⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-08 更新
Towards Smart Point-and-Shoot Photography
Authors:Jiawan Li, Fei Zhou, Zhipeng Zhong, Jiongzhi Lin, Guoping Qiu
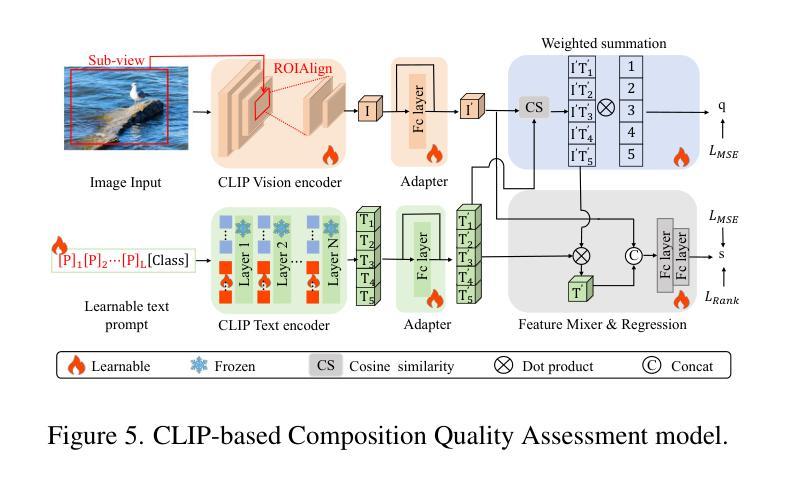
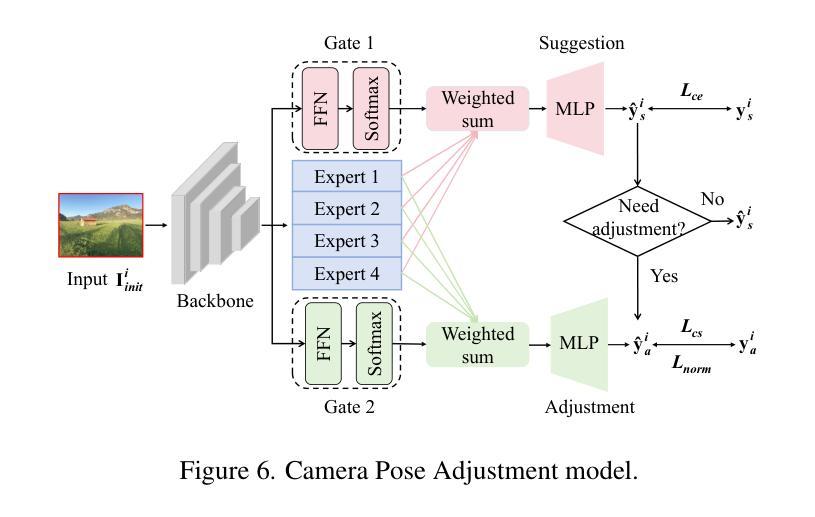
Hundreds of millions of people routinely take photos using their smartphones as point and shoot (PAS) cameras, yet very few would have the photography skills to compose a good shot of a scene. While traditional PAS cameras have built-in functions to ensure a photo is well focused and has the right brightness, they cannot tell the users how to compose the best shot of a scene. In this paper, we present a first of its kind smart point and shoot (SPAS) system to help users to take good photos. Our SPAS proposes to help users to compose a good shot of a scene by automatically guiding the users to adjust the camera pose live on the scene. We first constructed a large dataset containing 320K images with camera pose information from 4000 scenes. We then developed an innovative CLIP-based Composition Quality Assessment (CCQA) model to assign pseudo labels to these images. The CCQA introduces a unique learnable text embedding technique to learn continuous word embeddings capable of discerning subtle visual quality differences in the range covered by five levels of quality description words {bad, poor, fair, good, perfect}. And finally we have developed a camera pose adjustment model (CPAM) which first determines if the current view can be further improved and if so it outputs the adjust suggestion in the form of two camera pose adjustment angles. The two tasks of CPAM make decisions in a sequential manner and each involves different sets of training samples, we have developed a mixture-of-experts model with a gated loss function to train the CPAM in an end-to-end manner. We will present extensive results to demonstrate the performances of our SPAS system using publicly available image composition datasets.
数百万人经常使用智能手机作为即拍即摄(PAS)相机拍照,然而很少有人具备拍摄好场景照片的摄影技巧。虽然传统的PAS相机内置功能可以确保照片对焦清晰、亮度合适,但它们无法告诉用户如何拍摄场景的最佳镜头。在本文中,我们首次提出了一种智能即拍即摄(SPAS)系统,以帮助用户拍摄优质照片。我们的SPAS系统通过自动指导用户实时调整相机姿势来帮助用户拍摄好场景的照片。我们首先构建了一个大型数据集,包含来自4000个场景的320K张带有相机姿势信息的图像。然后,我们开发了一种基于CLIP的创新性构图质量评估(CCQA)模型,为这些图像分配伪标签。CCQA引入了一种独特的可学习文本嵌入技术,学习连续的单词嵌入,能够辨别五个质量描述词所涵盖范围内的细微视觉质量差异{差、较差、一般、好、完美}。最后,我们开发了一个相机姿势调整模型(CPAM),该模型首先确定当前视图是否可以进一步改进,如果可以,则输出以两个相机姿势调整角度形式的调整建议。CPAM的两个任务是按顺序进行的,每个任务涉及不同的训练样本集,因此我们采用了一种带有门控损失函数的混合专家模型,以端到端的方式训练CPAM。我们将通过使用公开的图像构图数据集来全面展示SPAS系统的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR2025 Accepted
Summary
本文介绍了一种新型的智能点拍系统(SPAS),旨在帮助用户拍摄高质量的照片。该系统通过自动引导用户调整相机姿态来实现。研究者构建了一个大型图像数据集,并利用CLIP技术的组合质量评估模型对图像进行伪标签标注。此外,他们还开发了一种相机姿态调整模型(CPAM),可判断当前视角是否需要改进,并给出调整建议。通过公开可用的图像组合数据集,展示了SPAS系统的性能表现。
Key Takeaways
- SPAS系统旨在帮助用户拍摄高质量照片,通过自动引导调整相机姿态实现。
- 研究者构建了一个包含320K张图片的大型数据集,每张图片都有相机姿态信息。
- 采用了基于CLIP的组合质量评估模型(CCQA),为图像赋予伪标签,能辨别细微的视觉质量差异。
- CCQA模型采用连续词嵌入技术,覆盖“坏、差、一般、好、完美”五个质量描述等级。
- 开发了相机姿态调整模型(CPAM),能判断当前视角是否需要改进,并提供调整建议。
- CPAM采用混合专家模型和门控损失函数进行训练,实现端到端的训练。
点此查看论文截图

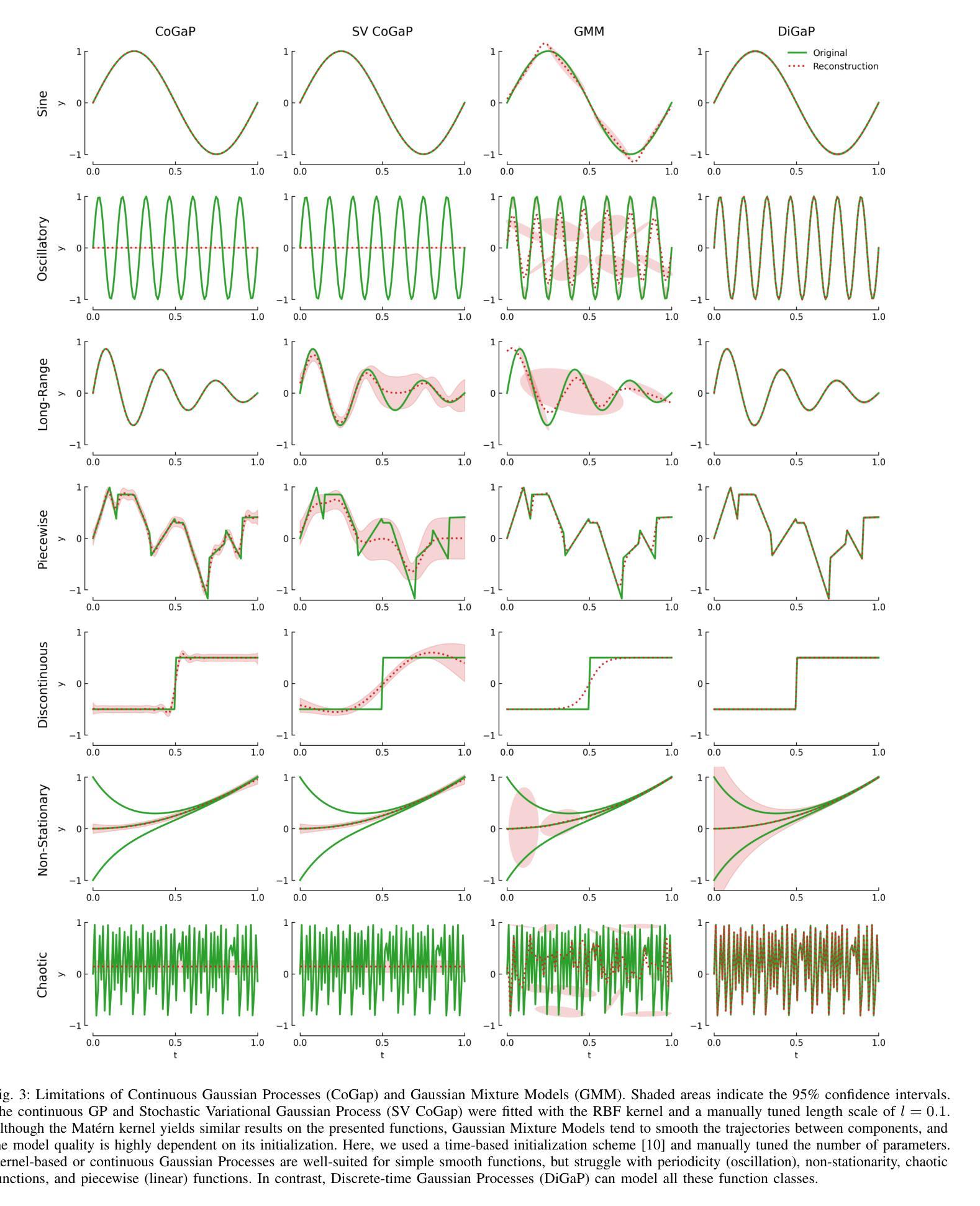
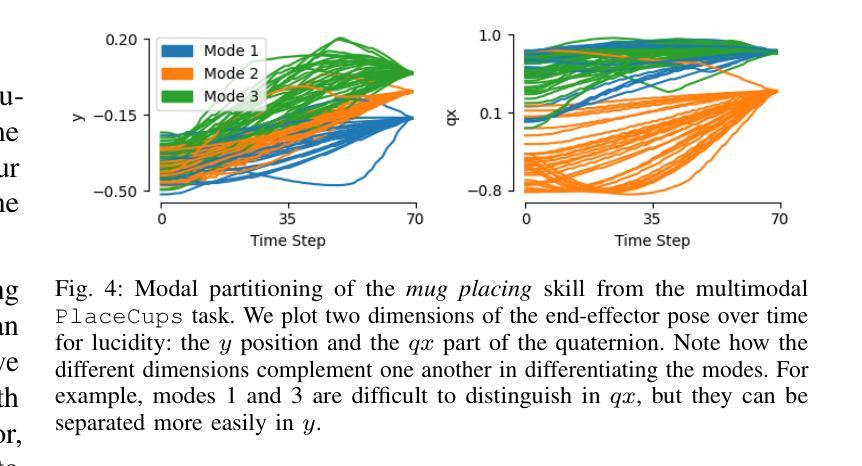
The Unreasonable Effectiveness of Discrete-Time Gaussian Process Mixtures for Robot Policy Learning
Authors:Jan Ole von Hartz, Adrian Röfer, Joschka Boedecker, Abhinav Valada
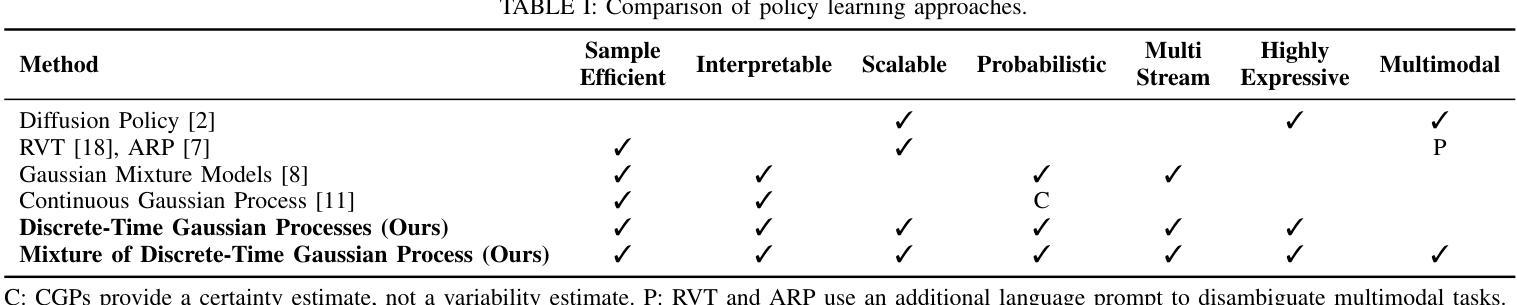
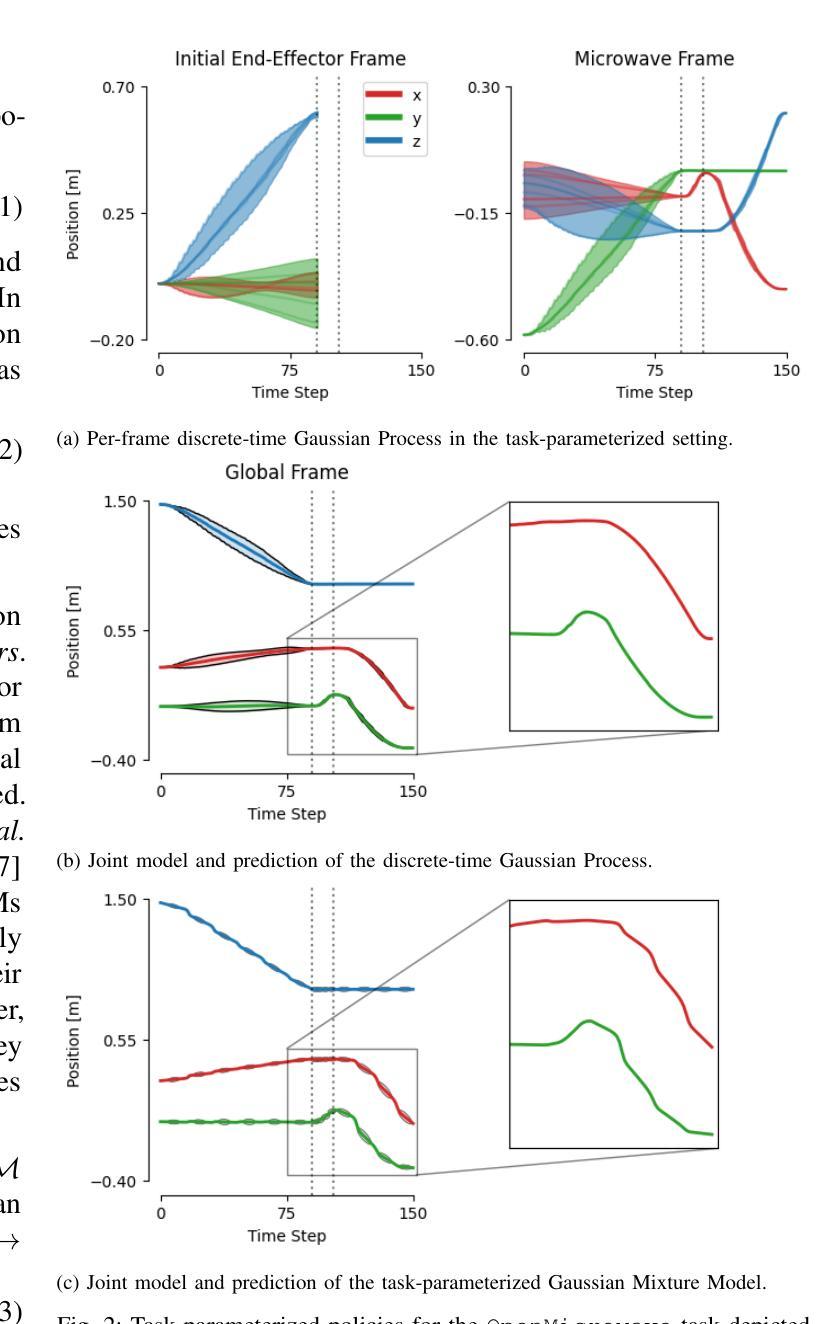
We present Mixture of Discrete-time Gaussian Processes (MiDiGap), a novel approach for flexible policy representation and imitation learning in robot manipulation. MiDiGap enables learning from as few as five demonstrations using only camera observations and generalizes across a wide range of challenging tasks. It excels at long-horizon behaviors such as making coffee, highly constrained motions such as opening doors, dynamic actions such as scooping with a spatula, and multimodal tasks such as hanging a mug. MiDiGap learns these tasks on a CPU in less than a minute and scales linearly to large datasets. We also develop a rich suite of tools for inference-time steering using evidence such as collision signals and robot kinematic constraints. This steering enables novel generalization capabilities, including obstacle avoidance and cross-embodiment policy transfer. MiDiGap achieves state-of-the-art performance on diverse few-shot manipulation benchmarks. On constrained RLBench tasks, it improves policy success by 76 percentage points and reduces trajectory cost by 67%. On multimodal tasks, it improves policy success by 48 percentage points and increases sample efficiency by a factor of 20. In cross-embodiment transfer, it more than doubles policy success. We make the code publicly available at https://midigap.cs.uni-freiburg.de.
我们提出了离散时间高斯过程混合(MiDiGap)方法,这是一种用于机器人操控中的灵活策略表示和模仿学习的新方法。MiDiGap能够从仅有的五个演示中学习,仅使用相机观察,并能广泛适应各种具有挑战性的任务。它擅长长远行为,如制作咖啡、高度约束的运动,如开门、动态动作,如用铲子铲东西以及多模式任务,如挂杯子。MiDiGap可以在CPU上学习这些任务不到一分钟的时间,并且线性扩展到大型数据集。我们还开发了一套丰富的工具,用于在推理时使用证据进行引导,如碰撞信号和机器人运动学约束。这种引导使新的泛化能力成为可能,包括避障和跨体态策略转移。MiDiGap在多样化的少样本操作基准测试中达到了最先进的性能。在受约束的RLBench任务中,它将策略成功率提高了76个百分点,轨迹成本降低了67%。在多模式任务中,它将策略成功率提高了48个百分点,提高了样本效率的20倍。在跨体态转移方面,它使策略成功率增加了一倍以上。我们的代码公开在https://midigap.cs.uni-freiburg.de。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted for publication to IEEE Transaction on Robotics
Summary
MiDiGap是一种用于机器人操作中的灵活策略表示和模仿学习的新方法。它能够从仅有的五个演示中学习,仅使用摄像头观察,并可以广泛适用于各种挑战任务。MiDiGap擅长处理长期行为、高度约束的运动、动态动作和多模式任务。其在CPU上的学习时间短于一分钟,并可线性扩展到大型数据集。此外,MiDiGap还开发了一套丰富的工具,用于基于证据进行推理时间控制,如碰撞信号和机器人运动学约束。这些控制功能带来了新颖的一般化能力,包括障碍避免和跨体态策略转移。MiDiGap在多样的少样本操作基准测试中达到了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- MiDiGap是一种用于机器人操作的新型策略表示和模仿学习方法。
- 它能够从仅有的五个演示中学习,仅使用摄像头观察。
- MiDiGap适用于各种挑战任务,包括长期行为、高度约束的运动、动态动作和多模式任务。
- MiDiGap在CPU上的学习时间短,并可快速扩展到大型数据集。
- MiDiGap提供丰富的工具进行推理时间控制,包括基于证据的控制功能。
- 这些控制功能带来了新颖的一般化能力,如障碍避免和跨体态策略转移。
点此查看论文截图

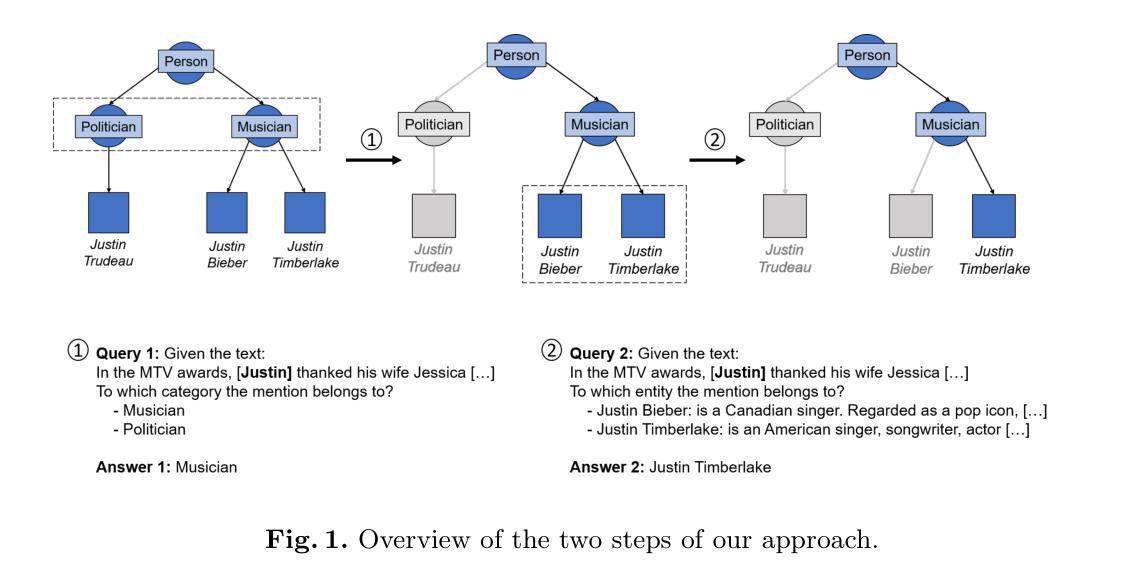
Knowledge Graphs for Enhancing Large Language Models in Entity Disambiguation
Authors:Gerard Pons, Besim Bilalli, Anna Queralt
Recent advances in Large Language Models (LLMs) have positioned them as a prominent solution for Natural Language Processing tasks. Notably, they can approach these problems in a zero or few-shot manner, thereby eliminating the need for training or fine-tuning task-specific models. However, LLMs face some challenges, including hallucination and the presence of outdated knowledge or missing information from specific domains in the training data. These problems cannot be easily solved by retraining the models with new data as it is a time-consuming and expensive process. To mitigate these issues, Knowledge Graphs (KGs) have been proposed as a structured external source of information to enrich LLMs. With this idea, in this work we use KGs to enhance LLMs for zero-shot Entity Disambiguation (ED). For that purpose, we leverage the hierarchical representation of the entities’ classes in a KG to gradually prune the candidate space as well as the entities’ descriptions to enrich the input prompt with additional factual knowledge. Our evaluation on popular ED datasets shows that the proposed method outperforms non-enhanced and description-only enhanced LLMs, and has a higher degree of adaptability than task-specific models. Furthermore, we conduct an error analysis and discuss the impact of the leveraged KG’s semantic expressivity on the ED performance.
最近的大型语言模型(LLM)的进步使它们成为自然语言处理任务的重要解决方案。值得注意的是,它们可以以零次或多次少量的方式解决问题,从而无需针对特定任务进行训练或微调模型。然而,LLM面临一些挑战,包括虚构和训练数据中特定领域的知识过时或缺失信息等问题。这些问题无法通过用新数据重新训练模型来轻松解决,因为这是一个耗时且昂贵的过程。为了缓解这些问题,知识图谱(KG)已被提议作为结构化的外部信息源来丰富LLM。基于这一理念,在这项工作中,我们使用知识图谱来增强LLM的零次实体消歧(ED)。为此,我们借助知识图谱中实体类别的层次表示来逐步缩小候选空间,并利用实体的描述来丰富输入提示以获取额外的事实知识。我们在流行的ED数据集上的评估表明,所提出的方法优于非增强型和仅描述增强的LLM,并且比特定任务的模型具有更高的适应性。此外,我们进行了错误分析,并讨论了所利用的知识图谱的语义表达力对ED性能的影响。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Pre-print submitted to ISWC 2024
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在自然语言处理任务中表现出显著的优势,尤其在零样本或少样本场景下表现突出。然而,LLM面临知识过时、缺失或幻觉等问题。为解决这些问题,利用知识图谱(KG)作为结构化外部信息源来丰富LLM成为一项解决方案。本研究采用知识图谱增强LLM进行零样本实体消歧(ED),通过利用知识图谱中实体类别的层次表示,逐步缩小候选空间,并借助实体描述来丰富输入提示中的事实知识。在流行ED数据集上的评估显示,该方法优于非增强和仅描述增强的LLM,且具有比特定任务模型更高的适应性。此外,还进行了误差分析,并讨论了所用知识图谱的语义表达能力对ED性能的影响。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)可在自然语言处理任务中表现优异,尤其在零样本或少样本情境下。
- LLM面临知识过时、缺失和幻觉等问题。
- 知识图谱(KG)可作为结构化外部信息源,用于增强LLM的性能。
- 本研究利用知识图谱进行实体消歧(ED),结合实体类别层次表示和实体描述来丰富输入提示。
- 在流行ED数据集上的评估显示,该方法优于其他LLM,且具有高适应性。
- 知识图谱的语义表达能力对实体消歧性能有影响。
点此查看论文截图

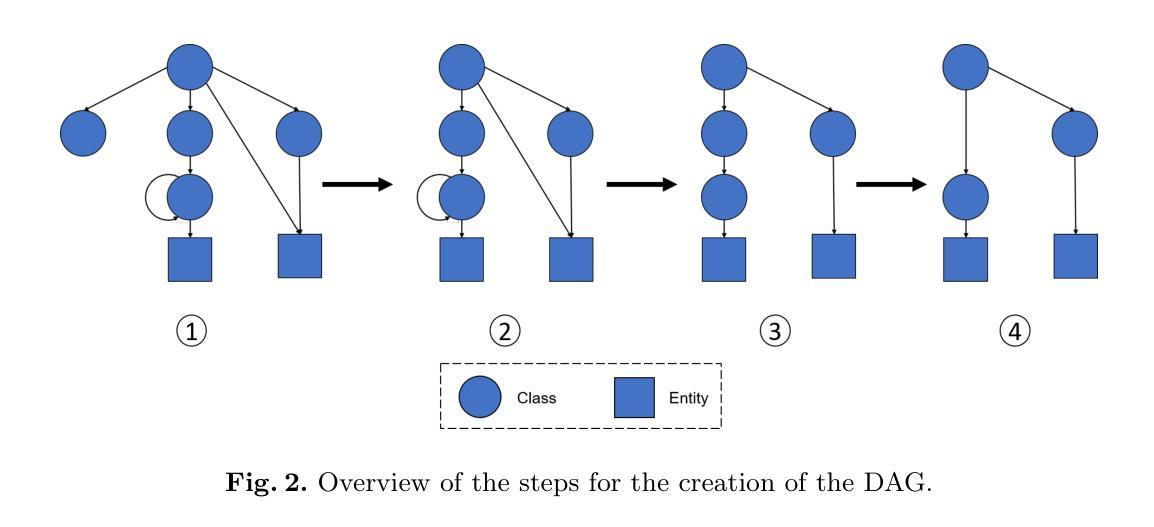
Identifying Legal Holdings with LLMs: A Systematic Study of Performance, Scale, and Memorization
Authors:Chuck Arvin
As large language models (LLMs) continue to advance in capabilities, it is essential to assess how they perform on established benchmarks. In this study, we present a suite of experiments to assess the performance of modern LLMs (ranging from 3B to 90B+ parameters) on CaseHOLD, a legal benchmark dataset for identifying case holdings. Our experiments demonstrate ``scaling effects’’ - performance on this task improves with model size, with more capable models like GPT4o and AmazonNovaPro achieving macro F1 scores of 0.744 and 0.720 respectively. These scores are competitive with the best published results on this dataset, and do not require any technically sophisticated model training, fine-tuning or few-shot prompting. To ensure that these strong results are not due to memorization of judicial opinions contained in the training data, we develop and utilize a novel citation anonymization test that preserves semantic meaning while ensuring case names and citations are fictitious. Models maintain strong performance under these conditions (macro F1 of 0.728), suggesting the performance is not due to rote memorization. These findings demonstrate both the promise and current limitations of LLMs for legal tasks with important implications for the development and measurement of automated legal analytics and legal benchmarks.
随着大型语言模型(LLM)的能力不断提升,评估它们在现有基准测试上的表现变得至关重要。本研究呈现了一系列实验,旨在评估现代LLM(参数范围从3B到90B+)在CaseHOLD这一法律基准数据集上的表现,该数据集用于识别判例法摘要。我们的实验展示了“规模效应”——在此任务上的表现会随着模型规模的扩大而提高,更强大的模型如GPT4o和AmazonNovaPro分别取得了宏观F1分数为0.744和0.720。这些分数与该数据集上已发布的最佳结果具有竞争力,并且不需要任何技术复杂模型的训练、微调或少样本提示。为确保这些强有力的结果并非由于训练数据中司法意见的刻板记忆所致,我们开发并采用了新型的引用匿名测试,该测试保留了语义含义,同时确保了案例名称和引用的虚构性。在这些条件下,模型保持了强大的性能(宏观F1为0.728),这表明其表现并非由于死记硬背。这些发现展示了LLM在法律任务上的潜力以及当前存在的局限性,对于自动化法律分析和法律基准的开发与衡量具有重要的影响。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Presented as a short paper at International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Law 2025 (Chicago, IL)
Summary
现代大型语言模型(LLM)在法律任务上的性能评估至关重要。本研究通过一系列实验,评估了不同规模LLM在CaseHOLD数据集上的表现。实验结果显示模型性能随规模提升而改善,GPT4o和AmazonNovaPro等大型模型表现出优异的性能。这些结果具有竞争力,且无需复杂模型训练、微调或少样本提示。通过新型引用匿名化测试,确保模型性能并非仅因记忆训练数据中的司法意见而达成。这一研究为自动化法律分析和法律基准的开发和评估提供了重要启示。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在法律任务性能评估中表现出规模效益,性能随模型规模提升而改善。
- GPT4o和AmazonNovaPro等模型在CaseHOLD数据集上的表现优异,宏观F1分数高且具有竞争力。
- 最佳模型性能不需要复杂的模型训练、微调或少样本提示。
- 通过引用匿名化测试验证了模型性能并非仅基于训练数据的记忆。
- 模型在法律任务上的表现显示自动化法律分析的潜力和当前局限性。
- 该研究对开发和应用法律基准的未来发展有重要意义。
点此查看论文截图



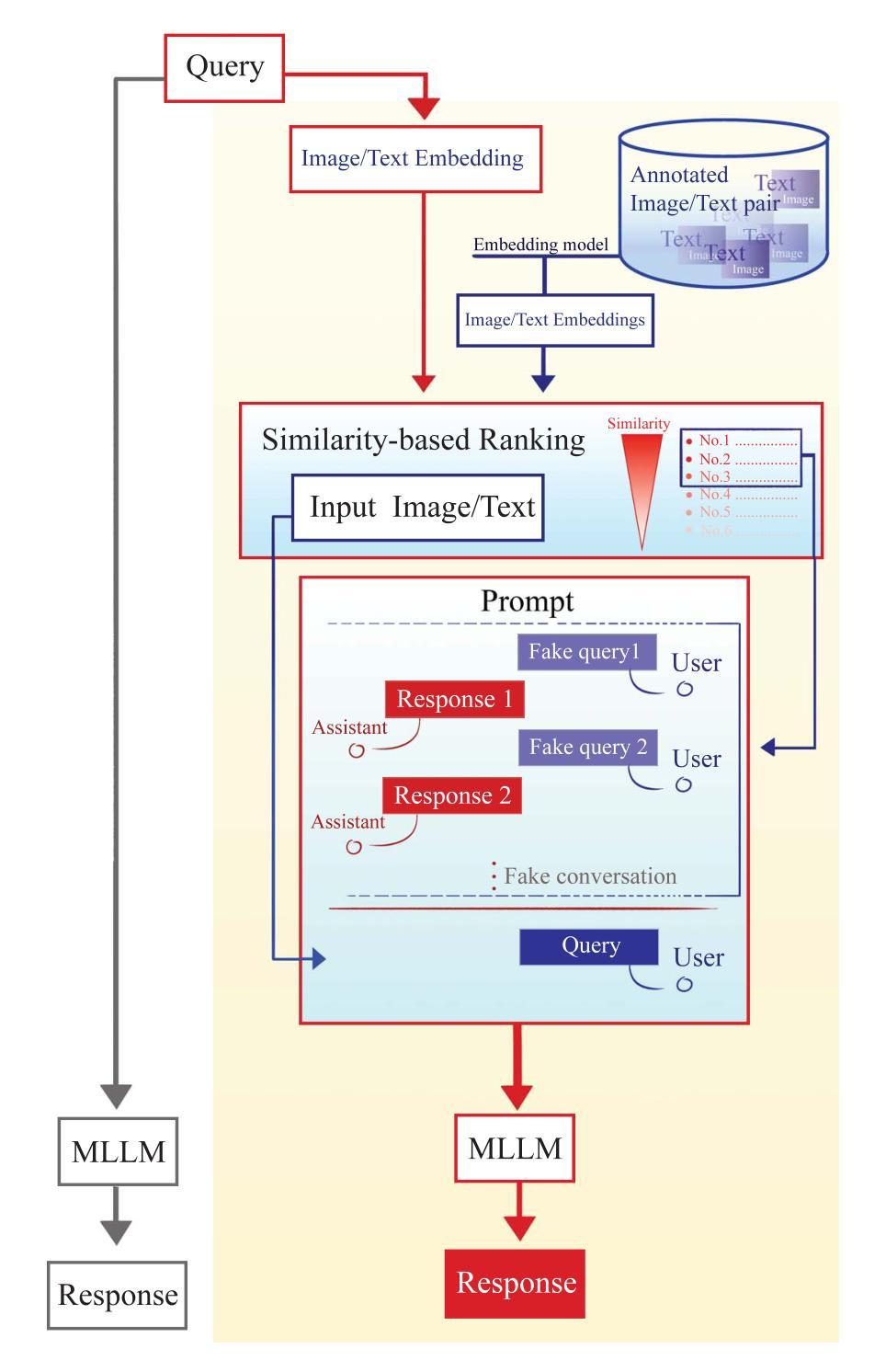
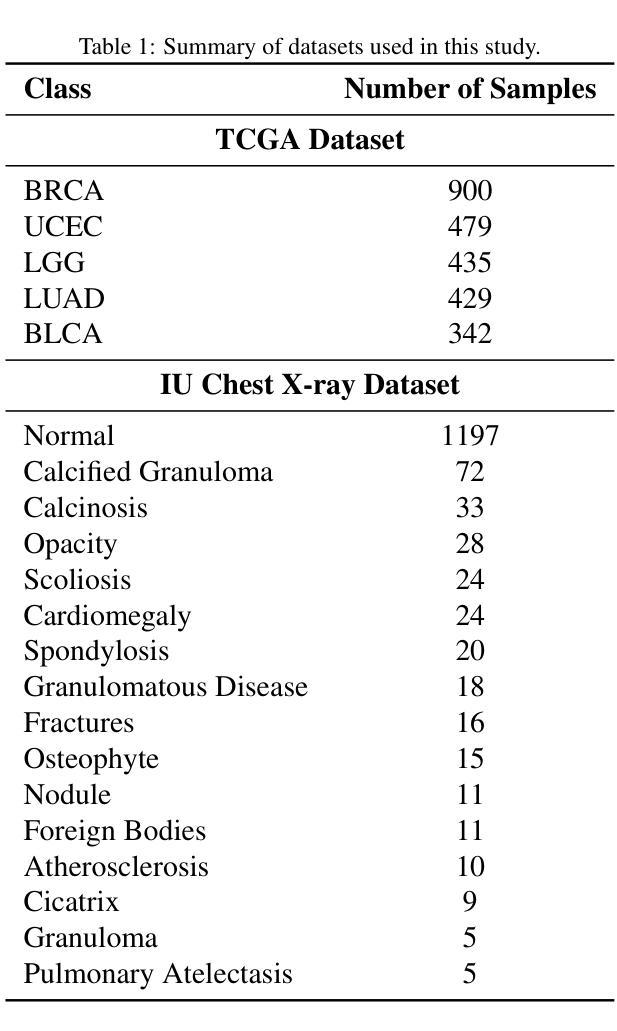
Retrieval-augmented in-context learning for multimodal large language models in disease classification
Authors:Zaifu Zhan, Shuang Zhou, Xiaoshan Zhou, Yongkang Xiao, Jun Wang, Jiawen Deng, He Zhu, Yu Hou, Rui Zhang
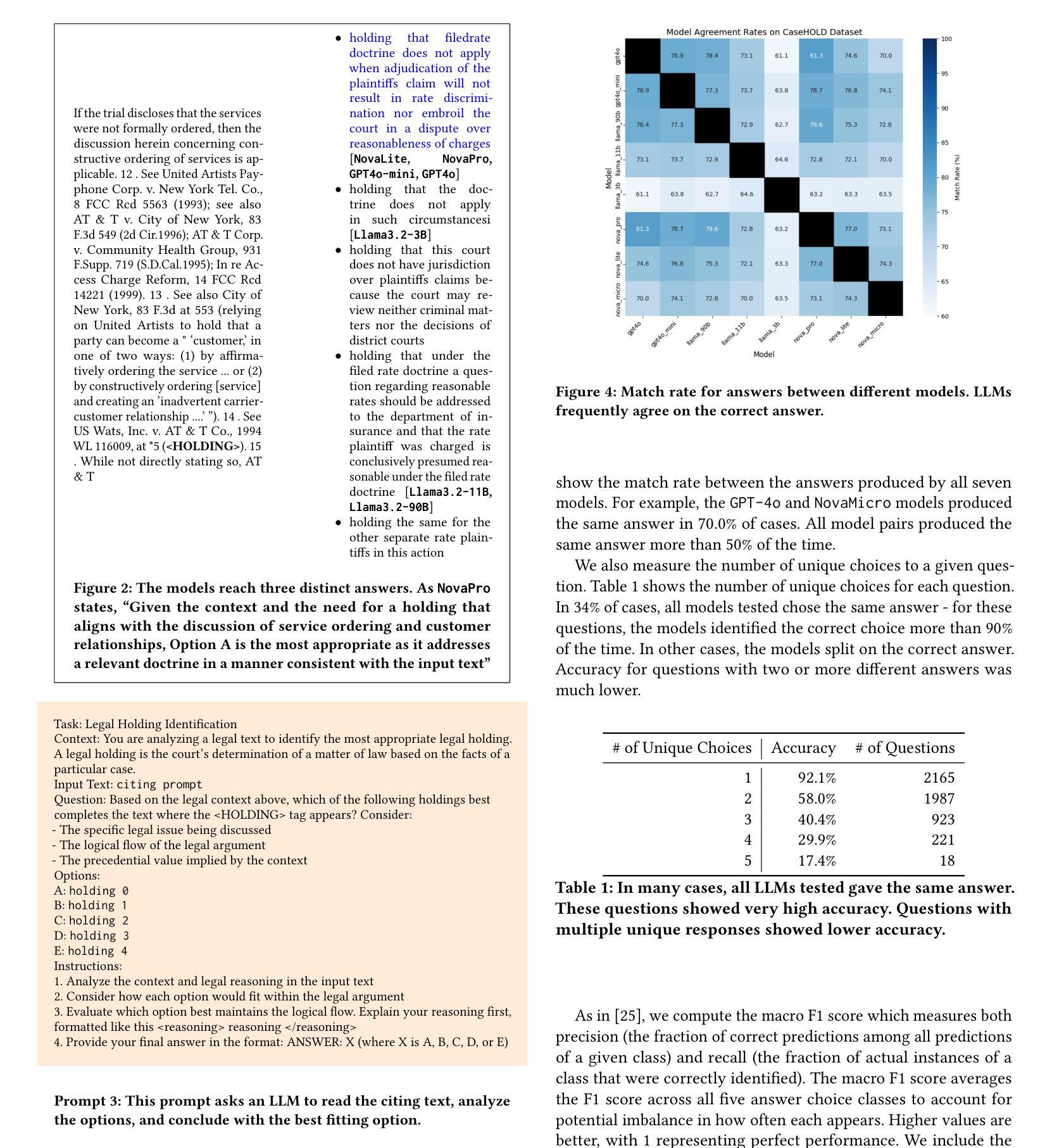
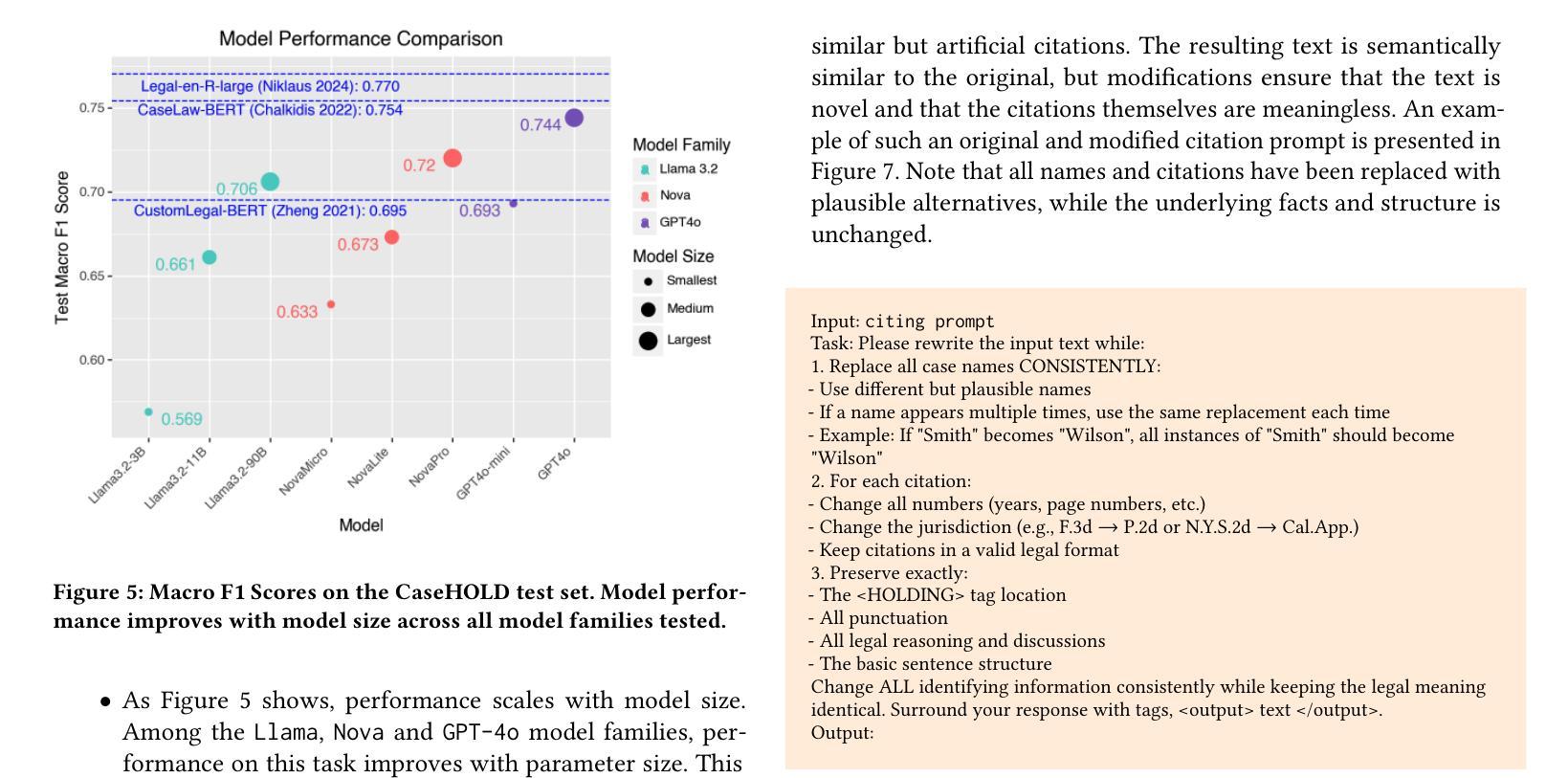
Objectives: We aim to dynamically retrieve informative demonstrations, enhancing in-context learning in multimodal large language models (MLLMs) for disease classification. Methods: We propose a Retrieval-Augmented In-Context Learning (RAICL) framework, which integrates retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) and in-context learning (ICL) to adaptively select demonstrations with similar disease patterns, enabling more effective ICL in MLLMs. Specifically, RAICL examines embeddings from diverse encoders, including ResNet, BERT, BioBERT, and ClinicalBERT, to retrieve appropriate demonstrations, and constructs conversational prompts optimized for ICL. We evaluated the framework on two real-world multi-modal datasets (TCGA and IU Chest X-ray), assessing its performance across multiple MLLMs (Qwen, Llava, Gemma), embedding strategies, similarity metrics, and varying numbers of demonstrations. Results: RAICL consistently improved classification performance. Accuracy increased from 0.7854 to 0.8368 on TCGA and from 0.7924 to 0.8658 on IU Chest X-ray. Multi-modal inputs outperformed single-modal ones, with text-only inputs being stronger than images alone. The richness of information embedded in each modality will determine which embedding model can be used to get better results. Few-shot experiments showed that increasing the number of retrieved examples further enhanced performance. Across different similarity metrics, Euclidean distance achieved the highest accuracy while cosine similarity yielded better macro-F1 scores. RAICL demonstrated consistent improvements across various MLLMs, confirming its robustness and versatility. Conclusions: RAICL provides an efficient and scalable approach to enhance in-context learning in MLLMs for multimodal disease classification.
目标:我们的目标是动态检索信息丰富的演示内容,以增强多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的上下文学习,用于疾病分类。方法:我们提出了一个名为RAICL(检索增强上下文学习)的框架,它结合了检索增强生成(RAG)和上下文学习(ICL),以自适应地选择具有相似疾病模式的演示内容,使MLLMs中的ICL更加有效。具体来说,RAICL会检查来自不同编码器的嵌入,包括ResNet、BERT、BioBERT和ClinicalBERT,以检索适当的演示内容,并构建针对ICL优化的对话提示。我们在两个真实世界的多模态数据集(TCGA和IU Chest X射线)上评估了框架的性能,评估其在多个MLLMs(Qwen、Llava、Gemma)、嵌入策略、相似度指标和不同数量的演示内容方面的表现。结果:RAICL持续提高了分类性能。TCGA上的准确率从0.7854提高到0.8368,IU Chest X射线上的准确率从0.7924提高到0.8658。多模态输入优于单模态输入,文本输入的效能强于图像。每种模态中嵌入的信息丰富程度将决定使用哪种嵌入模型可以获得更好的结果。少量样本的实验表明,增加检索到的示例数量可以进一步提高性能。在不同的相似度指标中,欧几里得距离实现了最高的准确率,而余弦相似度获得了更好的宏观F1分数。RAICL在各种MLLMs中表现出持续的性能改进,证明了其稳健性和通用性。结论:RAICL为多模态疾病分类在MLLMs中的上下文学习提供了一种高效且可扩展的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 Pages, 1 figure, 7 tables
Summary
本文旨在通过动态检索有信息量的演示示例,提高多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在疾病分类方面的上下文学习能力。提出了一种名为RAICL的检索增强上下文学习框架,该框架结合了检索增强生成(RAG)和上下文学习(ICL),可自适应地选择具有相似疾病模式的演示示例,从而更有效地在多模态大型语言模型中进行上下文学习。在真实世界的多模态数据集TCGA和IU Chest X-ray上的实验表明,RAICL提高了分类性能,并且在不同的多模态大型语言模型、嵌入策略、相似度度量以及不同数量的演示示例中都表现出了优越性。这表明RAICL是一个有效且可扩展的方法,可提高多模态大型语言模型在疾病分类方面的上下文学习能力。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种新的检索增强上下文学习(RAICL)框架,旨在提高多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在疾病分类方面的上下文学习能力。
- 结合了检索增强生成(RAG)和上下文学习(ICL),通过自适应选择演示示例来增强学习。
- 在真实世界的多模态数据集TCGA和IU Chest X-ray上的实验表明,RAICL能提高疾病分类的性能。
- 多模态输入优于单模态输入,文本输入比图像输入更有效。
- 不同嵌入模型的效果取决于其所嵌入信息的丰富程度。
- 增加检索到的示例数量能进一步提高性能。
点此查看论文截图

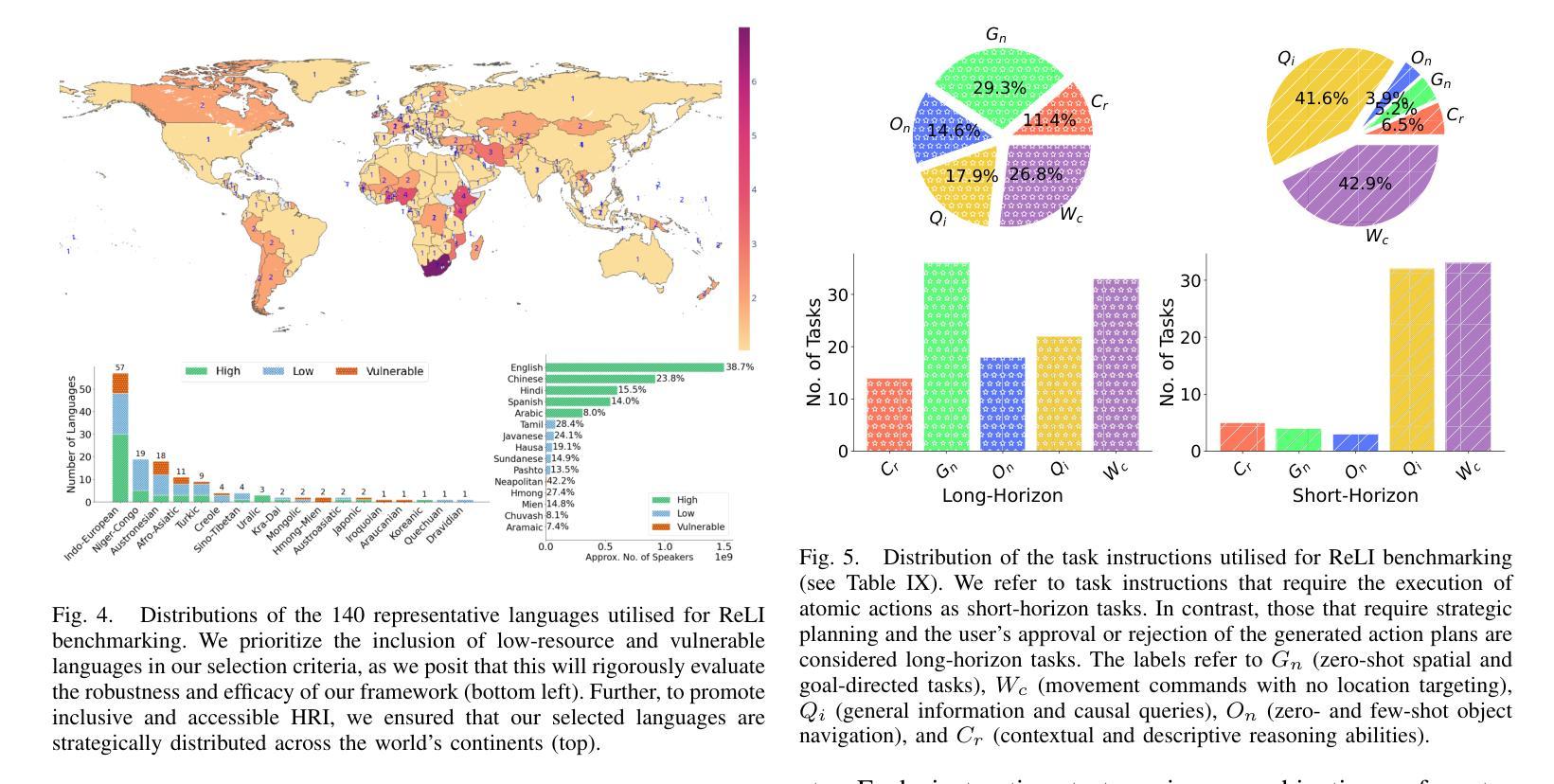
ReLI: A Language-Agnostic Approach to Human-Robot Interaction
Authors:Linus Nwankwo, Bjoern Ellensohn, Ozan Özdenizci, Elmar Rueckert
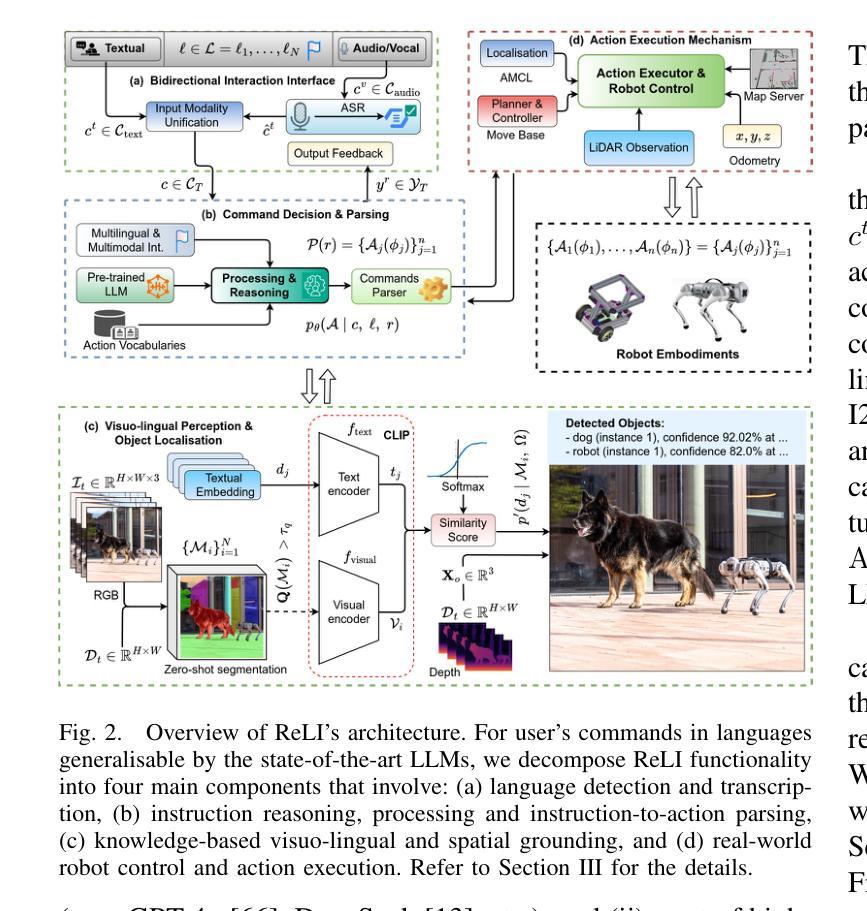
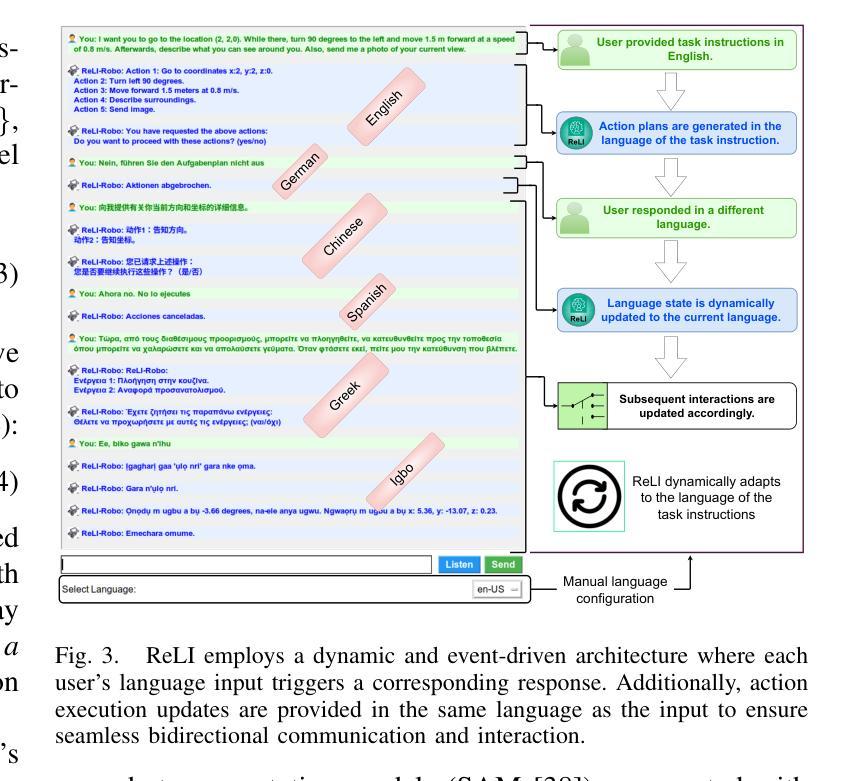
Adapting autonomous agents to industrial, domestic, and other daily tasks is currently gaining momentum. However, in the global or cross-lingual application contexts, ensuring effective interaction with the environment and executing unrestricted human task-specified instructions in diverse languages remains an unsolved problem. To address this challenge, we propose ReLI, a language-agnostic framework designed to enable autonomous agents to converse naturally, semantically reason about the environment, and to perform downstream tasks, regardless of the task instruction’s linguistic origin. First, we ground large-scale pre-trained foundation models and transform them into language-to-action models that can directly provide common-sense reasoning and high-level robot control through natural, free-flow human-robot conversational interactions. Further, we perform cross-lingual grounding of the models to ensure that ReLI generalises across the global languages. To demonstrate the ReLI’s robustness, we conducted extensive simulated and real-world experiments on various short- and long-horizon tasks, including zero-shot and few-shot spatial navigation, scene information retrieval, and query-oriented tasks. We benchmarked the performance on 140 languages involving over 70K multi-turn conversations. On average, ReLI achieved over 90%$\pm$0.2 accuracy in cross-lingual instruction parsing and task execution success rates. These results demonstrate the ReLI’s potential to enhance natural human-robot interaction in the real world while championing linguistic diversity. Demonstrations and resources will be publicly available at https://linusnep.github.io/ReLI/.
目前,将自主智能体适应于工业、家居和其他日常任务正在获得动力。然而,在全球或跨语言的应用场景中,确保与环境的有效互动并执行多样语言的非限制性人类任务指定指令仍是一个未解决的问题。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了ReLI,这是一个与语言无关的框架,旨在使自主智能体能够进行自然对话、对周围环境进行语义推理并执行下游任务,而无论任务指令的语言起源如何。首先,我们基于大规模预训练基础模型,将其转化为语言到行动模型,这些模型可以通过自然、流畅的人机对话互动,直接提供常识推理和高级机器人控制。此外,我们进行了跨语言模型接地,以确保ReLI在全球范围内推广各种语言。为了证明ReLI的稳健性,我们在各种短期和长期任务上进行了广泛的模拟和真实实验,包括零样本和少量样本的空间导航、场景信息检索和查询导向任务。我们在涉及超过7万多次对话的140种语言上进行了基准测试。平均而言,ReLI在跨语言指令解析和任务执行成功率方面达到了超过90%±0.2的准确率。这些结果证明了ReLI在实际世界中增强自然人机交互的潜力,同时支持语言多样性。演示和资源将在https://linusnep.github.io/ReLI/上公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一个名为ReLI的语言通用框架,它能实现自主代理在自然环境下进行交流、理解环境并进行下游任务操作,而无需受到任务指令语言来源的限制。该框架通过大型预训练基础模型建立语言到行动模型,支持自由流式的人机对话互动和机器人控制。经过跨语言训练,ReLI可推广到全球多种语言。实验结果显示,ReLI在多种短期和长期任务上表现出强大的稳健性,成功执行跨语言指令的准确率达到90%以上。
Key Takeaways
- ReLI是一个语言通用的框架,旨在使自主代理能够在各种环境下自然地交流、理解环境并执行任务,不受任务指令语言来源的限制。
- ReLI通过建立语言到行动模型,支持自由流式的人机对话互动和机器人控制。
- ReLI通过大型预训练基础模型实现,具备通用性和强大的学习能力。
- ReLI经过跨语言训练,可以推广到全球多种语言,增强了其在实际应用中的普适性。
- ReLI在模拟和真实世界的实验中表现出强大的稳健性,特别是在零基础和少量样本的空间导航、场景信息检索和查询导向任务中。
- ReLI在跨语言指令解析和任务执行方面的准确率超过90%,证明了其有效性和实用性。
点此查看论文截图

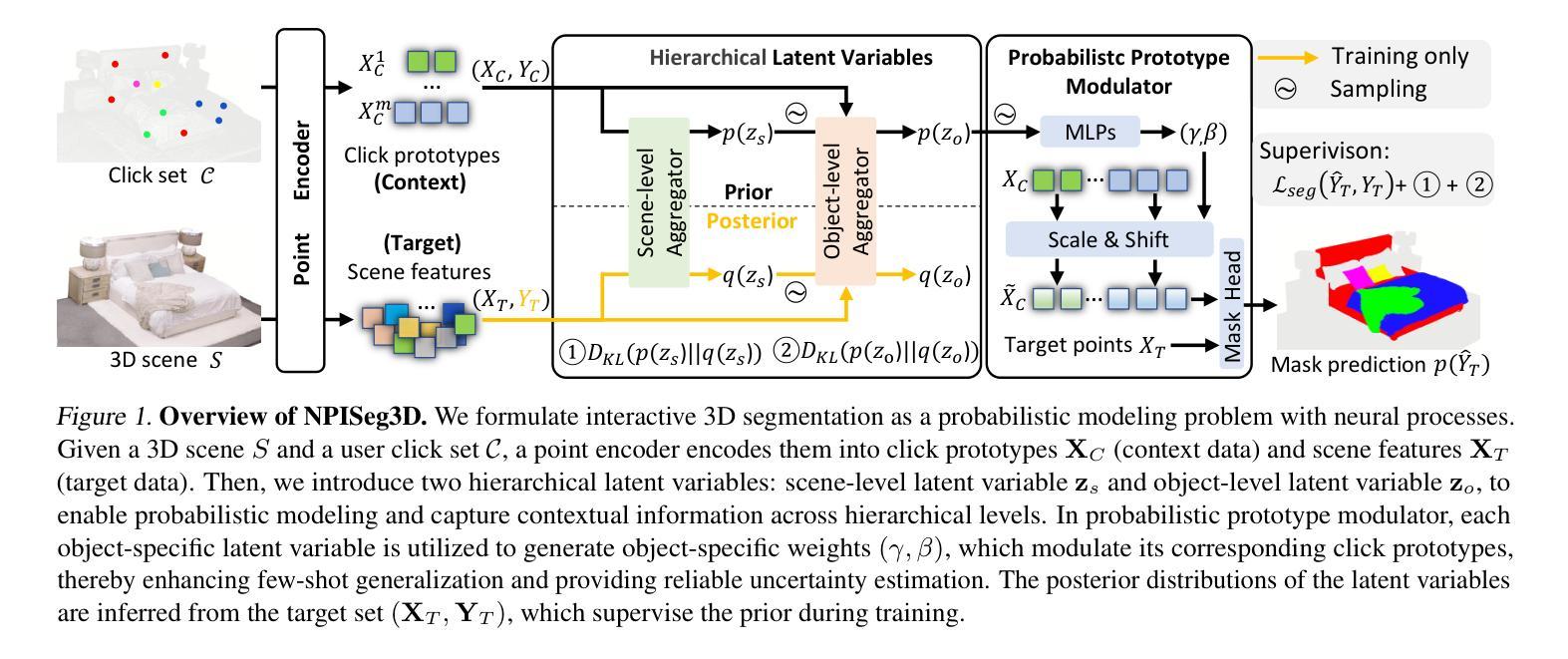
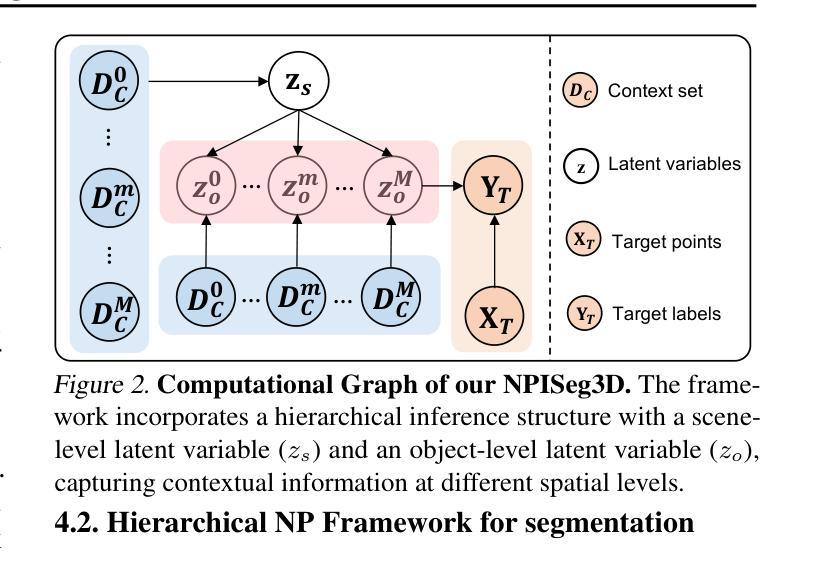
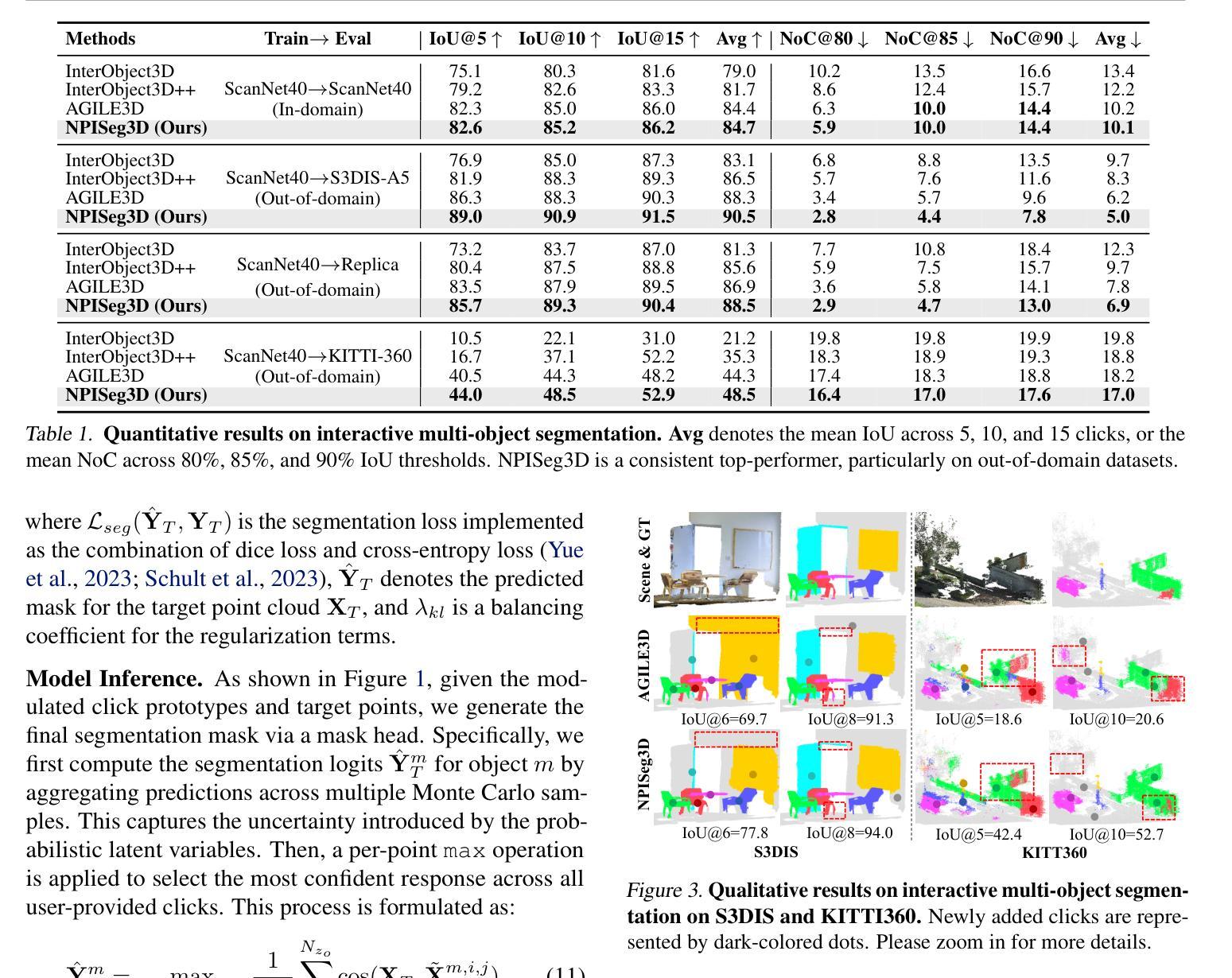
Probabilistic Interactive 3D Segmentation with Hierarchical Neural Processes
Authors:Jie Liu, Pan Zhou, Zehao Xiao, Jiayi Shen, Wenzhe Yin, Jan-Jakob Sonke, Efstratios Gavves
Interactive 3D segmentation has emerged as a promising solution for generating accurate object masks in complex 3D scenes by incorporating user-provided clicks. However, two critical challenges remain underexplored: (1) effectively generalizing from sparse user clicks to produce accurate segmentation, and (2) quantifying predictive uncertainty to help users identify unreliable regions. In this work, we propose NPISeg3D, a novel probabilistic framework that builds upon Neural Processes (NPs) to address these challenges. Specifically, NPISeg3D introduces a hierarchical latent variable structure with scene-specific and object-specific latent variables to enhance few-shot generalization by capturing both global context and object-specific characteristics. Additionally, we design a probabilistic prototype modulator that adaptively modulates click prototypes with object-specific latent variables, improving the model’s ability to capture object-aware context and quantify predictive uncertainty. Experiments on four 3D point cloud datasets demonstrate that NPISeg3D achieves superior segmentation performance with fewer clicks while providing reliable uncertainty estimations.
交互式3D分割技术通过结合用户提供的点击,在复杂的3D场景中生成精确的对象掩模方面展现出了巨大的潜力。然而,还有两大挑战尚未得到充分探索:(1)如何从稀疏的用户点击中有效泛化以产生精确的分割;(2)量化预测不确定性,以帮助用户识别不可靠的区域。在这项工作中,我们提出了NPISeg3D,这是一个新的概率框架,它基于神经过程(NPs)来解决这些挑战。具体来说,NPISeg3D引入了一种分层潜在变量结构,包括场景特定和对象特定的潜在变量,通过捕捉全局上下文和对象特定特征,增强少样本泛化能力。此外,我们设计了一个概率原型调制器,它自适应地利用对象特定的潜在变量调制点击原型,提高了模型捕捉对象感知上下文和量化预测不确定性的能力。在四个3D点云数据集上的实验表明,NPISeg3D在点击次数较少的情况下实现了优越的分割性能,同时提供了可靠的不确定性估计。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML 2025 Proceedings
Summary
基于用户点击的交互式三维分割技术为复杂三维场景中的精确对象掩模生成提供了有前景的解决方案。然而,两个关键问题尚未得到充分研究:(1)如何从稀疏的用户点击中有效泛化以产生精确的分割;(2)量化预测不确定性以帮助用户识别不可靠区域。本研究提出了NPISeg3D,一个基于神经过程(NPs)的新型概率框架,旨在解决这些问题。NPISeg3D引入了一种分层潜在变量结构,通过捕捉全局上下文和对象特定特征来增强小样本泛化能力。此外,设计了一种概率原型调制器,能够自适应地调整点击原型与对象特定的潜在变量,提高了模型捕捉对象感知上下文和量化预测不确定性的能力。在四个三维点云数据集上的实验表明,NPISeg3D在点击次数较少的情况下实现了优越的分割性能,同时提供了可靠的不确定性估计。
Key Takeaways
- 交互式三维分割技术通过结合用户点击,为复杂三维场景中的精确对象掩模生成提供了有效方法。
- 目前该技术面临两个挑战:从稀疏的用户点击中有效泛化以及量化预测不确定性。
- NPISeg3D是一个基于神经过程的概率框架,旨在解决上述挑战。
- NPISeg3D通过引入分层潜在变量结构,增强了小样本泛化能力,捕捉全局和局部特征。
- NPISeg3D设计的概率原型调制器能自适应调整点击原型与对象特定潜在变量,提高对象感知上下文的捕捉能力。
- 实验证明NPISeg3D在三维点云数据集上实现了优越性能,点击次数少且提供可靠的不确定性估计。
- NPISeg3D为用户与三维场景的交互提供了新的视角和工具,有望推动三维分割技术的发展。
点此查看论文截图

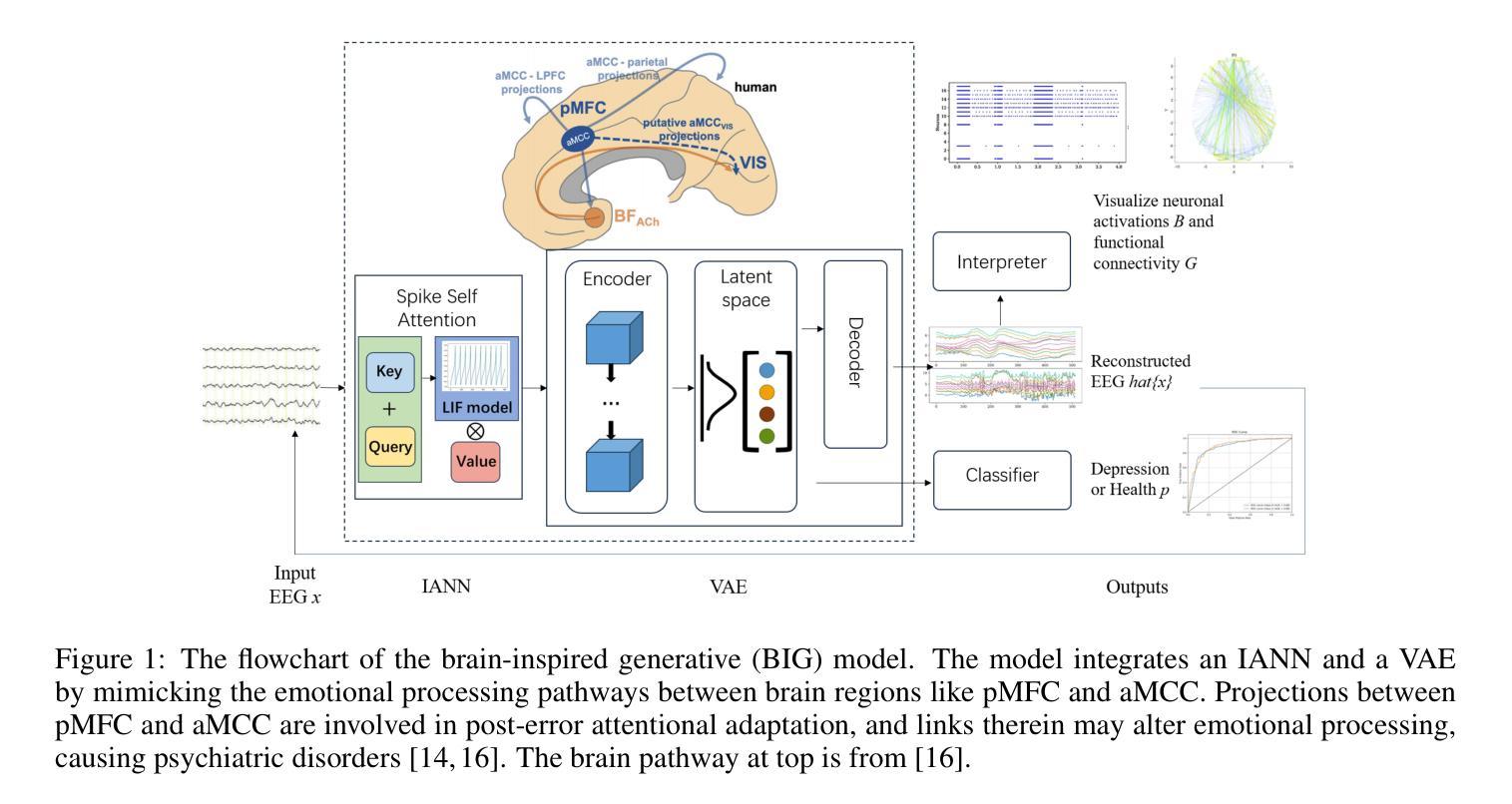
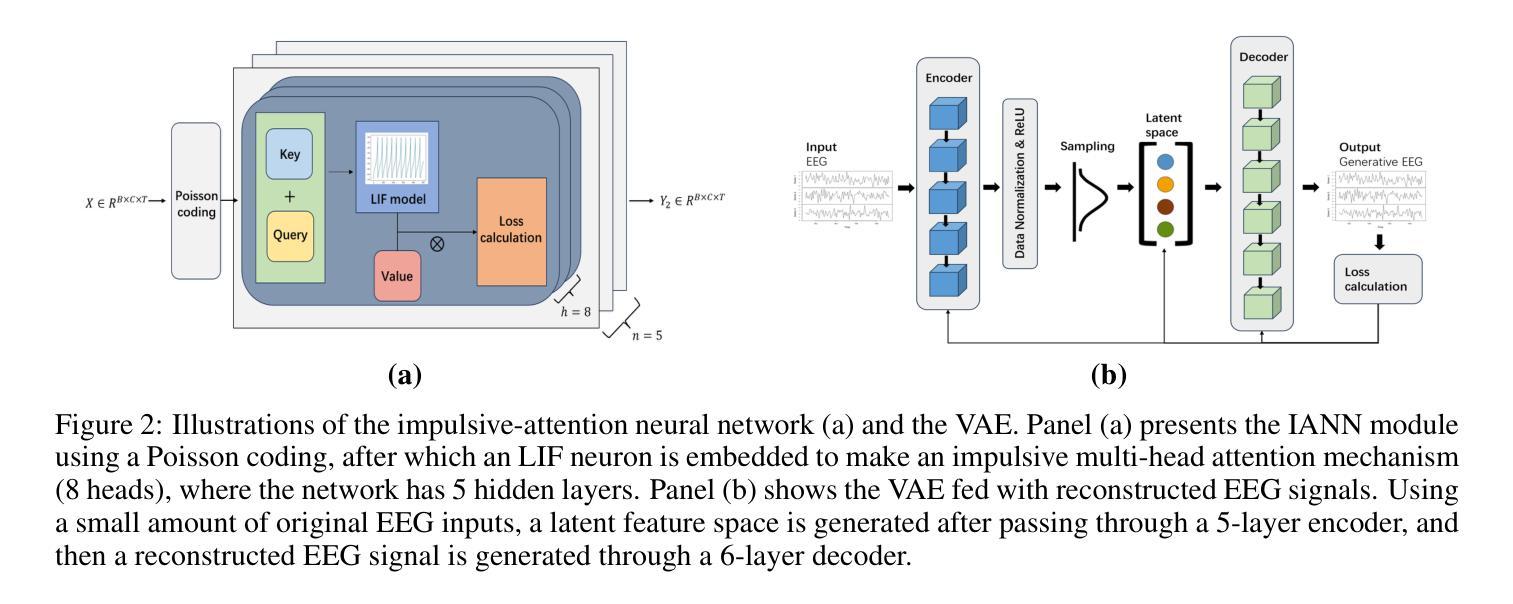
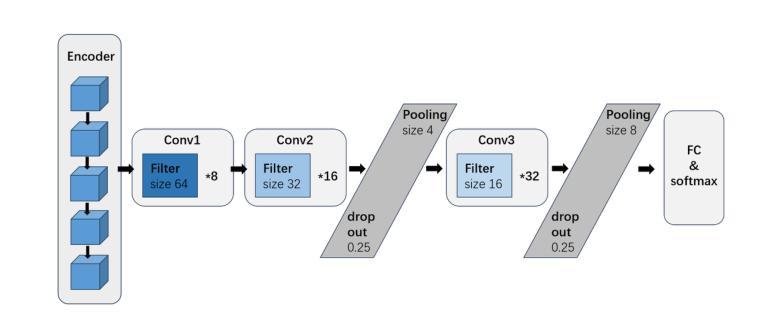
A brain-inspired generative model for EEG-based cognitive state identification
Authors:Bin Hu, Zhi-Hong Guan
This article proposes a brain-inspired generative (BIG) model that merges an impulsive-attention neural network and a variational autoencoder (VAE) for identifying cognitive states based on electroencephalography (EEG) data. A hybrid learning method is presented for training the model by integrating gradient-based learning and heteroassociative memory. The BIG model is capable of achieving multi-task objectives: classification, generating new EEG, and brain network interpretation, alleviating the limitations of excessive data training and high computational cost in conventional approaches. Experimental results on two public EEG datasets demonstrate that the BIG model achieves a classification accuracy above 89%, comparable with state-of-the-art methods, while reducing computational cost by nearly 11% over the baseline EEGNet. Incorporating the generated EEG data for training, the BIG model exhibits comparative performance in a few-shot pattern.Ablation studies justify the poised brain-inspired characteristic regarding the impulsive-attention module and the hybrid learning method. Thanks to the performance advantages with interpretable outputs, this BIG model has application potential for building digital twins of the brain.
本文提出了一种受大脑启发的生成(BIG)模型,该模型结合了冲动性注意神经网络和变分自编码器(VAE),可根据脑电图(EEG)数据识别认知状态。文章提出了一种混合学习方法来训练模型,将基于梯度的学习与异联想记忆相结合。BIG模型能够实现多任务目标:分类、生成新的EEG数据和解释脑网络,从而缓解传统方法中过度数据训练和计算成本过高的局限性。在两个公共EEG数据集上的实验结果表明,BIG模型的分类准确率高于89%,与最新方法相当,同时较基线EEGNet降低了近11%的计算成本。通过利用生成的EEG数据进行训练,BIG模型在少量样本情况下表现出相当的性能。通过消融研究验证了冲动性注意模块和混合学习方法在大脑启发特性方面的合理性。由于具有可解释的输出和性能优势,因此该BIG模型在构建大脑的数字化双胞胎方面具有应用潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种受大脑启发的生成(BIG)模型,该模型结合了冲动注意力神经网络和变分自编码器(VAE),用于基于脑电图(EEG)数据识别认知状态。文章展示了通过梯度学习和异联想记忆集成进行模型训练的混合学习方法。BIG模型能够完成多任务目标:分类、生成新的EEG数据和解释脑网络,缓解传统方法中过度数据训练和计算成本高昂的限制。在公共EEG数据集上的实验结果表明,BIG模型的分类准确率高于89%,与最新技术相当,且较基线EEGNet降低了近11%的计算成本。使用生成的EEG数据进行训练,BIG模型在少数样本模式中也表现出相当的性能。消融研究验证了冲动注意力模块和混合学习方法的稳健性。由于具有可解释的输出和性能优势,BIG模型在构建大脑的数字化双胞胎方面具有应用潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 文章提出了一种新的受大脑启发的生成(BIG)模型,融合了冲动注意力神经网络和变分自编码器(VAE)。
- BIG模型能够处理多任务,包括分类、生成新的EEG数据和解释脑网络。
- 模型通过混合学习方法进行训练,结合了梯度学习和异联想记忆。
- 在公共EEG数据集上的实验表明,BIG模型分类准确率高于89%,并降低了计算成本。
- 使用生成的EEG数据进行训练时,BIG模型在少数样本情况下表现出良好的性能。
- 消融研究验证了冲动注意力模块和混合学习方法的必要性。
点此查看论文截图

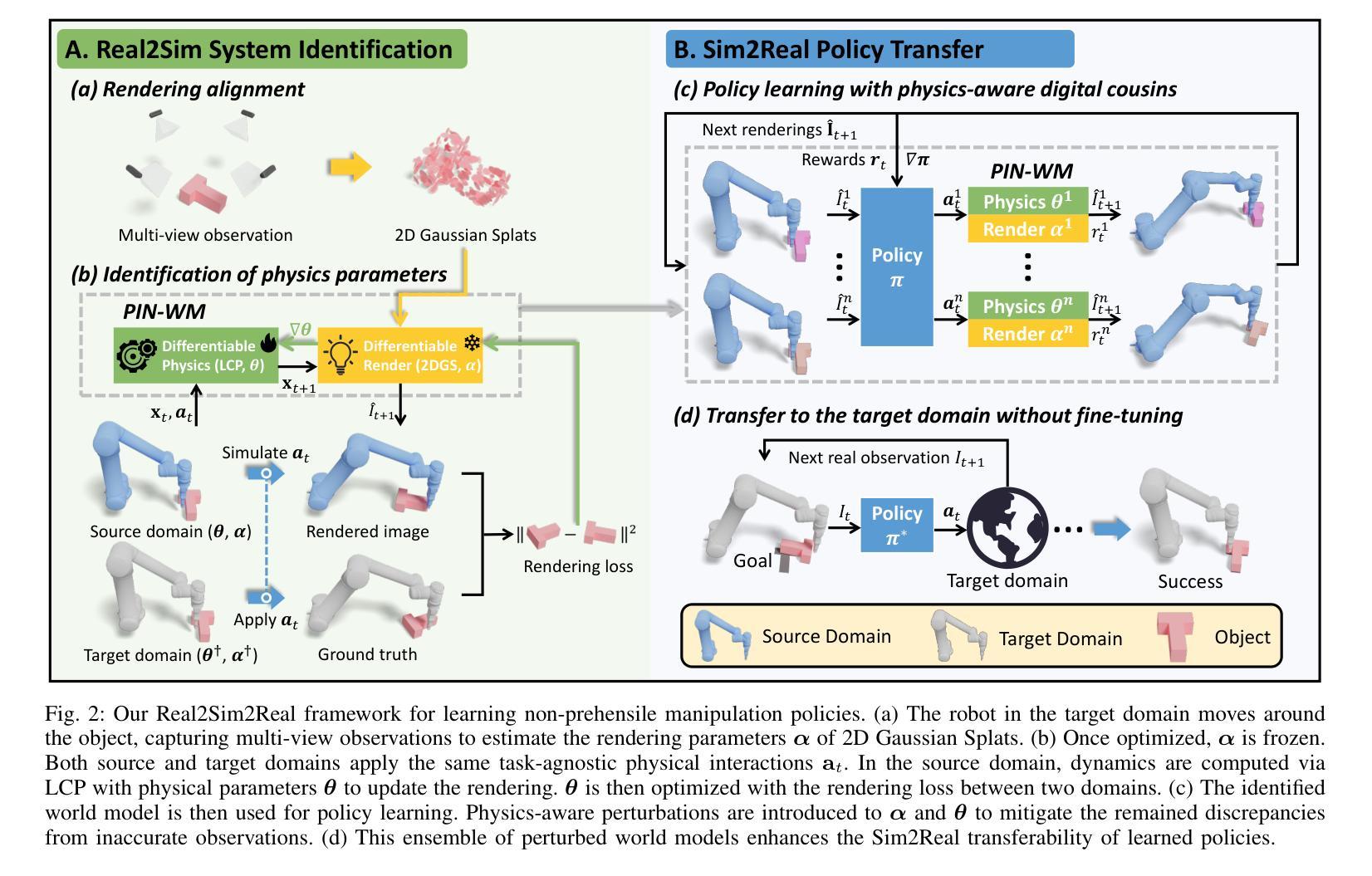
PIN-WM: Learning Physics-INformed World Models for Non-Prehensile Manipulation
Authors:Wenxuan Li, Hang Zhao, Zhiyuan Yu, Yu Du, Qin Zou, Ruizhen Hu, Kai Xu
While non-prehensile manipulation (e.g., controlled pushing/poking) constitutes a foundational robotic skill, its learning remains challenging due to the high sensitivity to complex physical interactions involving friction and restitution. To achieve robust policy learning and generalization, we opt to learn a world model of the 3D rigid body dynamics involved in non-prehensile manipulations and use it for model-based reinforcement learning. We propose PIN-WM, a Physics-INformed World Model that enables efficient end-to-end identification of a 3D rigid body dynamical system from visual observations. Adopting differentiable physics simulation, PIN-WM can be learned with only few-shot and task-agnostic physical interaction trajectories. Further, PIN-WM is learned with observational loss induced by Gaussian Splatting without needing state estimation. To bridge Sim2Real gaps, we turn the learned PIN-WM into a group of Digital Cousins via physics-aware randomizations which perturb physics and rendering parameters to generate diverse and meaningful variations of the PIN-WM. Extensive evaluations on both simulation and real-world tests demonstrate that PIN-WM, enhanced with physics-aware digital cousins, facilitates learning robust non-prehensile manipulation skills with Sim2Real transfer, surpassing the Real2Sim2Real state-of-the-arts.
非预握式操作(例如受控的推/戳)构成了基础机器人技能的一部分,但由于其对涉及摩擦和恢复力的复杂物理交互的高度敏感性,其学习仍然具有挑战性。为了实现稳健的政策学习和泛化,我们选择学习与非预握操作相关的3D刚体动力学世界模型,并将其用于基于模型的强化学习。我们提出了PIN-WM,这是一种物理信息世界模型,能够高效地从视觉观察中进行端到端的3D刚体动力学系统识别。通过采用可微分物理模拟,PIN-WM仅通过少量任务无关的物理交互轨迹即可学习。此外,PIN-WM通过高斯混合(Gaussian Splatting)产生的观察损失进行学习,无需进行状态估计。为了弥模拟与真实之间的差异,我们通过物理感知随机化将学到的PIN-WM变成一组“数字分身”,通过扰动物理和渲染参数来生成多样化和有意义的PIN-WM变化。在模拟和真实世界测试上的广泛评估表明,通过物理感知的数字分身增强的PIN-WM,有助于学习具有模拟到现实迁移能力的稳健的非预握操作技能,超越了最新的Real2Sim2Real技术水平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Robotics: Science and Systems 2025
Summary
非抓取操作(如控制推动/戳刺)是机器人技术中的基础技能,但由于涉及到摩擦和恢复等复杂物理交互,其学习仍然具有挑战性。为实现稳健的策略学习和泛化,我们选择了学习非抓取操作所涉及的3D刚体动力学世界模型,并用于基于模型强化学习。我们提出了PIN-WM,一种物理信息世界模型,能够高效地从视觉观察中进行端到端的3D刚体动力学系统识别。采用可微分物理模拟,PIN-WM仅通过少量任务无关的物理交互轨迹即可学习。此外,PIN-WM通过高斯散斑诱导的观察损失进行学习,无需状态估计。为弥仿真与真实之间的差距,我们将学到的PIN-WM转化为一系列物理感知随机化的数字分身,通过扰动物理和渲染参数生成多样且具意义的PIN-WM变化。在仿真和真实世界测试中的广泛评估表明,辅以物理感知数字分身的PIN-WM,能够促进具有Sim2Real迁移能力的稳健非抓取操作技能的学习,超越Real2Sim2Real当前最佳水平。
Key Takeaways
- 非抓取操作的机器人技术学习面临挑战,主要由于涉及复杂物理交互。
- 提出了PIN-WM模型,通过物理信息世界模型进行高效端到端识别。
- 仅通过少量任务无关的物理交互轨迹即可学习PIN-WM模型。
- 利用高斯散斑诱导的观察损失学习PIN-WM模型,无需状态估计。
- 通过转化为数字分身来缩小仿真与现实之间的差距。
- PIN-WM配合数字分身促进稳健的非抓取操作技能学习。
点此查看论文截图

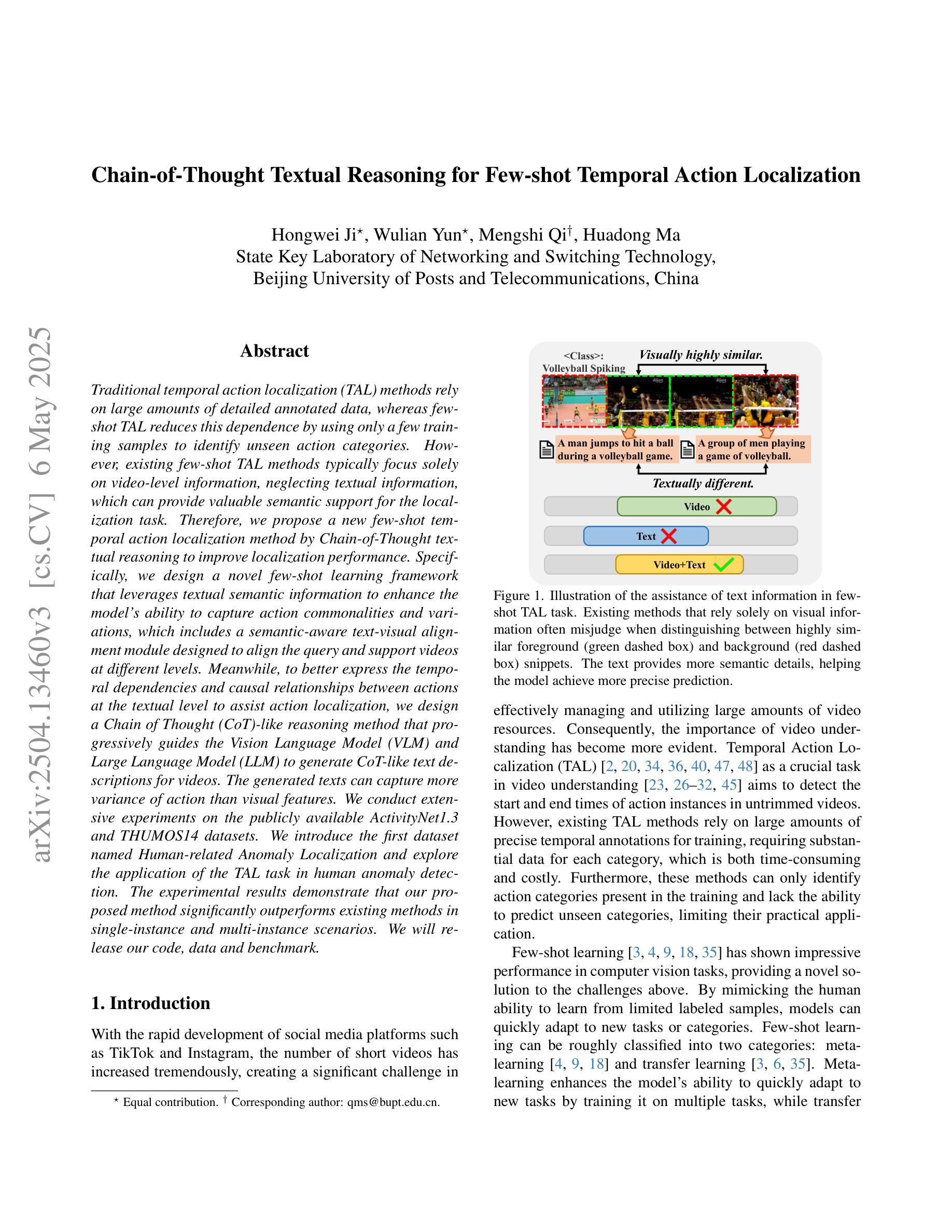
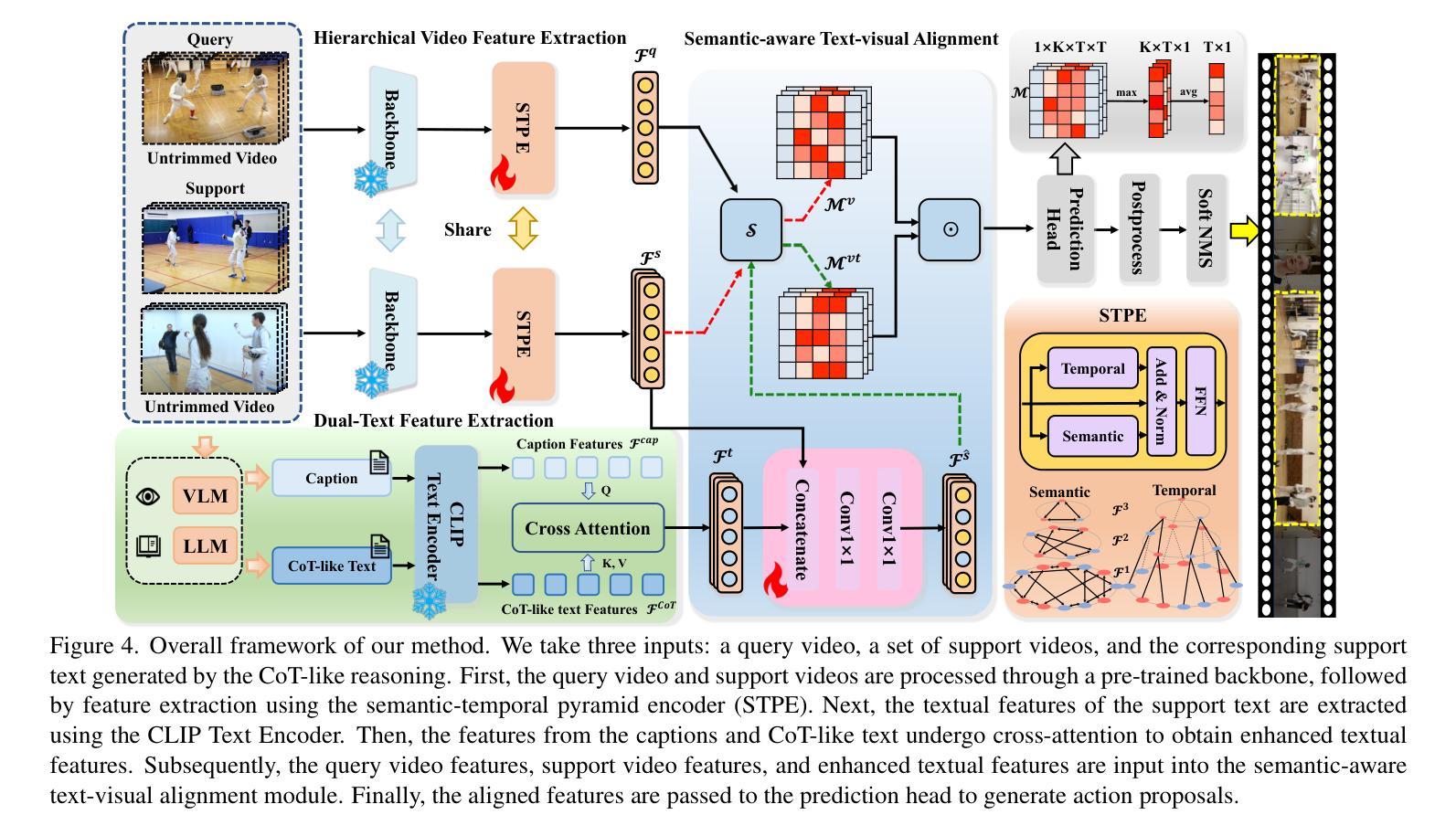
Chain-of-Thought Textual Reasoning for Few-shot Temporal Action Localization
Authors:Hongwei Ji, Wulian Yun, Mengshi Qi, Huadong Ma
Traditional temporal action localization (TAL) methods rely on large amounts of detailed annotated data, whereas few-shot TAL reduces this dependence by using only a few training samples to identify unseen action categories. However, existing few-shot TAL methods typically focus solely on video-level information, neglecting textual information, which can provide valuable semantic support for the localization task. Therefore, we propose a new few-shot temporal action localization method by Chain-of-Thought textual reasoning to improve localization performance. Specifically, we design a novel few-shot learning framework that leverages textual semantic information to enhance the model’s ability to capture action commonalities and variations, which includes a semantic-aware text-visual alignment module designed to align the query and support videos at different levels. Meanwhile, to better express the temporal dependencies and causal relationships between actions at the textual level to assist action localization, we design a Chain of Thought (CoT)-like reasoning method that progressively guides the Vision Language Model (VLM) and Large Language Model (LLM) to generate CoT-like text descriptions for videos. The generated texts can capture more variance of action than visual features. We conduct extensive experiments on the publicly available ActivityNet1.3 and THUMOS14 datasets. We introduce the first dataset named Human-related Anomaly Localization and explore the application of the TAL task in human anomaly detection. The experimental results demonstrate that our proposed method significantly outperforms existing methods in single-instance and multi-instance scenarios. We will release our code, data and benchmark.
传统的时间动作定位(TAL)方法依赖于大量的详细标注数据,而少样本TAL通过仅使用少量的训练样本来识别未见过的动作类别,减少了这种依赖。然而,现有的少样本TAL方法通常只关注视频级别的信息,忽略了文本信息,文本信息可以为定位任务提供有价值的语义支持。因此,我们提出了一种新的少样本时间动作定位方法,通过链式思维文本推理来提高定位性能。具体来说,我们设计了一种新的少样本学习框架,利用文本语义信息来提高模型捕捉动作共性和变化的能力,其中包括一个语义感知的文本-视觉对齐模块,旨在以不同级别对齐查询和支持视频。同时,为了更好地表达文本层面动作的时空依赖关系和因果关系,辅助动作定位,我们设计了类似链式思维(CoT)的推理方法,逐步引导视觉语言模型(VLM)和大型语言模型(LLM)生成类似CoT的文本描述视频。生成的文本可以捕捉比视觉特征更多的动作变化。我们在公开可用的ActivityNet1.3和THUMOS14数据集上进行了大量实验。我们引入了名为Human-related Anomaly Localization的第一个数据集,并探索了TAL任务在人类异常检测中的应用。实验结果表明,我们的方法在单实例和多实例场景中显著优于现有方法。我们将公开我们的代码、数据和基准测试。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本提出了一种基于Chain-of-Thought文本推理的少样本时序动作定位方法。该方法利用文本语义信息提高模型捕捉动作共性和变化的能力,并设计了语义感知文本视觉对齐模块,以在查询和支持视频的不同层次上进行对齐。同时,为了更好地表达文本层面动作的时空依赖和因果关系,辅助动作定位,该方法还设计了类似Chain of Thought的推理方法。实验结果表明,该方法在单实例和多实例场景下均显著优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 少样本时序动作定位(Few-Shot TAL)方法可以减少对大量详细标注数据的依赖,仅使用少量训练样本即可识别未见过的动作类别。
- 现有少样本TAL方法主要关注视频级别信息,忽略了文本信息,该文本提出利用文本语义信息提高模型性能。
- 文中设计了一个新型的少样本学习框架,包含语义感知文本视觉对齐模块,旨在在不同层次上对齐查询和支持视频。
- 引入了类似Chain of Thought的推理方法,在文本层面更好地表达动作的时空依赖和因果关系,辅助动作定位。
- 该方法在ActivityNet1.3和THUMOS14公开数据集上进行了广泛实验,并探索了人类异常检测中的TAL任务应用。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在单实例和多实例场景下均显著优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

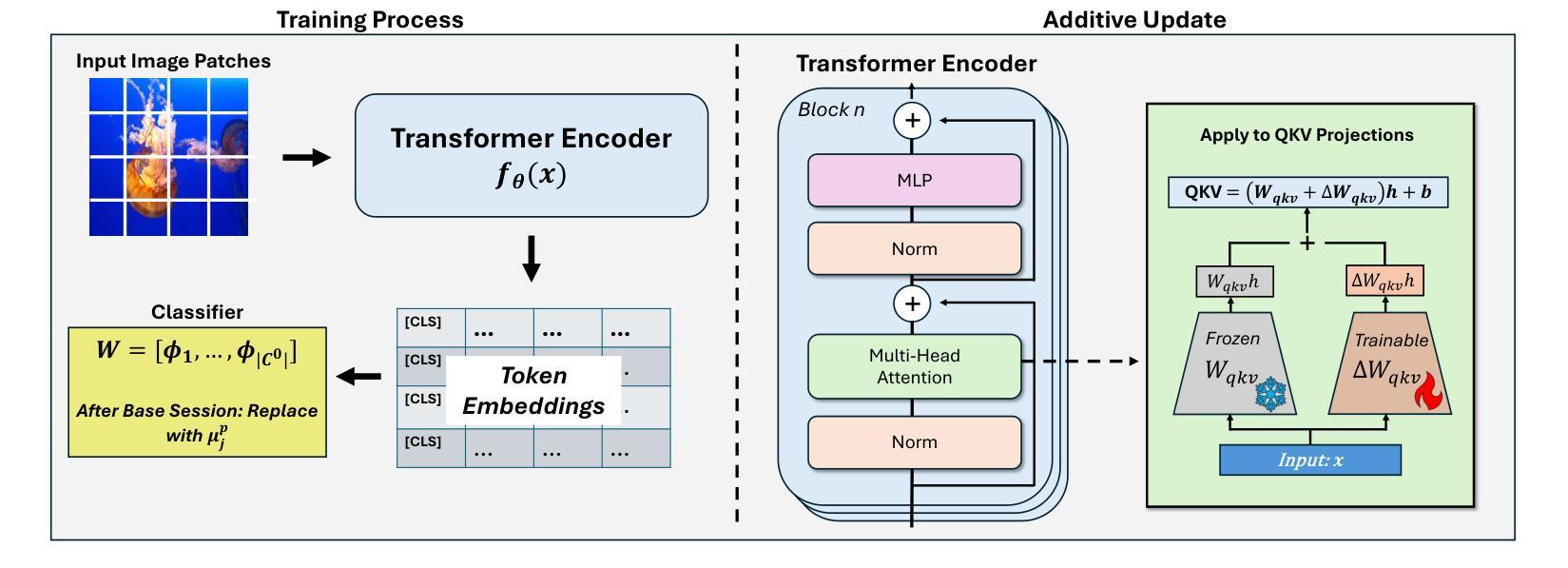
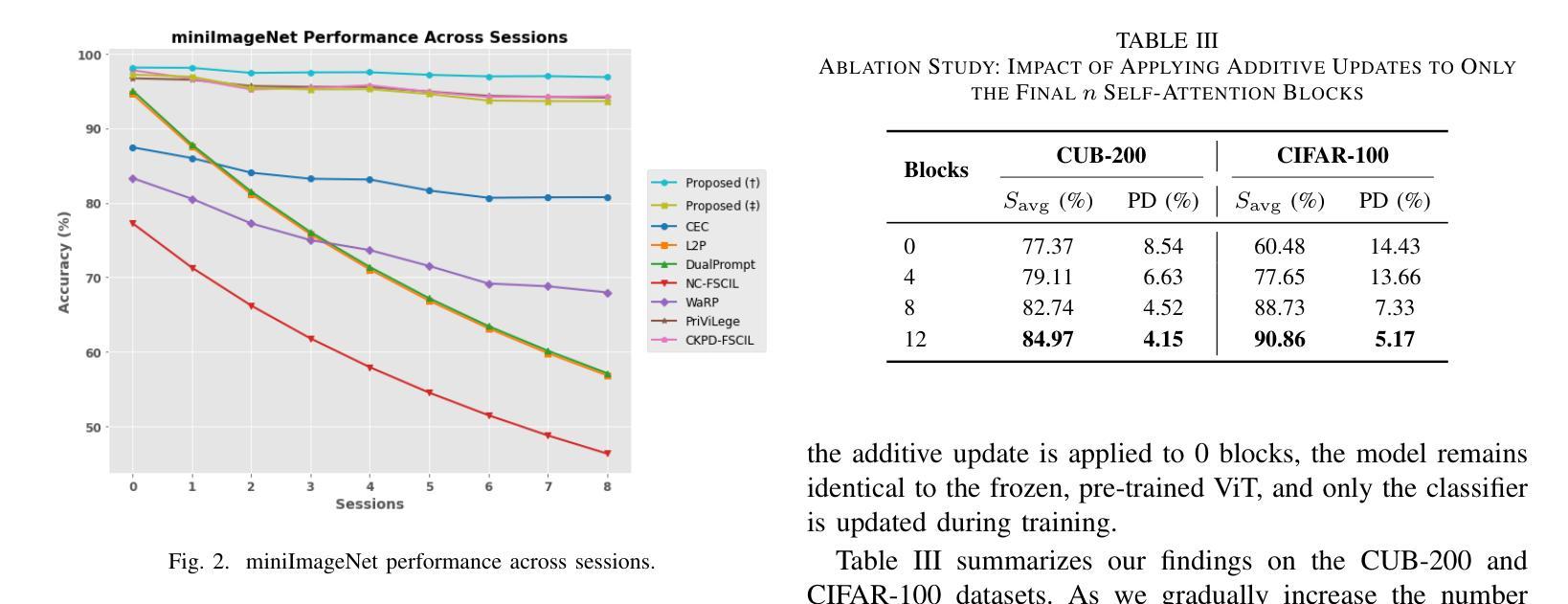
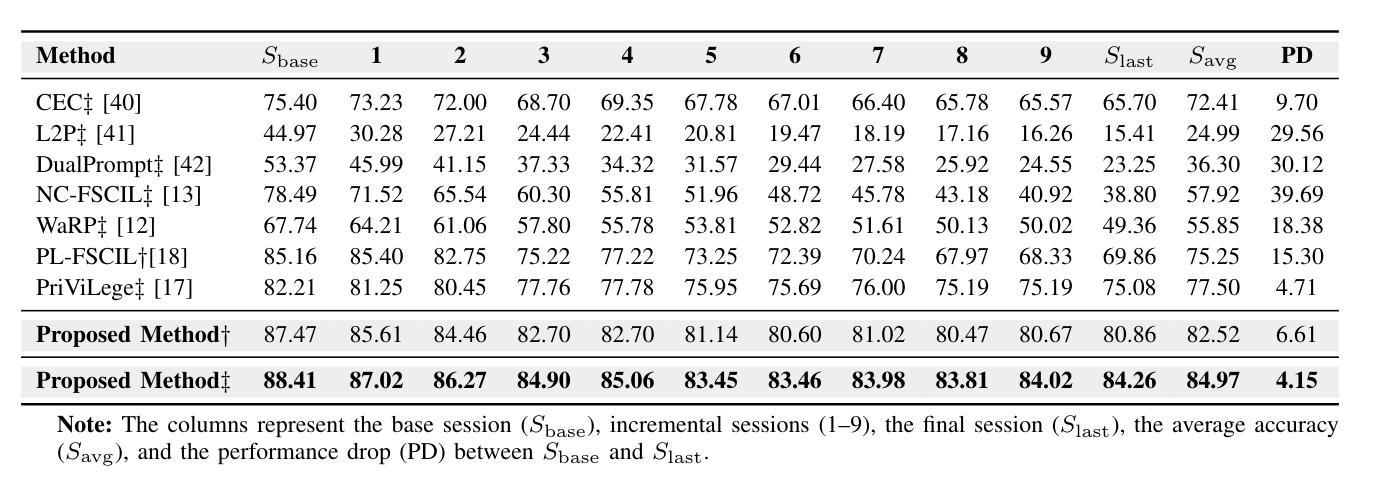
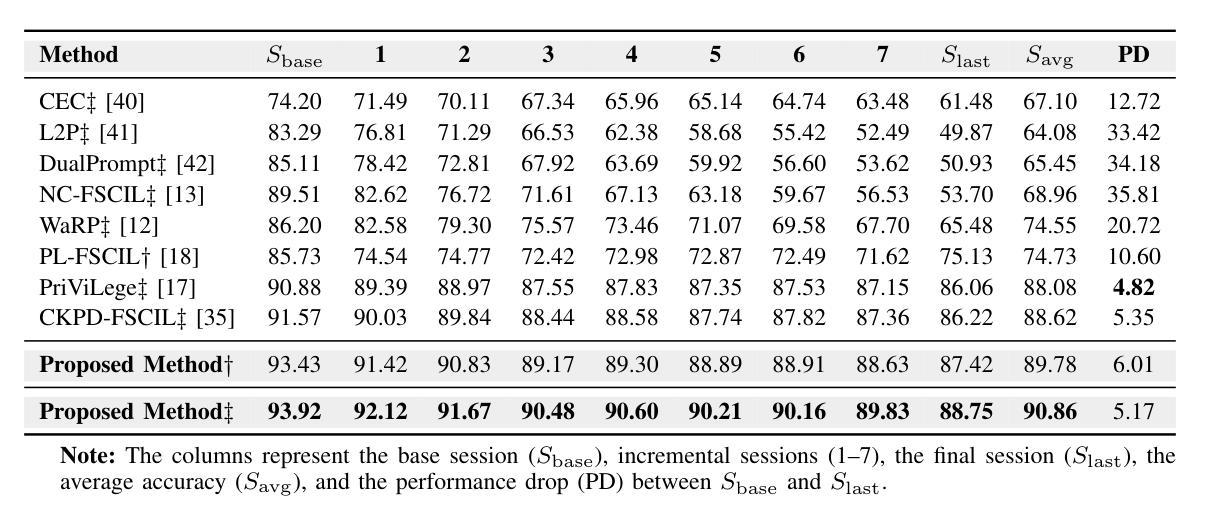
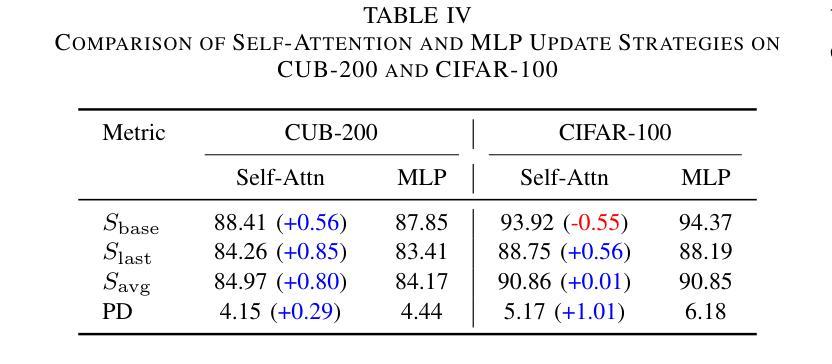
Adaptive Additive Parameter Updates of Vision Transformers for Few-Shot Continual Learning
Authors:Kyle Stein, Andrew Arash Mahyari, Guillermo Francia III, Eman El-Sheikh
Integrating new class information without losing previously acquired knowledge remains a central challenge in artificial intelligence, often referred to as catastrophic forgetting. Few-shot class incremental learning (FSCIL) addresses this by first training a model on a robust dataset of base classes and then incrementally adapting it in successive sessions using only a few labeled examples per novel class. However, this approach is prone to overfitting on the limited new data, which can compromise overall performance and exacerbate forgetting. In this work, we propose a simple yet effective novel FSCIL framework that leverages a frozen Vision Transformer (ViT) backbone augmented with parameter-efficient additive updates. Our approach freezes the pre-trained ViT parameters and selectively injects trainable weights into the self-attention modules via an additive update mechanism. This design updates only a small subset of parameters to accommodate new classes without sacrificing the representations learned during the base session. By fine-tuning a limited number of parameters, our method preserves the generalizable features in the frozen ViT while reducing the risk of overfitting. Furthermore, as most parameters remain fixed, the model avoids overwriting previously learned knowledge when small novel data batches are introduced. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that our approach yields state-of-the-art performance compared to baseline FSCIL methods.
在人工智能中,整合新类别信息而不丢失先前获得的知识仍然是一个核心挑战,通常被称为灾难性遗忘。少样本类别增量学习(FSCIL)通过首先在一个稳健的基础类别数据集上训练模型,然后在一系列连续的会话中仅使用每个新类别的少量标记示例来逐步适应模型来解决这个问题。然而,这种方法容易在新的有限数据上过拟合,这可能会损害整体性能并加剧遗忘。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种简单有效的FSCIL新框架,它利用冻结的Vision Transformer(ViT)主干并通过参数高效的加法更新进行增强。我们的方法冻结了预训练的ViT参数,并通过加法更新机制有选择地将可训练权重注入自注意力模块。这种设计只更新一小部分参数以适应新类别,同时不会牺牲基础会话期间学到的表示。通过微调有限数量的参数,我们的方法保留了冻结ViT中的可泛化特征,同时降低了过拟合的风险。此外,由于大多数参数保持不变,当引入少量新数据批次时,模型避免了覆盖先前学习的知识。在基准数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的方法相较于基线FSCIL方法达到了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一个简单有效的Few-Shot Class Incremental Learning(FSCIL)框架,该框架利用冻结的Vision Transformer(ViT)主干并通过参数有效的更新机制进行增强。通过冻结预训练的ViT参数,并在自注意力模块中选择性注入可训练权重,该方法在适应新类别时仅更新一小部分参数,同时保留基础会话中学习到的表示。通过微调有限的参数,该方法在冻结的ViT中保留了可泛化的特征,并降低了过拟合的风险。此外,由于大部分参数保持不变,模型在引入少量新数据批次时避免了覆盖先前学习的知识。实验表明,该方法在基准数据集上的性能达到了先进水平。
Key Takeaways
- Few-Shot Class Incremental Learning (FSCIL) 旨在解决人工智能中的灾难性遗忘问题,即在不失去先前学习知识的情况下整合新类别信息。
- 提出的FSCIL框架利用冻结的Vision Transformer (ViT) 主干,通过参数有效的更新机制进行增强。
- 框架通过冻结预训练的ViT参数并仅在自注意力模块中注入可训练权重来工作,以适应新类别。
- 该方法仅更新一小部分参数,以保留基础会话中学习到的表示,并在冻结的ViT中保留可泛化的特征。
- 通过微调有限的参数,该方法降低了过拟合的风险,并在引入新的少量数据批次时避免了覆盖先前学习的知识。
- 实验表明,该框架在基准数据集上的性能优于其他FSCIL方法,达到了先进水平。
点此查看论文截图

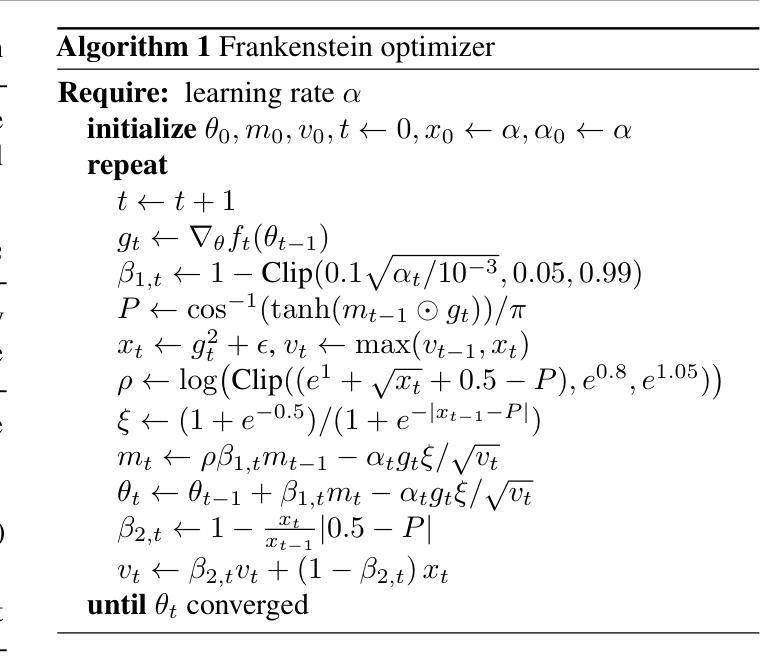
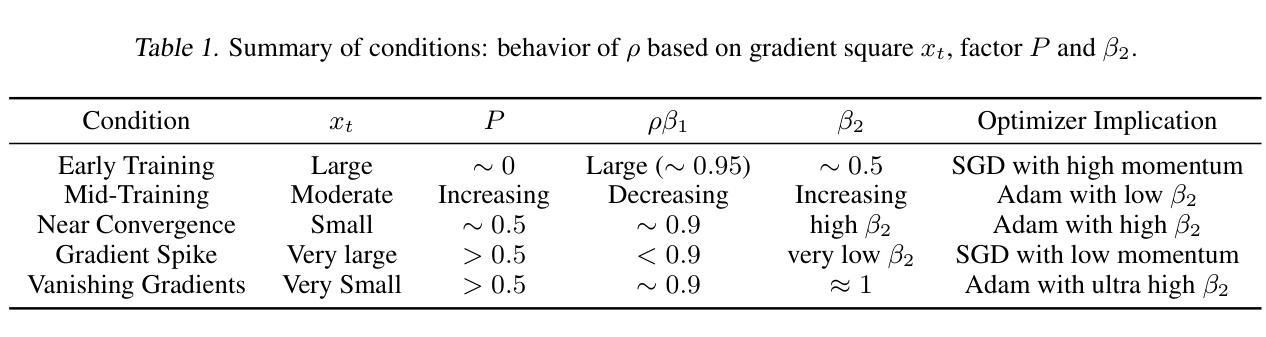
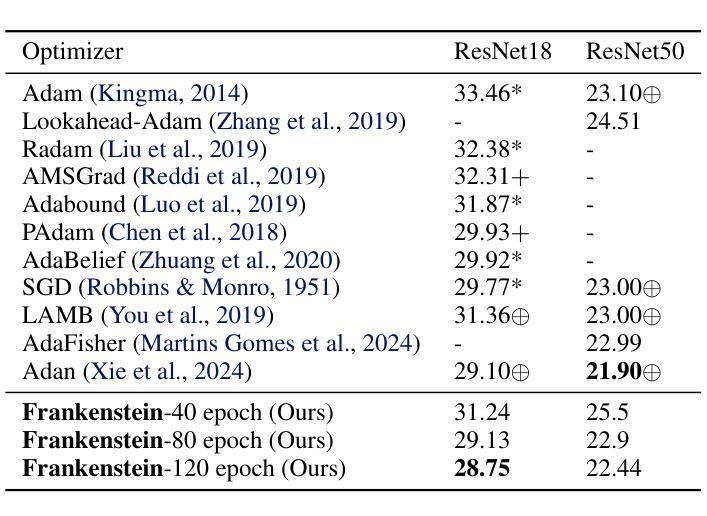
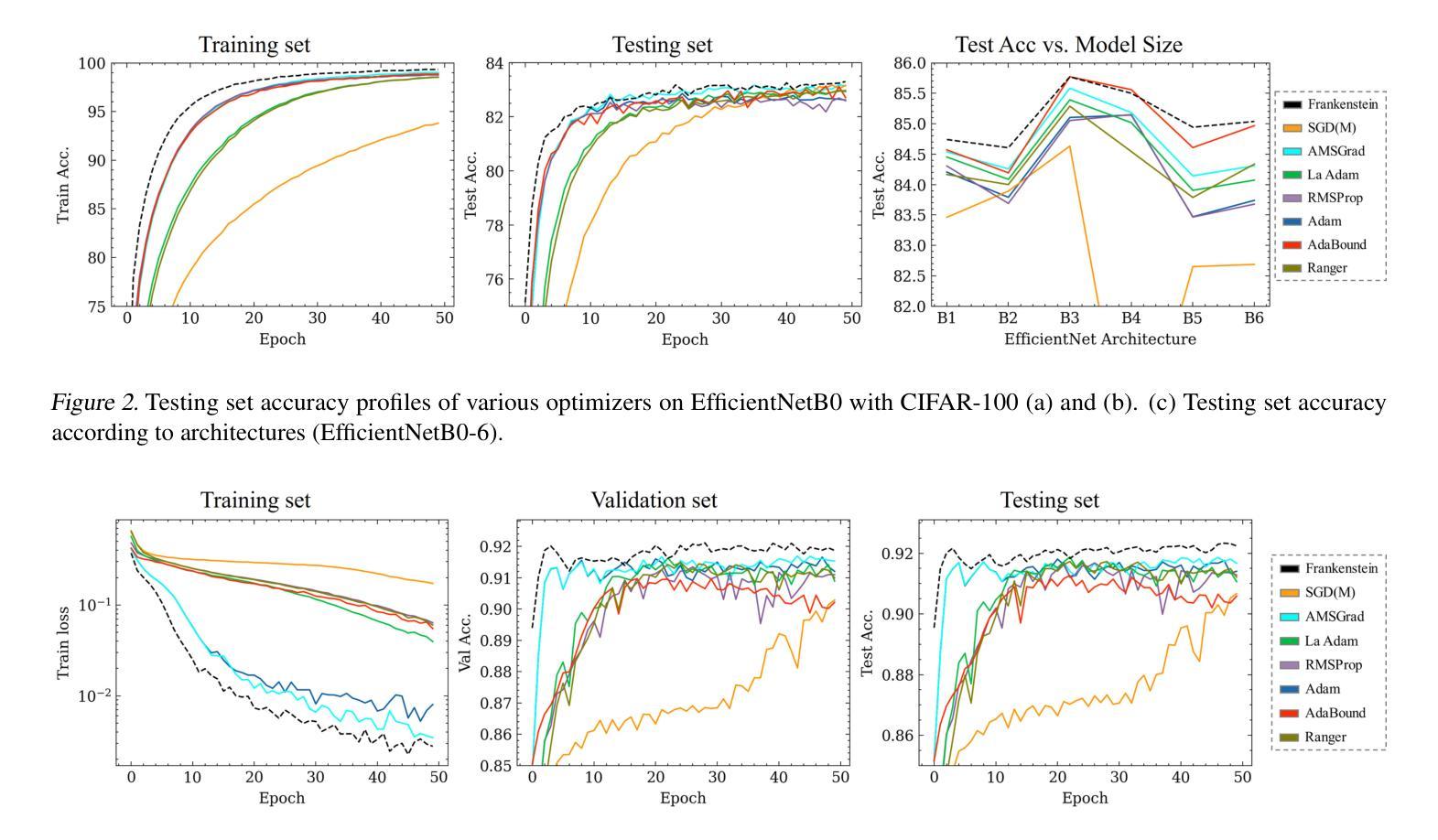
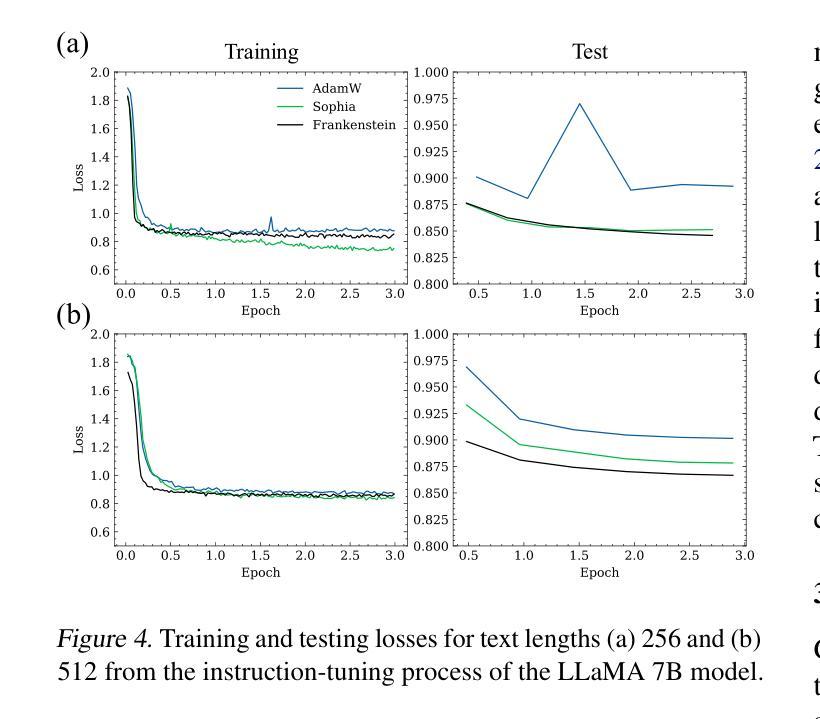
Frankenstein Optimizer: Harnessing the Potential by Revisiting Optimization Tricks
Authors:Chia-Wei Hsu, Nien-Ti Tsou, Yu-Cheng Chen, Yang Jeong Park, Ju Li
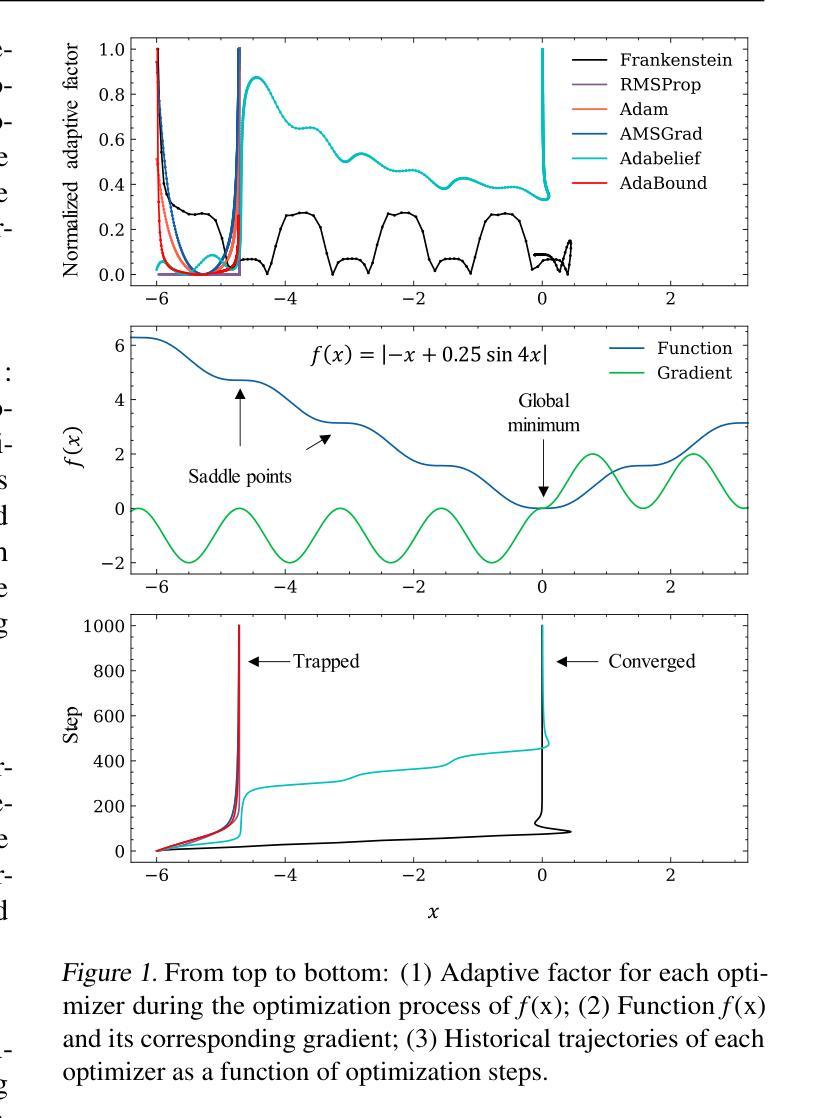
Gradient-based optimization drives the unprecedented performance of modern deep neural network models across diverse applications. Adaptive algorithms have accelerated neural network training due to their rapid convergence rates; however, they struggle to find ``flat minima” reliably, resulting in suboptimal generalization compared to stochastic gradient descent (SGD). By revisiting various adaptive algorithms’ mechanisms, we propose the Frankenstein optimizer, which combines their advantages. The proposed Frankenstein dynamically adjusts first- and second-momentum coefficients according to the optimizer’s current state to directly maintain consistent learning dynamics and immediately reflect sudden gradient changes. Extensive experiments across several research domains such as computer vision, natural language processing, few-shot learning, and scientific simulations show that Frankenstein surpasses existing adaptive algorithms and SGD empirically regarding convergence speed and generalization performance. Furthermore, this research deepens our understanding of adaptive algorithms through centered kernel alignment analysis and loss landscape visualization during the learning process. Code is available at https://github.com/acctouhou/Frankenstein_optimizer
基于梯度的优化推动了现代深度神经网络模型在多种应用中的前所未有的性能。自适应算法由于快速的收敛率而加速了神经网络训练;然而,它们在可靠地找到“平坦最小值”方面遇到困难,导致与随机梯度下降(SGD)相比次优的泛化能力。我们通过对各种自适应算法的机制进行重新审视,提出了结合了它们优势的Frankenstein优化器。所提出的Frankenstein会根据优化器的当前状态动态调整第一和第二动量系数,以直接保持一致的学习动力并立即反映突然的梯度变化。在计算机视觉、自然语言处理、小样本学习和科学模拟等多个研究领域的广泛实验表明,Frankenstein在收敛速度和泛化性能上超越了现有的自适应算法和SGD。此外,本研究通过中心核对齐分析和学习过程中的损失景观可视化,深化了我们对自适应算法的理解。代码可在https://github.com/acctouhou/Frankenstein_optimizer 中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
现代深度神经网络模型的卓越性能得益于梯度优化技术的推动。虽然自适应算法因其快速收敛率加速了神经网络训练,但在寻找“平坦最小值”方面存在可靠性问题,导致泛化性能不及随机梯度下降(SGD)。研究者提出结合各种自适应算法优势的Frankenstein优化器,可根据当前状态动态调整一、二阶动量系数,维持稳定学习动态并快速响应梯度突变。跨多个领域如计算机视觉、自然语言处理、小样本学习和科学模拟的实验显示,Frankenstein在收敛速度和泛化性能上超越现有自适应算法和SGD。此外,该研究还通过中心核对齐分析和学习过程损失景观可视化深化了对自适应算法的理解。
Key Takeaways
- 梯度优化是推动现代深度神经网络模型高性能的关键。
- 自适应算法虽加速神经网络训练,但在寻找平坦最小值方面存在挑战,影响泛化性能。
- Frankenstein优化器结合多种自适应算法的优势,动态调整动量系数以维持稳定学习并响应梯度变化。
- Frankenstein优化器在收敛速度和泛化性能上超越现有算法。
- 研究通过中心核对齐分析和损失景观可视化深化了对自适应算法的理解。
- Frankenstein优化器适用于多个领域,如计算机视觉、自然语言处理、小样本学习和科学模拟。
点此查看论文截图

Predicting potentially abusive clauses in Chilean terms of services with natural language processing
Authors:Christoffer Loeffler, Andrea Martínez Freile, Tomás Rey Pizarro
This study addresses the growing concern of information asymmetry in consumer contracts, exacerbated by the proliferation of online services with complex Terms of Service that are rarely even read. Even though research on automatic analysis methods is conducted, the problem is aggravated by the general focus on English-language Machine Learning approaches and on major jurisdictions, such as the European Union. We introduce a new methodology and a substantial dataset addressing this gap. We propose a novel annotation scheme with four categories and a total of 20 classes, and apply it on 50 online Terms of Service used in Chile. Our evaluation of transformer-based models highlights how factors like language- and/or domain-specific pre-training, few-shot sample size, and model architecture affect the detection and classification of potentially abusive clauses. Results show a large variability in performance for the different tasks and models, with the highest macro-F1 scores for the detection task ranging from 79% to 89% and micro-F1 scores up to 96%, while macro-F1 scores for the classification task range from 60% to 70% and micro-F1 scores from 64% to 80%. Notably, this is the first Spanish-language multi-label classification dataset for legal clauses, applying Chilean law and offering a comprehensive evaluation of Spanish-language models in the legal domain. Our work lays the ground for future research in method development for rarely considered legal analysis and potentially leads to practical applications to support consumers in Chile and Latin America as a whole.
本研究关注消费者合同中信息不对称问题的日益加剧,这一问题因在线服务的普及及其复杂的服务条款(很少被阅读)而愈发严重。尽管已经开展了关于自动分析方法的研究,但问题是由于研究主要集中在英语机器学习方法以及欧洲联盟等主要司法管辖区而加剧。我们提出了一种新的方法和大量的数据集来解决这一差距。我们提出了一个包含四个类别和总共20个子类别的全新注释方案,并对其应用于智利使用的50项在线服务条款。我们对基于转换器的模型进行了评估,强调了语言特定和/或领域特定的预训练、少量样本大小和模型架构等因素如何影响潜在滥用条款的检测和分类。结果显示,不同任务和模型的性能存在很大差异,检测任务的最高宏F1分数范围从79%到89%,微观F1分数高达96%,而分类任务的宏F1分数范围从60%到70%,微观F1分数从64%到80%。值得注意的是,这是第一个用于法律条款的西班牙语多标签分类数据集,它适用于智利法律,并对西班牙语模型在法律领域进行了全面评估。我们的工作为未来的方法开发研究奠定了基础,该研究对于很少考虑的法律分析具有实际意义,并有望为消费者在智利乃至整个拉丁美洲提供支持。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 39 pages, 2 figures, 8 tables, accepted for publication
Summary
本文关注消费者合同中信息不对称问题的日益严重,特别是在线服务协议的普及加剧了这一问题。研究介绍了新的方法论和大量数据集来解决这一差距,并提出了新的标注方案和四个类别下的二十个子类别。通过对智利使用的五十项在线服务协议的应用评估,发现语言特定和领域特定的预训练、少量样本大小和模型架构等因素会影响潜在滥用条款的检测和分类。研究结果显示,不同任务和模型的性能存在很大差异,检测任务的最高宏观F1分数在79%到89%之间,微观F1分数高达96%,而分类任务的宏观F1分数在60%到70%之间,微观F1分数在64%到80%之间。这为未来法律分析方法的发展提供了基础,并有望支持智利和拉丁美洲的消费者实际应用。
Key Takeaways
- 该研究关注消费者合同中信息不对称问题,特别是复杂的在线服务协议。
- 提出了新的方法论和标注方案来解决这一问题,数据集涵盖智利使用的在线服务协议。
- 研究评估了基于转换器的模型,发现语言特定和领域特定的预训练对检测潜在滥用条款至关重要。
- 不同任务和模型的性能差异显著,检测任务的F1分数较高。
- 这是首个针对法律条款的西班牙语多标签分类数据集,应用智利法律并全面评估西班牙语模型在法律领域的表现。
- 研究为未来法律分析方法的发展奠定了基础。
点此查看论文截图

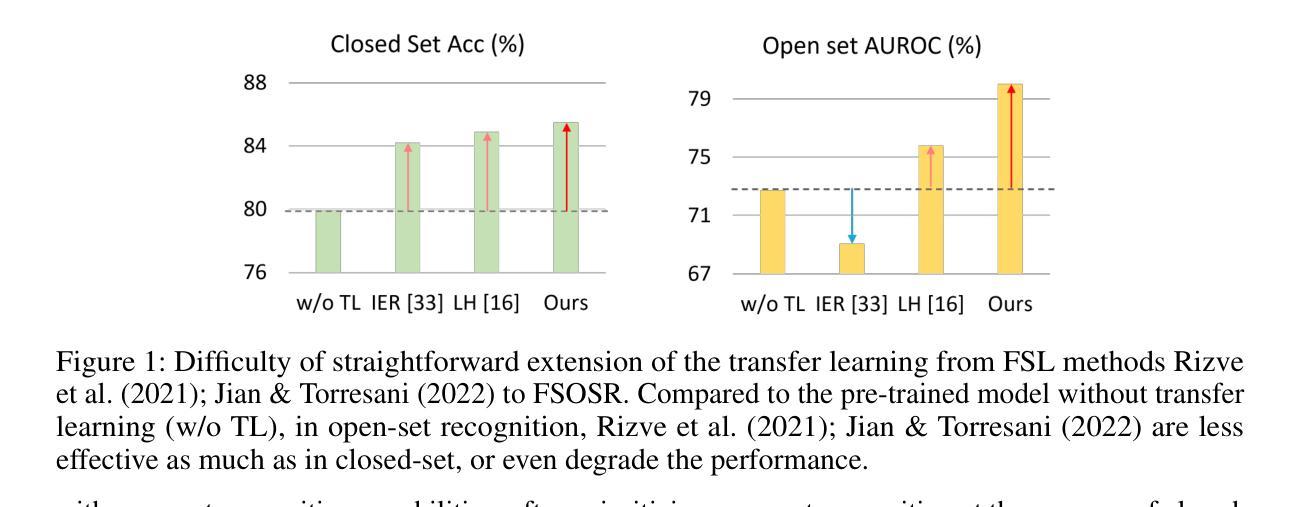
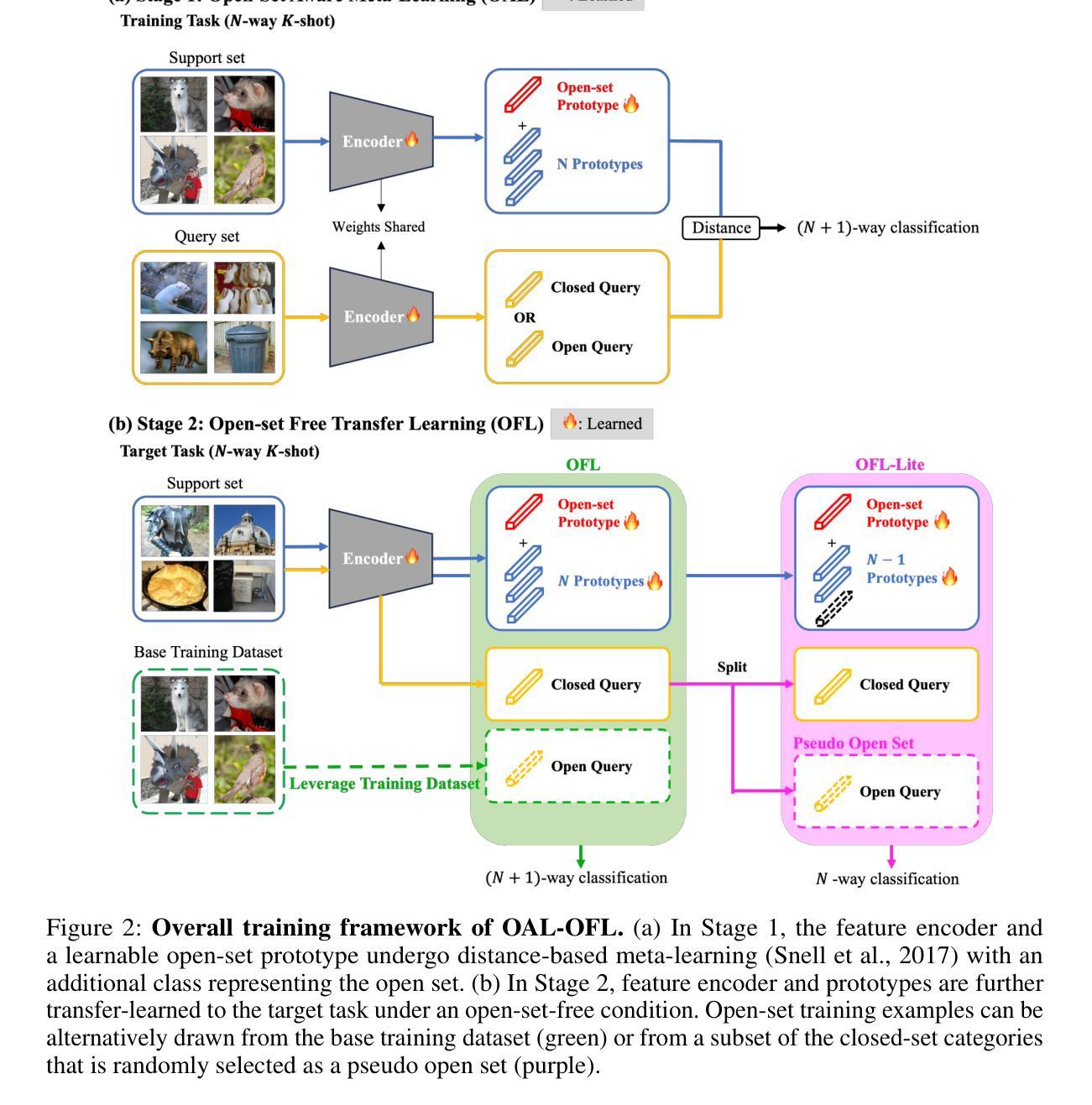
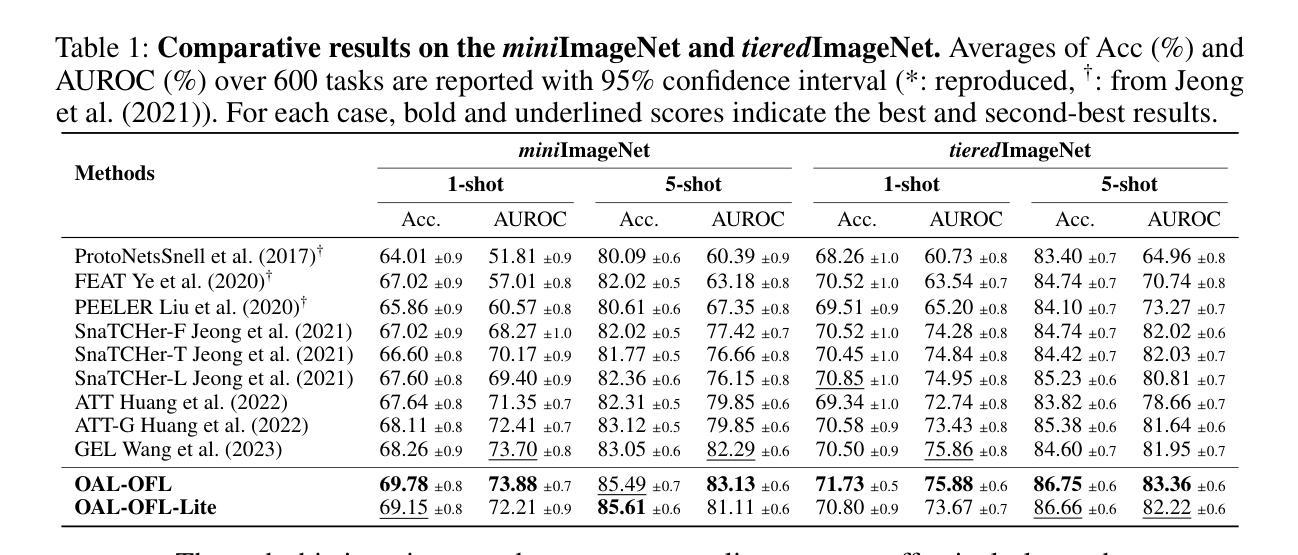
Unlocking Transfer Learning for Open-World Few-Shot Recognition
Authors:Byeonggeun Kim, Juntae Lee, Kyuhong Shim, Simyung Chang
Few-Shot Open-Set Recognition (FSOSR) targets a critical real-world challenge, aiming to categorize inputs into known categories, termed closed-set classes, while identifying open-set inputs that fall outside these classes. Although transfer learning where a model is tuned to a given few-shot task has become a prominent paradigm in closed-world, we observe that it fails to expand to open-world. To unlock this challenge, we propose a two-stage method which consists of open-set aware meta-learning with open-set free transfer learning. In the open-set aware meta-learning stage, a model is trained to establish a metric space that serves as a beneficial starting point for the subsequent stage. During the open-set free transfer learning stage, the model is further adapted to a specific target task through transfer learning. Additionally, we introduce a strategy to simulate open-set examples by modifying the training dataset or generating pseudo open-set examples. The proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance on two widely recognized benchmarks, miniImageNet and tieredImageNet, with only a 1.5% increase in training effort. Our work demonstrates the effectiveness of transfer learning in FSOSR.
少样本开放集识别(FSOSR)旨在应对现实世界中的一项关键挑战,旨在将输入分类为已知类别(称为封闭集类别),同时识别不属于这些类别的开放集输入。虽然迁移学习已成为封闭世界中一种突出的范式,其中模型被调整到给定的少样本任务,但我们发现它无法扩展到开放世界。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了一种两阶段的方法,包括开放集感知元学习与开放集自由迁移学习。在开放集感知元学习阶段,模型被训练以建立度量空间,作为后续阶段的有益起点。在开放集自由迁移学习阶段,模型通过迁移学习进一步适应特定的目标任务。此外,我们还介绍了一种通过修改训练数据集或生成伪开放集示例来模拟开放集示例的策略。所提出的方法在广泛认可的miniImageNet和tieredImageNet基准测试上实现了最新性能,仅增加了1.5%的训练努力。我们的工作证明了迁移学习在FSOSR中的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了Few-Shot Open-Set Recognition(FSOSR)的目标与挑战。它旨在将输入分类为已知类别(称为封闭集类别),同时识别不属于这些类别的开放集输入。虽然迁移学习已成为封闭世界中的主流范式,但在开放世界中却存在局限性。为此,研究者提出了一种两阶段的方法,包括开放集感知元学习与开放集自由迁移学习。在开放集感知元学习阶段,模型被训练以建立度量空间,作为后续阶段的起点。在开放集自由迁移学习阶段,模型通过迁移学习进一步适应特定目标任务。此外,通过修改训练数据集或生成伪开放集示例来模拟开放集示例的策略也被引入。该方法在miniImageNet和tieredImageNet两个广泛认可的基准测试上实现了最佳性能,仅增加了1.5%的训练努力。研究证明了迁移学习在FSOSR中的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- Few-Shot Open-Set Recognition (FSOSR) 旨在解决将输入分类为已知类别并识别开放集输入的问题。
- 迁移学习在封闭世界中很受欢迎,但在开放世界中存在局限性。
- 提出的两阶段方法包括开放集感知元学习和开放集自由迁移学习。
- 在开放集感知元学习阶段,模型建立度量空间作为后续阶段的起点。
- 开放集自由迁移学习阶段使模型适应特定目标任务。
- 通过模拟开放集示例的策略来提高模型性能。
点此查看论文截图