⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-08 更新
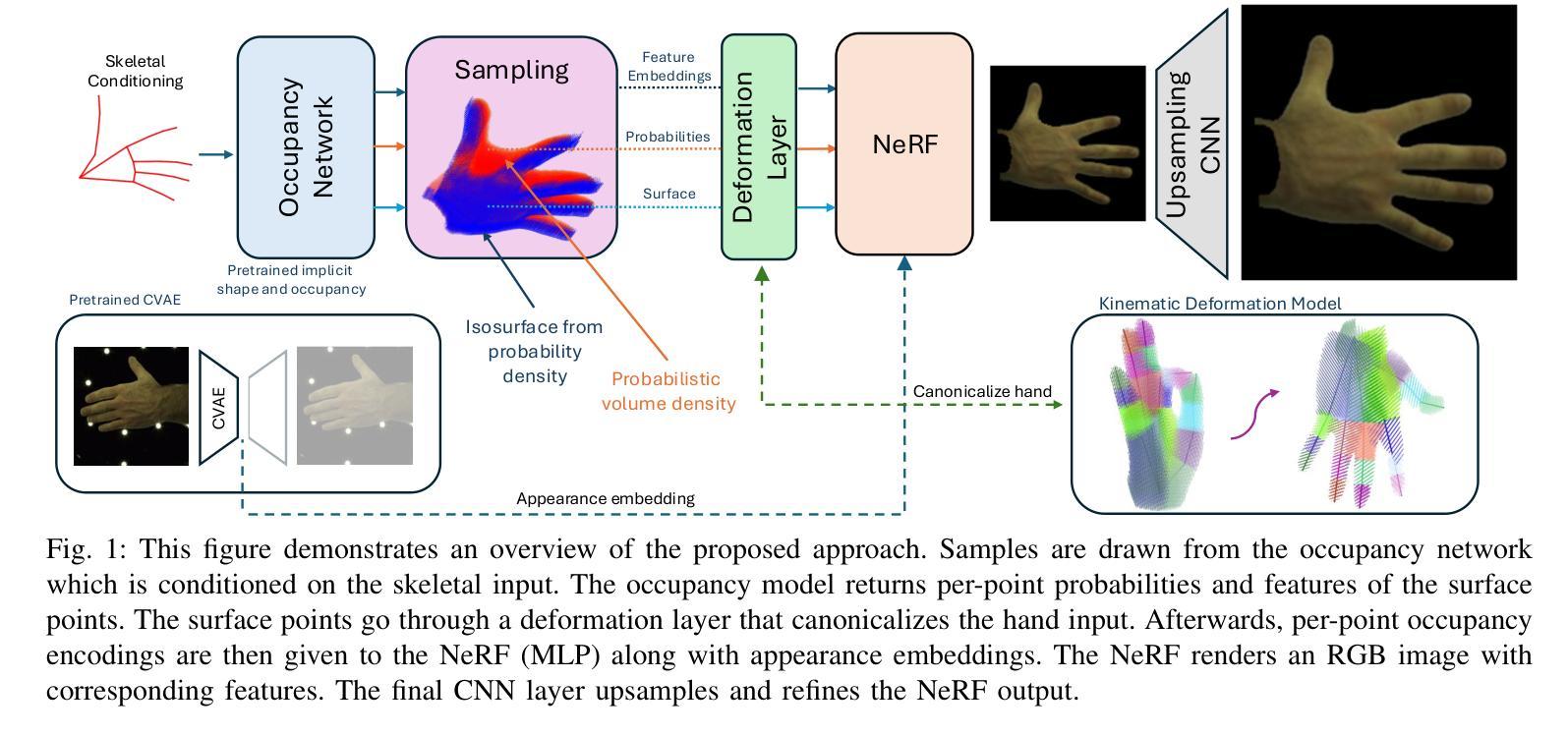
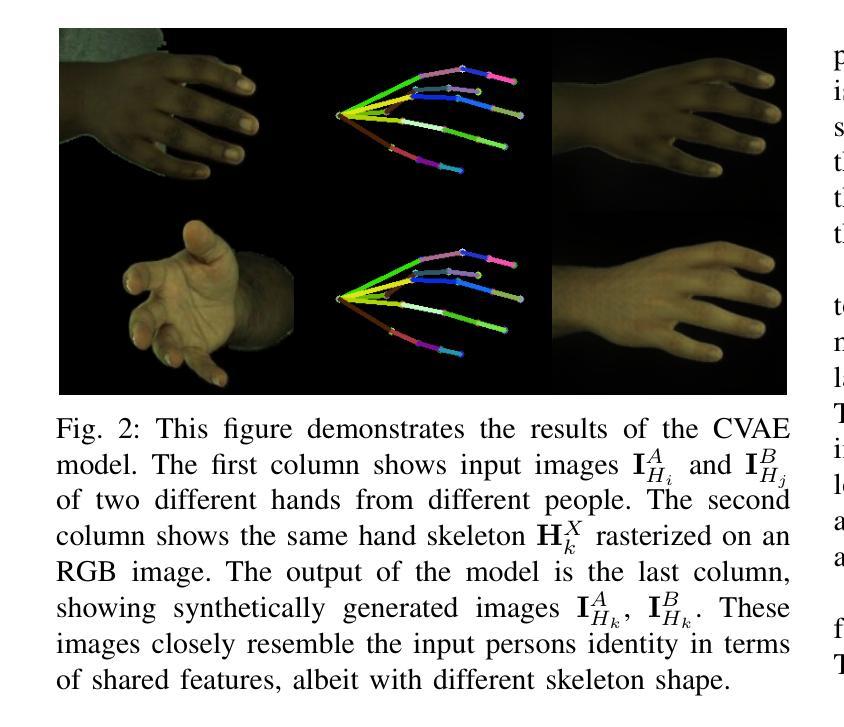
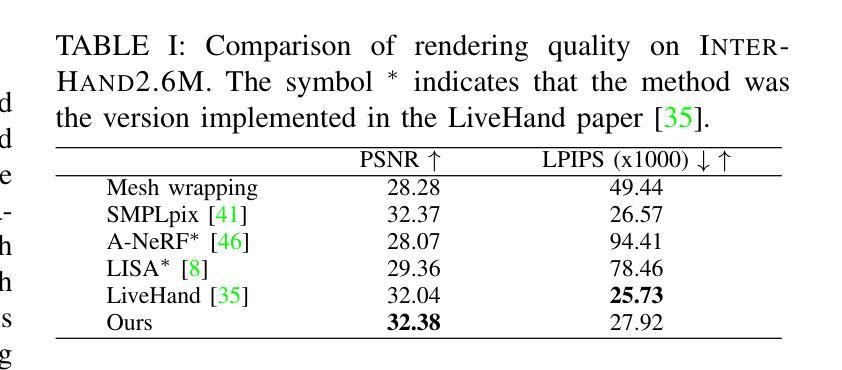
HandOcc: NeRF-based Hand Rendering with Occupancy Networks
Authors:Maksym Ivashechkin, Oscar Mendez, Richard Bowden
We propose HandOcc, a novel framework for hand rendering based upon occupancy. Popular rendering methods such as NeRF are often combined with parametric meshes to provide deformable hand models. However, in doing so, such approaches present a trade-off between the fidelity of the mesh and the complexity and dimensionality of the parametric model. The simplicity of parametric mesh structures is appealing, but the underlying issue is that it binds methods to mesh initialization, making it unable to generalize to objects where a parametric model does not exist. It also means that estimation is tied to mesh resolution and the accuracy of mesh fitting. This paper presents a pipeline for meshless 3D rendering, which we apply to the hands. By providing only a 3D skeleton, the desired appearance is extracted via a convolutional model. We do this by exploiting a NeRF renderer conditioned upon an occupancy-based representation. The approach uses the hand occupancy to resolve hand-to-hand interactions further improving results, allowing fast rendering, and excellent hand appearance transfer. On the benchmark InterHand2.6M dataset, we achieved state-of-the-art results.
我们提出了HandOcc,这是一种基于占用率的新型手渲染框架。流行的渲染方法,如NeRF,通常与参数化网格相结合,以提供可变形的手部模型。然而,这样做的方法在网格的保真度与参数模型的复杂性和维度之间存在权衡。参数化网格结构的简单性很有吸引力,但根本问题是它将方法绑定到网格初始化,使其无法推广到不存在参数模型的对象。这也意味着估计与网格分辨率和网格拟合的准确度有关。本文提出了一种无网格的3D渲染管道,我们将其应用于手部。仅通过提供3D骨架,通过卷积模型提取所需的外貌。我们通过利用基于占用率的表示条件NeRF渲染器来实现这一点。该方法利用手部占用率解决手部之间的交互问题,进一步改善结果,实现快速渲染和出色的手部外观转移。在InterHand2.6M数据集上,我们取得了最新的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
手渲染的新框架HandOcc被提出,基于占用率实现网格无关的渲染技术。该框架采用NeRF渲染器结合占用率表示,仅通过三维骨架实现期望的外观提取,通过卷积模型进行渲染,解决了传统网格模型存在的初始化和分辨率限制问题。该技术在解决手部互动和提升渲染效果上取得了突破性进展。在InterHand2.6M数据集上实现了业界领先的结果。
Key Takeaways
- HandOcc是一个基于占用率的新型手渲染框架,旨在解决传统网格模型在变形手渲染中的局限性。
- 该框架采用NeRF渲染器结合占用率表示,实现了网格无关的渲染技术。
- 仅通过三维骨架实现期望的外观提取,解决了对网格初始化的依赖问题。
- 通过卷积模型进行渲染,提高了手部的渲染速度和效果。
- 该技术解决了手部互动的问题,进一步提升了渲染效果。
- 在InterHand2.6M数据集上实现了业界领先的结果。
点此查看论文截图

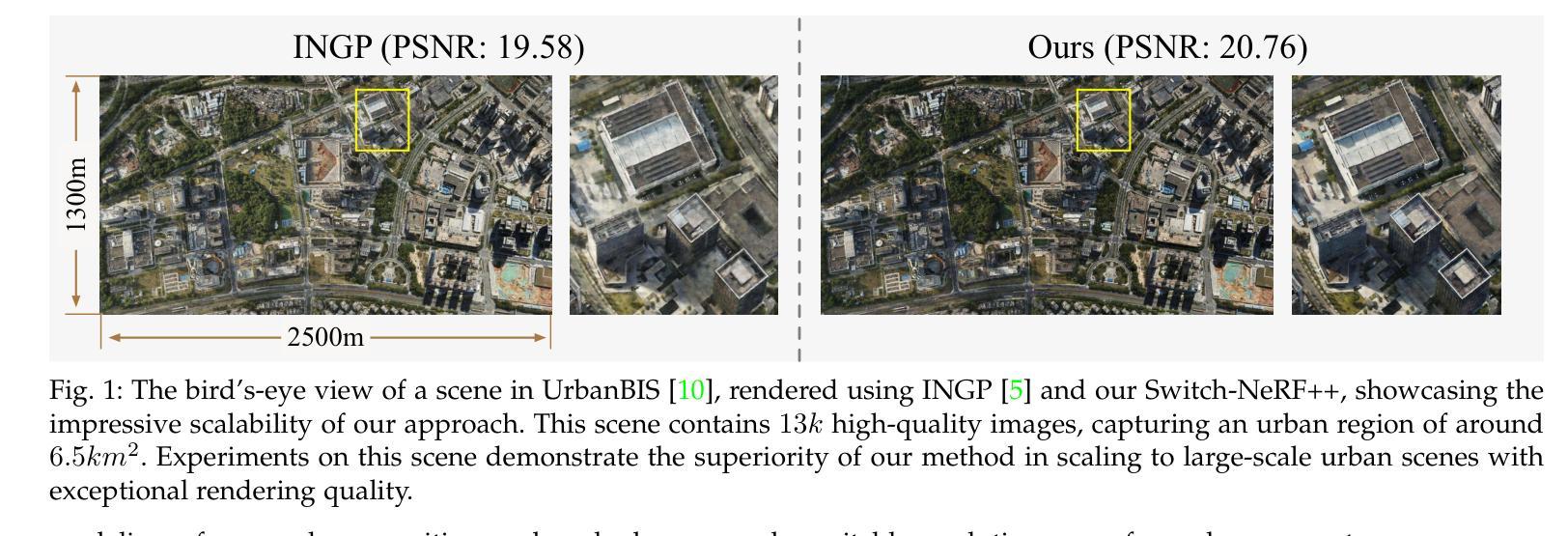
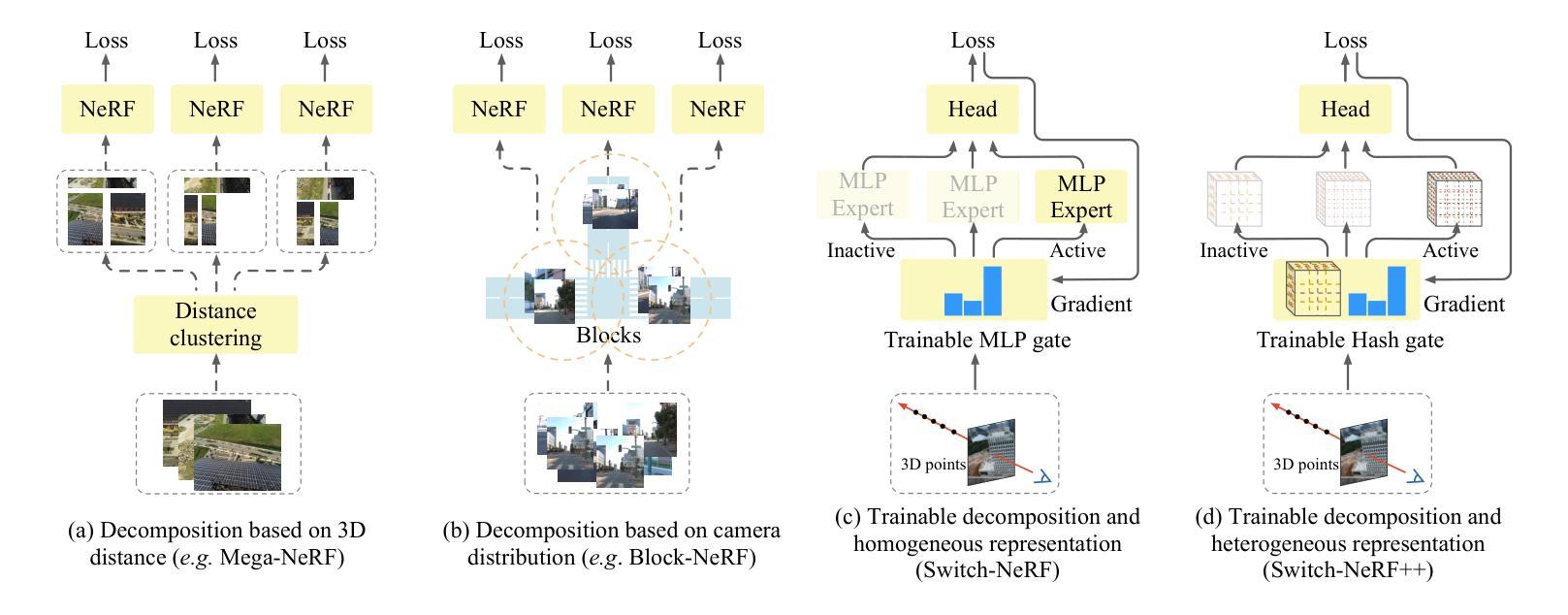
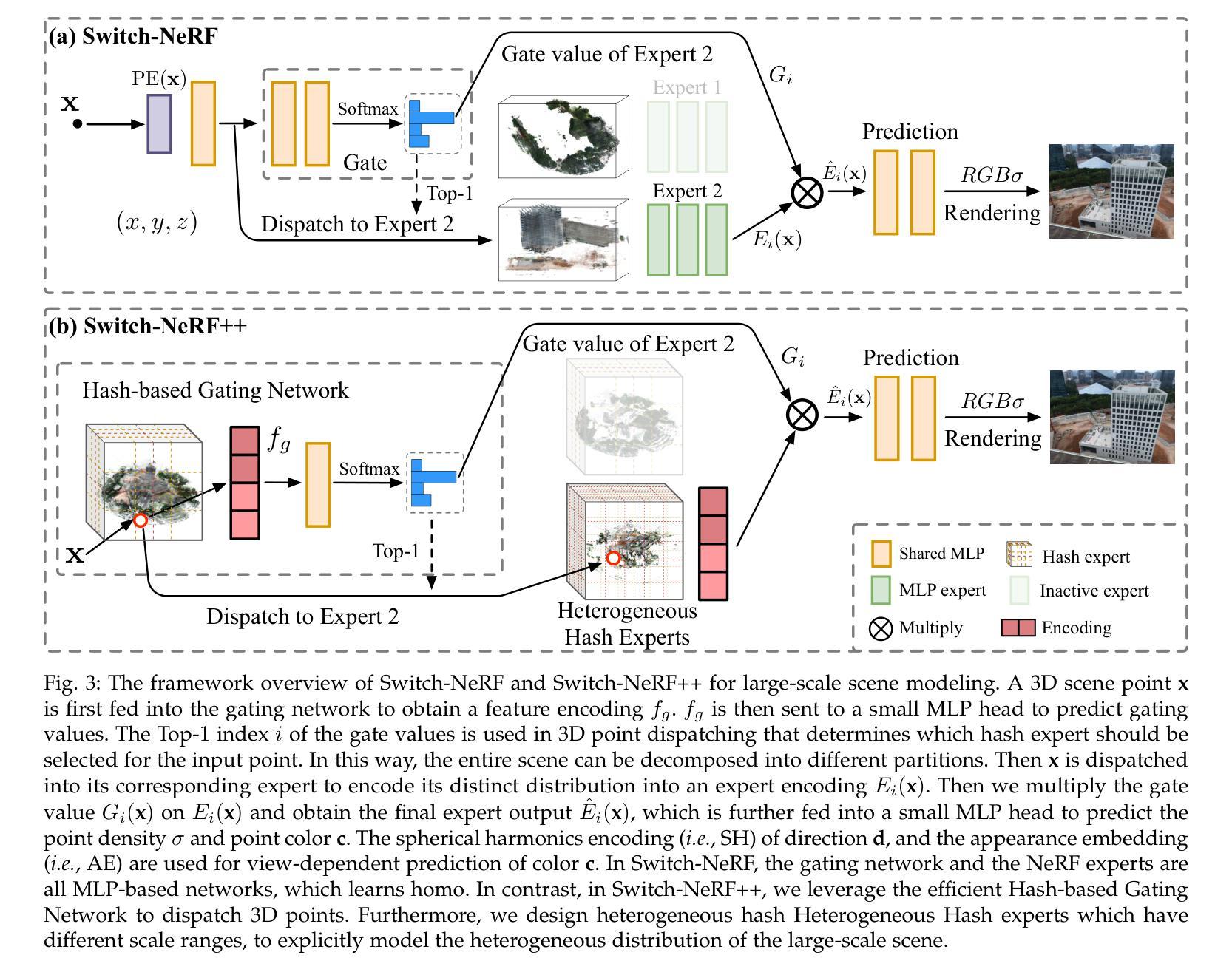
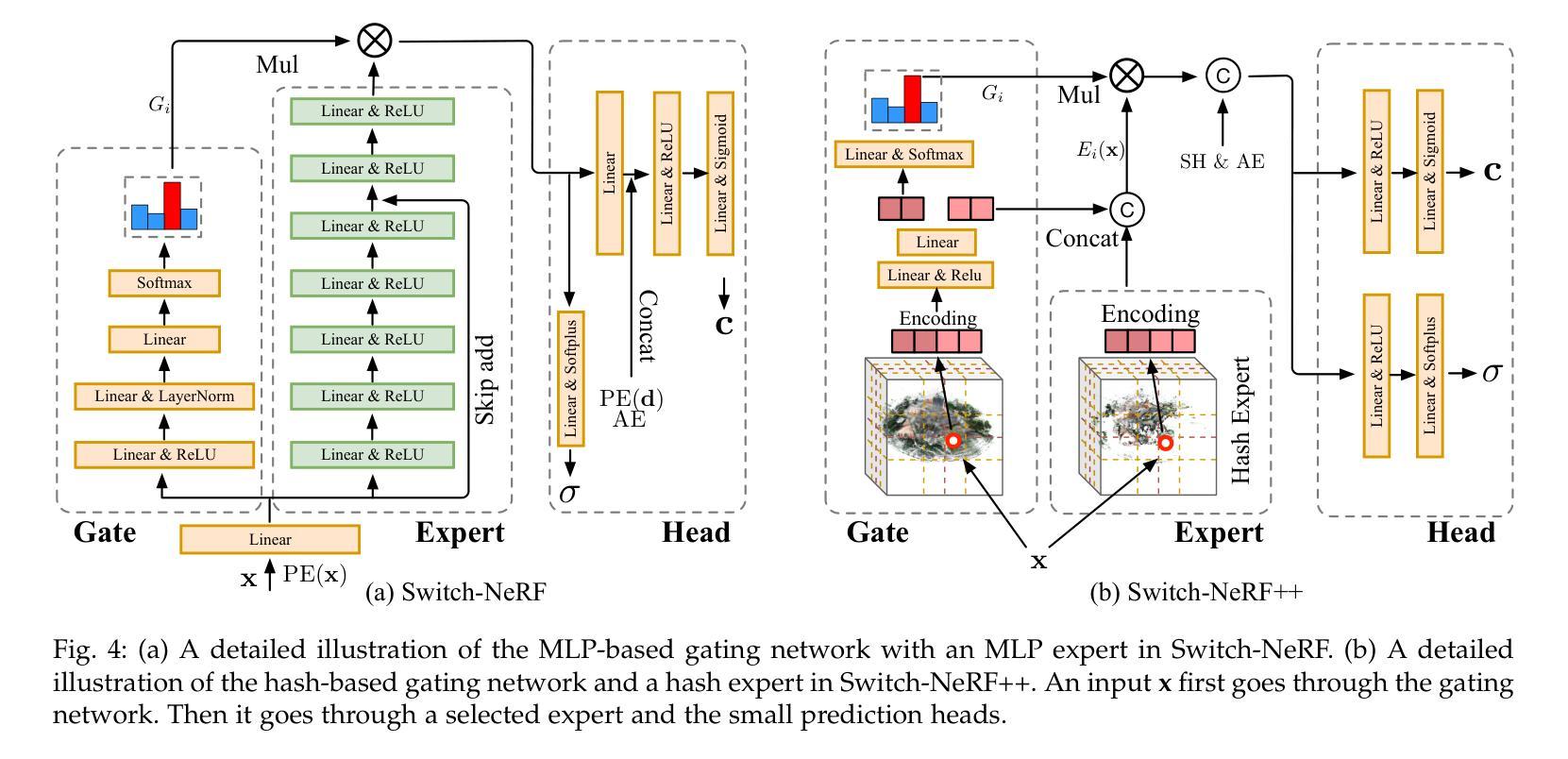
Learning Heterogeneous Mixture of Scene Experts for Large-scale Neural Radiance Fields
Authors:Zhenxing Mi, Ping Yin, Xue Xiao, Dan Xu
Recent NeRF methods on large-scale scenes have underlined the importance of scene decomposition for scalable NeRFs. Although achieving reasonable scalability, there are several critical problems remaining unexplored, i.e., learnable decomposition, modeling scene heterogeneity, and modeling efficiency. In this paper, we introduce Switch-NeRF++, a Heterogeneous Mixture of Hash Experts (HMoHE) network that addresses these challenges within a unified framework. It is a highly scalable NeRF that learns heterogeneous decomposition and heterogeneous NeRFs efficiently for large-scale scenes in an end-to-end manner. In our framework, a gating network learns to decomposes scenes and allocates 3D points to specialized NeRF experts. This gating network is co-optimized with the experts, by our proposed Sparsely Gated Mixture of Experts (MoE) NeRF framework. We incorporate a hash-based gating network and distinct heterogeneous hash experts. The hash-based gating efficiently learns the decomposition of the large-scale scene. The distinct heterogeneous hash experts consist of hash grids of different resolution ranges, enabling effective learning of the heterogeneous representation of different scene parts. These design choices make our framework an end-to-end and highly scalable NeRF solution for real-world large-scale scene modeling to achieve both quality and efficiency. We evaluate our accuracy and scalability on existing large-scale NeRF datasets and a new dataset with very large-scale scenes ($>6.5km^2$) from UrbanBIS. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach can be easily scaled to various large-scale scenes and achieve state-of-the-art scene rendering accuracy. Furthermore, our method exhibits significant efficiency, with an 8x acceleration in training and a 16x acceleration in rendering compared to Switch-NeRF. Codes will be released in https://github.com/MiZhenxing/Switch-NeRF.
近期的针对大规模场景的NeRF方法强调了场景分解对于可扩展NeRF的重要性。尽管已经实现了合理的可扩展性,但仍存在一些关键问题尚未探索,例如可学习的分解、场景异质性的建模和建模效率。在本文中,我们介绍了Switch-NeRF++,这是一种基于哈希专家的异质混合(HMoHE)网络,在一个统一的框架内解决这些挑战。它是一种高度可扩展的NeRF,能够以端到端的方式有效地对大规模场景进行异质分解和异质NeRF建模。在我们的框架中,门控网络学习分解场景并将三维点分配给专门的NeRF专家。通过我们提出的稀疏门控混合专家(MoE)NeRF框架,门控网络与专家共同进行优化。我们结合了基于哈希的门控网络和不同的异质哈希专家。基于哈希的门控网络有效地学习大规模场景的分解。不同的异质哈希专家由不同分辨率范围的哈希网格组成,能够实现不同场景部分的有效异质表示学习。这些设计选择使我们的框架成为针对现实世界大规模场景建模的端到端和高度可扩展的NeRF解决方案,以实现质量和效率。我们在现有的大规模NeRF数据集和来自UrbanBIS的大规模场景(> 6.5km²)的新数据集上评估了我们的准确性和可扩展性。大量实验表明,我们的方法可以轻松地扩展到各种大规模场景,并实现最先进的场景渲染精度。此外,我们的方法在训练和渲染方面表现出显著的高效性,与Switch-NeRF相比,训练速度提高了8倍,渲染速度提高了16倍。代码将在https://github.com/MiZhenxing/Switch-NeRF发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 9 figures
Summary
本文提出了Switch-NeRF++,一个基于Heterogeneous Mixture of Hash Experts (HMoHE)网络的端到端可伸缩NeRF解决方案。它通过引入门控网络和稀疏门控混合专家(MoE)NeRF框架,解决了大型场景的可扩展性和异质性问题。通过使用基于哈希的门控网络和不同的异质哈希专家,Switch-NeRF++能高效地进行场景分解和学习场景的异质表示。这一方法被评估为可在现实的大规模场景建模中实现高质量和高效率的解决方案。相较于Switch-NeRF,该方法在训练和渲染方面展现出显著的速度优势。
Key Takeaways
- Switch-NeRF++基于Heterogeneous Mixture of Hash Experts (HMoHE)网络进行大规模场景的NeRF建模。
- 通过引入门控网络和混合专家技术,实现了场景的高效分解和异质表示学习。
- 基于哈希的门控网络能高效地进行场景分解。
- 不同分辨率范围的异质哈希专家能更有效地学习场景的异质表示。
- 该方法可实现高质量的场景渲染,并且在可扩展性方面表现优异。
- Switch-NeRF++在大型场景数据集上的表现达到业界领先水平。
点此查看论文截图

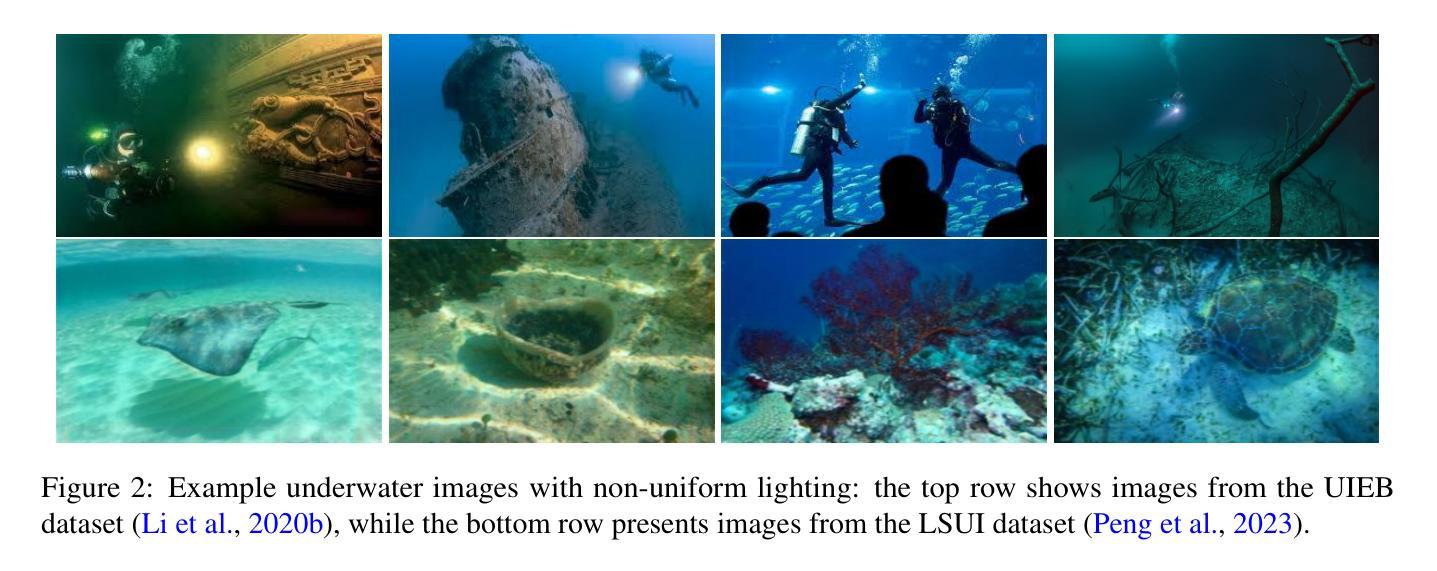
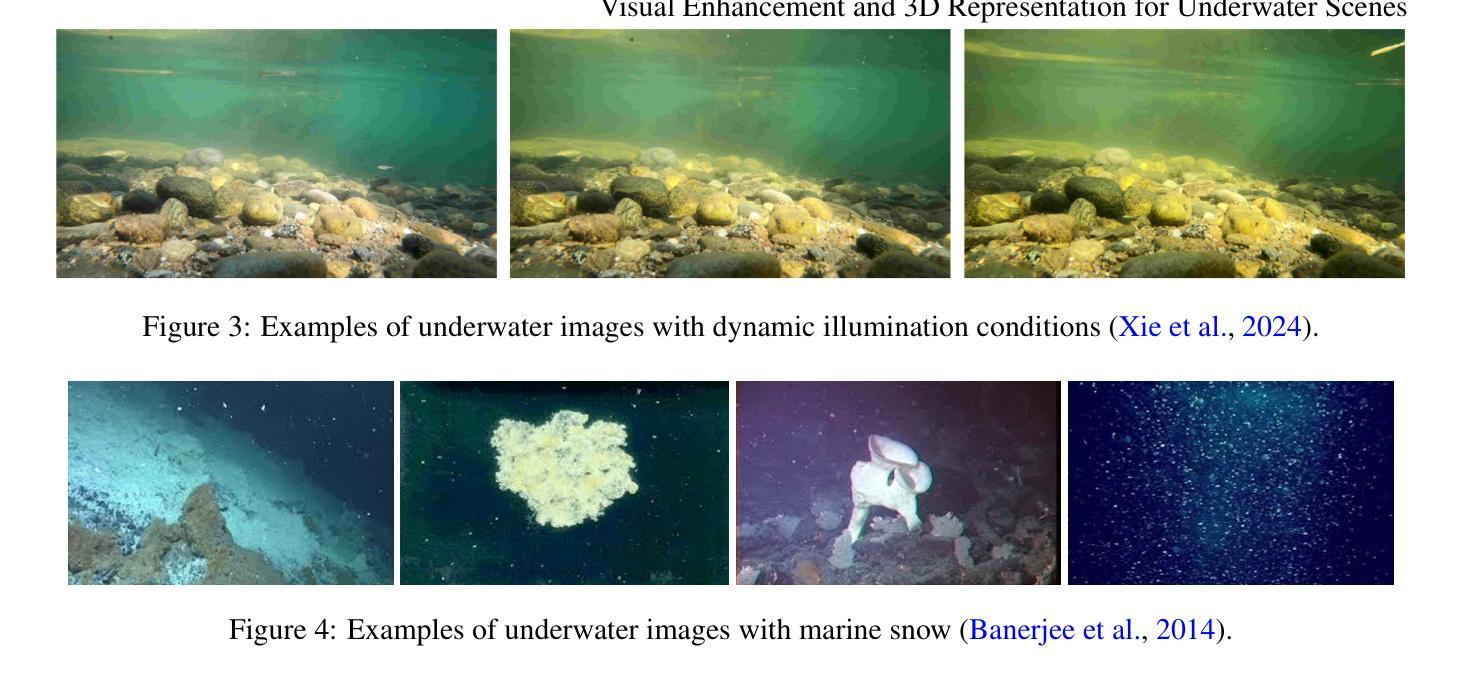
Visual enhancement and 3D representation for underwater scenes: a review
Authors:Guoxi Huang, Haoran Wang, Brett Seymour, Evan Kovacs, John Ellerbrock, Dave Blackham, Nantheera Anantrasirichai
Underwater visual enhancement (UVE) and underwater 3D reconstruction pose significant challenges in computer vision and AI-based tasks due to complex imaging conditions in aquatic environments. Despite the development of numerous enhancement algorithms, a comprehensive and systematic review covering both UVE and underwater 3D reconstruction remains absent. To advance research in these areas, we present an in-depth review from multiple perspectives. First, we introduce the fundamental physical models, highlighting the peculiarities that challenge conventional techniques. We survey advanced methods for visual enhancement and 3D reconstruction specifically designed for underwater scenarios. The paper assesses various approaches from non-learning methods to advanced data-driven techniques, including Neural Radiance Fields and 3D Gaussian Splatting, discussing their effectiveness in handling underwater distortions. Finally, we conduct both quantitative and qualitative evaluations of state-of-the-art UVE and underwater 3D reconstruction algorithms across multiple benchmark datasets. Finally, we highlight key research directions for future advancements in underwater vision.
水下视觉增强(UVE)和水下3D重建在计算机视觉和基于人工智能的任务中面临重大挑战,这主要是因为水上环境中复杂的成像条件。尽管有许多增强算法的发展,但涵盖UVE和水下3D重建的全面系统综述仍然缺失。为了促进这些领域的研究进展,我们从多个角度进行了深入的综述。首先,我们介绍了基本的物理模型,并强调了挑战传统技术的特性。我们调查了专门为水下场景设计的视觉增强和3D重建的先进方法。这篇论文从非学习方法到先进的数据驱动技术进行了各种方法的评估,包括神经辐射场和3D高斯喷涂,讨论了它们在处理水下失真方面的有效性。最后,我们在多个基准数据集上对最新的UVE和水下3D重建算法进行了定量和定性的评估。最后,我们强调了未来水下视觉研究的关键方向。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文全面综述了水下视觉增强(UVE)和水下三维重建在计算机视觉和人工智能领域面临的挑战。文章介绍了基本物理模型,评述了针对水下场景的视觉增强和三维重建的先进方法,并评估了多种方法的有效性。此外,本文还开展了对先进算法在多基准数据集上的定量和定性评估,并指出了未来水下视觉研究的关键方向。
Key Takeaways
- 水下视觉增强(UVE)和三维重建在水下环境中面临诸多挑战。
- 文章介绍了基本物理模型,强调其特殊性对常规技术的挑战。
- 文章综述了针对水下场景的先进视觉增强和三维重建方法。
- 文章评估了多种方法的有效性,包括非学习方法、数据驱动技术等。
- 文中提到了Neural Radiance Fields和3D Gaussian Splatting在水下失真处理中的应用。
- 文章通过多基准数据集对先进算法进行了定量和定性评估。
点此查看论文截图




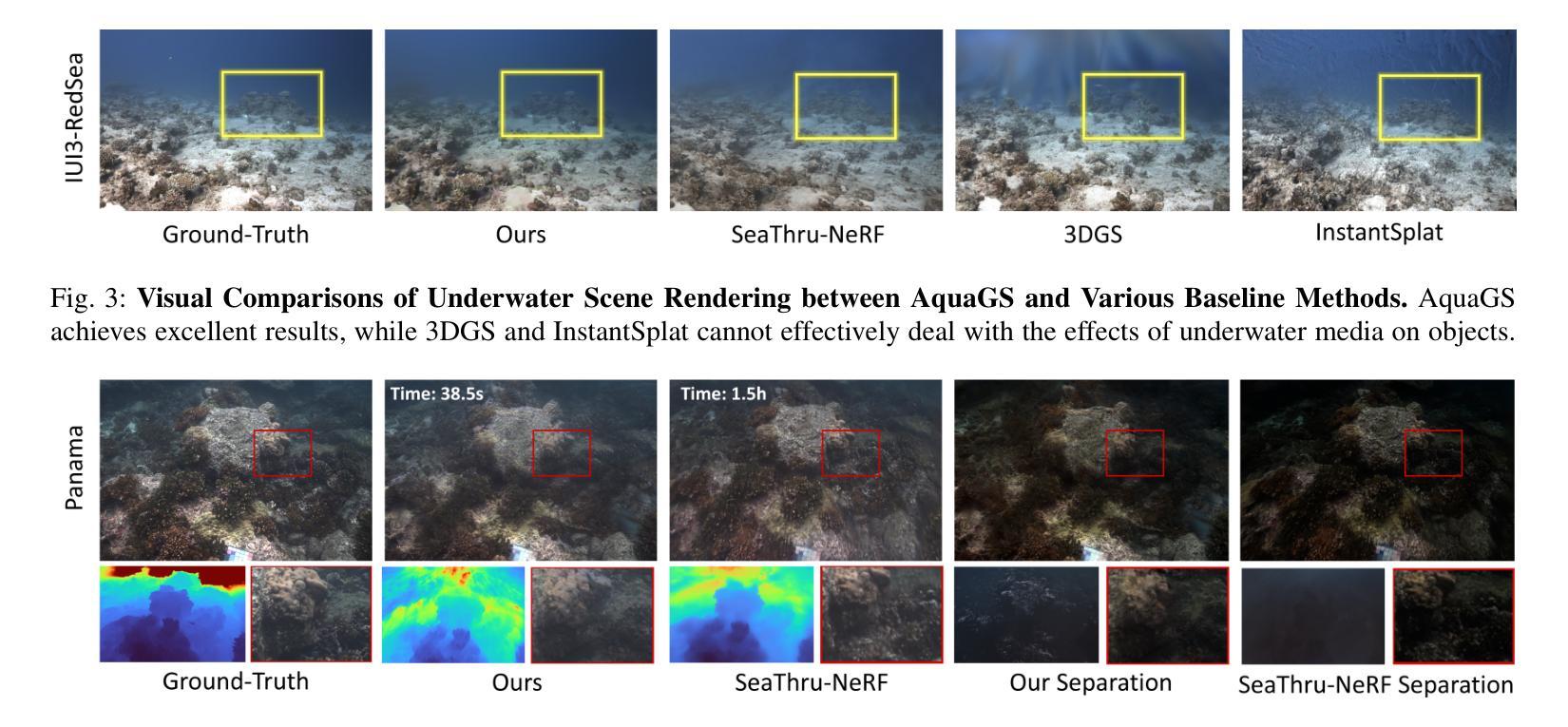
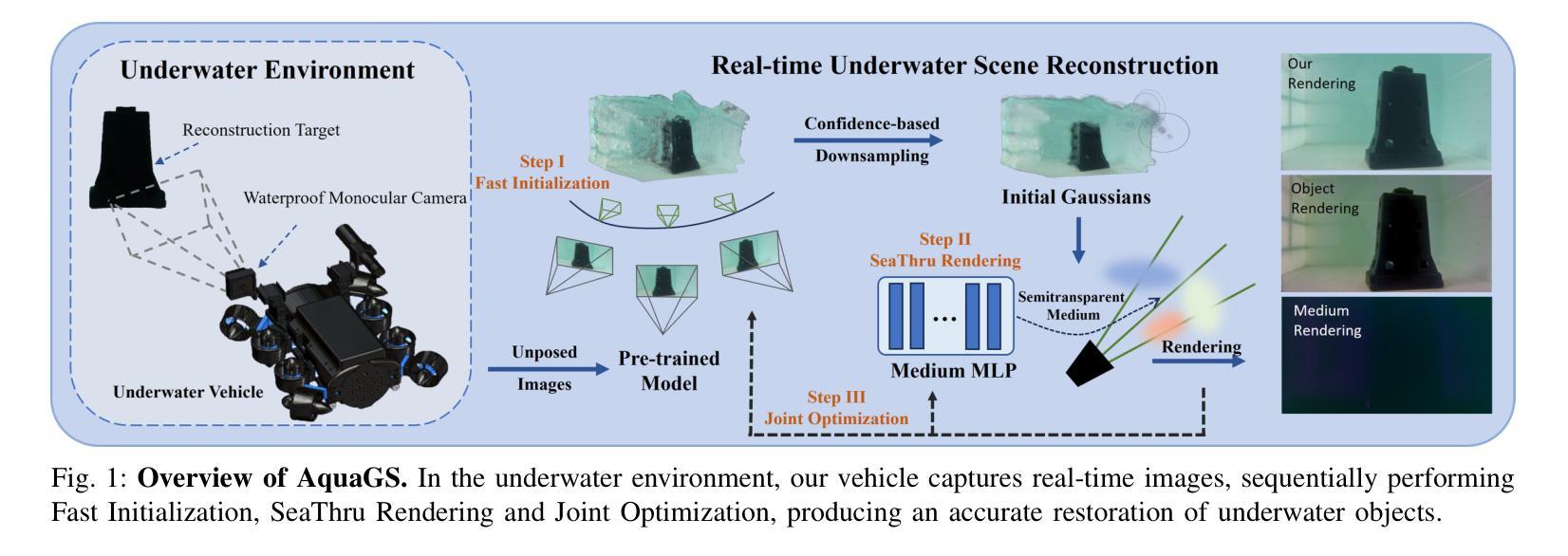
AquaGS: Fast Underwater Scene Reconstruction with SfM-Free Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Junhao Shi, Jisheng Xu, Jianping He, Zhiliang Lin
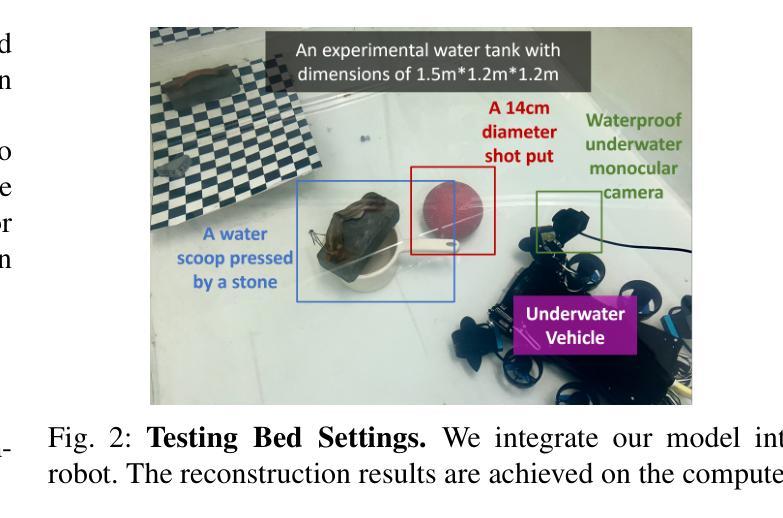
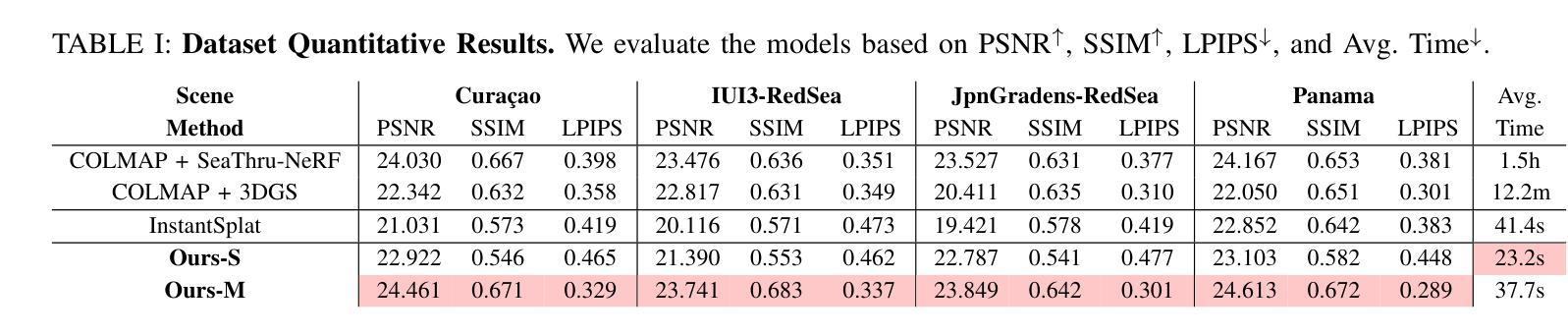
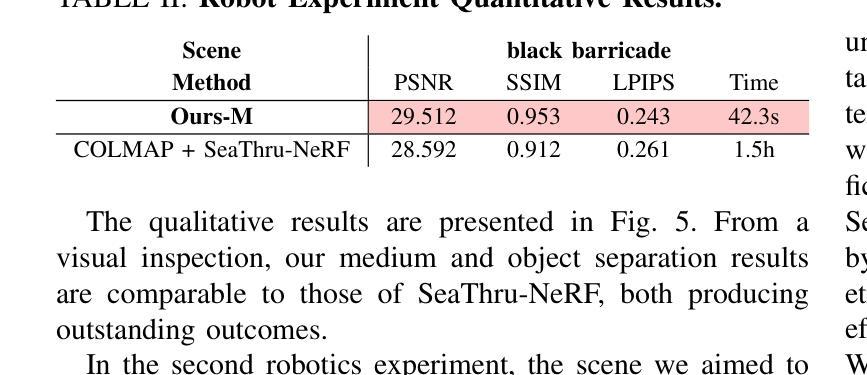
Underwater scene reconstruction is a critical tech-nology for underwater operations, enabling the generation of 3D models from images captured by underwater platforms. However, the quality of underwater images is often degraded due to medium interference, which limits the effectiveness of Structure-from-Motion (SfM) pose estimation, leading to subsequent reconstruction failures. Additionally, SfM methods typically operate at slower speeds, further hindering their applicability in real-time scenarios. In this paper, we introduce AquaGS, an SfM-free underwater scene reconstruction model based on the SeaThru algorithm, which facilitates rapid and accurate separation of scene details and medium features. Our approach initializes Gaussians by integrating state-of-the-art multi-view stereo (MVS) technology, employs implicit Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) for rendering translucent media and utilizes the latest explicit 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) technique to render object surfaces, which effectively addresses the limitations of traditional methods and accurately simulates underwater optical phenomena. Experimental results on the data set and the robot platform show that our model can complete high-precision reconstruction in 30 seconds with only 3 image inputs, significantly enhancing the practical application of the algorithm in robotic platforms.
水下场景重建是水下操作的关键技术,它能够从水下平台捕获的图像生成3D模型。然而,由于介质干扰,水下图像的质量往往下降,这限制了从运动结构(SfM)姿态估计的有效性,进而导致重建失败。此外,SfM方法通常运行速度较慢,进一步阻碍了在实时场景中的应用。在本文中,我们介绍了AquaGS,一种基于SeaThru算法的非SfM水下场景重建模型,它有助于快速准确地分离场景细节和介质特征。我们的方法通过集成最新的多视图立体(MVS)技术来初始化高斯分布,采用隐式神经辐射场(NeRF)进行半透明介质的渲染,并利用最新的显式3D高斯喷射(3DGS)技术来渲染物体表面,这有效地克服了传统方法的局限性,并准确地模拟了水下光学现象。在数据集和机器人平台上的实验结果表明,我们的模型仅需3张图像输入,就能在30秒内完成高精度重建,显著提高了该算法在机器人平台上的实际应用效果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在水下场景重建中,SfM方法受到水中干扰影响导致重建失败,且运行速度慢。本文提出一种基于SeaThru算法的无SfM水下场景重建模型AquaGS,可快速准确分离场景细节和介质特征,采用隐式NeRF渲染半透明介质,并利用最新的显式3D高斯贴图技术渲染物体表面,有效解决了传统方法的局限性,模拟水下光学现象更准确,在机器人平台上实现了高精度快速重建。
Key Takeaways
- 水下图像质量因介质干扰而降低,影响SfM姿态估计,导致重建失败。
- 现有SfM方法运行速度慢,难以应用于实时场景。
- AquaGS模型基于SeaThru算法,无需SfM技术,可快速准确分离场景细节和介质特征。
- AquaGS采用隐式NeRF渲染半透明介质,模拟水下光学现象更准确。
- 3DGS技术用于渲染物体表面,增强了模型的表达能力。
- 实验结果表明,AquaGS在30秒内仅用3张图像即可完成高精度重建。
点此查看论文截图



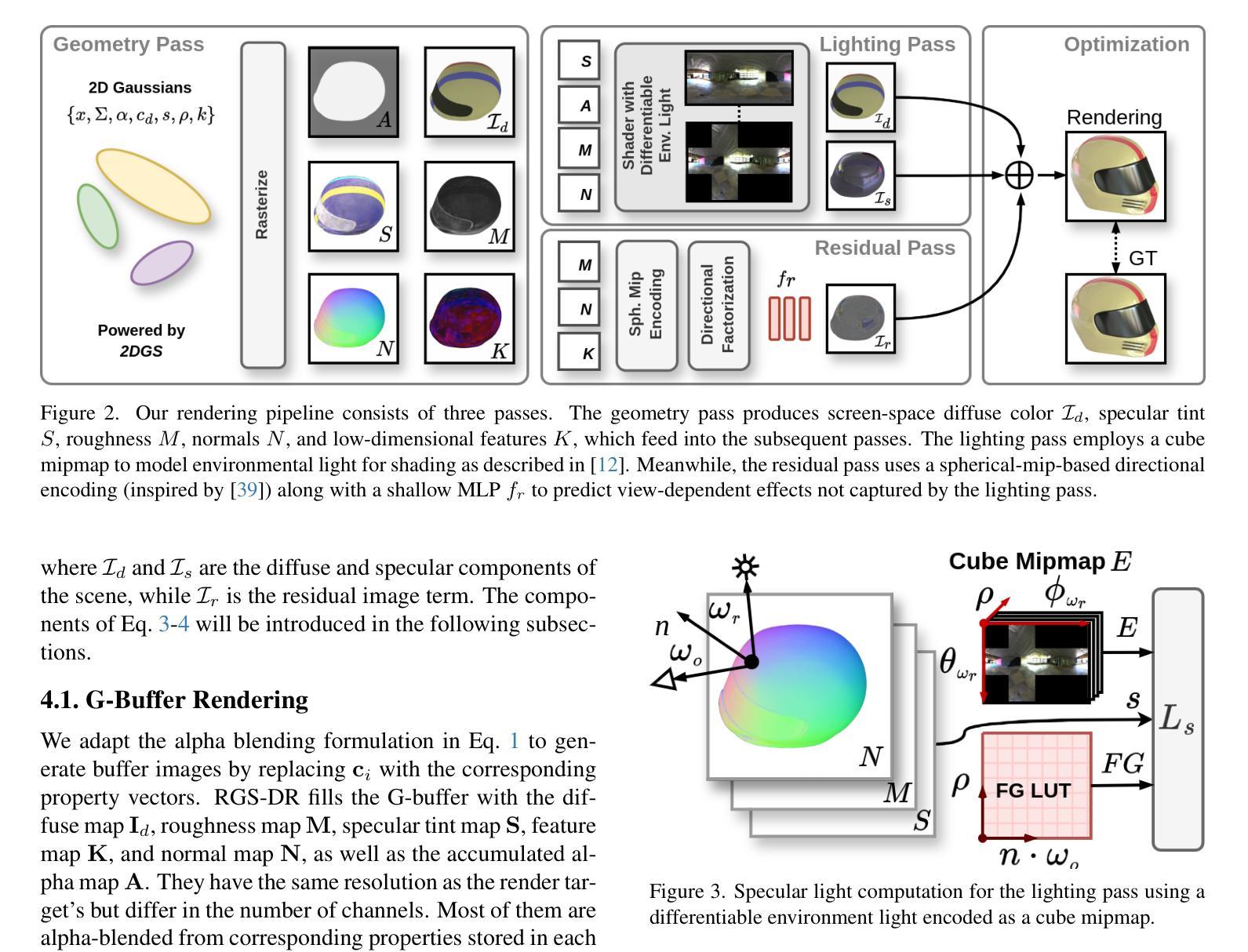
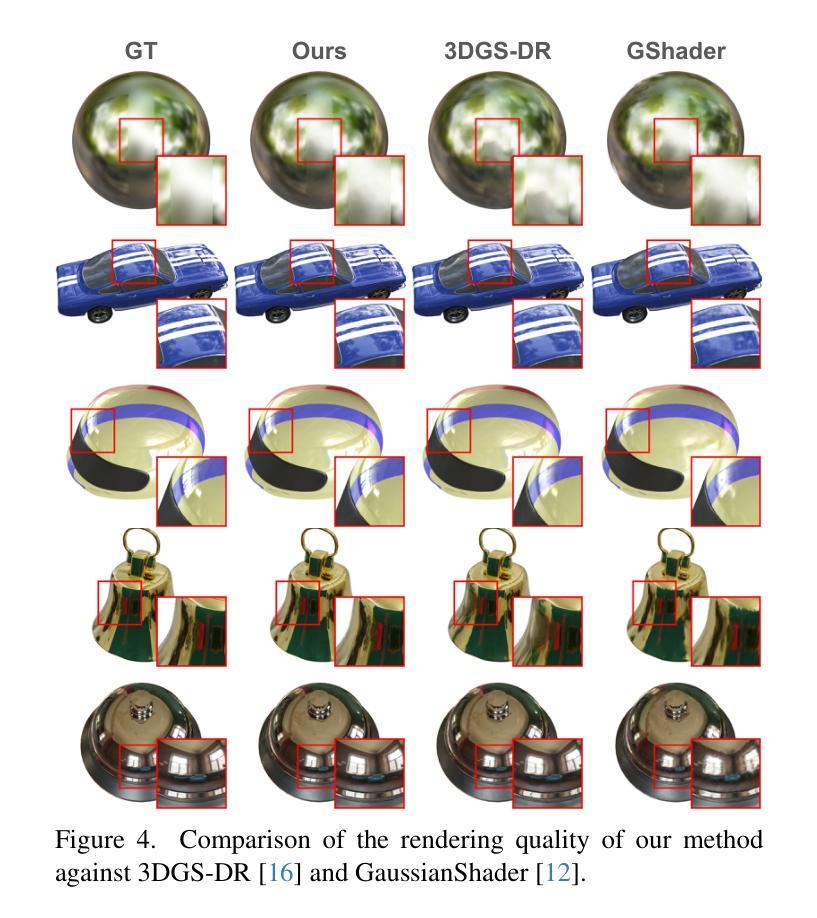
RGS-DR: Reflective Gaussian Surfels with Deferred Rendering for Shiny Objects
Authors:Georgios Kouros, Minye Wu, Tinne Tuytelaars
We introduce RGS-DR, a novel inverse rendering method for reconstructing and rendering glossy and reflective objects with support for flexible relighting and scene editing. Unlike existing methods (e.g., NeRF and 3D Gaussian Splatting), which struggle with view-dependent effects, RGS-DR utilizes a 2D Gaussian surfel representation to accurately estimate geometry and surface normals, an essential property for high-quality inverse rendering. Our approach explicitly models geometric and material properties through learnable primitives rasterized into a deferred shading pipeline, effectively reducing rendering artifacts and preserving sharp reflections. By employing a multi-level cube mipmap, RGS-DR accurately approximates environment lighting integrals, facilitating high-quality reconstruction and relighting. A residual pass with spherical-mipmap-based directional encoding further refines the appearance modeling. Experiments demonstrate that RGS-DR achieves high-quality reconstruction and rendering quality for shiny objects, often outperforming reconstruction-exclusive state-of-the-art methods incapable of relighting.
我们介绍了RGS-DR,这是一种用于重建和渲染光滑和反射物体的新型逆向渲染方法,支持灵活的重新打光和场景编辑。与现有方法(例如NeRF和3D高斯Splatting)不同,这些方法在处理视图相关效果时遇到困难,RGS-DR利用2D高斯surfel表示法准确估计几何和表面法线,这是高质量逆向渲染的基本属性。我们的方法通过可学习的原始元素显式建模几何和材料属性,并将其渲染到延迟着色管道中,这有效地减少了渲染伪影并保持了锐利的反射。通过采用多层次立方体mipmap,RGS-DR能够准确近似环境光照积分,从而实现高质量的重建和重新打光。基于球面mipmap的方向编码的残差传递进一步改进了外观建模。实验表明,RGS-DR实现了高质量的重建和渲染质量,尤其是对于光滑物体的渲染效果出众,往往超过了只能进行重建而不能重新打光的最新技术方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
高性能的逆向渲染方法RGS-DR被提出,用于重建和渲染光滑且具有反射特性的物体,并支持灵活的补光与场景编辑。不同于现有方法,RGS-DR使用二维高斯surfels表示法准确估计几何与表面法线,并显式建模几何与材质属性。通过多层次立方体mipmap,准确近似环境光照积分,实现高质量重建与补光。实验证明,RGS-DR对光泽物体的重建与渲染质量高,常优于仅支持重建的最新技术。
Key Takeaways
- RGS-DR是一种新颖的逆向渲染方法,用于重建和渲染具有光泽和反射特性的物体。
- 该方法支持灵活的补光和场景编辑。
- RGS-DR使用二维高斯surfels表示法来准确估计几何和表面法线,这是高质量逆向渲染的关键属性。
- 通过学习原始几何和材质属性的显式建模,RGS-DR减少了渲染伪影并保持了锐利的反射。
- 采用多层次立方体mipmap技术准确近似环境光照积分,提高重建和补光质量。
- 引入一个残差通道配合球形mipmap定向编码来进一步改善外观建模。
点此查看论文截图

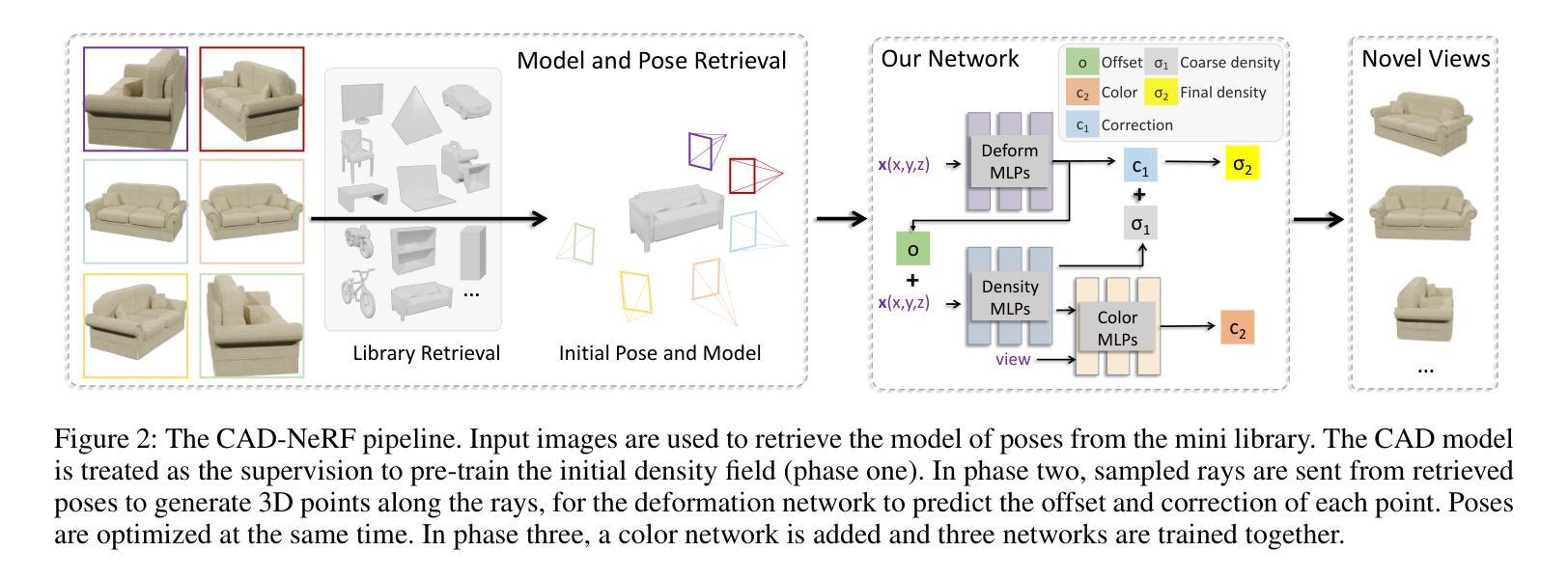
CAD-NeRF: Learning NeRFs from Uncalibrated Few-view Images by CAD Model Retrieval
Authors:Xin Wen, Xuening Zhu, Renjiao Yi, Zhifeng Wang, Chenyang Zhu, Kai Xu
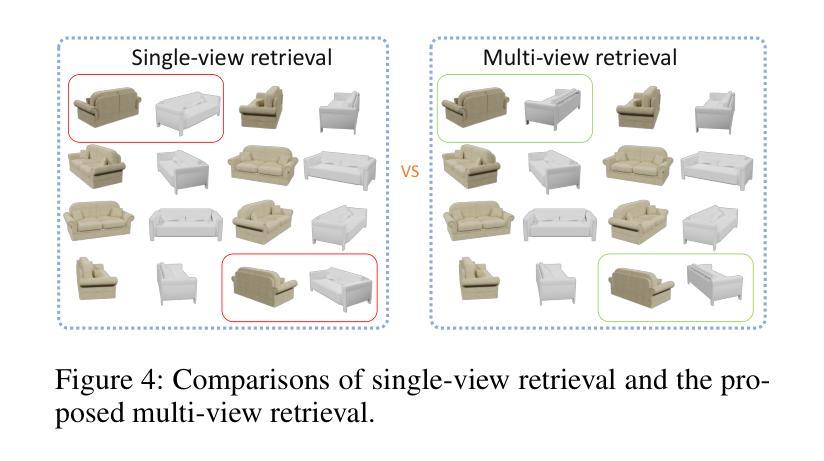
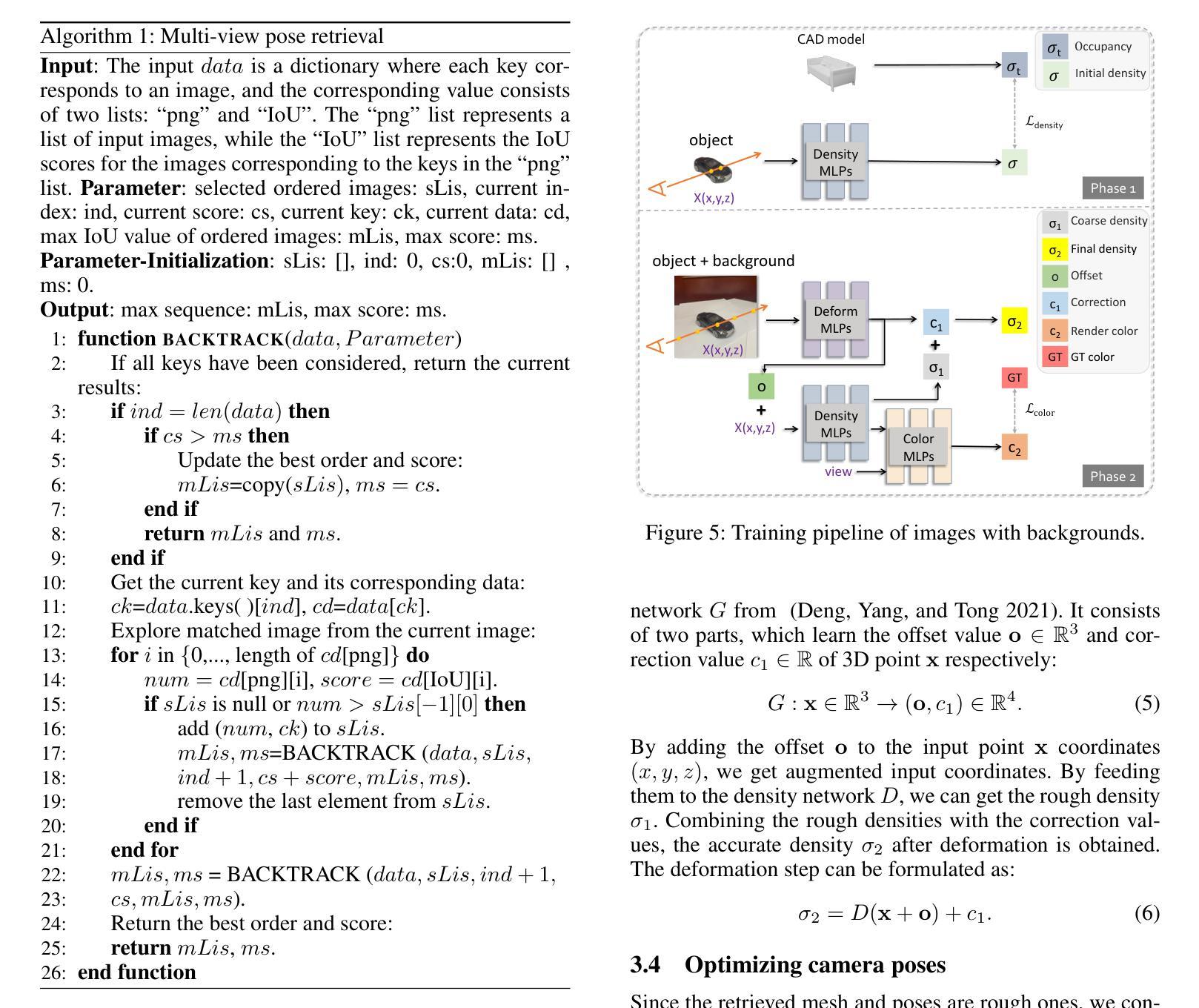
Reconstructing from multi-view images is a longstanding problem in 3D vision, where neural radiance fields (NeRFs) have shown great potential and get realistic rendered images of novel views. Currently, most NeRF methods either require accurate camera poses or a large number of input images, or even both. Reconstructing NeRF from few-view images without poses is challenging and highly ill-posed. To address this problem, we propose CAD-NeRF, a method reconstructed from less than 10 images without any known poses. Specifically, we build a mini library of several CAD models from ShapeNet and render them from many random views. Given sparse-view input images, we run a model and pose retrieval from the library, to get a model with similar shapes, serving as the density supervision and pose initializations. Here we propose a multi-view pose retrieval method to avoid pose conflicts among views, which is a new and unseen problem in uncalibrated NeRF methods. Then, the geometry of the object is trained by the CAD guidance. The deformation of the density field and camera poses are optimized jointly. Then texture and density are trained and fine-tuned as well. All training phases are in self-supervised manners. Comprehensive evaluations of synthetic and real images show that CAD-NeRF successfully learns accurate densities with a large deformation from retrieved CAD models, showing the generalization abilities.
从多视角图像重建是3D视觉中的一个长期存在的问题,神经辐射场(NeRF)在此展现出巨大潜力,并能呈现真实感的新视角渲染图像。当前,大多数NeRF方法需要准确的相机姿态或大量输入图像,甚至两者都需要。从少数视角图像无姿态地重建NeRF是具有挑战性和高度不适定的。为解决这一问题,我们提出CAD-NeRF方法,该方法可从不到10张图像中重建,而无需任何已知姿态。具体来说,我们从ShapeNet构建了几个CAD模型的迷你库,并从许多随机视角进行渲染。给定稀疏视角的输入图像,我们从库中运行模型和姿态检索,获得形状相似的模型,作为密度监督和姿态初始化。这里我们提出了一种多视角姿态检索方法,以避免各视角间的姿态冲突,这是在非校准NeRF方法中的新且未见的问题。然后,通过CAD指导训练物体的几何形状。密度场的变形和相机姿态进行优化结合。然后训练和微调纹理和密度。所有训练阶段都是自监督的。对合成图像和真实图像的综合评估表明,CAD-NeRF成功学习了从检索的CAD模型的准确密度,并展现出大变形和泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The article has been accepted by Frontiers of Computer Science (FCS)
Summary
本文介绍了利用神经网络辐射场(NeRF)技术从多角度图像重建三维物体的问题。针对现有NeRF方法需要大量输入图像和精确相机姿态的问题,提出了一种名为CAD-NeRF的新方法,能够从少数图像中重建NeRF,而无需知道相机姿态。通过构建ShapeNet中的CAD模型库,从多个随机视角进行渲染。在给定稀疏视图输入图像后,从库中检索相似形状模型和姿态,作为密度监督和姿态初始值。为避免未校准NeRF方法中的姿态冲突问题,提出了一种新的多视角姿态检索方法。在检索到的CAD模型的指导下训练物体的几何形状,并联合优化密度场的变形和相机姿态。最后,对纹理和密度进行训练和微调。所有训练阶段都是自我监督的。对合成图像和真实图像的综合评估表明,CAD-NeRF成功学习了从检索到的CAD模型中的准确密度,并显示出良好的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- NeRF技术用于从多角度图像重建三维物体。
- CAD-NeRF方法能够从少数图像中重建NeRF,无需知道相机姿态。
- 建立CAD模型库,从多个随机视角进行渲染。
- 通过模型与姿态检索,获取相似形状作为密度监督和姿态初始化。
- 引入多视角姿态检索方法,避免未校准NeRF中的姿态冲突问题。
- 在CAD模型的指导下训练物体的几何形状,联合优化密度场的变形和相机姿态。
点此查看论文截图


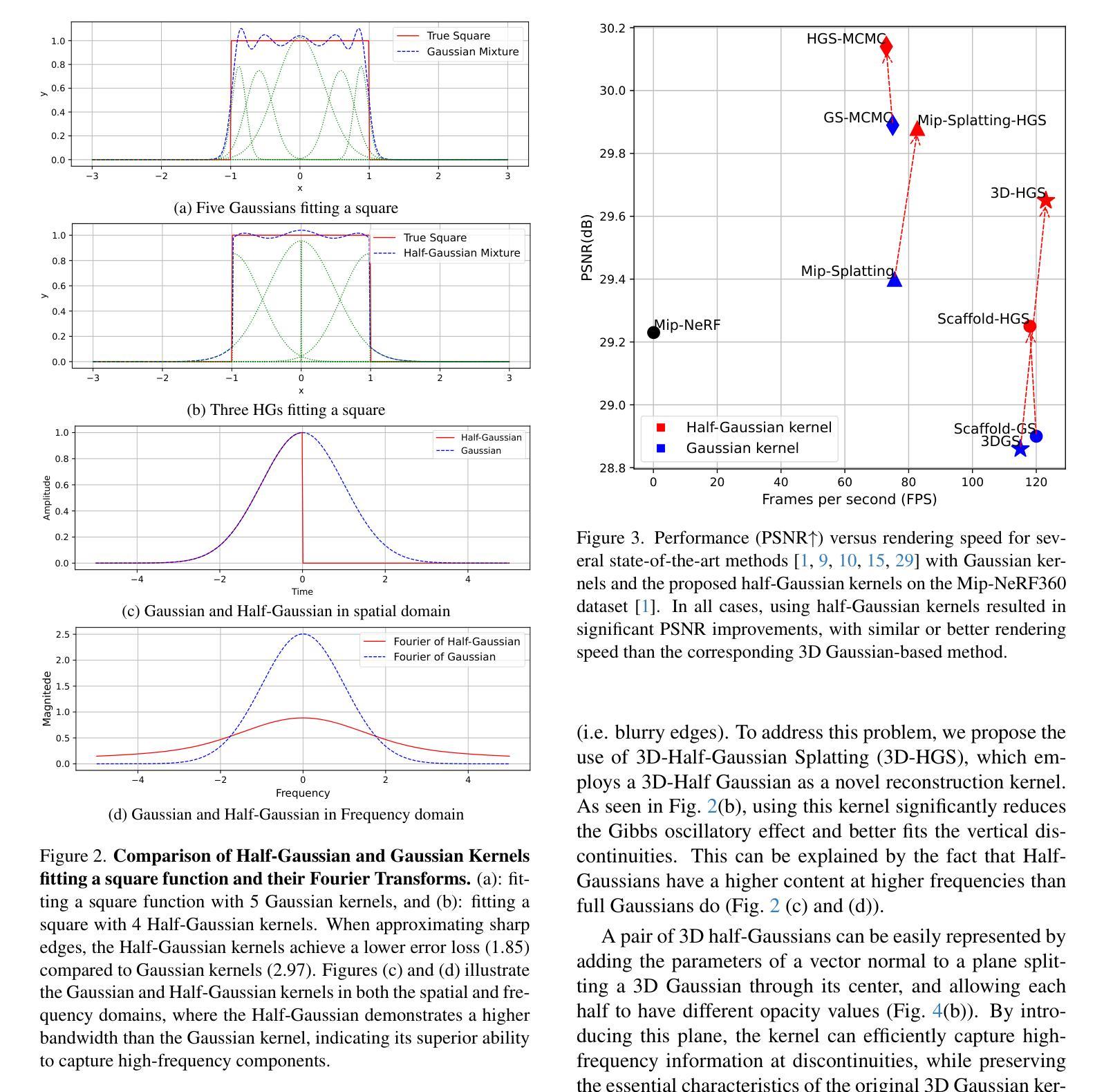
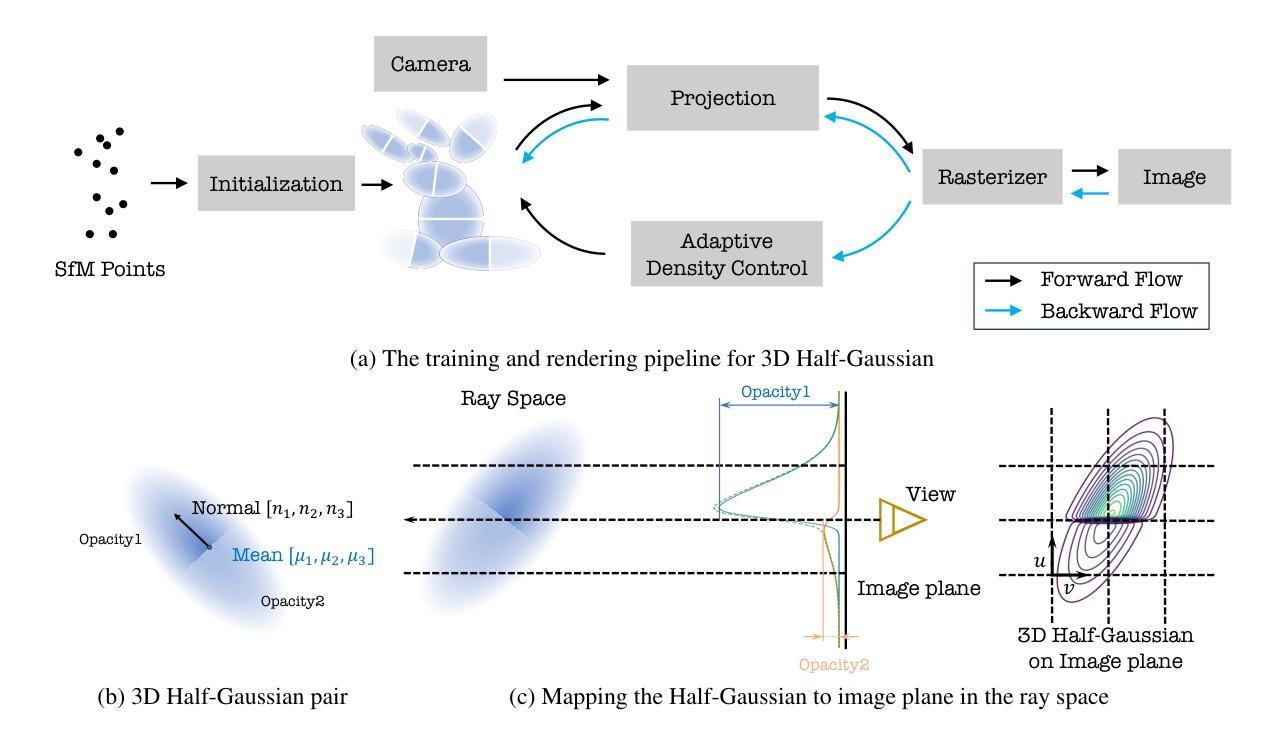
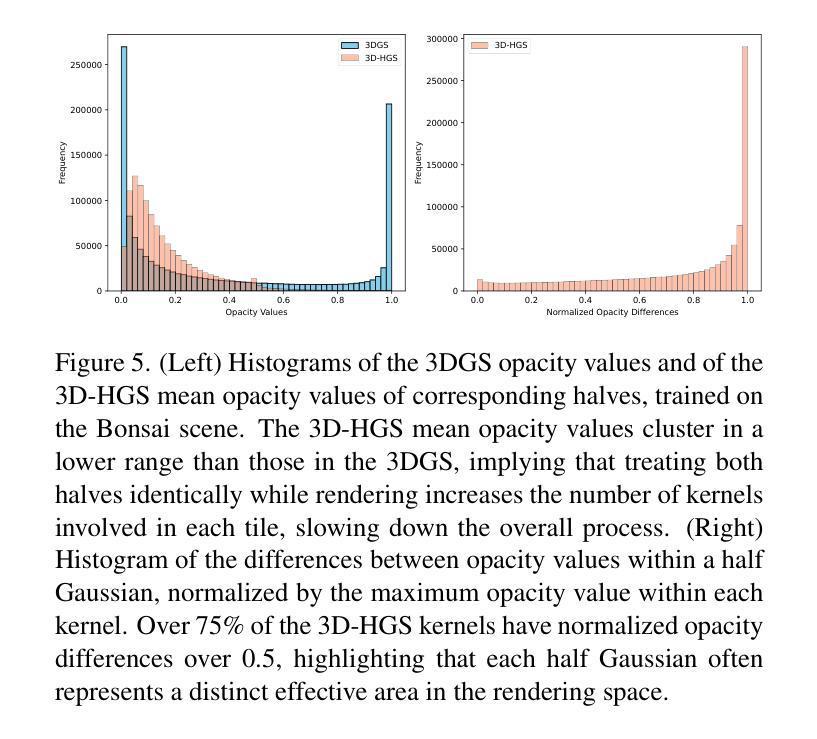
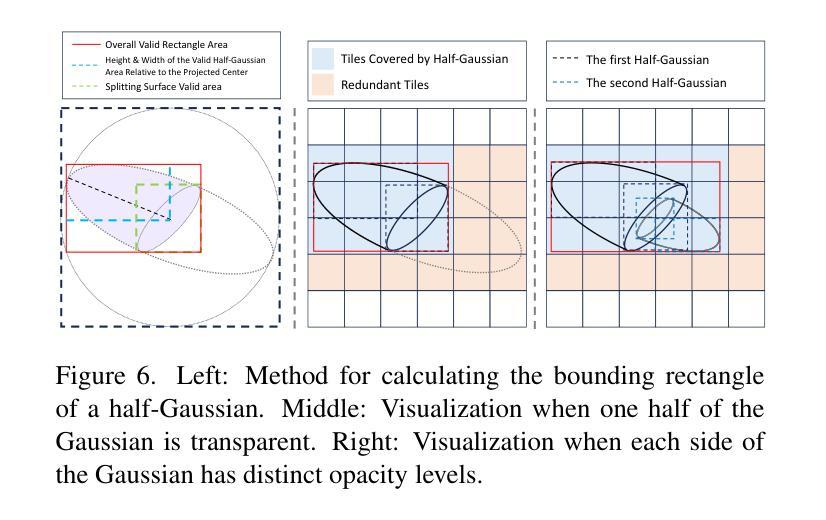
3D-HGS: 3D Half-Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Haolin Li, Jinyang Liu, Mario Sznaier, Octavia Camps
Photo-realistic image rendering from 3D scene reconstruction has advanced significantly with neural rendering techniques. Among these, 3D Gaussian Splatting (3D-GS) outperforms Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs) in quality and speed but struggles with shape and color discontinuities. We propose 3D Half-Gaussian (3D-HGS) kernels as a plug-and-play solution to address these limitations. Our experiments show that 3D-HGS enhances existing 3D-GS methods, achieving state-of-the-art rendering quality without compromising speed.
基于神经渲染技术的光栅化图像渲染从三维场景重建中得到了极大的发展。其中,三维高斯贴图(3D-GS)在质量和速度方面优于神经辐射场(NeRFs),但在形状和颜色不连续方面存在困难。我们提出使用三维半高斯(3D-HGS)核作为一种即插即用的解决方案来解决这些局限性。我们的实验表明,3D-HGS能够增强现有的3D-GS方法,在不牺牲速度的情况下实现最先进的渲染质量。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 9 figures
Summary
本文提出使用神经网络渲染技术进行三维场景重建,生成逼真的图像渲染。文章指出,相较于现有的神经网络渲染技术,如神经网络辐射场(NeRF),三维高斯拼贴(3D-GS)在质量和速度上表现更佳,但在处理形状和颜色断层方面存在局限。为解决这些问题,本文提出了使用三维半高斯(3D-HGS)核作为解决方案,并通过实验证明,它能显著提升现有三维高斯拼贴方法的性能,达到更高的渲染质量同时不牺牲速度。
Key Takeaways
- 神经网络渲染技术已显著提升了从三维场景重建生成逼真图像的效果。
- 三维高斯拼贴在质量和速度上优于神经网络辐射场技术。
- 三维高斯拼贴在处理形状和颜色断层方面存在局限。
- 三维半高斯核被提出作为解决方案,以改善三维高斯拼贴的性能。
- 三维半高斯核能显著提升渲染质量,同时保持高速性能。
- 使用该技术的图像渲染可以达到业界最佳效果。
点此查看论文截图