⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-08 更新
Not All Parameters Matter: Masking Diffusion Models for Enhancing Generation Ability
Authors:Lei Wang, Senmao Li, Fei Yang, Jianye Wang, Ziheng Zhang, Yuhan Liu, Yaxing Wang, Jian Yang
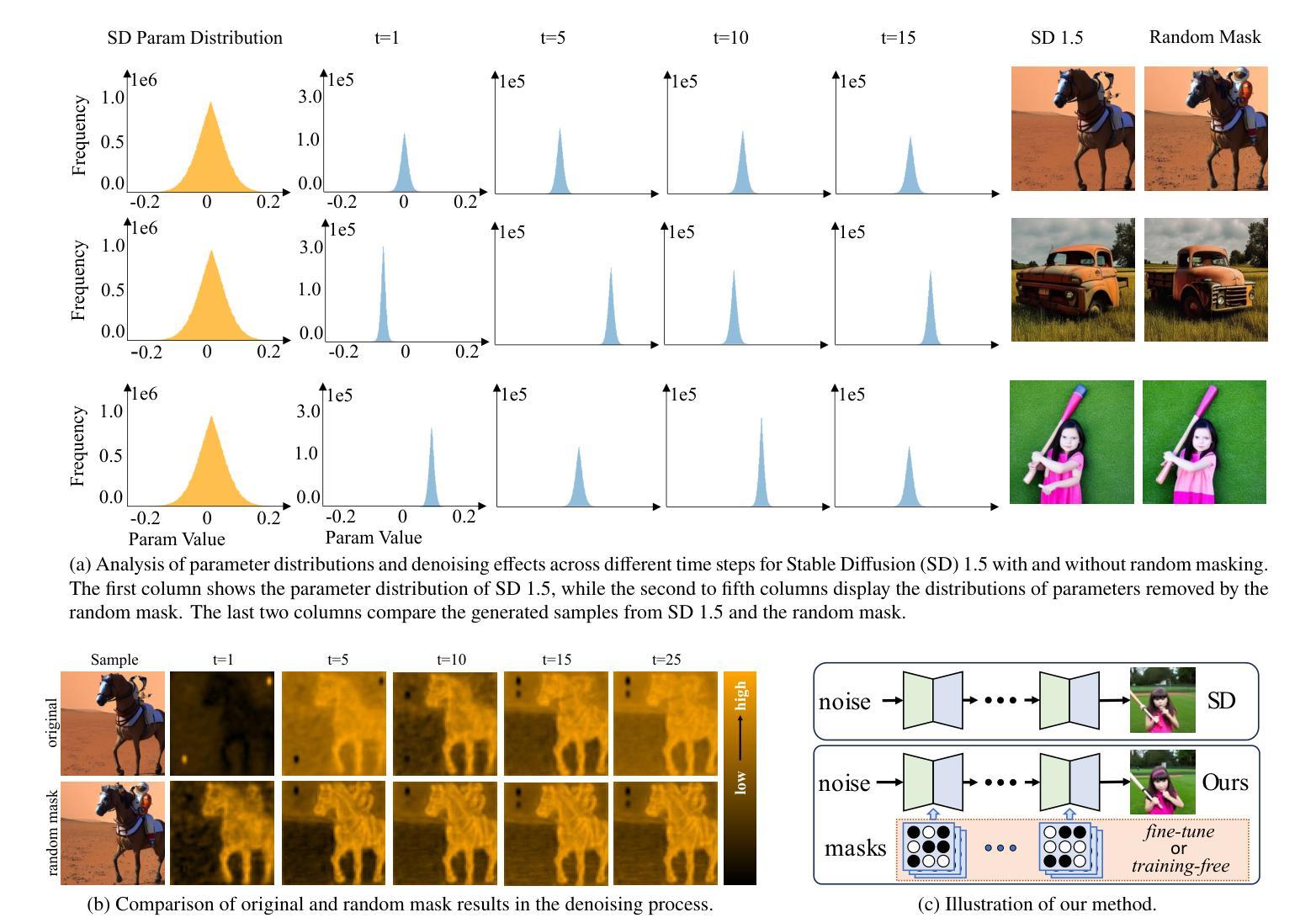
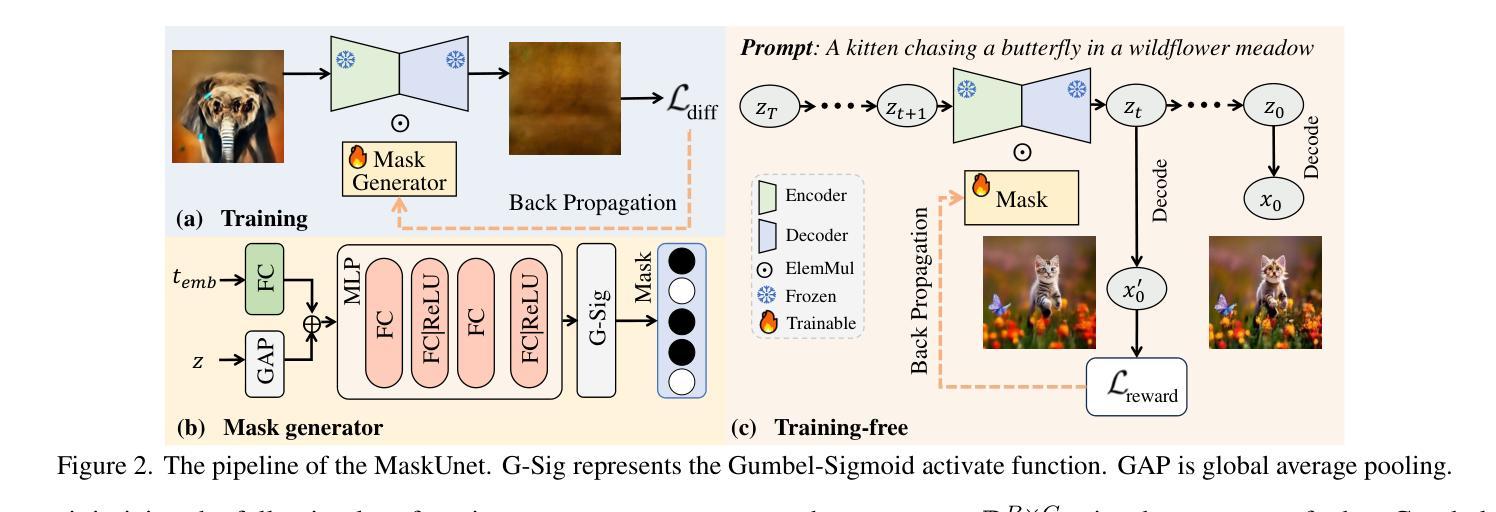
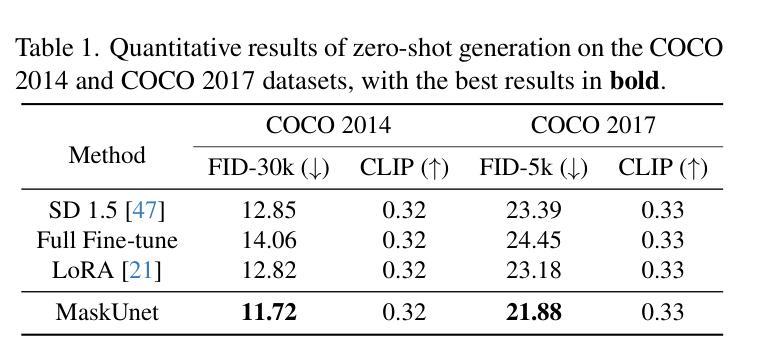
The diffusion models, in early stages focus on constructing basic image structures, while the refined details, including local features and textures, are generated in later stages. Thus the same network layers are forced to learn both structural and textural information simultaneously, significantly differing from the traditional deep learning architectures (e.g., ResNet or GANs) which captures or generates the image semantic information at different layers. This difference inspires us to explore the time-wise diffusion models. We initially investigate the key contributions of the U-Net parameters to the denoising process and identify that properly zeroing out certain parameters (including large parameters) contributes to denoising, substantially improving the generation quality on the fly. Capitalizing on this discovery, we propose a simple yet effective method-termed ``MaskUNet’’- that enhances generation quality with negligible parameter numbers. Our method fully leverages timestep- and sample-dependent effective U-Net parameters. To optimize MaskUNet, we offer two fine-tuning strategies: a training-based approach and a training-free approach, including tailored networks and optimization functions. In zero-shot inference on the COCO dataset, MaskUNet achieves the best FID score and further demonstrates its effectiveness in downstream task evaluations. Project page: https://gudaochangsheng.github.io/MaskUnet-Page/
扩散模型在早期阶段主要关注构建基本图像结构,而精细的细节,包括局部特征和纹理,是在后期阶段生成的。因此,相同的网络层被迫同时学习结构和纹理信息,这与传统的深度学习架构(例如ResNet或GAN)有很大不同,后者在不同的层捕获或生成图像语义信息。这种差异激发我们探索时间扩散模型。我们最初研究了U-Net参数对去噪过程的关键作用,并发现适当地将某些参数(包括大参数)清零有助于去噪,从而显著提高生成质量。基于这一发现,我们提出了一种简单而有效的方法,称为“MaskUNet”,它在几乎不影响参数数量的情况下提高了生成质量。我们的方法充分利用了与时间和样本相关的有效U-Net参数。为了优化MaskUNet,我们提供了两种微调策略:基于训练的方法和免训练的方法,包括定制的网络和优化函数。在COCO数据集上进行零样本推理时,MaskUNet获得了最佳的FID分数,并在下游任务评估中进一步证明了其有效性。项目页面:https://gudaochangsheng.github.io/MaskUnet-Page/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025
Summary
扩散模型分阶段构建图像结构并生成细节,与传统深度学习架构不同。研究U-Net参数对去噪过程的贡献,提出“MaskUNet”方法提高生成质量,并给出两种微调策略。MaskUNet在COCO数据集上实现最佳FID分数,并在下游任务评估中展现有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型分阶段构建图像,早期关注基本结构,后期生成精细细节。
- 传统深度学习架构与扩散模型在捕获或生成图像语义信息的方式上存在显著差异。
- U-Net参数对去噪过程有关键贡献,适当置零某些参数有助于提高生成质量。
- 提出名为“MaskUNet”的方法,在保持参数数量有限的情况下提高生成质量。
- MaskUNet充分利用时间步长和样本相关的有效U-Net参数。
- 提供两种MaskUNet优化策略:基于训练的方法和免训练方法。
点此查看论文截图


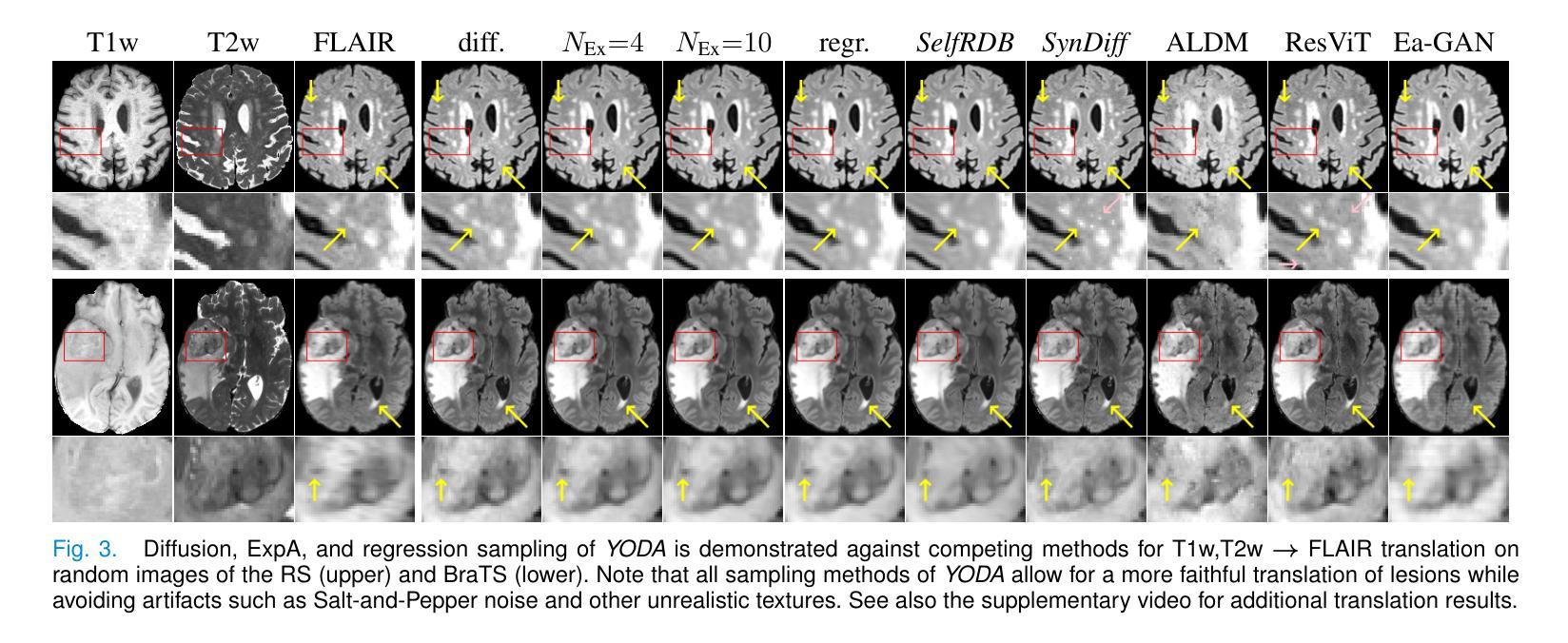
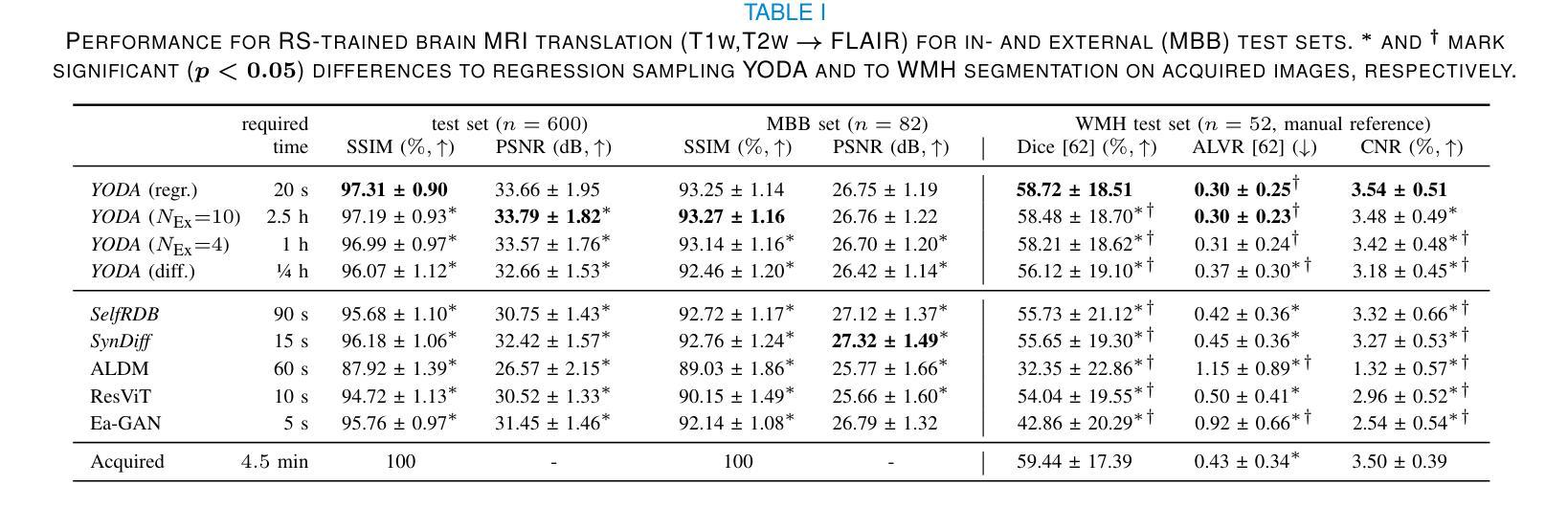
Regression is all you need for medical image translation
Authors:Sebastian Rassmann, David Kügler, Christian Ewert, Martin Reuter
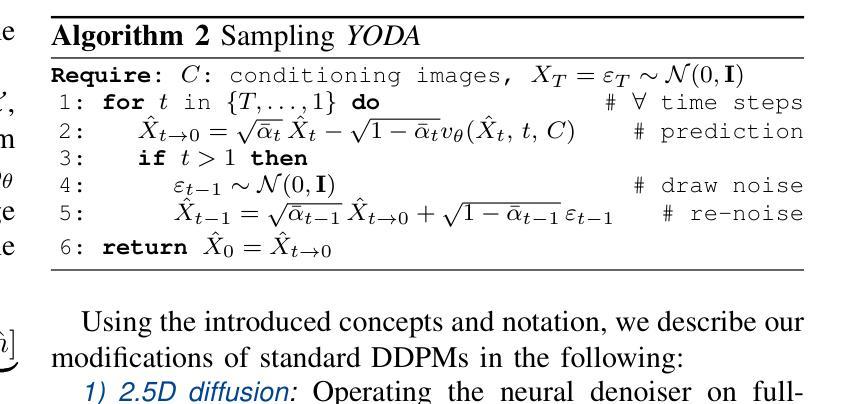
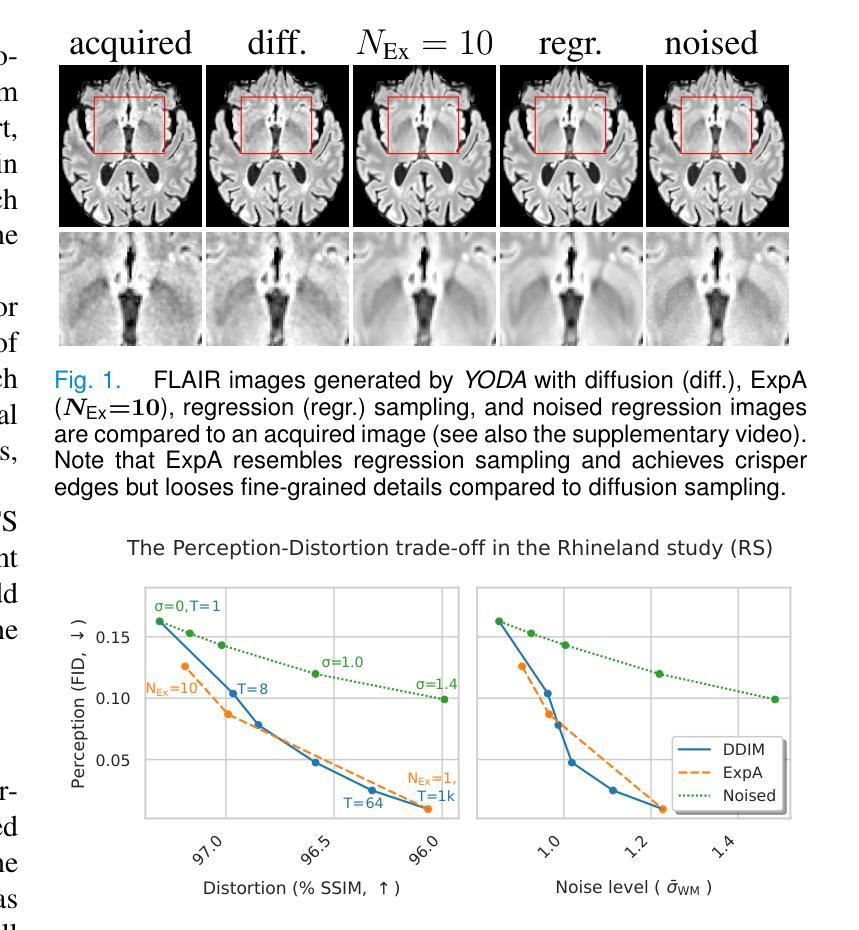
The acquisition of information-rich images within a limited time budget is crucial in medical imaging. Medical image translation (MIT) can help enhance and supplement existing datasets by generating synthetic images from acquired data. While Generative Adversarial Nets (GANs) and Diffusion Models (DMs) have achieved remarkable success in natural image generation, their benefits - creativity and image realism - do not necessarily transfer to medical applications where highly accurate anatomical information is required. In fact, the imitation of acquisition noise or content hallucination hinder clinical utility. Here, we introduce YODA (You Only Denoise once - or Average), a novel 2.5D diffusion-based framework for volumetric MIT. YODA unites diffusion and regression paradigms to produce realistic or noise-free outputs. Furthermore, we propose Expectation-Approximation (ExpA) DM sampling, which draws inspiration from MRI signal averaging. ExpA-sampling suppresses generated noise and, thus, eliminates noise from biasing the evaluation of image quality. Through extensive experiments on four diverse multi-modal datasets - comprising multi-contrast brain MRI and pelvic MRI-CT - we show that diffusion and regression sampling yield similar results in practice. As such, the computational overhead of diffusion sampling does not provide systematic benefits in medical information translation. Building on these insights, we demonstrate that YODA outperforms several state-of-the-art GAN and DM methods. Notably, YODA-generated images are shown to be interchangeable with, or even superior to, physical acquisitions for several downstream tasks. Our findings challenge the presumed advantages of DMs in MIT and pave the way for the practical application of MIT in medical imaging.
在医学影像中,在有限的时间预算内获取信息丰富的图像至关重要。医学图像翻译(MIT)可以通过从获取的数据生成合成图像来增强和补充现有的数据集。虽然生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型(DMs)在自然图像生成方面取得了显著的成功,它们在医学应用中并不一定能发挥出创意和图像逼真的优势,因为医学应用需要高度准确的解剖信息。实际上,模仿获取噪声或内容幻觉会阻碍其在临床上的应用。在这里,我们介绍了YODA(You Only Denoise once - or Average),这是一个基于体积的MIT的新型2.5D扩散框架。YODA结合了扩散和回归范式来产生逼真的或无噪声的输出。此外,我们提出了期望近似(ExpA)DM采样,它受到MRI信号平均的启发。ExpA采样抑制生成的噪声,从而消除噪声对图像质量评估的偏见。通过在四个不同的多模式数据集上进行广泛实验-包括多对比度脑部MRI和骨盆MRI-CT-我们显示扩散和回归采样在实践中产生相似结果。因此,扩散采样的计算开销在医学信息翻译中并没有提供系统性的优势。基于这些见解,我们证明了YODA优于几种先进的GAN和DM方法。值得注意的是,YODA生成的图像被证明可以互换或甚至优于多种下游任务的物理采集。我们的研究结果挑战了DM在MIT中的假定优势,并为MIT在医学影像中的实际应用铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对医学影像中有限时间内获取信息丰富图像的重要性,医学图像翻译(MIT)可以通过生成合成图像来增强和补充现有数据集。虽然生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型(DMs)在自然图像生成方面取得了显著成功,但它们带来的创造性和图像逼真度并不一定适用于医学应用中对高度准确的解剖信息的要求。本研究介绍了YODA(You Only Denoise once - or Average),一种用于体积MIT的新型2.5D扩散模型框架。YODA结合了扩散和回归范式,产生逼真的或无噪声输出。此外,提出了期望近似(ExpA)DM采样,其灵感来源于MRI信号平均技术。ExpA采样抑制生成噪声,从而消除噪声对图像质量评估的偏见。在四个不同模态的数据集上的实验表明,扩散和回归采样在实践中产生相似结果。基于这些见解,YODA被证明优于几种最先进的GAN和DM方法。值得注意的是,YODA生成的图像与物理采集的图像相当或更好,可用于多种下游任务。本研究挑战了DM在MIT中的预设优势,为医学成像中的MIT实际应用铺平了道路。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像翻译(MIT)可以通过生成合成图像来增强现有数据集,特别是在有限时间内获取丰富信息的医学影像中至关重要。
- 虽然GANs和DMs在自然图像生成方面表现出色,但它们并不必然适用于医学应用中要求高度准确的解剖信息的情况。
- 介绍了一种新型的2.5D扩散模型框架YODA,用于体积MIT,结合了扩散和回归范式产生逼真或无噪声输出。
- 提出了期望近似(ExpA)DM采样方法,灵感来源于MRI信号平均技术,能有效抑制生成噪声。
- 实验表明,扩散和回归采样在医学图像翻译中产生相似结果,扩散采样的计算开销并未带来系统性优势。
- YODA在多种下游任务中表现出优越性能,生成的图像与物理采集的图像相当或更好。
点此查看论文截图

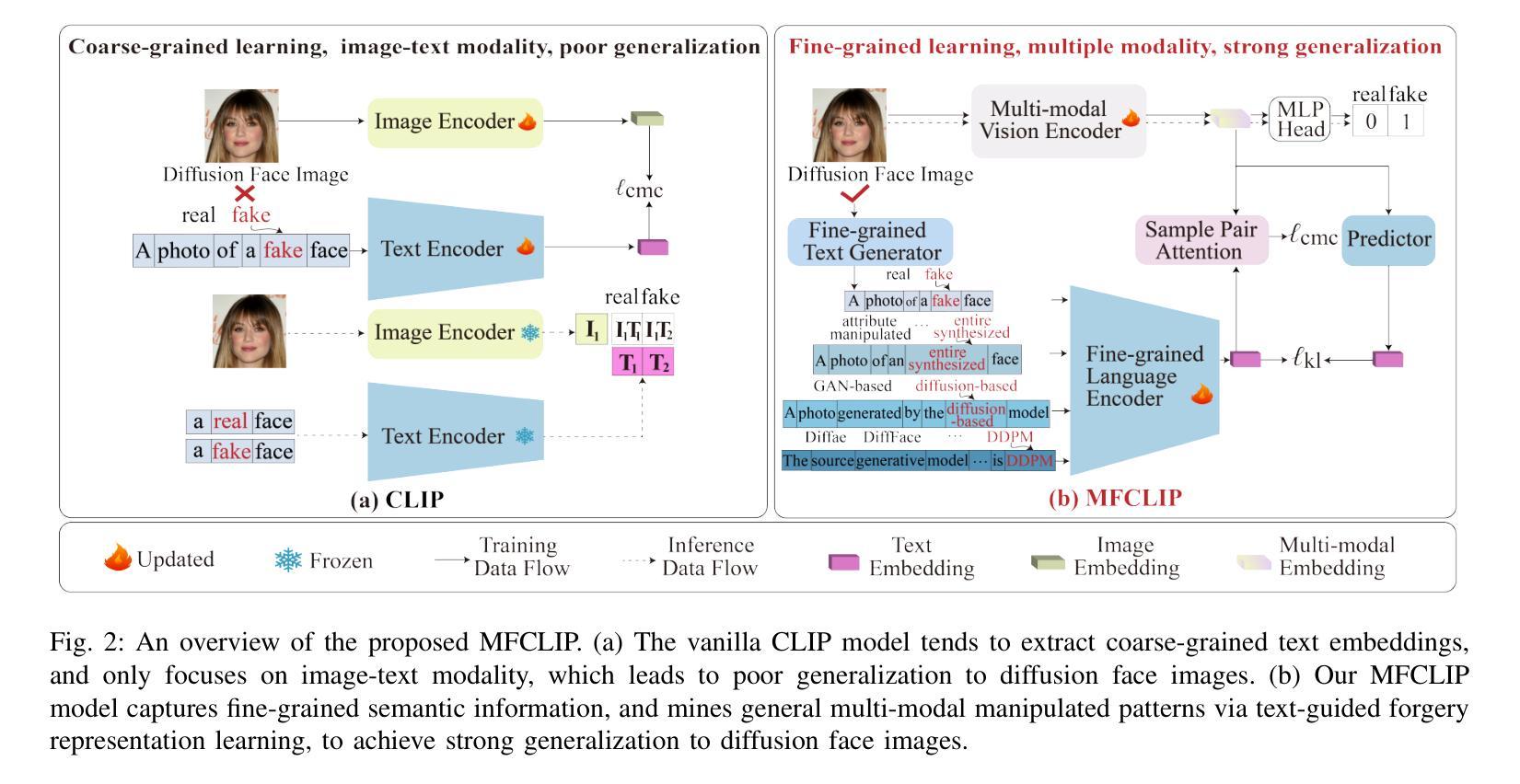
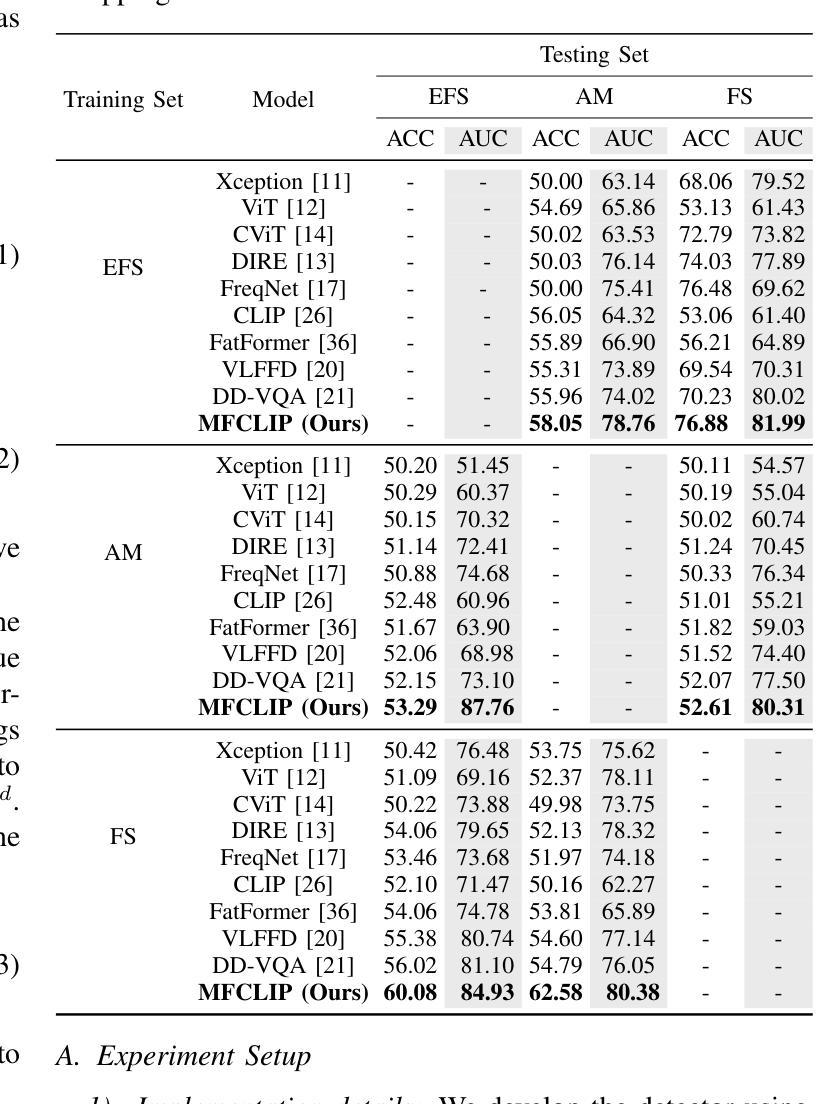
MFCLIP: Multi-modal Fine-grained CLIP for Generalizable Diffusion Face Forgery Detection
Authors:Yaning Zhang, Tianyi Wang, Zitong Yu, Zan Gao, Linlin Shen, Shengyong Chen
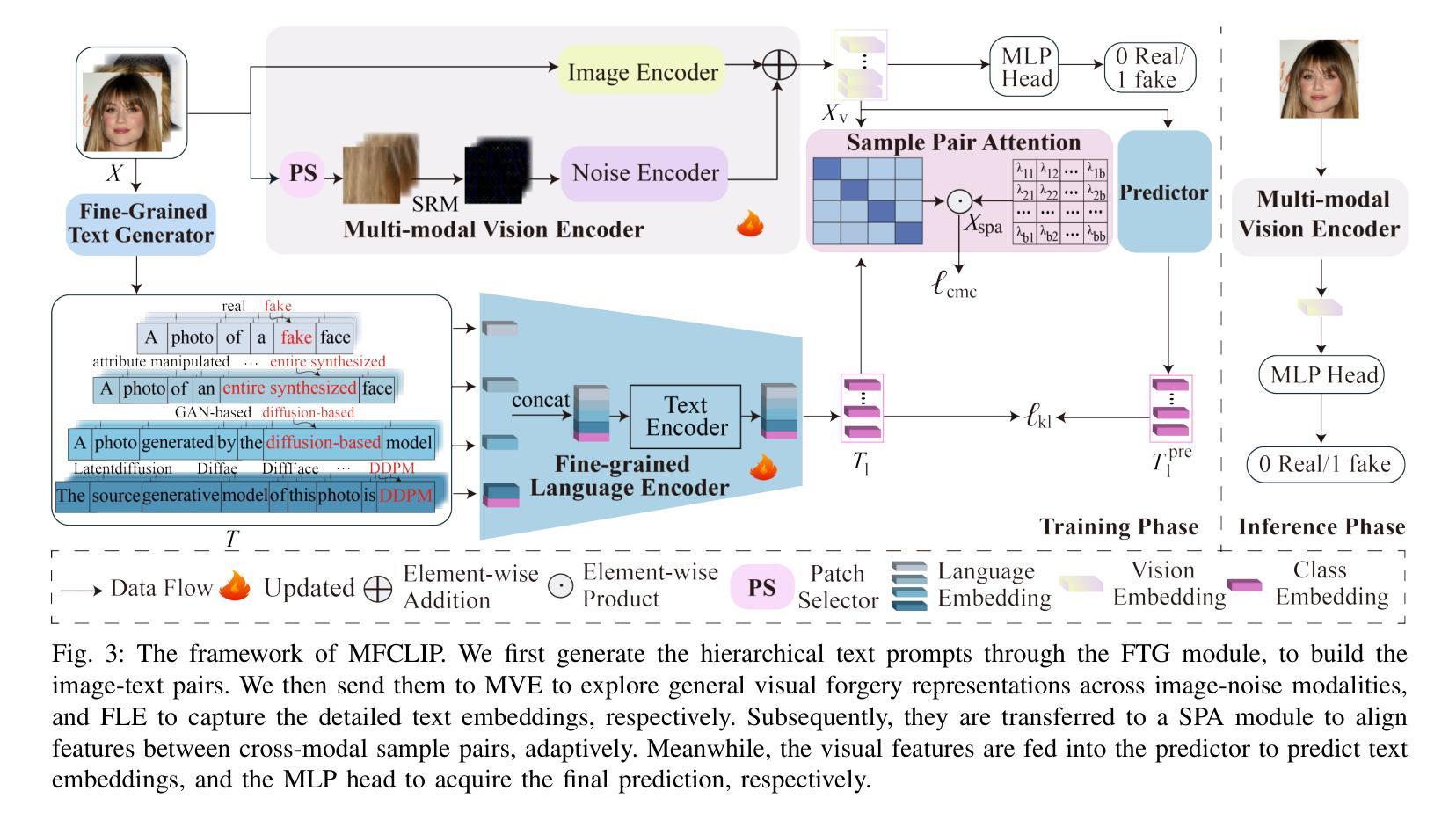
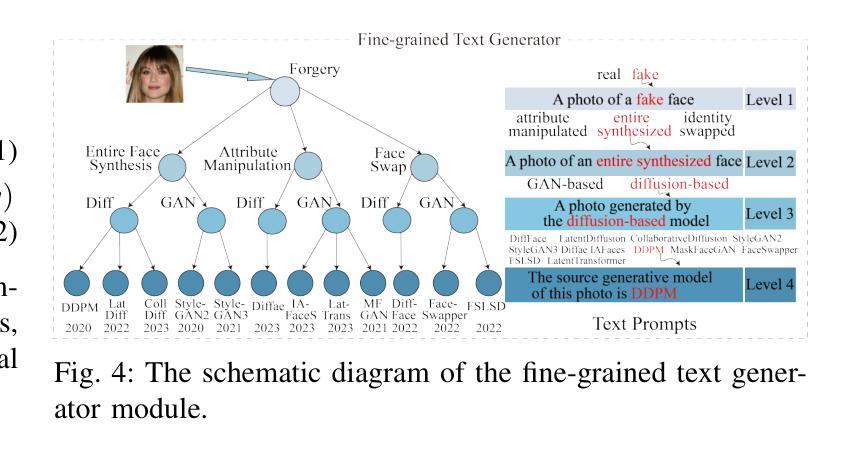
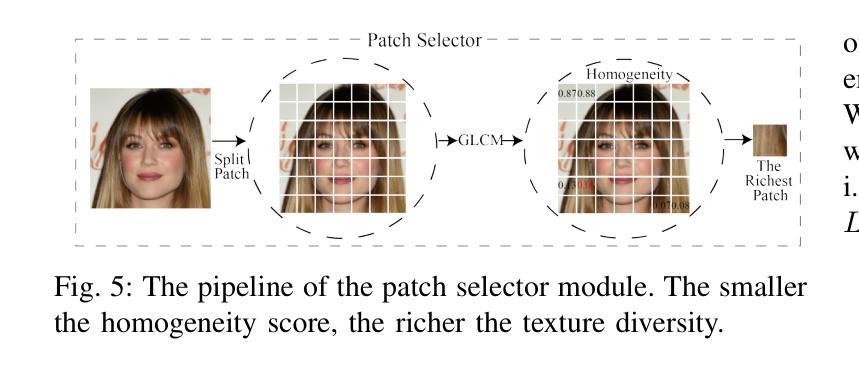
The rapid development of photo-realistic face generation methods has raised significant concerns in society and academia, highlighting the urgent need for robust and generalizable face forgery detection (FFD) techniques. Although existing approaches mainly capture face forgery patterns using image modality, other modalities like fine-grained noises and texts are not fully explored, which limits the generalization capability of the model. In addition, most FFD methods tend to identify facial images generated by GAN, but struggle to detect unseen diffusion-synthesized ones. To address the limitations, we aim to leverage the cutting-edge foundation model, contrastive language-image pre-training (CLIP), to achieve generalizable diffusion face forgery detection (DFFD). In this paper, we propose a novel multi-modal fine-grained CLIP (MFCLIP) model, which mines comprehensive and fine-grained forgery traces across image-noise modalities via language-guided face forgery representation learning, to facilitate the advancement of DFFD. Specifically, we devise a fine-grained language encoder (FLE) that extracts fine global language features from hierarchical text prompts. We design a multi-modal vision encoder (MVE) to capture global image forgery embeddings as well as fine-grained noise forgery patterns extracted from the richest patch, and integrate them to mine general visual forgery traces. Moreover, we build an innovative plug-and-play sample pair attention (SPA) method to emphasize relevant negative pairs and suppress irrelevant ones, allowing cross-modality sample pairs to conduct more flexible alignment. Extensive experiments and visualizations show that our model outperforms the state of the arts on different settings like cross-generator, cross-forgery, and cross-dataset evaluations.
随着写实主义人脸生成方法的快速发展,社会与学术界对此产生了重大关注,这突显了对稳健且可泛化的人脸伪造检测(FFD)技术的迫切需求。尽管现有方法主要使用图像模式捕捉人脸伪造特征,但其他模式(如精细纹理和文本)尚未得到完全探索,这限制了模型的泛化能力。此外,大多数FFD方法倾向于识别由生成对抗网络(GAN)生成的人脸图像,但难以检测未见过的扩散合成图像。为了解决这些限制,我们旨在利用最前沿的基础模型——对比语言图像预训练(CLIP),实现可泛化的扩散人脸伪造检测(DFFD)。在本文中,我们提出了一种新颖的多模式精细CLIP(MFCLIP)模型,它通过语言引导的人脸伪造表示学习,挖掘跨图像噪声模式的全面且精细的伪造痕迹,以促进DFFD的发展。具体来说,我们设计了一种精细语言编码器(FLE),用于从分层文本提示中提取精细的全局语言特征。我们设计了一种多模式视觉编码器(MVE),以捕获全局图像伪造嵌入以及从最具特征的补丁中提取的精细噪声伪造模式,并将它们集成在一起以挖掘通用的视觉伪造痕迹。此外,我们建立了一种创新的即插即用样本配对注意力(SPA)方法,以强调相关的负样本对并抑制不相关的样本对,从而实现跨模态样本对进行更灵活的对齐。广泛的实验和可视化结果表明,我们的模型在不同的设置(如跨生成器、跨伪造和跨数据集评估)上均优于最新技术。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于深度学习的面部生成技术引发了社会与学术界的关注,迫切需要具有鲁棒性和泛化能力的面部伪造检测(FFD)技术。当前方法主要基于图像模态捕捉面部伪造模式,但忽略了其他模态如精细噪声和文本的作用。针对现有技术的局限性,本文提出了一种基于CLIP预训练模型的多模态精细粒度CLIP(MFCLIP)模型,用于实现泛化扩散面部伪造检测(DFFD)。该模型通过语言引导的面伪造表示学习,挖掘图像噪声模态的全面精细伪造痕迹,促进DFFD的进步。实验表明,该模型在不同设置下均优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 面部生成技术的快速发展引发了社会和学术界对面部伪造检测(FFD)技术的关注,显示出对鲁棒性和泛化能力的迫切需求。
- 当前方法主要基于图像模态捕捉面部伪造模式,存在局限性。
- 为了解决这些局限性,引入了基于CLIP预训练模型的多模态精细粒度CLIP(MFCLIP)模型。
- MFCLIP模型通过语言引导的面伪造表示学习,挖掘图像噪声模态的全面精细伪造痕迹。
- MFCLIP模型设计了一个精细粒度语言编码器(FLE)和一个多模态视觉编码器(MVE),分别提取语言和图像伪造特征。
- 创新性的SPA方法强调相关的负样本对并抑制不相关的样本对,允许跨模态样本对进行更灵活的匹配。
点此查看论文截图