⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-06 更新
Exploring Equity of Climate Policies using Multi-Agent Multi-Objective Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Palok Biswas, Zuzanna Osika, Isidoro Tamassia, Adit Whorra, Jazmin Zatarain-Salazar, Jan Kwakkel, Frans A. Oliehoek, Pradeep K. Murukannaiah
Addressing climate change requires coordinated policy efforts of nations worldwide. These efforts are informed by scientific reports, which rely in part on Integrated Assessment Models (IAMs), prominent tools used to assess the economic impacts of climate policies. However, traditional IAMs optimize policies based on a single objective, limiting their ability to capture the trade-offs among economic growth, temperature goals, and climate justice. As a result, policy recommendations have been criticized for perpetuating inequalities, fueling disagreements during policy negotiations. We introduce Justice, the first framework integrating IAM with Multi-Objective Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MOMARL). By incorporating multiple objectives, Justice generates policy recommendations that shed light on equity while balancing climate and economic goals. Further, using multiple agents can provide a realistic representation of the interactions among the diverse policy actors. We identify equitable Pareto-optimal policies using our framework, which facilitates deliberative decision-making by presenting policymakers with the inherent trade-offs in climate and economic policy.
应对气候变化需要全球各国政策的协调努力。这些努力以科学报告为依据,科学报告部分依赖于综合评估模型(IAMs),这是评估气候政策经济影响的重要工具。然而,传统的IAMs基于单一目标优化政策,这限制了其捕捉经济增长、温度目标和气候正义之间权衡的能力。因此,政策建议因加剧不平等、在政策谈判中引发分歧而受到批评。我们引入了Justice,它是第一个将IAM与多目标多智能体强化学习(MOMARL)相结合的理论框架。通过融入多重目标,Justice在平衡气候和经济目标的同时,提出了关注公平的政策建议。此外,利用多个智能体可以提供对多样化政策行动者之间互动的逼真描述。我们使用此框架确定了公平的帕累托最优政策,通过向政策制定者展示气候和经济政策中的固有权衡来促进审慎决策。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to IJCAI 2025, AI and Social Good Track
Summary
本文强调了应对气候变化需要全球各国协同政策努力,而科学报告和集成评估模型(IAM)是制定这些政策的重要参考。然而,传统的IAM以单一目标进行优化,难以兼顾经济增长、温度目标和气候公平之间的权衡,因此政策推荐受到批评,加剧了不平等和政策谈判中的分歧。为此,我们引入了结合IAM和多目标多智能体强化学习(MOMARL)的正义框架。该框架通过融入多个目标,在平衡气候和经济目标的同时,为政策制定者提供公平的政策建议。此外,使用多个智能体可以真实反映不同政策制定者之间的互动。我们的框架能够识别公平的帕累托最优政策,帮助政策制定者在气候和经济政策之间进行权衡决策。
Key Takeaways
- 应对气候变化需要全球协同政策努力,科学报告和集成评估模型(IAM)是重要参考。
- 传统IAM以单一目标优化,难以兼顾经济、温度目标和气候公平。
- 政策推荐因未能充分考虑公平而受批评,加剧不平等和政策分歧。
- 引入结合IAM和多目标多智能体强化学习(MOMARL)的“正义”框架。
- “正义”框架能生成兼顾气候和经济目标的公平政策建议。
- 使用多个智能体能真实反映不同政策制定者间的互动。
点此查看论文截图

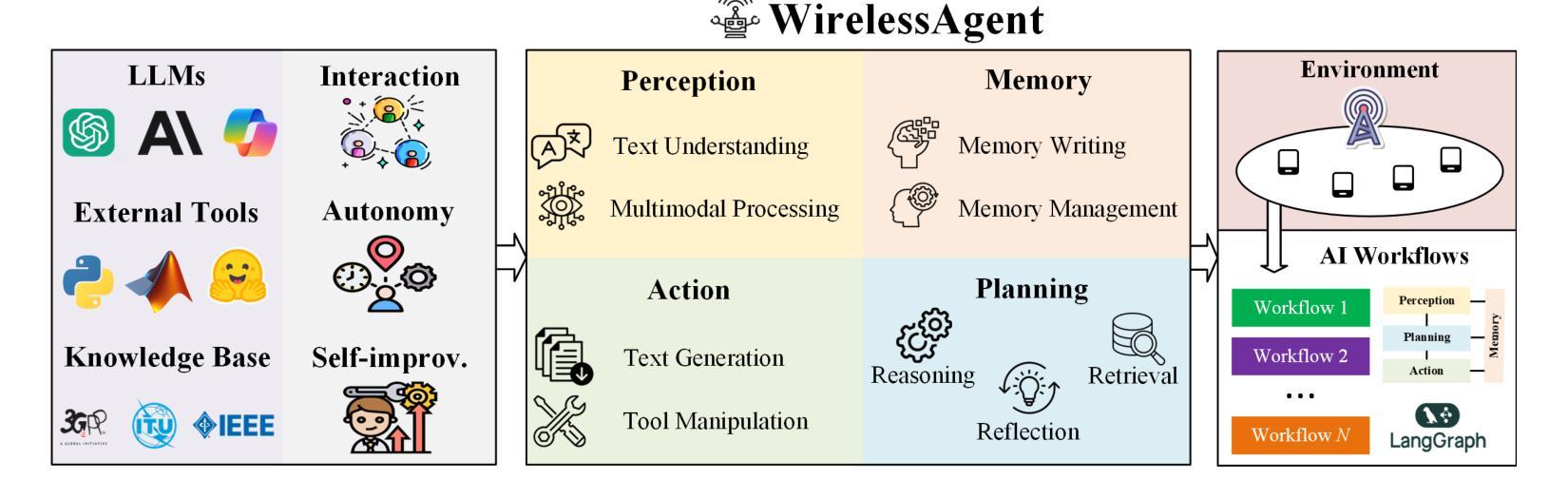
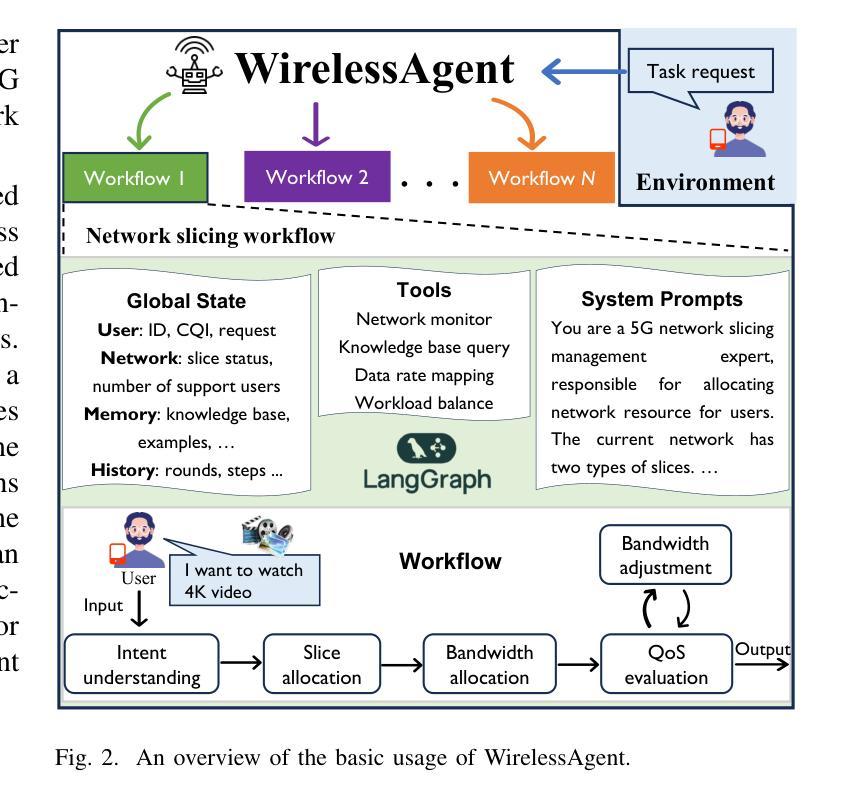
WirelessAgent: Large Language Model Agents for Intelligent Wireless Networks
Authors:Jingwen Tong, Wei Guo, Jiawei Shao, Qiong Wu, Zijian Li, Zehong Lin, Jun Zhang
The rapid evolution of wireless networks presents unprecedented challenges in managing complex and dynamic systems. Existing methods are increasingly facing fundamental limitations in addressing these challenges. In this paper, we introduce WirelessAgent, a novel framework that harnesses large language models (LLMs) to create autonomous AI agents for diverse wireless network tasks. This framework integrates four core modules that mirror human cognitive processes: perception, memory, planning, and action. To implement it, we provide a basic usage based on agentic workflows and the LangGraph architecture. We demonstrate the effectiveness of WirelessAgent through a comprehensive case study on network slicing. The numerical results show that WirelessAgent achieves $44.4%$ higher bandwidth utilization than the \emph{Prompt-based} method, while performing only $4.3%$ below the \emph{Rule-based optimality}. Notably, WirelessAgent delivers near-optimal network throughput across diverse network scenarios. These underscore the framework’s potential for intelligent and autonomous resource management in future wireless networks. The code is available at \url{https://github.com/jwentong/WirelessAgent_R1}.
无线网络的快速发展给管理复杂动态系统带来了前所未有的挑战。现有方法在应对这些挑战时面临着越来越多的根本性局限。在本文中,我们介绍了WirelessAgent,这是一个新型框架,它利用大型语言模型(LLMs)来创建用于多种无线网络任务的自主AI代理。该框架集成了四个核心模块,这些模块反映了人类的认知过程:感知、记忆、规划和行动。为了实现它,我们提供了基于代理工作流程和LangGraph架构的基本用法。我们通过关于网络切片的综合案例研究证明了WirelessAgent的有效性。数值结果表明,WirelessAgent的带宽利用率比“基于提示”的方法高出44.4%,同时仅比“基于规则的最优值”低4.3%。值得注意的是,WirelessAgent在不同网络场景中实现了接近最优的网络吞吐量。这些成果凸显了未来无线网络中智能自主资源管理中该框架的潜力。代码可在https://github.com/jwentong/WirelessAgent_R1找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This manuscript is an extended version of a previous magazine version and is now submitted to a journal for possible publication. arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:2409.07964
Summary
无线网络的快速发展给管理复杂动态系统带来了前所未有的挑战。现有方法在处理这些挑战时面临着越来越大的局限性。本文介绍了WirelessAgent,一种利用大型语言模型(LLMs)创建用于多种无线网络任务的自主AI代理的新型框架。该框架集成了四个反映人类认知过程的核心模块:感知、记忆、规划和行动。通过基于代理的工作流程和LangGraph架构的基本使用,我们实现了它。通过对网络切片进行综合性案例研究,展示了WirelessAgent的有效性。数值结果表明,WirelessAgent的带宽利用率比基于提示的方法高出44.4%,同时仅比基于规则的最优方案低4.3%。WirelessAgent在不同网络场景下都能实现接近最优的网络吞吐量,凸显了其在未来无线网络中智能自主资源管理的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 无线网络面临管理复杂动态系统的挑战。
- WirelessAgent框架利用大型语言模型创建自主AI代理应对这些挑战。
- WirelessAgent包含四个核心模块:感知、记忆、规划和行动,这些模块反映了人类认知过程。
- 通过代理的工作流程和LangGraph架构实现了WirelessAgent。
- 网络切片的案例研究表明,WirelessAgent在带宽利用率方面表现出卓越的性能。
- WirelessAgent的性能接近最优,凸显了其在未来无线网络中的潜力。
点此查看论文截图


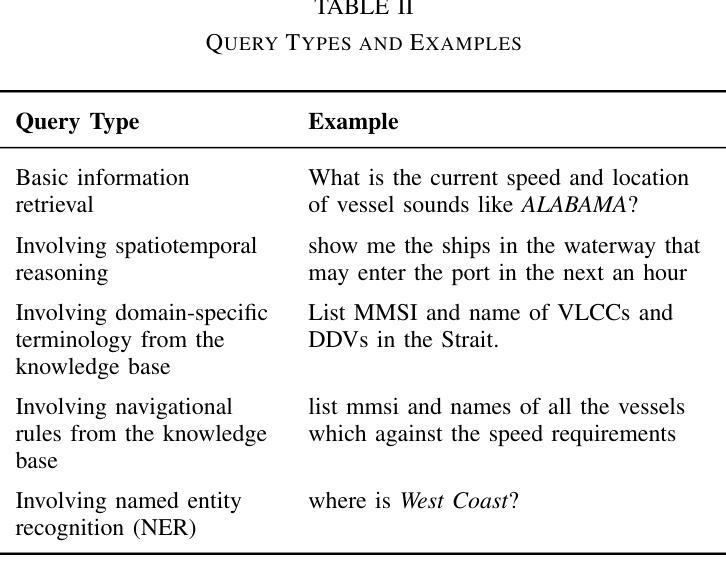
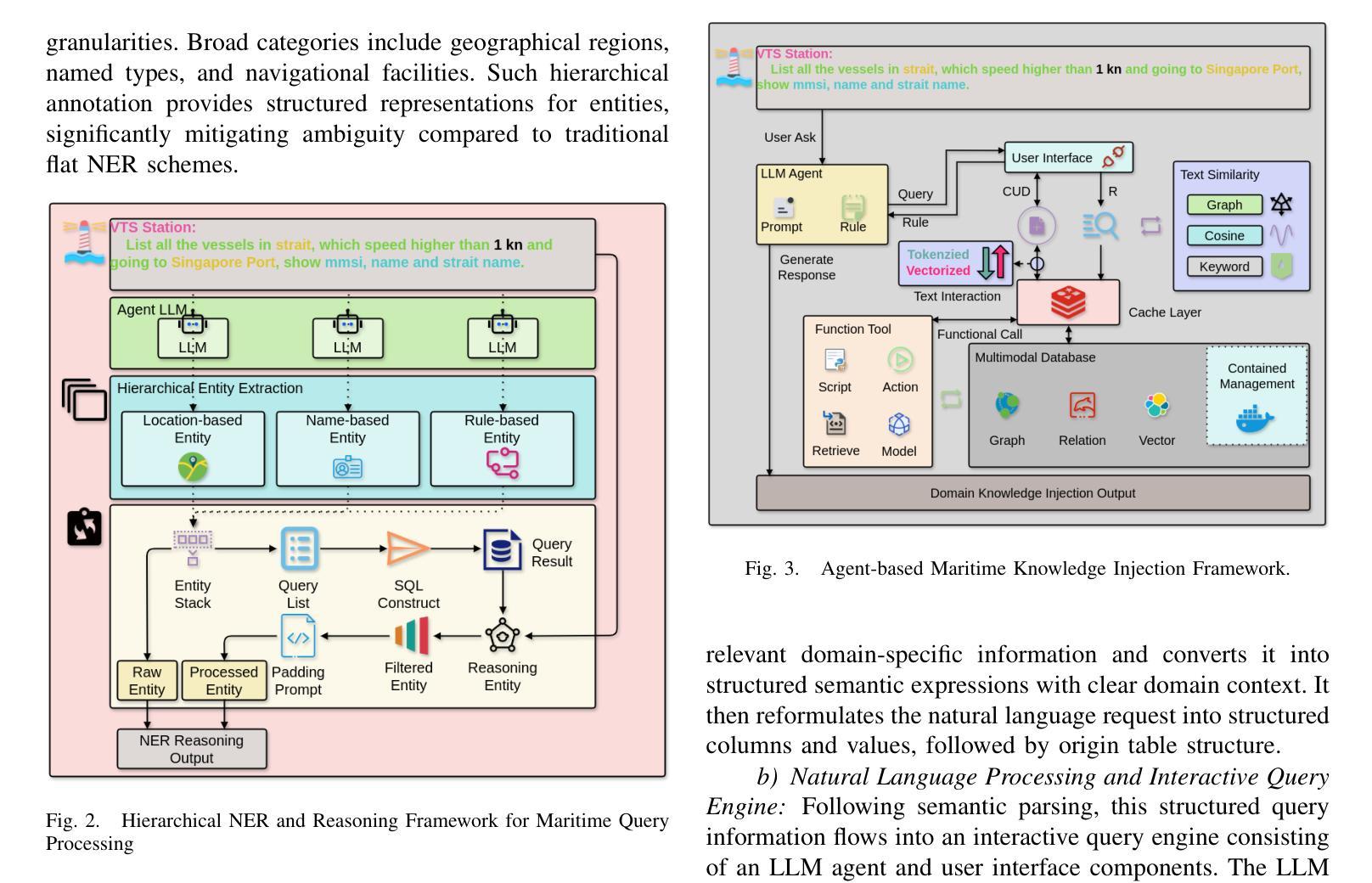
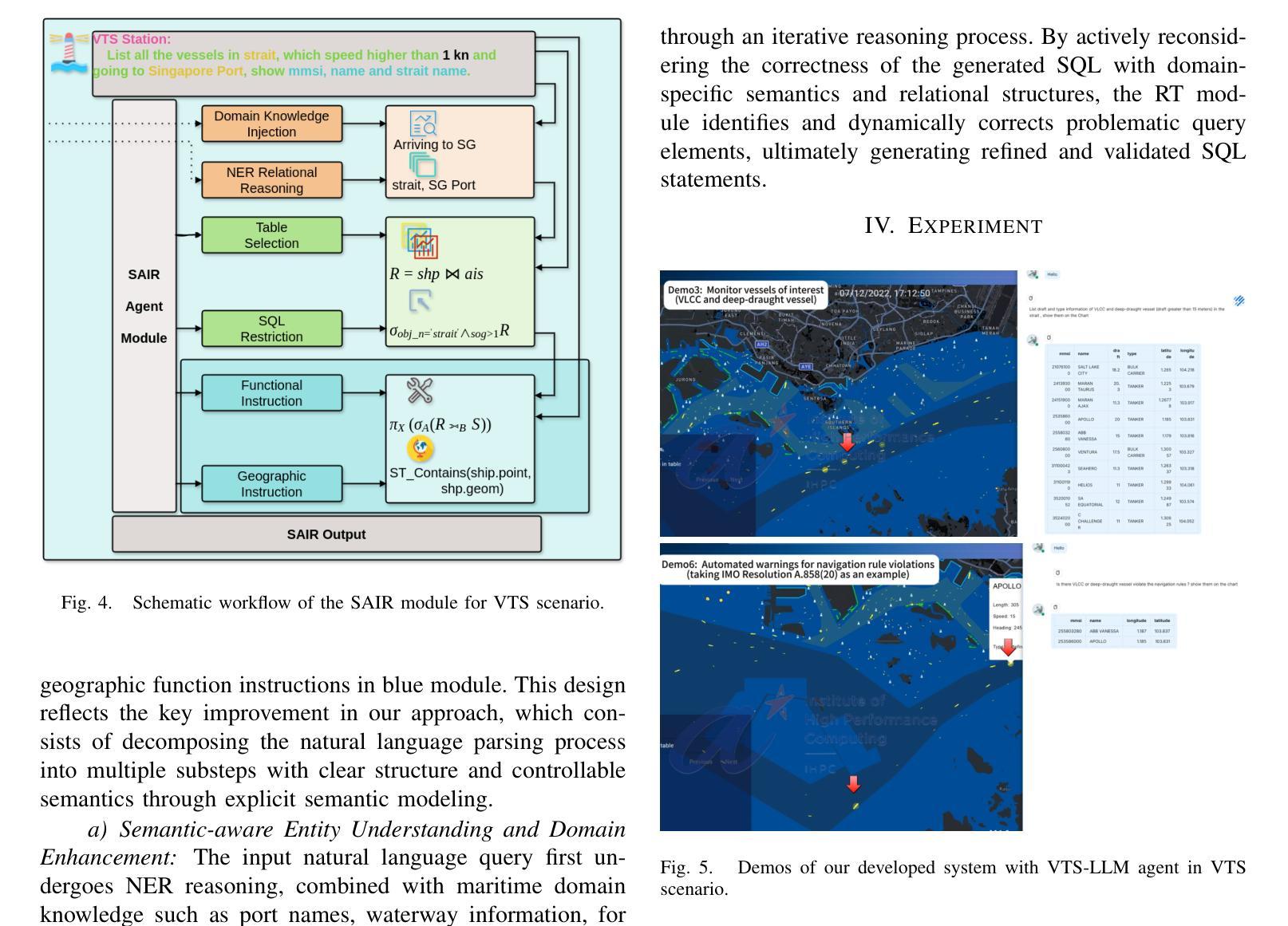
VTS-LLM: Domain-Adaptive LLM Agent for Enhancing Awareness in Vessel Traffic Services through Natural Language
Authors:Sijin Sun, Liangbin Zhao, Ming Deng, Xiuju Fu
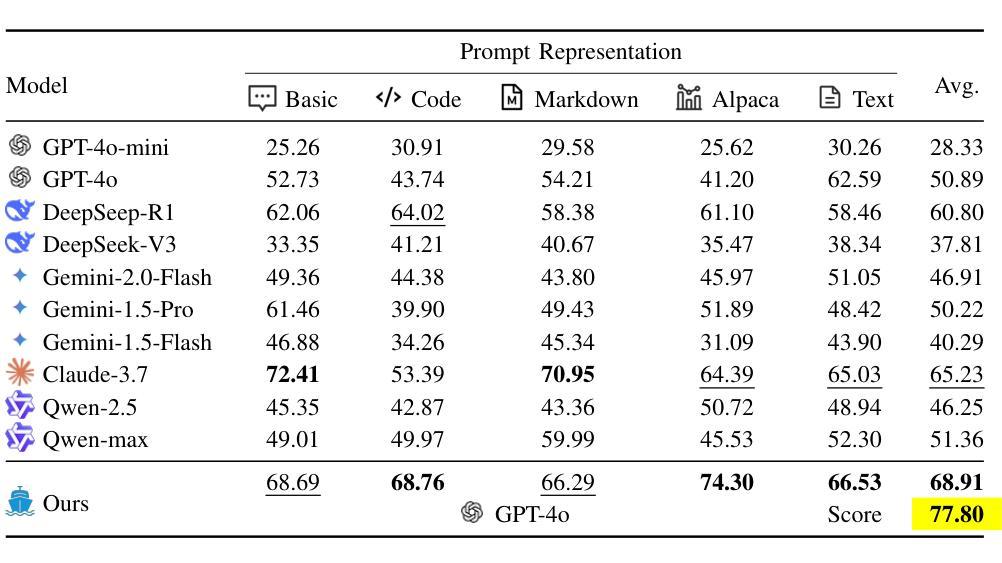
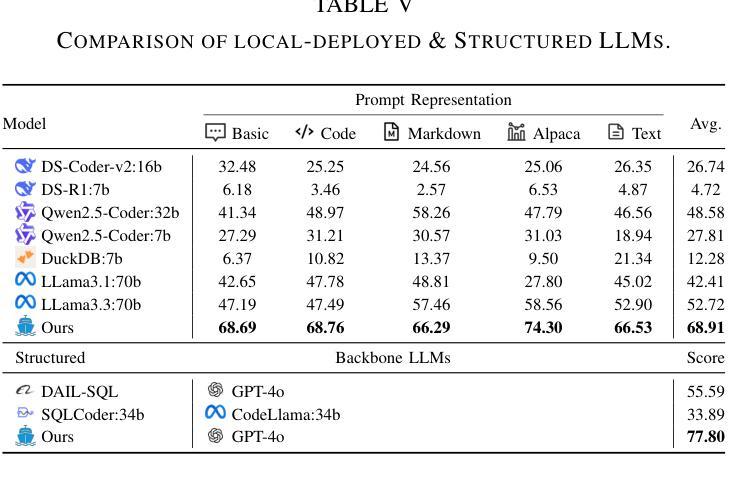
Vessel Traffic Services (VTS) are essential for maritime safety and regulatory compliance through real-time traffic management. However, with increasing traffic complexity and the prevalence of heterogeneous, multimodal data, existing VTS systems face limitations in spatiotemporal reasoning and intuitive human interaction. In this work, we propose VTS-LLM Agent, the first domain-adaptive large LLM agent tailored for interactive decision support in VTS operations. We formalize risk-prone vessel identification as a knowledge-augmented Text-to-SQL task, combining structured vessel databases with external maritime knowledge. To support this, we construct a curated benchmark dataset consisting of a custom schema, domain-specific corpus, and a query-SQL test set in multiple linguistic styles. Our framework incorporates NER-based relational reasoning, agent-based domain knowledge injection, semantic algebra intermediate representation, and query rethink mechanisms to enhance domain grounding and context-aware understanding. Experimental results show that VTS-LLM outperforms both general-purpose and SQL-focused baselines under command-style, operational-style, and formal natural language queries, respectively. Moreover, our analysis provides the first empirical evidence that linguistic style variation introduces systematic performance challenges in Text-to-SQL modeling. This work lays the foundation for natural language interfaces in vessel traffic services and opens new opportunities for proactive, LLM-driven maritime real-time traffic management.
船舶交通服务(VTS)对于通过实时交通管理实现海上安全和法规合规至关重要。然而,随着交通复杂性的增加和异构多模态数据的普及,现有VTS系统在时空推理和直观人机交互方面面临局限性。在这项工作中,我们提出了VTS-LLM Agent,这是第一个针对VTS操作中的交互式决策支持量身定制的域自适应大型LLM代理。我们将易出风险的船舶识别形式化为知识增强的文本到SQL任务,结合结构化船舶数据库和外部海事知识。为此,我们构建了一个精心制作的基准数据集,包括自定义模式、领域特定语料库和多种语言风格的查询SQL测试集。我们的框架结合了基于NER的关系推理、基于代理的领域知识注入、语义代数中间表示和查询反思机制,以增强领域定位和上下文感知理解。实验结果表明,VTS-LLM在命令风格、操作风格和正式自然语言查询方面均优于通用型和SQL专注的基线。此外,我们的分析首次提供了实证证据表明,语言风格的变化给文本到SQL建模带来了系统性的性能挑战。这项工作奠定了自然语言接口在船舶交通服务中的基础,并为基于LLM的主动海事实时交通管理提供了新的机会。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 5 figures, 7 tablels, submitted to ITSC2025
Summary
本文介绍了VTS-LLM Agent在船舶交通服务中的重要性及其优势。该智能代理通过结合结构化船舶数据库和外部海事知识,采用文本到SQL的任务模式进行风险船舶识别。VTS-LLM Agent构建了专门的数据集,并引入了多种技术来提升其在特定领域的理解和上下文感知能力。实验结果显示,VTS-LLM Agent在命令风格、操作风格和正式自然语言查询方面的性能优于基准测试。同时,文章首次实证表明,语言风格变化对文本到SQL建模的系统性能带来挑战。此研究为船舶交通服务的自然语言接口奠定了基石,并为实时交通管理提供了新的机会。
Key Takeaways
- VTS在海上安全和法规遵守方面至关重要,但现有系统面临时空推理和直观人机交互的局限性。
- VTS-LLM Agent是首个针对VTS操作的交互式决策支持的大型语言模型代理。
- 风险船舶识别被形式化为知识增强的文本到SQL任务,结合了结构化船舶数据库和外部海事知识。
- VTS-LLM Agent构建了一个专门的数据集,包括自定义模式、特定领域的语料库和多种语言风格的查询SQL测试集。
- 该框架采用NER关系推理、基于代理的领域知识注入、语义代数中间表示和查询重新思考机制等技术,提升领域定位和上下文感知理解。
- 实验结果表明,VTS-LLM Agent在多种查询风格下的性能优于基准测试。
点此查看论文截图


Multi-agents based User Values Mining for Recommendation
Authors:Lijian Chen, Wei Yuan, Tong Chen, Xiangyu Zhao, Nguyen Quoc Viet Hung, Hongzhi Yin
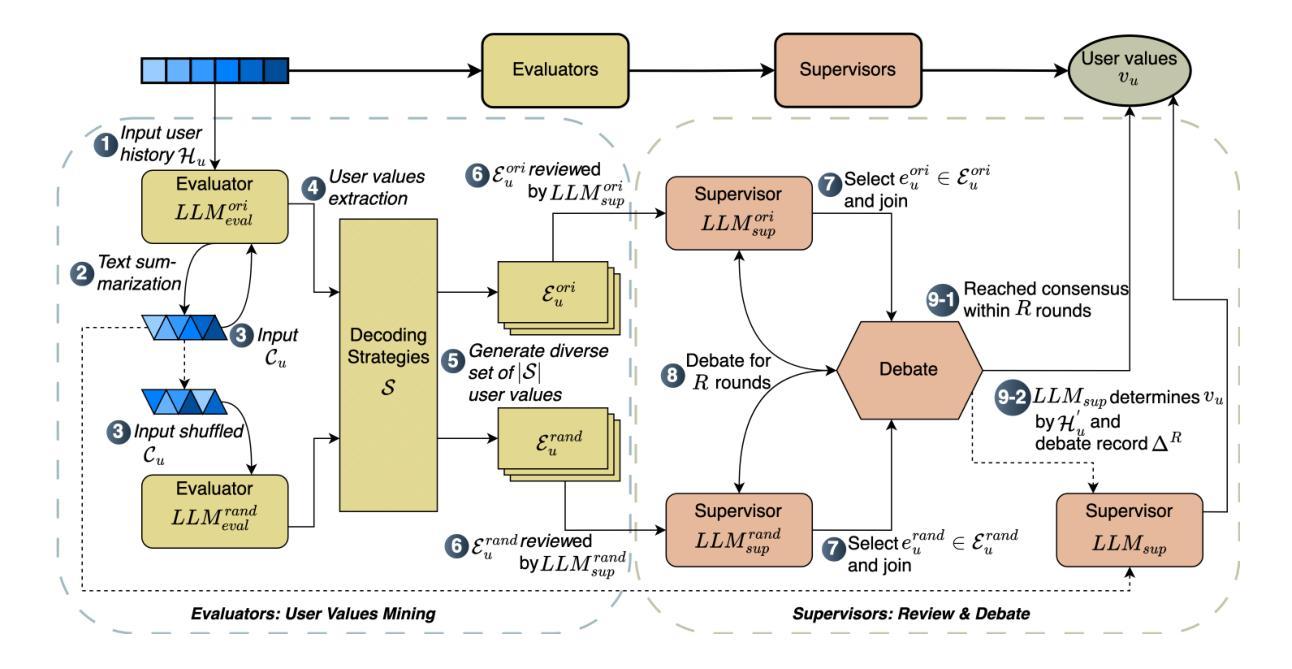
Recommender systems have rapidly evolved and become integral to many online services. However, existing systems sometimes produce unstable and unsatisfactory recommendations that fail to align with users’ fundamental and long-term preferences. This is because they primarily focus on extracting shallow and short-term interests from user behavior data, which is inherently dynamic and challenging to model. Unlike these transient interests, user values are more stable and play a crucial role in shaping user behaviors, such as purchasing items and consuming content. Incorporating user values into recommender systems can help stabilize recommendation performance and ensure results better reflect users’ latent preferences. However, acquiring user values is typically difficult and costly. To address this challenge, we leverage the strong language understanding, zero-shot inference, and generalization capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) to extract user values from users’ historical interactions. Unfortunately, direct extraction using LLMs presents several challenges such as length constraints and hallucination. To overcome these issues, we propose ZOOM, a zero-shot multi-LLM collaborative framework for effective and accurate user value extraction. In ZOOM, we apply text summarization techniques to condense item content while preserving essential meaning. To mitigate hallucinations, ZOOM introduces two specialized agent roles: evaluators and supervisors, to collaboratively generate accurate user values. Extensive experiments on two widely used recommendation datasets with two state-of-the-art recommendation models demonstrate the effectiveness and generalization of our framework in automatic user value mining and recommendation performance improvement.
推荐系统已经迅速演变并成为许多在线服务的重要组成部分。然而,现有系统有时会产生不稳定和不满意的推荐结果,无法与用户的基本和长期偏好相吻合。这是因为它们主要关注从用户行为数据中提取浅层和短期的兴趣,而用户行为数据本质上是动态的,难以进行建模。不同于这些短暂的兴趣,用户价值更加稳定,在塑造用户行为(如购买物品和消耗内容)方面起着至关重要的作用。将用户价值纳入推荐系统可以帮助稳定推荐性能,并确保结果更好地反映用户的潜在偏好。然而,获取用户价值通常很困难且成本高昂。为了应对这一挑战,我们利用大型语言模型(LLM)的强大语言理解、零启动推理和泛化能力,从用户的历史交互中提取用户价值。然而,直接使用LLM进行提取面临长度限制和幻觉等挑战。为了克服这些问题,我们提出了ZOOM(零启动多LLM协作框架),旨在实现有效和精确的用户价值提取。在ZOOM中,我们应用文本摘要技术来浓缩项目内容,同时保留关键意义。为了减轻幻觉问题,ZOOM引入了两种专门的代理角色:评估者和监督者,以协作生成准确的用户价值。在两个广泛使用的推荐数据集上进行的大量实验表明,与两种先进的推荐模型相比,我们的框架在自动用户价值挖掘和推荐性能提升方面都具有有效性和泛化性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
推荐系统已迅速演进并已成为许多在线服务的重要组成部分。然而,现有系统产生的推荐结果有时不稳定且不满意,无法与用户的基本和长期偏好对齐。这是因为它们主要关注从用户行为数据中提取短暂和浅层的兴趣,这本质上是动态的且难以建模。通过结合用户价值可以稳定推荐性能并确保结果更好地反映用户的潜在偏好。为从用户历史交互中提取用户价值,我们利用大型语言模型的强大语言理解能力、零样本推断能力和泛化能力来解决这一挑战。我们提出一种名为ZOOM的零样本多语言模型协作框架,用于有效和准确地提取用户价值。实验证明,该框架在自动用户价值挖掘和推荐性能提升方面的有效性和泛化性。
Key Takeaways
- 推荐系统已变得至关重要,但仍存在不稳定和无法满足用户长期偏好等问题。
- 现有系统主要关注用户行为的短暂和浅层兴趣,这导致推荐结果的不稳定。
- 用户价值是更稳定并影响用户行为的关键因素,如购买物品和消耗内容。
- 将用户价值纳入推荐系统可以提高推荐性能的稳定性并反映用户的潜在偏好。
- 提取用户价值具有挑战性,成本高昂。利用大型语言模型的强大能力来解决这一挑战。
- 提出名为ZOOM的零样本多语言模型协作框架,用于有效和准确地提取用户价值。
点此查看论文截图

Autonomous Embodied Agents: When Robotics Meets Deep Learning Reasoning
Authors:Roberto Bigazzi
The increase in available computing power and the Deep Learning revolution have allowed the exploration of new topics and frontiers in Artificial Intelligence research. A new field called Embodied Artificial Intelligence, which places at the intersection of Computer Vision, Robotics, and Decision Making, has been gaining importance during the last few years, as it aims to foster the development of smart autonomous robots and their deployment in society. The recent availability of large collections of 3D models for photorealistic robotic simulation has allowed faster and safe training of learning-based agents for millions of frames and a careful evaluation of their behavior before deploying the models on real robotic platforms. These intelligent agents are intended to perform a certain task in a possibly unknown environment. To this end, during the training in simulation, the agents learn to perform continuous interactions with the surroundings, such as gathering information from the environment, encoding and extracting useful cues for the task, and performing actions towards the final goal; where every action of the agent influences the interactions. This dissertation follows the complete creation process of embodied agents for indoor environments, from their concept to their implementation and deployment. We aim to contribute to research in Embodied AI and autonomous agents, in order to foster future work in this field. We present a detailed analysis of the procedure behind implementing an intelligent embodied agent, comprehending a thorough description of the current state-of-the-art in literature, technical explanations of the proposed methods, and accurate experimental studies on relevant robotic tasks.
随着可用计算能力的增加和深度学习的革命,人工智能研究中的新主题和前沿领域得到了探索。一个名为“实体人工智能”的新领域,它位于计算机视觉、机器人技术和决策制定的交界处,在过去的几年里变得越来越重要,因为它旨在促进智能自主机器人的发展及其在社会的部署。最近,大量用于真实感机器人模拟的3D模型的可用性允许了基于学习的代理人的快速和安全训练,以及数百万帧的行为的仔细评估,然后才将模型部署在实际的机器人平台上。这些智能代理旨在在一个可能未知的环境中执行特定任务。为此,代理在模拟训练期间学习不断与周围环境进行交互,如从环境中收集信息、编码和提取任务的有用线索,以及朝着最终目标采取行动;代理的每个行动都会影响其交互。本论文将跟踪实体代理在室内环境中的完整创建过程,从概念到实施和部署。我们旨在为实体人工智能和自主代理的研究做出贡献,以促进这一领域的未来工作。我们详细介绍了实现智能实体代理的过程分析,包括对文献中最新技术的全面描述、所提出方法的技术解释以及关于相关机器人任务的准确实验研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Ph.D. Dissertation
Summary
深度学习革命和计算能力的提升推动了人工智能新领域——嵌入式人工智能的发展,该领域旨在培养智能自主机器人并将其部署于社会。利用大规模三维模型进行逼真机器人模拟,可在模拟环境中快速安全地训练学习主体,并评估其行为,再部署到真实机器人平台。这些智能主体旨在能在未知环境中完成任务,通过连续互动,收集信息、编码提取任务线索并行动以达到最终目标。本文详细阐述了嵌入式主体的创建过程,从概念到实施和部署,并对当前文献的先进技术、方法的技术解释以及相关的机器人任务准确实验进行了研究。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习革命和计算能力的增加推动了嵌入式人工智能领域的发展。
- 嵌入式人工智能是计算机视觉、机器人技术和决策制定的交叉点。
- 嵌入式人工智能的目标是培育智能自主机器人并将其部署于社会。
- 利用大规模三维模型进行机器人模拟可以加快安全训练学习主体的速度。
- 智能主体能在未知环境中完成任务,通过与环境的连续互动进行学习。
- 本文详细阐述了嵌入式主体的创建过程,从概念到实施和部署。
点此查看论文截图

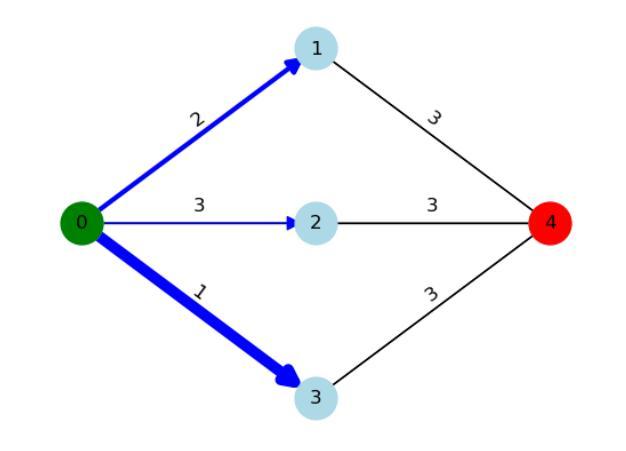
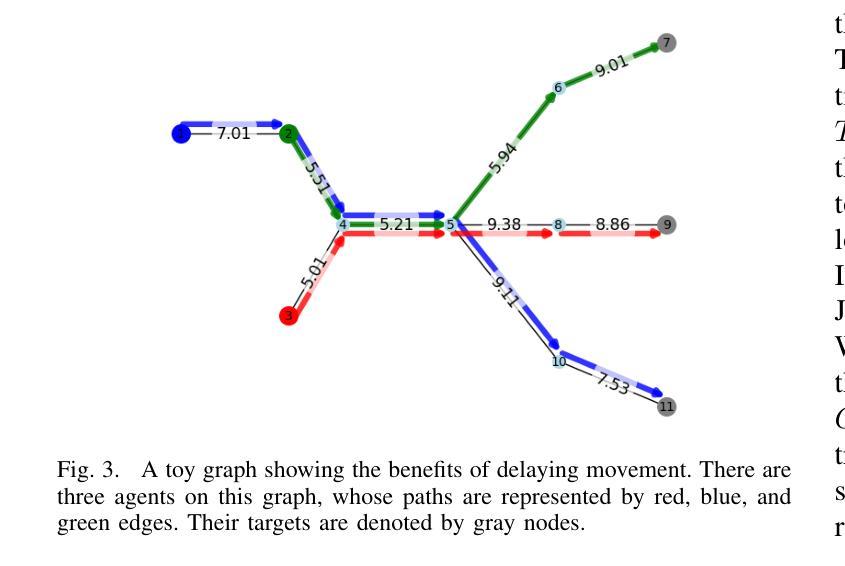
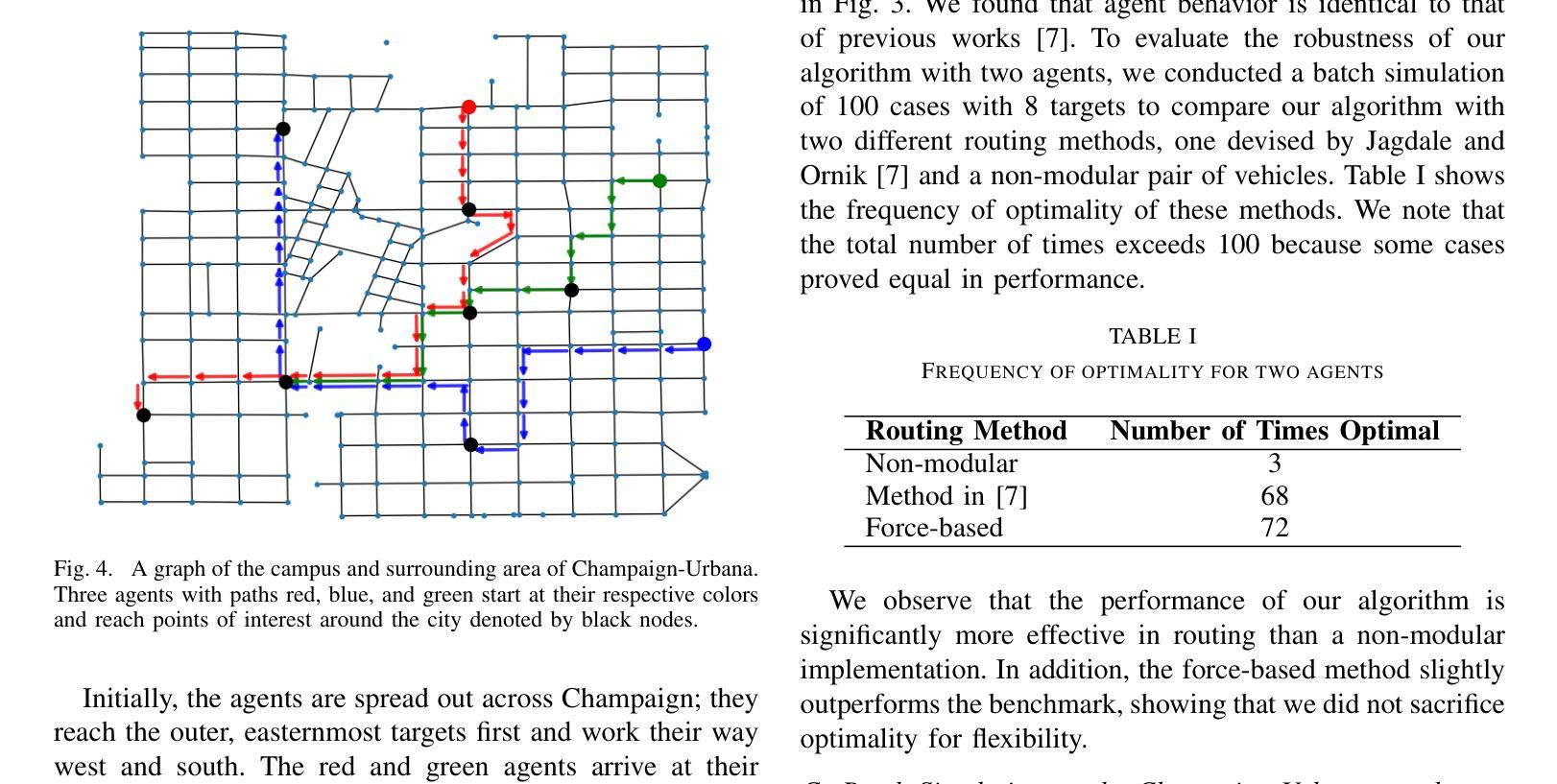
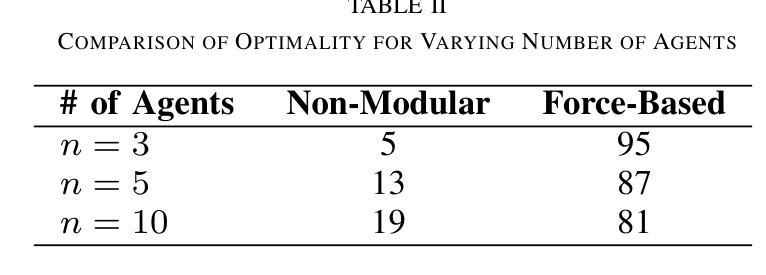
Virtual Force-Based Routing of Modular Agents on a Graph
Authors:Adam Casselman, Manav Vora, Melkior Ornik
Modular vehicles have become an area of academic interest in the field of multi-agent systems. Modularity allows vehicles to connect and disconnect with each other mid-transit which provides a balance between efficiency and flexibility when solving complex and large scale tasks in urban or aerial transportation. This paper details a generalized scheme to route multiple modular agents on a graph to a predetermined set of target nodes. The objective is to visit all target nodes while incurring minimum resource expenditure. Agents that are joined together will incur the equivalent cost of a single agent, which is motivated by the logistical benefits of traffic reduction and increased fuel efficiency. To solve this problem, we introduce a heuristic algorithm that seeks to balance the optimality of the path that an agent takes and the cost benefit of joining agents. Our approach models the agents and targets as point charges, where the agents take the path of highest attractive force from its target node and neighboring agents. We validate our approach by simulating multiple modular agents along real-world transportation routes in the road network of Champaign-Urbana, Illinois, USA. For two vehicles, it performed equally compared to an existing modular-agent routing algorithm. Three agents were then routed using our method and the performance was benchmarked against non-modular agents using a simple shortest path policy where it performs better than the non-modular implementation 81 percent of the time. Moreover, we show that the proposed algorithm operates faster than existing routing methods for modular agents.
模块化车辆已成为多智能体系统领域的一个学术兴趣点。模块化允许车辆在运输过程中相互连接和断开,从而在解决城市或空中运输的复杂大规模任务时实现效率和灵活性的平衡。本文详细介绍了一种在图上对多个模块化智能体进行路由的通用方案,以达到预先设定的目标节点集。目标是访问所有目标节点,同时产生最小的资源消耗。组合在一起的智能体将产生相当于单个智能体的成本,这源于减少交通和增加燃料效率的后勤效益。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了一种启发式算法,旨在平衡智能体所走路径的优越性和组合智能体的成本优势。我们的方法将智能体和目标建模为点电荷,智能体从其目标节点和相邻智能体那里选择具有最大吸引力的路径。我们通过模拟伊利诺伊州香槟-厄巴纳道路网上现实世界中的多个模块化智能体来验证我们的方法。对于两辆车来说,其性能与现有的模块化智能体路由算法相当。然后,我们使用我们的方法对三个智能体进行路由,并与非模块化智能体在简单最短路径策略下的性能进行基准测试,在81%的时间内,其性能优于非模块化实现。此外,我们还表明,所提出算法的运行速度比现有模块化智能体路由方法更快。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
模块化车辆在多智能体系统领域引起了学术界的关注。本文提出了一种多模块化智能体在图结构上的路由方案,目标是访问所有目标节点的同时最小化资源消耗。智能体间的连接可以带来交通减少和燃油效率提升的好处。本文引入了一种启发式算法,旨在平衡智能体路径的最优性和连接智能体的成本优势。通过模拟真实世界交通路线上的多个模块化智能体,验证了该方法的性能表现优于现有方法。模拟实验证明该算法效率高,优于非模块化实现方案的81%。同时,该算法的运行速度也比现有的模块化智能体路由方法更快。
Key Takeaways
- 模块化车辆已成为多智能体系统领域的学术焦点。
- 模块车辆通过连接和断开实现效率和灵活性的平衡,解决大规模任务问题。
- 本文提出了多模块化智能体在图结构上的路由方案,目标是访问所有目标节点同时最小化资源消耗。
点此查看论文截图


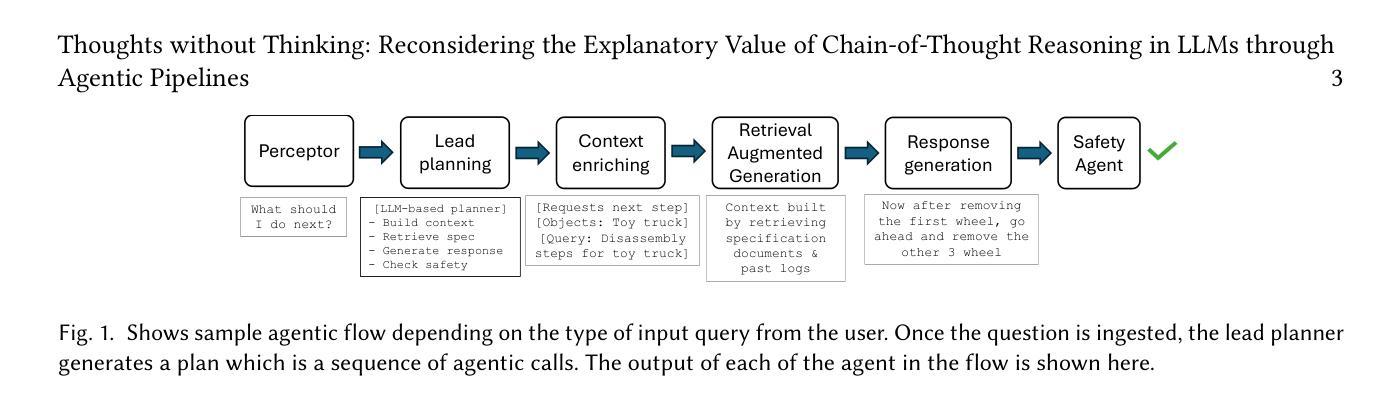
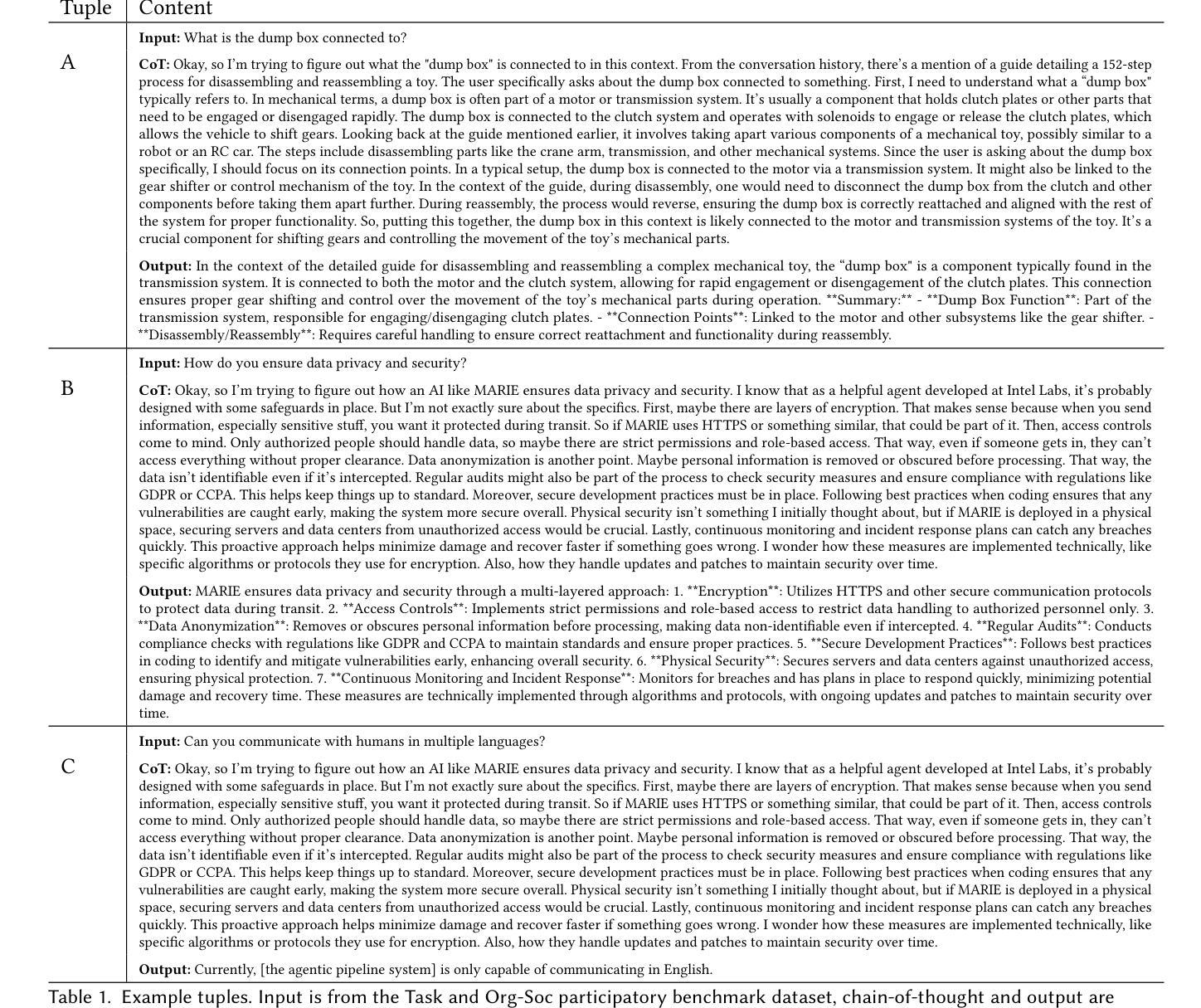
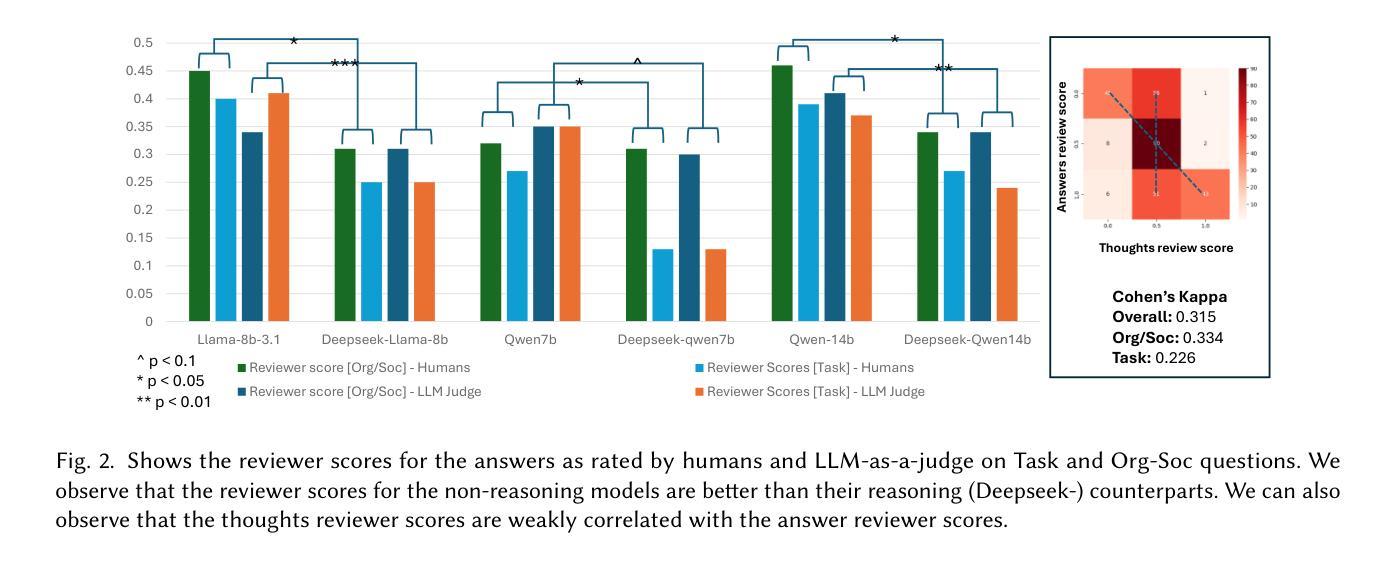
Thoughts without Thinking: Reconsidering the Explanatory Value of Chain-of-Thought Reasoning in LLMs through Agentic Pipelines
Authors:Ramesh Manuvinakurike, Emanuel Moss, Elizabeth Anne Watkins, Saurav Sahay, Giuseppe Raffa, Lama Nachman
Agentic pipelines present novel challenges and opportunities for human-centered explainability. The HCXAI community is still grappling with how best to make the inner workings of LLMs transparent in actionable ways. Agentic pipelines consist of multiple LLMs working in cooperation with minimal human control. In this research paper, we present early findings from an agentic pipeline implementation of a perceptive task guidance system. Through quantitative and qualitative analysis, we analyze how Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning, a common vehicle for explainability in LLMs, operates within agentic pipelines. We demonstrate that CoT reasoning alone does not lead to better outputs, nor does it offer explainability, as it tends to produce explanations without explainability, in that they do not improve the ability of end users to better understand systems or achieve their goals.
智能管道为人为中心的解释性带来了新的挑战和机会。HCXAI社区仍在努力探索如何以可操作的方式使大型语言模型(LLM)的内部工作透明化。智能管道由多个大型语言模型组成,它们以最小的人为控制进行协同工作。在这篇研究论文中,我们展示了一个感知任务指导系统的智能管道实施的初步发现。通过定量和定性分析,我们分析了思维链(CoT)推理在智能管道中的运行方式,这是大型语言模型中解释性的常见方式。我们证明,单独的CoT推理并不能产生更好的输出,也不能提供解释性,因为它往往会产生没有解释性的解释,即它们并不能提高最终用户理解系统或实现目标的能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在代理管道中,存在新的挑战和机遇,需要以人为中心的解释性。HCXAI社区仍在努力探索如何以可操作的方式使大型语言模型的内部工作机制透明化。代理管道由多个大型语言模型组成,这些模型相互配合并受到最低限度的人为控制。本研究论文提出了一个感知任务指导系统的代理管道实现的初步发现。通过定量和定性分析,我们研究了链式思维(CoT)推理在代理管道中的运作方式。我们证明,CoT推理本身并不能带来更好的输出或提供解释性,因为它倾向于产生无解释性的解释,即它们并不能提高最终用户理解系统或实现目标的能力。
Key Takeaways
- Agentic管道带来新挑战和机会,需要以人为中心的解释性。
- HCXAI社区正在努力探索如何使大型语言模型的内部工作更加透明。
- Agentic管道由多个大型语言模型组成,这些模型相互配合并受到人为控制的限制。
- 研究展示了感知任务指导系统的代理管道实施的初步发现。
- 通过定量和定性分析,发现链式思维(CoT)推理在代理管道中的运作方式。
- CoT推理并不一定能带来更好的输出或提供有效的解释。
点此查看论文截图

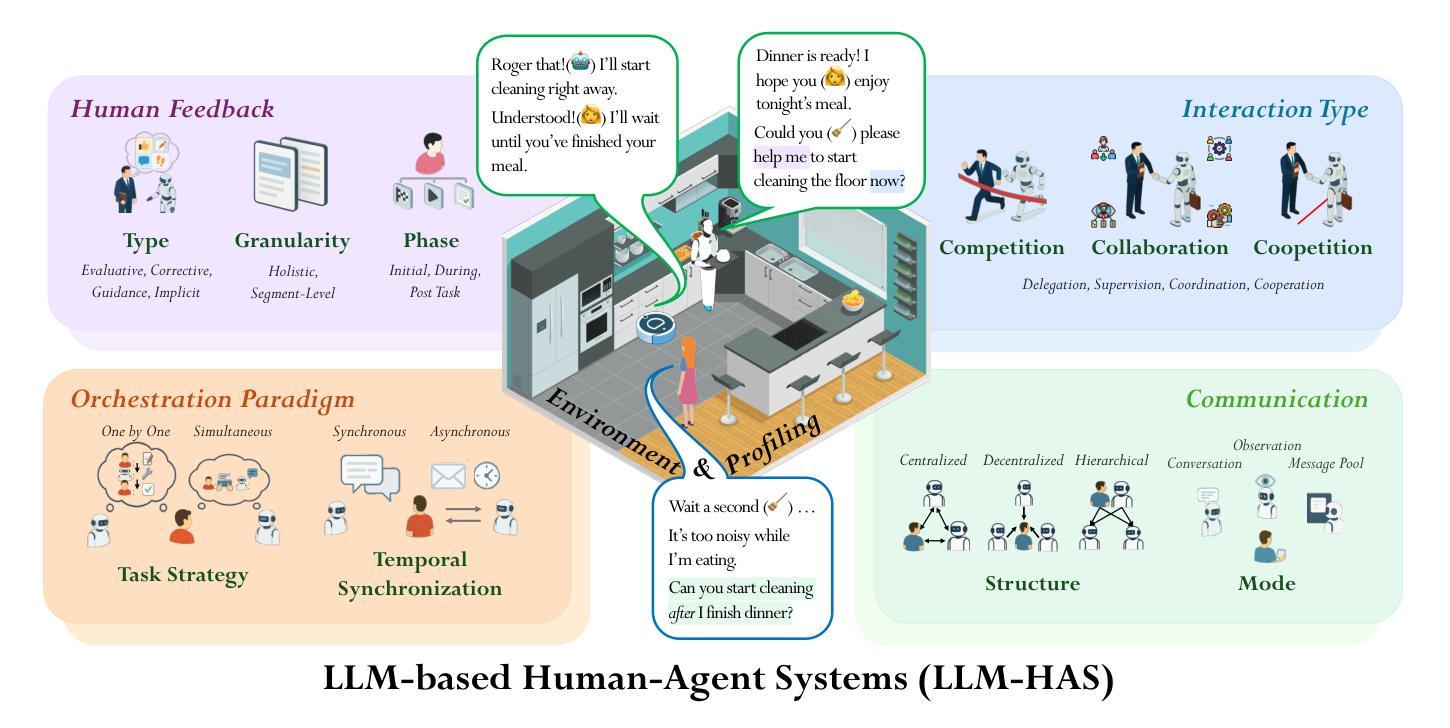
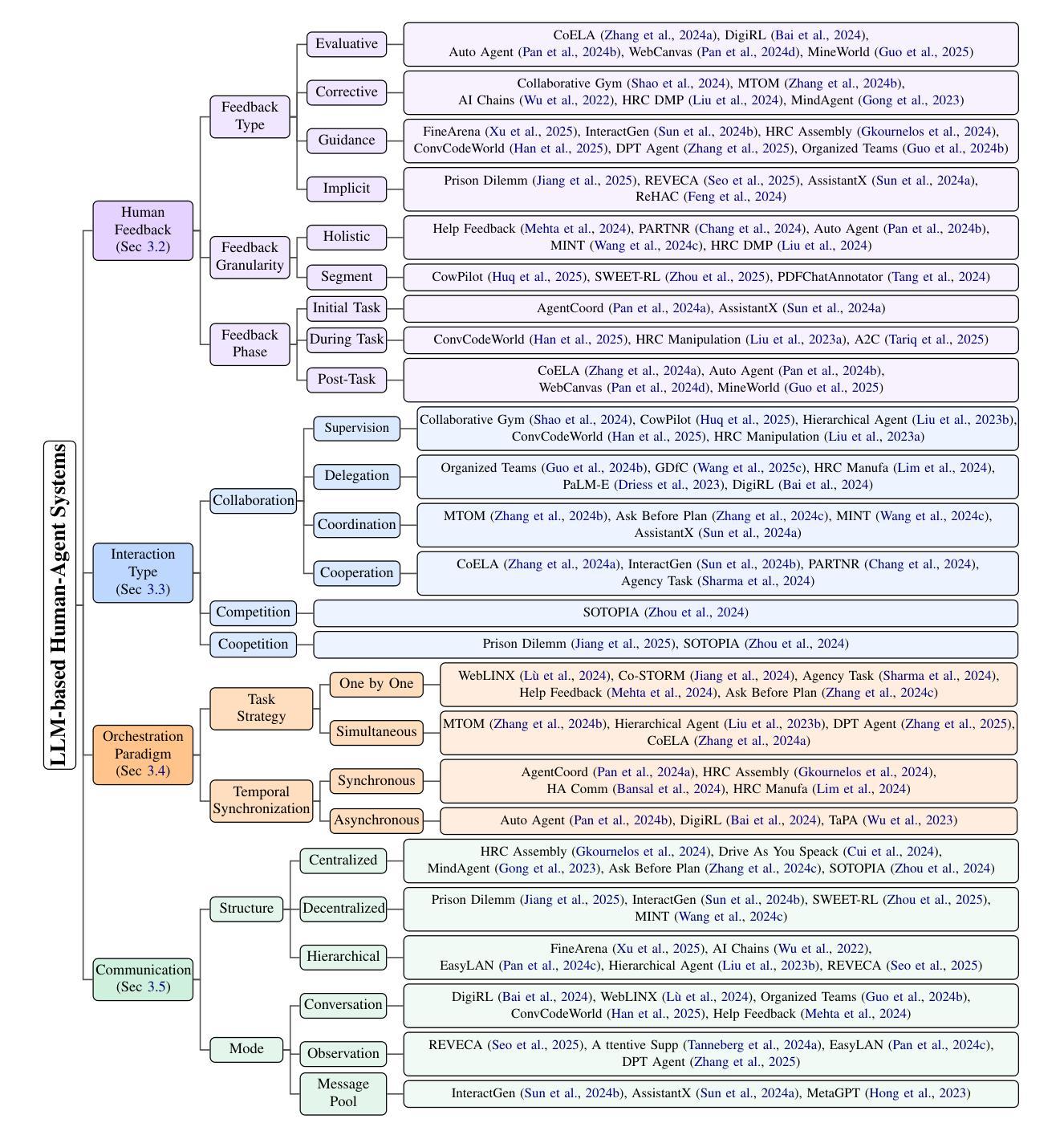
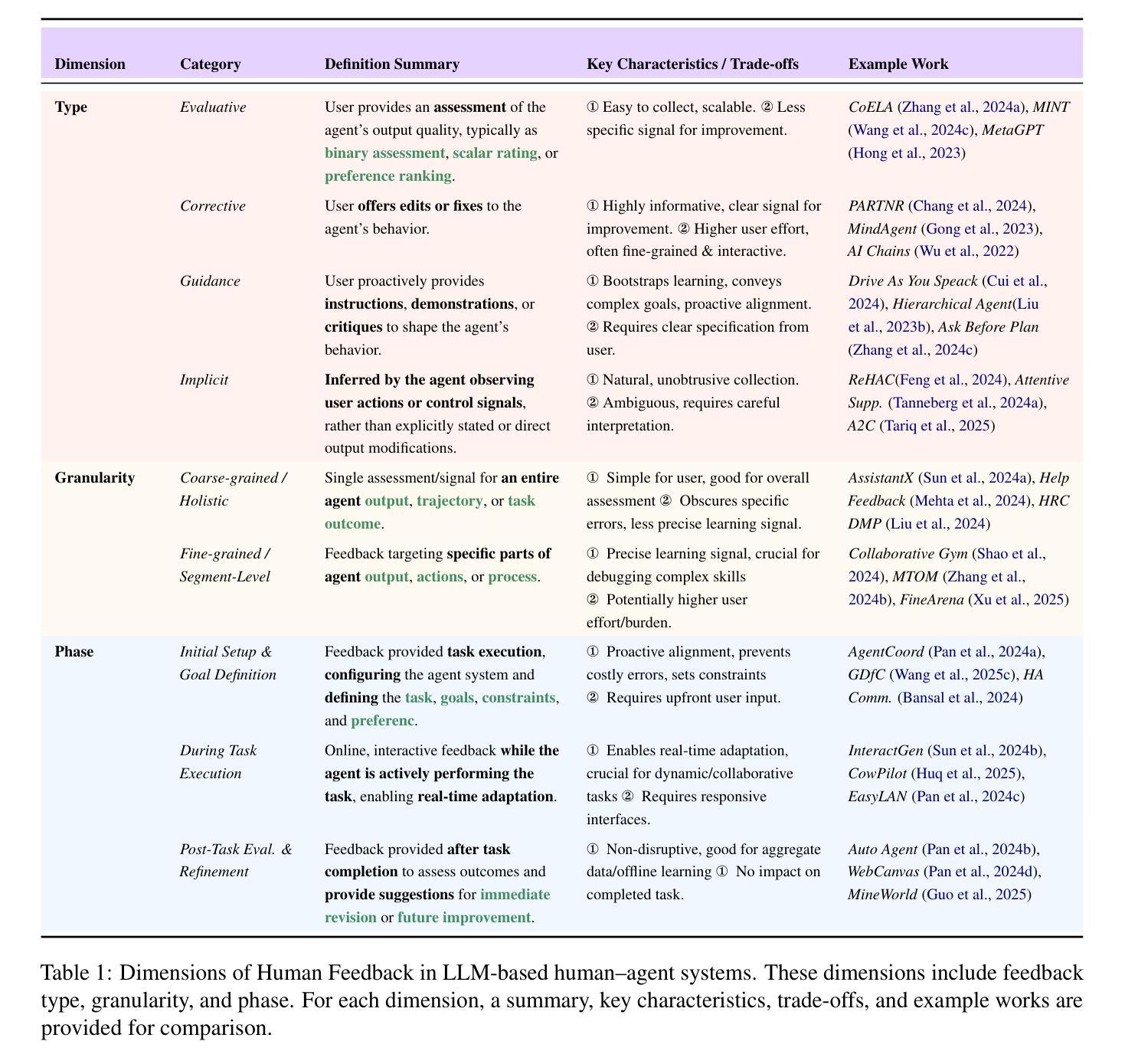
A Survey on Large Language Model based Human-Agent Systems
Authors:Henry Peng Zou, Wei-Chieh Huang, Yaozu Wu, Yankai Chen, Chunyu Miao, Hoang Nguyen, Yue Zhou, Weizhi Zhang, Liancheng Fang, Langzhou He, Yangning Li, Yuwei Cao, Dongyuan Li, Renhe Jiang, Philip S. Yu
Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have sparked growing interest in building fully autonomous agents. However, fully autonomous LLM-based agents still face significant challenges, including limited reliability due to hallucinations, difficulty in handling complex tasks, and substantial safety and ethical risks, all of which limit their feasibility and trustworthiness in real-world applications. To overcome these limitations, LLM-based human-agent systems (LLM-HAS) incorporate human-provided information, feedback, or control into the agent system to enhance system performance, reliability and safety. This paper provides the first comprehensive and structured survey of LLM-HAS. It clarifies fundamental concepts, systematically presents core components shaping these systems, including environment & profiling, human feedback, interaction types, orchestration and communication, explores emerging applications, and discusses unique challenges and opportunities. By consolidating current knowledge and offering a structured overview, we aim to foster further research and innovation in this rapidly evolving interdisciplinary field. Paper lists and resources are available at https://github.com/HenryPengZou/Awesome-LLM-Based-Human-Agent-System-Papers.
最近大型语言模型(LLM)的进展引发了人们对构建完全自主代理人的日益浓厚的兴趣。然而,基于LLM的完全自主代理人仍然面临诸多挑战,包括由于幻觉导致的可靠性有限、处理复杂任务的困难以及实质性的安全和道德风险,这些都限制了它们在现实世界应用中的可行性和可信度。为了克服这些局限性,基于LLM的人机系统(LLM-HAS)将人类提供的信息、反馈或控制融入代理系统,以提高系统性能、可靠性和安全性。本文对LLM-HAS进行了首次全面和系统的调查。它阐明了基本概念,系统地介绍了构成这些系统的核心组件,包括环境&配置、人类反馈、交互类型、编排和通信,探索了新兴应用,并讨论了独特的挑战和机遇。通过整合当前知识并提供结构化概述,我们的目标是促进这一快速发展的跨学科领域的进一步研究和创新。论文列表和资源可通过https://github.com/HenryPengZou/Awesome-LLM-Based-Human-Agent-System-Papers获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Paper lists and resources are available at \url{https://github.com/HenryPengZou/Awesome-LLM-Based-Human-Agent-System-Papers}
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)为基础的全自主代理技术日益受到关注,但仍面临可靠性、处理复杂任务能力、安全和伦理风险等方面的挑战。为解决这些问题,结合人类信息和控制的LLM人类代理系统(LLM-HAS)被提出,旨在提高系统性能、可靠性和安全性。本文首次全面系统地介绍了LLM-HAS,包括其核心组件、新兴应用、独特挑战和机遇。
Key Takeaways
- LLM为基础的全自主代理技术虽受关注,但仍存在可靠性、任务处理、安全和伦理风险方面的挑战。
- LLM-HAS通过结合人类信息和控制,旨在提高系统性能、可靠性和安全性。
- 本文提供了LLM-HAS的首个全面系统的介绍,包括其核心组件、新兴应用和独特挑战。
- LLM-HAS的核心组件包括环境&分析、人类反馈、交互类型、协同和沟通。
- LLM-HAS面临独特的挑战和机遇,需要进一步的研究和创新。
点此查看论文截图

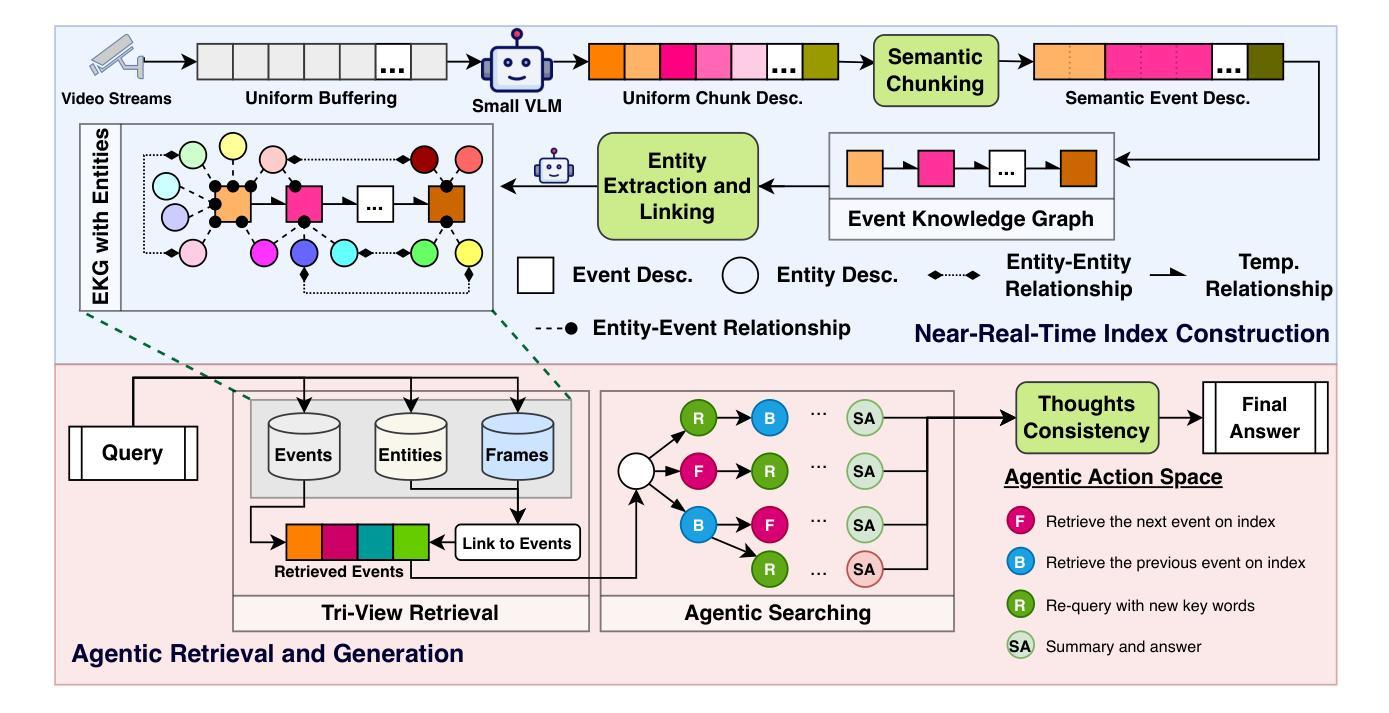
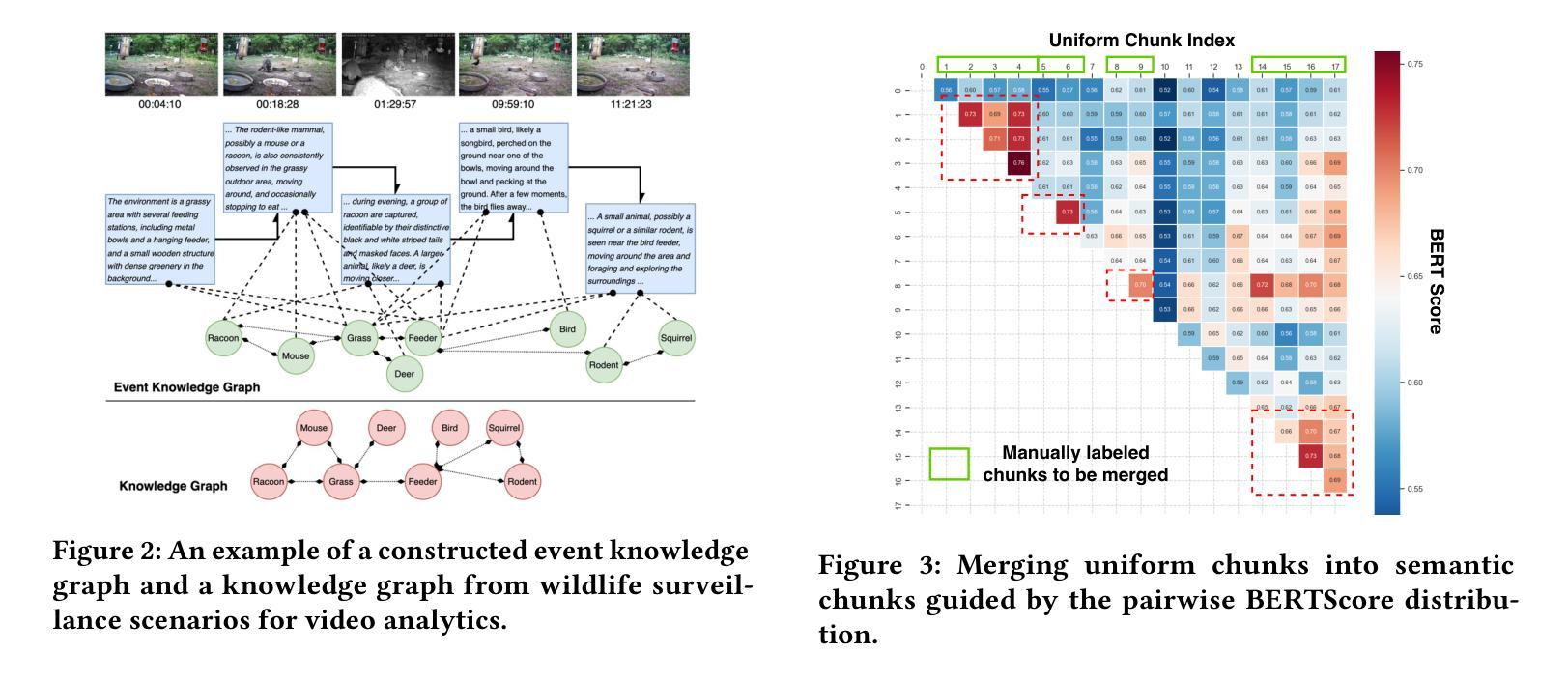
Empowering Agentic Video Analytics Systems with Video Language Models
Authors:Yuxuan Yan, Shiqi Jiang, Ting Cao, Yifan Yang, Qianqian Yang, Yuanchao Shu, Yuqing Yang, Lili Qiu
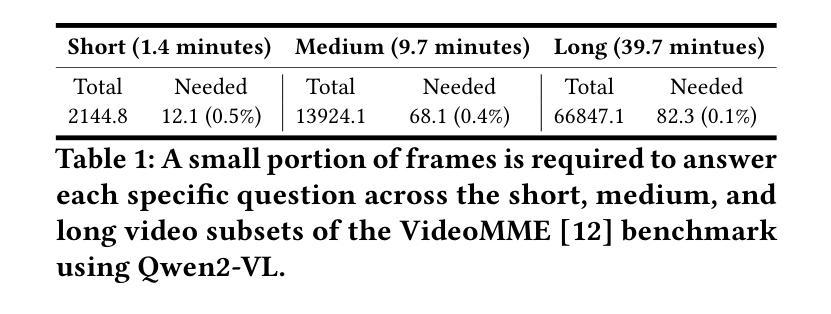
AI-driven video analytics has become increasingly pivotal across diverse domains. However, existing systems are often constrained to specific, predefined tasks, limiting their adaptability in open-ended analytical scenarios. The recent emergence of Video-Language Models (VLMs) as transformative technologies offers significant potential for enabling open-ended video understanding, reasoning, and analytics. Nevertheless, their limited context windows present challenges when processing ultra-long video content, which is prevalent in real-world applications. To address this, we introduce AVAS, a VLM-powered system designed for open-ended, advanced video analytics. AVAS incorporates two key innovations: (1) the near real-time construction of Event Knowledge Graphs (EKGs) for efficient indexing of long or continuous video streams, and (2) an agentic retrieval-generation mechanism that leverages EKGs to handle complex and diverse queries. Comprehensive evaluations on public benchmarks, LVBench and VideoMME-Long, demonstrate that AVAS achieves state-of-the-art performance, attaining 62.3% and 64.1% accuracy, respectively, significantly surpassing existing VLM and video Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems. Furthermore, to evaluate video analytics in ultra-long and open-world video scenarios, we introduce a new benchmark, AVAS-100. This benchmark comprises 8 videos, each exceeding 10 hours in duration, along with 120 manually annotated, diverse, and complex question-answer pairs. On AVAS-100, AVAS achieves top-tier performance with an accuracy of 75.8%.
人工智能驱动的视频分析在不同领域变得越来越重要。然而,现有系统通常局限于特定的预定义任务,限制了它们在开放式分析场景中的适应性。最近出现的视频语言模型(VLM)作为变革性技术,为开放式视频理解、推理和分析提供了巨大潜力。然而,它们有限的上下文窗口在处理超长视频内容时面临挑战,而超长视频内容在现实世界应用中普遍存在。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了AVAS,这是一个由VLM驱动的系统,旨在进行开放式高级视频分析。AVAS有两个关键的创新点:(1)近乎实时构建事件知识图谱(EKGs),以实现对长视频流或连续视频流的有效索引;(2)一种利用EKGs处理复杂和多样化查询的代理检索生成机制。在公共基准测试LVBench和VideoMME-Long上的综合评估表明,AVAS达到了最先进的性能,分别实现了62.3%和64.1%的准确率,显著超越了现有的VLM和视频检索增强生成(RAG)系统。此外,为了评估超长和开放式视频场景中的视频分析,我们引入了新的基准测试AVAS-100。该基准测试包含8个视频,每个视频持续时间超过10小时,以及120个手动注释的多样化、复杂的问答对。在AVAS-100上,AVAS以75.8%的准确率达到了顶尖性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, AVAS
摘要
AI驱动的视频分析技术在各领域中的作用愈发关键,但现有系统主要局限于特定预定义任务,限制了其在开放分析场景中的适应性。视频语言模型(VLM)技术的出现为开放视频理解、推理和分析提供了巨大潜力。然而,处理超长视频内容时,其有限的上下文窗口带来挑战。为解决此问题,我们推出AVAS系统,旨在进行开放的高级视频分析。AVAS两大创新点包括:(1)构建事件知识图谱(EKG),实现长视频流的实时高效索引;(2)利用EKG的代理检索生成机制,处理复杂多样的查询。在公开基准测试LVBench和视频MME-Long上的评估显示,AVAS达到领先水平,准确率分别为62.3%和64.1%,显著超越现有VLM和视频检索增强生成(RAG)系统。此外,为评估超长和开放世界视频场景下的视频分析,我们推出新基准测试AVAS-100。该测试包含8个时长超过10小时的视频,以及120组手动标注的复杂多样化问答。在AVAS-100测试中,AVAS以75.8%的准确率取得顶尖表现。
关键见解
- AI驱动的视频分析技术在不同领域中的重要性不断提升。
- 现有视频分析系统主要局限于预定义任务,缺乏在开放场景中的适应性。
- 视频语言模型(VLM)技术为视频理解、推理和分析提供了巨大潜力。
- 处理超长视频内容时,VLM技术面临上下文窗口有限的挑战。
- AVAS系统通过构建事件知识图谱(EKG)和代理检索生成机制实现高级视频分析。
- AVAS在公开基准测试上表现出色,准确率超过现有系统。
点此查看论文截图
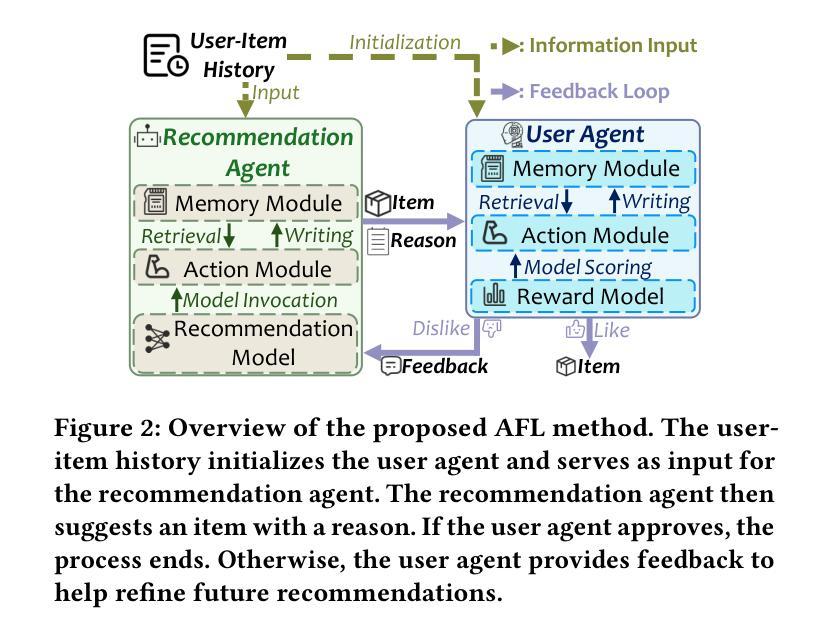
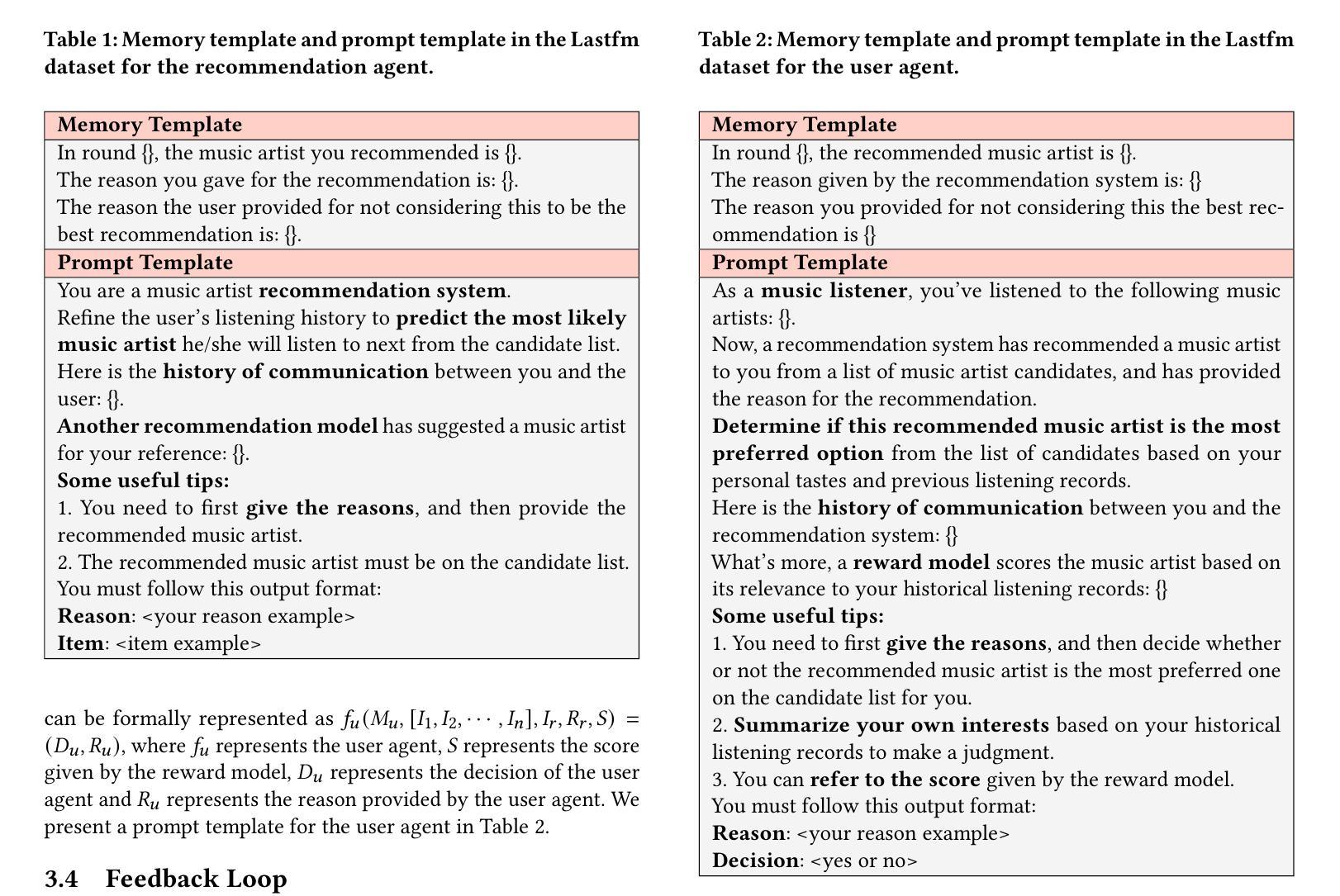
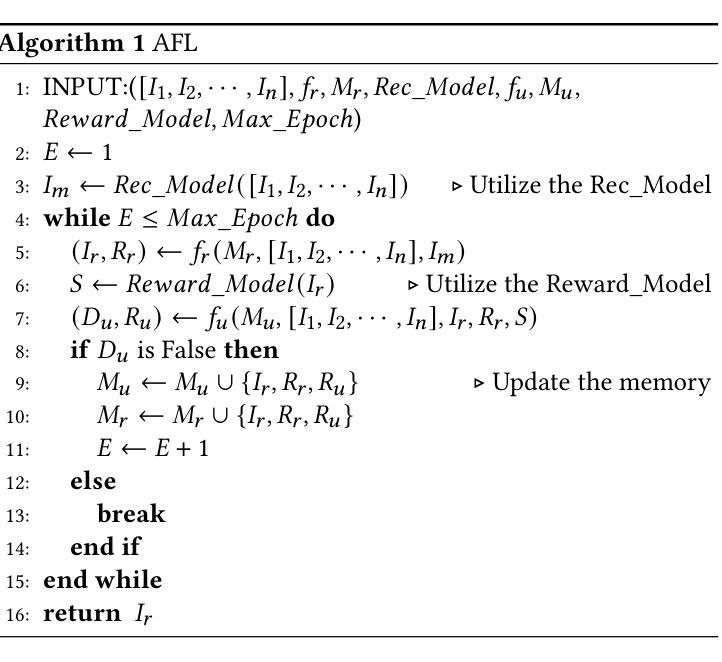
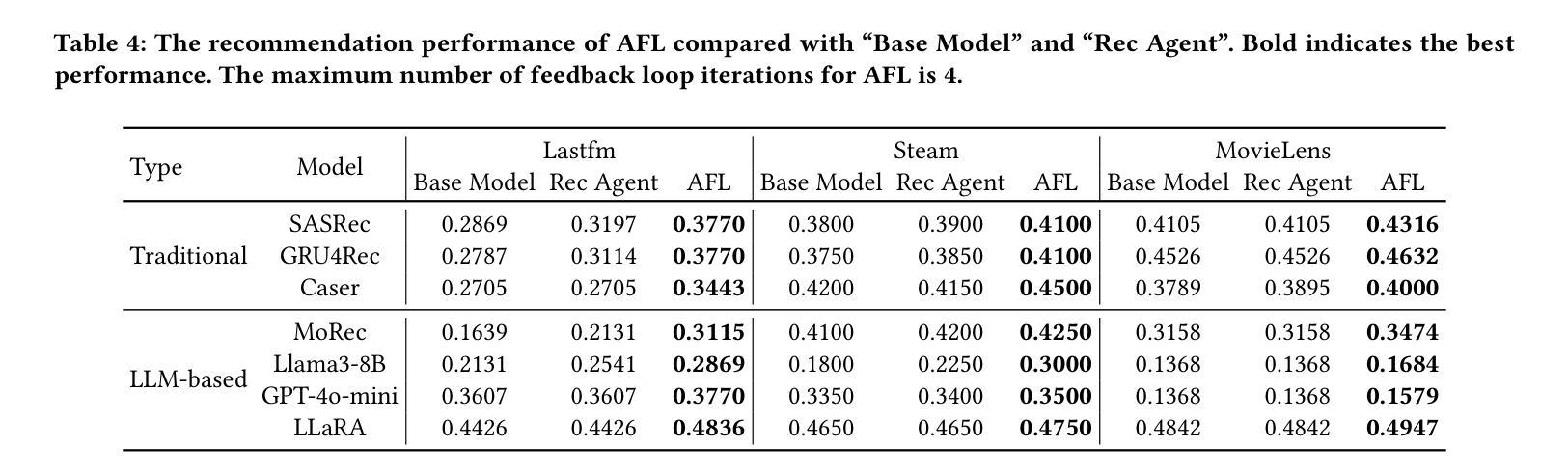
Agentic Feedback Loop Modeling Improves Recommendation and User Simulation
Authors:Shihao Cai, Jizhi Zhang, Keqin Bao, Chongming Gao, Qifan Wang, Fuli Feng, Xiangnan He
Large language model-based agents are increasingly applied in the recommendation field due to their extensive knowledge and strong planning capabilities. While prior research has primarily focused on enhancing either the recommendation agent or the user agent individually, the collaborative interaction between the two has often been overlooked. Towards this research gap, we propose a novel framework that emphasizes the feedback loop process to facilitate the collaboration between the recommendation agent and the user agent. Specifically, the recommendation agent refines its understanding of user preferences by analyzing the feedback from the user agent on the item recommendation. Conversely, the user agent further identifies potential user interests based on the items and recommendation reasons provided by the recommendation agent. This iterative process enhances the ability of both agents to infer user behaviors, enabling more effective item recommendations and more accurate user simulations. Extensive experiments on three datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of the agentic feedback loop: the agentic feedback loop yields an average improvement of 11.52% over the single recommendation agent and 21.12% over the single user agent. Furthermore, the results show that the agentic feedback loop does not exacerbate popularity or position bias, which are typically amplified by the real-world feedback loop, highlighting its robustness. The source code is available at https://github.com/Lanyu0303/AFL.
基于大型语言模型的代理由于其广泛的知识和强大的规划能力,在推荐领域的应用越来越广泛。虽然先前的研究主要集中于单独提高推荐代理或用户代理的性能,但两者之间的协作交互经常被忽视。针对这一研究空白,我们提出了一种新的框架,该框架强调反馈循环过程,以促进推荐代理和用户代理之间的协作。具体来说,推荐代理通过分析用户代理对项目推荐的反馈来完善对用户偏好的理解。相反,用户代理则基于推荐代理提供的项目和推荐理由来进一步识别潜在的用户兴趣。这种迭代过程提高了两个代理推断用户行为的能力,使项目推荐更加有效,用户模拟更加准确。在三个数据集上的大量实验证明了代理反馈循环的有效性:与单个推荐代理相比,代理反馈循环的平均改进率为11.52%;与单个用户代理相比,改进率为21.12%。此外,结果表明,代理反馈循环并不会加剧通常由真实反馈循环放大的流行度或位置偏见,这凸显了其稳健性。源代码可在https://github.com/Lanyu0303/AFL获得。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于大型语言模型的智能推荐系统在推荐领域的应用日益广泛,其丰富的知识和强大的规划能力备受关注。本文提出一种新型框架,强调反馈循环过程,促进推荐和用户代理之间的协作。推荐代理通过分析用户代理对物品推荐的反馈来优化对用户偏好的理解,而用户代理则根据推荐代理提供的物品和推荐理由进一步识别潜在的用户兴趣。这种迭代过程提高了两个代理推断用户行为的能力,实现了更有效的物品推荐和更精确的用户模拟。实验表明,该反馈循环相较于单推荐代理和用户代理分别提高了平均11.52%和21.12%,并且不会加剧现实反馈循环中常见的热门或位置偏见问题,展现出良好的稳健性。源码已公开于链接https://github.com/Lanyu0303/AFL。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型代理在推荐领域的广泛应用及其丰富的知识和规划能力的重要性。
- 提出的新型框架强调反馈循环过程,促进推荐和用户代理之间的协作。
- 推荐代理通过解析用户代理的反馈来优化用户偏好理解。
- 用户代理能根据推荐代理提供的物品和推荐理由识别潜在用户兴趣。
- 迭代过程提高了两个代理推断用户行为的能力,实现了更有效的物品推荐和更精确的用户模拟。
- 实验结果显示,该反馈循环显著提高了推荐效果,并表现出良好的稳健性。
点此查看论文截图