⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-09 更新
Active Sampling for MRI-based Sequential Decision Making
Authors:Yuning Du, Jingshuai Liu, Rohan Dharmakumar, Sotirios A. Tsaftaris
Despite the superior diagnostic capability of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), its use as a Point-of-Care (PoC) device remains limited by high cost and complexity. To enable such a future by reducing the magnetic field strength, one key approach will be to improve sampling strategies. Previous work has shown that it is possible to make diagnostic decisions directly from k-space with fewer samples. Such work shows that single diagnostic decisions can be made, but if we aspire to see MRI as a true PoC, multiple and sequential decisions are necessary while minimizing the number of samples acquired. We present a novel multi-objective reinforcement learning framework enabling comprehensive, sequential, diagnostic evaluation from undersampled k-space data. Our approach during inference actively adapts to sequential decisions to optimally sample. To achieve this, we introduce a training methodology that identifies the samples that contribute the best to each diagnostic objective using a step-wise weighting reward function. We evaluate our approach in two sequential knee pathology assessment tasks: ACL sprain detection and cartilage thickness loss assessment. Our framework achieves diagnostic performance competitive with various policy-based benchmarks on disease detection, severity quantification, and overall sequential diagnosis, while substantially saving k-space samples. Our approach paves the way for the future of MRI as a comprehensive and affordable PoC device. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/vios-s/MRI_Sequential_Active_Sampling
尽管磁共振成像(MRI)在诊断方面具有卓越的能力,但由于其高昂的成本和复杂性,作为即时检测(Point-of-Care,PoC)设备的使用仍然受到限制。通过降低磁场强度来实现未来技术的发展,关键方法之一是改进采样策略。先前的研究工作已经表明,从较少的样本中可以直接从k空间进行诊断决策。这样的工作证明了可以做出单一的诊断决策,但如果我们希望将MRI视为真正的即时检测工具,则需要在减少采集样本数量的同时,做出多次连续的诊断决策。我们提出了一种新型的多目标强化学习框架,能够从欠采样的k空间数据中实现全面、连续的诊断评估。在推理过程中,我们的方法能够主动适应连续决策以实现最优采样。为了实现这一点,我们引入了一种训练方法,该方法使用逐步加权奖励函数来确定对每个诊断目标贡献最大的样本。我们在两个连续的膝关节病理评估任务中评估了我们的方法:前交叉韧带扭伤检测和软骨厚度损失评估。我们的框架在疾病检测、严重程度量化和整体连续诊断方面的诊断性能与各种基于策略的标准相当,同时大幅减少了k空间样本的采集。我们的方法为磁共振成像作为全面且经济实惠的即时检测设备铺平了道路。我们的代码可在https://github.com/vios-s/MRI_Sequential_Active_Sampling上公开获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under Review
Summary
本文探讨了磁共振成像(MRI)在点医疗护理(PoC)设备中的应用限制,如高成本和复杂性。为提高MRI在PoC设备中的潜力,研究者提出改进采样策略是关键。利用欠采样的k-space数据进行综合诊断评估,研究团队采用一种新型多目标强化学习框架,实现连续决策过程的最优化采样。该研究在膝部病理评估任务中表现出良好的诊断性能,并显著节省了k-space样本。这为MRI作为全面且可负担的PoC设备铺平了道路。
Key Takeaways
- MRI在点医疗护理设备中的应用受限于高成本和复杂性。
- 改进采样策略是提高MRI在PoC设备中应用潜力的关键。
- 研究采用新型多目标强化学习框架,实现从欠采样的k-space数据中做出综合诊断评估。
- 该框架实现了连续决策过程的最优化采样。
- 在膝部病理评估任务中,该框架表现出良好的诊断性能,与各种政策基准相比具有竞争力。
- 该框架显著节省了k-space样本的采集。
点此查看论文截图

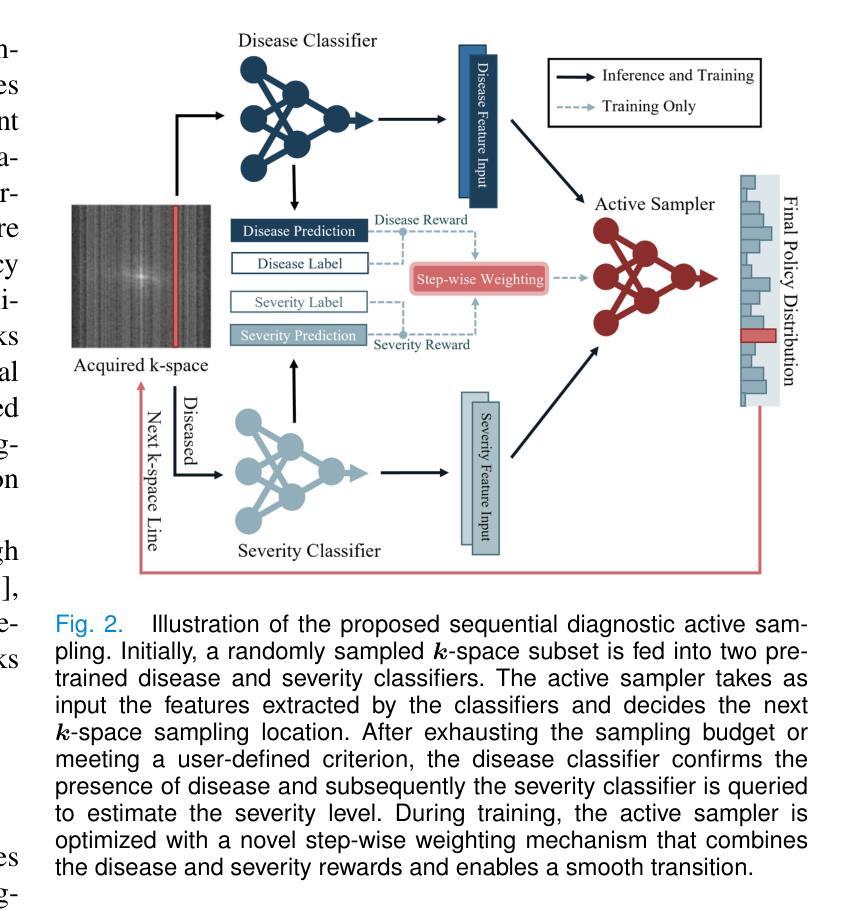
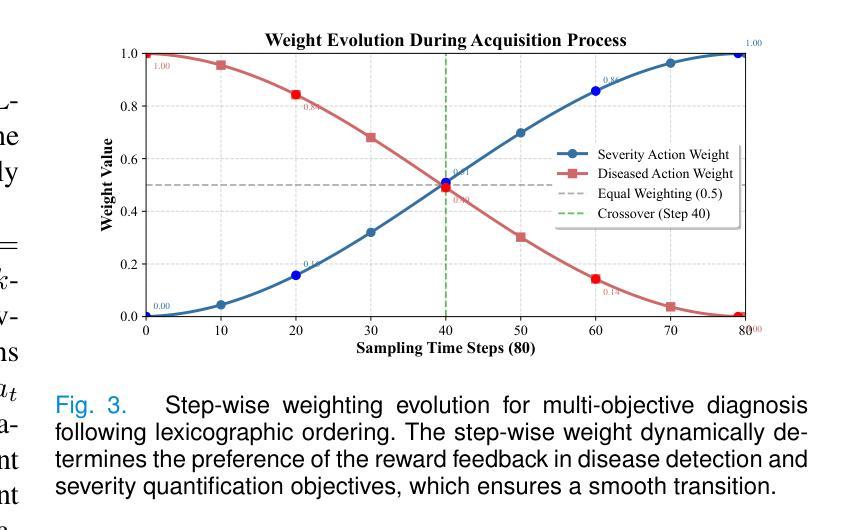
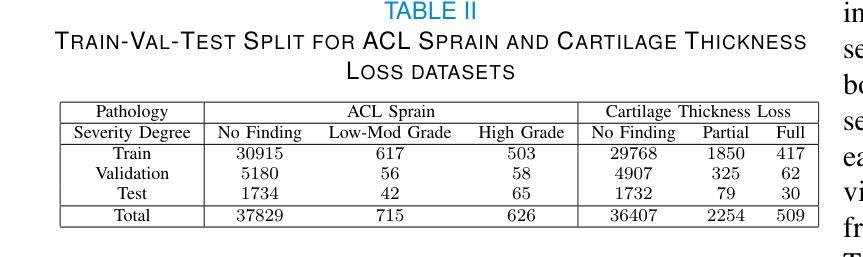
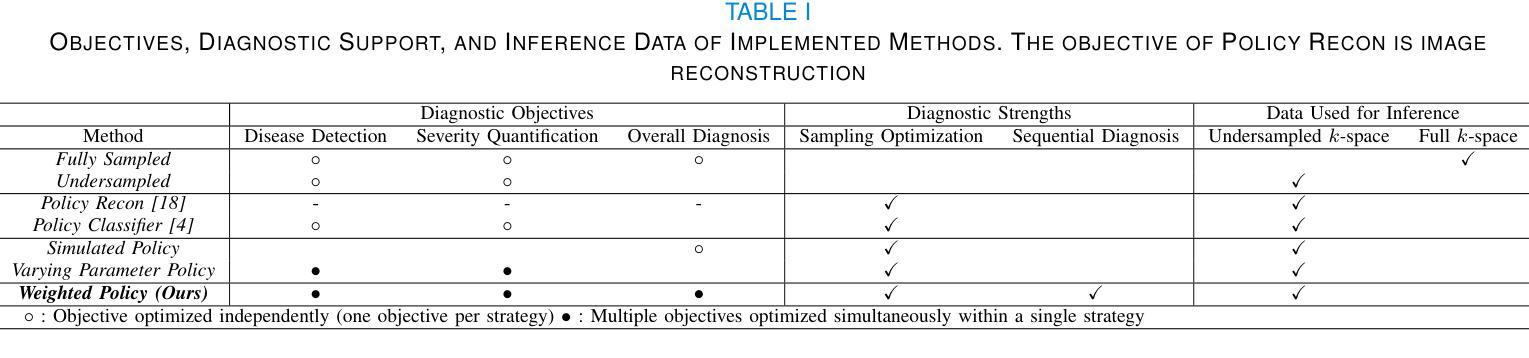
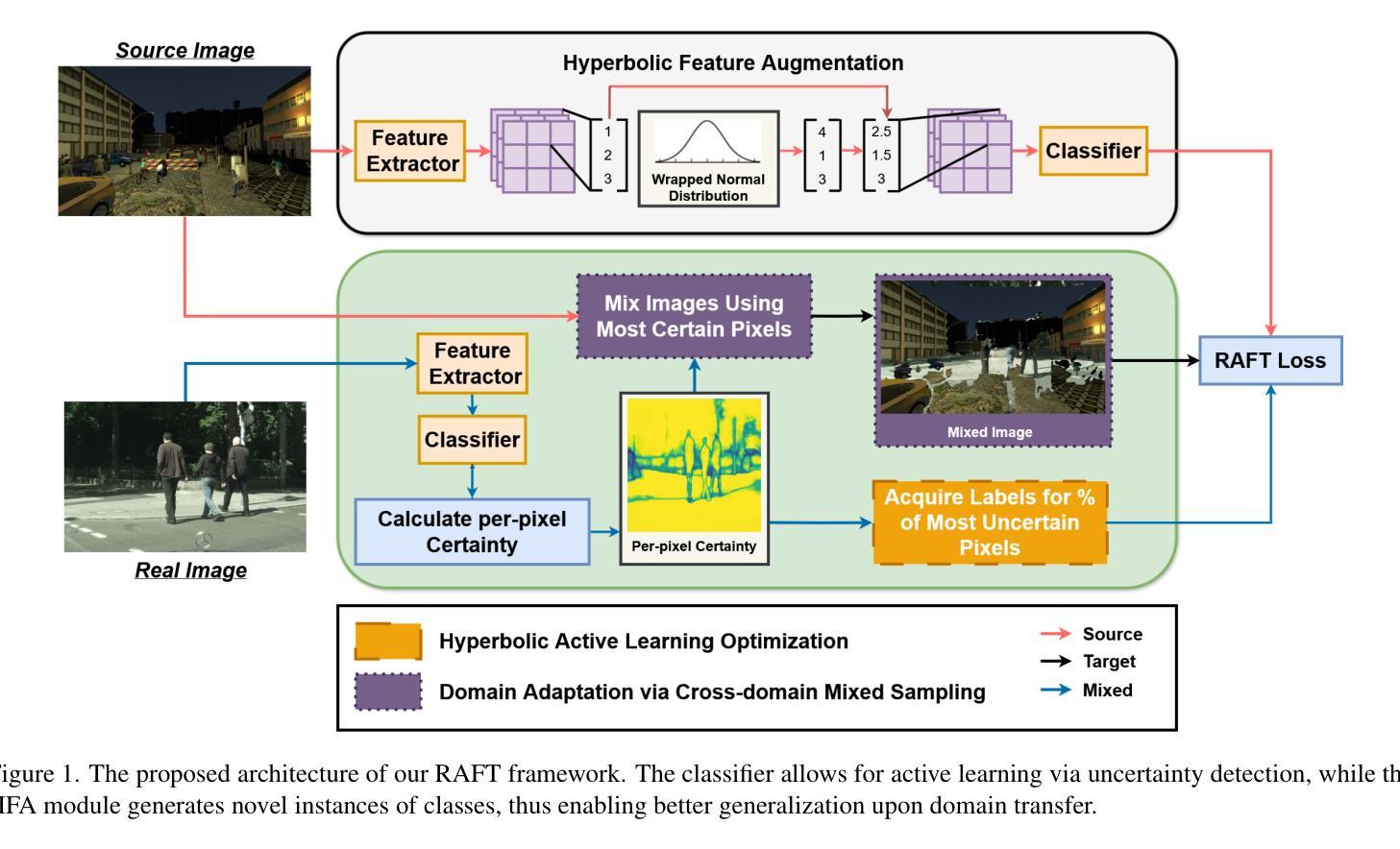
RAFT: Robust Augmentation of FeaTures for Image Segmentation
Authors:Edward Humes, Xiaomin Lin, Uttej Kallakuri, Tinoosh Mohsenin
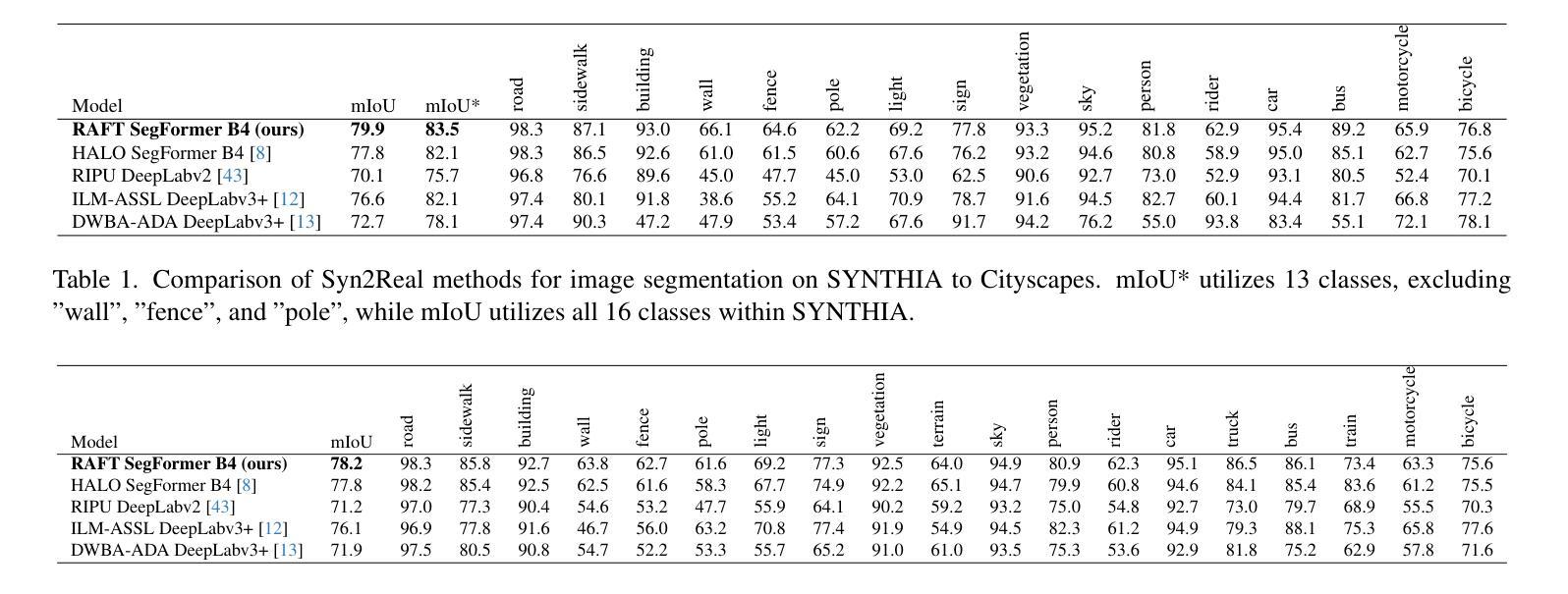
Image segmentation is a powerful computer vision technique for scene understanding. However, real-world deployment is stymied by the need for high-quality, meticulously labeled datasets. Synthetic data provides high-quality labels while reducing the need for manual data collection and annotation. However, deep neural networks trained on synthetic data often face the Syn2Real problem, leading to poor performance in real-world deployments. To mitigate the aforementioned gap in image segmentation, we propose RAFT, a novel framework for adapting image segmentation models using minimal labeled real-world data through data and feature augmentations, as well as active learning. To validate RAFT, we perform experiments on the synthetic-to-real “SYNTHIA->Cityscapes” and “GTAV->Cityscapes” benchmarks. We managed to surpass the previous state of the art, HALO. SYNTHIA->Cityscapes experiences an improvement in mIoU* upon domain adaptation of 2.1%/79.9%, and GTAV->Cityscapes experiences a 0.4%/78.2% improvement in mIoU. Furthermore, we test our approach on the real-to-real benchmark of “Cityscapes->ACDC”, and again surpass HALO, with a gain in mIoU upon adaptation of 1.3%/73.2%. Finally, we examine the effect of the allocated annotation budget and various components of RAFT upon the final transfer mIoU.
图像分割是场景理解的一种强大的计算机视觉技术。然而,真实世界的应用部署受到需要高质量、精细标注数据集的限制。合成数据提供了高质量标签,同时减少了手动数据收集和注释的需求。然而,在合成数据上训练的深度神经网络经常面临Syn2Real问题,导致在真实世界部署中的性能不佳。
为了缓解上述图像分割中的差距,我们提出了RAFT,这是一个新的框架,通过数据和特征增强以及主动学习,使用最少的标记真实世界数据来适应图像分割模型。为了验证RAFT,我们在合成到真实的“SYNTHIA->Cityscapes”和“GTAV->Cityscapes”基准测试集上进行了实验。我们超越了之前的先进技术HALO。SYNTHIA->Cityscapes在域适应方面提高了mIoU* 2.1%/79.9%,GTAV->Cityscapes提高了mIoU 0.4%/78.2%。此外,我们在“Cityscapes->ACDC”的真实到真实的基准测试集上测试了我们的方法,并再次超越了HALO,在适应后提高了mIoU 1.3%/73.2%。最后,我们研究了分配注释预算对RAFT最终迁移mIoU的影响以及各种组件的影响。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
图像分割是一种强大的计算机视觉场景理解技术,但在实际部署中需要高质量、精细标注的数据集。合成数据提供了高质量标签,减少了手动收集和标注的需要。然而,在合成数据上训练的深度神经网络常常面临合成到现实(Syn2Real)问题,导致在现实部署中表现不佳。为缓解图像分割中的上述差距,我们提出了RAFT框架,通过最小限度的真实世界标注数据,利用数据和特征增强以及主动学习方法,对图像分割模型进行适应。实验验证显示,我们在合成到现实的“SYNTHIA→Cityscapes”和“GTAV→Cityscapes”基准测试中超过了之前的最新水平HALO,在mIoU*指标上实现了显著改进。此外,我们在真实到真实的“Cityscapes→ACDC”基准测试中也验证了我们的方法的有效性。最后,我们研究了标注预算分配和RAFT的不同组件对最终迁移mIoU的影响。
Key Takeaways
- 图像分割是计算机视觉中的一项重要技术,用于场景理解,但在实际应用中受到高质量数据集的限制。
- 合成数据能减少手动数据收集和标注的工作量,但训练的模型在真实场景中表现不佳,存在合成到现实(Syn2Real)问题。
- 提出RAFT框架,通过数据增强、特征增强和主动学习策略,解决图像分割模型在现实场景部署中的性能差距。
- 在多个基准测试中验证了RAFT的有效性,包括“SYNTHIA→Cityscapes”,“GTAV→Cityscapes”,以及“Cityscapes→ACDC”,并超过了之前的最新水平HALO。
- RAFT框架能有效利用最小限度的真实世界标注数据,提高模型在现实场景中的性能。
- 实验结果显示,在mIoU*指标上实现了显著改进,具体数值根据不同基准测试而有所不同。
点此查看论文截图

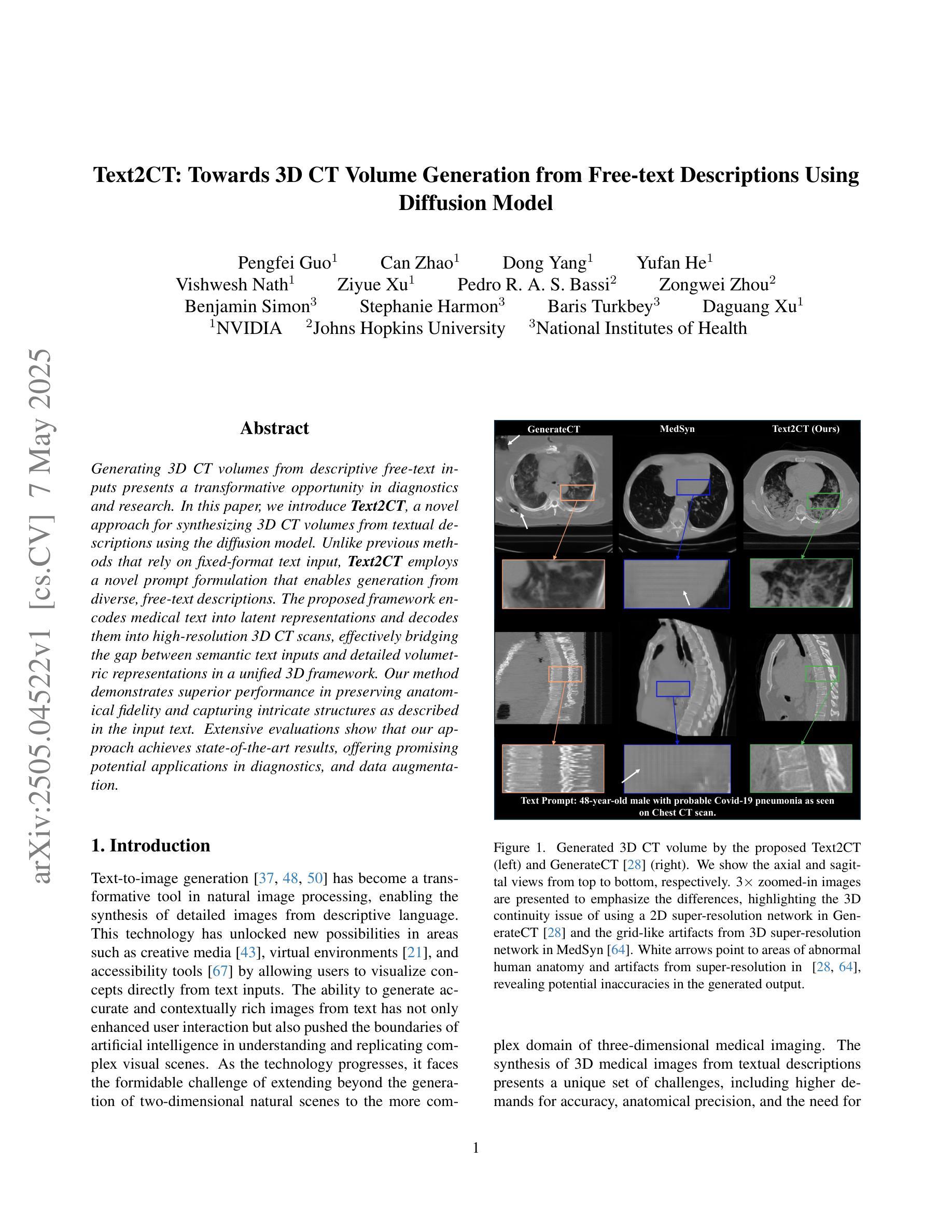
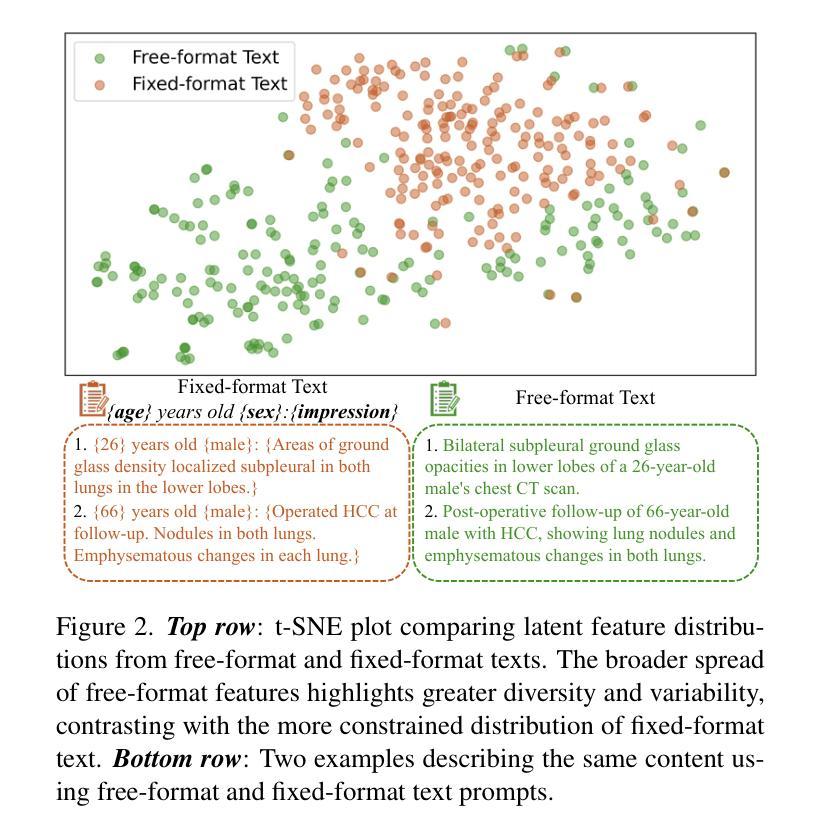
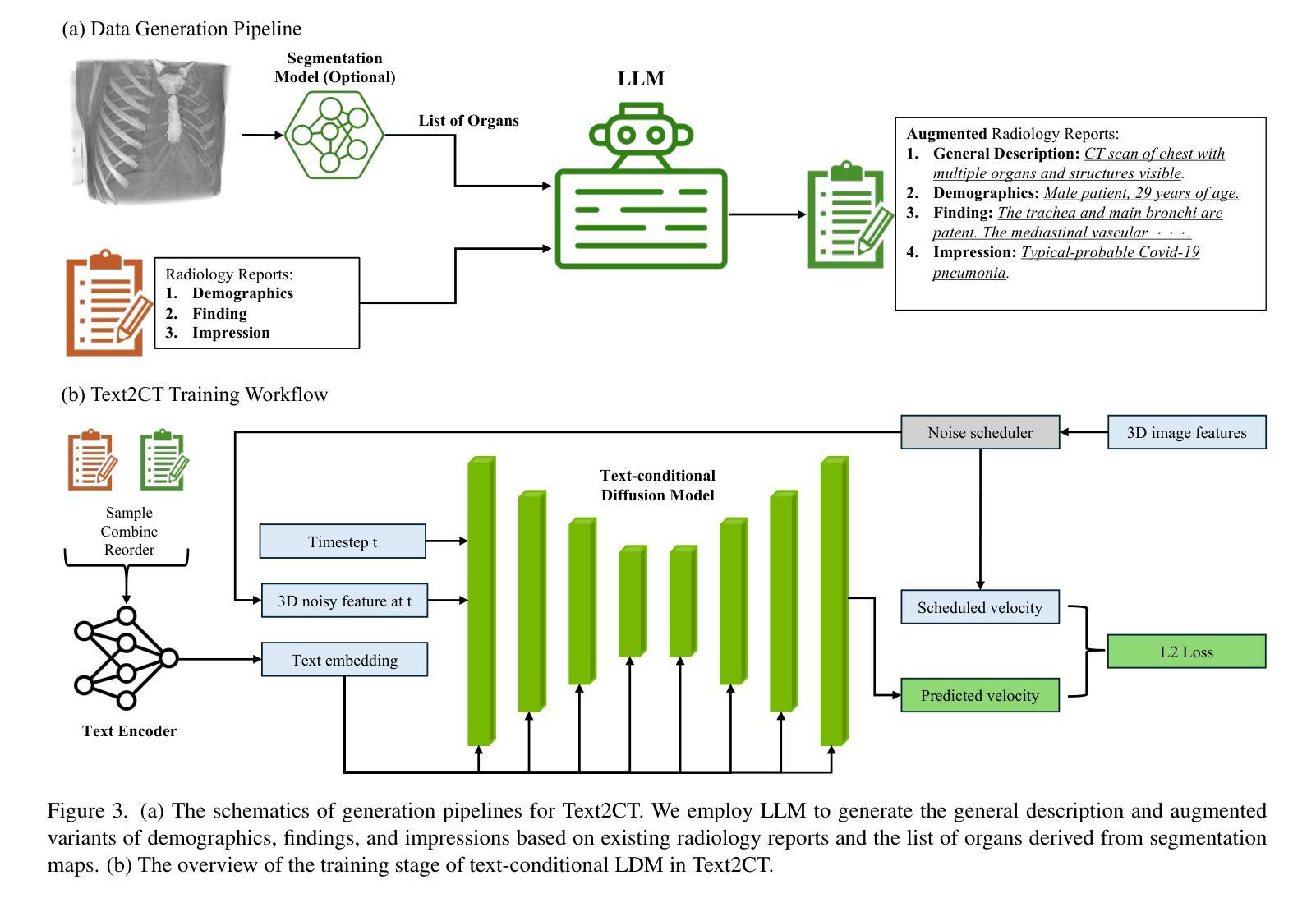
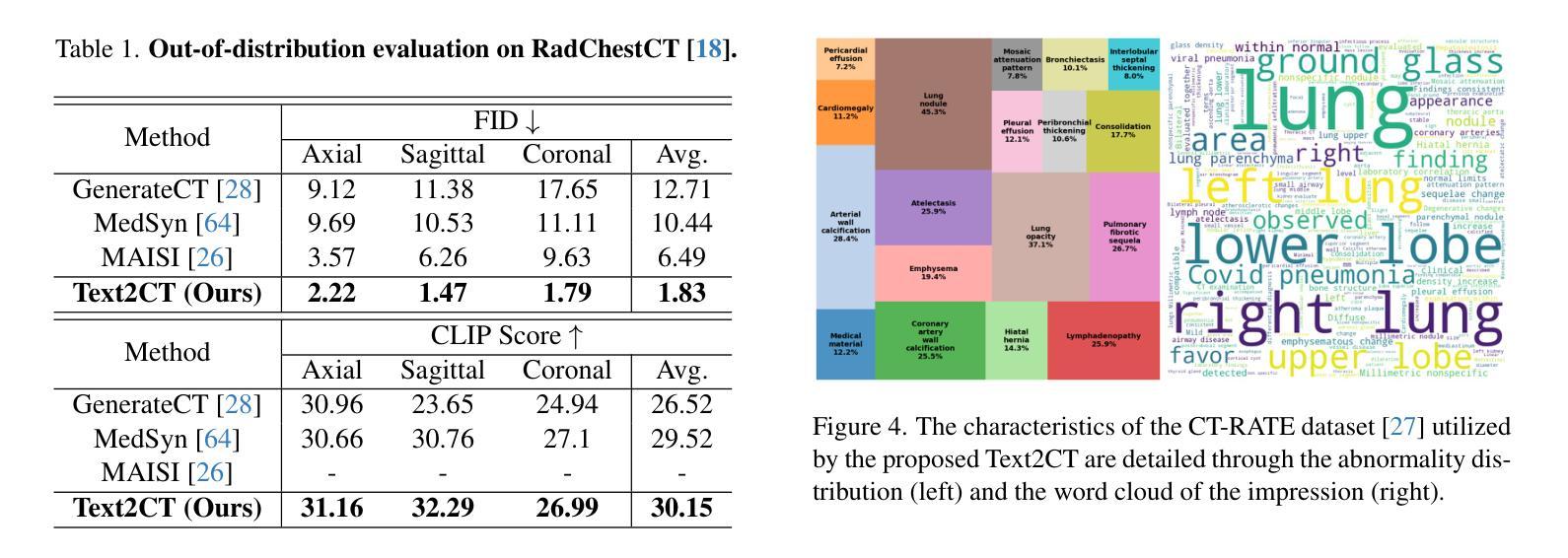
Text2CT: Towards 3D CT Volume Generation from Free-text Descriptions Using Diffusion Model
Authors:Pengfei Guo, Can Zhao, Dong Yang, Yufan He, Vishwesh Nath, Ziyue Xu, Pedro R. A. S. Bassi, Zongwei Zhou, Benjamin D. Simon, Stephanie Anne Harmon, Baris Turkbey, Daguang Xu
Generating 3D CT volumes from descriptive free-text inputs presents a transformative opportunity in diagnostics and research. In this paper, we introduce Text2CT, a novel approach for synthesizing 3D CT volumes from textual descriptions using the diffusion model. Unlike previous methods that rely on fixed-format text input, Text2CT employs a novel prompt formulation that enables generation from diverse, free-text descriptions. The proposed framework encodes medical text into latent representations and decodes them into high-resolution 3D CT scans, effectively bridging the gap between semantic text inputs and detailed volumetric representations in a unified 3D framework. Our method demonstrates superior performance in preserving anatomical fidelity and capturing intricate structures as described in the input text. Extensive evaluations show that our approach achieves state-of-the-art results, offering promising potential applications in diagnostics, and data augmentation.
从描述性自由文本输入生成3D CT体积在诊断和研究中提供了变革性的机会。在本文中,我们介绍了Text2CT,这是一种利用扩散模型从文本描述中合成3D CT体积的新方法。与之前依赖于固定格式文本输入的方法不同,Text2CT采用了一种新的提示制定方式,能够根据不同的自由文本描述进行生成。所提出的框架将医学文本编码为潜在表示,并将其解码为高分辨率的3D CT扫描,有效地在统一的3D框架中弥合了语义文本输入和详细体积表示之间的鸿沟。我们的方法在保持解剖保真度和捕捉输入文本中描述的复杂结构方面表现出卓越的性能。大量评估表明,我们的方法达到了最新水平的结果,在诊断和数据增强方面有着广阔的应用前景。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于扩散模型从文本描述中生成3D CT体积的新方法Text2CT。与传统的依赖于固定格式文本输入的方法不同,Text2CT采用了一种新颖的提示形式,支持从各种自由文本描述中进行生成。该方法将医学文本编码为潜在表示,然后解码为高质量的三维CT扫描图像,有效桥接了语义文本输入和详细体积表示之间的鸿沟。实验表明,该方法在保持解剖真实性和捕捉复杂结构方面表现出卓越性能,为诊断和医学数据增强领域带来了应用前景。
Key Takeaways
以下是文本中关键的见解摘要:
- Text2CT是一种将文本描述转化为3D CT体积的新型方法。它利用扩散模型,能在诊断和医学研究领域实现转化性进步。
- Text2CT不同于传统方法,支持多种自由文本描述作为输入,增强了生成的多样性和灵活性。
- 该方法通过将医学文本编码为潜在表示,再解码为高质量的三维CT扫描图像,有效融合了语义文本和体积表示。
- Text2CT在保持解剖真实性和捕捉复杂结构方面表现出卓越性能,能够有效生成细致的CT体积图像。
- 广泛评估显示,Text2CT的方法处于领先水平,这为诊断应用提供了潜力。
- 该方法可用于医学数据增强,有助于丰富医学图像数据集。
点此查看论文截图
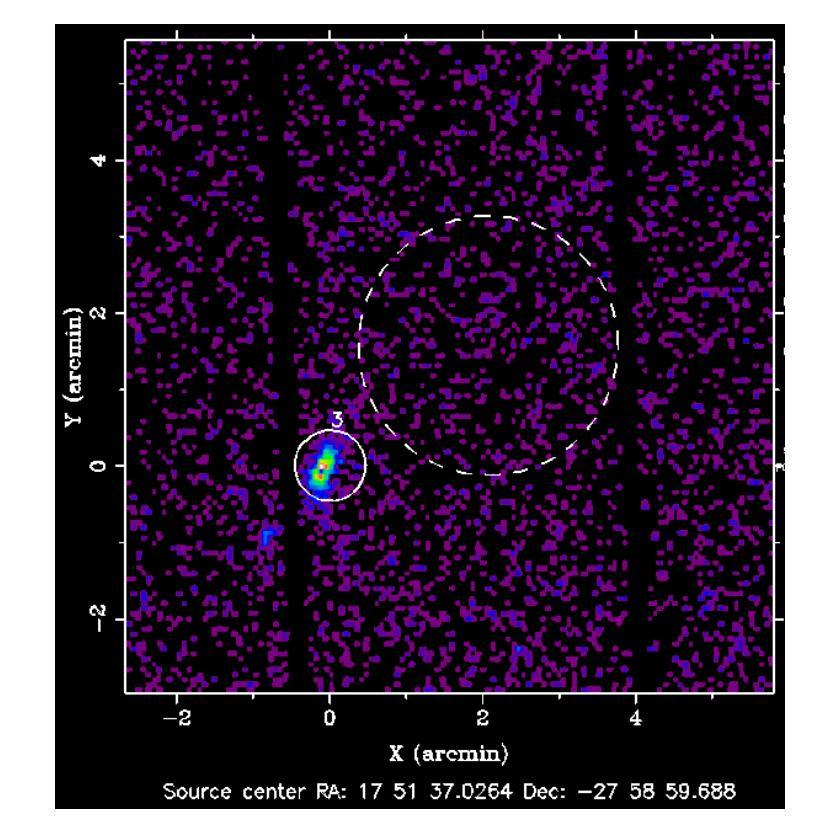
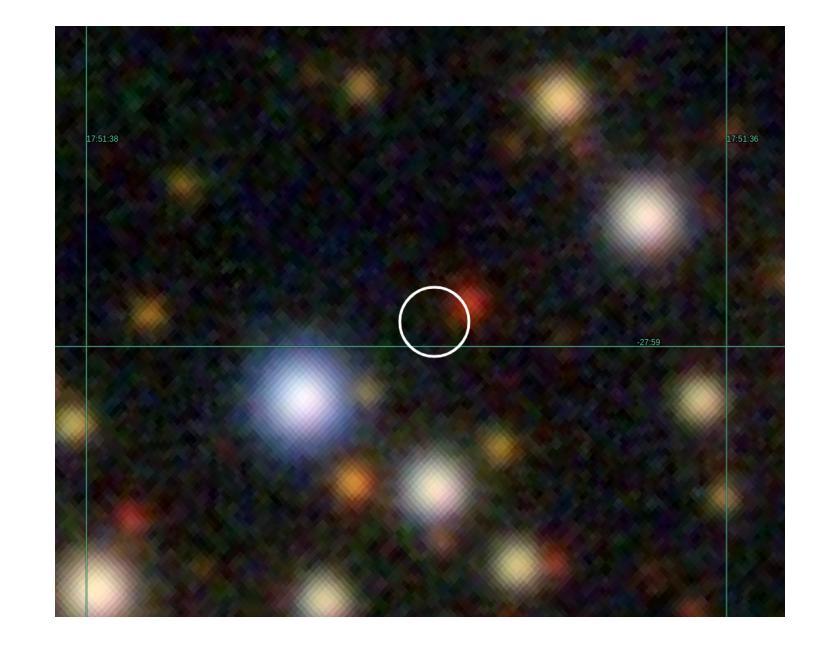
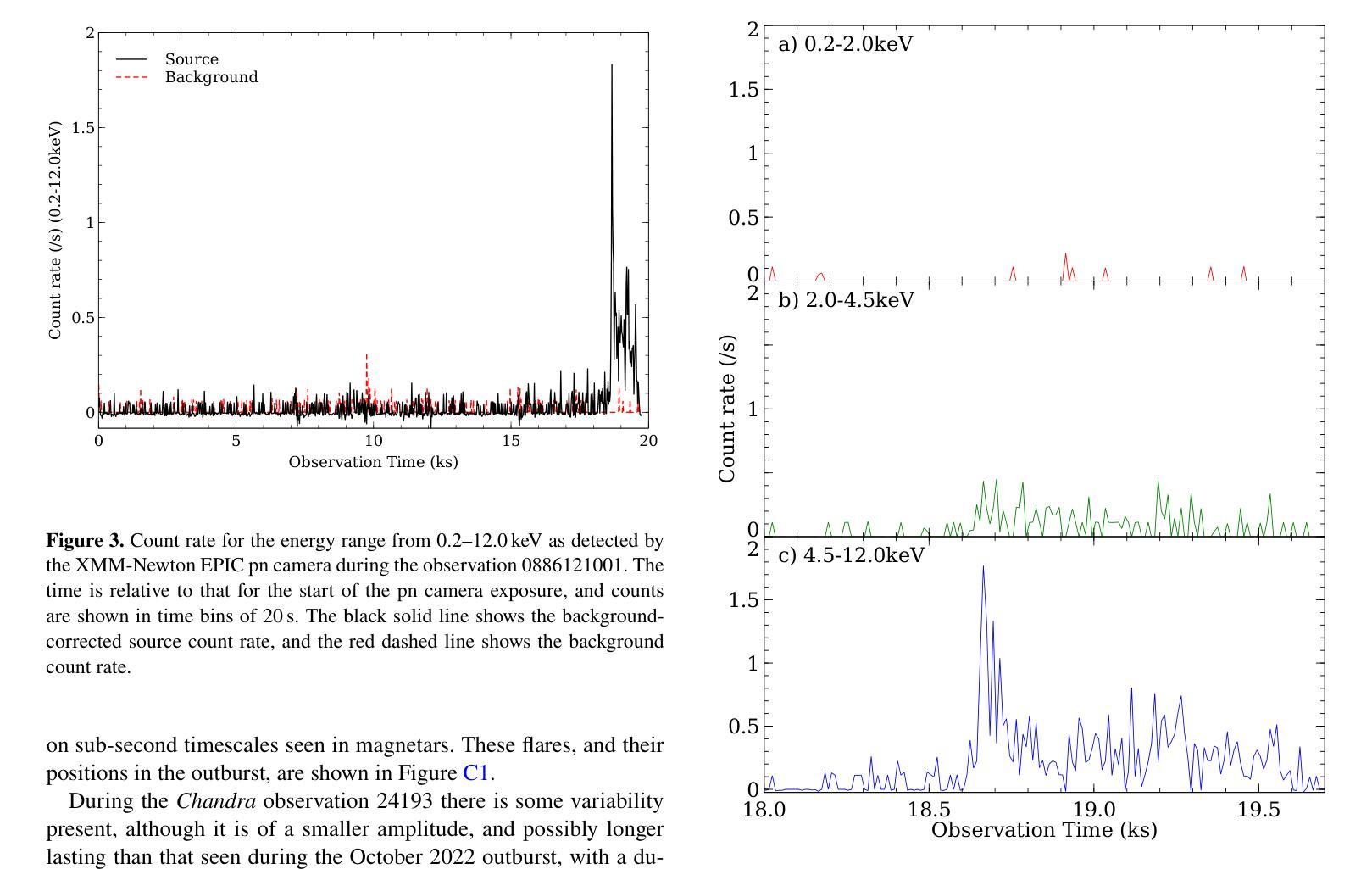
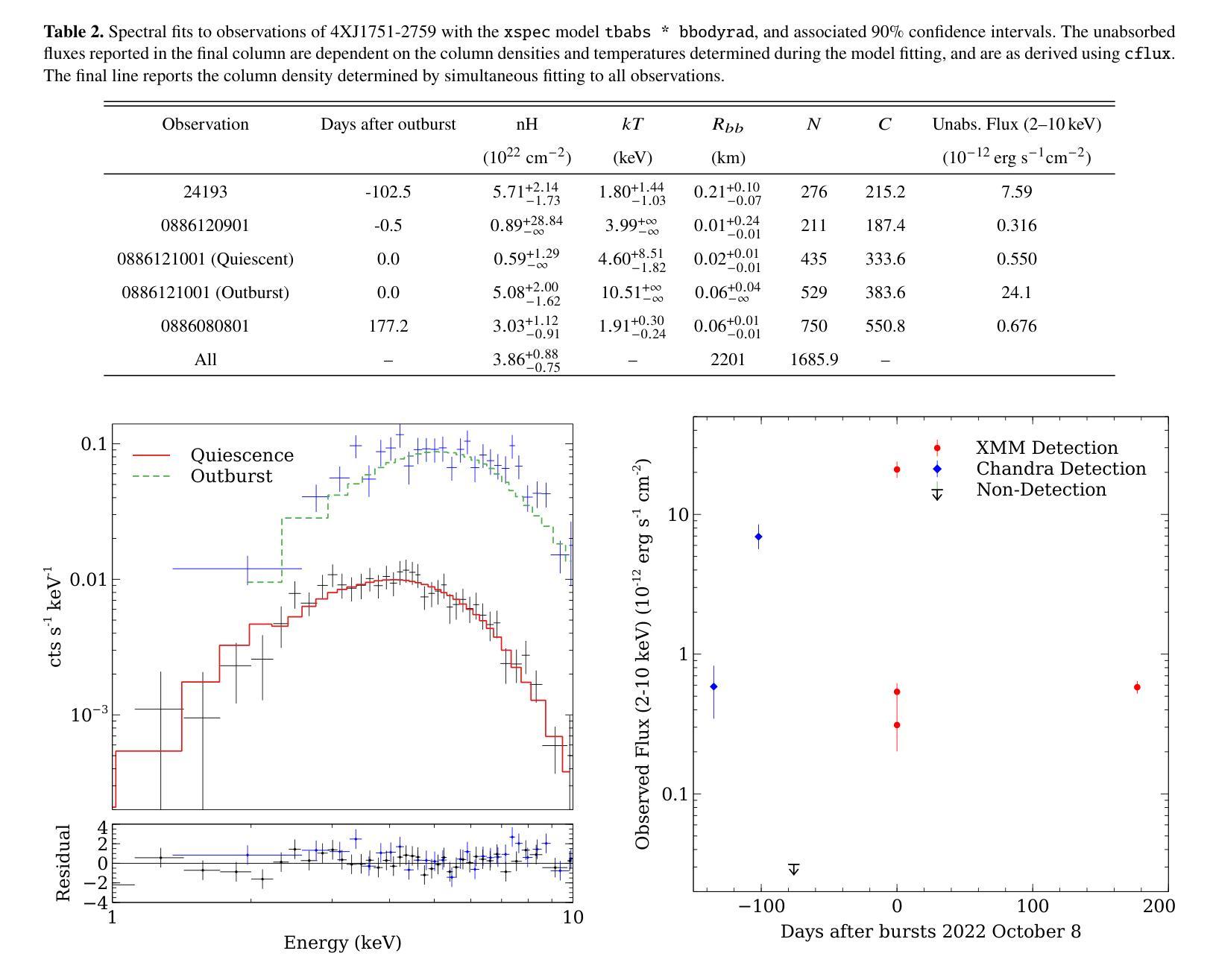
4XMM J175136.8-275858: A New Magnetar Candidate?
Authors:Robbie Webbe, Norman Khan, N. A. Webb, E. Quintin
Magnetars are very rare astrophysical objects, with $\sim$31 known to date. They are best understood as highly magnetised neutron stars, but a greater number need to be found to constrain their role in stellar evolution pathways. We apply a novel approach for the detection of fast, transient X-ray sources, using a revised version of the EPIC XMM-Newton Outburst Detector (EXOD) with the aim of detecting and identifying new and rare variable compact objects. We detect a transient, variable source notable for its strong variability and hard spectrum. The emission from 4XMM J175136.8-275858 is well characterised by a blackbody, with temperatures between $\sim$1.8–5,keV during its lower luminosity phase. Its temperature is poorly constrained during its brightest phase, and we observe an increase in luminosity by two orders of magnitude over timescales of a few ks. This is driven by increased emission of X-rays at energies above 2,keV, with a luminosity decay potentially over weeks or months. Derived luminosities for 4XJ1751-2759 range up to $\sim10^{35} \text{,erg s}^{-1}$ at 8,kpc at the Galactic centre, but neutral hydrogen column densities are greater than predicted Galactic values possibly implying a greater distance to the source, still within our galaxy, further increasing its luminosity. A consideration of optical and IR information in combination with the X-ray observations allow us to exclude the possibility that 4XJ1751-2759 is a star, rotationally powered pulsar or supergiant fast X-ray transient. This rapid, hard, variability is closest to that of outbursts in magnetars than any other known class of X-ray transient.
磁星是非常罕见的天体物理对象,至今已知约31个。它们最好被理解为高度磁化的中子星,但需要发现更多的磁星来限制它们在恒星演化途径中的作用。我们采用一种新颖的方法来检测快速、短暂的X射线源,使用修订后的EPICXMM-Newton爆发检测器(EXOD)版本,旨在检测和识别新的和罕见的可变紧凑型天体。我们检测到一个短暂、可变的源,以其强可变性以及硬谱而显著。来自4XMM J175136.8-275858的发射可以被黑体很好地表征,在其较低光度阶段时,温度约为~ 1.8至~ 5,keV之间。在其最亮的阶段,温度约束较差,我们观察到在几千秒内亮度增加了两个数量级。这是由高于~ 2,keV的X射线发射的增加所驱动的,亮度衰减可能在数周或数月内持续。对于位于银河系中心距离8kpc的磁星来说,其派生光度高达$\sim 10^{35} \text{ erg s}^{-1}$,但中性氢柱密度大于预测的银河系值,可能暗示该源的发射源距离更远。不过仍旧位于银河系内。这一事实连同与光学和红外观测结果综合考虑排除了它是一颗普通恒星、旋转脉冲星或超级巨星快速X射线瞬变的可能性。这种快速而强烈的可变性最接近磁星爆发的特征,与其他已知的X射线瞬变类型相比最为相似。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 10 figures. Accepted to MNRAS
Summary
利用修订后的EPICXMM-Newton爆发检测器(EXOD)新方法检测到了一种短暂、可变的强变量硬谱源。该源(4XMM J175136.8-275858)在较低光度时期的温度约为1.8-5keV,亮度在两个数量级内上升,时间跨度为数千秒。其X射线发射在高于2keV的能量处增强,光度衰减可能持续数周或数月。结合光学和红外信息,排除了其为恒星、旋转驱动脉冲星或超级巨星快速X射线短暂事件的可能性,被认为是最接近磁星爆发的短暂硬变源。
Key Takeaways
- Magnetars是罕见的天文现象,目前已知约31个,被认为是高度磁化的中子星,需要更多的发现来限制它们在恒星演化过程中的作用。
- 使用修订后的EXOD方法检测到新的短暂可变的强变量硬谱源。
- 源(4XMM J175136.8-275858)在较低光度时期的温度范围约为1.8-5keV。
- 源的亮度在短时间内增加了两个数量级。
- 源的X射线发射在较高能量处增强,光度衰减可能长达数周或数月。
- 结合光学和红外信息排除了该源为恒星、旋转驱动脉冲星的可能性。
点此查看论文截图

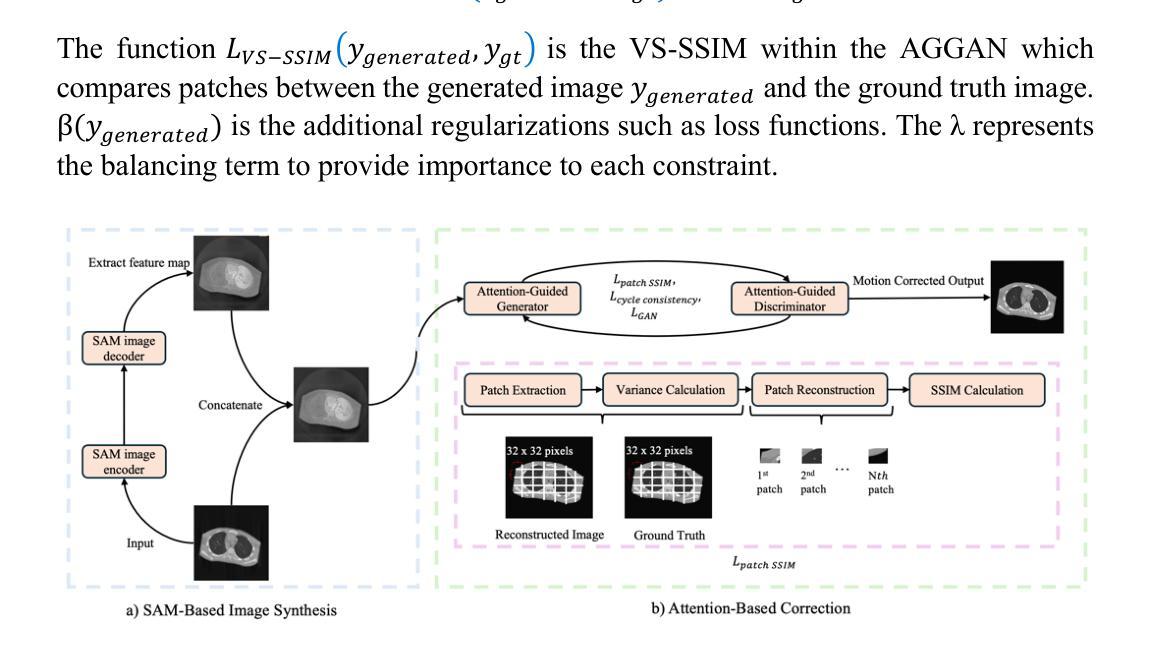
MAISY: Motion-Aware Image SYnthesis for MedicalImage Motion Correction
Authors:Andrew Zhang, Hao Wang, Shuchang Ye, Michael Fulham, Jinman Kim
Patient motion during medical image acquisition causes blurring, ghosting, and distorts organs, which makes image interpretation challenging.Current state-of-the-art algorithms using Generative Adversarial Network (GAN)-based methods with their ability to learn the mappings between corrupted images and their ground truth via Structural Similarity Index Measure (SSIM) loss effectively generate motion-free images. However, we identified the following limitations: (i) they mainly focus on global structural characteristics and therefore overlook localized features that often carry critical pathological information, and (ii) the SSIM loss function struggles to handle images with varying pixel intensities, luminance factors, and variance. In this study, we propose Motion-Aware Image SYnthesis (MAISY) which initially characterize motion and then uses it for correction by: (a) leveraging the foundation model Segment Anything Model (SAM), to dynamically learn spatial patterns along anatomical boundaries where motion artifacts are most pronounced and, (b) introducing the Variance-Selective SSIM (VS-SSIM) loss which adaptively emphasizes spatial regions with high pixel variance to preserve essential anatomical details during artifact correction. Experiments on chest and head CT datasets demonstrate that our model outperformed the state-of-the-art counterparts, with Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR) increasing by 40%, SSIM by 10%, and Dice by 16%.
患者在医学图像采集过程中的运动会导致图像模糊、鬼影和器官扭曲,这使得图像解读具有挑战性。当前最先进的算法使用基于生成对抗网络(GAN)的方法,通过学习被污染图像与真实图像之间的映射关系,通过结构相似性指数度量(SSIM)损失有效地生成无运动图像。然而,我们发现存在以下局限性:(i)它们主要关注全局结构特征,从而忽略了通常携带关键病理信息的局部特征;(ii)SSIM损失函数在处理像素强度、亮度因素和方差各异的图像时遇到困难。本研究提出了运动感知图像合成(MAISY),它首先表征运动,然后利用运动进行修正:(a)通过利用基础模型分割任何模型(SAM),动态学习解剖边界处的空间模式,这些边界处的运动伪影最为突出;(b)引入方差选择性SSIM(VS-SSIM)损失,在伪影修正过程中自适应地强调高像素方差的空间区域,以保留关键的解剖细节。在胸部和头部CT数据集上的实验表明,我们的模型超过了最先进的同行模型,峰值信噪比(PSNR)提高了40%,SSIM提高了10%,Dice系数提高了16%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了医学图像获取过程中患者运动导致的图像模糊、鬼影和器官扭曲问题,使得图像解读变得困难。现有算法主要关注全局结构特征,忽略了携带关键病理信息的局部特征,且SSIM损失函数在处理像素强度、亮度因素和方差变化的图像时存在困难。本研究提出了Motion-Aware Image SYnthesis(MAISY),首先进行运动特征表征,然后利用运动特征进行校正。通过利用Segment Anything Model(SAM)基础模型动态学习解剖边界的空间模式,并引入Variance-Selective SSIM(VS-SSIM)损失,以在保留重要解剖细节的同时自适应地强调高像素方差的空间区域。实验表明,该模型在胸部和头部CT数据集上的表现优于现有技术,PSNR提高40%,SSIM提高10%,Dice提高16%。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像获取过程中的患者运动会导致图像模糊、鬼影和器官扭曲,使得图像解读困难。
- 当前最先进的算法使用GAN和SSIM损失来生成无运动图像,但存在局限性:主要关注全局结构特征,忽略局部特征;SSIM损失函数在处理像素强度、亮度和方差变化的图像时表现不佳。
- 本研究提出了Motion-Aware Image SYnthesis(MAISY)模型,该模型首先进行运动特征表征并利用这些特征进行图像校正。
- MAISY模型利用Segment Anything Model(SAM)学习解剖边界的空间模式,并强调高像素方差区域以保留重要解剖细节。
- 实验结果表明,MAISY模型在胸部和头部CT数据集上的表现优于现有技术。
- MAISY模型提高了图像质量指标,如PSNR提高40%,SSIM提高10%,Dice提高16%。
点此查看论文截图

Device-Free Localization Using Multi-Link MIMO Channels in Distributed Antenna Networks
Authors:Minseok Kim, Gesi Teng, Keita Nishi, Togo Ikegami, Masamune Sato
This paper presented a novel device-free localization (DFL) framework based on distributed antenna networks (DANs), targeting integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) in future 6G radio access networks (RANs). In the proposed approach, radio tomographic imaging (RTI) leverages the spatial and temporal diversity of multi-link multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) channels in DANs to improve localization accuracy. Furthermore, a prototype system was developed using software-defined radios (SDRs) operating in the sub-6 GHz band, and comprehensive evaluations were conducted under indoor conditions involving varying node densities and target types. The results demonstrate that the framework achieves sub-meter localization accuracy in most scenarios and maintains robust performance under complex multipath environments. In addition, the use of Bayesian optimization to fine-tune key parameters, such as sparsity and path thickness, led to significant improvements in image reconstruction quality and target estimation accuracy. These results demonstrate the feasibility and effectiveness of DAN-based DFL systems for accurate, robust, and scalable localization.
本文提出了一种基于分布式天线网络(DANs)的新型无设备定位(DFL)框架,旨在用于未来6G无线接入网络(RANs)的综合感知和通信(ISAC)。在该方法中,通过利用分布天线网络的多个链接的多输入多输出(MIMO)通道的时空多样性,放射层析成像(RTI)提高了定位精度。此外,开发了一个采用工作在低于6 GHz频段的软件定义无线电(SDRs)的原型系统,并在涉及不同节点密度和目标类型的室内条件下进行了全面的评估。结果表明,该框架在大多数场景中实现了亚米级定位精度,并在复杂的多径环境中保持了稳健的性能。此外,使用贝叶斯优化对关键参数(如稀疏性和路径厚度)进行微调,显著提高了图像重建质量和目标估计精度。这些结果证明了基于DAN的DFL系统在实现准确、稳健和可扩展的定位方面的可行性和有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于分布式天线网络(DANs)的无设备定位(DFL)框架,适用于未来6G无线电接入网络(RANs)中的集成感知和通信(ISAC)。该框架利用无线电层析成像(RTI)技术,通过利用DANs中多链路多输入多输出(MIMO)通道的空间和时间多样性来提高定位精度。开发了一个采用软件定义无线电(SDRs)在低于6GHz频段运行的原型系统,并在室内条件下进行了全面的评估,包括不同的节点密度和目标类型。结果表明,该框架在大多数场景下实现了亚米级定位精度,并在复杂的多路径环境下保持了稳健的性能。此外,使用贝叶斯优化对稀疏性和路径厚度等关键参数进行微调,显著提高了图像重建质量和目标估计精度。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文介绍了一种新型的基于分布式天线网络(DANs)的无设备定位(DFL)框架,旨在用于未来6G网络的集成感知和通信。
- 通过无线电层析成像(RTI)技术,利用MIMO通道的空间和时间多样性提高定位精度。
- 开发了采用软件定义无线电(SDRs)的原型系统,并在低于6GHz的频段进行试验。
- 在室内环境下进行了全面的评估,测试环境涵盖不同的节点密度和目标类型。
- 该框架实现了亚米级定位精度,且在复杂多路径环境中表现稳健。
- 使用贝叶斯优化对关键参数进行微调,显著提升了图像重建质量和目标估计的准确性。
- 整体结果表明,基于DAN的DFL系统为实现准确、稳健和可扩展的定位是可行的和有效的。
点此查看论文截图

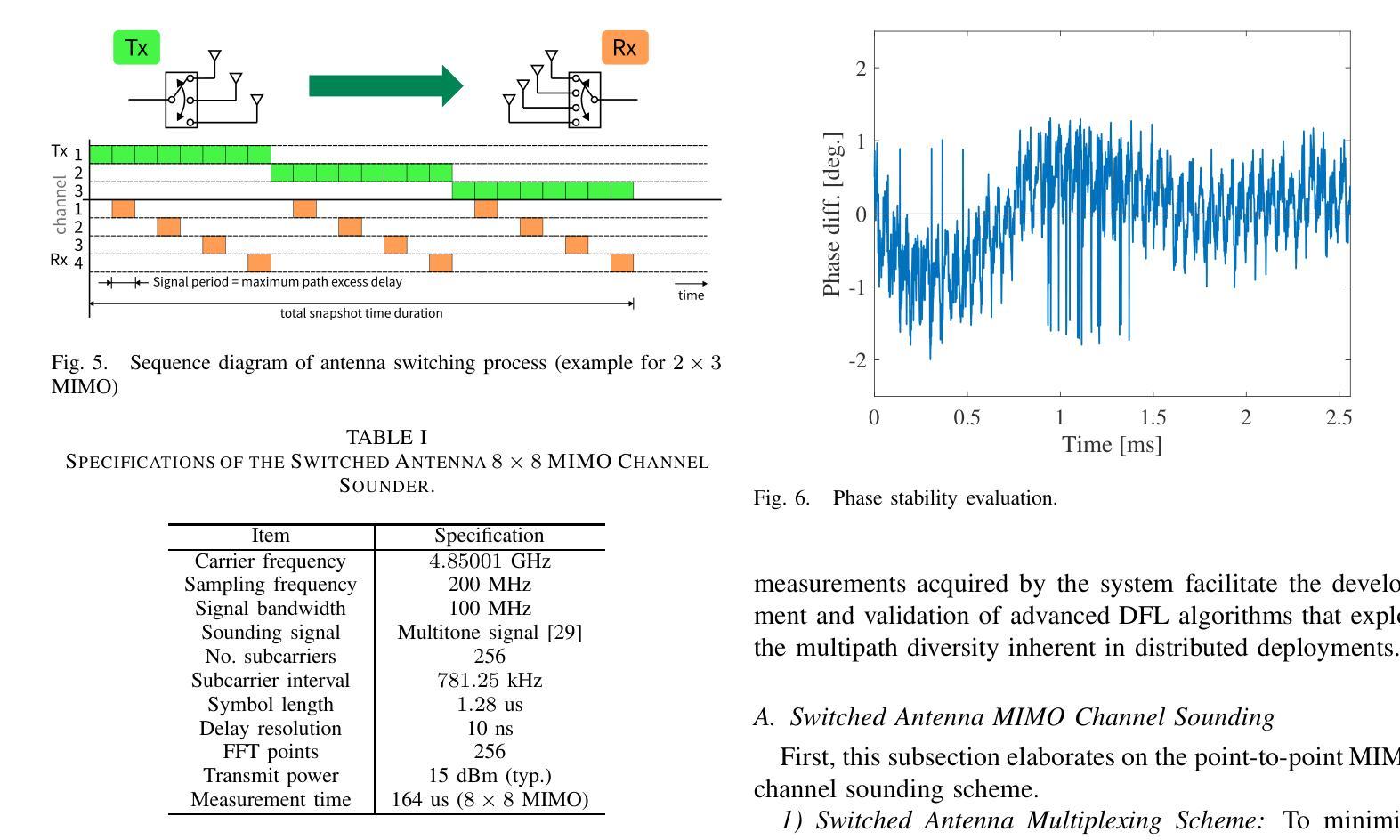
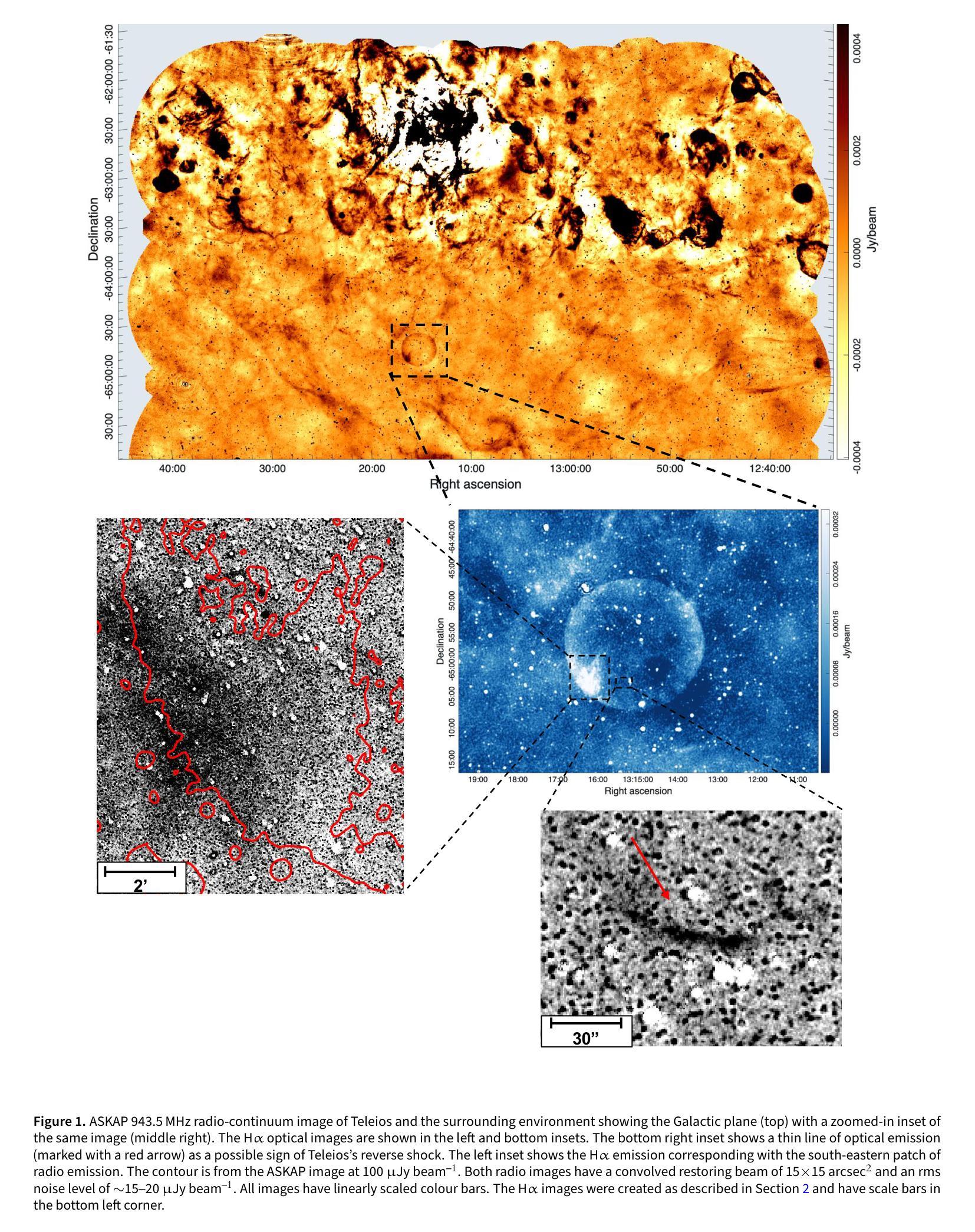
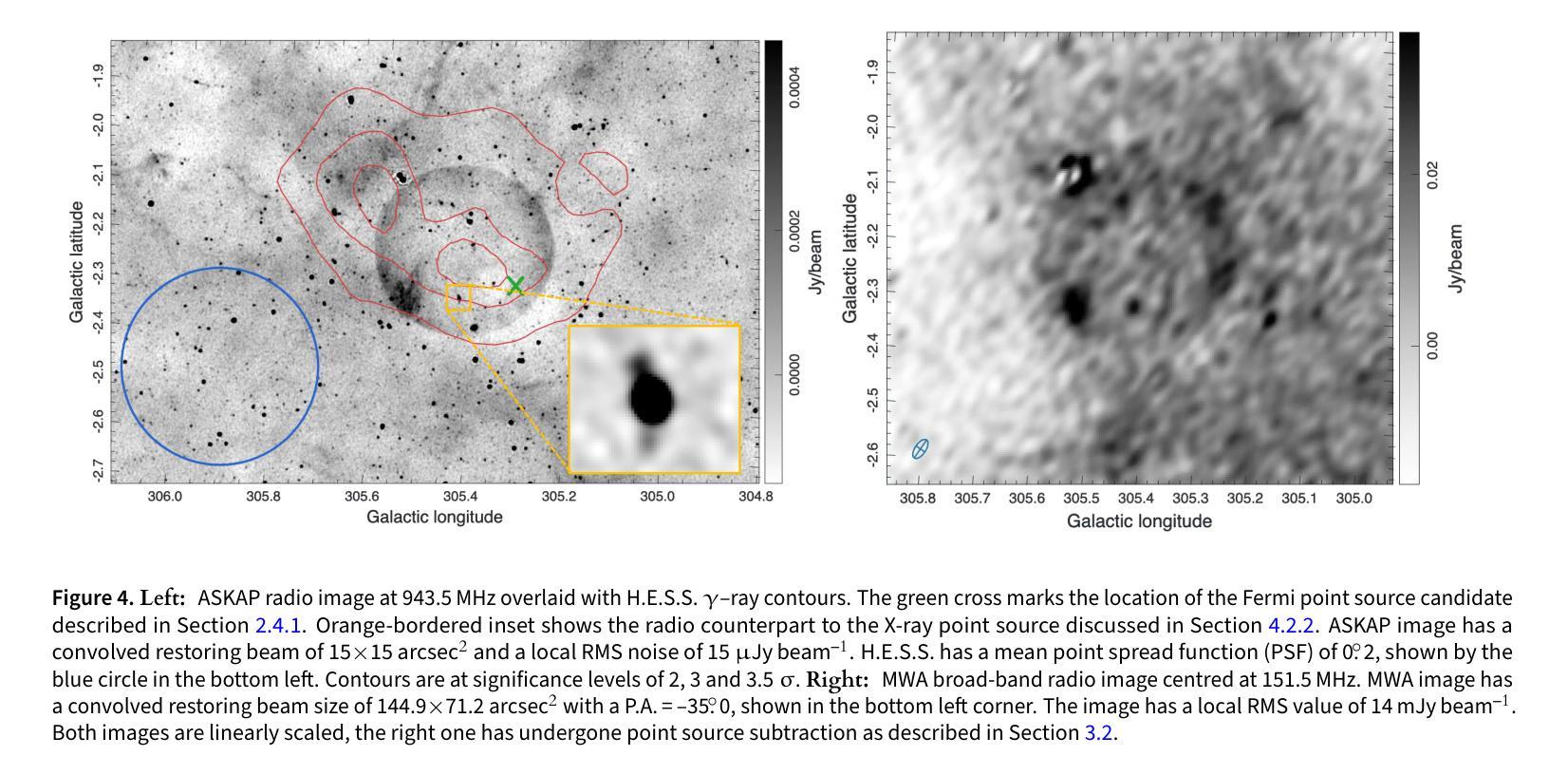
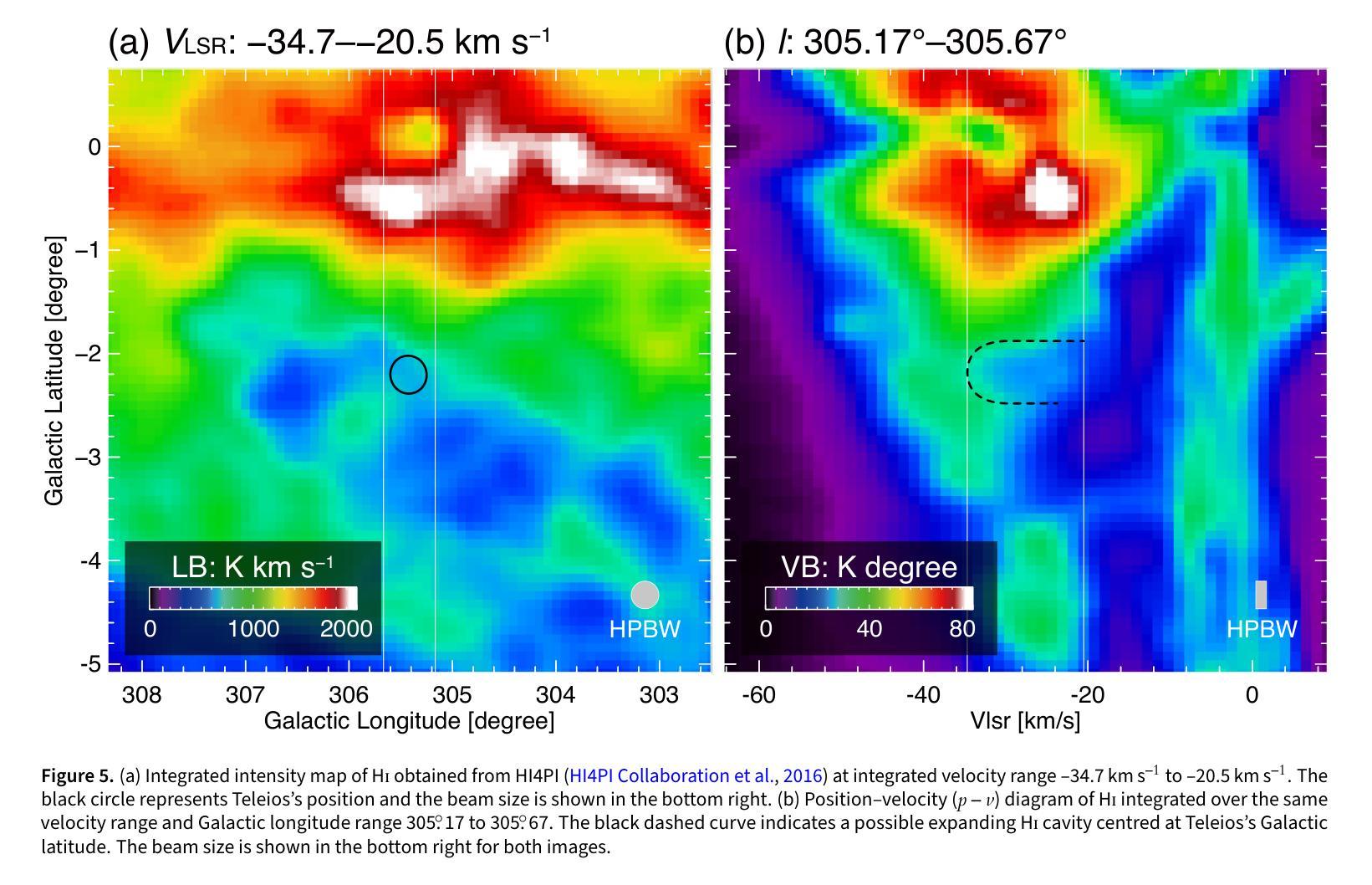
Teleios (G305.4-2.2) – the mystery of a perfectly shaped new Galactic supernova remnant
Authors:Miroslav D. Filipovic, Zachary J. Smeaton, Roland Kothes, Silvia Mantovanini, Petar Kostic, Denis Leahy, Adeel Ahmad, Gemma E. Anderson, Miguel Araya, Brianna Ball, Werner Becker, Cristobal Bordiu, Aaron C. Bradley, Robert Brose, Christopher Burger-Scheidlin, Shi Dai, Stefan Duchesne, Timothy J. Galvin, Andrew M. Hopkins, Natasha Hurley-Walker, Barbel S. Koribalski, Sanja Lazarevic, Peter Lundqvist, Jonathan Mackey, Pierrick Martin, Padric McGee, Ana Mitrasinovic, Jeffrey L. Payne, Simone Riggi, Kathryn Ross, Gavin Rowell, Lawrence Rudnick, Hidetoshi Sano, Manami Sasaki, Roberto Soria, Dejan Urosevic, Branislav Vukotic, Jennifer L. West
We present the serendipitous radio-continuum discovery of a likely Galactic supernova remnant (SNR) G305.4-2.2. This object displays a remarkable circular symmetry in shape, making it one of the most circular Galactic SNRs known. Nicknamed Teleios due to its symmetry, it was detected in the new Australian Square Kilometre Array Pathfinder (ASKAP) Evolutionary Map of the Universe (EMU) radio-continuum images with an angular size of 1320”x1260” and PA = 0 deg. While there is a hint of possible H$\alpha$ and gamma-ray emission, Teleios is exclusively seen at radio-continuum frequencies. Interestingly, Teleios is not only almost perfectly symmetric, but it also has one of the lowest surface brightnesses discovered among Galactic SNRs and a steep spectral index of $\alpha=-0.6\pm 0.3$. Our estimates from HI studies and the Sigma-D relation place Teleios as a type Ia SNR at a distance of either ~2.2 kpc of ~7.7 kpc. This indicates two possible scenarios, either a young (under 1000 yr) or an older SNR (over 10000 yr). With a corresponding diameter of 14/48 pc, our evolutionary studies place Teleios at the either early or late Sedov phase, depending on the distance estimate. However, our modelling also predicts X-ray emission, which we do not see in the present generation of eROSITA images. We also explored a type Iax explosion scenario that points to a much closer distance of <1 kpc and Teleios size of only ~3.3 pc, which would be similar to the only known type Iax remnant SN1181. Unfortunately, all examined scenarios have their challenges, and no definitive supernova (SN) origin type can be established at this stage. Teleios’s symmetrical shape suggests expansion into a rarefied and isotropic ambient medium. The low radio surface brightness and the lack of pronounced polarisation can be explained by a high level of ambient rotation measure (RM), with the largest RM being observed at centre.
我们意外发现了银河系超新星遗迹(SNR)G305.4-2.2的无线电连续谱发现。该对象呈现出显著的圆形对称性,使其成为已知最圆的银河系SNR之一。由于其对称性,它被命名为Teleios。它是在新的澳大利亚平方公里阵列探路者(ASKAP)宇宙演化图(EMU)无线电连续谱图像中检测到的,其角大小为1320”x1260”,位置角为0度。虽然有Hα和γ射线的可能发射提示,但Teleios仅在无线电连续谱频率下可见。有趣的是,Teleios不仅几乎完全对称,而且它还具有银河系SNR中发现的最低的表面亮度之一,以及α=-0.6±0.3的陡峭光谱指数。我们通过HI研究和Sigma-D关系估计,Teleios是Ia型SNR,距离约为2.2kpc或7.7kpc。这表明了两种可能的情况,一是年轻的(不到1000岁)SNR,二是较老的SNR(超过10000岁)。相应的直径为14/48秒差距,我们的进化研究将Teleios置于早期的塞多夫阶段或晚期塞多夫阶段,这取决于距离估计。然而,我们的模型还预测了X射线发射,这在当前的eROSITA图像中并未观察到。我们还探索了Iax型爆炸情景,这指向了小于1kpc的较近距离和Teleios只有约3.3秒差距的大小,这类似于已知的唯一Iax型遗迹SN1181。不幸的是,所有考察的情况都有其挑战,目前阶段无法确定超新星(SN)的起源类型。Teleios的对称形状表明其膨胀到一个稀疏的同位素环境中。低无线电表面亮度和缺乏明显的极化可以用高环境旋转度量(RM)来解释,最大的RM被观察到在中心。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Has been accepted for publication in PASA
Summary
发现一个新的可能银河系超新星遗迹G305.4-2.2,呈现显著圆形对称性,命名为Teleios。通过ASKAP和EMU的射电连续图像检测,初步判断为年轻的或年老的超新星遗迹,距离约为2.2kpc或7.7kpc。早期或晚期Sedov阶段模型预测有X射线发射,但在现有eROSITA图像中未见。同时探索了可能的Ia型或Iax型超新星爆炸情景,但仍无法确定其起源类型。周围介质被认为具有高的旋转度量(RM)。
Key Takeaways
- 发现新的银河系超新星遗迹G305.4-2.2(Teleios),具有显著的圆形对称性。
- Teleios在射电连续谱上被发现,且具有非常低的表面亮度和陡峭的谱指数α=-0.6±0.3。
- 基于HI研究和Sigma-D关系,推测Teleios的距离可能为约2.2kpc或约7.7kpc,分别对应年轻或年老的超新星遗迹。
- Teleios可能处于早期或晚期Sedov阶段,具体取决于距离估计。
- 预测存在X射线发射,但在现有的eROSITA图像中未见。
- 对可能的Ia型或Iax型超新星爆炸情景进行了探索,但无法确定其确切的SN起源类型。
点此查看论文截图

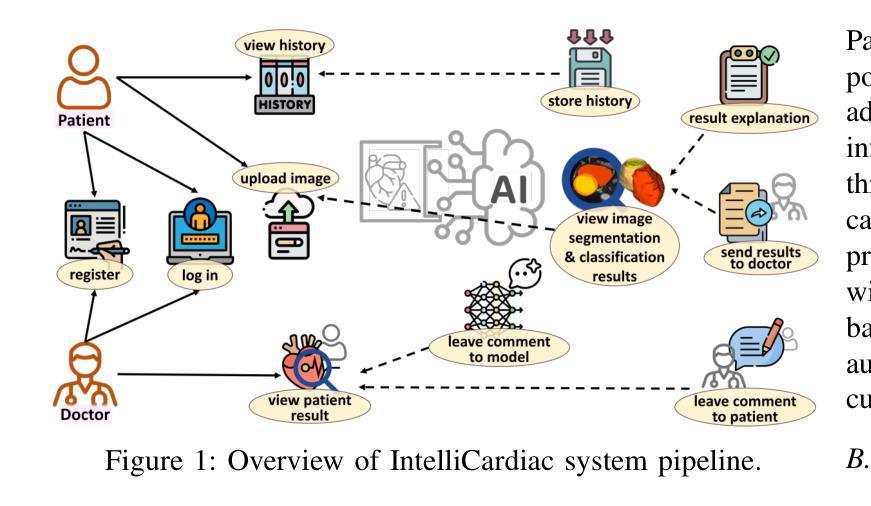
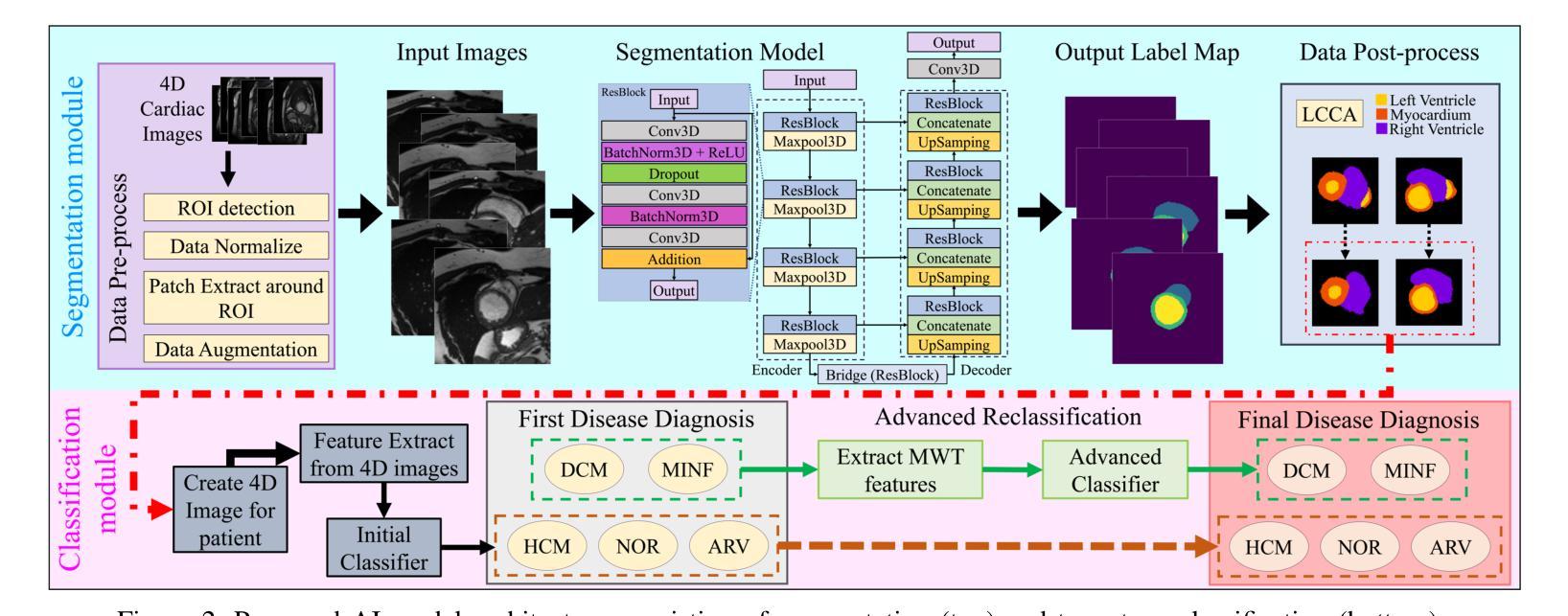
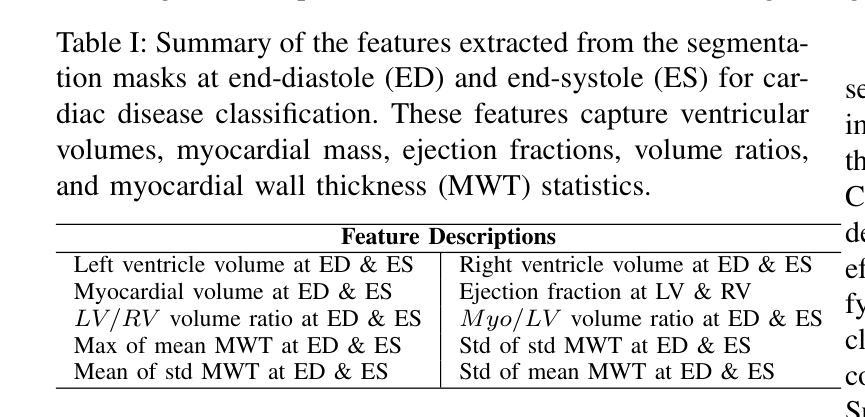
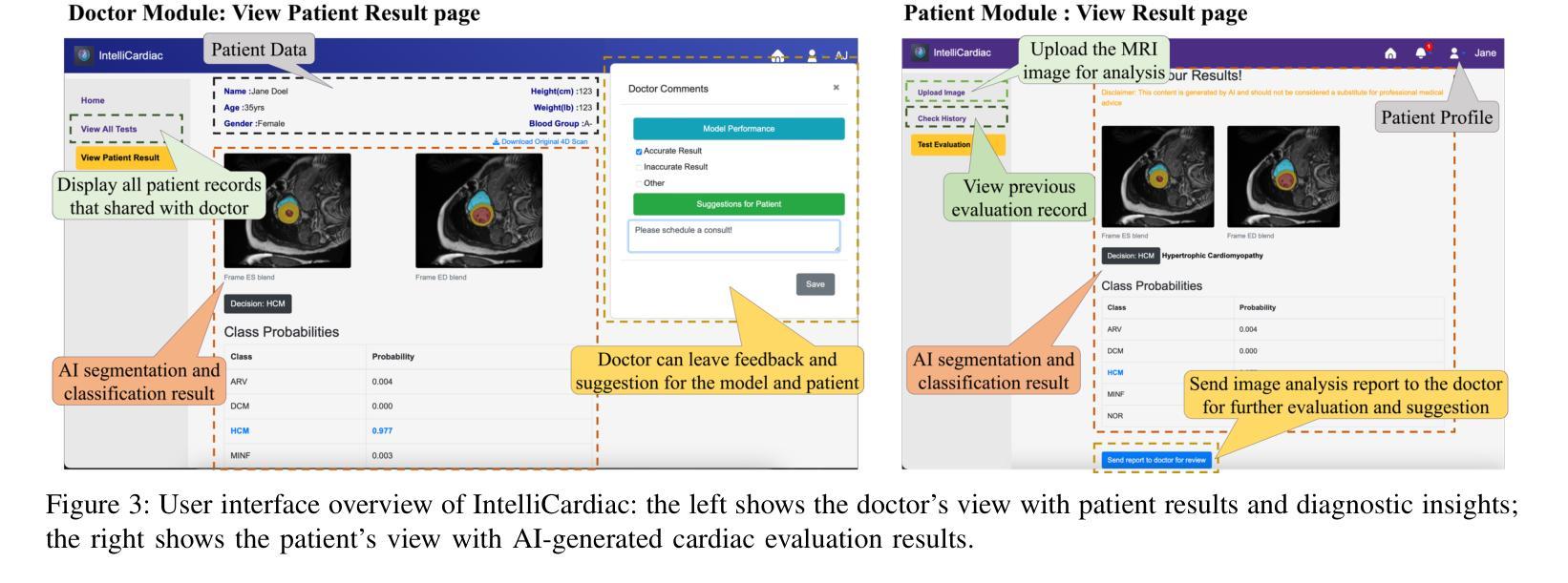
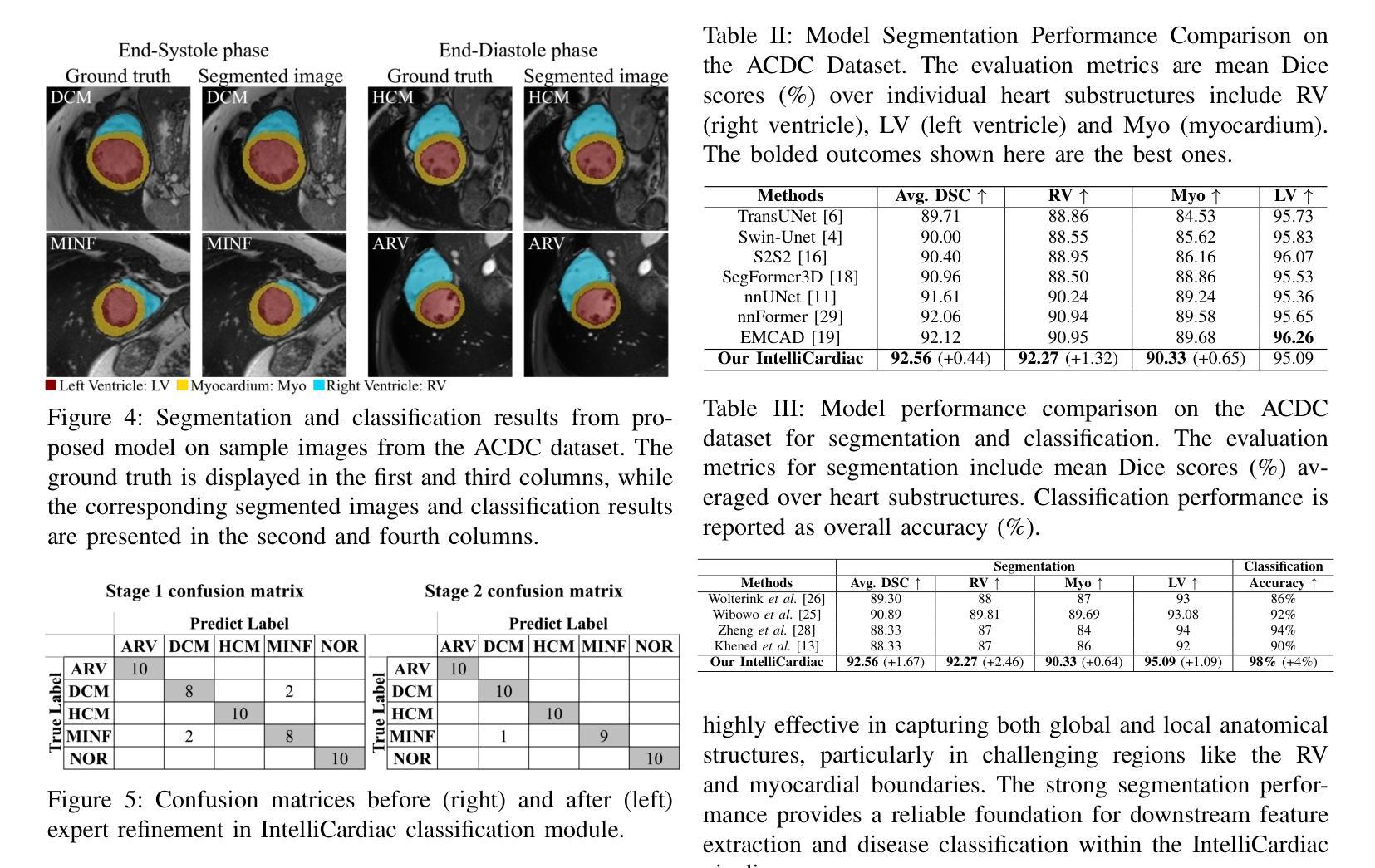
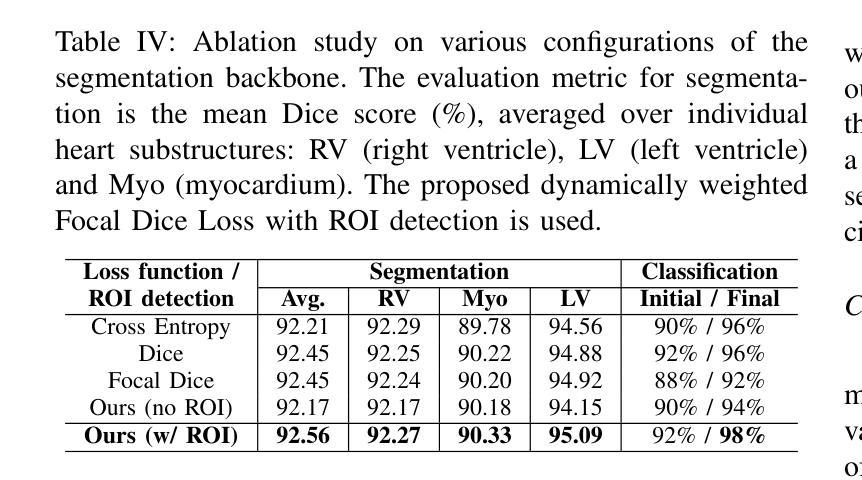
IntelliCardiac: An Intelligent Platform for Cardiac Image Segmentation and Classification
Authors:Ting Yu Tsai, An Yu, Meghana Spurthi Maadugundu, Ishrat Jahan Mohima, Umme Habiba Barsha, Mei-Hwa F. Chen, Balakrishnan Prabhakaran, Ming-Ching Chang
Precise and effective processing of cardiac imaging data is critical for the identification and management of the cardiovascular diseases. We introduce IntelliCardiac, a comprehensive, web-based medical image processing platform for the automatic segmentation of 4D cardiac images and disease classification, utilizing an AI model trained on the publicly accessible ACDC dataset. The system, intended for patients, cardiologists, and healthcare professionals, offers an intuitive interface and uses deep learning models to identify essential heart structures and categorize cardiac diseases. The system supports analysis of both the right and left ventricles as well as myocardium, and then classifies patient’s cardiac images into five diagnostic categories: dilated cardiomyopathy, myocardial infarction, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, right ventricular abnormality, and no disease. IntelliCardiac combines a deep learning-based segmentation model with a two-step classification pipeline. The segmentation module gains an overall accuracy of 92.6%. The classification module, trained on characteristics taken from segmented heart structures, achieves 98% accuracy in five categories. These results exceed the performance of the existing state-of-the-art methods that integrate both segmentation and classification models. IntelliCardiac, which supports real-time visualization, workflow integration, and AI-assisted diagnostics, has great potential as a scalable, accurate tool for clinical decision assistance in cardiac imaging and diagnosis.
精确且有效地处理心脏成像数据对于心血管疾病的识别和管理至关重要。我们推出IntelliCardiac,这是一款全面的基于网页的医学图像处理平台,用于自动分割4D心脏图像和疾病分类。它利用在公共可访问的ACDC数据集上训练的AI模型。此系统面向患者、心脏病专家以及医疗专业人士,提供直观界面,并使用深度学习模型来识别心脏的关键结构并对心脏疾病进行分类。系统支持对右心室和左心室以及心肌的分析,然后将患者的心脏图像分类为五种诊断类别:扩张型心肌病、心肌梗死、肥厚型心肌病、右心室异常以及无疾病。IntelliCardiac结合了基于深度学习的分割模型与两步分类流程。分割模块的整体准确率为92.6%。分类模块基于分割心脏结构的特征进行训练,在五个类别中达到98%的准确率。这些结果超过了现有最先进的集成分割和分类模型的方法的表现。IntelliCardiac支持实时可视化、工作流程集成和人工智能辅助诊断,作为心脏成像和诊断的临床决策辅助工具,具有可扩展性和准确性,具有巨大的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了IntelliCardiac这一基于网络的医学图像处理平台,用于自动分割四维心脏图像和疾病分类。它利用在公开可访问的ACDC数据集上训练的AI模型,提供对患者、心脏病专家和医疗保健专业人员的直观界面,并使用深度学习模型识别心脏结构并进行分类。该平台支持左右心室和心肌的分析,并将患者的心脏图像分为五个诊断类别。IntelliCardiac结合了深度学习分割模型和两步分类管道,其性能优于现有的最先进的集成分割和分类模型的方法。它具有良好的可扩展性和准确性,可作为心脏成像和诊断的临床决策辅助工具。
Key Takeaways
- IntelliCardiac是一个用于自动分割四维心脏图像和疾病分类的医学图像处理平台。
- 平台使用深度学习模型进行心脏结构识别和疾病分类。
- 支持左右心室和心肌的分析,分为五个诊断类别。
- IntelliCardiac结合了深度学习分割模型和两步分类管道。
- 分割模型的准确度为92.6%,分类模型的准确度为98%。
- 与现有的集成分割和分类模型的方法相比,IntelliCardiac的性能更为优越。
点此查看论文截图

mAIstro: an open-source multi-agentic system for automated end-to-end development of radiomics and deep learning models for medical imaging
Authors:Eleftherios Tzanis, Michail E. Klontzas
Agentic systems built on large language models (LLMs) offer promising capabilities for automating complex workflows in healthcare AI. We introduce mAIstro, an open-source, autonomous multi-agentic framework for end-to-end development and deployment of medical AI models. The system orchestrates exploratory data analysis, radiomic feature extraction, image segmentation, classification, and regression through a natural language interface, requiring no coding from the user. Built on a modular architecture, mAIstro supports both open- and closed-source LLMs, and was evaluated using a large and diverse set of prompts across 16 open-source datasets, covering a wide range of imaging modalities, anatomical regions, and data types. The agents successfully executed all tasks, producing interpretable outputs and validated models. This work presents the first agentic framework capable of unifying data analysis, AI model development, and inference across varied healthcare applications, offering a reproducible and extensible foundation for clinical and research AI integration. The code is available at: https://github.com/eltzanis/mAIstro
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的Agentic系统为医疗保健AI中复杂工作流的自动化提供了有前途的能力。我们介绍了mAIstro,这是一个开源的、自主的多Agentic框架,用于端到端的医疗AI模型开发和部署。该系统通过自然语言接口协调探索性数据分析、放射学特征提取、图像分割、分类和回归,无需用户编写代码。mAIstro采用模块化架构,支持开源和闭源的LLM,并使用涵盖广泛成像模式、解剖部位和数据类型的16个开源数据集的大型和多样化的提示集进行评估。代理成功执行了所有任务,产生了可解释的输出和经过验证的模型。这项工作提出了第一个能够在各种医疗保健应用中统一数据分析、AI模型开发和推理的Agentic框架,为临床和研究AI集成提供了可复制和可扩展的基础。代码可在https://github.com/eltzanis/mAIstro找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的Agentic系统为医疗保健AI自动化复杂工作流程提供了有前景的能力。本文介绍了mAIstro,一个开源的、自主的多Agentic框架,用于端到端医疗AI模型的开发和部署。该系统通过自然语言接口协调探索性分析、放射特征提取、图像分割、分类和回归,无需用户编程。在跨多个开源数据集、涵盖多种成像模式、解剖部位和数据类型的广泛评估中,agents成功执行了所有任务,产生了可解释的输出和经过验证的模型。这项工作是第一个能够在各种医疗保健应用中统一数据分析、AI模型开发和推理的Agentic框架,为临床和研究AI的融合提供了可复制和可扩展的基础。
Key Takeaways
- Agentic系统基于大型语言模型(LLM),为医疗保健AI自动化提供前景。
- mAIstro是一个开源的、自主的多Agentic框架,支持医疗AI模型端到端的开发和部署。
- mAIstro通过自然语言接口进行探索性分析、放射特征提取、图像分割等任务。
- 系统无需用户编程,可协调多种任务。
- mAIstro支持开源和闭源的LLM。
- Agents在广泛的数据集上成功执行任务,产生可解释的输出和经过验证的模型。
- mAIstro为临床和研究AI的融合提供了可复制和可扩展的基础。
点此查看论文截图

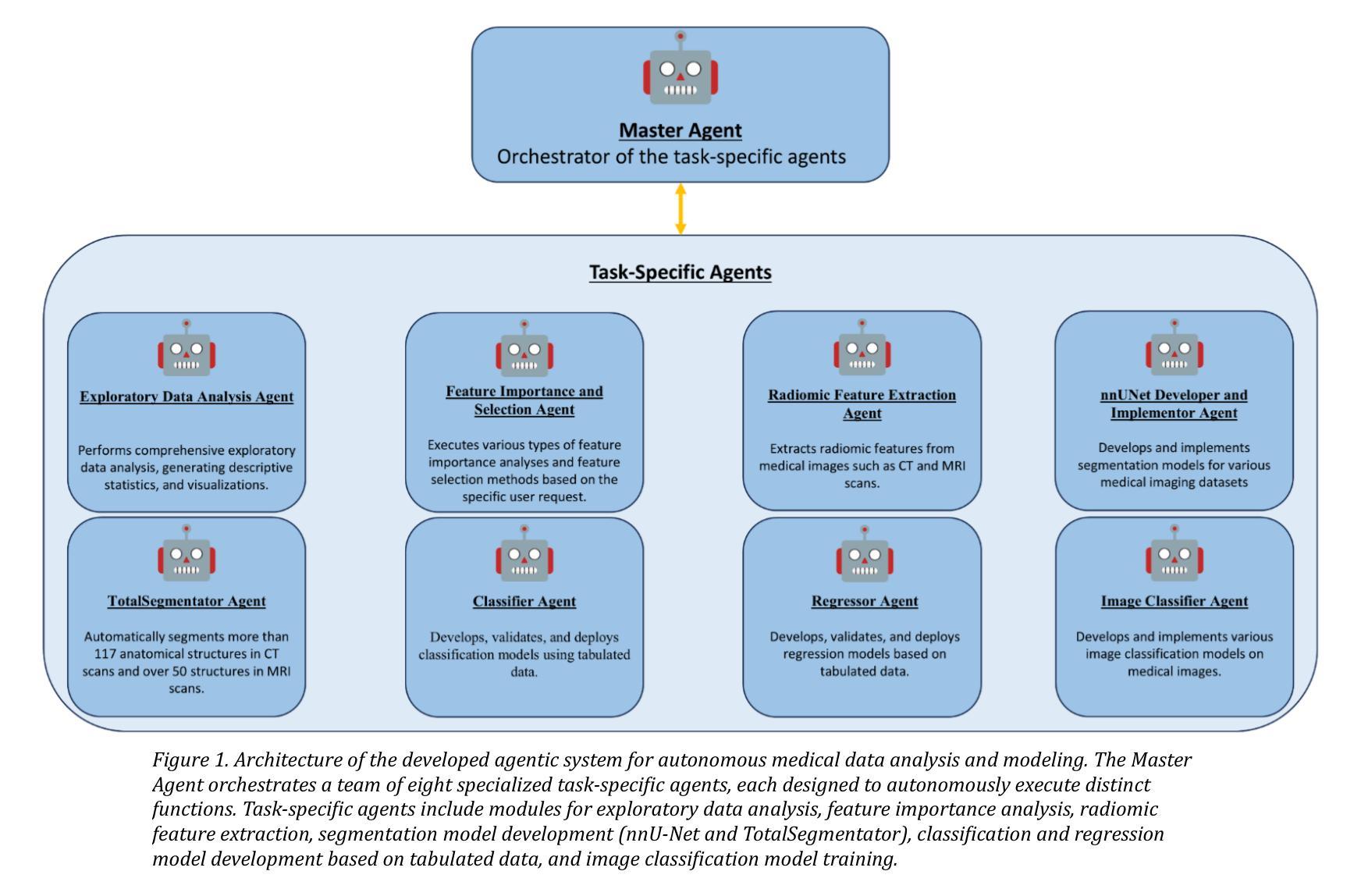
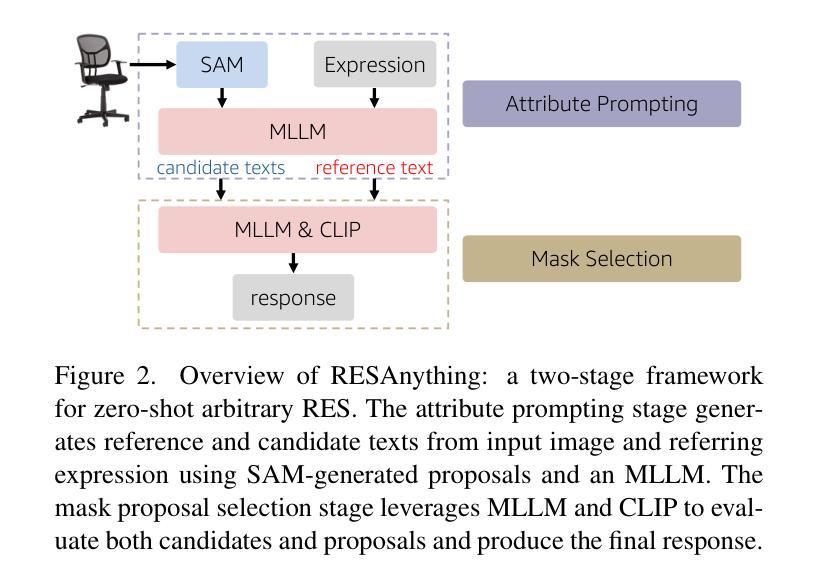
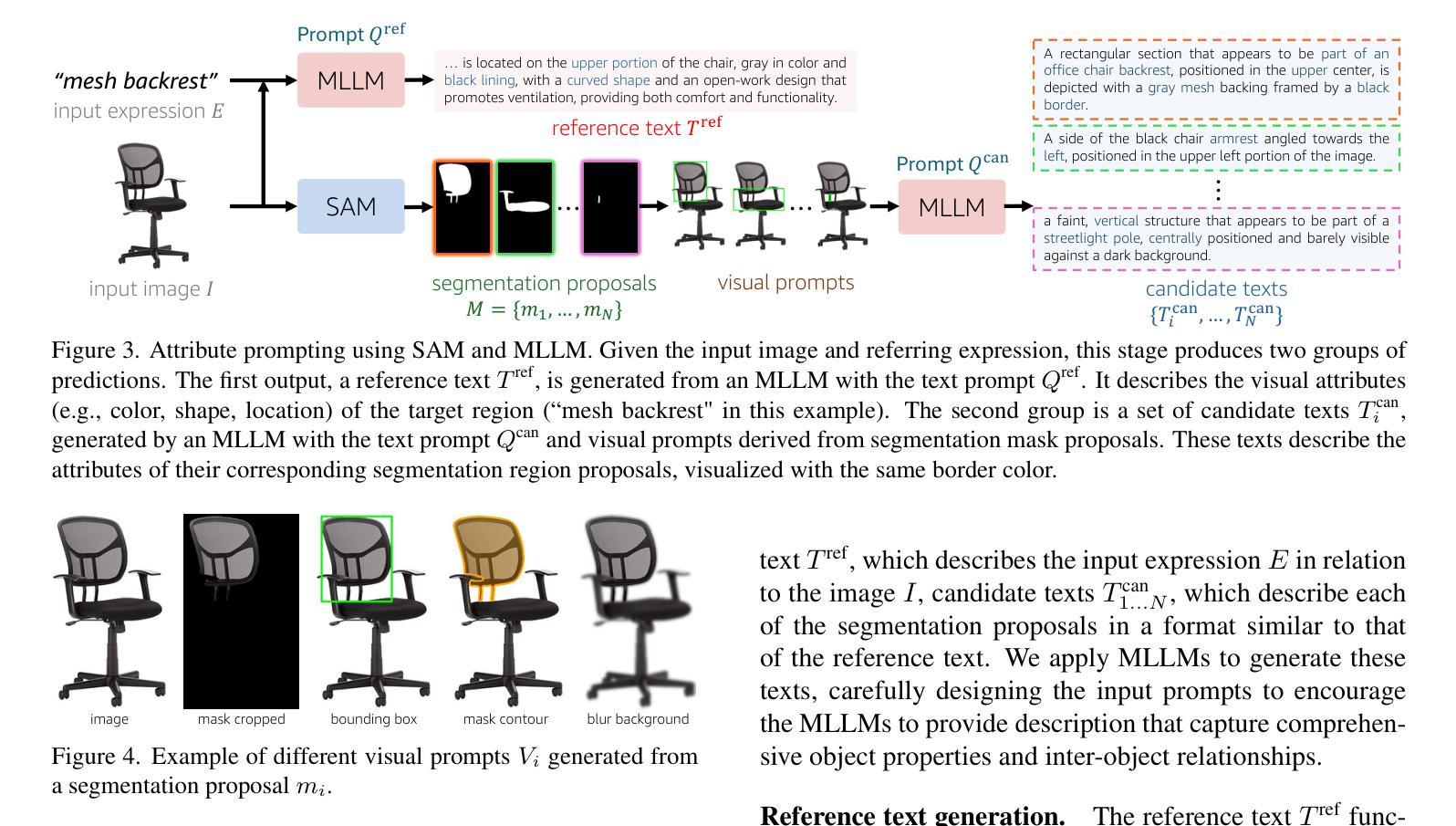
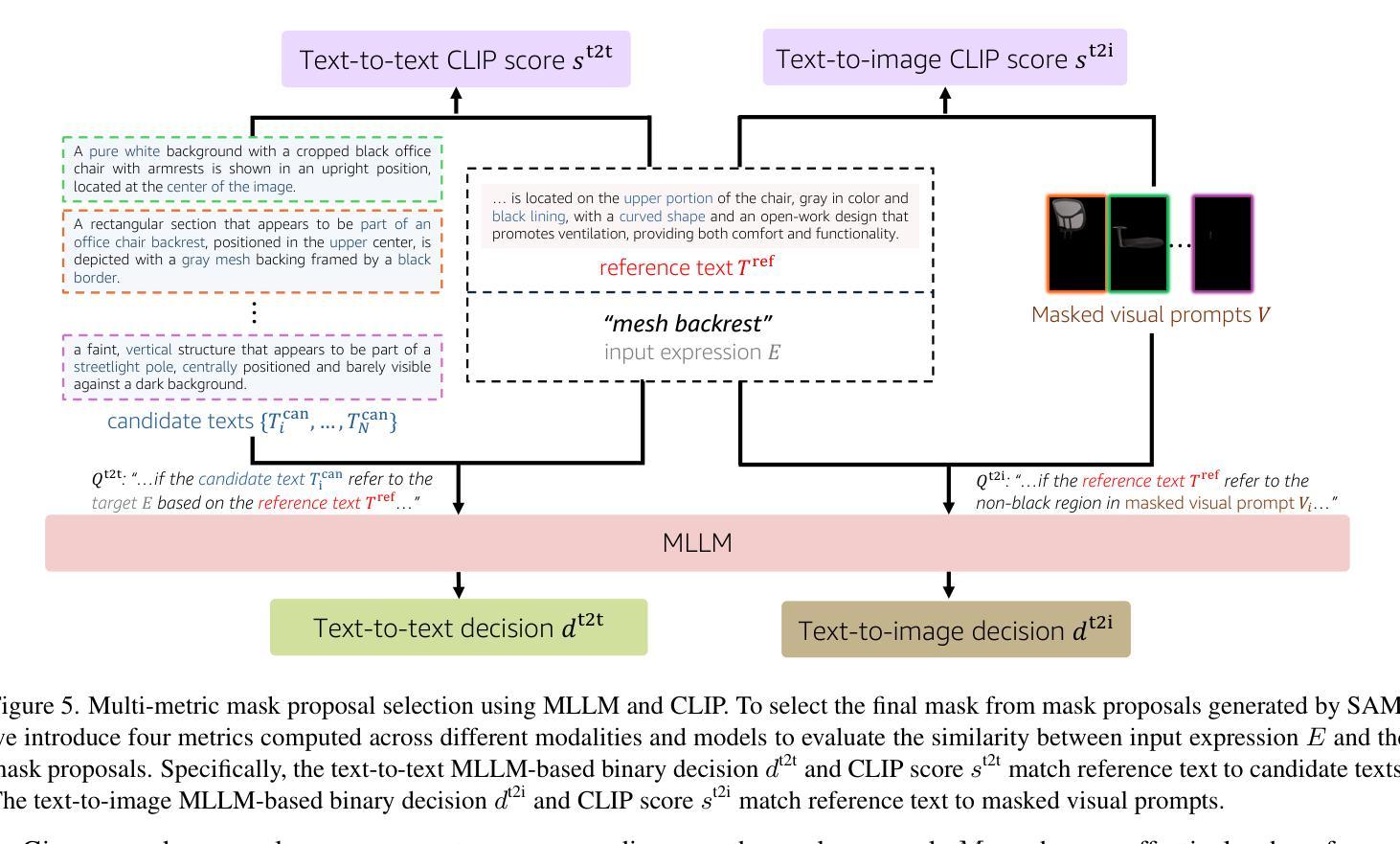
RESAnything: Attribute Prompting for Arbitrary Referring Segmentation
Authors:Ruiqi Wang, Hao Zhang
We present an open-vocabulary and zero-shot method for arbitrary referring expression segmentation (RES), targeting input expressions that are more general than what prior works were designed to handle. Specifically, our inputs encompass both object- and part-level labels as well as implicit references pointing to properties or qualities of object/part function, design, style, material, etc. Our model, coined RESAnything, leverages Chain-of-Thoughts (CoT) reasoning, where the key idea is attribute prompting. We generate detailed descriptions of object/part attributes including shape, color, and location for potential segment proposals through systematic prompting of a large language model (LLM), where the proposals are produced by a foundational image segmentation model. Our approach encourages deep reasoning about object or part attributes related to function, style, design, etc., enabling the system to handle implicit queries without any part annotations for training or fine-tuning. As the first zero-shot and LLM-based RES method, RESAnything achieves clearly superior performance among zero-shot methods on traditional RES benchmarks and significantly outperforms existing methods on challenging scenarios involving implicit queries and complex part-level relations. Finally, we contribute a new benchmark dataset to offer ~3K carefully curated RES instances to assess part-level, arbitrary RES solutions.
我们提出了一种用于任意引用表达式分割(RES)的开放词汇和零样本方法,针对的输入表达式比以往工作设计的更为通用。具体来说,我们的输入涵盖了对象级和部件级标签,以及指向对象/部件功能、设计、风格、材质等属性的隐含引用。我们的模型被称为RESAnything,它利用Chain-of-Thoughts(CoT)推理,关键思想是属性提示。我们通过系统提示大型语言模型(LLM)来生成对象/部件属性的详细描述,包括形状、颜色和位置等,为潜在的分段提案提供支持。这些提案由基础图像分割模型生成。我们的方法鼓励对对象或部件属性(如功能、风格、设计等)进行深度推理,使系统能够处理隐式查询,而无需任何部分注释进行训练或微调。作为基于零样本和LLM的RES方法,RESAnything在传统的RES基准测试上实现了明显的优势性能,并且在涉及隐式查询和复杂部件级关系的挑战性场景中显著优于现有方法。最后,我们贡献了一个新的基准数据集,提供了约3K个精心策划的RES实例,以评估部件级、任意RES解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 42 pages, 31 figures. For more details: https://suikei-wang.github.io/RESAnything/
Summary
本文介绍了一种开放词汇表和零样本方法,用于处理任意引用表达式分割(RES),该方法能够处理比以往研究更一般的输入表达式。通过Chain-of-Thoughts(CoT)推理和属性提示,模型RESAnything能够详细描述对象/部分的属性,如形状、颜色和位置,以产生潜在的分段建议。该方法鼓励对对象或部分的属性进行深度推理,能够处理隐式查询,无需对训练或微调进行部分注释。作为第一个基于零样本和大型语言模型(LLM)的RES方法,RESAnything在传统的RES基准测试上的表现优于其他零样本方法,在处理涉及隐式查询和复杂部分级关系的挑战场景时表现出显著的优势。最后,本文贡献了一个新的基准数据集,包含约3K个精心挑选的RES实例,以评估部分级、任意的RES解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种开放词汇表和零样本方法用于任意引用表达式分割(RES)。
- 模型RESAnything能够处理更一般的输入表达式,涵盖对象级和部分级的标签以及指向属性或功能的隐式引用。
- 采用Chain-of-Thoughts(CoT)推理和属性提示,生成详细的对象/部分属性描述。
- 鼓励对对象或部分的属性进行深度推理,能处理隐式查询,无需对训练或微调进行部分注释。
- RESAnything在RES基准测试上的表现优于其他零样本方法,特别擅长处理复杂场景和隐式查询。
- 引入了一个新的基准数据集,包含约3K个RES实例,用于评估部分级、任意的RES解决方案。
- 该方法推动了医学图像分割技术的发展,尤其是任意引用表达式分割的处理能力。
点此查看论文截图


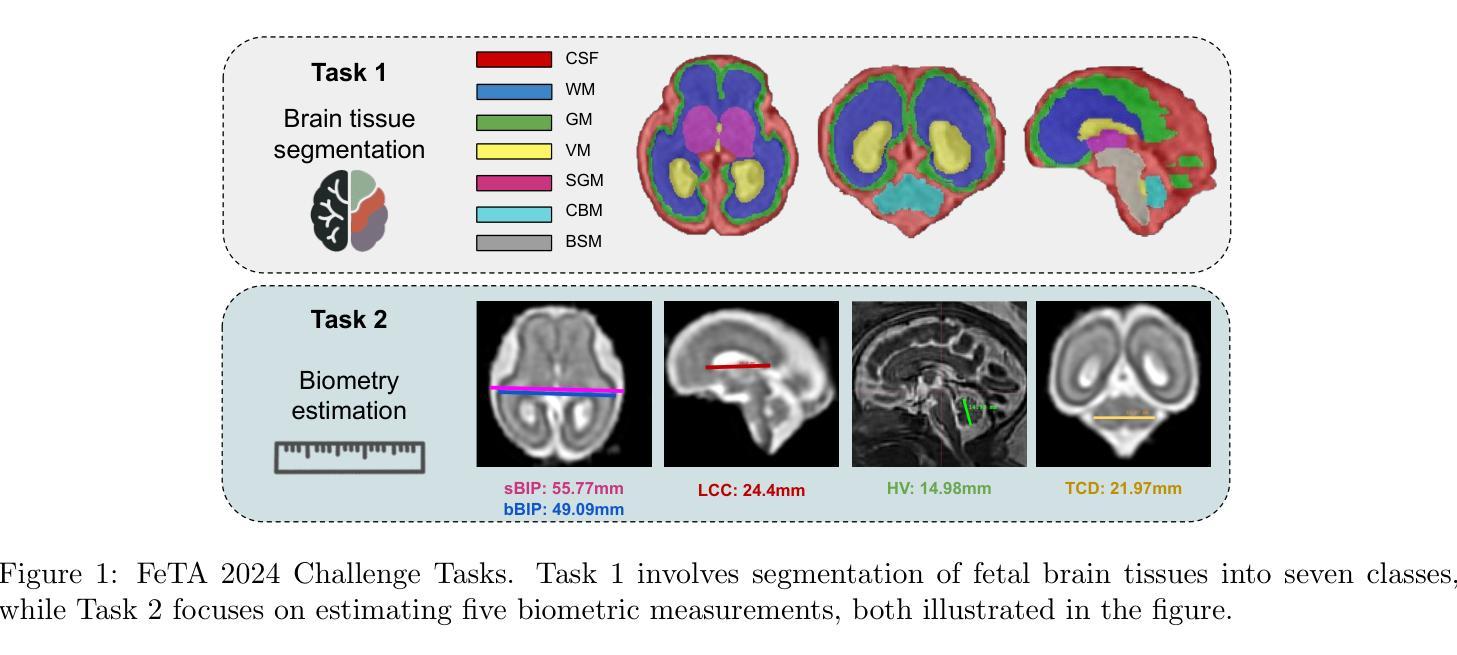
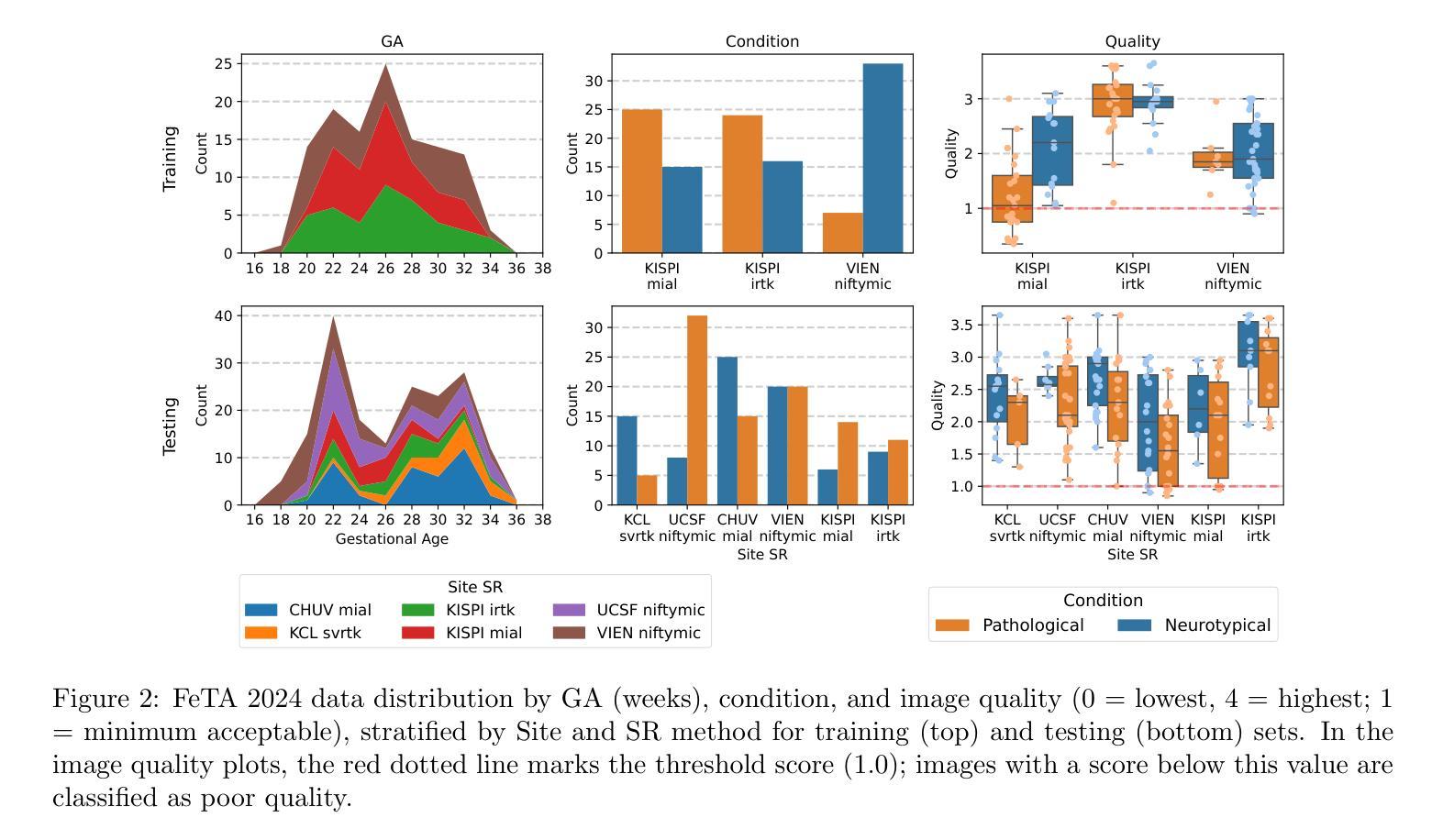
Advances in Automated Fetal Brain MRI Segmentation and Biometry: Insights from the FeTA 2024 Challenge
Authors:Vladyslav Zalevskyi, Thomas Sanchez, Misha Kaandorp, Margaux Roulet, Diego Fajardo-Rojas, Liu Li, Jana Hutter, Hongwei Bran Li, Matthew Barkovich, Hui Ji, Luca Wilhelmi, Aline Dändliker, Céline Steger, Mériam Koob, Yvan Gomez, Anton Jakovčić, Melita Klaić, Ana Adžić, Pavel Marković, Gracia Grabarić, Milan Rados, Jordina Aviles Verdera, Gregor Kasprian, Gregor Dovjak, Raphael Gaubert-Rachmühl, Maurice Aschwanden, Qi Zeng, Davood Karimi, Denis Peruzzo, Tommaso Ciceri, Giorgio Longari, Rachika E. Hamadache, Amina Bouzid, Xavier Lladó, Simone Chiarella, Gerard Martí-Juan, Miguel Ángel González Ballester, Marco Castellaro, Marco Pinamonti, Valentina Visani, Robin Cremese, Keïn Sam, Fleur Gaudfernau, Param Ahir, Mehul Parikh, Maximilian Zenk, Michael Baumgartner, Klaus Maier-Hein, Li Tianhong, Yang Hong, Zhao Longfei, Domen Preloznik, Žiga Špiclin, Jae Won Choi, Muyang Li, Jia Fu, Guotai Wang, Jingwen Jiang, Lyuyang Tong, Bo Du, Milton O. Candela-Leal, Andrea Gondova, Sungmin You, Abdul Qayyum, Moona Mazher, Steven A Niederer, Andras Jakab, Roxane Licandro, Kelly Payette, Meritxell Bach Cuadra
Accurate fetal brain tissue segmentation and biometric analysis are essential for studying brain development in utero. The FeTA Challenge 2024 advanced automated fetal brain MRI analysis by introducing biometry prediction as a new task alongside tissue segmentation. For the first time, our diverse multi-centric test set included data from a new low-field (0.55T) MRI dataset. Evaluation metrics were also expanded to include the topology-specific Euler characteristic difference (ED). Sixteen teams submitted segmentation methods, most of which performed consistently across both high- and low-field scans. However, longitudinal trends indicate that segmentation accuracy may be reaching a plateau, with results now approaching inter-rater variability. The ED metric uncovered topological differences that were missed by conventional metrics, while the low-field dataset achieved the highest segmentation scores, highlighting the potential of affordable imaging systems when paired with high-quality reconstruction. Seven teams participated in the biometry task, but most methods failed to outperform a simple baseline that predicted measurements based solely on gestational age, underscoring the challenge of extracting reliable biometric estimates from image data alone. Domain shift analysis identified image quality as the most significant factor affecting model generalization, with super-resolution pipelines also playing a substantial role. Other factors, such as gestational age, pathology, and acquisition site, had smaller, though still measurable, effects. Overall, FeTA 2024 offers a comprehensive benchmark for multi-class segmentation and biometry estimation in fetal brain MRI, underscoring the need for data-centric approaches, improved topological evaluation, and greater dataset diversity to enable clinically robust and generalizable AI tools.
准确胎儿脑组织分割和生物测定分析对于研究胎儿期的大脑发育至关重要。FeTA Challenge 2024通过引入生物测定预测作为新任务,推动了胎儿脑部MRI分析的自动化发展,同时辅以组织分割。我们的多样化多中心测试集首次包含来自新低场(0.55T)MRI数据集的数据。评估指标也得以扩充,包括针对拓扑特性的欧拉特征差异(ED)。有十六支队伍提交了分割方法,其中大多数在高场和低场扫描中都表现稳定。然而纵向趋势表明,分割精度可能已达到一个瓶颈期,其结果现已接近观察者间变异度。ED指标发现了传统指标未能覆盖的拓扑差异,同时低场数据集获得了最高的分割得分,这突显了当与高质量重建相结合时,平价成像系统的潜力。有七支队伍参与了生物测定任务,但大多数方法未能超越一个简单基线,该基线仅根据胎龄进行预测测量,这突显了仅从图像数据中提取可靠生物测定估计的挑战性。域偏移分析确定了图像质量是影响模型泛化的最重要因素,超分辨率流程也发挥了重要作用。其他因素,如胎龄、病理和采集地点的影响较小,但仍可衡量。总体而言,FeTA 2024为多类分割和胎儿脑部MRI生物测定估计提供了全面的基准测试,这突显了对数据中心方法、改进拓扑评估和更大数据集多样性的需求,以实现临床稳健且可推广的人工智能工具。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了FeTA Challenge 2024在胎儿脑部MRI分析方面的进展,包括组织分割和生物计量预测两个任务。研究使用了多中心测试集,包括来自低场(0.55T)MRI数据集的数据。评价指标扩展到了拓扑特定的Euler特征差异(ED)。尽管大多数团队在高场和低场扫描中表现稳定,但分割精度可能已经达到一个平台期。低场数据集获得了最高的分割分数,突显出低成本成像系统与高质重建相结合时的潜力。对于生物计量任务,大多数方法未能超越基于胎龄的简单基线预测,表明仅从图像数据中提取可靠生物计量估计的挑战性。领域偏移分析表明,图像质量是影响模型泛化的最重要因素。
Key Takeaways
- FeTA Challenge 2024扩展了胎儿脑部MRI分析,包括生物计量预测这一新任务。
- 多样化的多中心测试集包含来自低场MRI数据集的数据。
- 评价指标新增了Euler特征差异(ED),用于捕捉拓扑特性。
- 大多数团队在高场和低场扫描中表现稳定,但分割精度接近饱和。
- 低场数据集获得最高分割分数,显示低成本成像系统结合高质量重建的潜力。
- 生物计量预测任务面临挑战,简单基线模型基于胎龄的预测表现较好。
- 领域偏移分析显示,模型泛化受影响最大的因素是图像质量,其次是超分辨率管道、胎龄、病理和采集地点。
点此查看论文截图

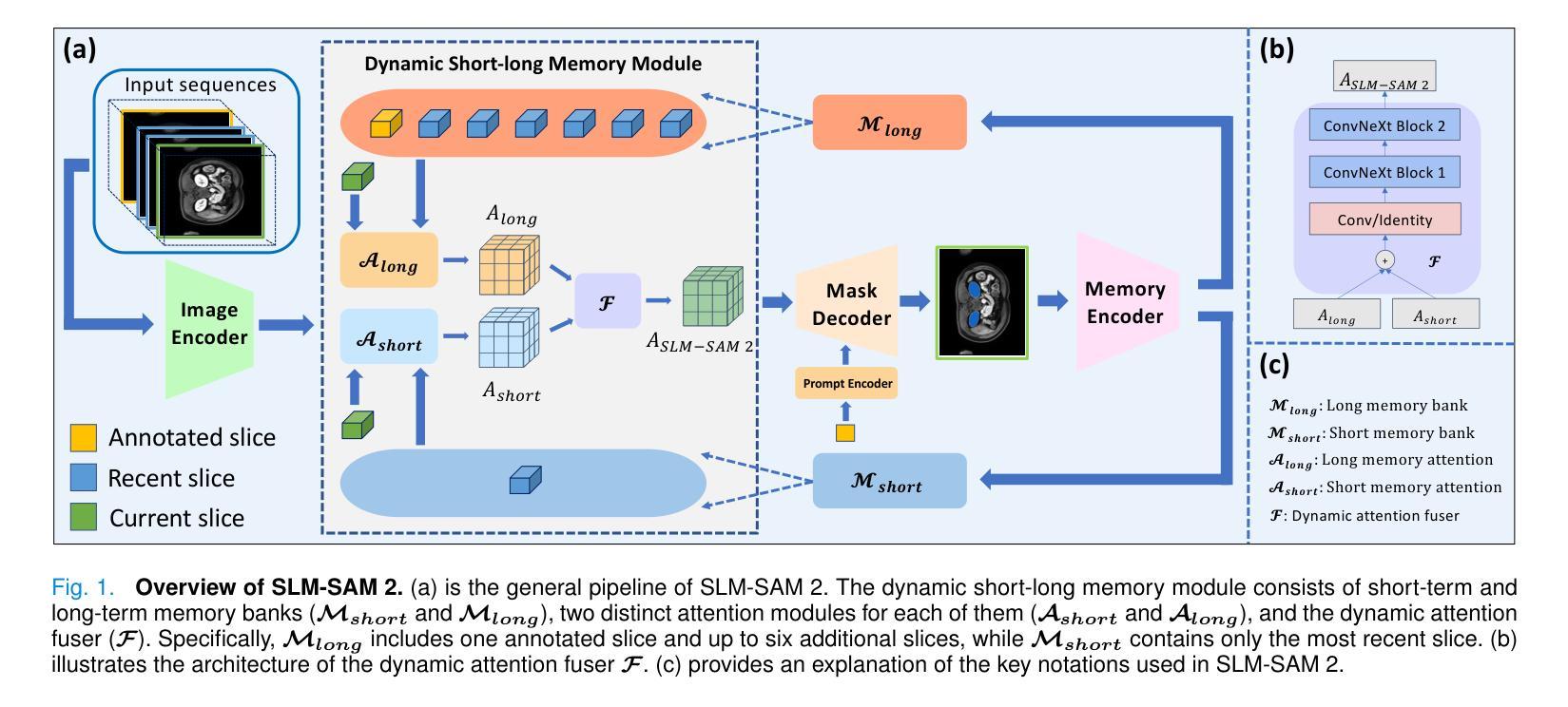
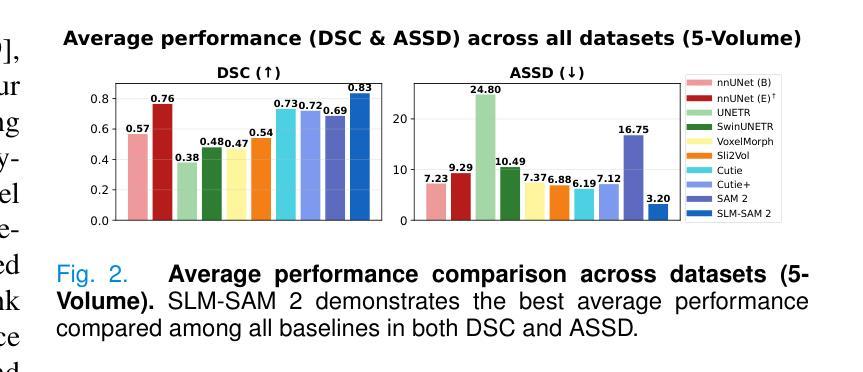
Accelerating Volumetric Medical Image Annotation via Short-Long Memory SAM 2
Authors:Yuwen Chen, Zafer Yildiz, Qihang Li, Yaqian Chen, Haoyu Dong, Hanxue Gu, Nicholas Konz, Maciej A. Mazurowski
Manual annotation of volumetric medical images, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT), is a labor-intensive and time-consuming process. Recent advancements in foundation models for video object segmentation, such as Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM 2), offer a potential opportunity to significantly speed up the annotation process by manually annotating one or a few slices and then propagating target masks across the entire volume. However, the performance of SAM 2 in this context varies. Our experiments show that relying on a single memory bank and attention module is prone to error propagation, particularly at boundary regions where the target is present in the previous slice but absent in the current one. To address this problem, we propose Short-Long Memory SAM 2 (SLM-SAM 2), a novel architecture that integrates distinct short-term and long-term memory banks with separate attention modules to improve segmentation accuracy. We evaluate SLM-SAM 2 on three public datasets covering organs, bones, and muscles across MRI and CT modalities. We show that the proposed method markedly outperforms the default SAM 2, achieving average Dice Similarity Coefficient improvement of 0.14 and 0.11 in the scenarios when 5 volumes and 1 volume are available for the initial adaptation, respectively. SLM-SAM 2 also exhibits stronger resistance to over-propagation, making a notable step toward more accurate automated annotation of medical images for segmentation model development.
医学图像(如磁共振成像(MRI)和计算机断层扫描(CT))的手动标注是一个劳动密集型且耗时的工作过程。近期视频对象分割基础模型(例如分割任何模型 2 (SAM 2))的最新进展提供了一个潜在的机会,可以通过手动标注一个或多个切片,然后将其传播到整个体积,从而显著加快标注过程。然而,SAM 2 在此背景下的表现有所不同。我们的实验表明,依赖单一内存银行和注意力模块容易出现误差传播,特别是在目标出现在前一个切片中而在当前切片中不存在的边界区域。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了长短记忆SAM 2(SLM-SAM 2),这是一种新型架构,融合了不同的短期和长期内存银行以及单独的注意力模块,以提高分割精度。我们在三个公共数据集上评估了SLM-SAM 2,这些数据集涵盖了MRI和CT模态下的器官、骨骼和肌肉。我们展示的方法在初始适应时显著优于默认SAM 2,在可用体积为5个和1个的情况下,平均Dice相似系数分别提高了0.14和0.11。SLM-SAM 2 还展现出更强的抵抗过度传播的能力,在更准确自动标注医学图像以开发分割模型方面迈出了重要一步。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于医学图像(如MRI和CT)的自动标注技术改进方案,名为Short-Long Memory SAM 2(SLM-SAM 2)。该技术通过整合短期和长期记忆库以及独立注意力模块,解决了现有技术如SAM 2在标注过程中出现的误差传播问题,特别是在目标在前后切片间边界区域的标注问题。实验表明,SLM-SAM 2在公开数据集上的表现优于原版SAM 2,Dice相似系数平均提升0.14和0.11。此外,SLM-SAM 2还展现出更强的抗过度传播能力,为医学图像分割模型的更准确自动标注迈出了重要一步。
Key Takeaways
- 手动标注医学图像如MRI和CT是劳动密集且耗时的过程。
- Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM 2)等视频物体分割基础模型可用于加速标注过程。
- SAM 2在医学图像标注中存在误差传播问题,特别是在目标边界区域。
- Short-Long Memory SAM 2(SLM-SAM 2)是一种新技术,通过结合短期和长期记忆库及独立注意力模块,提高了分割准确性。
- SLM-SAM 2在公开数据集上的表现优于SAM 2,Dice相似系数有所提升。
点此查看论文截图


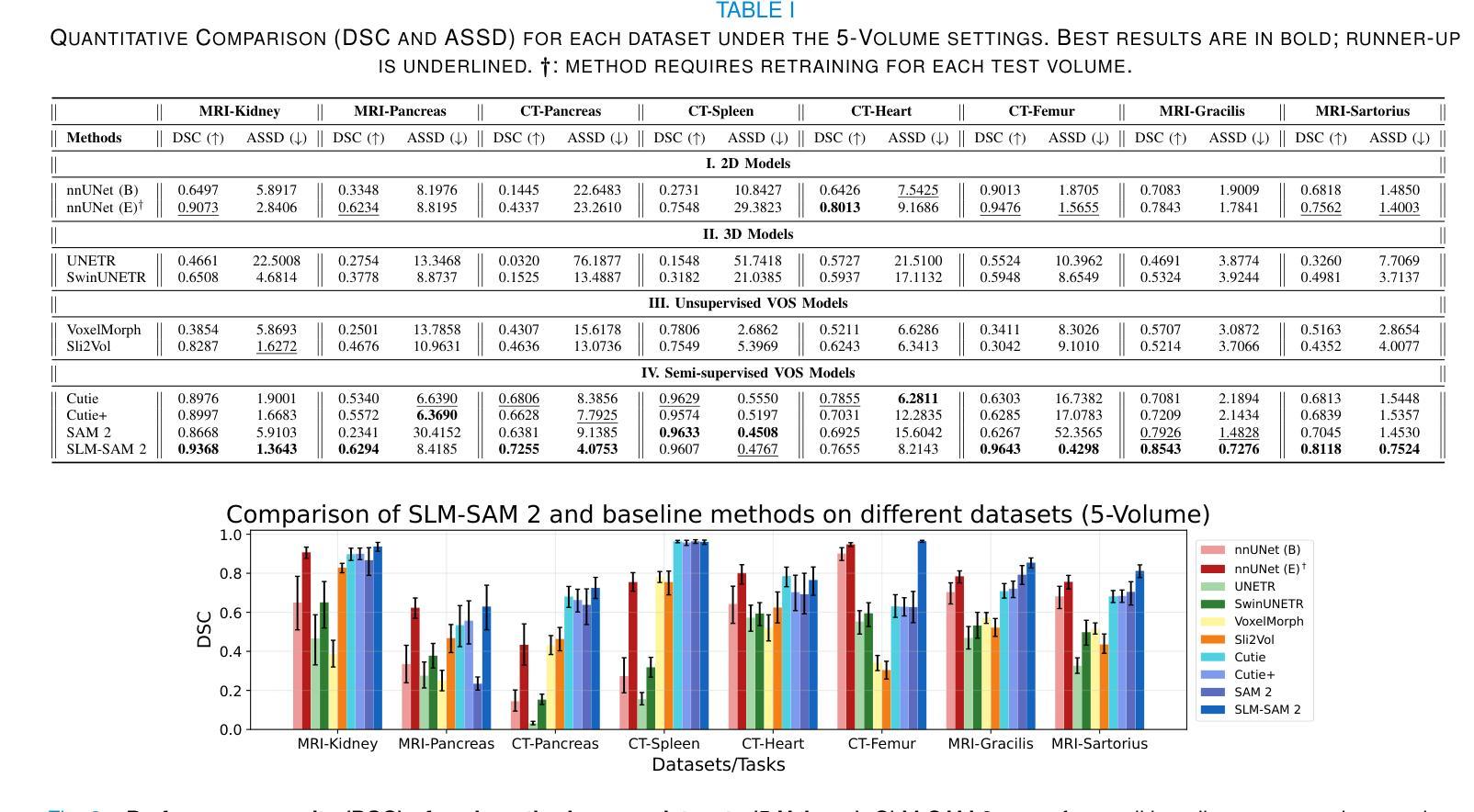
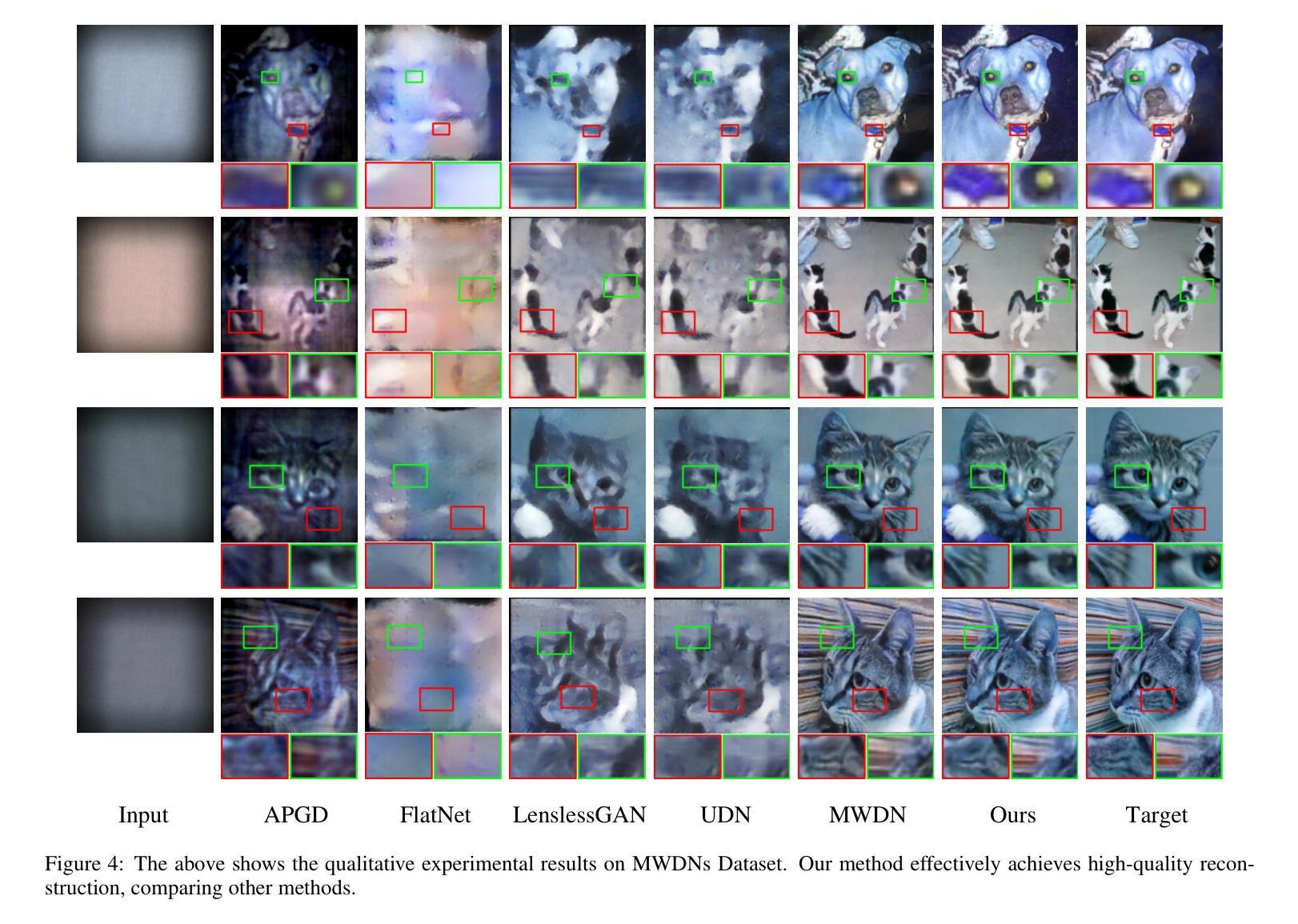
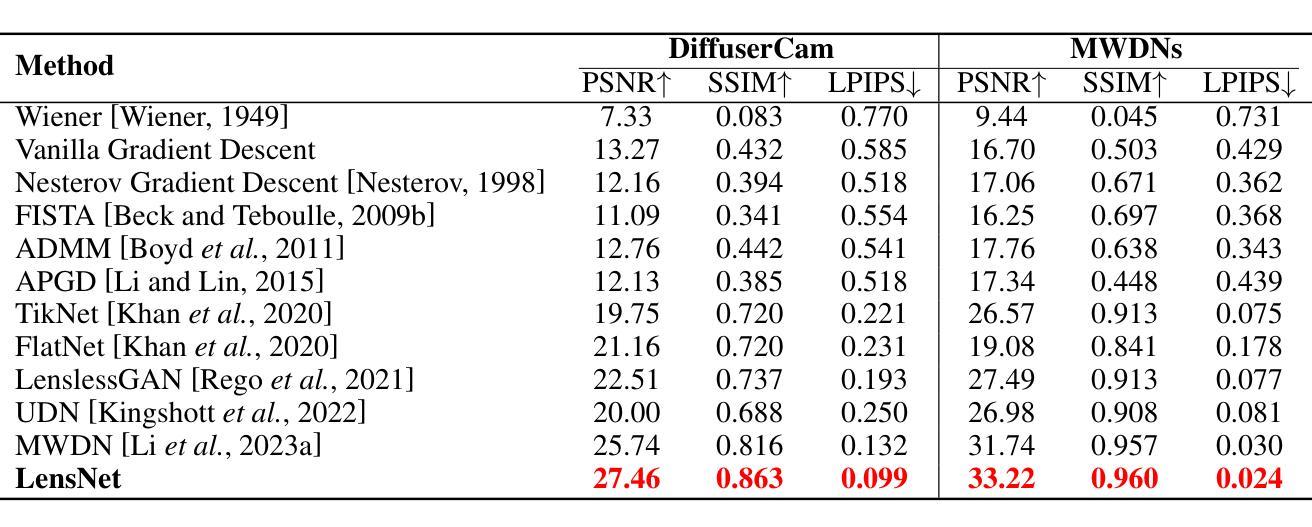
LensNet: An End-to-End Learning Framework for Empirical Point Spread Function Modeling and Lensless Imaging Reconstruction
Authors:Jiesong Bai, Yuhao Yin, Yihang Dong, Xiaofeng Zhang, Chi-Man Pun, Xuhang Chen
Lensless imaging stands out as a promising alternative to conventional lens-based systems, particularly in scenarios demanding ultracompact form factors and cost-effective architectures. However, such systems are fundamentally governed by the Point Spread Function (PSF), which dictates how a point source contributes to the final captured signal. Traditional lensless techniques often require explicit calibrations and extensive pre-processing, relying on static or approximate PSF models. These rigid strategies can result in limited adaptability to real-world challenges, including noise, system imperfections, and dynamic scene variations, thus impeding high-fidelity reconstruction. In this paper, we propose LensNet, an end-to-end deep learning framework that integrates spatial-domain and frequency-domain representations in a unified pipeline. Central to our approach is a learnable Coded Mask Simulator (CMS) that enables dynamic, data-driven estimation of the PSF during training, effectively mitigating the shortcomings of fixed or sparsely calibrated kernels. By embedding a Wiener filtering component, LensNet refines global structure and restores fine-scale details, thus alleviating the dependency on multiple handcrafted pre-processing steps. Extensive experiments demonstrate LensNet’s robust performance and superior reconstruction quality compared to state-of-the-art methods, particularly in preserving high-frequency details and attenuating noise. The proposed framework establishes a novel convergence between physics-based modeling and data-driven learning, paving the way for more accurate, flexible, and practical lensless imaging solutions for applications ranging from miniature sensors to medical diagnostics. The link of code is https://github.com/baijiesong/Lensnet.
无透镜成像作为传统基于透镜系统的有前途的替代方案脱颖而出,特别是在要求超紧凑外形尺寸和成本效益高的架构的场景中。然而,此类系统从根本上受到点扩散函数(PSF)的支配,PSF决定了点源如何贡献于最终捕获的信号。传统的无透镜技术通常需要明确的校准和广泛的预处理,依赖于静态或近似PSF模型。这些僵硬策略对现实世界挑战的可适应性有限,包括噪声、系统缺陷和动态场景变化,从而阻碍高保真重建。在本文中,我们提出了LensNet,这是一个端到端的深度学习框架,它将空间域和频率域表示集成到一个统一的管道中。我们的方法的核心是可学习的编码掩膜模拟器(CMS),它能够在训练过程中实现PSF的动态数据驱动估计,有效地弥补了固定或稀疏校准内核的缺点。通过嵌入维纳滤波组件,LensNet细化全局结构并恢复细微细节,从而减少对多个手工预处理步骤的依赖。大量实验表明,LensNet的性能稳健,重建质量优越,特别是能够保持高频细节并减少噪声。所提出的框架在基于物理的建模和数据驱动学习之间建立了新的融合,为从微型传感器到医学诊断等各种应用提供了更准确、更灵活、更实用的无透镜成像解决方案。代码链接是https://github.com/baijiesong/Lensnet。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IJCAI 2025
Summary
本文介绍了无透镜成像作为一种对传统透镜系统有前景的替代方案的特点与优势,尤其在超紧凑形式因素和成本效益型架构方面的应用。但由于受到点扩散函数(PSF)的影响,其面临诸多挑战。针对这些问题,本文提出了一种名为LensNet的端到端深度学习框架,该框架结合了空间域和频率域表示,并引入了一个可学习的编码掩膜模拟器(CMS),能够动态、数据驱动地估计PSF。此外,LensNet通过嵌入维纳滤波组件,改进了全局结构并恢复了细节,减少了对手动预处理步骤的依赖。实验结果证明了LensNet的鲁棒性能和优越的重建质量。该框架为物理建模和数据驱动学习之间建立了新的融合点,为从微型传感器到医疗诊断等领域的无透镜成像提供了更准确、灵活和实用的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 无透镜成像作为传统透镜系统的替代方案,尤其在超紧凑和成本效益型架构方面表现出潜力。
- 点扩散函数(PSF)在无透镜成像中起到关键作用,影响最终捕获信号的点源贡献。
- 传统无透镜技术依赖于静态或近似PSF模型,存在对现实世界挑战的适应性有限的缺点。
- LensNet框架结合了空间域和频率域表示,通过深度学习实现动态、数据驱动的PSF估计。
- LensNet引入编码掩膜模拟器(CMS)和维纳滤波组件,改进全局结构并恢复细节。
- LensNet减少了对手动预处理步骤的依赖,并展示了在噪声衰减和高频细节保留方面的优势。
点此查看论文截图
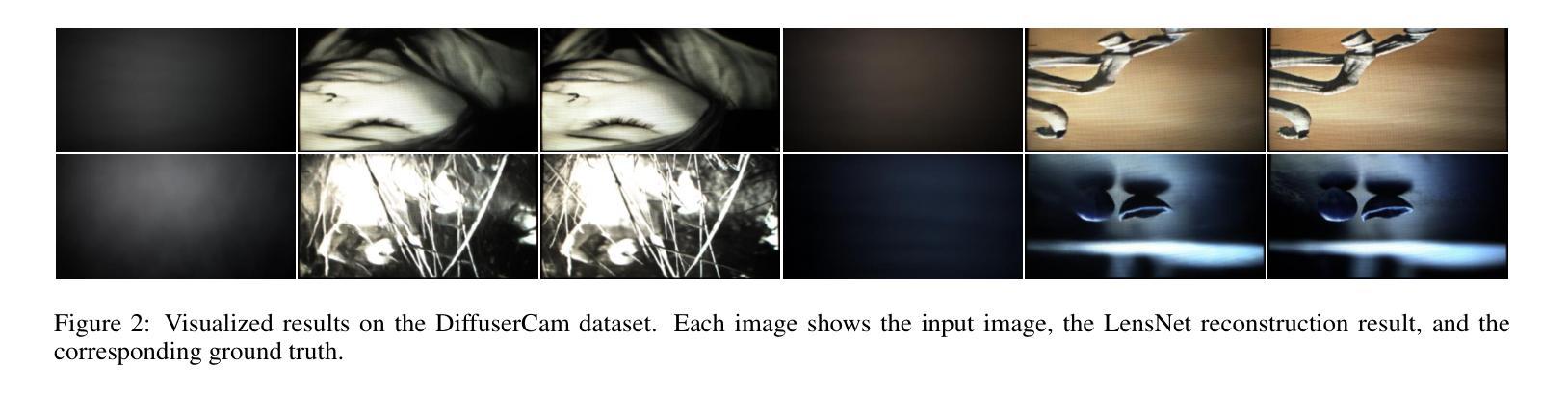
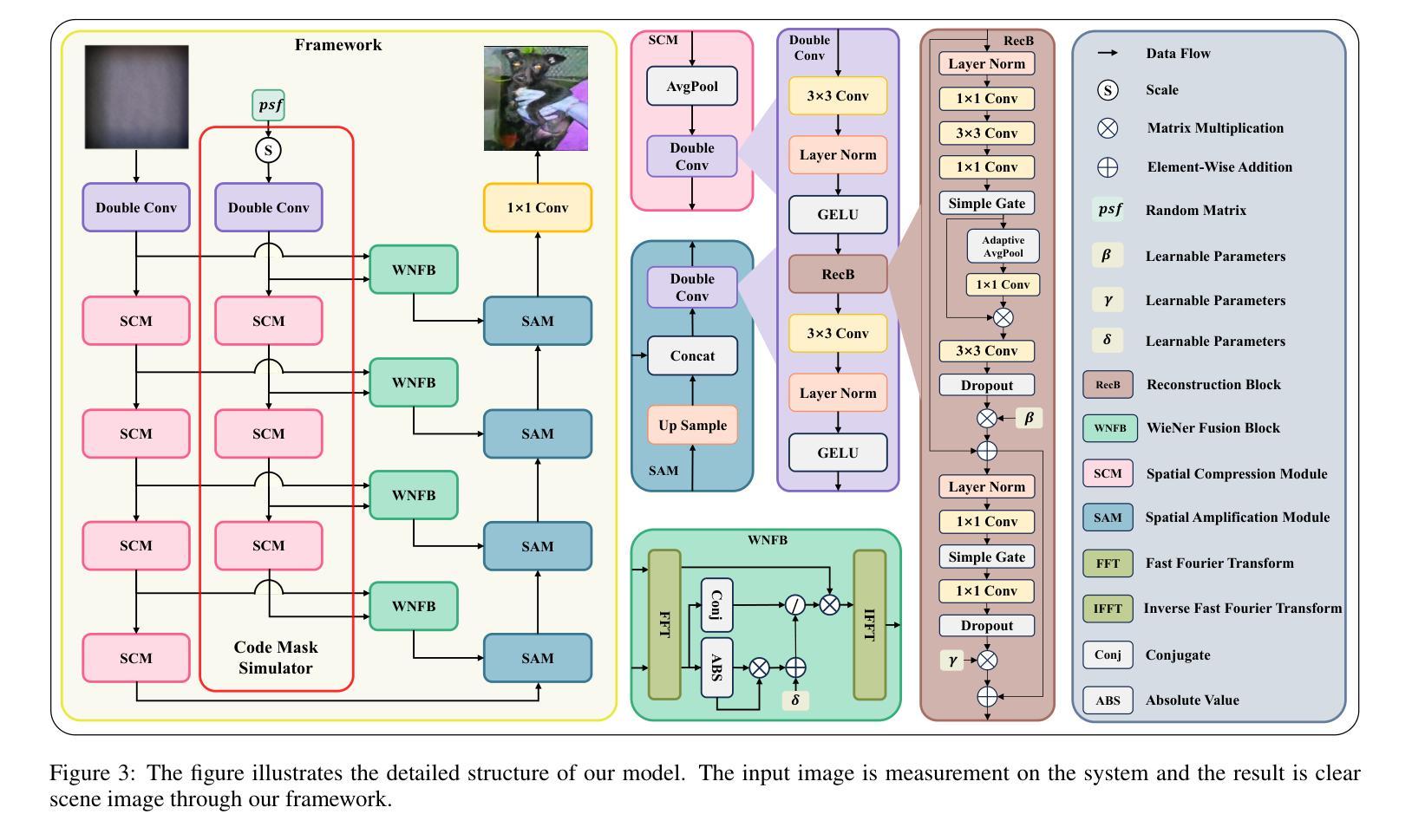

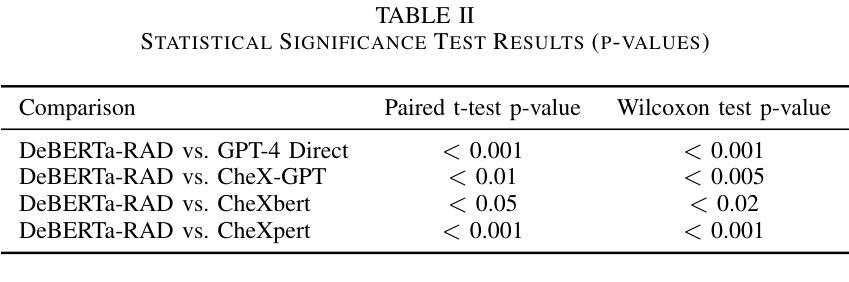
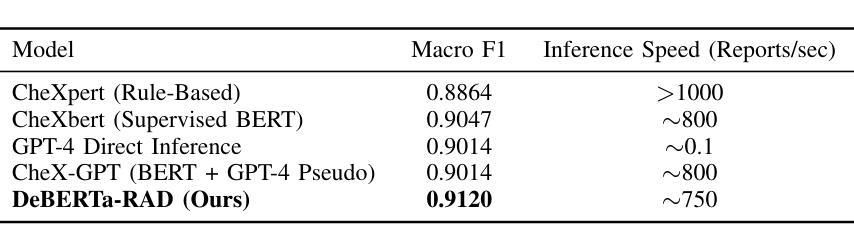
High-Fidelity Pseudo-label Generation by Large Language Models for Training Robust Radiology Report Classifiers
Authors:Brian Wong, Kaito Tanaka
Automated labeling of chest X-ray reports is essential for enabling downstream tasks such as training image-based diagnostic models, population health studies, and clinical decision support. However, the high variability, complexity, and prevalence of negation and uncertainty in these free-text reports pose significant challenges for traditional Natural Language Processing methods. While large language models (LLMs) demonstrate strong text understanding, their direct application for large-scale, efficient labeling is limited by computational cost and speed. This paper introduces DeBERTa-RAD, a novel two-stage framework that combines the power of state-of-the-art LLM pseudo-labeling with efficient DeBERTa-based knowledge distillation for accurate and fast chest X-ray report labeling. We leverage an advanced LLM to generate high-quality pseudo-labels, including certainty statuses, for a large corpus of reports. Subsequently, a DeBERTa-Base model is trained on this pseudo-labeled data using a tailored knowledge distillation strategy. Evaluated on the expert-annotated MIMIC-500 benchmark, DeBERTa-RAD achieves a state-of-the-art Macro F1 score of 0.9120, significantly outperforming established rule-based systems, fine-tuned transformer models, and direct LLM inference, while maintaining a practical inference speed suitable for high-throughput applications. Our analysis shows particular strength in handling uncertain findings. This work demonstrates a promising path to overcome data annotation bottlenecks and achieve high-performance medical text processing through the strategic combination of LLM capabilities and efficient student models trained via distillation.
胸部X光报告自动标注对于下游任务至关重要,如基于图像的诊断模型训练、人群健康研究和临床决策支持。然而,这些自由文本报告中存在的高变异性、复杂性和否定以及不确定性的普遍存在,给传统自然语言处理方法带来了巨大的挑战。虽然大型语言模型(LLM)表现出强大的文本理解能力,但直接应用于大规模、高效的标注却受到计算成本和速度的限制。
本文介绍了DeBERTa-RAD,这是一种新颖的两阶段框架,结合了最先进的LLM伪标注的能力和基于DeBERTa的高效知识蒸馏,用于准确快速地完成胸部X光报告标注。我们利用先进的LLM为大量报告生成高质量伪标签,包括确定性状态。随后,使用定制的知识蒸馏策略,在伪标记数据上训练DeBERTa-Base模型。在专家注释的MIMIC-500基准测试上进行评估,DeBERTa-RAD取得了宏观F1得分为0.9120的业界最佳成绩,显著优于基于规则的系统、微调后的transformer模型和直接LLM推理,同时保持了适用于高吞吐量应用的实际推理速度。我们的分析显示在处理不确定的检查结果时具有特别的优势。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文提出一种基于自然语言处理技术的自动标注胸部X光报告的方法。针对传统自然语言处理方法难以处理报告中存在的否定和不确定性等问题,本文引入了一种新型的两阶段框架——DeBERTa-RAD。该框架结合了最先进的大型语言模型的伪标注能力与高效的DeBERTa知识蒸馏技术,以实现快速准确的胸部X光报告标注。利用先进的LLM生成高质量伪标签(包括确定状态),用于大规模报告数据集。随后,使用定制的知识蒸馏策略在伪标签数据上训练DeBERTa-Base模型。在专家标注的MIMIC-500基准测试上评估,DeBERTa-RAD取得了宏平均F1分数为0.912的业界最佳成绩,显著优于基于规则的系统、微调过的transformer模型和直接LLM推理,同时保持了适合高吞吐量应用的实际推理速度。特别在处理不确定结果方面表现突出。本文展示了通过结合LLM能力和高效学生模型训练克服数据标注瓶颈,实现高性能医学文本处理的途径。
关键见解
- 自动化标记胸部X光报告对下游任务至关重要,如训练基于图像的诊断模型、人群健康研究和临床决策支持。
- 传统自然语言处理方法面临报告中否定和不确定性的高变异性、复杂性和普遍性所带来的挑战。
- DeBERTa-RAD框架结合了大型语言模型的伪标注能力和DeBERTa知识蒸馏技术,以实现快速准确的胸部X光报告标注。
- 利用伪标签数据训练DeBERTa-Base模型,在MIMIC-500基准测试中取得业界最佳性能。
- DeBERTa-RAD在处理不确定结果方面表现优异。
- 该研究展示了结合大型语言模型能力和高效学生模型训练的战略组合,以克服数据标注瓶颈并实现高性能医学文本处理。
点此查看论文截图

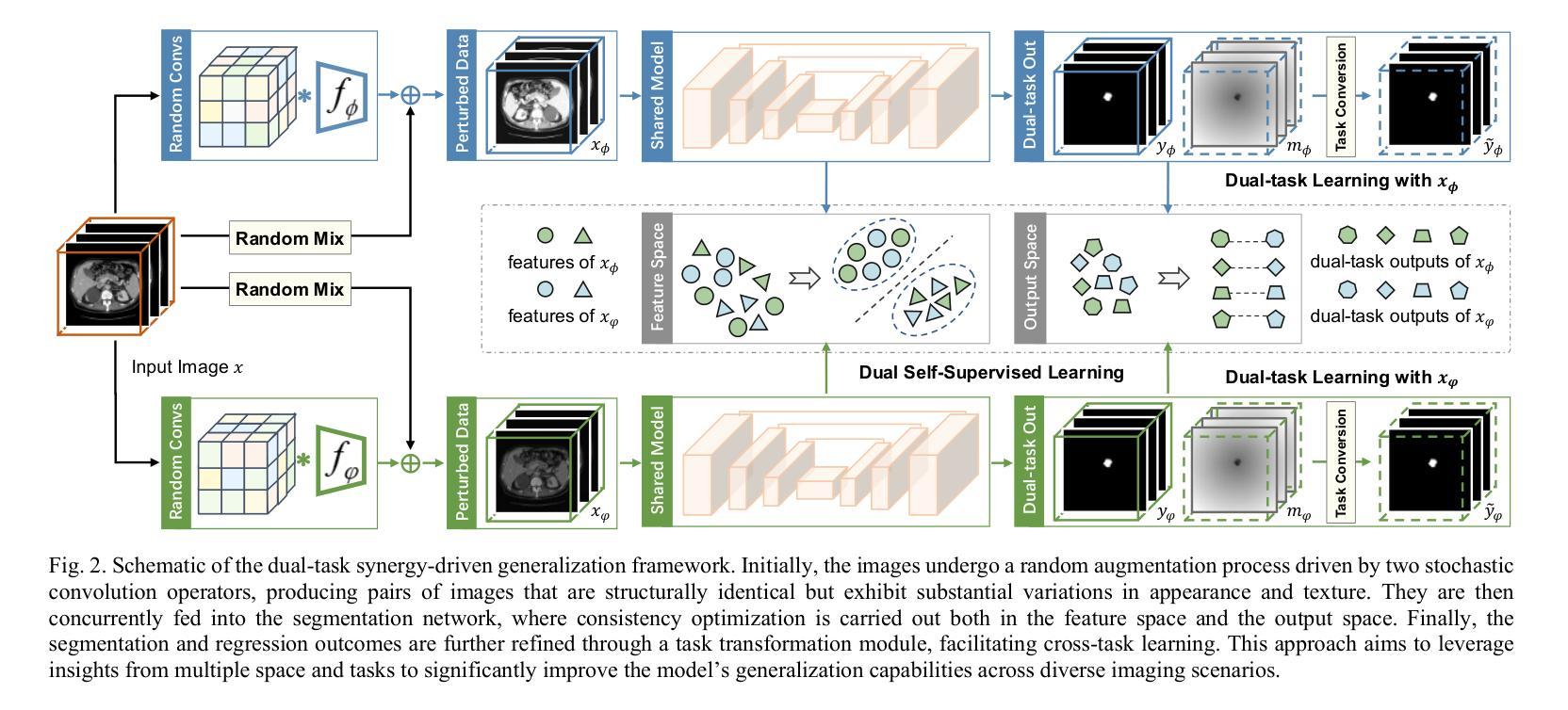
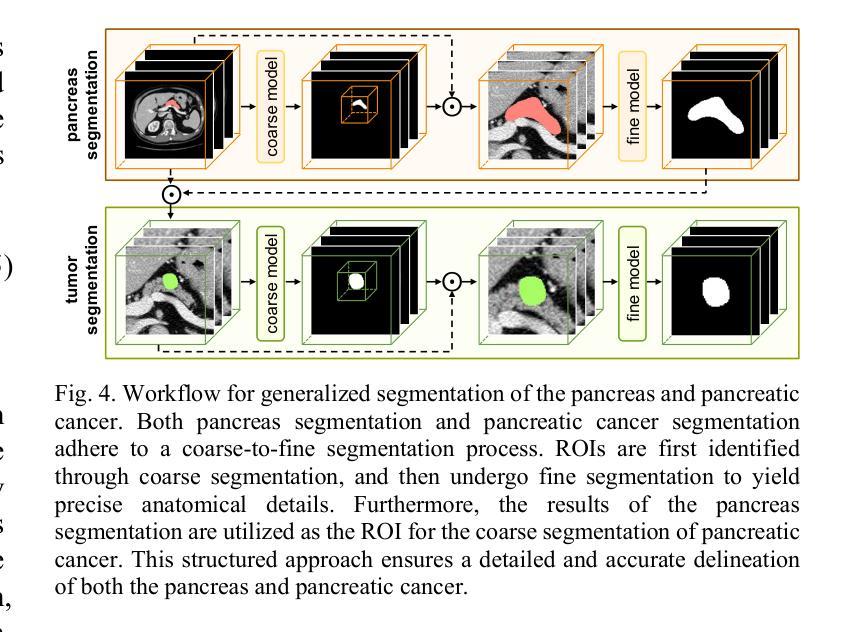
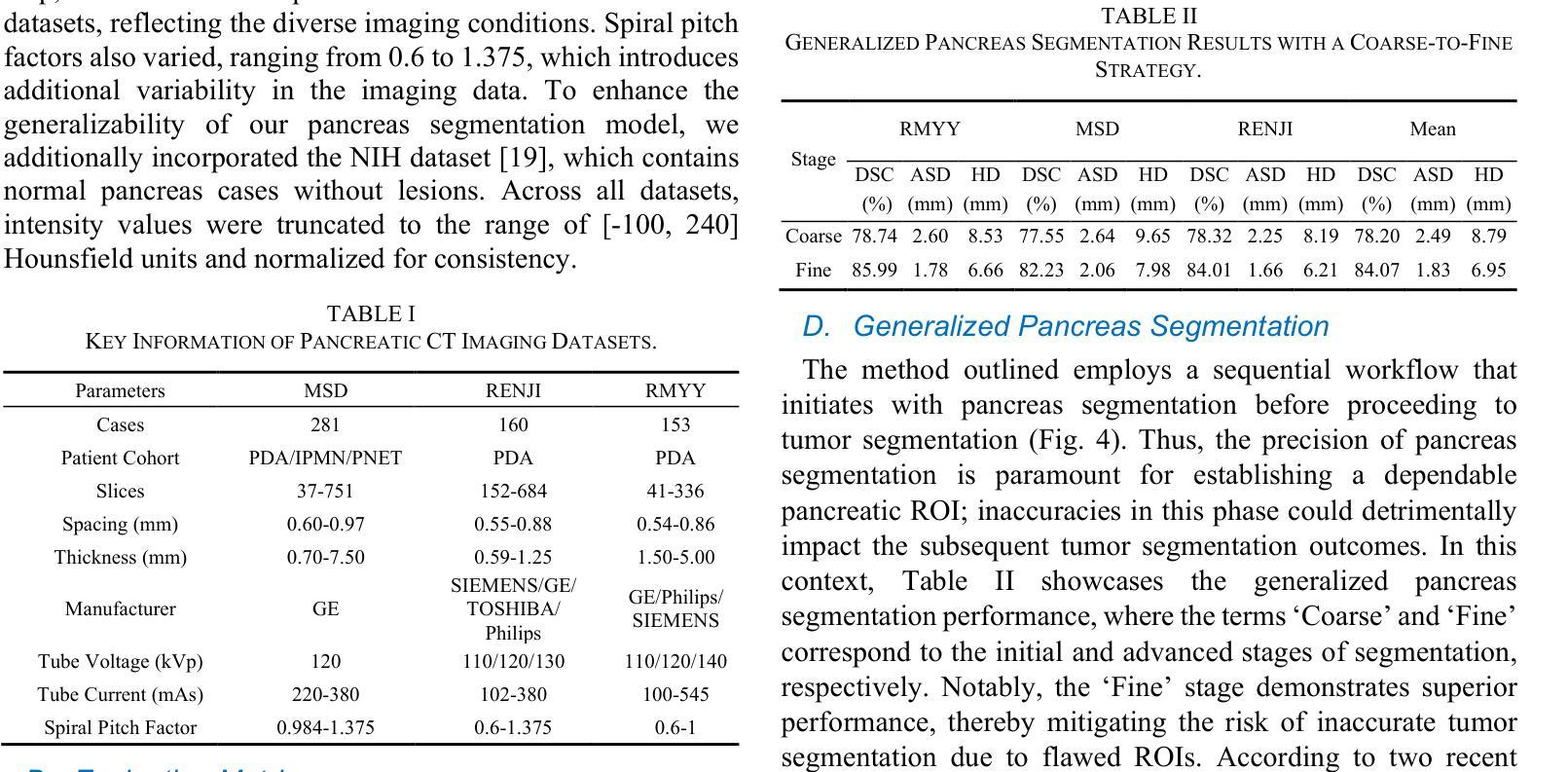
A Dual-Task Synergy-Driven Generalization Framework for Pancreatic Cancer Segmentation in CT Scans
Authors:Jun Li, Yijue Zhang, Haibo Shi, Minhong Li, Qiwei Li, Xiaohua Qian
Pancreatic cancer, characterized by its notable prevalence and mortality rates, demands accurate lesion delineation for effective diagnosis and therapeutic interventions. The generalizability of extant methods is frequently compromised due to the pronounced variability in imaging and the heterogeneous characteristics of pancreatic lesions, which may mimic normal tissues and exhibit significant inter-patient variability. Thus, we propose a generalization framework that synergizes pixel-level classification and regression tasks, to accurately delineate lesions and improve model stability. This framework not only seeks to align segmentation contours with actual lesions but also uses regression to elucidate spatial relationships between diseased and normal tissues, thereby improving tumor localization and morphological characterization. Enhanced by the reciprocal transformation of task outputs, our approach integrates additional regression supervision within the segmentation context, bolstering the model’s generalization ability from a dual-task perspective. Besides, dual self-supervised learning in feature spaces and output spaces augments the model’s representational capability and stability across different imaging views. Experiments on 594 samples composed of three datasets with significant imaging differences demonstrate that our generalized pancreas segmentation results comparable to mainstream in-domain validation performance (Dice: 84.07%). More importantly, it successfully improves the results of the highly challenging cross-lesion generalized pancreatic cancer segmentation task by 9.51%. Thus, our model constitutes a resilient and efficient foundational technological support for pancreatic disease management and wider medical applications. The codes will be released at https://github.com/SJTUBME-QianLab/Dual-Task-Seg.
胰腺癌以其较高的发病率和死亡率而著称,需要进行准确的病灶勾画以实现有效的诊断和干预治疗。由于成像的明显差异性和胰腺病灶的异质性特征(可能模拟正常组织并表现出显著的病人间差异),现有方法的通用性经常受到威胁。因此,我们提出了一个综合像素级分类和回归任务的通用框架,以准确勾画病灶并提高模型稳定性。该框架不仅致力于使分割轮廓与实际病灶对齐,还使用回归来阐明病变组织与正常组织之间的空间关系,从而提高肿瘤定位和形态表征。通过任务输出的相互转换,我们的方法将额外的回归监督整合到分割背景中,从双重任务的角度增强模型的通用性能力。此外,特征空间和输出空间中的双重自监督学习增强了模型的表示能力和稳定性,适用于不同的成像视图。在由三个具有显著差异的数据集组成的594个样本上进行的实验表明,我们的通用胰腺分割结果与主流的同域验证性能相当(Dice系数为84.07%)。更重要的是,它成功提高了具有挑战性的跨病灶通用胰腺癌分割任务的结果达9.51%。因此,我们的模型为胰腺疾病管理和更广泛的医学应用提供了稳健高效的基础技术支持。代码将发布在https://github.com/SJTUBME-QianLab/Dual-Task-Seg。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF accept by IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging (TMI) 2025
摘要
胰腺癌因其高发病率和高死亡率而备受关注,准确地进行病灶勾画对于有效的诊断和干预治疗至关重要。由于成像的显著变异性和胰腺病灶的异质性特征(可能模拟正常组织并表现出显著的患者间差异),现有方法的通用性往往受到影响。因此,我们提出了一个融合像素级分类和回归任务的通用框架,以准确勾画病灶并提高模型稳定性。该框架不仅寻求将分割轮廓与实际病灶对齐,而且利用回归来阐明病灶与正常组织之间的空间关系,从而改善肿瘤定位和形态表征。通过任务输出的相互转换,我们的方法将额外的回归监督整合到分割背景中,从双重任务的角度增强了模型的泛化能力。此外,特征空间和输出空间中的双重自监督学习增强了模型的表征能力和稳定性,适用于不同的成像视图。在由三个数据集组成的594个样本上进行实验,结果表明我们的泛化胰腺分割结果与主流的同域验证性能相当(Dice:84.07%)。更重要的是,它成功提高了极具挑战性的跨病灶泛化胰腺癌分割任务的结果达9.51%。因此,我们的模型为胰腺疾病管理和更广泛的医疗应用提供了稳健有效的基本技术支持。代码将发布在https://github.com/SJTUBME-QianLab/Dual-Task-Seg。
要点
- 胰腺癌由于其高发病率和死亡率,需要准确进行病灶勾画以进行有效诊断和治疗。
- 现有方法由于成像的变异性和胰腺病灶的异质性而缺乏泛化能力。
- 提出的框架融合了像素级分类和回归任务,以提高病灶勾画的准确性并增强模型稳定性。
- 该框架通过任务输出的相互转换和双重自监督学习增强了模型的泛化能力和表征能力。
- 实验结果表明,该框架在泛化胰腺分割任务上具有良好的性能,并在跨病灶分割任务上取得了显著改进。
- 该模型为胰腺疾病管理提供了稳健有效的技术支持,并有望应用于更广泛的医疗领域。
点此查看论文截图

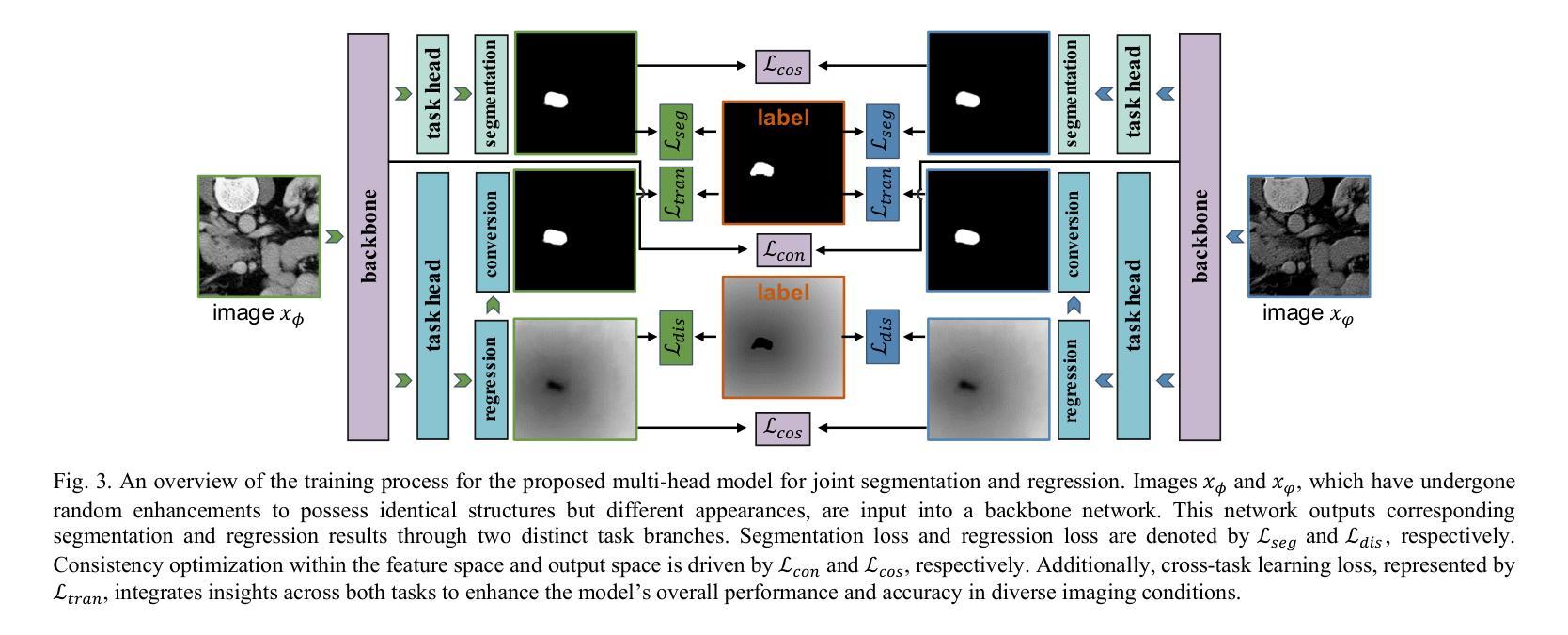
Towards Accurate and Interpretable Neuroblastoma Diagnosis via Contrastive Multi-scale Pathological Image Analysis
Authors:Zhu Zhu, Shuo Jiang, Jingyuan Zheng, Yawen Li, Yifei Chen, Manli Zhao, Weizhong Gu, Feiwei Qin, Jinhu Wang, Gang Yu
Neuroblastoma, adrenal-derived, is among the most common pediatric solid malignancies, characterized by significant clinical heterogeneity. Timely and accurate pathological diagnosis from hematoxylin and eosin-stained whole-slide images is critical for patient prognosis. However, current diagnostic practices primarily rely on subjective manual examination by pathologists, leading to inconsistent accuracy. Existing automated whole-slide image classification methods encounter challenges such as poor interpretability, limited feature extraction capabilities, and high computational costs, restricting their practical clinical deployment. To overcome these limitations, we propose CMSwinKAN, a contrastive-learning-based multi-scale feature fusion model tailored for pathological image classification, which enhances the Swin Transformer architecture by integrating a Kernel Activation Network within its multilayer perceptron and classification head modules, significantly improving both interpretability and accuracy. By fusing multi-scale features and leveraging contrastive learning strategies, CMSwinKAN mimics clinicians’ comprehensive approach, effectively capturing global and local tissue characteristics. Additionally, we introduce a heuristic soft voting mechanism guided by clinical insights to bridge patch-level predictions to whole-slide image-level classifications seamlessly. We verified the CMSwinKAN on the publicly available BreakHis dataset and the PpNTs dataset, which was established by our hospital. Results demonstrate that CMSwinKAN performs better than existing state-of-the-art pathology-specific models pre-trained on large datasets. Our source code is available at https://github.com/JSLiam94/CMSwinKAN.
神经母细胞瘤是肾上腺来源的最常见的儿童实体恶性肿瘤之一,具有显著的临床异质性。及时而准确的病理诊断对于患者的预后至关重要,这些诊断通常基于苏木精和伊红染色的全切片图像。然而,当前的诊断方法主要依赖于病理医师的主观手动检查,导致诊断准确性不一致。现有的全自动切片图像分类方法面临可解释性差、特征提取能力有限以及计算成本高的挑战,限制了其在临床实践中的部署应用。为了克服这些限制,我们提出了CMSwinKAN,这是一种基于对比学习的多尺度特征融合模型,专为病理图像分类而定制。我们通过将内核激活网络集成到Swin Transformer架构的多层感知器和分类头模块中,增强了其可解释性和准确性。通过融合多尺度特征并利用对比学习策略,CMSwinKAN模仿了临床医生全面的诊断方法,有效地捕捉了全局和局部组织特征。此外,我们还引入了一种受临床见解启发的新型软投票机制,将斑块级别的预测无缝地桥接到全切片图像级别的分类。我们在公开可用的BreakHis数据集和由我们医院建立PpNTs数据集上验证了CMSwinKAN。结果表明,CMSwinKAN的性能优于现有最先进的、在大数据集上预训练的病理学专用模型。我们的源代码可在https://github.com/JSLiam94/CMSwinKAN获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10pages, 8 figures
Summary
本文提出了一种基于对比学习的多尺度特征融合模型CMSwinKAN,用于神经母细胞瘤等肾上腺衍生固体肿瘤的病理图像分类。该模型结合了Swin Transformer架构和Kernel Activation Network,提高了模型的解释性和准确性。通过融合多尺度特征和采用对比学习策略,CMSwinKAN有效捕捉全局和局部组织特征,模拟医生的综合诊断方法。此外,还引入了一种基于临床见解的启发式软投票机制,将补丁级别的预测无缝地桥接到整个幻灯片图像级别的分类。在公开可用的BreakHis数据集和我们医院建立的PpNTs数据集上的验证结果表明,CMSwinKAN的性能优于现有的最新病理学预训练模型。
Key Takeaways
- 神经母细胞瘤是常见的儿童固体肿瘤,病理诊断对其预后至关重要。
- 当前诊断方法主要依赖病理医师的主观手动检查,存在准确性不一致的问题。
- CMSwinKAN模型结合了Swin Transformer和Kernel Activation Network,提高病理图像分类的准确性和解释性。
- CMSwinKAN通过融合多尺度特征和对比学习策略,有效捕捉全局和局部组织特性,模拟医生的诊断过程。
- 引入启发式软投票机制,将补丁级别预测无缝转换为整个幻灯片图像级别分类。
- 在公开和医院内部数据集上的验证结果表明,CMSwinKAN性能优于现有最新病理学预训练模型。
点此查看论文截图

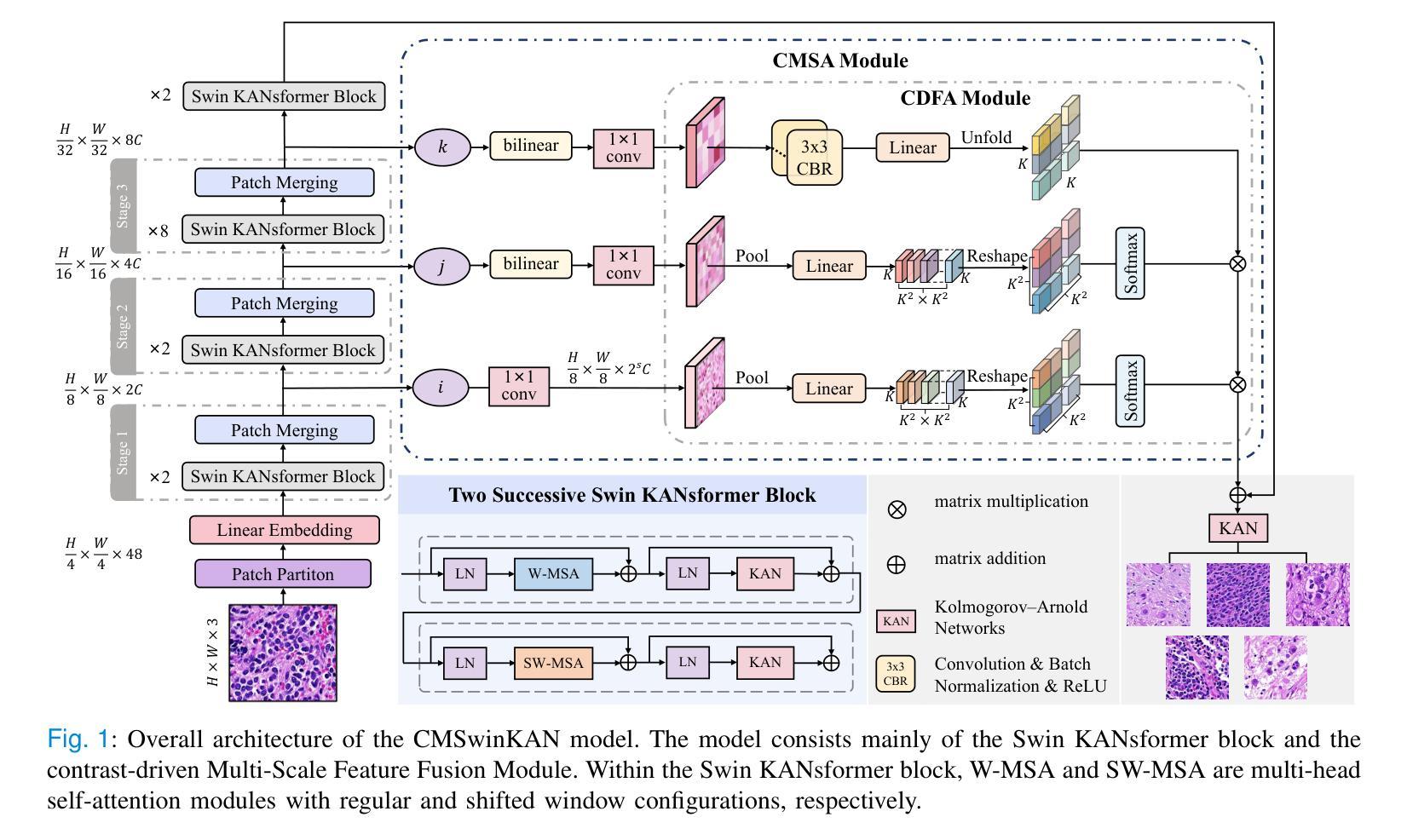
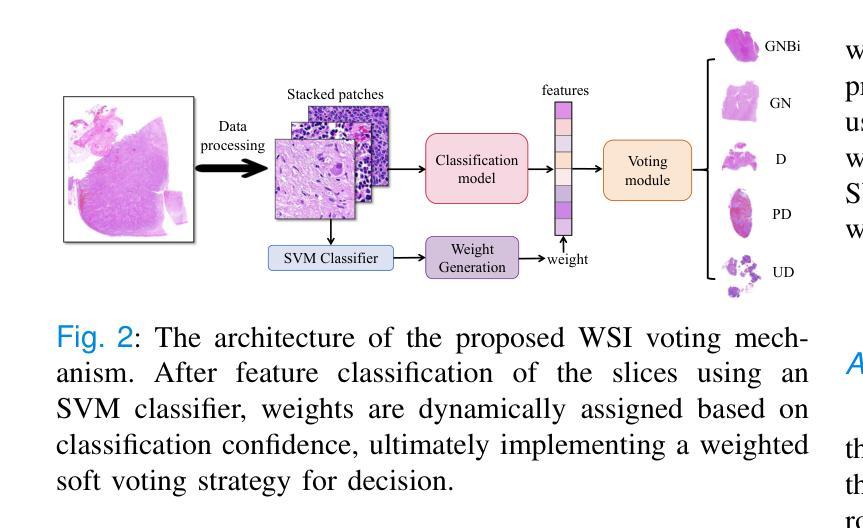
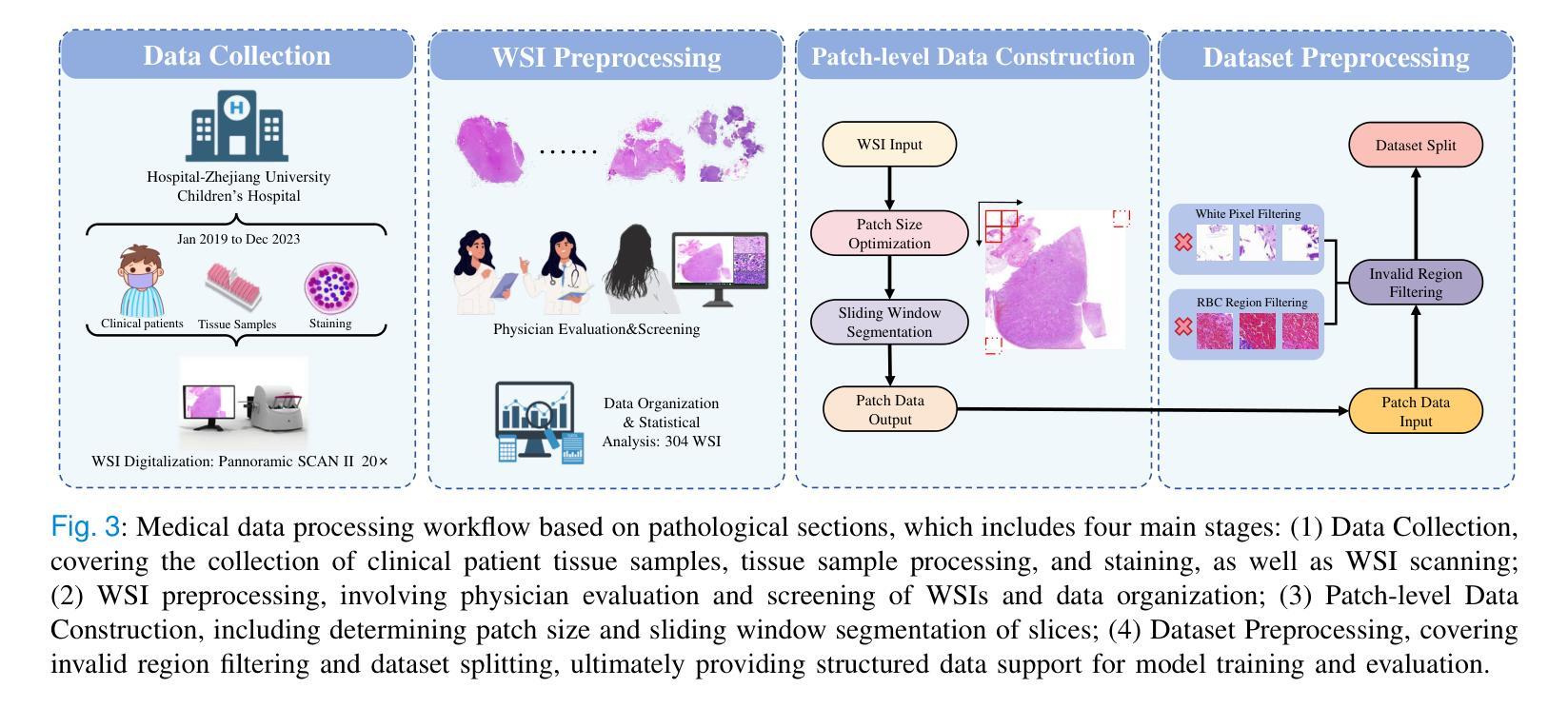
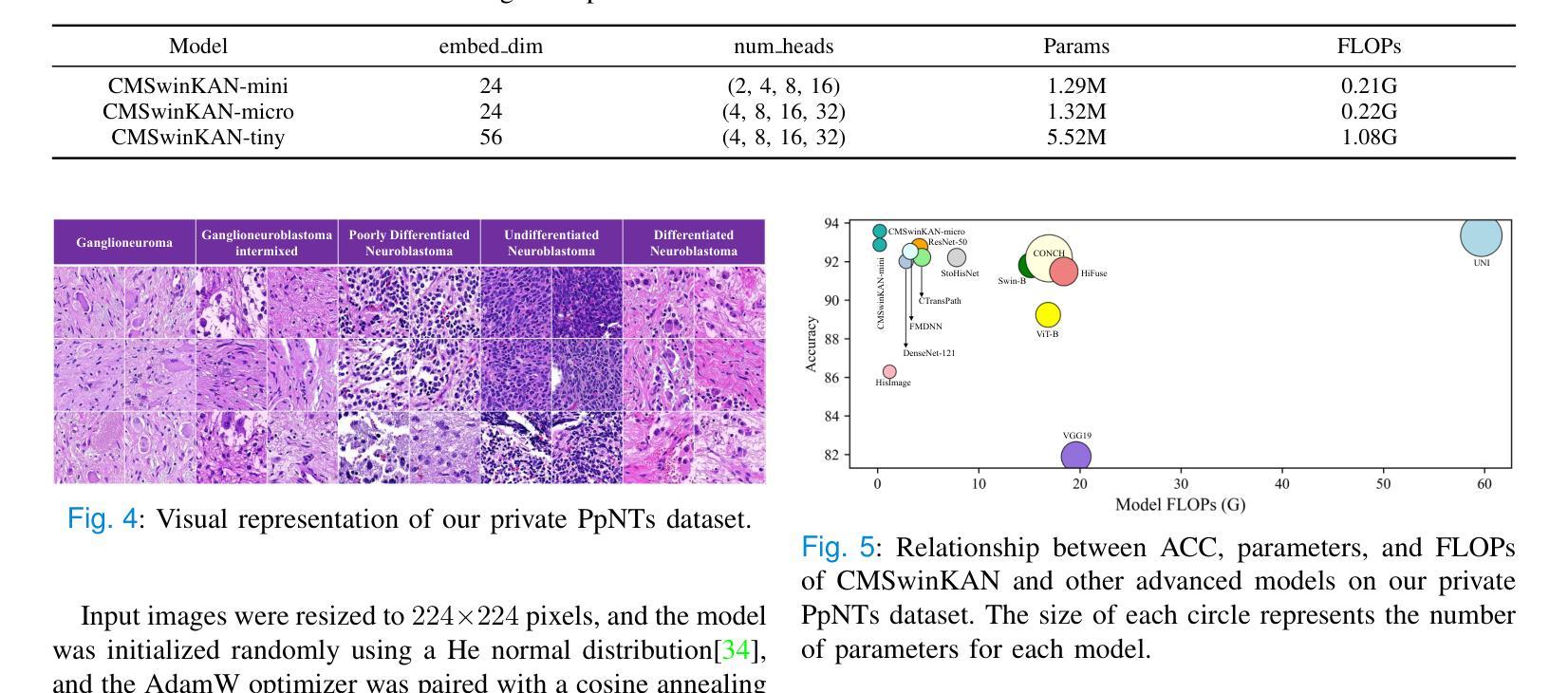
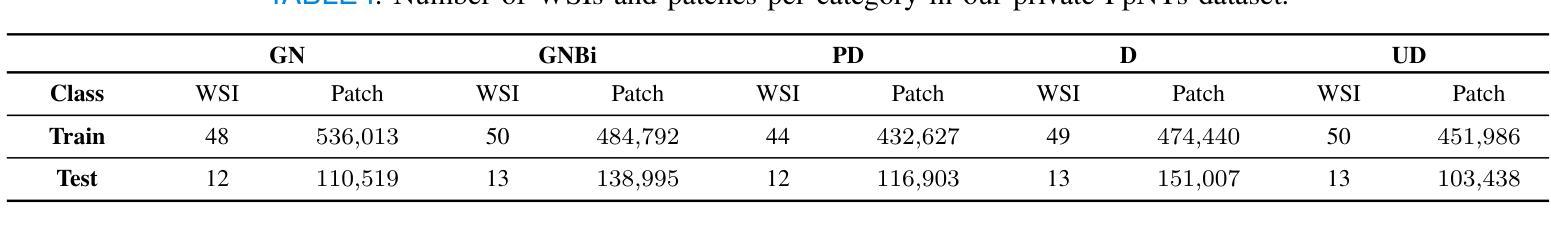
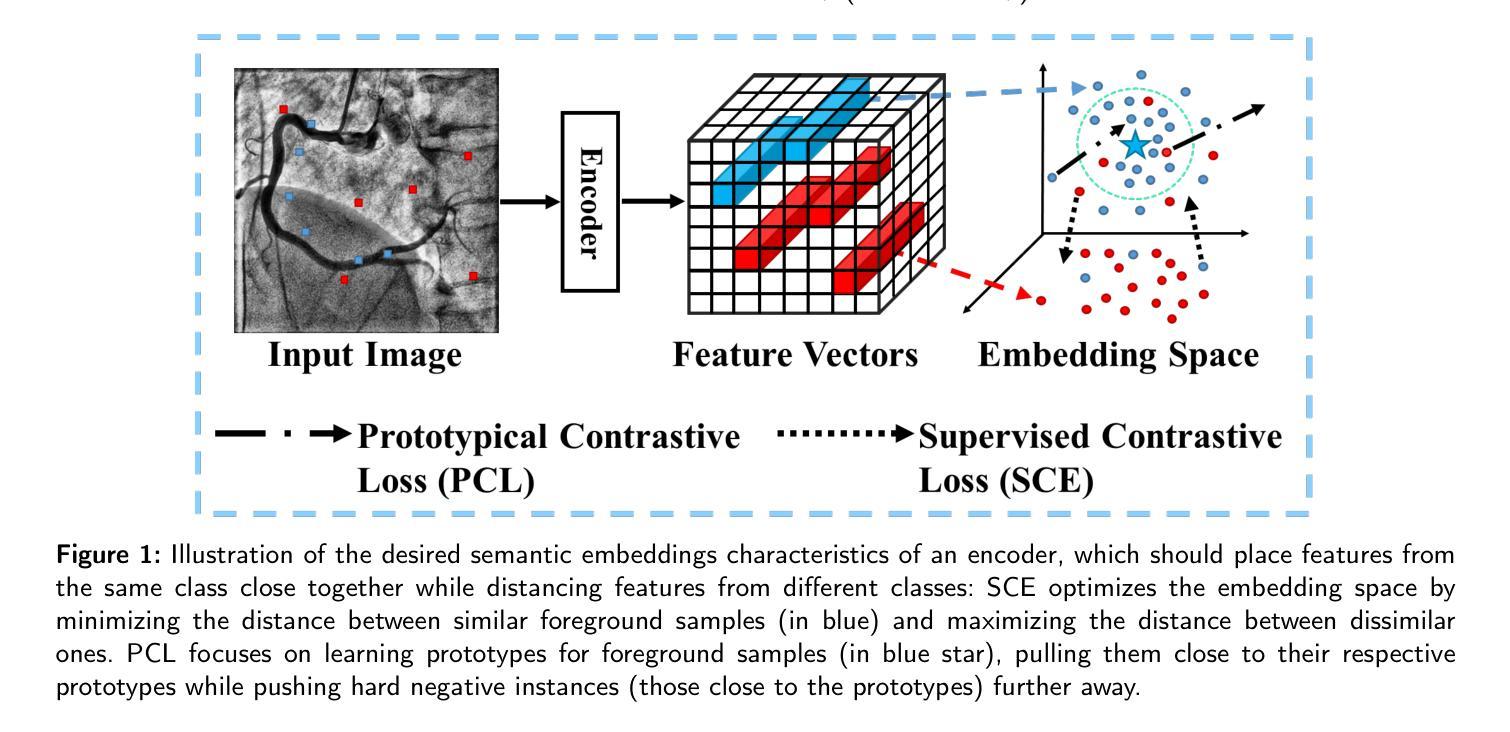
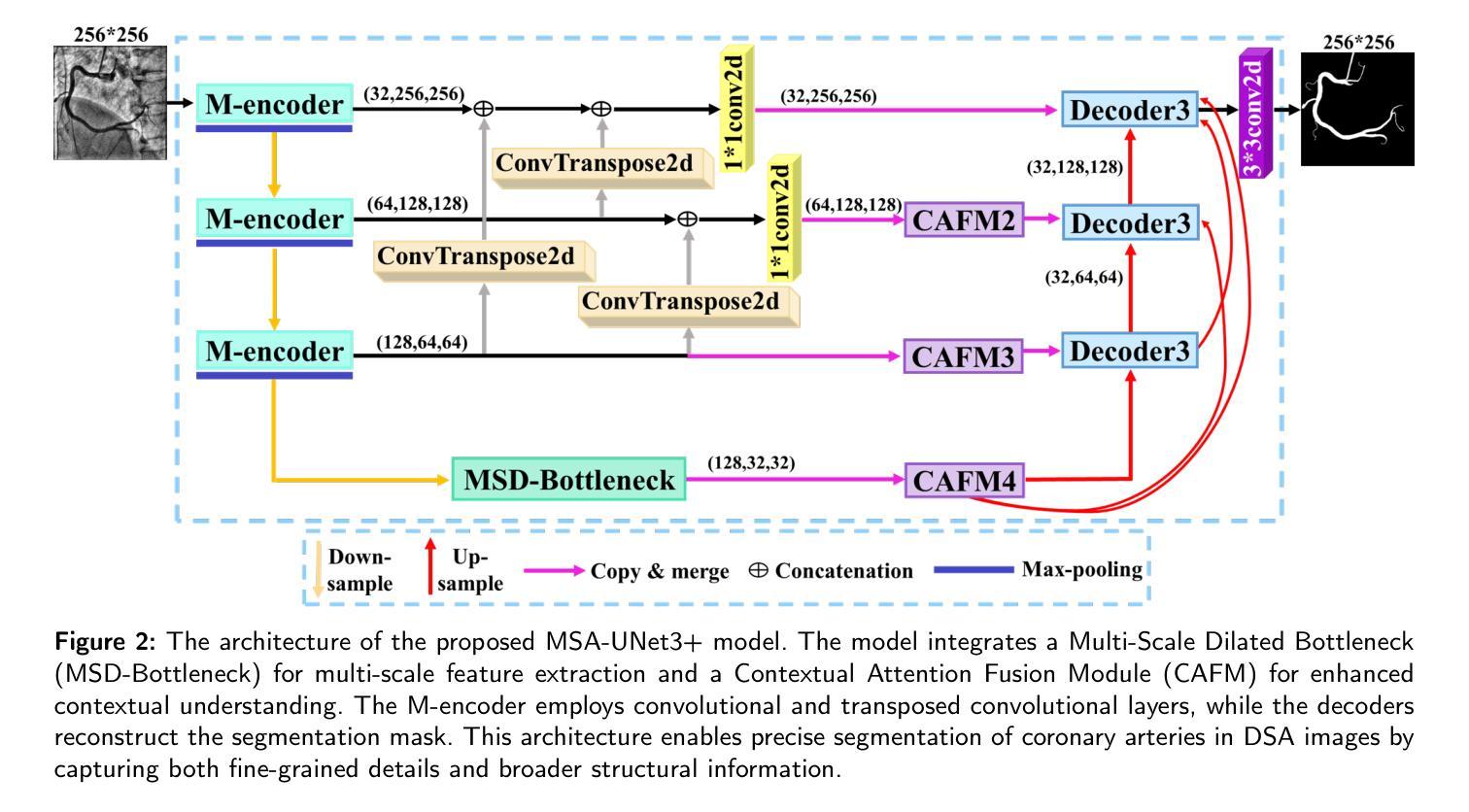
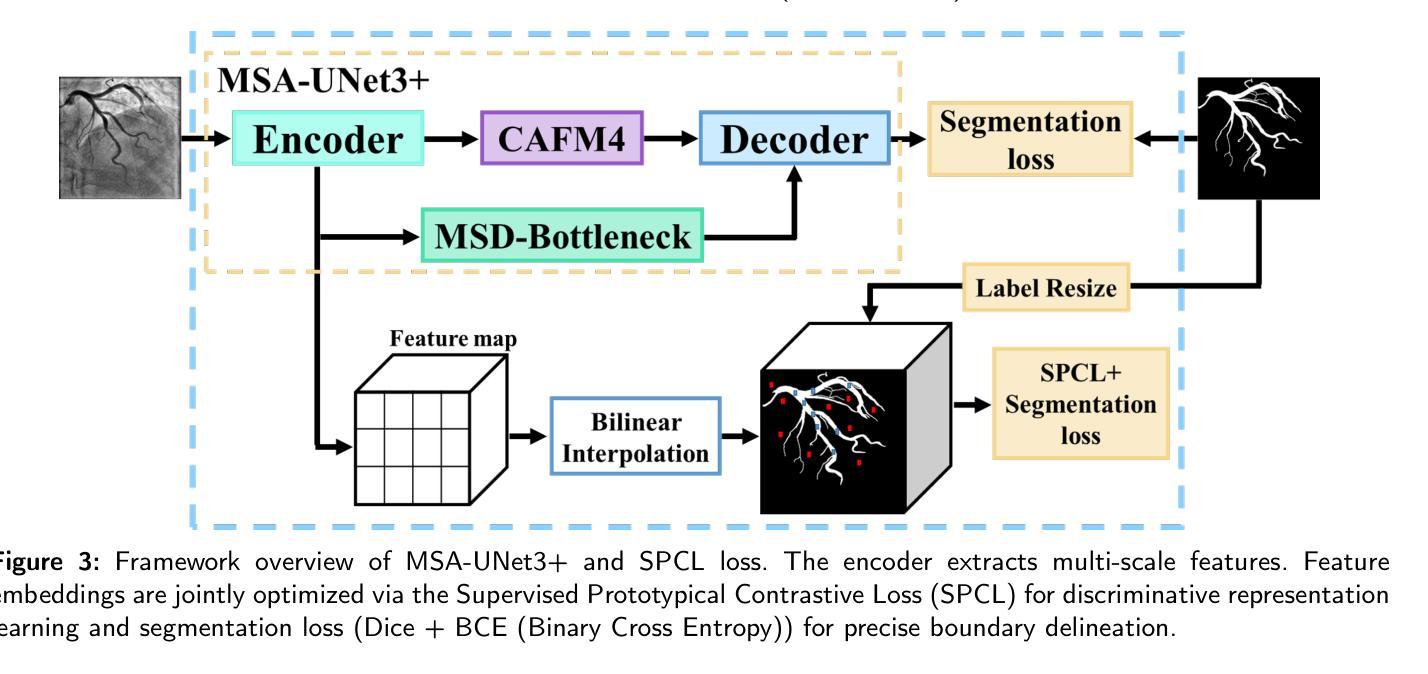
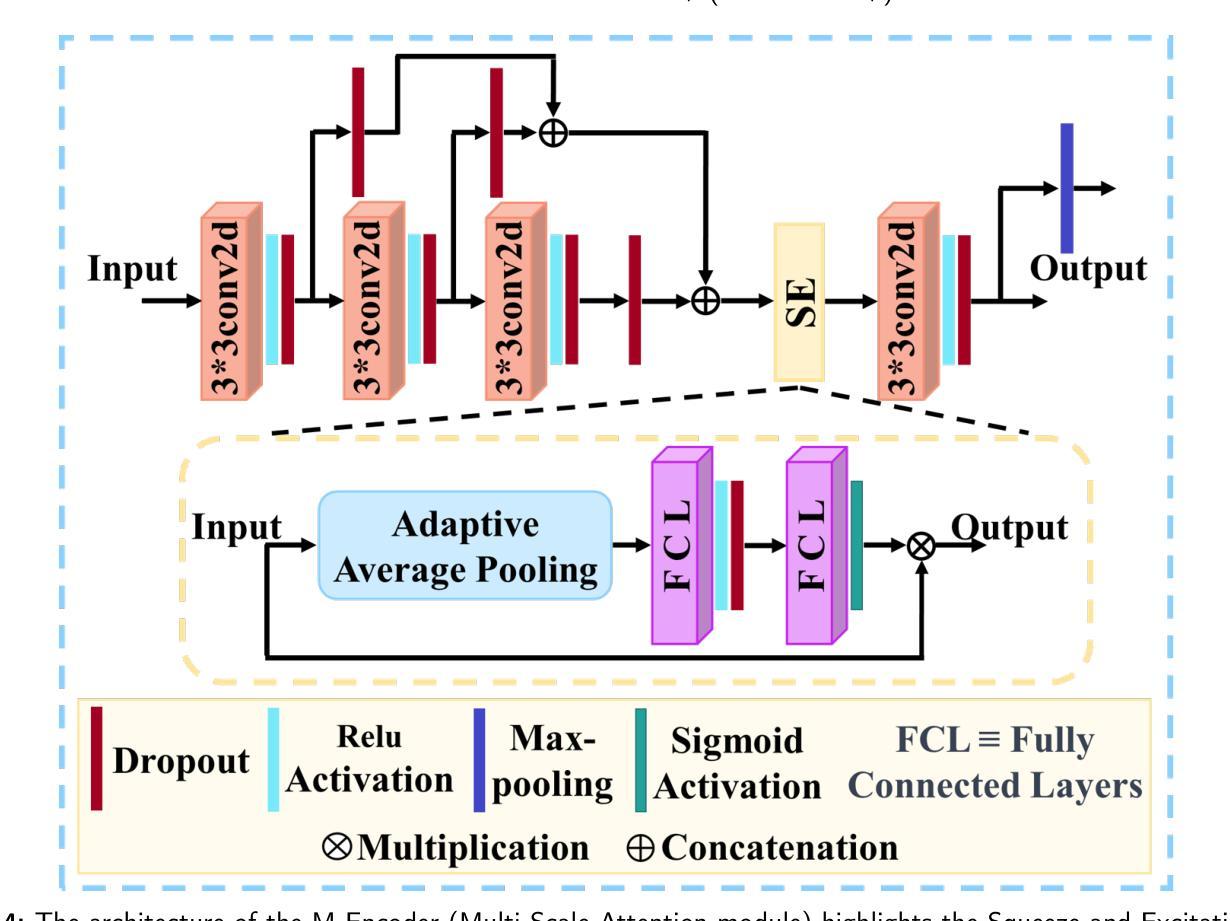
MSA-UNet3+: Multi-Scale Attention UNet3+ with New Supervised Prototypical Contrastive Loss for Coronary DSA Image Segmentation
Authors:Rayan Merghani Ahmed, Adnan Iltaf, Mohamed Elmanna, Gang Zhao, Hongliang Li, Yue Du, Bin Li, Shoujun Zhou
Accurate segmentation of coronary Digital Subtraction Angiography images is essential to diagnose and treat coronary artery diseases. Despite advances in deep learning, challenges such as high intra-class variance and class imbalance limit precise vessel delineation. Most existing approaches for coronary DSA segmentation cannot address these issues. Also, existing segmentation network’s encoders do not directly generate semantic embeddings, which could enable the decoder to reconstruct segmentation masks effectively from these well-defined features. We propose a Supervised Prototypical Contrastive Loss that fuses supervised and prototypical contrastive learning to enhance coronary DSA image segmentation. The supervised contrastive loss enforces semantic embeddings in the encoder, improving feature differentiation. The prototypical contrastive loss allows the model to focus on the foreground class while alleviating the high intra-class variance and class imbalance problems by concentrating only on the hard-to-classify background samples. We implement the proposed SPCL loss within an MSA-UNet3+: a Multi-Scale Attention-Enhanced UNet3+ architecture. The architecture integrates key components: a Multi-Scale Attention Encoder and a Multi-Scale Dilated Bottleneck designed to enhance multi-scale feature extraction and a Contextual Attention Fusion Module built to keep fine-grained details while improving contextual understanding. Experiments on a private coronary DSA dataset show that MSA-UNet3+ outperforms state-of-the-art methods, achieving the highest Dice coefficient and F1-score and significantly reducing ASD and ACD. The developed framework provides clinicians with precise vessel segmentation, enabling accurate identification of coronary stenosis and supporting informed diagnostic and therapeutic decisions. The code will be released at https://github.com/rayanmerghani/MSA-UNet3plus.
冠状动脉数字减影血管造影(DSA)图像的准确分割对于冠状动脉疾病的诊断和治疗至关重要。尽管深度学习有所进展,但类内高方差和类不平衡等挑战仍然限制了血管精确勾勒。大多数现有的冠状动脉DSA分割方法无法解决这些问题。此外,现有分割网络的编码器并没有直接生成语义嵌入,这可能会使解码器无法从这些定义明确的功能中有效地重建分割掩模。我们提出了一种有监督原型对比损失(Supervised Prototypical Contrastive Loss),它将有监督学习和原型对比学习相结合,以提高冠状动脉DSA图像分割的效果。有监督对比损失在编码器中实施语义嵌入,提高特征差异。原型对比损失允许模型专注于前景类,并通过仅关注难以分类的背景样本,缓解类内高方差和类不平衡问题。我们在MSA-UNet3+中实现了所提出的SPCL损失:一种集多尺度注意力增强UNet3+架构。该架构集成了关键组件:多尺度注意力编码器和多尺度膨胀瓶颈,旨在增强多尺度特征提取和上下文理解,以及构建用于保持精细细节的同时改善上下文理解的上下文注意力融合模块。在私有冠状动脉DSA数据集上的实验表明,MSA-UNet3+优于最先进的方法,获得了最高的Dice系数和F1分数,并显著降低了ASD和ACD。所开发的框架为临床医生提供了精确的血管分割,能够准确识别冠状动脉狭窄,并支持做出明智的诊断和治疗决策。代码将在https://github.com/rayanmerghani/MSA-UNet3plus发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Work in progress
Summary
本文提出一种融合监督对比损失和原型对比损失的冠状动脉数字减影血管造影图像分割方法,以解决现有方法面临的高内类方差和类别不平衡等问题。该方法通过加强编码器中的语义嵌入来提高特征区分度,并通过原型对比损失使模型专注于前景类别,从而减轻高内类方差和类别不平衡问题。实验结果表明,该方法在私有冠状动脉DSA数据集上优于现有先进技术,实现了最高的Dice系数和F1分数,并显著降低了ASD和ACD。此框架可为临床医生提供精确的血管分割,有助于准确识别冠状动脉狭窄并支持医生做出诊断和治疗的决策。
Key Takeaways
- 冠状动脉数字减影血管造影(DSA)图像的准确分割对诊断和治疗冠状动脉疾病至关重要。
- 现有方法面临高内类方差和类别不平衡的挑战,影响精确血管轮廓的描绘。
- 提出的监督原型对比损失(SPCL)融合了监督对比学习和原型对比学习,旨在提高冠状动脉DSA图像分割的效果。
- SPCL损失在编码器阶段强制生成语义嵌入,改善特征区分度,并通过原型对比损失关注前景类别,减轻高内类方差和类别不平衡问题。
- 采用多尺度注意力增强UNet3+架构(MSA-UNet3+)实现SPCL损失,包括多尺度注意力编码器、多尺度扩张瓶颈和上下文注意力融合模块,旨在提高多尺度特征提取和上下文理解能力。
- 在私有冠状动脉DSA数据集上的实验表明,MSA-UNet3+方法优于现有技术,提高了Dice系数和F1分数,并降低了ASD和ACD。
点此查看论文截图

Instance Segmentation of Scene Sketches Using Natural Image Priors
Authors:Mia Tang, Yael Vinker, Chuan Yan, Lvmin Zhang, Maneesh Agrawala
Sketch segmentation involves grouping pixels within a sketch that belong to the same object or instance. It serves as a valuable tool for sketch editing tasks, such as moving, scaling, or removing specific components. While image segmentation models have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in recent years, sketches present unique challenges for these models due to their sparse nature and wide variation in styles. We introduce InkLayer, a method for instance segmentation of raster scene sketches. Our approach adapts state-of-the-art image segmentation and object detection models to the sketch domain by employing class-agnostic fine-tuning and refining segmentation masks using depth cues. Furthermore, our method organizes sketches into sorted layers, where occluded instances are inpainted, enabling advanced sketch editing applications. As existing datasets in this domain lack variation in sketch styles, we construct a synthetic scene sketch segmentation dataset, InkScenes, featuring sketches with diverse brush strokes and varying levels of detail. We use this dataset to demonstrate the robustness of our approach.
草图分割涉及将属于同一对象或实例的草图内的像素进行分组。它作为草图编辑任务(如移动、缩放或删除特定组件)的宝贵工具。近年来,图像分割模型表现出了显著的能力,但由于草图的稀疏性和风格上的巨大差异,这些模型面临着独特的挑战。我们引入了InkLayer,这是一种基于矢量的场景草图实例分割方法。我们的方法通过采用类无关的微调和使用深度线索细化分割掩膜,将最先进的图像分割和对象检测模型适应到草图领域。此外,我们的方法将草图组织成有序的层,其中遮挡的实例被填充,从而实现高级的草图编辑应用程序。由于该领域的现有数据集缺乏草图风格的多样性,我们构建了一个合成场景草图分割数据集InkScenes,其中包含具有不同笔触和细节级别的草图。我们使用此数据集来展示我们方法的稳健性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project website: https://inklayer.github.io
Summary
本文介绍了InkLayer方法,用于对场景草图进行实例分割。该方法采用先进的图像分割和对象检测模型,通过类别无关的微调并利用深度线索完善分割掩模,以适应草图领域。此外,该方法可将草图组织成有序层,对遮挡的实例进行填充,实现高级草图编辑应用。为解决现有数据集风格缺乏变化的问题,构建了一个合成场景草图分割数据集InkScenes。
Key Takeaways
- Sketch segmentation旨在将同一对象或实例的像素进行分组,对于草图编辑任务(如移动、缩放或删除特定组件)具有重要价值。
- InkLayer方法采用先进的图像分割和对象检测模型,通过类别无关的微调来适应草图领域。
- InkLayer方法利用深度线索完善分割掩模,提高模型的适应性。
- 该方法将草图组织成有序层,便于进行高级草图编辑应用。
- 现存数据集缺乏草图风格的变化,缺乏足够的多样性以适应不同的模型需求。
- 为解决上述问题,构建了一个合成场景草图分割数据集InkScenes,包含不同笔触和细节层次的草图。
点此查看论文截图

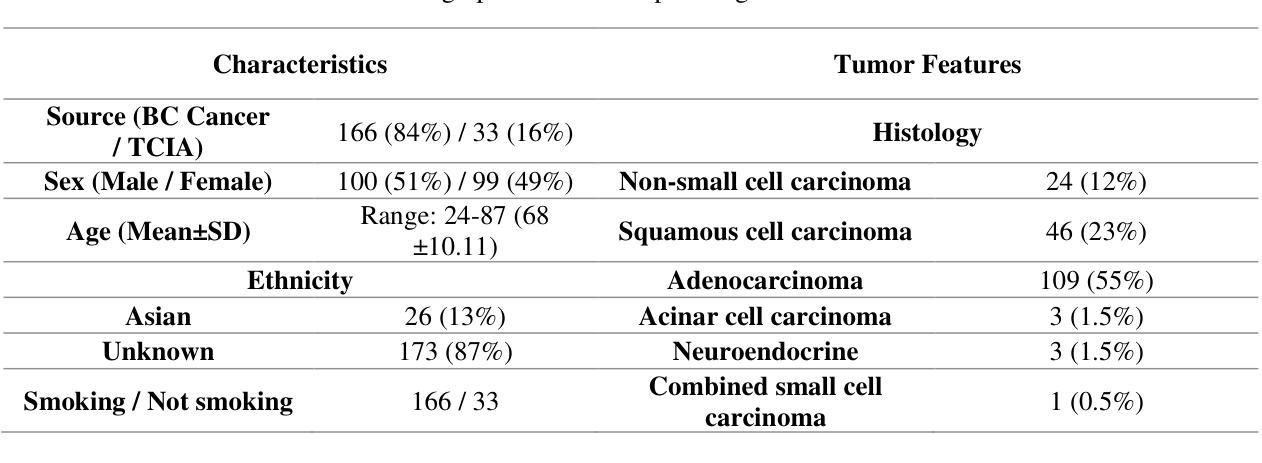
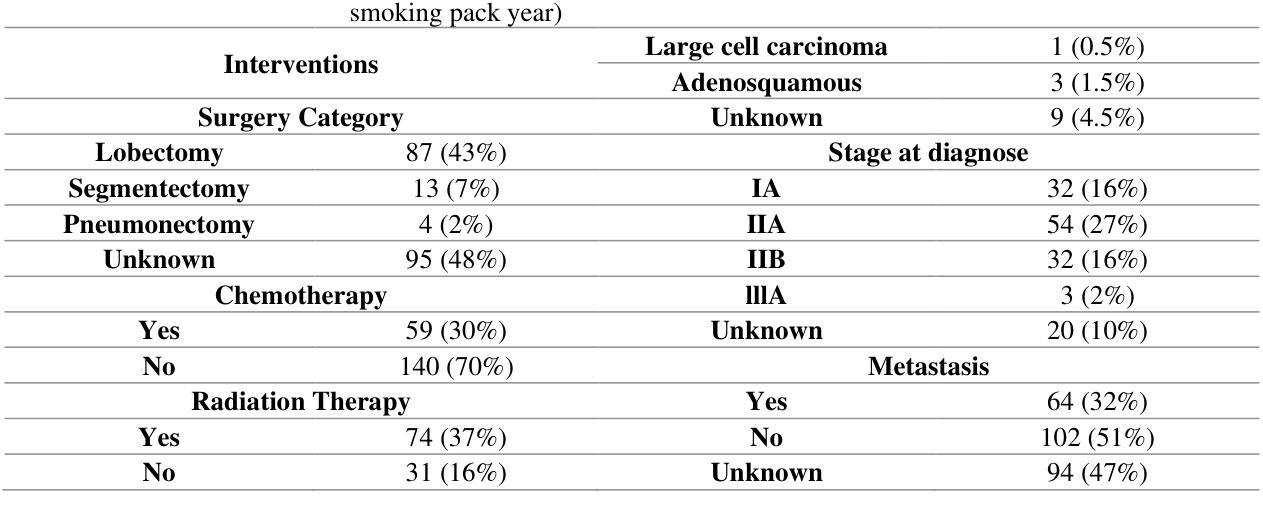
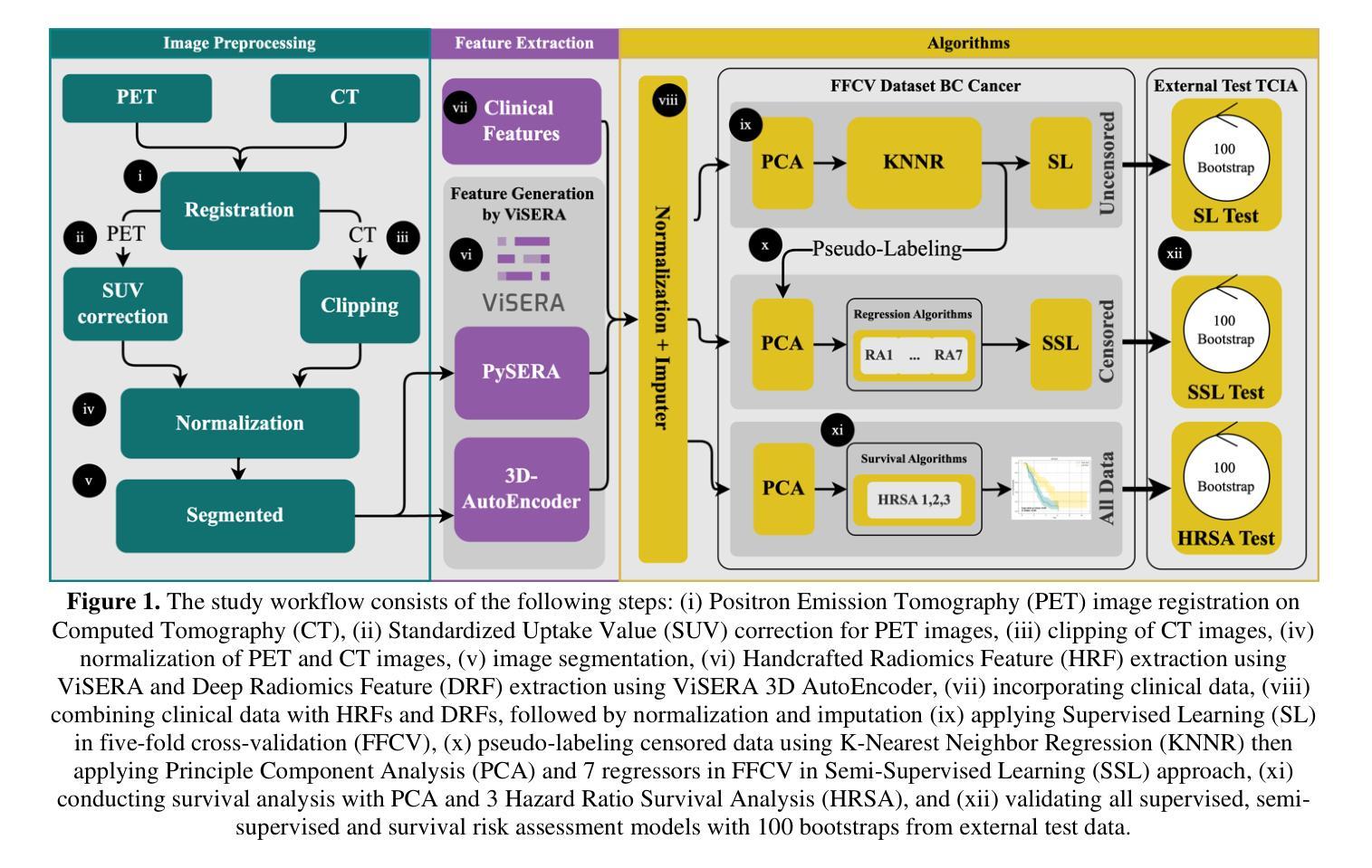
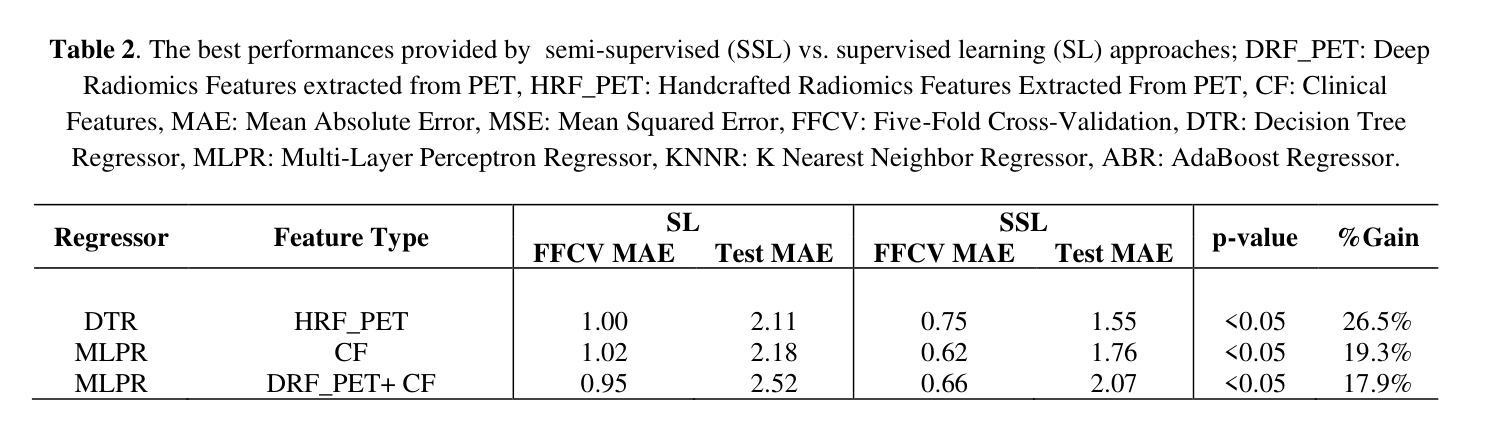
Censor-Aware Semi-Supervised Survival Time Prediction in Lung Cancer Using Clinical and Radiomics Features
Authors:Arman Gorji, Ali Fathi Jouzdani, Nima Sanati, Amir Mahmoud Ahmadzadeh, Ren Yuan, Arman Rahmim, Mohammad R. Salmanpour
Objectives: Lung cancer poses a significant global health challenge, necessitating improved prognostic methods for personalized treatment. This study introduces a censor-aware semi-supervised learning (SSL) framework that integrates clinical and imaging data, addressing biases in traditional models handling censored data. Methods: We analyzed clinical, PET and CT data from 199 lung cancer patients from public and local data respositories, focusing on overall survival (OS) time as the primary outcome. Handcrafted (HRF) and Deep Radiomics features (DRF) were extracted after preprocessing using ViSERA software and were combined with clinical features (CF). Feature dimensions were optimized using Principal Component Analysis (PCA), followed by the application of supervised learning (SL) and SSL. SSL incorporated pseudo-labeling of censored data to improve performance. Seven regressors and three hazard ratio survival analysis (HRSA) algorithms were optimized using five-fold cross-validation, grid search and external test bootstrapping. Results: For PET HRFs, SSL reduced the mean absolute error (MAE) by 26.5%, achieving 1.55 years with PCA+decision tree regression, compared to SL’s 2.11 years with PCA+KNNR (p<0.05). Combining HRFs (CT_HRF) and DRFs from CT images using SSL+PCA+KNNR achieved an MAE of 2.08 years, outperforming SL’s 2.26 years by 7.96% (p<0.05). In HRSA, CT_HRF applied to PCA+Component Wise Gradient Boosting Survival Analysis achieved an external c-index of 0.65, effectively differentiating high- and low-risk groups. Conclusions: We demonstrated that the SSL strategy significantly outperforms SL across PET, CT, and CF. As such, censor-aware SSL applied to HRFs from PET images significantly improved survival prediction performance by 26.5% compared to the SL approach.
目标:肺癌构成一项重大的全球健康挑战,需要改进预测方法以实现个性化治疗。本研究引入了一种有审查意识的半监督学习(SSL)框架,该框架结合了临床和成像数据,解决了传统模型在处理审查数据时的偏见问题。
方法:我们分析了来自公共和本地数据仓库的199名肺癌患者的临床、PET和CT数据,以总生存期(OS)时间为主要结果。使用ViSERA软件预处理后,提取了手工特征(HRF)和深度放射学特征(DRF),并与临床特征(CF)相结合。使用主成分分析(PCA)优化特征维度,然后应用监督学习(SL)和SSL。SSL通过伪标记审查数据来提高性能。使用五折交叉验证、网格搜索和外部测试自助法对七个回归器和三种风险比率生存分析(HRSA)算法进行了优化。
结果:对于PET的HRF,SSL将平均绝对误差(MAE)降低了26.5%,使用PCA+决策树回归达到1.55年,而SL使用PCA+KNNR为2.11年(p<0.05)。使用SSL+PCA+KNNR结合来自CT图像的HRF和DRF,MAE为2.08年,优于SL的2.26年,提高了7.96%(p<0.05)。在HRSA中,将CT_HRF应用于PCA+组件智慧梯度提升生存分析达到了外部c指数为0.65,有效地区分了高风险组和低风险组。
结论:我们证明SSL策略在PET、CT和CF方面显著优于SL。因此,与SL方法相比,应用于PET图像HRF的有审查意识的SSL将生存预测性能提高了26.5%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 4 Figures and 4 Tables
Summary:本研究旨在应对肺癌预后预测方法的挑战,提出一种融合临床与成像数据的半监督学习框架,该框架能够处理带有审查的数据中的偏见问题。通过对PET和CT影像数据以及临床数据的分析,本研究发现该半监督学习方法能够提高预后预测的准确度。对比只使用监督学习方法,该半监督学习方法的预测误差降低了近百分之二十五。对影像特征的有效组合进一步提升了模型的性能。研究结论表明半监督学习框架在处理肺癌患者的预后预测问题上表现优异。
Key Takeaways:
- 本研究引入了半监督学习框架以整合临床和成像数据,解决传统模型处理审查数据时存在的偏见问题。
- 研究采用了PET和CT影像数据以及临床数据,关注的主要结果是患者的总体生存时间。
- 半监督学习方法相较于传统监督学习方法显著提高了预后预测的准确度,预测误差降低了约百分之二十五。
- 结合影像特征的临床特征可以进一步优化模型性能。
- 通过使用主成分分析(PCA)对特征维度进行优化后,模型性能得到进一步提升。
- HRSA算法对于区分高风险和低风险患者群体具有良好的效果,其外部一致性指数达到了0.65。
点此查看论文截图

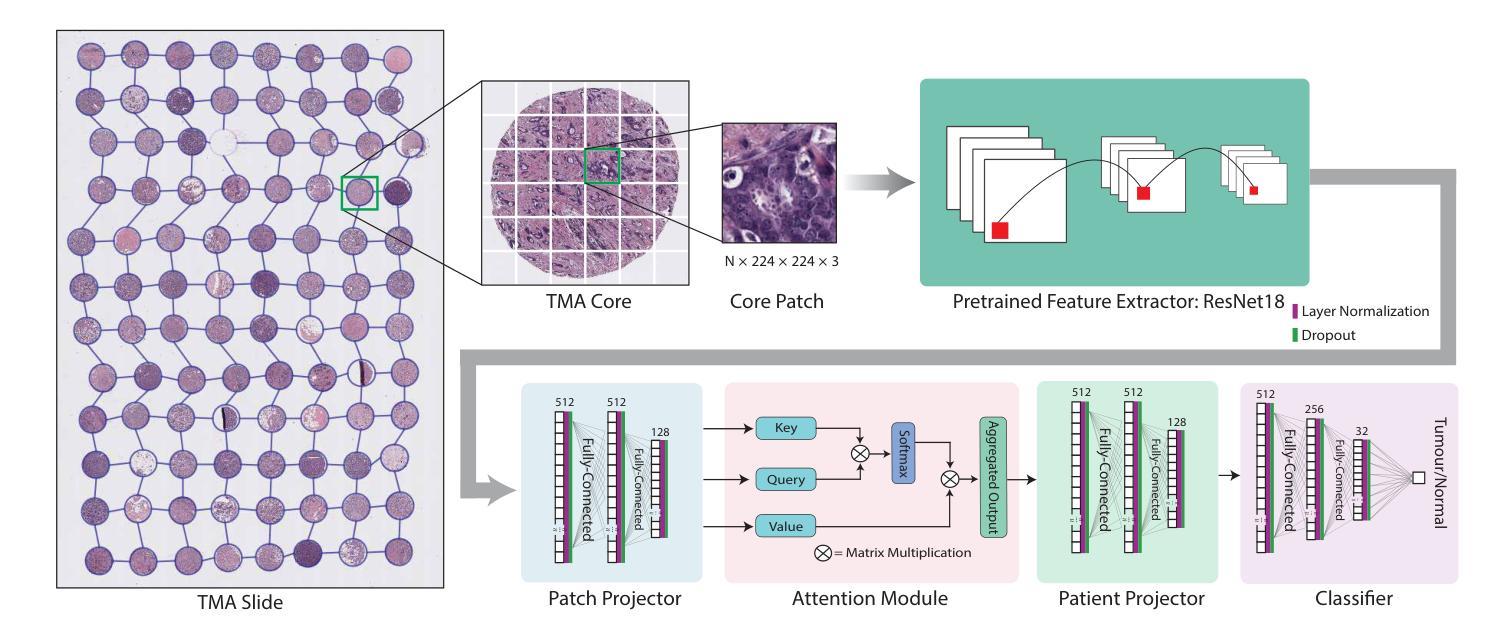
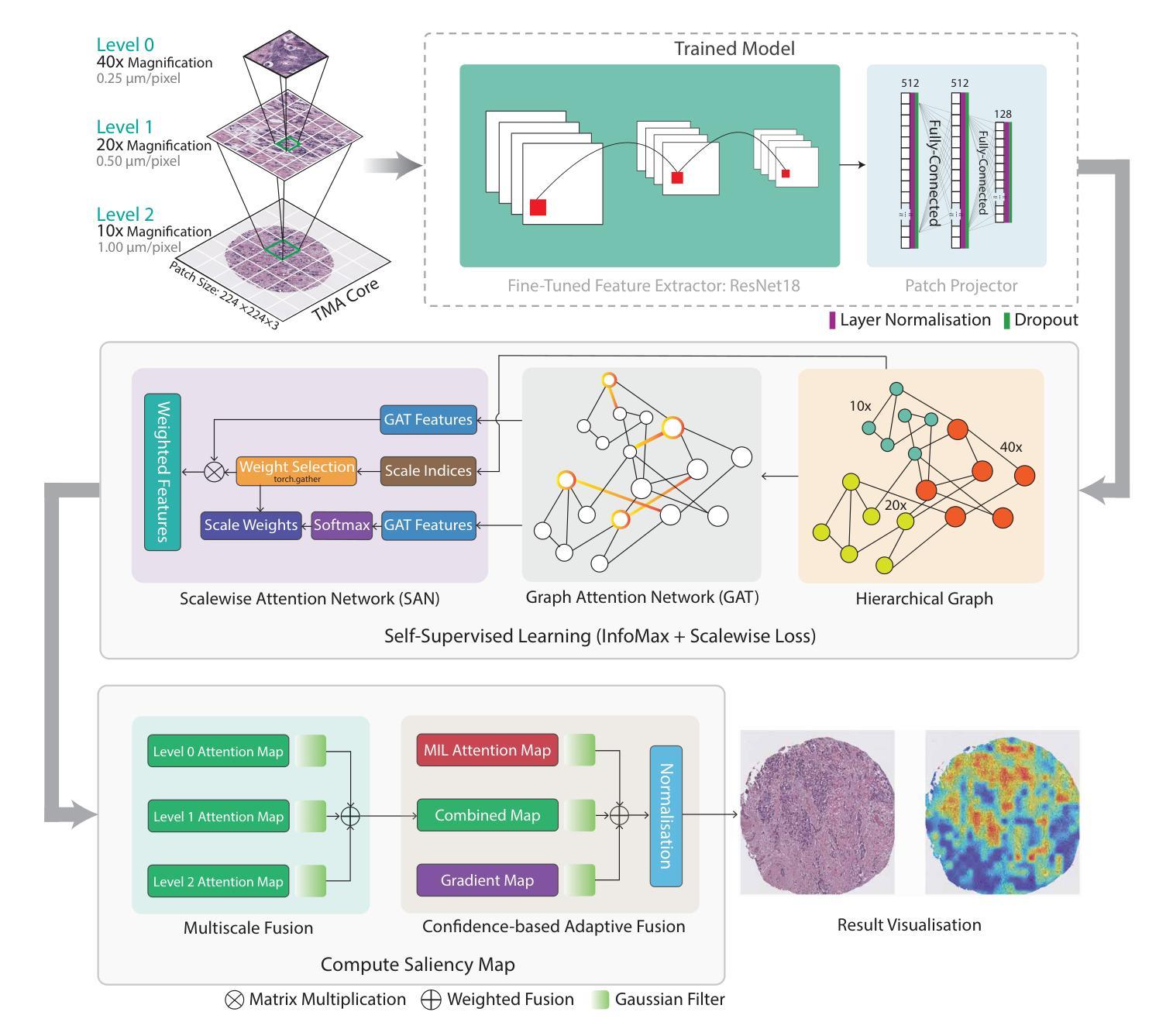
GRAPHITE: Graph-Based Interpretable Tissue Examination for Enhanced Explainability in Breast Cancer Histopathology
Authors:Raktim Kumar Mondol, Ewan K. A. Millar, Peter H. Graham, Lois Browne, Arcot Sowmya, Erik Meijering
Explainable AI (XAI) in medical histopathology is essential for enhancing the interpretability and clinical trustworthiness of deep learning models in cancer diagnosis. However, the black-box nature of these models often limits their clinical adoption. We introduce GRAPHITE (Graph-based Interpretable Tissue Examination), a post-hoc explainable framework designed for breast cancer tissue microarray (TMA) analysis. GRAPHITE employs a multiscale approach, extracting patches at various magnification levels, constructing an hierarchical graph, and utilising graph attention networks (GAT) with scalewise attention (SAN) to capture scale-dependent features. We trained the model on 140 tumour TMA cores and four benign whole slide images from which 140 benign samples were created, and tested it on 53 pathologist-annotated TMA samples. GRAPHITE outperformed traditional XAI methods, achieving a mean average precision (mAP) of 0.56, an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) of 0.94, and a threshold robustness (ThR) of 0.70, indicating that the model maintains high performance across a wide range of thresholds. In clinical utility, GRAPHITE achieved the highest area under the decision curve (AUDC) of 4.17e+5, indicating reliable decision support across thresholds. These results highlight GRAPHITE’s potential as a clinically valuable tool in computational pathology, providing interpretable visualisations that align with the pathologists’ diagnostic reasoning and support precision medicine.
在医学病理学中,可解释人工智能(XAI)对于提高癌症诊断中深度学习模型的解释性和临床可信度至关重要。然而,这些模型的“黑箱”性质常常限制了它们在临床上的采纳。我们引入了GRAPHITE(基于图的可解释组织检查),这是一种针对乳腺癌组织微阵列(TMA)分析的事后可解释框架。GRAPHITE采用多尺度方法,在不同放大级别提取斑块,构建分层图,并利用具有尺度相关注意力(SAN)的图注意力网络(GAT)来捕获尺度相关特征。我们在由肿瘤组织微阵列核心中的140个样本和由四张良性全切片图像创建的另外140个良性样本上训练模型,并在由病理学家注释的53个TMA样本上进行测试。与传统的XAI方法相比,GRAPHITE表现更佳,其平均精度均值(mAP)达到0.56,在受试者工作特征曲线下的面积(AUROC)达到0.94,阈值稳健性(ThR)达到0.70,这表明模型在广泛阈值范围内均表现出良好性能。在临床应用中,GRAPHITE的决策曲线下的面积(AUDC)达到最高值,即每观察小时后多决策后计算的校正因子等于常数计算值为十万分之一的最大可能累计得分之和等于万分之一点八四零三加量数字的最高积分域数据取得了一次达到每个可接受模型的判别,证明其提供了解释性可视化,这些可视化与病理医师的诊断推理相一致,为精准医学提供了可靠的决策支持。结果证明了GRAPHITE在人工智能临床病理领域的潜在应用价值,它可以为医学决策分析提供有意义的可解释工具并促进精准医疗的发展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 25 Pages, 10 Figures, 1 Tables
摘要
GRAPHITE(基于图的解释性组织检测)是一种用于乳腺癌组织微阵列(TMA)分析的后验可解释框架。它采用多尺度方法,利用图注意力网络(GAT)和尺度注意力(SAN)捕获尺度相关特征,提高深度学习模型在癌症诊断中的可解释性和临床可信度。在肿瘤TMA芯和全幻灯片图像上的实验表明,GRAPHITE优于传统XAI方法,具有高平均精度、高曲线下面积和阈值稳健性。这为临床决策支持提供了可靠的依据,凸显了其在计算病理学中的临床价值。
关键见解
- XAI在医学病理学中对于增强深度学习模型在癌症诊断中的可解释性和临床信任度至关重要。
- GRAPHITE框架被引入以解决深度学习模型的“黑箱”问题,提高临床采纳率。
- GRAPHITE采用多尺度方法,捕获尺度相关特征,构建层次图来提高解释性能。
- GRAPHITE在肿瘤TMA芯和全幻灯片图像上进行训练并测试,表现出优越性能。
- GRAPHITE相对于传统XAI方法具有更高的平均精度、曲线下面积和阈值稳健性。
- GRAPHITE在临床决策支持中表现出可靠性,与病理医师的诊断推理相符,支持精准医疗。
- 结果凸显了GRAPHITE在计算病理学中的潜在临床价值。
点此查看论文截图