⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-09 更新
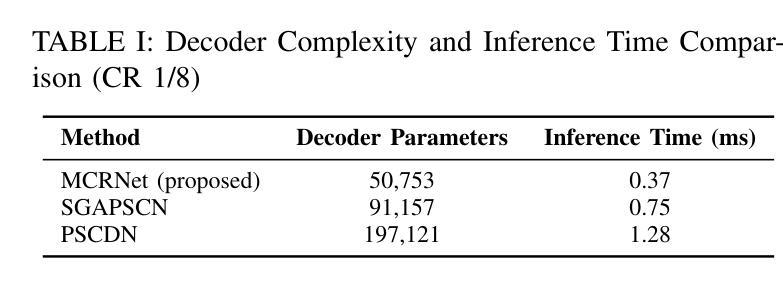
Meta-Learning Driven Lightweight Phase Shift Compression for IRS-Assisted Wireless Systems
Authors:Xianhua Yu, Dong Li, Bowen Gu, Xiaoye Jing, Wen Wu, Tuo Wu, Kan Yu
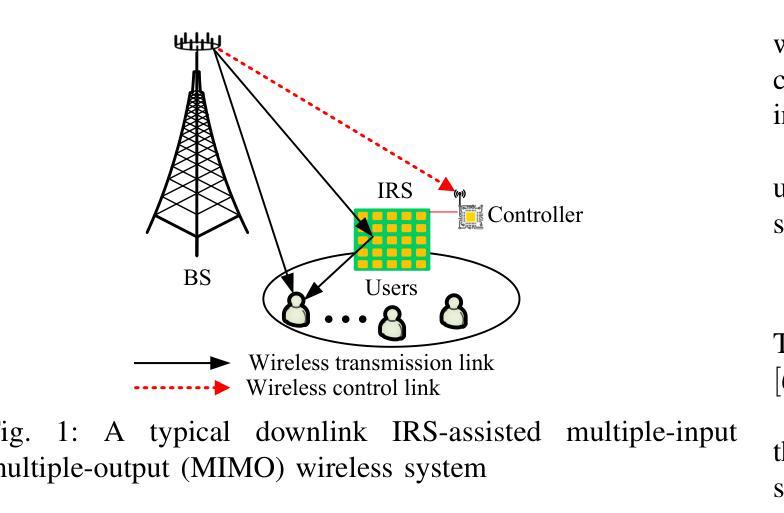
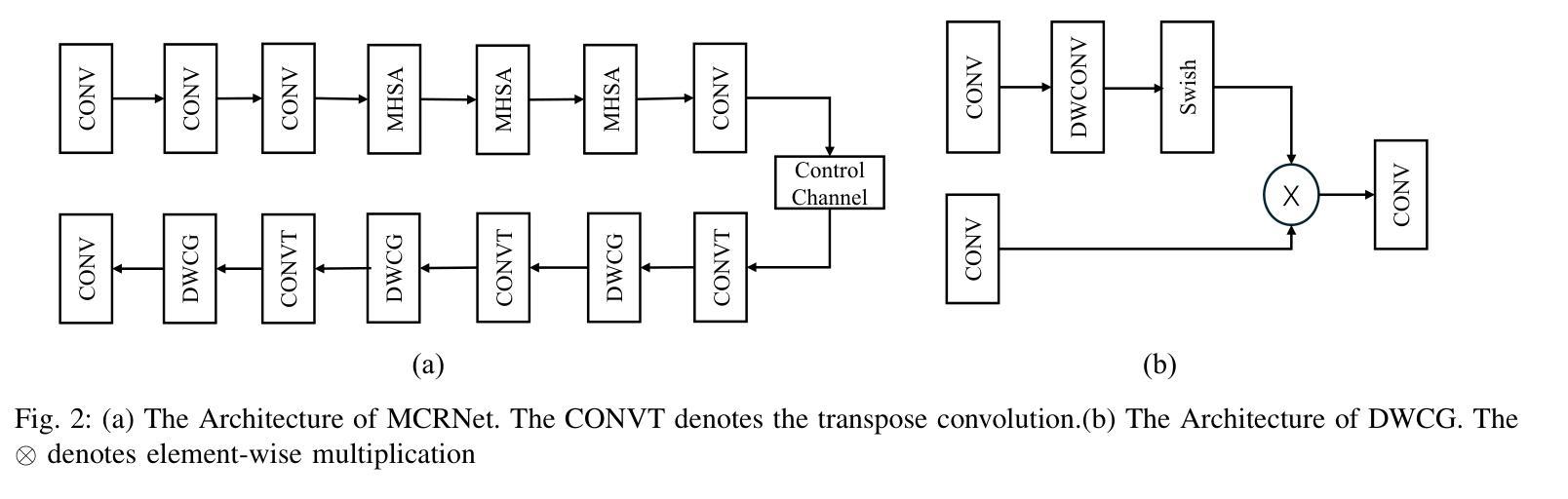
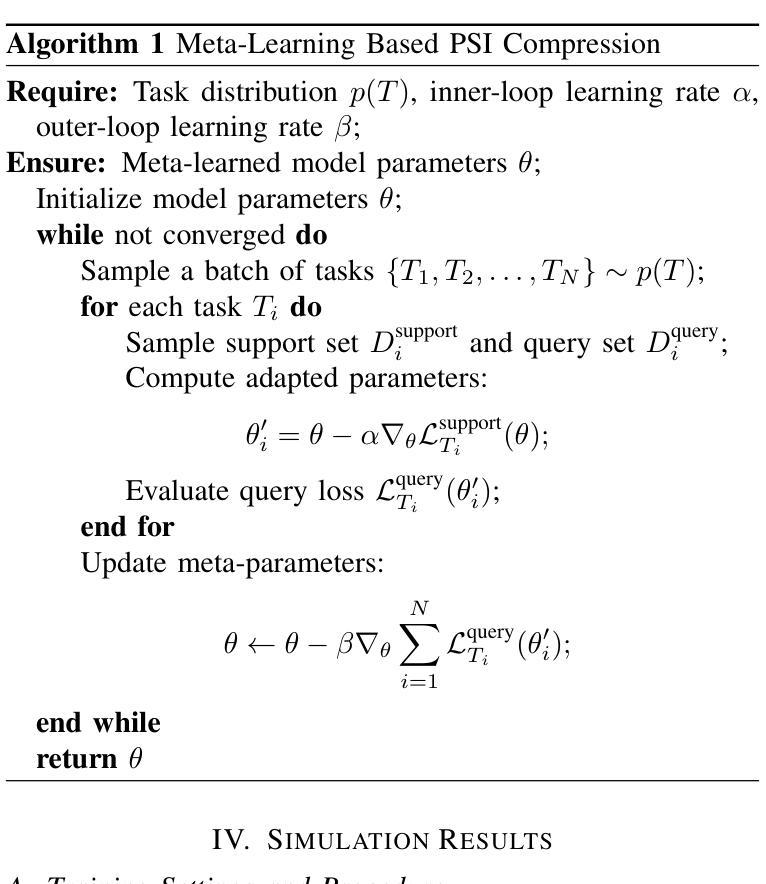
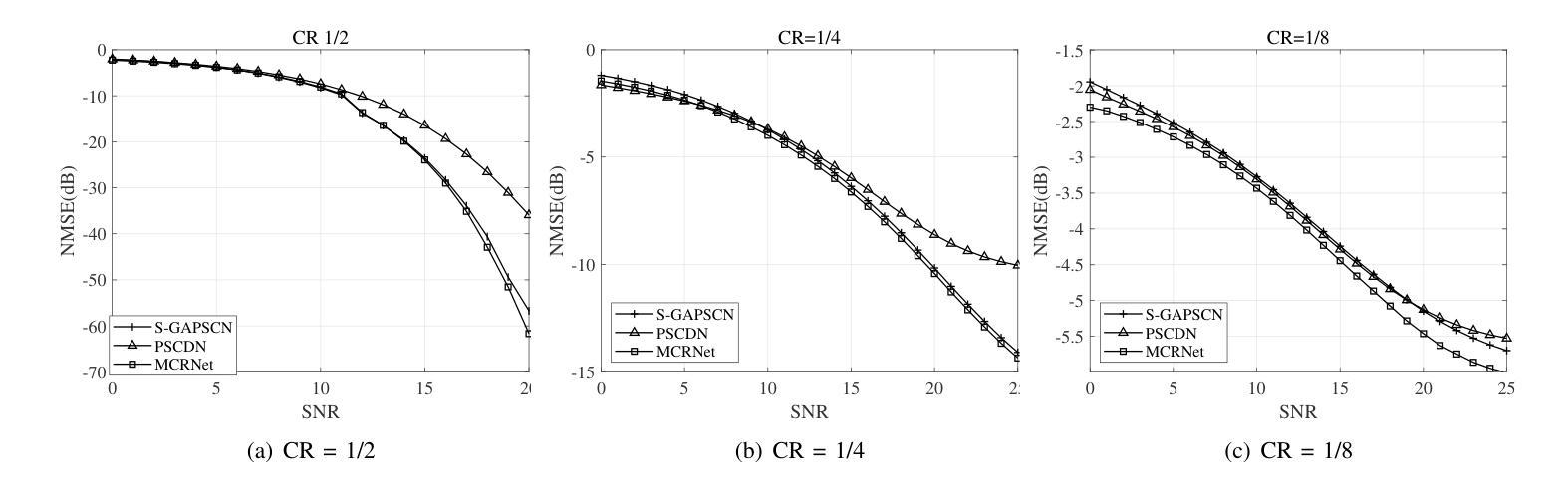
The phase shift information (PSI) overhead poses a critical challenge to enabling real-time intelligent reflecting surface (IRS)-assisted wireless systems, particularly under dynamic and resource-constrained conditions. In this paper, we propose a lightweight PSI compression framework, termed meta-learning-driven compression and reconstruction network (MCRNet). By leveraging a few-shot adaptation strategy via model-agnostic meta-learning (MAML), MCRNet enables rapid generalization across diverse IRS configurations with minimal retraining overhead. Furthermore, a novel depthwise convolutional gating (DWCG) module is incorporated into the decoder to achieve adaptive local feature modulation with low computational cost, significantly improving decoding efficiency. Extensive simulations demonstrate that MCRNet achieves competitive normalized mean square error performance compared to state-of-the-art baselines across various compression ratios, while substantially reducing model size and inference latency. These results validate the effectiveness of the proposed asymmetric architecture and highlight the practical scalability and real-time applicability of MCRNet for dynamic IRS-assisted wireless deployments.
相位偏移信息(PSI)开销为实时智能反射表面(IRS)辅助无线系统带来了重大挑战,特别是在动态和资源受限的条件下。本文提出了一种轻量级的PSI压缩框架,称为元学习驱动压缩与重建网络(MCRNet)。通过利用模型无关元学习(MAML)进行小样本适应策略,MCRNet能够在各种IRS配置中快速推广,并且只需要最小的再训练开销。此外,解码器中还融入了一种新型深度卷积门控(DWCG)模块,以实现具有低计算成本的自适应局部特征调制,从而大大提高了解码效率。大量模拟结果表明,与最新基线相比,MCRNet在各种压缩率下实现了具有竞争力的归一化均方误差性能,同时大大减少了模型大小和推理延迟。这些结果验证了所提出的不对称架构的有效性,并突出了MCRNet在实际动态IRS辅助无线部署中的实用可扩展性和实时适用性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于元学习驱动的压缩与重建网络(MCRNet)的相位偏移信息(PSI)压缩框架,用于实时智能反射表面(IRS)辅助的无线系统。该框架利用模型无关元学习(MAML)的少样本适应策略,实现快速泛化到不同的IRS配置,并加入深度可分离卷积门控模块以在低计算成本下实现自适应局部特征调制,提高解码效率。模拟结果表明,MCRNet在多种压缩比下实现了具有竞争力的归一化均方误差性能,同时显著减少了模型大小和推理延迟。验证了不对称架构的有效性以及MCRNet在实际动态IRS辅助无线部署中的实时适用性和可扩展性。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种新型的PSI压缩框架,称为MCRNet。
- 利用模型无关的元学习技术(MAML)进行少样本适应,可快速泛化到多种IRS配置。
- 采用深度可分离卷积门控模块实现自适应局部特征调制,提高解码效率并降低计算成本。
- 通过广泛的模拟实验验证了MCRNet的性能优于其他现有技术基准。
- MCRNet在各种压缩比下实现了具有竞争力的归一化均方误差性能。
- 显著减少了模型大小和推理延迟,增强了实际应用中的实时性和可扩展性。
点此查看论文截图

A Large Language Model for Feasible and Diverse Population Synthesis
Authors:Sung Yoo Lim, Hyunsoo Yun, Prateek Bansal, Dong-Kyu Kim, Eui-Jin Kim
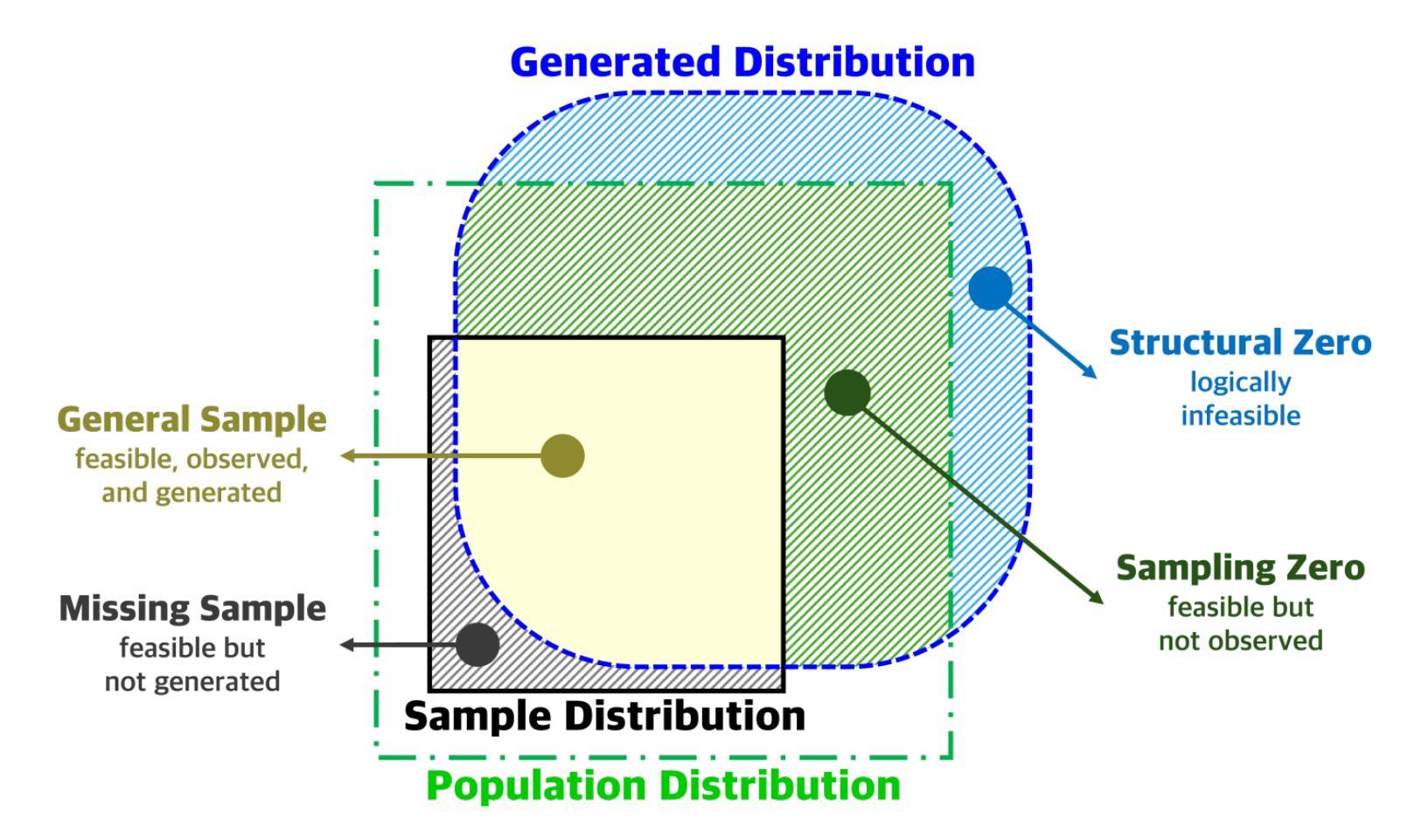
Generating a synthetic population that is both feasible and diverse is crucial for ensuring the validity of downstream activity schedule simulation in activity-based models (ABMs). While deep generative models (DGMs), such as variational autoencoders and generative adversarial networks, have been applied to this task, they often struggle to balance the inclusion of rare but plausible combinations (i.e., sampling zeros) with the exclusion of implausible ones (i.e., structural zeros). To improve feasibility while maintaining diversity, we propose a fine-tuning method for large language models (LLMs) that explicitly controls the autoregressive generation process through topological orderings derived from a Bayesian Network (BN). Experimental results show that our hybrid LLM-BN approach outperforms both traditional DGMs and proprietary LLMs (e.g., ChatGPT-4o) with few-shot learning. Specifically, our approach achieves approximately 95% feasibility, significantly higher than the ~80% observed in DGMs, while maintaining comparable diversity, making it well-suited for practical applications. Importantly, the method is based on a lightweight open-source LLM, enabling fine-tuning and inference on standard personal computing environments. This makes the approach cost-effective and scalable for large-scale applications, such as synthesizing populations in megacities, without relying on expensive infrastructure. By initiating the ABM pipeline with high-quality synthetic populations, our method improves overall simulation reliability and reduces downstream error propagation. The source code for these methods is available for research and practical application.
在活动基于模型(ABM)中生成既可行又多样化的合成人口对于确保下游活动日程模拟的有效性至关重要。虽然深度生成模型(DGM),如变分自动编码器和生成对抗网络,已经应用于这项任务,但它们往往难以平衡包含罕见但合理的组合(例如,采样零值)与排除不合理的组合之间的矛盾。为了在提高可行性的同时保持多样性,我们提出了一种针对大型语言模型(LLM)的微调方法,该方法通过贝叶斯网络(BN)得出的拓扑排序来显式控制自回归生成过程。实验结果表明,我们的混合LLM-BN方法在传统DGM和专有LLM(例如ChatGPT-4o)上的少样本学习表现更好。具体来说,我们的方法实现了大约95%的可行性,明显高于DGM中的约80%,同时保持相当的多样性,使其非常适合实际应用。重要的是,该方法基于轻量级的开源LLM,能够在标准的个人计算环境上进行微调并推断。这使得该方法对于大规模应用,如合成大城市人口等,具有经济实惠和可扩展性优势,无需依赖昂贵的基础设施。通过以高质量合成人口启动ABM管道,我们的方法提高了整体模拟的可靠性并减少了下游误差传播。这些方法的相关源代码可供研究和实践应用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 28 pages, 7 figures, 6 tables. Submitted to Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies. Preprint version
Summary
该文强调了在活动基于模型(ABM)中生成既可行又多样化的人口的综合人口生成的重要性。为了改进可行性和保持多样性,文章提出了一种大型语言模型(LLM)的微调方法,该方法通过贝叶斯网络(BN)派生的拓扑顺序显式控制自回归生成过程。实验结果显示,与传统的深度生成模型(DGM)和专有大型语言模型相比,该混合LLM-BN方法具有更高的可行性和相当多样性。此外,该方法基于轻量级开源大型语言模型,可在标准个人计算环境中进行微调并推断,成本效益高且适用于大规模应用。因此,通过提高ABM管道中合成人口的可靠性,该方法提高了整体模拟的可靠性并减少了下游误差传播。
Key Takeaways
- 生成可行且多样化的合成人口对于确保活动基于模型(ABM)的下游活动模拟有效性至关重要。
- 深度的生成模型在平衡罕见但可能的组合与不可能的结构零的问题上遇到挑战。
- 提出了一种混合的大型语言模型(LLM)-贝叶斯网络(BN)方法,以提高人口生成的可行性和多样性。
- 与传统的深度生成模型和专有大型语言模型相比,混合LLM-BN方法具有更高的可行性和相当多样性。
- 该方法基于轻量级开源大型语言模型,适用于标准个人计算环境,成本效益高且适用于大规模应用。
- 该方法提高了活动模拟的可靠性并减少了下游误差传播。
点此查看论文截图

Can Large Language Models Predict Parallel Code Performance?
Authors:Gregory Bolet, Giorgis Georgakoudis, Harshitha Menon, Konstantinos Parasyris, Niranjan Hasabnis, Hayden Estes, Kirk W. Cameron, Gal Oren
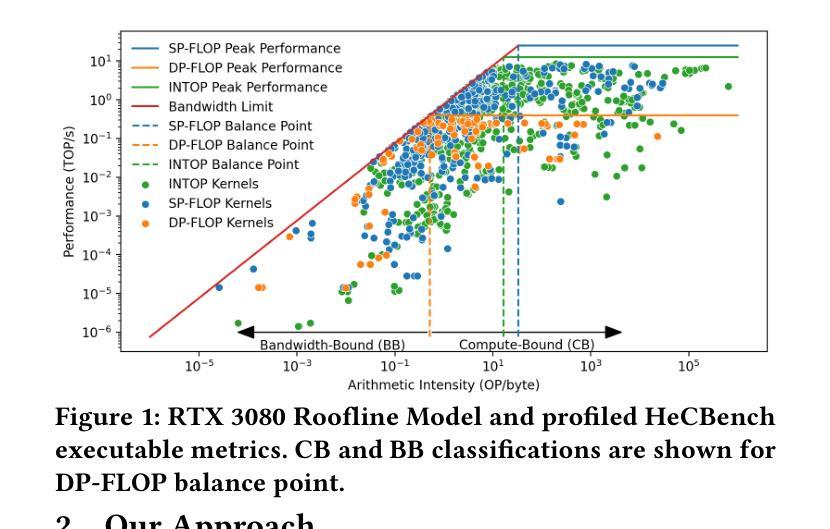
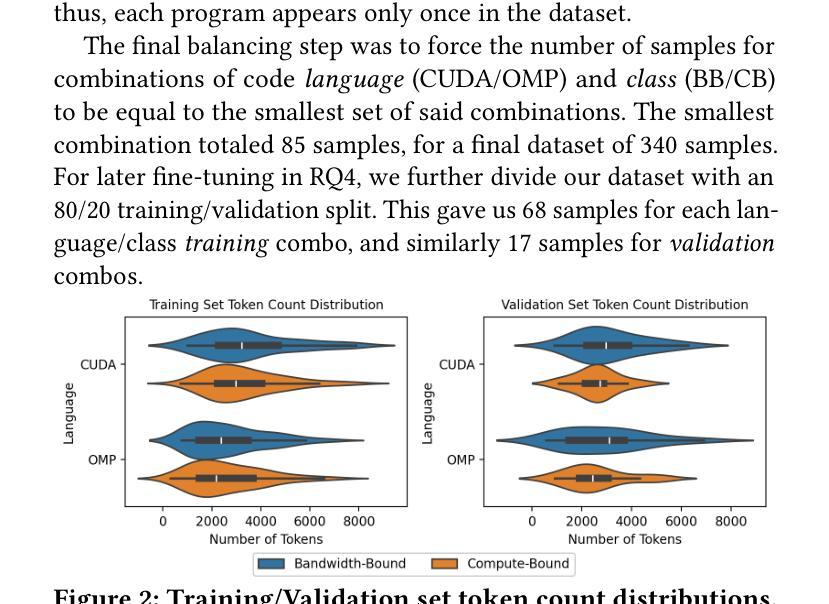
Accurate determination of the performance of parallel GPU code typically requires execution-time profiling on target hardware – an increasingly prohibitive step due to limited access to high-end GPUs. This paper explores whether Large Language Models (LLMs) can offer an alternative approach for GPU performance prediction without relying on hardware. We frame the problem as a roofline classification task: given the source code of a GPU kernel and the hardware specifications of a target GPU, can an LLM predict whether the GPU kernel is compute-bound or bandwidth-bound? For this study, we build a balanced dataset of 340 GPU kernels, obtained from HeCBench benchmark and written in CUDA and OpenMP, along with their ground-truth labels obtained via empirical GPU profiling. We evaluate LLMs across four scenarios: (1) with access to profiling data of the kernel source, (2) zero-shot with source code only, (3) few-shot with code and label pairs, and (4) fine-tuned on a small custom dataset. Our results show that state-of-the-art LLMs have a strong understanding of the Roofline model, achieving 100% classification accuracy when provided with explicit profiling data. We also find that reasoning-capable LLMs significantly outperform standard LLMs in zero- and few-shot settings, achieving up to 64% accuracy on GPU source codes, without profiling information. Lastly, we find that LLM fine-tuning will require much more data than what we currently have available. This work is among the first to use LLMs for source-level roofline performance prediction via classification, and illustrates their potential to guide optimization efforts when runtime profiling is infeasible. Our findings suggest that with better datasets and prompt strategies, LLMs could become practical tools for HPC performance analysis and performance portability.
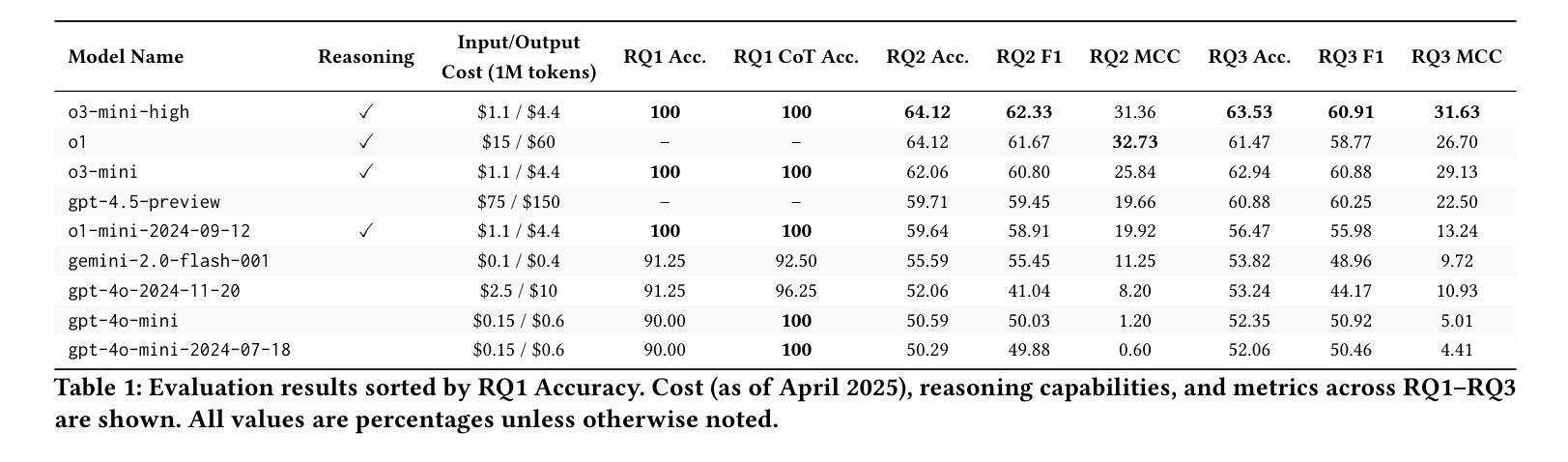
准确确定并行GPU代码的性能通常需要在目标硬件上进行执行时间分析,这是一个由于高端GPU访问有限而越来越不可行的步骤。本文探讨了大型语言模型(LLM)是否能在不依赖硬件的情况下为GPU性能预测提供替代方法。我们将问题框架设定为屋顶线分类任务:给定GPU内核的源代码和目标GPU的硬件规格,LLM能否预测GPU内核是计算受限还是带宽受限?
为了这项研究,我们构建了包含340个GPU内核的平衡数据集,这些内核来自HeCBench基准测试,采用CUDA和OpenMP编写,还结合了通过实证GPU分析获得的真实标签。我们对LLM在四种场景下的表现进行了评估:(1)能够访问内核源代码的分析数据,(2)仅使用源代码的零样本情景,(3)使用代码和标签对的少量情景,以及(4)在小规模自定义数据集上进行微调。
我们的结果表明,尖端LLM对屋顶线模型有深刻的理解,在提供明确的分析数据时,分类准确率可达100%。我们还发现,能够推理的LLM在零样本和少量样本场景中显著优于标准LLM,在没有分析信息的情况下,对GPU源代码的准确率高达64%。最后,我们发现LLM的微调将需要比当前可用的数据更多的数据。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, 4 figures, accepted to AI4Sys Workshop at HPDC 2025
摘要
本文探索了大型语言模型(LLMs)在无需硬件的情况下对GPU性能进行预测的可能性。研究将问题定位为屋顶线分类任务:给定GPU内核的源代码和目标GPU的硬件规格,LLM能否预测GPU内核是计算受限还是带宽受限?研究构建了包含340个GPU内核的平衡数据集,这些数据集来自HeCBench基准测试,并使用CUDA和OpenMP编写,以及通过实证GPU分析获得的真实标签。评估LLMs在四种场景下的表现:(1)可访问内核源代码的剖析数据,(2)仅使用源代码的零镜头,(3)带有代码和标签对的镜头,(4)在小规模自定义数据集上进行微调。结果显示,最先进的LLMs对屋顶线模型有深刻的理解,在提供明确的剖析数据时,分类准确率高达百分之百。此外,发现推理能力强的大型语言模型在零和少量镜头设置中显著优于标准大型语言模型,在没有剖析信息的情况下,对GPU源代码的准确率高达百分之六十四。最后,发现大型语言模型的微调将需要比现有更多的数据。这项工作率先使用大型语言模型进行源代码屋顶线性能分类预测,并证明了其在无法进行运行时分析时指导优化工作的潜力。
关键见解
- 大型语言模型能够在无需硬件的情况下预测GPU性能。
- LLMs对屋顶线模型有深刻理解,在提供剖析数据时分类准确率极高。
- 推理能力强的大型语言模型在没有剖析信息的情况下也能达到较高的准确率。
- LLMs在零镜头和少量镜头设置中的表现优于标准大型语言模型。
- 大型语言模型的微调需要大量数据。
- LLMs在指导优化工作和性能分析方面具有潜力。
点此查看论文截图

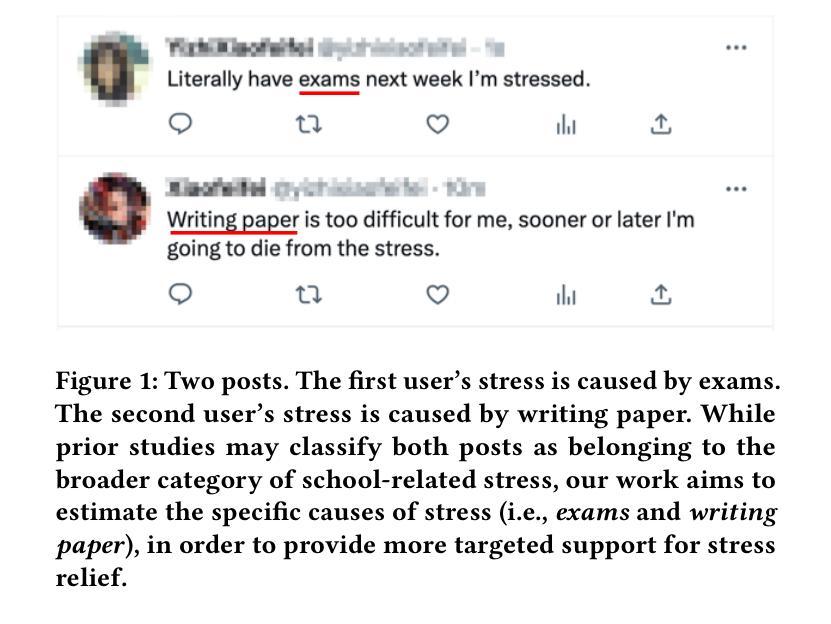
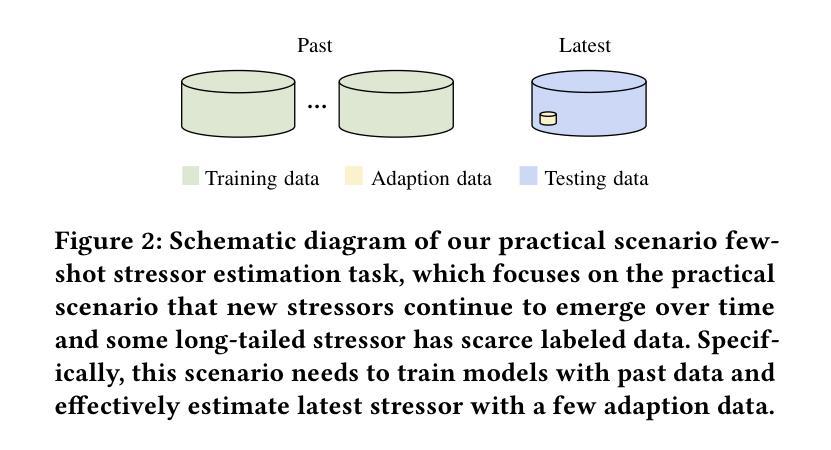
MISE: Meta-knowledge Inheritance for Social Media-Based Stressor Estimation
Authors:Xin Wang, Ling Feng, Huijun Zhang, Lei Cao, Kaisheng Zeng, Qi Li, Yang Ding, Yi Dai, David Clifton
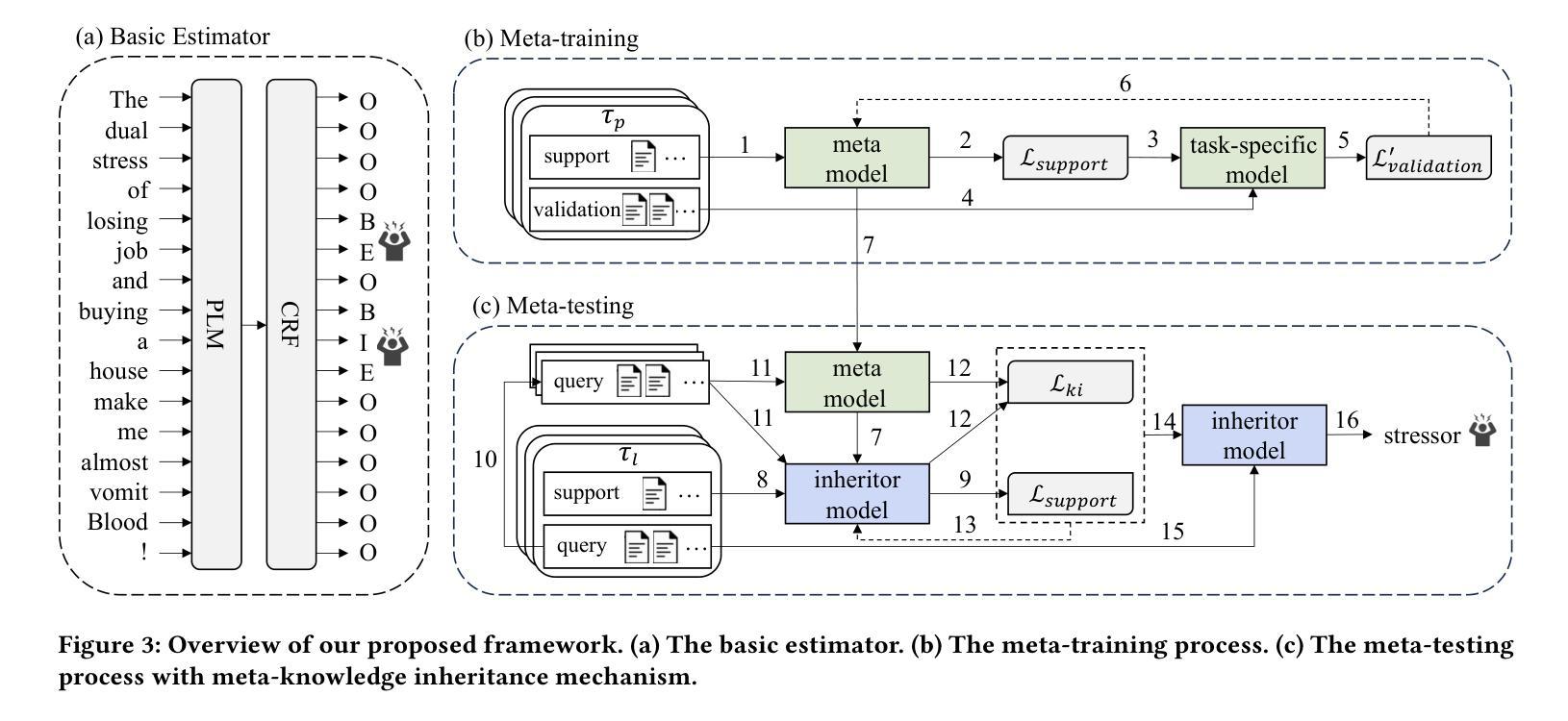
Stress haunts people in modern society, which may cause severe health issues if left unattended. With social media becoming an integral part of daily life, leveraging social media to detect stress has gained increasing attention. While the majority of the work focuses on classifying stress states and stress categories, this study introduce a new task aimed at estimating more specific stressors (like exam, writing paper, etc.) through users’ posts on social media. Unfortunately, the diversity of stressors with many different classes but a few examples per class, combined with the consistent arising of new stressors over time, hinders the machine understanding of stressors. To this end, we cast the stressor estimation problem within a practical scenario few-shot learning setting, and propose a novel meta-learning based stressor estimation framework that is enhanced by a meta-knowledge inheritance mechanism. This model can not only learn generic stressor context through meta-learning, but also has a good generalization ability to estimate new stressors with little labeled data. A fundamental breakthrough in our approach lies in the inclusion of the meta-knowledge inheritance mechanism, which equips our model with the ability to prevent catastrophic forgetting when adapting to new stressors. The experimental results show that our model achieves state-of-the-art performance compared with the baselines. Additionally, we construct a social media-based stressor estimation dataset that can help train artificial intelligence models to facilitate human well-being. The dataset is now public at \href{https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/xinwangcs/stressor-cause-of-mental-health-problem-dataset}{\underline{Kaggle}} and \href{https://huggingface.co/datasets/XinWangcs/Stressor}{\underline{Hugging Face}}.
在现代社会,压力困扰着人们,如果置之不理,可能会导致严重的健康问题。随着社交媒体成为日常生活的重要组成部分,利用社交媒体检测压力越来越受到关注。虽然大多数工作都集中在分类压力状态和压力类别上,但这项研究介绍了一个新任务,旨在通过用户在社交媒体上的帖子来估计更具体的压力源(如考试、写论文等)。然而,压力源的多样性具有许多不同的类别,每一类别只有很少的示例,以及随时间不断出现的新压力源,阻碍了机器对压力源的理解。为此,我们将压力源估计问题置于实际场景的小样本学习环境中,并提出了一种基于元学习的压力源估计新框架,该框架通过元知识继承机制得到了增强。该模型不仅可以利用元学习获得通用的压力源上下文,而且具有良好的泛化能力,可以估计新的压力源而无需大量标记数据。我们的方法的一个基本突破在于引入了元知识继承机制,使我们的模型在适应新压力源时能够防止灾难性遗忘。实验结果表明,与基线相比,我们的模型达到了最先进的性能。此外,我们构建了一个基于社交媒体的压力源估计数据集,可以帮助训练人工智能模型以促进人类福祉。数据集现在已在\underline{Kaggle}和\underline{Hugging Face)上公开。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF WWW2025, Oral Presentation
Summary
社交媒体在现代社会中成为检测压力的重要工具。当前多数研究集中在分类压力状态和类别上,而本研究旨在通过社交媒体帖子来估计更具体的压力源(如考试、写作论文等)。然而,压力源的多样性以及每类样本数量较少且不断出现新的压力源,给机器理解压力源带来挑战。本研究将压力源估计问题置于实际场景中,采用小样本学习设置,并提出基于元学习的压力源估计框架,通过元知识继承机制进行增强。该模型不仅能通过元学习学习通用压力源上下文,而且在新压力源少量标注数据的情况下具有良好的泛化能力。其关键突破在于引入元知识继承机制,使模型在适应新压力源时能够防止灾难性遗忘。实验结果证明该模型较基线方法达到最佳性能。此外,本研究还构建了社交媒体基于的压力源估计数据集,帮助训练人工智能模型以促进人类福祉。数据集已在Kaggle和Hugging Face上公开。
Key Takeaways
- 现代社会中压力问题严重,可通过社交媒体检测压力。
- 现有研究多关注压力状态和类别的分类,本研究致力于通过社交媒体帖子估计具体压力源。
- 压力源的多样性和样本数量限制给机器理解带来挑战。
- 采用小样本学习设置,提出基于元学习的压力源估计框架,结合元知识继承机制。
- 模型具有良好泛化能力,能在少量标注数据下估计新压力源。
- 元知识继承机制防止模型在适应新压力源时发生灾难性遗忘。
点此查看论文截图