⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-08 更新
Accelerating the development of oxynitride thin films: A combinatorial investigation of the Al-Si-O-N system
Authors:Stefanie Frick, Oleksandr Pshyk, Arnold Müller, Alexander Wieczorek, Kerstin Thorwarth, Sebastian Siol
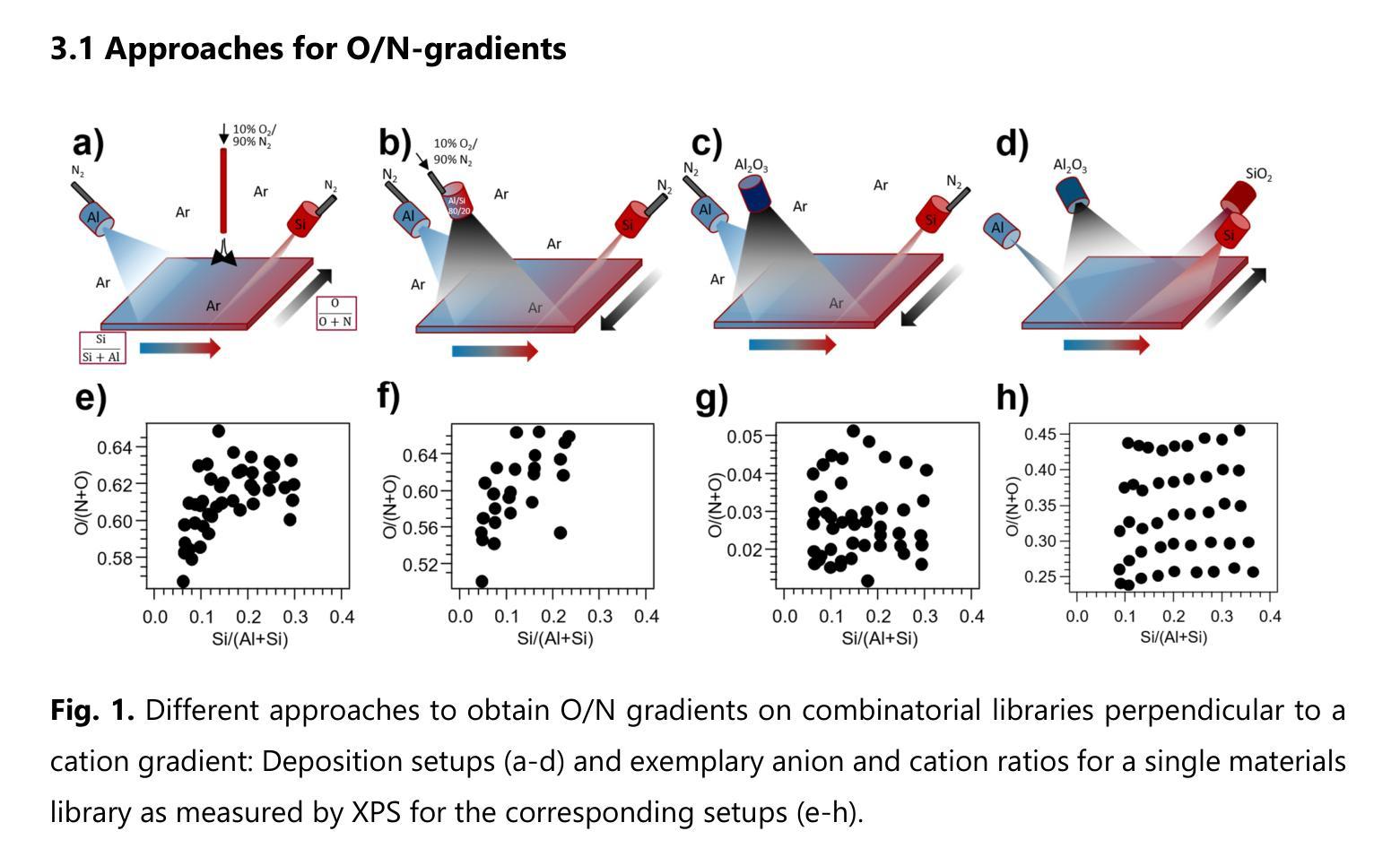
Oxynitrides are used in a variety of applications including photocatalysts, high-k dielectrics or wear-resistant coatings and often show intriguing multi-functionality. To accelerate the co-optimization of the relevant material properties of these compositionally complex oxynitride systems, high-throughput synthesis and characterization methods are desirable. In the present work, three approaches were investigated to obtain orthogonal anion and cation gradients on the same substrate by magnetron sputtering. The different approaches included varying positions of the local reactive gas inlets and different combinations of target materials. The best performing approach was applied to screen a large two-dimensional area of the quaternary phase space within the Al-Si-O-N system. This material system is a promising candidate for transparent protective coatings with variable refractive indices. With only five depositions of combinatorial libraries, an anion composition range of 2-46% O/(N+O) and a cation composition range of 4-44% Si/(Al+Si) is covered. For lower oxygen and silicon contents, a region with hardness of up to 25 GPa is observed, where the material exhibits either wurtzite AlN or a composite microstructure. By increasing the deposition temperature to 400 {\deg}C, an extension of this region can be achieved. At higher oxygen and silicon contents, the structure of the samples is X-ray amorphous. In this structural region, an intimate correlation between hardness and refractive index is confirmed. The results of this study introduce a practical approach to perform high-throughput development of mixed anion materials, which is transferable to many materials systems and applications.
氧氮化物被广泛应用于光催化剂、高介电常数介质或耐磨涂层等多个领域,并展现出令人着迷的多功能性。为了加速这些成分复杂的氧氮化物系统的相关材料属性的协同优化,需要采用高通量合成和表征方法。在本研究中,我们研究了三种方法,通过磁控溅射在同一基板上获得正交的阴离子和阳离子梯度。这三种方法包括改变局部反应气体入口的位置以及靶材料的不同组合。最佳方法被应用于在Al-Si-O-N系统内筛选一个大的二维区域。该材料系统是一个有望用于具有可变折射率的透明保护涂层的候选材料。通过仅沉积五次组合库,就覆盖了阴离子组成范围在2-46%的O/(N+O),以及阳离子组成范围在4-44%的Si/(Al+Si)。对于较低的氧和硅含量,观察到硬度高达25 GPa的区域,该材料呈现出纤锌矿结构AlN或复合微观结构。通过将沉积温度提高到400°C,可以实现此区域的扩展。在较高的氧和硅含量下,样品的结构为X射线非晶态。在此结构区域中,证实了硬度与折射率之间的密切联系。本研究的结果介绍了一种实际可行的方法来执行混合阴离子材料的高通量开发,这种方法可应用于多种材料系统和应用。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本研究针对氧氮化合物在多领域应用中的材料性能优化问题,探索了高通量合成及表征方法。研究采用磁控溅射技术,在同一基底上实现阴离子和阳离子的正交梯度。最佳方案在Al-Si-O-N系统内的大范围二维区域进行了筛选,该系统在可变折射率的透明防护涂层中具有应用前景。仅通过五次沉积组合库,就覆盖了氧阴离子2%~46%及硅阳离子4%~44%的范围。在较低氧和硅含量区域,观察到硬度达25 GPa的材料,表现为纤锌矿结构氮化铝或复合微观结构。提高沉积温度至400°C可扩大此区域。在较高氧和硅含量区域,样品结构呈X射线非晶态,硬度与折射率之间存在密切关联。本研究为混合阴离子材料的高通量开发提供了实用方法,可广泛应用于其他材料体系和应用领域。
关键见解
- 氧氮化合物在多种应用中表现出多功能性,如光催化剂、高介电常数介质和耐磨涂层。
- 研究采用磁控溅射技术,探索了在同一基底上实现阴离子和阳离子梯度的三种方法。
- 最佳性能方法用于筛选Al-Si-O-N系统内的广阔二维区域,该系统对于透明防护涂层具有应用潜力。
- 通过沉积组合库,实现了氧阴离子和硅阳离子的广泛组成范围。
- 在特定成分区域,材料表现出高达25 GPa的硬度,并观察到纤锌矿结构氮化铝或复合微观结构。
- 提高沉积温度可以扩大某些成分区域的材料性能。
点此查看论文截图

Crystal structural evolution of Ru$_3$Sn$_7$ under pressure and its implication on possible electronic changes
Authors:K. A. Irshad, P. Anees, Hrudananda Jena, Boby Joseph
Ru$_3$Sn$_7$, an intermetallic compound with advanced catalytic properties, exhibits a complex crystal structure and intriguing electronic properties, making it an attractive candidate for investigations under high-pressure (HP). The structural, vibrational and electronic band structure of this compound were investigated at HP up to ~ 20 GPa using synchrotron x-ray powder diffraction, micro-Raman, and density functional theory (DFT), respectively. Despite the local structural changes implied by a discernible reduction in the compressibility and distinct slope changes in the pressure evolution of the symmetric stretching vibrations of the Ru and Sn atoms around 8 GPa, the cubic structure is found to be stable throughout the pressure range. In support, our calculated phonon dispersion relation confirmed the stability of the cubic phase till the highest pressures. A comprehensive analysis of the Raman spectrum reveals the signatures of the pressure induced sudden strengthening of electron-phonon coupling as early as 3 GPa which is backed by a bounce in the phonon and electron density of states (DoS). Electronic structure calculations demonstrate that the metallic nature of Ru$_3$Sn$_7$ is preserved in the studied pressure range with a minor redistribution of electronic DoS across the Fermi level (EF). The band structure calculations predict intriguing changes in the electronic structure, revealing the pressure induced dp hybridization through the high symmetry point of the Brillouin zone which is largely responsible for the observed reduction in the compressibility and enhancement of the electron-phonon coupling in Ru$_3$Sn$_7$.
Ru$_3$Sn$_7$是一种具有先进催化性能的金属间化合物,其晶体结构复杂且电子特性有趣,使其成为高压(HP)研究中的理想候选物。该化合物的结构、振动和电子带结构在高压下至约20 GPa使用同步加速器X射线粉末衍射、微拉曼光谱和密度泛函理论(DFT)进行了研究。尽管在压力演化中观察到对称伸缩振动的压缩性明显降低和斜率明显变化,且局部结构发生变化,特别是在大约8 GPa时Ru和Sn原子的周围,但立方结构在整个压力范围内被证明是稳定的。我们的计算声子色散关系支持了这一发现,证实了立方相在最高压力下也是稳定的。对拉曼光谱的综合分析揭示了压力诱导的电子-声子耦合突然增强的迹象,早在3 GPa时就开始了,这得到了声子和电子态密度(DoS)跳跃的支持。电子结构计算表明,在研究的压力范围内保持了Ru$_3$Sn$_7$的金属性质,费米能级(EF)附近的电子态密度略有重新分布。带结构计算预测电子结构会发生有趣的变化,显示出压力诱导的dp杂化通过布里渊区的高对称点,这在很大程度上导致观察到的压缩性降低和电子-声子耦合增强在Ru$_3$Sn$_7$中。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
Ru$_3$Sn$_7$在高压下的性质研究。通过同步辐射X射线粉末衍射、微拉曼光谱和密度泛函理论等方法,发现其在高压下的晶体结构、振动和电子结构发生变化,但立方结构在测试压力范围内保持稳定。压力诱导下,电子-声子耦合作用增强,电子结构发生有趣变化。
Key Takeaways
- Ru$_3$Sn$_7$是一种具有先进催化性能的金属间化合物,其晶体结构复杂且电子特性引人入胜。
- 在高压下(HP)对其结构、振动和电子结构进行了研究,压力范围高达约20 GPa。
- 尽管在大约8 GPa的压力下,Ru和Sn原子的对称伸缩振动的压缩性和斜率发生变化,但立方结构在整个压力范围内保持稳定。
- 拉曼光谱分析显示,压力诱导的电子-声子耦合作用在3 GPa时突然增强。
- 电子结构计算表明,Ru$_3$Sn$_7$的金属性质在研究的压力范围内得以保持,费米能级附近的电子态密度有所变化。
- 带结构计算预测了电子结构的有趣变化,包括压力引起的dp杂化,这主要导致了观察到的压缩性降低和电子-声子耦合的增强。
点此查看论文截图

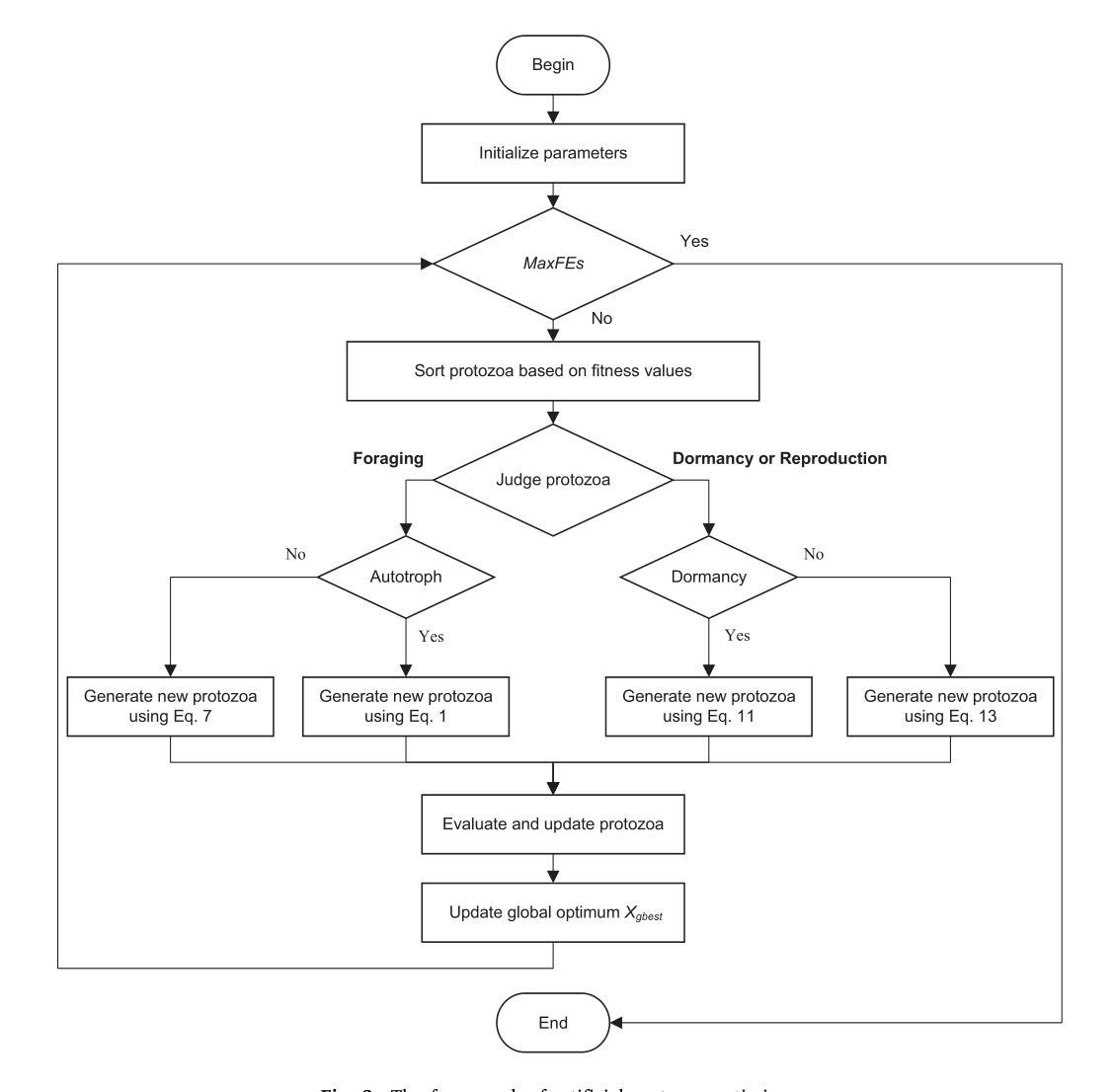
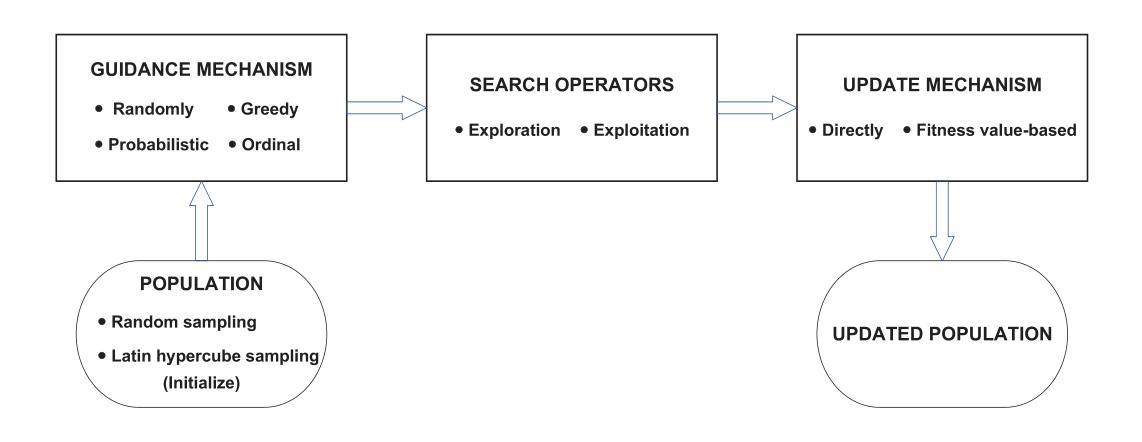
Artificial Protozoa Optimizer (APO): A novel bio-inspired metaheuristic algorithm for engineering optimization
Authors:Xiaopeng Wang, Vaclav Snasel, Seyedali Mirjalili, Jeng-Shyang Pan, Lingping Kong, Hisham A. Shehadeh
This study proposes a novel artificial protozoa optimizer (APO) that is inspired by protozoa in nature. The APO mimics the survival mechanisms of protozoa by simulating their foraging, dormancy, and reproductive behaviors. The APO was mathematically modeled and implemented to perform the optimization processes of metaheuristic algorithms. The performance of the APO was verified via experimental simulations and compared with 32 state-of-the-art algorithms. Wilcoxon signed-rank test was performed for pairwise comparisons of the proposed APO with the state-of-the-art algorithms, and Friedman test was used for multiple comparisons. First, the APO was tested using 12 functions of the 2022 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation benchmark. Considering practicality, the proposed APO was used to solve five popular engineering design problems in a continuous space with constraints. Moreover, the APO was applied to solve a multilevel image segmentation task in a discrete space with constraints. The experiments confirmed that the APO could provide highly competitive results for optimization problems. The source codes of Artificial Protozoa Optimizer are publicly available at https://seyedalimirjalili.com/projects and https://ww2.mathworks.cn/matlabcentral/fileexchange/162656-artificial-protozoa-optimizer.
本研究提出了一种受自然界原生动物启发的新型人工原生动物优化器(APO)。APO通过模拟原生动物的觅食、休眠和繁殖行为来模仿其生存机制。APO在数学上被建模和实现,以执行元启发式算法的优化过程。通过仿真实验验证了APO的性能,并与32种最新算法进行了比较。采用Wilcoxon符号秩检验对提出 APO与最新算法进行配对比较,并采用Friedman检验进行多重比较。首先,使用2022年IEEE进化计算大会基准测试的12个函数对APO进行了测试。考虑到实用性,所提出的APO被用于解决连续空间中具有约束的五个流行的工程设计问题。此外,APO还被应用于解决离散空间中具有约束的多级图像分割任务。实验证实,APO在优化问题处理方面能提供极具竞争力的结果。人工原生动物优化器的源代码可在https://seyedalimirjalili.com/projects和https://ww2.mathworks.cn/matlabcentral/fileexchange/162656-人工原生动物优化器公开获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于自然界原生动物生存策略启发的新型人工原生动物优化器(APO)被提出。APO模拟原生动物的觅食、休眠和繁殖行为,通过数学建模实现元启发式算法的优化过程。经实验仿真验证,APO与32种最新算法相比表现出良好性能,并在多个工程设计和图像分割问题中展现出竞争力。
Key Takeaways
- APO基于自然原生动物的生存策略设计,模拟其觅食、休眠和繁殖行为。
- APO通过数学建模实现元启发式算法的优化过程。
- 经实验仿真验证,APO在解决优化问题上表现出良好性能。
- APO在解决多个工程设计和图像分割问题中展现竞争力。
- APO能够处理不同空间类型的约束问题。
- 与其他先进的算法相比,APO在性能和竞争力方面具有优势。
点此查看论文截图


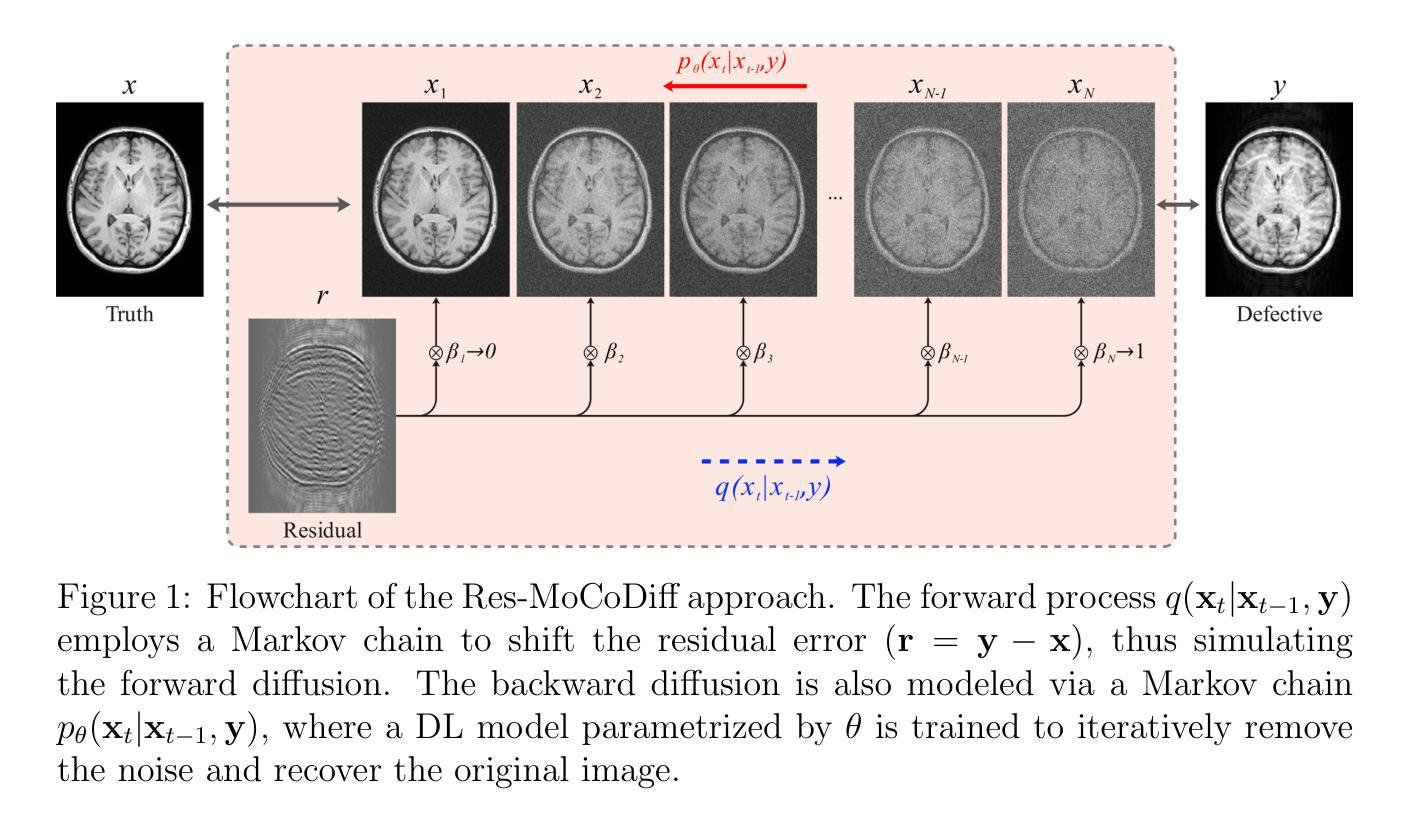
MRI motion correction via efficient residual-guided denoising diffusion probabilistic models
Authors:Mojtaba Safari, Shansong Wang, Qiang Li, Zach Eidex, Richard L. J. Qiu, Chih-Wei Chang, Hui Mao, Xiaofeng Yang
Purpose: Motion artifacts in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) significantly degrade image quality and impair quantitative analysis. Conventional mitigation strategies, such as repeated acquisitions or motion tracking, are costly and workflow-intensive. This study introduces Res-MoCoDiff, an efficient denoising diffusion probabilistic model tailored for MRI motion artifact correction. Methods: Res-MoCoDiff incorporates a novel residual error shifting mechanism in the forward diffusion process, aligning the noise distribution with motion-corrupted data and enabling an efficient four-step reverse diffusion. A U-net backbone enhanced with Swin-Transformer blocks conventional attention layers, improving adaptability across resolutions. Training employs a combined l1+l2 loss, which promotes image sharpness and reduces pixel-level errors. Res-MoCoDiff was evaluated on synthetic dataset generated using a realistic motion simulation framework and on an in-vivo dataset. Comparative analyses were conducted against established methods, including CycleGAN, Pix2pix, and MT-DDPM using quantitative metrics such as peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR), structural similarity index measure (SSIM), and normalized mean squared error (NMSE). Results: The proposed method demonstrated superior performance in removing motion artifacts across all motion severity levels. Res-MoCoDiff consistently achieved the highest SSIM and the lowest NMSE values, with a PSNR of up to 41.91+-2.94 dB for minor distortions. Notably, the average sampling time was reduced to 0.37 seconds per batch of two image slices, compared with 101.74 seconds for conventional approaches.
目的:磁共振成像(MRI)中的运动伪影会显著降低图像质量并影响定量分析。传统的缓解策略,如重复采集或运动跟踪,成本高昂且工作流程复杂。本研究介绍了Res-MoCoDiff,这是一种针对MRI运动伪影校正的高效去噪扩散概率模型。方法:Res-MoCoDiff在正向扩散过程中融入了一种新颖的残差误差转移机制,使噪声分布与运动失真数据相匹配,并实现了一个高效的四步反向扩散。使用U-net主干并结合Swin-Transformer块替代传统注意力层,提高了跨分辨率的适应性。训练采用l1+l2损失组合,这促进了图像清晰度并减少了像素级误差。Res-MoCoDiff在利用现实运动模拟框架生成的综合数据集和体内数据集上进行了评估。与包括CycleGAN、Pix2pix和MT-DDPM等方法进行了比较性分析,采用了峰值信噪比(PSNR)、结构相似性指数度量(SSIM)和归一化均方误差(NMSE)等定量指标。结果:所提方法在所有运动严重程度级别中均表现出优异的去运动伪影性能。Res-MoCoDiff持续获得最高的SSIM和最低的NMSE值,对于轻微失真,PSNR高达41.91±2.94 dB。值得注意的是,平均采样时间减少到每批两个图像切片0.37秒,而传统方法需要101.74秒。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究介绍了一种针对磁共振成像(MRI)运动伪影校正的高效去噪扩散概率模型——Res-MoCoDiff。该方法通过在前向扩散过程中引入新型残差误差转移机制,与运动失真数据对齐噪声分布,并实现四步反向扩散,提高图像质量和定量分析效率。在合成和真实数据集上的评估显示,Res-MoCoDiff在去除运动伪影方面表现出卓越性能,平均采样时间大幅减少。
Key Takeaways
- Res-MoCoDiff是一种针对MRI运动伪影校正的先进去噪扩散概率模型。
- 该方法结合了一种新型的残差误差转移机制,有效对齐噪声分布与运动失真数据。
- Res-MoCoDiff实现了高效四步反向扩散,提高了图像质量和定量分析效率。
- 在合成和真实数据集上的评估显示,Res-MoCoDiff性能卓越,适用于不同运动严重程度级别的伪影去除。
- 与传统方法相比,Res-MoCoDiff的采样时间大幅减少,提高了工作效率。
- 研究采用了结合l1+l2损失的训练方法,促进了图像清晰度的提升并减少了像素级误差。
点此查看论文截图

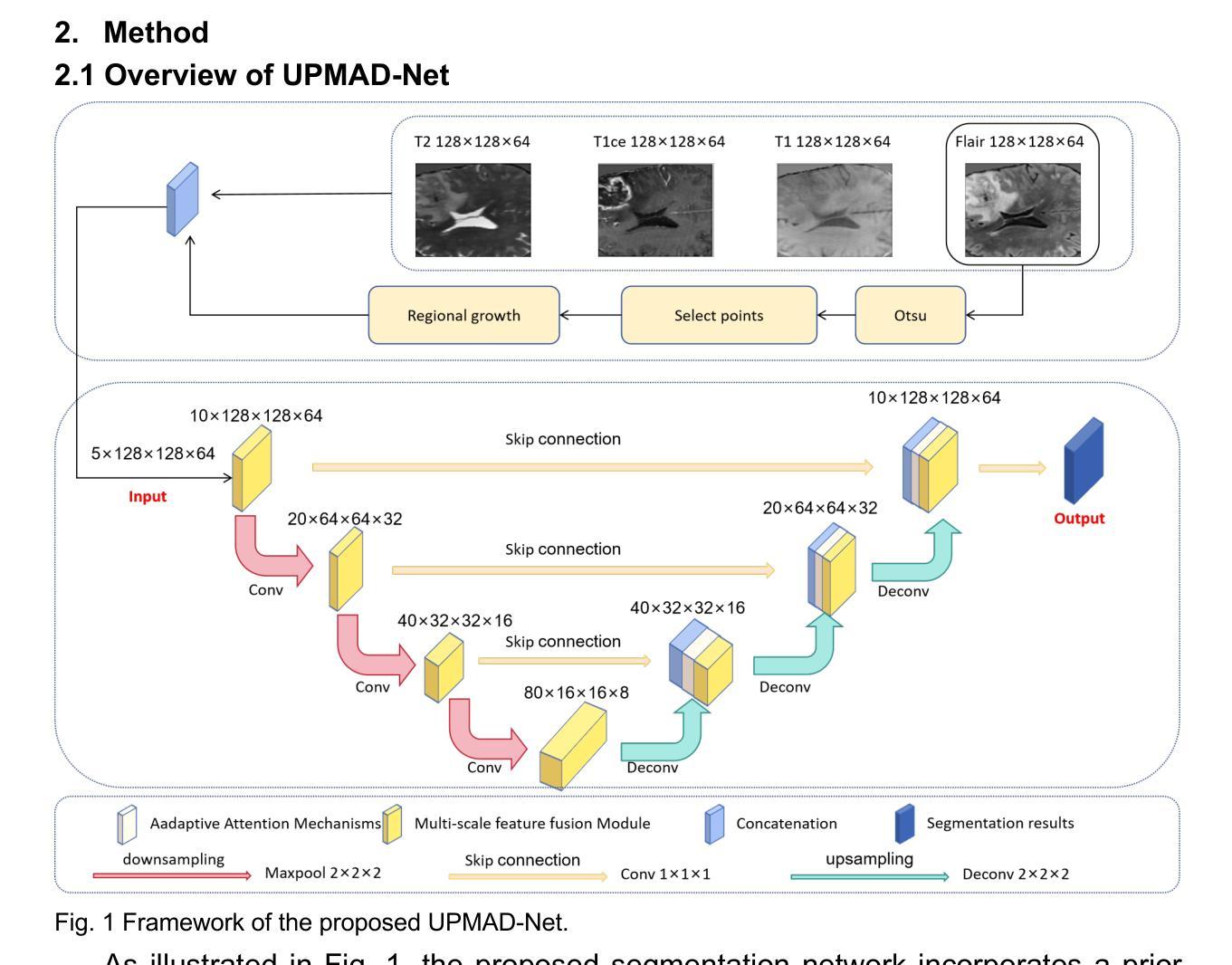
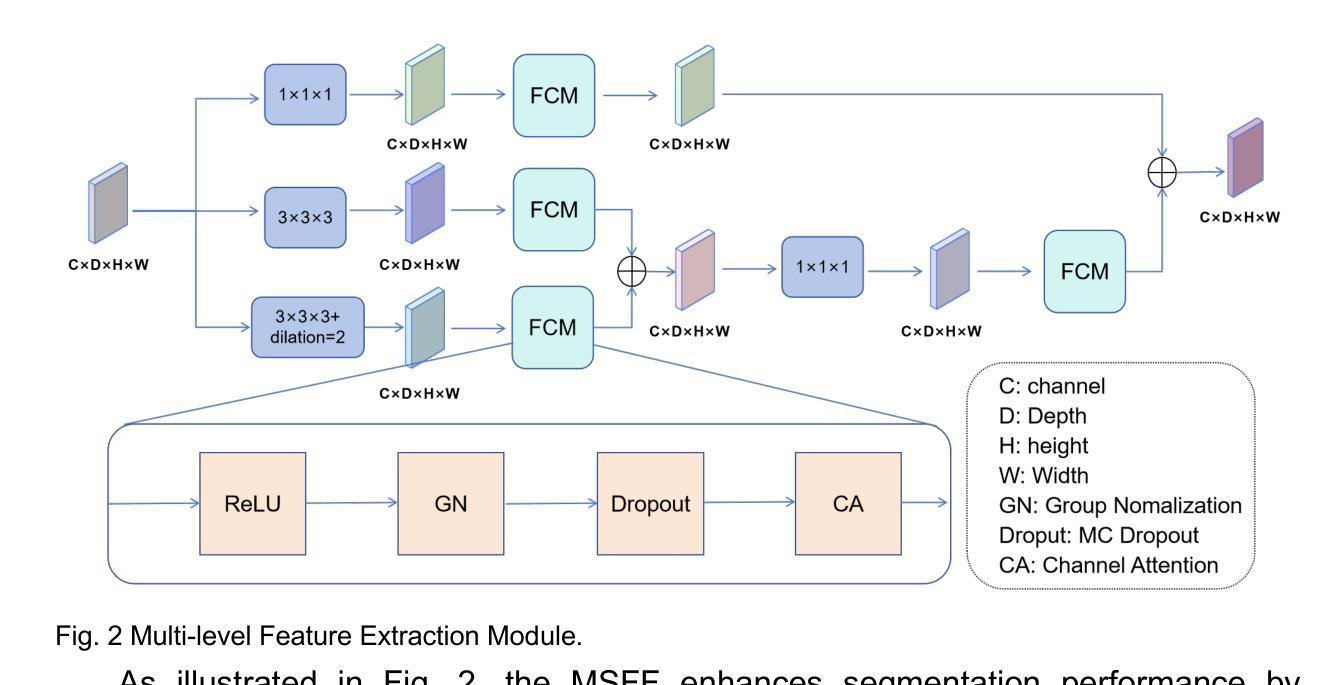
UPMAD-Net: A Brain Tumor Segmentation Network with Uncertainty Guidance and Adaptive Multimodal Feature Fusion
Authors:Zhanyuan Jia, Ni Yao, Danyang Sun, Chuang Han, Yanting Li, Jiaofen Nan, Fubao Zhu, Chen Zhao, Weihua Zhou
Background: Brain tumor segmentation has a significant impact on the diagnosis and treatment of brain tumors. Accurate brain tumor segmentation remains challenging due to their irregular shapes, vague boundaries, and high variability. Objective: We propose a brain tumor segmentation method that combines deep learning with prior knowledge derived from a region-growing algorithm. Methods: The proposed method utilizes a multi-scale feature fusion (MSFF) module and adaptive attention mechanisms (AAM) to extract multi-scale features and capture global contextual information. To enhance the model’s robustness in low-confidence regions, the Monte Carlo Dropout (MC Dropout) strategy is employed for uncertainty estimation. Results: Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed method achieves superior performance on Brain Tumor Segmentation (BraTS) datasets, significantly outperforming various state-of-the-art methods. On the BraTS2021 dataset, the test Dice scores are 89.18% for Enhancing Tumor (ET) segmentation, 93.67% for Whole Tumor (WT) segmentation, and 91.23% for Tumor Core (TC) segmentation. On the BraTS2019 validation set, the validation Dice scores are 87.43%, 90.92%, and 90.40% for ET, WT, and TC segmentation, respectively. Ablation studies further confirmed the contribution of each module to segmentation accuracy, indicating that each component played a vital role in overall performance improvement. Conclusion: This study proposed a novel 3D brain tumor segmentation network based on the U-Net architecture. By incorporating the prior knowledge and employing the uncertainty estimation method, the robustness and performance were improved. The code for the proposed method is available at https://github.com/chenzhao2023/UPMAD_Net_BrainSeg.
背景:脑肿瘤分割对脑肿瘤的诊断和治疗具有重要影响。由于脑肿瘤的形态不规则、边界模糊以及高度异质性,准确的脑肿瘤分割仍然具有挑战性。
目标:我们提出了一种结合深度学习与区域增长算法所派生先验知识的脑肿瘤分割方法。
方法:所提出的方法利用多尺度特征融合(MSFF)模块和自适应注意力机制(AAM)来提取多尺度特征和捕捉全局上下文信息。为了提高模型在低置信度区域的稳健性,采用蒙特卡洛Dropout(MC Dropout)策略进行不确定性估计。
结果:大量实验表明,所提出的方法在脑肿瘤分割(BraTS)数据集上表现优越,显著优于各种最先进的方法。在BraTS2021数据集上,增强肿瘤(ET)分割的Dice得分为89.18%,整个肿瘤(WT)分割的Dice得分为93.67%,肿瘤核心(TC)分割的Dice得分为91.23%。在BraTS2019验证集上,ET、WT和TC分割的验证Dice得分分别为87.43%、90.92%和90.40%。消融研究进一步证实了每个模块对分割精度的贡献,表明每个组件在总体性能提升中都起到了至关重要的作用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 21 pages, 7 figures
Summary
本文提出了一种结合深度学习与区域增长算法先验知识的脑肿瘤分割方法。该方法利用多尺度特征融合模块和自适应注意力机制来提取多尺度特征并捕捉全局上下文信息。同时,采用蒙特卡洛Dropout策略进行不确定性估计,以提高模型在低置信区域的稳健性。在Brain Tumor Segmentation(BraTS)数据集上的实验表明,该方法性能卓越,显著优于多种最新方法。
Key Takeaways
- 脑肿瘤分割在诊断与治疗中有重要影响,但由于肿瘤形状不规则、边界模糊和高变异性,准确分割具有挑战性。
- 提出了一种结合深度学习与区域增长算法先验知识的脑肿瘤分割方法。
- 利用多尺度特征融合模块和自适应注意力机制来提取多尺度特征和捕捉全局上下文信息。
- 采用蒙特卡洛Dropout策略进行不确定性估计,提高模型在低置信区域的稳健性。
- 在BraTS数据集上的实验结果表明,该方法性能优越,特别是在BraTS2021和BraTS2019数据集上。
- 消融研究证实了每个模块对分割精度的贡献,表明每个组件在整体性能提升中都起到了关键作用。
点此查看论文截图

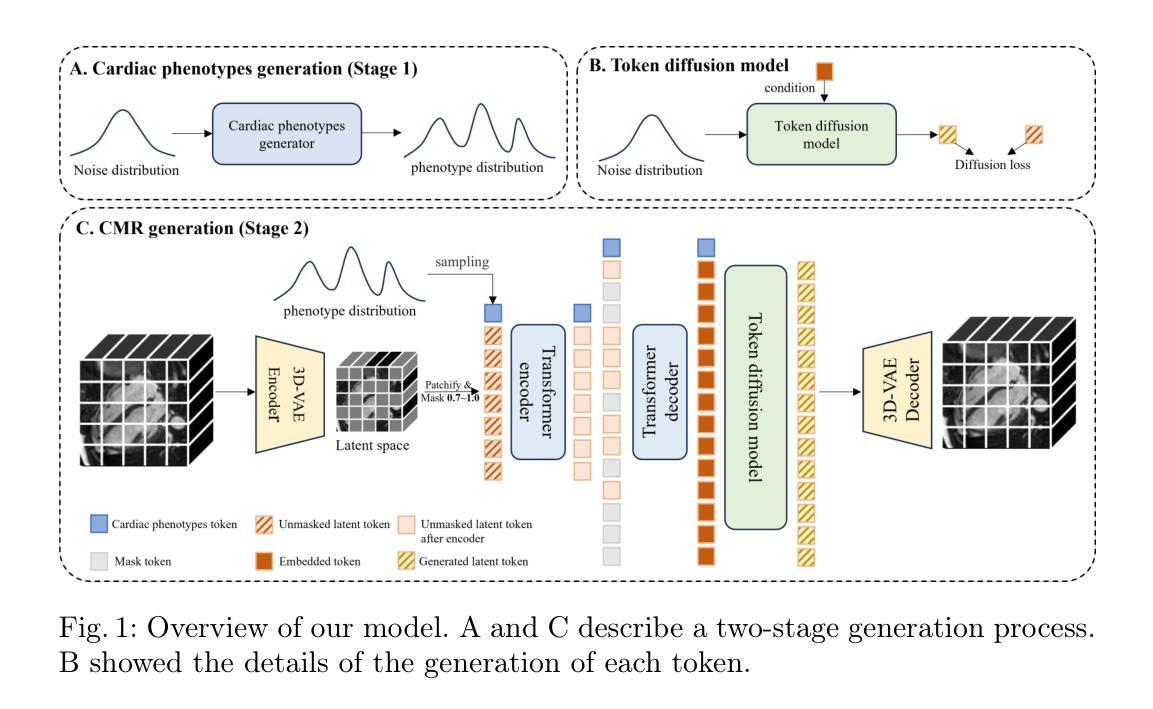
Phenotype-Guided Generative Model for High-Fidelity Cardiac MRI Synthesis: Advancing Pretraining and Clinical Applications
Authors:Ziyu Li, Yujian Hu, Zhengyao Ding, Yiheng Mao, Haitao Li, Fan Yi, Hongkun Zhang, Zhengxing Huang
Cardiac Magnetic Resonance (CMR) imaging is a vital non-invasive tool for diagnosing heart diseases and evaluating cardiac health. However, the limited availability of large-scale, high-quality CMR datasets poses a major challenge to the effective application of artificial intelligence (AI) in this domain. Even the amount of unlabeled data and the health status it covers are difficult to meet the needs of model pretraining, which hinders the performance of AI models on downstream tasks. In this study, we present Cardiac Phenotype-Guided CMR Generation (CPGG), a novel approach for generating diverse CMR data that covers a wide spectrum of cardiac health status. The CPGG framework consists of two stages: in the first stage, a generative model is trained using cardiac phenotypes derived from CMR data; in the second stage, a masked autoregressive diffusion model, conditioned on these phenotypes, generates high-fidelity CMR cine sequences that capture both structural and functional features of the heart in a fine-grained manner. We synthesized a massive amount of CMR to expand the pretraining data. Experimental results show that CPGG generates high-quality synthetic CMR data, significantly improving performance on various downstream tasks, including diagnosis and cardiac phenotypes prediction. These gains are demonstrated across both public and private datasets, highlighting the effectiveness of our approach. Code is availabel at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/CPGG.
心脏磁共振(CMR)成像是一种非常重要的无创工具,可用于诊断心脏病并评估心脏健康。然而,大规模高质量CMR数据集的有限可用性给人工智能(AI)在此领域的有效应用带来了重大挑战。即使是无标签数据及其所涵盖的健康状况也难以满足模型预训练的需求,这阻碍了AI模型在下游任务上的性能。在本研究中,我们提出了心脏表型引导CMR生成(CPGG)方法,这是一种生成多样化CMR数据的新方法,涵盖了广泛的心脏健康状况。CPGG框架分为两个阶段:在第一阶段,使用从CMR数据中得出的心脏表型来训练生成模型;在第二阶段,基于这些表型,使用带掩码的自动回归扩散模型生成高保真CMR电影序列,以精细的方式捕捉心脏的结构和功能特征。我们合成了大量CMR数据以扩充预训练数据。实验结果表明,CPGG生成的高质量合成CMR数据显著提高了各种下游任务(包括诊断和心脏表型预测)的性能。这些收益在公共和私有数据集上都得到了证明,凸显了我们的方法的有效性。代码可通过https://anonymous.4open.science/r/CPGG获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
心脏磁共振(CMR)成像在诊断心脏病和评估心脏健康方面具有重要意义。然而,大规模高质量CMR数据集有限,给人工智能在该领域的应用带来挑战。本研究提出一种新型方法——心脏表型引导CMR生成(CPGG),旨在生成覆盖广泛心脏健康状态的多样化CMR数据。CPGG框架包括两个阶段:第一阶段利用来源于CMR数据的心脏表型训练生成模型;第二阶段利用条件化的遮罩自回归扩散模型生成精细捕捉心脏结构和功能特征的高保真度CMR电影序列。合成大量CMR数据以扩充预训练数据,实验结果显示CPGG生成的合成CMR数据质量高,显著提高诊断和各种下游任务的性能,包括心脏表型预测。相关代码可访问(https://anonymous.4open.science/r/CPGG)。
Key Takeaways
- CMR成像在心脏疾病诊断和治疗中扮演重要角色。
- 大规模高质量CMR数据集的有限性限制了人工智能在心脏健康领域的应用。
- 本研究提出一种新型方法CPGG,旨在生成覆盖广泛心脏健康状态的多样化CMR数据。
- CPGG框架包括两个阶段:训练生成模型和使用条件化的遮罩自回归扩散模型生成高保真度CMR电影序列。
- 合成大量CMR数据用于扩充预训练数据,提高模型性能。
- 实验结果显示CPGG生成的合成CMR数据质量高,能提高诊断和下游任务的性能。
点此查看论文截图

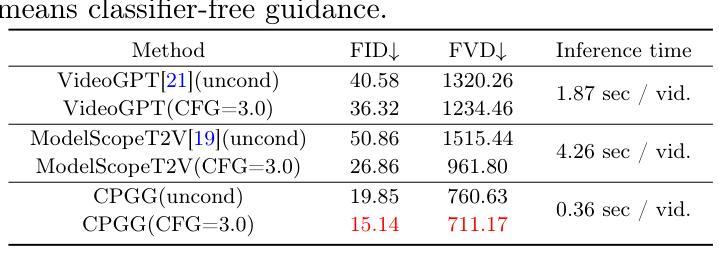
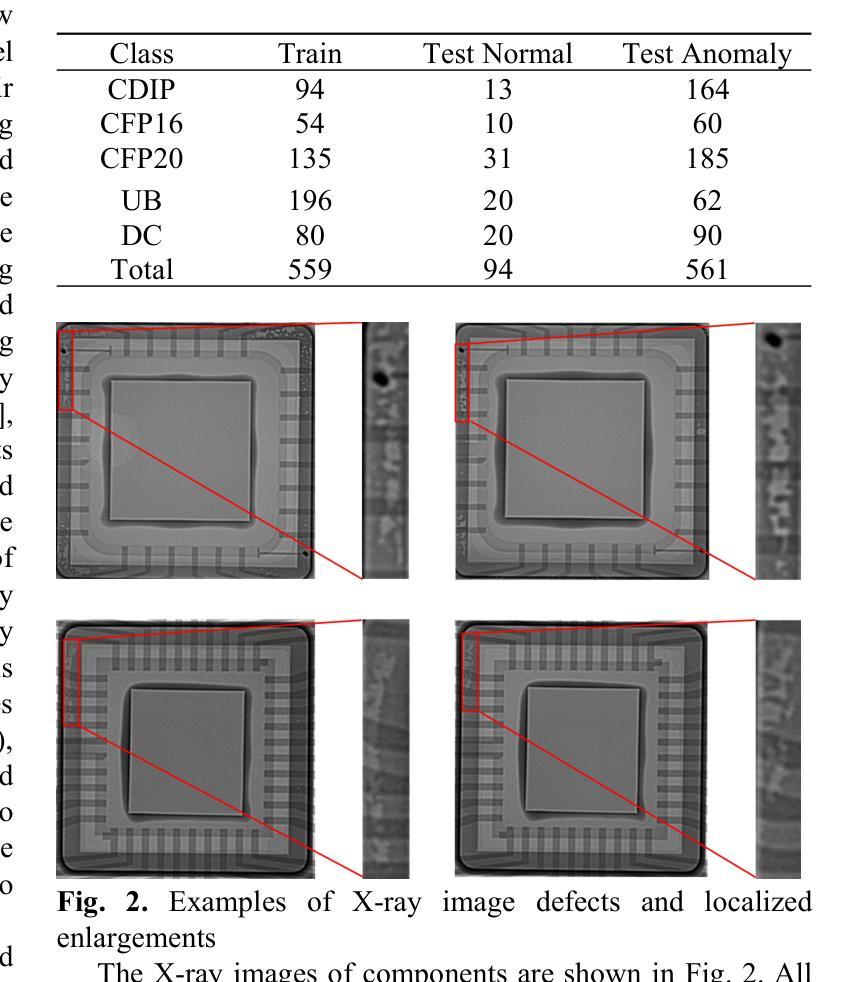
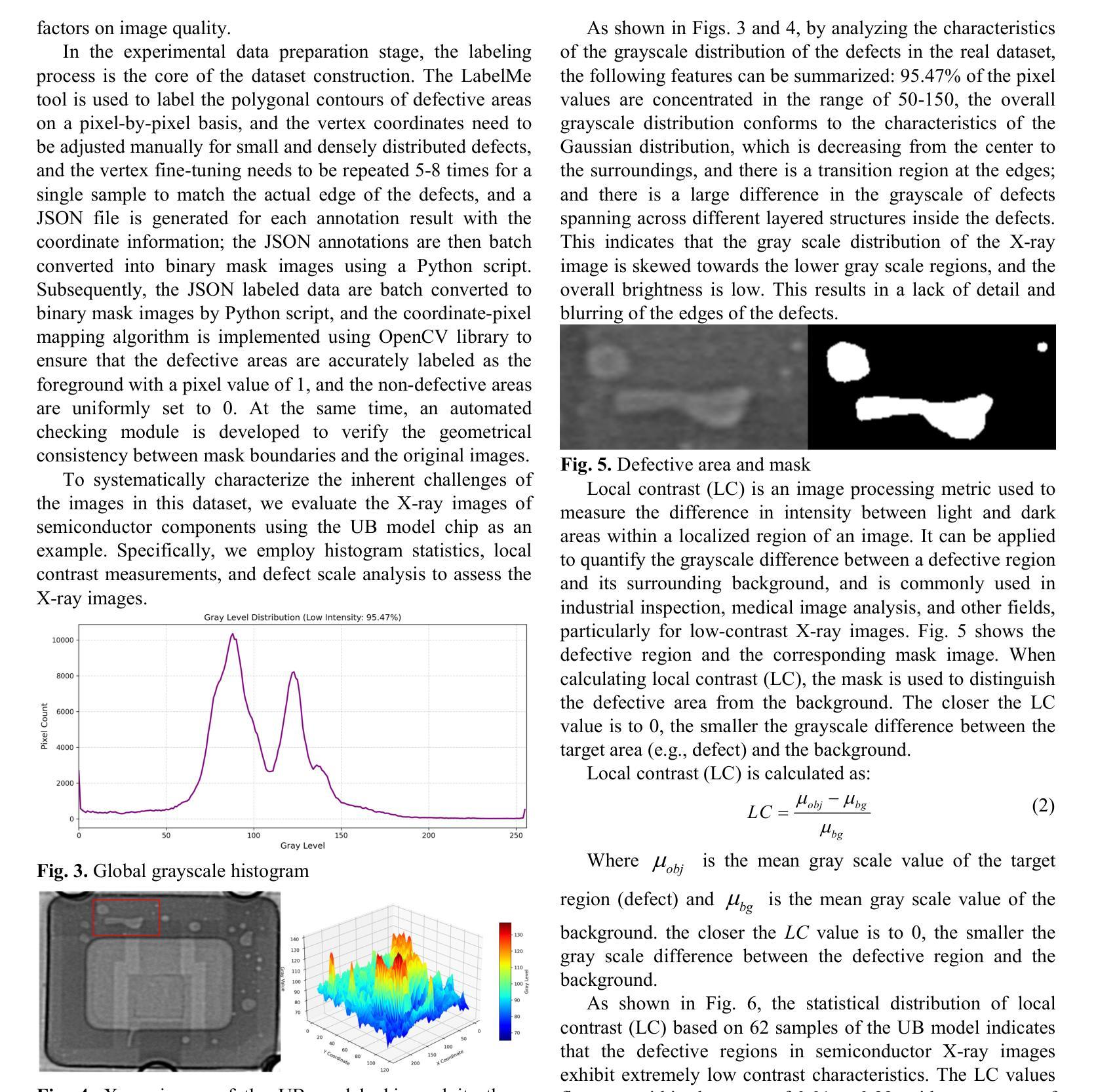
CXR-AD: Component X-ray Image Dataset for Industrial Anomaly Detection
Authors:Haoyu Bai, Jie Wang, Gaomin Li, Xuan Li, Xiaohu Zhang, Xia Yang
Internal defect detection constitutes a critical process in ensuring component quality, for which anomaly detection serves as an effective solution. However, existing anomaly detection datasets predominantly focus on surface defects in visible-light images, lacking publicly available X-ray datasets targeting internal defects in components. To address this gap, we construct the first publicly accessible component X-ray anomaly detection (CXR-AD) dataset, comprising real-world X-ray images. The dataset covers five industrial component categories, including 653 normal samples and 561 defect samples with precise pixel-level mask annotations. We systematically analyze the dataset characteristics and identify three major technical challenges: (1) strong coupling between complex internal structures and defect regions, (2) inherent low contrast and high noise interference in X-ray imaging, and (3) significant variations in defect scales and morphologies. To evaluate dataset complexity, we benchmark three state-of-the-art anomaly detection frameworks (feature-based, reconstruction-based, and zero-shot learning methods). Experimental results demonstrate a 29.78% average performance degradation on CXR-AD compared to MVTec AD, highlighting the limitations of current algorithms in handling internal defect detection tasks. To the best of our knowledge, CXR-AD represents the first publicly available X-ray dataset for component anomaly detection, providing a real-world industrial benchmark to advance algorithm development and enhance precision in internal defect inspection technologies.
内部缺陷检测是确保组件质量的关键过程,异常检测是有效的解决方案。然而,现有的异常检测数据集主要集中在可见光图像的表面缺陷上,缺乏针对组件内部缺陷的公开X射线数据集。为了解决这一空白,我们构建了第一个可公开访问的组件X射线异常检测(CXR-AD)数据集,包含真实世界的X射线图像。该数据集涵盖五个工业组件类别,包括653个正常样本和561个带有精确像素级掩膜注释的缺陷样本。我们系统地分析了数据集的特点,并识别出三个主要技术挑战:(1)复杂内部结构区域与缺陷区域之间的强耦合,(2)X射线成像中固有的低对比度和高噪声干扰,(3)缺陷规模和形态的显著变化。为了评估数据集的复杂性,我们对三种最先进的异常检测框架(基于特征、基于重建和零样本学习方法)进行了基准测试。实验结果表明,与MVTec AD相比,CXR-AD上的平均性能下降29.78%,这突显了当前算法在处理内部缺陷检测任务时的局限性。据我们所知,CXR-AD是第一个公开的用于组件异常检测的X射线数据集,它为算法的发展提供了一个真实的工业基准,提高了内部缺陷检测技术的精度。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文构建了一个首个公开可用的组件X射线异常检测(CXR-AD)数据集,包含真实世界的X射线图像,涵盖五种工业部件类别,包括正常样本和带精确像素级掩膜标注的缺陷样本。文章分析了数据集特性,并指出其在复杂内部结构、低对比度和高噪声干扰、缺陷尺度和形态多样等三个方面的技术挑战。通过实验评估,当前异常检测算法在CXR-AD上的性能平均下降29.78%,凸显了现有算法在处理内部缺陷检测任务时的局限性。CXR-AD为组件异常检测提供了首个公开的X射线数据集,为算法发展和内部缺陷检测技术的精确性提升提供了工业基准。
Key Takeaways
- 文章提出了构建首个公开可用的组件X射线异常检测(CXR-AD)数据集的需求。
- 数据集涵盖五种工业部件类别,包括正常和缺陷样本,且带有精确像素级标注。
- 分析了数据集特性,并指出了其在内部结构复杂性、X射线成像的低对比度和高噪声干扰以及缺陷尺度和形态的多样性等方面的技术挑战。
- 对比评估了三种先进异常检测算法在CXR-AD上的性能表现,发现平均性能下降29.78%。
- CXR-AD数据集是目前首个公开的用于组件异常检测的X射线数据集。
- CXR-AD数据集为算法发展提供工业基准,有助于推动内部缺陷检测技术的进步。
点此查看论文截图


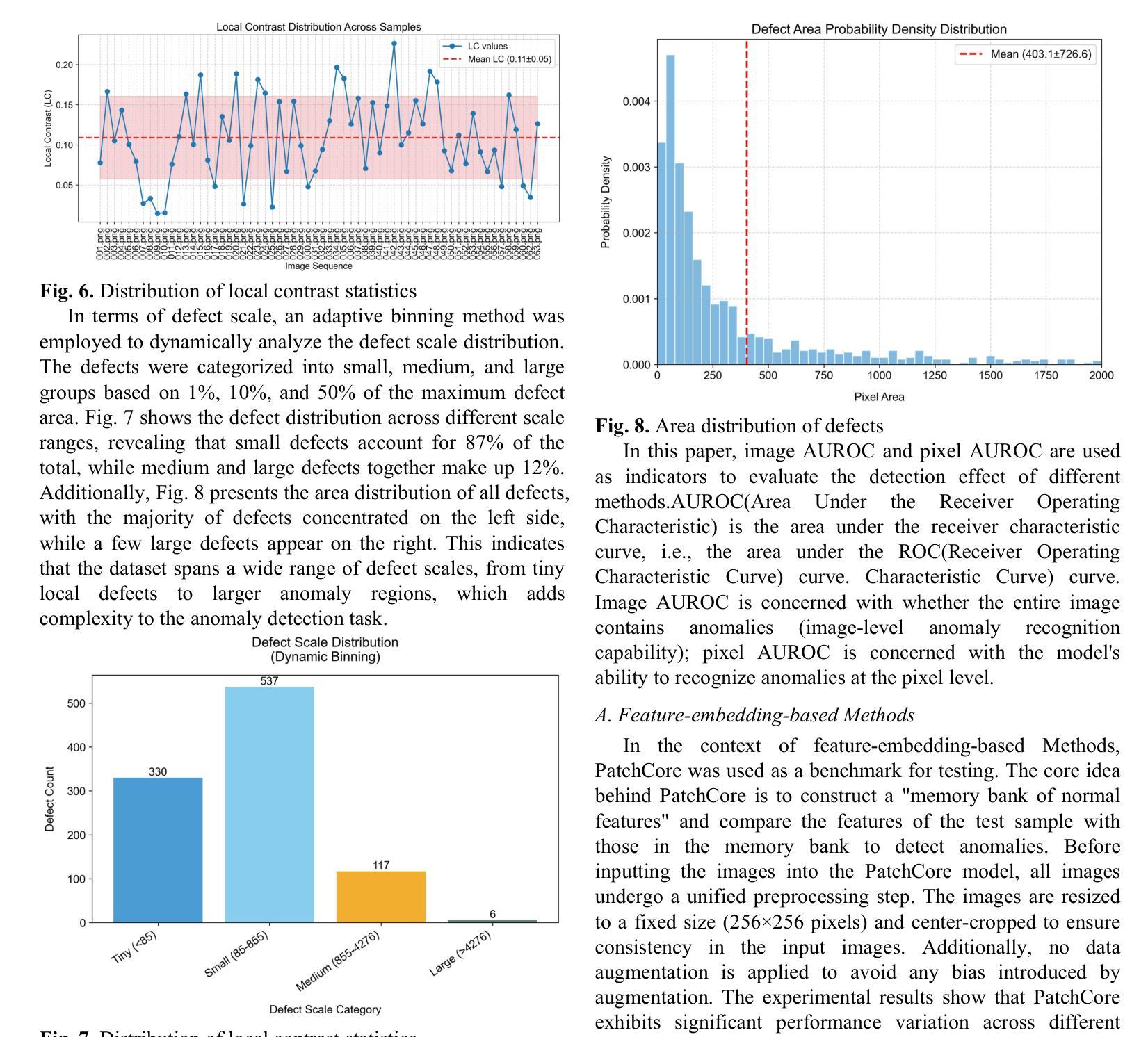
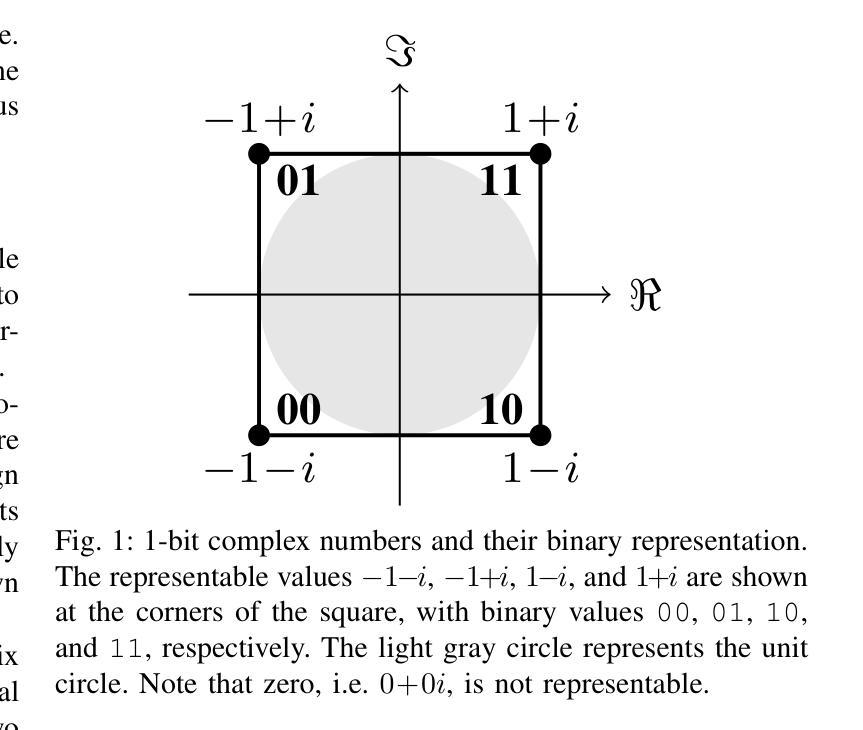
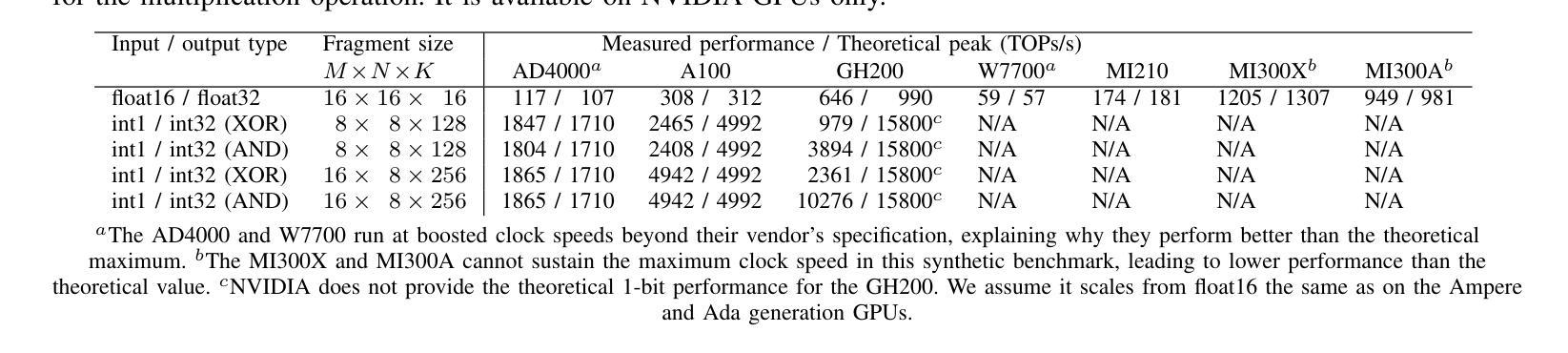
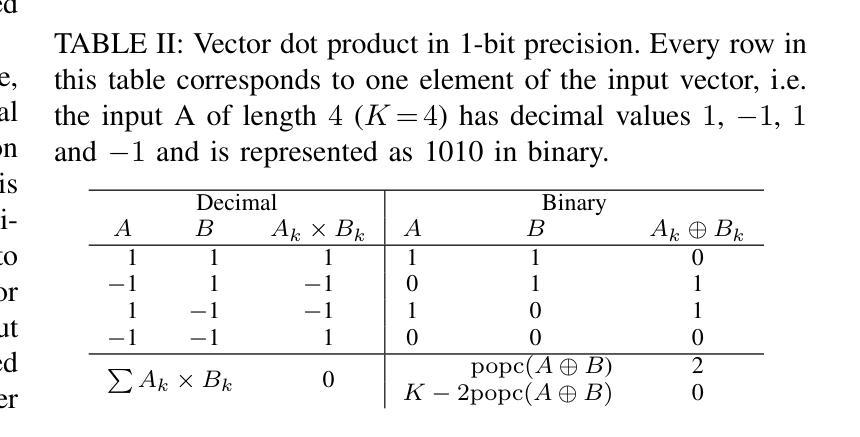
The Tensor-Core Beamformer: A High-Speed Signal-Processing Library for Multidisciplinary Use
Authors:Leon Oostrum, Bram Veenboer, Ronald Rook, Michael Brown, Pieter Kruizinga, John W. Romein
Beamforming is a well-known technique to combine signals from multiple sensors. It has a wide range of application domains. This paper introduces the Tensor-Core Beamformer: a generic, optimized beamformer library that harnesses the computational power of GPU tensor cores to accelerate beamforming computations. The library hides the complexity of tensor cores from the user, and supports 16-bit and 1-bit precision. An extensive performance evaluation on NVIDIA and AMD GPUs shows that the library outperforms traditional beamforming on regular GPU cores by a wide margin, at much higher energy efficiency. In the 16-bit mode, it achieves over 600 TeraOps/s on an AMD MI300X GPU, while approaching 1 TeraOp/J. In the 1-bit mode, it breaks the 3 PetaOps/s barrier and achieves over 10 TeraOps/J on an NVIDIA A100 GPU. The beamforming library can be easily integrated into existing pipelines. We demonstrate its use for medical ultrasound and radio-astronomical instruments.
波束形成是一种众所周知的从多个传感器组合信号的技术,具有广泛的应用领域。本文介绍了Tensor-Core Beamformer:一个通用、优化的波束形成库,它利用GPU张量核心的计算能力来加速波束形成的计算。该库向用户隐藏了张量核心的复杂性,并支持16位和1位精度。在NVIDIA和AMD GPU上进行的大规模性能评估表明,该库在常规GPU核心上大幅超越了传统波束形成,且能效更高。在16位模式下,它在AMD MI300X GPU上实现了超过600 TeraOps/s的性能,接近1 TeraOp/J。在1位模式下,它突破了3 PetaOps/s的障碍,并在NVIDIA A100 GPU上实现了超过10 TeraOps/J的性能。波束形成库可以轻松地集成到现有管道中。我们展示了其在医疗超声和射电天文仪器中的应用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 7 figures, accepted at the IEEE International Parallel & Distributed Processing Symposium (IPDPS) 2025
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为Tensor-Core Beamformer的通用优化波束形成库,它利用GPU张量核心的计算能力来加速波束形成计算。该库支持16位和1位精度,并且易于集成到现有管道中。在AMD和NVIDIA GPU上的性能评估表明,与传统波束形成相比,该库具有更高的能效和计算性能。
Key Takeaways
- Tensor-Core Beamformer是一个利用GPU张量核心加速波束形成计算的通用优化库。
- 该库支持16位和1位精度计算,提供了更高的计算性能和能效。
- 在AMD MI300X GPU上,Tensor-Core Beamformer的16位模式实现了超过600 TeraOps/s的性能,接近1 TeraOp/J的能效。
- 在NVIDIA A100 GPU上,该库的1位模式突破了3 PetaOps/s的性能障碍,实现了超过10 TeraOps/J的能效。
- Tensor-Core Beamformer库可以轻松地集成到现有的管道中。
- 该库在医疗超声和射电天文仪器等应用中得到了演示。
点此查看论文截图

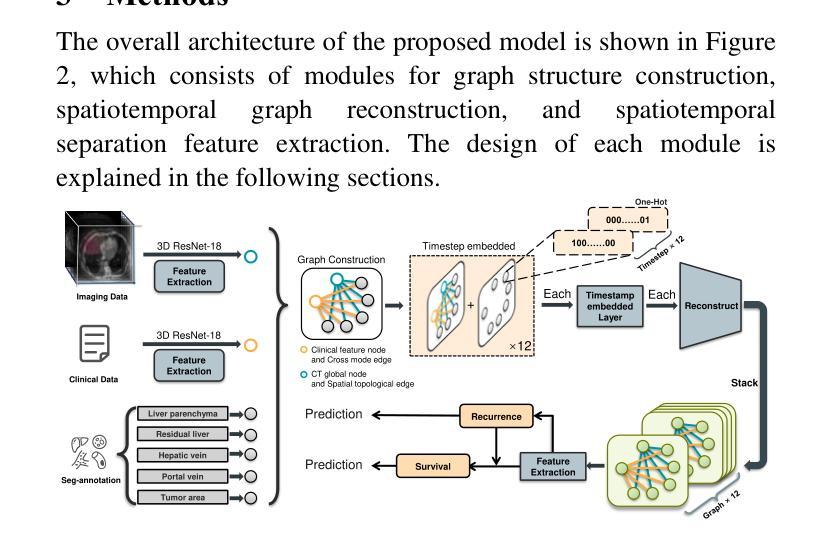
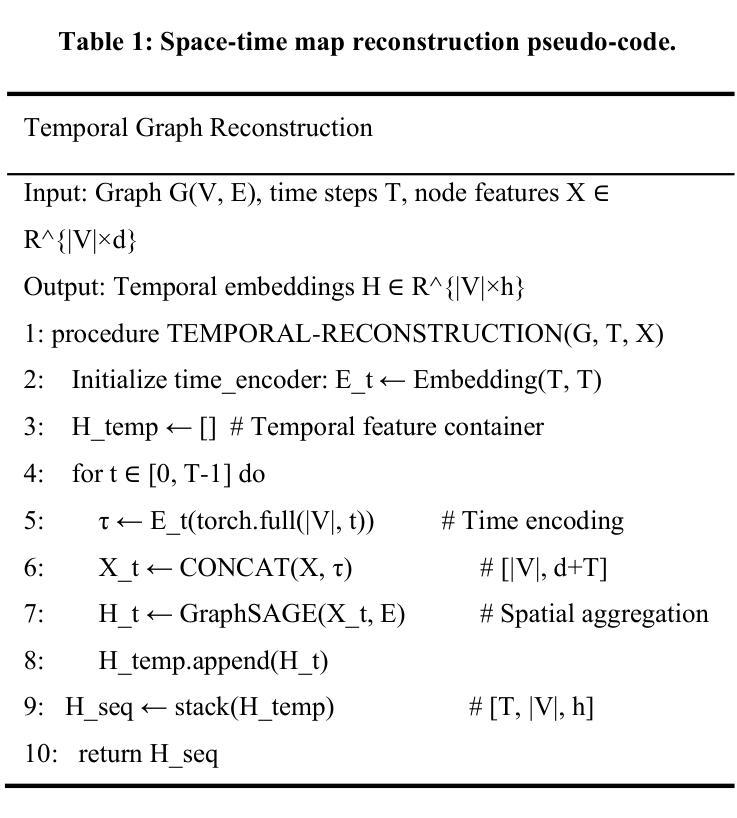
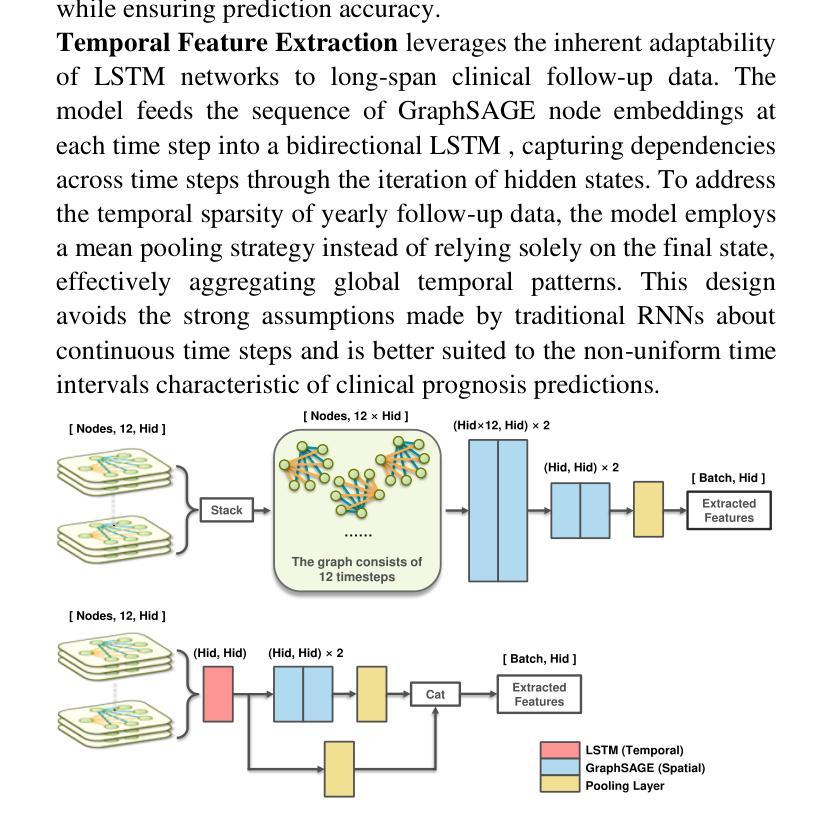
STG: Spatiotemporal Graph Neural Network with Fusion and Spatiotemporal Decoupling Learning for Prognostic Prediction of Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastasis
Authors:Yiran Zhu, Wei Yang, Yan su, Zesheng Li, Chengchang Pan, Honggang Qi
We propose a multimodal spatiotemporal graph neural network (STG) framework to predict colorectal cancer liver metastasis (CRLM) progression. Current clinical models do not effectively integrate the tumor’s spatial heterogeneity, dynamic evolution, and complex multimodal data relationships, limiting their predictive accuracy. Our STG framework combines preoperative CT imaging and clinical data into a heterogeneous graph structure, enabling joint modeling of tumor distribution and temporal evolution through spatial topology and cross-modal edges. The framework uses GraphSAGE to aggregate spatiotemporal neighborhood information and leverages supervised and contrastive learning strategies to enhance the model’s ability to capture temporal features and improve robustness. A lightweight version of the model reduces parameter count by 78.55%, maintaining near-state-of-the-art performance. The model jointly optimizes recurrence risk regression and survival analysis tasks, with contrastive loss improving feature representational discriminability and cross-modal consistency. Experimental results on the MSKCC CRLM dataset show a time-adjacent accuracy of 85% and a mean absolute error of 1.1005, significantly outperforming existing methods. The innovative heterogeneous graph construction and spatiotemporal decoupling mechanism effectively uncover the associations between dynamic tumor microenvironment changes and prognosis, providing reliable quantitative support for personalized treatment decisions.
我们提出了一种多模态时空图神经网络(STG)框架,用于预测结直肠癌肝转移(CRLM)的进展。当前的临床模型不能有效地整合肿瘤的空间异质性、动态演变和复杂的多模态数据关系,从而限制了其预测精度。我们的STG框架将术前CT影像和临床数据整合到异质图结构中,通过空间拓扑和跨模态边缘,实现对肿瘤分布和动态演变的联合建模。该框架使用GraphSAGE聚合时空邻域信息,并利用有监督和对比学习策略,增强模型捕捉时间特征的能力,提高模型的稳健性。模型的轻量级版本通过减少78.55%的参数数量,维持了近乎最前沿的性能。该模型联合优化了复发风险回归和生存分析任务,对比损失提高了特征表示的辨别力和跨模态的一致性。在MSKCC CRLM数据集上的实验结果显示,时间相邻准确率为85%,平均绝对误差为1.1005,显著优于现有方法。创新的异质图构建和时空解耦机制,有效地揭示了动态肿瘤微环境变化和预后之间的关联,为个性化的治疗决策提供了可靠的定量支持。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 4 figures, 5 tables
Summary
提出了一种多模态时空图神经网络(STG)框架,用于预测结肠癌肝转移(CRLM)的进展。该框架结合了术前CT影像和临床数据,创新地使用异质图结构进行肿瘤分布和动态演变的联合建模。通过时空拓扑和跨模态边缘,模型能有效捕捉肿瘤的空间异质性和动态演变。采用GraphSAGE聚合时空邻域信息,并利用监督学习和对比学习策略提高模型捕捉时序特征的能力和稳健性。实验结果显示,该模型在MSKCC CRLM数据集上的时间邻近准确率为85%,平均绝对误差为1.1005,显著优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种多模态时空图神经网络(STG)框架,用于预测结肠癌肝转移(CRLM)的进展。
- 框架结合了术前CT影像和临床数据,形成异质图结构,以联合建模肿瘤分布和动态演变。
- 通过时空拓扑和跨模态边缘,有效捕捉肿瘤的空间异质性和动态演变。
- 使用GraphSAGE聚合时空邻域信息,增强模型捕捉时序特征的能力。
- 采用了监督学习和对比学习策略,提高了模型的稳健性。
- 实验结果显示,该模型在MSKCC CRLM数据集上表现优异,时间邻近准确率高,平均绝对误差小。
点此查看论文截图

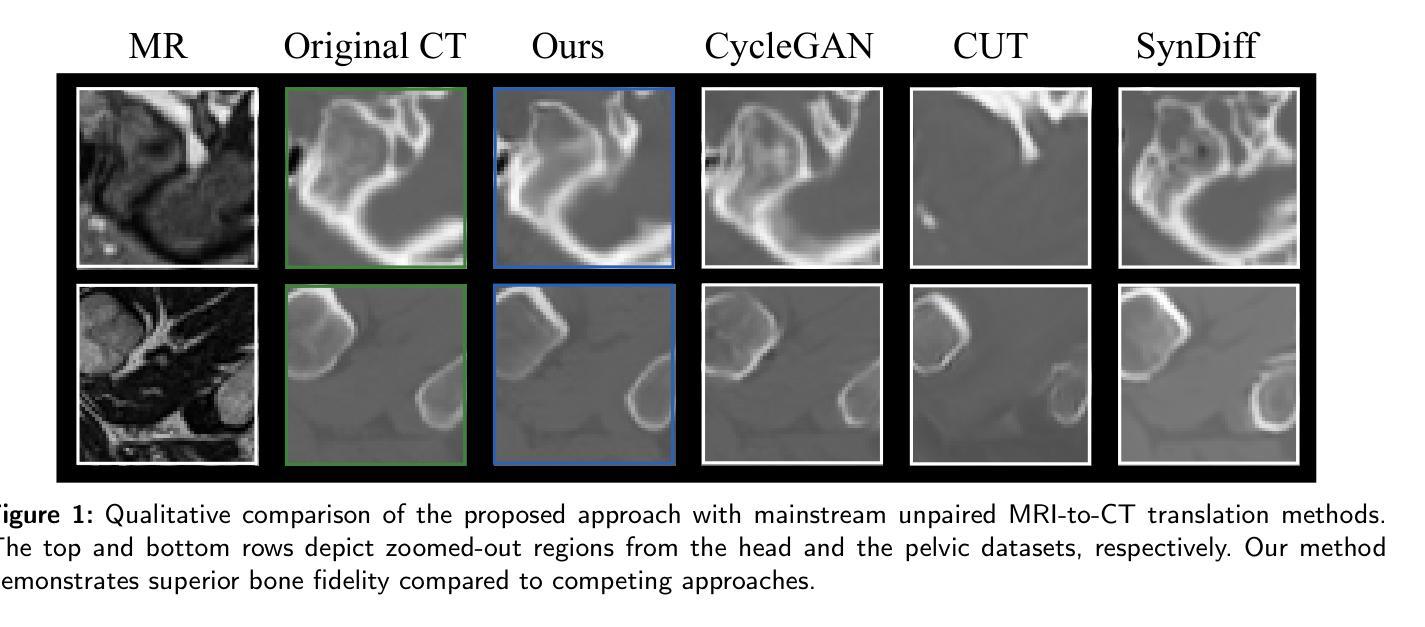
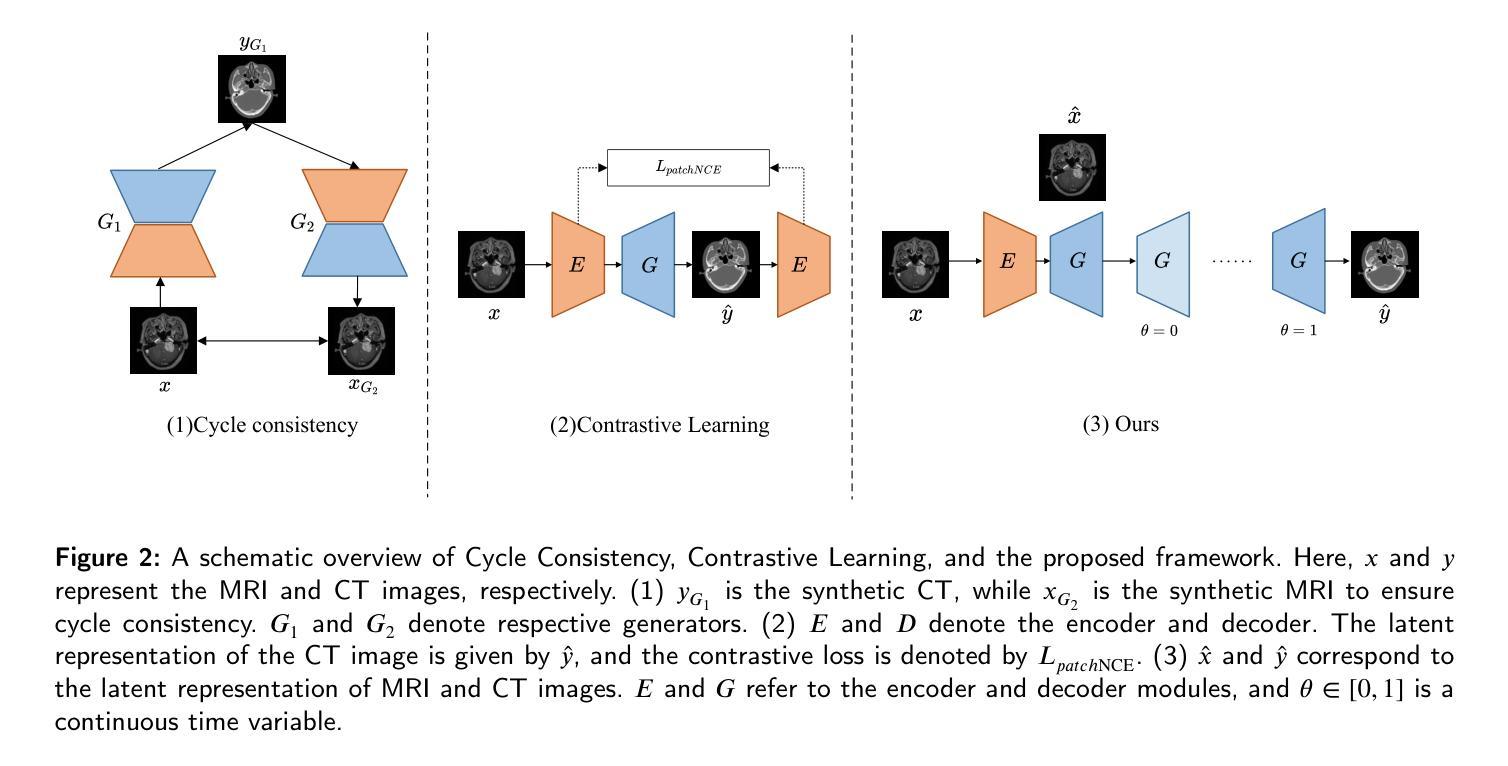
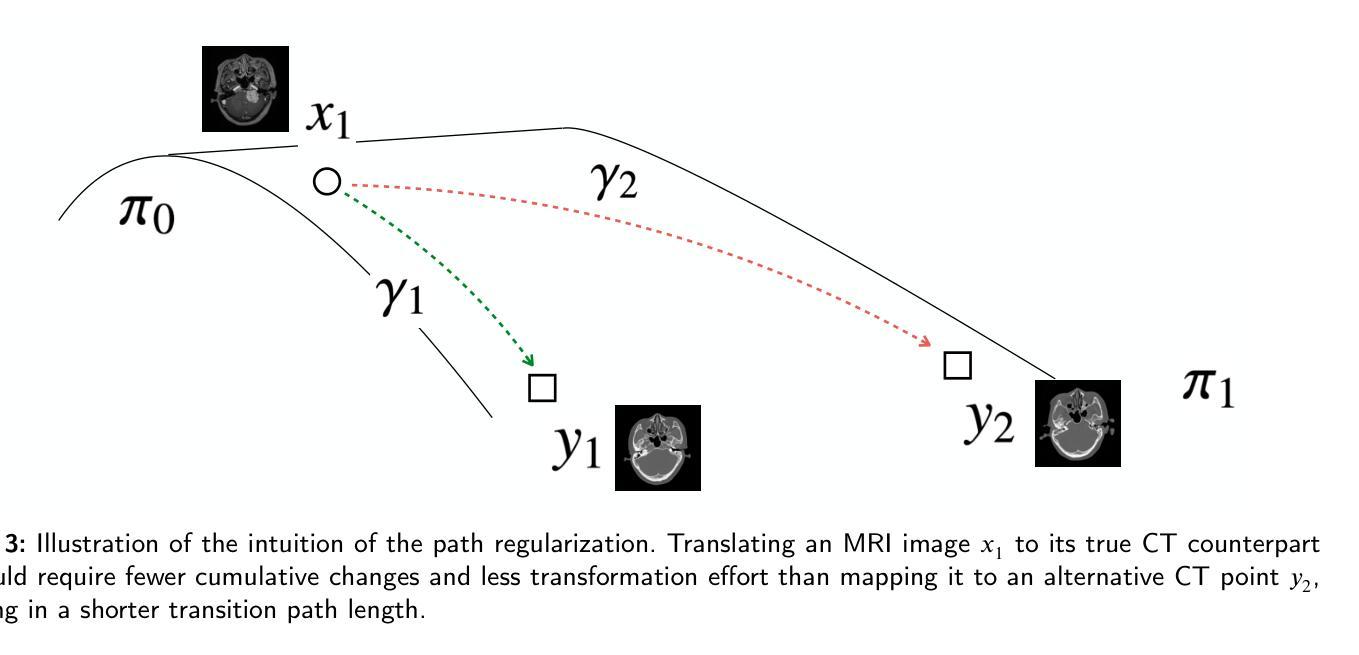
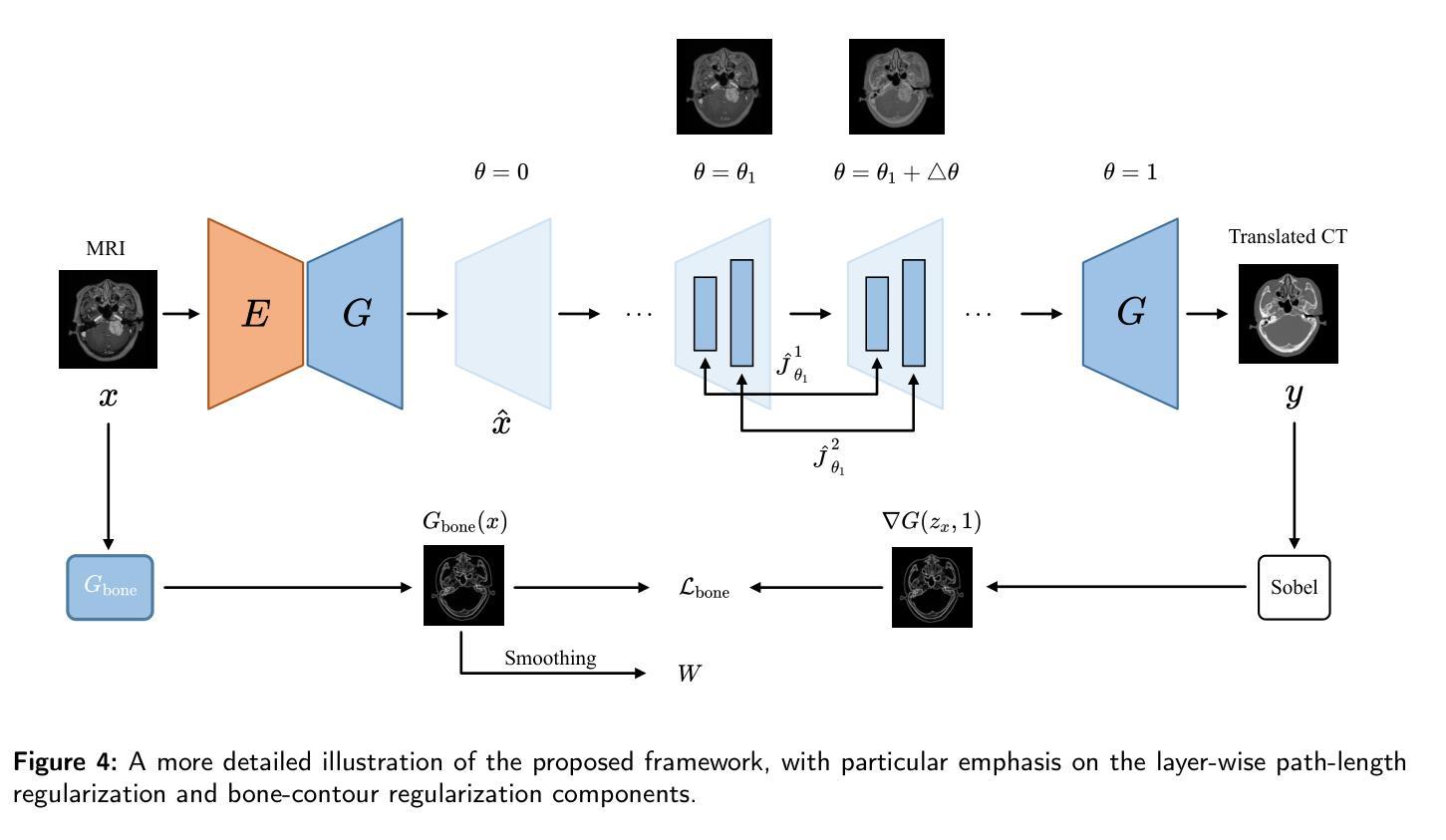
Path and Bone-Contour Regularized Unpaired MRI-to-CT Translation
Authors:Teng Zhou, Jax Luo, Yuping Sun, Yiheng Tan, Shun Yao, Nazim Haouchine, Scott Raymond
Accurate MRI-to-CT translation promises the integration of complementary imaging information without the need for additional imaging sessions. Given the practical challenges associated with acquiring paired MRI and CT scans, the development of robust methods capable of leveraging unpaired datasets is essential for advancing the MRI-to-CT translation. Current unpaired MRI-to-CT translation methods, which predominantly rely on cycle consistency and contrastive learning frameworks, frequently encounter challenges in accurately translating anatomical features that are highly discernible on CT but less distinguishable on MRI, such as bone structures. This limitation renders these approaches less suitable for applications in radiation therapy, where precise bone representation is essential for accurate treatment planning. To address this challenge, we propose a path- and bone-contour regularized approach for unpaired MRI-to-CT translation. In our method, MRI and CT images are projected to a shared latent space, where the MRI-to-CT mapping is modeled as a continuous flow governed by neural ordinary differential equations. The optimal mapping is obtained by minimizing the transition path length of the flow. To enhance the accuracy of translated bone structures, we introduce a trainable neural network to generate bone contours from MRI and implement mechanisms to directly and indirectly encourage the model to focus on bone contours and their adjacent regions. Evaluations conducted on three datasets demonstrate that our method outperforms existing unpaired MRI-to-CT translation approaches, achieving lower overall error rates. Moreover, in a downstream bone segmentation task, our approach exhibits superior performance in preserving the fidelity of bone structures. Our code is available at: https://github.com/kennysyp/PaBoT.
准确的MRI到CT转换技术能够在不需要额外的成像时间的情况下,整合互补的成像信息。考虑到获取配对MRI和CT扫描的实际挑战,开发能够利用未配对数据集的方法对于推动MRI到CT转换技术的发展至关重要。当前的未配对MRI到CT转换方法主要依赖于循环一致性和对比学习框架,但在准确转换那些在CT上清晰可见但在MRI上较难区分的解剖特征时,经常面临挑战,例如骨骼结构。这一局限性使得这些方法不太适合放疗应用,因为在放疗计划中精确的骨骼表示至关重要。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了一种用于未配对MRI到CT转换的路径和骨骼轮廓正则化方法。在我们的方法中,MRI和CT图像被投射到一个共享潜在空间,其中MRI到CT的映射被建模为受神经常微分方程控制的连续流。最佳映射是通过最小化流的过渡路径长度来获得的。为了提高翻译后的骨骼结构的准确性,我们引入了一个可训练的神经网络来从MRI生成骨骼轮廓,并实施了直接和间接鼓励模型关注骨骼轮廓及其邻近区域的机制。在三个数据集上的评估表明,我们的方法优于现有的未配对MRI到CT转换方法,总体误差率更低。此外,在下游的骨骼分割任务中,我们的方法在保持骨骼结构保真度方面表现出卓越的性能。我们的代码可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/kennysyp/PaBoT。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种解决MRI与CT成像信息融合难题的方法。鉴于获得配对MRI和CT扫描的实际挑战,研究团队提出了一个基于路径和骨轮廓正则化的无配对MRI-CT转换方法。通过建模MRI到CT的连续映射,并利用神经常微分方程优化映射路径,提高了骨结构的翻译准确性。该方法在三个数据集上的表现优于现有方法,并在下游骨分割任务中展现了优越的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 研究解决了MRI与CT成像融合中的挑战,尤其是针对骨骼结构的准确翻译问题。
- 提出了基于路径和骨轮廓正则化的无配对MRI-CT转换方法,适用于放射治疗等应用场景。
- 方法通过将MRI和CT图像投影到共享潜在空间,并利用神经常微分方程建模连续映射,优化了映射路径长度。
- 引入可训练的神经网络生成骨轮廓,提高了翻译准确性。
- 在三个数据集上的表现优于现有方法,并在下游骨分割任务中展现出优越性能。
点此查看论文截图

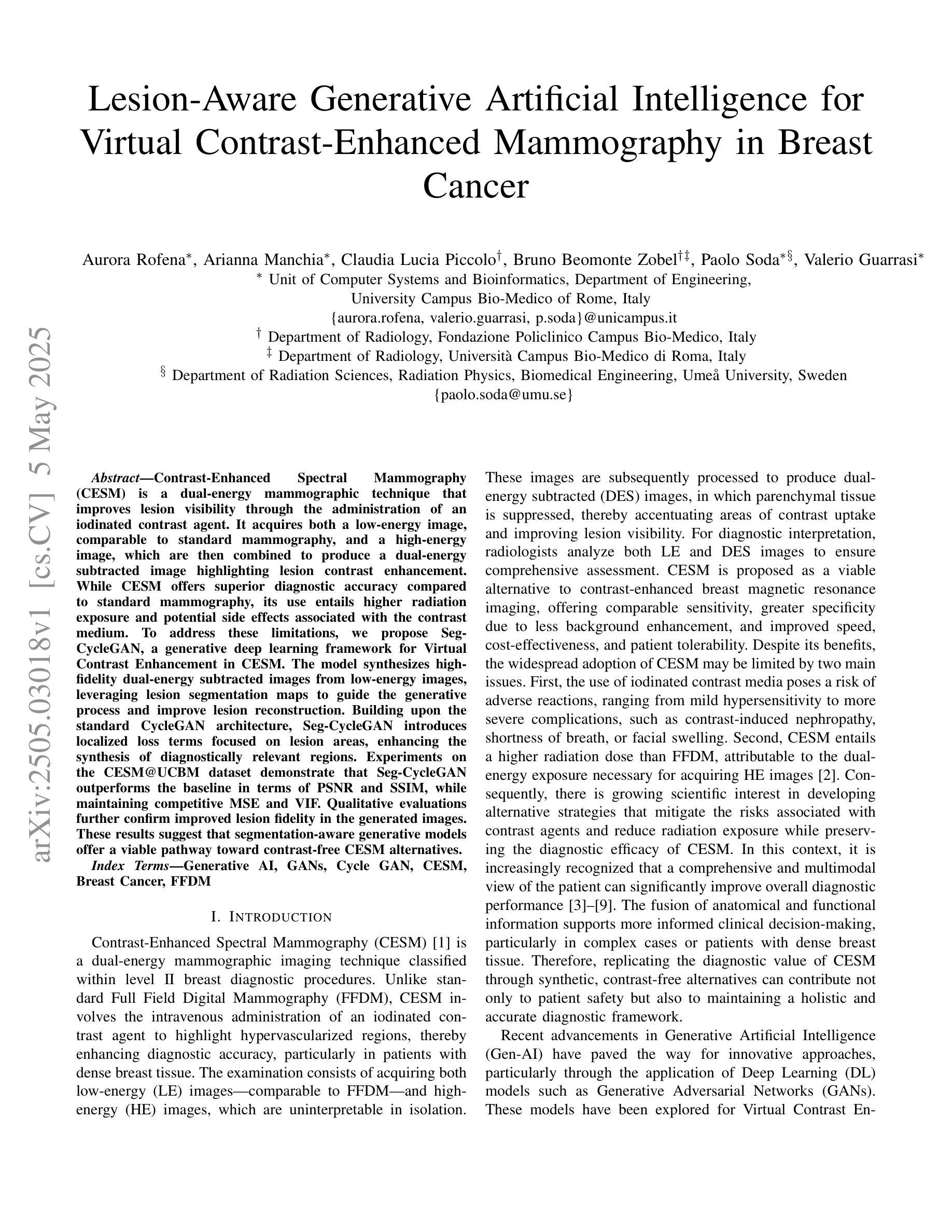
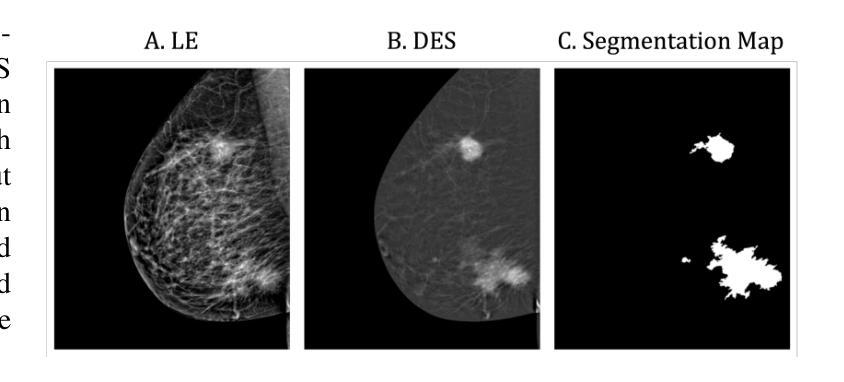
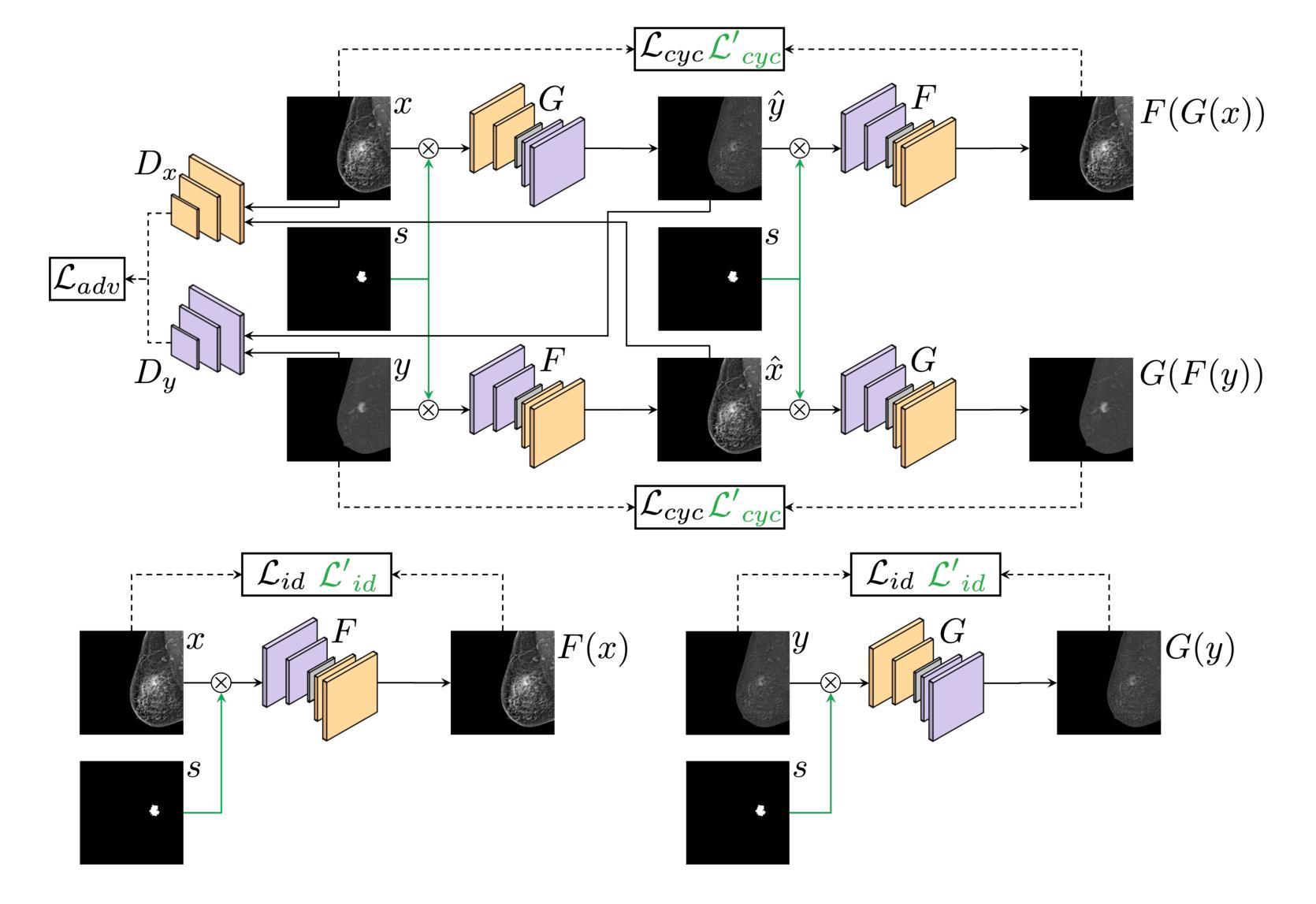
Lesion-Aware Generative Artificial Intelligence for Virtual Contrast-Enhanced Mammography in Breast Cancer
Authors:Aurora Rofena, Arianna Manchia, Claudia Lucia Piccolo, Bruno Beomonte Zobel, Paolo Soda, Valerio Guarrasi
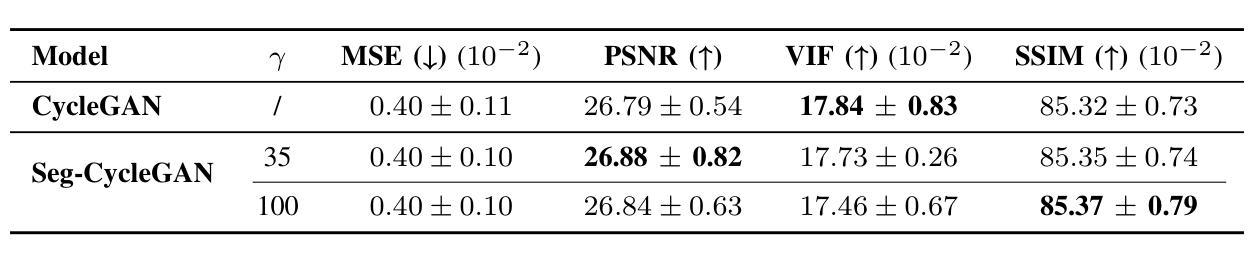
Contrast-Enhanced Spectral Mammography (CESM) is a dual-energy mammographic technique that improves lesion visibility through the administration of an iodinated contrast agent. It acquires both a low-energy image, comparable to standard mammography, and a high-energy image, which are then combined to produce a dual-energy subtracted image highlighting lesion contrast enhancement. While CESM offers superior diagnostic accuracy compared to standard mammography, its use entails higher radiation exposure and potential side effects associated with the contrast medium. To address these limitations, we propose Seg-CycleGAN, a generative deep learning framework for Virtual Contrast Enhancement in CESM. The model synthesizes high-fidelity dual-energy subtracted images from low-energy images, leveraging lesion segmentation maps to guide the generative process and improve lesion reconstruction. Building upon the standard CycleGAN architecture, Seg-CycleGAN introduces localized loss terms focused on lesion areas, enhancing the synthesis of diagnostically relevant regions. Experiments on the CESM@UCBM dataset demonstrate that Seg-CycleGAN outperforms the baseline in terms of PSNR and SSIM, while maintaining competitive MSE and VIF. Qualitative evaluations further confirm improved lesion fidelity in the generated images. These results suggest that segmentation-aware generative models offer a viable pathway toward contrast-free CESM alternatives.
对比增强光谱乳腺摄影(CESM)是一种双能乳腺摄影技术,通过注射碘化造影剂提高病灶的可见性。它获取与标准乳腺摄影相当的低能图像和高能图像,然后将它们组合以产生突出病灶对比增强的双能减影图像。虽然CESM在诊断准确性方面优于标准乳腺摄影,但其使用会带来更高的辐射暴露和与造影剂相关的潜在副作用。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了Seg-CycleGAN,这是一种用于CESM虚拟对比增强的生成深度学习框架。该模型从低能图像中合成高保真双能减影图像,利用病灶分割图来指导生成过程并提高病灶重建。基于标准CycleGAN架构,Seg-CycleGAN引入了局部损失项,重点关注病灶区域,提高了诊断相关区域的合成效果。在CESM@UCBM数据集上的实验表明,Seg-CycleGAN在PSNR和SSIM方面优于基线,同时保持竞争的MSE和VIF。定性评估进一步证实了生成图像中病灶的保真度有所提高。这些结果提示,分割感知生成模型为无对比剂的CESM替代品提供了可行的途径。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
对比增强光谱成像(CESM)是一种双能乳腺X线摄影技术,通过注射碘对比剂提高病灶的可见性。它获取低能量图像(与标准乳腺X线摄影相当)和高能量图像,然后结合产生双能量减去图像,突出病灶的对比度增强。虽然CESM相比标准乳腺X线摄影具有更高的诊断准确性,但其使用会带来更高的辐射暴露和与对比剂相关的潜在副作用。为解决这些局限性,我们提出Seg-CycleGAN,一种用于CESM虚拟对比度增强的生成深度学习框架。该模型从低能量图像中合成高保真双能量减去图像,利用病灶分割图引导生成过程,提高病灶重建。实验表明,Seg-CycleGAN在PSNR和SSIM方面优于基线,同时保持竞争力的MSE和VIF。定性评估进一步证实生成图像中病灶的保真度有所提高。这些结果提示,分割感知生成模型为无对比剂CESM替代品提供了可行的途径。
Key Takeaways
- 对比增强光谱成像(CESM)是一种双能乳腺X线摄影技术,能提高病灶的可见性。
- CESM通过获取低能量和高能量图像,然后结合产生双能量减去图像来突出病灶。
- CESM相较于标准乳腺X线摄影有更高的诊断准确性,但伴随更高的辐射暴露和对比剂潜在副作用。
- Seg-CycleGAN是一种生成深度学习框架,用于CESM的虚拟对比度增强。
- Seg-CycleGAN能从低能量图像中合成高保真双能量减去图像,利用病灶分割图改善生成过程。
- 实验显示Seg-CycleGAN在多种评估标准上表现优异,合成图像的病灶保真度有所提高。
点此查看论文截图
Adversarial Robustness Analysis of Vision-Language Models in Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Anjila Budathoki, Manish Dhakal
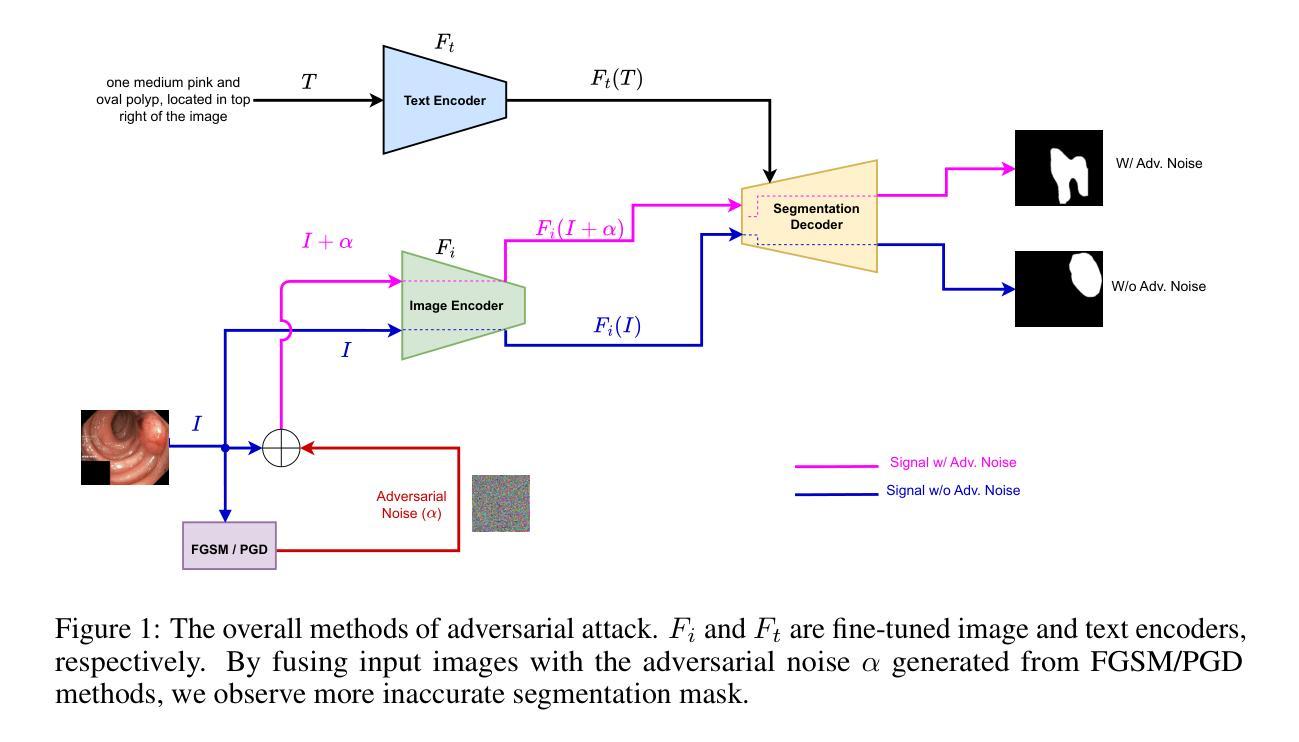
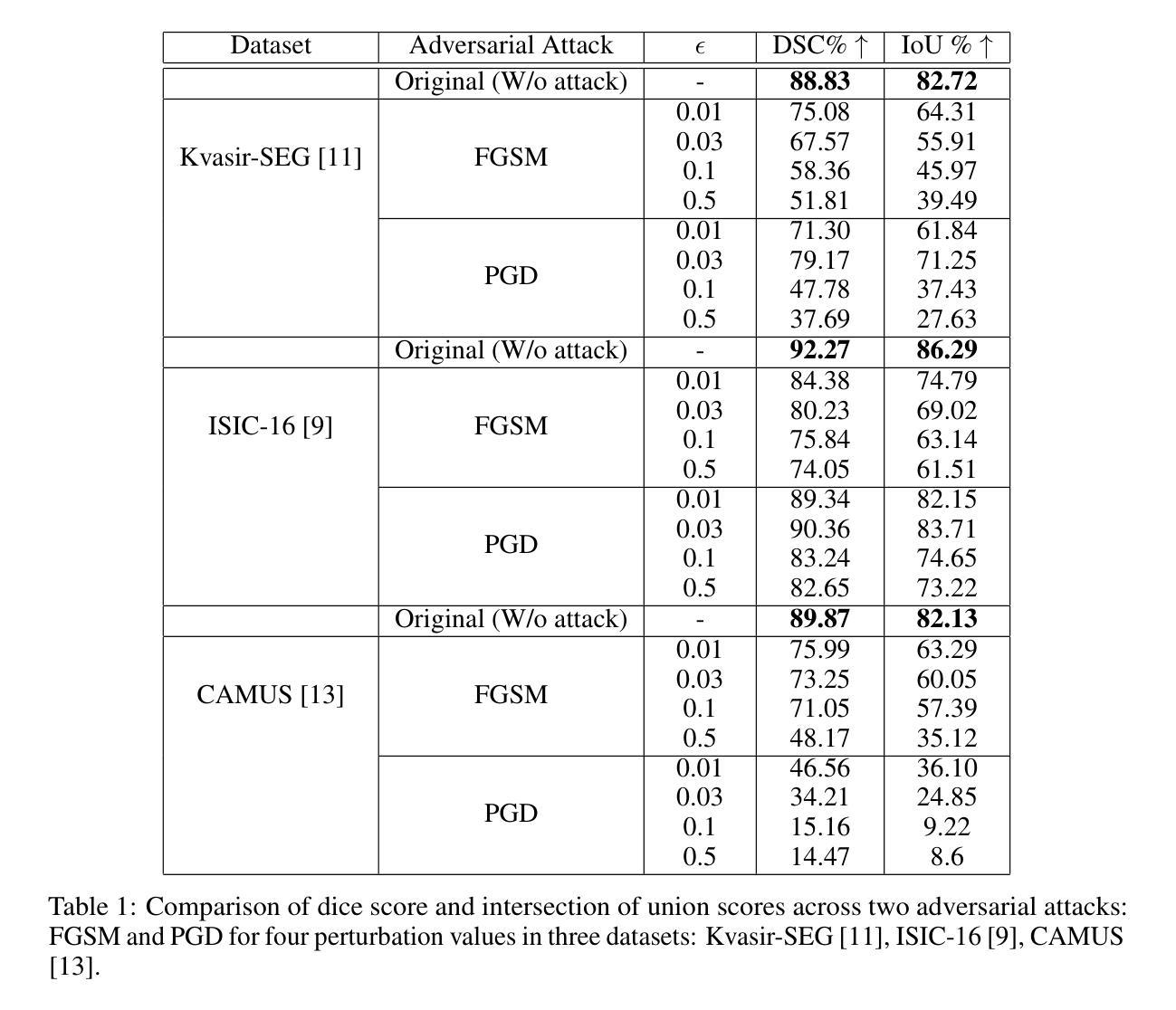
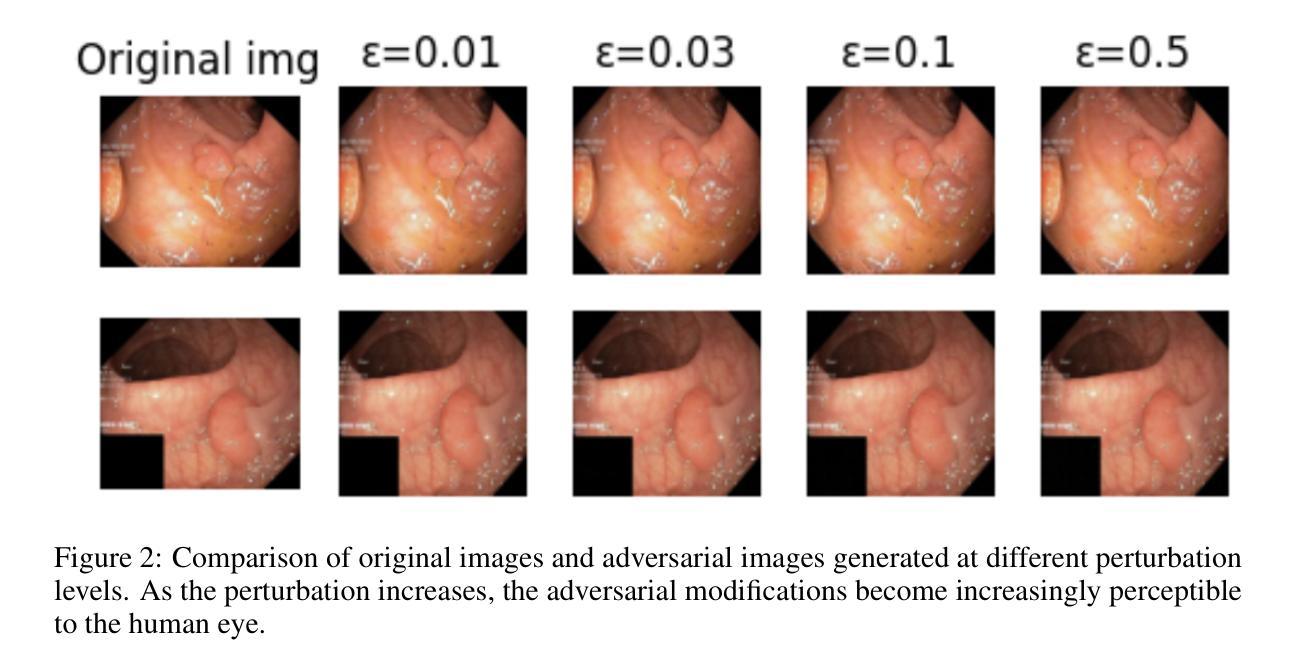
Adversarial attacks have been fairly explored for computer vision and vision-language models. However, the avenue of adversarial attack for the vision language segmentation models (VLSMs) is still under-explored, especially for medical image analysis. Thus, we have investigated the robustness of VLSMs against adversarial attacks for 2D medical images with different modalities with radiology, photography, and endoscopy. The main idea of this project was to assess the robustness of the fine-tuned VLSMs specially in the medical domain setting to address the high risk scenario. First, we have fine-tuned pre-trained VLSMs for medical image segmentation with adapters. Then, we have employed adversarial attacks – projected gradient descent (PGD) and fast gradient sign method (FGSM) – on that fine-tuned model to determine its robustness against adversaries. We have reported models’ performance decline to analyze the adversaries’ impact. The results exhibit significant drops in the DSC and IoU scores after the introduction of these adversaries. Furthermore, we also explored universal perturbation but were not able to find for the medical images. \footnote{https://github.com/anjilab/secure-private-ai}
对抗性攻击在计算机视觉和视觉语言模型方面已经得到了广泛的研究。然而,针对视觉语言分割模型(VLSMs)的对抗性攻击途径,尤其是在医学图像分析方面,仍被较少探索。因此,我们研究了VLSMs对不同模态的二维医学图像(如放射学、摄影和内镜)的对抗性攻击的鲁棒性。此项目的主要目的是评估经过精细调整的VLSMs在医学领域设置中的稳健性,以解决高风险场景问题。首先,我们使用适配器对预训练的VLSMs进行医学图像分割的微调。然后,我们对微调模型采用对抗性攻击——投影梯度下降法(PGD)和快速梯度符号法(FGSM),以确定其对对手的稳健性。我们报告了模型性能下降的情况,以分析对手的影响。结果显示,引入这些对手后,DSC和IoU分数出现了显著下降。此外,我们还探索了通用扰动,但未能针对医学图像找到适用的方法。\footnote{https://github.com/anjilab/secure-private-ai}
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探索了针对二维医学图像的视觉语言分割模型(VLSMs)在医学图像分析领域的对抗攻击研究。通过对预训练的VLSMs进行微调并使用梯度下降投影法和快速梯度符号法进行对抗攻击测试,发现模型性能在引入对抗样本后出现显著下降。尚未实现针对医学图像的全局扰动研究。如需了解更多详情,可访问链接https://github.com/anjilab/secure-private-ai进行查看。
Key Takeaways
- 对抗攻击在医学图像分析领域的视觉语言分割模型(VLSMs)上尚未得到充分研究。
- 通过微调预训练的VLSMs模型并对其进行对抗攻击测试,发现模型性能显著下降。
- 对抗攻击方法包括梯度下降投影法(PGD)和快速梯度符号法(FGSM)。
- 在医学图像分析领域引入对抗样本后,模型的DSC和IoU得分明显下降。
- 目前尚未实现针对医学图像的全局扰动研究。
- 项目旨在评估精细调整的VLSMs在医学领域设置中的稳健性,以应对高风险场景。
点此查看论文截图

Unsupervised Deep Learning-based Keypoint Localization Estimating Descriptor Matching Performance
Authors:David Rivas-Villar, Álvaro S. Hervella, José Rouco, Jorge Novo
Retinal image registration, particularly for color fundus images, is a challenging yet essential task with diverse clinical applications. Existing registration methods for color fundus images typically rely on keypoints and descriptors for alignment; however, a significant limitation is their reliance on labeled data, which is particularly scarce in the medical domain. In this work, we present a novel unsupervised registration pipeline that entirely eliminates the need for labeled data. Our approach is based on the principle that locations with distinctive descriptors constitute reliable keypoints. This fully inverts the conventional state-of-the-art approach, conditioning the detector on the descriptor rather than the opposite. First, we propose an innovative descriptor learning method that operates without keypoint detection or any labels, generating descriptors for arbitrary locations in retinal images. Next, we introduce a novel, label-free keypoint detector network which works by estimating descriptor performance directly from the input image. We validate our method through a comprehensive evaluation on four hold-out datasets, demonstrating that our unsupervised descriptor outperforms state-of-the-art supervised descriptors and that our unsupervised detector significantly outperforms existing unsupervised detection methods. Finally, our full registration pipeline achieves performance comparable to the leading supervised methods, while not employing any labeled data. Additionally, the label-free nature and design of our method enable direct adaptation to other domains and modalities.
视网膜图像配准,尤其是对于彩色眼底图像来说,是一项具有挑战性的但至关重要的任务,在临床应用中具有多种应用。现有的彩色眼底图像配准方法通常依赖于关键点及其描述符来进行对齐;然而,它们的一个重大局限性是依赖于标记数据,这在医学领域尤为稀缺。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新型的无监督配准流程,完全消除了对标记数据的需要。我们的方法基于这样一个原则:具有独特描述符的地点构成可靠的关键点。这完全颠倒了现有的最先进的方法,将探测器置于描述符之上而不是相反。首先,我们提出了一种创新的描述符学习方法,它可以在没有关键点检测或任何标签的情况下运行,为视网膜图像中的任意位置生成描述符。接下来,我们介绍了一种新型的无标签关键点检测网络,它通过直接从输入图像估计描述符性能来工作。我们通过四个独立数据集的综合评估验证了我们的方法,结果表明我们的无监督描述符优于最先进的监督描述符,我们的无监督检测器也显著优于现有的无监督检测方法。最后,我们的完整配准流程在不使用任何标记数据的情况下实现了与领先的有监督方法相当的性能。此外,我们方法的无标签特性和设计使其能够直接适应其他领域和模态。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种无需标注数据的新型视网膜图像注册方法。该方法基于具有独特描述符的地点构成可靠关键点的原理,完全颠覆了传统方法。通过创新的无监督描述符学习方法和标签无关的关键点检测网络,该方法在四个独立数据集上的表现验证了其有效性。此方法无需任何标注数据,性能与领先的监督方法相当,并可直接适应到其他领域和模态。
Key Takeaways
- 视网膜图像注册是颜色眼底图像的重要任务,具有多种临床应用。
- 传统注册方法依赖于关键点和描述符进行对齐,但依赖标注数据存在局限性。
- 本文提出了一种新型无监督注册方法,无需标注数据。
- 该方法基于具有独特描述符的地点构成可靠关键点的原理。
- 创新的无监督描述符学习方法和标签无关的关键点检测网络被提出。
- 方法在四个独立数据集上的表现验证了其有效性。
点此查看论文截图

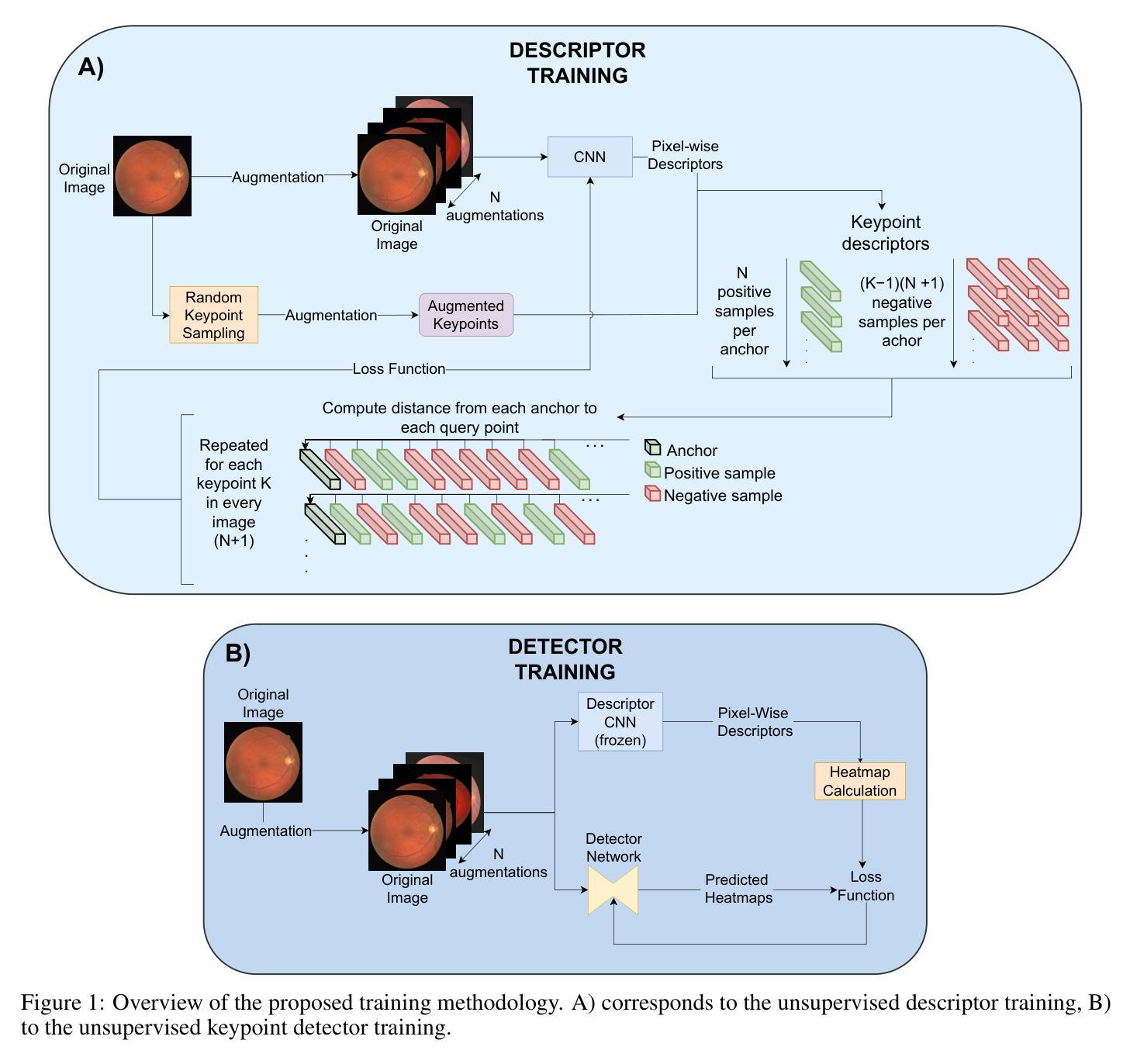
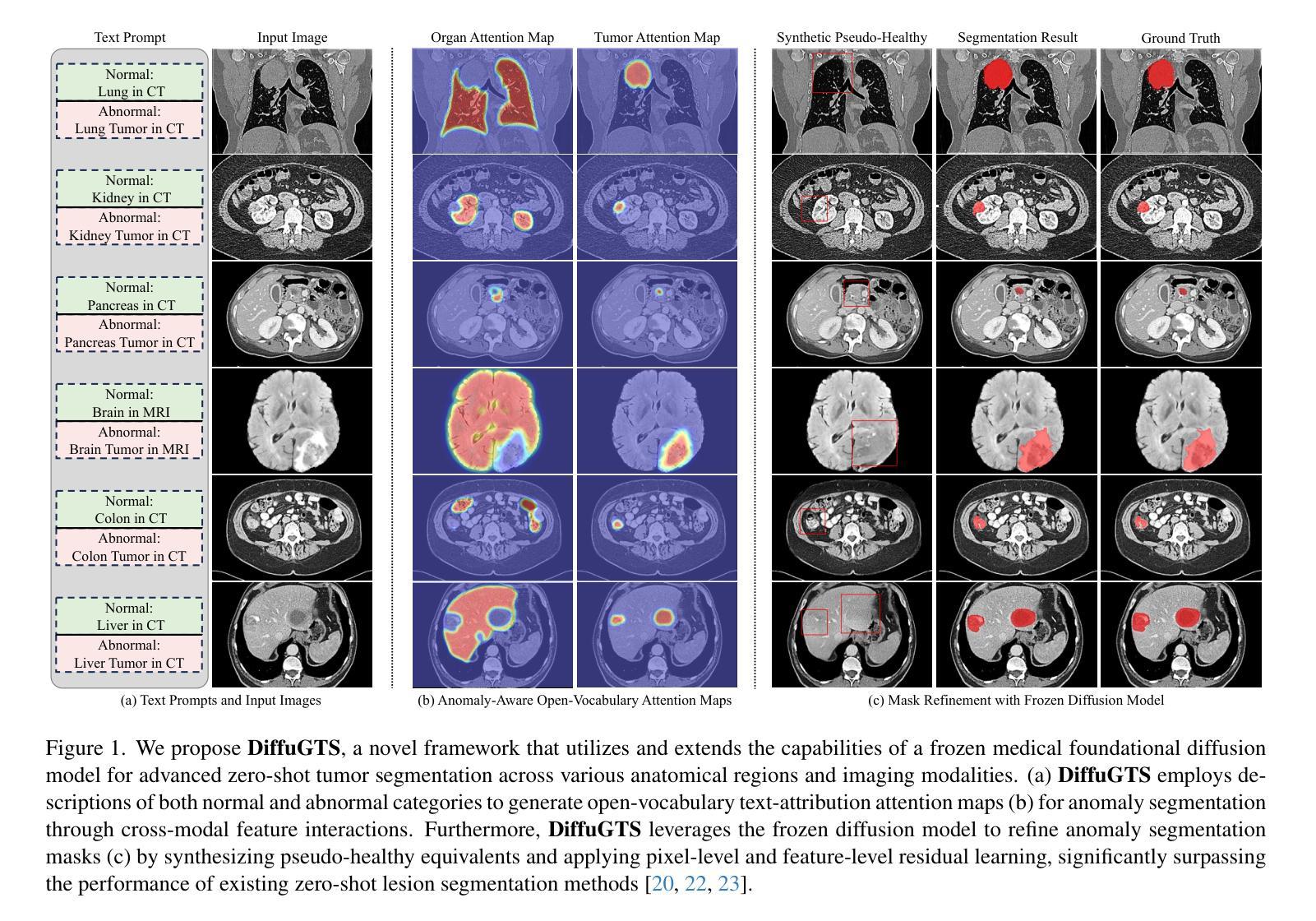
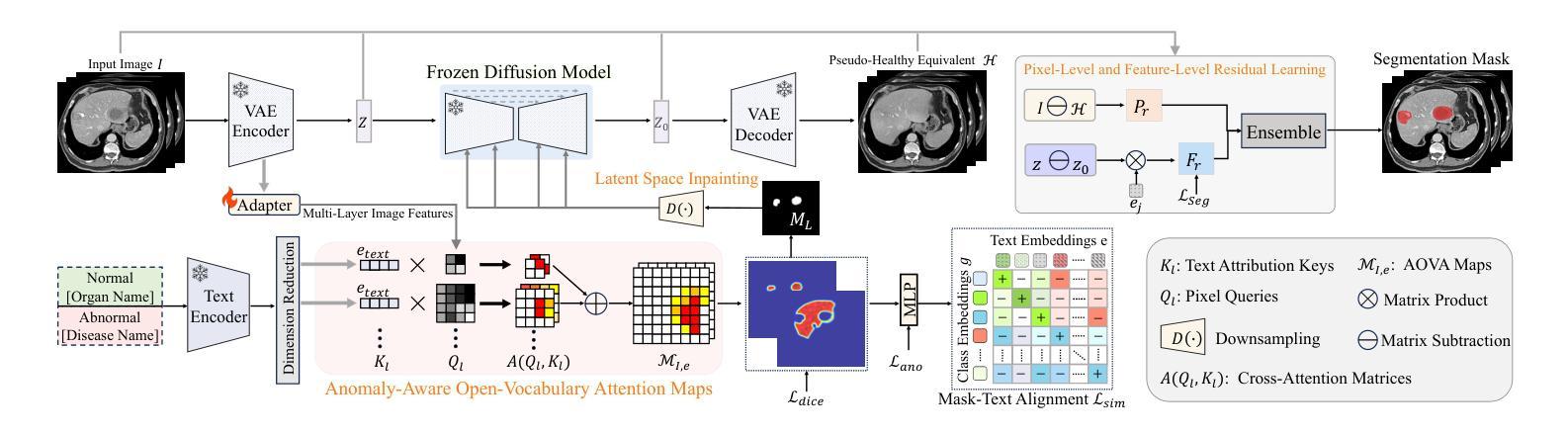
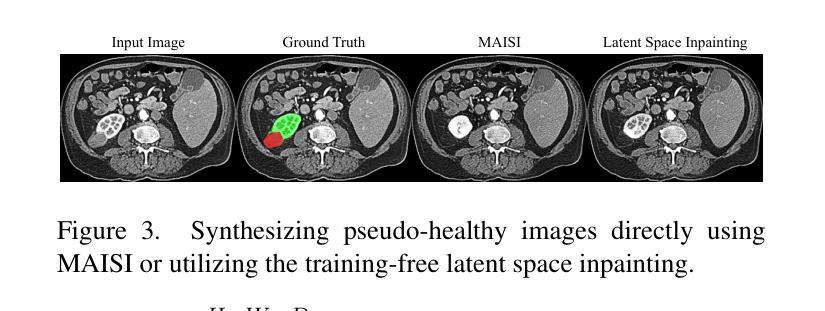
Advancing Generalizable Tumor Segmentation with Anomaly-Aware Open-Vocabulary Attention Maps and Frozen Foundation Diffusion Models
Authors:Yankai Jiang, Peng Zhang, Donglin Yang, Yuan Tian, Hai Lin, Xiaosong Wang
We explore Generalizable Tumor Segmentation, aiming to train a single model for zero-shot tumor segmentation across diverse anatomical regions. Existing methods face limitations related to segmentation quality, scalability, and the range of applicable imaging modalities. In this paper, we uncover the potential of the internal representations within frozen medical foundation diffusion models as highly efficient zero-shot learners for tumor segmentation by introducing a novel framework named DiffuGTS. DiffuGTS creates anomaly-aware open-vocabulary attention maps based on text prompts to enable generalizable anomaly segmentation without being restricted by a predefined training category list. To further improve and refine anomaly segmentation masks, DiffuGTS leverages the diffusion model, transforming pathological regions into high-quality pseudo-healthy counterparts through latent space inpainting, and applies a novel pixel-level and feature-level residual learning approach, resulting in segmentation masks with significantly enhanced quality and generalization. Comprehensive experiments on four datasets and seven tumor categories demonstrate the superior performance of our method, surpassing current state-of-the-art models across multiple zero-shot settings. Codes are available at https://github.com/Yankai96/DiffuGTS.
我们探索了可推广的肿瘤分割技术,旨在针对多个解剖区域进行零样本肿瘤分割训练单个模型。现有方法存在与分割质量、可扩展性和适用成像模式范围相关的局限性。在本文中,我们通过引入一个新的框架DiffuGTS,发现了冻结医疗基础扩散模型内部表示在肿瘤分割中的潜力,作为一种高效的零样本学习者。DiffuGTS基于文本提示创建异常感知开放词汇注意力图,实现了可推广的异常分割,不再局限于预定义的训练类别列表。为了进一步提高和改进异常分割掩膜,DiffuGTS利用扩散模型,通过潜在空间修复将病理区域转换为高质量伪健康对应物,并应用新的像素级和特征级残差学习方法,得到质量显著提高和泛化能力增强的分割掩膜。在四个数据集和七个肿瘤类别的综合实验表明,我们的方法性能优越,在多个零样本设置中超越了当前最先进的模型。代码可在https://github.com/Yankai96/DiffuGTS获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper is accepted to CVPR 2025
Summary
本文探索了通用肿瘤分割技术,旨在针对多种解剖区域进行零样本肿瘤分割的单模型训练。文章引入了一个名为DiffuGTS的新型框架,利用冻结的医疗基础扩散模型内的内部表征作为零样本肿瘤分割的高效学习者。DiffuGTS创建基于文本提示的异常感知开放词汇注意力图,以实现可推广的异常分割,而不受预设训练类别列表的限制。通过扩散模型改进和细化异常分割掩膜,通过将病理区域转化为高质量的伪健康对应物,并在像素级别和特征级别应用新型的残差学习方法,获得质量更高、泛化性更强的分割掩膜。在四个数据集和七个肿瘤类别上的综合实验表明,该方法性能卓越,在多零样本设置中超越了当前最先进的模型。
Key Takeaways
- 研究目标是实现通用肿瘤分割,旨在训练一个单一模型来适应多种解剖区域的零样本肿瘤分割。
- 引入新型框架DiffuGTS,利用冻结的医疗基础扩散模型的内部表征进行零样本学习。
- DiffuGTS通过创建异常感知开放词汇注意力图,实现可推广的异常分割。
- 扩散模型用于改进和细化异常分割掩膜,通过转化病理区域并应用新型的像素级和特征级残差学习方法提高分割质量。
- 方法在四个数据集和七个肿瘤类别上的实验表现卓越,超越了现有的最先进模型。
- 研究提供的代码可在公开代码库中找到(https://github.com/Yankai96/DiffuGTS)。
点此查看论文截图

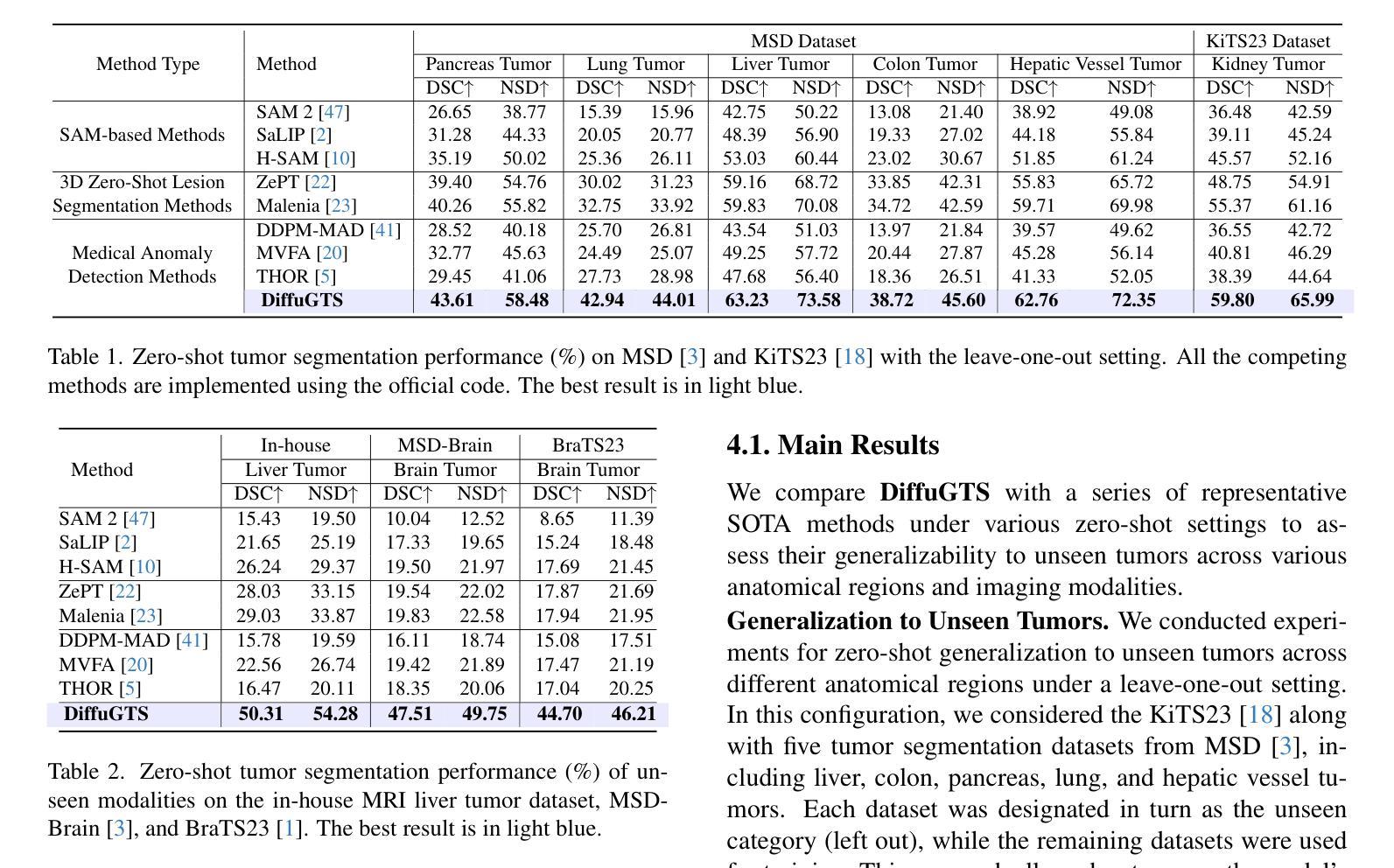
Timing Is Everything: Finding the Optimal Fusion Points in Multimodal Medical Imaging
Authors:Valerio Guarrasi, Klara Mogensen, Sara Tassinari, Sara Qvarlander, Paolo Soda
Multimodal deep learning harnesses diverse imaging modalities, such as MRI sequences, to enhance diagnostic accuracy in medical imaging. A key challenge is determining the optimal timing for integrating these modalities-specifically, identifying the network layers where fusion modules should be inserted. Current approaches often rely on manual tuning or exhaustive search, which are computationally expensive without any guarantee of converging to optimal results. We propose a sequential forward search algorithm that incrementally activates and evaluates candidate fusion modules at different layers of a multimodal network. At each step, the algorithm retrains from previously learned weights and compares validation loss to identify the best-performing configuration. This process systematically reduces the search space, enabling efficient identification of the optimal fusion timing without exhaustively testing all possible module placements. The approach is validated on two multimodal MRI datasets, each addressing different classification tasks. Our algorithm consistently identified configurations that outperformed unimodal baselines, late fusion, and a brute-force ensemble of all potential fusion placements. These architectures demonstrated superior accuracy, F-score, and specificity while maintaining competitive or improved AUC values. Furthermore, the sequential nature of the search significantly reduced computational overhead, making the optimization process more practical. By systematically determining the optimal timing to fuse imaging modalities, our method advances multimodal deep learning for medical imaging. It provides an efficient and robust framework for fusion optimization, paving the way for improved clinical decision-making and more adaptable, scalable architectures in medical AI applications.
多模态深度学习利用多种成像模态(如MRI序列)来提高医学成像的诊断准确性。一个关键挑战是确定整合这些模态的最佳时机,特别是确定应插入融合模块的网络层。当前的方法通常依赖于手动调整或穷举搜索,这不仅计算成本高,而且无法保证收敛到最优结果。我们提出了一种顺序前向搜索算法,该算法可以在多模态网络的不同层级逐步激活并评估候选融合模块。在每一步中,该算法都会根据先前学习的权重进行再训练,并通过比较验证损失来识别表现最佳的配置。这个过程系统地减少了搜索空间,能够高效确定最优融合时间,而无需对所有可能的模块放置进行全面测试。该方法在两个多模态MRI数据集上进行了验证,每个数据集都针对不同的分类任务。我们的算法始终能够识别出优于单模态基准、后期融合以及所有潜在融合放置的暴力组合的配置。这些架构在保持竞争力或提高AUC值的同时,展示了更高的准确性、F分数和特异性。此外,搜索的顺序性显著减少了计算开销,使优化过程更加实用。通过系统确定融合成像模态的最佳时机,我们的方法为医学成像中的多模态深度学习提供了先进的优化框架。这为改进临床决策制定和医学人工智能应用中的更灵活、可扩展架构铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了多模态深度学习在医学成像中的应用,通过融合多种成像模态(如MRI序列)提高诊断准确性。针对如何确定融合模态的最优时机问题,提出了一种基于序贯前向搜索算法的多模态融合优化方法。该方法能够在不同层的多模态网络中逐步激活和评估候选融合模块,通过比较验证损失来识别最佳配置,有效减少搜索空间,避免昂贵的计算成本。在两种多模态MRI数据集上的实验表明,该方法能够有效识别出优于单模态基线、后期融合及所有潜在融合放置的暴力组合的配置,具有更高的准确性、F值和特异性,同时保持竞争力或提高AUC值。该方法的优化过程更为实用和高效,为临床决策制定提供了先进的多模态深度学习框架,促进了医学人工智能应用的适应性和可扩展性。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态深度学习通过融合多种成像模态提高医学成像诊断准确性。
- 确定融合模态的最优时机是重要挑战。
- 现有方法依赖手动调整或穷举搜索,计算成本高且无法保证最优结果。
- 提出了基于序贯前向搜索算法的多模态融合优化方法。
- 方法能有效减少搜索空间,高效确定最优融合时机。
- 实验证明该方法在多种配置下优于其他方法,具有更高的准确性、F值和特异性。
点此查看论文截图

Sampling Kantorovich operators for speckle noise reduction using a Down-Up scaling approach and gap filling in remote sensing images
Authors:Danilo Costarelli, Mariarosaria Natale
In the literature, several approaches have been proposed for restoring and enhancing remote sensing images, including methods based on interpolation, filtering, and deep learning. In this paper, we investigate the application of multivariate sampling Kantorovich (SK) operators for image reconstruction, with a particular focus on gap filling and speckle noise reduction. To understand the accuracy performances of the proposed algorithms, we first derive a quantitative estimate in $C(\R^n)$ for the error of approximation using the Euler-Maclaurin summation formula, which provides sharper error bounds under minimal regularity conditions. We also establish a convergence result and a quantitative estimate with respect to the dissimilarity index measured by the continuous SSIM for functions in Lebesgue spaces. Additionally, we prove a multidimensional linear prediction result, which is used to design a new SK-based reconstruction algorithm to handle missing data, that we call LP-SK algorithm. To address speckle noise, we integrate SK operators into a newly proposed Down-Up scaling approach. Numerical tests are presented on synthetic and real SAR images to validate the proposed methods. Performance is assessed using similarity metrics such as SSIM and PSNR, along with speckle-specific indexes. Comparative analysis with state-of-the-art techniques highlights the effectiveness of the proposed approaches.
在文献中,已经提出了多种恢复和增强遥感图像的方法,包括基于插值、滤波和深度学习的方法。本文研究了多元采样Kantorovich(SK)算子在图像重建中的应用,特别关注间隙填充和斑点噪声减少。为了了解所提出算法的准确性能,我们首先使用Euler-Maclaurin求和公式对误差进行定量估计,在最小的正规性条件下提供更精确的误差界限。我们还针对黎曼空间中的函数建立了关于连续结构相似性指标的不相似性指数的收敛性和定量估计结果。此外,我们还证明了多维线性预测结果,用于设计一种新型的基于SK的重建算法来处理缺失数据,我们称之为LP-SK算法。为了解决斑点噪声问题,我们将SK算子集成到一种新提出的自下而上缩放方法中。对合成和真实SAR图像进行了数值测试,以验证所提出的方法。性能评估采用结构相似性度量(SSIM)和峰值信噪比(PSNR)以及斑点特定指标。与最新技术的对比分析突显了所提出方法的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究探讨了多元采样Kantorovich算子在遥感图像重建中的应用,重点关注了数据填充和斑点噪声降低。研究内容包括误差估计、收敛性结果、基于连续SSIM的勒贝格空间中的定量评估,以及用于处理缺失数据的新SK重建算法设计。同时,研究将SK算子与新的Down-Up缩放方法相结合以解决斑点噪声问题。通过合成和真实SAR图像的数值测试验证了方法的有效性,并与最新技术进行了比较分析。
Key Takeaways
- 研究提出使用多元采样Kantorovich(SK)算子进行遥感图像重建。
- 重点关注数据填充和斑点噪声降低问题。
- 通过Euler-Maclaurin求和公式进行误差估计,并提供了更精确的误差边界。
- 建立了关于连续SSIM的收敛性和定量评估结果。
- 设计了一种新的基于SK算子的重建算法(LP-SK算法)来处理缺失数据。
- 将SK算子与Down-Up缩放方法结合,以解决斑点噪声问题。
点此查看论文截图

Regression is all you need for medical image translation
Authors:Sebastian Rassmann, David Kügler, Christian Ewert, Martin Reuter
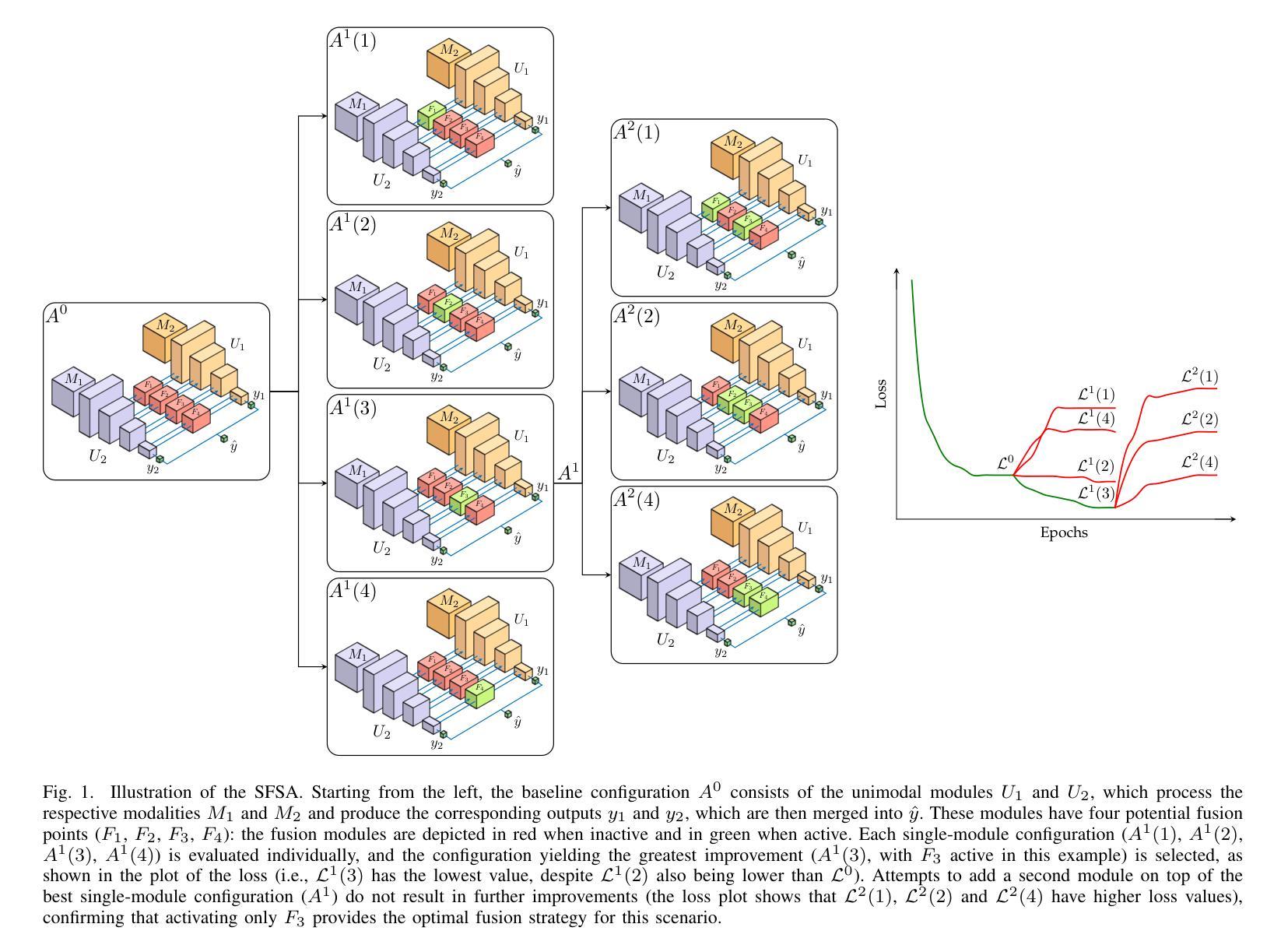
The acquisition of information-rich images within a limited time budget is crucial in medical imaging. Medical image translation (MIT) can help enhance and supplement existing datasets by generating synthetic images from acquired data. While Generative Adversarial Nets (GANs) and Diffusion Models (DMs) have achieved remarkable success in natural image generation, their benefits - creativity and image realism - do not necessarily transfer to medical applications where highly accurate anatomical information is required. In fact, the imitation of acquisition noise or content hallucination hinder clinical utility. Here, we introduce YODA (You Only Denoise once - or Average), a novel 2.5D diffusion-based framework for volumetric MIT. YODA unites diffusion and regression paradigms to produce realistic or noise-free outputs. Furthermore, we propose Expectation-Approximation (ExpA) DM sampling, which draws inspiration from MRI signal averaging. ExpA-sampling suppresses generated noise and, thus, eliminates noise from biasing the evaluation of image quality. Through extensive experiments on four diverse multi-modal datasets - comprising multi-contrast brain MRI and pelvic MRI-CT - we show that diffusion and regression sampling yield similar results in practice. As such, the computational overhead of diffusion sampling does not provide systematic benefits in medical information translation. Building on these insights, we demonstrate that YODA outperforms several state-of-the-art GAN and DM methods. Notably, YODA-generated images are shown to be interchangeable with, or even superior to, physical acquisitions for several downstream tasks. Our findings challenge the presumed advantages of DMs in MIT and pave the way for the practical application of MIT in medical imaging.
在医学成像中,在有限的时间预算内获取信息丰富的图像至关重要。医学图像翻译(MIT)可以通过从获取的数据生成合成图像来增强和补充现有的数据集。虽然生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型(DMs)在自然图像生成方面取得了显著的成功,它们在医学应用中并不一定能发挥出创造性和图像真实性的优势,因为医学应用需要高度准确的解剖信息。事实上,模仿获取噪声或内容幻觉会阻碍其在临床上的实用性。在这里,我们介绍了YODA(You Only Denoise once - or Average),这是一个新型的基于2.5D扩散的体积医学图像翻译框架。YODA结合了扩散和回归范式,以产生逼真的或无噪声的输出。此外,我们提出了期望近似(ExpA)DM采样,它受到MRI信号平均的启发。ExpA采样抑制生成的噪声,从而消除噪声对图像质量评估的偏见。通过在四个不同的多模式数据集上进行的大量实验(包括多对比度脑部MRI和盆腔MRI-CT),我们证明了扩散采样和回归采样在实践中可以得到类似的结果。因此,扩散采样在计算上的开销并没有在医学信息翻译中提供系统性的优势。基于这些见解,我们证明了YODA优于几种最先进的GAN和DM方法。值得注意的是,YODA生成的图像被证明可以替换或甚至优于某些下游任务的物理采集。我们的研究挑战了DM在MIT中的既定优势,为医学成像中MIT的实际应用铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
医学信息成像中,在有限的时间预算内获取信息丰富的图像至关重要。医学图像翻译(MIT)可以通过生成合成图像来增强和补充现有数据集。虽然生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型(DMs)在自然图像生成方面取得了显著的成功,但其在医学应用中却存在挑战,因为医学应用要求高度的解剖准确性。事实上,对采集噪声的模仿或内容幻觉阻碍了其在临床上的效用。本文介绍了一种新型的2.5D扩散式医学图像翻译框架YODA(You Only Denoise once - or Average)。YODA结合了扩散和回归范式,生成逼真的或无噪声的输出。此外,本文还提出了期望近似(ExpA)DM采样方法,该方法从MRI信号平均中获得灵感。ExpA采样抑制生成噪声,从而消除噪声对图像质量评估的偏见。在包含多对比度脑部MRI和盆腔MRI-CT的四个不同多模式数据集上进行的广泛实验表明,扩散采样和回归采样在实践中产生相似结果。因此,扩散采样在医学信息翻译中的计算开销并未带来系统性优势。基于这些见解,我们证明YODA优于几种最先进的GAN和DM方法。值得注意的是,YODA生成的图像被证明可与物理采集互换,甚至在某些下游任务中表现更佳。我们的研究结果挑战了DM在MIT中的假设优势,为医学成像中的MIT实际应用铺平了道路。
关键见解
- 医学成像中,有限时间内获取丰富信息的图像至关重要。
- 医学图像翻译(MIT)可以通过生成合成图像增强和补充现有数据集。
- 虽然GANs和DMs在自然图像生成方面表现出色,但它们在医学应用中并不总能保持同样的优势,因为医学应用要求图像的解剖信息高度准确。
- 提出的YODA框架结合了扩散和回归范式,生成逼真的或无噪声的输出。
- ExpA-sampling方法能从MRI信号平均中获得灵感,有效抑制生成噪声。
- 扩散采样与回归采样在实践中效果相似,计算开销未带来显著优势。
点此查看论文截图

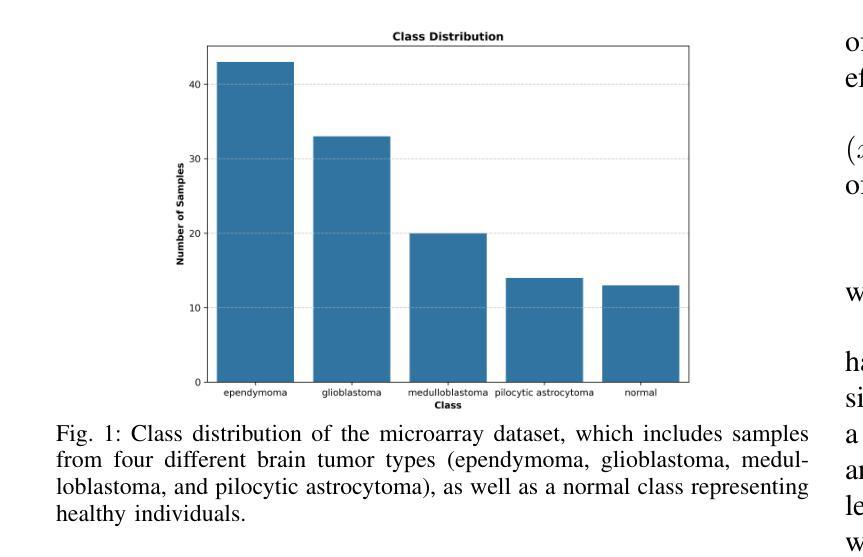
Quantum-Enhanced Classification of Brain Tumors Using DNA Microarray Gene Expression Profiles
Authors:Emine Akpinar, Batuhan Hangun, Murat Oduncuoglu, Oguz Altun, Onder Eyecioglu, Zeynel Yalcin
DNA microarray technology enables the simultaneous measurement of expression levels of thousands of genes, thereby facilitating the understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying complex diseases such as brain tumors and the identification of diagnostic genetic signatures. To derive meaningful biological insights from the high-dimensional and complex gene features obtained through this technology and to analyze gene properties in detail, classical AI-based approaches such as machine learning and deep learning are widely employed. However, these methods face various limitations in managing high-dimensional vector spaces and modeling the intricate relationships among genes. In particular, challenges such as hyperparameter tuning, computational costs, and high processing power requirements can hinder their efficiency. To overcome these limitations, quantum computing and quantum AI approaches are gaining increasing attention. Leveraging quantum properties such as superposition and entanglement, quantum methods enable more efficient parallel processing of high-dimensional data and offer faster and more effective solutions to problems that are computationally demanding for classical methods. In this study, a novel model called “Deep VQC” is proposed, based on the Variational Quantum Classifier approach. Developed using microarray data containing 54,676 gene features, the model successfully classified four different types of brain tumors-ependymoma, glioblastoma, medulloblastoma, and pilocytic astrocytoma-alongside healthy samples with high accuracy. Furthermore, compared to classical ML algorithms, our model demonstrated either superior or comparable classification performance. These results highlight the potential of quantum AI methods as an effective and promising approach for the analysis and classification of complex structures such as brain tumors based on gene expression features.
DNA微阵列技术可以同时测量数千个基因的表达水平,从而有助于了解脑肿瘤等复杂疾病的分子机制,并确定诊断基因特征。为了从该技术获得的高维和复杂的基因特征中得出有意义的生物学见解,并详细分析基因属性,广泛采用了基于机器学习和深度学习等经典的人工智能方法。然而,这些方法在处理高维向量空间以及建模基因之间复杂关系方面存在各种局限性。特别是,超参数调整、计算成本和高度处理功率要求等挑战可能会阻碍其效率。为了克服这些局限性,量子计算和量子人工智能方法越来越受到关注。利用量子叠加和纠缠等量子属性,量子方法能够更有效地并行处理高维数据,并为经典方法计算上难以处理的问题提供更快速和有效的解决方案。本研究提出了一种基于变分量子分类器方法的新型模型,名为“Deep VQC”。该模型使用包含54676个基因特征的微阵列数据开发而成,成功地将四种不同类型的脑肿瘤(室管膜瘤、胶质母细胞瘤、髓母细胞瘤和星形细胞瘤)以及健康样本进行了高准确度的分类。此外,与经典机器学习算法相比,我们的模型表现出优越或相当的分类性能。这些结果突出了量子人工智能方法在脑肿瘤等复杂结构的分析和分类中的潜力和前景,有望成为一种基于基因表达特征的有效且前景广阔的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
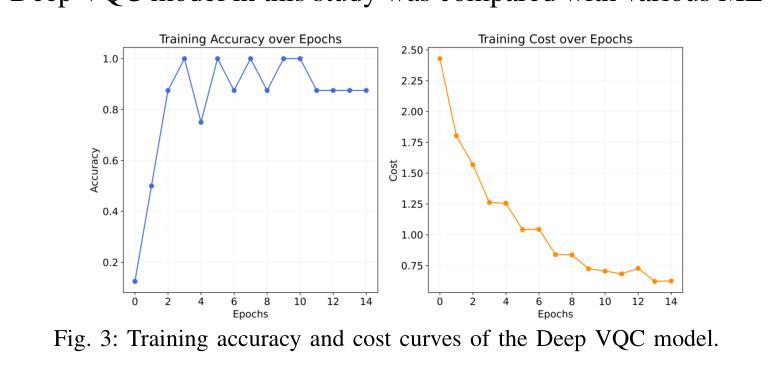
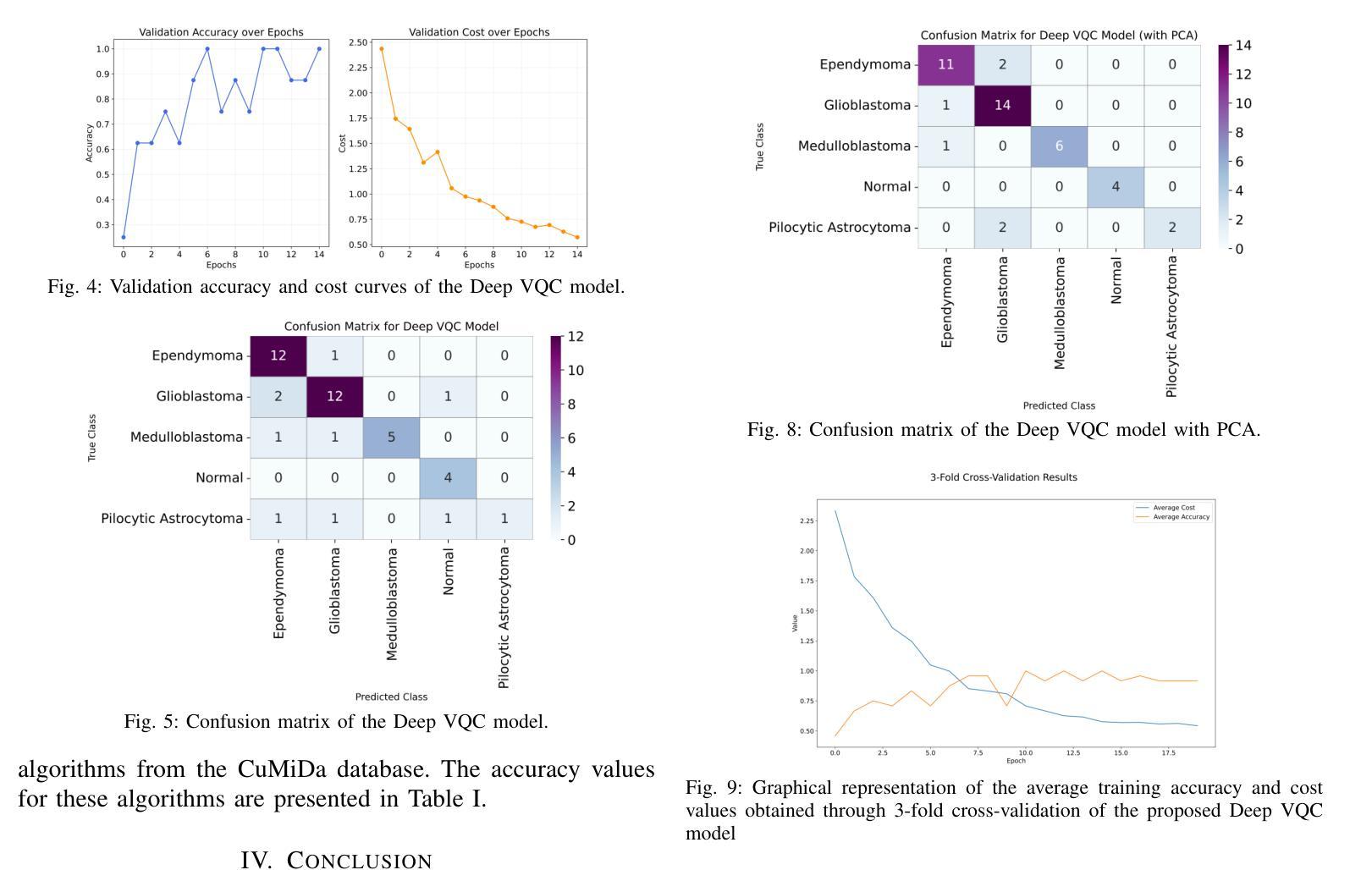
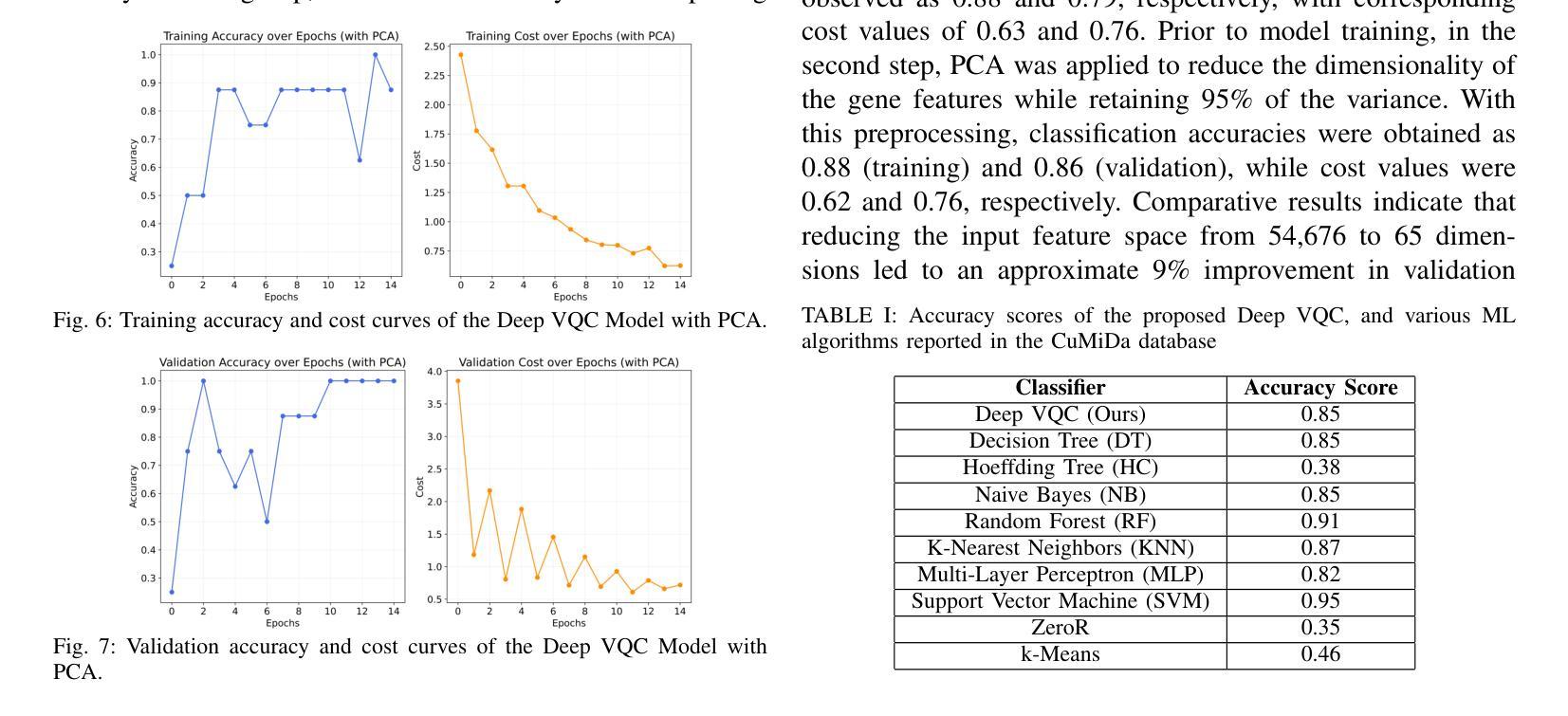
Summary
本文介绍了DNA微阵列技术在基因表达水平检测方面的应用,并指出其在理解复杂疾病如脑肿瘤分子机制和诊断遗传特征方面的作用。为了从该技术获得的高维复杂基因特征中获取有意义的生物学见解并详细分析基因属性,普遍采用基于机器学习和深度学习等古典人工智能方法。然而,这些方法在高维向量空间管理和基因间复杂关系建模方面存在局限。为此,量子计算和量子人工智能方法正受到越来越多的关注。本研究提出了一种基于变分量子分类器的新型模型“Deep VQC”,该模型成功利用微阵列数据对四种不同类型的脑肿瘤进行分类,并表现出优越或相当的性能。这突显了量子人工智能方法在脑肿瘤分析和分类中的潜力和前景。
Key Takeaways
- DNA微阵列技术能同时检测数千个基因的表达水平,有助于理解复杂疾病的分子机制和诊断遗传特征。
- 机器学习和深度学习等古典人工智能方法广泛应用于分析基因属性,但在处理高维数据和建模复杂关系方面存在局限。
- 量子计算和量子人工智能方法具备处理高维数据的潜力,并能在解决计算密集型问题上提供更高效解决方案。
- “Deep VQC”模型成功利用微阵列数据对脑肿瘤进行分类,表现出优越或相当的性能。
- 此研究突显了量子人工智能在分析和分类复杂结构如脑肿瘤方面的潜力。
点此查看论文截图

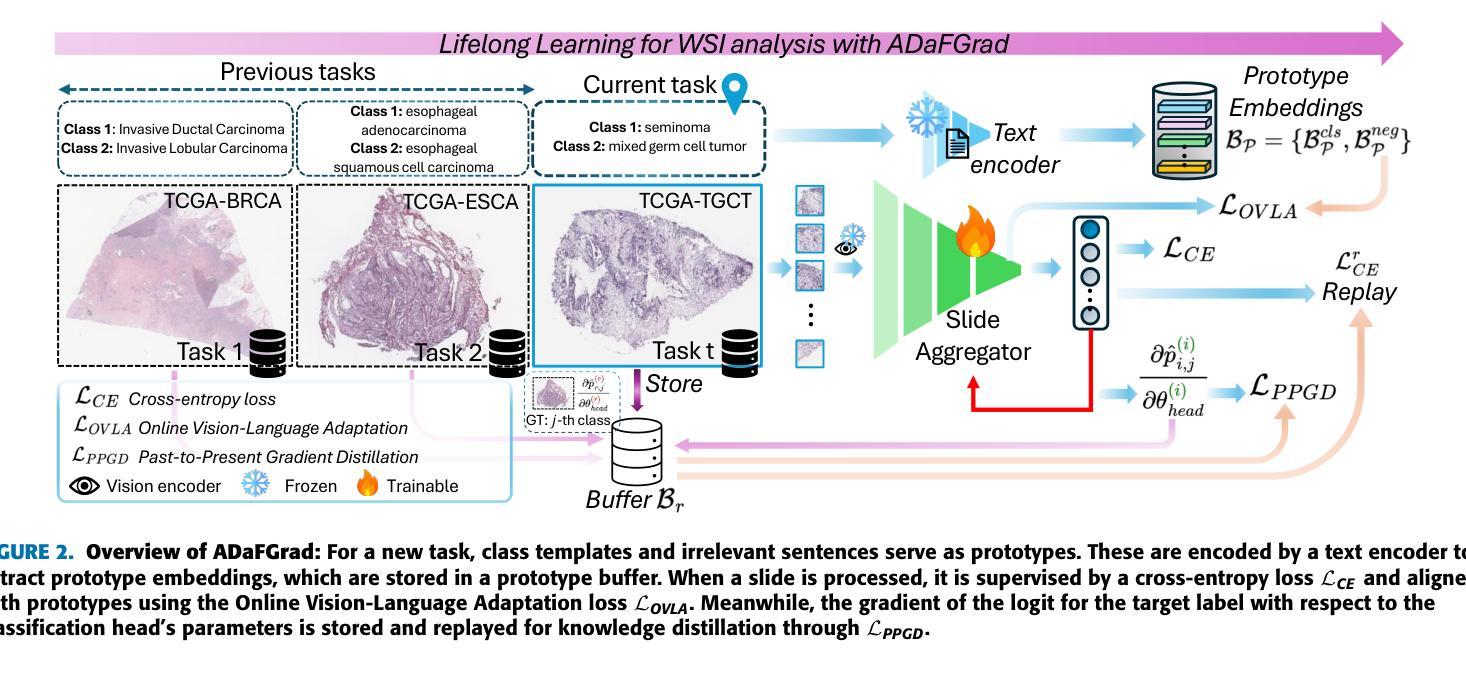
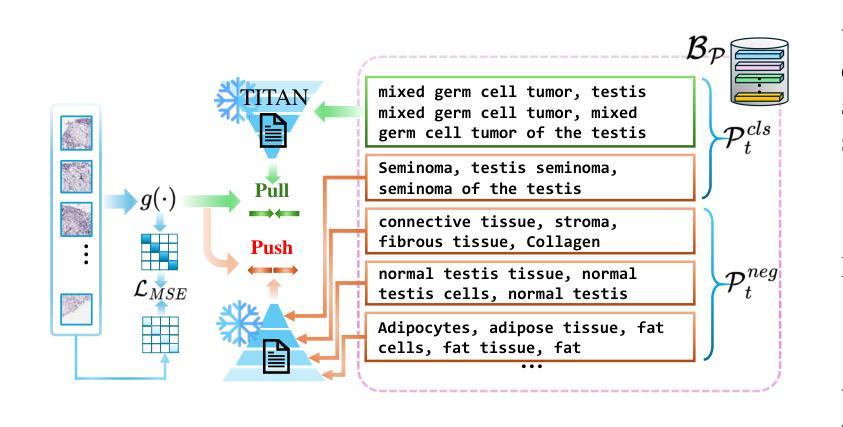
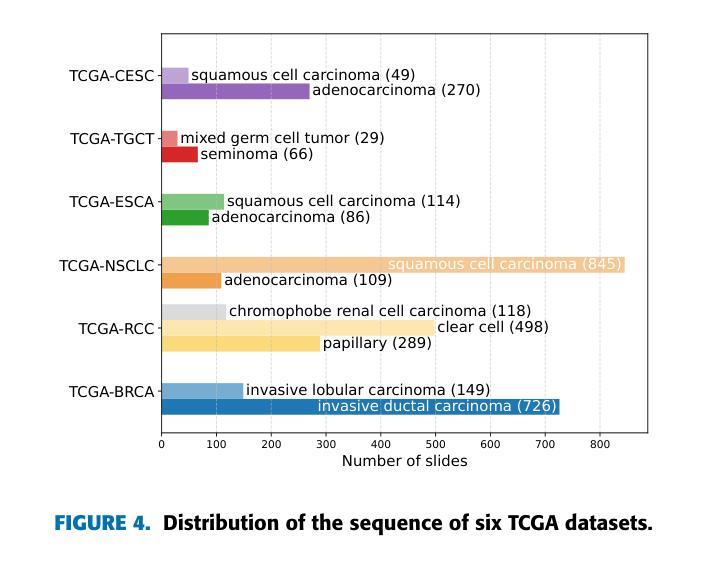
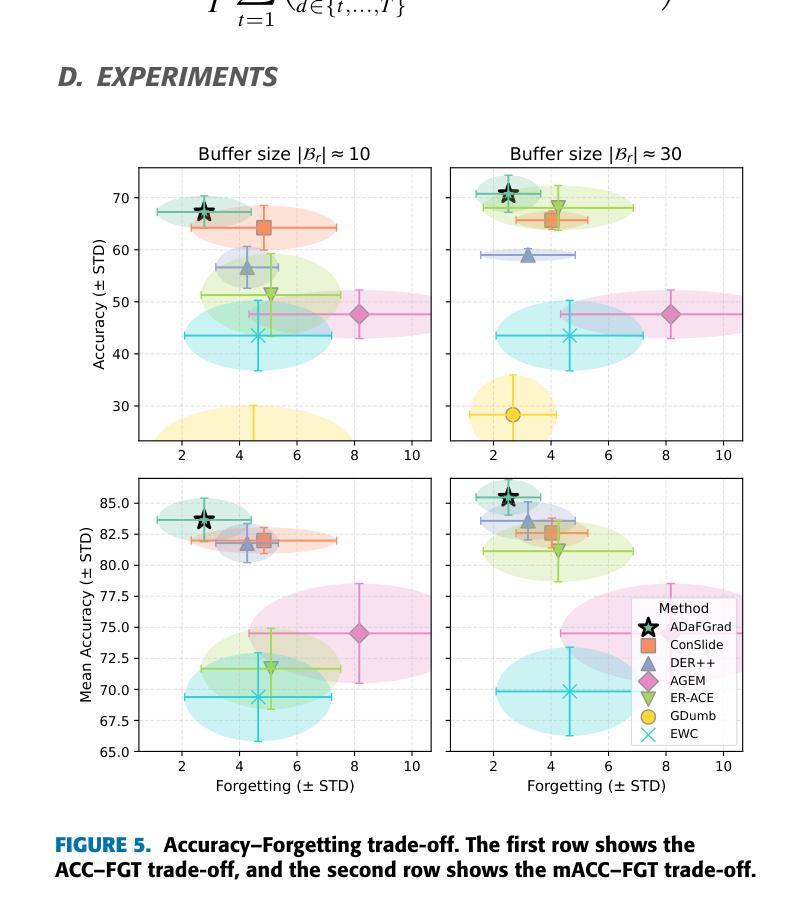
Lifelong Whole Slide Image Analysis: Online Vision-Language Adaptation and Past-to-Present Gradient Distillation
Authors:Doanh C. Bui, Hoai Luan Pham, Vu Trung Duong Le, Tuan Hai Vu, Van Duy Tran, Khang Nguyen, Yasuhiko Nakashima
Whole Slide Images (WSIs) play a crucial role in accurate cancer diagnosis and prognosis, as they provide tissue details at the cellular level. However, the rapid growth of computational tasks involving WSIs poses significant challenges. Given that WSIs are gigapixels in size, they present difficulties in terms of storage, processing, and model training. Therefore, it is essential to develop lifelong learning approaches for WSI analysis. In scenarios where slides are distributed across multiple institutes, we aim to leverage them to develop a unified online model as a computational tool for cancer diagnosis in clinical and hospital settings. In this study, we introduce ADaFGrad, a method designed to enhance lifelong learning for whole-slide image (WSI) analysis. First, we leverage pathology vision-language foundation models to develop a framework that enables interaction between a slide’s regional tissue features and a predefined text-based prototype buffer. Additionally, we propose a gradient-distillation mechanism that mimics the gradient of a logit with respect to the classification-head parameters across past and current iterations in a continual-learning setting. We construct a sequence of six TCGA datasets for training and evaluation. Experimental results show that ADaFGrad outperforms both state-of-the-art WSI-specific and conventional continual-learning methods after only a few training epochs, exceeding them by up to +5.068% in the class-incremental learning scenario while exhibiting the least forgetting (i.e., retaining the most knowledge from previous tasks). Moreover, ADaFGrad surpasses its baseline by as much as +40.084% in accuracy, further demonstrating the effectiveness of the proposed modules.
全切片图像(Whole Slide Images,WSIs)在准确的癌症诊断和治疗中起着至关重要的作用,因为它们能够提供细胞层面的组织细节。然而,涉及WSIs的计算任务的快速增长带来了重大挑战。鉴于WSIs的千兆像素大小,它们在存储、处理和模型训练方面存在困难。因此,开发用于WSI分析的终身学习方法至关重要。在幻灯片(slides)分布在多个机构的情况下,我们的目标是利用它们来开发一个统一的在线模型,作为临床和医院环境中癌症诊断的计算工具。本研究中,我们介绍了ADaFGrad方法,该方法旨在提高全切片图像(WSI)分析的终身学习效能。首先,我们利用病理视觉语言基础模型来构建一个框架,该框架可以实现对幻灯片区域组织特征与基于文本的预先定义原型缓冲区之间的交互。此外,我们提出了一种梯度蒸馏机制,该机制模仿了连续学习环境中过去迭代和当前迭代之间的分类头参数的梯度对数似然度。我们构建了六个TCGA数据集用于训练和评估。实验结果表明,在仅经过几个训练周期后,ADaFGrad在类增量学习场景中超越了最先进的WSI特定方法和传统的持续学习方法,高出+5.068%,同时展现出最少的遗忘(即保留最多的先前任务知识)。此外,ADaFGrad的准确率比基线高出+40.084%,这进一步证明了所提出模块的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
全滑图像(WSIs)在癌症诊断和预后中扮演关键角色,它们以细胞层面提供组织细节。然而,涉及WSIs的计算任务的快速增长带来了巨大的挑战。WSIs的千兆像素大小导致存储、处理和模型训练方面的困难。因此,开发WSI分析的终身学习方法是至关重要的。在幻灯片分布在多个机构的情况下,我们旨在利用它们开发一个统一的在线模型,作为临床和医院环境中癌症诊断的计算工具。本研究中,我们介绍了ADaFGrad方法,旨在增强全滑图像(WSI)分析的终身学习。首先,我们利用病理学视觉语言基础模型,建立一个框架,使幻灯片的区域组织特征与基于文本的原型缓冲区能够进行交互。此外,我们提出了一种梯度蒸馏机制,它模仿了连续学习环境中过去迭代和当前迭代分类头参数梯度的对数。我们使用六个TCGA数据集进行训练和评估。实验结果表明,ADaFGrad在仅经过几个训练周期后,在类增量学习场景中优于最新的WSI特定和传统持续学习方法,高出最多+5.068%,并且遗忘最少(即保留最多的先前任务知识)。此外,ADaFGrad的准确率比基线高出+40.084%,这进一步证明了所提出模块的有效性。
关键见解
- 全滑图像(WSIs)在癌症诊断和预后中起关键作用,对计算任务提出了挑战。
- WSIs的千兆像素大小带来了存储、处理和模型训练的难题。
- 开发了ADaFGrad方法,以增强WSI分析的终身学习。
- 利用病理学视觉语言基础模型建立框架,实现幻灯片区域组织特征与文本原型缓冲区的交互。
- 梯度蒸馏机制模仿连续学习环境中梯度的变化。
- ADaFGrad在类增量学习场景中表现出卓越性能,优于其他方法。
点此查看论文截图

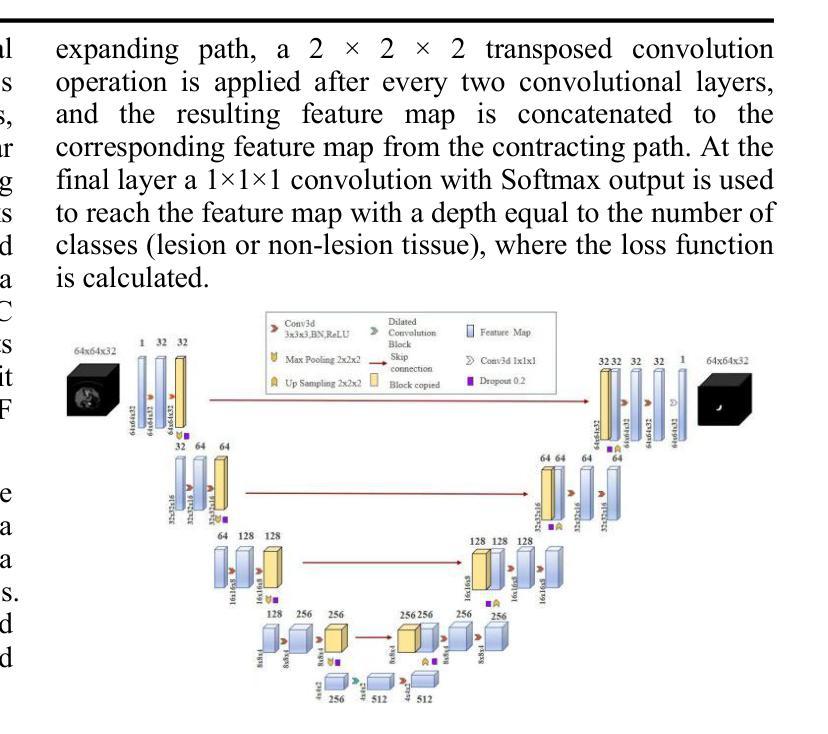
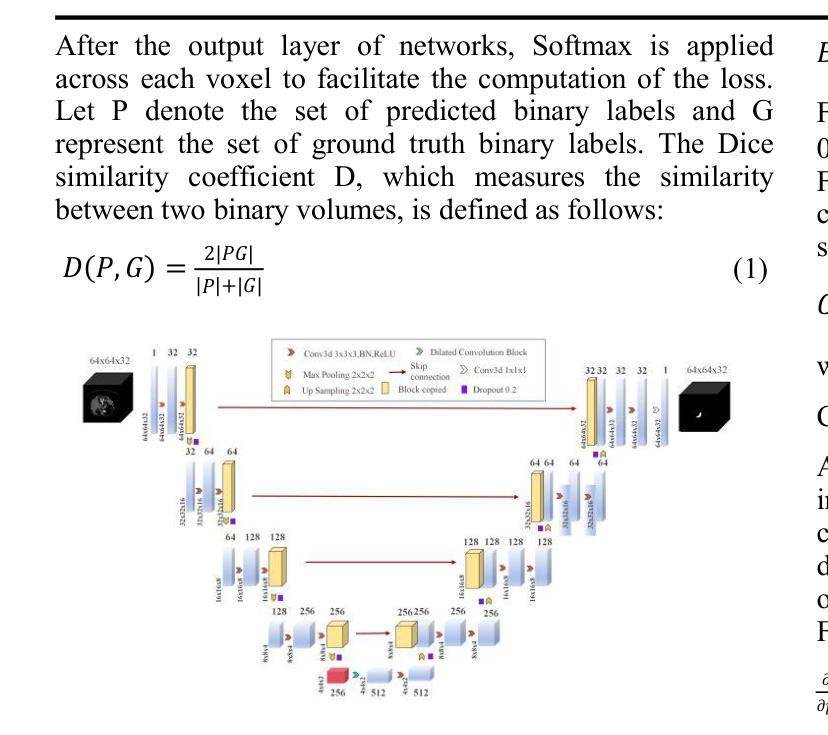
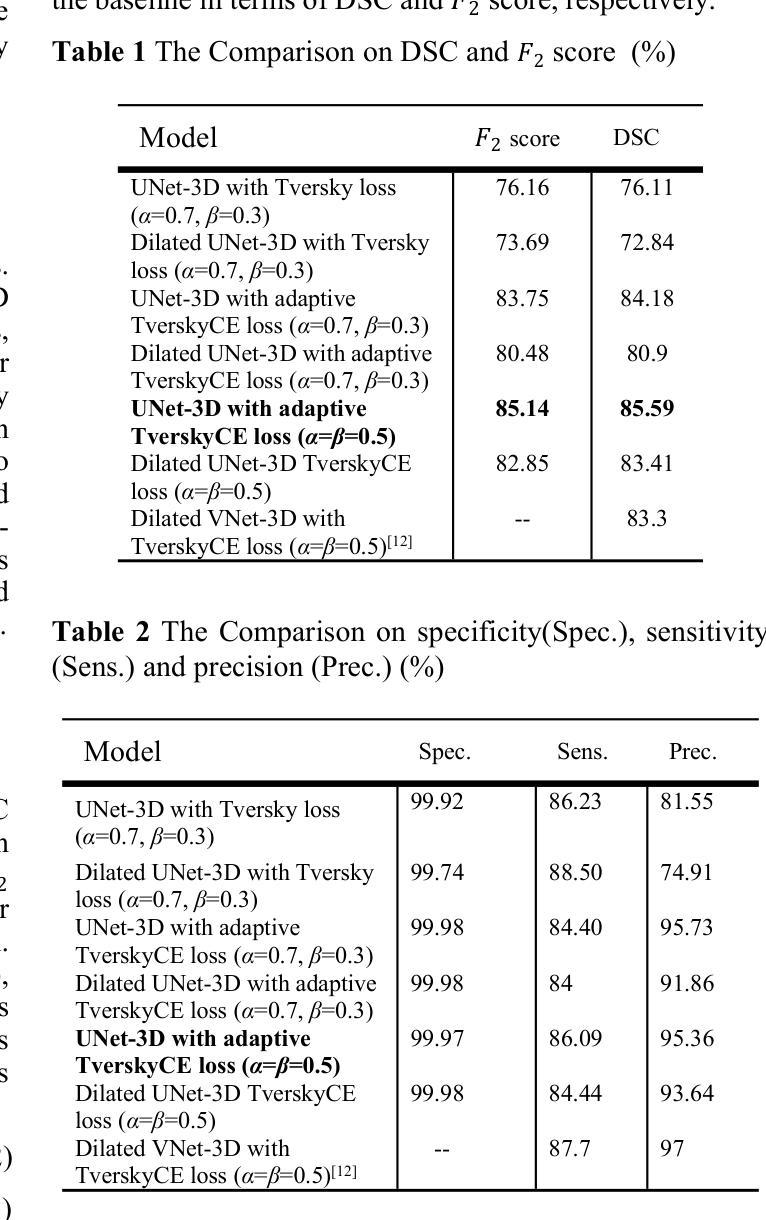
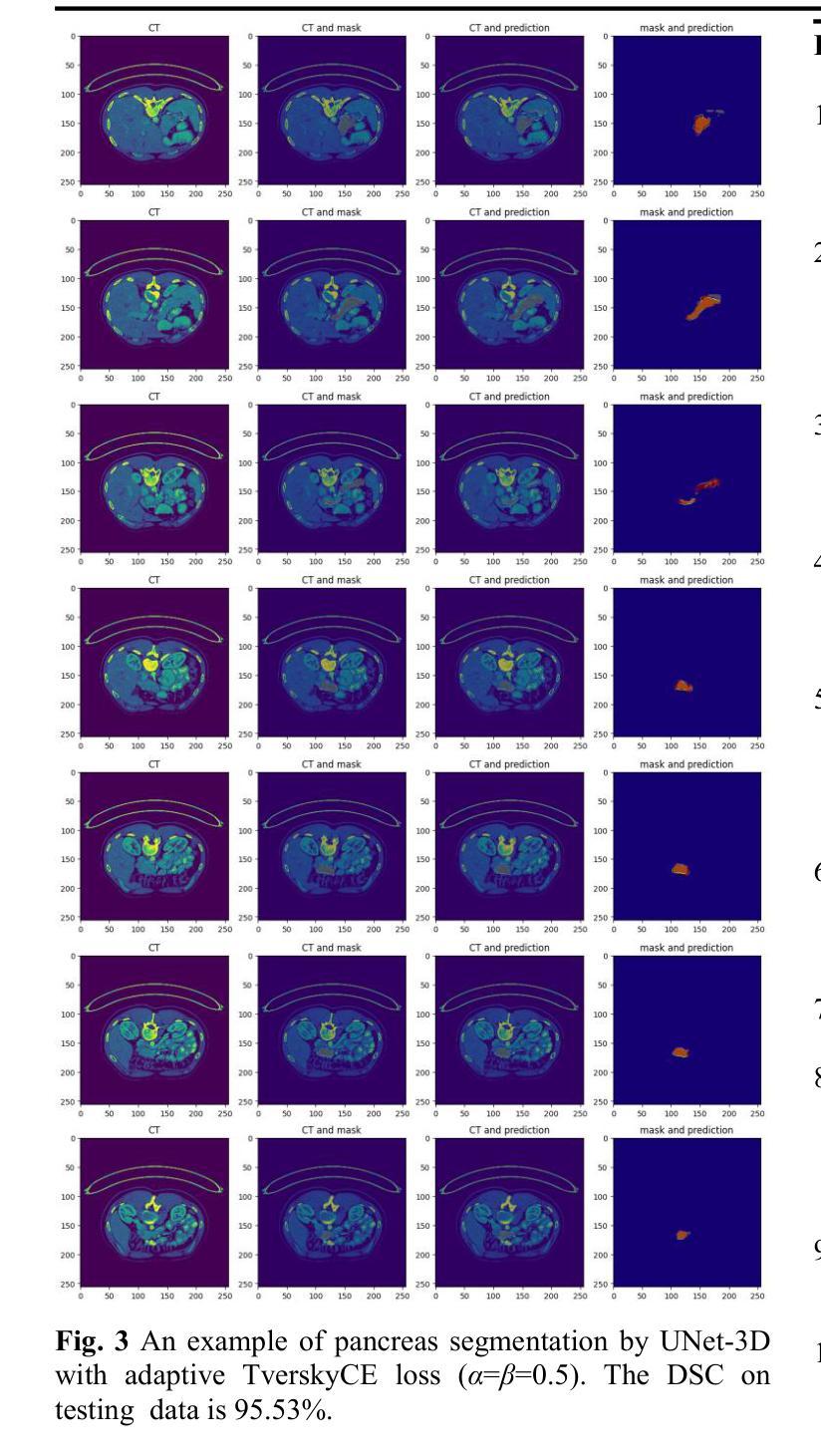
UNet-3D with Adaptive TverskyCE Loss for Pancreas Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Xubei Zhang, Mikhail Y. Shalaginov, Tingying Helen Zeng
Pancreatic cancer, which has a low survival rate, is the most intractable one among all cancers. Most diagnoses of this cancer heavily depend on abdominal computed tomography (CT) scans. Therefore, pancreas segmentation is crucial but challenging. Because of the obscure position of the pancreas, surrounded by other large organs, and its small area, the pancreas has often been impeded and difficult to detect. With these challenges , the segmentation results based on Deep Learning (DL) models still need to be improved. In this research, we propose a novel adaptive TverskyCE loss for DL model training, which combines Tversky loss with cross-entropy loss using learnable weights. Our method enables the model to adjust the loss contribution automatically and find the best objective function during training. All experiments were conducted on the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Pancreas-CT dataset. We evaluated the adaptive TverskyCE loss on the UNet-3D and Dilated UNet-3D, and our method achieved a Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC) of 85.59%, with peak performance up to 95.24%, and the score of 85.14%. DSC and the score were improved by 9.47% and 8.98% respectively compared with the baseline UNet-3D with Tversky loss for pancreas segmentation. Keywords: Pancreas segmentation, Tversky loss, Cross-entropy loss, UNet-3D, Dilated UNet-3D
胰腺癌是恶性程度极高的一种癌症,在所有癌症中最为棘手。其诊断大多依赖于腹部计算机断层扫描(CT扫描)。因此,胰腺分割至关重要且极具挑战性。胰腺位置隐蔽,被其他大型器官包围,且面积较小,因此经常受到阻碍,难以检测。面对这些挑战,基于深度学习的分割结果仍需改进。在这项研究中,我们提出了一种新型的自适应TverskyCE损失,用于深度学习模型训练,它将Tversky损失与交叉熵损失相结合,使用可学习的权重。我们的方法使模型能够自动调整损失的贡献,并在训练过程中找到最佳目标函数。所有实验均在国立卫生研究院的胰腺CT数据集上进行。我们对UNet-3D和Dilated UNet-3D模型评估了自适应TverskyCE损失,该方法实现了85.59%的Dice相似系数(DSC),最高性能达到95.24%,评分为85.14%。与基线UNet-3D模型使用Tversky损失进行胰腺分割相比,DSC和评分分别提高了9.47%和8.98%。关键词:胰腺分割、Tversky损失、交叉熵损失、UNet-3D、膨胀UNet-3D。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages and 3 figures
Summary
胰腺癌是一种难以治愈且生存率较低的癌症,其诊断高度依赖于腹部计算机断层扫描(CT扫描)。胰腺分割至关重要但具有挑战性,因为其位置隐蔽且面积小。本研究提出了一种新型自适应TverskyCE损失函数,用于深度学习模型训练,结合了Tversky损失和交叉熵损失,并自动调整损失贡献,找到最佳目标函数。在NIH胰腺CT数据集上进行实验,使用UNet-3D和膨胀UNet-3D评估自适应TverskyCE损失,实现了85.59%的Dice相似系数(DSC),最高性能达到95.24%,较基线UNet-3D使用Tversky损失进行胰腺分割的性能提升分别为DSC和得分提高9.47%和提高了整体的模型表现。自适应TverskyCE损失有助于改进胰腺分割的深度学习模型性能。
Key Takeaways
- 胰腺癌诊断高度依赖腹部CT扫描,胰腺分割是重要且具有挑战性的任务。
- 胰腺位置隐蔽且面积小,导致分割困难。
- 本研究提出了一种新型自适应TverskyCE损失函数,结合Tversky损失和交叉熵损失。
- 该方法能够自动调整损失贡献并找到最佳目标函数。
- 在NIH胰腺CT数据集上进行的实验表明,使用自适应TverskyCE损失的UNet-3D和膨胀UNet-3D性能有所提升。
- 实验结果显示Dice相似系数(DSC)达到85.59%,最高性能为95.24%。
点此查看论文截图