni Superpoint Transformer
Authors:Jiajun Deng, Tianyu He, Li Jiang, Tianyu Wang, Feras Dayoub, Ian Reid
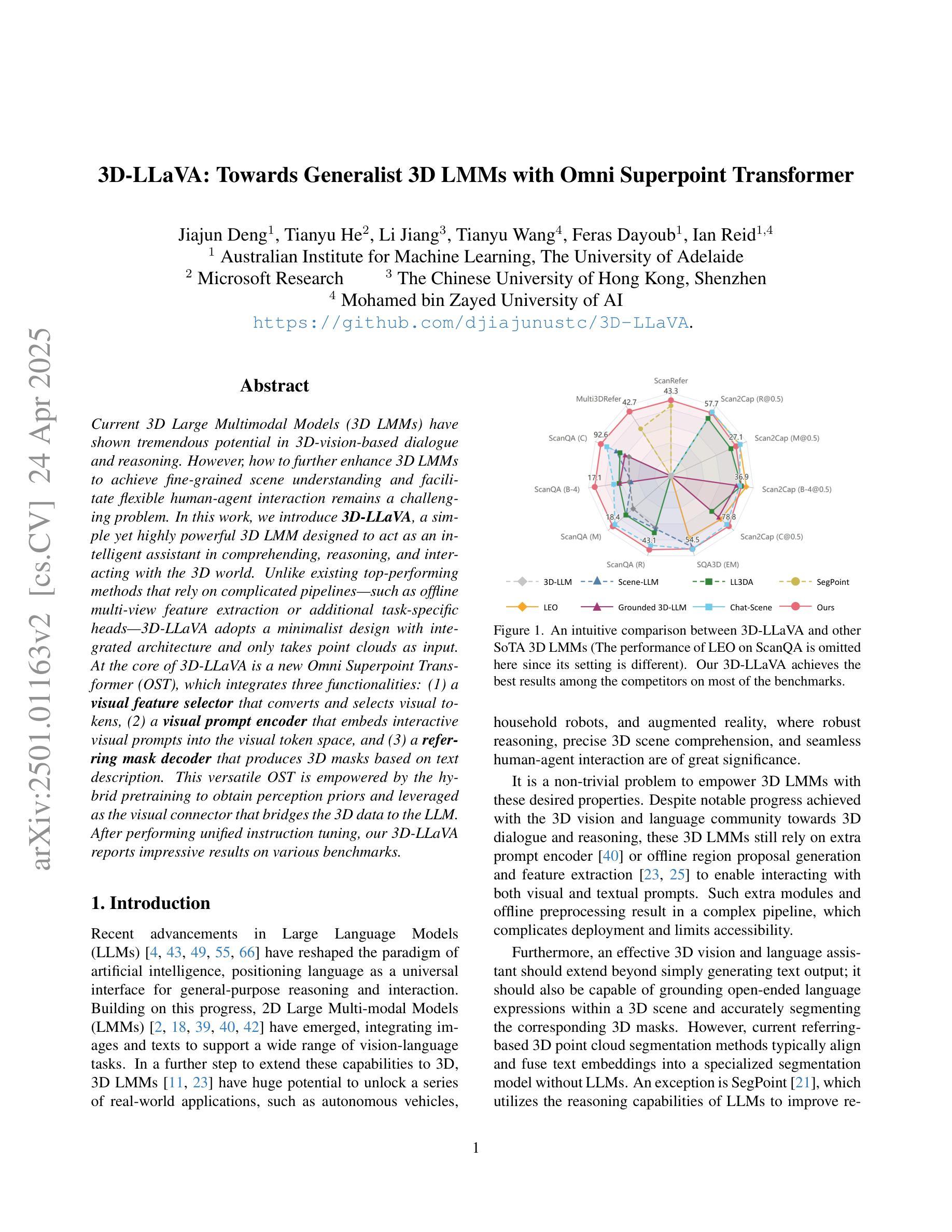
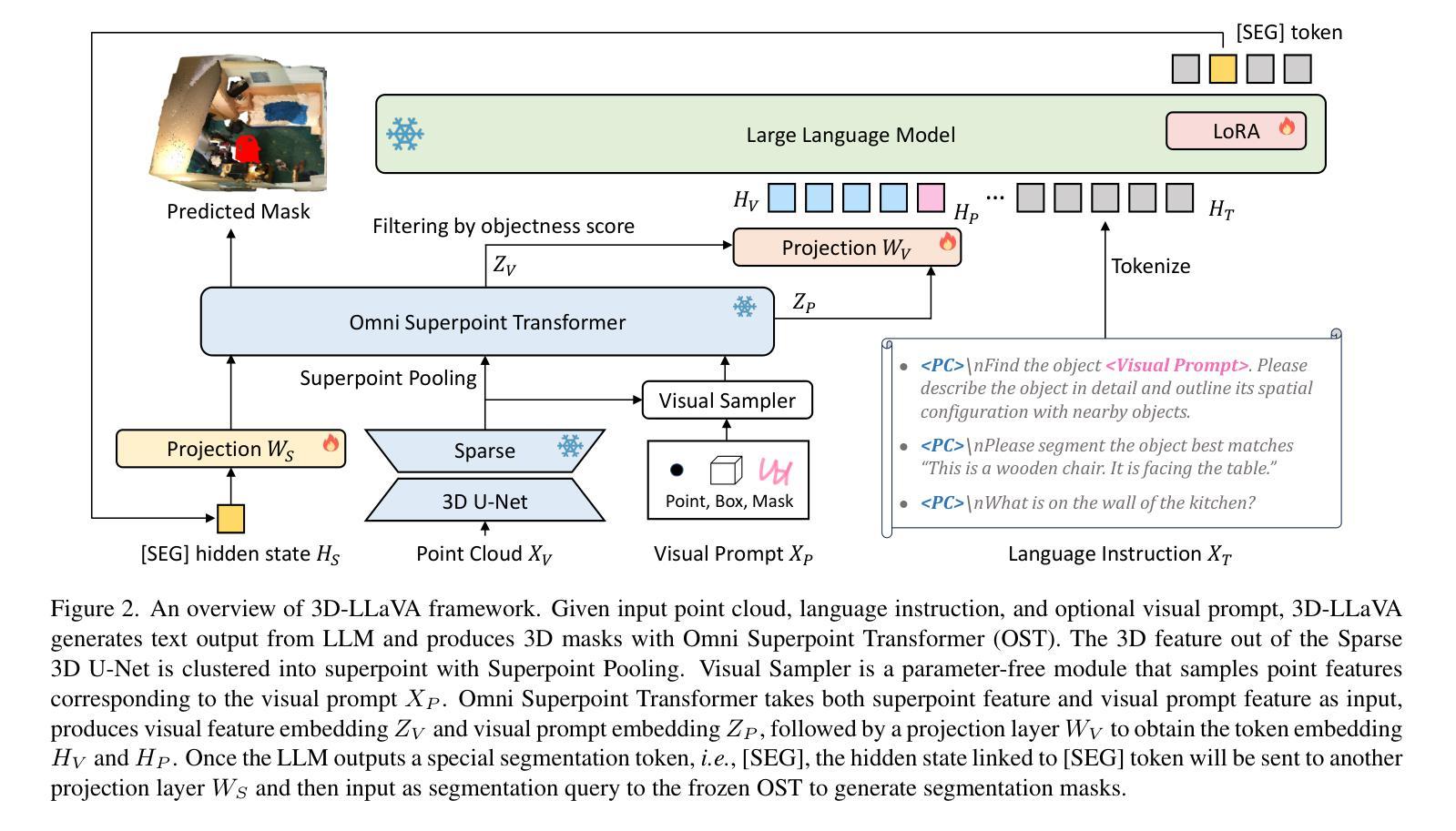
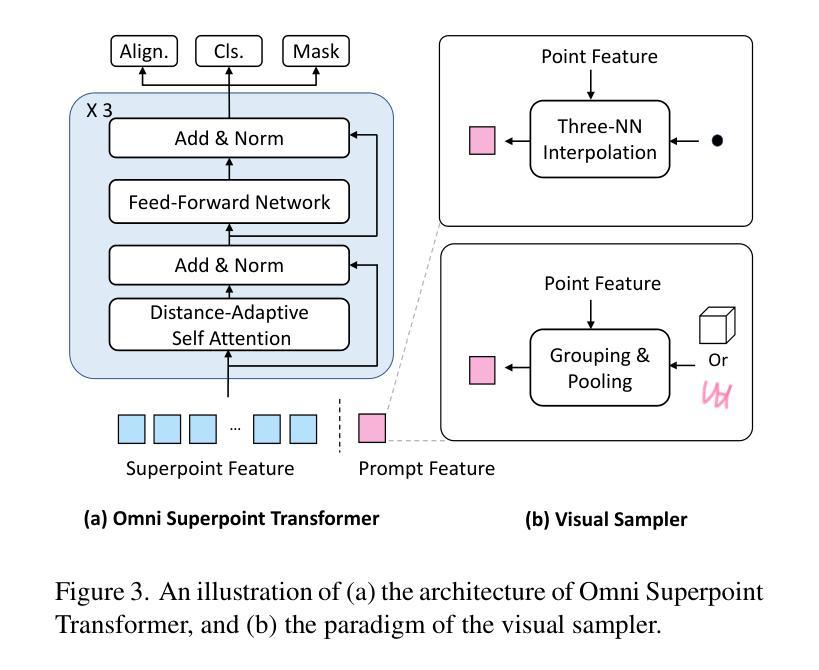
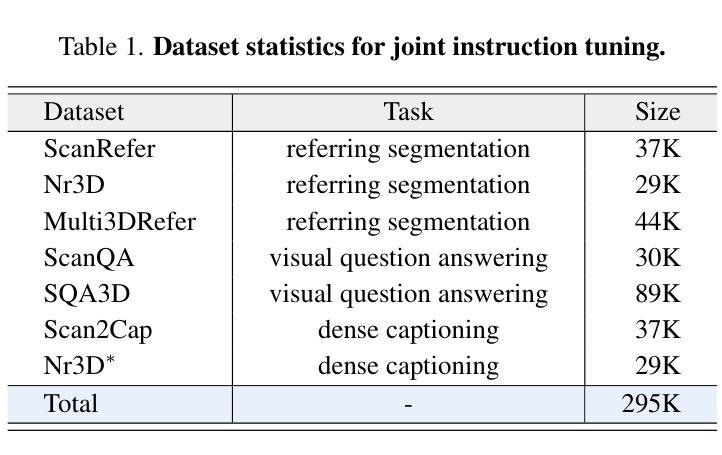
Current 3D Large Multimodal Models (3D LMMs) have shown tremendous potential in 3D-vision-based dialogue and reasoning. However, how to further enhance 3D LMMs to achieve fine-grained scene understanding and facilitate flexible human-agent interaction remains a challenging problem. In this work, we introduce 3D-LLaVA, a simple yet highly powerful 3D LMM designed to act as an intelligent assistant in comprehending, reasoning, and interacting with the 3D world. Unlike existing top-performing methods that rely on complicated pipelines-such as offline multi-view feature extraction or additional task-specific heads-3D-LLaVA adopts a minimalist design with integrated architecture and only takes point clouds as input. At the core of 3D-LLaVA is a new Omni Superpoint Transformer (OST), which integrates three functionalities: (1) a visual feature selector that converts and selects visual tokens, (2) a visual prompt encoder that embeds interactive visual prompts into the visual token space, and (3) a referring mask decoder that produces 3D masks based on text description. This versatile OST is empowered by the hybrid pretraining to obtain perception priors and leveraged as the visual connector that bridges the 3D data to the LLM. After performing unified instruction tuning, our 3D-LLaVA reports impressive results on various benchmarks.
当前3D大型多模态模型(3D LMMs)在基于3D视觉的对话和推理方面显示出巨大的潜力。然而,如何进一步增强3D LMMs以实现精细场景理解和促进灵活的人机交互仍然是一个具有挑战性的问题。在这项工作中,我们引入了3D-LLaVA,这是一个简单而强大的3D LMM,旨在作为智能助理,在理解、推理和与3D世界交互方面发挥作用。与依赖复杂管道(如离线多视图特征提取或特定任务附加头)的现有顶尖方法不同,3D-LLaVA采用极简设计,具有集成架构,仅将点云作为输入。3D-LLaVA的核心是一个新型Omni Superpoint Transformer(OST),它集成了三种功能:(1)视觉特征选择器,用于转换和选择视觉令牌;(2)视觉提示编码器,将交互式视觉提示嵌入视觉令牌空间;(3)参照掩码解码器,根据文本描述生成3D掩码。这种通用OST通过混合预训练获得感知先验,并被用作连接3D数据和LLM的视觉连接器。经过统一的指令调整后,我们的3D-LLaVA在各种基准测试上取得了令人印象深刻的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR 2025
Summary
本文介绍了3D-LLaVA模型,它是一个针对3D世界的智能助理。与传统的复杂模型不同,该模型采用简洁设计并接受点云输入。其核心是Omni Superpoint Transformer(OST),集成了视觉特征选择、交互式视觉提示嵌入和基于文本描述的3D掩码生成三大功能。该模型在多个基准测试中表现卓越。它不仅具有场景理解的精细度,还与人类互动更为灵活。通过混合预训练获得感知先验,作为连接3D数据和大型语言模型的视觉连接器。统一指令调整后,在各种基准测试中表现出惊人的性能。总的来说,它为解决进一步实现三维场景的精细理解问题提供了一种新方法。它还具有成为智能助理的潜力,可以在理解和互动方面与人类进行交流。同时,它还具备在各种任务中取得卓越表现的能力。这不仅是一种全新的设计概念,也是实现先进智能交互的关键步骤。这些功能共同构建了3D-LLaVA的强大功能。这是一个对人工智能发展的重要贡献。简化了先前大型多模态模型的复杂性并推动了领域内的技术进步和潜在应用方向的创新与发展趋势。该模型展示了其卓越的性能和潜力,在人工智能领域具有广泛的应用前景。随着技术的不断进步和应用的广泛推广,未来该模型将发挥更大的作用并推动相关领域的发展。我们相信这一领域的未来将充满无限可能性和创新机遇。随着研究的深入和技术的不断进步,我们期待看到更多令人兴奋的成果和突破性的进展。总的来说,这是一个令人鼓舞的进步并表明了强大的前景发展机会潜力。我们正在见证一项创新性的技术和行业发展的到来这是对未来研究的展望和发展方向提出了一种全新和前沿的解决方案这是为更复杂的理解和应对人类生活的需求奠定了坚实的基础提供了坚实的基础和方向引领着未来的人工智能发展趋势和发展方向提供了一个强有力的支撑点未来我们期待看到更多的突破和创新推动着领域向更加广泛的边界推进让这项技术持续展现出更高的效率水平和应用能力进一步增强应用的价值和智慧并在提高生产效率改善生活质量等方面发挥更大的作用为未来社会创造更多的价值实现可持续发展与科技进步的双赢局面这是一个具有划时代意义的进步它开启了新的可能性并引领着未来的发展趋势为人类社会的未来发展提供了强有力的支持。Key Takeaways
以下是文本中的关键要点:
- 当前的大型多模态模型在理解和推理方面显示出巨大潜力,但仍面临精细场景理解和灵活人机交互的挑战。
点此查看论文截图
Online Video Understanding: OVBench and VideoChat-Online
Authors:Zhenpeng Huang, Xinhao Li, Jiaqi Li, Jing Wang, Xiangyu Zeng, Cheng Liang, Tao Wu, Xi Chen, Liang Li, Limin Wang
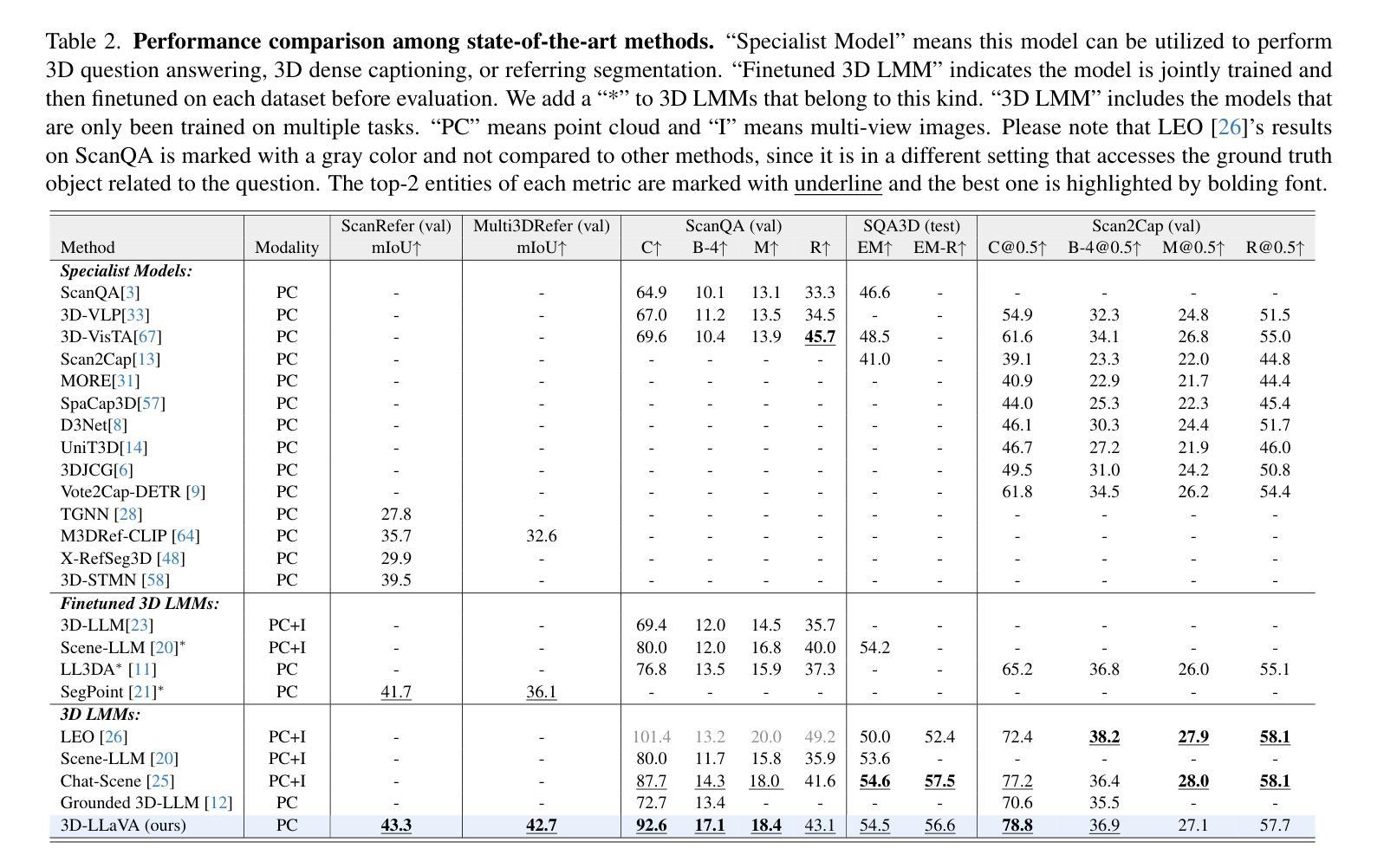
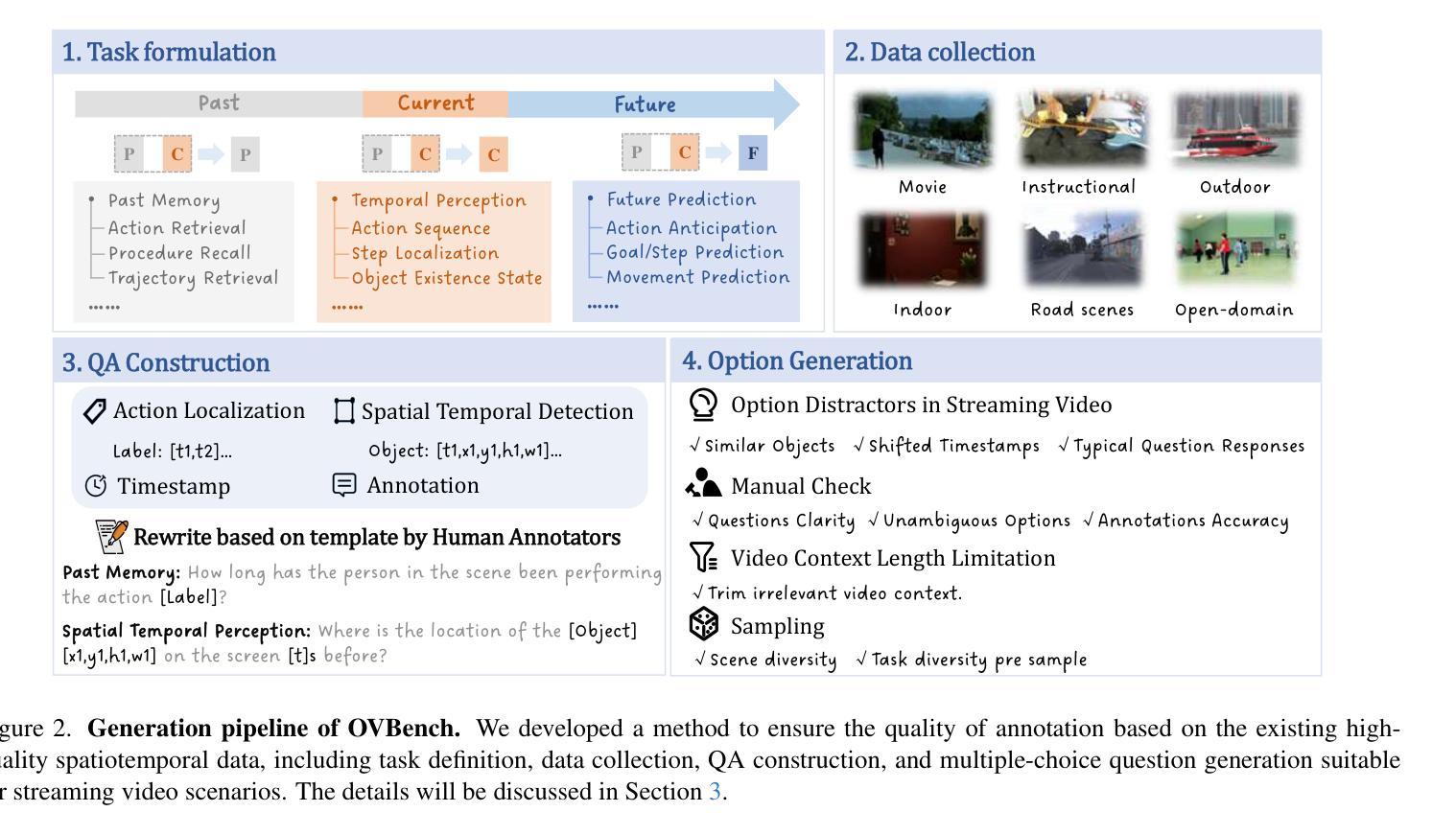
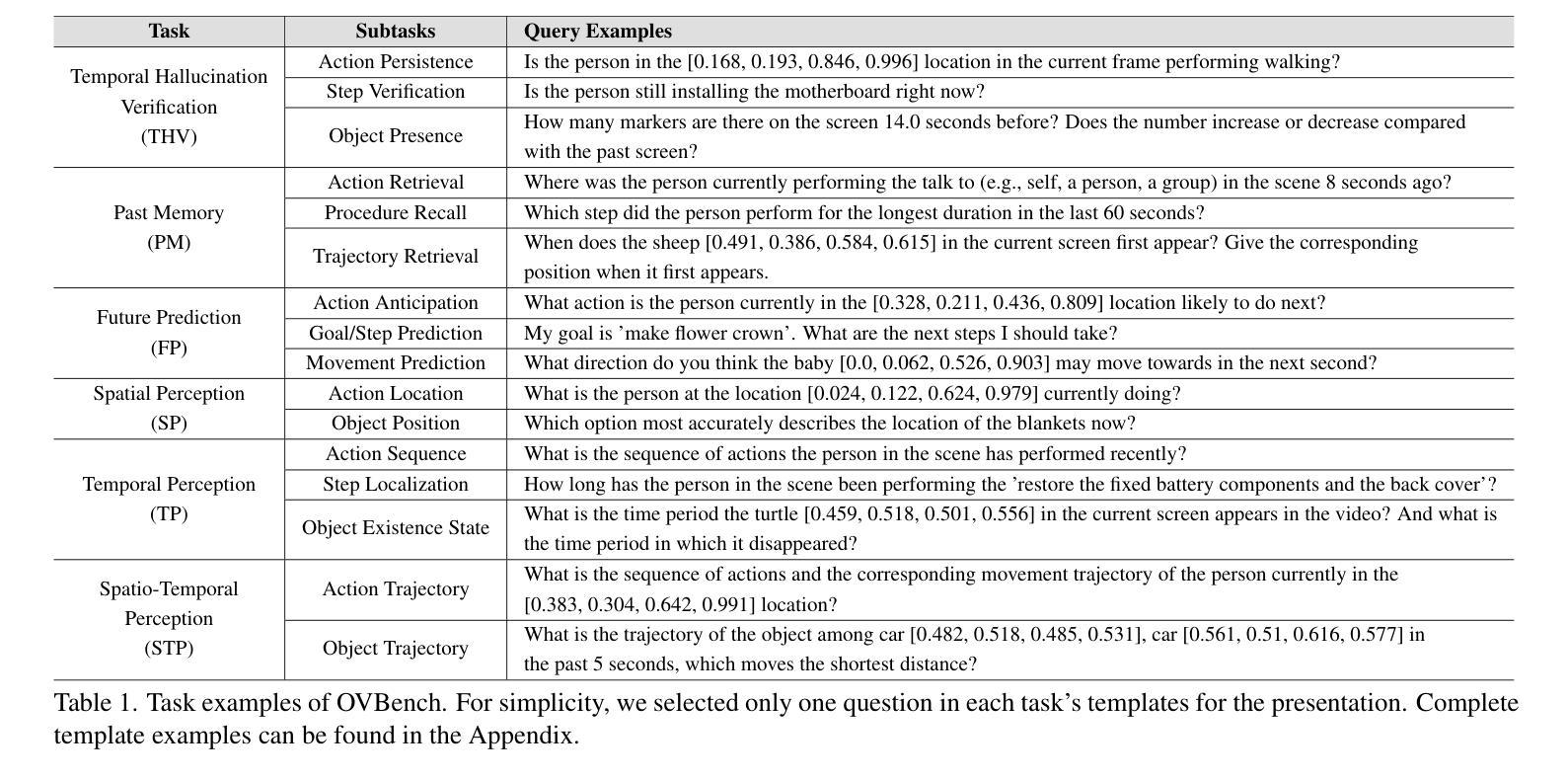
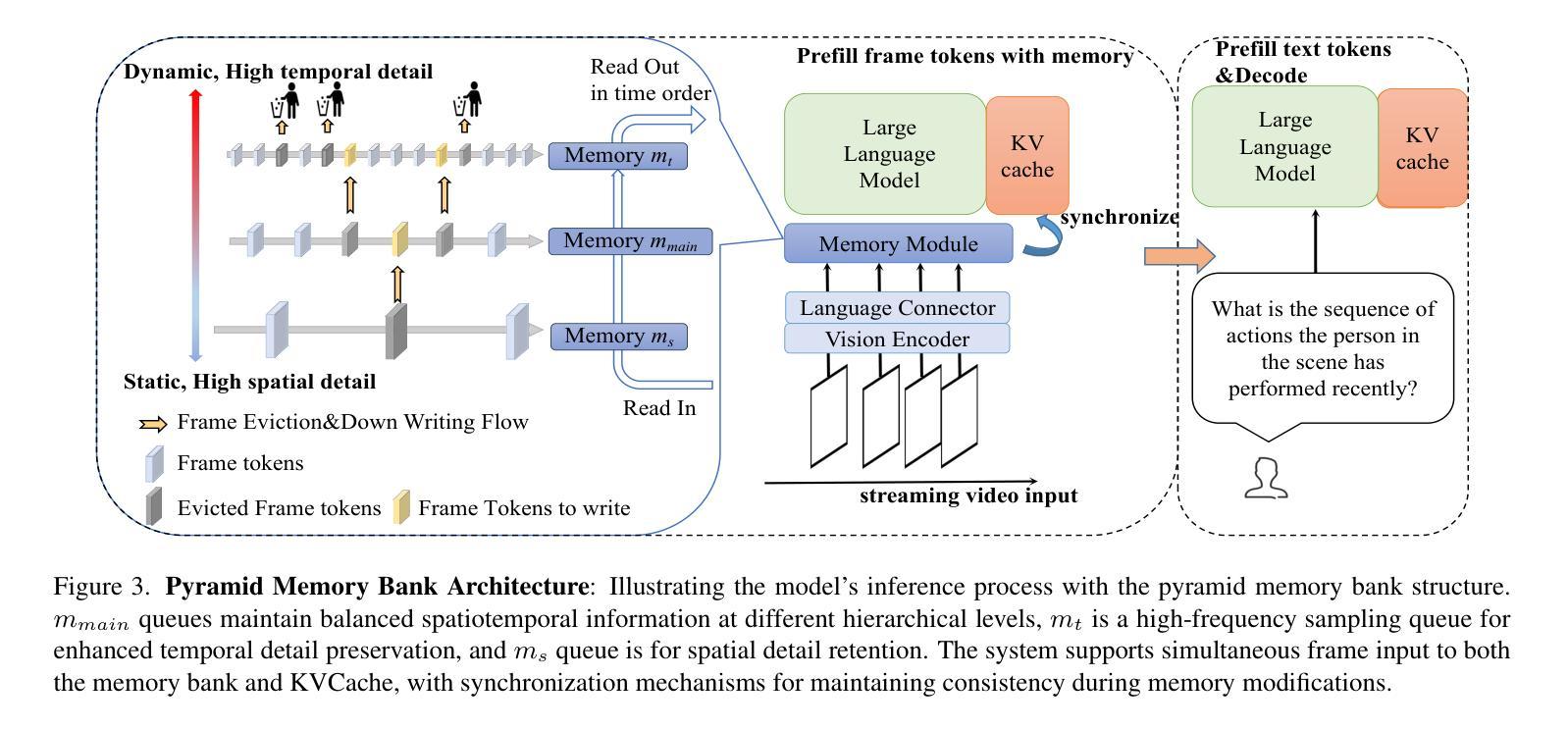
Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have significantly progressed in offline video understanding. However, applying these models to real-world scenarios, such as autonomous driving and human-computer interaction, presents unique challenges due to the need for real-time processing of continuous online video streams. To this end, this paper presents systematic efforts from three perspectives: evaluation benchmark, model architecture, and training strategy. First, we introduce OVBench, a comprehensive question-answering benchmark designed to evaluate models’ ability to perceive, memorize, and reason within online video contexts. It features 6 core task types across three temporal contexts-past, current, and future-forming 16 subtasks from diverse datasets. Second, we propose a new Pyramid Memory Bank (PMB) that effectively retains key spatiotemporal information in video streams. Third, we proposed an offline-to-online learning paradigm, designing an interleaved dialogue format for online video data and constructing an instruction-tuning dataset tailored for online video training. This framework led to the development of VideoChat-Online, a robust and efficient model for online video understanding. Despite the lower computational cost and higher efficiency, VideoChat-Online outperforms existing state-of-the-art offline and online models across popular offline video benchmarks and OVBench, demonstrating the effectiveness of our model architecture and training strategy. % Our approach surpasses existing state-of-the-art offline models Qwen2-VL 7B and online models Flash-VStream, by 4.19% and 23.7% on OVBench, respectively.
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在离线视频理解方面取得了显著进展。然而,将这些模型应用于自动驾驶和人机交互等现实世界场景,由于需要对连续的在线视频流进行实时处理,面临着独特的挑战。为此,本文从评估基准、模型架构和训练策略三个方面进行了系统的努力。首先,我们介绍了OVBench,这是一个旨在评估模型在在线视频上下文中的感知、记忆和推理能力的综合问答基准。它涵盖了三种时间上下文——过去、现在和未来——形成16个子任务,涉及各种数据集,包括6种核心任务类型。其次,我们提出了一种新的金字塔存储器(PMB),它能够有效地保留视频流中的关键时空信息。第三,我们提出了从离线到在线的学习范式,为在线视频数据设计了一种交替对话格式,并构建了一个用于在线视频训练的指令调整数据集。这一框架催生了VideoChat-Online,一个用于在线视频理解的稳健高效模型。尽管计算成本较低,效率更高,VideoChat-Online在流行的离线视频基准测试和OVBench上的表现仍优于现有的最先进的离线模型和在线模型,证明了我们的模型架构和训练策略的有效性。我们的方法在OVBench上的表现超过了现有的最先进的离线模型Qwen2-VL 7B和在线模型Flash-VStream,分别高出4.19%和23.7%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025 Camera Ready Version. Project Page: https://videochat-online.github.io
摘要
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在离线视频理解方面取得了显著进展。然而,将这些模型应用于自动驾驶和人机交互等现实场景时,由于需要实时处理连续的在线视频流,面临着独特挑战。本文从评估基准、模型架构和训练策略三个方面进行了系统努力。首先,我们介绍了OVBench,这是一个旨在评估模型在线视频语境中的感知、记忆和推理能力的综合问答基准。其次,我们提出了金字塔记忆库(PMB),它有效地保留了视频流中的关键时空信息。此外,我们提出了从离线到在线的学习范式,为在线视频数据设计了一种交替对话格式,并构建了一个专为在线视频训练设计的指令调整数据集。这些努力促成了VideoChat-Online模型的开发,该模型具有稳健性和高效性,在在线视频理解方面表现出卓越性能。VideoChat-Online在流行的离线视频基准测试和OVBench上超越了现有的最先进的离线模型和在线模型,证明了我们的模型架构和训练策略的有效性。
关键见解
- MLLMs在离线视频理解方面取得显著进展,但在处理连续在线视频流方面面临挑战。
- OVBench基准用于评估模型在线视频语境中的感知、记忆和推理能力。
- 引入金字塔记忆库(PMB)以保留视频流中的关键时空信息。
- 提出了从离线到在线的学习范式,包括设计交替对话格式和构建指令调整数据集。
- VideoChat-Online模型具有稳健性和高效性,适用于在线视频理解。
- VideoChat-Online在OVBench上超越了现有最先进的离线模型和在线模型。
- 研究结果表明模型架构和训练策略的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

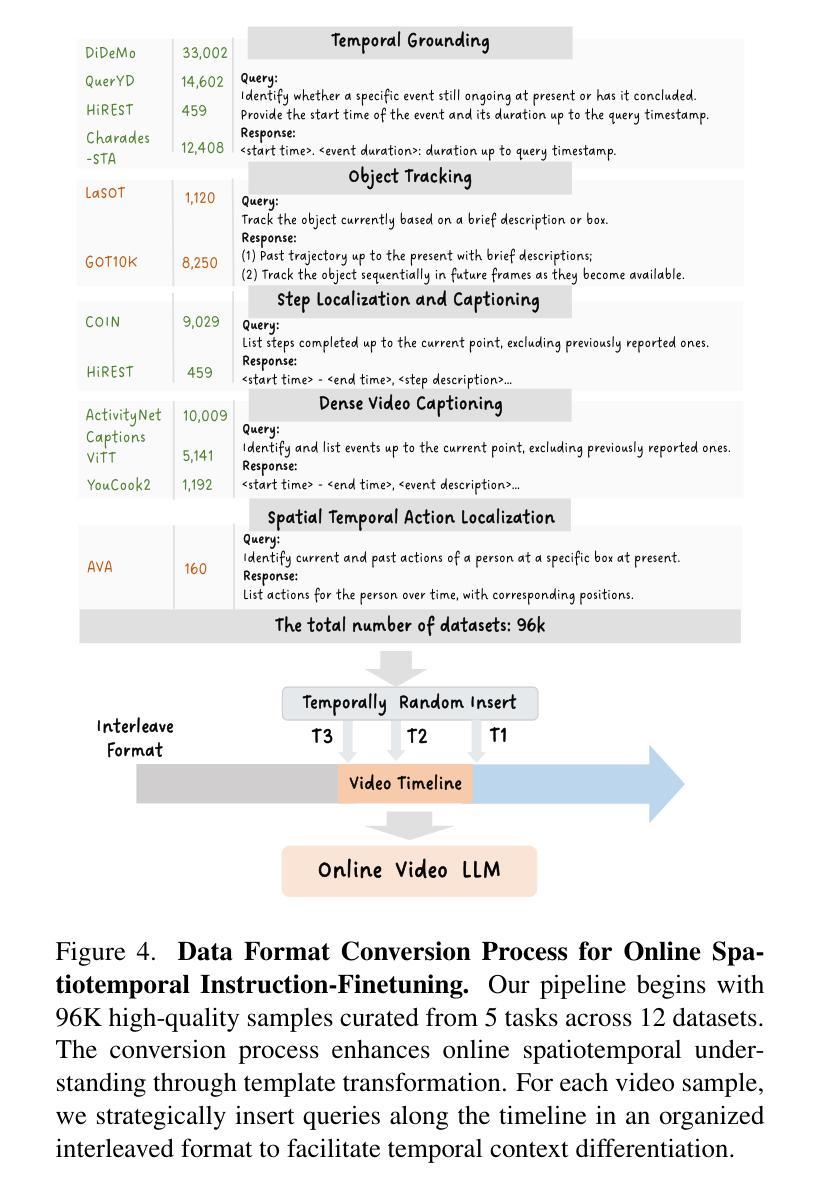
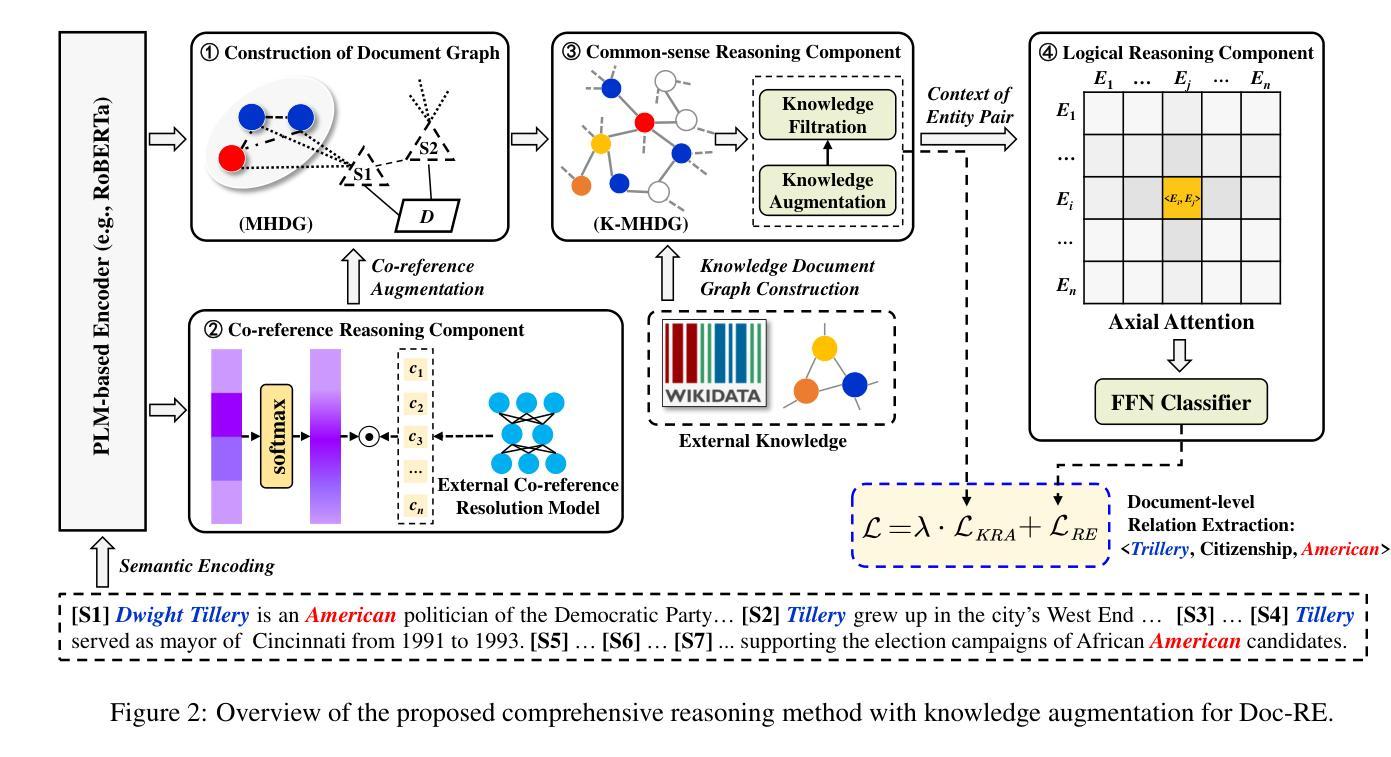
KnowRA: Knowledge Retrieval Augmented Method for Document-level Relation Extraction with Comprehensive Reasoning Abilities
Authors:Chengcheng Mai, Yuxiang Wang, Ziyu Gong, Hanxiang Wang, Yihua Huang
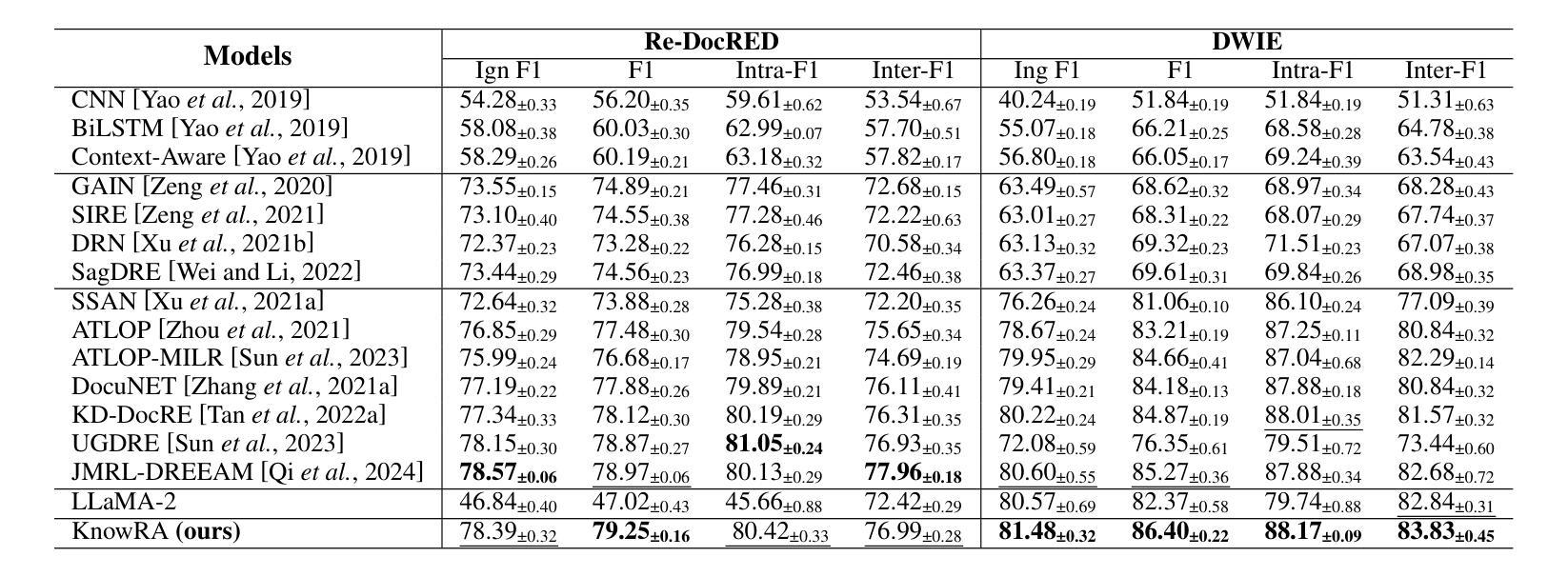
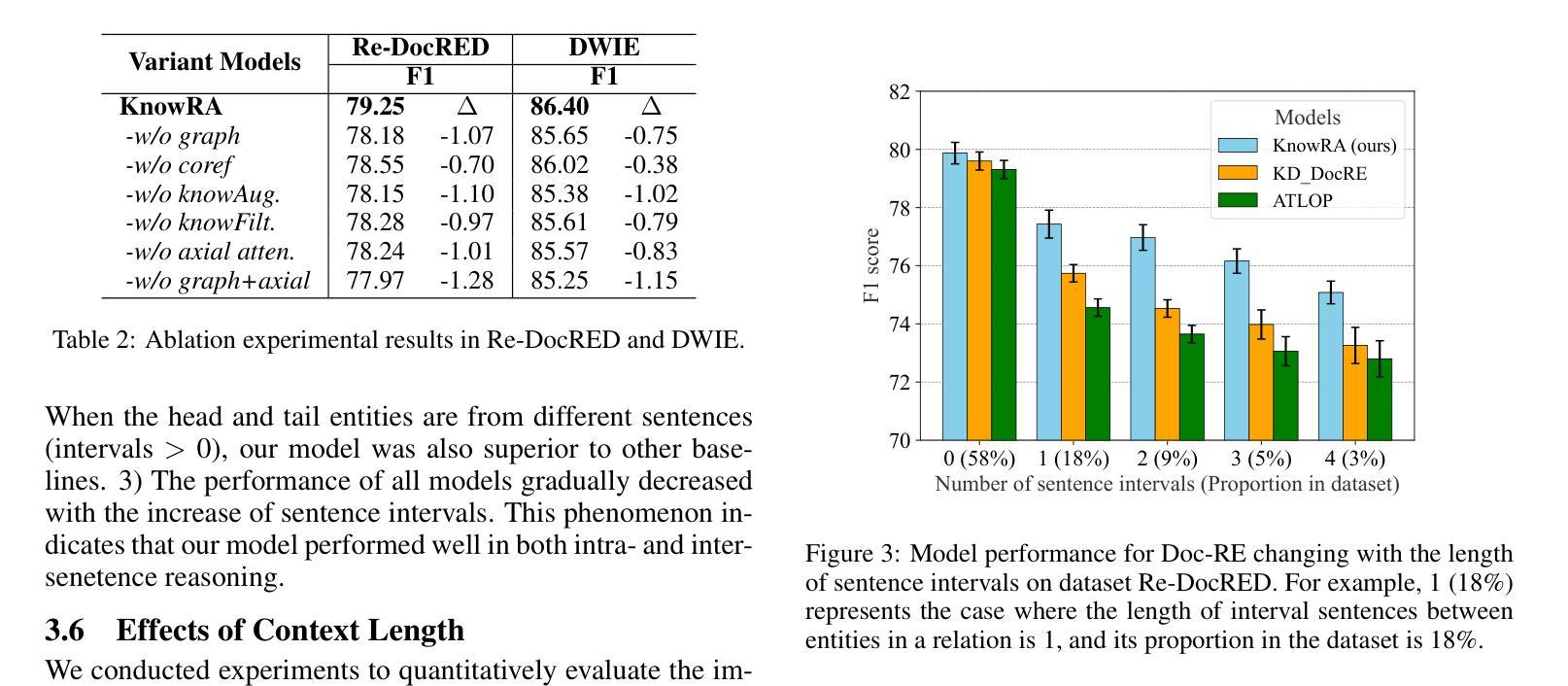
Document-level relation extraction (Doc-RE) aims to extract relations between entities across multiple sentences. Therefore, Doc-RE requires more comprehensive reasoning abilities like humans, involving complex cross-sentence interactions between entities, contexts, and external general knowledge, compared to the sentence-level RE. However, most existing Doc-RE methods focus on optimizing single reasoning ability, but lack the ability to utilize external knowledge for comprehensive reasoning on long documents. To solve these problems, a knowledge retrieval augmented method, named KnowRA, was proposed with comprehensive reasoning to autonomously determine whether to accept external knowledge to assist DocRE. Firstly, we constructed a document graph for semantic encoding and integrated the co-reference resolution model to augment the co-reference reasoning ability. Then, we expanded the document graph into a document knowledge graph by retrieving the external knowledge base for common-sense reasoning and a novel knowledge filtration method was presented to filter out irrelevant knowledge. Finally, we proposed the axis attention mechanism to build direct and indirect associations with intermediary entities for achieving cross-sentence logical reasoning. Extensive experiments conducted on two datasets verified the effectiveness of our method compared to the state-of-the-art baselines. Our code is available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/KnowRA.
文档级关系抽取(Doc-RE)旨在提取多个句子中实体之间的关系。因此,与句子级的RE相比,Doc-RE需要更全面的推理能力,涉及实体、上下文和外部通用知识之间的复杂跨句交互。然而,现有的大多数Doc-RE方法侧重于优化单一的推理能力,但缺乏在长篇文档中进行综合推理和利用外部知识的能力。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种名为KnowRA的知识检索增强方法,以综合推理来自主决定是否接受外部知识来辅助DocRE。首先,我们构建了文档图进行语义编码,并集成了引用解析模型来增强引用推理能力。然后,我们通过检索外部知识库将文档图扩展为文档知识图,用于常识推理,并提出了一种新的知识过滤方法来过滤出无关的知识。最后,我们提出了轴注意力机制,与中介实体建立直接或间接关联,以实现跨句逻辑推理。在两个数据集上进行的广泛实验验证了我们的方法与最新基线相比的有效性。我们的代码可在https://anonymous.4open.science/r/KnowRA访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This work has been accepted by IJCAI 2025 (CCF A)
Summary
在这个文本中,描述了文档级关系抽取(Doc-RE)的重要性,以及相比于句子级关系抽取(RE),它需要的更全面的人类推理能力。为了解决现有Doc-RE方法缺乏利用外部知识进行综合推理的问题,提出了一种名为KnowRA的知识检索增强方法。该方法通过构建文档图进行语义编码,集成共引用解析模型增强共引用推理能力,并通过检索外部知识库将文档图扩展为文档知识图进行常识推理。还提出了一种新的知识过滤方法来过滤掉无关的知识。最后,通过轴注意力机制建立与中介实体的直接或间接关联,实现跨句逻辑推理。在两个数据集上的大量实验验证了该方法的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 文档级关系抽取(Doc-RE)需要更全面的人类推理能力,包括跨句子的实体交互、上下文和外部通用知识。
- 现有Doc-RE方法主要侧重于优化单一推理能力,缺乏利用外部知识进行全面推理的能力。
- KnowRA是一种解决这些问题的知识检索增强方法,具有全面推理能力,可自主决定是否接受外部知识来帮助Doc-RE。
- KnowRA通过构建文档图进行语义编码,并集成共引用解析模型以增强共引用推理能力。
- 通过检索外部知识库,将文档图扩展为文档知识图,进行常识推理。
- KnowRA采用新的知识过滤方法来过滤掉无关的知识。
点此查看论文截图

7B Fully Open Source Moxin-LLM – From Pretraining to GRPO-based Reinforcement Learning Enhancement
Authors:Pu Zhao, Xuan Shen, Zhenglun Kong, Yixin Shen, Sung-En Chang, Timothy Rupprecht, Lei Lu, Enfu Nan, Changdi Yang, Yumei He, Weiyan Shi, Xingchen Xu, Yu Huang, Wei Jiang, Wei Wang, Yue Chen, Yong He, Yanzhi Wang
Recently, Large Language Models (LLMs) have undergone a significant transformation, marked by a rapid rise in both their popularity and capabilities. Leading this evolution are proprietary LLMs like GPT-4 and GPT-o1, which have captured widespread attention in the AI community due to their remarkable performance and versatility. Simultaneously, open-source LLMs, such as LLaMA, have made great contributions to the ever-increasing popularity of LLMs due to the ease to customize and deploy the models across diverse applications. Although open-source LLMs present unprecedented opportunities for innovation and research, the commercialization of LLMs has raised concerns about transparency, reproducibility, and safety. Many open-source LLMs fail to meet fundamental transparency requirements by withholding essential components like training code and data, which may hinder further innovations on LLMs. To mitigate this issue, we introduce Moxin 7B, a fully open-source LLM developed, adhering to principles of open science, open source, open data, and open access. We release the pre-training code and configurations, training and fine-tuning datasets, and intermediate and final checkpoints, aiming to make continuous commitments to fully open-source LLMs. After pre-training and obtaining the base model, we finetune the Moxin Base model with SOTA post-training framework and instruction data to obtain Moxin Instruct model. To improve the reasoning capability, we further finetune our Instruct model with chain-of-thought data distilled from DeepSeek R1, and then use Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO), an efficient and effective reinforcement learning algorithm following DeepSeek R1, to finetune our model, leading to the Moxin Reasoning model. Experiments show that our models achieve superior performance in various evaluations such as zero-shot evaluation, few-shot evaluation, and CoT evaluation.
最近,大型语言模型(LLM)经历了重大转变,其知名度和能力都迅速上升。引领这一变革的是专有大型语言模型,如GPT-4和GPT-o1,由于它们出色的性能和多功能性,它们在人工智能领域引起了广泛关注。同时,开源大型语言模型,如LLaMA,由于其易于定制和部署在各种应用程序中,为大型语言模型日益普及做出了巨大贡献。尽管开源大型语言模型为创新和研发提供了前所未有的机会,但大型语言模型的商业化引发了关于透明度、可重复性和安全的担忧。许多开源大型语言模型未能满足基本的透明度要求,隐瞒了关键组件,如训练代码和数据,这可能阻碍大型语言模型的进一步创新。为了缓解这个问题,我们推出了Moxin 7B,这是一个完全开源的大型语言模型,遵循开放科学、开源、开放数据和开放访问的原则。我们发布了预训练代码和配置、训练和微调数据集以及中间和最终检查点,致力于完全开源的大型语言模型。在预训练并获取基础模型后,我们使用最先进的后训练框架和指令数据对Moxin Base模型进行微调,以获得Moxin Instruct模型。为了提高推理能力,我们进一步使用来自DeepSeek R1的链式思维数据进行微调我们的Instruct模型,然后使用遵循DeepSeek R1的高效且有效的强化学习算法——Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO)来微调我们的模型,从而得到Moxin Reasoning模型。实验表明,我们的模型在零样本评估、少样本评估和CoT评估等各种评估中均表现出卓越的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大规模语言模型(LLM)近期经历了显著变革,受到广泛关注并不断提升能力。GPT-4和GPT-o1等专有LLM引领了这一发展潮流,在AI社区引起了广泛关注。同时,开源LLM,如LLaMA,对LLM日益普及做出了巨大贡献。然而,LLM的商业化引发了关于透明度、可重复性和安全性的担忧。许多开源LLM未能满足基本的透明度要求,隐瞒了训练代码和数据等关键组件,可能阻碍了LLM的进一步创新。为解决这一问题,我们推出了遵循公开科学、开源、开放数据和开放访问原则的完全开源LLM——Moxin 7B。我们公开了预训练代码和配置、训练和微调数据集以及中间和最终检查点,致力于推动完全开源的LLM。通过微调Moxin基础模型并借助最新颖的博士后训练框架和指令数据,获得了Moxin Instruct模型。为提高推理能力,我们进一步使用来自DeepSeek R1的思维链数据微调了我们的Instruct模型,并采用DeepSeek R1之后的强大且高效的强化学习算法Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO)对模型进行了微调,产生了Moxin Reasoning模型。实验表明,我们的模型在零样本评估、少样本评估和思维链评估等方面均表现出卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 大规模语言模型(LLM)近期经历显著变革,GPT-4和GPT-o1等专有模型备受关注。
- 开源LLM如LLaMA推动了LLM的普及,但商业化引发透明度、可重复性和安全性担忧。
- 许多开源LLM存在透明度问题,缺乏训练代码和数据等关键信息,可能阻碍进一步创新。
- Moxin 7B是一个完全开源的LLM,致力于解决上述问题,遵循开放科学、开源、开放数据和开放访问原则。
- Moxin 7B公开了预训练代码、配置、数据集和检查点,以推动完全开源的LLM发展。
- Moxin Instruct模型通过微调基础模型并结合最新颖的博士后训练框架和指令数据而生成。
点此查看论文截图


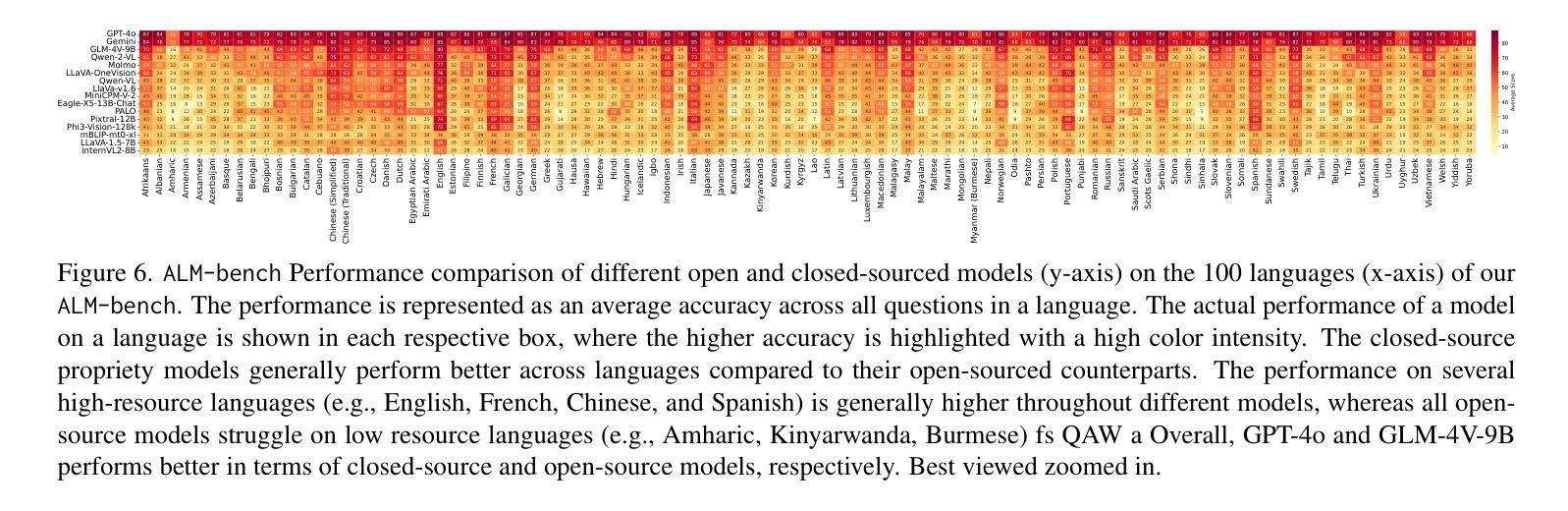
All Languages Matter: Evaluating LMMs on Culturally Diverse 100 Languages
Authors:Ashmal Vayani, Dinura Dissanayake, Hasindri Watawana, Noor Ahsan, Nevasini Sasikumar, Omkar Thawakar, Henok Biadglign Ademtew, Yahya Hmaiti, Amandeep Kumar, Kartik Kuckreja, Mykola Maslych, Wafa Al Ghallabi, Mihail Mihaylov, Chao Qin, Abdelrahman M Shaker, Mike Zhang, Mahardika Krisna Ihsani, Amiel Esplana, Monil Gokani, Shachar Mirkin, Harsh Singh, Ashay Srivastava, Endre Hamerlik, Fathinah Asma Izzati, Fadillah Adamsyah Maani, Sebastian Cavada, Jenny Chim, Rohit Gupta, Sanjay Manjunath, Kamila Zhumakhanova, Feno Heriniaina Rabevohitra, Azril Amirudin, Muhammad Ridzuan, Daniya Kareem, Ketan More, Kunyang Li, Pramesh Shakya, Muhammad Saad, Amirpouya Ghasemaghaei, Amirbek Djanibekov, Dilshod Azizov, Branislava Jankovic, Naman Bhatia, Alvaro Cabrera, Johan Obando-Ceron, Olympiah Otieno, Fabian Farestam, Muztoba Rabbani, Sanoojan Baliah, Santosh Sanjeev, Abduragim Shtanchaev, Maheen Fatima, Thao Nguyen, Amrin Kareem, Toluwani Aremu, Nathan Xavier, Amit Bhatkal, Hawau Toyin, Aman Chadha, Hisham Cholakkal, Rao Muhammad Anwer, Michael Felsberg, Jorma Laaksonen, Thamar Solorio, Monojit Choudhury, Ivan Laptev, Mubarak Shah, Salman Khan, Fahad Khan
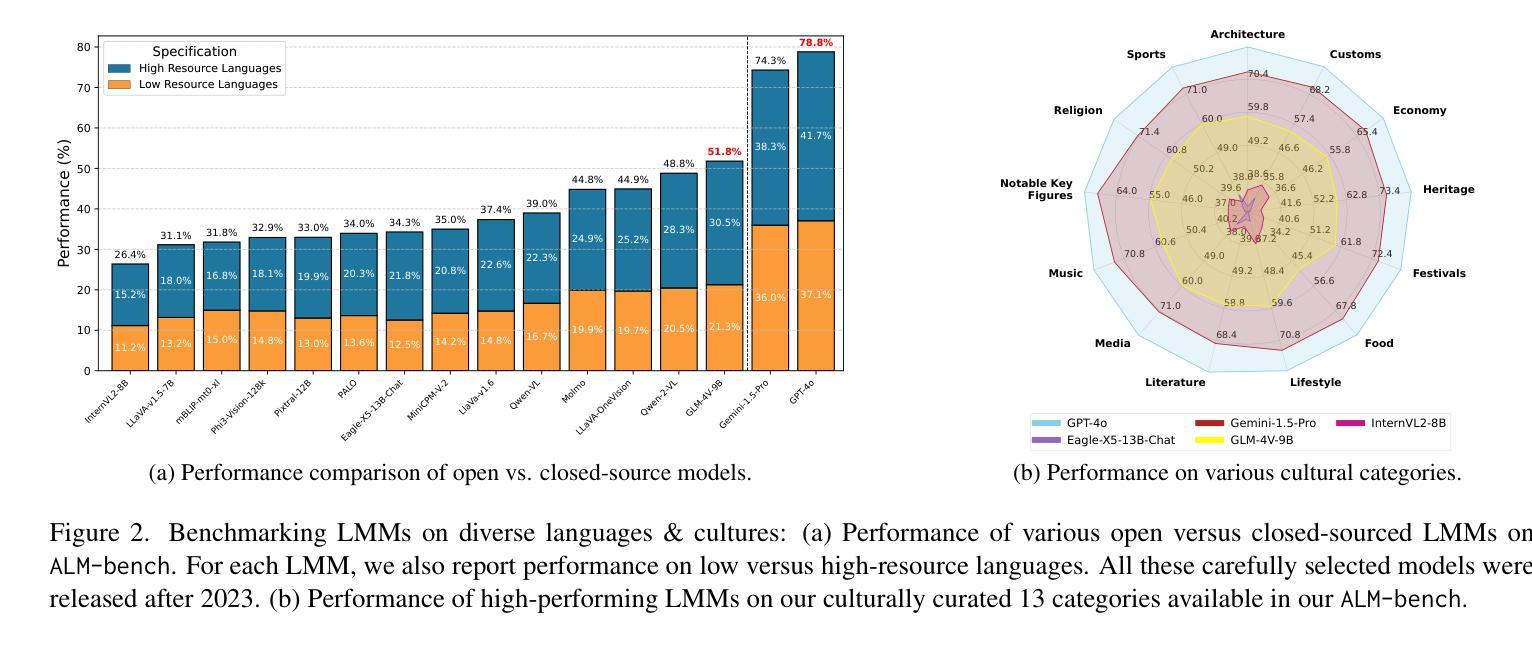
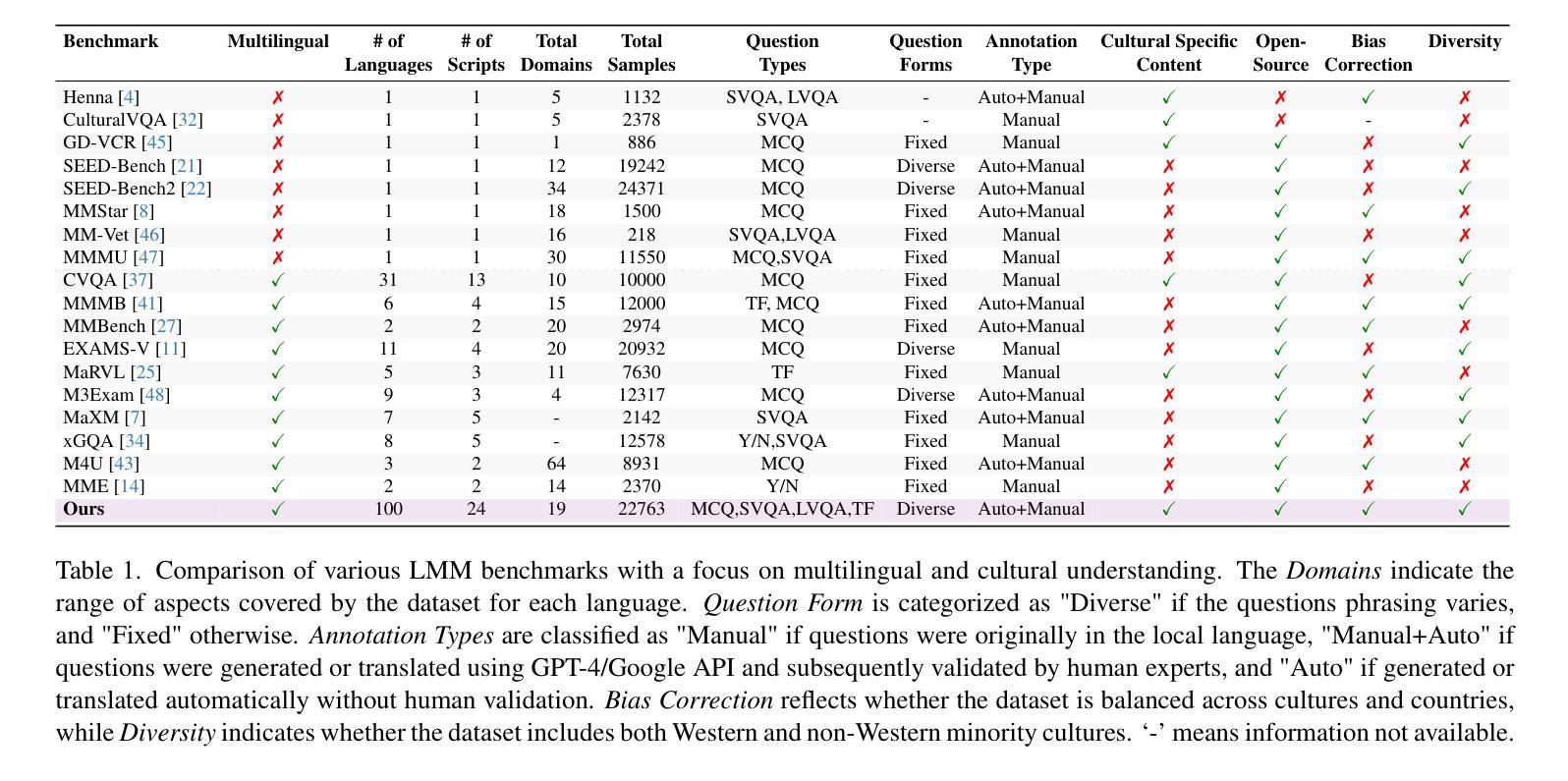
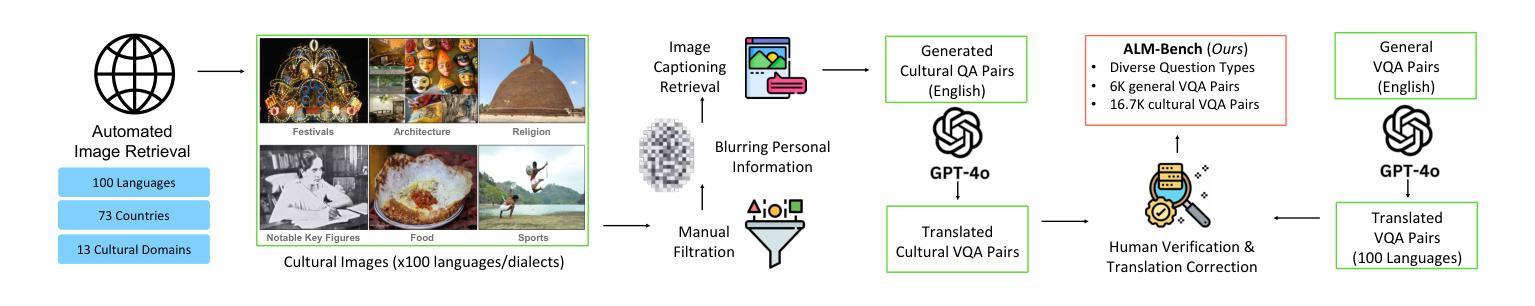
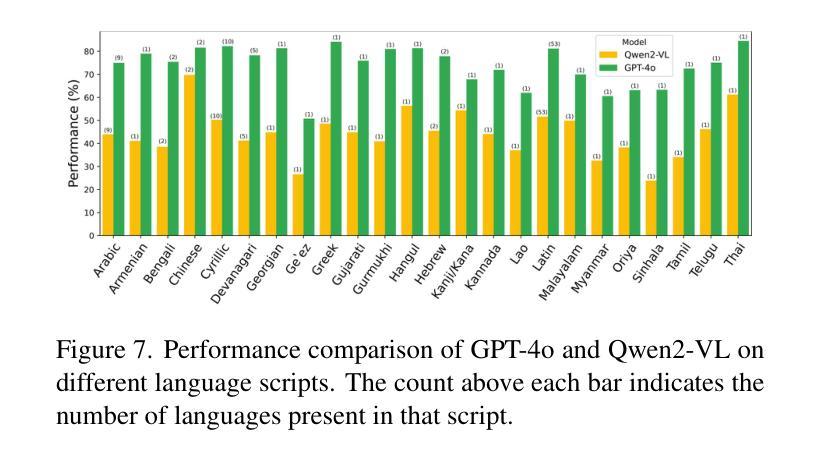
Existing Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) generally focus on only a few regions and languages. As LMMs continue to improve, it is increasingly important to ensure they understand cultural contexts, respect local sensitivities, and support low-resource languages, all while effectively integrating corresponding visual cues. In pursuit of culturally diverse global multimodal models, our proposed All Languages Matter Benchmark (ALM-bench) represents the largest and most comprehensive effort to date for evaluating LMMs across 100 languages. ALM-bench challenges existing models by testing their ability to understand and reason about culturally diverse images paired with text in various languages, including many low-resource languages traditionally underrepresented in LMM research. The benchmark offers a robust and nuanced evaluation framework featuring various question formats, including true/false, multiple choice, and open-ended questions, which are further divided into short and long-answer categories. ALM-bench design ensures a comprehensive assessment of a model’s ability to handle varied levels of difficulty in visual and linguistic reasoning. To capture the rich tapestry of global cultures, ALM-bench carefully curates content from 13 distinct cultural aspects, ranging from traditions and rituals to famous personalities and celebrations. Through this, ALM-bench not only provides a rigorous testing ground for state-of-the-art open and closed-source LMMs but also highlights the importance of cultural and linguistic inclusivity, encouraging the development of models that can serve diverse global populations effectively. Our benchmark is publicly available.
现有的大型多模态模型(LMM)通常只关注少数地区和语言。随着LMM的不断发展,确保它们理解文化背景、尊重当地敏感性、支持低资源语言,同时有效地整合相应的视觉线索变得越来越重要。为了打造文化多元的全球多模态模型,我们提出的多语言基准测试(ALM-bench)代表了迄今为止评估LMM跨100种语言性能的最大和最全面的努力。ALM-bench通过测试现有模型理解和推理文化多样图像以及与各种语言文本配对的能力来挑战现有模型,包括传统上在LMM研究中被低估的许多低资源语言。该基准测试提供了一个稳健而细致的评价框架,包括多种题型,包括是非题、选择题和开放性问题,这些题型进一步分为短回答和长回答类别。ALM-bench的设计确保了对模型在视觉和语言推理中处理不同难度能力的全面评估。为了捕捉全球文化的丰富面貌,ALM-bench精心挑选了来自13个不同文化方面的内容,从传统和仪式到著名人物和庆祝活动。因此,ALM-bench不仅为最新开源和封闭源LMM提供了严格的测试环境,而且还强调了文化和语言包容性的重要性,鼓励开发能够有效服务于多元化全球人群模型。我们的基准测试可公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF A Multilingual Multimodal cultural benchmark for 100 languages
Summary
本文提出全新的跨文化多元全球多模态模型评估基准——ALM-bench,旨在全面评估大型多模态模型在全球范围内的跨文化表现。ALM-bench不仅覆盖全球多种语言,包括低资源语言,而且注重文化语境和视觉线索的整合。通过多元化的评估框架,包括多种题型和丰富的文化内容,ALM-bench为当前最前沿的开源和闭源多模态模型提供了严格的测试环境,并强调文化和语言多样性的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- ALM-bench是专为评估大型多模态模型在全球范围内的跨文化表现而设计的基准。
- 它涵盖了全球100多种语言,包括通常被忽视的许多低资源语言。
- ALM-bench注重文化语境和视觉线索的整合,确保模型理解文化背景和尊重当地敏感性。
- 基准包括多种题型,如选择题、简答题等,以全面评估模型的视觉和语言推理能力。
- 内容涵盖了全球文化的丰富多样性,包括传统、仪式、名人以及庆祝活动等。
- ALM-bench提供了一个严格的测试环境,用于评估最前沿的开源和闭源多模态模型的表现。
点此查看论文截图


GLOVER: Generalizable Open-Vocabulary Affordance Reasoning for Task-Oriented Grasping
Authors:Teli Ma, Zifan Wang, Jiaming Zhou, Mengmeng Wang, Junwei Liang
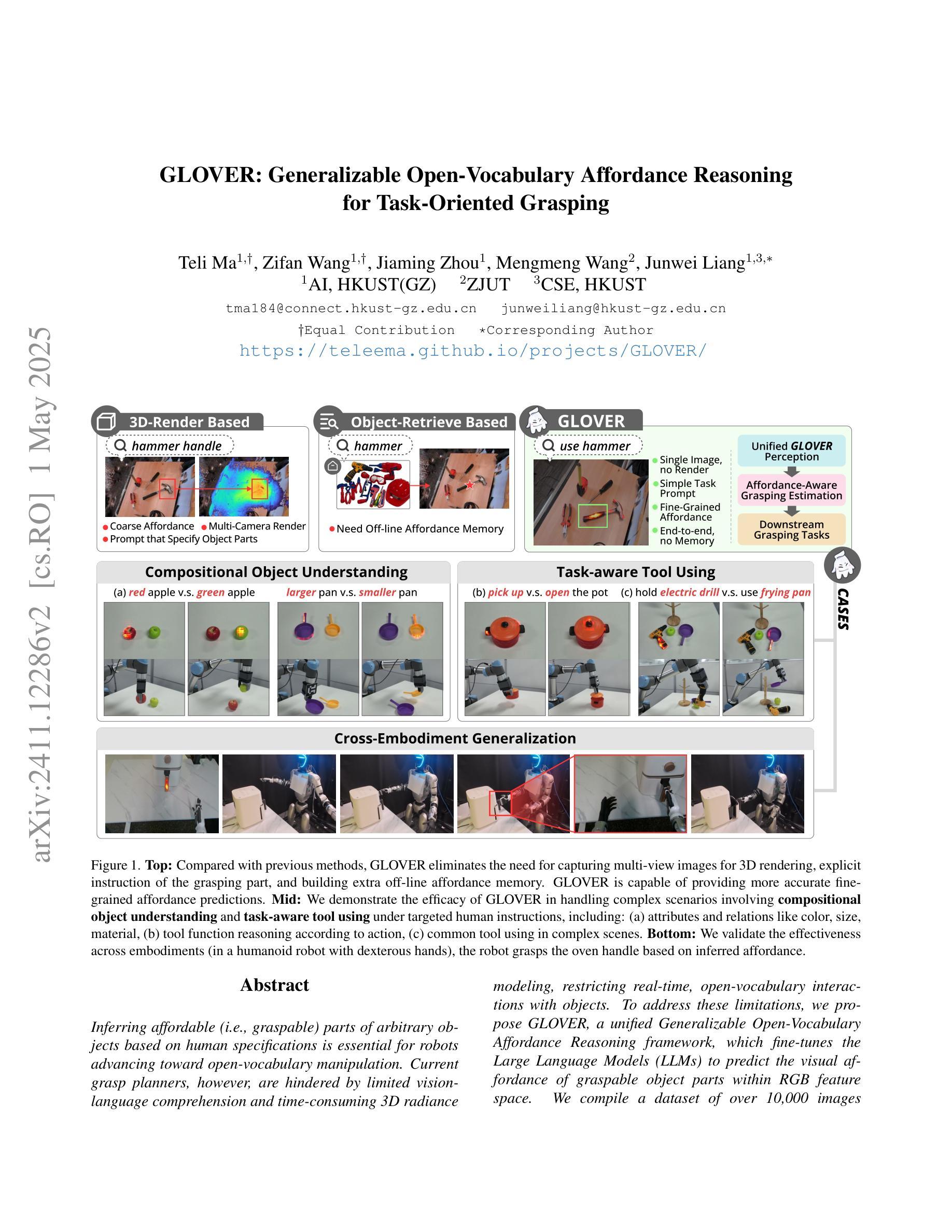
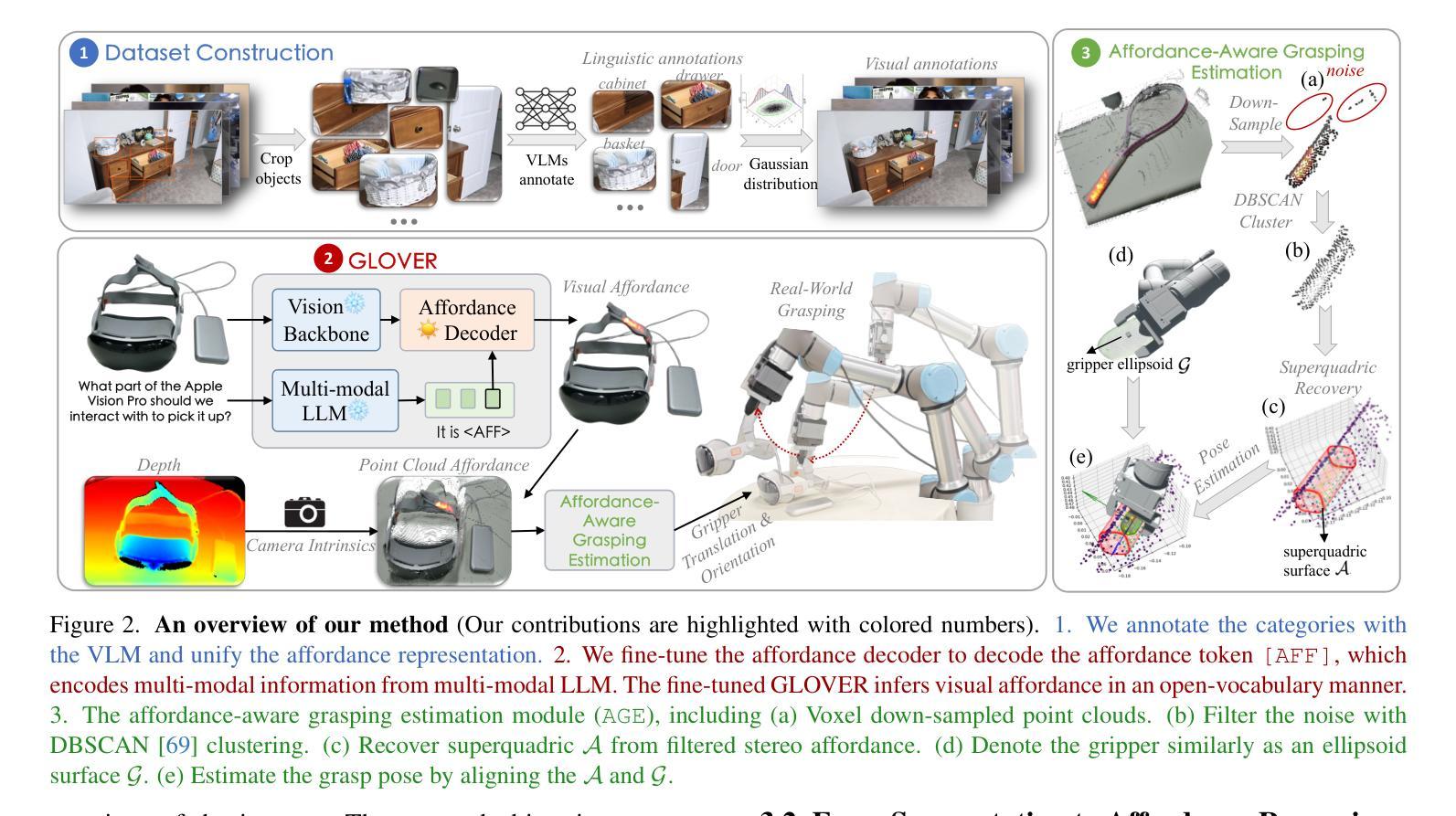
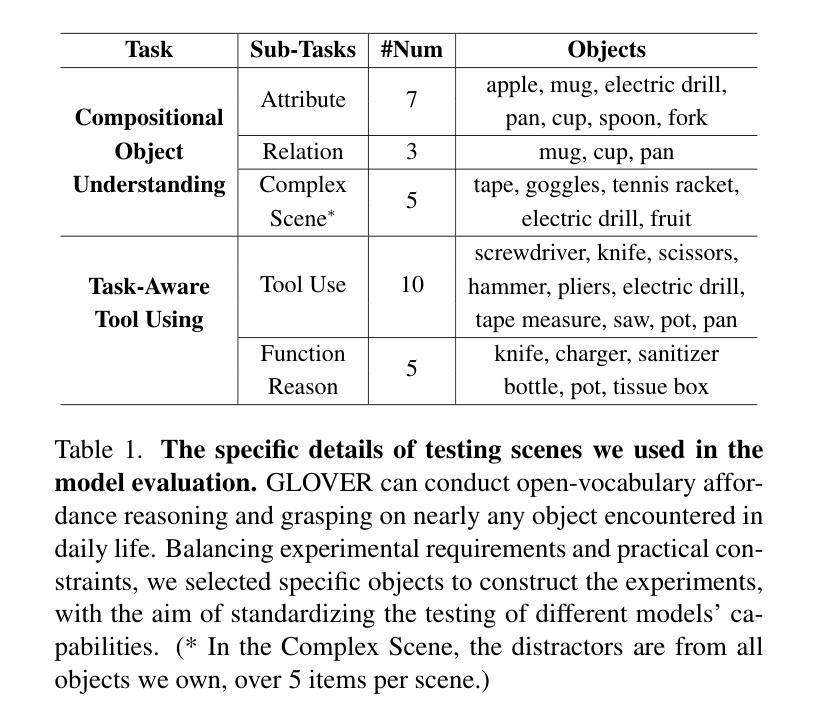
Inferring affordable (i.e., graspable) parts of arbitrary objects based on human specifications is essential for robots advancing toward open-vocabulary manipulation. Current grasp planners, however, are hindered by limited vision-language comprehension and time-consuming 3D radiance modeling, restricting real-time, open-vocabulary interactions with objects. To address these limitations, we propose GLOVER, a unified Generalizable Open-Vocabulary Affordance Reasoning framework, which fine-tunes the Large Language Models (LLMs) to predict the visual affordance of graspable object parts within RGB feature space. We compile a dataset of over 10,000 images from human-object interactions, annotated with unified visual and linguistic affordance labels, to enable multi-modal fine-tuning. GLOVER inherits world knowledge and common-sense reasoning from LLMs, facilitating more fine-grained object understanding and sophisticated tool-use reasoning. To enable effective real-world deployment, we present Affordance-Aware Grasping Estimation (AGE), a non-parametric grasp planner that aligns the gripper pose with a superquadric surface derived from affordance data. In evaluations across 30 table-top real-world scenes, GLOVER achieves success rates of 86.0% in part identification and 76.3% in grasping, with speeds approximately 29 times faster in affordance reasoning and 40 times faster in grasping pose estimation than the previous state-of-the-art. We also validate the generalization across embodiments, showing effectiveness in humanoid robots with dexterous hands.
根据人类指令推断任意对象的可负担(即抓握)部分,对于朝着开放词汇操作发展的机器人来说至关重要。然而,当前的抓握规划器受到有限的视觉语言理解和耗时的3D辐射建模的阻碍,限制了与对象的实时开放词汇交互。为了解决这些限制,我们提出了GLOVER,一个通用的开放词汇可负担性推理框架,它通过对大型语言模型(LLM)进行微调,以预测RGB特征空间中可抓握对象部分的视觉可负担性。我们编译了一个包含超过10,000张人类与物体交互图像的数据集,并统一标注了视觉和语言可负担性标签,以实现多模态微调。GLOVER从LLM继承世界知识和常识推理,促进更精细的对象理解和复杂的工具使用推理。为了实现现实世界的有效部署,我们提出了可负担性感知抓取估计(AGE),这是一种非参数化的抓握规划器,它将夹爪姿态与从可负担性数据中得出的超二次曲面进行对齐。在跨越30个真实桌面场景的评估中,GLOVER在部件识别方面的成功率为86.0%,在抓取方面的成功率为76.3%,在可负担性推理方面速度比先前最先进的技术快约29倍,在抓取姿态估计方面快约40倍。我们还通过人形机器人验证了跨实体的泛化能力,显示出在各种灵巧手上的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为GLOVER的通用开放词汇表的可承担性推理框架,旨在解决机器人在进行开放式词汇操作时所面临的视觉语言理解有限和三维辐射建模耗时的问题。通过微调大型语言模型(LLM)在RGB特征空间内预测可抓取物体部分的视觉可承担性,GLOVER框架编译了超过一万张人类与物体交互的图像数据集,并标注了统一的视觉和语言可承担性标签,以实现多模态微调。此外,框架引入了世界知识和常识推理,促进了更精细的对象理解和复杂的工具使用推理。为了在实际世界中进行有效部署,还推出了基于可承担性的抓取估算(AGE)的非参数化抓取规划器,该规划器根据可承担性数据调整夹持器的姿态,与超二次曲面相符。在三十个实际桌面场景中的评估显示,GLOVER在部件识别方面的成功率为86.0%,在抓取方面的成功率为76.3%,在可承担性推理和抓取姿态估计方面比现有技术快大约29倍和40倍。验证了在不同实体机器人上的有效性,包括人形机器人和灵巧手等。
Key Takeaways
- GLOVER是一个通用开放词汇表的可承担性推理框架,旨在解决机器人在开放式词汇操作中的限制。
- GLOVER通过微调大型语言模型预测物体视觉可承担性。
- GLOVER利用统一视觉和语言标注的图像数据集进行多模态微调。
- 世界知识和常识推理有助于更精细的对象理解和复杂的工具使用推理。
- AGE是一种非参数化抓取规划器,根据可承担性数据调整夹持器姿态。
- 在桌面场景中,GLOVER在部件识别和抓取方面表现出高成功率。
点此查看论文截图