⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-08 更新
Lesion-Aware Generative Artificial Intelligence for Virtual Contrast-Enhanced Mammography in Breast Cancer
Authors:Aurora Rofena, Arianna Manchia, Claudia Lucia Piccolo, Bruno Beomonte Zobel, Paolo Soda, Valerio Guarrasi
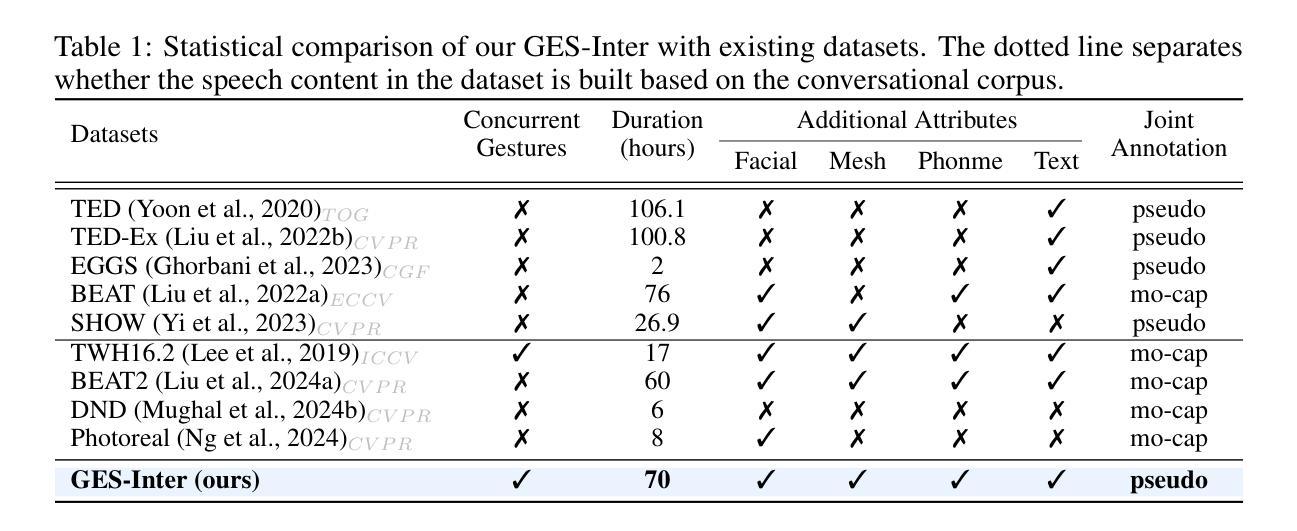
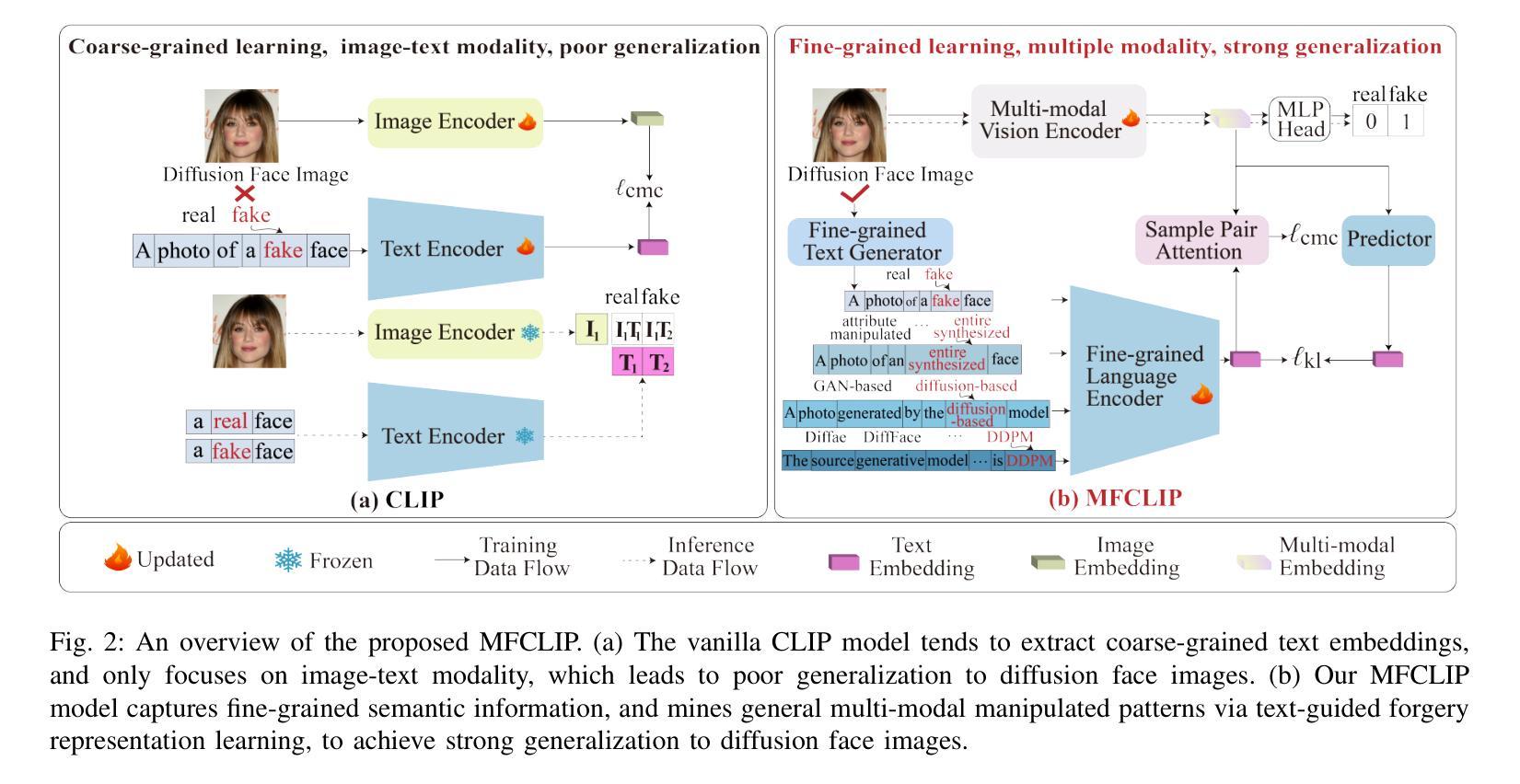
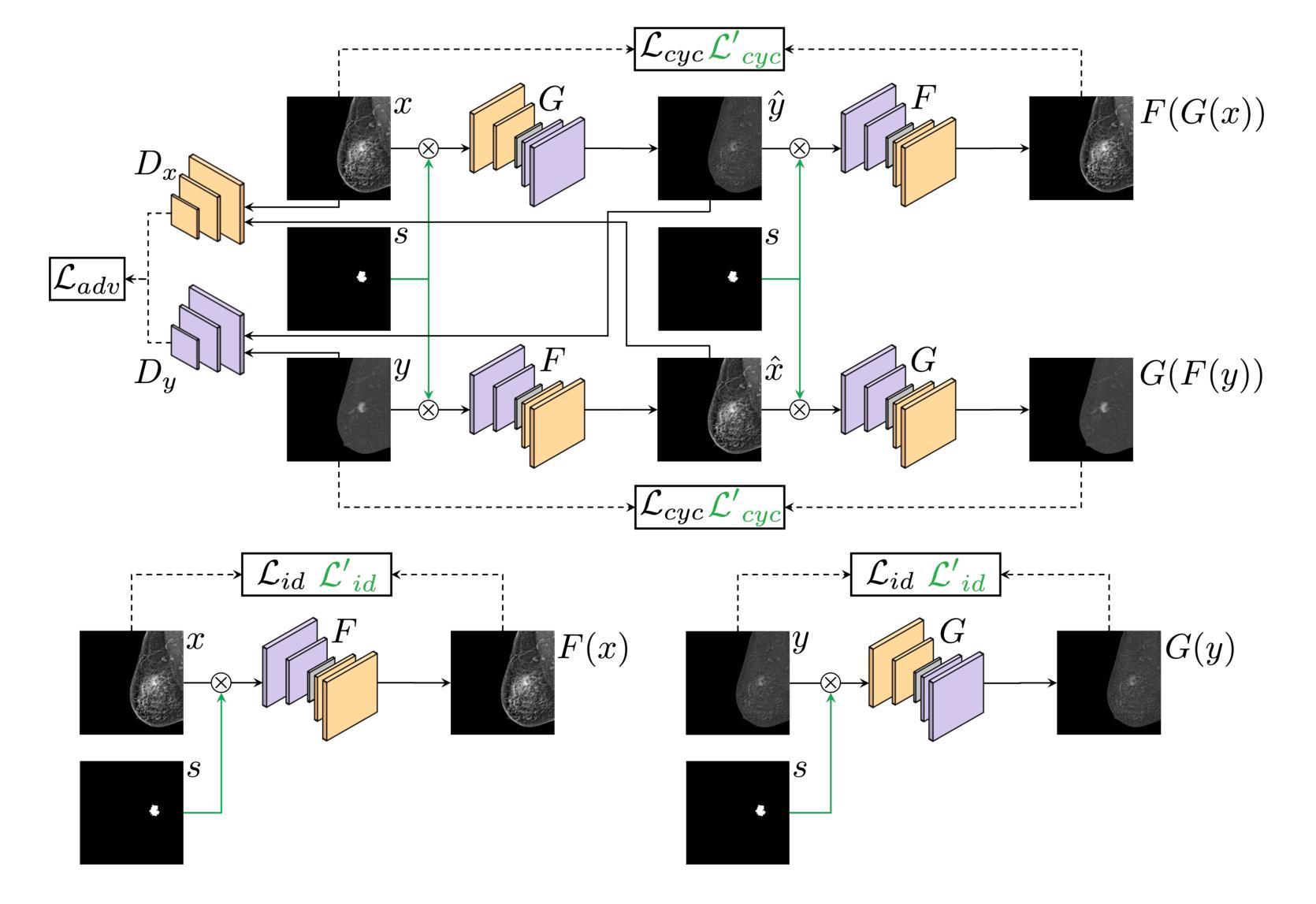
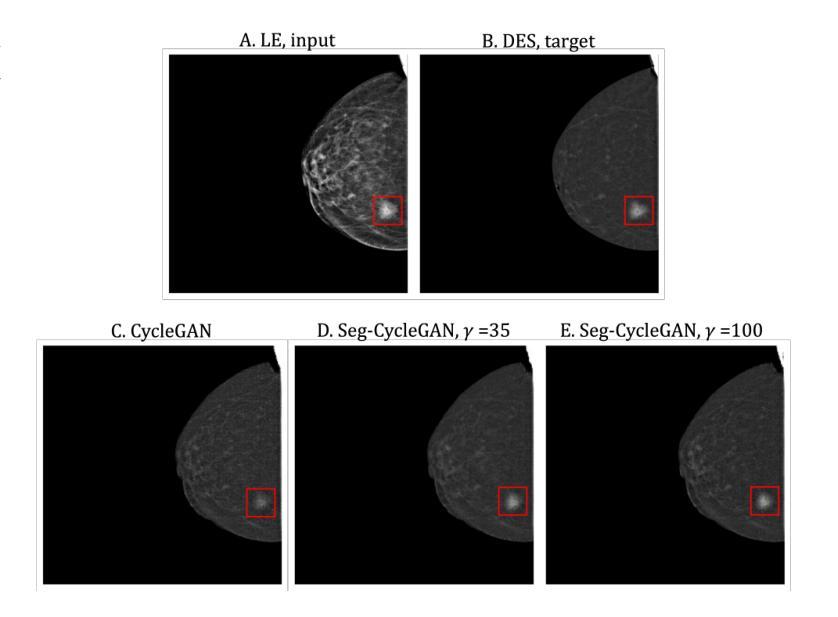
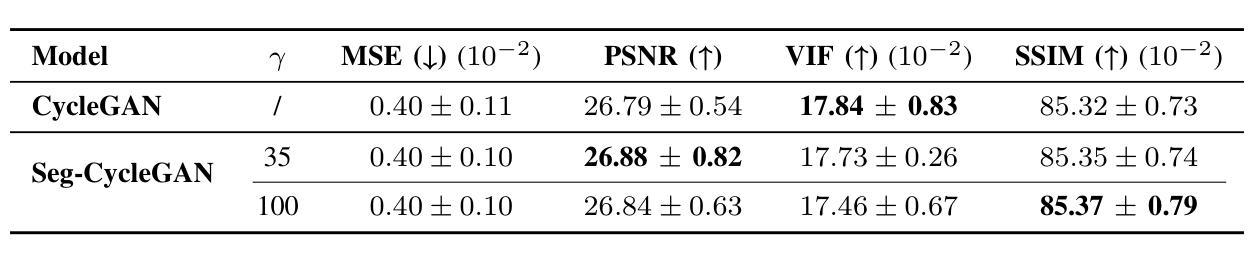
Contrast-Enhanced Spectral Mammography (CESM) is a dual-energy mammographic technique that improves lesion visibility through the administration of an iodinated contrast agent. It acquires both a low-energy image, comparable to standard mammography, and a high-energy image, which are then combined to produce a dual-energy subtracted image highlighting lesion contrast enhancement. While CESM offers superior diagnostic accuracy compared to standard mammography, its use entails higher radiation exposure and potential side effects associated with the contrast medium. To address these limitations, we propose Seg-CycleGAN, a generative deep learning framework for Virtual Contrast Enhancement in CESM. The model synthesizes high-fidelity dual-energy subtracted images from low-energy images, leveraging lesion segmentation maps to guide the generative process and improve lesion reconstruction. Building upon the standard CycleGAN architecture, Seg-CycleGAN introduces localized loss terms focused on lesion areas, enhancing the synthesis of diagnostically relevant regions. Experiments on the CESM@UCBM dataset demonstrate that Seg-CycleGAN outperforms the baseline in terms of PSNR and SSIM, while maintaining competitive MSE and VIF. Qualitative evaluations further confirm improved lesion fidelity in the generated images. These results suggest that segmentation-aware generative models offer a viable pathway toward contrast-free CESM alternatives.
对比增强光谱乳腺摄影(CESM)是一种双能乳腺摄影技术,通过注射碘化造影剂提高病灶的可见性。它获取与标准乳腺摄影相当的低能图像和高能图像,然后将它们组合以产生突出病灶对比度增强的双能减影图像。虽然CESM在诊断准确性方面优于标准乳腺摄影,但其使用会带来更高的辐射暴露和与造影剂相关的潜在副作用。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了Seg-CycleGAN,这是一种用于CESM虚拟对比度增强的生成深度学习框架。该模型从低能图像中合成高保真双能减影图像,利用病灶分割图来指导生成过程,提高病灶重建效果。基于标准CycleGAN架构,Seg-CycleGAN引入了局部损失项,重点关注病灶区域,提高了诊断相关区域的合成效果。在UCBM数据集上的实验表明,Seg-CycleGAN在PSNR和SSIM方面优于基线,同时保持竞争性的MSE和VIF。定性评估进一步证实了生成图像中病灶的保真度有所提高。这些结果表明,分割感知生成模型为无对比剂的CESM替代品提供了可行的途径。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
基于对比增强光谱成像(CESM)技术的局限性,研究团队提出Seg-CycleGAN深度学习框架,通过利用病变分割图谱进行虚拟对比增强,生成高质量的双能减影图像。该模型从低能图像中合成双能减影图像,通过局部损失函数提高病变区域的合成效果。在UCBM数据集上的实验表明,Seg-CycleGAN在PSNR和SSIM指标上优于基线方法,同时保持MSE和VIF的竞争性能。这些结果表明分割感知生成模型是实现无对比剂CESM的可行途径。
Key Takeaways:
- 对比增强光谱成像(CESM)通过碘造影剂提高病变可见性。
- CESM具有比传统乳腺X线摄影更高的诊断准确性,但伴随更高的辐射暴露和造影剂的潜在副作用。
- 提出Seg-CycleGAN模型,通过深度学习技术合成高质量的双能减影图像。
- Seg-CycleGAN利用病变分割图谱引导生成过程,提高病变重建效果。
- 模型在UCBM数据集上的实验表现优越,特别是在PSNR和SSIM指标上。
- 定性评价进一步证实了生成图像中病变的保真度有所提高。
点此查看论文截图
Towards Accurate and Interpretable Neuroblastoma Diagnosis via Contrastive Multi-scale Pathological Image Analysis
Authors:Zhu Zhu, Shuo Jiang, Jingyuan Zheng, Yawen Li, Yifei Chen, Manli Zhao, Weizhong Gu, Feiwei Qin, Jinhu Wang, Gang Yu
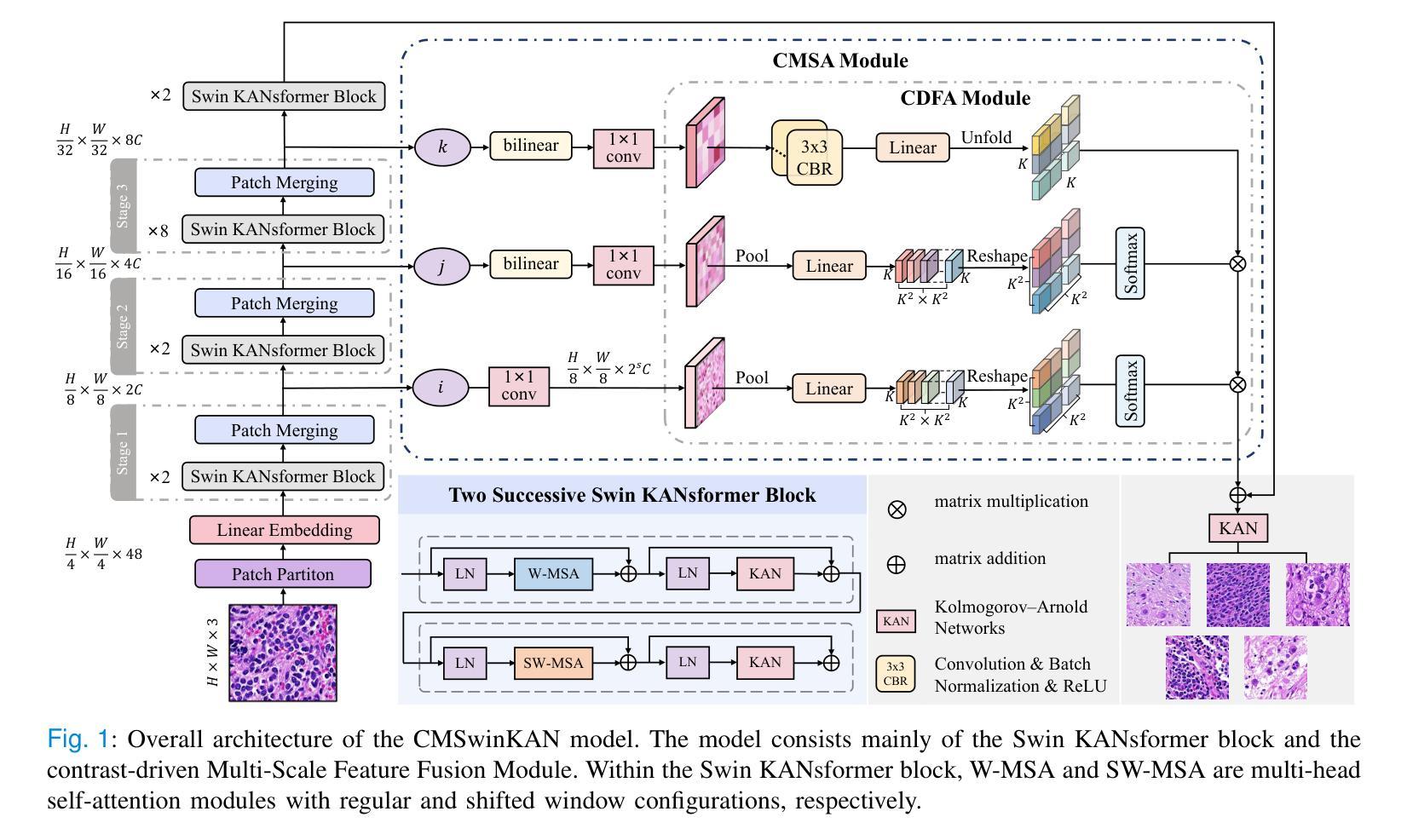
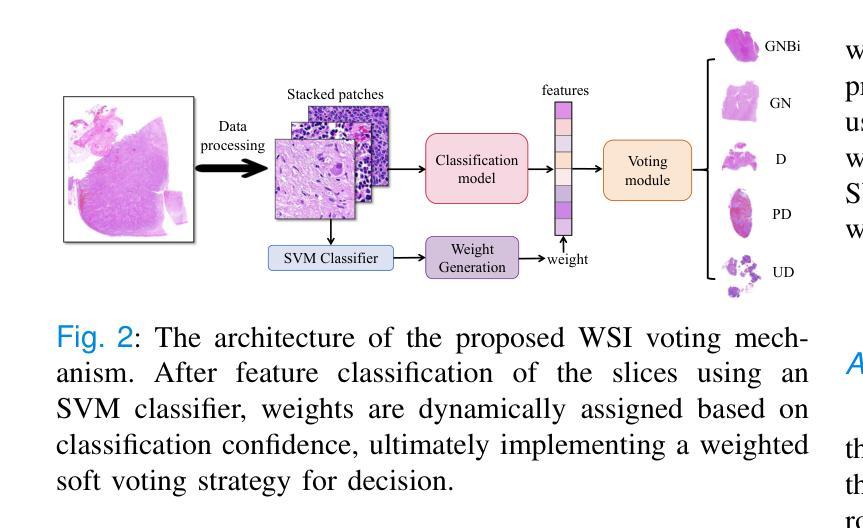
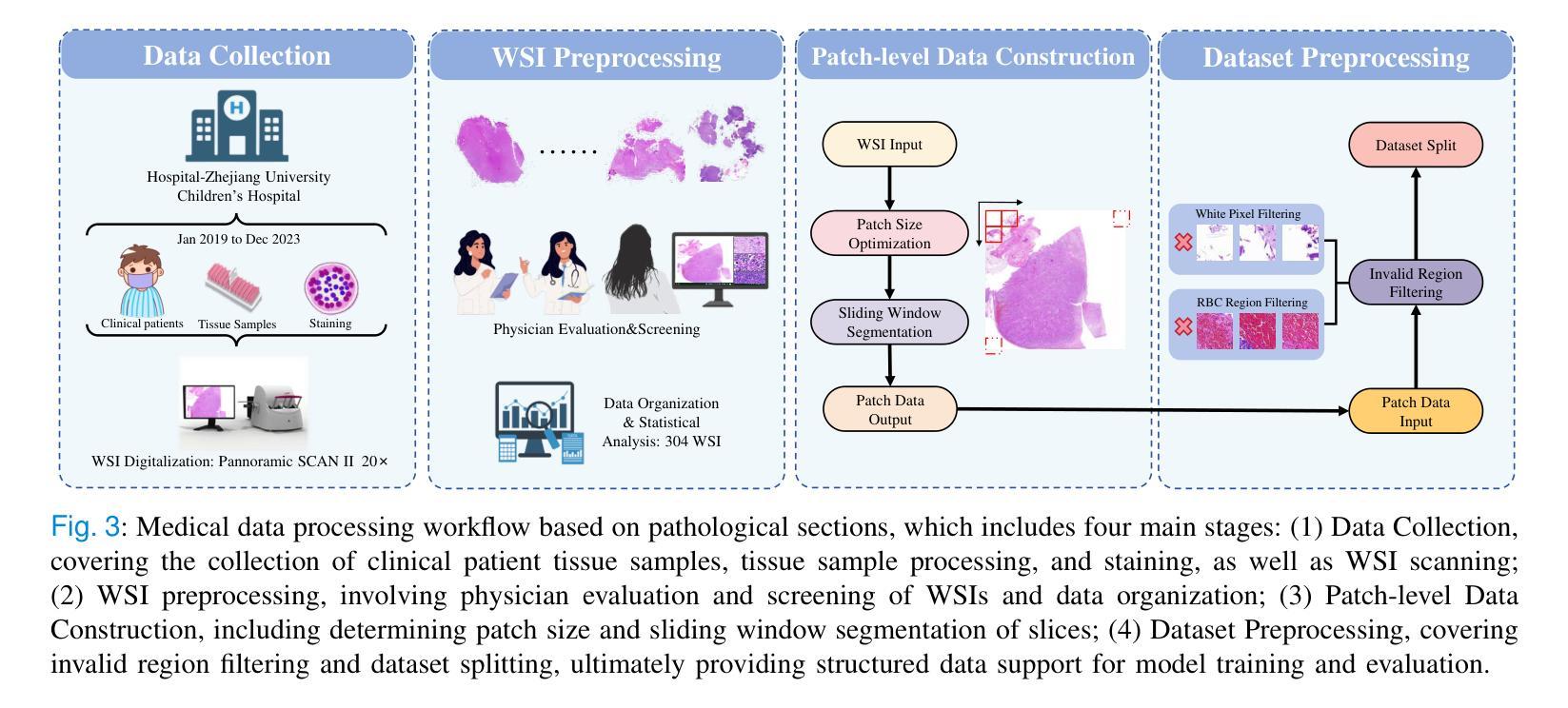
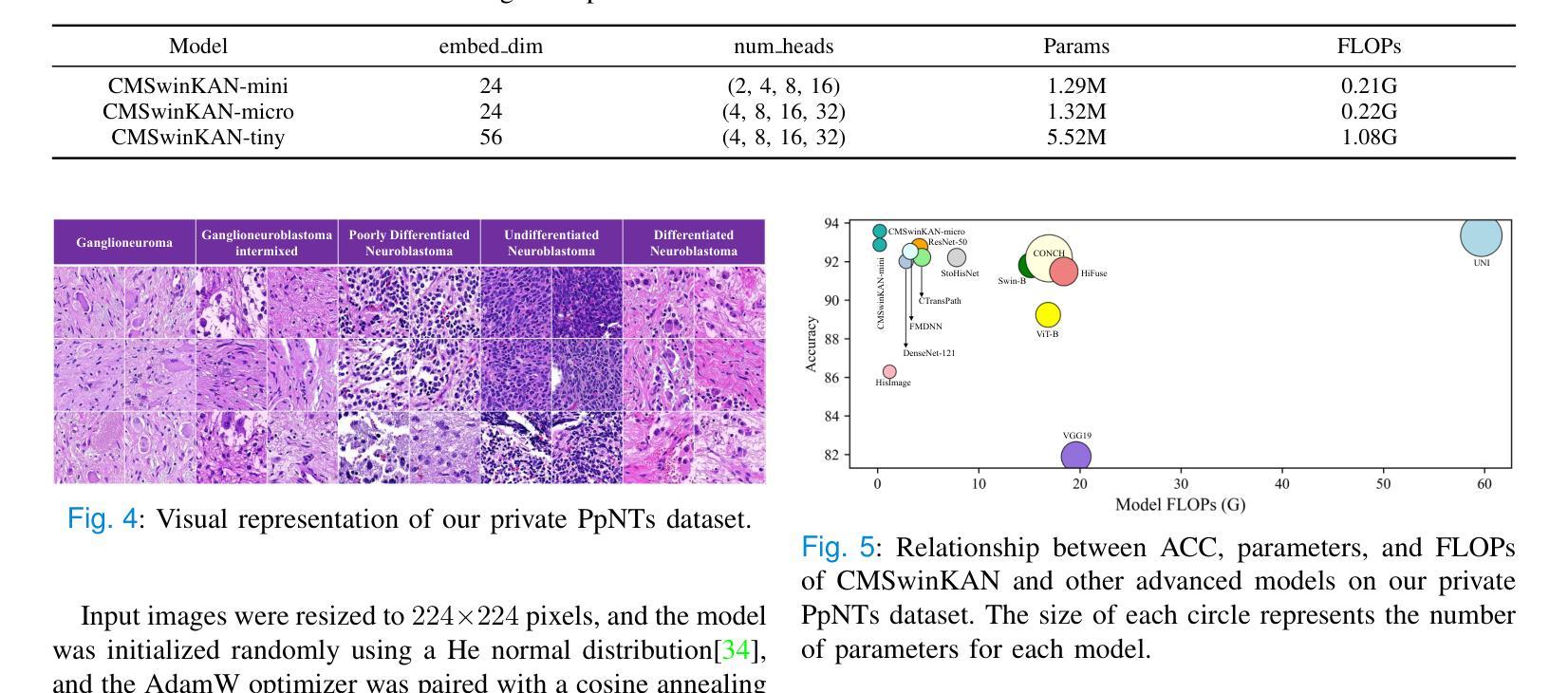
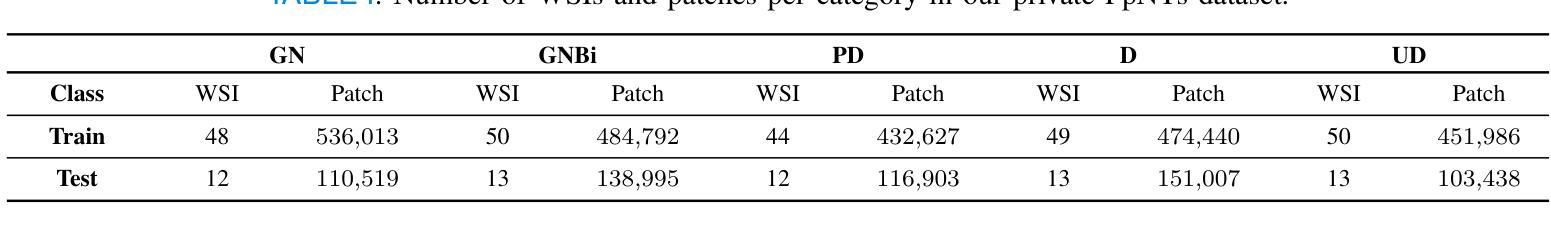
Neuroblastoma, adrenal-derived, is among the most common pediatric solid malignancies, characterized by significant clinical heterogeneity. Timely and accurate pathological diagnosis from hematoxylin and eosin-stained whole-slide images is critical for patient prognosis. However, current diagnostic practices primarily rely on subjective manual examination by pathologists, leading to inconsistent accuracy. Existing automated whole-slide image classification methods encounter challenges such as poor interpretability, limited feature extraction capabilities, and high computational costs, restricting their practical clinical deployment. To overcome these limitations, we propose CMSwinKAN, a contrastive-learning-based multi-scale feature fusion model tailored for pathological image classification, which enhances the Swin Transformer architecture by integrating a Kernel Activation Network within its multilayer perceptron and classification head modules, significantly improving both interpretability and accuracy. By fusing multi-scale features and leveraging contrastive learning strategies, CMSwinKAN mimics clinicians’ comprehensive approach, effectively capturing global and local tissue characteristics. Additionally, we introduce a heuristic soft voting mechanism guided by clinical insights to bridge patch-level predictions to whole-slide image-level classifications seamlessly. We verified the CMSwinKAN on the publicly available BreakHis dataset and the PpNTs dataset, which was established by our hospital. Results demonstrate that CMSwinKAN performs better than existing state-of-the-art pathology-specific models pre-trained on large datasets. Our source code is available at https://github.com/JSLiam94/CMSwinKAN.
神经母细胞瘤(肾上腺起源)是最常见的儿童实体恶性肿瘤之一,具有显著的临床异质性。及时而准确的病理诊断对于患者的预后至关重要,诊断依据来源于苏木精和伊红染色的全切片图像。然而,目前的诊断方法主要依赖于病理医师的主观手动检查,导致诊断准确性不一致。现有的全自动切片图像分类方法面临可解释性差、特征提取能力有限和计算成本高的挑战,限制了其在临床实践中的部署应用。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了CMSwinKAN,这是一种基于对比学习的多尺度特征融合模型,专为病理图像分类而定制。CMSwinKAN增强了Swin Transformer架构,通过在其多层感知器和分类头模块中集成内核激活网络,显著提高了可解释性和准确性。通过融合多尺度特征和利用对比学习策略,CMSwinKAN模仿了临床医生全面的诊断方法,有效地捕捉了全局和局部组织特征。此外,我们还引入了一种受临床见解启发的主观软投票机制,以无缝连接补丁级别的预测和整个切片图像级别的分类。我们在公开可用的BreakHis数据集和我们医院建立的的PpNTs数据集上验证了CMSwinKAN。结果表明,CMSwinKAN的性能优于现有最先进的病理学专用模型,这些模型是在大型数据集上进行预训练的。我们的源代码可在https://github.com/JSLiam94/CMSwinKAN获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10pages, 8 figures
Summary
本文提出了一种基于对比学习的多尺度特征融合模型CMSwinKAN,用于神经母细胞瘤等小儿实体恶性肿瘤的病理图像分类。该模型改进了Swin Transformer架构,通过集成Kernel Activation Network,提高了模型的解释性和准确性。通过多尺度特征融合和对比学习策略,CMSwinKAN能够模拟医生的综合判断方式,有效捕捉组织和细胞的全球和局部特征。此外,还引入了一种基于临床见解的启发式软投票机制,实现了斑块级别预测到全幻灯片图像级别分类的顺畅过渡。在公开数据集BreakHis和本院建立的PpNTs数据集上的验证结果表明,CMSwinKAN的性能优于现有的预训练病理模型。
Key Takeaways
- 神经母细胞瘤是常见的儿童实体恶性肿瘤,具有显著的临床异质性,及时准确的病理诊断对预后至关重要。
- 当前诊断方法主要依赖病理医生的主观手动检查,存在准确性不一致的问题。
- CMSwinKAN模型基于对比学习,融合了多尺度特征,提高了病理图像分类的准确性和解释性。
- CMSwinKAN通过集成Kernel Activation Network在Swin Transformer架构中,有效捕捉全局和局部组织特性,模拟医生的综合判断方式。
- 引入的启发式软投票机制能够实现斑块级别预测到全幻灯片图像级别分类的过渡,提高了模型的实用性。
- 在公开和本院建立的数据集上的验证结果表明,CMSwinKAN的性能优于现有预训练病理模型。
点此查看论文截图

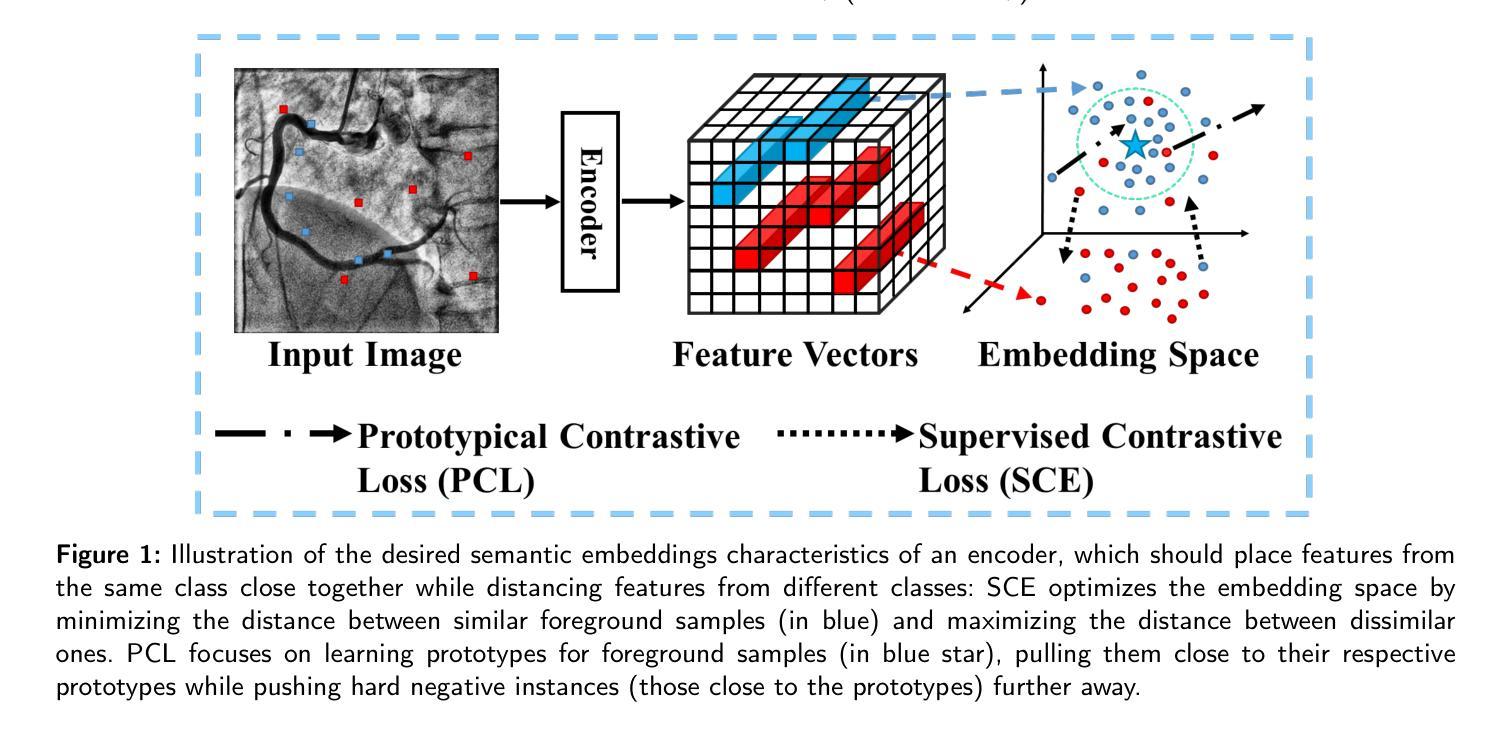
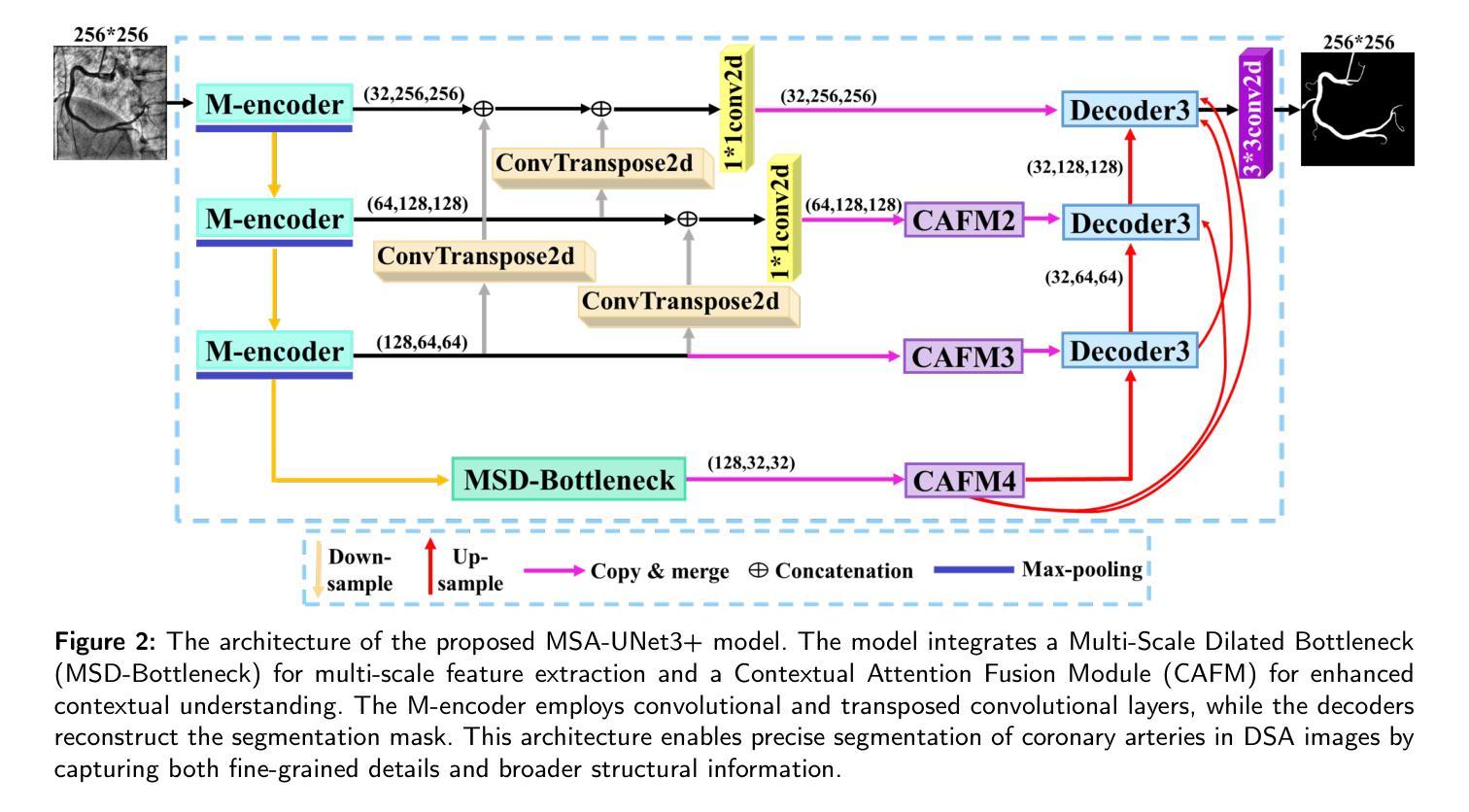
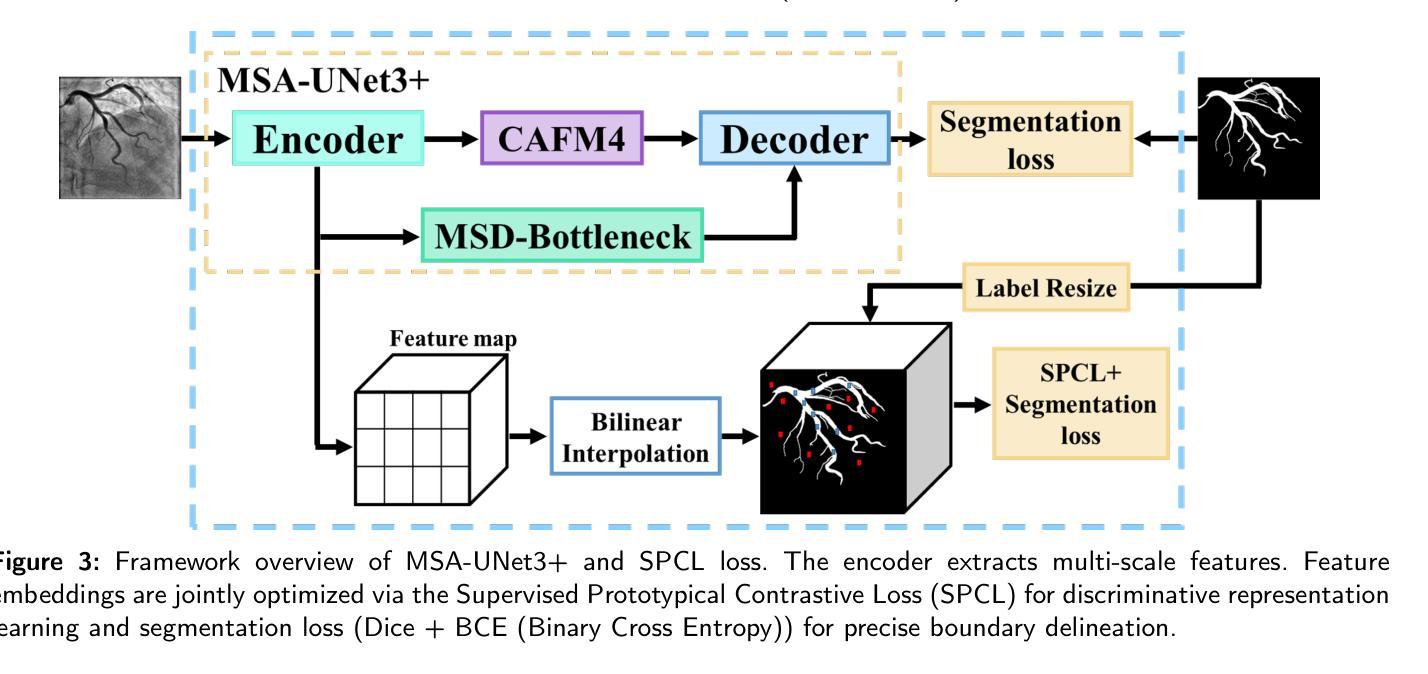
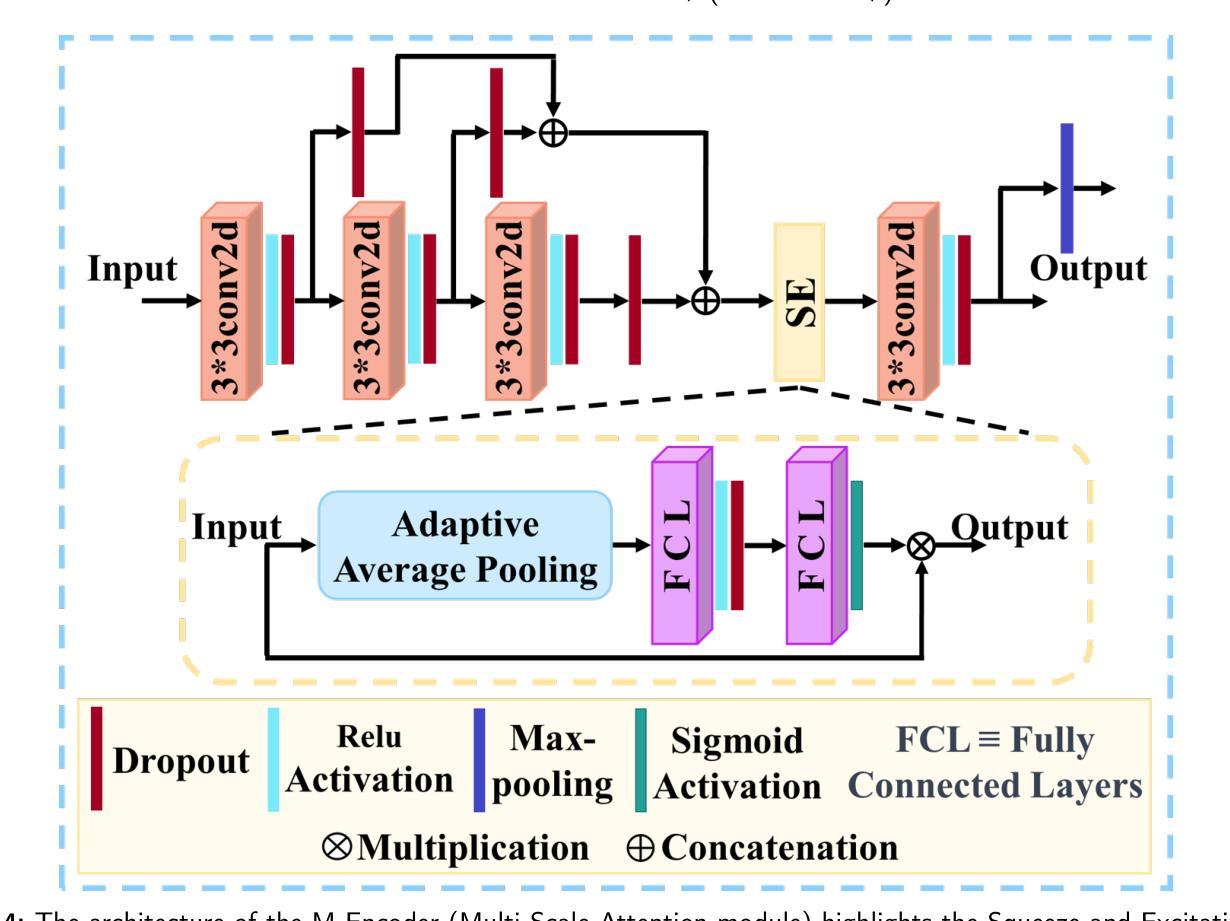
MSA-UNet3+: Multi-Scale Attention UNet3+ with New Supervised Prototypical Contrastive Loss for Coronary DSA Image Segmentation
Authors:Rayan Merghani Ahmed, Adnan Iltaf, Bin Li, Shoujun Zhou
The accurate segmentation of coronary Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA) images is essential for diagnosing and treating coronary artery diseases. Despite advances in deep learning-based segmentation, challenges such as low contrast, noise, overlapping structures, high intra-class variance, and class imbalance limit precise vessel delineation. To overcome these limitations, we propose the MSA-UNet3+: a Multi-Scale Attention enhanced UNet3+ architecture for coronary DSA image segmentation. The framework combined Multi-Scale Dilated Bottleneck (MSD-Bottleneck) with Contextual Attention Fusion Module (CAFM), which not only enhances multi-scale feature extraction but also preserve fine-grained details, and improve contextual understanding. Furthermore, we propose a new Supervised Prototypical Contrastive Loss (SPCL), which combines supervised and prototypical contrastive learning to minimize class imbalance and high intra-class variance by focusing on hard-to-classified background samples. Experiments carried out on a private coronary DSA dataset demonstrate that MSA-UNet3+ outperforms state-of-the-art methods, achieving a Dice coefficient of 87.73%, an F1-score of 87.78%, and significantly reduced Average Surface Distance (ASD) and Average Contour Distance (ACD). The developed framework provides clinicians with precise vessel segmentation, enabling accurate identification of coronary stenosis and supporting informed diagnostic and therapeutic decisions. The code will be released at the following GitHub profile link https://github.com/rayanmerghani/MSA-UNet3plus.
冠状动脉数字减影血管造影(DSA)图像的准确分割对于冠状动脉疾病的诊断和治疗至关重要。尽管基于深度学习的分割技术有所进展,但低对比度、噪声、结构重叠、高类内方差和类别不平衡等挑战仍然限制了精确血管勾勒的实现。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了MSA-UNet3+:一种用于冠状动脉DSA图像分割的多尺度注意力增强UNet3+架构。该框架结合了多尺度膨胀瓶颈(MSD-Bottleneck)和上下文注意力融合模块(CAFM),这不仅增强了多尺度特征提取,还保留了精细细节,并提高了上下文理解。此外,我们提出了一种新的监督原型对比损失(SPCL),它将监督学习和原型对比学习相结合,通过关注难以分类的背景样本,最小化类别不平衡和高类内方差。在私有冠状动脉DSA数据集上进行的实验表明,MSA-UNet3+优于最新方法,达到87.73%的Dice系数,87.78%的F1分数,以及显著降低的平均表面距离(ASD)和平均轮廓距离(ACD)。所开发的框架为临床医生提供了精确的血管分割,能够准确识别冠状动脉狭窄,并支持做出有根据的诊断和治疗决策。代码将在以下GitHub个人主页链接发布:https://github.com/rayanmerghani/MSA-UNet3plus。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Work in progress
Summary
本文提出一种基于深度学习的新型冠状动脉数字减影血管造影(DSA)图像分割方法MSA-UNet3+,通过多尺度注意力机制增强UNet3+架构的性能。该方法结合了多尺度膨胀瓶颈(MSD-Bottleneck)与上下文注意力融合模块(CAFM),提高了多尺度特征提取能力,同时保留精细细节并改善上下文理解。此外,还提出了一种新的监督原型对比损失(SPCL),通过结合监督学习和原型对比学习,减少类别不平衡和高类内方差问题,重点关注难以分类的背景样本。实验表明,MSA-UNet3+在私人冠状动脉DSA数据集上的表现优于现有方法,实现了87.73%的Dice系数、87.78%的F1分数,并显著降低了平均表面距离(ASD)和平均轮廓距离(ACD)。这为临床医生提供了精确的血管分割,有助于准确识别冠状动脉狭窄,为诊断和治疗决策提供有力支持。
Key Takeaways
- 冠状动脉数字减影血管造影(DSA)图像的准确分割对诊断与治疗至关重要。
- 现有深度学习分割方法面临低对比度、噪声、结构重叠等挑战。
- 提出了一种新型架构MSA-UNet3+,结合多尺度注意力机制增强特征提取和上下文理解。
- 引入了新的监督原型对比损失(SPCL),以解决类别不平衡和高类内方差问题。
- 实验证明,MSA-UNet3+在冠状动脉DSA图像分割上表现优异。
- 该方法能提高医生对血管病变的识别准确性,为诊断与治疗决策提供有力支持。
点此查看论文截图