⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-08 更新
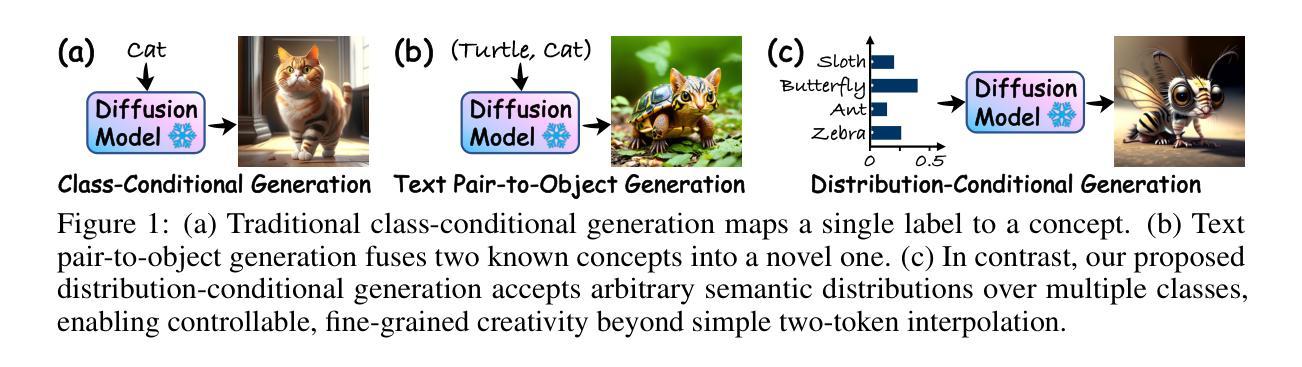
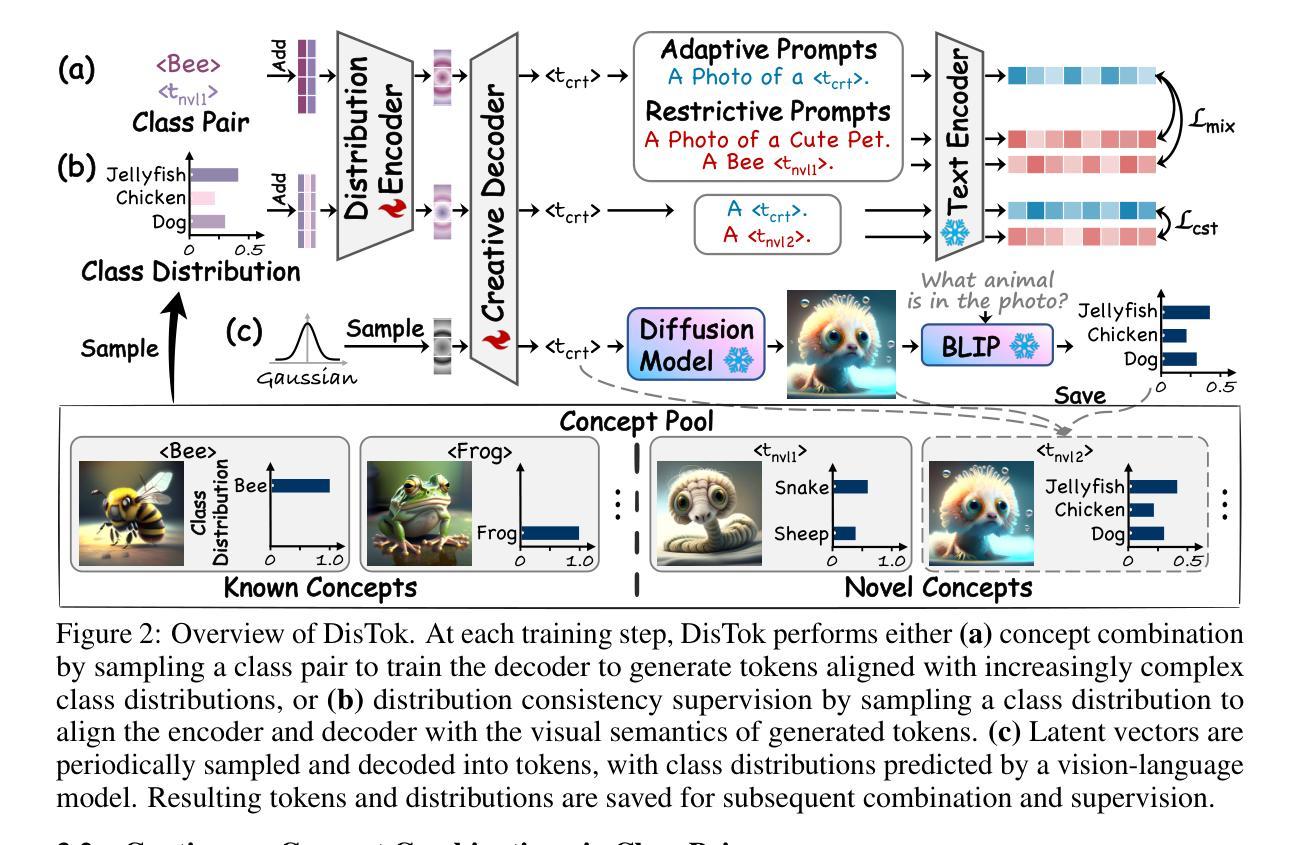
Distribution-Conditional Generation: From Class Distribution to Creative Generation
Authors:Fu Feng, Yucheng Xie, Xu Yang, Jing Wang, Xin Geng
Text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models are effective at producing semantically aligned images, but their reliance on training data distributions limits their ability to synthesize truly novel, out-of-distribution concepts. Existing methods typically enhance creativity by combining pairs of known concepts, yielding compositions that, while out-of-distribution, remain linguistically describable and bounded within the existing semantic space. Inspired by the soft probabilistic outputs of classifiers on ambiguous inputs, we propose Distribution-Conditional Generation, a novel formulation that models creativity as image synthesis conditioned on class distributions, enabling semantically unconstrained creative generation. Building on this, we propose DisTok, an encoder-decoder framework that maps class distributions into a latent space and decodes them into tokens of creative concept. DisTok maintains a dynamic concept pool and iteratively sampling and fusing concept pairs, enabling the generation of tokens aligned with increasingly complex class distributions. To enforce distributional consistency, latent vectors sampled from a Gaussian prior are decoded into tokens and rendered into images, whose class distributions-predicted by a vision-language model-supervise the alignment between input distributions and the visual semantics of generated tokens. The resulting tokens are added to the concept pool for subsequent composition. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DisTok, by unifying distribution-conditioned fusion and sampling-based synthesis, enables efficient and flexible token-level generation, achieving state-of-the-art performance with superior text-image alignment and human preference scores.
文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型在生成语义对齐的图像方面非常有效,但它们对训练数据分布的依赖限制了其合成真正新颖、超出分布概念的能力。现有方法通常通过结合已知概念对来增强创造力,从而产生超出分布但仍然是语言可描述且存在于现有语义空间内的组合。我们受到分类器在模糊输入上的软概率输出的启发,提出了分布条件生成,这是一种新的模型创造力的方法,即将图像合成条件化为类分布,从而实现语义上无约束的创造性生成。在此基础上,我们提出了DisTok,这是一种编码器解码器框架,它将类分布映射到潜在空间并解码为创造性概念的标记。DisTok维护一个动态概念池,并迭代采样和融合概念对,以生成与日益复杂的类分布对齐的标记。为了强制实施分布一致性,从高斯先验中采样的潜在向量被解码为标记并呈现为图像,其类分布由视觉语言模型预测,监督输入分布与生成标记的视觉语义之间的对齐。生成的标记被添加到概念池中以供后续组合。大量实验表明,DisTok通过统一分布条件下的融合和基于采样的合成,实现了高效灵活的标记级别生成,以卓越的性能实现了文本与图像之间的对齐和人类偏好得分。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型在生成语义对齐的图像方面非常有效,但其对训练数据分布的依赖限制了其合成真正新颖、超出分布概念的能力。本文受分类器对模糊输入软概率输出的启发,提出了分布条件生成这一新模型,将创造力视为基于类别分布的图像合成条件,从而实现语义上无约束的创造性生成。在此基础上,本文提出了DisTok,一种编码器-解码器框架,将类别分布映射到潜在空间并解码为创造性概念的标记。DisTok维持一个动态概念池,通过迭代采样和融合概念对,生成与复杂类别分布对齐的标记。通过从高斯先验中采样潜在向量,并将其解码为标记和图像,利用视觉语言模型预测的类别分布来监督输入分布与生成标记之间的一致性。生成的标记被添加到概念池中用于后续组合。实验表明,DisTok通过统一分布条件下的融合和基于采样的合成,实现了高效且灵活的标记级别生成,达到了最先进的性能,具有出色的文本-图像对齐和更高的人类偏好评分。
Key Takeaways
- T2I扩散模型虽能有效生成语义对齐图像,但受限于训练数据分布,难以合成真正新颖、超出分布的概念。
- 本文提出了分布条件生成的新模型,以类别分布为条件进行图像合成,推动语义无约束的创造性生成。
- DisTok作为一种编码器-解码器框架,能将类别分布映射到潜在空间并解码为创造性概念的标记。
- DisTok通过动态概念池实现迭代采样和概念对融合,生成与复杂类别分布对齐的标记。
- 通过从高斯先验采样潜在向量并解码为标记和图像,DisTok利用视觉语言模型的类别分布预测来监督输入分布与生成标记之间的对齐。
- 实验表明DisTok在文本到图像生成任务上达到了最先进的性能。
点此查看论文截图


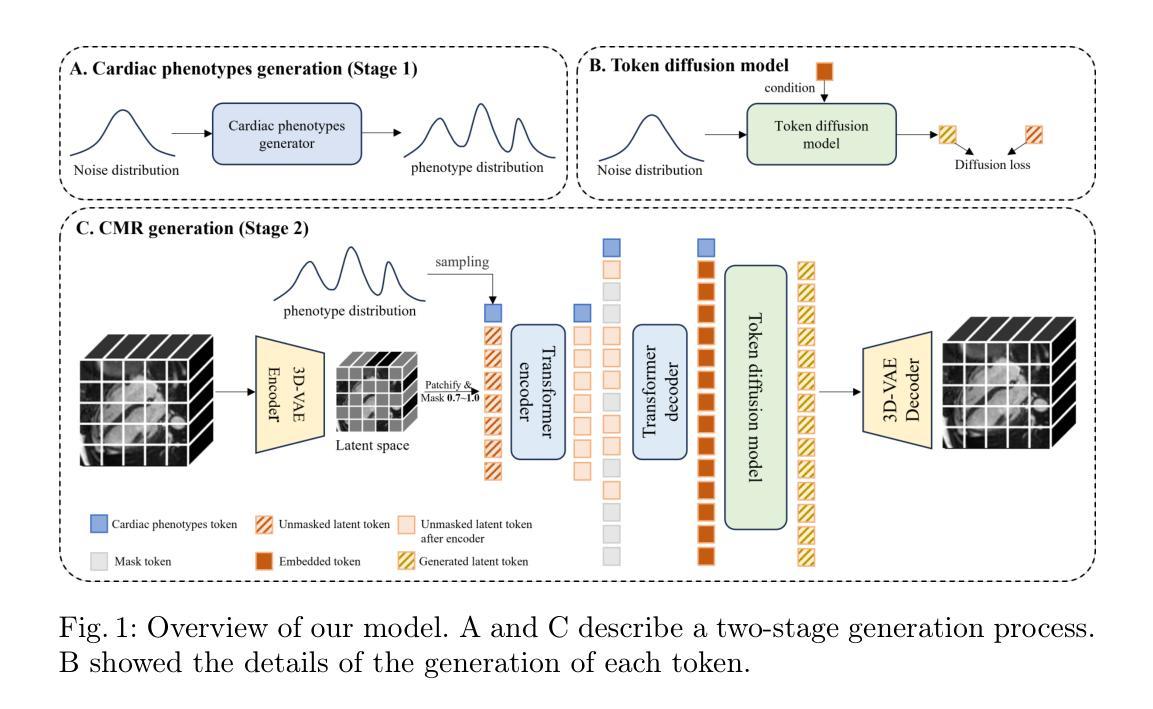
Phenotype-Guided Generative Model for High-Fidelity Cardiac MRI Synthesis: Advancing Pretraining and Clinical Applications
Authors:Ziyu Li, Yujian Hu, Zhengyao Ding, Yiheng Mao, Haitao Li, Fan Yi, Hongkun Zhang, Zhengxing Huang
Cardiac Magnetic Resonance (CMR) imaging is a vital non-invasive tool for diagnosing heart diseases and evaluating cardiac health. However, the limited availability of large-scale, high-quality CMR datasets poses a major challenge to the effective application of artificial intelligence (AI) in this domain. Even the amount of unlabeled data and the health status it covers are difficult to meet the needs of model pretraining, which hinders the performance of AI models on downstream tasks. In this study, we present Cardiac Phenotype-Guided CMR Generation (CPGG), a novel approach for generating diverse CMR data that covers a wide spectrum of cardiac health status. The CPGG framework consists of two stages: in the first stage, a generative model is trained using cardiac phenotypes derived from CMR data; in the second stage, a masked autoregressive diffusion model, conditioned on these phenotypes, generates high-fidelity CMR cine sequences that capture both structural and functional features of the heart in a fine-grained manner. We synthesized a massive amount of CMR to expand the pretraining data. Experimental results show that CPGG generates high-quality synthetic CMR data, significantly improving performance on various downstream tasks, including diagnosis and cardiac phenotypes prediction. These gains are demonstrated across both public and private datasets, highlighting the effectiveness of our approach. Code is availabel at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/CPGG.
心脏磁共振(CMR)成像是一种用于诊断心脏病和评估心脏健康的重要无创工具。然而,大规模高质量CMR数据集的有限可用性给人工智能(AI)在该领域的有效应用带来了重大挑战。即使是无标签数据的数量和它所涵盖的健康状况也难以满足模型预训练的需求,这阻碍了AI模型在下游任务上的性能。在这项研究中,我们提出了Cardiac Phenotype-Guided CMR Generation(CPGG),这是一种生成多样化CMR数据的新方法,涵盖了广泛的心脏健康状况。CPGG框架分为两个阶段:在第一阶段,使用从CMR数据中得出的心脏表型来训练生成模型;在第二阶段,使用一个基于这些表型的掩码自回归扩散模型,生成高保真度的CMR电影序列,以精细的方式捕捉心脏的结构和功能特征。我们合成了大量的CMR数据来扩展预训练数据。实验结果表明,CPGG生成的高质量合成CMR数据显著提高了各种下游任务(包括诊断和心脏表型预测)的性能。这些收益在公共和私有数据集上都得到了证明,凸显了我们的方法的有效性。代码可在https://anonymous.4open.science/r/CPGG获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本摘要介绍了一项重要研究,该研究解决了心脏磁共振成像(CMR)数据稀缺的问题,限制了人工智能在该领域的应用。该研究提出了心脏表型引导CMR生成(CPGG)的新方法,通过生成涵盖广泛心脏健康状态的多样的CMR数据来扩展预训练数据。CPGG框架分为两个阶段:首先利用从CMR数据中得出的心脏表型训练生成模型,然后使用掩模自回归扩散模型基于这些表型生成高质量的CMR电影序列。此方法能精细捕捉心脏的结构和功能特征,并合成大量CMR数据以扩展预训练数据。实验结果显示,CPGG生成的合成CMR数据质量高,能显著提高诊断和各种下游任务的性能,包括心脏表型预测。代码已公开。
Key Takeaways
- CMR成像在心脏疾病诊断和治疗评估中至关重要,但大规模高质量CMR数据的有限可用性限制了人工智能在该领域的应用。
- 提出了一种新的方法——心脏表型引导CMR生成(CPGG),以生成涵盖广泛心脏健康状态的多样化CMR数据。
- CPGG框架分为两个阶段:首先使用心脏表型训练生成模型,然后使用掩模自回归扩散模型生成高质量的CMR电影序列。
- 合成大量CMR数据以扩展预训练数据,显著提高诊断和各种下游任务的性能,包括心脏表型预测。
- 实验结果显示,CPGG生成的合成CMR数据质量高。
- 此方法能捕捉心脏的结构和功能特征的细节,这是其成功的关键因素之一。
点此查看论文截图

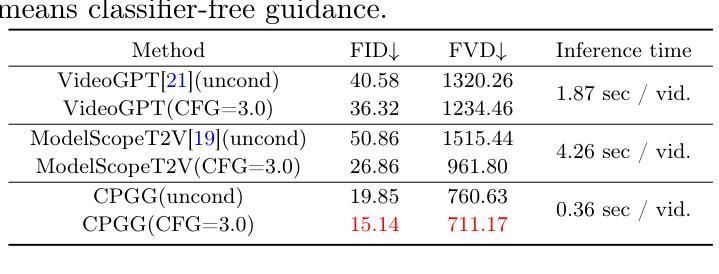
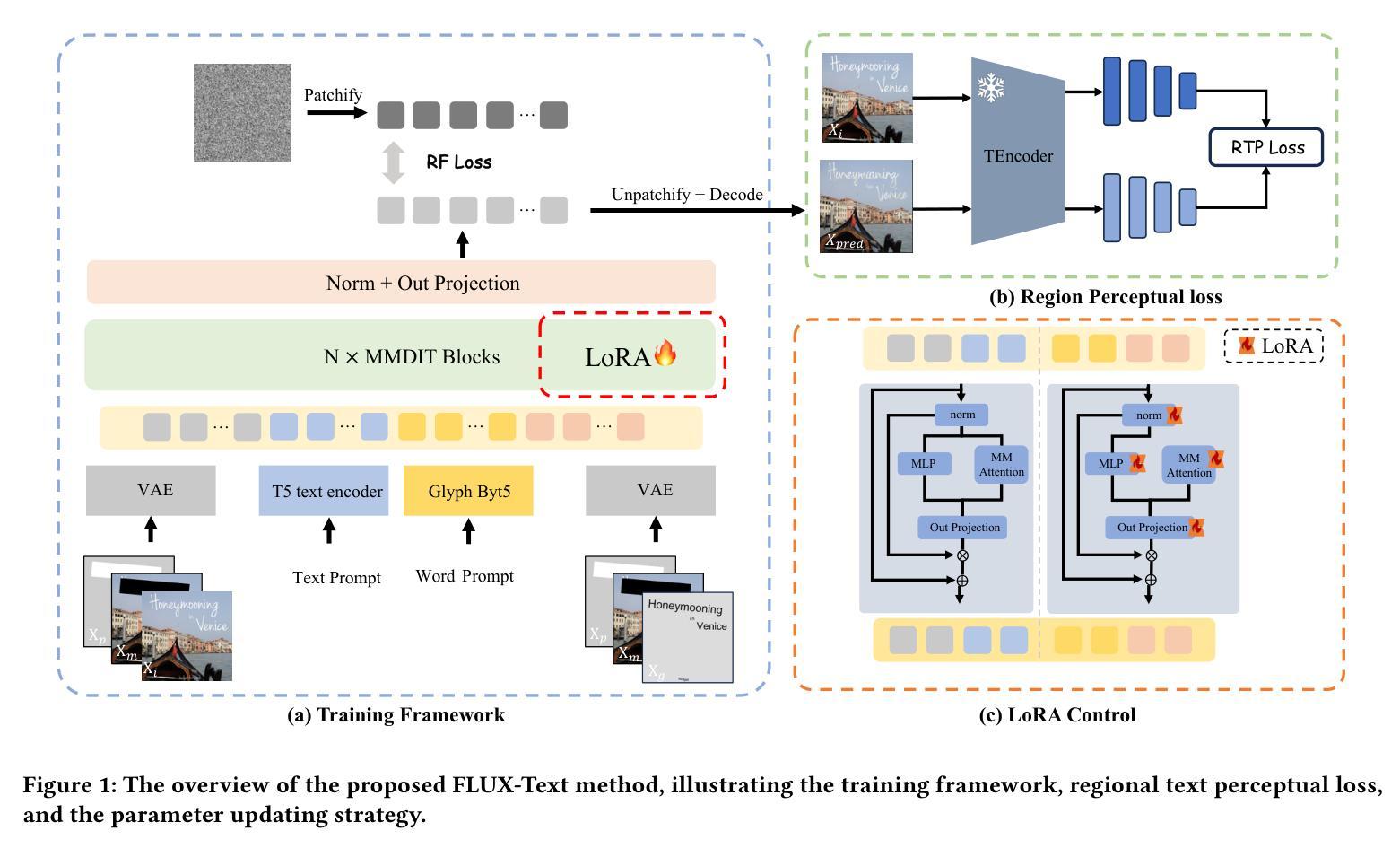
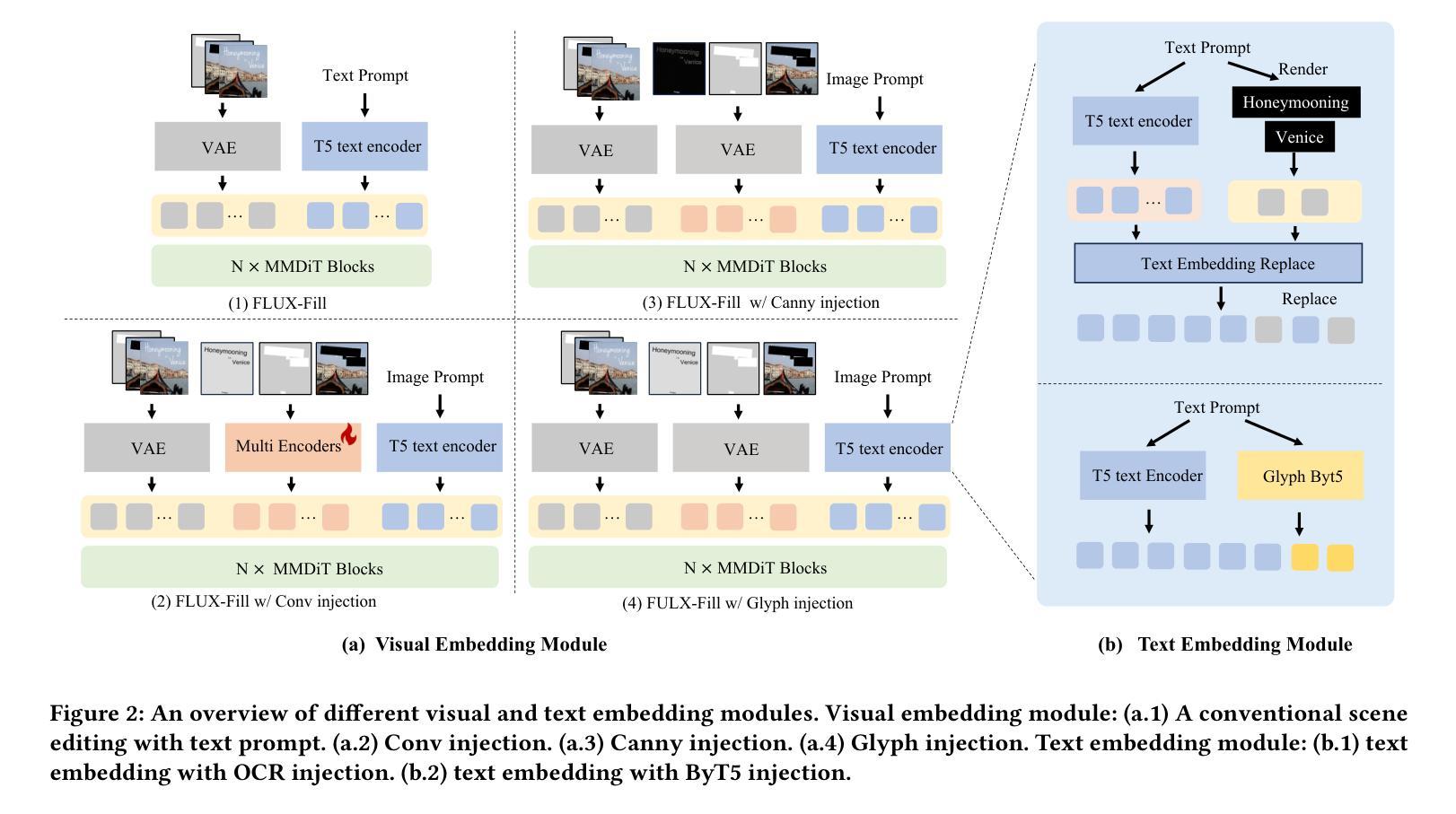
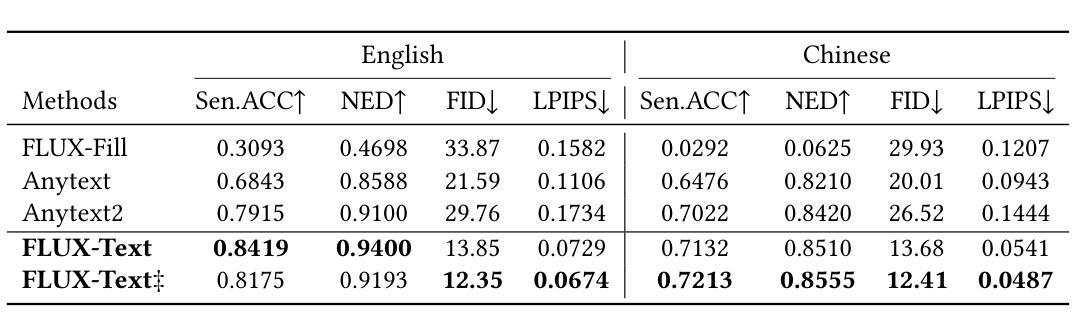
FLUX-Text: A Simple and Advanced Diffusion Transformer Baseline for Scene Text Editing
Authors:Rui Lan, Yancheng Bai, Xu Duan, Mingxing Li, Lei Sun, Xiangxiang Chu
The task of scene text editing is to modify or add texts on images while maintaining the fidelity of newly generated text and visual coherence with the background. Recent works based on latent diffusion models (LDM) show improved text editing results, yet still face challenges and often generate inaccurate or unrecognizable characters, especially for non-Latin ones (\eg, Chinese), which have complex glyph structures. To address these issues, we present FLUX-Text, a simple and advanced multilingual scene text editing framework based on FLUX-Fill. Specifically, we carefully investigate glyph conditioning, considering both visual and textual modalities. To retain the original generative capabilities of FLUX-Fill while enhancing its understanding and generation of glyphs, we propose lightweight glyph and text embedding modules. Owning to the lightweight design, FLUX-Text is trained only with $100K$ training examples compared to current popular methods trained with 2.9M ones. With no bells and whistles, our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on text editing tasks. Qualitative and quantitative experiments on the public datasets demonstrate that our method surpasses previous works in text fidelity.
场景文本编辑的任务是在保持新生成文本的保真度和与背景视觉连贯性的同时,对图像上的文本进行修改或添加。基于潜在扩散模型(LDM)的近期工作在文本编辑结果方面显示出改进,但仍面临挑战,并且经常生成不准确或不可识别的字符,特别是非拉丁字符(例如中文),这是由于中文等字符具有复杂的字形结构。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了基于FLUX-Fill的简洁先进的多语言场景文本编辑框架FLUX-Text。具体来说,我们仔细研究了字形条件,考虑了视觉和文本模式。为了保留FLUX-Fill的原始生成能力,同时提高其字形理解和生成能力,我们提出了轻量级字形和文本嵌入模块。由于设计轻量级,FLUX-Text仅使用100K训练样本进行训练,而当前流行的方法则使用290万训练样本。我们的方法在没有额外修饰的情况下,在文本编辑任务上实现了最先进的性能。在公开数据集上的定性和定量实验表明,我们的方法在文本保真度方面超越了以前的工作。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 4 figures
Summary
基于潜在扩散模型(LDM)的FLUX-Text场景文本编辑框架,通过轻量级字形和文本嵌入模块,提高了对非拉丁字符(如中文)的识别与生成能力,训练样本数量大幅减少至仅10万,实现了高效的多语言文本编辑性能。
Key Takeaways
- 基于潜在扩散模型(LDM)进行场景文本编辑。
- 面临对非拉丁字符(如中文)的复杂字形结构处理挑战。
- 提出FLUX-Text框架,结合FLUX-Fill技术增强字形处理和理解能力。
- 采用轻量级字形和文本嵌入模块提高生成文本的质量和准确性。
- 仅用10万训练样本,相较于当前流行方法大幅降低训练成本。
- 在公开数据集上的实验证明,FLUX-Text在文本保真度上超越先前方法。
点此查看论文截图

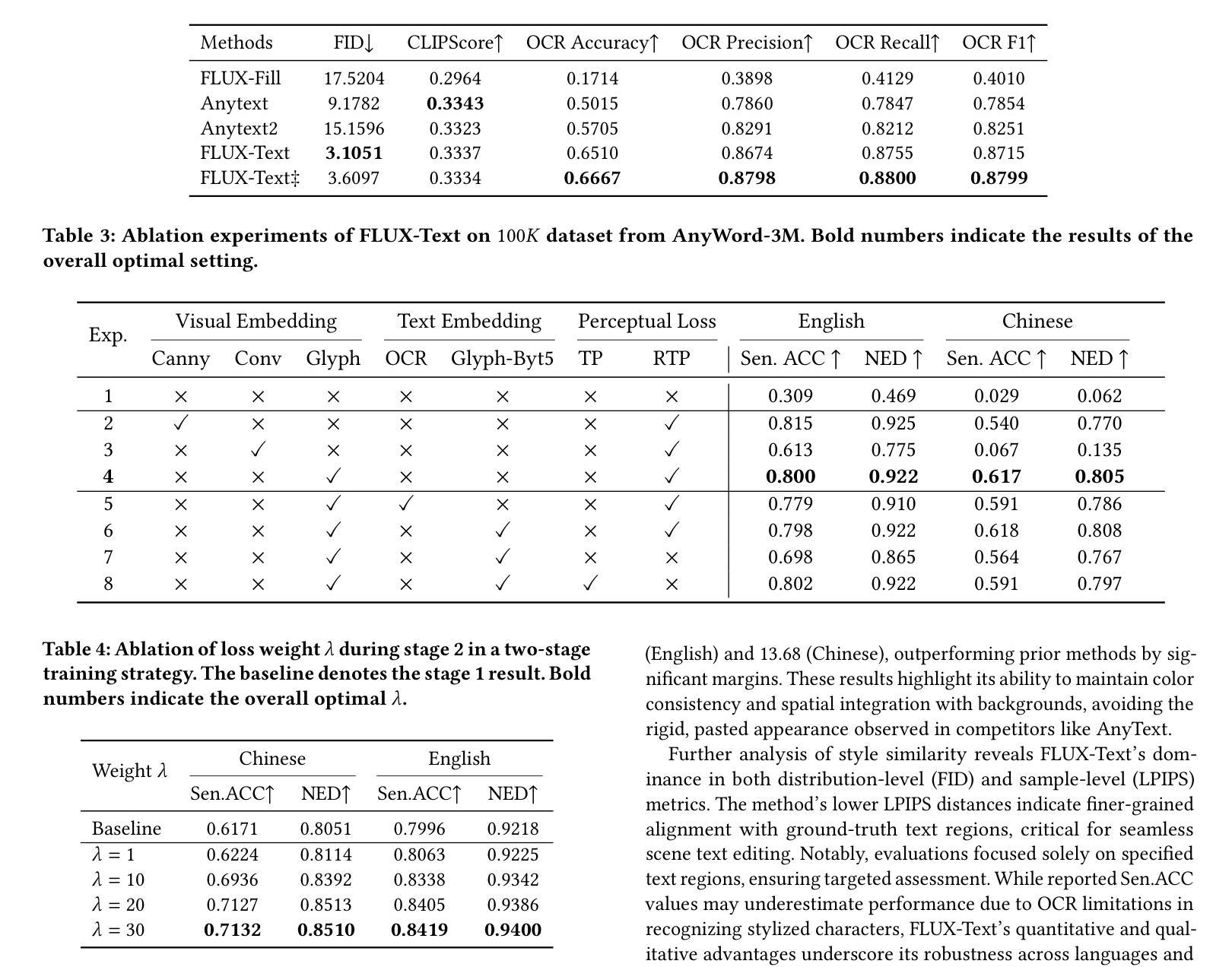
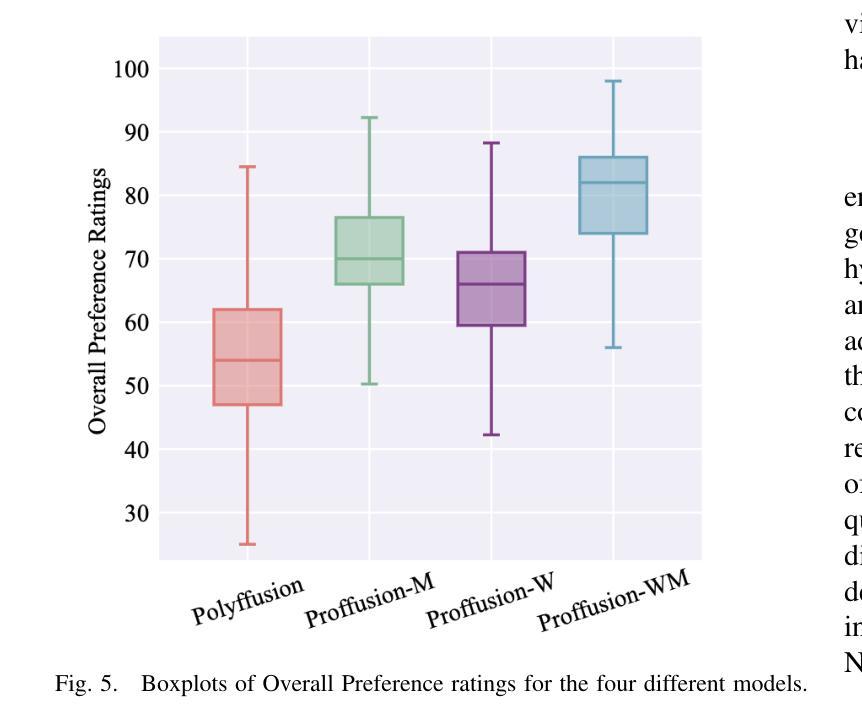
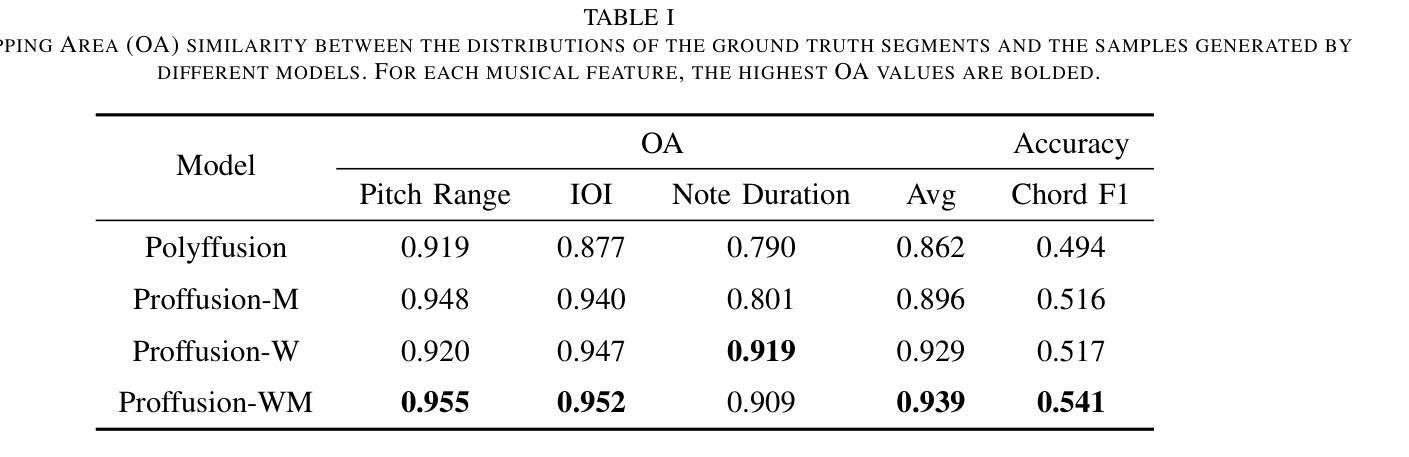
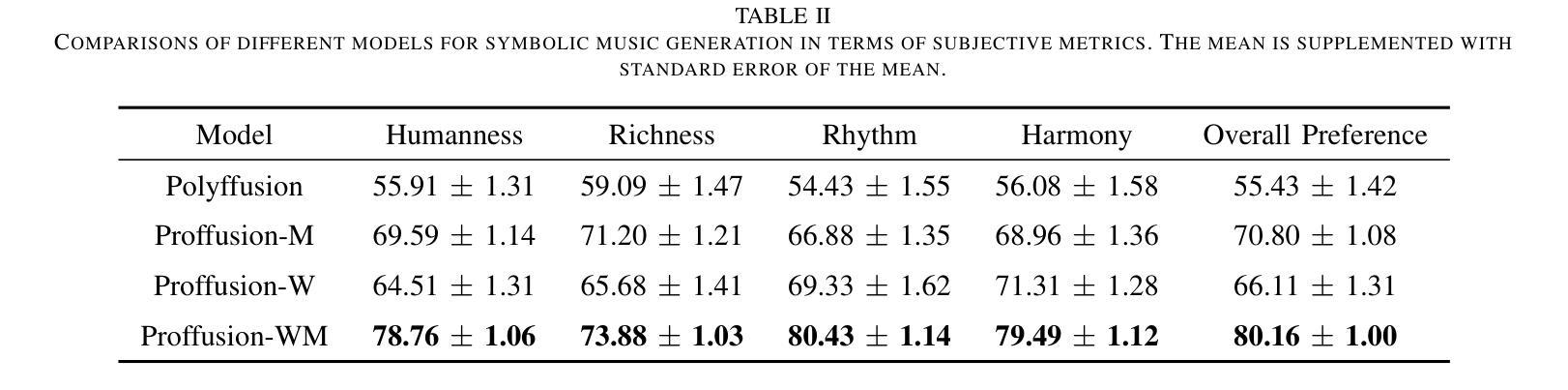
Mamba-Diffusion Model with Learnable Wavelet for Controllable Symbolic Music Generation
Authors:Jincheng Zhang, György Fazekas, Charalampos Saitis
The recent surge in the popularity of diffusion models for image synthesis has attracted new attention to their potential for generation tasks in other domains. However, their applications to symbolic music generation remain largely under-explored because symbolic music is typically represented as sequences of discrete events and standard diffusion models are not well-suited for discrete data. We represent symbolic music as image-like pianorolls, facilitating the use of diffusion models for the generation of symbolic music. Moreover, this study introduces a novel diffusion model that incorporates our proposed Transformer-Mamba block and learnable wavelet transform. Classifier-free guidance is utilised to generate symbolic music with target chords. Our evaluation shows that our method achieves compelling results in terms of music quality and controllability, outperforming the strong baseline in pianoroll generation. Our code is available at https://github.com/jinchengzhanggg/proffusion.
最近扩散模型在图像合成中的流行引起了人们对这些模型在其他领域生成任务潜力的新关注。然而,它们在符号音乐生成中的应用仍然在很大程度上被忽视,因为符号音乐通常被表示为离散事件的序列,而标准扩散模型并不适合处理离散数据。我们将符号音乐表示为类似图像的钢琴卷,便于使用扩散模型生成符号音乐。此外,本研究引入了一种新型扩散模型,该模型融入了我们所提出的Transformer-Mamba模块和可学习的小波变换。使用无分类器指导来生成具有目标和弦的符号音乐。我们的评估表明,我们的方法在音质和可控性方面取得了令人信服的结果,在钢琴卷生成方面超越了强大的基线。我们的代码可在https://github.com/jinchengzhanggg/proffusion找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散模型在图像合成领域的普及引起了人们对其在其他领域生成任务的关注。然而,由于符号音乐通常表示为离散事件的序列,标准扩散模型不适用于离散数据,因此符号音乐的生成应用仍然被忽视。本研究将符号音乐表示为图像式钢琴卷(pianorolls),促进了扩散模型在符号音乐生成中的应用。此外,本研究引入了一种新型的扩散模型,其中包含我们提出的Transformer-Mamba模块和学习小波变换。通过无分类器引导生成目标和弦的符号音乐。评估表明,该方法在音乐质量和可控性方面取得了令人信服的结果,在钢琴卷生成方面优于强大的基线。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在图像合成领域的普及促使人们关注其在其他领域的应用。
- 符号音乐生成的应用使用扩散模型仍然有限,因为符号音乐表示为离散事件序列,标准扩散模型不适用。
- 本研究通过将符号音乐表示为图像式钢琴卷(pianorolls),为扩散模型在符号音乐生成中的应用提供了便利。
- 引入了一种新型的扩散模型,包含Transformer-Mamba模块和学习小波变换。
- 使用无分类器引导生成目标和弦的符号音乐。
- 该方法在音乐质量和可控性方面取得了显著成果,优于现有基线。
点此查看论文截图

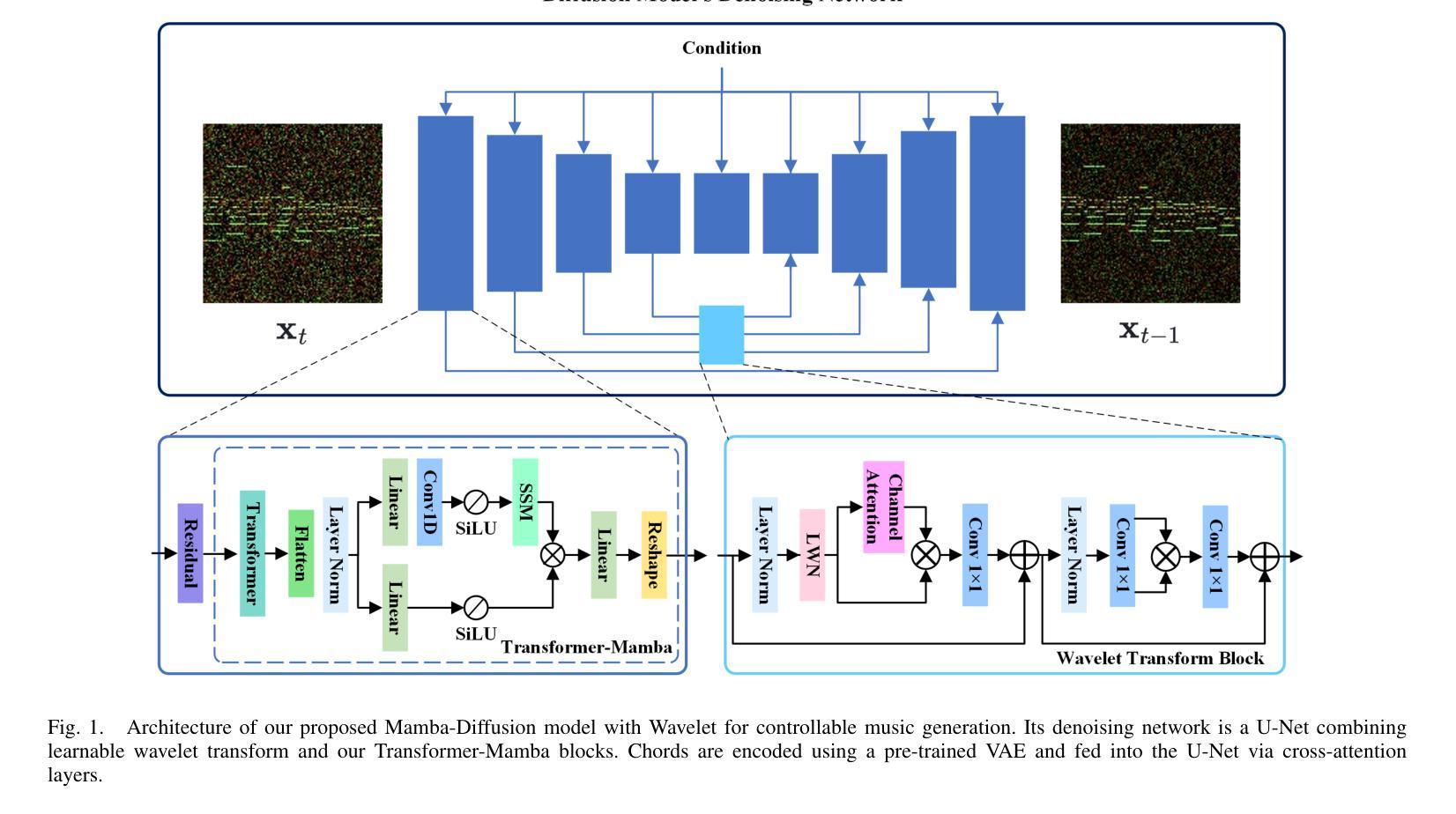
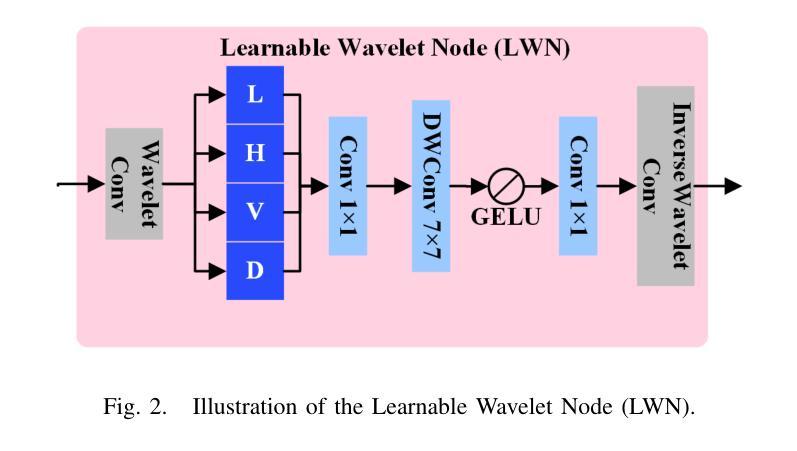

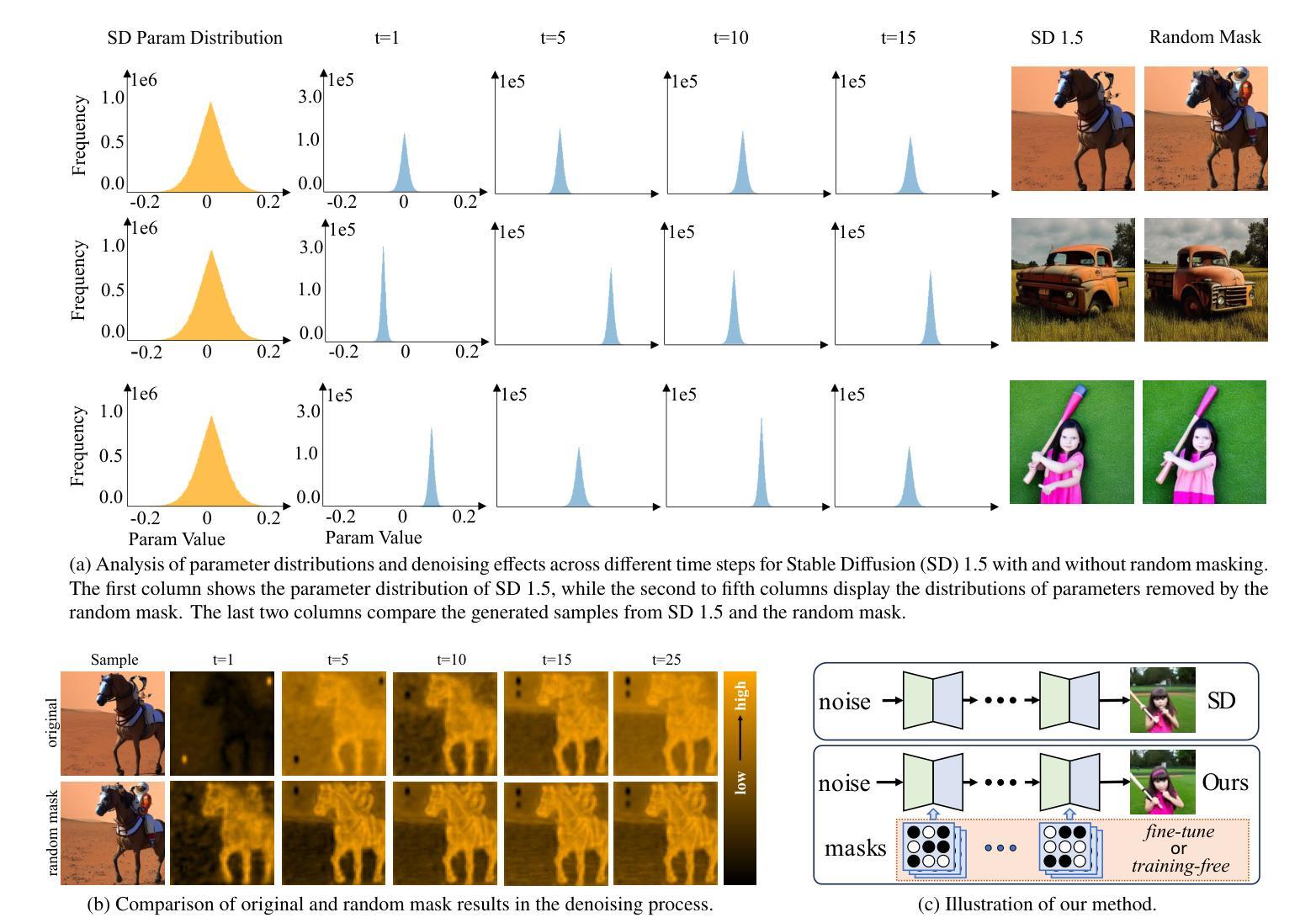
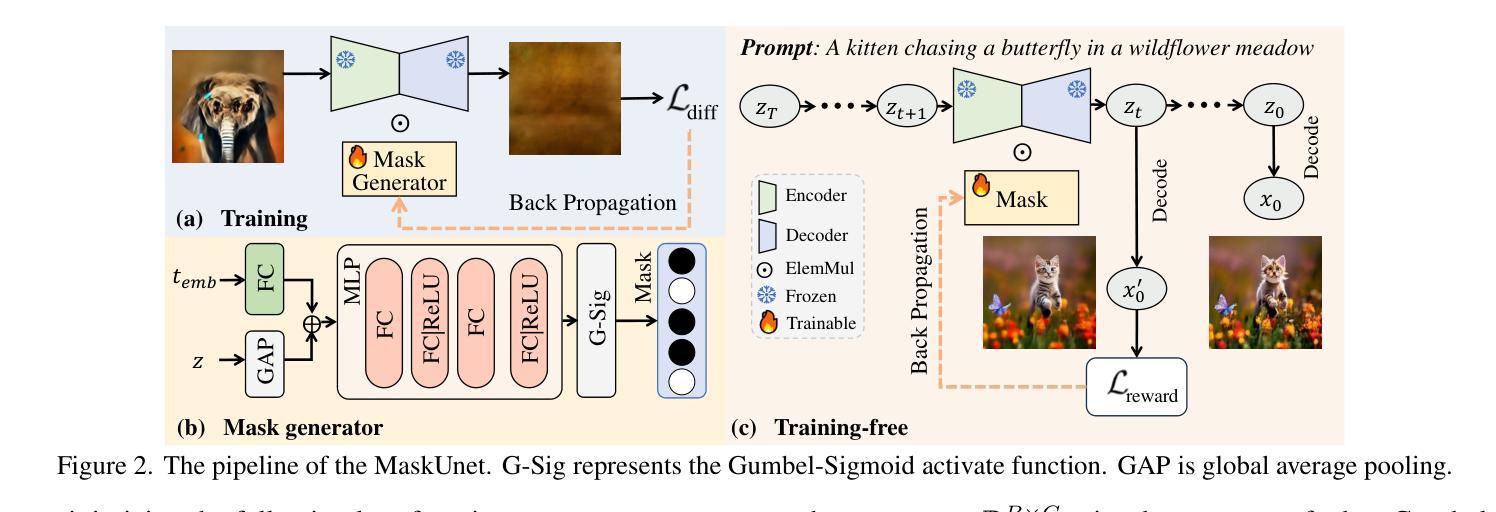
Not All Parameters Matter: Masking Diffusion Models for Enhancing Generation Ability
Authors:Lei Wang, Senmao Li, Fei Yang, Jianye Wang, Ziheng Zhang, Yuhan Liu, Yaxing Wang, Jian Yang
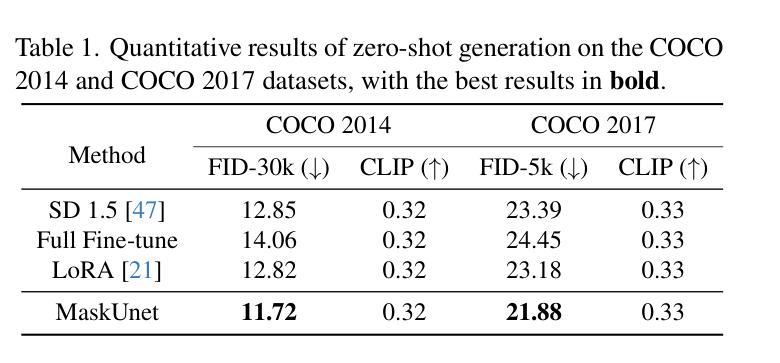
The diffusion models, in early stages focus on constructing basic image structures, while the refined details, including local features and textures, are generated in later stages. Thus the same network layers are forced to learn both structural and textural information simultaneously, significantly differing from the traditional deep learning architectures (e.g., ResNet or GANs) which captures or generates the image semantic information at different layers. This difference inspires us to explore the time-wise diffusion models. We initially investigate the key contributions of the U-Net parameters to the denoising process and identify that properly zeroing out certain parameters (including large parameters) contributes to denoising, substantially improving the generation quality on the fly. Capitalizing on this discovery, we propose a simple yet effective method-termed ``MaskUNet’’- that enhances generation quality with negligible parameter numbers. Our method fully leverages timestep- and sample-dependent effective U-Net parameters. To optimize MaskUNet, we offer two fine-tuning strategies: a training-based approach and a training-free approach, including tailored networks and optimization functions. In zero-shot inference on the COCO dataset, MaskUNet achieves the best FID score and further demonstrates its effectiveness in downstream task evaluations. Project page: https://gudaochangsheng.github.io/MaskUnet-Page/
扩散模型在早期阶段主要关注构建基本图像结构,而在后期阶段则生成精细的详细信息,包括局部特征和纹理。因此,相同的网络层被迫同时学习结构和纹理信息,这与传统的深度学习架构(例如ResNet或GANs)有很大不同,后者在不同的层捕获或生成图像语义信息。这种差异激发我们探索时间扩散模型。我们最初研究了U-Net参数对去噪过程的关键作用,并确定适当地将某些参数(包括大参数)置零有助于去噪,从而大大提高了生成质量。利用这一发现,我们提出了一种简单有效的方法,称为“MaskUNet”,它在参数数量很少的情况下提高了生成质量。我们的方法充分利用了时间步长和样本相关的有效U-Net参数。为了优化MaskUNet,我们提供了两种微调策略:基于训练的方法和无需训练的方法,包括定制的网络和优化函数。在COCO数据集上进行零样本推理时,MaskUNet获得了最佳的FID分数,并在下游任务评估中进一步证明了其有效性。项目页面:https://gudaochangsheng.github.io/MaskUnet-Page/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025
Summary
本文介绍了扩散模型的工作机制,该模型在初期关注构建基本图像结构,后期生成精细细节,如局部特征和纹理。与传统深度学习架构不同,扩散模型在同一网络层中同时学习结构和纹理信息。研究团队探索了U-Net参数对去噪过程的贡献,并提出了一种名为“MaskUNet”的方法,该方法通过有效利用时间步长和样本相关的有效U-Net参数,在保持参数数量很少的同时提高了生成质量。此外,团队还提供了两种微调策略来优化MaskUNet的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型分阶段构建图像结构和纹理信息,与传统深度学习架构不同。
- MaskUNet方法通过有效利用时间步长和样本相关的有效U-Net参数,提高了生成质量。
- 研究发现,正确地将某些参数(包括大参数)置零有助于去噪。
- MaskUNet实现了最佳FID分数,并在下游任务评估中证明了其有效性。
- MaskUNet方法简单有效,参数数量少。
- 研究团队提供了两种优化MaskUNet的策略:基于训练的方法和无需训练的方法。
点此查看论文截图


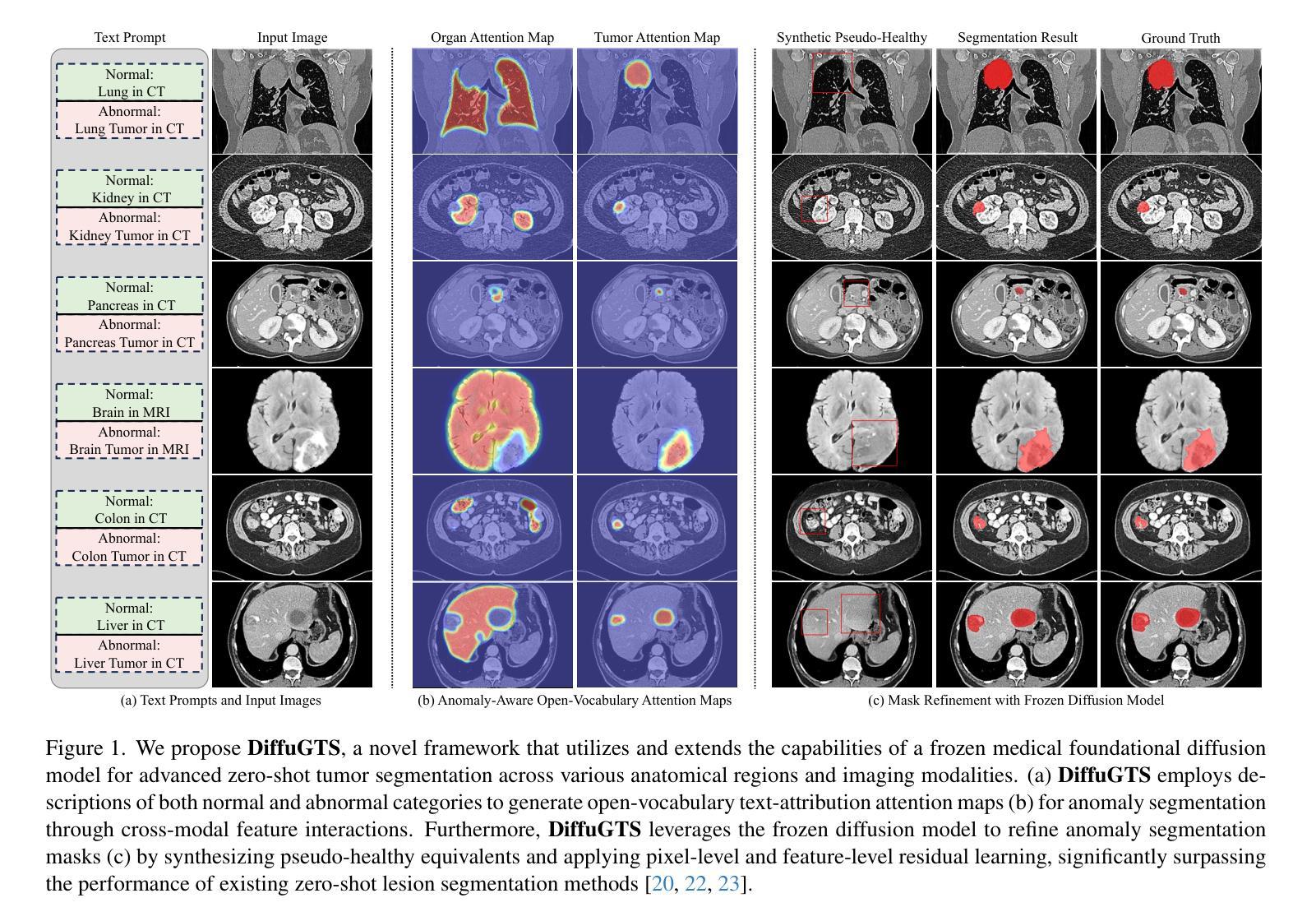
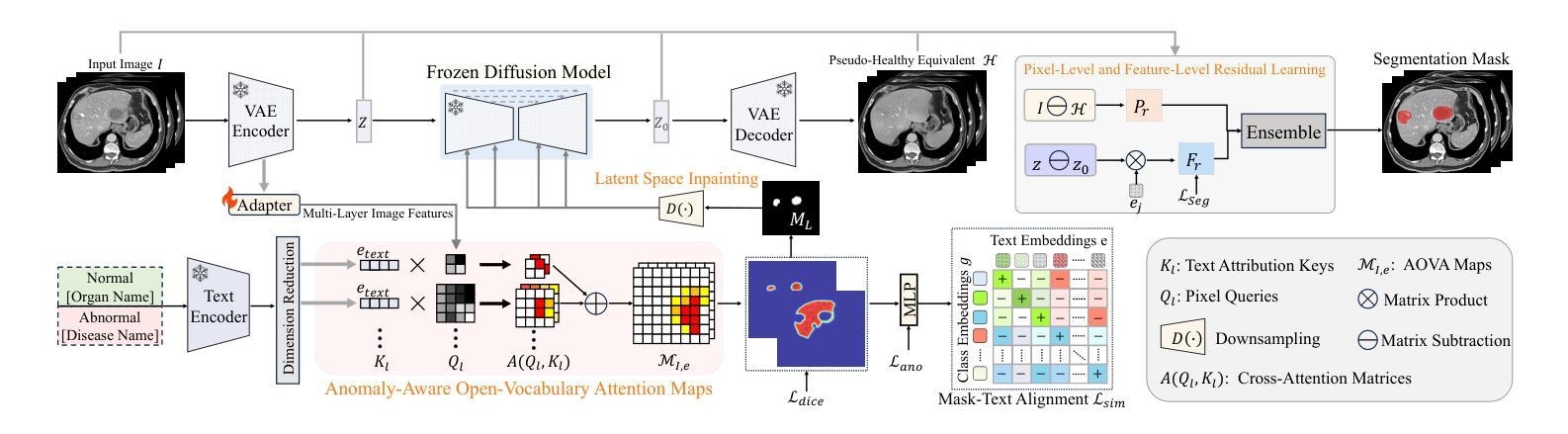
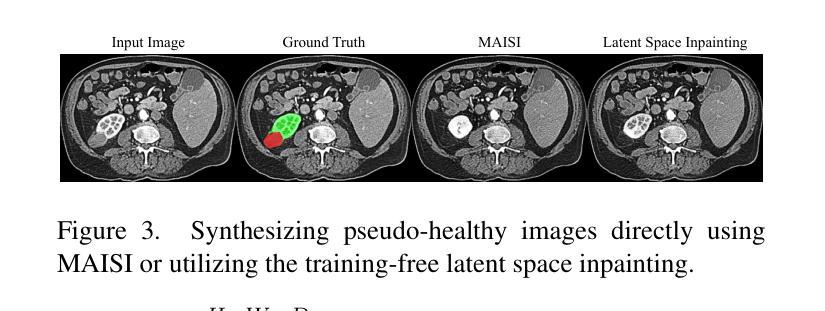
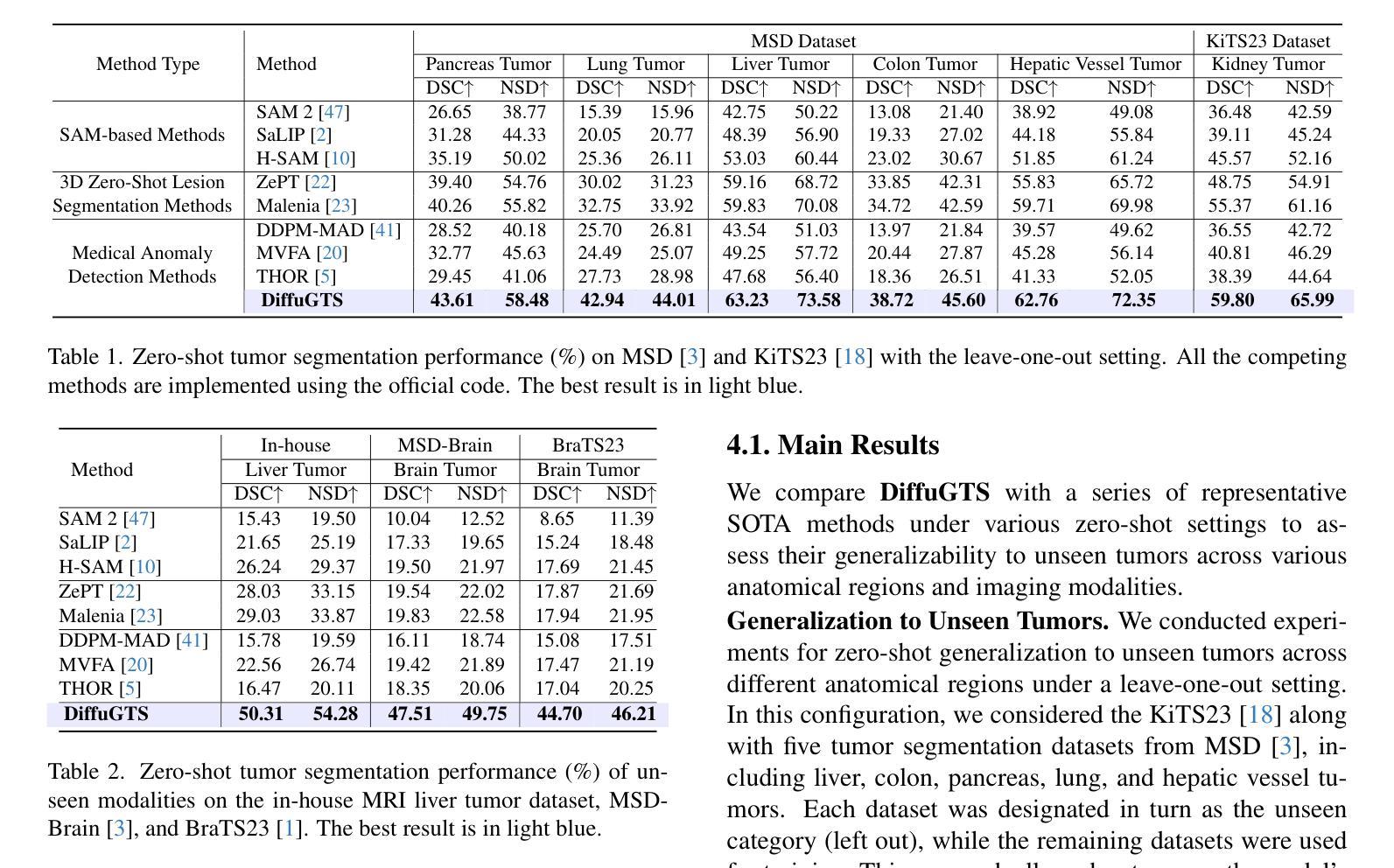
Advancing Generalizable Tumor Segmentation with Anomaly-Aware Open-Vocabulary Attention Maps and Frozen Foundation Diffusion Models
Authors:Yankai Jiang, Peng Zhang, Donglin Yang, Yuan Tian, Hai Lin, Xiaosong Wang
We explore Generalizable Tumor Segmentation, aiming to train a single model for zero-shot tumor segmentation across diverse anatomical regions. Existing methods face limitations related to segmentation quality, scalability, and the range of applicable imaging modalities. In this paper, we uncover the potential of the internal representations within frozen medical foundation diffusion models as highly efficient zero-shot learners for tumor segmentation by introducing a novel framework named DiffuGTS. DiffuGTS creates anomaly-aware open-vocabulary attention maps based on text prompts to enable generalizable anomaly segmentation without being restricted by a predefined training category list. To further improve and refine anomaly segmentation masks, DiffuGTS leverages the diffusion model, transforming pathological regions into high-quality pseudo-healthy counterparts through latent space inpainting, and applies a novel pixel-level and feature-level residual learning approach, resulting in segmentation masks with significantly enhanced quality and generalization. Comprehensive experiments on four datasets and seven tumor categories demonstrate the superior performance of our method, surpassing current state-of-the-art models across multiple zero-shot settings. Codes are available at https://github.com/Yankai96/DiffuGTS.
我们探索了通用肿瘤分割技术,旨在针对多个解剖学区域训练单一模型来实现零样本肿瘤分割。现有方法存在与分割质量、可扩展性和适用的成像模式范围相关的局限性。在本文中,我们通过引入名为DiffuGTS的新型框架,揭示了冻结医疗基础扩散模型内部表示作为肿瘤分割的高效零样本学习者的潜力。DiffuGTS基于文本提示创建异常感知开放词汇注意力图,以实现可通用的异常分割,而不受预设训练类别列表的限制。为了进一步提高和完善异常分割掩膜,DiffuGTS利用扩散模型,通过潜在空间补全技术将病理区域转换为高质量伪健康对应物,并应用新颖的像素级和特征级残差学习方法,从而得到质量显著提高且更具通用性的分割掩膜。在四个数据集和七个肿瘤类别上的综合实验表明,我们的方法性能卓越,在多个零样本设置上超越了当前最先进的模型。代码可在https://github.com/Yankai96/DiffuGTS获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper is accepted to CVPR 2025
Summary
本文探索了通用肿瘤分割技术,旨在使用单一模型实现跨不同解剖区域的零样本肿瘤分割。文章提出了一种新型框架DiffuGTS,利用冻结的医疗基础扩散模型的内部表示作为零样本肿瘤分割的高效学习者。DiffuGTS创建基于文本提示的异常感知开放词汇注意力图,以实现对肿瘤的一般性分割,而不受预设训练类别列表的限制。为进一步改善和细化异常分割掩膜,DiffuGTS利用扩散模型将病理区域转化为高质量的伪健康对应物,并通过像素级和特征级残差学习的方法应用,得到质量更高、泛化性更强的分割掩膜。在四个数据集和七个肿瘤类别的综合实验表明,该方法性能优越,在多种零样本设置中超越了当前最先进模型。
Key Takeaways
- 文章研究了通用肿瘤分割技术,目标是使用单一模型在不同解剖区域进行零样本肿瘤分割。
- 提出了一种新型框架DiffuGTS,利用冻结的医疗基础扩散模型进行高效零样本肿瘤分割学习。
- DiffuGTS通过创建基于文本提示的异常感知开放词汇注意力图,实现肿瘤的一般性分割。
- 利用扩散模型将病理区域转化为高质量的伪健康对应物,提高了异常分割掩膜的质量和泛化性。
- 采用了像素级和特征级的残差学习方法来进一步优化分割效果。
- 在多个数据集和肿瘤类别上的实验表明,DiffuGTS性能优越,显著超越了当前最先进模型。
点此查看论文截图

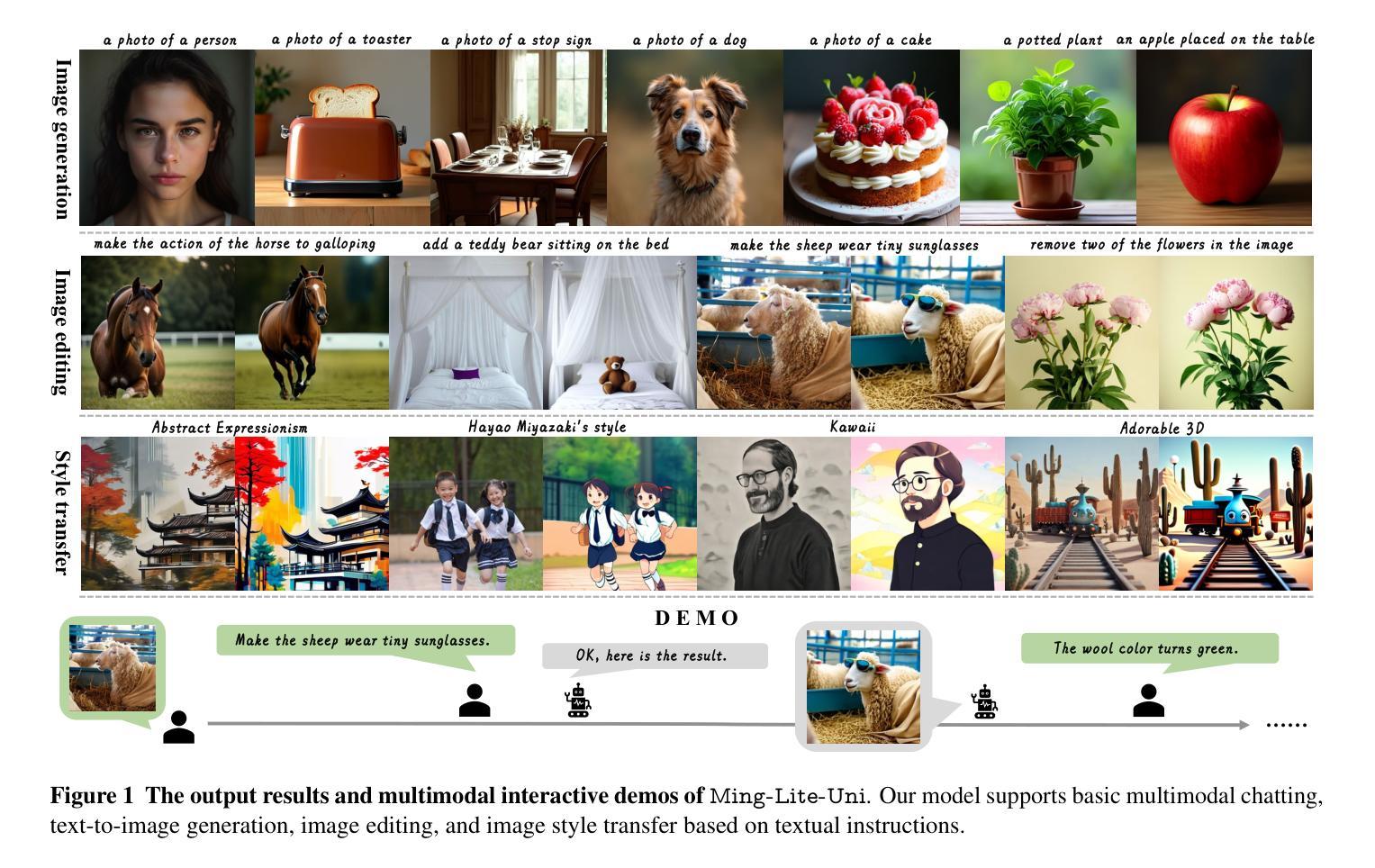
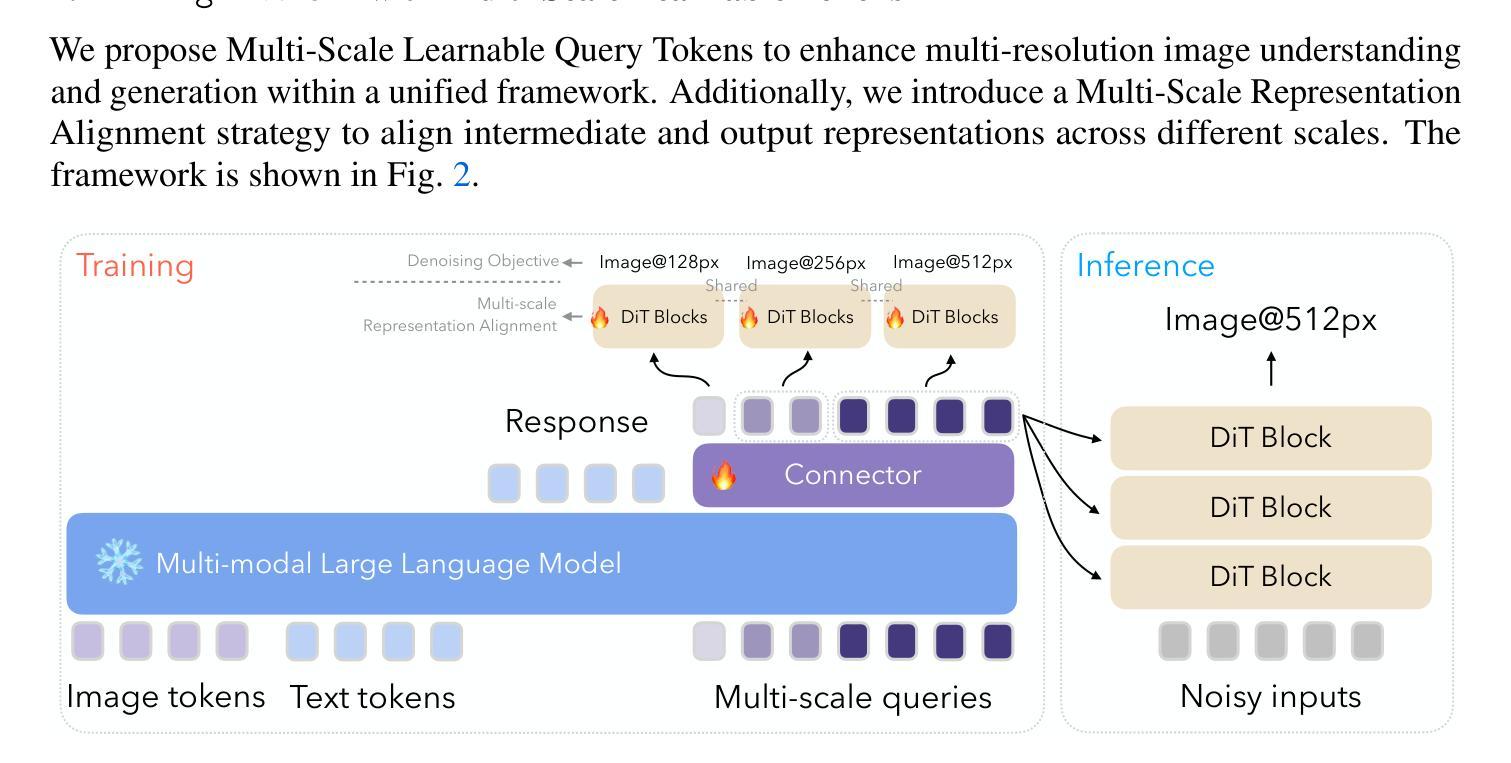
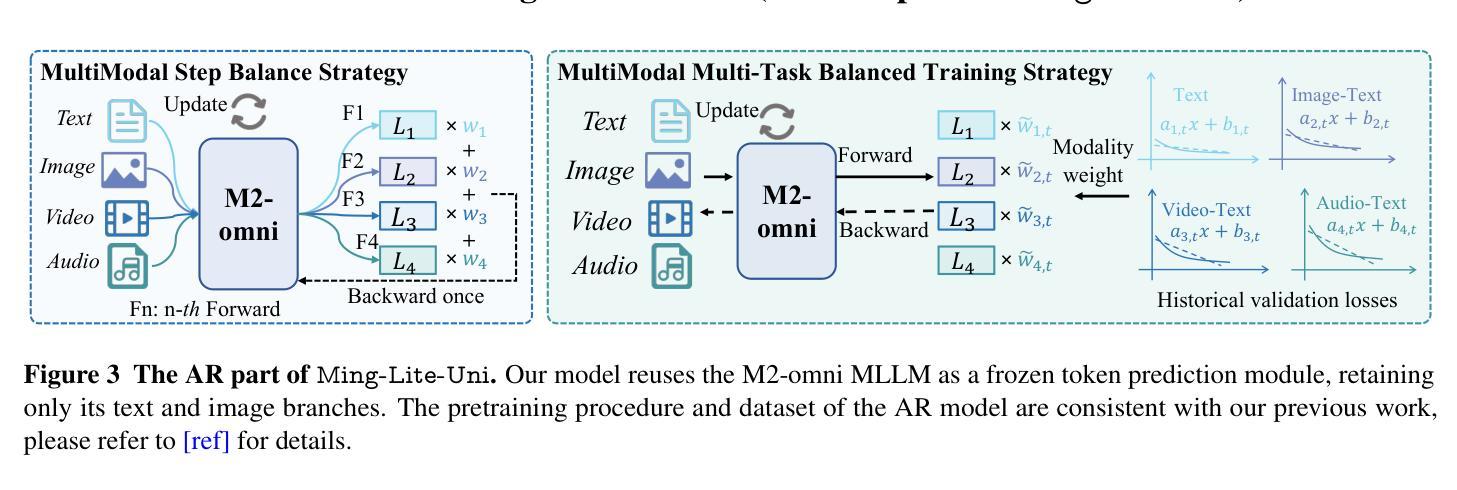
Ming-Lite-Uni: Advancements in Unified Architecture for Natural Multimodal Interaction
Authors:Biao Gong, Cheng Zou, Dandan Zheng, Hu Yu, Jingdong Chen, Jianxin Sun, Junbo Zhao, Jun Zhou, Kaixiang Ji, Lixiang Ru, Libin Wang, Qingpei Guo, Rui Liu, Weilong Chai, Xinyu Xiao, Ziyuan Huang
We introduce Ming-Lite-Uni, an open-source multimodal framework featuring a newly designed unified visual generator and a native multimodal autoregressive model tailored for unifying vision and language. Specifically, this project provides an open-source implementation of the integrated MetaQueries and M2-omni framework, while introducing the novel multi-scale learnable tokens and multi-scale representation alignment strategy. By leveraging a fixed MLLM and a learnable diffusion model, Ming-Lite-Uni enables native multimodal AR models to perform both text-to-image generation and instruction based image editing tasks, expanding their capabilities beyond pure visual understanding. Our experimental results demonstrate the strong performance of Ming-Lite-Uni and illustrate the impressive fluid nature of its interactive process. All code and model weights are open-sourced to foster further exploration within the community. Notably, this work aligns with concurrent multimodal AI milestones - such as ChatGPT-4o with native image generation updated in March 25, 2025 - underscoring the broader significance of unified models like Ming-Lite-Uni on the path toward AGI. Ming-Lite-Uni is in alpha stage and will soon be further refined.
我们介绍Ming-Lite-Uni,这是一个开源的多模式框架,具有新设计的统一视觉生成器和针对视觉和语言的融合任务量身定制的本地图像生成模型。具体来说,该项目提供了集成MetaQueries和M2-omni框架的开源实现,同时引入了新型的多尺度可学习令牌和多尺度表示对齐策略。通过利用固定的多模态语言模型和可学习的扩散模型,Ming-Lite-Uni使本地多模式AR模型能够执行文本到图像生成和基于指令的图像编辑任务,扩展了其超越纯视觉理解的能力。我们的实验结果证明了Ming-Lite-Uni的强大性能,并展示了其交互过程的流畅性。所有代码和模型权重都已开源,以促进社区内的进一步探索。值得注意的是,这项工作与同期发布的多模式人工智能里程碑事件相一致,如于三月二十五日更新的具有本地图像生成的ChatGPT-4o等,突显出像Ming-Lite-Uni这样的统一模型在通往人工智能通用化道路上的重要性。Ming-Lite-Uni目前处于Alpha阶段,并即将进行进一步的完善。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF https://github.com/inclusionAI/Ming/tree/main/Ming-unify
Summary
本文介绍了Ming-Lite-Uni这一开源多模态框架,其特点为全新设计的统一视觉生成器以及针对视觉和语言统一化的本地多模态自回归模型。该项目实现了集成MetaQueries和M2-omni框架的开源实现,并引入新型多尺度可学习令牌和多尺度表示对齐策略。Ming-Lite-Uni利用固定的MLLM和可学习的扩散模型,使本地多模态AR模型能够执行文本到图像生成和基于指令的图像编辑任务,超越了纯视觉理解的能力。实验结果显示其强大性能,并且交互过程流畅。所有代码和模型权重均已开源,以促进社区内的进一步探索。该工作与当前的多媒体人工智能里程碑(如ChatGPT-4o)保持一致,显示出统一模型在迈向通用人工智能过程中的重要性。目前Ming-Lite-Uni仍处于Alpha阶段,未来会进一步进行优化改进。
Key Takeaways
- Ming-Lite-Uni是一个开源多模态框架,集成了视觉和语言处理。
- 它包含统一视觉生成器和本地多模态自回归模型。
- 该项目实现了MetaQueries和M2-omni框架的集成。
- 引入多尺度可学习令牌和多尺度表示对齐策略为新颖特点。
- Ming-Lite-Uni能执行文本到图像生成和基于指令的图像编辑任务。
- 实验结果展示了其强大的性能,并且交互过程非常流畅。
点此查看论文截图




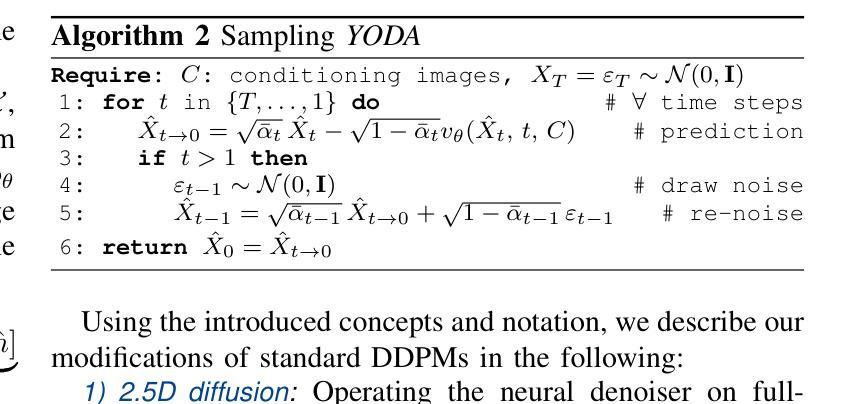
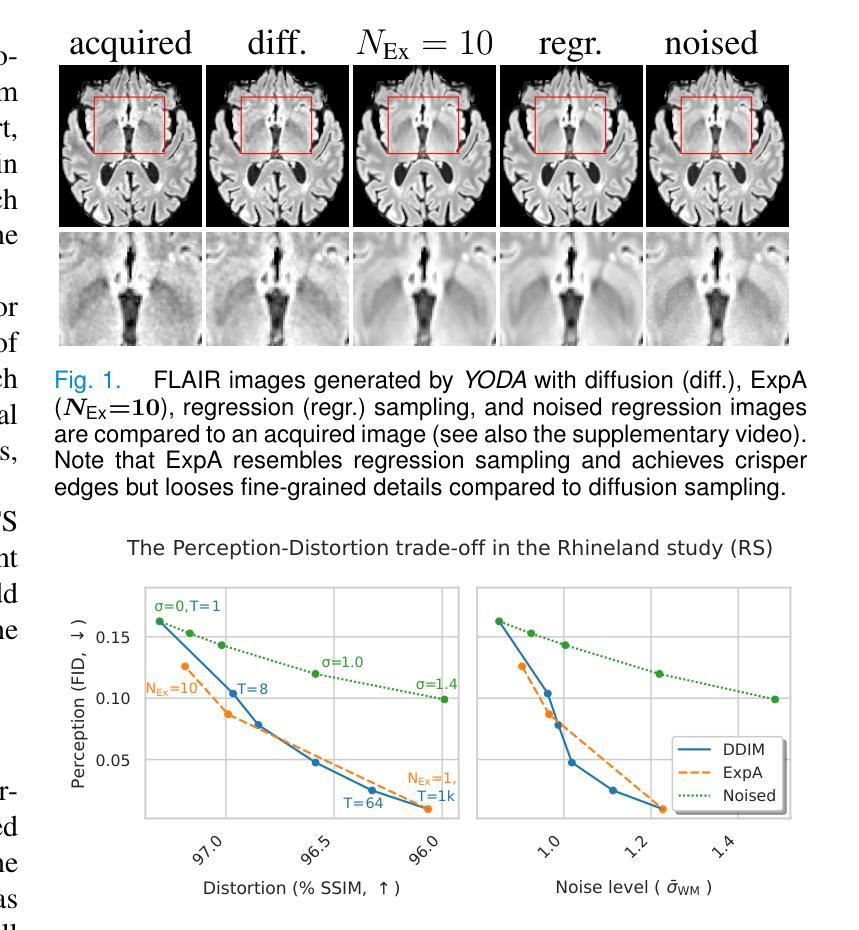
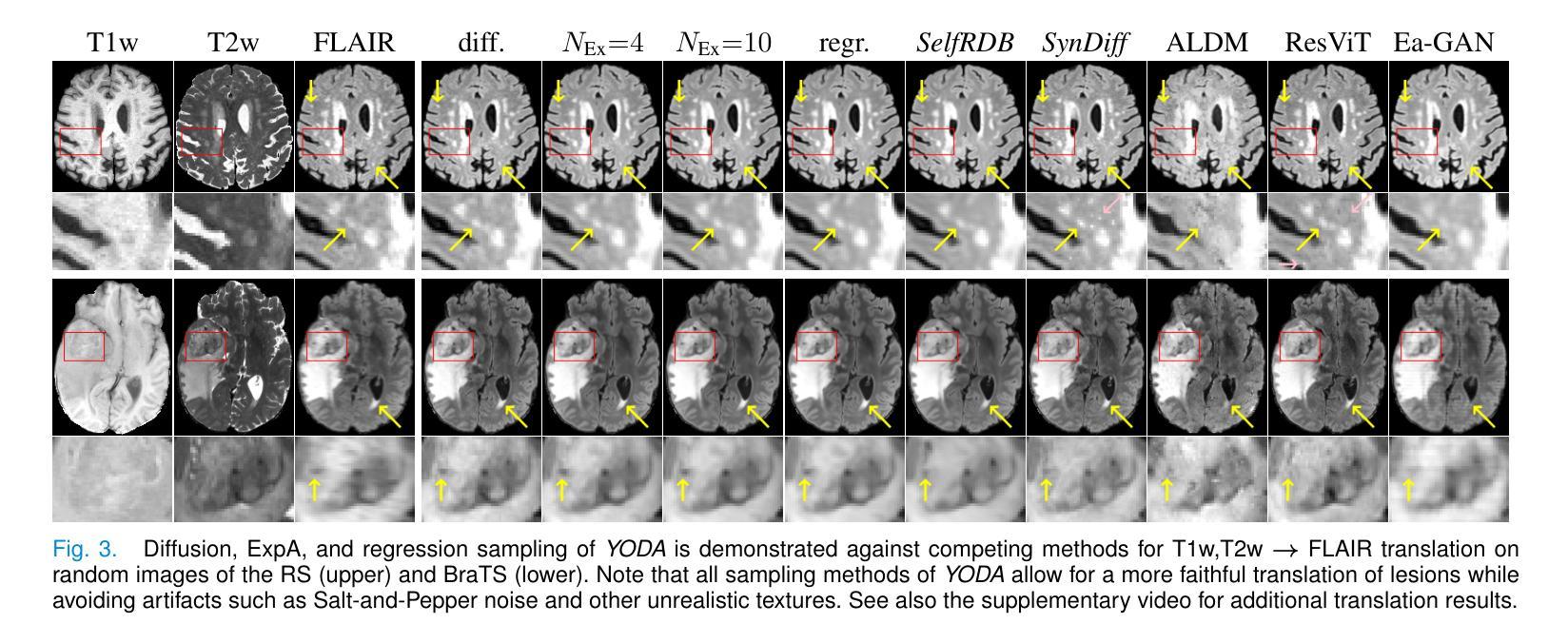
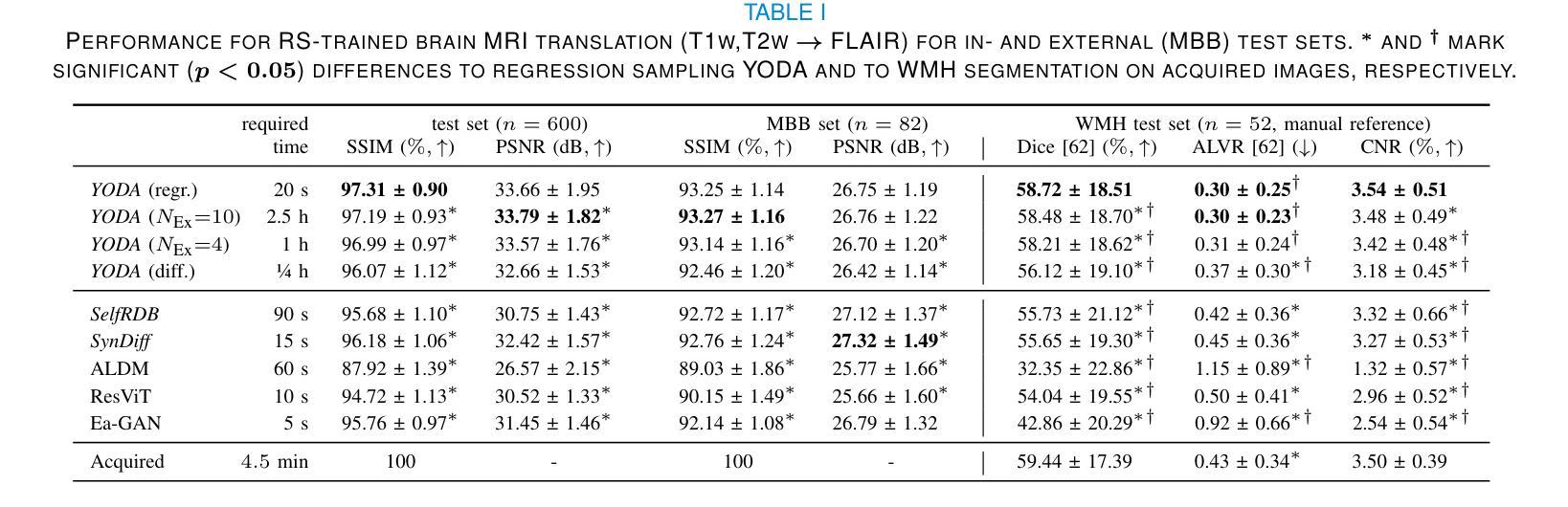
Regression is all you need for medical image translation
Authors:Sebastian Rassmann, David Kügler, Christian Ewert, Martin Reuter
The acquisition of information-rich images within a limited time budget is crucial in medical imaging. Medical image translation (MIT) can help enhance and supplement existing datasets by generating synthetic images from acquired data. While Generative Adversarial Nets (GANs) and Diffusion Models (DMs) have achieved remarkable success in natural image generation, their benefits - creativity and image realism - do not necessarily transfer to medical applications where highly accurate anatomical information is required. In fact, the imitation of acquisition noise or content hallucination hinder clinical utility. Here, we introduce YODA (You Only Denoise once - or Average), a novel 2.5D diffusion-based framework for volumetric MIT. YODA unites diffusion and regression paradigms to produce realistic or noise-free outputs. Furthermore, we propose Expectation-Approximation (ExpA) DM sampling, which draws inspiration from MRI signal averaging. ExpA-sampling suppresses generated noise and, thus, eliminates noise from biasing the evaluation of image quality. Through extensive experiments on four diverse multi-modal datasets - comprising multi-contrast brain MRI and pelvic MRI-CT - we show that diffusion and regression sampling yield similar results in practice. As such, the computational overhead of diffusion sampling does not provide systematic benefits in medical information translation. Building on these insights, we demonstrate that YODA outperforms several state-of-the-art GAN and DM methods. Notably, YODA-generated images are shown to be interchangeable with, or even superior to, physical acquisitions for several downstream tasks. Our findings challenge the presumed advantages of DMs in MIT and pave the way for the practical application of MIT in medical imaging.
在医疗成像中,在有限的时间预算内获取信息丰富的图像至关重要。医学图像翻译(MIT)可以通过从获取的数据生成合成图像来帮助增强和补充现有数据集。虽然生成对抗网络(GAN)和扩散模型(DM)在自然图像生成方面取得了显著的成功,它们在医疗应用中的益处——创造性和图像逼真性——并不一定会转移到需要高度准确的解剖信息的应用场景。事实上,模仿获取噪声或内容幻觉会阻碍其在临床上的实用性。在这里,我们介绍了YODA(You Only Denoise once - or Average),这是一个基于体积的新型2.5D扩散模型框架用于医学图像翻译。YODA结合了扩散和回归范式来产生逼真的或无噪声的输出。此外,我们提出了期望近似(ExpA)DM采样方法,该方法受到MRI信号平均的启发。ExpA采样抑制生成的噪声,从而消除噪声对图像质量评估的偏见。通过在四个不同的多模态数据集上进行广泛实验——包括多对比度脑部MRI和盆腔MRI-CT——我们证明扩散采样和回归采样在实践中可以得到类似的结果。因此,扩散采样在医学翻译中的计算开销并没有提供系统性的好处。基于这些见解,我们证明YODA优于几种最先进的GAN和DM方法。值得注意的是,YODA生成的图像被证明可以与多个下游任务中的物理采集互换使用,甚至在某些情况下表现更优越。我们的研究挑战了DM在MIT中的预设优势,并为MIT在医疗成像中的实际应用铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了在医学成像中,信息丰富的图像在有限时间预算内的获取至关重要。医学图像翻译(MIT)可以通过生成合成图像来增强和补充现有数据集。虽然生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型(DMs)在自然图像生成方面取得了显著的成功,但其在医学应用中并不一定能发挥出创造性和图像真实性的优势,因为医学应用需要高度准确的解剖信息。为此,本文提出了一种新型的2.5D扩散基于体积的医学图像翻译框架YODA,它将扩散和回归范式结合起来,产生逼真的或无噪声的输出。此外,还提出了受MRI信号平均启发的Expectation-Approximation(ExpA)DM采样,用于抑制生成的噪声,从而提高图像质量评估的客观性。通过实验证明,YODA在多种模态数据集上的表现优于一些最先进的GAN和DM方法,生成的图像甚至可与真实物理采集的图像互换或更优越。
Key Takeaways
- 医学成像中,在有限时间预算内获取信息丰富的图像至关重要。
- 医学图像翻译(MIT)能通过生成合成图像来增强和补充现有数据集。
- 虽然GANs和DMs在自然图像生成上表现出色,但在医学应用中不一定能发挥出其创造性和图像真实性的优势。
- 本文提出了一种新型的医学图像翻译框架YODA,结合了扩散和回归范式,能生成逼真的或无噪声的图像。
- YODA采用了受MRI信号平均启发的Expectation-Approximation(ExpA)DM采样,以提高图像质量评估的客观性。
- 实验证明,YODA在多种数据集上的表现优于其他先进方法。
点此查看论文截图

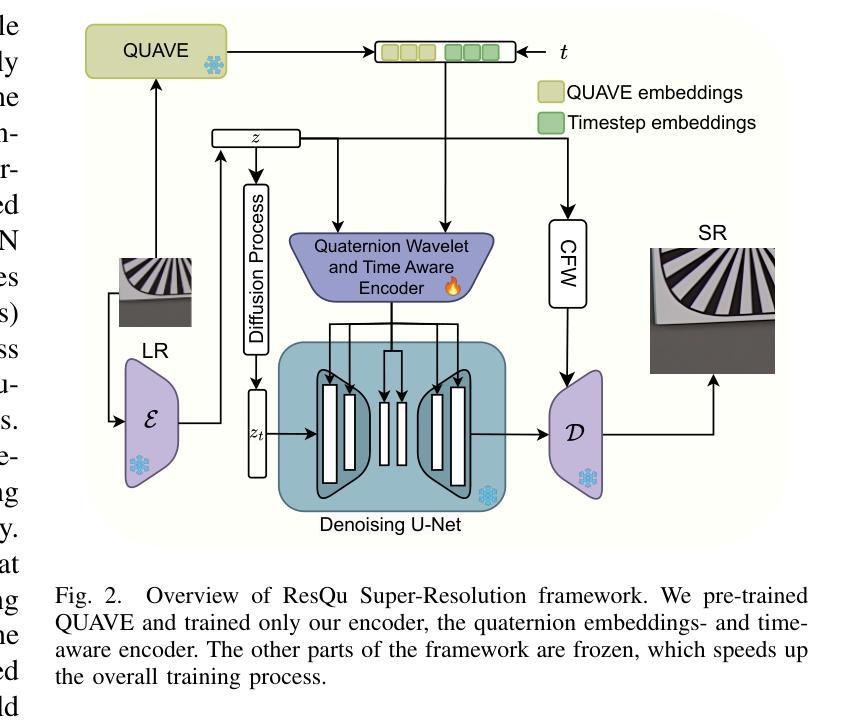
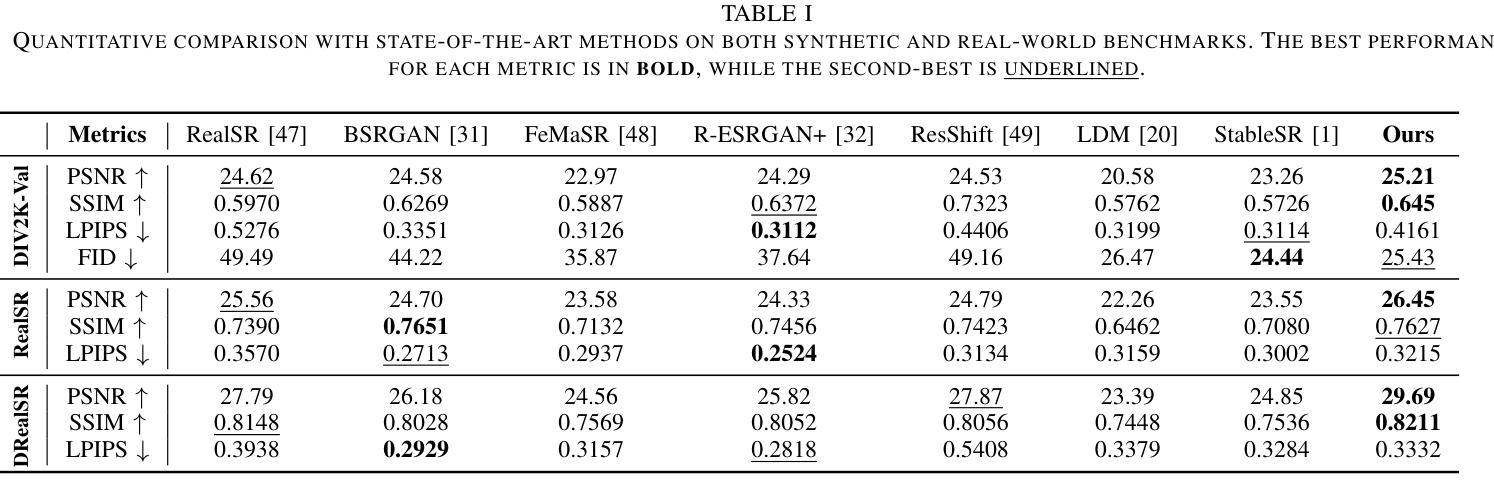
Quaternion Wavelet-Conditioned Diffusion Models for Image Super-Resolution
Authors:Luigi Sigillo, Christian Bianchi, Aurelio Uncini, Danilo Comminiello
Image Super-Resolution is a fundamental problem in computer vision with broad applications spacing from medical imaging to satellite analysis. The ability to reconstruct high-resolution images from low-resolution inputs is crucial for enhancing downstream tasks such as object detection and segmentation. While deep learning has significantly advanced SR, achieving high-quality reconstructions with fine-grained details and realistic textures remains challenging, particularly at high upscaling factors. Recent approaches leveraging diffusion models have demonstrated promising results, yet they often struggle to balance perceptual quality with structural fidelity. In this work, we introduce ResQu a novel SR framework that integrates a quaternion wavelet preprocessing framework with latent diffusion models, incorporating a new quaternion wavelet- and time-aware encoder. Unlike prior methods that simply apply wavelet transforms within diffusion models, our approach enhances the conditioning process by exploiting quaternion wavelet embeddings, which are dynamically integrated at different stages of denoising. Furthermore, we also leverage the generative priors of foundation models such as Stable Diffusion. Extensive experiments on domain-specific datasets demonstrate that our method achieves outstanding SR results, outperforming in many cases existing approaches in perceptual quality and standard evaluation metrics. The code will be available after the revision process.
图像超分辨率是计算机视觉中的一个基本问题,其应用领域广泛,从医学影像到卫星分析都有涉及。从低分辨率输入重建高分辨率图像的能力对于提高下游任务(如目标检测和分割)至关重要。虽然深度学习已经大大推动了超分辨率技术的发展,但实现具有精细细节和逼真纹理的高质量重建仍然是一个挑战,尤其是在高放大倍数时。最近利用扩散模型的方法已经取得了有前景的结果,但它们往往难以在感知质量和结构保真度之间取得平衡。在这项工作中,我们介绍了ResQu,这是一个新的超分辨率框架,它将四元小波预处理框架与潜在扩散模型相结合,并引入了一个新的四元小波和时间感知编码器。不同于那些在扩散模型中简单应用小波变换的方法,我们的方法通过利用四元小波嵌入来增强条件过程,这些嵌入在不同的去噪阶段被动态集成。此外,我们还利用了基础模型的生成先验知识,如Stable Diffusion。在特定领域数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的方法实现了出色的超分辨率结果,在许多情况下,在感知质量和标准评估指标上都超越了现有方法。代码将在修订后提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for presentation at IJCNN 2025
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于扩散模型的新型图像超分辨率重建框架ResQu,结合了四元小波预处理框架和潜在扩散模型。该方法通过利用四元小波嵌入并动态集成于去噪的不同阶段,提高了条件过程的性能。此外,它还利用基础模型的生成先验,如Stable Diffusion。在特定领域数据集上的广泛实验表明,该方法在感知质量和标准评估指标方面取得了出色的超分辨率重建结果,并在许多情况下优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 图像超分辨率是计算机视觉中的基本问题,具有广泛的应用领域,如医学影像和卫星分析。
- 深度学习在SR中有很大进展,但在实现高质量重建方面仍然存在挑战,特别是在高放大倍数时。
- 扩散模型在图像超分辨率重建中显示出良好前景,但需要在感知质量和结构保真之间取得平衡。
- 提出的ResQu框架结合了四元小波预处理框架和潜在扩散模型,提高了条件过程的性能。
- ResQu通过在不同阶段的去噪过程中动态利用四元小波嵌入,提高了图像重建的精细度和纹理真实性。
- 该方法还利用基础模型的生成先验,如Stable Diffusion,来提高超分辨率重建的质量。
点此查看论文截图
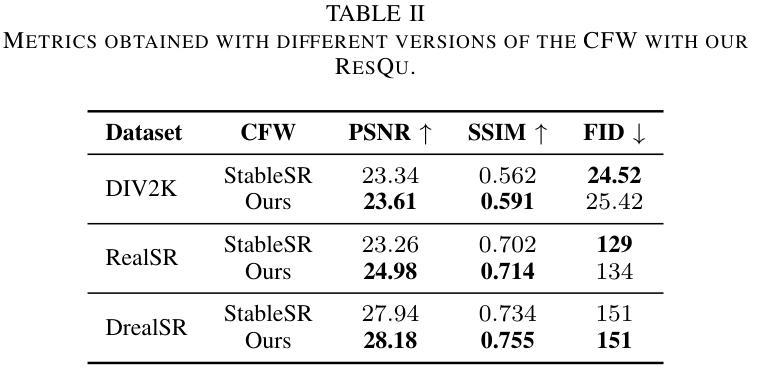

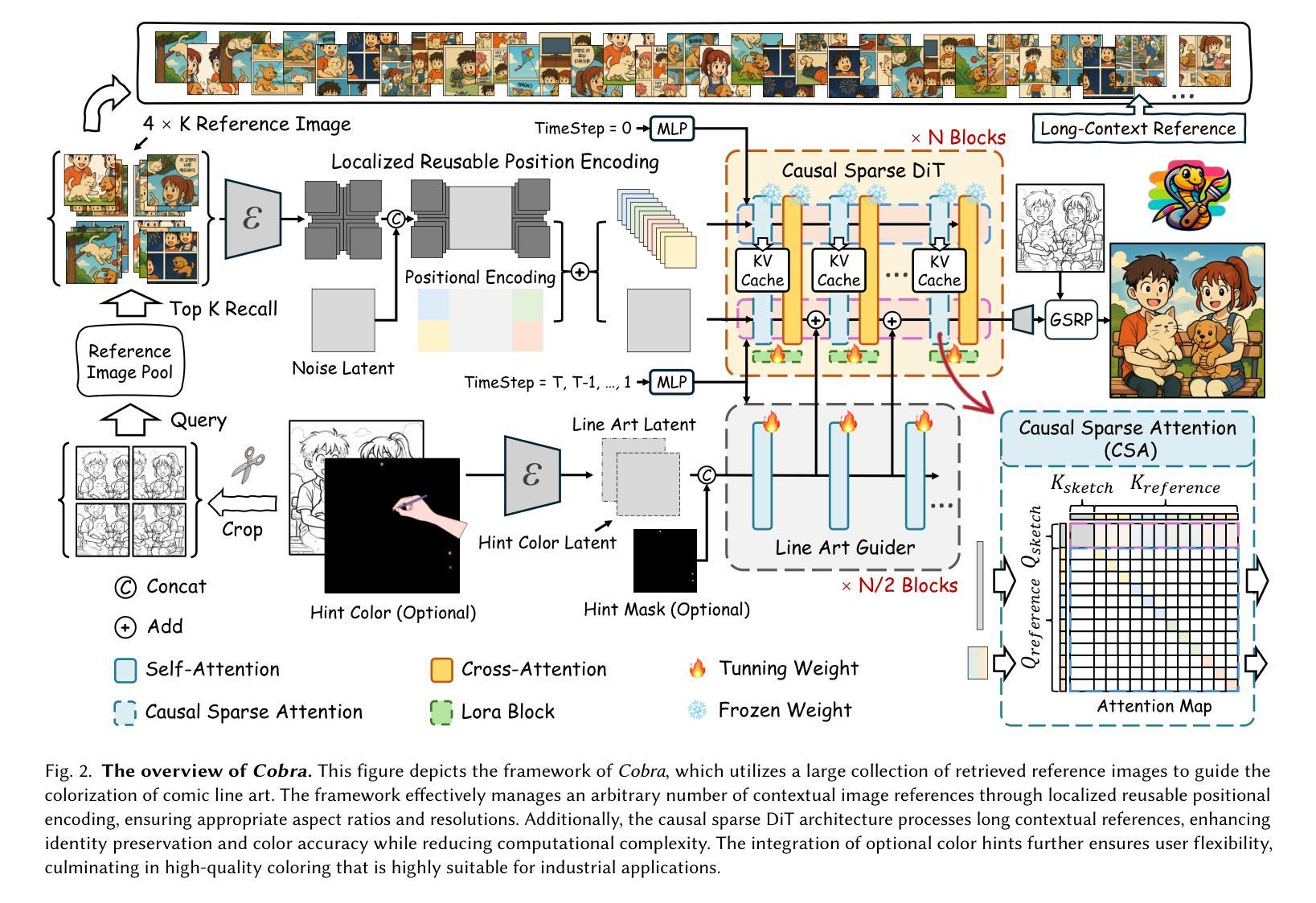
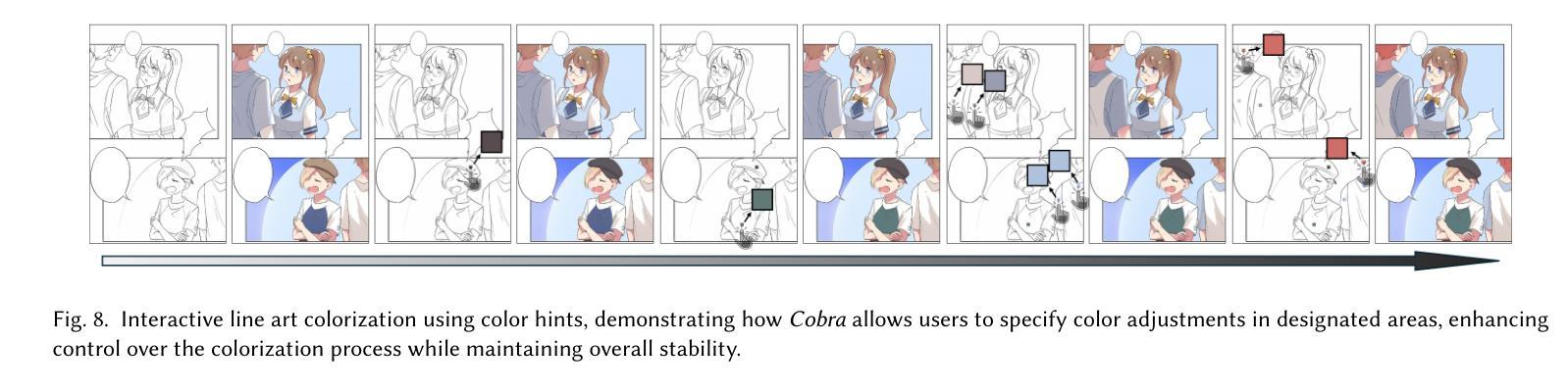
Cobra: Efficient Line Art COlorization with BRoAder References
Authors:Junhao Zhuang, Lingen Li, Xuan Ju, Zhaoyang Zhang, Chun Yuan, Ying Shan
The comic production industry requires reference-based line art colorization with high accuracy, efficiency, contextual consistency, and flexible control. A comic page often involves diverse characters, objects, and backgrounds, which complicates the coloring process. Despite advancements in diffusion models for image generation, their application in line art colorization remains limited, facing challenges related to handling extensive reference images, time-consuming inference, and flexible control. We investigate the necessity of extensive contextual image guidance on the quality of line art colorization. To address these challenges, we introduce Cobra, an efficient and versatile method that supports color hints and utilizes over 200 reference images while maintaining low latency. Central to Cobra is a Causal Sparse DiT architecture, which leverages specially designed positional encodings, causal sparse attention, and Key-Value Cache to effectively manage long-context references and ensure color identity consistency. Results demonstrate that Cobra achieves accurate line art colorization through extensive contextual reference, significantly enhancing inference speed and interactivity, thereby meeting critical industrial demands. We release our codes and models on our project page: https://zhuang2002.github.io/Cobra/.
漫画制作行业需要基于参考的高精度、高效率、上下文一致性和灵活控制的线艺彩色化。漫画页面通常涉及多种角色、物体和背景,这使着色过程复杂化。尽管扩散模型在图像生成方面取得了进展,但在线艺彩色化的应用仍然有限,面临着处理大量参考图像、耗时推理和灵活控制等挑战。本研究探讨了大量上下文图像指导对线艺彩色化质量的必要性。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了Cobra,这是一种高效且通用的方法,支持颜色提示,同时使用超过200张参考图像,同时保持低延迟。Cobra的核心是因果稀疏DiT架构,它利用专门设计的位置编码、因果稀疏注意力和键值缓存来有效管理长上下文引用并确保颜色身份一致性。结果表明,Cobra通过大量的上下文参考实现了准确的线艺彩色化,大大提高了推理速度和交互性,从而满足了行业的关键需求。我们已在项目页面发布代码和模型:https://zhuang2002.github.io/Cobra/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page with code: https://zhuang2002.github.io/Cobra/
Summary
该文本介绍了漫画制作行业对基于参考的线艺术色彩化的高准确性、高效率、上下文一致性和灵活控制的需求。文中指出,尽管扩散模型在图像生成方面有所进展,但在线艺术色彩化方面的应用仍然有限,面临处理大量参考图像、推理耗时以及灵活控制等挑战。为解决这些挑战,研究团队引入了Cobra方法,该方法支持颜色提示并利用超过200张参考图像,同时保持低延迟。Cobra的核心是一种因果稀疏DiT架构,它通过专门设计的位置编码、因果稀疏注意力机制和键值缓存来有效管理长上下文参考并确保颜色一致性。实验结果表明,Cobra通过广泛的上下文参考实现了准确的线艺术色彩化,大大提高了推理速度和交互性,从而满足了行业的关键需求。
Key Takeaways
- 漫画制作需要高准确性、高效率、上下文一致性和灵活控制的线艺术色彩化。
- 扩散模型在图像生成方面的应用在线艺术色彩化方面仍面临挑战。
- Cobra是一种支持颜色提示并利用大量参考图像的方法,同时保持低延迟。
- Cobra的核心是因果稀疏DiT架构,能有效管理长上下文参考和确保颜色一致性。
- Cobra实现了准确的线艺术色彩化,通过广泛的上下文参考。
- Cobra提高了推理速度和交互性,满足了行业关键需求。
- 研究团队已在其项目页面上发布了代码和模型。
点此查看论文截图


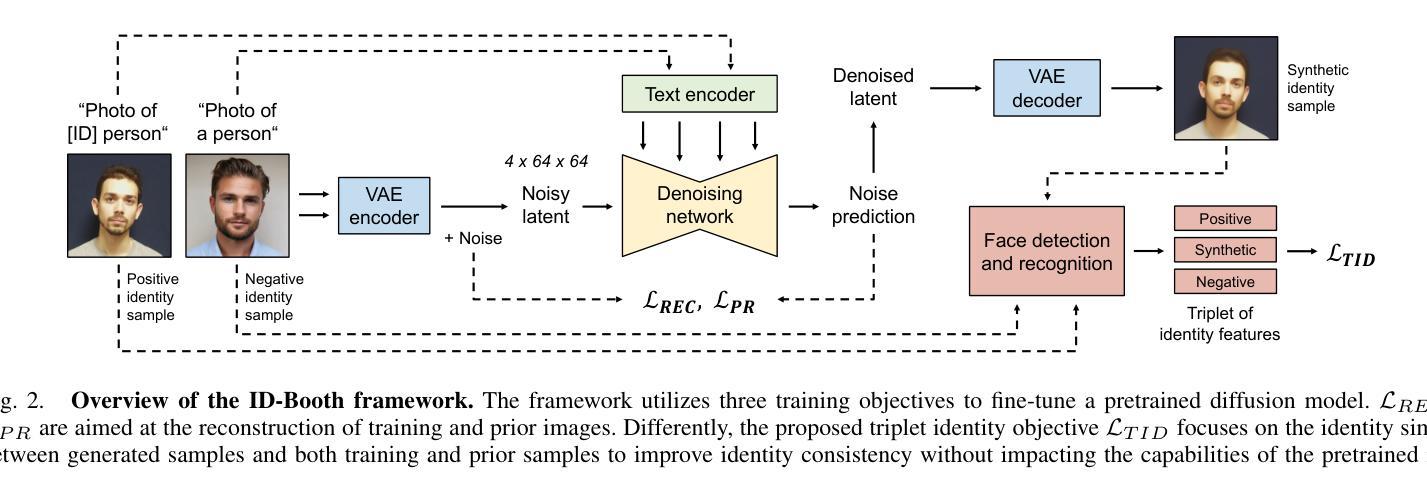
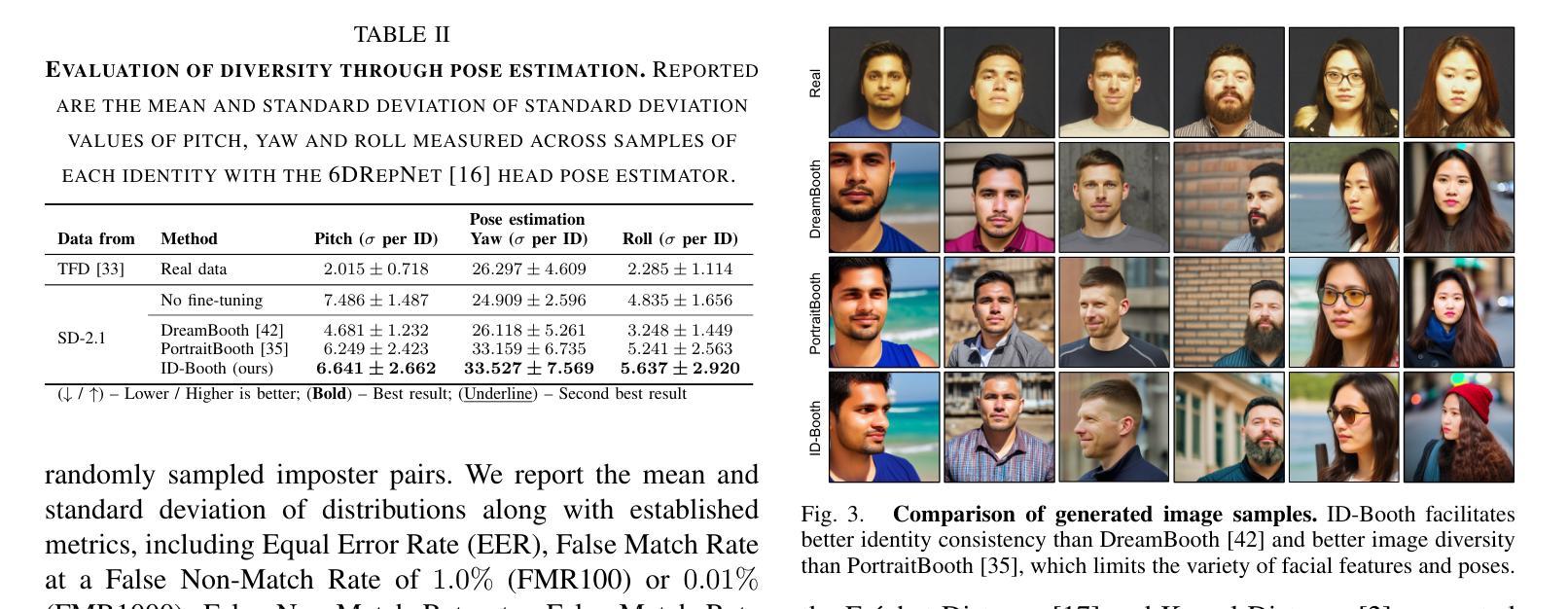
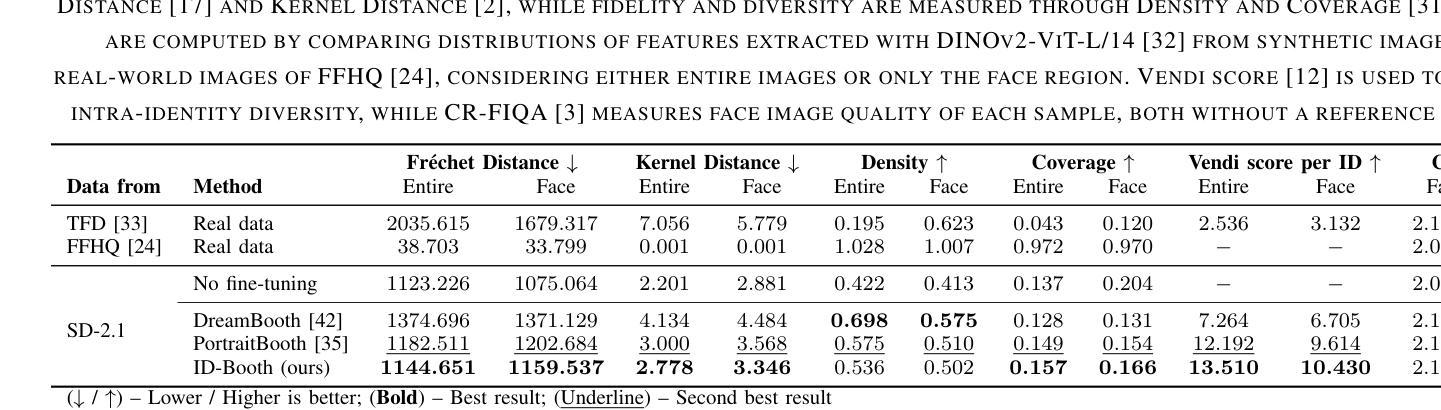
ID-Booth: Identity-consistent Face Generation with Diffusion Models
Authors:Darian Tomašević, Fadi Boutros, Chenhao Lin, Naser Damer, Vitomir Štruc, Peter Peer
Recent advances in generative modeling have enabled the generation of high-quality synthetic data that is applicable in a variety of domains, including face recognition. Here, state-of-the-art generative models typically rely on conditioning and fine-tuning of powerful pretrained diffusion models to facilitate the synthesis of realistic images of a desired identity. Yet, these models often do not consider the identity of subjects during training, leading to poor consistency between generated and intended identities. In contrast, methods that employ identity-based training objectives tend to overfit on various aspects of the identity, and in turn, lower the diversity of images that can be generated. To address these issues, we present in this paper a novel generative diffusion-based framework, called ID-Booth. ID-Booth consists of a denoising network responsible for data generation, a variational auto-encoder for mapping images to and from a lower-dimensional latent space and a text encoder that allows for prompt-based control over the generation procedure. The framework utilizes a novel triplet identity training objective and enables identity-consistent image generation while retaining the synthesis capabilities of pretrained diffusion models. Experiments with a state-of-the-art latent diffusion model and diverse prompts reveal that our method facilitates better intra-identity consistency and inter-identity separability than competing methods, while achieving higher image diversity. In turn, the produced data allows for effective augmentation of small-scale datasets and training of better-performing recognition models in a privacy-preserving manner. The source code for the ID-Booth framework is publicly available at https://github.com/dariant/ID-Booth.
近期生成建模技术的进步使得能够生成适用于多种领域的高质量合成数据,其中包括人脸识别。在此情况下,最先进的生成模型通常依赖于强大预训练扩散模型的条件和微调,以促进所需身份的逼真图像合成。然而,这些模型在训练过程中往往不考虑主体的身份,导致生成图像与预期身份之间的一致性较差。相比之下,采用基于身份训练目标的方法往往会在身份的各个方面的拟合过度,从而降低了可以生成的图像多样性。为解决这些问题,本文提出了一种新颖的基于扩散的生成框架,称为ID-Booth。ID-Booth包括一个用于数据生成的去噪网络、一个用于将图像映射到和从低维潜在空间的变自动编码器和一个文本编码器,该编码器可以通过提示来控制生成过程。该框架利用新型的三重身份训练目标,能够在保持预训练扩散模型的合成能力的同时,实现身份一致的图像生成。使用最先进的潜在扩散模型和多种提示进行的实验表明,我们的方法比竞争方法具有更好的身份内部一致性和身份间可分离性,同时保持了较高的图像多样性。反过来,所生成的数据可以有效地增强小规模数据集并用于训练性能更好的识别模型,同时保护隐私。ID-Booth框架的源代码可在https://github.com/dariant/ID-Booth上公开获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FG) 2025, 14 pages
摘要
本文介绍了一种基于扩散的新型生成模型ID-Booth,该模型解决了现有生成模型在面部识别等领域合成图像时面临的身份不一致和图像多样性不足的问题。ID-Booth包括一个用于数据生成的降噪网络、一个用于将图像映射到低维潜在空间的变分自编码器和一个文本编码器,以实现基于提示的生成过程控制。该框架采用新型的三元组身份训练目标,能够在保留预训练扩散模型的合成能力的同时,实现身份一致的图像生成。实验证明,与其他方法相比,ID-Booth在身份内一致性和身份间可分性方面表现更佳,同时保持了较高的图像多样性。此外,生成的数据能够有效增强小规模数据集,并可用于训练性能更佳的隐私保护识别模型。ID-Booth框架的源代码已公开在https://github.com/dariant/ID-Booth。
关键见解
- 新型生成模型ID-Booth基于扩散模型,解决了合成图像时身份不一致和图像多样性不足的问题。
- ID-Booth包括降噪网络、变分自编码器和文本编码器,可实现基于提示的生成过程控制。
- 该框架采用三元组身份训练目标,提高了身份一致性,同时保留了图像多样性。
- ID-Booth在实验中表现出优秀的性能,与其他方法相比,具有更好的身份内一致性和身份间可分性。
- ID-Booth能够增强小规模数据集,并可用于训练性能更佳的隐私保护识别模型。
- ID-Booth框架的源代码已公开,方便研究者和开发者使用。
- 该框架的提出为面部识别等领域的数据合成和模型训练提供了新的思路和方法。
点此查看论文截图

Dynamic Importance in Diffusion U-Net for Enhanced Image Synthesis
Authors:Xi Wang, Ziqi He, Yang Zhou
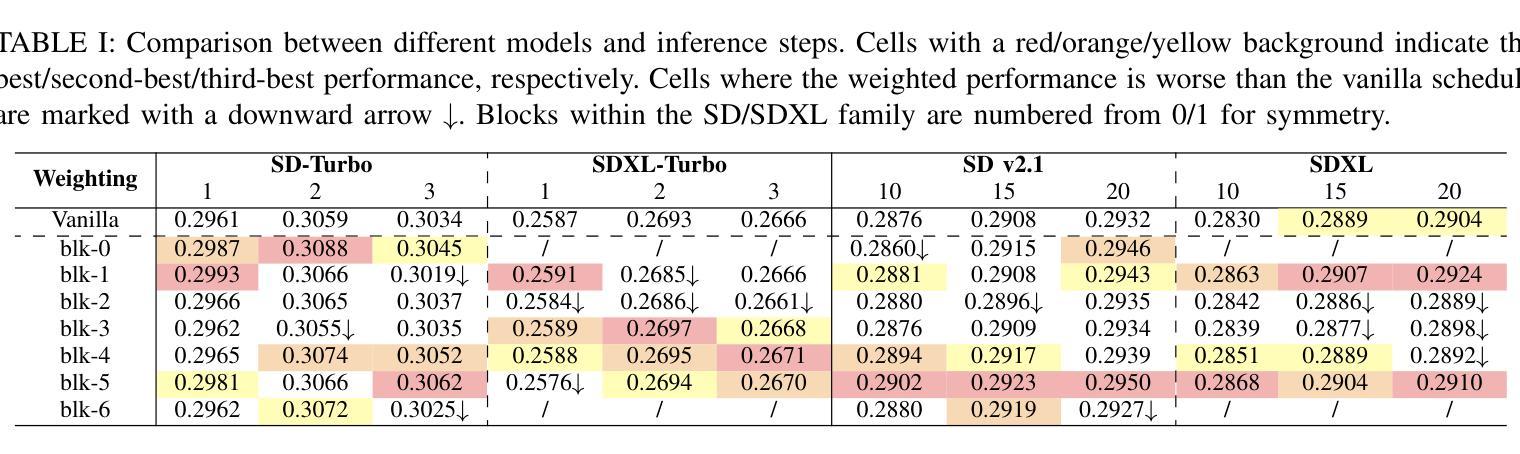
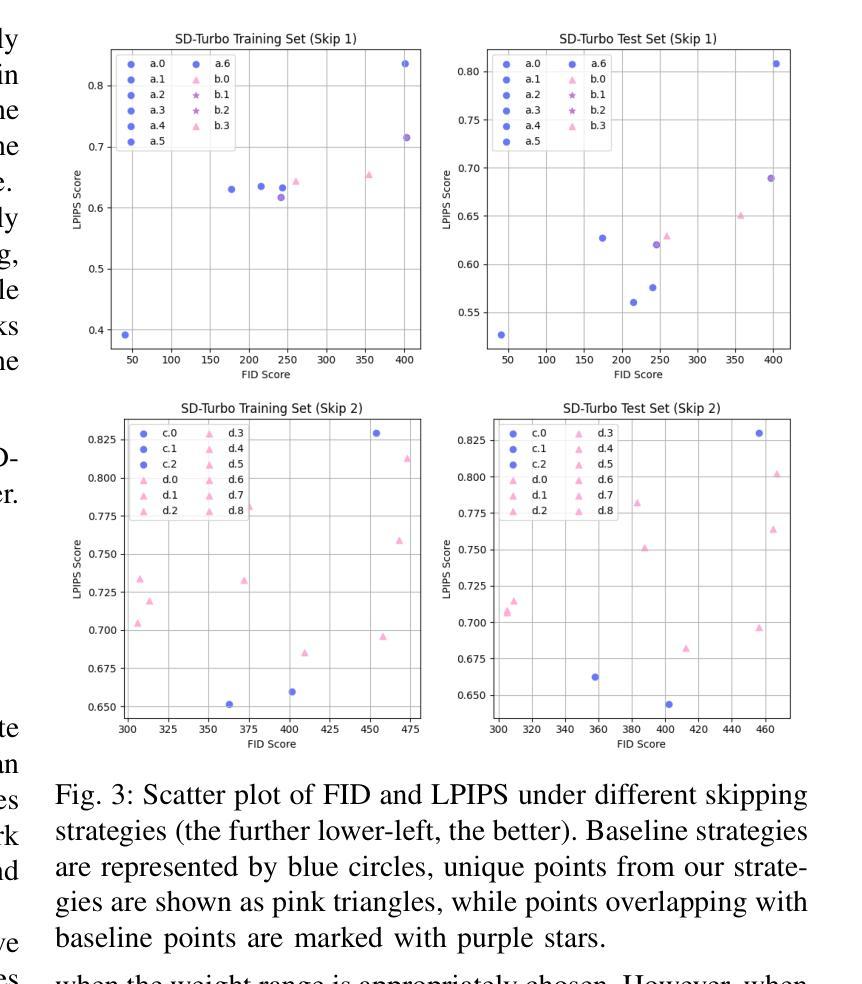
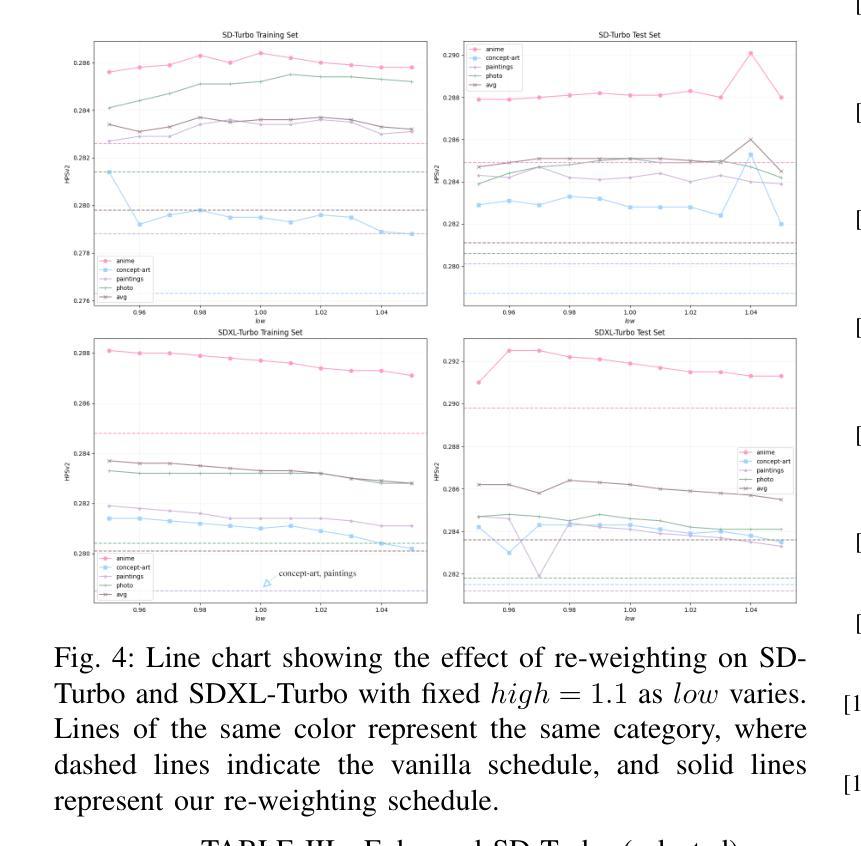
Traditional diffusion models typically employ a U-Net architecture. Previous studies have unveiled the roles of attention blocks in the U-Net. However, they overlook the dynamic evolution of their importance during the inference process, which hinders their further exploitation to improve image applications. In this study, we first theoretically proved that, re-weighting the outputs of the Transformer blocks within the U-Net is a “free lunch” for improving the signal-to-noise ratio during the sampling process. Next, we proposed Importance Probe to uncover and quantify the dynamic shifts in importance of the Transformer blocks throughout the denoising process. Finally, we design an adaptive importance-based re-weighting schedule tailored to specific image generation and editing tasks. Experimental results demonstrate that, our approach significantly improves the efficiency of the inference process, and enhances the aesthetic quality of the samples with identity consistency. Our method can be seamlessly integrated into any U-Net-based architecture. Code: https://github.com/Hytidel/UNetReweighting
传统扩散模型通常采用U-Net架构。之前的研究已经揭示了注意力块在U-Net中的作用。然而,他们忽略了推理过程中注意力块重要性动态变化的重要性,这阻碍了其进一步开发以提高图像应用的效果。在本研究中,我们首先从理论上证明了重新调整U-Net中Transformer块的输出可以提高采样过程中的信噪比。接下来,我们提出了重要性探针(Importance Probe),以揭示和量化降噪过程中Transformer块重要性的动态变化。最后,我们设计了一种基于自适应重要性的重新调整权重调度策略,可针对特定的图像生成和编辑任务进行定制。实验结果表明,我们的方法显著提高了推理过程的效率,并提高了样本的美学质量和一致性。我们的方法可以无缝集成到任何基于U-Net的架构中。代码:https://github.com/Hytidel/UNetReweighting
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ICME 2025. Appendix & Code: https://github.com/Hytidel/UNetReweighting
Summary
本文研究了传统扩散模型中的U-Net架构,并指出以往研究忽视了注意力块在推理过程中的动态重要性变化。本研究通过理论证明了重新加权U-Net中Transformer块的输出可以提高采样过程中的信号噪声比。同时,提出了重要性探针(Importance Probe)来揭示和量化去噪过程中Transformer块重要性的动态变化。最终设计了一种基于自适应重要性的重新加权调度,适用于特定的图像生成和编辑任务。实验结果表明,该方法显著提高了推理效率,并提高了样本的美学质量和身份一致性。此方法可无缝集成到任何基于U-Net的架构中。
Key Takeaways
- 传统扩散模型采用U-Net架构,但之前的研究未充分关注注意力块在推理过程中的动态重要性变化。
- 重新加权U-Net中Transformer块的输出可以提高采样过程中的信号噪声比。
- 提出了重要性探针(Importance Probe)来量化去噪过程中Transformer块的重要性变化。
- 设计了一种基于自适应重要性的重新加权调度,适用于图像生成和编辑任务。
- 方法显著提高了推理效率,增强了样本的美学质量和身份一致性。
- 该方法可无缝集成到任何基于U-Net的架构中。
点此查看论文截图


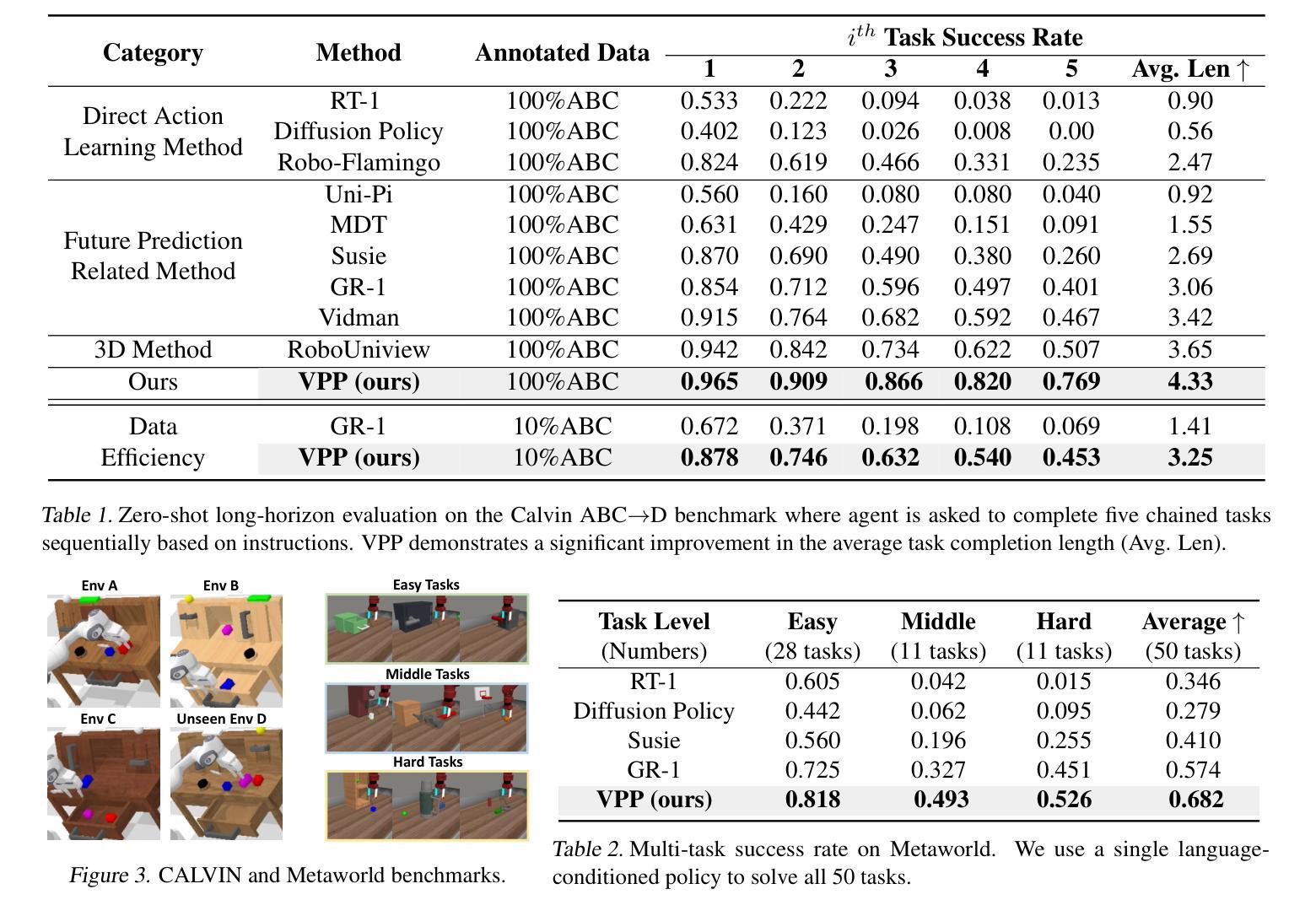
Video Prediction Policy: A Generalist Robot Policy with Predictive Visual Representations
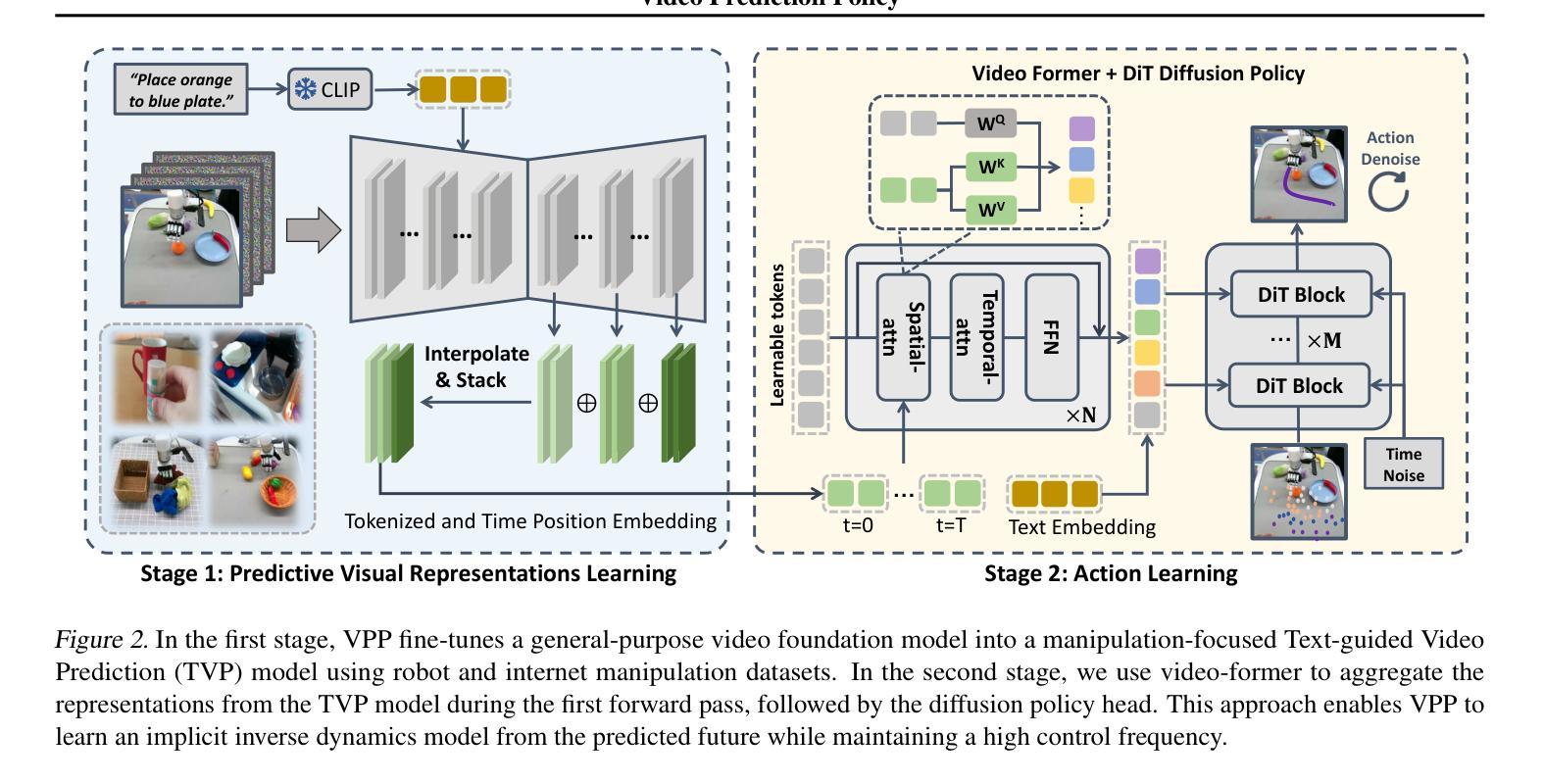
Authors:Yucheng Hu, Yanjiang Guo, Pengchao Wang, Xiaoyu Chen, Yen-Jen Wang, Jianke Zhang, Koushil Sreenath, Chaochao Lu, Jianyu Chen
Visual representations play a crucial role in developing generalist robotic policies. Previous vision encoders, typically pre-trained with single-image reconstruction or two-image contrastive learning, tend to capture static information, often neglecting the dynamic aspects vital for embodied tasks. Recently, video diffusion models (VDMs) demonstrate the ability to predict future frames and showcase a strong understanding of physical world. We hypothesize that VDMs inherently produce visual representations that encompass both current static information and predicted future dynamics, thereby providing valuable guidance for robot action learning. Based on this hypothesis, we propose the Video Prediction Policy (VPP), which learns implicit inverse dynamics model conditioned on predicted future representations inside VDMs. To predict more precise future, we fine-tune pre-trained video foundation model on robot datasets along with internet human manipulation data. In experiments, VPP achieves a 18.6% relative improvement on the Calvin ABC-D generalization benchmark compared to the previous state-of-the-art, and demonstrates a 31.6% increase in success rates for complex real-world dexterous manipulation tasks. Project page at https://video-prediction-policy.github.io
视觉表示在开发通用机器人策略中发挥了至关重要的作用。以前的视觉编码器通常使用单图像重建或双图像对比学习进行预训练,更偏向于捕捉静态信息,往往忽略了对于实体任务至关重要的动态方面。最近,视频扩散模型(VDMs)展示了预测未来帧的能力,并展示了对物理世界的深刻理解。我们假设VDMs会生成包含当前静态信息和预测的未来动态信息的视觉表示,从而为机器人动作学习提供有价值的指导。基于这一假设,我们提出了视频预测策略(VPP),它学习基于VDMs内部预测的未来表示的隐式逆动力学模型。为了预测更精确的未来,我们在机器人数据集以及互联网人类操作数据上对预训练的视频基础模型进行了微调。在实验中,VPP在Calvin ABC-D泛化基准测试上相对于之前的最先进水平实现了18.6%的相对改进,并且在复杂的真实世界精细操作任务中成功率提高了31.6%。项目页面为:https://video-prediction-policy.github.io。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML 2025 Spotlight Paper. The first two authors contribute equally
Summary
视觉表示在开发通用机器人策略中起到关键作用。传统的视觉编码器主要捕捉静态信息,忽略了动态方面,这对于实体任务至关重要。视频扩散模型(VDMs)能够预测未来帧,并展示对物理世界的深刻理解。基于此,我们假设VDMs产生的视觉表示包含当前静态信息和预测的未来动态,为机器人动作学习提供宝贵指导。我们提出了基于视频预测的策略(VPP),它学习基于VDMs内预测未来表示的隐逆动力学模型。在实验中,VPP在Calvin ABC-D通用化基准测试上相对于之前的最优策略实现了18.6%的相对改进,并在复杂的真实世界精细操作任务上成功率提高了31.6%。
Key Takeaways
- 视频扩散模型(VDMs)能预测未来帧,展现对物理世界的深刻理解。
- VDMs产生的视觉表示包含当前静态信息和预测的未来动态。
- 基于视频预测的策略(VPP)结合了VDMs和机器人动作学习。
- VPP通过隐逆动力学模型预测未来表现,基于预测未来表示。
- 对预训练的视频基础模型进行微调,以提高对未来预测的精确度。
- VPP在Calvin ABC-D基准测试上实现了显著的性能提升。
- VPP在真实世界的精细操作任务上表现出较高的成功率。
点此查看论文截图

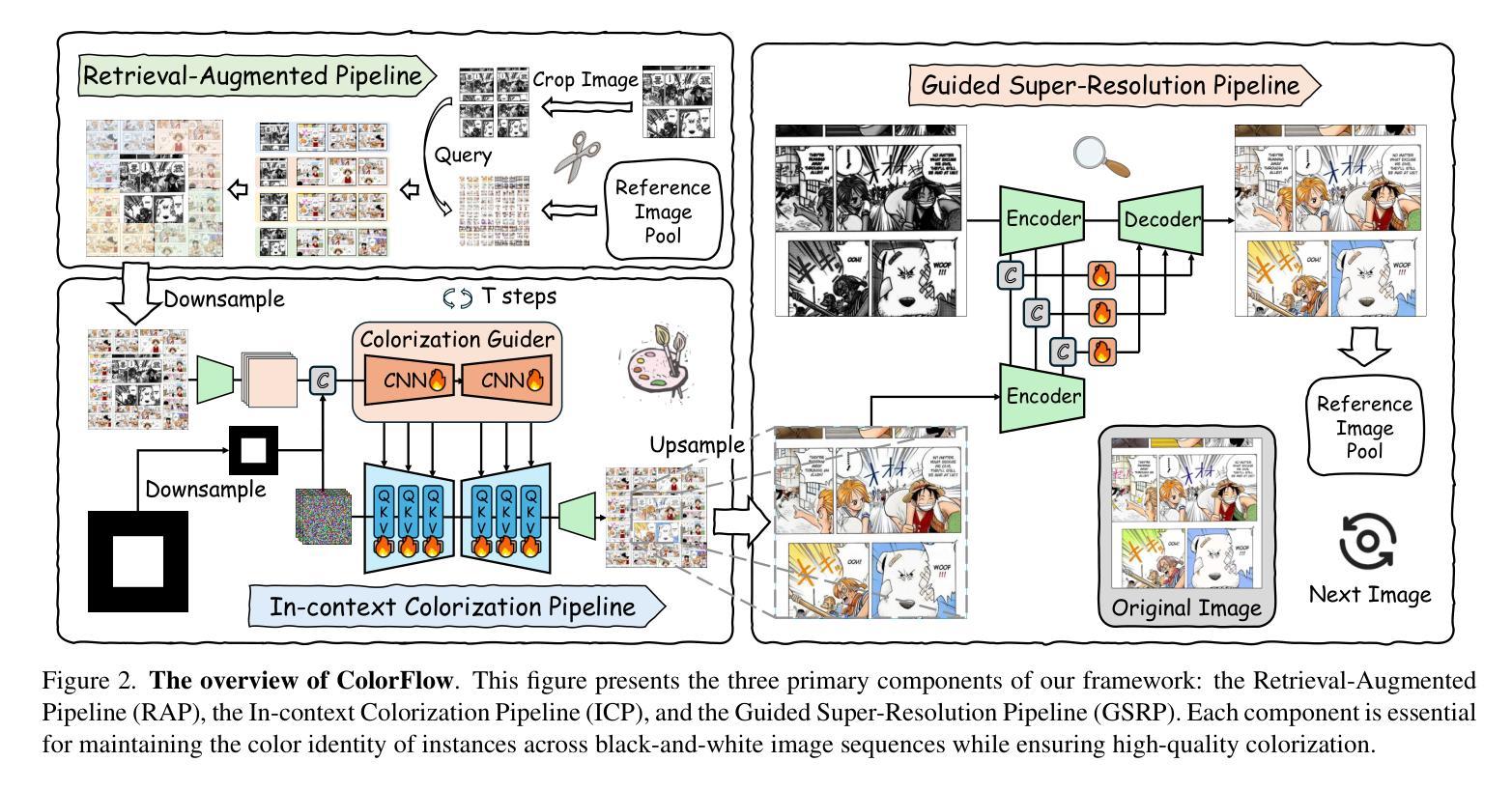
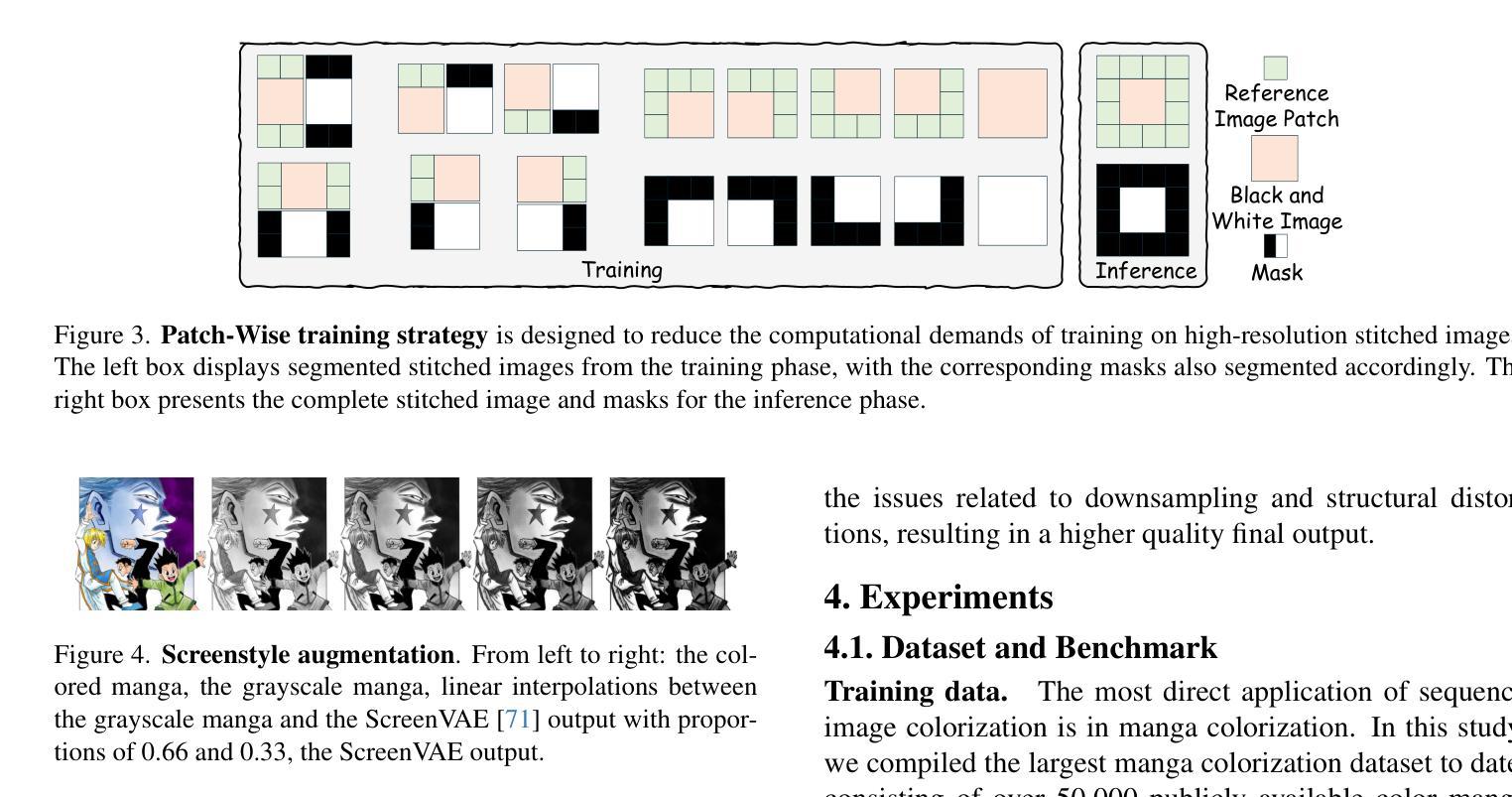
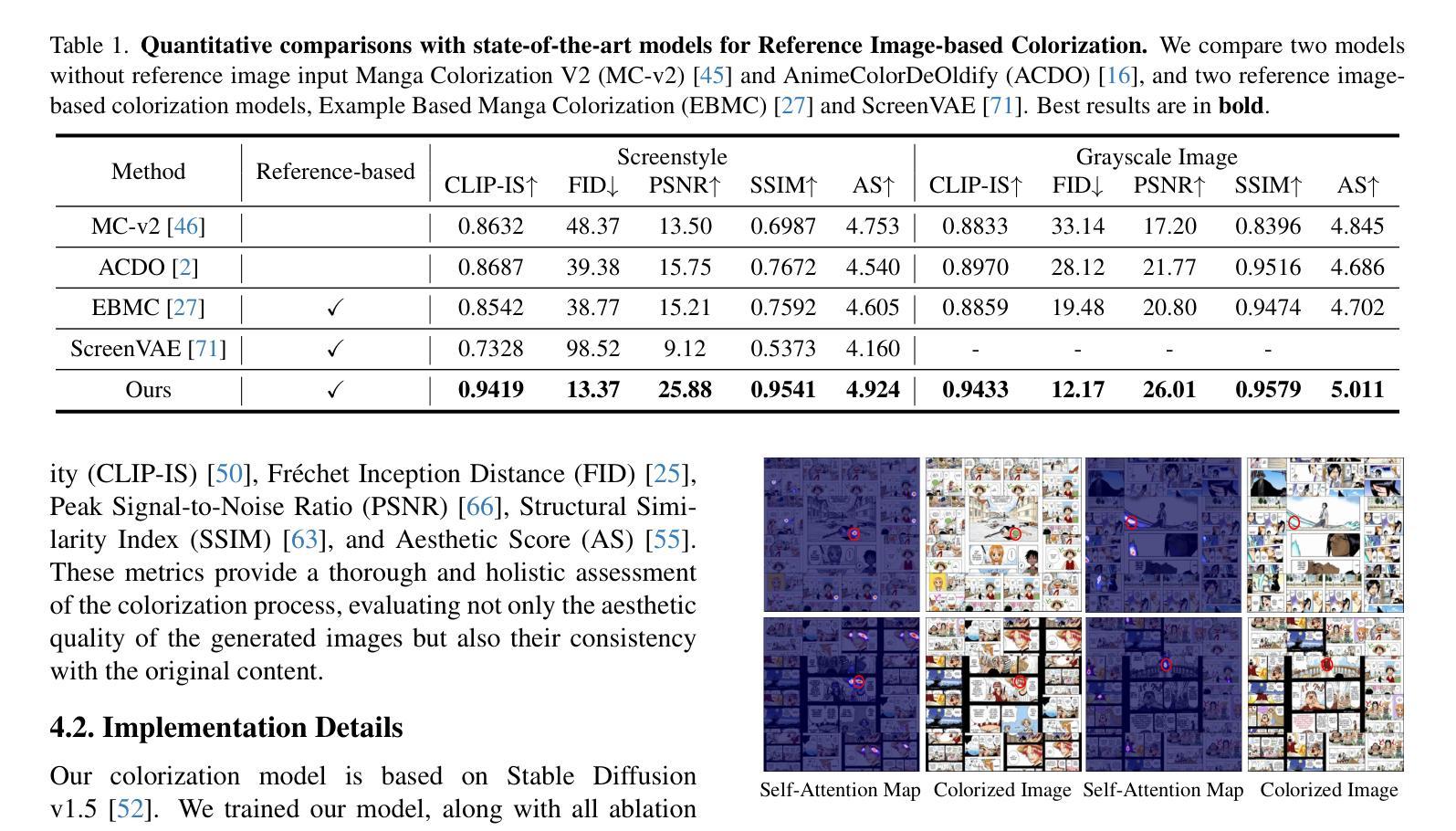
ColorFlow: Retrieval-Augmented Image Sequence Colorization
Authors:Junhao Zhuang, Xuan Ju, Zhaoyang Zhang, Yong Liu, Shiyi Zhang, Chun Yuan, Ying Shan
Automatic black-and-white image sequence colorization while preserving character and object identity (ID) is a complex task with significant market demand, such as in cartoon or comic series colorization. Despite advancements in visual colorization using large-scale generative models like diffusion models, challenges with controllability and identity consistency persist, making current solutions unsuitable for industrial application.To address this, we propose ColorFlow, a three-stage diffusion-based framework tailored for image sequence colorization in industrial applications. Unlike existing methods that require per-ID finetuning or explicit ID embedding extraction, we propose a novel robust and generalizable Retrieval Augmented Colorization pipeline for colorizing images with relevant color references. Our pipeline also features a dual-branch design: one branch for color identity extraction and the other for colorization, leveraging the strengths of diffusion models. We utilize the self-attention mechanism in diffusion models for strong in-context learning and color identity matching. To evaluate our model, we introduce ColorFlow-Bench, a comprehensive benchmark for reference-based colorization. Results show that ColorFlow outperforms existing models across multiple metrics, setting a new standard in sequential image colorization and potentially benefiting the art industry. We release our codes and models on our project page: https://zhuang2002.github.io/ColorFlow/.
自动黑白图像序列上色,同时保留人物和物体身份(ID),是一项具有显著市场需求的复杂任务,例如在卡通或漫画系列的上色中。尽管使用大规模生成模型(如扩散模型)的视觉上色技术有所进步,但可控性和身份一致性的挑战仍然存在,使得当前解决方案不适合工业应用。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了ColorFlow,这是一个用于工业应用图像序列上色的三阶段扩散模型框架。与现有方法不同,我们不需要针对每个ID进行微调或显式ID嵌入提取,提出了一种新颖、稳健和通用的检索增强上色管道,用于以上色相关的颜色参考图像。我们的管道还采用双分支设计:一个分支用于颜色身份提取,另一个分支用于上色,利用扩散模型的优点。我们利用扩散模型中的自注意力机制进行强大的上下文学习和颜色身份匹配。为了评估我们的模型,我们引入了ColorFlow-Bench,这是一个基于参考的上色综合基准测试。结果表明,ColorFlow在多个指标上超过了现有模型,为序列图像上色设定了新的标准,并有望惠及艺术产业。我们将在项目页面发布我们的代码和模型:https://zhuang2002.github.io/ColorFlow/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://zhuang2002.github.io/ColorFlow/
Summary
本文提出了一种名为ColorFlow的三阶段扩散模型框架,用于工业应用中图像序列的自动黑白图像色彩化,同时保留角色和物体身份。该框架具有强大的检索增强色彩化管道,可基于相关颜色参考进行色彩化,无需对每个身份进行微调或显式身份嵌入提取。通过双分支设计利用扩散模型的优点,通过自注意力机制实现强上下文学习和颜色身份匹配。此外,引入了一个新的基准测试ColorFlow-Bench用于评估模型在参考基础上的色彩化效果。实验结果显示,ColorFlow在多个指标上超越了现有模型,为艺术产业带来了潜在好处。有关代码和模型的详细信息可在我们的项目页面找到。
Key Takeaways
- ColorFlow是一个三阶段的扩散模型框架,专门用于图像序列的色彩化,适用于工业应用。
- 提出了一个强大的检索增强色彩化管道,无需针对每个身份进行微调或提取显式身份嵌入。
- 采用双分支设计,一个分支用于颜色身份提取,另一个分支用于色彩化,利用扩散模型的自注意力机制。
- 引入ColorFlow-Bench基准测试,用于评估模型在基于参考的色彩化性能。
- ColorFlow在多个指标上超越了现有模型,展现出优秀的性能。
- 该研究为艺术产业带来潜在好处,并能为黑白图像(如卡通或漫画系列)带来色彩化应用。
点此查看论文截图

Efficient Diversity-Preserving Diffusion Alignment via Gradient-Informed GFlowNets
Authors:Zhen Liu, Tim Z. Xiao, Weiyang Liu, Yoshua Bengio, Dinghuai Zhang
While one commonly trains large diffusion models by collecting datasets on target downstream tasks, it is often desired to align and finetune pretrained diffusion models with some reward functions that are either designed by experts or learned from small-scale datasets. Existing post-training methods for reward finetuning of diffusion models typically suffer from lack of diversity in generated samples, lack of prior preservation, and/or slow convergence in finetuning. In response to this challenge, we take inspiration from recent successes in generative flow networks (GFlowNets) and propose a reinforcement learning method for diffusion model finetuning, dubbed Nabla-GFlowNet (abbreviated as $\nabla$-GFlowNet), that leverages the rich signal in reward gradients for probabilistic diffusion finetuning. We show that our proposed method achieves fast yet diversity- and prior-preserving finetuning of Stable Diffusion, a large-scale text-conditioned image diffusion model, on different realistic reward functions.
通常人们通过收集目标下游任务的数据集来训练大型扩散模型,但有时人们希望使用专家设计的奖励函数或与从小规模数据集中学习到的奖励函数对齐并微调预先训练的扩散模型。现有的用于扩散模型奖励微调的后训练方法通常面临生成样本缺乏多样性、缺乏先验知识保留以及微调收敛缓慢等问题。为了应对这一挑战,我们从生成流网络(GFlowNets)的最新成功中汲取灵感,提出了一种用于扩散模型微调的强化学习方法,名为Nabla-GFlowNet(简称$\nabla$-GFlowNet),该方法利用奖励梯度中的丰富信号进行概率扩散微调。我们证明了所提出的方法能够在不同的现实奖励函数上快速、多样化和保留先验地对大型文本条件图像扩散模型Stable Diffusion进行微调。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical Report (37 pages, 31 figures), Accepted at ICLR 2025
Summary
本文提出一种基于强化学习的方法,用于对扩散模型进行微调,称为Nabla-GFlowNet。该方法利用奖励梯度中的丰富信号进行概率扩散微调,解决了现有扩散模型奖励微调方法的样本多样性不足、先验知识丢失以及微调收敛慢的问题。实验表明,该方法在Stable Diffusion模型上实现了快速、多样性和保持先验知识的微调,适用于不同的真实奖励函数。
Key Takeaways
- 本文介绍了强化学习在扩散模型微调中的应用,提出Nabla-GFlowNet方法。
- Nabla-GFlowNet利用奖励梯度中的丰富信号进行概率扩散微调。
- 现有扩散模型奖励微调方法存在样本多样性不足、先验知识丢失和微调收敛慢的问题。
- Nabla-GFlowNet在Stable Diffusion模型上进行了实验验证。
- 该方法实现了快速、多样性和保持先验知识的微调。
- Nabla-GFlowNet适用于不同的真实奖励函数。
点此查看论文截图


OSMamba: Omnidirectional Spectral Mamba with Dual-Domain Prior Generator for Exposure Correction
Authors:Gehui Li, Bin Chen, Chen Zhao, Lei Zhang, Jian Zhang
Exposure correction is a fundamental problem in computer vision and image processing. Recently, frequency domain-based methods have achieved impressive improvement, yet they still struggle with complex real-world scenarios under extreme exposure conditions. This is due to the local convolutional receptive fields failing to model long-range dependencies in the spectrum, and the non-generative learning paradigm being inadequate for retrieving lost details from severely degraded regions. In this paper, we propose Omnidirectional Spectral Mamba (OSMamba), a novel exposure correction network that incorporates the advantages of state space models and generative diffusion models to address these limitations. Specifically, OSMamba introduces an omnidirectional spectral scanning mechanism that adapts Mamba to the frequency domain to capture comprehensive long-range dependencies in both the amplitude and phase spectra of deep image features, hence enhancing illumination correction and structure recovery. Furthermore, we develop a dual-domain prior generator that learns from well-exposed images to generate a degradation-free diffusion prior containing correct information about severely under- and over-exposed regions for better detail restoration. Extensive experiments on multiple-exposure and mixed-exposure datasets demonstrate that the proposed OSMamba achieves state-of-the-art performance both quantitatively and qualitatively.
曝光校正(Exposure Correction)是计算机视觉和图像处理中的一个基本问题。虽然基于频域的方法近期取得了令人印象深刻的改进,但在极端曝光条件下的复杂现实场景中仍然面临挑战。这是因为局部卷积感受野无法对光谱中的长距离依赖关系进行建模,且非生成性学习范式无法从严重退化的区域中检索丢失的细节。针对这些限制,本文提出了全方位光谱Mamba(OSMamba)网络。它结合了状态空间模型和生成扩散模型的优势。具体来说,OSMamba引入了一种全方位频谱扫描机制,使Mamba能够适应频域,捕获深度图像特征的幅度和相位谱中的全面长距离依赖关系,从而增强照明校正和结构恢复。此外,我们开发了一个双域先验生成器,它从曝光良好的图像中学习,生成一个无退化扩散先验,其中包含关于严重欠曝光和过曝光区域的正确信息,以更好地恢复细节。在多种曝光和混合曝光数据集上的大量实验表明,所提出的OSMamba在定量和定性方面都达到了最新水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为Omnidirectional Spectral Mamba(OSMamba)的新型曝光校正网络,结合了状态空间模型和生成扩散模型的优点,解决了现有频率域方法在复杂现实世界场景下的局限性。OSMamba通过引入全方向频谱扫描机制,适应Mamba到频率域,捕捉深度图像特征的幅度和相位频谱中的全面长程依赖关系,从而提高照明校正和结构恢复能力。此外,还开发了一种双域先验生成器,从曝光良好的图像中学习,生成不含降质的扩散先验,包含关于严重欠曝和过曝区域的正确信息,以更好地恢复细节。在多个曝光和混合曝光数据集上的广泛实验表明,所提出的OSMamba在量和质上均达到最新技术水平。
Key Takeaways
- 曝光校正是计算机视觉和图像处理中的基础问题,近期频率域方法虽然有所改进,但在极端曝光条件下仍面临复杂现实世界场景的挑战。
- 现有方法因局部卷积感受野无法建模长程依赖关系和非生成学习范式不足,难以从严重退化区域中检索丢失的细节。
- 提出的OSMamba网络结合了状态空间模型和生成扩散模型的优点,旨在解决这些问题。
- OSMamba通过全方向频谱扫描机制适应Mamba到频率域,在深度图像特征的幅度和相位频谱中捕捉全面的长程依赖关系。
- 开发了一种双域先验生成器,可以从良好曝光的图像中学习,生成扩散先验以更好地恢复细节。
- OSMamba在多个曝光和混合曝光数据集上实现了先进性能。
点此查看论文截图



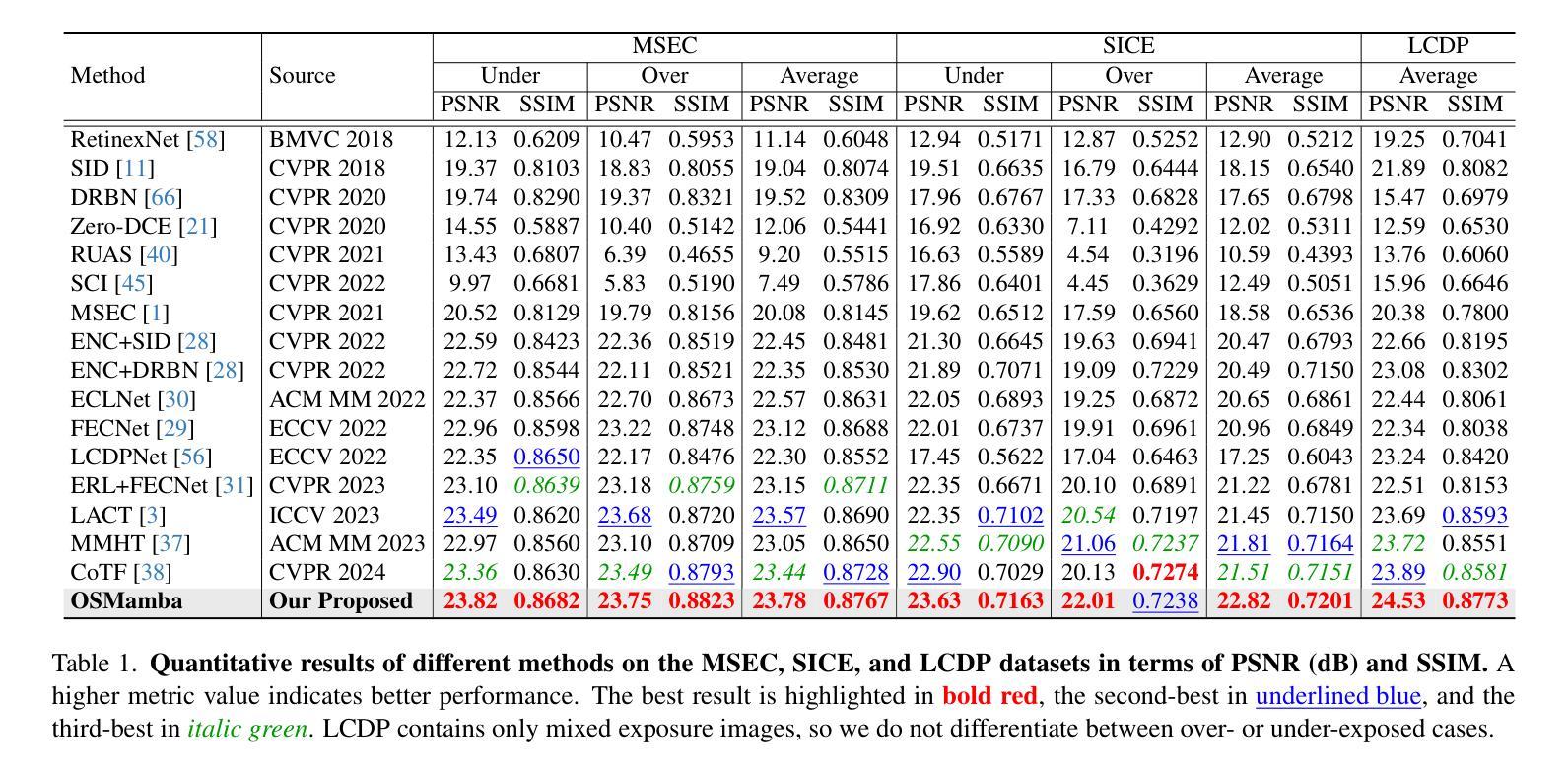
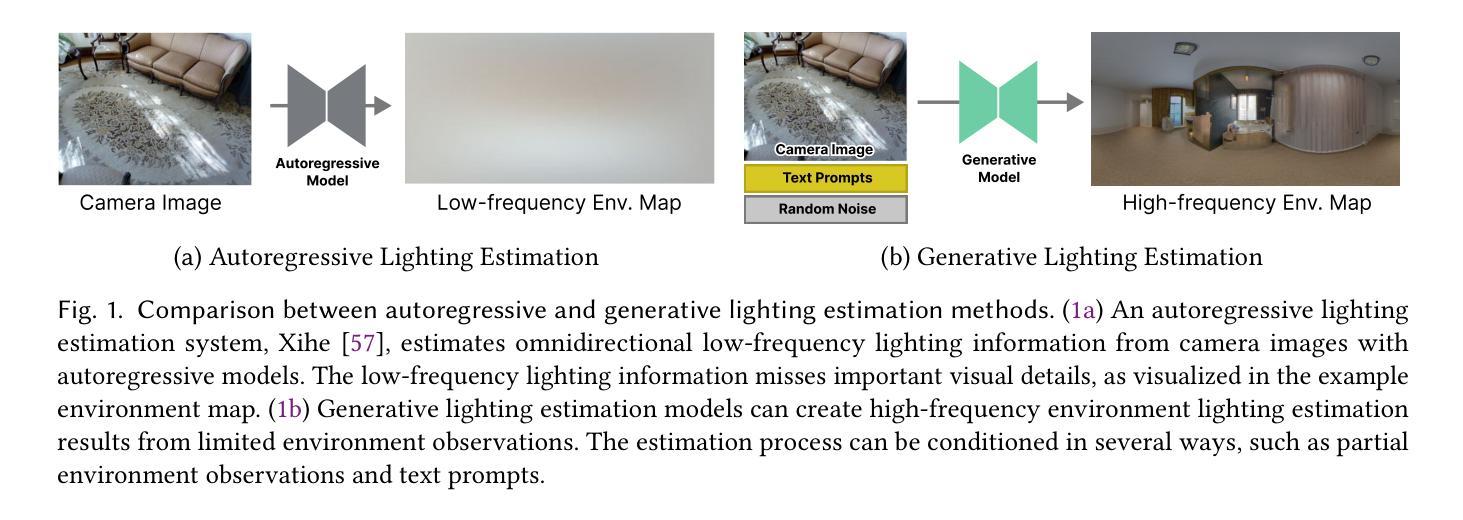
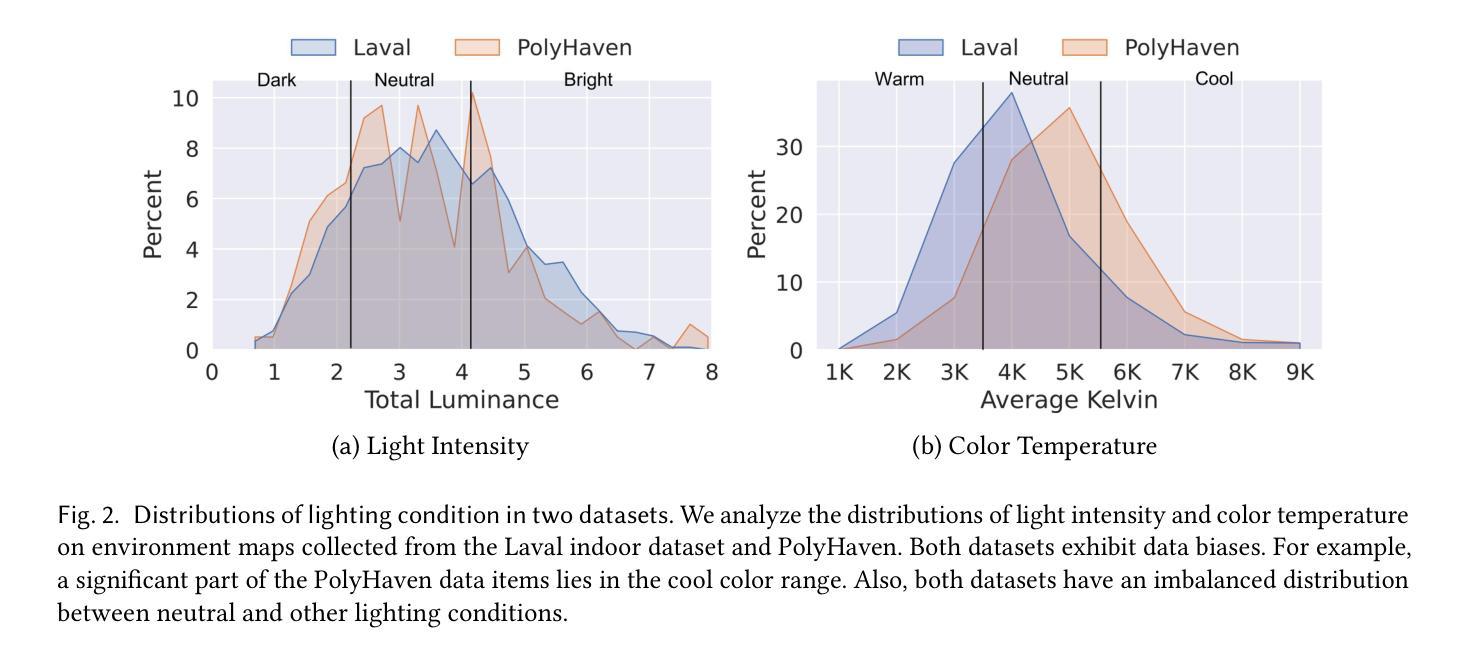
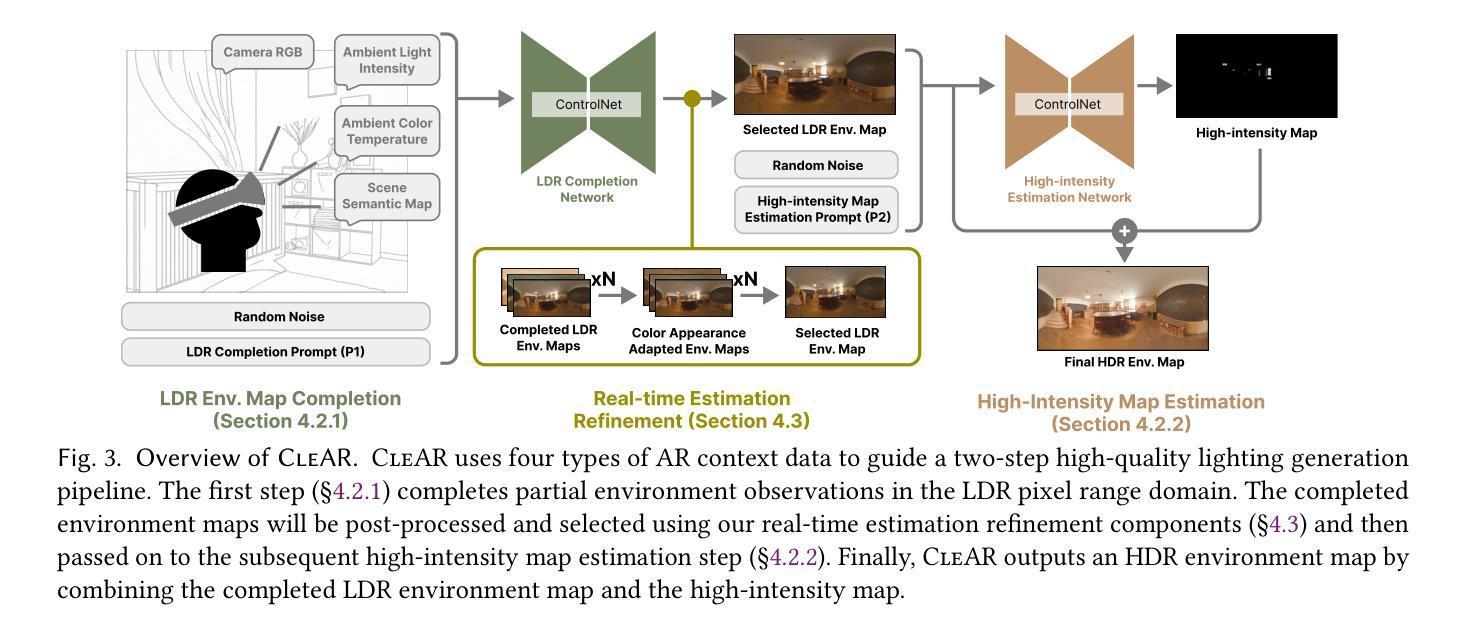
CleAR: Robust Context-Guided Generative Lighting Estimation for Mobile Augmented Reality
Authors:Yiqin Zhao, Mallesham Dasari, Tian Guo
High-quality environment lighting is essential for creating immersive mobile augmented reality (AR) experiences. However, achieving visually coherent estimation for mobile AR is challenging due to several key limitations in AR device sensing capabilities, including low camera FoV and limited pixel dynamic ranges. Recent advancements in generative AI, which can generate high-quality images from different types of prompts, including texts and images, present a potential solution for high-quality lighting estimation. Still, to effectively use generative image diffusion models, we must address two key limitations of content quality and slow inference. In this work, we design and implement a generative lighting estimation system called CleAR that can produce high-quality, diverse environment maps in the format of 360{\deg} HDR images. Specifically, we design a two-step generation pipeline guided by AR environment context data to ensure the output aligns with the physical environment’s visual context and color appearance. To improve the estimation robustness under different lighting conditions, we design a real-time refinement component to adjust lighting estimation results on AR devices. Through a combination of quantitative and qualitative evaluations, we show that CleAR outperforms state-of-the-art lighting estimation methods on both estimation accuracy, latency, and robustness, and is rated by 31 participants as producing better renderings for most virtual objects. For example, CleAR achieves 51% to 56% accuracy improvement on virtual object renderings across objects of three distinctive types of materials and reflective properties. CleAR produces lighting estimates of comparable or better quality in just 3.2 seconds – over 110X faster than state-of-the-art methods.
高质量的环境照明对于创建沉浸式的移动增强现实(AR)体验至关重要。然而,由于AR设备感知能力的几个关键限制,如相机视野较小和像素动态范围有限,实现移动AR的视觉一致性估计具有挑战性。最近,生成式人工智能的发展可以从不同类型的提示生成高质量图像,包括文本和图像,这为高质量照明估计提供了潜在的解决方案。然而,为了有效地使用生成式图像扩散模型,我们必须解决内容质量和推理速度慢的两个关键局限性。在这项工作中,我们设计并实现了一个名为CleAR的生成式照明估计系统,可以生成高质量、多样化的环境地图,以360°HDR图像格式呈现。具体来说,我们设计了一个由AR环境上下文数据引导的两步生成管道,以确保输出与物理环境的视觉上下文和颜色外观保持一致。为了提高不同照明条件下的估计稳健性,我们设计了一个实时修正组件来调整AR设备上的照明估计结果。通过定量和定性评估的结合,我们证明了CleAR在估计精度、延迟和稳健性方面优于最新的照明估计方法,并被31名参与者评价为对大多数虚拟对象产生了更好的渲染效果。例如,CleAR在三种不同材质和反射属性的对象上实现了虚拟对象渲染的51%至56%的准确度提升。CleAR仅需3.2秒即可生成相当或更高质量的照明估计——比最先进的方法快超过110倍。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
高质量的环境光照对于创建沉浸式的移动增强现实(AR)体验至关重要。然而,由于AR设备感知能力的关键限制,如低相机视野和有限的像素动态范围,实现移动AR的视觉连贯性估计具有挑战性。最近生成式AI的进展,可以从不同类型的提示生成高质量图像,为解决高质量光照估计问题提供了潜在解决方案。然而,为了有效地使用图像扩散模型,我们必须解决内容质量和推理速度慢的两个关键局限性。本研究设计并实施了一个名为CleAR的生成式光照估计系统,能够生成高质量、多样化的环境地图,以360°HDR图像格式呈现。本研究通过结合定量和定性评估,验证了CleAR在估计精度、延迟和稳健性方面的表现均优于当前先进的光照估计方法,并被31位参与者评价为对大多数虚拟物体的渲染效果更好。例如,CleAR在三种不同材质和反射属性的物体上实现了对虚拟物体渲染的51%至56%的准确性改进,且在仅3.2秒内生成了质量相当或更好的光照估计——比当前最先进的方法快超过110倍。
Key Takeaways
- 高质量环境光照对移动AR体验至关重要,但实现视觉连贯性估计具有挑战性。
- 生成式AI为解决高质量光照估计问题提供了潜在解决方案。
- 研究设计并实施了一个名为CleAR的生成式光照估计系统,可生成多样化的高质量环境地图。
- CleAR在估计精度、延迟和稳健性方面优于现有方法。
- CleAR能够有效提高虚拟物体渲染的准确度,尤其是对三种不同材质和反射属性的物体。
- CleAR在快速生成高质量光照估计方面表现出色,仅需要3.2秒,比现有方法快超过110倍。
点此查看论文截图

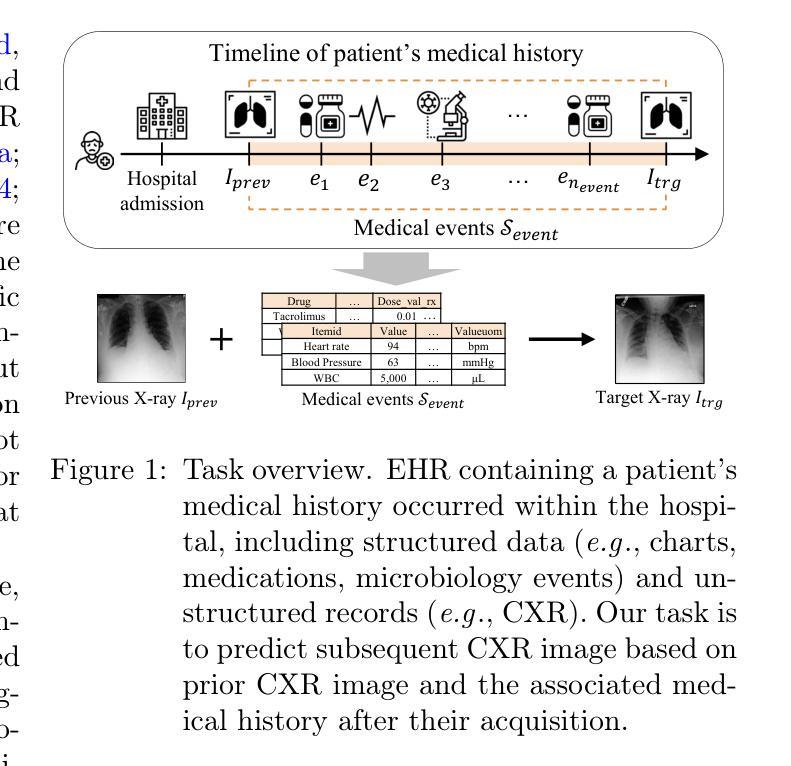
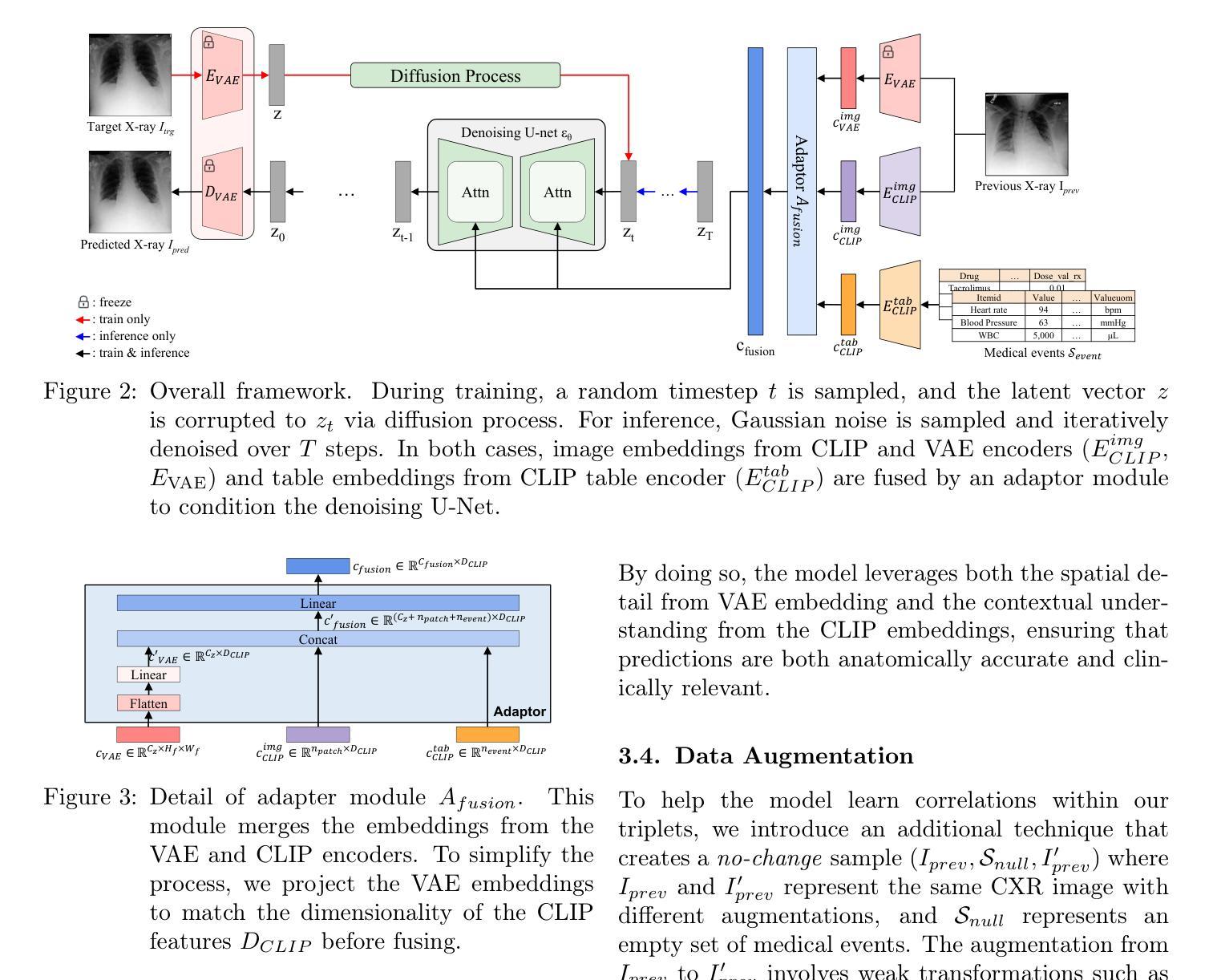
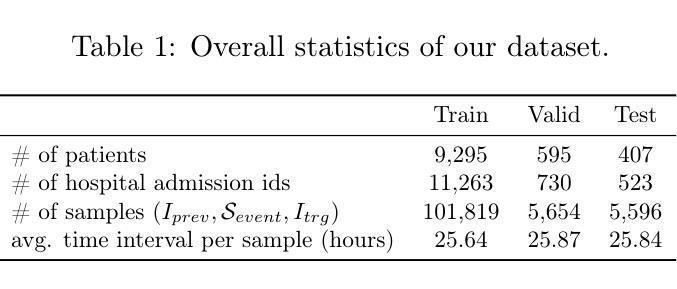
Towards Predicting Temporal Changes in a Patient’s Chest X-ray Images based on Electronic Health Records
Authors:Daeun Kyung, Junu Kim, Tackeun Kim, Edward Choi
Chest X-ray (CXR) is an important diagnostic tool widely used in hospitals to assess patient conditions and monitor changes over time. Recently, generative models, specifically diffusion-based models, have shown promise in generating realistic synthetic CXRs. However, these models mainly focus on conditional generation using single-time-point data, i.e., generating CXRs conditioned on their corresponding reports from a specific time. This limits their clinical utility, particularly for capturing temporal changes. To address this limitation, we propose a novel framework, EHRXDiff, which predicts future CXR images by integrating previous CXRs with subsequent medical events, e.g., prescriptions, lab measures, etc. Our framework dynamically tracks and predicts disease progression based on a latent diffusion model, conditioned on the previous CXR image and a history of medical events. We comprehensively evaluate the performance of our framework across three key aspects, including clinical consistency, demographic consistency, and visual realism. Results show that our framework generates high-quality, realistic future images that effectively capture potential temporal changes. This suggests that our framework could be further developed to support clinical decision-making and provide valuable insights for patient monitoring and treatment planning in the medical field. The code is available at https://github.com/dek924/EHRXDiff.
胸部X光(CXR)是医院中广泛使用的重要诊断工具,用于评估患者状况和监测随时间的变化。最近,生成式模型,特别是基于扩散的模型,在生成逼真的合成CXR方面显示出巨大的潜力。然而,这些模型主要集中在使用单时间点数据的条件生成上,即根据特定时间的相应报告生成CXR。这限制了它们在临床上的实用性,尤其是用于捕捉时间变化的能力。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了一种新的框架EHRXDiff,它通过整合先前的CXR和随后的医疗事件(如处方、实验室测量等)来预测未来的CXR图像。我们的框架基于潜在扩散模型动态跟踪和预测疾病进展,以先前的CXR图像和医疗事件历史为条件。我们从临床一致性、人口统计学一致性和视觉真实性三个方面全面评估了我们的框架性能。结果表明,我们的框架生成的高质量、逼真的未来图像能够有效地捕捉潜在的临时变化。这表明我们的框架可以进一步发展,以支持临床决策制定,为医学领域的患者监测和治疗计划提供有价值的见解。代码可在https://github.com/dek924/EHRXDiff找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at Proc. of Conference on Health, Inference, and Learning (CHIL) 2025 (10 pages for main text, 3 pages for references, 8 pages for supplementary materials)
Summary
本文提出了一种新的框架EHRXDiff,该框架利用扩散模型预测未来的胸部X光图像。它不仅基于先前的CXR图像,还结合了后续医疗事件,如处方、实验室测量等,以动态追踪和预测疾病进展。该框架在临床一致性、人口统计一致性和视觉逼真度方面表现出色,生成的未来图像高质量且真实,能有效捕捉潜在的暂时变化。这有助于临床决策制定、患者监测和治疗计划。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在生成真实的合成胸部X光图像方面显示出潜力。
- 当前模型主要关注基于单时间点数据的条件生成,限制了其在临床上的用途。
- EHRXDiff框架通过结合先前的CXR图像和后续医疗事件,如处方和实验室测量,来预测未来的CXR图像。
- EHRXDiff框架利用潜伏扩散模型动态追踪和预测疾病进展。
- 该框架在临床一致性、人口统计一致性和视觉逼真度方面表现出色。
- EHRXDiff生成的未来图像高质量且真实,能有效捕捉潜在的临时变化。
点此查看论文截图

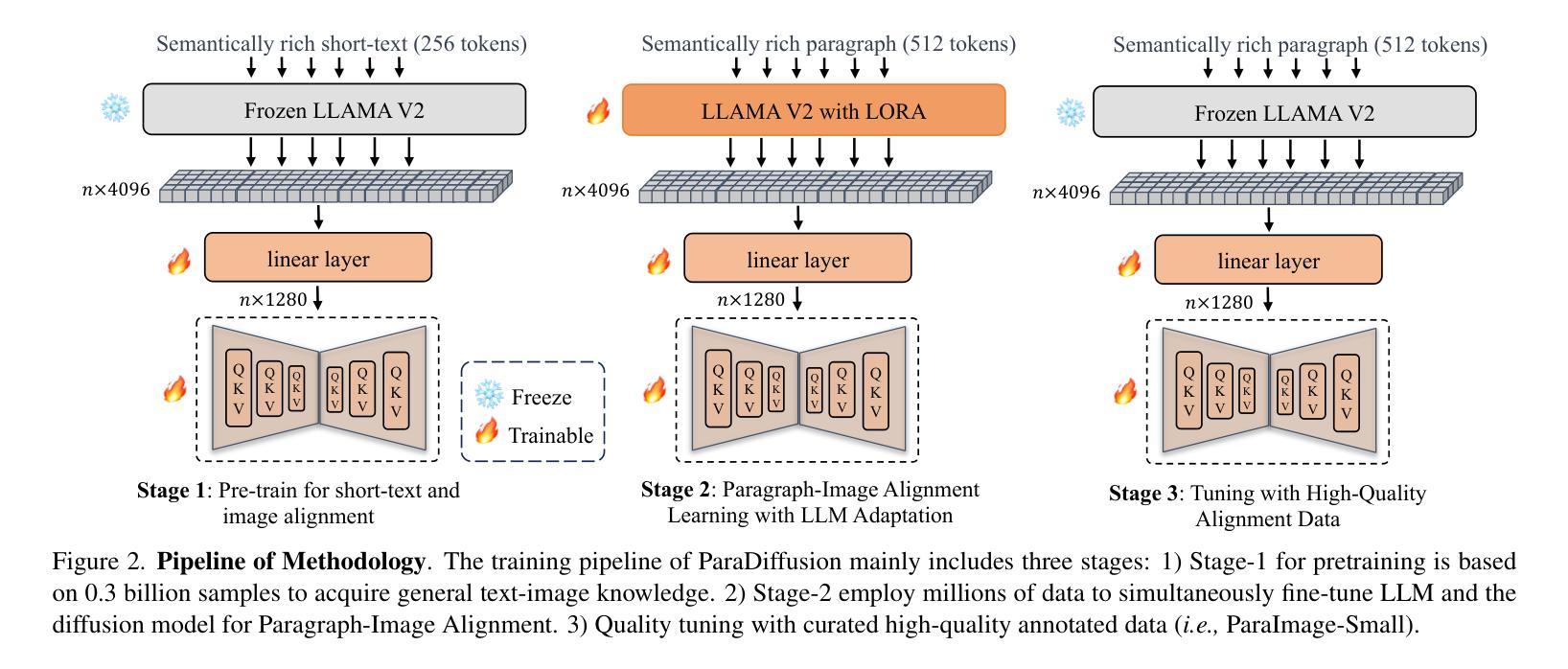
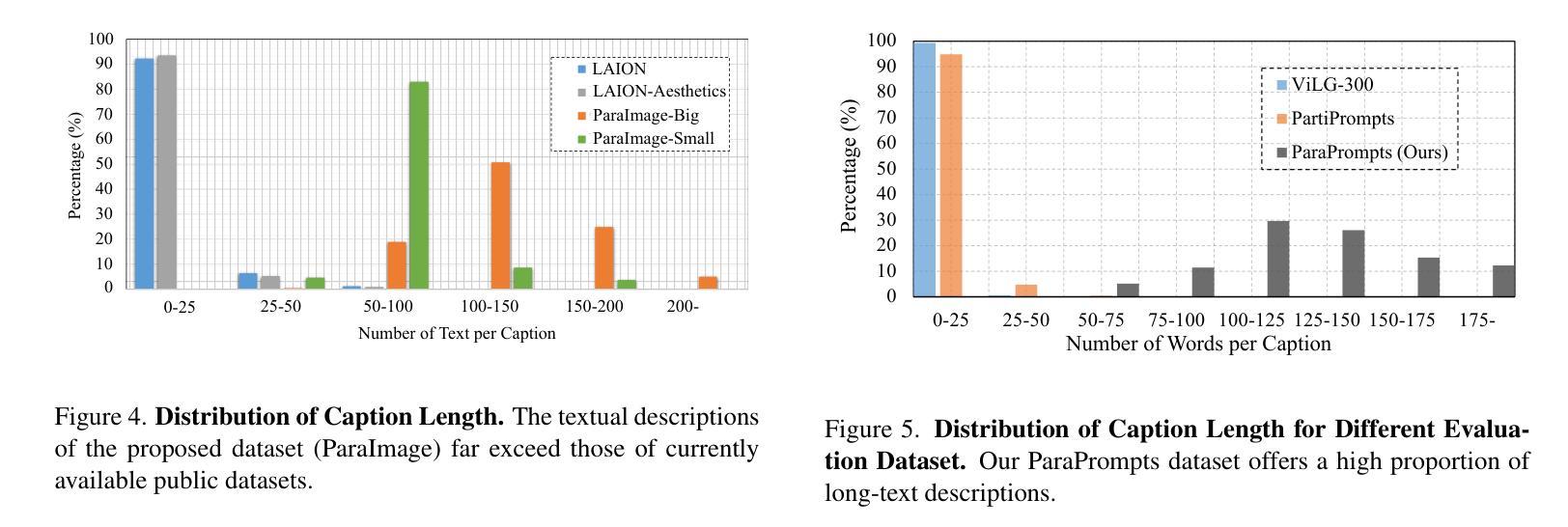
Paragraph-to-Image Generation with Information-Enriched Diffusion Model
Authors:Weijia Wu, Zhuang Li, Yefei He, Mike Zheng Shou, Chunhua Shen, Lele Cheng, Yan Li, Tingting Gao, Di Zhang
Text-to-image (T2I) models have recently experienced rapid development, achieving astonishing performance in terms of fidelity and textual alignment capabilities. However, given a long paragraph (up to 512 words), these generation models still struggle to achieve strong alignment and are unable to generate images depicting complex scenes. In this paper, we introduce an information-enriched diffusion model for paragraph-to-image generation task, termed ParaDiffusion, which delves into the transference of the extensive semantic comprehension capabilities of large language models to the task of image generation. At its core is using a large language model (e.g., Llama V2) to encode long-form text, followed by fine-tuning with LORA to alignthe text-image feature spaces in the generation task. To facilitate the training of long-text semantic alignment, we also curated a high-quality paragraph-image pair dataset, namely ParaImage. This dataset contains a small amount of high-quality, meticulously annotated data, and a large-scale synthetic dataset with long text descriptions being generated using a vision-language model. Experiments demonstrate that ParaDiffusion outperforms state-of-the-art models (SD XL, DeepFloyd IF) on ViLG-300 and ParaPrompts, achieving up to 15% and 45% human voting rate improvements for visual appeal and text faithfulness, respectively. The code and dataset will be released to foster community research on long-text alignment.
文本到图像(T2I)模型最近经历了快速发展,在保真度和文本对齐能力方面取得了惊人的性能。然而,对于长达512字的段落,这些生成模型仍然难以实现对齐,并且无法生成描述复杂场景的图像。在本文中,我们介绍了一种用于段落到图像生成任务的丰富信息扩散模型,称为ParaDiffusion,它深入研究了大语言模型的广泛语义理解能力的转移到图像生成任务。其核心是使用大型语言模型(例如Llama V2)对长文本进行编码,然后使用LORA进行微调,以在生成任务中对齐文本图像特征空间。为了训练长文本语义对齐,我们还精心制作了一个高质量段落图像对数据集,即ParaImage。该数据集包含少量高质量、精心注释的数据,以及一个大规模合成数据集,使用视觉语言模型生成具有长文本描述的数据。实验表明,ParaDiffusion在ViLG-300和ParaPrompts上优于现有模型(SD XL、DeepFloyd IF),在视觉吸引力和文本忠实度方面分别提高了高达15%和45%的人类投票率。代码和数据集将发布,以促进社区对长文本对齐的研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The project website is at: https://weijiawu.github.io/ParaDiffusionPage/. Code: https://github.com/weijiawu/ParaDiffusion
摘要
本文提出了一种信息丰富的扩散模型——ParaDiffusion,用于段落到图像的生成任务。该模型利用大型语言模型(如Llama V2)对长文本进行编码,并使用LORA微调以在生成任务中对齐文本图像特征空间。为训练长文本语义对齐,还推出了高质量的段落图像配对数据集ParaImage。实验表明,ParaDiffusion在ViLG-300和ParaPrompts上优于其他模型(SD XL、DeepFloyd IF),视觉吸引力和文本忠实度分别提高了高达15%和45%。代码和数据集将发布,以促进社区对长文本对齐的研究。
关键见解
- T2I模型在段落(长达512字)生成图像时面临对齐困难,无法生成描述复杂场景的图像。
- 提出了信息丰富的扩散模型ParaDiffusion,用于段落到图像的生成任务。
- ParaDiffusion利用大型语言模型(如Llama V2)对长文本进行编码。
- 使用LORA微调以在生成任务中对齐文本图像特征空间。
- 推出了高质量的段落图像配对数据集ParaImage,包含少量高质量、精心注释的数据和大规模合成数据集。
- 实验表明,ParaDiffusion在视觉吸引力和文本忠实度方面优于其他模型。
- 代码和数据集的发布将促进社区对长文本对齐的研究。
点此查看论文截图