⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-08 更新
3D Can Be Explored In 2D: Pseudo-Label Generation for LiDAR Point Clouds Using Sensor-Intensity-Based 2D Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Andrew Caunes, Thierry Chateau, Vincent Frémont
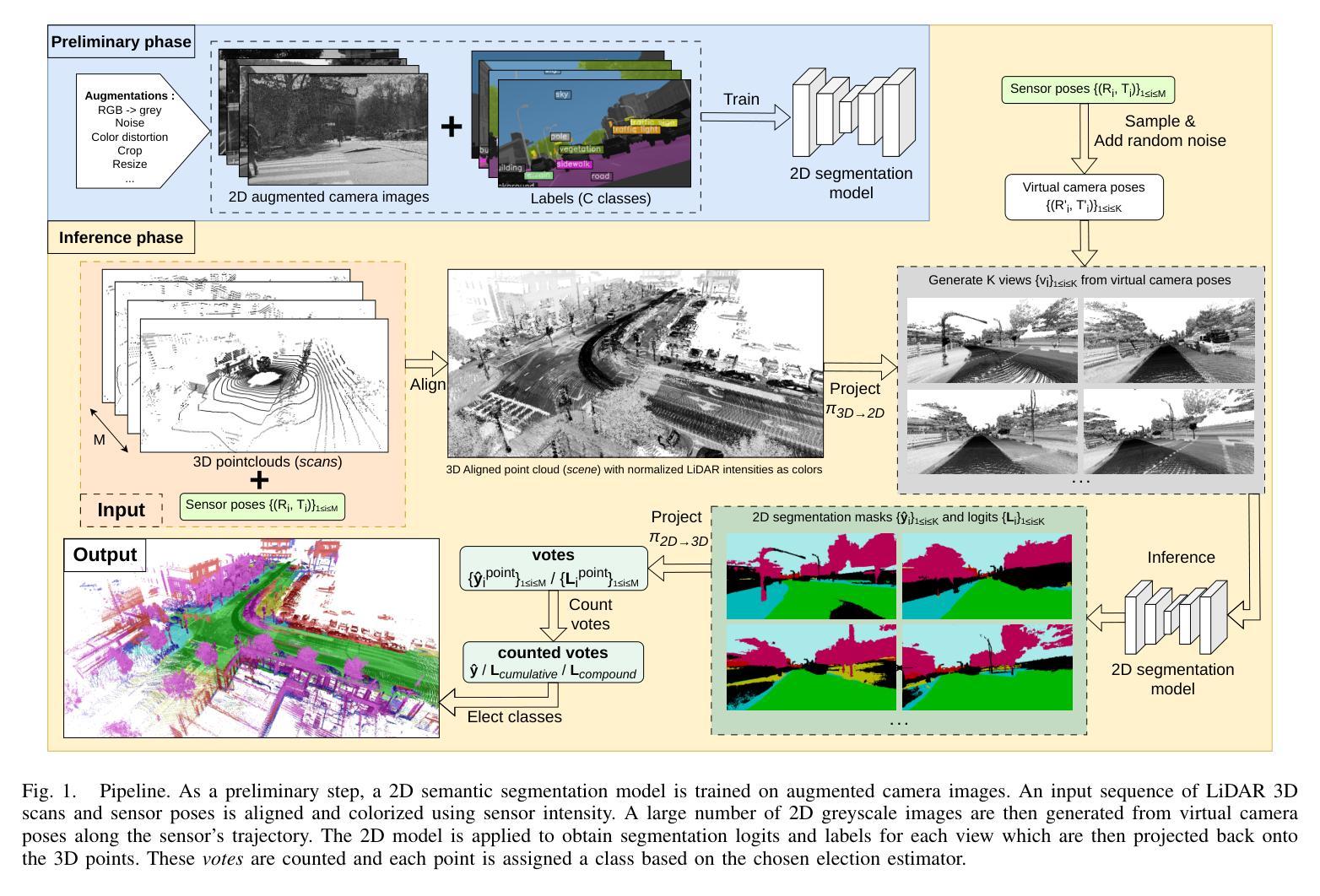
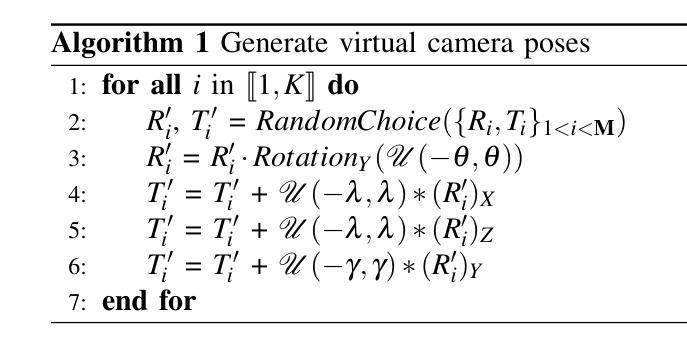
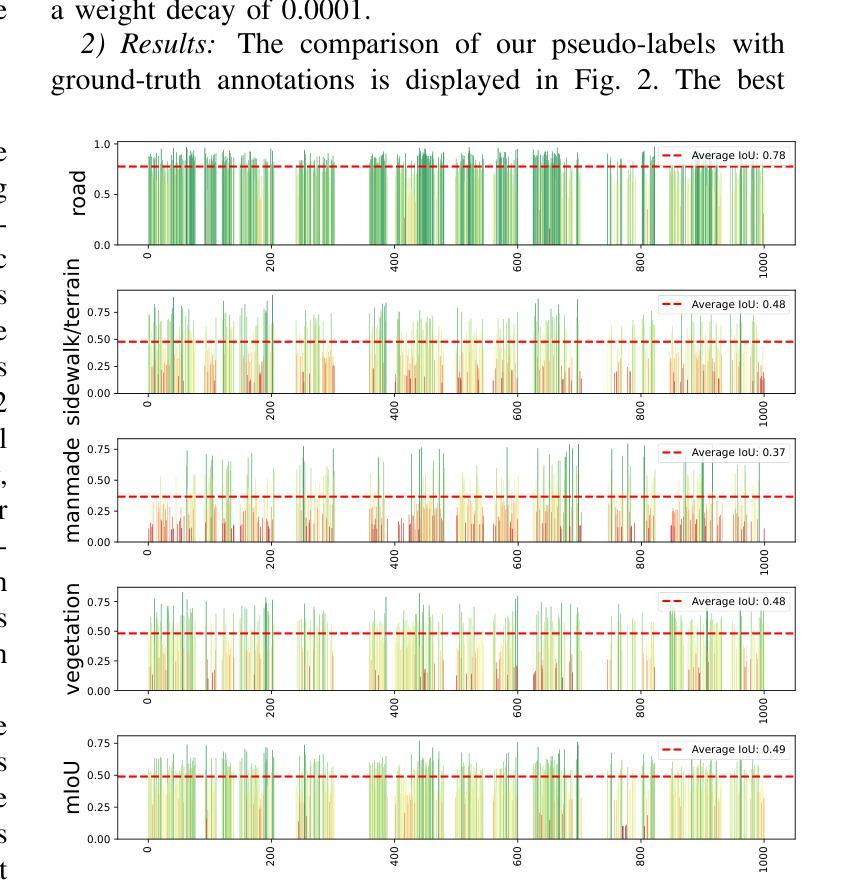
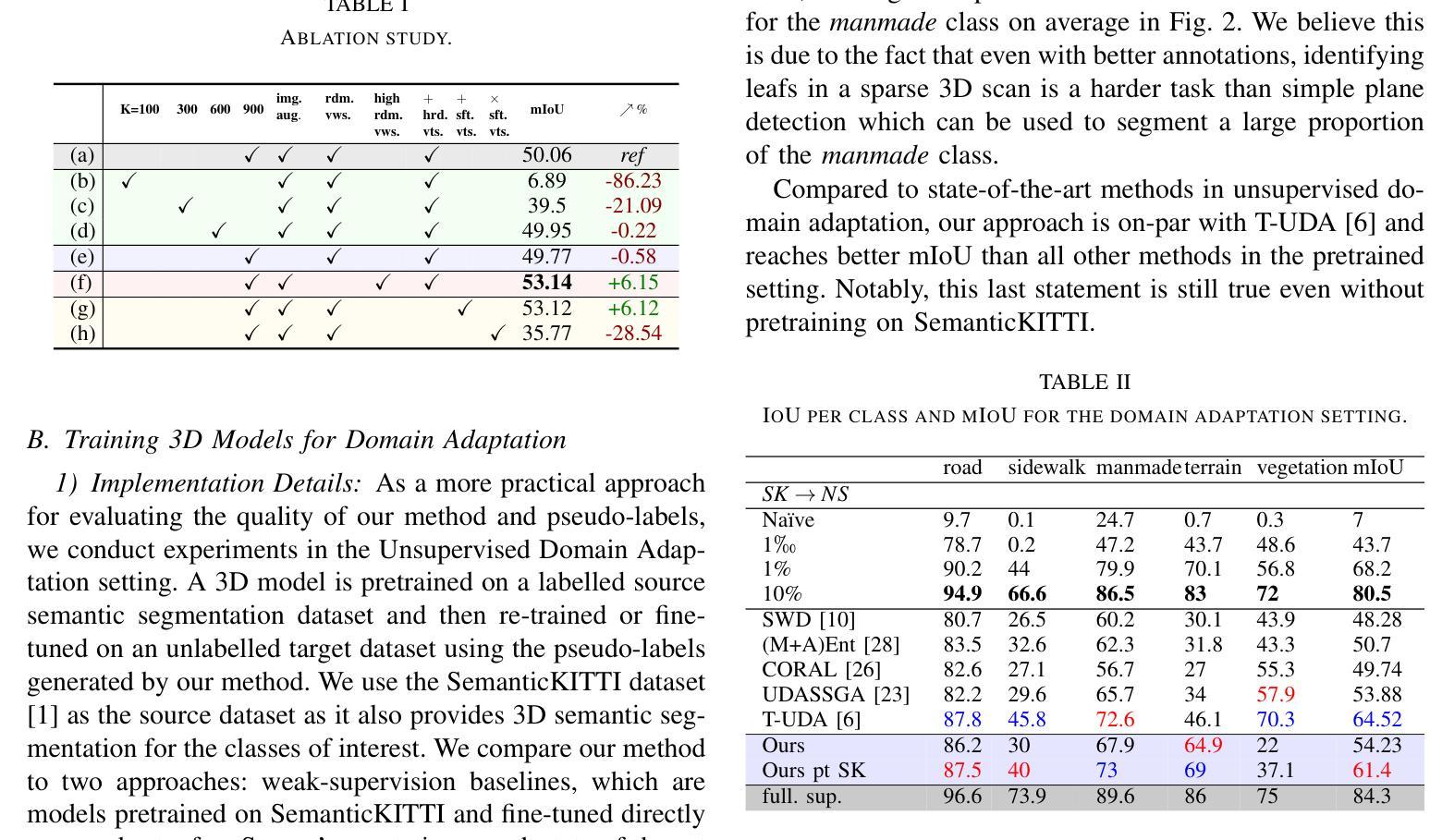
Semantic segmentation of 3D LiDAR point clouds, essential for autonomous driving and infrastructure management, is best achieved by supervised learning, which demands extensive annotated datasets and faces the problem of domain shifts. We introduce a new 3D semantic segmentation pipeline that leverages aligned scenes and state-of-the-art 2D segmentation methods, avoiding the need for direct 3D annotation or reliance on additional modalities such as camera images at inference time. Our approach generates 2D views from LiDAR scans colored by sensor intensity and applies 2D semantic segmentation to these views using a camera-domain pretrained model. The segmented 2D outputs are then back-projected onto the 3D points, with a simple voting-based estimator that merges the labels associated to each 3D point. Our main contribution is a global pipeline for 3D semantic segmentation requiring no prior 3D annotation and not other modality for inference, which can be used for pseudo-label generation. We conduct a thorough ablation study and demonstrate the potential of the generated pseudo-labels for the Unsupervised Domain Adaptation task.
3D激光雷达点云的语义分割对于自动驾驶和基础设施管理至关重要,最好通过监督学习来实现。然而,监督学习需要大量的标注数据集,并面临领域偏移的问题。我们引入了一种新的3D语义分割流程,它利用对齐的场景和最新的2D分割方法,避免了在推理阶段对直接3D标注的依赖或对附加模式(如相机图像)的依赖。我们的方法通过传感器强度对激光雷达扫描进行着色以生成二维视图,并使用针对相机领域进行预训练的模型对这些视图应用二维语义分割。然后,将分割后的二维输出重新投影到三维点上,使用基于简单投票的估计器合并与每个三维点相关的标签。我们的主要贡献是一个全局的3D语义分割流程,无需事先的3D标注,并且推理不需要其他模式,可用于生成伪标签。我们进行了全面的消融研究,并展示了生成的伪标签在无需监督的领域自适应任务中的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to IV2024
Summary
本文介绍了一种新的3D语义分割管道,它通过利用对齐场景和最新的2D分割方法,实现了无需直接3D标注和依赖其他模态(如摄像头图像)的推理。该方法通过从激光雷达扫描生成彩色2D视图,并应用预训练的摄像头模型进行2D语义分割。分割后的2D输出被重新投影到3D点上,通过简单的投票估算器合并每个3D点的标签。本文的主要贡献是一个全局的3D语义分割管道,它无需预先的3D标注,且推理过程不需要其他模态的支持,可用于生成伪标签。此外,文章还进行了全面的消融研究,证明了生成的伪标签在监督域自适应任务中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了一种新的3D语义分割方法,利用对齐场景和先进的2D分割技术。
- 方法通过生成彩色2D视图并利用预训练的摄像头模型进行分割来实现3D语义分割。
- 不需要直接的3D标注和额外的模态(如摄像头图像)进行推理。
- 通过将分割后的2D输出重新投影到3D点,并采用基于投票的估算器来合并标签。
- 提出了一种全局的3D语义分割管道,可用于生成伪标签。
点此查看论文截图

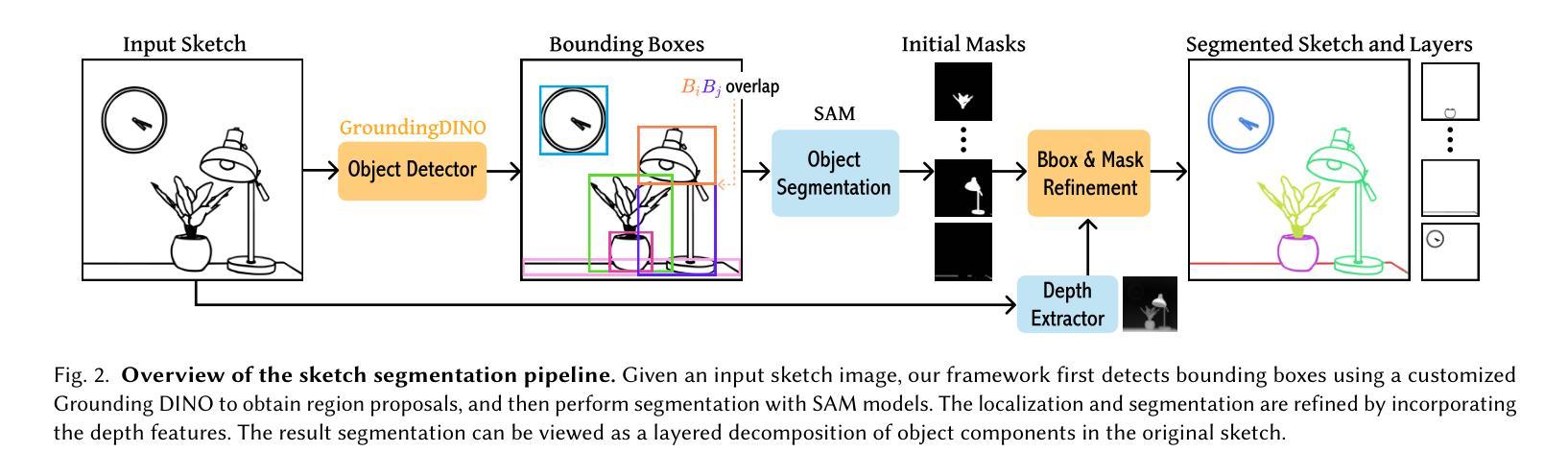
Instance Segmentation of Scene Sketches Using Natural Image Priors
Authors:Mia Tang, Yael Vinker, Chuan Yan, Lvmin Zhang, Maneesh Agrawala
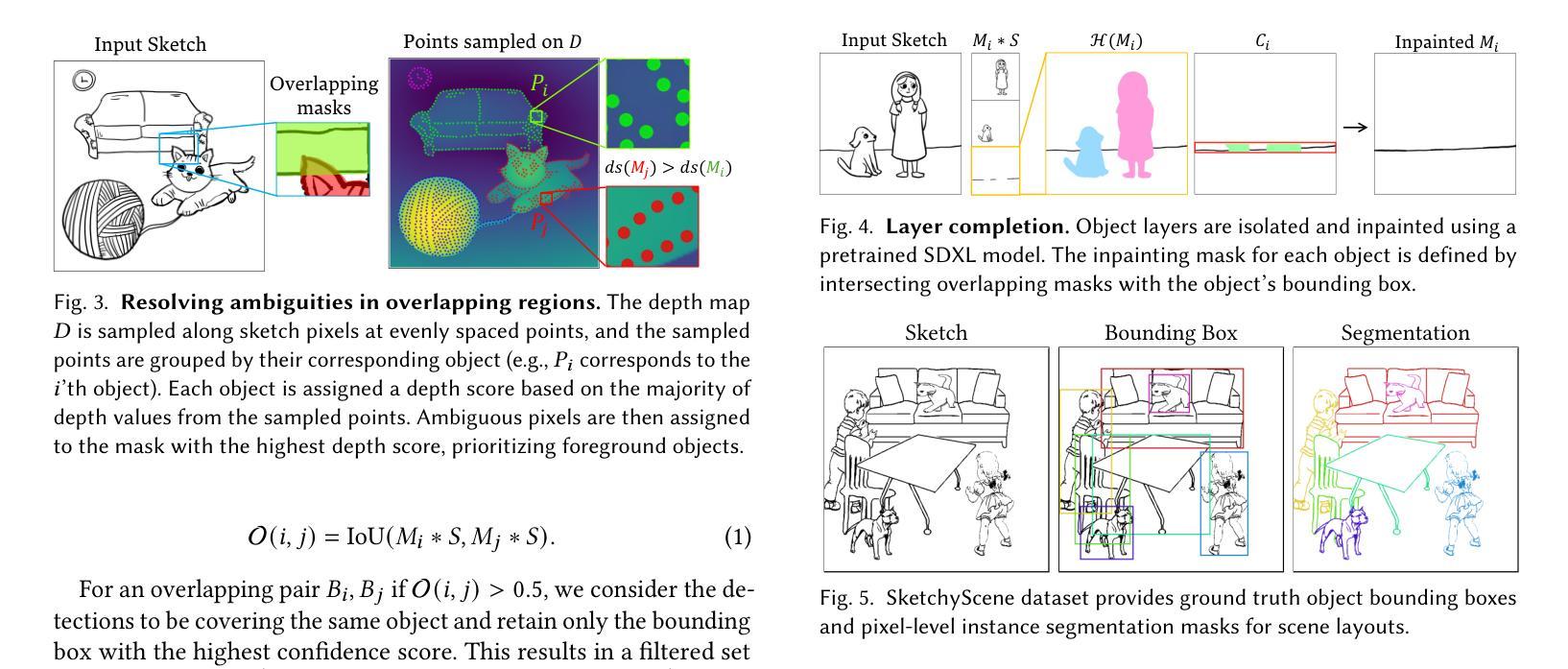
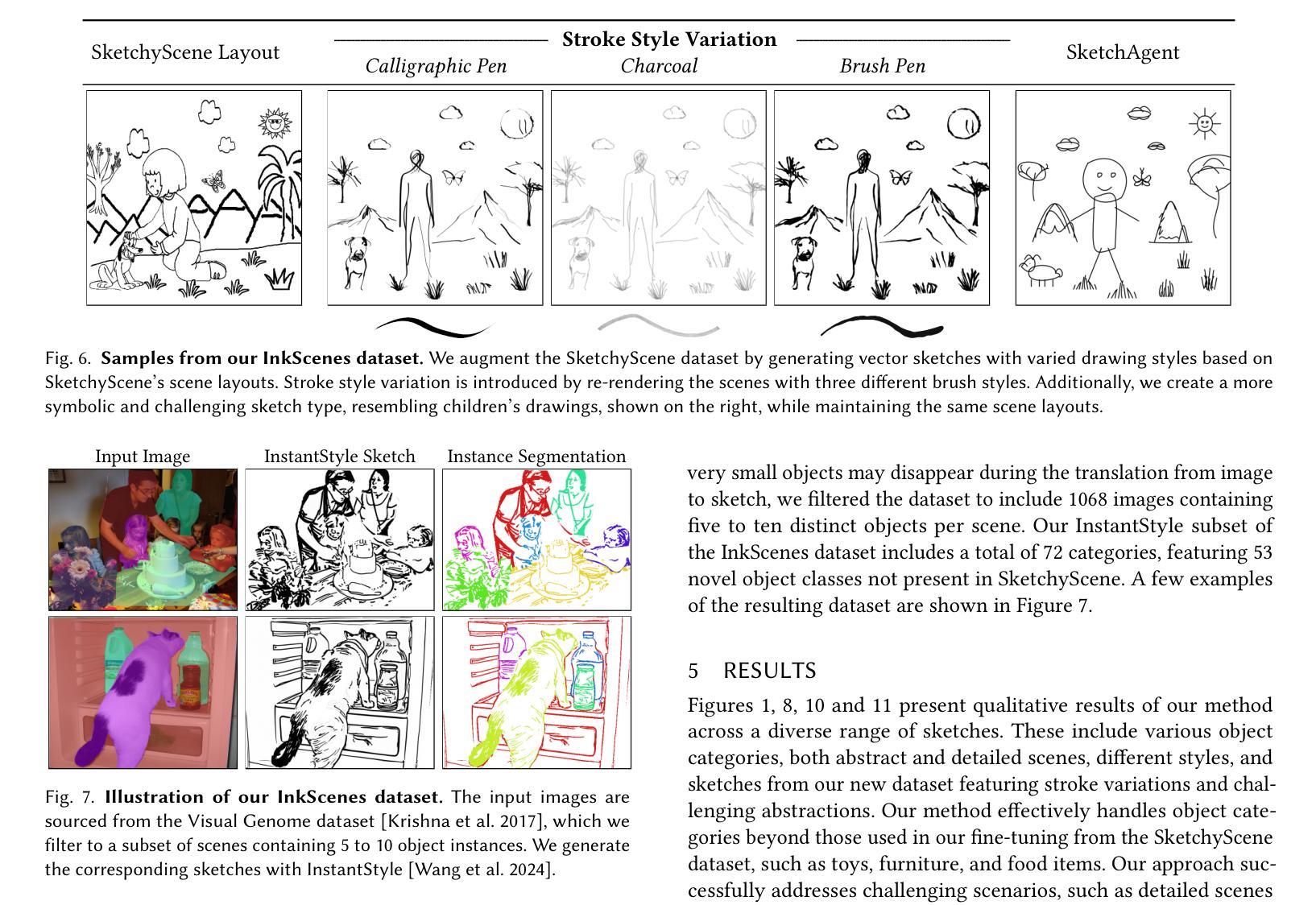
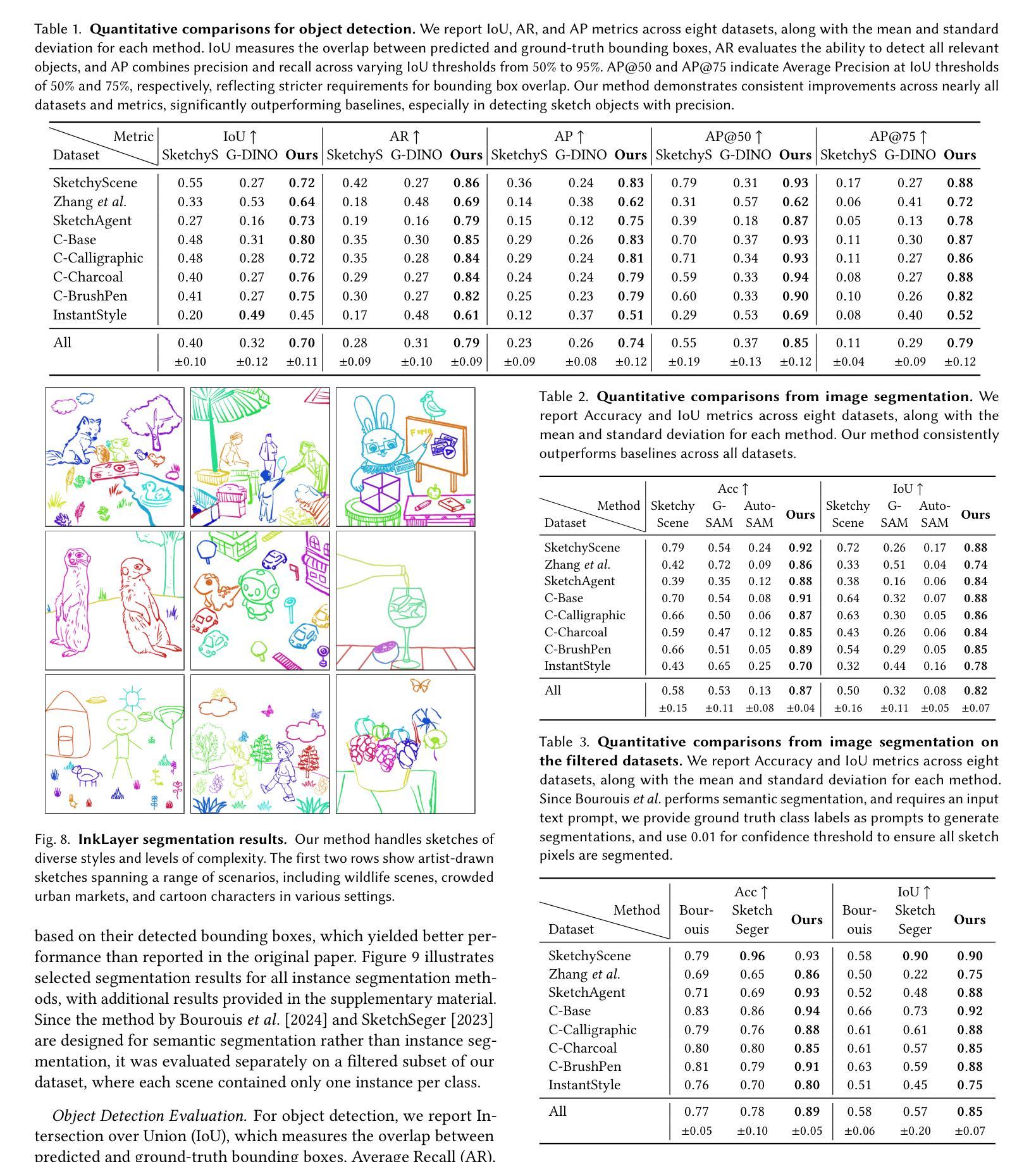
Sketch segmentation involves grouping pixels within a sketch that belong to the same object or instance. It serves as a valuable tool for sketch editing tasks, such as moving, scaling, or removing specific components. While image segmentation models have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in recent years, sketches present unique challenges for these models due to their sparse nature and wide variation in styles. We introduce InkLayer, a method for instance segmentation of raster scene sketches. Our approach adapts state-of-the-art image segmentation and object detection models to the sketch domain by employing class-agnostic fine-tuning and refining segmentation masks using depth cues. Furthermore, our method organizes sketches into sorted layers, where occluded instances are inpainted, enabling advanced sketch editing applications. As existing datasets in this domain lack variation in sketch styles, we construct a synthetic scene sketch segmentation dataset, InkScenes, featuring sketches with diverse brush strokes and varying levels of detail. We use this dataset to demonstrate the robustness of our approach.
草图分割涉及将属于同一对象或实例的草图内的像素进行分组。它是草图编辑任务(如移动、缩放或删除特定组件)的重要工具。虽然图像分割模型近年来表现出了显著的能力,但由于草图的稀疏性和风格上的巨大差异,这些模型面临着独特的挑战。我们引入了InkLayer,这是一种基于矢量场景草图的实例分割方法。我们的方法通过采用类无关的微调和使用深度线索细化分割掩膜,将最先进的图像分割和对象检测模型适应到草图领域。此外,我们的方法将草图组织成有序的层,其中遮挡的实例会被涂上颜色,从而实现高级的草图编辑应用程序。由于该领域的现有数据集缺乏草图风格的多样性,我们构建了一个合成场景草图分割数据集InkScenes,其中包含具有不同笔触和细节层次的草图。我们使用此数据集来展示我们方法的稳健性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project website: https://inklayer.github.io
Summary
本文介绍了InkLayer方法,这是一种针对矢量场景素描的实例分割方法。它通过采用类无关的微调技术,将先进的图像分割和对象检测模型适应到素描领域。此外,该方法利用深度线索对分割掩膜进行细化,并将素描整理成有序的层,支持高级素描编辑应用。为解决现有数据集在素描风格上的缺乏多样性问题,本文构建了一个合成场景素描分割数据集InkScenes。
Key Takeaways
- Sketch segmentation是指将同一对象或实例的像素进行分组,对于素描编辑任务(如移动、缩放或删除特定组件)具有重要意义。
- InkLayer方法是一种针对矢量场景素描的实例分割方法,通过适应先进的图像分割和对象检测模型来进行分割。
- InkLayer方法采用类无关的微调技术,并结合深度线索对分割掩膜进行细化。
- 该方法将素描整理成有序的层,使被遮挡的实例可以进行填充,支持高级素描编辑应用。
- 现有素描分割数据集在素描风格上缺乏多样性。
- 为解决此问题,本文构建了一个合成场景素描分割数据集InkScenes,包含不同笔触和细节层次的素描。
点此查看论文截图