⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-06 更新
Compensating Spatiotemporally Inconsistent Observations for Online Dynamic 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Youngsik Yun, Jeongmin Bae, Hyunseung Son, Seoha Kim, Hahyun Lee, Gun Bang, Youngjung Uh
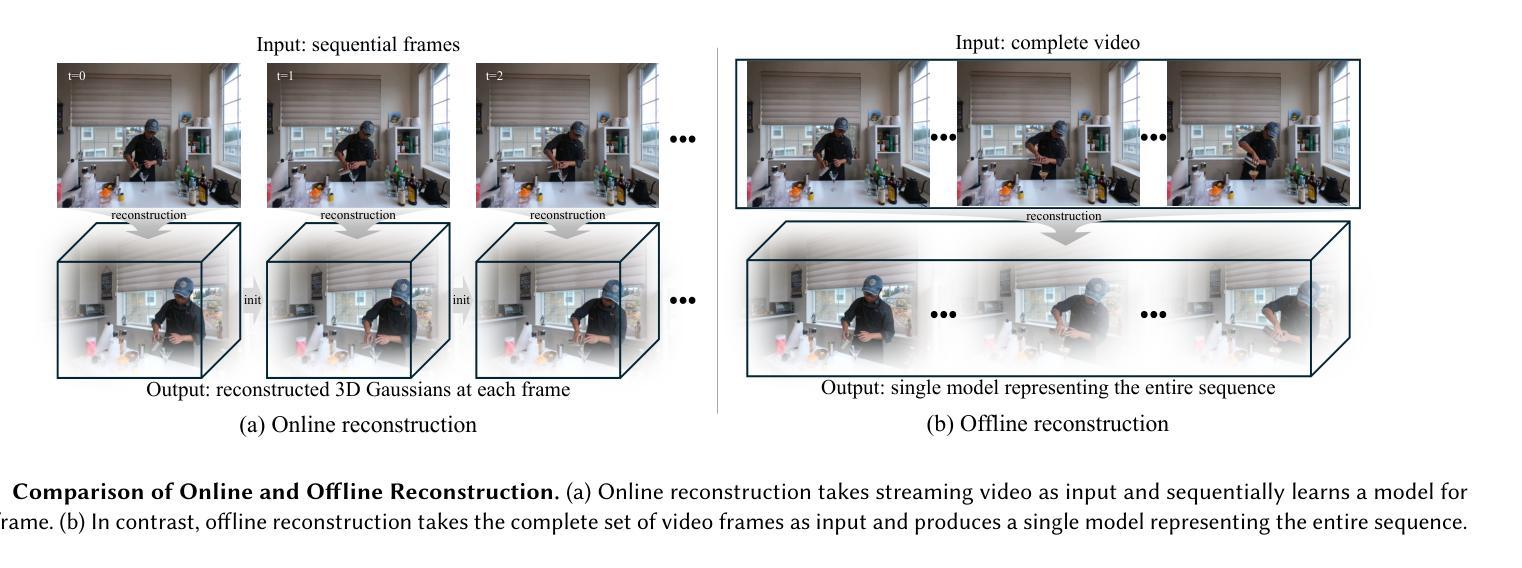
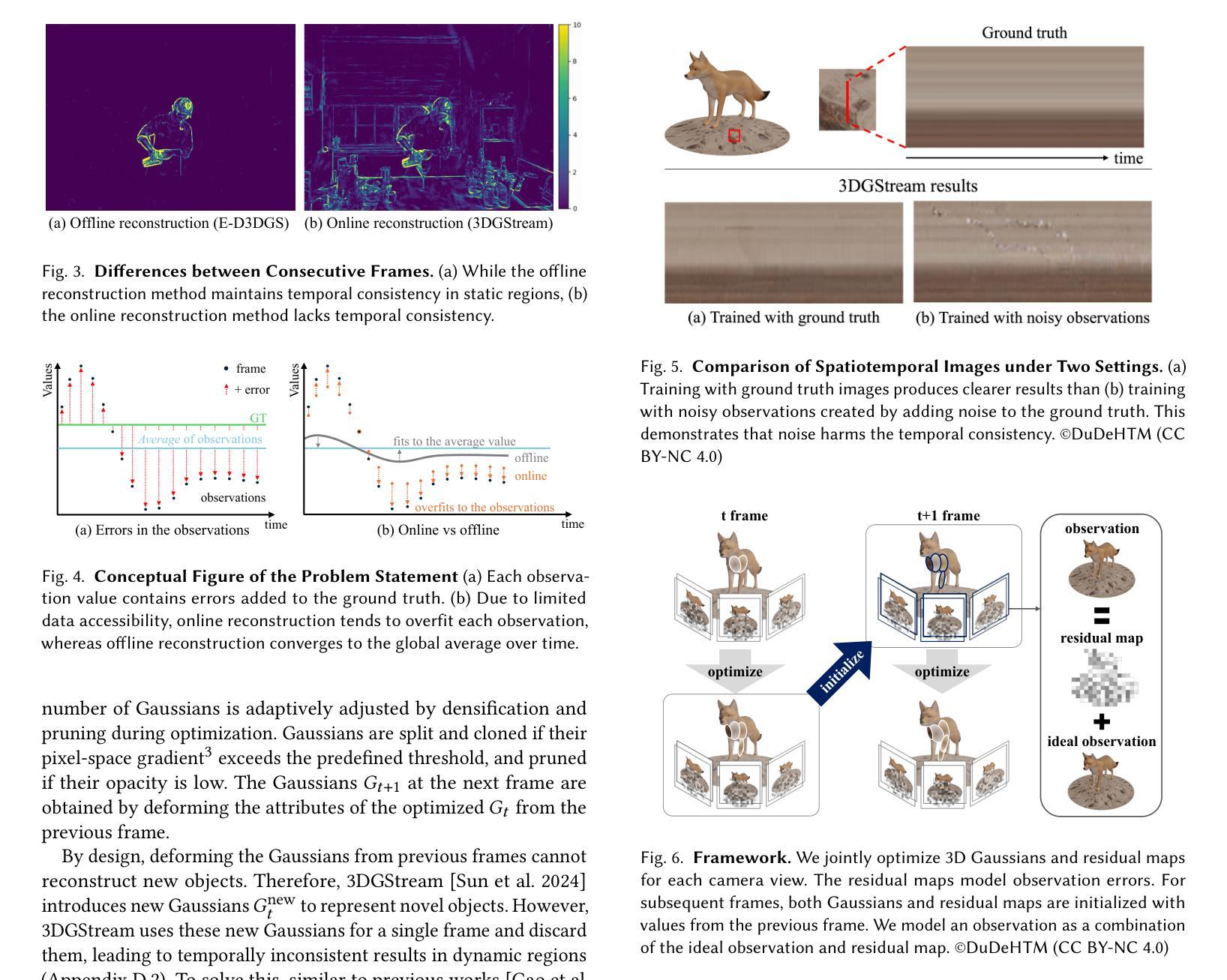
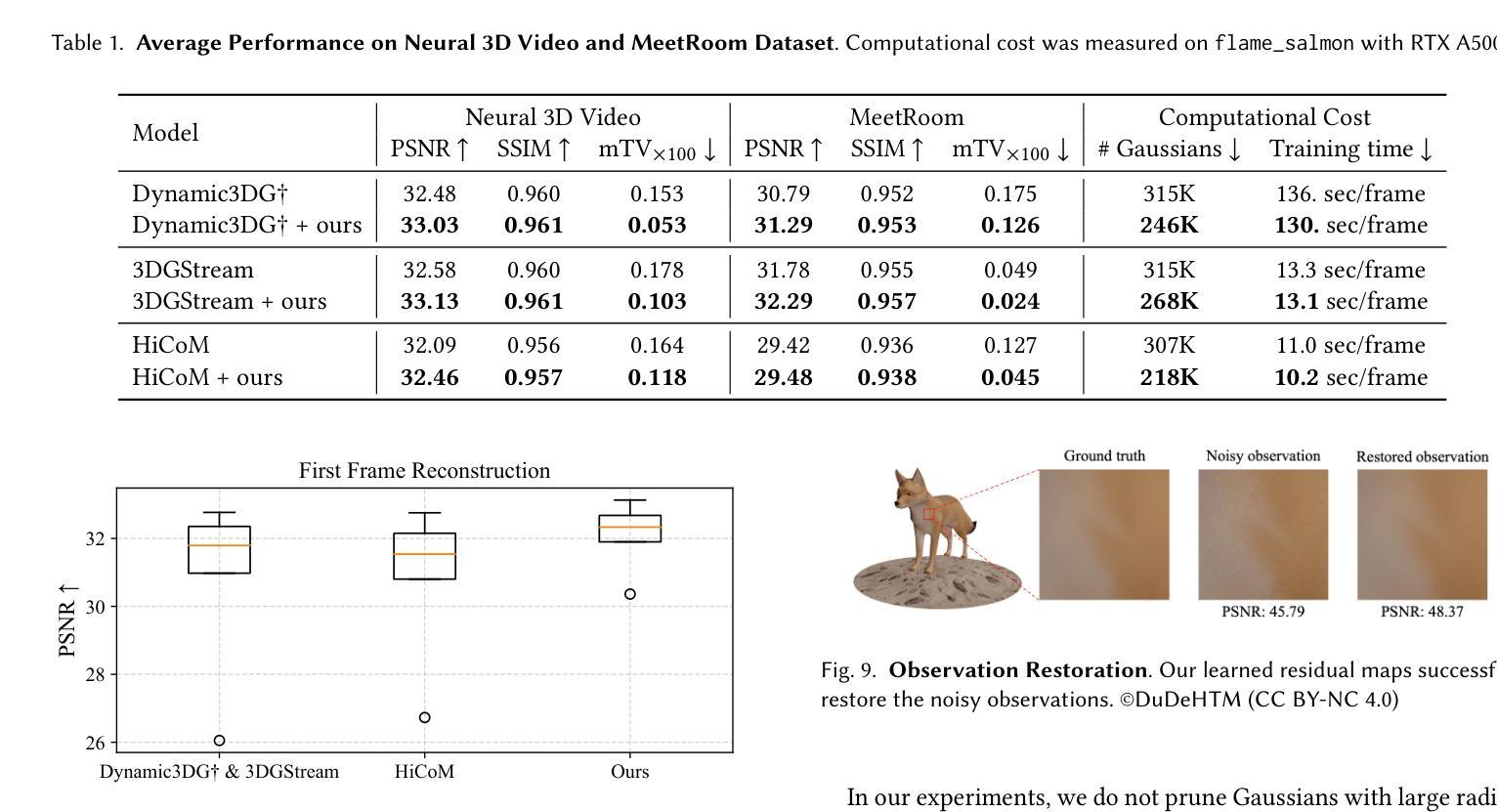
Online reconstruction of dynamic scenes is significant as it enables learning scenes from live-streaming video inputs, while existing offline dynamic reconstruction methods rely on recorded video inputs. However, previous online reconstruction approaches have primarily focused on efficiency and rendering quality, overlooking the temporal consistency of their results, which often contain noticeable artifacts in static regions. This paper identifies that errors such as noise in real-world recordings affect temporal inconsistency in online reconstruction. We propose a method that enhances temporal consistency in online reconstruction from observations with temporal inconsistency which is inevitable in cameras. We show that our method restores the ideal observation by subtracting the learned error. We demonstrate that applying our method to various baselines significantly enhances both temporal consistency and rendering quality across datasets. Code, video results, and checkpoints are available at https://bbangsik13.github.io/OR2.
动态场景的在线重建具有重要意义,因为它能够从直播视频输入中学习场景,而现有的离线动态重建方法则依赖于录制的视频输入。然而,之前的在线重建方法主要关注效率和渲染质量,忽视了其结果的时序一致性,这在静态区域中往往会产生明显的伪影。本文指出,现实世界记录中的噪声等错误会影响在线重建中的时序不一致性。我们提出了一种方法,通过观测增强在线重建中的时序一致性,而摄像头拍摄中不可避免地会出现时序不一致的现象。我们展示,通过减去学习到的误差,我们的方法可以恢复理想观测值。我们证明,将我们的方法应用于各种基准线,可以显著提高跨数据集的时序一致性和渲染质量。代码、视频结果和检查点均可在https://bbangsik13.github.io/OR2找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF SIGGRAPH 2025, Project page: https://bbangsik13.github.io/OR2
Summary
本文探讨了在线动态场景重建的重要性及其面临的挑战。现有方法主要关注效率和渲染质量,忽视了结果的时序一致性,导致在静态区域出现明显的伪影。本文提出一种增强在线重建时序一致性的方法,通过学习和减去误差来恢复理想观测值,并证明该方法可显著提高不同基准测试的时序一致性和渲染质量。
Key Takeaways
- 在线重建动态场景允许从实时流媒体视频输入中学习场景,而现有离线动态重建方法依赖于录制视频输入。
- 现有在线重建方法主要关注效率和渲染质量,忽视了时序一致性,导致静态区域出现伪影。
- 本文指出真实世界录制中的误差会影响在线重建的时序一致性。
- 提出一种增强在线重建时序一致性的方法,通过减去学习到的误差来恢复理想观测值。
- 方法在多个基准测试上显著提高了时序一致性和渲染质量。
- 方法和代码可在指定网站找到。
点此查看论文截图


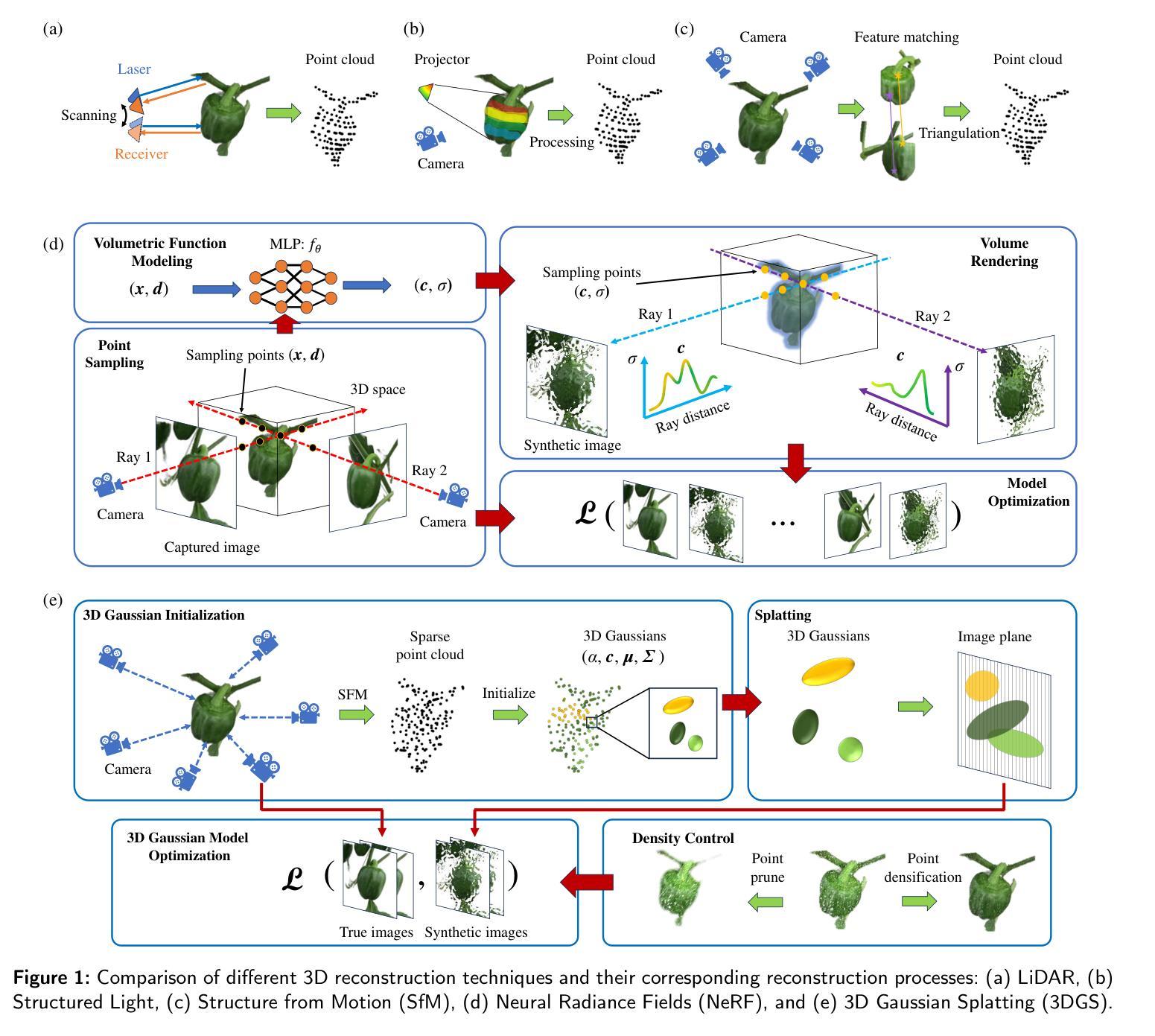
A Survey on 3D Reconstruction Techniques in Plant Phenotyping: From Classical Methods to Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF), 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), and Beyond
Authors:Jiajia Li, Xinda Qi, Seyed Hamidreza Nabaei, Meiqi Liu, Dong Chen, Xin Zhang, Xunyuan Yin, Zhaojian Li
Plant phenotyping plays a pivotal role in understanding plant traits and their interactions with the environment, making it crucial for advancing precision agriculture and crop improvement. 3D reconstruction technologies have emerged as powerful tools for capturing detailed plant morphology and structure, offering significant potential for accurate and automated phenotyping. This paper provides a comprehensive review of the 3D reconstruction techniques for plant phenotyping, covering classical reconstruction methods, emerging Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF), and the novel 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) approach. Classical methods, which often rely on high-resolution sensors, are widely adopted due to their simplicity and flexibility in representing plant structures. However, they face challenges such as data density, noise, and scalability. NeRF, a recent advancement, enables high-quality, photorealistic 3D reconstructions from sparse viewpoints, but its computational cost and applicability in outdoor environments remain areas of active research. The emerging 3DGS technique introduces a new paradigm in reconstructing plant structures by representing geometry through Gaussian primitives, offering potential benefits in both efficiency and scalability. We review the methodologies, applications, and performance of these approaches in plant phenotyping and discuss their respective strengths, limitations, and future prospects (https://github.com/JiajiaLi04/3D-Reconstruction-Plants). Through this review, we aim to provide insights into how these diverse 3D reconstruction techniques can be effectively leveraged for automated and high-throughput plant phenotyping, contributing to the next generation of agricultural technology.
植物表型分析在理解植物特性及其与环境互动方面扮演着关键角色,对于推动精准农业和作物改良至关重要。三维重建技术已崭露头角,成为捕捉植物详细形态和结构的有力工具,为准确和自动化的表型分析提供了巨大潜力。本文全面综述了用于植物表型分析的三维重建技术,包括经典重建方法、新兴的神经辐射场(NeRF)以及新颖的三维高斯喷涂(3DGS)方法。经典方法通常依赖于高分辨率传感器,在表示植物结构方面简单灵活,广泛应用于实践中。但它们面临着数据密度、噪声和可扩展性等方面的挑战。NeRF是最新的进展,能够从稀疏视角实现高质量、逼真的三维重建,但其计算成本和在户外环境的适用性仍是活跃的研究领域。新兴的3DGS技术通过高斯基元表示几何结构,为植物结构重建提供了新的范式,在效率和可扩展性方面可能带来潜在的优势。我们回顾了这些方法在植物表型分析中的方法学、应用和性能,并讨论了其各自的优点、局限性和未来前景(https://github.com/JiajiaLi04/3D-Reconstruction-Plants)。通过本次综述,我们旨在深入了解这些不同的三维重建技术如何有效地用于自动化和高通量的植物表型分析,为下一代农业技术做出贡献。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages, 7 figures, 4 tables
摘要
植物表型分析对了解植物特征及其与环境互动至关重要,是推动精准农业和作物改良的关键。3D重建技术已成为捕捉植物形态结构的强大工具,为精准自动表型分析提供显著潜力。本文全面综述了用于植物表型分析的3D重建技术,包括传统重建方法、新兴的神经辐射场(NeRF)和新颖的3D高斯喷涂(3DGS)方法。传统方法虽简单易用,能灵活表现植物结构,但存在数据密度、噪声和可扩展性挑战。NeRF虽能实现高质量、逼真的3D重建,但其计算成本和户外环境的适用性仍是研究热点。新兴的3DGS技术通过高斯原始数据表现几何结构,为植物重建提供了新的模式,可能在效率和可扩展性方面带来优势。本文评述了这些方法在植物表型分析中的方法、应用与性能,讨论了其优缺点与未来前景。本文旨在为如何利用这些3D重建技术为自动、高通量的植物表型分析提供有效见解,为下一代农业技术做出贡献。
关键见解
- 植物表型分析在理解植物特征及其与环境的互动中起到关键作用,对精准农业和作物改良至关重要。
- 3D重建技术已成为捕捉植物形态结构的强大工具,为精准自动表型分析提供潜力。
- 传统3D重建方法在植物表型分析中应用广泛,但面临数据密度、噪声和可扩展性挑战。
- NeRF技术能实现高质量3D重建,但计算成本和户外环境应用仍是研究热点。
- 新兴的3DGS技术在植物重建领域提供新的模式,可能在效率和扩展性方面具备优势。
- 综述了各种3D重建技术在植物表型分析中的应用、方法和性能,为下一代农业技术提供见解。
点此查看论文截图

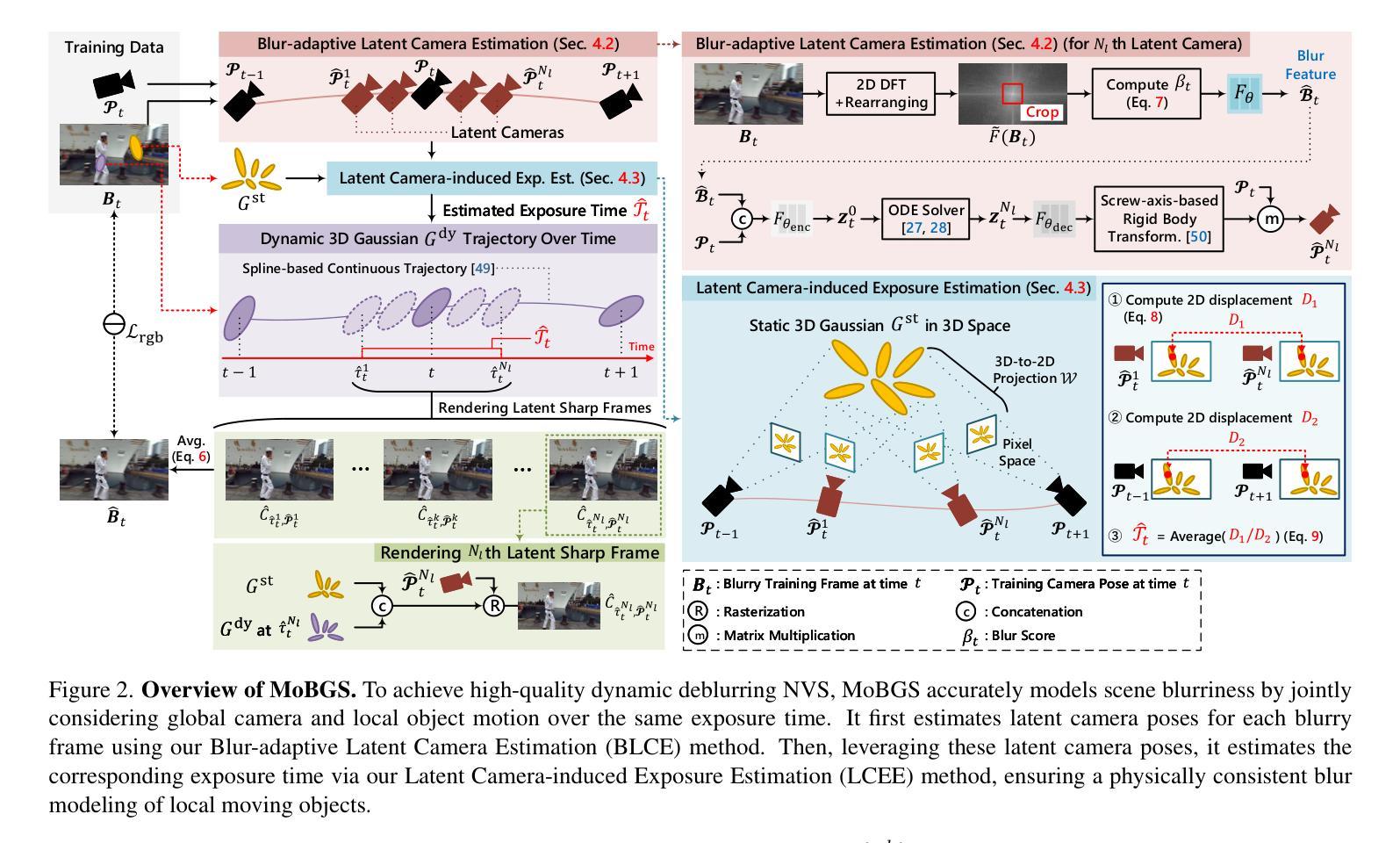
MoBGS: Motion Deblurring Dynamic 3D Gaussian Splatting for Blurry Monocular Video
Authors:Minh-Quan Viet Bui, Jongmin Park, Juan Luis Gonzalez Bello, Jaeho Moon, Jihyong Oh, Munchurl Kim
We present MoBGS, a novel deblurring dynamic 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) framework capable of reconstructing sharp and high-quality novel spatio-temporal views from blurry monocular videos in an end-to-end manner. Existing dynamic novel view synthesis (NVS) methods are highly sensitive to motion blur in casually captured videos, resulting in significant degradation of rendering quality. While recent approaches address motion-blurred inputs for NVS, they primarily focus on static scene reconstruction and lack dedicated motion modeling for dynamic objects. To overcome these limitations, our MoBGS introduces a novel Blur-adaptive Latent Camera Estimation (BLCE) method for effective latent camera trajectory estimation, improving global camera motion deblurring. In addition, we propose a physically-inspired Latent Camera-induced Exposure Estimation (LCEE) method to ensure consistent deblurring of both global camera and local object motion. Our MoBGS framework ensures the temporal consistency of unseen latent timestamps and robust motion decomposition of static and dynamic regions. Extensive experiments on the Stereo Blur dataset and real-world blurry videos show that our MoBGS significantly outperforms the very recent advanced methods (DyBluRF and Deblur4DGS), achieving state-of-the-art performance for dynamic NVS under motion blur.
我们提出了MoBGS,这是一种新型的去模糊动态三维高斯拼贴(3DGS)框架,能够以端到端的方式从模糊的单目视频中重建清晰、高质量的新时空视图。现有的动态新颖视图合成(NVS)方法对随意拍摄的视频中的运动模糊高度敏感,导致渲染质量显著下降。虽然最近的方法解决了运动模糊输入下的NVS问题,但它们主要关注静态场景的重建,缺乏针对动态对象的专用运动建模。为了克服这些局限性,我们的MoBGS引入了一种新的模糊自适应潜在相机估计(BLCE)方法,用于有效的潜在相机轨迹估计,改进全局相机运动去模糊。此外,我们提出了一种受物理启发的潜在相机诱导曝光估计(LCEE)方法,以确保全局相机和局部对象运动的持续去模糊。我们的MoBGS框架确保了未见潜在时间戳的时空一致性以及静态和动态区域的稳健运动分解。在立体模糊数据集和真实世界的模糊视频上的大量实验表明,我们的MoBGS显著优于最新的高级方法(DyBluRF和Deblur4DGS),在运动模糊的动态NVS中达到最新性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The first two authors contributed equally to this work (equal contribution). The last two authors are co-corresponding authors. Please visit our project page at https://kaist-viclab.github.io/mobgs-site/
摘要
提出一种新型动态3D高斯拼贴(MoBGS)框架,可从模糊的单目视频中重建清晰、高质量的新时空视图。现有动态新视图合成(NVS)方法对运动模糊敏感,导致渲染质量显著下降。MoBGS引入模糊自适应潜在相机估计(BLCE)方法,改进全局相机运动去模糊。同时,提出受物理启发的潜在相机诱导曝光估计(LCEE)方法,确保全局相机和局部对象运动的持续去模糊。MoBGS框架确保未见潜在时间戳的时空一致性及静态和动态区域的稳健运动分解。在Stereo Blur数据集和真实世界模糊视频上的广泛实验表明,MoBGS显著优于最近的高级方法(DyBluRF和Deblur4DGS),在运动模糊情况下实现动态NVS的卓越性能。
关键见解
- 提出MoBGS框架,结合动态3D高斯拼贴技术,能从模糊的单目视频中重建高质量的新时空视图。
- 现有动态NVS方法对运动模糊敏感,导致渲染质量下降。
- MoBGS通过引入BLCE方法改进全局相机运动去模糊,同时处理局部对象运动。
- LCEE方法确保相机和对象运动的持续去模糊。
- MoBGS框架实现未见潜在时间戳的时空一致性。
- MoBGS在静态和动态区域之间实现稳健的运动分解。
点此查看论文截图