⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-06 更新
TRAVELER: A Benchmark for Evaluating Temporal Reasoning across Vague, Implicit and Explicit References
Authors:Svenja Kenneweg, Jörg Deigmöller, Philipp Cimiano, Julian Eggert
Understanding and resolving temporal references is essential in Natural Language Understanding as we often refer to the past or future in daily communication. Although existing benchmarks address a system’s ability to reason about and resolve temporal references, systematic evaluation of specific temporal references remains limited. Towards closing this gap, we introduce TRAVELER, a novel synthetic benchmark dataset that follows a Question Answering paradigm and consists of questions involving temporal references with the corresponding correct answers. TRAVELER assesses models’ abilities to resolve explicit, implicit relative to speech time, and vague temporal references. Beyond investigating the performance of state-of-the-art LLMs depending on the type of temporal reference, our benchmark also allows evaluation of performance in relation to the length of the set of events. For the category of vague temporal references, ground-truth answers were established via human surveys on Prolific, following a procedure similar to the one from Kenneweg et al. To demonstrate the benchmark’s applicability, we evaluate four state-of-the-art LLMs using a question-answering task encompassing 3,300 questions. Our findings show that while the benchmarked LLMs can answer questions over event sets with a handful of events and explicit temporal references successfully, performance clearly deteriorates with larger event set length and when temporal references get less explicit. Notably, the vague question category exhibits the lowest performance across all models. The benchmark is publicly available at: https://gitlab.ub.uni-bielefeld.de/s.kenneweg/TRAVELER
理解和解决时间参照对于自然语言理解至关重要,因为我们在日常交流中经常提及过去或未来。尽管现有的基准测试可以评估系统在推理和解决时间参照方面的能力,但对特定时间参照的评估仍然有限。为了缩小这一差距,我们引入了旅行者(TRAVELER)这一新型合成基准数据集,它遵循问答模式,包含涉及时间参照的问题和相应的正确答案。旅行者评估模型解决明确时间参照、隐含相对语时和模糊时间参照的能力。除了根据时间参照类型调查当前最前沿的大型语言模型性能外,我们的基准测试还允许根据事件集长度评估性能。对于模糊时间参照类别,我们通过Prolific上的人类调查来确定真实答案,采用与Kenneweg等人相似的方法。为了证明基准测试的适用性,我们使用包含3300个问题的问答任务评估了四种最前沿的大型语言模型。我们的研究结果表明,虽然所评估的大型语言模型能够成功回答涉及少量事件和明确时间参照的事件集问题,但随着事件集长度的增加和时间参照的模糊性增加,性能明显下降。值得注意的是,模糊问题类别在所有模型中的表现最差。基准测试公开可用:https://gitlab.ub.uni-bielefeld.de/s.kenneweg/TRAVELER。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 24 pages, 6 figures, submitted to Springer Nature Computer Science
Summary
本文介绍了理解并解决时间参考在自然语言理解中的重要性。为解决现有时间参考解析的评估缺口,提出一个名为“旅行者”(TRAVELER)的新合成基准数据集。该数据集遵循问答模式,包含涉及不同类型时间引用的相关问题及其正确答案。旅行者不仅评估模型对明确、隐含和模糊时间引用的解析能力,还允许根据事件集的长度评估性能。为模糊时间引用类别,通过类似人类调查的方式建立基准答案。为了证明该基准的适用性,对四种先进的LLMS进行了评估。发现虽然这些模型可以成功回答涉及少量事件和明确时间引用的问绝,但随着事件集长度的增加和时间引用的不明确性,性能明显下降。特别是模糊问题类别的表现尤为不佳。该基准数据集已在指定链接中公开。
Key Takeaways
- 时间参考理解和解析在自然语言处理中至关重要。
- 现有时间参考解析的评估标准存在缺口。
- 引入新的合成基准数据集“旅行者”(TRAVELER),用于评估模型处理不同类型时间引用的能力。
- 旅行者评估模型在解决明确、隐含和模糊时间引用方面的能力。
- 旅行者允许根据事件集的长度评估性能差异。
- 通过类似的人类调查方式确定模糊时间引用的基准答案。
点此查看论文截图

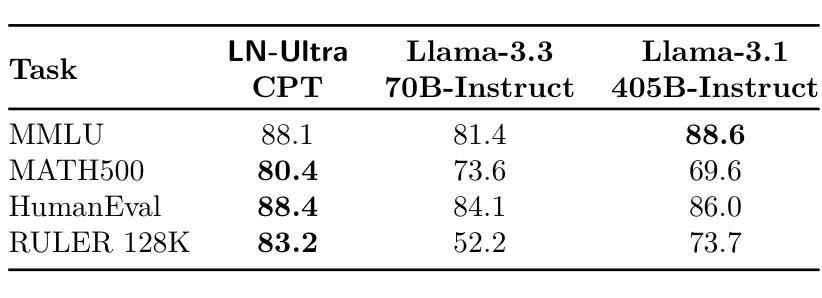
Llama-Nemotron: Efficient Reasoning Models
Authors:Akhiad Bercovich, Itay Levy, Izik Golan, Mohammad Dabbah, Ran El-Yaniv, Omri Puny, Ido Galil, Zach Moshe, Tomer Ronen, Najeeb Nabwani, Ido Shahaf, Oren Tropp, Ehud Karpas, Ran Zilberstein, Jiaqi Zeng, Soumye Singhal, Alexander Bukharin, Yian Zhang, Tugrul Konuk, Gerald Shen, Ameya Sunil Mahabaleshwarkar, Bilal Kartal, Yoshi Suhara, Olivier Delalleau, Zijia Chen, Zhilin Wang, David Mosallanezhad, Adi Renduchintala, Haifeng Qian, Dima Rekesh, Fei Jia, Somshubra Majumdar, Vahid Noroozi, Wasi Uddin Ahmad, Sean Narenthiran, Aleksander Ficek, Mehrzad Samadi, Jocelyn Huang, Siddhartha Jain, Igor Gitman, Ivan Moshkov, Wei Du, Shubham Toshniwal, George Armstrong, Branislav Kisacanin, Matvei Novikov, Daria Gitman, Evelina Bakhturina, Jane Polak Scowcroft, John Kamalu, Dan Su, Kezhi Kong, Markus Kliegl, Rabeeh Karimi, Ying Lin, Sanjeev Satheesh, Jupinder Parmar, Pritam Gundecha, Brandon Norick, Joseph Jennings, Shrimai Prabhumoye, Syeda Nahida Akter, Mostofa Patwary, Abhinav Khattar, Deepak Narayanan, Roger Waleffe, Jimmy Zhang, Bor-Yiing Su, Guyue Huang, Terry Kong, Parth Chadha, Sahil Jain, Christine Harvey, Elad Segal, Jining Huang, Sergey Kashirsky, Robert McQueen, Izzy Putterman, George Lam, Arun Venkatesan, Sherry Wu, Vinh Nguyen, Manoj Kilaru, Andrew Wang, Anna Warno, Abhilash Somasamudramath, Sandip Bhaskar, Maka Dong, Nave Assaf, Shahar Mor, Omer Ullman Argov, Scot Junkin, Oleksandr Romanenko, Pedro Larroy, Monika Katariya, Marco Rovinelli, Viji Balas, Nicholas Edelman, Anahita Bhiwandiwalla, Muthu Subramaniam, Smita Ithape, Karthik Ramamoorthy, Yuting Wu, Suguna Varshini Velury, Omri Almog, Joyjit Daw, Denys Fridman, Erick Galinkin, Michael Evans, Katherine Luna, Leon Derczynski, Nikki Pope, Eileen Long, Seth Schneider, Guillermo Siman, Tomasz Grzegorzek, Pablo Ribalta, Monika Katariya, Joey Conway, Trisha Saar, Ann Guan, Krzysztof Pawelec, Shyamala Prayaga, Oleksii Kuchaiev, Boris Ginsburg, Oluwatobi Olabiyi, Kari Briski, Jonathan Cohen, Bryan Catanzaro, Jonah Alben, Yonatan Geifman, Eric Chung
We introduce the Llama-Nemotron series of models, an open family of heterogeneous reasoning models that deliver exceptional reasoning capabilities, inference efficiency, and an open license for enterprise use. The family comes in three sizes – Nano (8B), Super (49B), and Ultra (253B) – and performs competitively with state-of-the-art reasoning models such as DeepSeek-R1 while offering superior inference throughput and memory efficiency. In this report, we discuss the training procedure for these models, which entails using neural architecture search from Llama 3 models for accelerated inference, knowledge distillation, and continued pretraining, followed by a reasoning-focused post-training stage consisting of two main parts: supervised fine-tuning and large scale reinforcement learning. Llama-Nemotron models are the first open-source models to support a dynamic reasoning toggle, allowing users to switch between standard chat and reasoning modes during inference. To further support open research and facilitate model development, we provide the following resources: 1. We release the Llama-Nemotron reasoning models – LN-Nano, LN-Super, and LN-Ultra – under the commercially permissive NVIDIA Open Model License Agreement. 2. We release the complete post-training dataset: Llama-Nemotron-Post-Training-Dataset. 3. We also release our training codebases: NeMo, NeMo-Aligner, and Megatron-LM.
我们介绍了Llama-Nemotron系列模型,这是一个开放的异质推理模型家族,具有出色的推理能力、推理效率和开放的企业使用许可。该系列有三种型号:Nano(8B)、Super(49B)和Ultra(253B),与DeepSeek-R1等最先进的推理模型相比具有竞争力,同时提供卓越的推理吞吐量和内存效率。在本报告中,我们讨论了这些模型的训练流程,包括使用Llama 3模型的神经网络架构搜索以加速推理、知识蒸馏和持续预训练,随后是注重推理的后期训练阶段,包括两个主要部分:监督微调和大规模增强学习。Llama-Nemotron模型是第一个支持动态推理切换的开源模型,允许用户在推理过程中切换标准聊天和推理模式。为了进一步支持开放研究和促进模型开发,我们提供了以下资源:1.我们在商业许可的NVIDIA开放模型许可协议下发布了Llama-Nemotron推理模型——LN-Nano、LN-Super和LN-Ultra。2.我们发布了完整的后期训练数据集:Llama-Nemotron-Post-Training-Dataset。3.我们还发布了我们的训练代码库:NeMo、NeMo-Aligner和Megatron-LM。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于Llama 3模型的神经网络架构搜索、知识蒸馏和持续预训练等训练程序,我们推出了Llama-Nemotron系列模型,包括Nano、Super和Ultra三种规模。该系列模型具备出色的推理能力、推理效率和开放企业使用许可。它们是第一个支持动态推理切换的开源模型,可在推理过程中在标准聊天和推理模式之间进行切换。
Key Takeaways
- Llama-Nemotron系列模型是一个开放的异质推理模型家族,提供Nano、Super和Ultra三种规模,具有出色的推理能力和效率。
- 该系列模型采用Llama 3模型的神经网络架构搜索进行加速推理,并结合知识蒸馏和持续预训练。
- 模型在推理聚焦的后训练阶段包括监督微调和大规模强化学习两个主要部分。
- Llama-Nemotron模型是第一个支持动态推理切换的开源模型,用户可在推理过程中在标准聊天和推理模式之间切换。
- 模型资源包括发布Llama-Nemotron推理模型(LN-Nano、LN-Super、LN-Ultra)、完整的后训练数据集以及训练代码库。
- 模型采用NVIDIA的开放模型许可协议,允许商业使用。
点此查看论文截图

Autonomous Embodied Agents: When Robotics Meets Deep Learning Reasoning
Authors:Roberto Bigazzi
The increase in available computing power and the Deep Learning revolution have allowed the exploration of new topics and frontiers in Artificial Intelligence research. A new field called Embodied Artificial Intelligence, which places at the intersection of Computer Vision, Robotics, and Decision Making, has been gaining importance during the last few years, as it aims to foster the development of smart autonomous robots and their deployment in society. The recent availability of large collections of 3D models for photorealistic robotic simulation has allowed faster and safe training of learning-based agents for millions of frames and a careful evaluation of their behavior before deploying the models on real robotic platforms. These intelligent agents are intended to perform a certain task in a possibly unknown environment. To this end, during the training in simulation, the agents learn to perform continuous interactions with the surroundings, such as gathering information from the environment, encoding and extracting useful cues for the task, and performing actions towards the final goal; where every action of the agent influences the interactions. This dissertation follows the complete creation process of embodied agents for indoor environments, from their concept to their implementation and deployment. We aim to contribute to research in Embodied AI and autonomous agents, in order to foster future work in this field. We present a detailed analysis of the procedure behind implementing an intelligent embodied agent, comprehending a thorough description of the current state-of-the-art in literature, technical explanations of the proposed methods, and accurate experimental studies on relevant robotic tasks.
计算能力的增强和深度学习的革命为人工智能研究带来了新的课题和前沿领域。一个名为“实体人工智能”的新领域在计算机视觉、机器人技术和决策制定的交汇点应运而生,并在过去几年中越来越重要。实体人工智能旨在促进智能自主机器人的发展及其在社会的部署。最近出现的庞大三维模型集合,可用于创建逼真的机器人模拟,这允许基于学习的代理进行更快、更安全的训练,并在实际机器人平台上部署前对行为进行评估。这些智能代理旨在在一个可能未知的环境中执行特定任务。为此,代理在模拟训练期间学习不断与周围环境进行交互,例如从环境中收集信息、编码和提取任务的有用线索以及朝着最终目标采取行动;代理的每个行动都会影响其交互方式。本论文将跟踪实体代理在室内环境中的完整创建过程,从概念到实施和部署。我们旨在为实体人工智能和自主代理的研究做出贡献,以促进该领域的未来发展。我们详细分析了实现智能实体代理的程序背后的步骤,包括对当前文献的彻底描述、所提出方法的技术解释以及关于相关机器人任务的精确实验性研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Ph.D. Dissertation
Summary
深度学习革命和计算能力的提升推动了人工智能新领域——具象人工智能的发展。该领域旨在培育智能自主机器人及其在社会的部署。利用大量3D模型进行逼真的机器人模拟,可以更快、更安全地对基于学习的代理进行训练,并对其行为进行仔细评估,再部署到真实的机器人平台上。该领域的目标是贡献于具象人工智能和自主代理的研究,以推动未来在这一领域的工作。本文详细阐述了构建室内环境具象代理的完整过程,从概念到实施和部署。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习革命和计算能力的提升推动了人工智能新领域的发展,即具象人工智能。
- 具象人工智能的目标在于培育智能自主机器人及其在社会的部署。
- 利用大量3D模型进行逼真的机器人模拟可以更快、更安全地训练基于学习的代理。
- 智能代理在模拟环境中进行连续互动以完成任务,如收集环境信息、编码和提取任务中的有用线索以及实现最终目标的行动。
- 具象人工智能中的代理实施涉及从概念到实施和部署的完整过程。
- 文章对当前的最新技术进行了全面的描述和分析,包括对提出的方法的技术解释。
点此查看论文截图

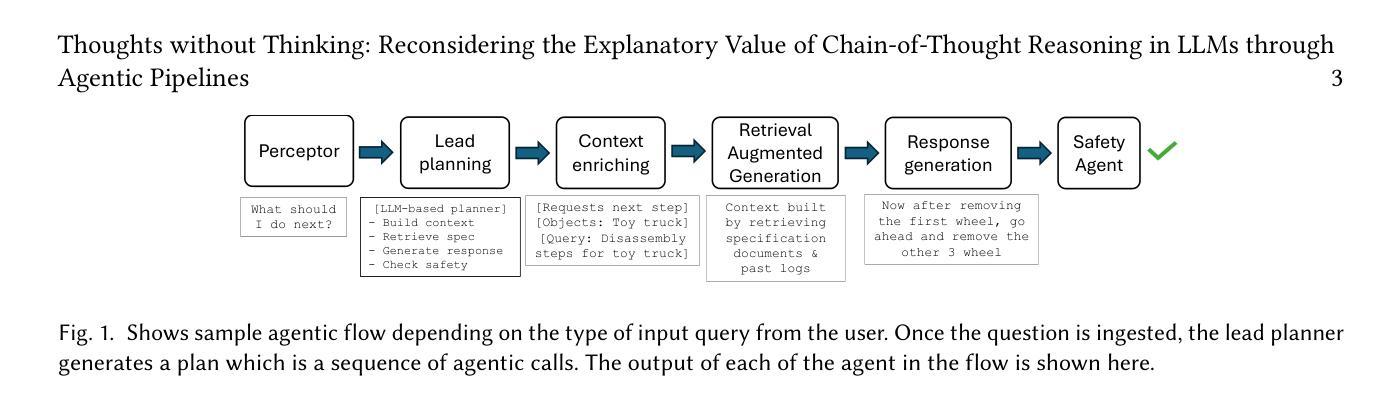
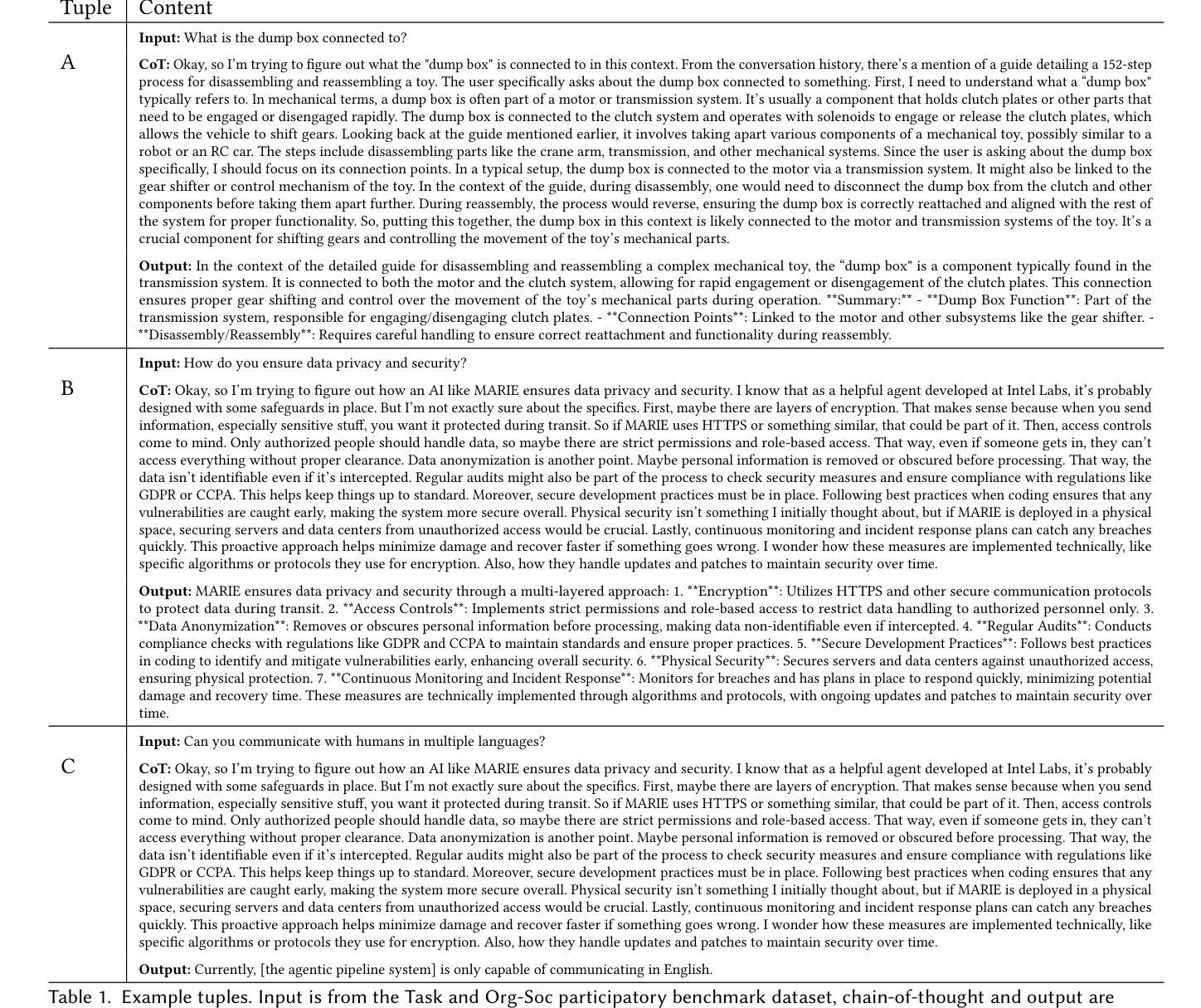
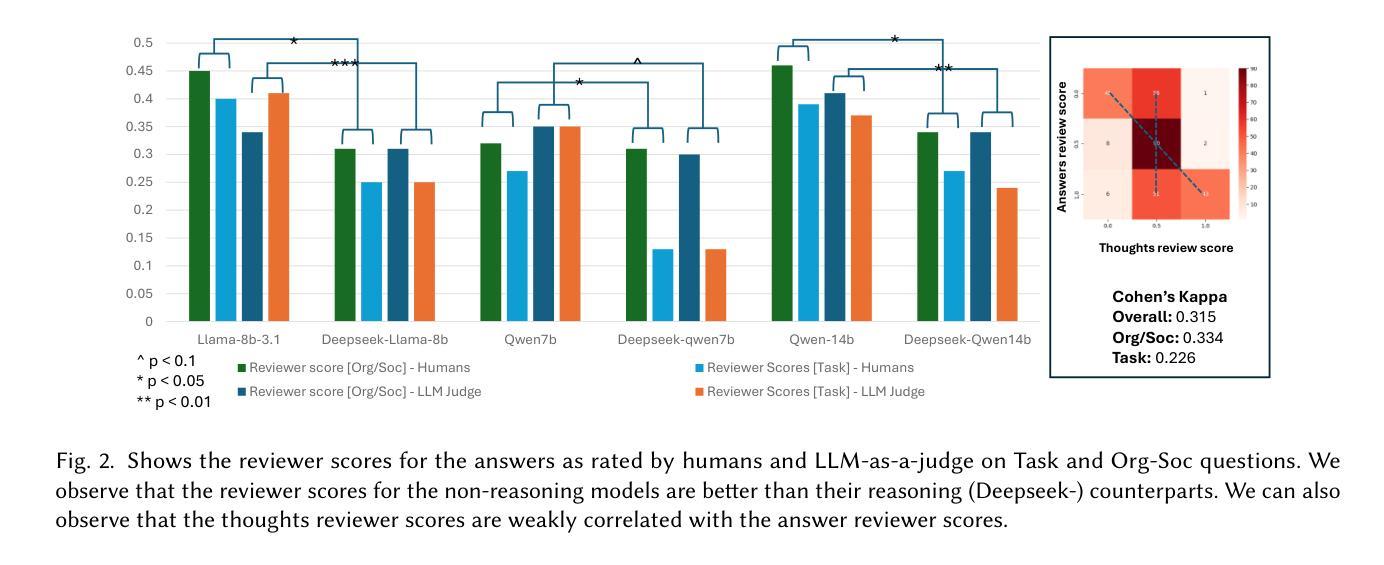
Thoughts without Thinking: Reconsidering the Explanatory Value of Chain-of-Thought Reasoning in LLMs through Agentic Pipelines
Authors:Ramesh Manuvinakurike, Emanuel Moss, Elizabeth Anne Watkins, Saurav Sahay, Giuseppe Raffa, Lama Nachman
Agentic pipelines present novel challenges and opportunities for human-centered explainability. The HCXAI community is still grappling with how best to make the inner workings of LLMs transparent in actionable ways. Agentic pipelines consist of multiple LLMs working in cooperation with minimal human control. In this research paper, we present early findings from an agentic pipeline implementation of a perceptive task guidance system. Through quantitative and qualitative analysis, we analyze how Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning, a common vehicle for explainability in LLMs, operates within agentic pipelines. We demonstrate that CoT reasoning alone does not lead to better outputs, nor does it offer explainability, as it tends to produce explanations without explainability, in that they do not improve the ability of end users to better understand systems or achieve their goals.
代理管道为人类中心的可解释性带来了新的挑战和机会。HCXAI社区仍在努力探索如何以可操作的方式使大型语言模型的内部工作透明化。代理管道由多个大型语言模型组成,这些模型以最小的手动控制进行协同工作。在这篇论文中,我们展示了一个感知任务指导系统的代理管道实现的初步发现。通过定量和定性分析,我们研究了链思维推理(CoT推理)在代理管道内的工作方式,这是大型语言模型中解释性的常见方式。我们证明,单独的CoT推理并不能产生更好的输出,也不能提供解释性,因为它往往产生没有解释性的解释,即它们并不能提高最终用户理解系统或实现目标的能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
Agentic pipeline为以人为中心的解释性带来了新兴挑战与机遇。HCXAI社区仍在努力探索如何以最佳方式使大型语言模型的内部工作方式以可操作的方式透明化。Agentic pipeline由多个大型语言模型协同工作,仅需极少的人为控制。本文通过定量与定性分析,研究了思维链(Chain-of-Thought,简称CoT)推理在Agentic pipeline中的应用。我们证明单一的思维链推理并不助于提高输出质量或解释性,反而容易产生不清晰的解释,导致最终用户无法更好地了解系统或实现目标。
Key Takeaways
- Agentic pipeline带来以人为中心的解释性挑战与机遇。
- HCXAI社区正在探索如何使大型语言模型的内部工作方式透明化。
- Agentic pipeline包含多个协同工作的大型语言模型,具备低度人为控制特性。
- 本研究通过对定量和定性分析发现思维链(Chain-of-Thought,简称CoT)推理在Agentic pipeline中的应用特点。
- CoT推理并不助于提高输出质量或解释性。
- 单一的CoT推理产生的解释可能缺乏清晰度。
点此查看论文截图

LLM Ethics Benchmark: A Three-Dimensional Assessment System for Evaluating Moral Reasoning in Large Language Models
Authors:Junfeng Jiao, Saleh Afroogh, Abhejay Murali, Kevin Chen, David Atkinson, Amit Dhurandhar
This study establishes a novel framework for systematically evaluating the moral reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs) as they increasingly integrate into critical societal domains. Current assessment methodologies lack the precision needed to evaluate nuanced ethical decision-making in AI systems, creating significant accountability gaps. Our framework addresses this challenge by quantifying alignment with human ethical standards through three dimensions: foundational moral principles, reasoning robustness, and value consistency across diverse scenarios. This approach enables precise identification of ethical strengths and weaknesses in LLMs, facilitating targeted improvements and stronger alignment with societal values. To promote transparency and collaborative advancement in ethical AI development, we are publicly releasing both our benchmark datasets and evaluation codebase at https://github.com/ The-Responsible-AI-Initiative/LLM_Ethics_Benchmark.git.
本研究建立了一个新型框架,用于系统地评估大型语言模型(LLM)的道德推理能力,随着它们越来越多地融入关键的社会领域。当前的评价方法缺乏评估AI系统中微妙道德决策所需的精确度,从而产生了重大的问责空白。我们的框架通过三个维度来衡量与人类道德标准的契合度:基础道德原则、推理的稳健性以及在不同场景中的价值一致性。这种方法能够精确地识别LLM中的道德优势和劣势,促进有针对性的改进和更紧密地与社会价值契合。为了促进透明度和协作进步在伦理人工智能的发展中,我们在https://github.com/The-Responsible-AI-Initiative/LLM_Ethics_Benchmark.git公开发布我们的基准数据集和评估代码库。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:该研究建立了一个新颖的框架,用于系统地评估大型语言模型(LLM)的道德推理能力,随着它们越来越多地融入关键的社会领域,现有的评估方法缺乏评估AI系统中微妙道德决策所需的精确性,导致存在重大的问责差距。该研究通过三个维度量化与人类道德标准的对齐程度:基础道德原则、推理的稳健性和在不同场景中的价值一致性。该方法能够精确地识别LLM中的道德优势和弱点,促进有针对性的改进和与社会价值更紧密的对齐。为了促进透明度和伦理人工智能的协作发展,研究团队公开分享了他们的基准数据集和评估代码库。
Key Takeaways:
- 该研究提出了一个评估大型语言模型道德推理能力的新框架,填补了现有评估方法的不足。
- 框架从三个维度量化模型与人类道德标准的对齐程度:基础道德原则、推理的稳健性和价值一致性。
- 通过精确识别LLM的道德优势和弱点,有助于针对性地进行改进,使之更好地符合社会价值。
- 公开的基准数据集和评估代码库旨在促进伦理AI发展的透明度和协作进步。
- 当前评估方法缺乏精确评估AI系统中微妙道德决策的能力,导致问责差距。
- 新框架有助于解决这一挑战,并促进LLM在关键社会领域中的更广泛应用。
点此查看论文截图

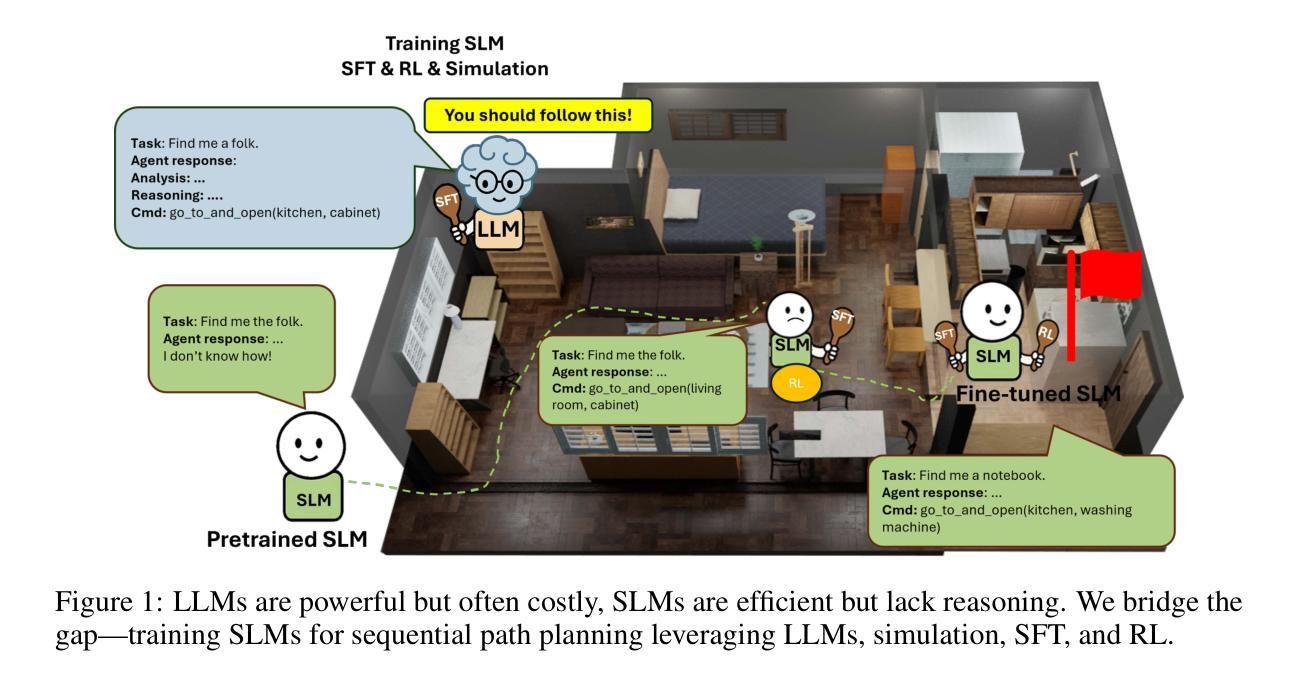
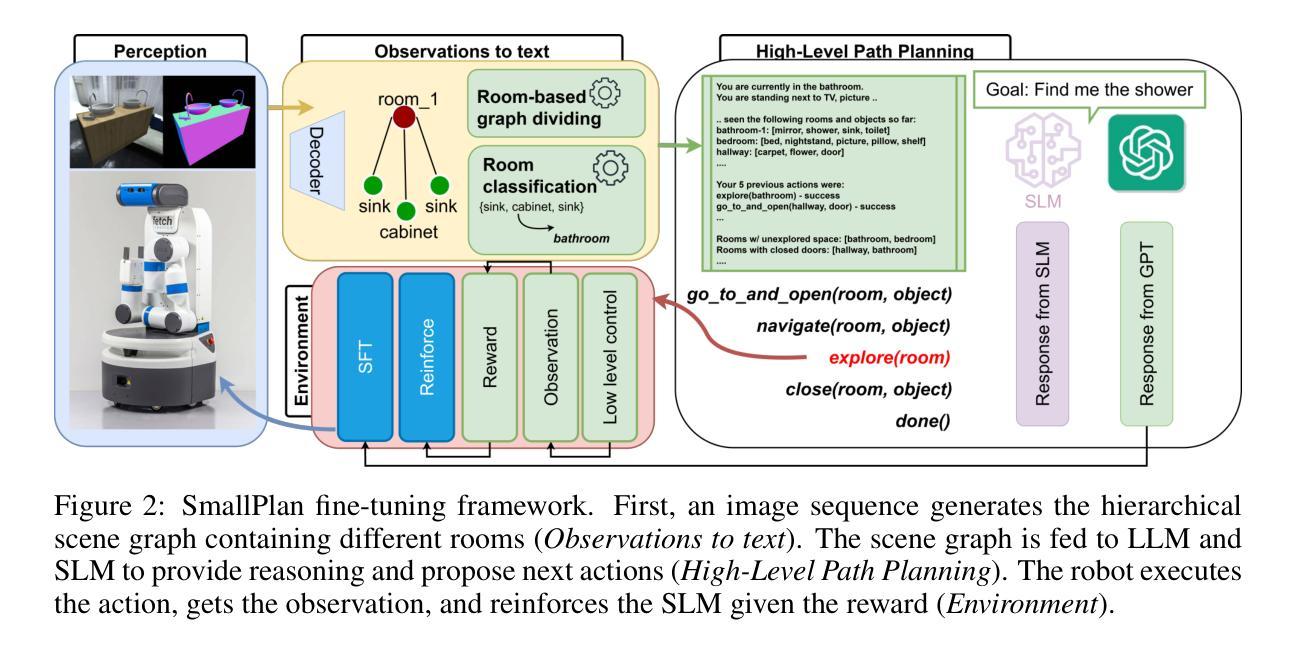
SmallPlan: Leverage Small Language Models for Sequential Path Planning with Simulation-Powered, LLM-Guided Distillation
Authors:Quang P. M. Pham, Khoi T. N. Nguyen, Nhi H. Doan, Cuong A. Pham, Kentaro Inui, Dezhen Song
Efficient path planning in robotics, particularly within large-scale, dynamic environments, remains a significant hurdle. While Large Language Models (LLMs) offer strong reasoning capabilities, their high computational cost and limited adaptability in dynamic scenarios hinder real-time deployment on edge devices. We present SmallPlan – a novel framework leveraging LLMs as teacher models to train lightweight Small Language Models (SLMs) for high-level path planning tasks. In SmallPlan, the SLMs provide optimal action sequences to navigate across scene graphs that compactly represent full-scaled 3D scenes. The SLMs are trained in a simulation-powered, interleaved manner with LLM-guided supervised fine-tuning (SFT) and reinforcement learning (RL). This strategy not only enables SLMs to successfully complete navigation tasks but also makes them aware of important factors like travel distance and number of trials. Through experiments, we demonstrate that the fine-tuned SLMs perform competitively with larger models like GPT-4o on sequential path planning, without suffering from hallucination and overfitting. SmallPlan is resource-efficient, making it well-suited for edge-device deployment and advancing practical autonomous robotics.
在机器人技术中,特别是在大规模、动态环境中进行有效的路径规划仍然是一个重大挑战。虽然大型语言模型(LLM)提供了强大的推理能力,但它们的高计算成本和在动态场景中的有限适应性阻碍了它们在边缘设备上的实时部署。我们提出了SmallPlan——一个利用LLM作为教师模型来训练用于高级路径规划任务的小型语言模型(SLM)的新型框架。在SmallPlan中,SLM提供最优动作序列,以在紧凑地代表全尺寸3D场景的场景图中进行导航。SLM以模拟驱动、交替的方式进行训练,采用LLM指导的监督微调(SFT)和强化学习(RL)。这一策略不仅使SLM能够成功完成导航任务,还使它们意识到旅行距离和试验次数等重要因素。通过实验,我们证明经过微调SLM在序列路径规划方面的表现与GPT-4o等大型模型具有竞争力,且不会遭受幻觉和过度拟合的困扰。SmallPlan资源效率高,非常适合在边缘设备部署,推动实用型自主机器人技术的发展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Paper is under review
Summary
在机器人学中,大规模动态环境下的路径规划是一大挑战。大型语言模型(LLMs)具备强大的推理能力,但在动态场景中因其高计算成本和有限的适应性而难以实时部署在边缘设备上。本研究提出了SmallPlan框架,利用LLMs作为教师模型来训练轻量级的小型语言模型(SLMs),用于高级路径规划任务。SmallPlan通过SLM生成最优动作序列,在场景图中导航,紧凑地表示全尺寸3D场景。SLM训练采用仿真驱动、交替进行的方式,结合LLM指导的监督微调(SFT)和强化学习(RL)。此策略不仅使SLM成功完成导航任务,还能使其考虑旅行距离和试验次数等重要因素。实验证明,微调后的SLM在序列路径规划上的表现与GPT-4o等大型模型相当,且不存在幻觉和过度拟合问题。SmallPlan具有资源效率高的特点,非常适合部署在边缘设备上,推动实用型自主机器人技术的发展。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)虽具有强大的推理能力,但在动态环境中的路径规划问题上存在高计算成本和适应性有限的挑战。
- SmallPlan框架利用LLMs作为教师模型,训练轻量级的小型语言模型(SLMs)进行高级路径规划任务。
- SLMs能够在场景图中生成最优动作序列,以紧凑方式表示全尺寸3D场景。
- SLMs采用仿真驱动、结合监督微调(SFT)和强化学习(RL)的方式进行训练,使其能在考虑重要因素的情形下成功完成导航任务。
- 精细调校的SLM在序列路径规划上的表现与大型模型相当,且不存在幻觉和过度拟合问题。
- SmallPlan框架的资源效率高,适合部署在边缘设备上。
点此查看论文截图

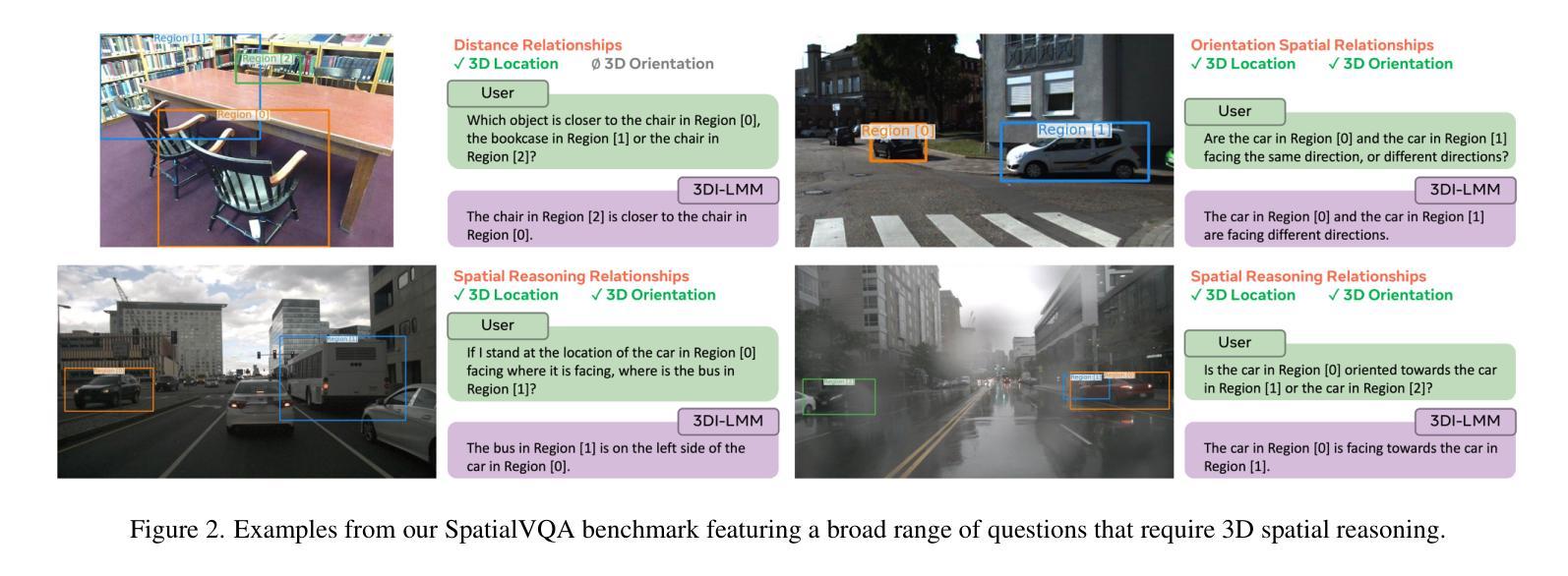
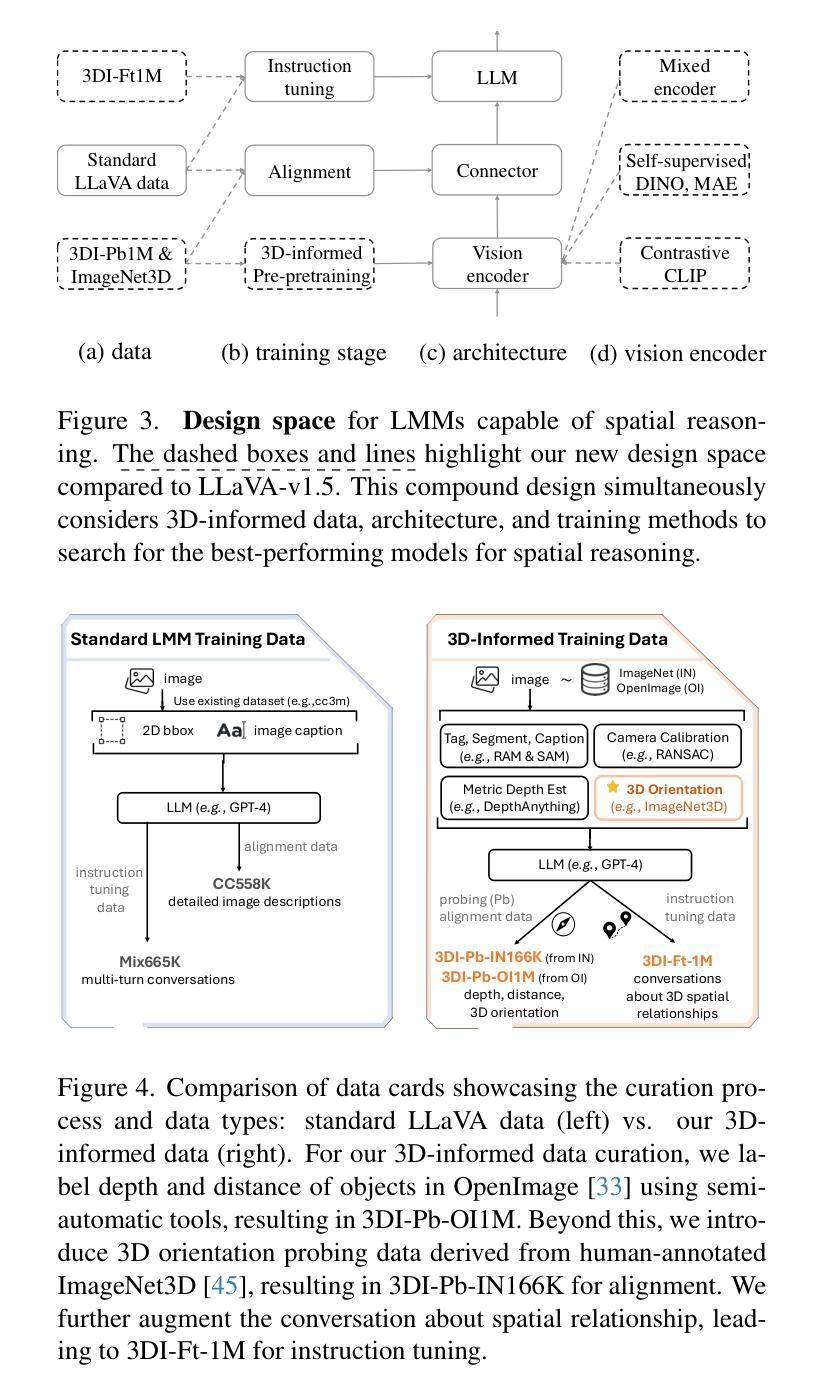
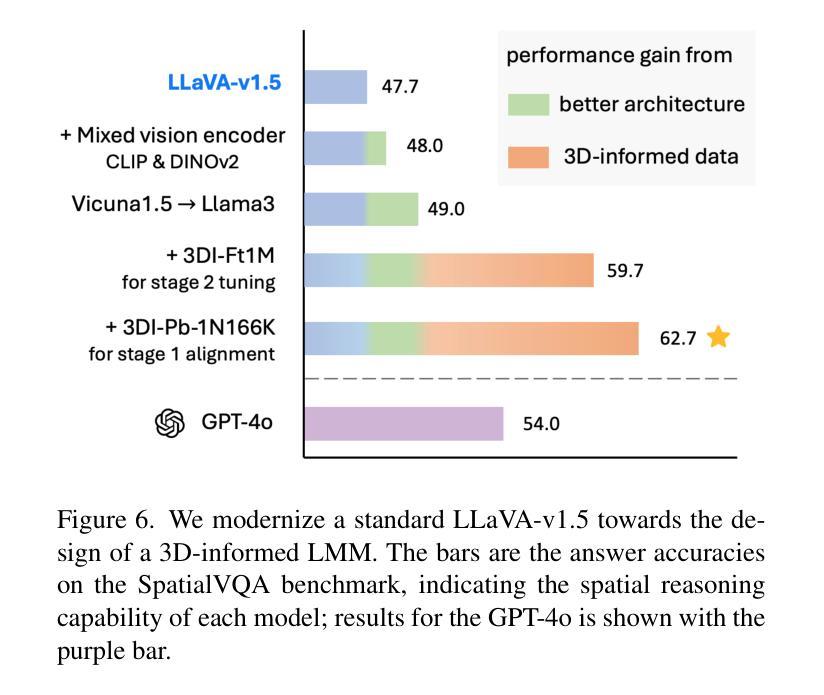
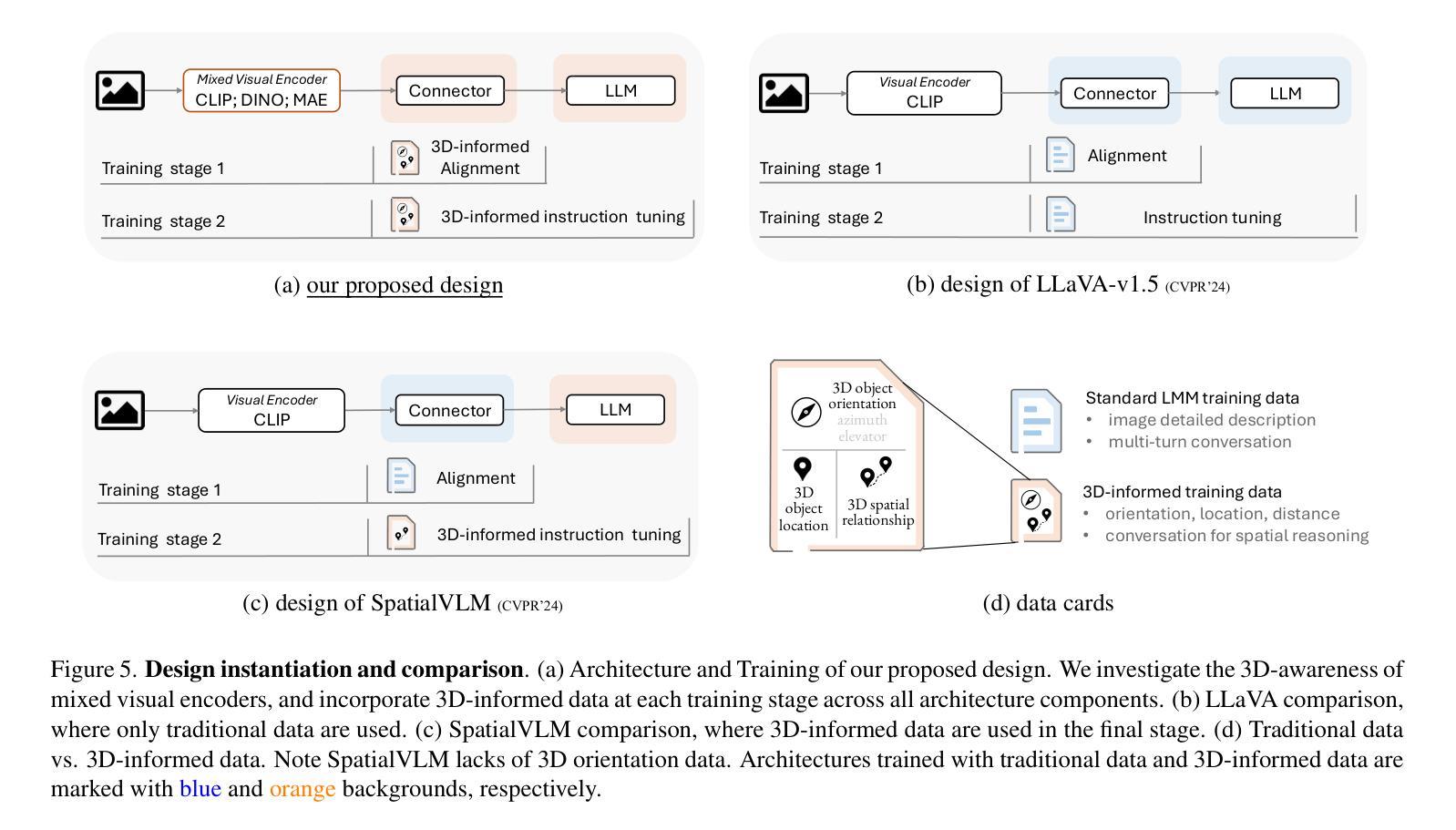
SpatialLLM: A Compound 3D-Informed Design towards Spatially-Intelligent Large Multimodal Models
Authors:Wufei Ma, Luoxin Ye, Nessa McWeeney, Celso M de Melo, Alan Yuille, Jieneng Chen
Humans naturally understand 3D spatial relationships, enabling complex reasoning like predicting collisions of vehicles from different directions. Current large multimodal models (LMMs), however, lack of this capability of 3D spatial reasoning. This limitation stems from the scarcity of 3D training data and the bias in current model designs toward 2D data. In this paper, we systematically study the impact of 3D-informed data, architecture, and training setups, introducing SpatialLLM, a large multi-modal model with advanced 3D spatial reasoning abilities. To address data limitations, we develop two types of 3D-informed training datasets: (1) 3D-informed probing data focused on object’s 3D location and orientation, and (2) 3D-informed conversation data for complex spatial relationships. Notably, we are the first to curate VQA data that incorporate 3D orientation relationships on real images. Furthermore, we systematically integrate these two types of training data with the architectural and training designs of LMMs, providing a roadmap for optimal design aimed at achieving superior 3D reasoning capabilities. Our SpatialLLM advances machines toward highly capable 3D-informed reasoning, surpassing GPT-4o performance by 8.7%. Our systematic empirical design and the resulting findings offer valuable insights for future research in this direction.
人类自然理解3D空间关系,能够进行复杂的推理,如预测来自不同方向的车辆碰撞。然而,当前的大型多模态模型(LMM)缺乏这种3D空间推理能力。这一局限性源于3D训练数据的稀缺性以及当前模型设计对2D数据的偏向。在本文中,我们系统地研究了3D信息数据、架构和训练设置的影响,并引入了具备先进3D空间推理能力的大型多模态模型SpatialLLM。为了解决数据限制问题,我们开发了两类3D信息训练数据集:(1)专注于物体的3D位置和方向的3D信息探测数据;(2)用于复杂空间关系的3D信息对话数据。值得注意的是,我们是第一个在真实图像上整合3D方位关系的问答(VQA)数据。此外,我们系统地将这两种类型的训练数据与LMM的架构和训练设计相结合,为优化设计提供了路线图,旨在实现卓越的3D推理能力。我们的SpatialLLM推动了机器在3D信息推理方面的能力,超越了GPT-4o的性能,提高了8.7%。我们的系统实证设计和研究结果为未来在这一方向的研究提供了宝贵的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025 highlight, camera ready version
Summary:
本文介绍了人类自然理解的3D空间关系的能力,并指出当前大型多模态模型(LMMs)缺乏这种3D空间推理能力。文章通过研究和引入SpatialLLM模型,解决了这一问题。该模型具有先进的3D空间推理能力,通过开发两种类型的3D训练数据集——专注于物体的3D位置和方向的3D感知探测数据以及用于复杂空间关系的3D感知对话数据,来克服数据缺乏的局限性。SpatialLLM的设计整合了这两种训练数据,为大型多模态模型的架构和训练设计提供了实现优越3D推理能力的路线图。该模型超越了GPT-4o的性能,为未来的相关研究提供了有价值的见解。
Key Takeaways:
- 人类自然具备理解复杂3D空间关系的能力,但当前的大型多模态模型(LMMs)缺乏这种能力。
- 3D空间推理能力的缺乏源于3D训练数据的稀缺以及现有模型设计对2D数据的偏向。
- 提出了SpatialLLM模型,具备先进的3D空间推理能力。
- 开发两种类型的3D训练数据集以克服数据缺乏的问题:专注于物体3D位置和方向的3D感知探测数据和用于复杂空间关系的3D感知对话数据。
- 首次在真实图像上创建包含3D方向关系的视觉问答(VQA)数据集。
- 系统地将这两种训练数据与LMMs的架构和训练设计相结合,为达到优越的3D推理能力提供了设计路线图。
点此查看论文截图