⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-09 更新
Using anomaly detection to search for technosignatures in Breakthrough Listen observations
Authors:Snir Pardo, Dovi Poznanski, Steve Croft, Andrew P. V. Siemion, Matthew Lebofsky
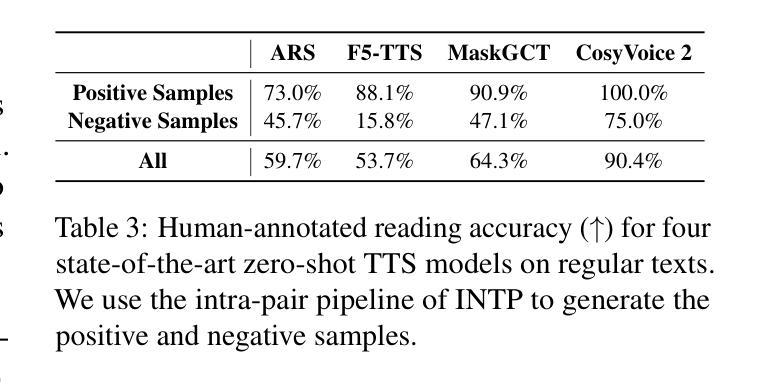
We implement a machine learning algorithm to search for extra-terrestrial technosignatures in radio observations of several hundred nearby stars, obtained with the Parkes and Green Bank Telescopes by the Breakthrough Listen collaboration. Advances in detection technology have led to an exponential growth in data, necessitating innovative and efficient analysis methods. This problem is exacerbated by the large variety of possible forms an extraterrestrial signal might take, and the size of the multidimensional parameter space that must be searched. It is then made markedly worse by the fact that our best guess at the properties of such a signal is that it might resemble the signals emitted by human technology and communications, the main (yet diverse) contaminant in radio observations. We address this challenge by using a combination of simulations and machine learning methods for anomaly detection. We rank candidates by how unusual they are in frequency, and how persistent they are in time, by measuring the similarity between consecutive spectrograms of the same star. We validate that our filters significantly improve the quality of the candidates that are selected for human vetting when compared to a random selection. Of the ~ 10^11 spectrograms that we analyzed, we visually inspected thousands of the most promising spectrograms, and thousands more for validation, about 20,000 in total, and report that no candidate survived basic scrutiny.
我们实现了一种机器学习算法,用于在突破聆听合作通过帕克斯和格林班克望远镜获得的数百颗附近恒星的无线电观测中寻找外星技术迹象。检测技术的进步导致了数据的指数级增长,需要创新和高效的分析方法。这个问题因外星信号可能采取的多种形式和必须搜索的多维参数空间的大小而加剧。更糟糕的是,我们对此类信号属性的最佳猜测是它可能类似于人类技术和通信中发出的信号,这是无线电观测中的主要(但多样化)污染物。我们通过模拟和机器学习方法的结合来解决这一挑战,进行异常检测。我们通过测量同一恒星连续光谱图之间的相似性,对候选者进行排名,看他们频率上有多不寻常,时间上有多持久。我们验证了我们的过滤器与随机选择相比,显着提高了所选候选人的质量,这些候选人需要经过人工审核。在我们分析的约10^11个光谱图中,我们对数千个最有希望的光谱图进行了视觉检查,还有数千个用于验证的光谱图,总计约2万个。我们报告说,没有候选者通过基本审查。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF AJ accepted
Summary:
我们利用机器学习算法在来自帕克望远镜和格林班克望远镜的数百颗附近恒星的无线电观测中寻找外星技术迹象。由于检测技术的指数级增长,产生了大量数据,需要创新和高效的分析方法。我们面临的挑战在于外星信号可能呈现的形式多种多样,以及必须搜索的多维参数空间的规模巨大。我们通过结合模拟和机器学习方法进行异常检测来解决这一挑战。我们对候选对象根据其在频率上的不寻常程度和在时间上的持久性进行排名。验证我们的过滤器在所选候选人的质量上,与随机选择相比有明显改善。经过视觉检查数十万张最富希望的谱图后,未发现任何符合要求的候选人。
Key Takeaways:
- 利用机器学习算法在恒星无线电观测中搜索外星技术迹象。
- 数据增长迅速,需要创新和高效的分析方法。
- 外星信号的形式多种多样,搜索多维参数空间规模巨大。
- 通过模拟和结合机器学习方法进行异常检测来解决挑战。
- 对候选对象进行排名,考虑其在频率上的不寻常程度和在时间上的持久性。
- 过滤器在所选候选人的质量上显著改善,相较于随机选择。
点此查看论文截图

VividListener: Expressive and Controllable Listener Dynamics Modeling for Multi-Modal Responsive Interaction
Authors:Shiying Li, Xingqun Qi, Bingkun Yang, Chen Weile, Zezhao Tian, Muyi Sun, Qifeng Liu, Man Zhang, Zhenan Sun
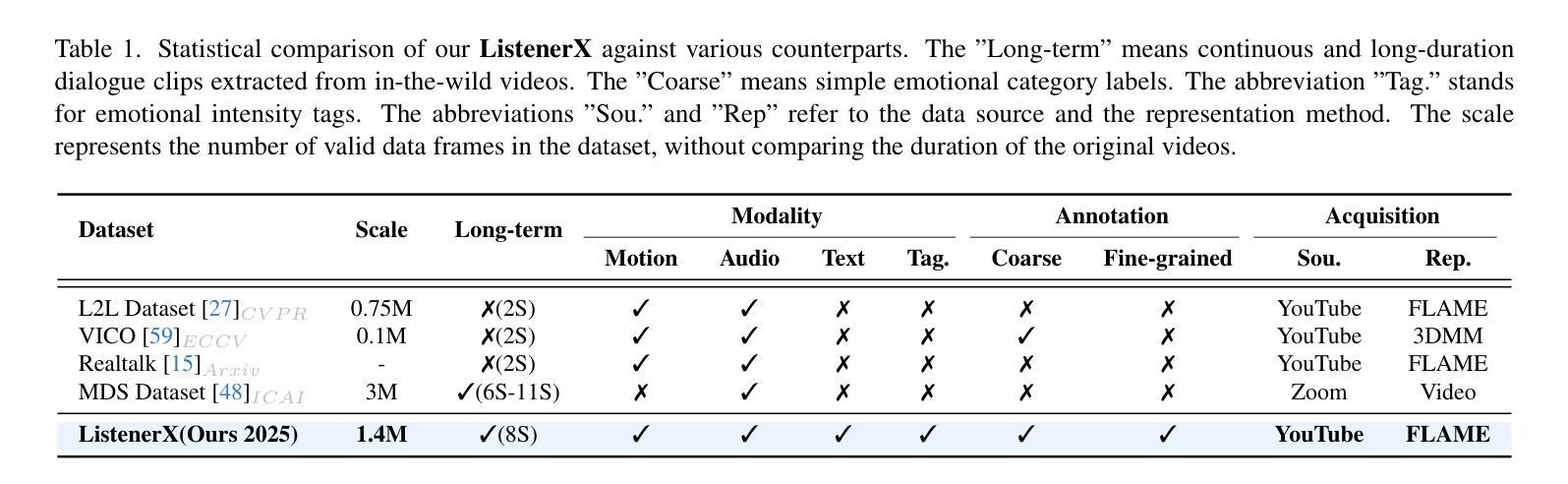
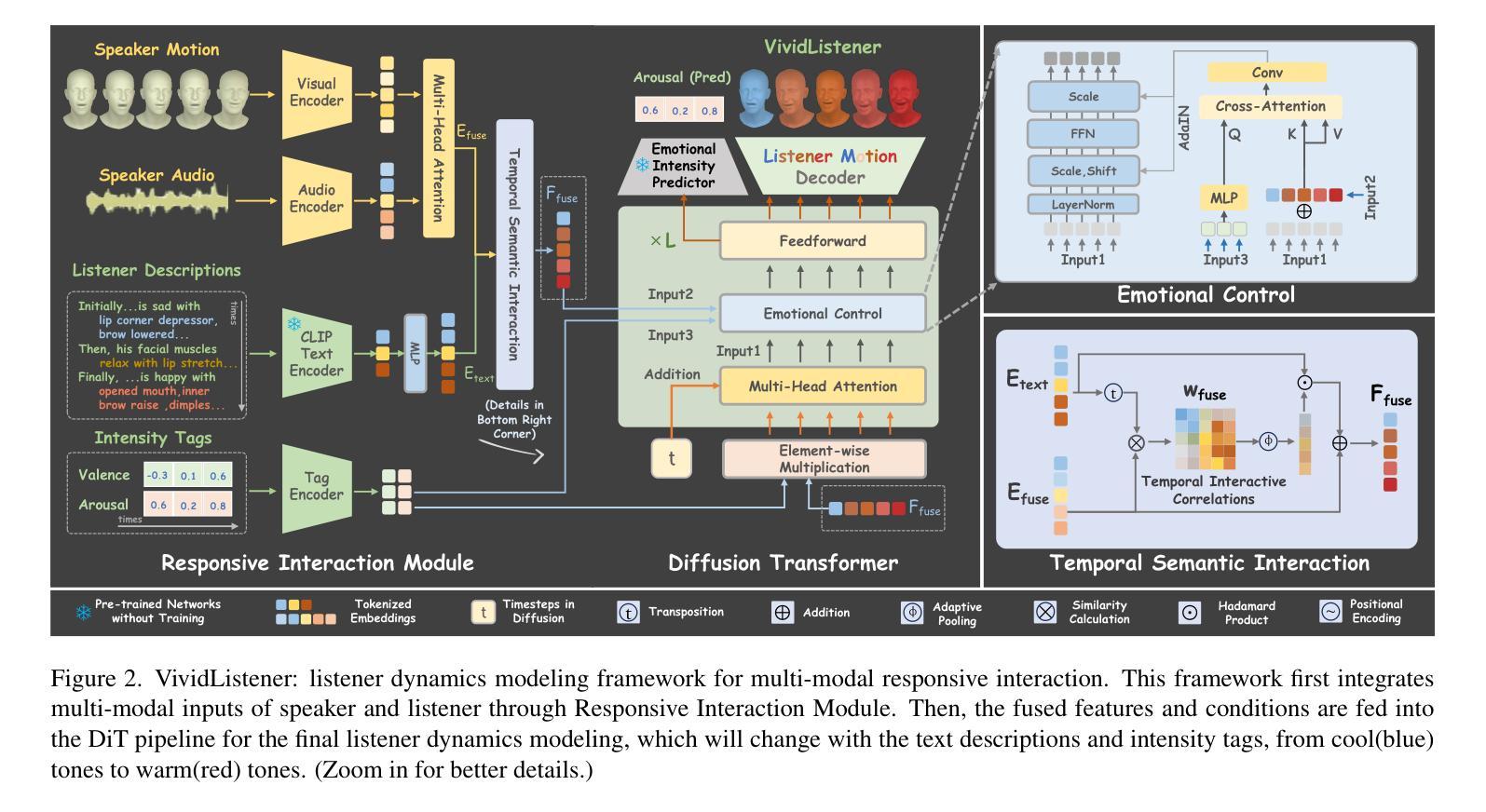
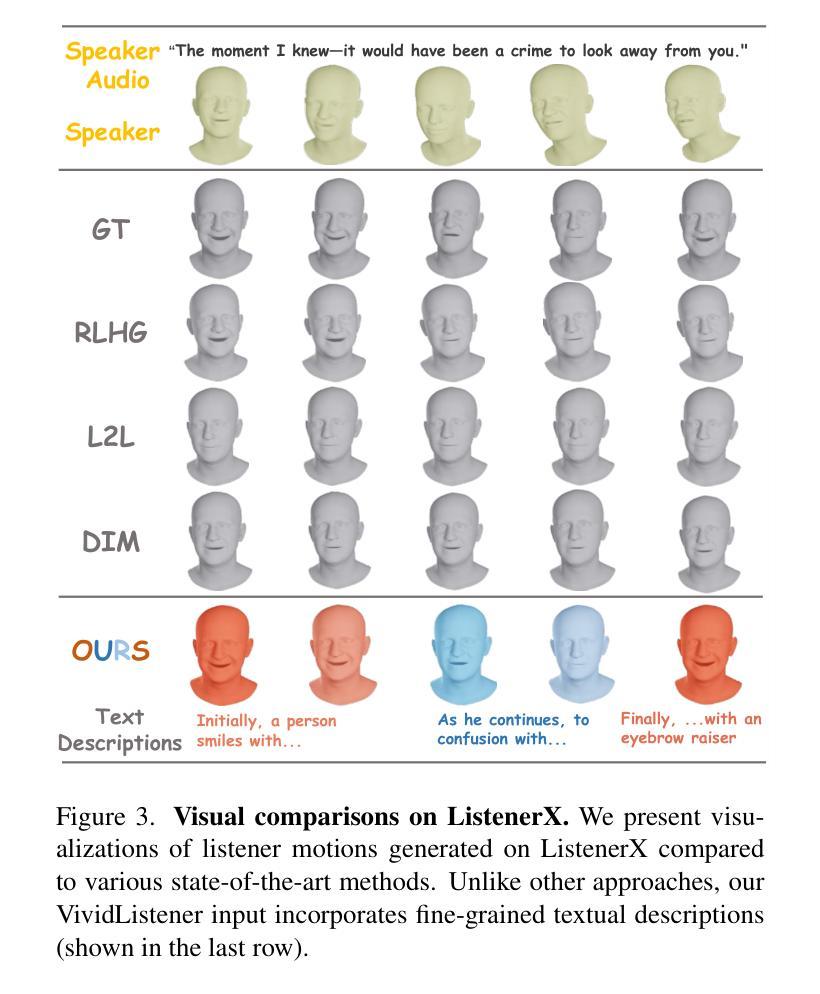
Generating responsive listener head dynamics with nuanced emotions and expressive reactions is crucial for practical dialogue modeling in various virtual avatar animations. Previous studies mainly focus on the direct short-term production of listener behavior. They overlook the fine-grained control over motion variations and emotional intensity, especially in long-sequence modeling. Moreover, the lack of long-term and large-scale paired speaker-listener corpora including head dynamics and fine-grained multi-modality annotations (e.g., text-based expression descriptions, emotional intensity) also limits the application of dialogue modeling.Therefore, we first newly collect a large-scale multi-turn dataset of 3D dyadic conversation containing more than 1.4M valid frames for multi-modal responsive interaction, dubbed ListenerX. Additionally, we propose VividListener, a novel framework enabling fine-grained, expressive and controllable listener dynamics modeling. This framework leverages multi-modal conditions as guiding principles for fostering coherent interactions between speakers and listeners.Specifically, we design the Responsive Interaction Module (RIM) to adaptively represent the multi-modal interactive embeddings. RIM ensures the listener dynamics achieve fine-grained semantic coordination with textual descriptions and adjustments, while preserving expressive reaction with speaker behavior. Meanwhile, we design the Emotional Intensity Tags (EIT) for emotion intensity editing with multi-modal information integration, applying to both text descriptions and listener motion amplitude.Extensive experiments conducted on our newly collected ListenerX dataset demonstrate that VividListener achieves state-of-the-art performance, realizing expressive and controllable listener dynamics.
生成具有细微情绪和生动反应的响应式听者头部动态,对于各种虚拟角色动画中的实际对话建模至关重要。以往的研究主要集中在听者行为的直接短期生成上,忽视了运动变化的精细控制以及情绪强度,特别是在长序列建模中。此外,缺乏长期大规模配对的说-听者语料库,包括头部动态和精细的多模式注释(如基于文本的表情描述、情绪强度等),也限制了对话建模的应用。因此,我们首先新收集了一个大规模的多轮三维二元对话数据集ListenerX,包含超过140万个有效帧的多模式响应交互。此外,我们提出了VividListener这一新型框架,能够实现精细、生动且可控的听者动态建模。该框架利用多模式条件作为指导原则,促进说话人和听者之间的连贯互动。具体来说,我们设计了交互式模块(Responsive Interaction Module,RIM),自适应地表示多模式交互嵌入。RIM确保听者动态与文本描述和调整实现精细的语义协调,同时保持与说话者行为的生动反应。同时,我们为情绪强度编辑设计了情绪强度标签(Emotional Intensity Tags,EIT),通过多模式信息整合,既适用于文本描述也适用于听者运动幅度。在我们新收集的ListenerX数据集上进行的广泛实验表明,VividListener达到了最先进的性能,实现了生动且可控的听者动态。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文关注虚拟对话模型中听众头部动态的情感反应与表达。文章强调了对听众行为的精细控制和对情感强度的精准把握在对话建模中的重要性,特别是在长序列建模中。为解决缺乏大规模、长期的带说话者和听众的语料库问题,文章首次收集了一个大规模的3D双人对话数据集ListenerX,并提出了一种新型的框架VividListener,用于精细、表达和可控的听众动态建模。该框架利用多模态条件作为指导原则,促进说话者和听众之间的连贯互动。通过设计响应交互模块(RIM)和情感强度标签(EIT),VividListener在表达和控制听众动态方面取得了显著的效果。
Key Takeaways
- 虚拟对话模型中,听众头部动态的情感反应与表达建模是关键。
- 现有研究主要关注短期内的听众行为产生,缺乏对运动变化和情感强度的精细控制,尤其在长序列建模中。
- 缺乏大规模、长期的带说话者和听众的语料库,包括头部动态和精细的多模式注释(如基于文本的表达描述、情感强度)。
- ListenerX数据集的建立,包含超过140万有效帧的多模式交互数据,为对话建模提供了新资源。
- VividListener框架实现精细、表达和可控的听众动态建模。
- VividListener利用多模态条件作为指导原则,促进说话者和听众之间的连贯互动。
点此查看论文截图