⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-09 更新
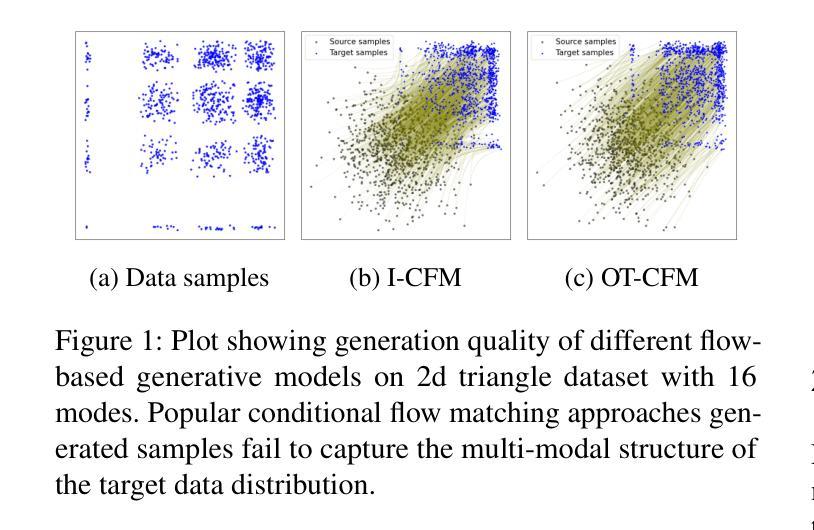
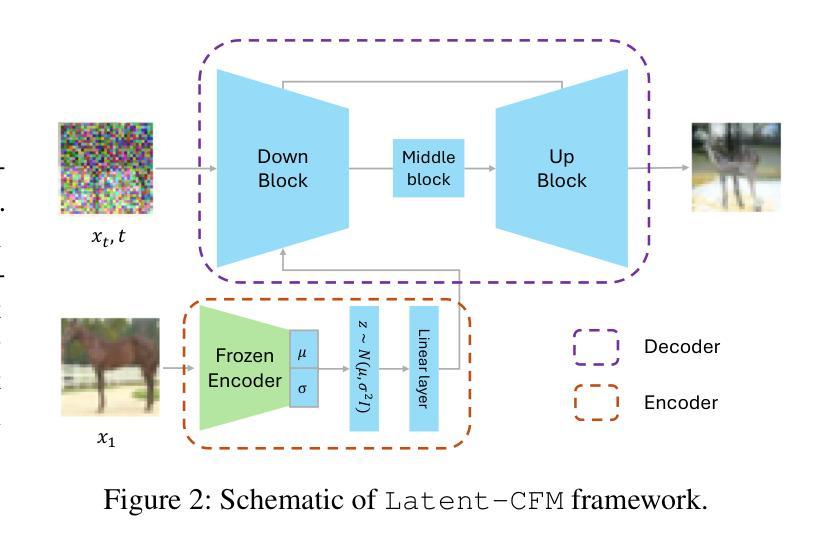
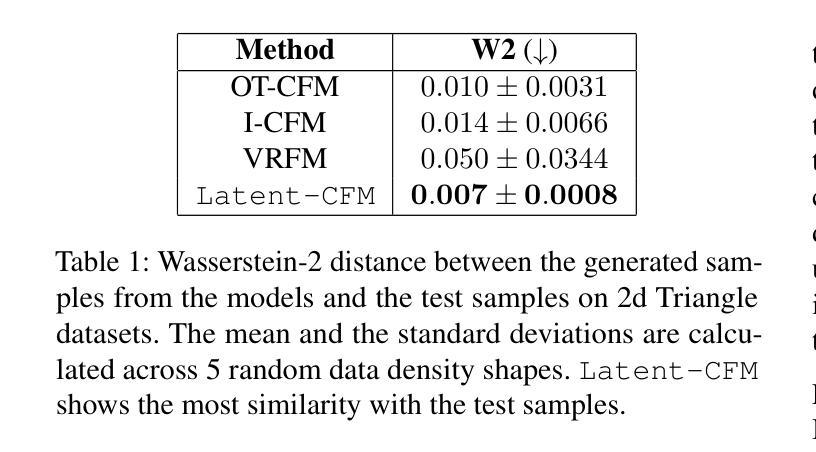
Efficient Flow Matching using Latent Variables
Authors:Anirban Samaddar, Yixuan Sun, Viktor Nilsson, Sandeep Madireddy
Flow matching models have shown great potential in image generation tasks among probabilistic generative models. Building upon the ideas of continuous normalizing flows, flow matching models generalize the transport path of the diffusion models from a simple prior distribution to the data. Most flow matching models in the literature do not explicitly model the underlying structure/manifold in the target data when learning the flow from a simple source distribution like the standard Gaussian. This leads to inefficient learning, especially for many high-dimensional real-world datasets, which often reside in a low-dimensional manifold. Existing strategies of incorporating manifolds, including data with underlying multi-modal distribution, often require expensive training and hence frequently lead to suboptimal performance. To this end, we present \texttt{Latent-CFM}, which provides simplified training/inference strategies to incorporate multi-modal data structures using pretrained deep latent variable models. Through experiments on multi-modal synthetic data and widely used image benchmark datasets, we show that \texttt{Latent-CFM} exhibits improved generation quality with significantly less training ($\sim 50%$ less in some cases) and computation than state-of-the-art flow matching models. Using a 2d Darcy flow dataset, we demonstrate that our approach generates more physically accurate samples than competitive approaches. In addition, through latent space analysis, we demonstrate that our approach can be used for conditional image generation conditioned on latent features.
流体匹配模型在概率生成模型中的图像生成任务中表现出了巨大的潜力。基于连续归一化流的思想,流体匹配模型将扩散模型的传输路径从简单的先验分布推广到数据。文献中的大多数流体匹配模型在学习从标准高斯等简单源分布到目标的流体时,并没有显式地建模目标数据的底层结构/流形。这导致了学习的不高效,特别是对于许多高维的现实世界数据集,它们经常居住在低维流形中。现有的结合流形的策略,包括具有潜在多元分布的数据,通常需要昂贵的训练成本,因此经常导致次优性能。为此,我们提出了“潜在CFM”,它提供了简化的训练/推理策略,利用预训练的深度潜在变量模型来结合多模态数据结构。通过对多模态合成数据和广泛使用的图像基准数据集进行实验,我们证明了“潜在CFM”在生成质量上的提高,并且在训练量和计算量上大大减少了(在某些情况下减少了约50%)相比于最先进的流体匹配模型。使用二维达西流数据集,我们证明了我们的方法生成的样本比竞争方法更具有物理准确性。此外,通过潜在空间分析,我们证明了我们的方法可用于基于潜在特征的条件图像生成。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
流匹配模型在概率生成模型中在图像生成任务中显示出巨大潜力。基于连续归一化流的思想,流匹配模型将数据从简单先验分布推广到扩散模型的传输路径。现有文献中的大多数流匹配模型在学习从简单源分布(如标准高斯分布)开始的流时,并没有显式地建模目标数据的底层结构/流形。这导致了对许多高维现实数据集的无效学习,尤其是那些经常处于低维流形中的数据集。尽管现有的结合流形策略包括具有潜在多模态分布的数据,但其训练成本高昂且经常导致性能不佳。为此,我们提出了基于预训练的深度潜在变量模型的“Latent-CFM”,它可以通过简化训练和推理策略来结合多模态数据结构。通过实验表明,Latent-CFM在生成质量上有所提升,并且在某些情况下训练时间减少了约一半,计算效率也显著提高。此外,我们的方法还能用于基于潜在特征的条件图像生成。
Key Takeaways
- 流匹配模型在图像生成任务中具有潜力。
- 流匹配模型基于连续归一化流推广数据传输路径。
- 现有流匹配模型未显式建模目标数据的底层结构,导致对高维现实数据集的学习效率低下。
- Latent-CFM通过简化训练和推理策略,能够结合多模态数据结构。
- Latent-CFM提高了生成质量,并显著减少了训练时间和计算成本。
- Latent-CFM在物理样本生成方面表现出更准确的性能。
点此查看论文截图

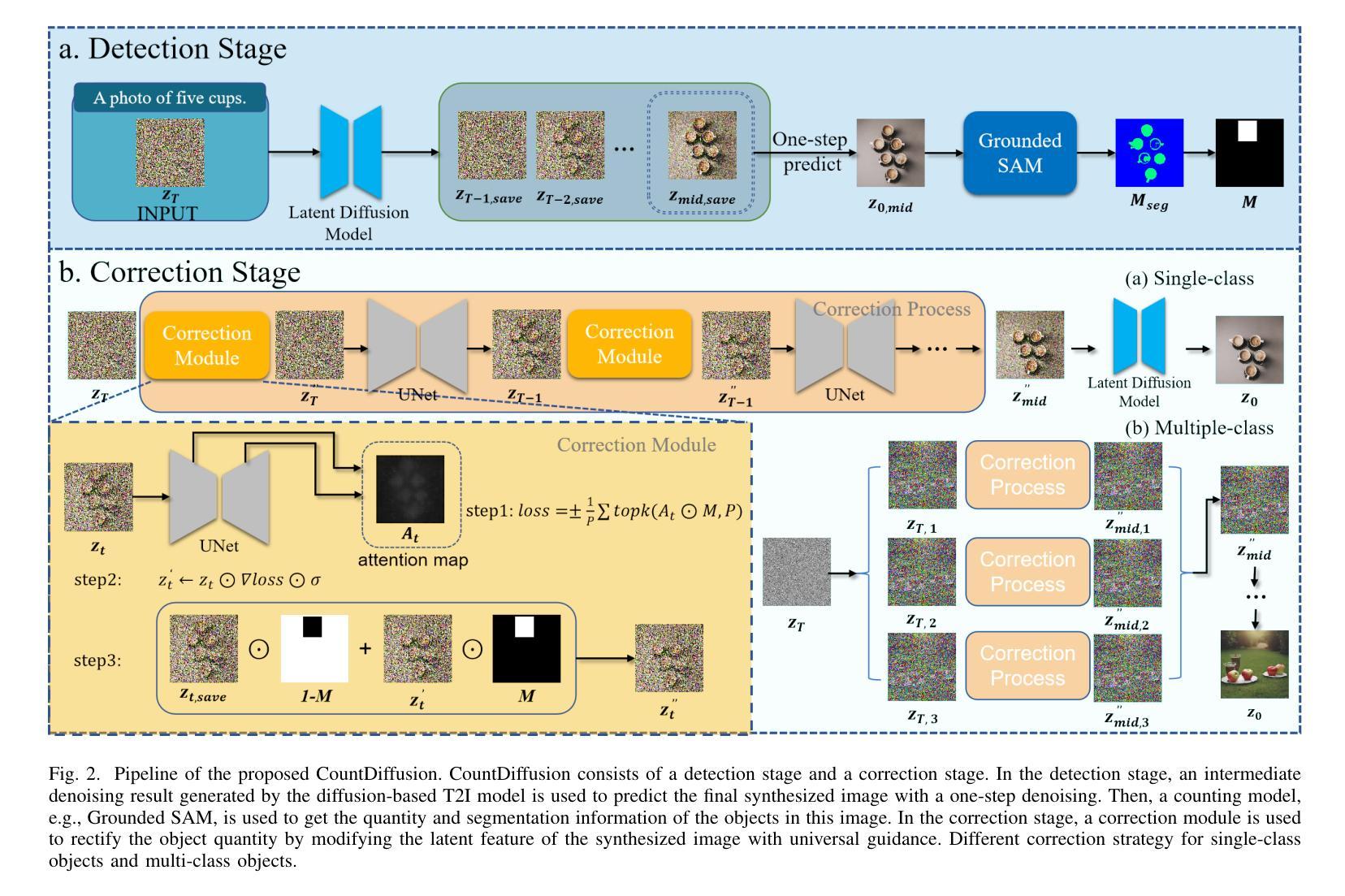
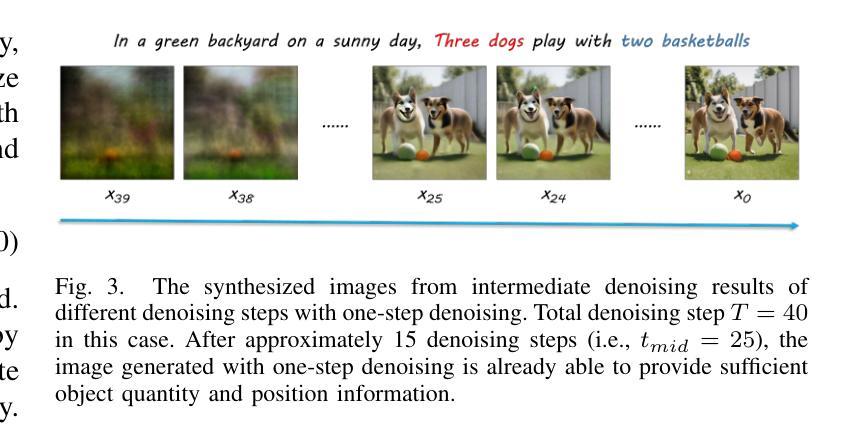
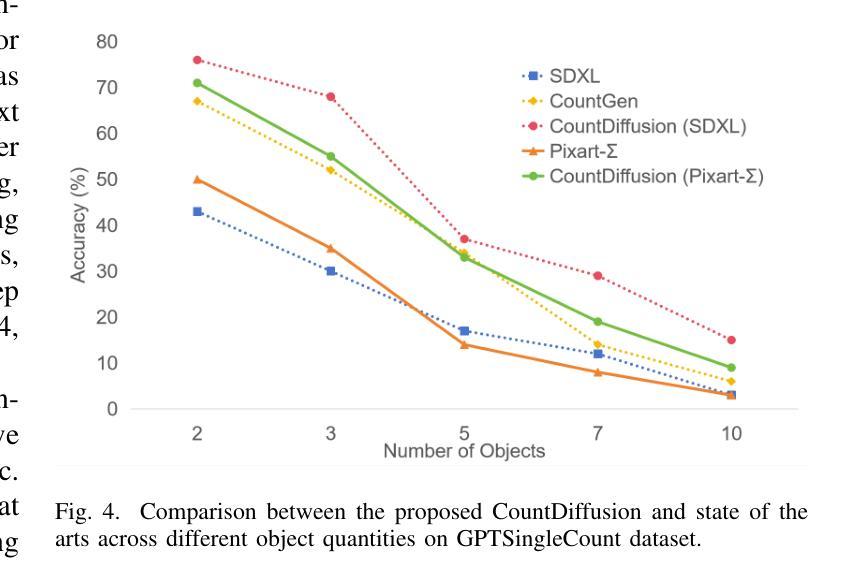
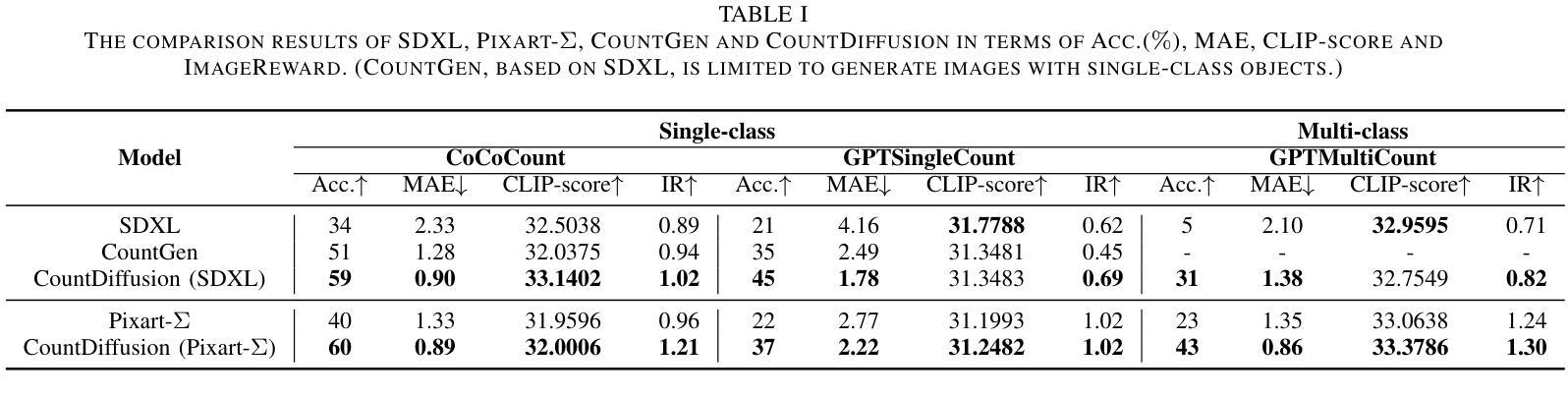
CountDiffusion: Text-to-Image Synthesis with Training-Free Counting-Guidance Diffusion
Authors:Yanyu Li, Pencheng Wan, Liang Han, Yaowei Wang, Liqiang Nie, Min Zhang
Stable Diffusion has advanced text-to-image synthesis, but training models to generate images with accurate object quantity is still difficult due to the high computational cost and the challenge of teaching models the abstract concept of quantity. In this paper, we propose CountDiffusion, a training-free framework aiming at generating images with correct object quantity from textual descriptions. CountDiffusion consists of two stages. In the first stage, an intermediate denoising result is generated by the diffusion model to predict the final synthesized image with one-step denoising, and a counting model is used to count the number of objects in this image. In the second stage, a correction module is used to correct the object quantity by changing the attention map of the object with universal guidance. The proposed CountDiffusion can be plugged into any diffusion-based text-to-image (T2I) generation models without further training. Experiment results demonstrate the superiority of our proposed CountDiffusion, which improves the accurate object quantity generation ability of T2I models by a large margin.
Stable Diffusion已经实现了先进的文本到图像合成技术,但由于计算成本高昂以及教授模型理解数量这一抽象概念具有挑战性,训练模型以生成具有准确对象数量的图像仍然很困难。在本文中,我们提出了CountDiffusion,这是一个无需训练即可生成正确对象数量的图像的目标框架。CountDiffusion分为两个阶段。在第一阶段,通过扩散模型生成中间去噪结果,以通过一步去噪预测最终的合成图像,并使用计数模型计算图像中的对象数量。在第二阶段,使用校正模块通过改变对象的注意力图进行通用指导来校正对象数量。所提出的CountDiffusion可以插入任何基于扩散的文本到图像(T2I)生成模型中而无需进一步训练。实验结果表明,我们所提出的CountDiffusion具有显著优势,能大幅度提高T2I模型生成准确对象数量的能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 9 figures, 3 tables
Summary
稳定扩散已提升了文本到图像的合成技术,但生成具有准确对象数量的图像仍存在困难,因涉及高计算成本及教授模型抽象数量概念的挑战。本文提出CountDiffusion,一种无需训练、旨在从文本描述生成具有正确对象数量的图像框架。CountDiffusion分两个阶段,第一阶段利用扩散模型生成中间去噪结果,通过一步去噪预测最终合成图像,并利用计数模型计算图像中对象的数量。第二阶段采用校正模块,通过改变对象的注意力图进行通用指导,以校正对象数量。CountDiffusion可无缝集成任何基于扩散的文本到图像生成模型,无需进一步训练。实验结果表明,CountDiffusion大幅提升了文本到图像模型的准确对象数量生成能力。
Key Takeaways
- 稳定扩散虽已提升文本到图像的合成技术,但生成具有准确对象数量的图像仍然具有挑战。
- CountDiffusion是一种无需训练的框架,可从文本描述生成具有正确对象数量的图像。
- CountDiffusion分为两个阶段:第一阶段预测图像并计算对象数量,第二阶段校正对象数量。
- CountDiffusion可无缝集成到任何扩散基础的文本到图像生成模型中。
- CountDiffusion通过改变对象的注意力图进行通用指导以校正对象数量。
- 实验结果表明CountDiffusion显著提高了文本到图像模型的准确对象数量生成能力。
- 该方法面对的挑战包括高计算成本和教授模型抽象数量概念的困难。
点此查看论文截图


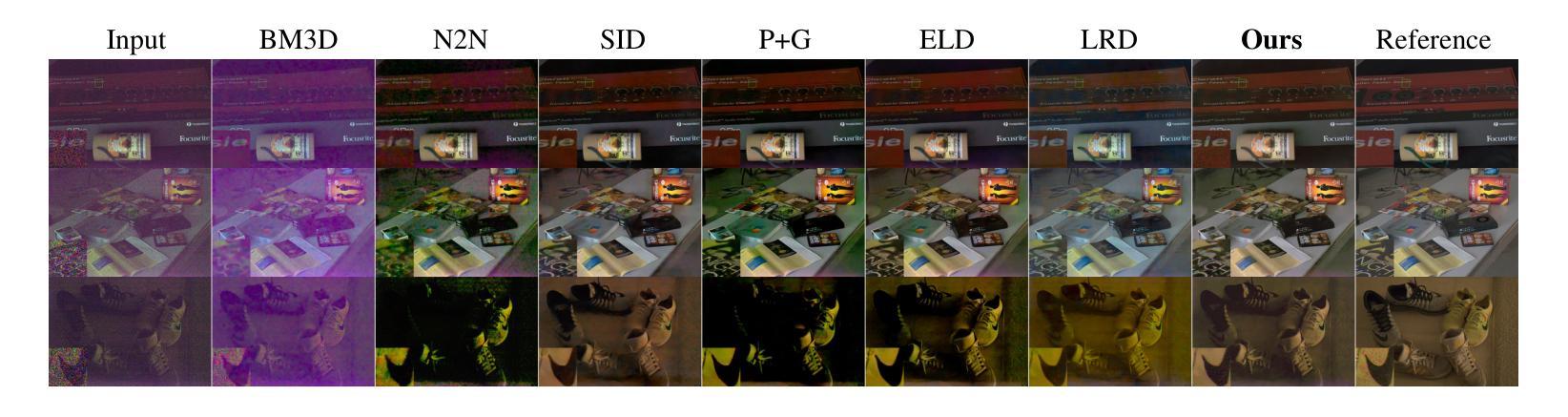
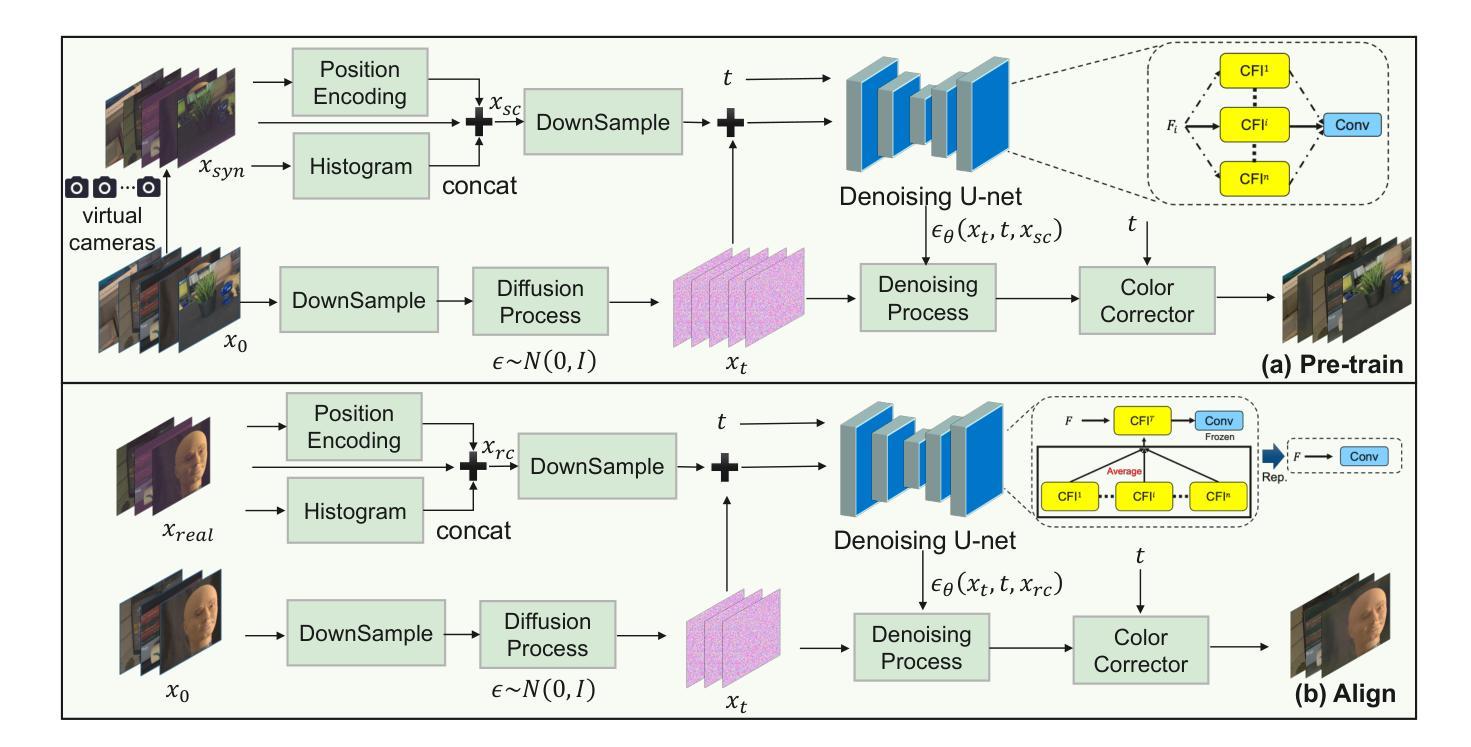
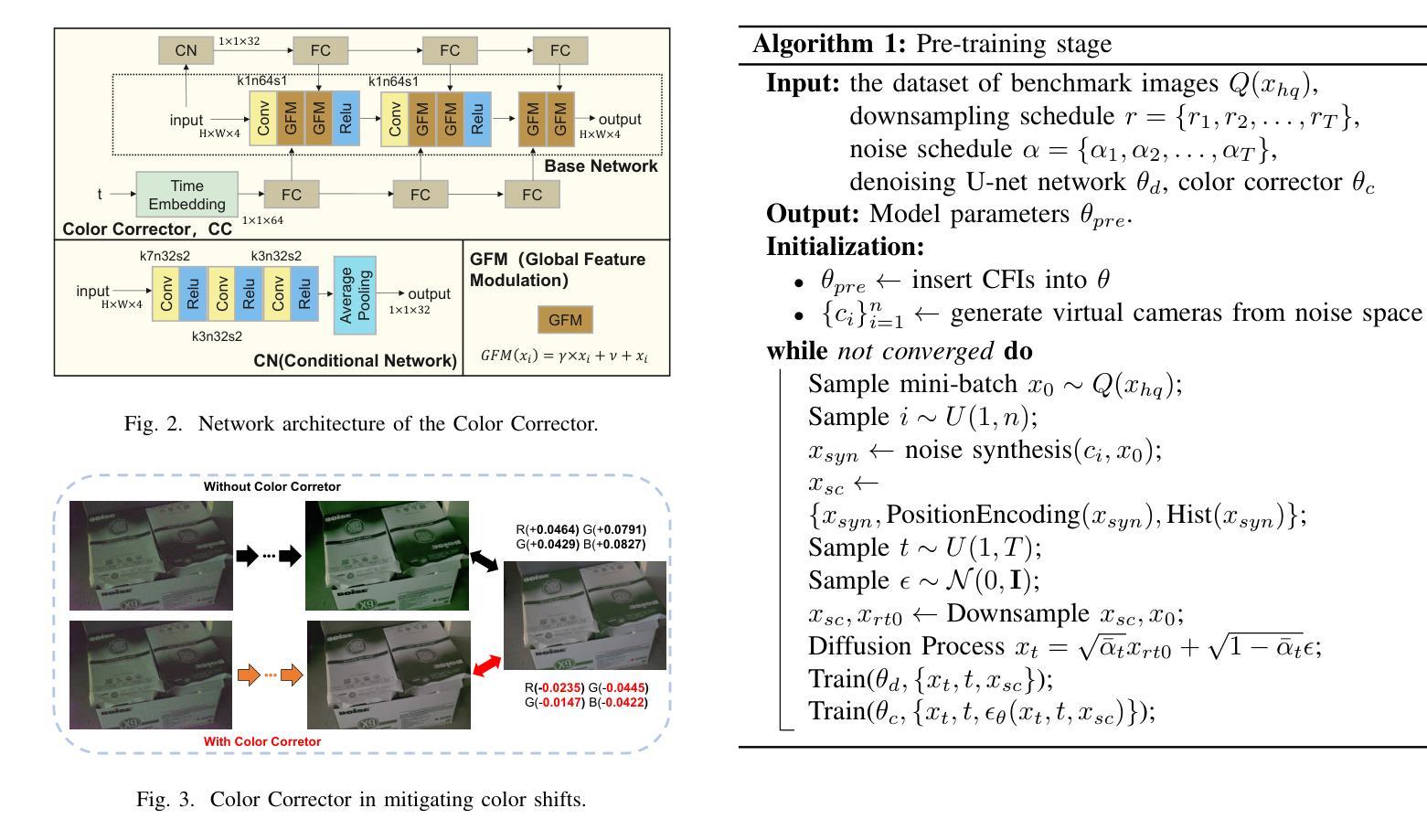
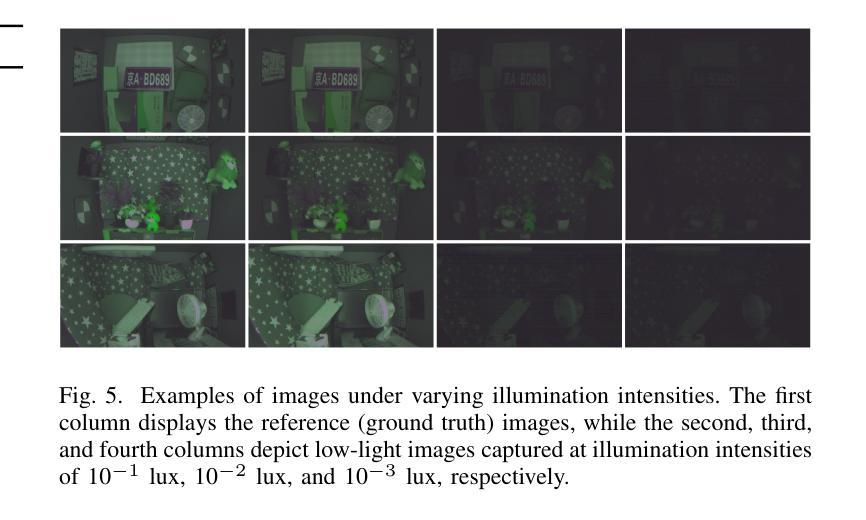
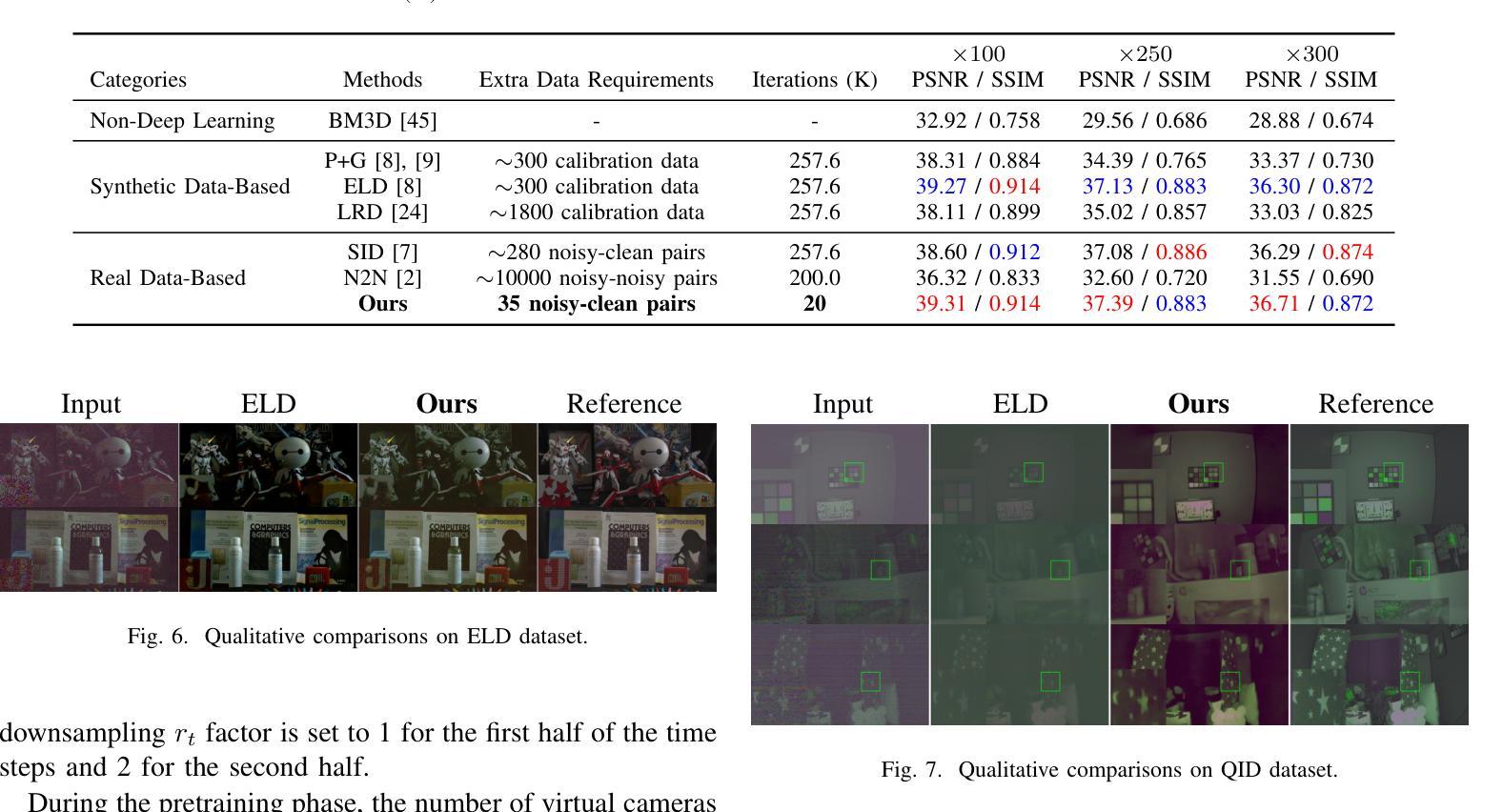
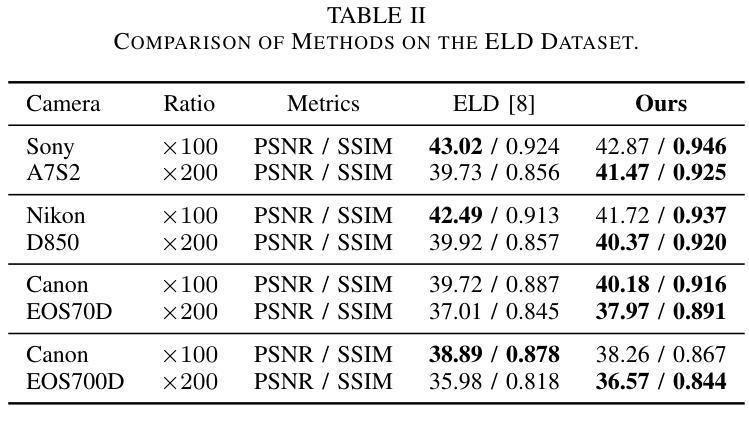
TS-Diff: Two-Stage Diffusion Model for Low-Light RAW Image Enhancement
Authors:Yi Li, Zhiyuan Zhang, Jiangnan Xia, Jianghan Cheng, Qilong Wu, Junwei Li, Yibin Tian, Hui Kong
This paper presents a novel Two-Stage Diffusion Model (TS-Diff) for enhancing extremely low-light RAW images. In the pre-training stage, TS-Diff synthesizes noisy images by constructing multiple virtual cameras based on a noise space. Camera Feature Integration (CFI) modules are then designed to enable the model to learn generalizable features across diverse virtual cameras. During the aligning stage, CFIs are averaged to create a target-specific CFI$^T$, which is fine-tuned using a small amount of real RAW data to adapt to the noise characteristics of specific cameras. A structural reparameterization technique further simplifies CFI$^T$ for efficient deployment. To address color shifts during the diffusion process, a color corrector is introduced to ensure color consistency by dynamically adjusting global color distributions. Additionally, a novel dataset, QID, is constructed, featuring quantifiable illumination levels and a wide dynamic range, providing a comprehensive benchmark for training and evaluation under extreme low-light conditions. Experimental results demonstrate that TS-Diff achieves state-of-the-art performance on multiple datasets, including QID, SID, and ELD, excelling in denoising, generalization, and color consistency across various cameras and illumination levels. These findings highlight the robustness and versatility of TS-Diff, making it a practical solution for low-light imaging applications. Source codes and models are available at https://github.com/CircccleK/TS-Diff
本文提出了一种新型的两阶段扩散模型(TS-Diff),用于增强极低光照的RAW图像。在预训练阶段,TS-Diff通过构建基于噪声空间的多个虚拟相机来合成噪声图像。随后设计了相机特征融合(CFI)模块,使模型能够在各种虚拟相机上学习可推广的特征。在对齐阶段,CFIs被平均化以创建目标特定的CFI$^T$,并使用少量真实RAW数据进行微调,以适应特定相机的噪声特性。一种结构再参数化技术进一步简化了CFI$^T$,以便有效部署。为了解决扩散过程中的颜色偏移问题,引入了一种颜色校正器,通过动态调整全局颜色分布来确保颜色一致性。此外,还构建了一个新型数据集QID,具有可量化的照明水平和宽动态范围,为极端低光照条件下的训练和评估提供了全面的基准测试。实验结果证明,TS-Diff在多数据集(包括QID、SID和ELD)上达到了最新技术水平,在降噪、通用性和跨不同相机和光照级别的颜色一致性方面表现出色。这些发现突出了TS-Diff的稳健性和多功能性,使其成为低光成像应用的实用解决方案。相关源代码和模型可在https://github.com/CircccleK/TS-Diff 获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN)
摘要
本文提出了一种新型的两阶段扩散模型(TS-Diff),用于增强极低光照下的RAW图像。在预训练阶段,TS-Diff通过构建多个基于噪声空间的虚拟相机合成噪声图像。设计了相机特征融合(CFI)模块,使模型能够在不同的虚拟相机上学习通用特征。在调整阶段,CFIs经过平均化处理以创建目标特定的CFI^T,并使用少量真实RAW数据进行微调,以适应特定相机的噪声特性。通过结构再参数化技术进一步简化CFI^T,以便有效部署。为解决扩散过程中的色彩偏移问题,引入了色彩校正器,通过动态调整全局色彩分布来确保色彩一致性。此外,还构建了一个新型数据集QID,具有可量化的照明水平和宽动态范围,为极端低光照条件下的训练和评估提供了全面的基准。实验结果证明,TS-Diff在多个数据集(包括QID、SID和ELD)上实现了最先进的性能,在降噪、通用性和色彩一致性方面表现出色,适用于各种相机和光照水平。
关键见解
- TS-Diff模型通过构建虚拟相机合成噪声图像,为极低光照下的RAW图像增强提供了新方法。
- 引入相机特征融合(CFI)模块,使模型能在不同的虚拟相机上学习通用特征。
- 通过创建目标特定的CFI^T并微调,模型能适应特定相机的噪声特性。
- 结构再参数化技术简化了CFI^T的部署。
- 引入色彩校正器来解决扩散过程中的色彩偏移问题,确保色彩一致性。
- 新型数据集QID的构建为极端低光照条件下的训练和评估提供了基准。
- TS-Diff在多个数据集上实现了最先进的性能,尤其在降噪、通用性和色彩一致性方面表现突出。
点此查看论文截图


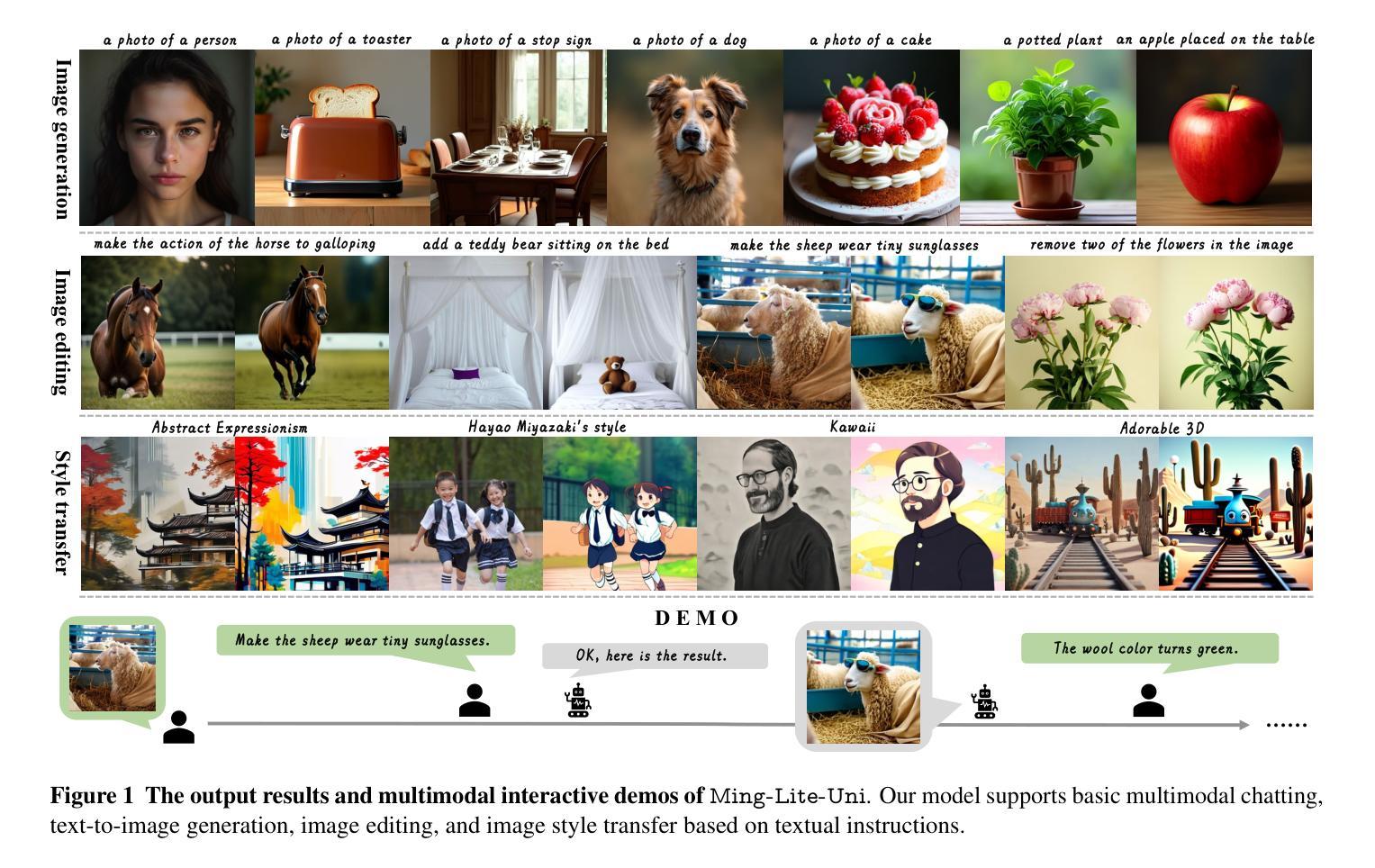
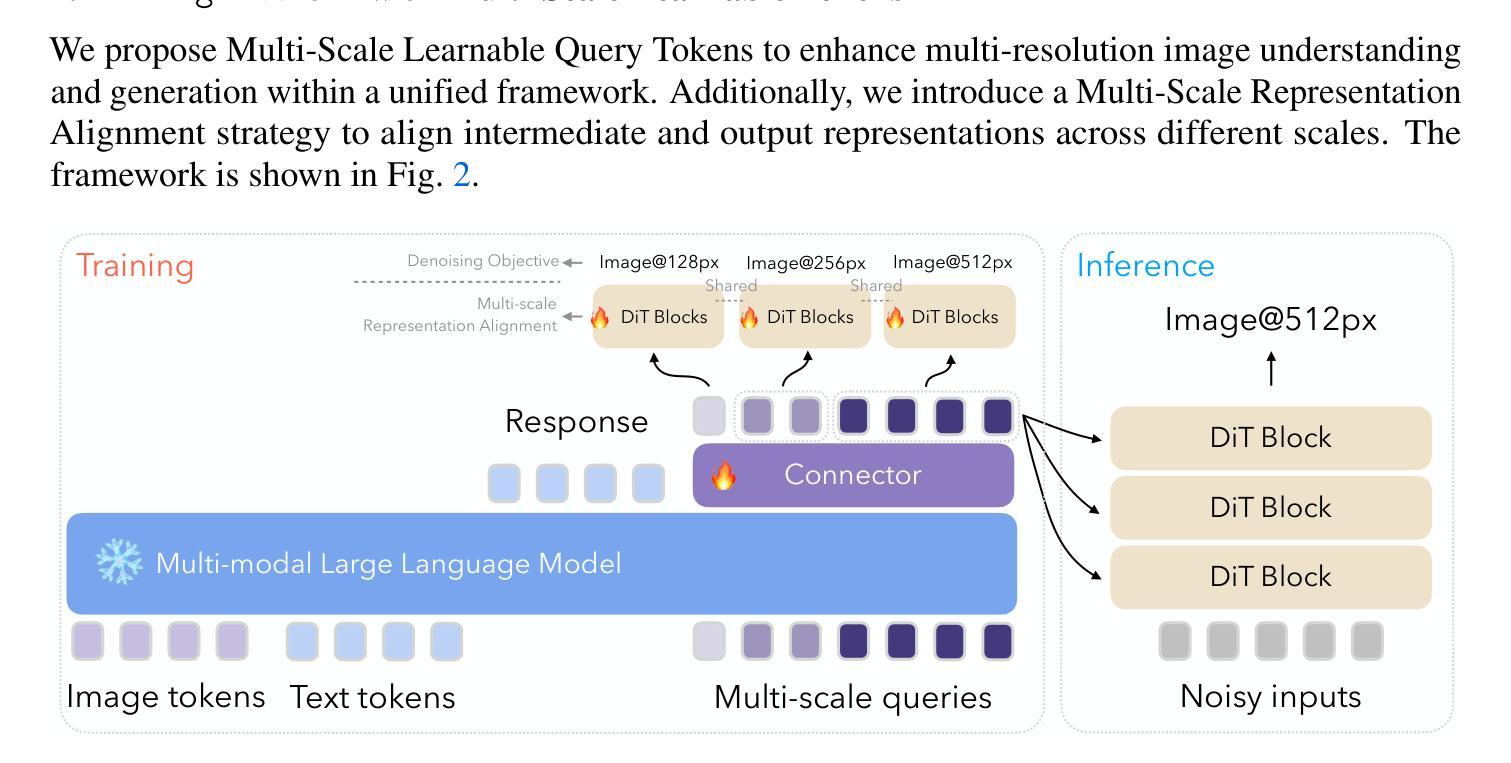
Ming-Lite-Uni: Advancements in Unified Architecture for Natural Multimodal Interaction
Authors:Inclusion AI, Biao Gong, Cheng Zou, Dandan Zheng, Hu Yu, Jingdong Chen, Jianxin Sun, Junbo Zhao, Jun Zhou, Kaixiang Ji, Lixiang Ru, Libin Wang, Qingpei Guo, Rui Liu, Weilong Chai, Xinyu Xiao, Ziyuan Huang
We introduce Ming-Lite-Uni, an open-source multimodal framework featuring a newly designed unified visual generator and a native multimodal autoregressive model tailored for unifying vision and language. Specifically, this project provides an open-source implementation of the integrated MetaQueries and M2-omni framework, while introducing the novel multi-scale learnable tokens and multi-scale representation alignment strategy. By leveraging a fixed MLLM and a learnable diffusion model, Ming-Lite-Uni enables native multimodal AR models to perform both text-to-image generation and instruction based image editing tasks, expanding their capabilities beyond pure visual understanding. Our experimental results demonstrate the strong performance of Ming-Lite-Uni and illustrate the impressive fluid nature of its interactive process. All code and model weights are open-sourced to foster further exploration within the community. Notably, this work aligns with concurrent multimodal AI milestones - such as ChatGPT-4o with native image generation updated in March 25, 2025 - underscoring the broader significance of unified models like Ming-Lite-Uni on the path toward AGI. Ming-Lite-Uni is in alpha stage and will soon be further refined.
我们介绍了Ming-Lite-Uni,这是一个开源的多模式框架,具有新设计的统一视觉生成器和针对视觉和语言的融合量身定制的本土多模式自回归模型。具体来说,此项目提供了集成MetaQueries和M2-omni框架的开源实现,同时引入了新型的多尺度可学习令牌和多尺度表示对齐策略。通过利用固定的MLLM和可学习的扩散模型,Ming-Lite-Uni使本土多模式自回归模型能够执行文本到图像生成和基于指令的图像编辑任务,扩展了其超越纯视觉理解的能力。我们的实验结果证明了Ming-Lite-Uni的强大性能,并展示了其交互过程的惊人流畅性。所有代码和模型权重均开源,以促进社区内的进一步探索。值得注意的是,这项工作与同期的多模式人工智能里程碑事件相符,如2025年3月25日更新的具有原生图像生成的ChatGPT-4o,突显出像Ming-Lite-Uni这样的统一模型在通往人工智能通用性(AGI)道路上的重要性。目前Ming-Lite-Uni处于Alpha阶段,未来将会进一步完善。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF https://github.com/inclusionAI/Ming/tree/main/Ming-unify
Summary
本文介绍了Ming-Lite-Uni这一开源多模态框架,其特点为全新设计的统一视觉生成器以及针对视觉和语言统一化的本地多模态自回归模型。该项目实现了集成MetaQueries和M2-omni框架的开源实现,引入新型多尺度可学习令牌和多尺度表示对齐策略。利用固定的MLLM和可学习的扩散模型,Ming-Lite-Uni使本地多模态AR模型能够执行文本到图像生成和基于指令的图像编辑任务,超越了纯视觉理解的能力。实验结果证明了Ming-Lite-Uni的强大性能,其交互过程表现出令人印象深刻的流畅性。所有代码和模型权重均开源,以促进社区内的进一步探索。该工作与当前的多元模态人工智能里程碑(如ChatGPT-4o等)相吻合,显示出统一模型在迈向人工智能通用性过程中的重要性。Ming-Lite-Uni尚处于Alpha阶段,未来将有进一步的改进。
Key Takeaways
- Ming-Lite-Uni是一个开源多模态框架,集成了视觉和语言处理功能。
- 它采用统一视觉生成器和本地多模态自回归模型设计。
- 该项目实现了MetaQueries和M2-omni框架的集成。
- 引入新型的多尺度可学习令牌和多尺度表示对齐策略是该框架的创新点。
- Ming-Lite-Uni支持文本到图像生成以及基于指令的图像编辑任务。
- 该框架的实验结果表现优秀,与当前的多元模态人工智能里程碑相符。
点此查看论文截图




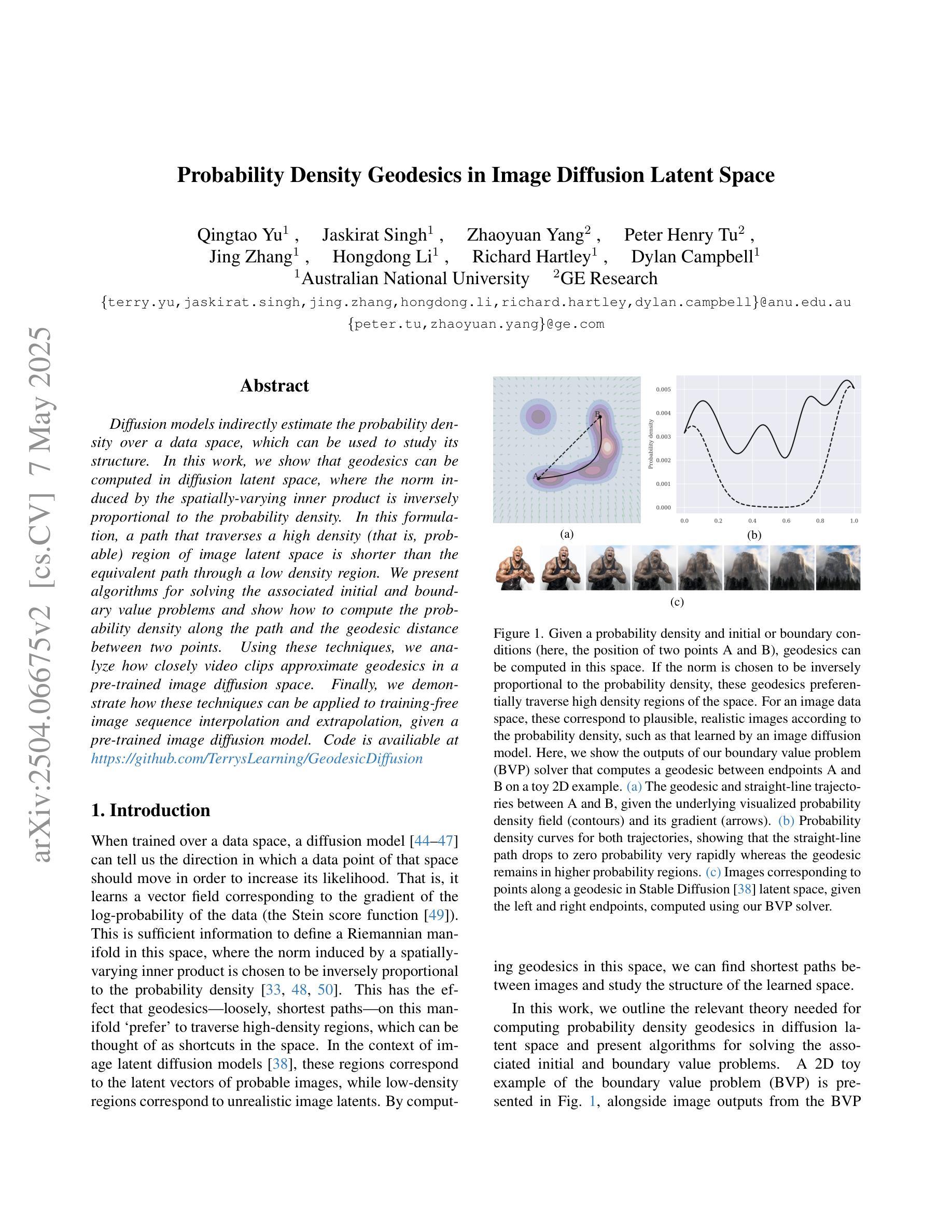
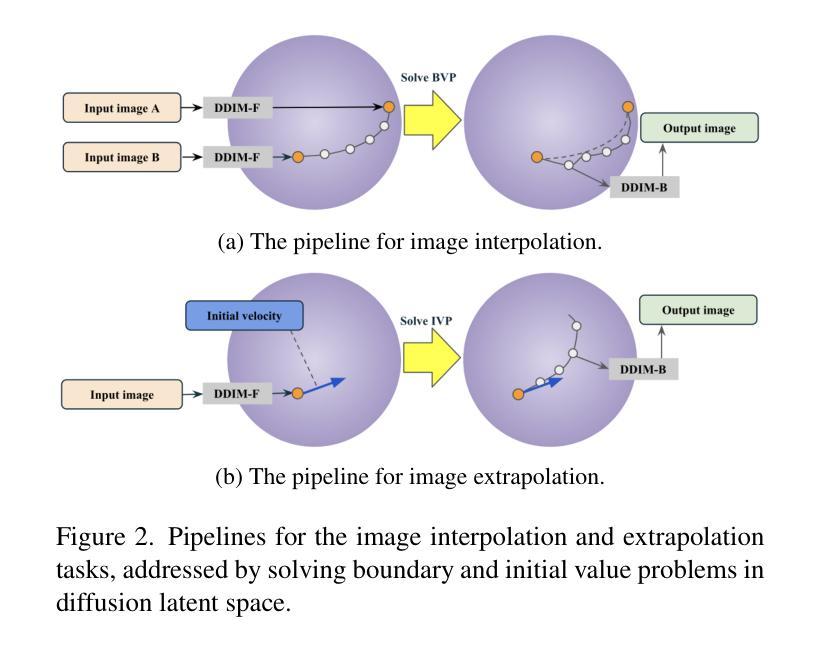
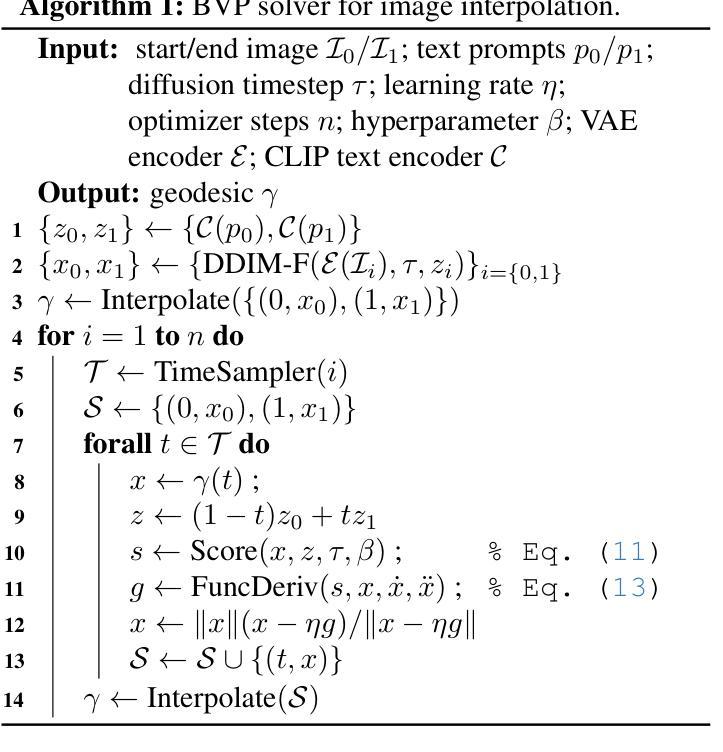
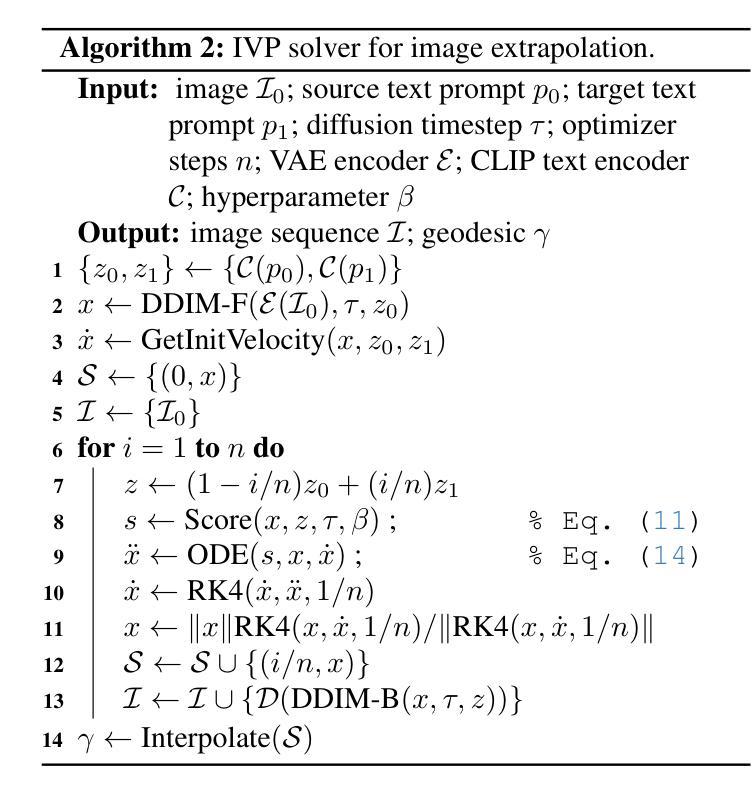
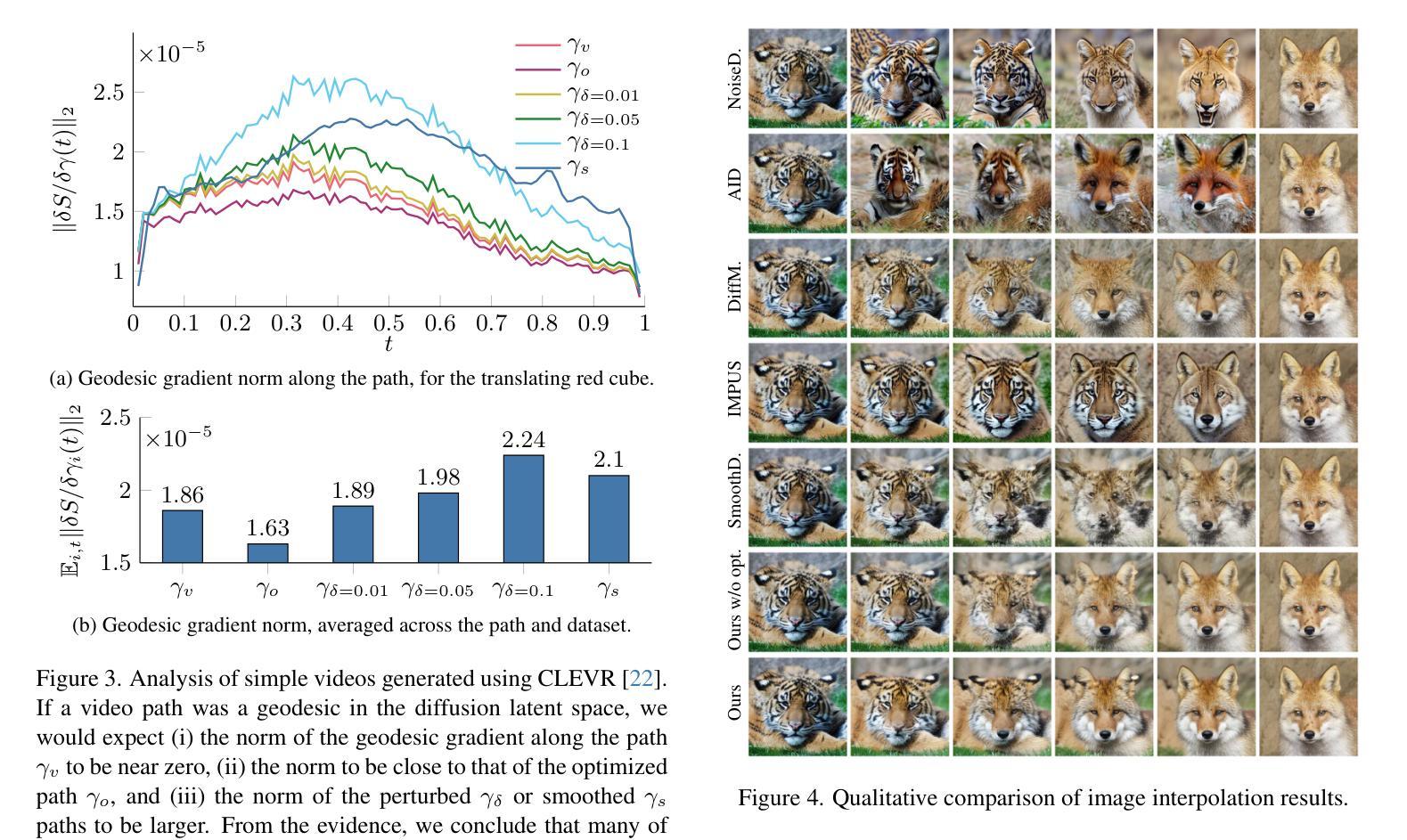
Probability Density Geodesics in Image Diffusion Latent Space
Authors:Qingtao Yu, Jaskirat Singh, Zhaoyuan Yang, Peter Henry Tu, Jing Zhang, Hongdong Li, Richard Hartley, Dylan Campbell
Diffusion models indirectly estimate the probability density over a data space, which can be used to study its structure. In this work, we show that geodesics can be computed in diffusion latent space, where the norm induced by the spatially-varying inner product is inversely proportional to the probability density. In this formulation, a path that traverses a high density (that is, probable) region of image latent space is shorter than the equivalent path through a low density region. We present algorithms for solving the associated initial and boundary value problems and show how to compute the probability density along the path and the geodesic distance between two points. Using these techniques, we analyze how closely video clips approximate geodesics in a pre-trained image diffusion space. Finally, we demonstrate how these techniques can be applied to training-free image sequence interpolation and extrapolation, given a pre-trained image diffusion model.
扩散模型通过间接估计数据空间的概率密度,可用于研究其结构。在这项工作中,我们展示了如何在扩散潜在空间中计算测地线,其中由空间变化的内积引起的范数与概率密度成反比。在这种表述中,遍历图像潜在空间的高密度(即可能的)区域的路径比通过低密度区域的等效路径更短。我们提出了解决相关初始值和边界值问题的算法,并展示了如何计算路径上的概率密度以及两点之间的测地距离。使用这些技术,我们分析了视频剪辑在预训练的图像扩散空间中如何近似测地线。最后,我们展示了如何在给定预训练的图像扩散模型的情况下,将这些技术应用于无训练图像序列的插值和外推。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR2025
Summary
本文介绍了扩散模型在数据空间概率密度估计方面的应用,并展示了如何在扩散潜在空间中进行测地线计算。研究发现,由空间变化内积诱导的范数与概率密度成反比,高密度区域的路径比低密度区域的路径短。本文提出了解决相关初始和边界值问题的算法,并展示了如何计算路径上的概率密度和两点之间的测地距离。此外,本文还分析了视频剪辑在预训练图像扩散空间中的近似测地线路情况,并展示了如何将该技术应用于训练图像序列的插值与外延预测。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型可估计数据空间的概率密度。
- 在扩散潜在空间中进行测地线计算。
- 空间变化内积诱导的范数与概率密度成反比。
- 高密度区域路径短于低密度区域路径。
- 提出了解决初始和边界值问题的算法。
- 分析了视频剪辑在预训练图像扩散空间中的近似测地线路情况。
点此查看论文截图
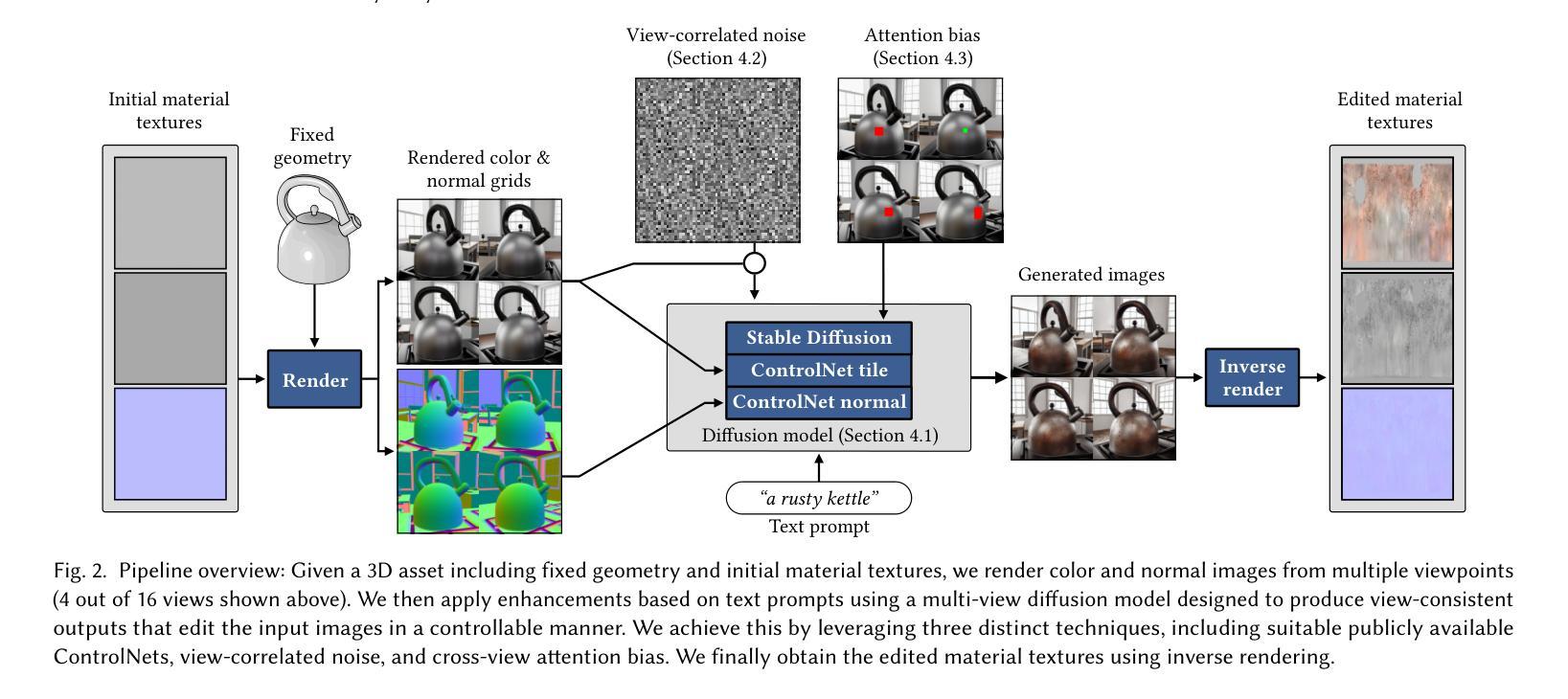
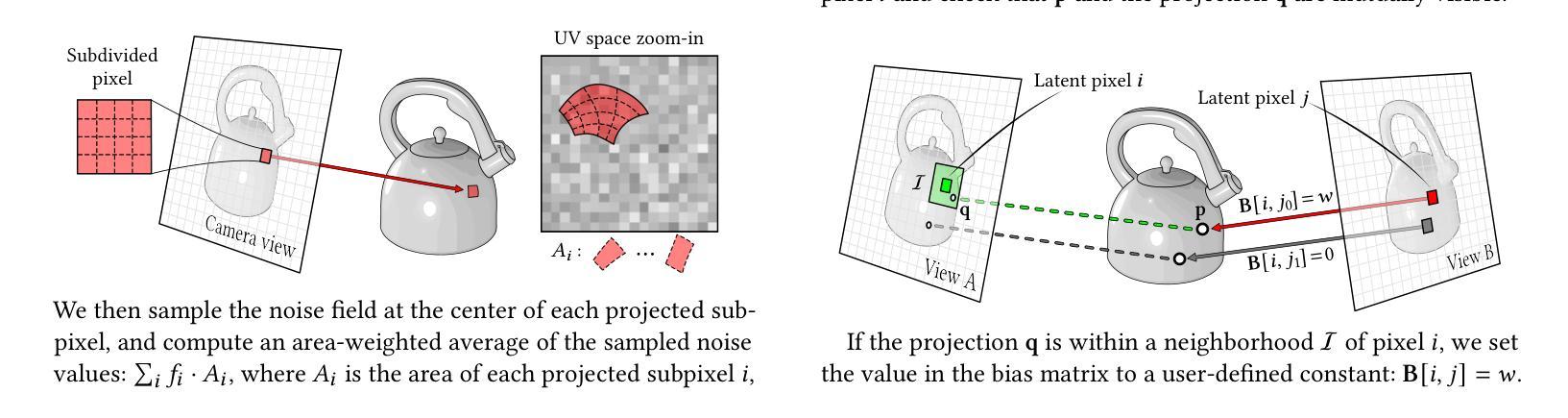
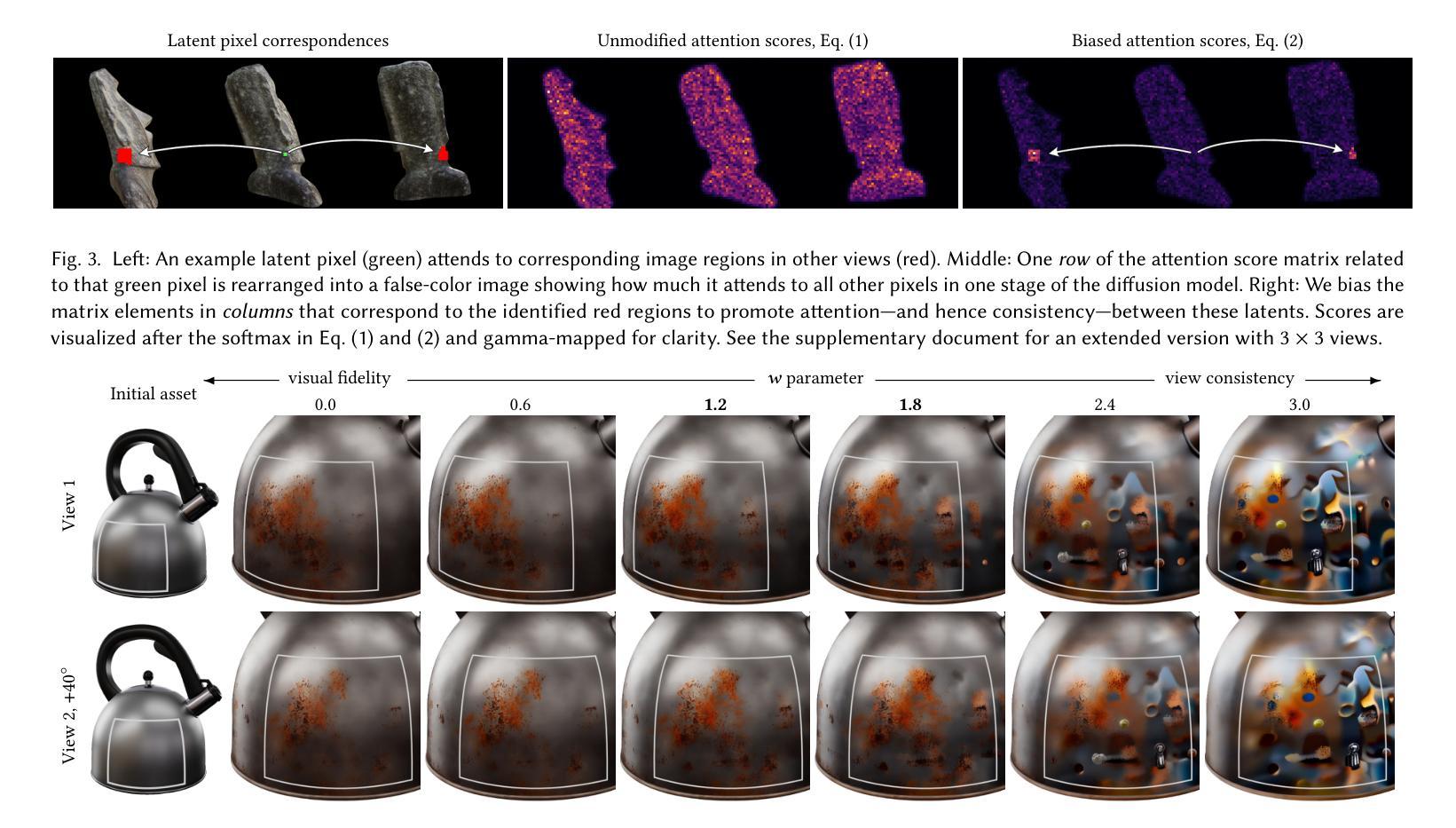
Generative Detail Enhancement for Physically Based Materials
Authors:Saeed Hadadan, Benedikt Bitterli, Tizian Zeltner, Jan Novák, Fabrice Rousselle, Jacob Munkberg, Jon Hasselgren, Bartlomiej Wronski, Matthias Zwicker
We present a tool for enhancing the detail of physically based materials using an off-the-shelf diffusion model and inverse rendering. Our goal is to enhance the visual fidelity of materials with detail that is often tedious to author, by adding signs of wear, aging, weathering, etc. As these appearance details are often rooted in real-world processes, we leverage a generative image model trained on a large dataset of natural images with corresponding visuals in context. Starting with a given geometry, UV mapping, and basic appearance, we render multiple views of the object. We use these views, together with an appearance-defining text prompt, to condition a diffusion model. The details it generates are then backpropagated from the enhanced images to the material parameters via inverse differentiable rendering. For inverse rendering to be successful, the generated appearance has to be consistent across all the images. We propose two priors to address the multi-view consistency of the diffusion model. First, we ensure that the initial noise that seeds the diffusion process is itself consistent across views by integrating it from a view-independent UV space. Second, we enforce geometric consistency by biasing the attention mechanism via a projective constraint so that pixels attend strongly to their corresponding pixel locations in other views. Our approach does not require any training or finetuning of the diffusion model, is agnostic of the material model used, and the enhanced material properties, i.e., 2D PBR textures, can be further edited by artists. This project is available at https://generative-detail.github.io.
我们提出了一种利用现成的扩散模型和逆向渲染技术,提高基于物理材质细节的工具。我们的目标是通过添加磨损、老化、风化等迹象,提高材质的视觉保真度和细节。由于这些外观细节往往源于现实世界的过程,我们利用在大规模自然图像数据集上训练的生成图像模型,以及相应的上下文视觉。从给定的几何形状、UV贴图和基本外观开始,我们渲染对象的多个视图。我们使用这些视图以及定义外观的文本提示,对扩散模型进行条件化处理。它生成的细节然后会从增强图像反向传播到材质参数,通过逆向可微分渲染。为了逆向渲染成功,生成的外观必须在所有图像中保持一致。我们提出了两种先验知识来解决扩散模型的多视图一致性。首先,我们通过从与视图无关的UV空间进行积分,确保种子扩散过程的初始噪声本身在不同视图中是一致的。其次,我们通过投影约束来引导注意力机制,强制几何一致性,使像素强烈关注其他视图中的对应像素位置。我们的方法不需要对扩散模型进行任何训练或微调,不受所使用的材料模型的影响,并且增强的材料属性(即2D PBR纹理)可以进一步由艺术家进行编辑。此项目在https://generative-detail.github.io上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种利用现成的扩散模型和逆向渲染技术提升物理基础材料的细节丰富度的工具。其目标是通过添加磨损、老化、风化等迹象,提高材料的视觉逼真度,这些外观细节通常难以制作。该研究利用大型自然图像数据集训练的生成图像模型,结合物体的多个视图和定义外观的文本提示,来调控扩散模型。生成的细节通过逆向可微渲染从增强图像传播回材料参数。该研究提出了两种优先策略,以确保扩散模型在多视图一致性方面的成功。一是确保扩散过程初始噪声在视图间是一致,通过从与视图无关的UV空间进行整合实现;二是通过投影约束引导注意力机制,实现几何一致性。该方法无需对扩散模型进行任何训练或微调,对使用的材料模型具有通用性,且增强的材料属性(如2D PBR纹理)可进一步由艺术家编辑。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了一种利用扩散模型和逆向渲染增强物理基础材料细节的方法。
- 方法的目的是提高材料的视觉逼真度,特别是添加磨损、老化、风化等细节。
- 利用生成图像模型和对物体的多个视图以及定义外观的文本提示来调控扩散模型。
- 通过逆向可微渲染将生成的细节从增强图像传播回材料参数。
- 提出了两种策略确保多视图一致性:整合UV空间的初始噪声和通过投影约束引导注意力机制。
- 该方法无需对扩散模型进行训练或微调,适用于各种材料模型。
- 增强的材料属性(如2D PBR纹理)可由艺术家进一步编辑。
点此查看论文截图


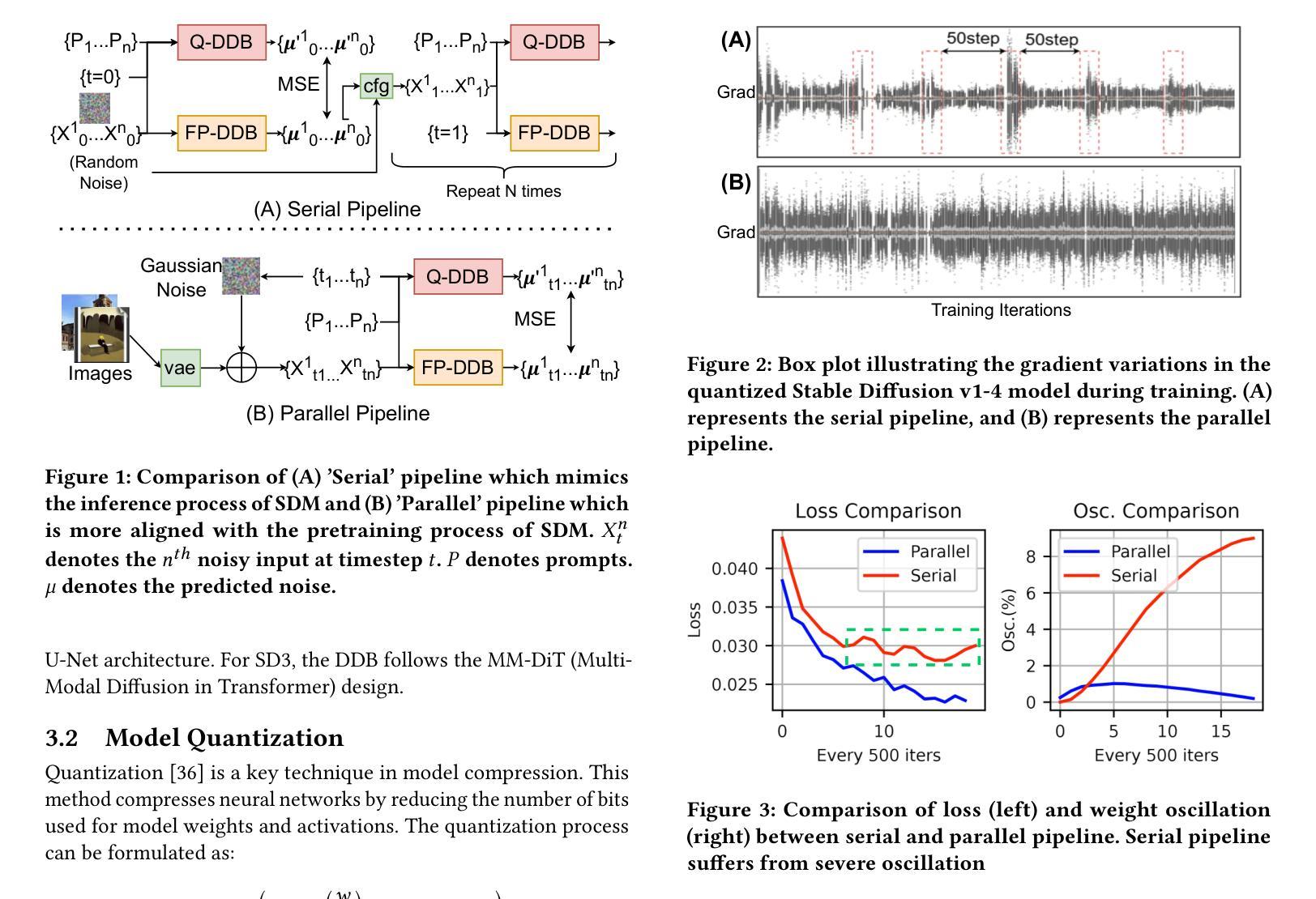
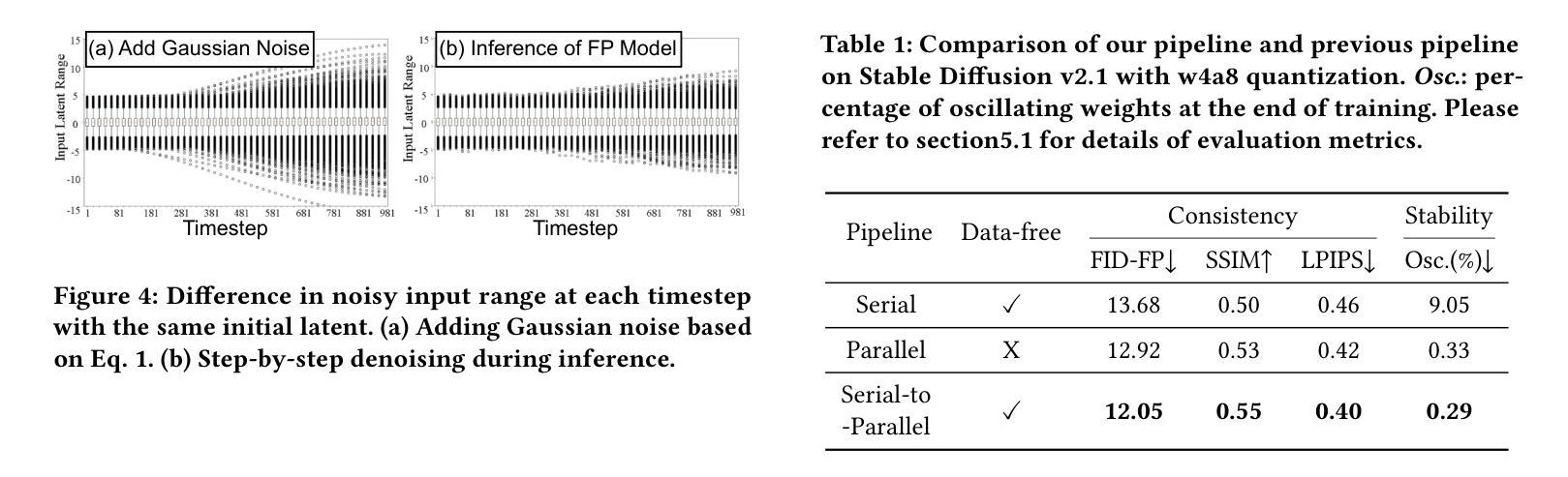
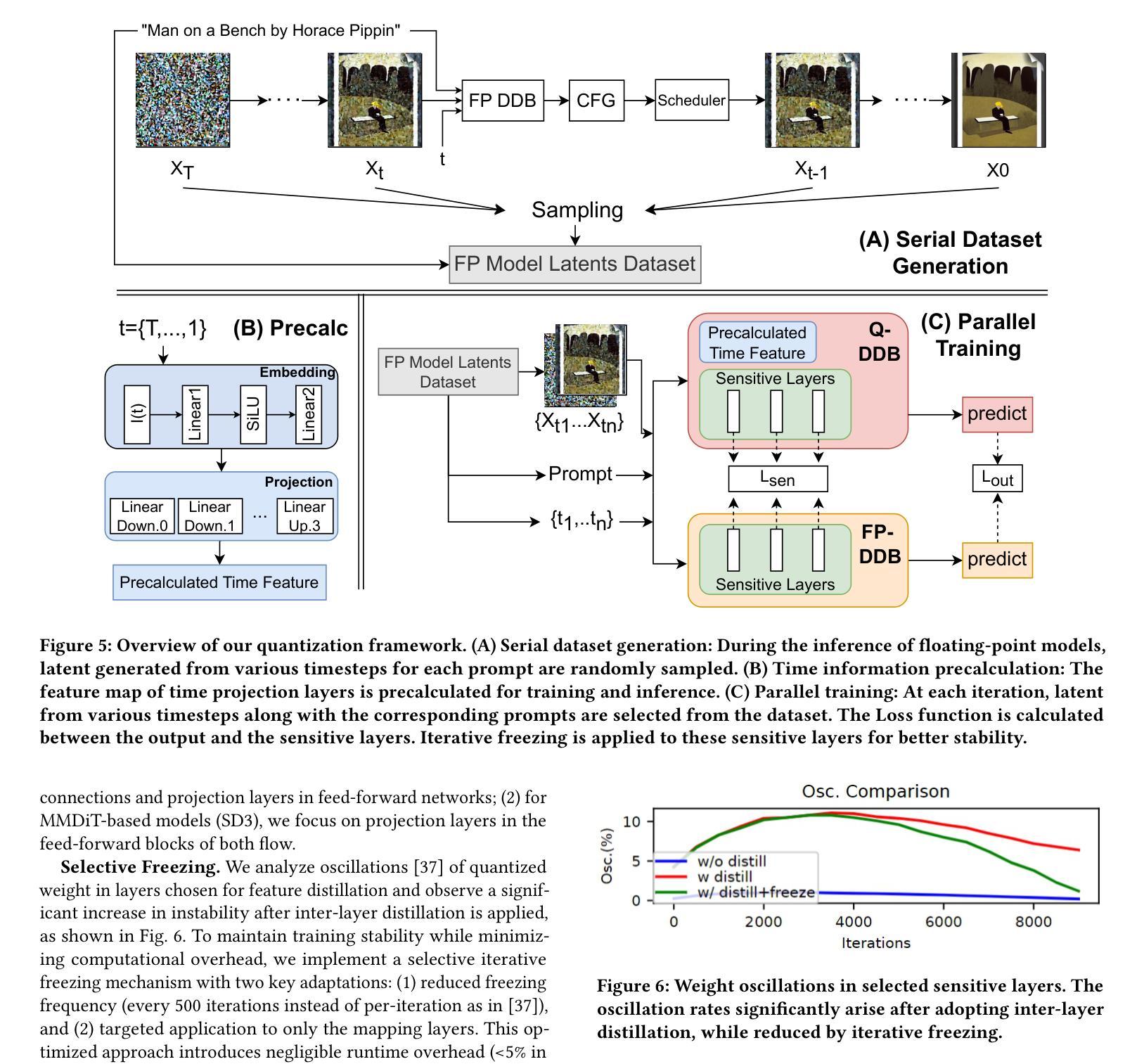
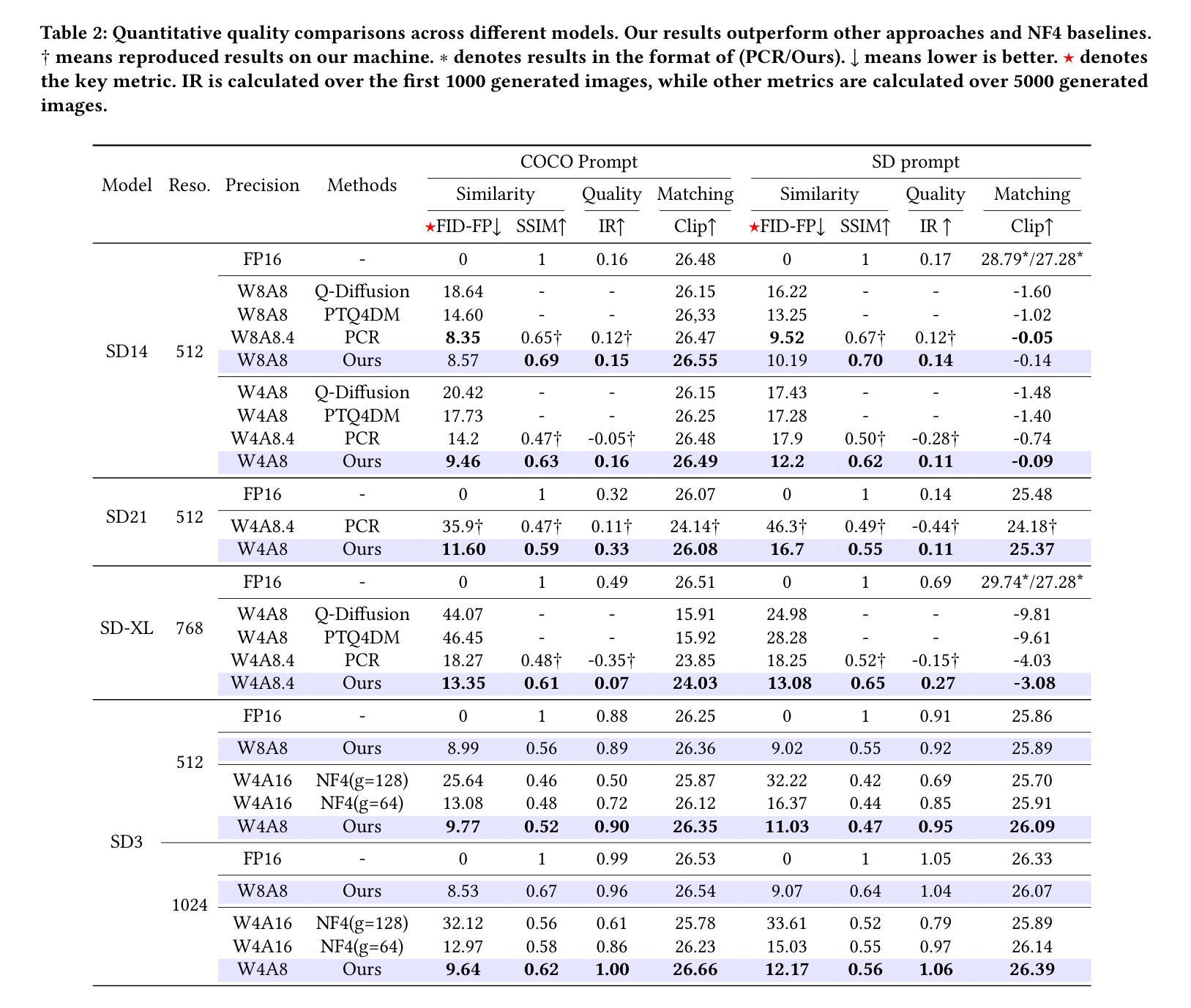
Efficiency Meets Fidelity: A Novel Quantization Framework for Stable Diffusion
Authors:Shuaiting Li, Juncan Deng, Zeyu Wang, Kedong Xu, Rongtao Deng, Hong Gu, Haibin Shen, Kejie Huang
Text-to-image generation via Stable Diffusion models (SDM) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities. However, their computational intensity, particularly in the iterative denoising process, hinders real-time deployment in latency-sensitive applications. While Recent studies have explored post-training quantization (PTQ) and quantization-aware training (QAT) methods to compress Diffusion models, existing methods often overlook the consistency between results generated by quantized models and those from floating-point models. This consistency is paramount for professional applications where both efficiency and output reliability are essential. To ensure that quantized SDM generates high-quality and consistent images, we propose an efficient quantization framework for SDM. Our framework introduces a Serial-to-Parallel pipeline that simultaneously maintains training-inference consistency and ensures optimization stability. Building upon this foundation, we further develop several techniques including multi-timestep activation quantization, time information precalculation, inter-layer distillation, and selective freezing, to achieve high-fidelity generation in comparison to floating-point models while maintaining quantization efficiency. Through comprehensive evaluation across multiple Stable Diffusion variants (v1-4, v2-1, XL 1.0, and v3), our method demonstrates superior performance over state-of-the-art approaches with shorter training times. Under W4A8 quantization settings, we achieve significant improvements in both distribution similarity and visual fidelity, while preserving a high image quality.
通过稳定扩散模型(SDM)进行的文本到图像生成已经显示出显著的能力。然而,其计算强度,特别是在迭代去噪过程中,阻碍了其在延迟敏感应用中的实时部署。虽然最近的研究已经探索了训练后量化(PTQ)和量化感知训练(QAT)方法来压缩扩散模型,但现有方法往往忽视了量化模型生成的结果与浮点模型生成的结果之间的一致性。对于既需要效率又需要输出可靠性的专业应用而言,这种一致性至关重要。为了确保量化的SDM生成高质量且一致的图像,我们为SDM提出了一个高效的量化框架。我们的框架引入了一个串行到并行的流水线,同时保持训练推理的一致性和确保优化稳定性。在此基础上,我们进一步开发了几种技术,包括多时间步激活量化、时间信息预计算、层间蒸馏和选择性冻结,以实现与浮点模型相比的高保真生成,同时保持量化效率。通过对多个稳定扩散变体(v1-4、v2-1、XL 1.0和v3)的综合评估,我们的方法在训练时间上优于最新方法,表现出卓越的性能。在W4A8量化设置下,我们在分布相似性和视觉保真度方面取得了显著的改进,同时保持了高图像质量。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于Stable Diffusion模型(SDM)的文本转图像生成技术展现出卓越的能力,但其计算密集型的迭代去噪过程阻碍了其在延迟敏感场景中的实时部署。为确保量化后的SDM生成高质量且一致的图像,研究团队提出一个高效量化框架,采用串行转并行管道,保持训练推理一致性并优化稳定性。通过多项技术,包括多时间步激活量化、时间信息预计算、层间蒸馏和选择性冻结等,该框架相较于浮点模型在保持量化效率的同时实现了高保真生成。经过对多个Stable Diffusion版本的综合评估,该方法在性能和训练时间上均表现出超越现有技术的优势。在W4A8量化设置下,其在分布相似性和视觉保真度方面取得了显著改进,同时保持了高图像质量。
Key Takeaways
- Stable Diffusion模型在文本转图像生成上表现卓越,但计算密集型的去噪过程导致实时部署受限。
- 量化框架用于提高SDM的效率并生成高质量、一致的图像。
- 框架采用串行转并行管道,旨在保持训练推理一致性并优化稳定性。
- 通过多项技术实现高保真生成,包括多时间步激活量化、时间信息预计算等。
- 框架在多个Stable Diffusion版本评估中表现优越,训练时间缩短。
- 在W4A8量化设置下,框架在分布相似性和视觉保真度上取得显著改进。
点此查看论文截图

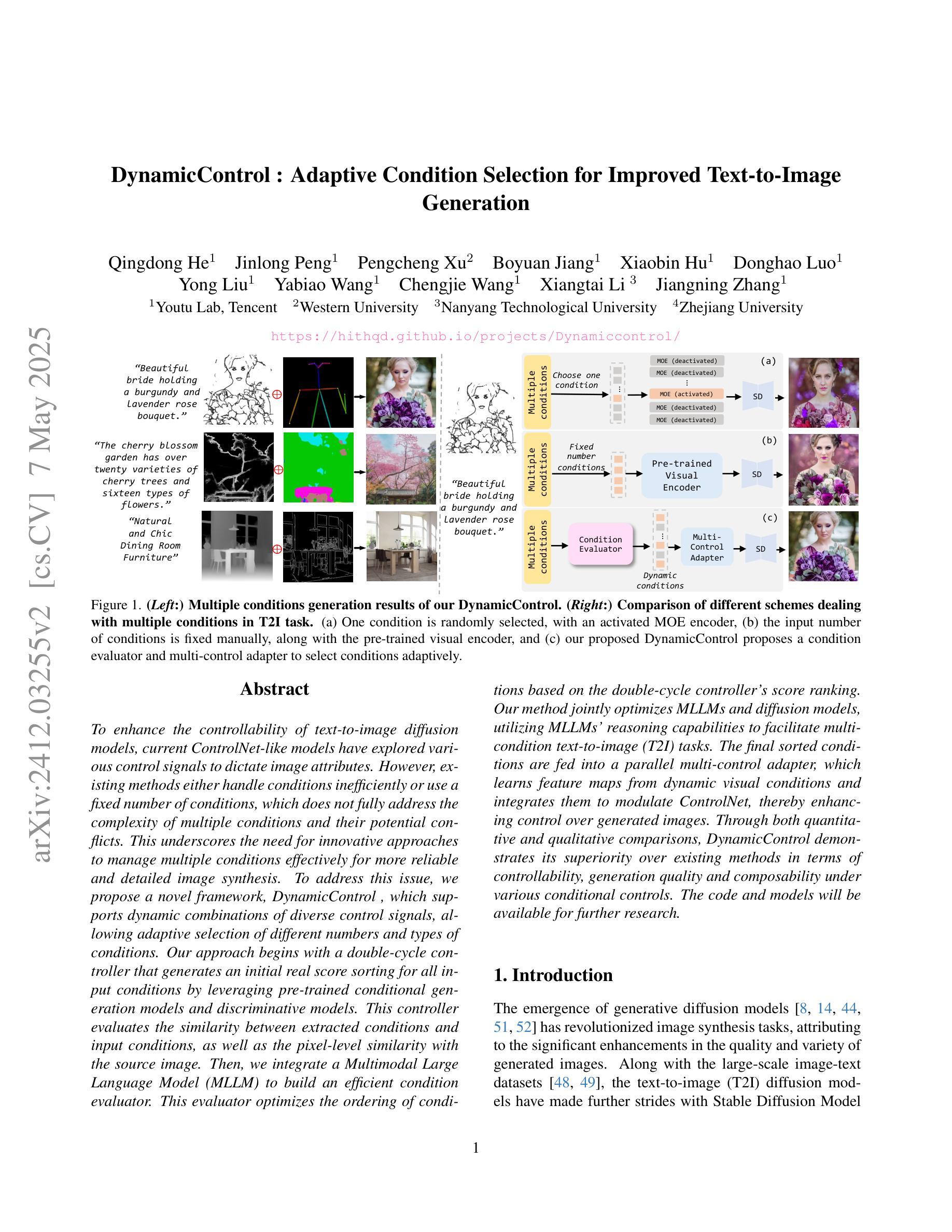
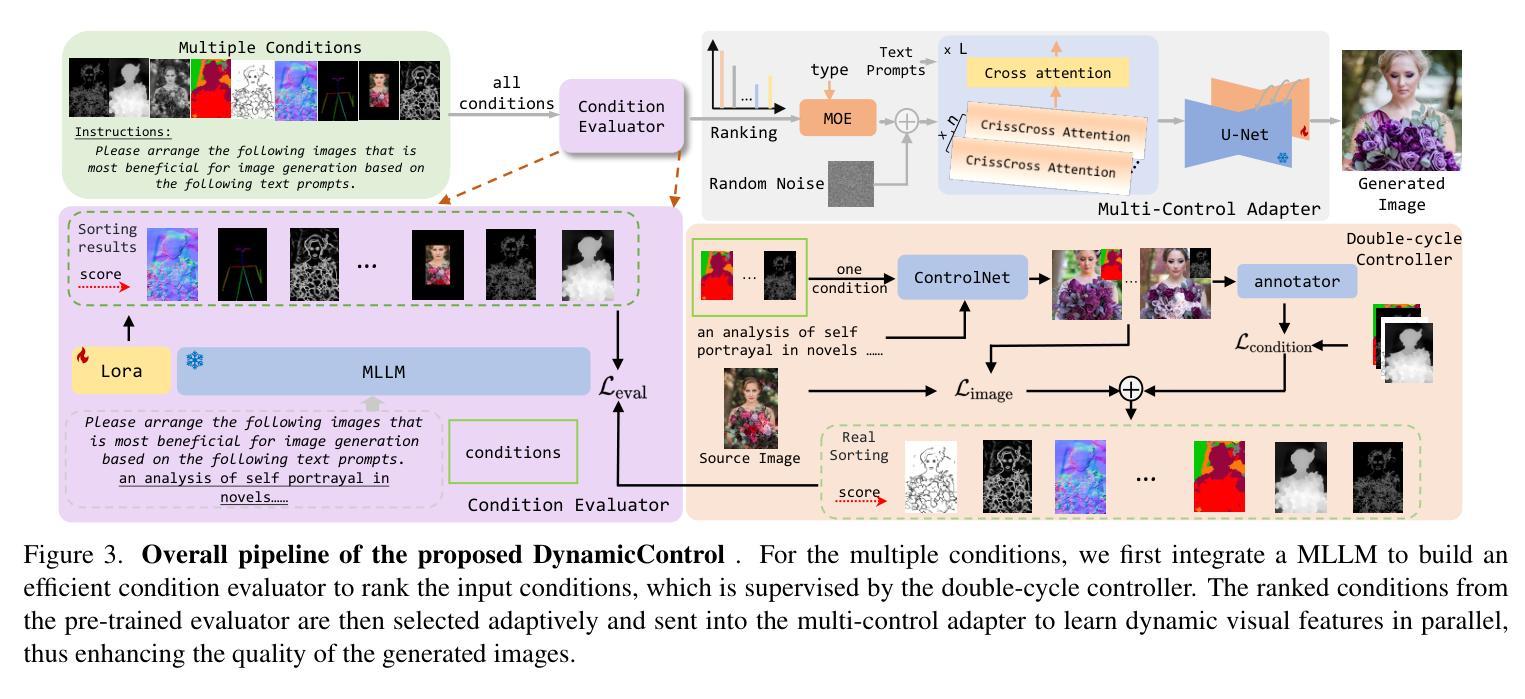
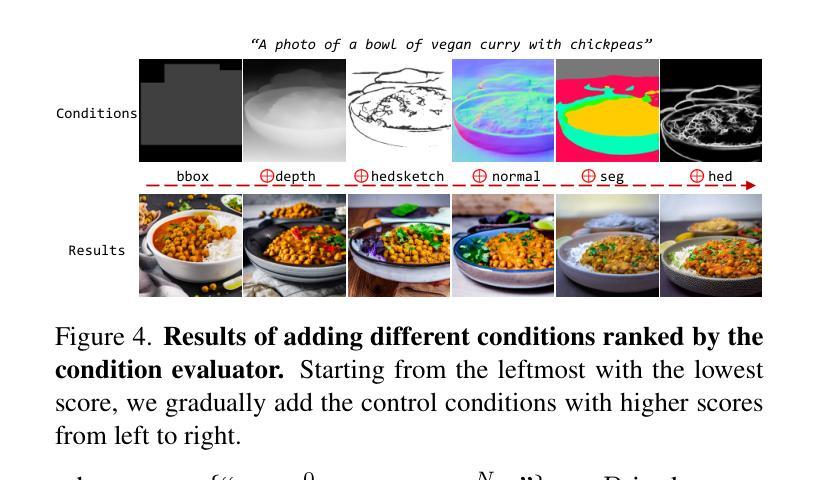
DynamicControl: Adaptive Condition Selection for Improved Text-to-Image Generation
Authors:Qingdong He, Jinlong Peng, Pengcheng Xu, Boyuan Jiang, Xiaobin Hu, Donghao Luo, Yong Liu, Yabiao Wang, Chengjie Wang, Xiangtai Li, Jiangning Zhang
To enhance the controllability of text-to-image diffusion models, current ControlNet-like models have explored various control signals to dictate image attributes. However, existing methods either handle conditions inefficiently or use a fixed number of conditions, which does not fully address the complexity of multiple conditions and their potential conflicts. This underscores the need for innovative approaches to manage multiple conditions effectively for more reliable and detailed image synthesis. To address this issue, we propose a novel framework, DynamicControl, which supports dynamic combinations of diverse control signals, allowing adaptive selection of different numbers and types of conditions. Our approach begins with a double-cycle controller that generates an initial real score sorting for all input conditions by leveraging pre-trained conditional generation models and discriminative models. This controller evaluates the similarity between extracted conditions and input conditions, as well as the pixel-level similarity with the source image. Then, we integrate a Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) to build an efficient condition evaluator. This evaluator optimizes the ordering of conditions based on the double-cycle controller’s score ranking. Our method jointly optimizes MLLMs and diffusion models, utilizing MLLMs’ reasoning capabilities to facilitate multi-condition text-to-image (T2I) tasks. The final sorted conditions are fed into a parallel multi-control adapter, which learns feature maps from dynamic visual conditions and integrates them to modulate ControlNet, thereby enhancing control over generated images. Through both quantitative and qualitative comparisons, DynamicControl demonstrates its superiority over existing methods in terms of controllability, generation quality and composability under various conditional controls.
为了增强文本到图像扩散模型的可控性,当前的ControlNet类模型已经探索了各种控制信号来指示图像属性。然而,现有方法要么处理条件效率低下,要么使用固定数量的条件,这并没有完全解决多个条件的复杂性及其潜在冲突。这强调了需要采用创新方法有效管理多个条件,以实现更可靠和更详细的图像合成。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种新型框架DynamicControl,它支持各种控制信号的动态组合,并允许自适应选择不同数量和类型的条件。我们的方法始于双重循环控制器,该控制器利用预训练的条件生成模型和判别模型,对所有输入条件生成初始真实分数排序。该控制器评估提取的条件与输入条件之间的相似性,以及与源图像的像素级相似性。然后,我们集成了多模态大型语言模型(MLLM),以构建高效的条件评估器。该评估器根据双重循环控制器的得分排名优化条件的顺序。我们的方法联合优化MLLMs和扩散模型,利用MLLMs的推理能力促进多条件文本到图像(T2I)任务。最终的排序条件被输入到并行多控制适配器中,该适配器从动态视觉条件中学习特征映射并将其集成,以调制ControlNet,从而提高对生成图像的控制能力。通过定量和定性比较,DynamicControl在各种条件控制下,在可控性、生成质量和组合性方面均表现出其优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
为提高文本到图像扩散模型的可控性,当前ControlNet类模型已尝试使用各种控制信号来指示图像属性。然而,现有方法要么处理条件效率低下,要么使用固定数量的条件,这并未充分解决多个条件的复杂性及其潜在冲突。因此,需要创新方法有效管理多个条件,以实现更可靠和详细的图像合成。为解决这一问题,我们提出了DynamicControl框架,支持各种控制信号的动态组合,可实现不同数量和类型的条件的自适应选择。我们的方法首先通过利用预训练的条件生成模型和判别模型,构建一个双循环控制器,生成所有输入条件的初始真实分数排序。该控制器评估提取的条件与输入条件的相似性,以及与源图像的像素级相似性。然后,我们整合了一个多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)来构建一个高效的条件评估器。该评估器基于双循环控制器的分数排名优化条件的排序。我们的方法联合优化MLLMs和扩散模型,利用MLLMs的推理能力促进多条件文本到图像(T2I)任务。最终排序的条件被输入到并行多控制适配器中,该适配器从动态视觉条件中学习特征映射并将其集成以调制ControlNet,从而提高对生成图像的控制能力。通过定量和定性比较,DynamicControl在可控性、生成质量和各种条件控制的组合性方面均优于现有方法。
要点摘要
- 当前文本到图像扩散模型面临可控性问题,需要有效管理多个条件的方法。
- DynamicControl框架支持动态组合多种控制信号,实现条件数量和类型的自适应选择。
- 利用双循环控制器生成初始真实分数排序,评估条件相似性。
- 集成多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)构建高效条件评估器,优化条件排序。
- 联合优化MLLMs和扩散模型,利用MLLMs的推理能力促进多条件文本到图像任务。
- 最后的条件排序被输入到并行多控制适配器中,该适配器学习并集成动态视觉条件以调制ControlNet。
点此查看论文截图
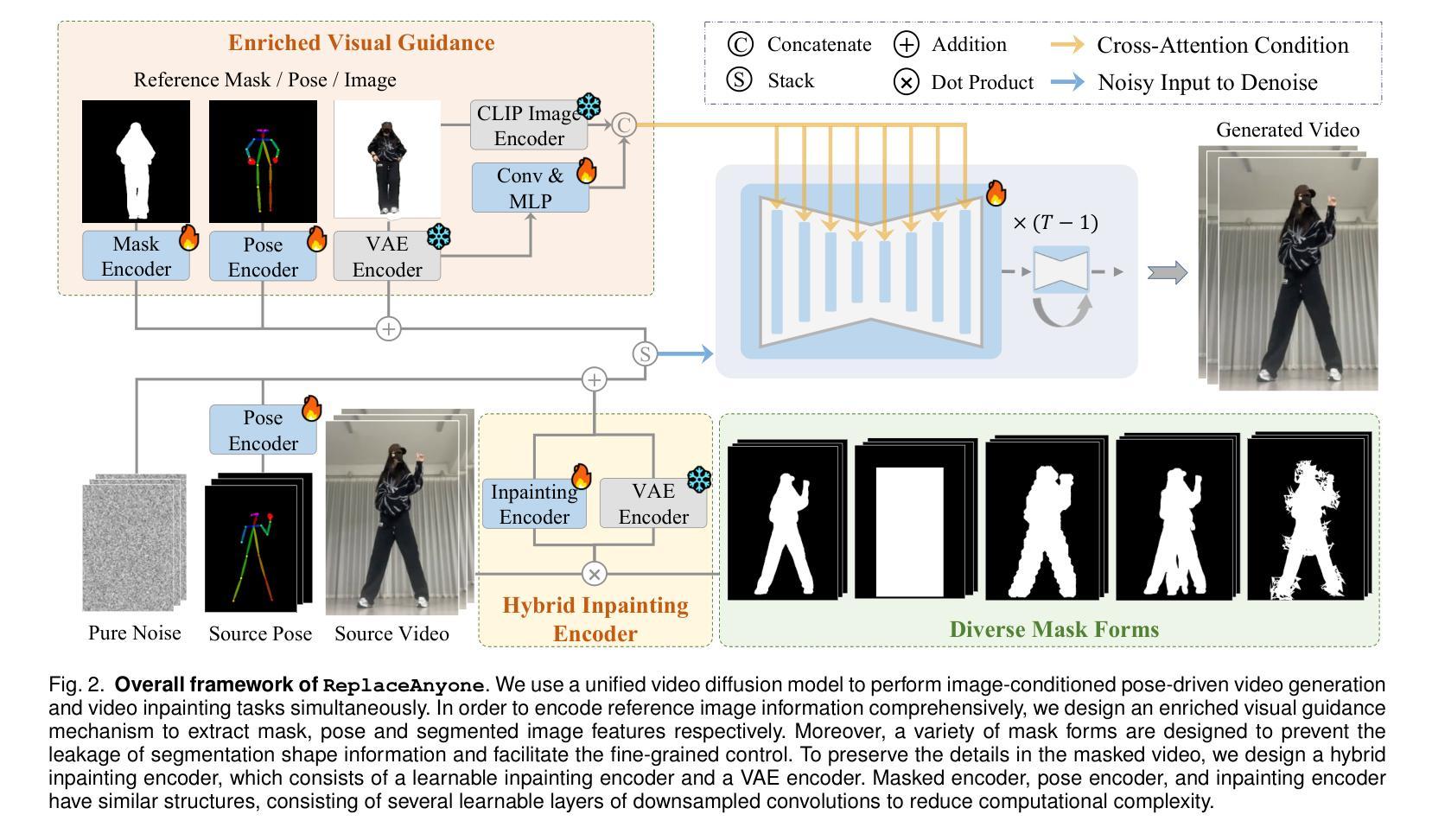
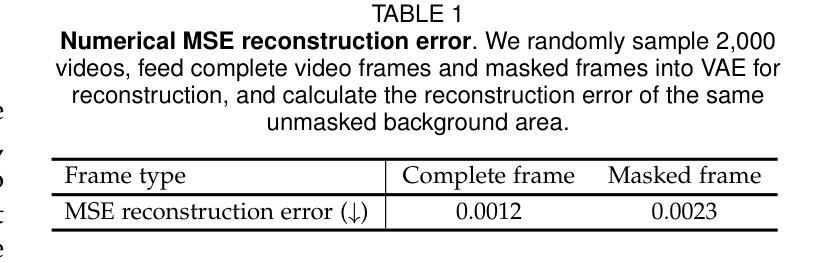
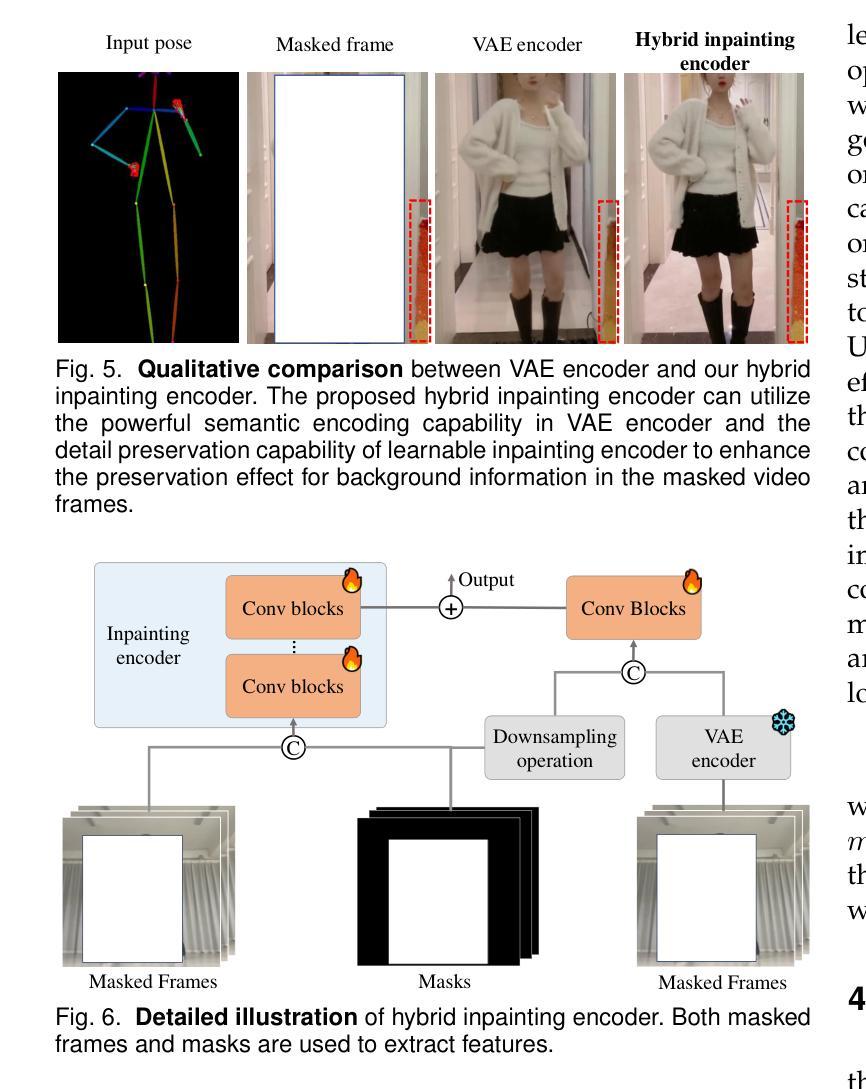
Replace Anyone in Videos
Authors:Xiang Wang, Shiwei Zhang, Haonan Qiu, Ruihang Chu, Zekun Li, Yingya Zhang, Changxin Gao, Yuehuan Wang, Chunhua Shen, Nong Sang
The field of controllable human-centric video generation has witnessed remarkable progress, particularly with the advent of diffusion models. However, achieving precise and localized control over human motion in videos, such as replacing or inserting individuals while preserving desired motion patterns, still remains a formidable challenge. In this work, we present the ReplaceAnyone framework, which focuses on localized human replacement and insertion featuring intricate backgrounds. Specifically, we formulate this task as an image-conditioned video inpainting paradigm with pose guidance, utilizing a unified end-to-end video diffusion architecture that facilitates image-conditioned video inpainting within masked regions. To prevent shape leakage and enable granular local control, we introduce diverse mask forms involving both regular and irregular shapes. Furthermore, we implement an enriched visual guidance mechanism to enhance appearance alignment, a hybrid inpainting encoder to further preserve the detailed background information in the masked video, and a two-phase optimization methodology to simplify the training difficulty. ReplaceAnyone enables seamless replacement or insertion of characters while maintaining the desired pose motion and reference appearance within a single framework. Extensive experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our method in generating realistic and coherent video content. The proposed ReplaceAnyone can be seamlessly applied not only to traditional 3D-UNet base models but also to DiT-based video models such as Wan2.1. The code will be available at https://github.com/ali-vilab/UniAnimate-DiT.
可控以人为中心的视频生成领域已经取得了显著的进步,特别是随着扩散模型的兴起。然而,在视频中对人类动作进行精确和局部化的控制,如替换或插入个体同时保持期望的动作模式,仍然是一个巨大的挑战。在这项工作中,我们提出了ReplaceAnyone框架,该框架专注于具有复杂背景的局部人类替换和插入。具体来说,我们将此任务制定为图像条件视频修复模式带有姿势指导,利用统一端到端视频扩散架构,便于在遮罩区域内进行图像条件视频修复。为了防止形状泄露并实现精细的局部控制,我们引入了多种形式的遮罩,包括规则和不规则形状。此外,我们实现了丰富的视觉引导机制以增强外观对齐,混合修复编码器以进一步保留遮罩视频中的详细背景信息,以及两阶段优化方法来简化训练难度。ReplaceAnyone能够在单一框架内无缝替换或插入角色,同时保持期望的姿势动作和参考外观。大量的实验结果证明了我们的方法在生成现实和连贯的视频内容方面的有效性。所提出的ReplaceAnyone不仅可以无缝应用于传统的3D-UNet基础模型,还可以应用于基于DiT的视频模型,如Wan 2.1。相关代码将发布在:https://github.com/ali-vilab/UniAnimate-DiT。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着扩散模型的发展,以人为中心的可控视频生成领域取得了显著进步,但在视频中实现精确和局部化的运动控制,如在保留所需运动模式的同时替换或插入个体,仍是一项艰巨的挑战。本研究提出了ReplaceAnyone框架,专注于局部人物替换和插入,带有复杂背景。我们将此任务制定为图像条件视频修复范式,采用统一的端到端视频扩散架构,在掩码区域内进行图像条件视频修复。为预防形状泄露并实现精细局部控制,我们引入了多种掩码形式,包括规则和不规则形状。此外,我们还实施了丰富的视觉引导机制,以提高外观对齐度,混合修复编码器以进一步保留掩码视频中的详细背景信息,以及两阶段优化方法以简化训练难度。ReplaceAnyone能够在单一框架内无缝替换或插入角色,同时保持所需的姿势运动和参考外观。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在以人为中心的可控视频生成领域取得显著进步。
- 实现精确和局部化的运动控制(如替换或插入视频中的个体)仍是一个挑战。
- ReplaceAnyone框架专注于局部人物替换和插入,带有复杂背景。
- 该任务被制定为图像条件视频修复范式,利用统一的端到端视频扩散架构。
- 为实现精细局部控制,引入了多种掩码形式和丰富的视觉引导机制。
- ReplaceAnyone能无缝替换或插入角色,同时保持姿势运动和外观。
- 该方法不仅适用于传统的3D-UNet基础模型,也适用于DiT-based视频模型,如Wan2.1。
点此查看论文截图