⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-08 更新
Learning Unknown Spoof Prompts for Generalized Face Anti-Spoofing Using Only Real Face Images
Authors:Fangling Jiang, Qi Li, Weining Wang, Wei Shen, Bing Liu, Zhenan Sun
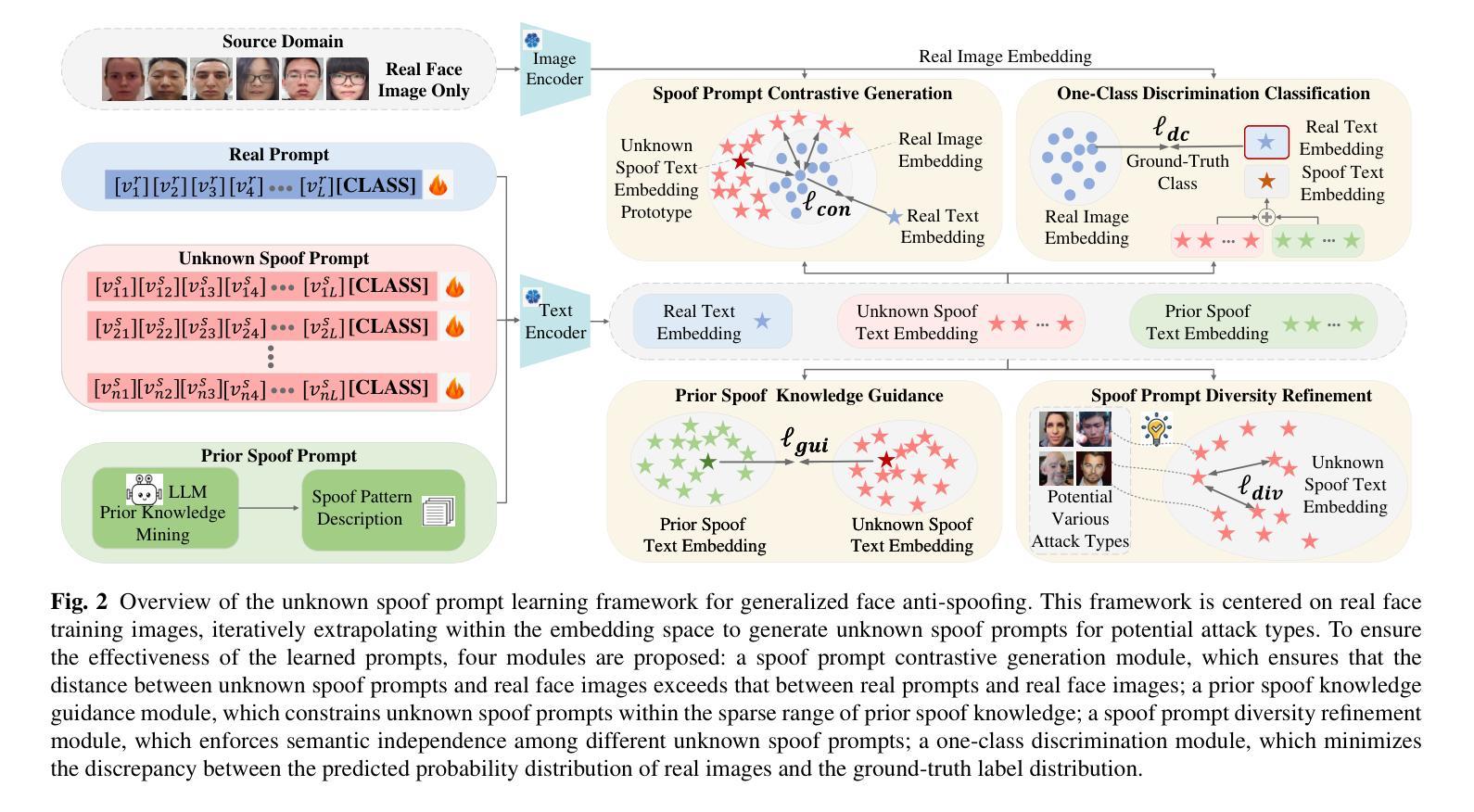
Face anti-spoofing is a critical technology for ensuring the security of face recognition systems. However, its ability to generalize across diverse scenarios remains a significant challenge. In this paper, we attribute the limited generalization ability to two key factors: covariate shift, which arises from external data collection variations, and semantic shift, which results from substantial differences in emerging attack types. To address both challenges, we propose a novel approach for learning unknown spoof prompts, relying solely on real face images from a single source domain. Our method generates textual prompts for real faces and potential unknown spoof attacks by leveraging the general knowledge embedded in vision-language models, thereby enhancing the model’s ability to generalize to unseen target domains. Specifically, we introduce a diverse spoof prompt optimization framework to learn effective prompts. This framework constrains unknown spoof prompts within a relaxed prior knowledge space while maximizing their distance from real face images. Moreover, it enforces semantic independence among different spoof prompts to capture a broad range of spoof patterns. Experimental results on nine datasets demonstrate that the learned prompts effectively transfer the knowledge of vision-language models, enabling state-of-the-art generalization ability against diverse unknown attack types across unseen target domains without using any spoof face images.
人脸识别反欺骗技术是保证人脸识别系统安全的关键技术。然而,其在不同场景下的泛化能力仍然是一个巨大的挑战。在本文中,我们将有限的泛化能力归因于两个关键因素:由外部数据采集变化引起的协变量偏移,以及由新兴攻击类型中的巨大差异引起的语义偏移。为了解决这两个挑战,我们提出了一种应对未知欺骗提示的新型学习方法,该方法仅依赖于单一源域的真实人脸图像。我们的方法通过利用视觉语言模型中的通用知识,为真实人脸和潜在的未知欺骗攻击生成文本提示,从而提高模型对未见目标域的泛化能力。具体来说,我们引入了一个多样化的欺骗提示优化框架来学习有效的提示。该框架在放宽的先验知识空间内约束未知的欺骗提示,同时最大化其与真实人脸图像之间的距离。此外,它强制执行不同欺骗提示之间的语义独立性,以捕获广泛的欺骗模式。在九个数据集上的实验结果表明,学习到的提示有效地转移了视觉语言模型的知识,实现了对未见目标域中多种未知攻击类型的最先进的泛化能力,且无需使用任何欺骗人脸图像。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一个基于真实人脸图像生成文本提示的方法,用于应对未知攻击类型的面部抗欺骗问题。通过利用视觉语言模型中的通用知识,该方法能够生成针对真实人脸和潜在未知欺骗攻击的提示,从而提高模型对未见目标域的泛化能力。引入了一个多样化的欺骗提示优化框架来学习有效的提示,该框架在放松的先验知识空间中约束未知欺骗提示,同时最大化其与真实人脸图像的距离。此外,它还强制不同欺骗提示之间的语义独立性,以捕捉广泛的欺骗模式。实验结果表明,所学习的提示有效地转移了视觉语言模型的知识,在未见目标域上实现了对多种未知攻击类型的最先进的泛化能力,且无需使用任何欺骗人脸图像。
Key Takeaways
- 面部抗欺骗技术是确保人脸识别系统安全的关键技术。
- 当前技术面临的主要挑战是其在不同场景下的泛化能力有限。
- 文中将泛化能力受限归因于两个关键因素:源自外部数据采集变化的协变量偏移和新兴攻击类型间的语义偏移。
- 提出了一种基于真实人脸图像生成文本提示的新方法,以应对未知欺骗攻击。
- 该方法利用视觉语言模型中的通用知识,增强了模型对未见目标域的泛化能力。
- 引入了一个多样化的欺骗提示优化框架,以学习有效的提示,该框架能够在放松的先验知识空间内约束未知欺骗提示。
点此查看论文截图

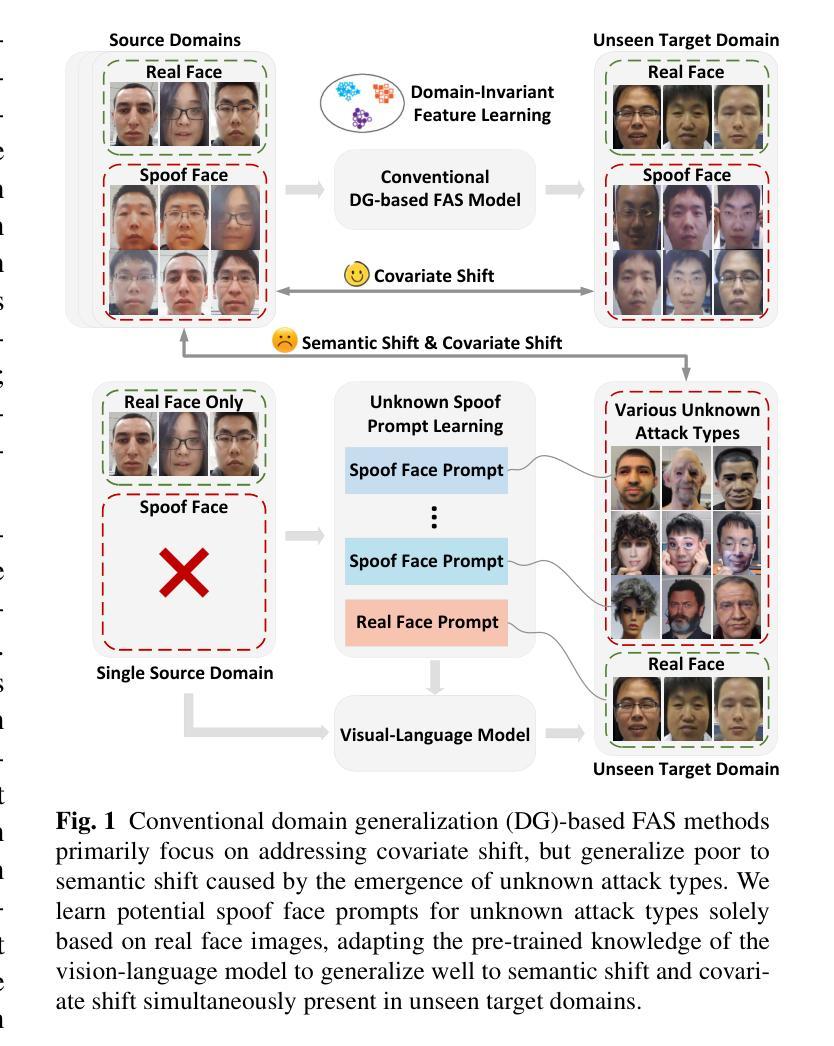
Learning Knowledge-based Prompts for Robust 3D Mask Presentation Attack Detection
Authors:Fangling Jiang, Qi Li, Bing Liu, Weining Wang, Caifeng Shan, Zhenan Sun, Ming-Hsuan Yang
3D mask presentation attack detection is crucial for protecting face recognition systems against the rising threat of 3D mask attacks. While most existing methods utilize multimodal features or remote photoplethysmography (rPPG) signals to distinguish between real faces and 3D masks, they face significant challenges, such as the high costs associated with multimodal sensors and limited generalization ability. Detection-related text descriptions offer concise, universal information and are cost-effective to obtain. However, the potential of vision-language multimodal features for 3D mask presentation attack detection remains unexplored. In this paper, we propose a novel knowledge-based prompt learning framework to explore the strong generalization capability of vision-language models for 3D mask presentation attack detection. Specifically, our approach incorporates entities and triples from knowledge graphs into the prompt learning process, generating fine-grained, task-specific explicit prompts that effectively harness the knowledge embedded in pre-trained vision-language models. Furthermore, considering different input images may emphasize distinct knowledge graph elements, we introduce a visual-specific knowledge filter based on an attention mechanism to refine relevant elements according to the visual context. Additionally, we leverage causal graph theory insights into the prompt learning process to further enhance the generalization ability of our method. During training, a spurious correlation elimination paradigm is employed, which removes category-irrelevant local image patches using guidance from knowledge-based text features, fostering the learning of generalized causal prompts that align with category-relevant local patches. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method achieves state-of-the-art intra- and cross-scenario detection performance on benchmark datasets.
三维掩膜展示攻击检测对于保护人脸识别系统免受日益严重的三维掩膜攻击威胁至关重要。虽然大多数现有方法利用多模式特征或远程光体积描记术(rPPG)信号来区分真实面孔和三维掩膜,但它们面临巨大的挑战,例如多模式传感器的高成本和有限的泛化能力。检测相关的文本描述提供了简洁且普遍的信息,并且成本低廉、易于获取。然而,利用视觉语言多模式特征进行三维掩膜展示攻击检测潜力尚未得到探索。在本文中,我们提出了一种基于知识提示学习框架来探索预训练视觉语言模型对三维掩膜展示攻击检测的强泛化能力。具体来说,我们的方法将知识图谱中的实体和三元组融入提示学习过程,生成精细粒度的、任务特定的明确提示,有效利用嵌入在预训练视觉语言模型中的知识。此外,考虑到不同的输入图像可能会强调不同的知识图谱元素,我们引入了一种基于注意力机制的视觉特定知识过滤器,以根据视觉上下文精炼相关元素。我们还利用因果图理论的见解来促进提示学习过程,进一步增强了方法的泛化能力。在训练过程中,采用了一种消除偶然性关联的范式,该范式利用基于知识的文本特征来去除与类别无关的局部图像斑块,促进学习符合类别相关局部斑块的通用因果提示。实验结果表明,该方法在基准数据集上实现了先进的内部和跨场景检测性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在人脸识别系统中,保护系统免受日益增长的3D面具攻击至关重要。现有的方法主要使用多模态特征或远程光体积法(rPPG)信号来区分真实人脸和3D面具,但它们面临高成本、泛化能力有限的挑战。文本描述检测相关文本提供简洁、通用信息且成本效益高。本文探索了基于知识的提示学习框架在利用视觉语言模型进行3D面具攻击检测方面的强大泛化能力。通过融入知识图谱中的实体和三元组,生成精细的任务特定显式提示,有效挖掘预训练的视觉语言模型中的知识。考虑到不同输入图像可能强调不同的知识图谱元素,我们引入了基于注意力机制的视觉特定知识过滤器来根据视觉上下文调整相关元素。此外,我们利用因果图论的见解来促进提示学习过程,增强方法的泛化能力。训练期间采用消除偶然性相关性的模式,通过利用基于知识的文本特征来移除类别不相关的局部图像补丁,促使学习符合类别相关的局部补丁的通用因果提示。实验结果表明,该方法在基准数据集上实现了先进的内部和跨场景检测性能。
Key Takeaways
- 3D面具攻击对人脸识别系统构成威胁,需要有效的检测方法来保护系统。
- 现有方法主要使用多模态特征和远程光体积法信号检测3D面具,但存在高成本和泛化能力有限的问题。
- 本文首次探索了视觉语言模型在3D面具攻击检测中的潜力,利用知识图谱中的实体和三元组生成任务特定提示。
- 引入视觉特定知识过滤器,根据输入图像的不同内容调整相关知识图谱元素的重要性。
- 结合因果图理论来提升方法的泛化能力,通过消除偶然相关性来提高检测性能。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在基准数据集上实现了先进的检测性能,适用于不同场景。
点此查看论文截图

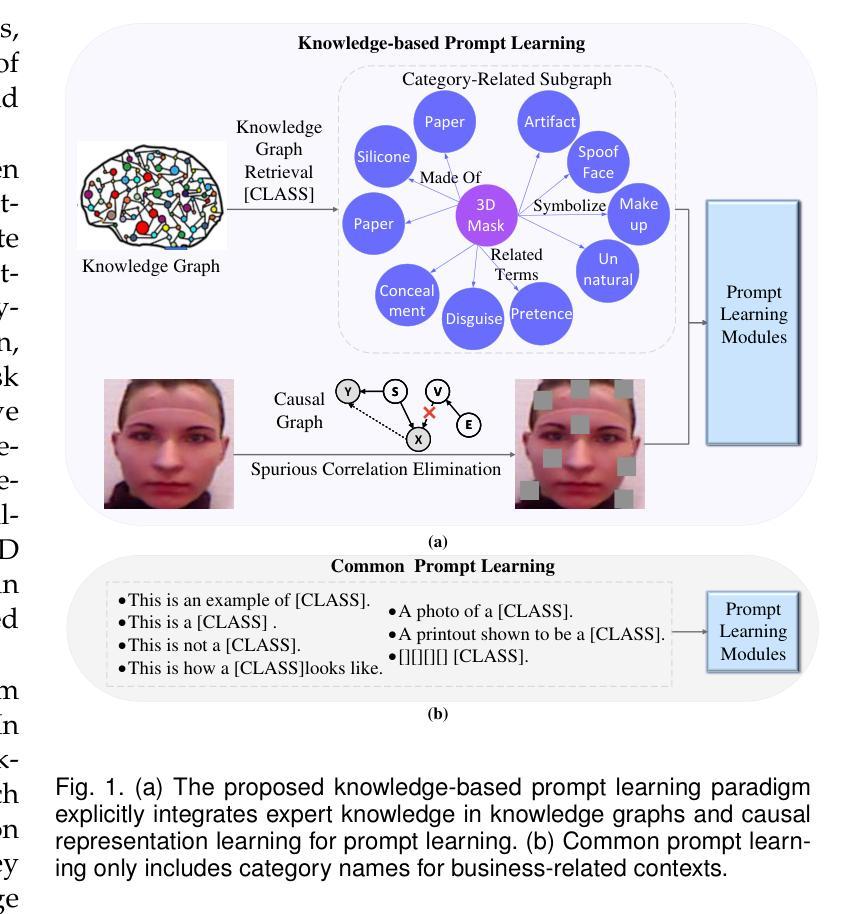
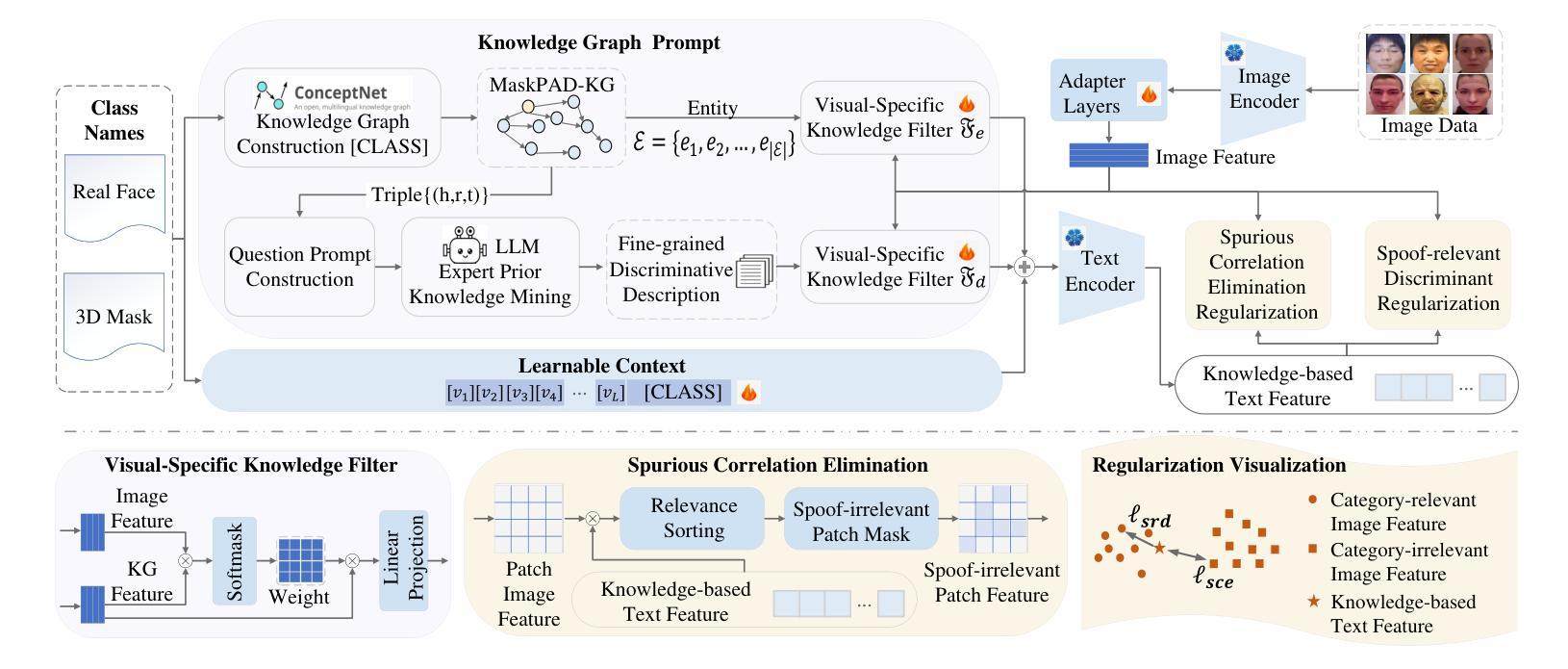
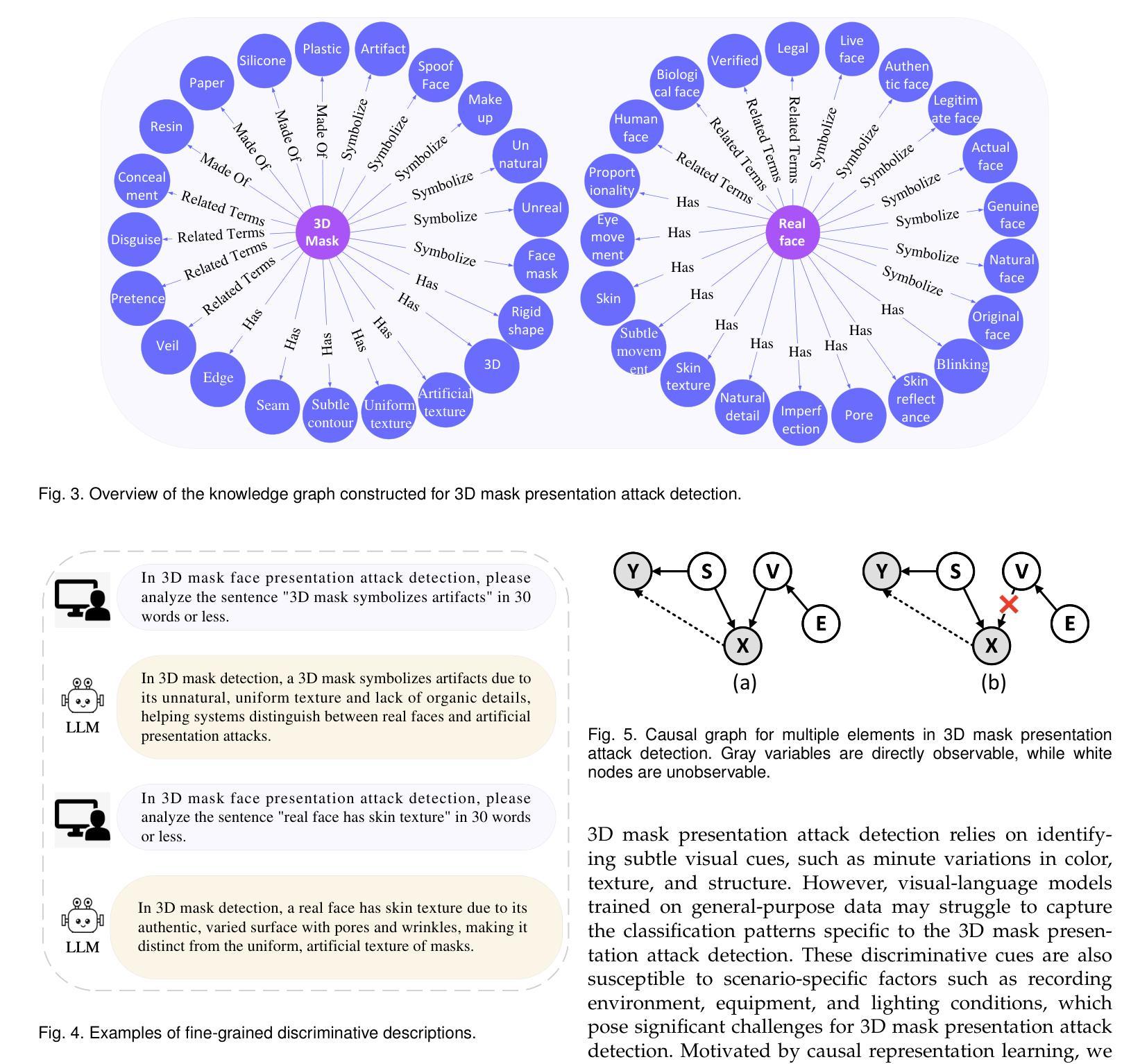
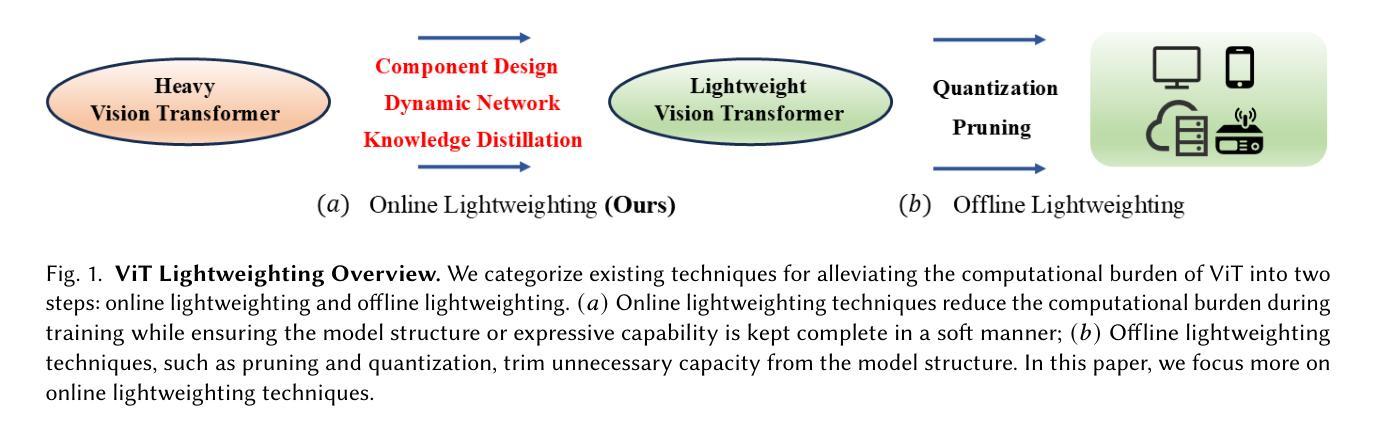
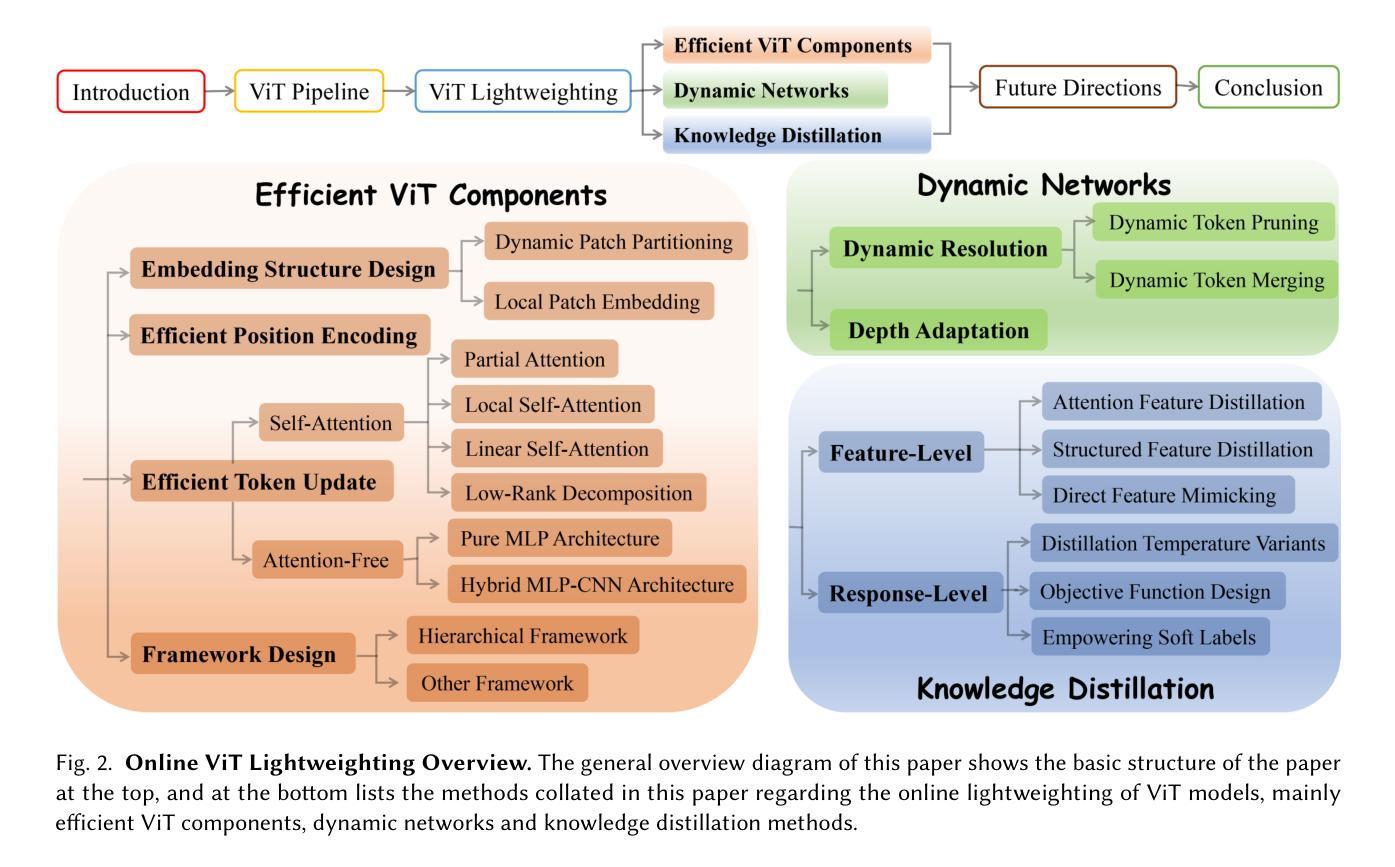
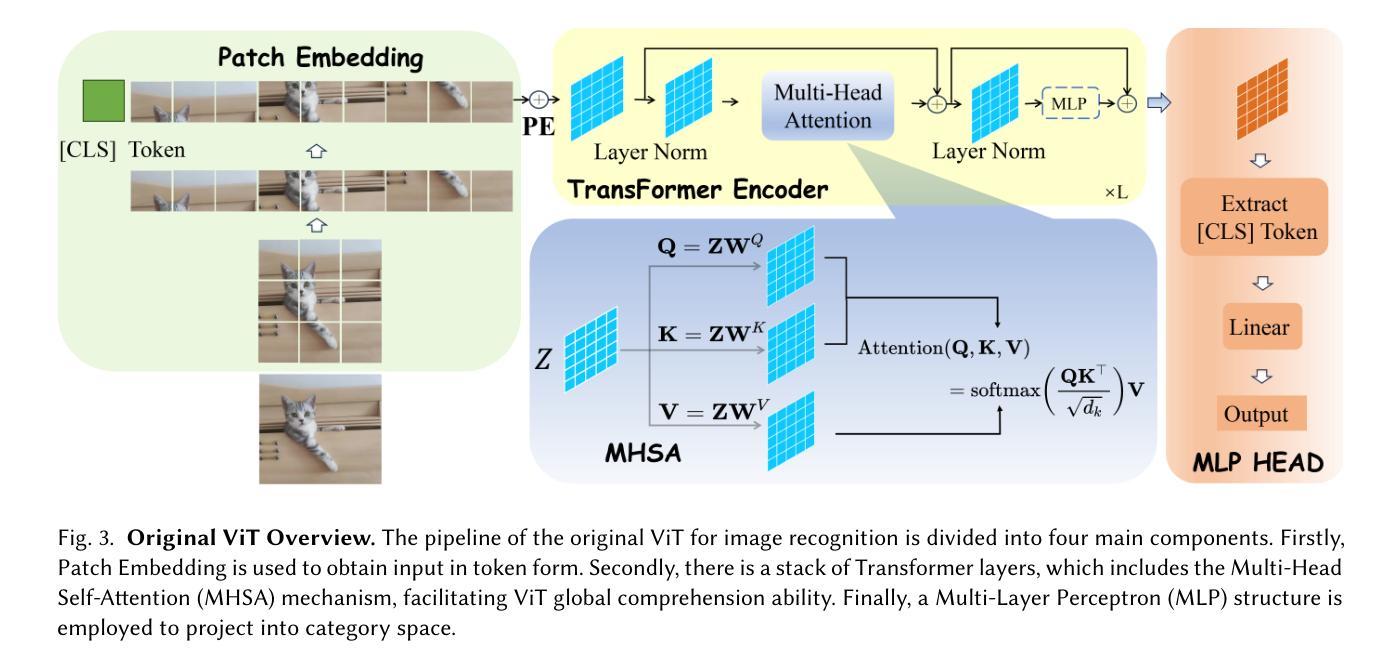
Image Recognition with Online Lightweight Vision Transformer: A Survey
Authors:Zherui Zhang, Rongtao Xu, Jie Zhou, Changwei Wang, Xingtian Pei, Wenhao Xu, Jiguang Zhang, Li Guo, Longxiang Gao, Wenbo Xu, Shibiao Xu
The Transformer architecture has achieved significant success in natural language processing, motivating its adaptation to computer vision tasks. Unlike convolutional neural networks, vision transformers inherently capture long-range dependencies and enable parallel processing, yet lack inductive biases and efficiency benefits, facing significant computational and memory challenges that limit its real-world applicability. This paper surveys various online strategies for generating lightweight vision transformers for image recognition, focusing on three key areas: Efficient Component Design, Dynamic Network, and Knowledge Distillation. We evaluate the relevant exploration for each topic on the ImageNet-1K benchmark, analyzing trade-offs among precision, parameters, throughput, and more to highlight their respective advantages, disadvantages, and flexibility. Finally, we propose future research directions and potential challenges in the lightweighting of vision transformers with the aim of inspiring further exploration and providing practical guidance for the community. Project Page: https://github.com/ajxklo/Lightweight-VIT
Transformer架构在自然语言处理领域取得了巨大成功,这激发了将其适应计算机视觉任务的动机。与卷积神经网络不同,视觉Transformer天生就能捕捉长距离依赖关系并实现并行处理,但缺乏归纳偏见和效率优势,面临计算量和内存方面的挑战,这些挑战限制了其在现实世界中的应用。本文调查了在线生成轻量级视觉Transformer用于图像识别的各种策略,重点关注三个关键领域:高效组件设计、动态网络和知识蒸馏。我们在ImageNet-1K基准测试上评估了每个主题的相关探索,分析了精确度、参数、吞吐量等之间的权衡,以突出各自的优势、劣势和灵活性。最后,我们提出了轻量级视觉Transformer的未来研究方向和潜在挑战,旨在激发进一步探索,为社区提供实用指导。项目页面:https://github.com/ajxklo/Lightweight-VIT
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了将Transformer架构应用于计算机视觉任务的策略,特别是针对图像识别的轻量级视觉Transformer的研究。文章聚焦于三个关键领域:高效组件设计、动态网络和知识蒸馏。文章评估了每个主题在ImageNet-1K基准测试上的相关研究,并分析了精度、参数、吞吐量和灵活性之间的权衡,提出了未来研究的方向和挑战。
Key Takeaways
- Transformer架构在计算机视觉任务中的适用性及其与卷积神经网络的区别。
- 长程依赖性的捕捉和并行处理在视觉Transformer中的优势。
- 视觉Transformer面临的主要挑战,包括缺乏归纳偏见和效率优势。
- 文中介绍的轻量级视觉Transformer的在线策略,包括高效组件设计、动态网络和知识蒸馏。
- 在ImageNet-1K基准测试上对各种策略的评估结果。
- 精度、参数、吞吐量和灵活性之间的权衡在视觉Transformer轻量化设计中的重要性。
点此查看论文截图

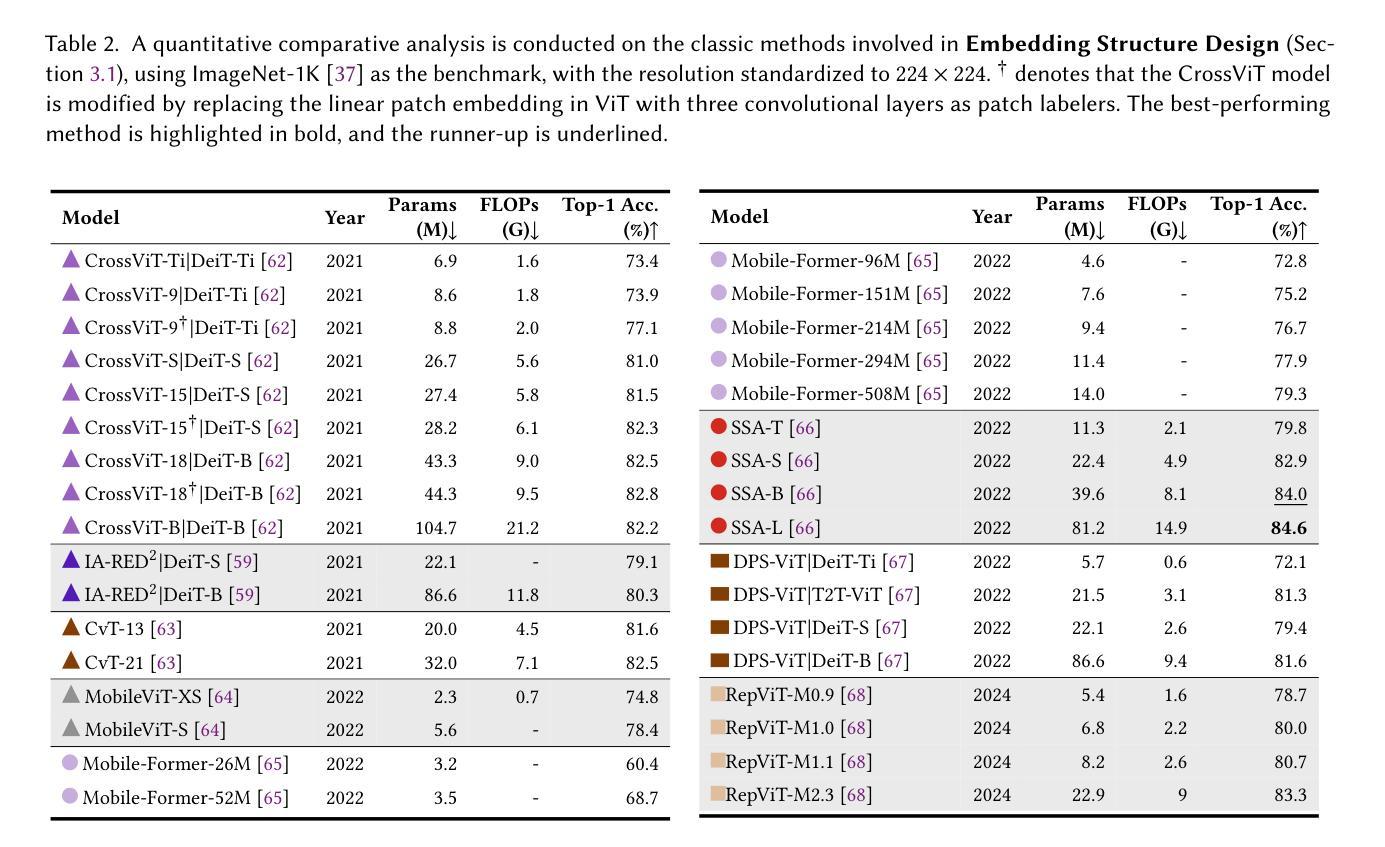
Deep learning of personalized priors from past MRI scans enables fast, quality-enhanced point-of-care MRI with low-cost systems
Authors:Tal Oved, Beatrice Lena, Chloé F. Najac, Sheng Shen, Matthew S. Rosen, Andrew Webb, Efrat Shimron
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) offers superb-quality images, but its accessibility is limited by high costs, posing challenges for patients requiring longitudinal care. Low-field MRI provides affordable imaging with low-cost devices but is hindered by long scans and degraded image quality, including low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and tissue contrast. We propose a novel healthcare paradigm: using deep learning to extract personalized features from past standard high-field MRI scans and harnessing them to enable accelerated, enhanced-quality follow-up scans with low-cost systems. To overcome the SNR and contrast differences, we introduce ViT-Fuser, a feature-fusion vision transformer that learns features from past scans, e.g. those stored in standard DICOM CDs. We show that \textit{a single prior scan is sufficient}, and this scan can come from various MRI vendors, field strengths, and pulse sequences. Experiments with four datasets, including glioblastoma data, low-field ($50mT$), and ultra-low-field ($6.5mT$) data, demonstrate that ViT-Fuser outperforms state-of-the-art methods, providing enhanced-quality images from accelerated low-field scans, with robustness to out-of-distribution data. Our freely available framework thus enables rapid, diagnostic-quality, low-cost imaging for wide healthcare applications.
磁共振成像(MRI)提供了高质量的图像,但由于成本高昂,其普及程度受到限制,这对于需要长期护理的患者来说具有挑战性。低场MRI通过使用低成本设备提供可负担的成像,但受到扫描时间长和图像质量下降(包括低信噪比(SNR)和组织对比度)的阻碍。我们提出了一种新的医疗范式:使用深度学习从过去的标准高场MRI扫描中提取个性化特征,并利用这些特征实现低成本系统的加速、高质量随访扫描。为了克服信噪比和对比度差异,我们引入了ViT-Fuser,这是一种特征融合视觉变压器,可以从过去的扫描中学习特征,例如存储在标准DICOM光盘中的扫描。我们证明只需一次先验扫描,这次扫描可以来自不同的MRI供应商、磁场强度和脉冲序列。使用包括胶质母细胞瘤数据、低场(50mT)和超低场(6.5mT)数据的四个数据集进行的实验表明,ViT-Fuser优于最先进的方法,能够提供加速低场扫描的高质量图像,并对异常数据具有稳健性。我们提供的免费框架因此能够实现快速、诊断质量、低成本成像,广泛应用于医疗保健领域。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:利用深度学习从过去的高场MRI扫描中提取个性化特征,并利用这些特征实现低成本系统的加速、高质量随访扫描。提出ViT-Fuser愿景转换器,学习过去扫描的特征,如存储在标准DICOM CD中的扫描。实验证明,单次先验扫描即可,且该扫描可来自不同的MRI供应商、场强和脉冲序列。ViT-Fuser在加速低场扫描中提供高质量图像,具有对离群数据的稳健性,为广泛的应用提供了快速、诊断性、低成本的成像。
Key Takeaways:
- 深度学习用于从过去的高场MRI扫描中提取个性化特征。
- 使用这些特征可实现低成本系统的加速、高质量随访扫描。
- 引入ViT-Fuser愿景转换器,学习过去扫描的特征。
- 单次先验扫描即可满足需求,且来源广泛。
- ViT-Fuser在多种数据集上的实验表现优异,包括胶质母细胞瘤数据、低场和超低场数据。
- ViT-Fuser能提供加速低场扫描的高质量图像,并具有对离群数据的稳健性。
点此查看论文截图

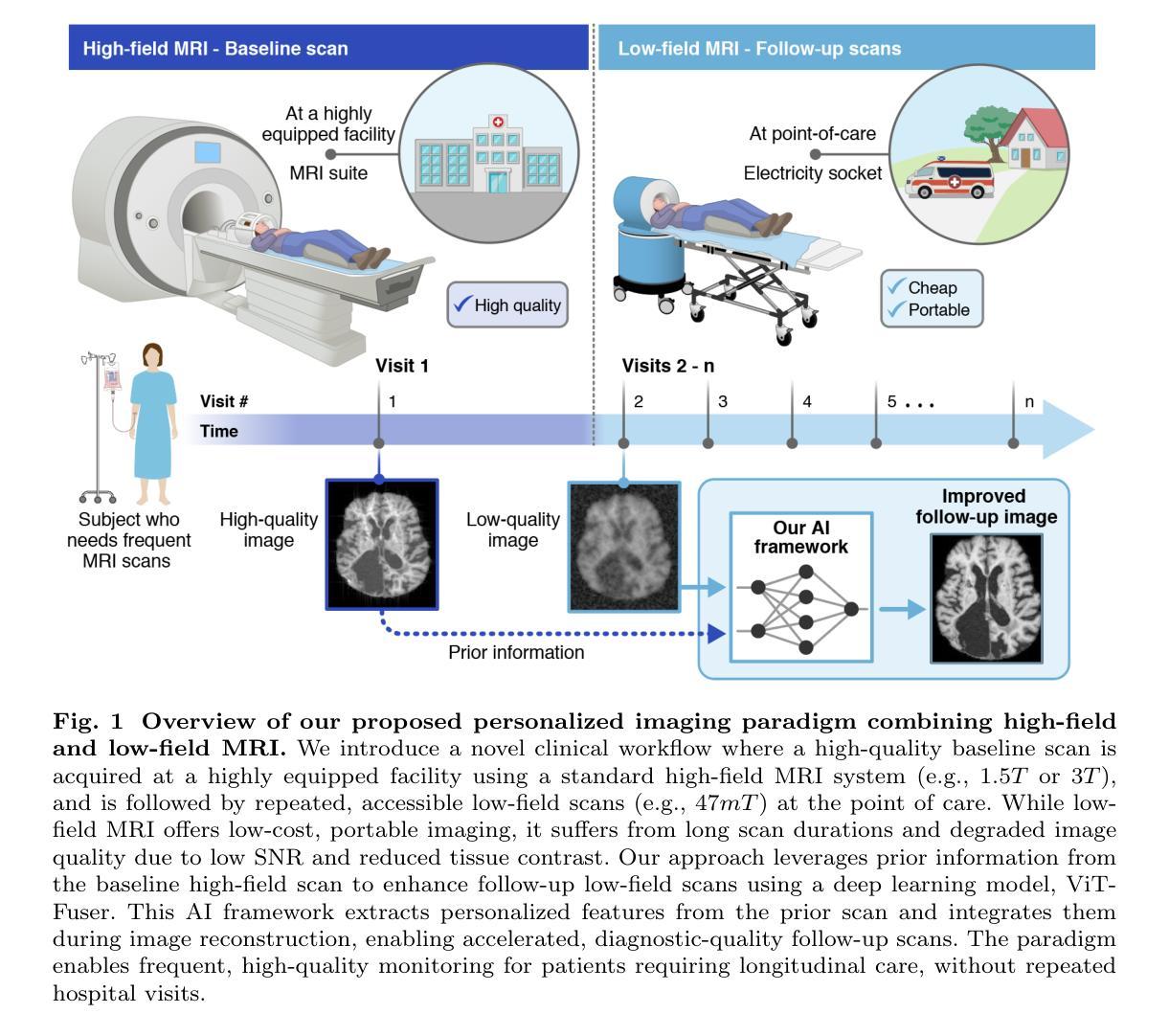
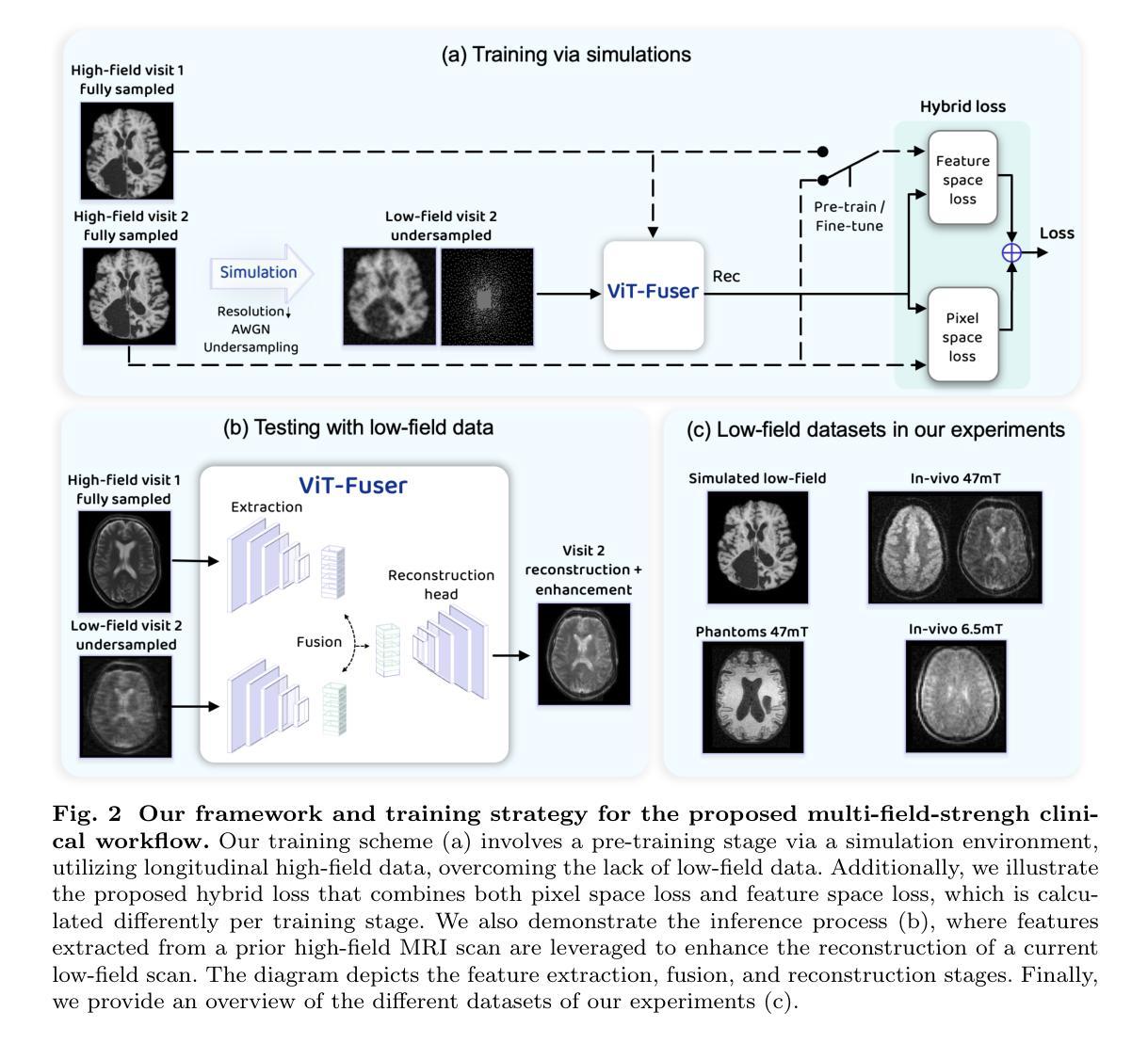
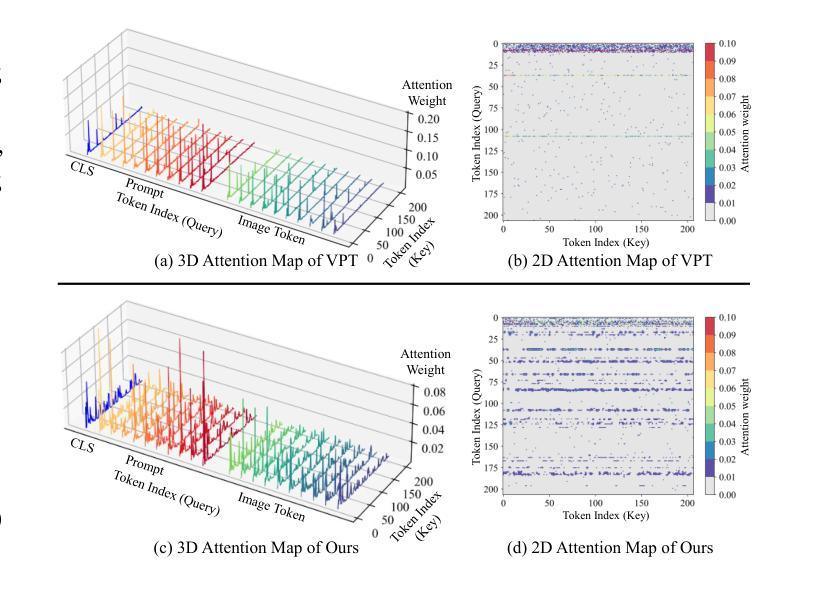
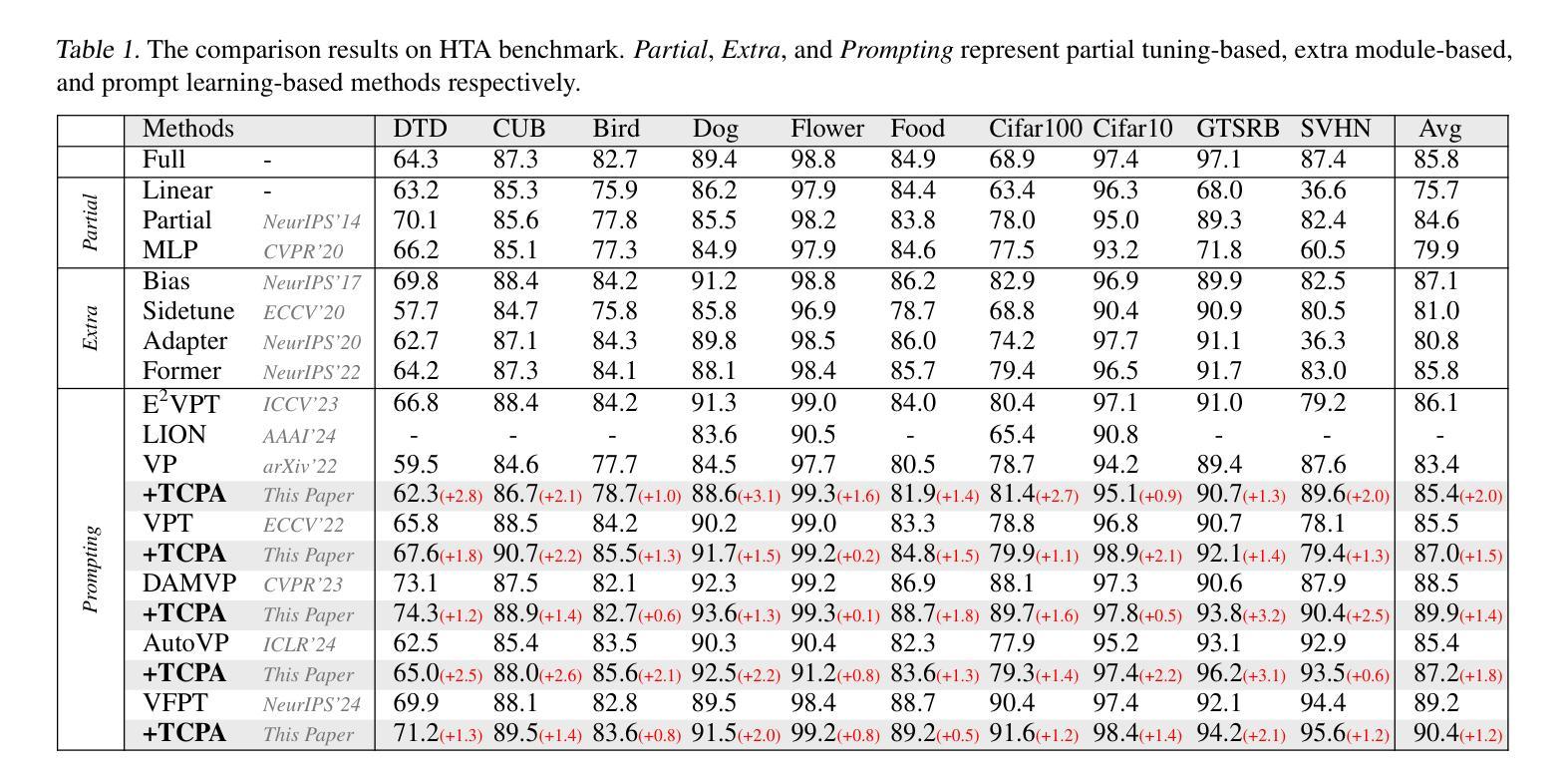
Token Coordinated Prompt Attention is Needed for Visual Prompting
Authors:Zichen Liu, Xu Zou, Gang Hua, Jiahuan Zhou
Visual prompting techniques are widely used to efficiently fine-tune pretrained Vision Transformers (ViT) by learning a small set of shared prompts for all tokens. However, existing methods overlook the unique roles of different tokens in conveying discriminative information and interact with all tokens using the same prompts, thereby limiting the representational capacity of ViT. This often leads to indistinguishable and biased prompt-extracted features, hindering performance. To address this issue, we propose a plug-and-play Token Coordinated Prompt Attention (TCPA) module, which assigns specific coordinated prompts to different tokens for attention-based interactions. Firstly, recognizing the distinct functions of CLS and image tokens-global information aggregation and local feature extraction, we disentangle the prompts into CLS Prompts and Image Prompts, which interact exclusively with CLS tokens and image tokens through attention mechanisms. This enhances their respective discriminative abilities. Furthermore, as different image tokens correspond to distinct image patches and contain diverse information, we employ a matching function to automatically assign coordinated prompts to individual tokens. This enables more precise attention interactions, improving the diversity and representational capacity of the extracted features. Extensive experiments across various benchmarks demonstrate that TCPA significantly enhances the diversity and discriminative power of the extracted features. The code is available at https://github.com/zhoujiahuan1991/ICML2025-TCPA.
视觉提示技术被广泛用于通过学习一组共享提示来微调预训练的视觉转换器(ViT)。然而,现有方法忽视了不同标记在传递判别信息方面的独特作用,并使用相同的提示与所有标记进行交互,从而限制了ViT的表征容量。这通常会导致难以区分和偏向提示提取的特征,阻碍性能。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种即插即用的标记协调提示注意力(TCPA)模块,该模块为不同的标记分配特定的协调提示,以进行基于注意力的交互。首先,我们认识到CLS和图像标记的不同功能——全局信息聚合和局部特征提取,我们将提示分解为CLS提示和图像提示,它们通过注意力机制与CLS标记和图像标记进行独家交互,增强了各自的判别能力。此外,由于不同的图像标记对应于不同的图像块并包含各种信息,我们采用匹配函数来自动为单个标记分配协调提示。这能够实现更精确的关注力交互,提高提取特征的多样性和表征容量。在各种基准测试上的大量实验表明,TCPA显著增强了提取特征的多样性和判别力。代码可在https://github.com/zhoujiahuan1991/ICML2025-TCPA上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
视觉提示技术广泛应用于微调预训练的Vision Transformers(ViT),通过学习一小套共享提示来完成所有令牌的效率优化。然而,现有方法忽略了不同令牌在传递鉴别信息方面的独特作用,并使用相同的提示与所有令牌进行交互,从而限制了ViT的代表性容量。为解决此问题,我们提出了即插即用的令牌协调提示注意力(TCPA)模块,该模块为不同的令牌分配特定的协调提示进行基于注意力的交互。我们认识到CLS和图像令牌的不同功能——全局信息聚合和局部特征提取,将提示分为CLS提示和图像提示,它们通过注意力机制与CLS令牌和图像令牌进行独家互动,增强了各自的鉴别能力。此外,由于不同的图像令牌对应于不同的图像补丁并包含各种信息,我们采用匹配功能自动为个别令牌分配协调提示。这实现了更精确的关注力交互,提高了提取特征的多样性和代表性容量。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉提示技术用于微调预训练的Vision Transformers(ViT)。
- 现有方法忽略不同令牌在传递鉴别信息中的独特作用。
- 提出了Token Coordinated Prompt Attention(TCPA)模块,为不同令牌分配特定的协调提示。
- TCPA模块增强CLS令牌和图像令牌各自的鉴别能力。
- 通过注意力机制,TCPA模块实现CLS提示和图像提示与相应令牌的独家互动。
- 采用匹配功能自动为图像令牌分配协调提示,提高特征提取的多样性和代表性容量。
点此查看论文截图

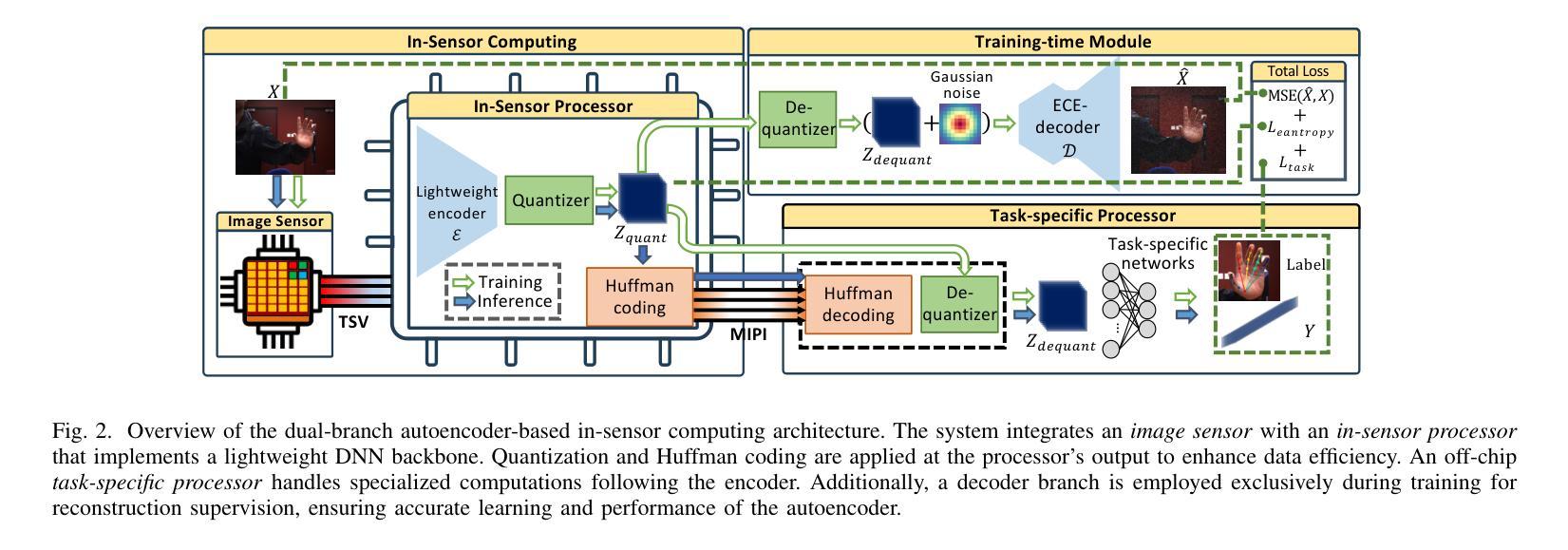
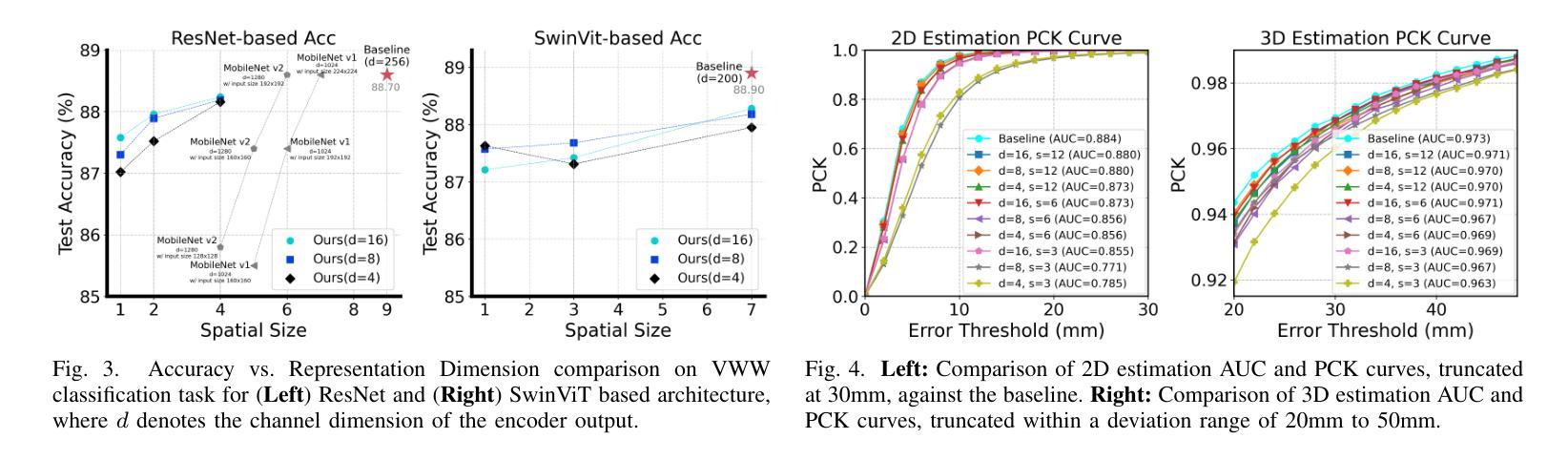
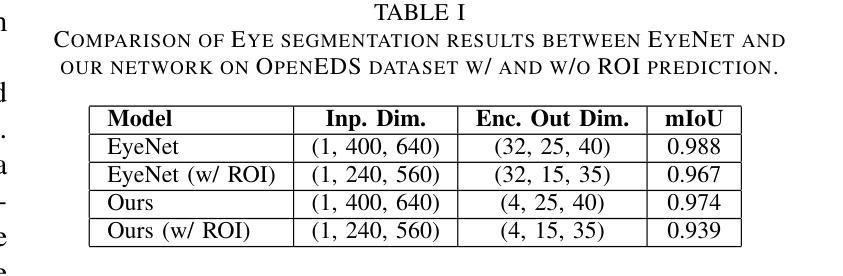
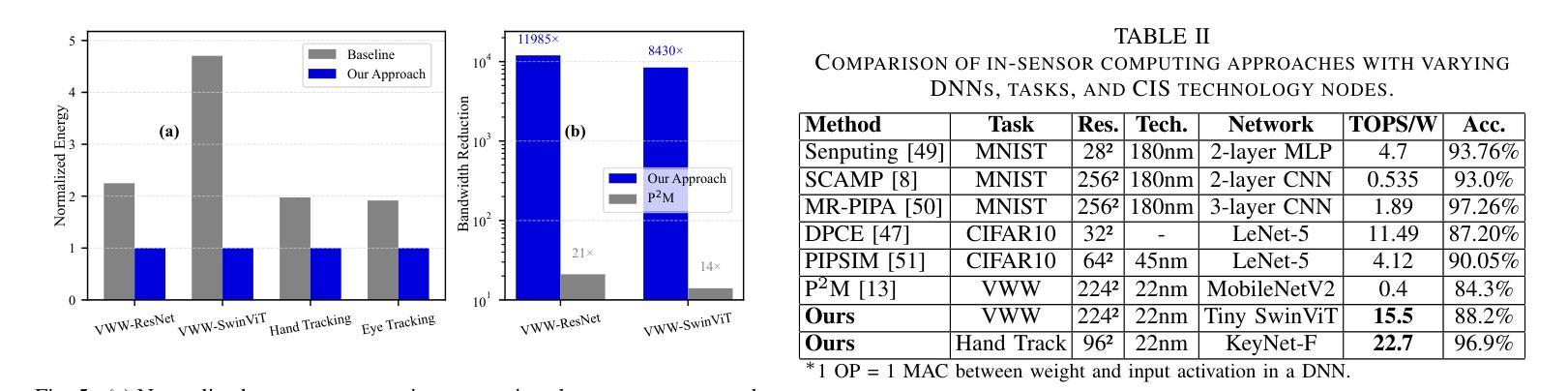
OASIS: Optimized Lightweight Autoencoder System for Distributed In-Sensor computing
Authors:Chengwei Zhou, Sreetama Sarkar, Yuming Li, Arnab Sanyal, Gourav Datta
In-sensor computing, which integrates computation directly within the sensor, has emerged as a promising paradigm for machine vision applications such as AR/VR and smart home systems. By processing data on-chip before transmission, it alleviates the bandwidth bottleneck caused by high-resolution, high-frame-rate image transmission, particularly in video applications. We envision a system architecture that integrates a CMOS image sensor (CIS) with a logic chip via advanced packaging, where the logic chip processes early-stage deep neural network (DNN) layers. However, its limited compute and memory make deploying advanced DNNs challenging. A simple solution is to split the model, executing the first part on the logic chip and the rest off-chip. However, modern DNNs require multiple layers before dimensionality reduction, limiting their ability to achieve the primary goal of in-sensor computing: minimizing data bandwidth. To address this, we propose a dual-branch autoencoder-based vision architecture that deploys a lightweight encoder on the logic chip while the task-specific network runs off-chip. The encoder is trained using a triple loss function: (1) task-specific loss to optimize accuracy, (2) entropy loss to enforce compact and compressible representations, and (3) reconstruction loss (mean-square error) to preserve essential visual information. This design enables a four-order-of-magnitude reduction in output activation dimensionality compared to input images, resulting in a $2{-}4.5\times$ decrease in energy consumption, as validated by our hardware-backed semi-analytical energy models. We evaluate our approach on CNN and ViT-based models across applications in smart home and augmented reality domains, achieving state-of-the-art accuracy with energy efficiency of up to 22.7 TOPS/W.
将计算直接集成到传感器中的感器计算(In-sensor computing)已成为AR/VR和智能家居系统等机器视觉应用的前景看好的范式。它在传输前在芯片上处理数据,从而减轻了由高分辨率、高帧率图像传输引起的带宽瓶颈,特别是在视频应用中。我们设想了一种通过先进封装技术将CMOS图像传感器(CIS)与逻辑芯片集成的系统架构,逻辑芯片处理早期深度神经网络(DNN)层。然而,其有限的计算和内存使部署先进的DNN面临挑战。一种简单的解决方案是将模型拆分,在逻辑芯片上执行第一部分,其余部分在芯片外执行。然而,现代DNN需要在降维之前进行多层计算,这限制了其实现感器计算主要目标的能力,即最小化数据带宽。为解决这一问题,我们提出了一种基于双分支自动编码器的视觉架构,该架构在逻辑芯片上部署轻量级编码器,而任务特定网络在芯片外运行。编码器使用三重损失函数进行训练:(1)任务特定损失以优化准确性,(2)熵损失以实施紧凑且可压缩的表示形式,(3)重建损失(均方误差)以保留必要的视觉信息。这一设计实现了输出激活维度相对于输入图像的四个数量级的降低,从而实现了能量消耗的减少(减少幅度为2-4.5倍),这已由我们的硬件支持半分析能量模型验证。我们的方法在智能家居和增强现实领域的应用中,对基于CNN和ViT的模型进行了评估,在具有高达22.7 TOPS/W的能量效率的同时实现了最先进的准确性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review; 8 pages, 5 figures
Summary
该文本介绍了一种在传感器内部进行计算的新型计算模式——在传感器计算。该模式对于机器视觉应用如AR/VR和智能家居系统具有前景。通过直接在芯片上处理数据,它解决了高分辨率、高帧率图像传输引起的带宽瓶颈问题。作者提出了一种结合CMOS图像传感器和逻辑芯片的系统架构,通过先进封装技术实现。为了解决在逻辑芯片上部署高级深度神经网络(DNN)的挑战,提出了基于自编码机的双分支视觉架构。编码器使用三重损失函数进行训练,以实现优化精度、紧凑和可压缩的表示以及关键视觉信息的保留。这种设计实现了输出激活维度相对于输入图像的四个数量级的降低,减少了能源消耗。该方法的能量效率和准确率在智能家庭和增强现实领域均达到领先水平。
Key Takeaways
- 在传感器计算是一种新兴的计算模式,它在机器视觉应用中具有前景,特别是在AR/VR和智能家居系统中。
- 在传感器计算模式通过在传感器内部直接处理数据来解决带宽瓶颈问题。
- 一种系统架构结合了CMOS图像传感器和逻辑芯片,通过先进封装技术实现集成。
- 在部署高级DNN时,受到计算和内存限制的挑战,提出了一种基于自编码机的双分支视觉架构解决方案。
- 编码器使用三重损失函数进行训练,以优化精度、实现紧凑和可压缩的表示,并保留关键视觉信息。
- 该设计实现了输出激活维度相对于输入图像的显著降低,降低了能源消耗。
- 该方法在智能家庭和增强现实领域的能量效率和准确率均达到领先水平。
点此查看论文截图

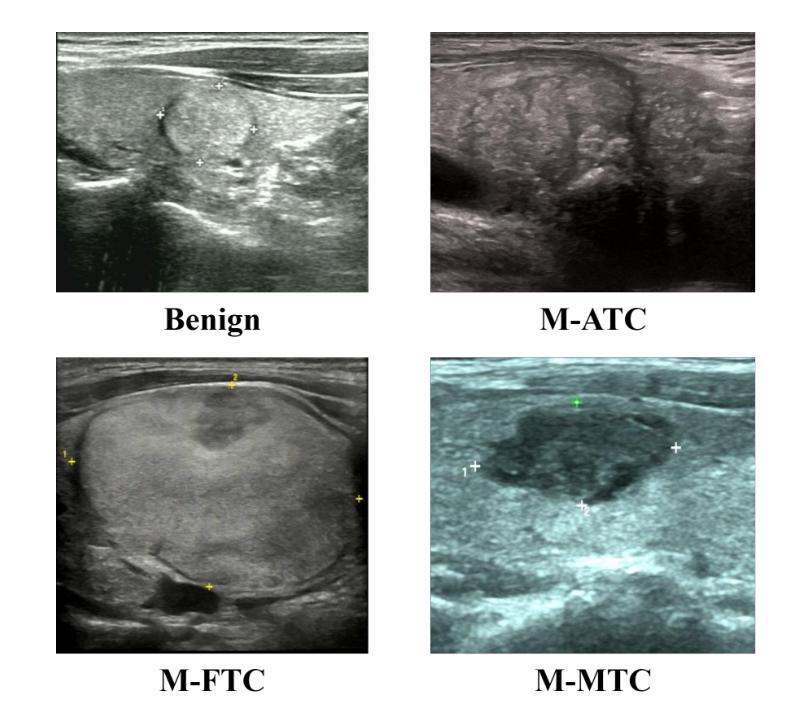
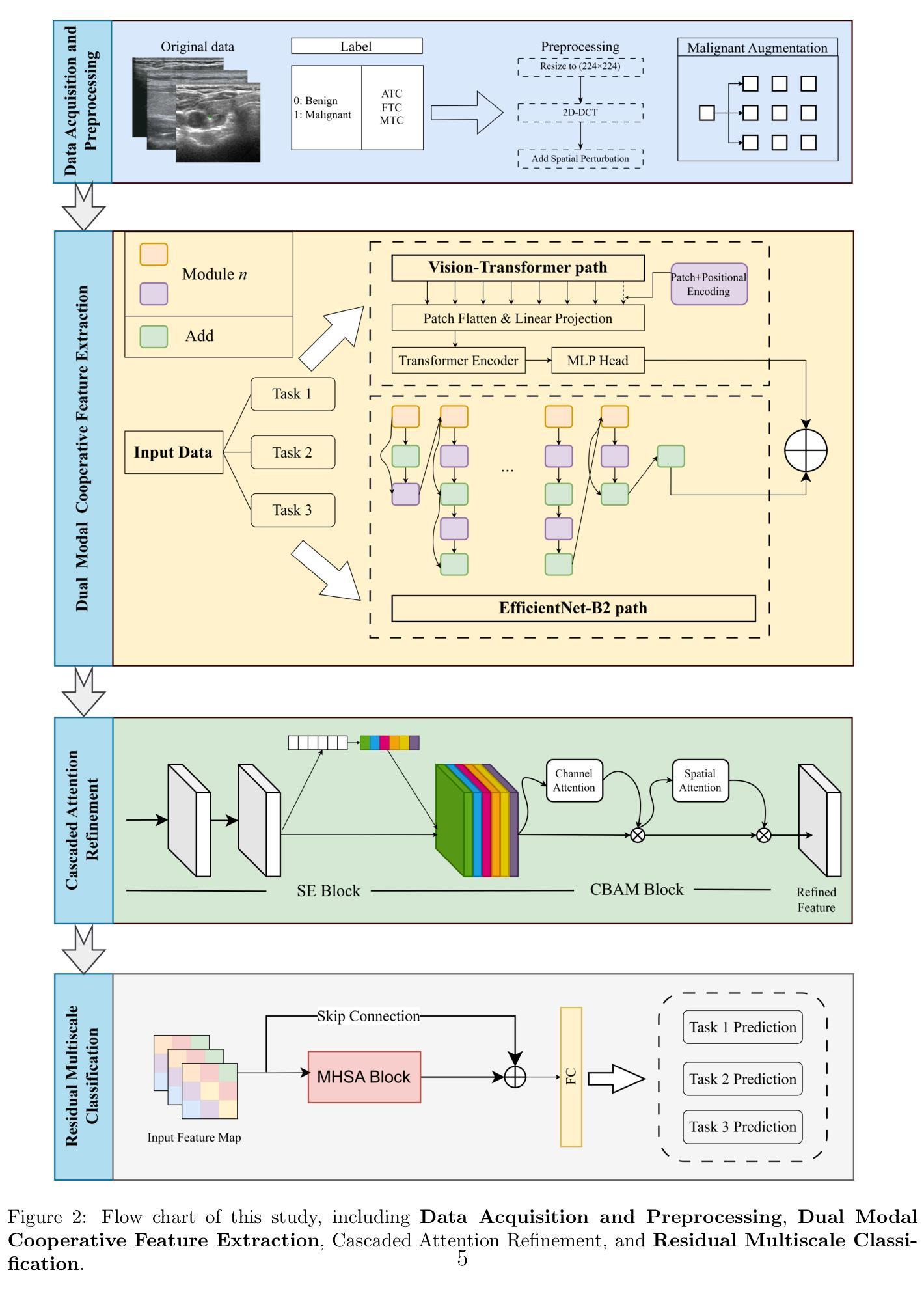
CSASN: A Multitask Attention-Based Framework for Heterogeneous Thyroid Carcinoma Classification in Ultrasound Images
Authors:Peiqi Li, Yincheng Gao, Renxing Li, Haojie Yang, Yunyun Liu, Boji Liu, Jiahui Ni, Ying Zhang, Yulu Wu, Xiaowei Fang, Lehang Guo, Liping Sun, Jiangang Chen
Heterogeneous morphological features and data imbalance pose significant challenges in rare thyroid carcinoma classification using ultrasound imaging. To address this issue, we propose a novel multitask learning framework, Channel-Spatial Attention Synergy Network (CSASN), which integrates a dual-branch feature extractor - combining EfficientNet for local spatial encoding and ViT for global semantic modeling, with a cascaded channel-spatial attention refinement module. A residual multiscale classifier and dynamically weighted loss function further enhance classification stability and accuracy. Trained on a multicenter dataset comprising more than 2000 patients from four clinical institutions, our framework leverages a residual multiscale classifier and dynamically weighted loss function to enhance classification stability and accuracy. Extensive ablation studies demonstrate that each module contributes significantly to model performance, particularly in recognizing rare subtypes such as FTC and MTC carcinomas. Experimental results show that CSASN outperforms existing single-stream CNN or Transformer-based models, achieving a superior balance between precision and recall under class-imbalanced conditions. This framework provides a promising strategy for AI-assisted thyroid cancer diagnosis.
在超声成像中,异质形态特征和数据不平衡给罕见甲状腺癌的分类带来了重大挑战。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种新型的多任务学习框架——通道空间注意力协同网络(CSASN)。该框架整合了一个双分支特征提取器,结合了EfficientNet进行局部空间编码和ViT进行全局语义建模,并配备了一个级联的通道空间注意力优化模块。残差多尺度分类器和动态加权损失函数进一步提高了分类的稳定性和准确性。我们的框架是在一个包含超过2000名患者的多中心数据集上训练的,该数据集来自四个临床机构。通过广泛的消融研究证明,每个模块都对模型性能做出了重大贡献,特别是在识别罕见亚型如FTC和MTC癌方面。实验结果表明,CSASN优于现有的单流CNN或基于Transformer的模型,在类别不平衡的条件下,在精度和召回率之间取得了优越的平衡。该框架为人工智能辅助甲状腺癌诊断提供了有前景的策略。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 10 figures, 4 tables
Summary
一篇关于使用超声成像对稀有甲状腺癌进行分类的研究,提出了一个新型多任务学习框架CSASN,通过结合EfficientNet进行局部空间编码和ViT进行全局语义建模,解决异质形态特征和不平衡数据带来的挑战。该框架采用级联通道空间注意力优化模块,并通过残差多尺度分类器和动态加权损失函数提高分类的稳定性和准确性。经过超过两千名患者的多中心数据集训练,该框架能够有效识别罕见亚型如FTC和MTC癌。研究结果表明,CSASN优于现有的单流CNN或Transformer模型,在类别不平衡条件下实现了精度和召回率的平衡,为AI辅助甲状腺癌诊断提供了有力支持。
Key Takeaways
- 面对超声成像中罕见的甲状腺癌分类的挑战,提出了CSASN多任务学习框架来解决异质形态特征和不平衡数据的问题。
- CSASN结合了EfficientNet和ViT两种技术,分别进行局部空间编码和全局语义建模。
- 通过级联通道空间注意力优化模块来提高模型的性能。
- 采用残差多尺度分类器和动态加权损失函数,增强了分类的稳定性和准确性。
- 该框架在多中心数据集上进行了训练,包括超过两千名患者,能有效识别罕见癌症状如FTC和MTC。
- CSASN在类别不平衡条件下表现出优越的性能,实现了精度和召回率的平衡。
点此查看论文截图

Heart Failure Prediction using Modal Decomposition and Masked Autoencoders for Scarce Echocardiography Databases
Authors:Andrés Bell-Navas, María Villalba-Orero, Enrique Lara-Pezzi, Jesús Garicano-Mena, Soledad Le Clainche
Heart diseases constitute the main cause of international human defunction. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), approximately 18 million deaths happen each year due to precisely heart diseases. In particular, heart failures (HF) press the healthcare industry to develop systems for their early, rapid, and effective prediction. This work presents an automatic system based on a novel deep learning framework which analyses in real-time echocardiography video sequences for the challenging and more specific task of heart failure time prediction. This system works in two stages. The first one transforms the data from a database of echocardiography video sequences into a machine learning-compatible collection of annotated images which can be used in the training phase of any machine learning-based framework, including a deep learning-based one. This stage includes the use of the Higher Order Dynamic Mode Decomposition (HODMD) algorithm for both data augmentation and feature extraction. The second stage builds and trains a Vision Transformer (ViT). Self-supervised learning (SSL) methods, so far barely explored in the literature about heart failure prediction, are adopted to effectively train the ViT from scratch, even with scarce databases. The designed neural network analyses images from echocardiography sequences to estimate the time in which a heart failure will happen. The results obtained show the efficacy of the HODMD algorithm and the superiority of the proposed system with respect to several established ViT and Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) architectures. The source code will be incorporated into the next version release of the ModelFLOWs-app software (https://github.com/modelflows/ModelFLOWs-app).
心脏病是国际人类功能障碍的主要诱因。据世界卫生组织(WHO)统计,每年约有1800万人因心脏病而死亡。特别是,心力衰竭(HF)迫使医疗行业需要开发系统以进行早期、快速和有效的预测。本文介绍了一个基于新型深度学习框架的自动系统,该系统可实时分析超声心动图视频序列,以进行更具挑战性的心力衰竭时间预测任务。该系统分为两个阶段。第一阶段将超声心动图视频序列数据库的数据转换为机器学习兼容的注释图像集合,可用于任何基于机器学习(包括深度学习)的框架的训练阶段。这一阶段包括使用高阶动态模式分解(HODMD)算法进行数据增强和特征提取。第二阶段构建并训练Vision Transformer(ViT)。采用迄今为止在心力衰竭预测文献中很少探索的自我监督学习(SSL)方法来有效地从头开始训练ViT,即使数据库稀缺也是如此。所设计的神经网络分析超声心动图序列的图像,以估计心力衰竭发生的时间。获得的结果显示了HODMD算法的有效性以及所提出的系统在多个已建立的ViT和卷积神经网络(CNN)架构方面的优越性。源代码将包含在ModelFLOWs-app软件的下一个版本发布中(https://github.com/modelflows/ModelFLOWs-app)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 39 pages, 7 figures. arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:2404.19579
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于深度学习的自动系统,用于实时分析超声心动图视频序列,预测心脏衰竭的时间。系统分为两个阶段,第一阶段将数据转换为机器学习兼容的标注图像集合,第二阶段构建并训练Vision Transformer(ViT)。采用自监督学习方法有效训练ViT,即使数据库稀缺也能从头开始训练。所设计的神经网络通过分析超声心动图序列的图像来估计心脏衰竭发生的时间。
Key Takeaways
- 本文提出一种自动系统,基于深度学习的框架,用于实时分析超声心动图视频序列,挑战性地预测心脏衰竭的时间。
- 系统包括两个主要阶段:数据转换和ViT的构建与训练。
- 使用高阶动态模式分解(HODMD)算法进行数据增强和特征提取。
- 首次在心脏衰竭预测领域采用自监督学习方法训练ViT。
- 设计的神经网络能够通过分析超声心动图序列的图像来预测心脏衰竭发生的时间。
- 实验结果证明了HODMD算法的有效性以及该系统相较于其他ViT和CNN架构的优越性。
点此查看论文截图

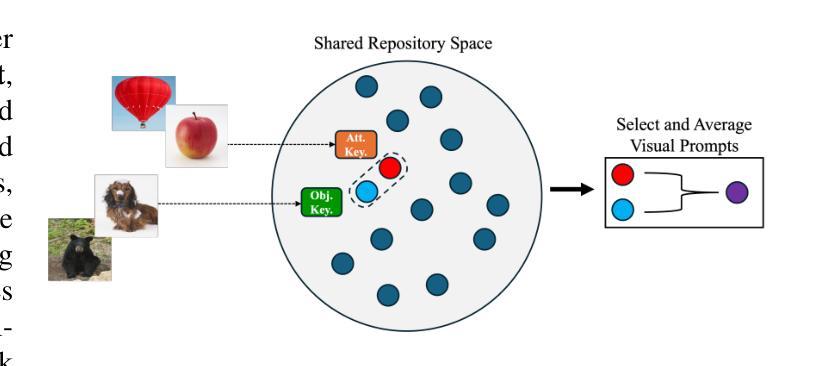
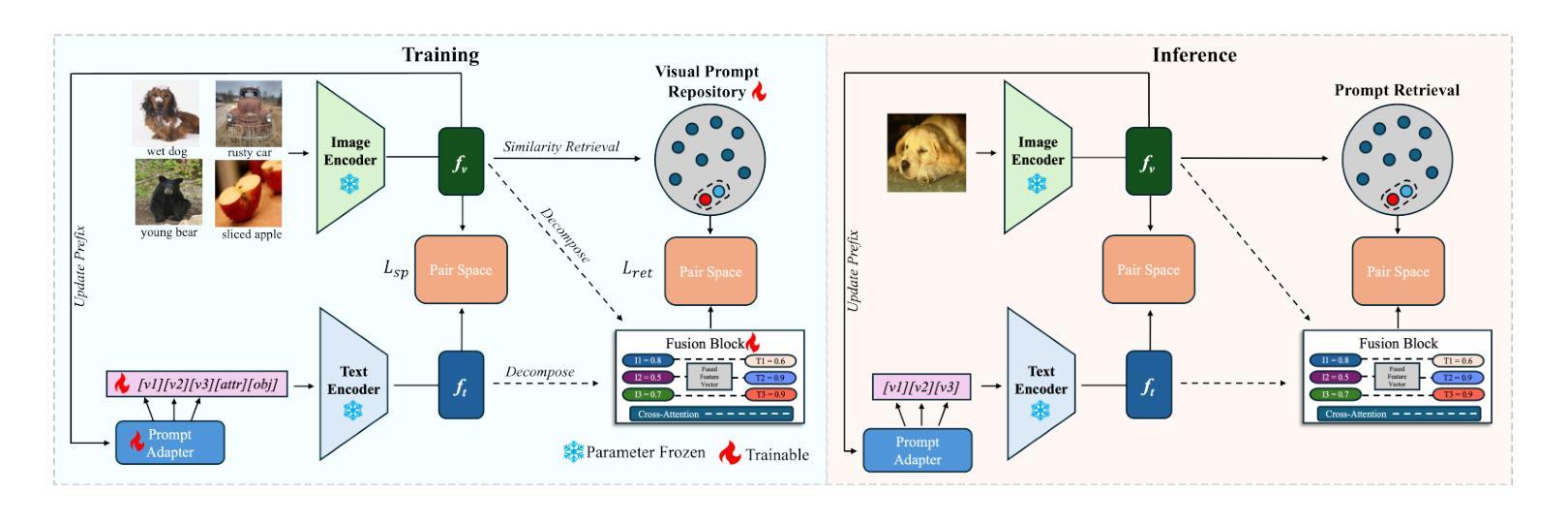
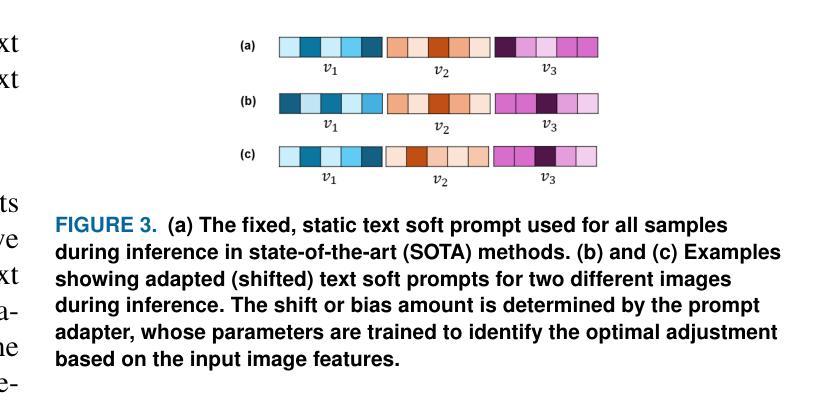
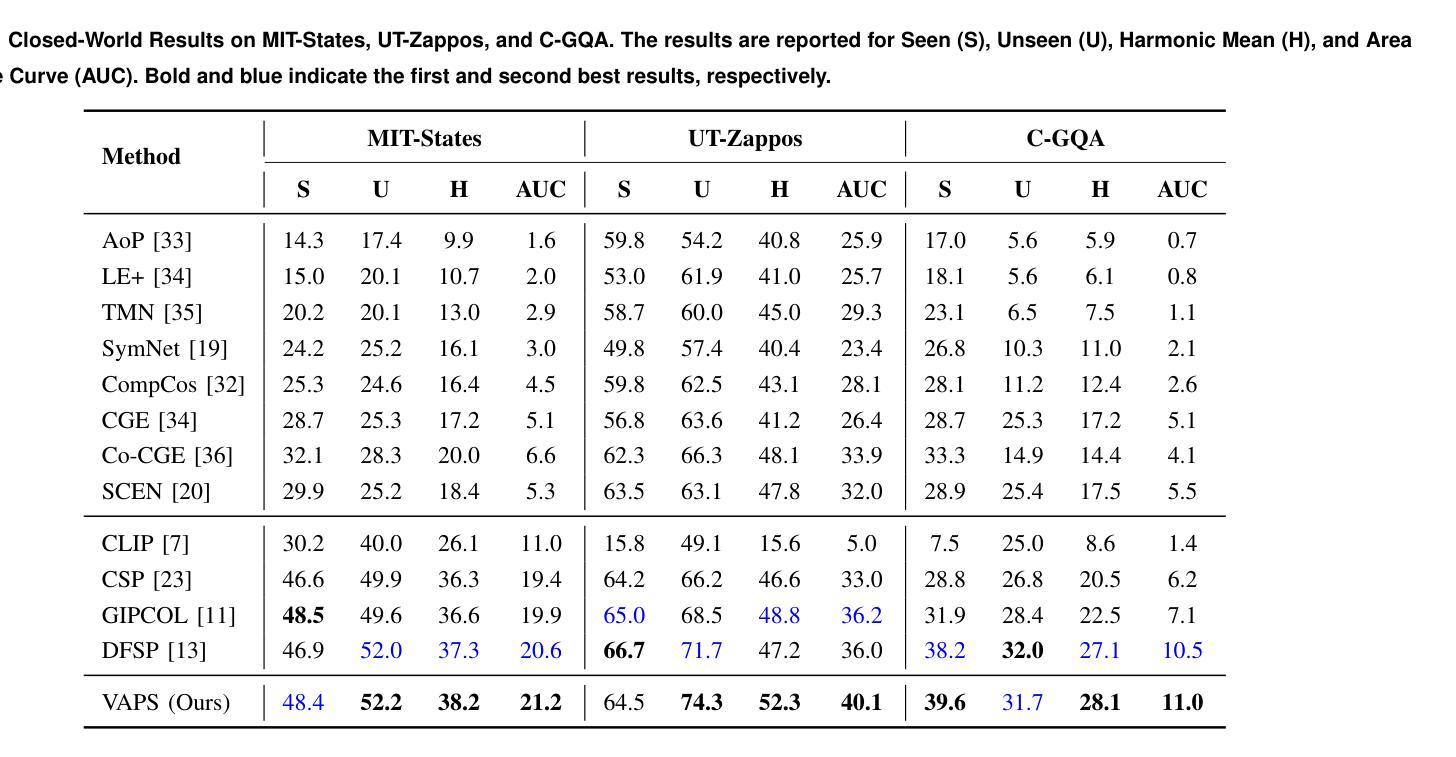
Visual Adaptive Prompting for Compositional Zero-Shot Learning
Authors:Kyle Stein, Arash Mahyari, Guillermo Francia, Eman El-Sheikh
Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have demonstrated impressive capabilities in learning joint representations of visual and textual data, making them powerful tools for tasks such as Compositional Zero-Shot Learning (CZSL). CZSL requires models to generalize to novel combinations of visual primitives-such as attributes and objects-that were not explicitly encountered during training. Recent works in prompting for CZSL have focused on modifying inputs for the text encoder, often using static prompts that do not change across varying visual contexts. However, these approaches struggle to fully capture varying visual contexts, as they focus on text adaptation rather than leveraging visual features for compositional reasoning. To address this, we propose Visual Adaptive Prompting System (VAPS) that leverages a learnable visual prompt repository and similarity-based retrieval mechanism within the framework of VLMs to bridge the gap between semantic and visual features. Our method introduces a dynamic visual prompt repository mechanism that selects the most relevant attribute and object prompts based on the visual features of the image. Our proposed system includes a visual prompt adapter that encourages the model to learn a more generalizable embedding space. Experiments on three CZSL benchmarks, across both closed and open-world scenarios, demonstrate state-of-the-art results.
视觉语言模型(VLMs)在视觉和文本数据的联合表示学习方面表现出了令人印象深刻的能力,使其成为用于组合零射击学习(CZSL)等任务的强大工具。CZSL要求模型能够推广到训练期间未明确遇到的新组合的视觉元素,如属性和对象。最近关于CZSL提示的工作主要集中在修改文本编码器的输入,通常使用在多种视觉上下文中不会改变的静态提示。然而,这些方法在捕捉多变的视觉上下文时遇到困难,因为它们专注于文本适应,而不是利用视觉特征进行组合推理。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了视觉自适应提示系统(VAPS),该系统利用可学习的视觉提示存储库和基于相似性的检索机制,在视觉语言模型的框架内缩小语义和视觉特征之间的差距。我们的方法引入了一个动态视觉提示存储库机制,该机制根据图像的视觉特征选择最相关的属性和对象提示。我们提出的系统包括一个视觉提示适配器,鼓励模型学习一个更具泛化能力的嵌入空间。在三种CZSL基准测试上的实验,无论是在封闭世界还是开放世界场景中,都取得了最新技术成果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
视觉语言模型(VLMs)在联合表示视觉和文本数据方面表现出强大的能力,适用于组合零射学习(CZSL)等任务。为应对CZSL中对于视觉上下文的捕捉难题,提出了一种视觉自适应提示系统(VAPS),该系统利用可学习的视觉提示库和基于相似性的检索机制,缩小语义和视觉特征之间的差距。通过动态视觉提示库机制,系统根据图像视觉特征选择最相关的属性和对象提示。实验证明,该系统在三种CZSL基准测试中均达到最佳状态。
Key Takeaways
- VLMs具备强大的联合表示视觉和文本数据的能力。
- CZSL任务需要模型对未在训练中明确遇到的新组合的视觉原始数据进行泛化。
- 现有提示方法主要侧重于文本适应,难以充分利用视觉特征进行组合推理。
- VAPS通过利用可学习的视觉提示库和基于相似性的检索机制来缩小语义和视觉特征之间的差距。
- VAPS包括一个动态视觉提示库机制,能够根据图像选择相关提示。
- VAPS包括一个视觉提示适配器,鼓励模型学习更具泛化能力的嵌入空间。
点此查看论文截图

Underwater Image Enhancement via Dehazing and Color Restoration
Authors:Chengqin Wu, Shuai Yu, Tuyan Luo, Qiuhua Rao, Qingson Hu, Jingxiang Xu, Lijun Zhang
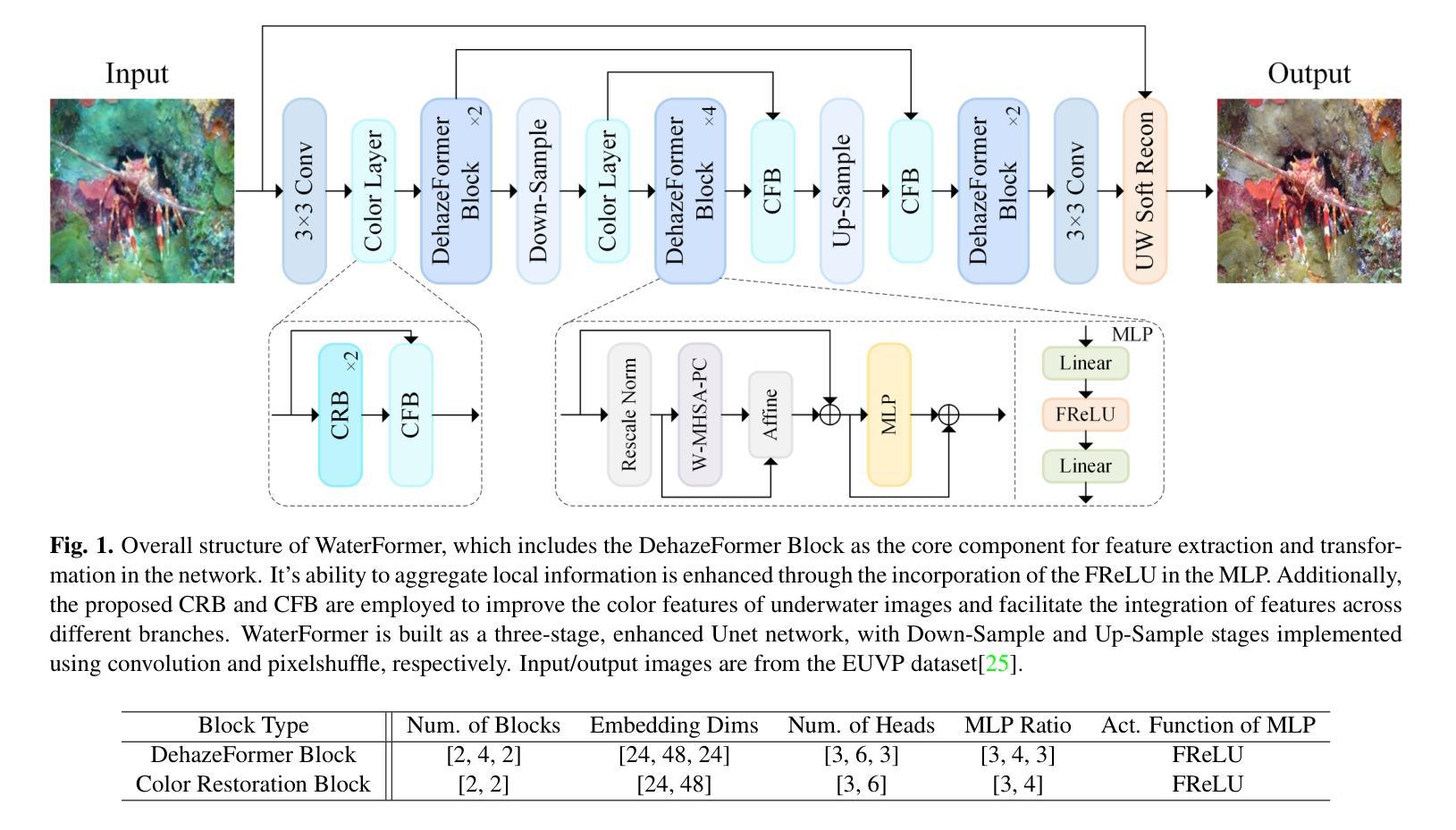
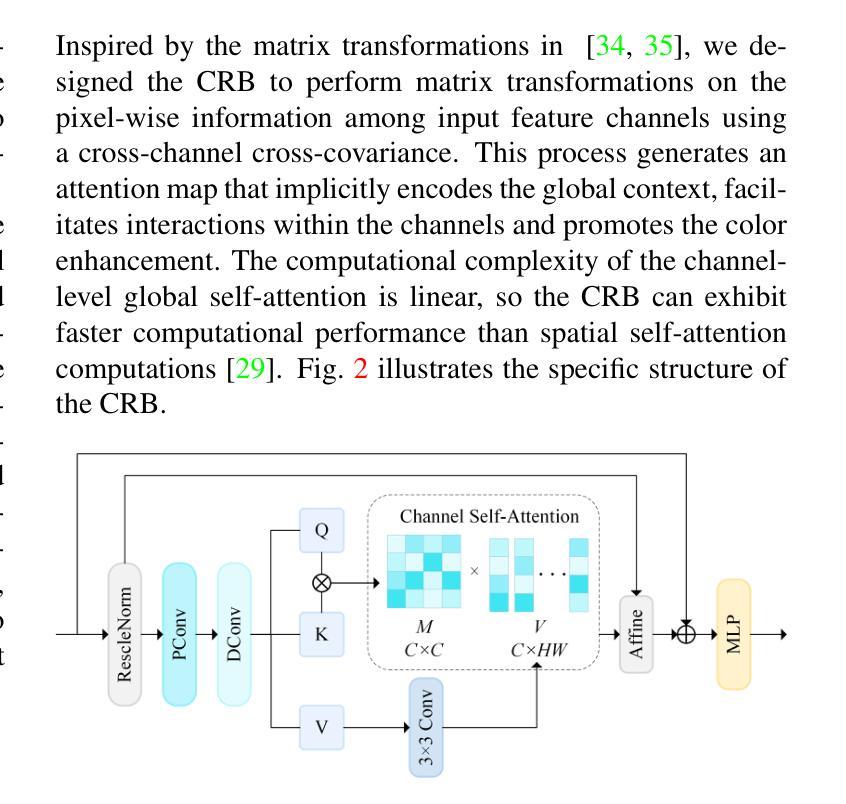
Underwater visual imaging is crucial for marine engineering, but it suffers from low contrast, blurriness, and color degradation, which hinders downstream analysis. Existing underwater image enhancement methods often treat the haze and color cast as a unified degradation process, neglecting their inherent independence while overlooking their synergistic relationship. To overcome this limitation, we propose a Vision Transformer (ViT)-based network (referred to as WaterFormer) to improve underwater image quality. WaterFormer contains three major components: a dehazing block (DehazeFormer Block) to capture the self-correlated haze features and extract deep-level features, a Color Restoration Block (CRB) to capture self-correlated color cast features, and a Channel Fusion Block (CFB) that dynamically integrates these decoupled features to achieve comprehensive enhancement. To ensure authenticity, a soft reconstruction layer based on the underwater imaging physics model is included. Further, a Chromatic Consistency Loss and Sobel Color Loss are designed to respectively preserve color fidelity and enhance structural details during network training. Comprehensive experimental results demonstrate that WaterFormer outperforms other state-of-the-art methods in enhancing underwater images.
水下视觉成像对于海洋工程至关重要,但它受到低对比度、模糊和颜色退化等因素的影响,阻碍了后续分析。现有的水下图像增强方法通常将雾霾和色彩投射视为统一的退化过程,忽略了它们内在的独立性,同时忽视了它们之间的协同关系。为了克服这一局限性,我们提出了一种基于Vision Transformer(ViT)的网络(称为WaterFormer)来改善水下图像质量。WaterFormer包含三个主要组件:去雾块(DehazeFormer Block)用于捕获自相关的雾特征并提取深层特征,色彩恢复块(CRB)用于捕获自相关的色彩投射特征,以及通道融合块(CFB)动态融合这些解耦特征以实现全面增强。为了保证真实性,还加入了一个基于水下成像物理模型的软重建层。此外,还设计了色度一致性损失和Sobel色彩损失,以在网络训练过程中分别保持颜色保真度和增强结构细节。大量的实验结果证明,WaterFormer在增强水下图像方面优于其他最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于Vision Transformer(ViT)的水下图像增强网络(WaterFormer),旨在解决水下视觉成像中的低对比度和色彩失真问题。该网络包含三个主要组件:去雾块(DehazeFormer Block)、色彩恢复块(CRB)和通道融合块(CFB)。去雾块用于捕捉雾气特征并提取深层特征,色彩恢复块则负责捕捉颜色偏差特征。通道融合块则动态结合了这些独立特征以实现全面增强。此外,网络还包含基于水下成像物理模型的软重建层,并设计了色度一致性损失和Sobel色彩损失,以在训练过程中保持色彩保真度和增强结构细节。实验结果表明,WaterFormer在增强水下图像方面优于其他先进方法。
Key Takeaways
- 水下视觉成像面临低对比度和色彩失真问题,影响下游分析。
- 现有水下图像增强方法往往将雾气和色彩偏移视为统一退化过程,忽略了它们的独立性和相互作用关系。
- 提出一种基于Vision Transformer(ViT)的水下图像增强网络(WaterFormer)来解决这一问题。
- WaterFormer包含三个主要组件:去雾块、色彩恢复块和通道融合块,分别负责捕捉雾气特征、颜色偏差特征,并动态结合这些特征以实现增强。
- 网络包含基于水下成像物理模型的软重建层,确保增强的真实性。
- 设计了色度一致性损失和Sobel色彩损失,以在训练过程中保持色彩保真度和增强结构细节。
点此查看论文截图

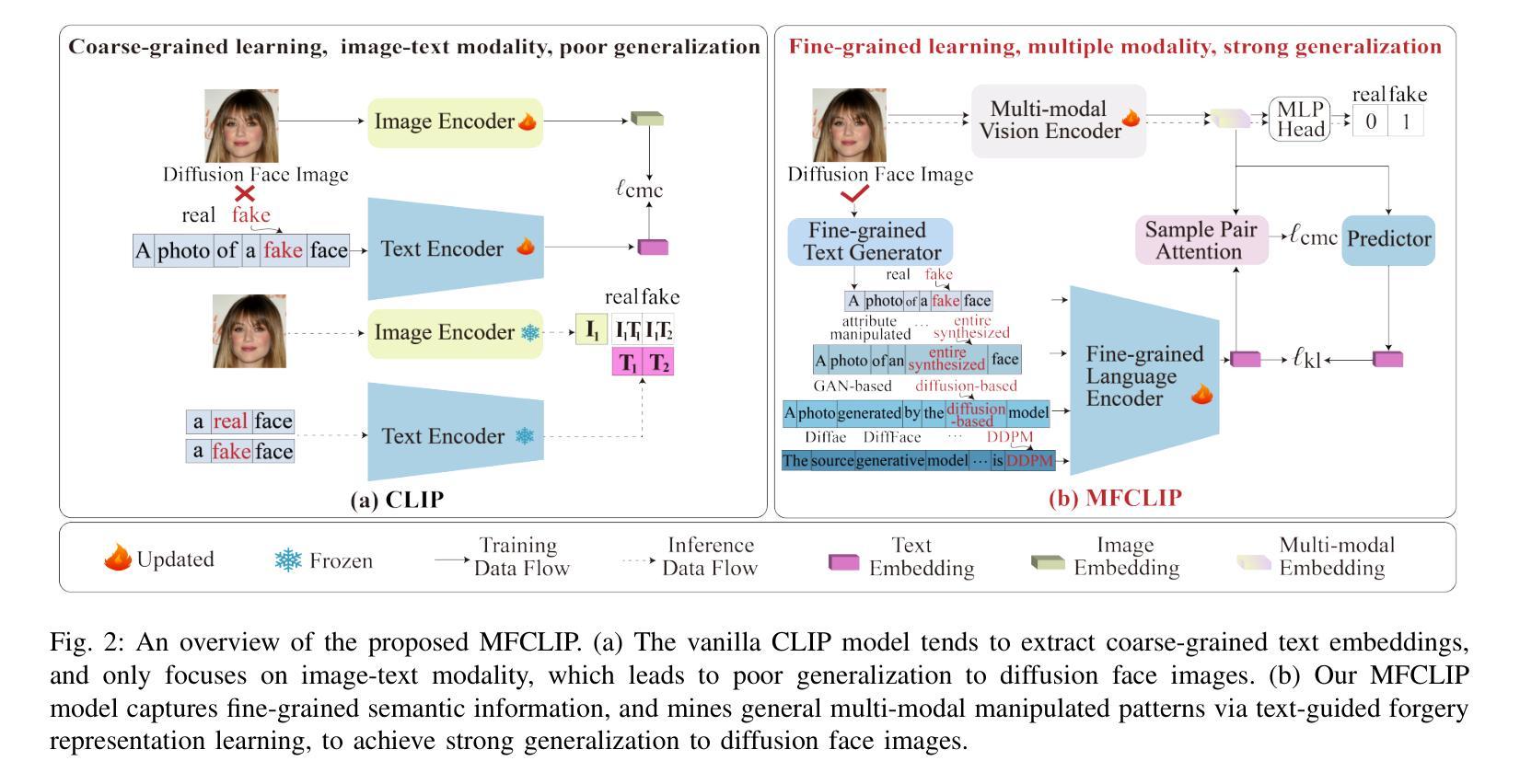
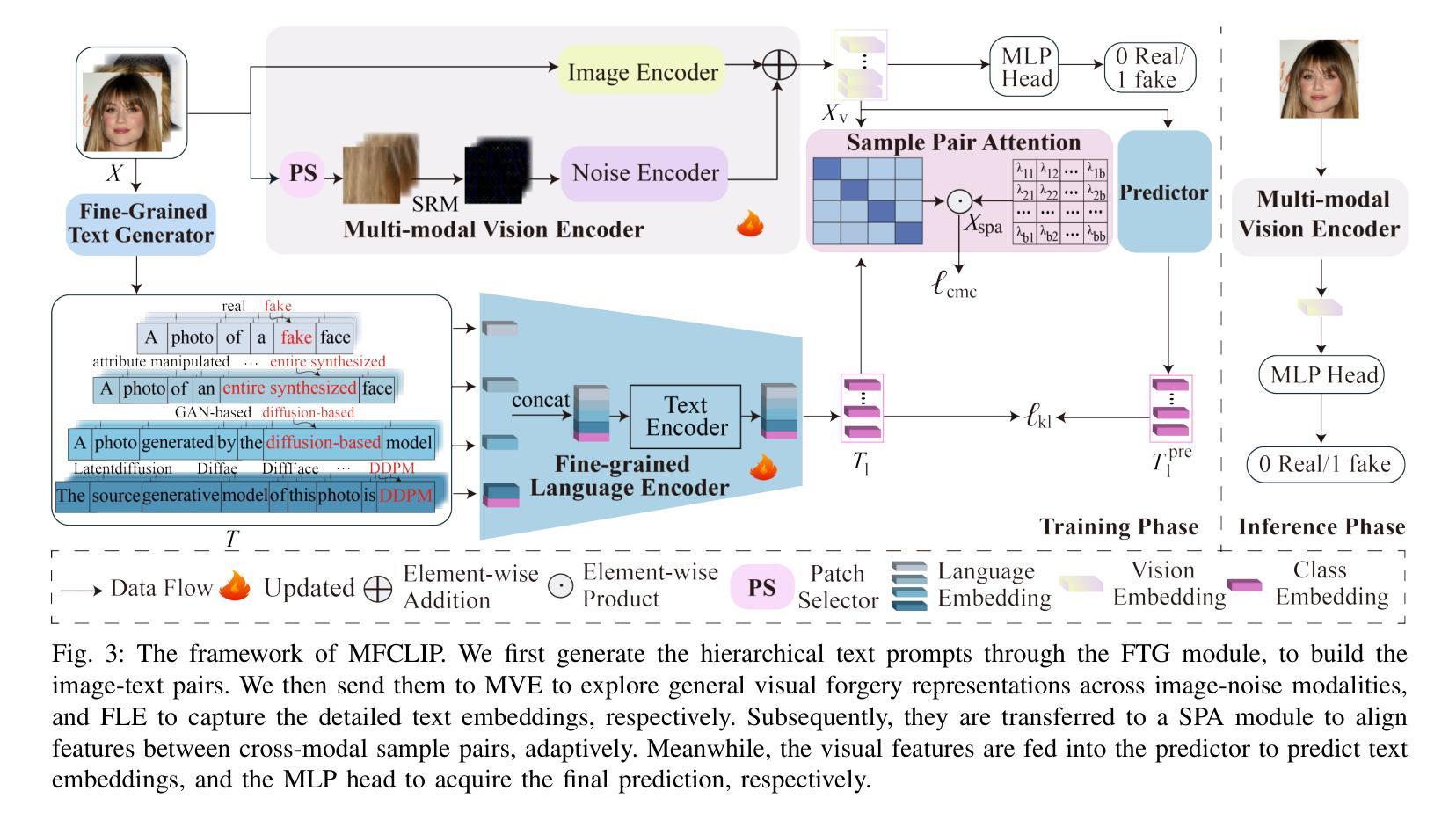
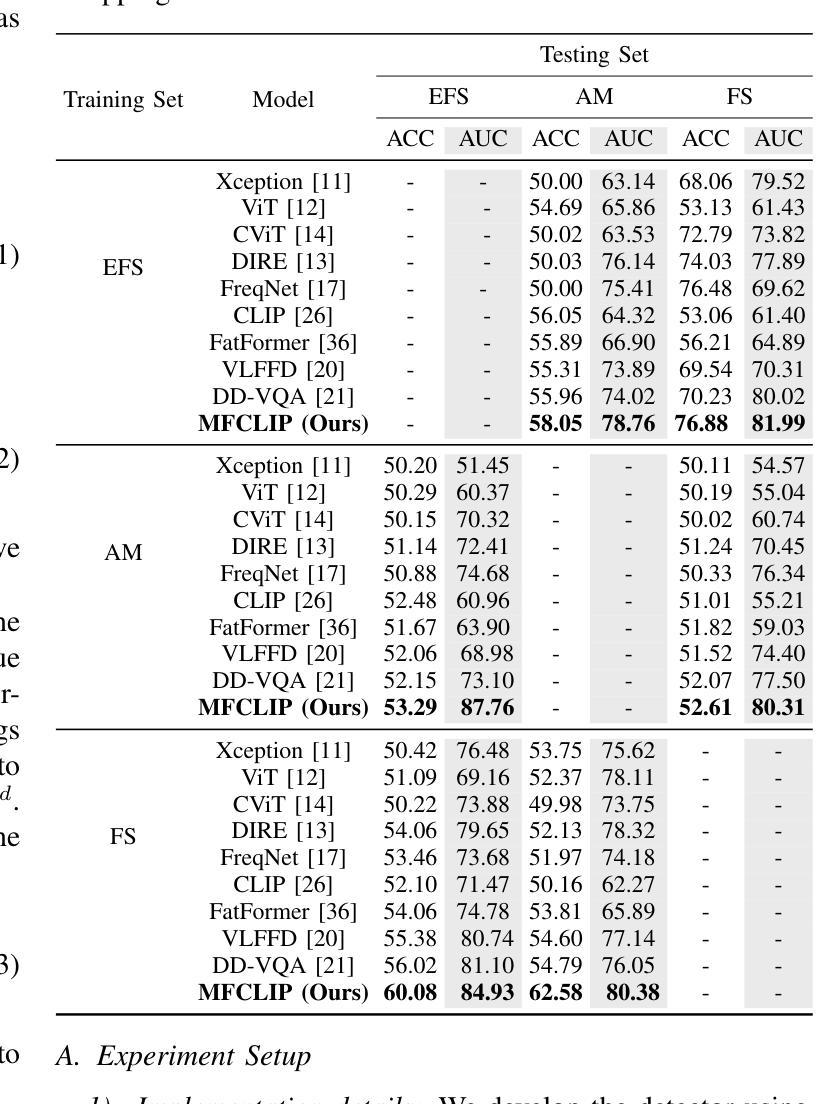
MFCLIP: Multi-modal Fine-grained CLIP for Generalizable Diffusion Face Forgery Detection
Authors:Yaning Zhang, Tianyi Wang, Zitong Yu, Zan Gao, Linlin Shen, Shengyong Chen
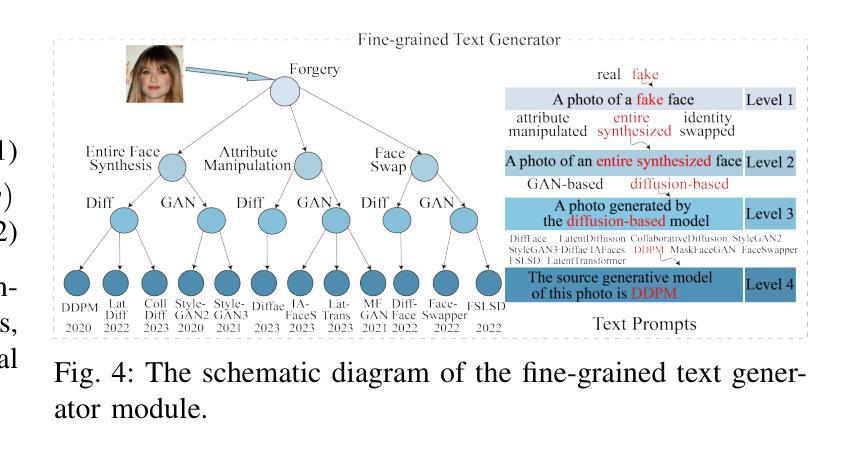
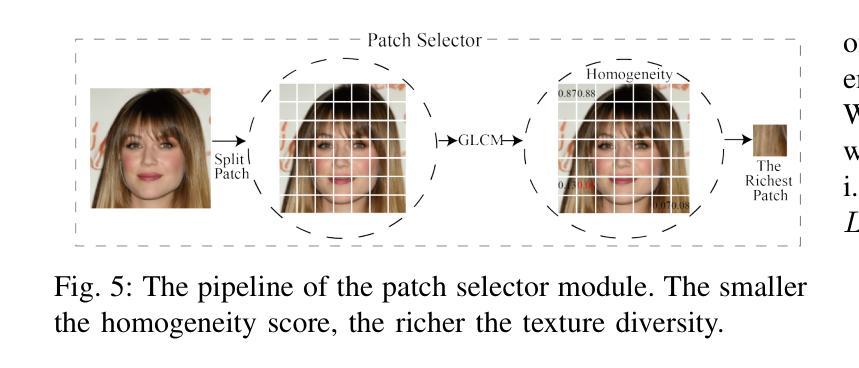
The rapid development of photo-realistic face generation methods has raised significant concerns in society and academia, highlighting the urgent need for robust and generalizable face forgery detection (FFD) techniques. Although existing approaches mainly capture face forgery patterns using image modality, other modalities like fine-grained noises and texts are not fully explored, which limits the generalization capability of the model. In addition, most FFD methods tend to identify facial images generated by GAN, but struggle to detect unseen diffusion-synthesized ones. To address the limitations, we aim to leverage the cutting-edge foundation model, contrastive language-image pre-training (CLIP), to achieve generalizable diffusion face forgery detection (DFFD). In this paper, we propose a novel multi-modal fine-grained CLIP (MFCLIP) model, which mines comprehensive and fine-grained forgery traces across image-noise modalities via language-guided face forgery representation learning, to facilitate the advancement of DFFD. Specifically, we devise a fine-grained language encoder (FLE) that extracts fine global language features from hierarchical text prompts. We design a multi-modal vision encoder (MVE) to capture global image forgery embeddings as well as fine-grained noise forgery patterns extracted from the richest patch, and integrate them to mine general visual forgery traces. Moreover, we build an innovative plug-and-play sample pair attention (SPA) method to emphasize relevant negative pairs and suppress irrelevant ones, allowing cross-modality sample pairs to conduct more flexible alignment. Extensive experiments and visualizations show that our model outperforms the state of the arts on different settings like cross-generator, cross-forgery, and cross-dataset evaluations.
快速逼真面部生成方法的开发引起了社会和学术界的广泛关注,这凸显了对稳健且通用的面部伪造检测(FFD)技术的迫切需求。尽管现有方法主要使用图像模式捕捉面部伪造模式,但其他模式(如细微噪声和文本)尚未得到完全探索,这限制了模型的泛化能力。此外,大多数FFD方法倾向于识别由GAN生成的面部图像,但难以检测未见过的扩散合成图像。为了解决这些限制,我们旨在利用最前沿的基础模型——对比语言图像预训练(CLIP),实现可通用的扩散面部伪造检测(DFFD)。在本文中,我们提出了一种新的多模式精细CLIP(MFCLIP)模型,它通过语言引导的面部伪造表示学习,挖掘图像噪声模式之间的全面和精细的伪造痕迹,以促进DFFD的发展。具体来说,我们设计了一种精细的语言编码器(FLE),它从分层的文本提示中提取精细的全局语言特征。我们设计了一个多模式视觉编码器(MVE),以捕获全局图像伪造嵌入以及从最丰富的补丁中提取的精细噪声伪造模式,并将它们整合起来挖掘通用的视觉伪造痕迹。此外,我们建立了一种创新的可插拔式样本配对注意力(SPA)方法,以强调相关的负样本对并抑制不相关的样本对,使跨模态样本对能够进行更灵活的对齐。广泛的实验和可视化结果表明,我们的模型在不同的设置(如跨生成器、跨伪造和跨数据集评估)上均超过了现有技术。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该方法旨在解决社会与学术界对于逼真的面部生成技术快速发展所引发的担忧,特别是对面部伪造检测技术的迫切需求。现有方法主要依赖图像模态捕捉面部伪造模式,但忽略了其他模态如精细噪声和文本的重要性,限制了模型的泛化能力。本研究旨在利用前沿的CLIP模型,实现可泛化的扩散面部伪造检测(DFFD)。为此,提出了一种新颖的多模态精细CLIP(MFCLIP)模型,通过语言引导的面伪造表示学习,挖掘图像噪声模态的全面精细伪造痕迹。设计精细语言编码器(FLE)和多模态视觉编码器(MVE),整合全局图像伪造嵌入和从丰富区域提取的精细噪声伪造模式,挖掘通用视觉伪造痕迹。此外,开发了创新的即插即用样本配对注意力(SPA)方法,强调相关的负样本对并抑制无关的样本对,实现跨模态样本对更灵活的配对。实验和可视化显示,该模型在不同设置上均超越了现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 现有面部伪造检测技术主要关注图像模态,忽视了其他如精细噪声和文本等模态的重要性。
- 提出利用CLIP模型实现可泛化的扩散面部伪造检测(DFFD)。
- 引入多模态精细CLIP(MFCLIP)模型,通过语言引导学习挖掘全面的精细伪造痕迹。
- 设计了精细语言编码器(FLE)和多模态视觉编码器(MVE),用于提取全局和精细的伪造特征。
- 创新提出即插即用样本配对注意力(SPA)方法,强化相关样本对的配对。
- 该模型在跨生成器、跨伪造和跨数据集评估等不同设置上均表现出卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图