⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-09 更新
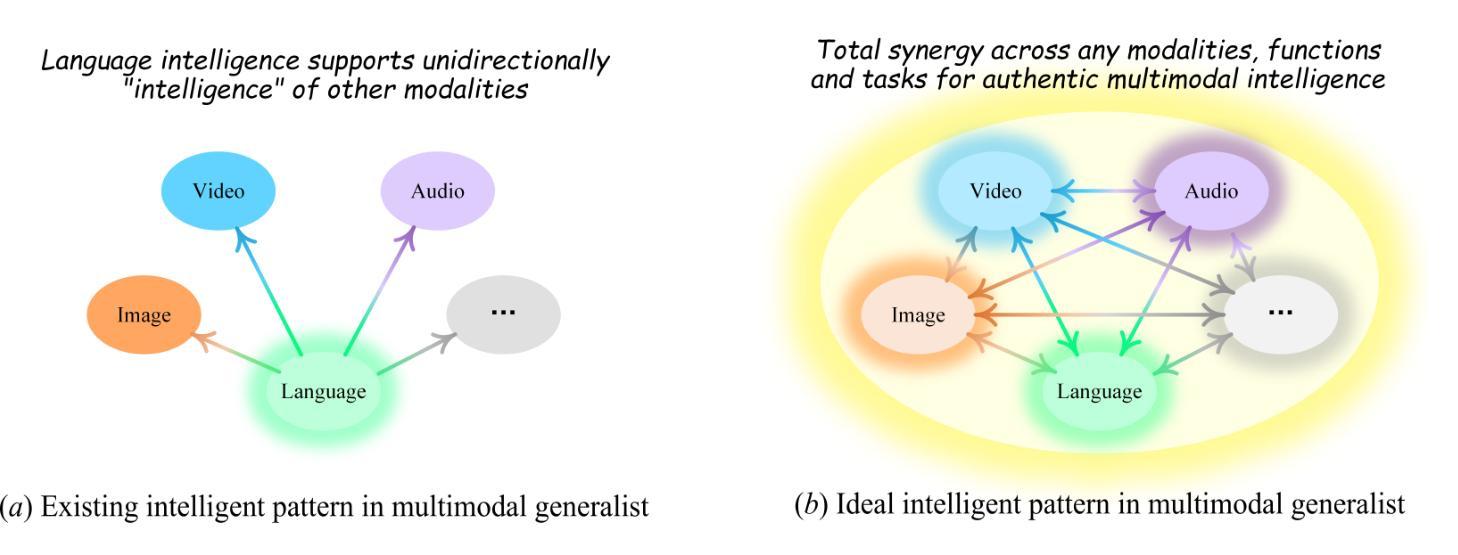
On Path to Multimodal Generalist: General-Level and General-Bench
Authors:Hao Fei, Yuan Zhou, Juncheng Li, Xiangtai Li, Qingshan Xu, Bobo Li, Shengqiong Wu, Yaoting Wang, Junbao Zhou, Jiahao Meng, Qingyu Shi, Zhiyuan Zhou, Liangtao Shi, Minghe Gao, Daoan Zhang, Zhiqi Ge, Weiming Wu, Siliang Tang, Kaihang Pan, Yaobo Ye, Haobo Yuan, Tao Zhang, Tianjie Ju, Zixiang Meng, Shilin Xu, Liyu Jia, Wentao Hu, Meng Luo, Jiebo Luo, Tat-Seng Chua, Shuicheng Yan, Hanwang Zhang
The Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) is currently experiencing rapid growth, driven by the advanced capabilities of LLMs. Unlike earlier specialists, existing MLLMs are evolving towards a Multimodal Generalist paradigm. Initially limited to understanding multiple modalities, these models have advanced to not only comprehend but also generate across modalities. Their capabilities have expanded from coarse-grained to fine-grained multimodal understanding and from supporting limited modalities to arbitrary ones. While many benchmarks exist to assess MLLMs, a critical question arises: Can we simply assume that higher performance across tasks indicates a stronger MLLM capability, bringing us closer to human-level AI? We argue that the answer is not as straightforward as it seems. This project introduces General-Level, an evaluation framework that defines 5-scale levels of MLLM performance and generality, offering a methodology to compare MLLMs and gauge the progress of existing systems towards more robust multimodal generalists and, ultimately, towards AGI. At the core of the framework is the concept of Synergy, which measures whether models maintain consistent capabilities across comprehension and generation, and across multiple modalities. To support this evaluation, we present General-Bench, which encompasses a broader spectrum of skills, modalities, formats, and capabilities, including over 700 tasks and 325,800 instances. The evaluation results that involve over 100 existing state-of-the-art MLLMs uncover the capability rankings of generalists, highlighting the challenges in reaching genuine AI. We expect this project to pave the way for future research on next-generation multimodal foundation models, providing a robust infrastructure to accelerate the realization of AGI. Project page: https://generalist.top/
多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)目前正在经历快速发展,其动力来源于LLM的先进功能。与早期的专家不同,现有的MLLM正在向多模态通才模式发展。这些模型最初仅限于理解多种模式,现已发展进步,不仅能理解也能生成多种模式的内容。它们的能力已从粗粒度的多模态理解扩展到精细粒度的多模态理解,并且从支持有限的模式扩展到任意模式。虽然存在许多基准测试来评估MLLM,但有一个关键问题:我们能否简单地假设跨任务的高性能就表明MLLM能力更强,更能实现人类水平的AI?我们认为答案并不像看起来那么简单。此项目引入了通用级别评估框架,该框架定义了MLLM性能的五个级别以及一般性,提供了一种比较MLLM并衡量现有系统朝着更稳健的多模态通才和最终实现AGI的进展的方法。框架的核心在于协同概念,它衡量的是模型在理解和生成方面以及多个模式之间是否保持了一致的能力。为了支持这一评估,我们推出了General-Bench,它涵盖了更广泛的技能、模式、格式和能力,包括超过700个任务和325,800个实例。涉及超过100个现有最先进的MLLM的评估结果揭示了通才的能力排名,突出了实现真正AI的挑战。我们希望这个项目能为下一代多模态基础模型的进一步研究铺平道路,提供加速实现AGI的稳健基础设施。项目页面:https://generalist.top/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML’25, 305 pages, 115 tables, 177 figures, project page: https://generalist.top/
Summary
本文介绍了多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)的最新进展。MLLM正朝着多模态通用主义模式发展,不仅能理解多种模态,还能生成多种模态的内容。文章提出了一个评估MLLM性能与通用性的五层次评价框架,并引入了“协同”这一核心概念来比较模型在不同理解和生成任务中的表现,并评价不同模型之间的综合能力差距。通过构建大规模的评测基准数据集General-Bench,包括广泛的技能、模态、格式和能力以及超过百万级别的数据点来训练和验证MLLM性能等级评估模型的能力水平排名和挑战,期望为下一代多模态基础模型的实现提供稳健的框架和加速人工智能通用智能(AGI)的实现。
Key Takeaways
- MLLM正在迅速发展和演进,展现出了对多种模态的理解和生成能力。
- 文章提出了一个评估MLLM性能与通用性的五层次评价框架,该框架旨在评估模型在不同任务中的表现,并衡量其向更稳健的多模态通用主义和人工智能通用智能(AGI)迈进的进度。
- 引入了“协同”这一核心评估概念,旨在比较模型在不同理解和生成任务中的一致性表现。
- 构建了一个大规模的评测基准数据集General-Bench,用于训练和验证MLLM性能等级评估模型的能力水平排名和挑战。
- 通过超过百万级别的数据点来评估模型在各种技能和模态方面的表现。
点此查看论文截图

OmniGIRL: A Multilingual and Multimodal Benchmark for GitHub Issue Resolution
Authors:Lianghong Guo, Wei Tao, Runhan Jiang, Yanlin Wang, Jiachi Chen, Xilin Liu, Yuchi Ma, Mingzhi Mao, Hongyu Zhang, Zibin Zheng
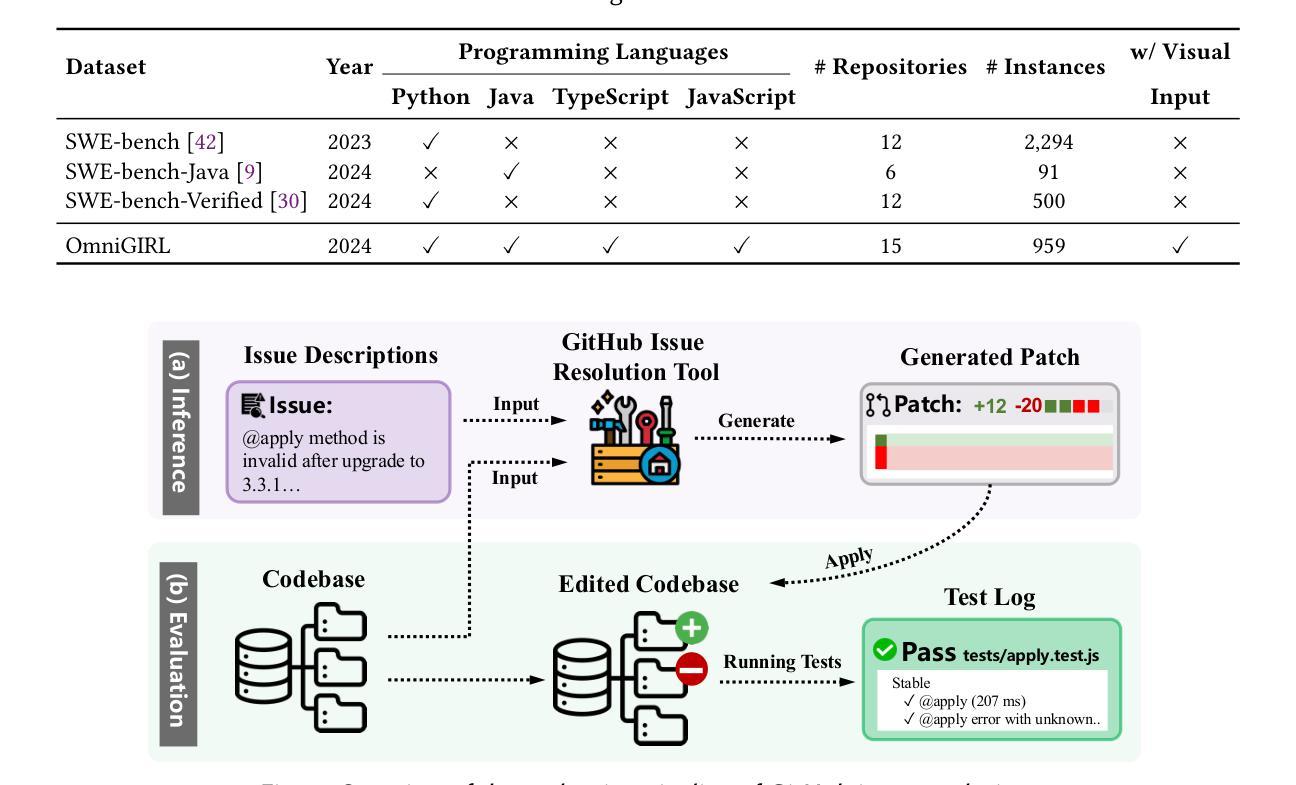
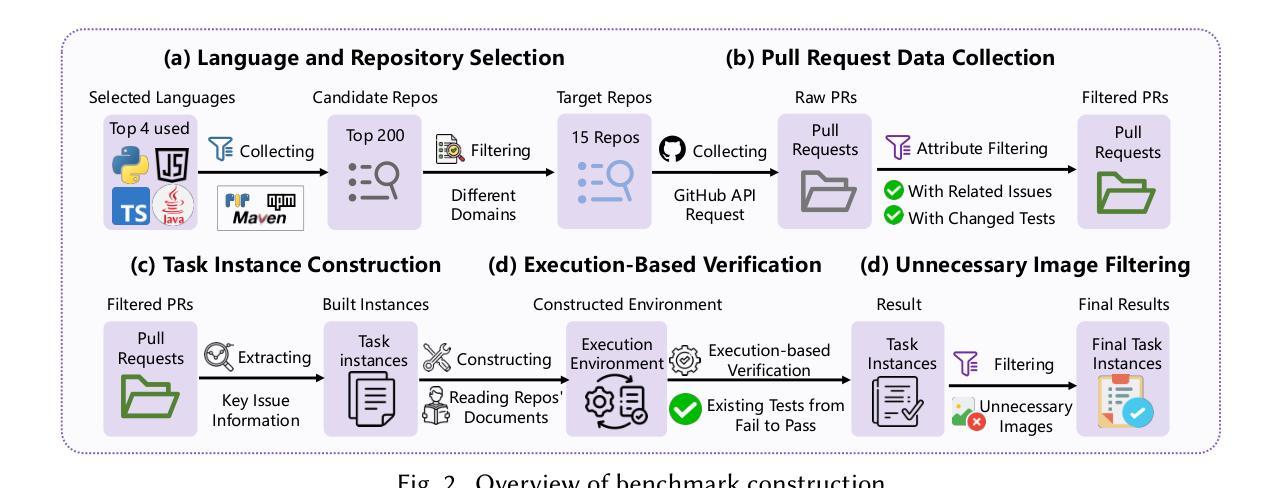
The GitHub issue resolution task aims to resolve issues reported in repositories automatically. With advances in large language models (LLMs), this task has gained increasing attention, and several benchmarks are proposed to evaluate the issue resolution ability of LLMs. However, existing benchmarks have three main limitations. First, current benchmarks focus on a single programming language, limiting the evaluation of issues from repositories across different languages. Second, they usually cover a narrow range of domains, which may fail to represent the diversity of real-world issues. Third, existing benchmarks rely solely on textual information in issue descriptions, overlooking multimodal information such as images in issues. In this paper, we propose OmniGIRL, a GitHub Issue ResoLution benchmark that is multilingual, multimodal, and multi-domain. OmniGIRL includes 959 task instances, which are collected from repositories across four programming languages (i.e., Python, JavaScript, TypeScript, and Java) and eight different domains. Our evaluation shows that current LLMs show limited performances on OmniGIRL. Notably, the best-performing model, GPT-4o, resolves only 8.6% of the issues. Besides, we find that current LLMs struggle to resolve issues requiring understanding images. The best performance is achieved by Claude-3.5-Sonnet, which resolves only 10.5% of the issues with image information. Finally, we analyze the reasons behind current LLMs’ failure on OmniGIRL, providing insights for future improvements.
GitHub问题解答任务旨在自动解决仓库中报告的问题。随着大型语言模型(LLM)的进步,此任务越来越受到关注,并提出了多个基准测试来评估LLM的问题解决能力。然而,现有的基准测试存在三个主要局限性。首先,当前的基准测试专注于单一编程语言,这限制了从不同语言的仓库中评估问题。其次,它们通常涉及范围狭窄的领域,可能无法代表真实世界问题的多样性。第三,现有基准测试仅依赖于问题描述中的文本信息,而忽略了问题中的多模态信息,如图像。在本文中,我们提出了OmniGIRL,这是一个多语言、多模态和多领域的GitHub问题解答基准测试。OmniGIRL包含959个任务实例,这些实例是从四种编程语言(即Python、JavaScript、TypeScript和Java)的仓库中以及八个不同领域收集的。我们的评估显示,当前的LLM在OmniGIRL上的表现有限。值得注意的是,表现最佳的模型GPT-4o只能解决8.6%的问题。此外,我们发现当前LLM在解决需要理解图像的问题时面临困难。成绩最好的是Claude-3.5-Sonnet,它只能解决带有图像信息的10.5%的问题。最后,我们分析了当前LLM在OmniGIRL上失败的原因,为未来的改进提供了见解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To appear at ISSTA’25
Summary
随着大型语言模型(LLM)的发展,GitHub问题自动解决任务得到了越来越多的关注。然而,当前存在几个主要的局限性。本文提出了OmniGIRL基准测试,这是一个多语言、多模态和多领域的GitHub问题解决方案基准测试。然而,LLM模型在该测试中的表现受限,解决问题的最佳模型GPT-4o仅占解决率的8.6%。并且LLM在处理涉及图像理解的问题时尤为困难。因此,需要深入分析和改进未来的LLM模型以提高解决率。本文同时探讨了原因,并提供了对未来改进的启示。
Key Takeaways
- GitHub问题自动解决任务旨在自动解决仓库中报告的问题。
- 当前存在的基准测试主要关注单一编程语言和狭窄领域的问题评价,限制了问题的评估范围。
- OmniGIRL是一个多语言、多模态和多领域的GitHub问题解决方案基准测试。它涵盖了四种编程语言和八个不同领域,包括图像在内的多种信息。
- 当前LLM在OmniGIRL上的表现受限,最佳模型GPT-4o的解决率仅为8.6%。
- LLM在处理涉及图像理解的问题时面临困难,最佳模型Claude-3.5-Sonnet的解决率为仅10.5%。这表明LLM在处理复杂问题时仍需要改进。
点此查看论文截图

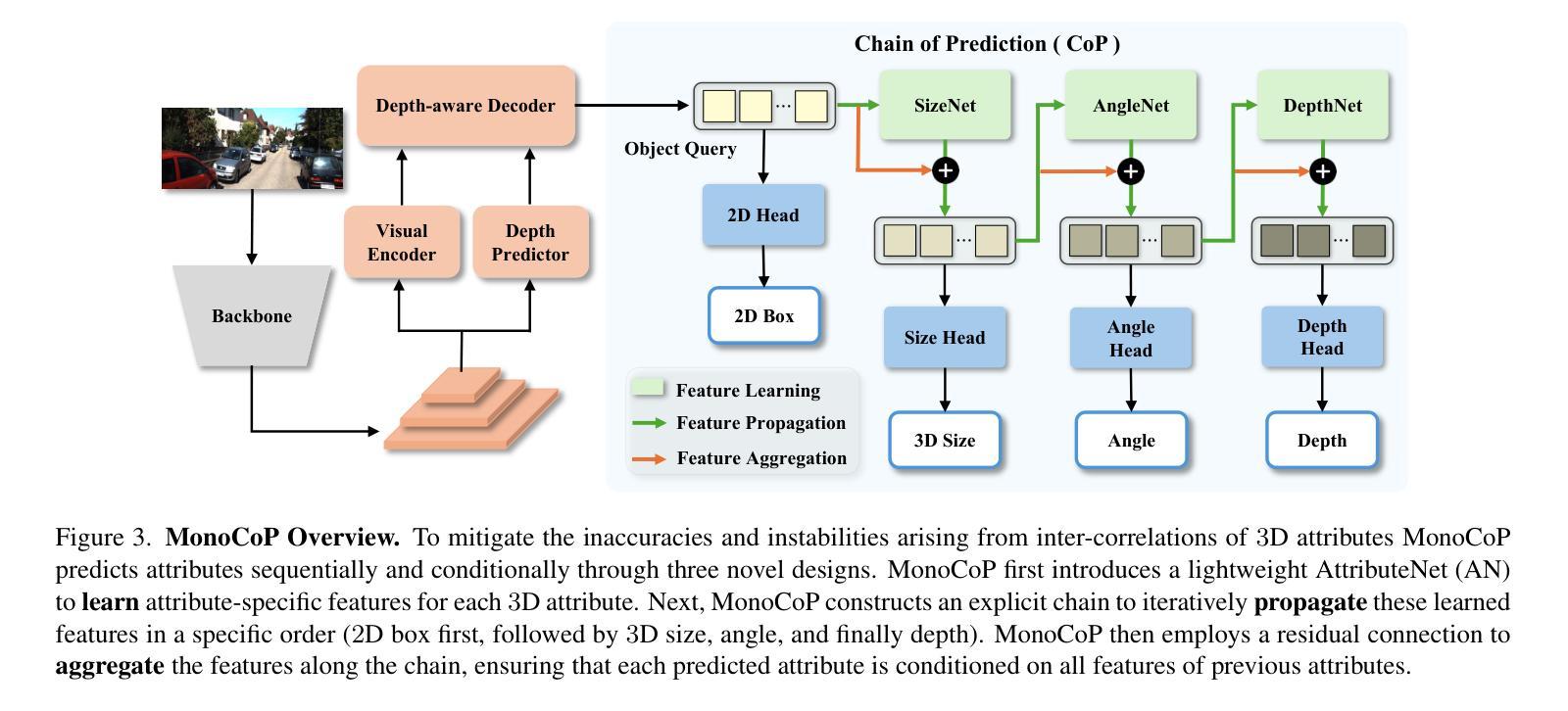
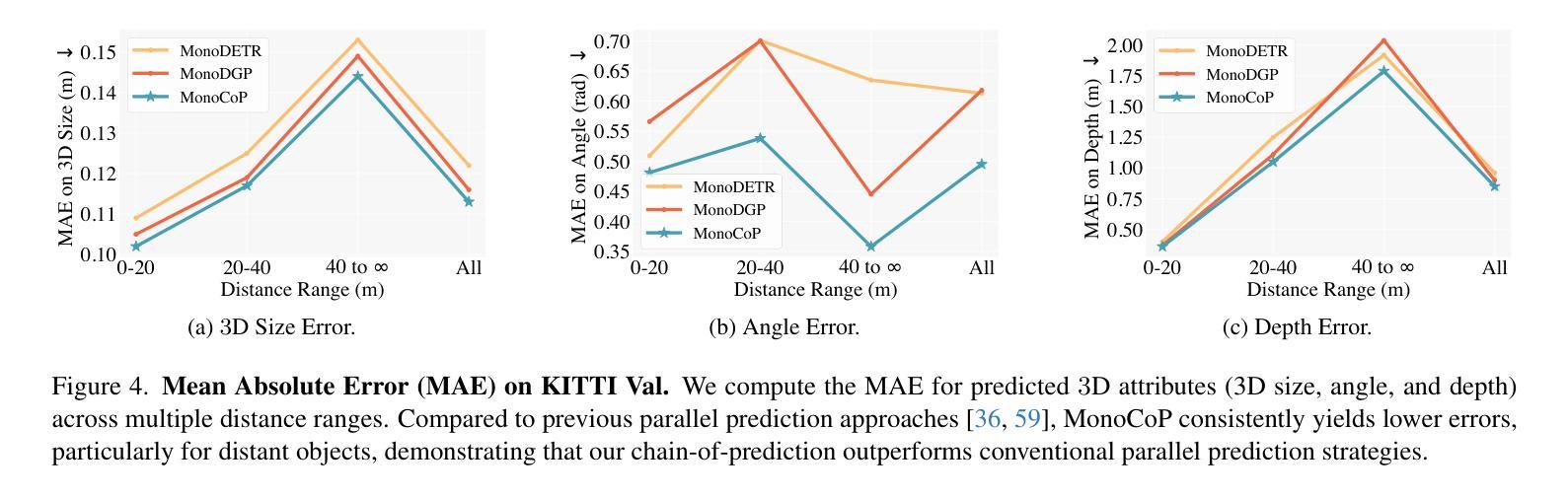
MonoCoP: Chain-of-Prediction for Monocular 3D Object Detection
Authors:Zhihao Zhang, Abhinav Kumar, Girish Chandar Ganesan, Xiaoming Liu
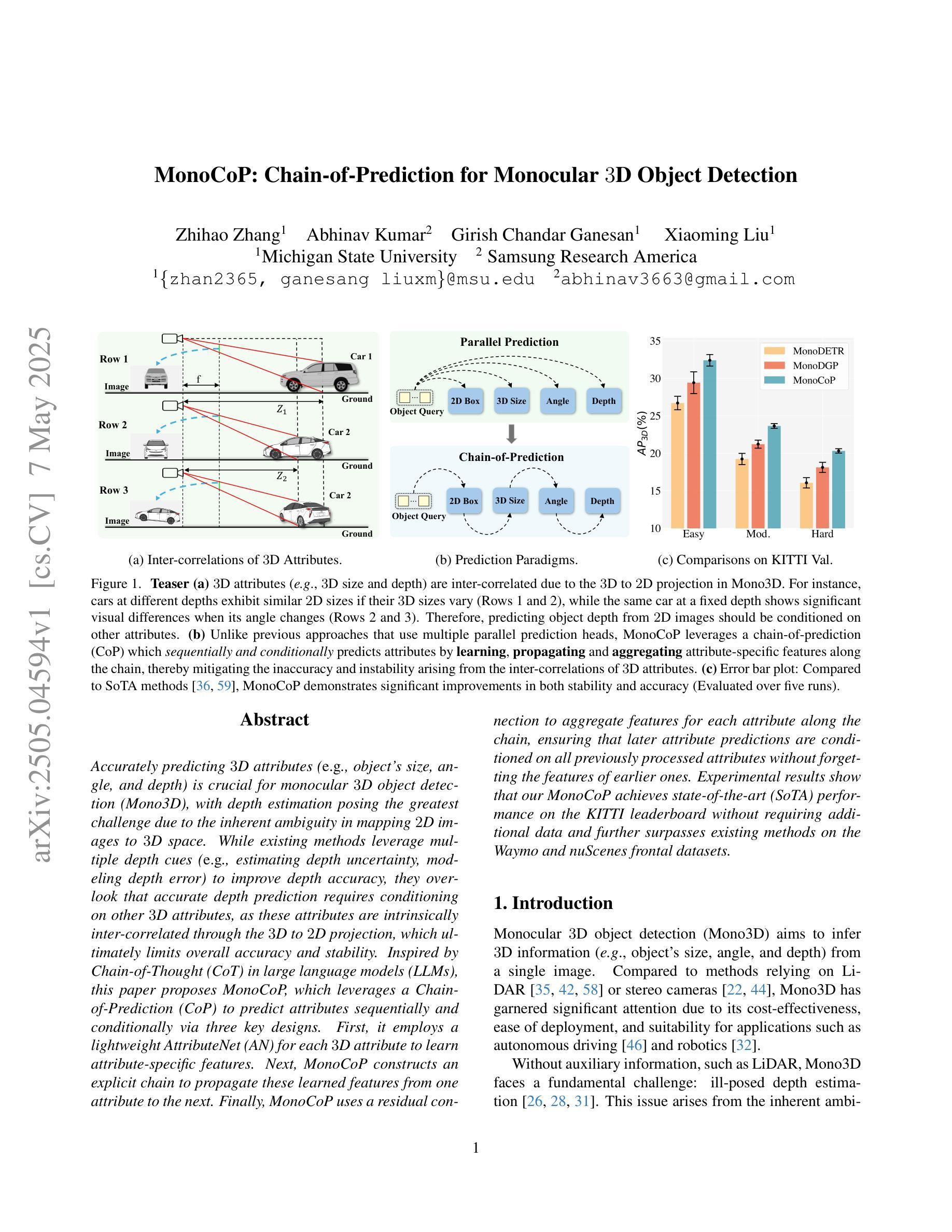
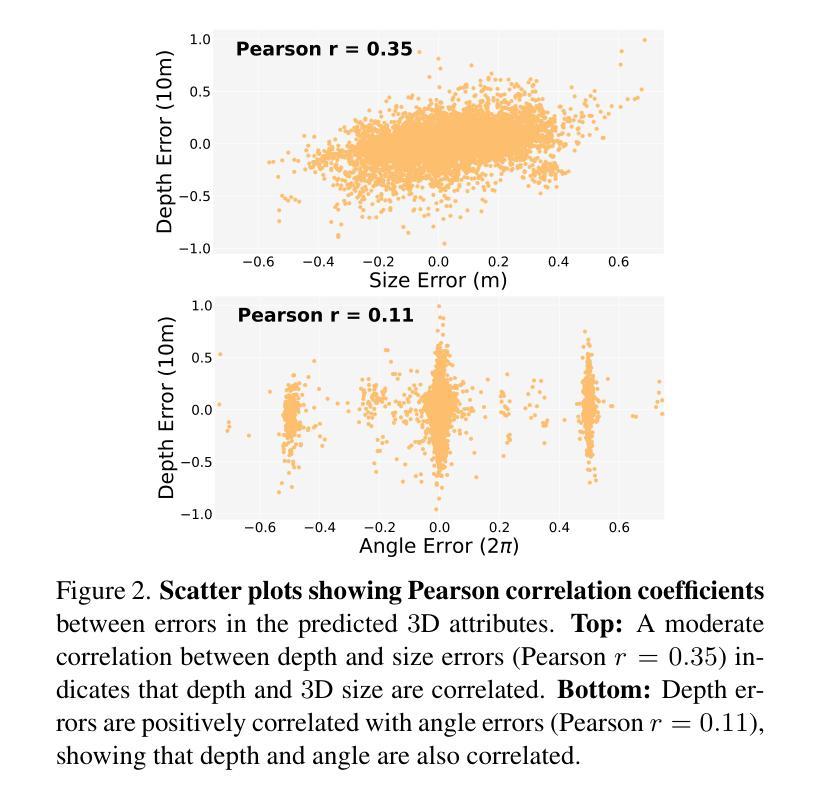
Accurately predicting 3D attributes is crucial for monocular 3D object detection (Mono3D), with depth estimation posing the greatest challenge due to the inherent ambiguity in mapping 2D images to 3D space. While existing methods leverage multiple depth cues (e.g., estimating depth uncertainty, modeling depth error) to improve depth accuracy, they overlook that accurate depth prediction requires conditioning on other 3D attributes, as these attributes are intrinsically inter-correlated through the 3D to 2D projection, which ultimately limits overall accuracy and stability. Inspired by Chain-of-Thought (CoT) in large language models (LLMs), this paper proposes MonoCoP, which leverages a Chain-of-Prediction (CoP) to predict attributes sequentially and conditionally via three key designs. First, it employs a lightweight AttributeNet (AN) for each 3D attribute to learn attribute-specific features. Next, MonoCoP constructs an explicit chain to propagate these learned features from one attribute to the next. Finally, MonoCoP uses a residual connection to aggregate features for each attribute along the chain, ensuring that later attribute predictions are conditioned on all previously processed attributes without forgetting the features of earlier ones. Experimental results show that our MonoCoP achieves state-of-the-art (SoTA) performance on the KITTI leaderboard without requiring additional data and further surpasses existing methods on the Waymo and nuScenes frontal datasets.
准确预测3D属性对于单目3D物体检测(Mono3D)至关重要,深度估计由于将2D图像映射到3D空间时固有的模糊性而构成最大的挑战。虽然现有方法利用多种深度线索(例如估计深度不确定性、建模深度误差)来提高深度准确性,但它们忽略了准确的深度预测需要依赖于其他3D属性,因为这些属性通过3D到2D的投影固有地相互关联,这最终限制了整体准确性和稳定性。本文受大型语言模型(LLM)中的思维链(CoT)启发,提出了一种名为MonoCoP的方法,它利用预测链(CoP)按顺序和有条件地预测属性,主要通过三个关键设计实现。首先,它采用轻量级的AttributeNet(AN)来学习每个3D属性的特定特征。接下来,MonoCoP构建了一个明确的链条,以传播从一个属性学到的特征到下一个属性。最后,MonoCoP使用残差连接来沿链条聚合每个属性的特征,确保后续的属性预测依赖于所有先前处理的属性,同时不会忘记较早属性的特征。实验结果表明,我们的MonoCoP在KITTI排行榜上达到了最先进的性能,并且无需额外数据,在Waymo和nuScenes正面数据集上超越了现有方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了基于Chain-of-Prediction(CoP)的单眼三维物体检测新方法MonoCoP。该方法通过构建预测链,利用属性特定的特征进行三维属性的顺序和条件预测。通过实验结果,证明了MonoCoP在KITTI排行榜上达到了领先水平,同时在Waymo和nuScenes正面数据集上超越了现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 单眼三维物体检测(Mono3D)中,准确预测三维属性至关重要,深度估计是一大挑战。
- 现有方法虽利用多种深度线索提高深度准确性,但忽略了准确深度预测需要依赖其他三维属性的条件。
- 本文受大型语言模型中“Chain-of-Thought”(CoT)的启发,提出了MonoCoP方法。
- MonoCoP通过构建预测链进行三维属性的顺序和条件预测,利用AttributeNet(AN)学习属性特定特征。
- MonoCoP通过显式链传播这些学习到的特征从一个属性到下一个属性。
- MonoCoP使用残差连接来聚合预测链中每个属性的特征,确保后来的属性预测依赖于所有先前处理的属性。
点此查看论文截图
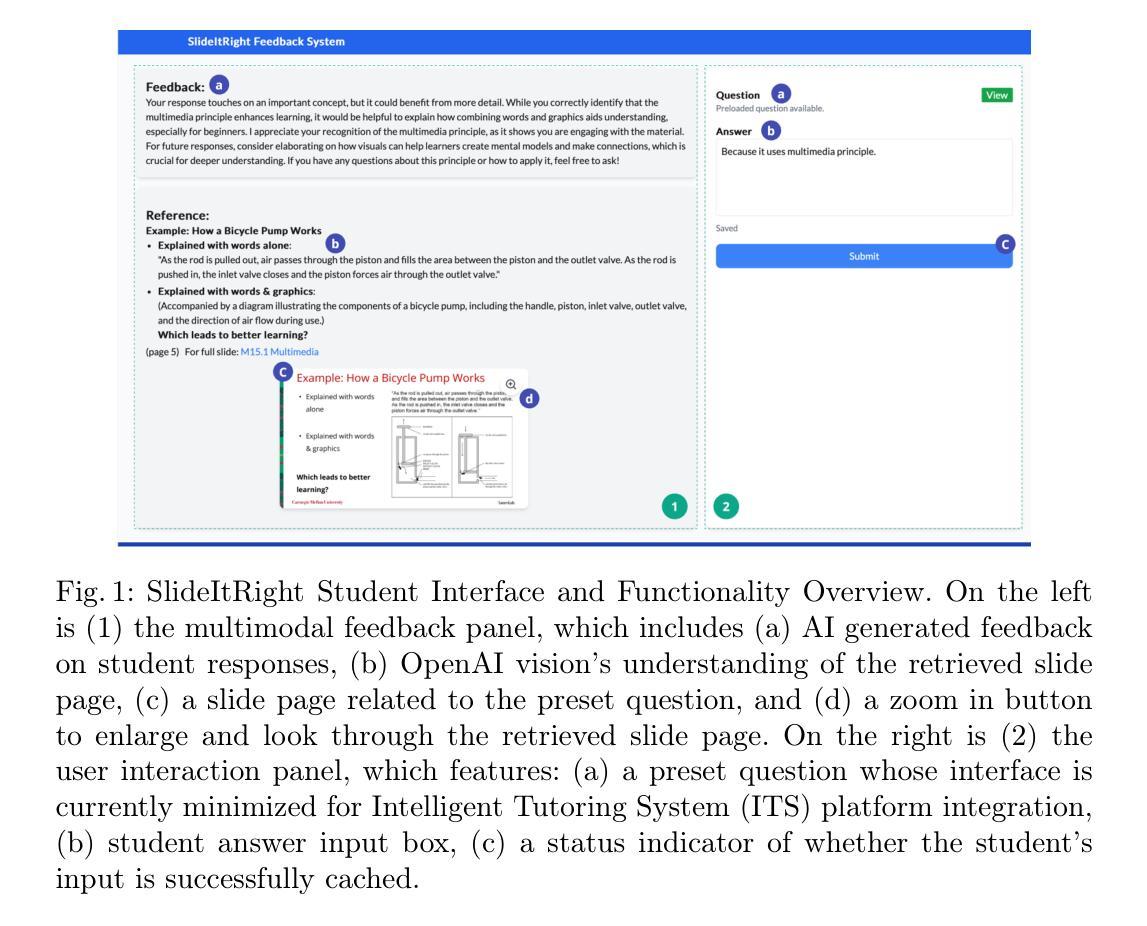
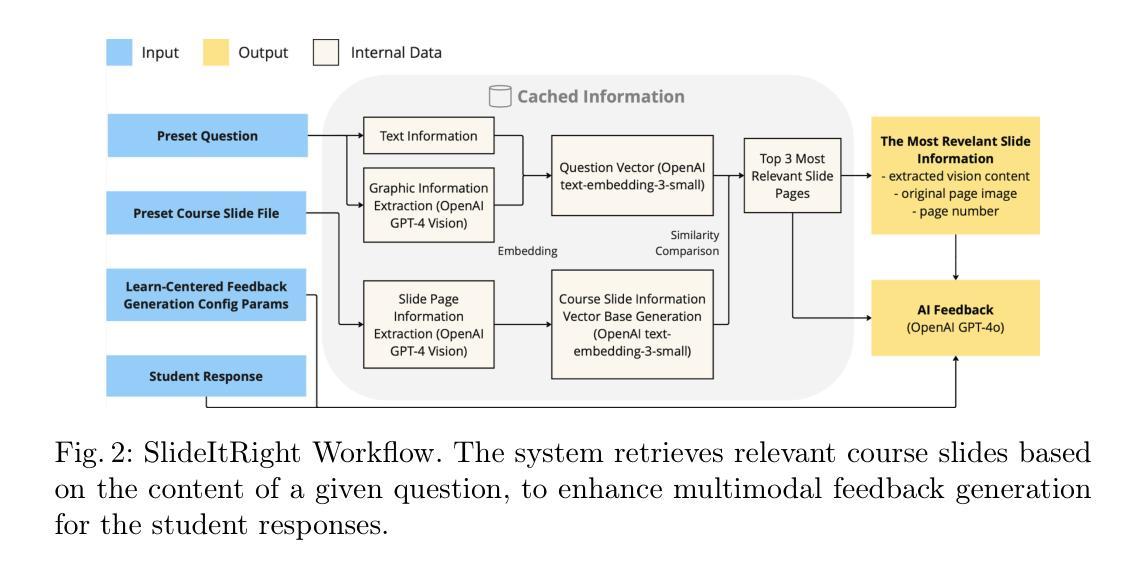
SlideItRight: Using AI to Find Relevant Slides and Provide Feedback for Open-Ended Questions
Authors:Chloe Qianhui Zhao, Jie Cao, Eason Chen, Kenneth R. Koedinger, Jionghao Lin
Feedback is important in supporting student learning. While various automated feedback systems have been implemented to make the feedback scalable, many existing solutions only focus on generating text-based feedback. As is indicated in the multimedia learning principle, learning with more modalities could help utilize more separate channels, reduce the cognitive load and facilitate students’ learning. Hence, it is important to explore the potential of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in feedback generation from and to different modalities. Our study leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) for textual feedback with the supplementary guidance from other modality - relevant lecture slide retrieved from the slides hub. Through an online crowdsourcing study (N=91), this study investigates learning gains and student perceptions using a 2x2 design (i.e., human feedback vs. AI feedback and with vs. without relevant slide), evaluating the clarity, engagement, perceived effectiveness, and reliability) of AI-facilitated multimodal feedback. We observed significant pre-to-post learning gains across all conditions. However, the differences in these gains were not statistically significant between conditions. The post-survey revealed that students found the slide feedback helpful in their learning process, though they reported difficulty in understanding it. Regarding the AI-generated open-ended feedback, students considered it personalized and relevant to their responses, but they expressed lower trust in the AI feedback compared to human-generated feedback.
反馈对于支持学生学习非常重要。虽然已实施各种自动化反馈系统以实现反馈的规模化,但许多现有解决方案仅专注于生成基于文本的反馈。正如多媒体学习原理所指示的,使用更多模式进行学习可以帮助利用更多独立通道,减少认知负荷并促进学生学习。因此,探索人工智能(AI)在不同模式反馈生成中的潜力非常重要。我们的研究利用大型语言模型(LLM)进行文本反馈,并辅以其他模式的指导——从幻灯片中心检索的相关讲义幻灯片。通过一项在线众包研究(N=91),本研究采用2x2设计(即人工反馈与AI反馈,有与无相关幻灯片),对学习收获和学生感知进行调查,评估AI辅助多模式反馈的清晰度、参与度、感知有效性和可靠性。我们观察到所有条件下的学习收获都有显著提高。然而,这些收益之间的差异在条件之间并没有统计学上的显著差异。调查显示,学生们认为幻灯片反馈对他们的学习过程很有帮助,尽管他们表示理解起来有困难。关于AI生成的开放式反馈,学生认为它针对他们的回答进行了个性化且相关的反馈,但他们表示对AI反馈的信任度低于人类生成的反馈。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, to be published at the 26th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education (AIED ‘25)
Summary
本文探讨了人工智能在多模态反馈生成中的潜力,研究利用大型语言模型(LLM)提供文本反馈,辅以相关讲座幻灯片。通过在线众包研究(N=91),本研究调查了使用人工智能促进的多模式反馈的学习收获和学生感知。研究观察到所有条件下的学习收获都有显著提高,但不同条件之间的差异并不显著。学生们发现幻灯片的反馈在他们的学习过程中很有帮助,尽管他们报告说难以理解。对于AI生成的开放性反馈,学生们认为它是个性化的并且与他们的回答相关,但他们表示对AI反馈的信任度较低。
Key Takeaways
- 反馈在学生学习中非常重要,需要探索人工智能在多模态反馈生成中的潜力。
- 本研究利用大型语言模型(LLM)提供文本反馈,并辅以相关讲座幻灯片以增强学习效果。
- 通过在线众包研究,发现所有条件下的学习收获都有显著提高,但不同条件间的差异并不显著。
- 学生们认为幻灯片反馈对学习过程有帮助,但存在理解困难的问题。
- AI生成的开放性反馈被认为是与回答相关的个性化反馈,但学生对AI反馈的信任度较低。
- 学习效果的评价包括清晰度、参与度、感知效果和可靠性等方面。
点此查看论文截图


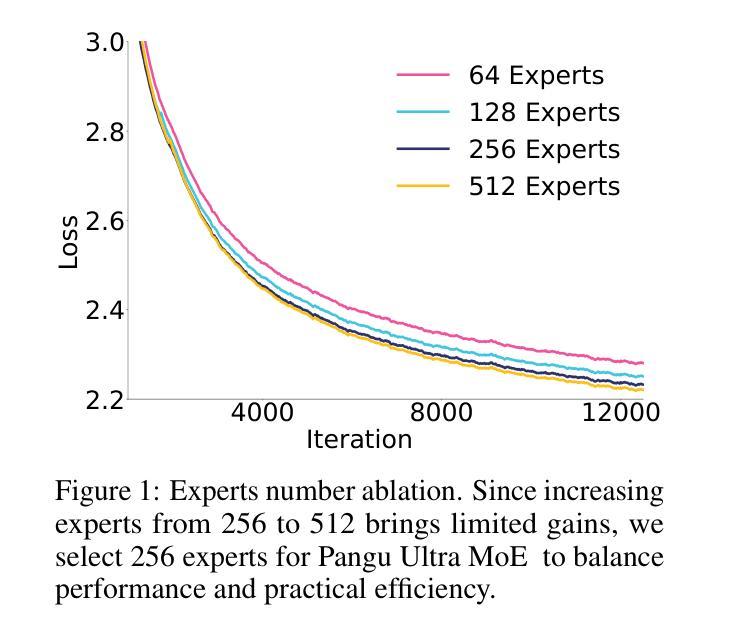
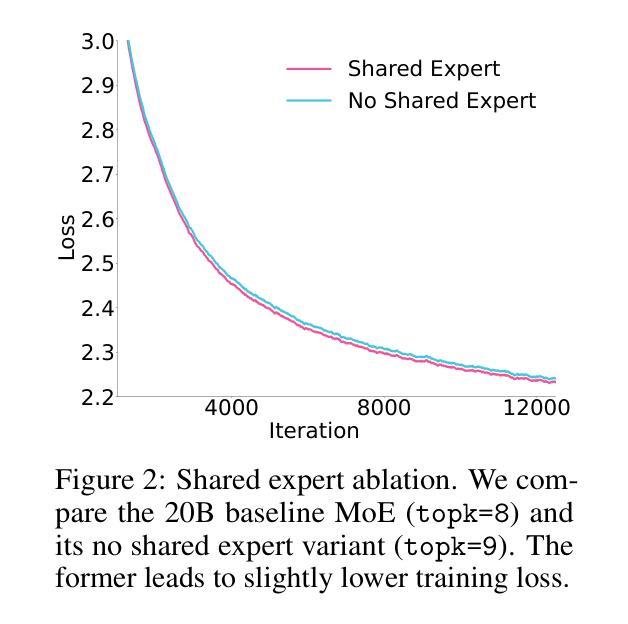
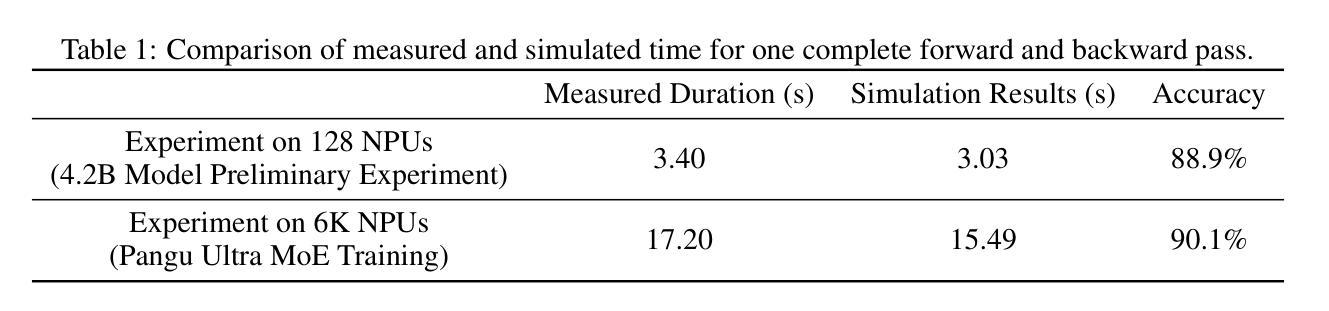
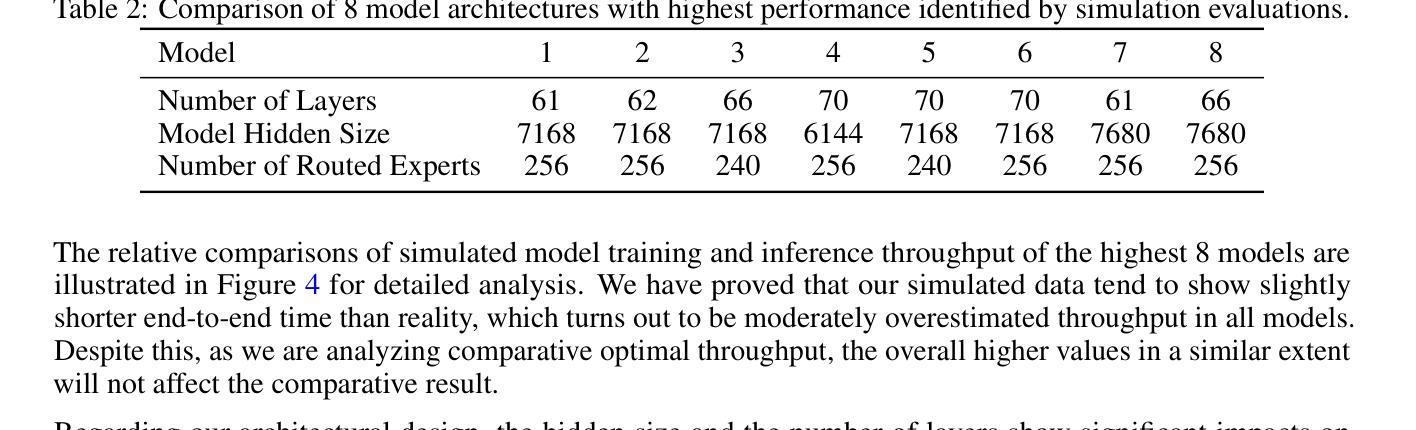
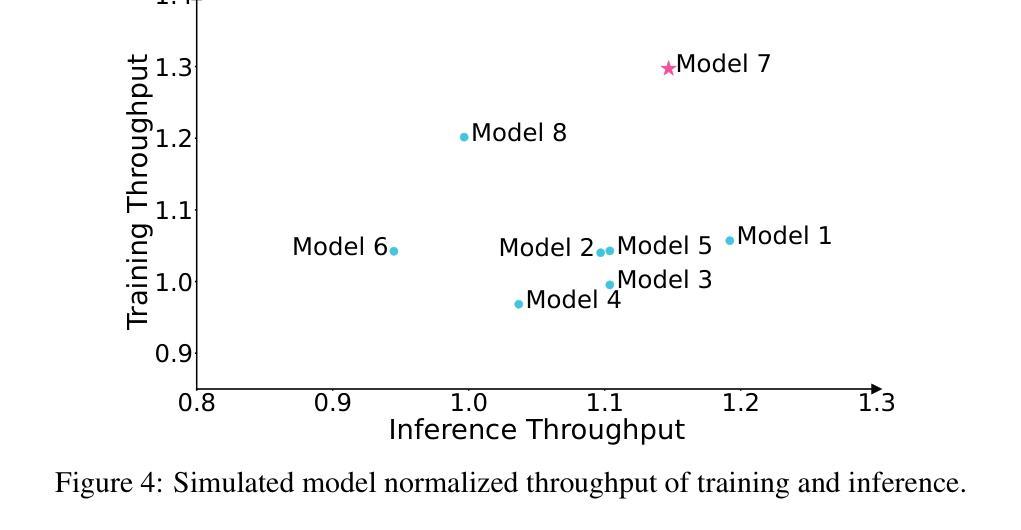
Pangu Ultra MoE: How to Train Your Big MoE on Ascend NPUs
Authors:Yehui Tang, Yichun Yin, Yaoyuan Wang, Hang Zhou, Yu Pan, Wei Guo, Ziyang Zhang, Miao Rang, Fangcheng Liu, Naifu Zhang, Binghan Li, Yonghan Dong, Xiaojun Meng, Yasheng Wang, Dong Li, Yin Li, Dandan Tu, Can Chen, Youliang Yan, Fisher Yu, Ruiming Tang, Yunhe Wang, Botian Huang, Bo Wang, Boxiao Liu, Changzheng Zhang, Da Kuang, Fei Liu, Gang Huang, Jiansheng Wei, Jiarui Qin, Jie Ran, Jinpeng Li, Jun Zhao, Liang Dai, Lin Li, Liqun Deng, Peifeng Qin, Pengyuan Zeng, Qiang Gu, Shaohua Tang, Shengjun Cheng, Tao Gao, Tao Yu, Tianshu Li, Tianyu Bi, Wei He, Weikai Mao, Wenyong Huang, Wulong Liu, Xiabing Li, Xianzhi Yu, Xueyu Wu, Xu He, Yangkai Du, Yan Xu, Ye Tian, Yimeng Wu, Yongbing Huang, Yong Tian, Yong Zhu, Yue Li, Yufei Wang, Yuhang Gai, Yujun Li, Yu Luo, Yunsheng Ni, Yusen Sun, Zelin Chen, Zhe Liu, Zhicheng Liu, Zhipeng Tu, Zilin Ding, Zongyuan Zhan
Sparse large language models (LLMs) with Mixture of Experts (MoE) and close to a trillion parameters are dominating the realm of most capable language models. However, the massive model scale poses significant challenges for the underlying software and hardware systems. In this paper, we aim to uncover a recipe to harness such scale on Ascend NPUs. The key goals are better usage of the computing resources under the dynamic sparse model structures and materializing the expected performance gain on the actual hardware. To select model configurations suitable for Ascend NPUs without repeatedly running the expensive experiments, we leverage simulation to compare the trade-off of various model hyperparameters. This study led to Pangu Ultra MoE, a sparse LLM with 718 billion parameters, and we conducted experiments on the model to verify the simulation results. On the system side, we dig into Expert Parallelism to optimize the communication between NPU devices to reduce the synchronization overhead. We also optimize the memory efficiency within the devices to further reduce the parameter and activation management overhead. In the end, we achieve an MFU of 30.0% when training Pangu Ultra MoE, with performance comparable to that of DeepSeek R1, on 6K Ascend NPUs, and demonstrate that the Ascend system is capable of harnessing all the training stages of the state-of-the-art language models. Extensive experiments indicate that our recipe can lead to efficient training of large-scale sparse language models with MoE. We also study the behaviors of such models for future reference.
具有专家混合(MoE)的稀疏大型语言模型(LLM)接近万亿参数,正在成为最强大的语言模型领域的主导。然而,巨大的模型规模给底层软硬件系统带来了巨大的挑战。本文旨在揭示在Ascend NPUs上利用这种规模的秘诀。我们的主要目标是更好地利用动态稀疏模型结构下的计算资源,并在实际硬件上实现预期的性能提升。为了选择适合Ascend NPUs的模型配置,而避免反复运行昂贵的实验,我们利用仿真来比较各种模型超参数的权衡。这项研究促成了Pangu Ultra MoE的诞生,这是一个具有718亿参数的稀疏LLM,我们对该模型进行了实验以验证仿真结果。在系统方面,我们深入挖掘专家并行性,优化NPU设备之间的通信,以减少同步开销。我们还优化设备内的内存效率,进一步减少参数和激活管理开销。最终,我们在训练Pangu Ultra MoE时实现了30.0%的MFU,在6K Ascend NPUs上的性能与DeepSeek R1相当,证明Ascend系统能够驾驭最新语言模型的所有训练阶段。大量实验表明,我们的秘诀可以导致具有MoE的大规模稀疏语言模型的高效训练。我们还研究了此类模型的行为以供未来参考。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
稀疏大型语言模型(LLM)结合专家混合(MoE)技术,拥有接近万亿参数,成为当前最强大的语言模型领域的主导者。然而,大规模模型对底层软硬件系统提出了巨大挑战。本文旨在揭示在Ascend NPUs上利用这种规模的模型的方法。我们的主要目标是在动态稀疏模型结构下更好地利用计算资源,并在实际硬件上实现预期的性能提升。我们通过模拟比较不同模型超参数的权衡,以选择适合Ascend NPUs的模型配置。这项研究诞生了庞古Ultra MoE这一稀疏LLM,拥有718亿参数。我们对该模型进行实验,验证了模拟结果。在系统层面,我们深入研究了专家并行性以优化NPU设备之间的通信,减少同步开销。我们还优化了设备内的内存效率,进一步减少了参数和激活管理开销。最终,我们在训练庞古Ultra MoE时实现了30.0%的MFU(一种性能指标),在6K Ascend NPUs上的性能与DeepSeek R1相当,证明了Ascend系统能够应对最先进语言模型的所有训练阶段。大量实验表明,我们的方法能够实现大规模稀疏语言模型的高效训练。我们还研究了此类模型的行为,以供未来参考。
关键见解
- 稀疏大型语言模型(LLM)结合专家混合(MoE)成为当前领先的强大语言模型。
- 面临大规模模型的挑战,需要在Ascend NPUs上优化利用计算资源的方法。
- 通过模拟比较不同模型超参数的权衡来选择适合Ascend NPUs的模型配置。
- 庞古Ultra MoE是一个稀疏LLM,拥有718亿参数,通过实验验证了其性能。
- 优化专家并行性以减少NPU设备间的同步开销,同时优化内存效率。
- 在训练庞古Ultra MoE时实现了较高的MFU性能,与DeepSeek R1相当。
点此查看论文截图

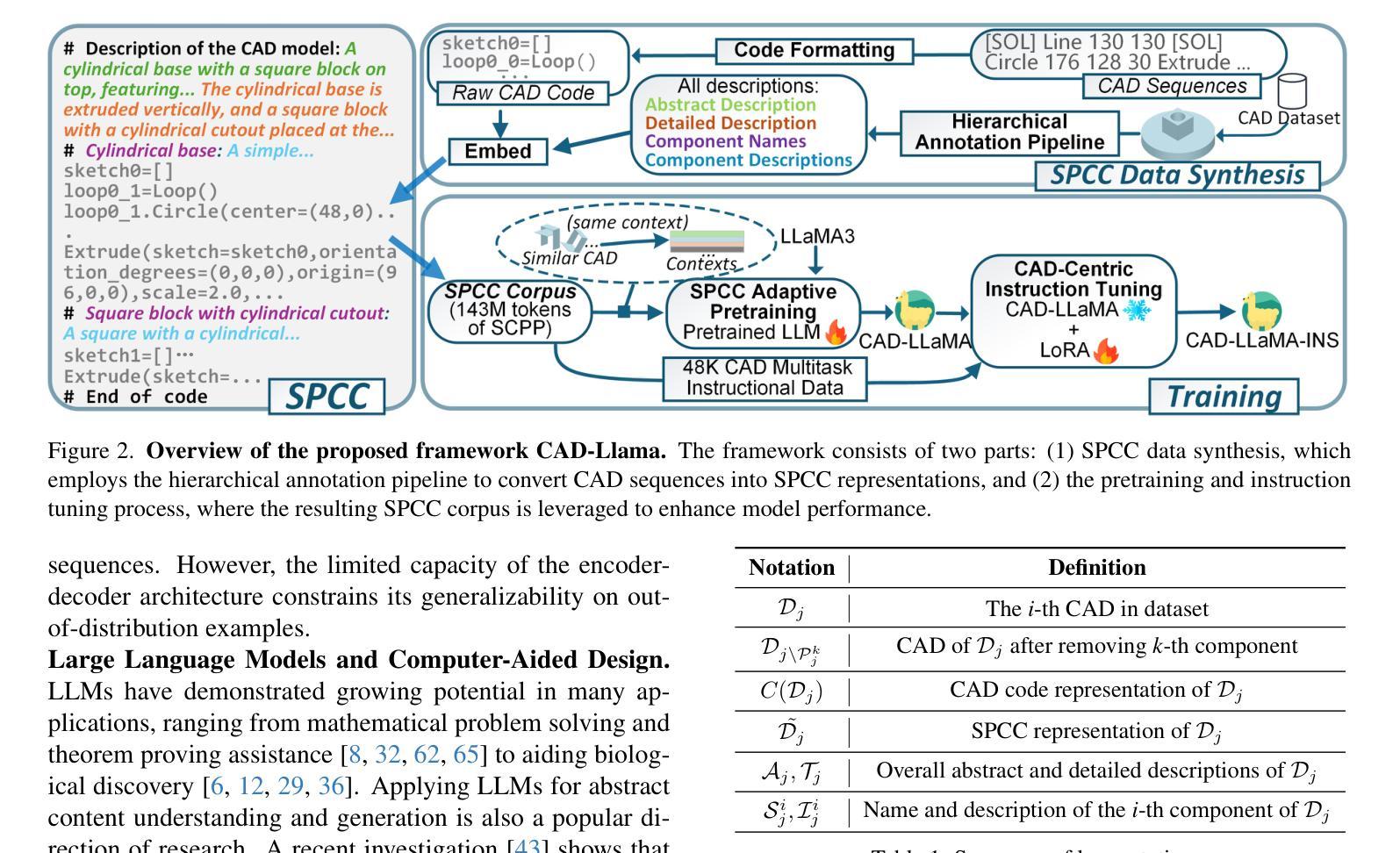
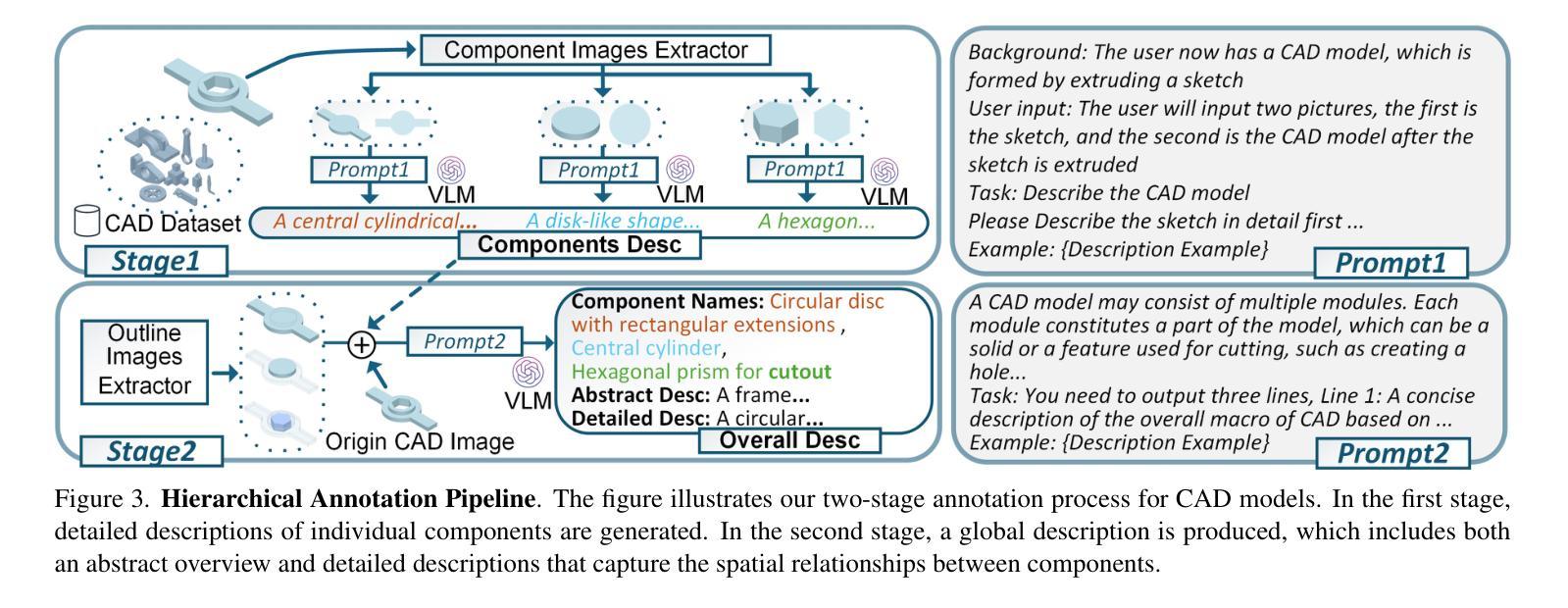
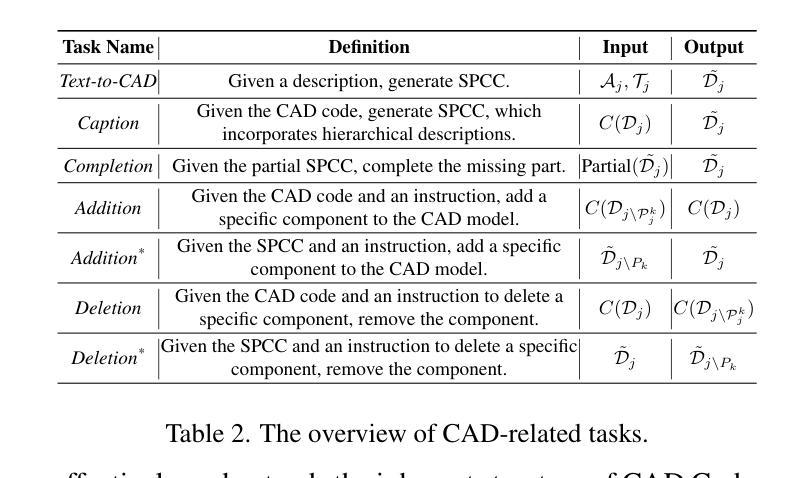
CAD-Llama: Leveraging Large Language Models for Computer-Aided Design Parametric 3D Model Generation
Authors:Jiahao Li, Weijian Ma, Xueyang Li, Yunzhong Lou, Guichun Zhou, Xiangdong Zhou
Recently, Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved significant success, prompting increased interest in expanding their generative capabilities beyond general text into domain-specific areas. This study investigates the generation of parametric sequences for computer-aided design (CAD) models using LLMs. This endeavor represents an initial step towards creating parametric 3D shapes with LLMs, as CAD model parameters directly correlate with shapes in three-dimensional space. Despite the formidable generative capacities of LLMs, this task remains challenging, as these models neither encounter parametric sequences during their pretraining phase nor possess direct awareness of 3D structures. To address this, we present CAD-Llama, a framework designed to enhance pretrained LLMs for generating parametric 3D CAD models. Specifically, we develop a hierarchical annotation pipeline and a code-like format to translate parametric 3D CAD command sequences into Structured Parametric CAD Code (SPCC), incorporating hierarchical semantic descriptions. Furthermore, we propose an adaptive pretraining approach utilizing SPCC, followed by an instruction tuning process aligned with CAD-specific guidelines. This methodology aims to equip LLMs with the spatial knowledge inherent in parametric sequences. Experimental results demonstrate that our framework significantly outperforms prior autoregressive methods and existing LLM baselines.
最近,大型语言模型(LLM)取得了巨大成功,引发了对其生成能力从一般文本扩展到特定领域兴趣的增加。本研究探讨了使用LLM为计算机辅助设计(CAD)模型生成参数序列。这一努力是朝着使用LLM创建参数化3D形状的第一步,因为CAD模型参数直接与三维空间中的形状相关联。尽管LLM具有强大的生成能力,但这一任务仍然具有挑战性,因为这些模型在预训练阶段并未遇到参数序列,也不具备对三维结构的直接意识。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了CAD-Llama框架,旨在增强预训练的LLM生成参数化3D CAD模型的能力。具体而言,我们开发了一种分层注释管道和一种类似于代码的格式,将参数化的三维CAD命令序列翻译成结构化参数CAD代码(SPCC),并融入分层语义描述。此外,我们提出了一种利用SPCC的自适应预训练方法,随后是一个与CAD特定准则对齐的指令调整过程。该方法旨在让LLM具备参数序列中固有的空间知识。实验结果表明,我们的框架显著优于先前的自回归方法和现有的LLM基线。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在生成通用文本方面取得了显著成功,现在正扩展到特定领域的生成能力。本研究探讨了使用LLM生成计算机辅助设计(CAD)模型的参数序列。这是向利用LLM创建参数化三维形状迈出的初步尝试,因为CAD模型参数与三维空间中的形状直接相关。尽管LLM具有强大的生成能力,但此任务仍然具有挑战性,因为这些模型在预训练阶段并未遇到参数序列,也缺乏对三维结构的直接了解。为解决这一问题,我们提出了CAD-Llama框架,旨在增强预训练的LLM生成参数化三维CAD模型的能力。通过开发层次化注释管道和类似代码的格式,将参数化三维CAD命令序列翻译成结构化参数化CAD代码(SPCC),并结合层次化语义描述。我们还提出了一种利用SPCC的自适应预训练方法,随后是符合CAD特定指导的指令调整过程。该方法旨在赋予LLM参数序列中的空间知识。实验结果表明,我们的框架显著优于先前的自回归方法和现有的LLM基线。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在生成通用文本方面的成功促使了对扩展其在特定领域生成能力的研究。
- 本研究关注使用LLM生成计算机辅助设计(CAD)模型的参数序列,为创建参数化三维形状迈出了初步尝试。
- LLM在预训练阶段并未遇到参数序列,因此此任务具有挑战性。
- CAD-Llama框架旨在增强LLM生成参数化三维CAD模型的能力。
- CAD-Llama通过开发层次化注释管道和类似代码的格式来实现对参数化三维CAD命令序列的翻译。
- 该框架结合了自适应预训练方法和指令调整过程,以赋予LLM参数序列中的空间知识。
点此查看论文截图

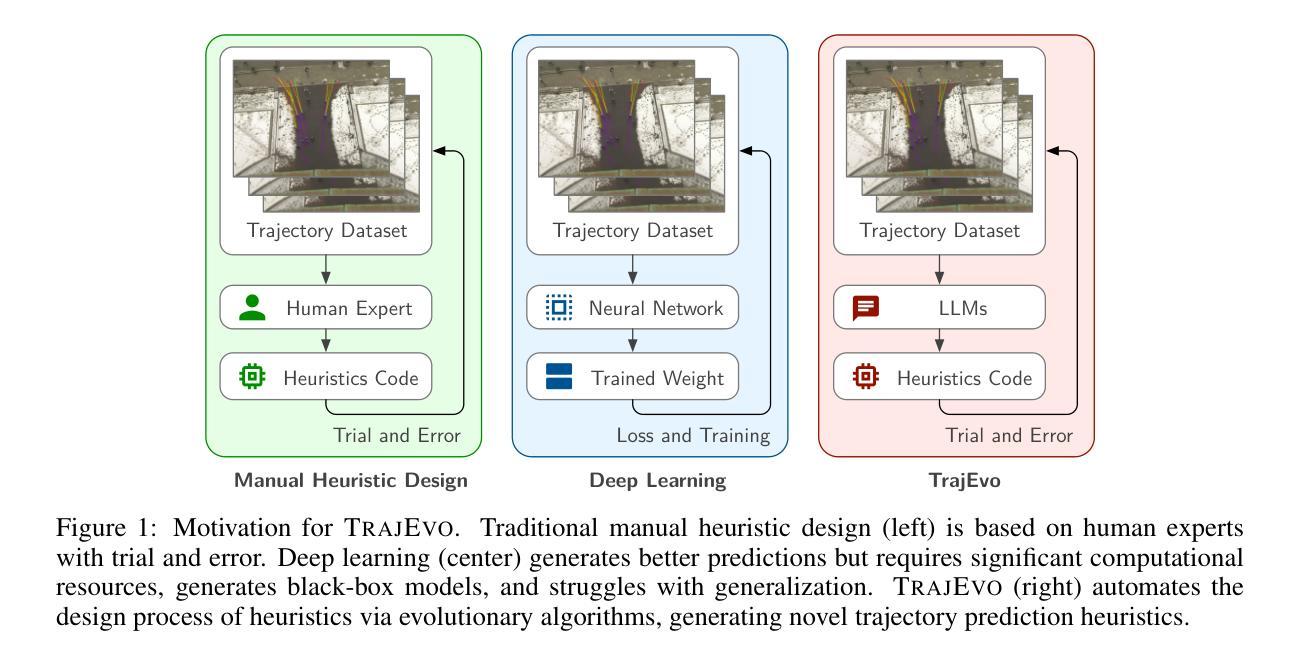
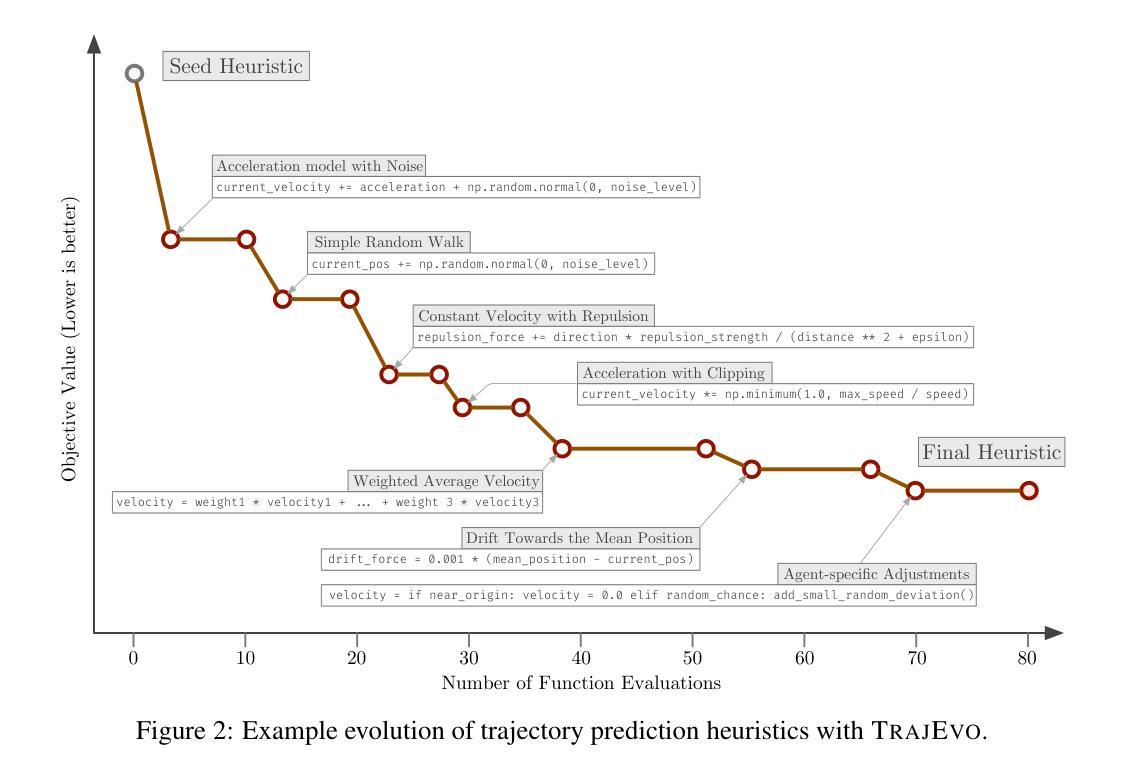
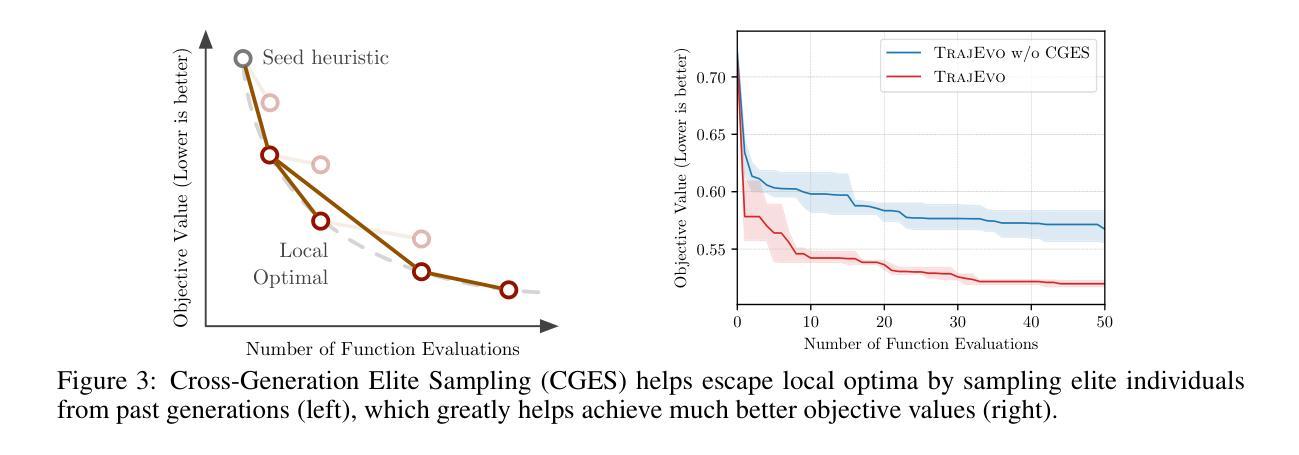
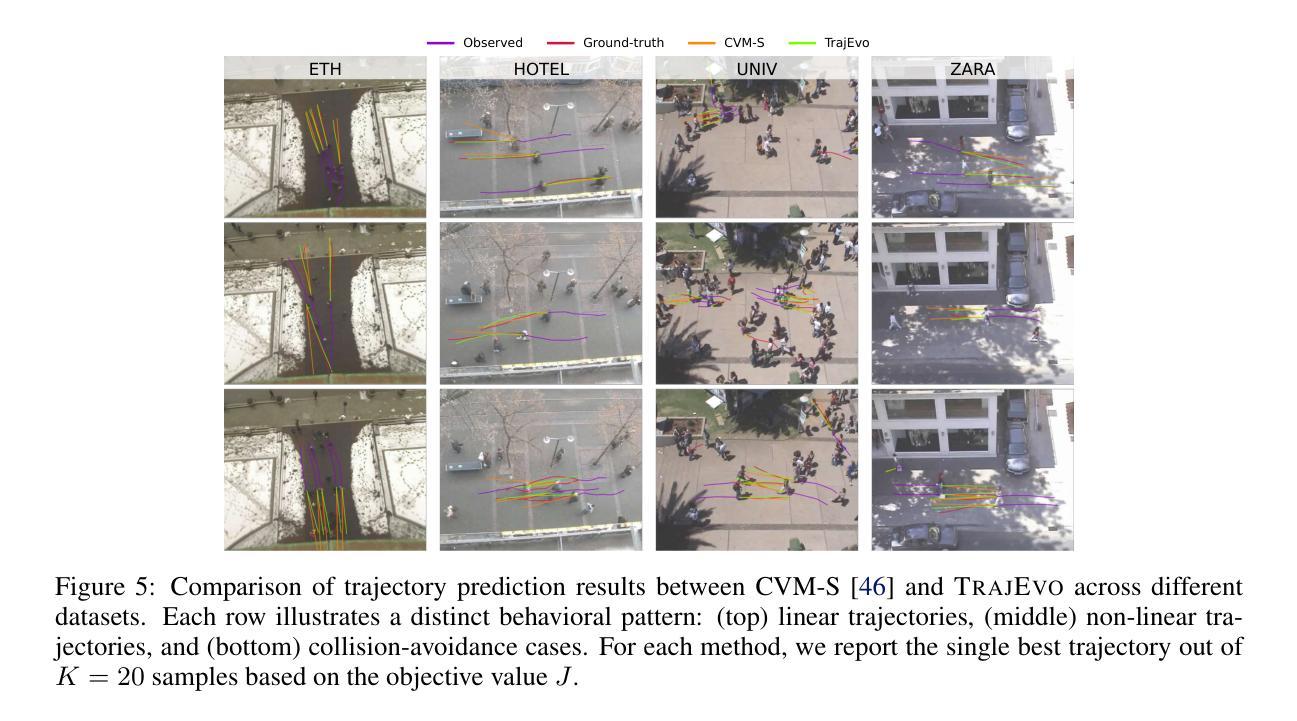
TrajEvo: Designing Trajectory Prediction Heuristics via LLM-driven Evolution
Authors:Zhikai Zhao, Chuanbo Hua, Federico Berto, Kanghoon Lee, Zihan Ma, Jiachen Li, Jinkyoo Park
Trajectory prediction is a crucial task in modeling human behavior, especially in fields as social robotics and autonomous vehicle navigation. Traditional heuristics based on handcrafted rules often lack accuracy, while recently proposed deep learning approaches suffer from computational cost, lack of explainability, and generalization issues that limit their practical adoption. In this paper, we introduce TrajEvo, a framework that leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to automatically design trajectory prediction heuristics. TrajEvo employs an evolutionary algorithm to generate and refine prediction heuristics from past trajectory data. We introduce a Cross-Generation Elite Sampling to promote population diversity and a Statistics Feedback Loop allowing the LLM to analyze alternative predictions. Our evaluations show TrajEvo outperforms previous heuristic methods on the ETH-UCY datasets, and remarkably outperforms both heuristics and deep learning methods when generalizing to the unseen SDD dataset. TrajEvo represents a first step toward automated design of fast, explainable, and generalizable trajectory prediction heuristics. We make our source code publicly available to foster future research at https://github.com/ai4co/trajevo.
轨迹预测是模拟人类行为的重要任务,特别是在社交机器人和自动驾驶导航等领域。基于手工规则的传统启发式方法通常缺乏准确性,而最近提出的深度学习方法则存在计算成本高、缺乏可解释性和泛化问题,这些问题限制了它们的实际应用。在本文中,我们介绍了TrajEvo框架,该框架利用大型语言模型(LLM)自动设计轨迹预测启发式方法。TrajEvo采用进化算法,根据过去的轨迹数据生成和细化预测启发式方法。我们引入了跨代精英采样法以促进种群多样性,并建立了统计反馈循环,使LLM能够分析替代预测。我们的评估显示,TrajEvo在ETH-UCY数据集上的表现优于先前的启发式方法,并且在推广到未见过的SDD数据集时,它显著优于启发式方法和深度学习方法。TrajEvo朝着自动设计快速、可解释和通用的轨迹预测启发式方法迈出了第一步。为了让未来的研究得以发展,我们在https://github.com/ai4co/trajevo公开了我们的源代码。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
轨迹预测是模拟人类行为的重要任务,尤其在社交机器人和自动驾驶导航等领域。传统基于手工规则的方法常常缺乏准确性,而新近提出的深度学习方法则存在计算成本高、缺乏可解释性和泛化问题等实践应用中的局限。本文介绍TrajEvo框架,它利用大语言模型(LLM)自动设计轨迹预测规则。TrajEvo采用进化算法从过去的轨迹数据中生成和优化预测规则。通过引入跨代精英采样以促进种群多样性和统计反馈环,使LLM能够分析替代预测。评估表明,TrajEvo在ETH-UCY数据集上优于传统启发式方法,并且在未见过的SDD数据集上显著优于启发式和深度学习方法。TrajEvo朝着自动设计快速、可解释和通用的轨迹预测规则迈出了第一步。我们的源代码可在https://github.com/ai4co/trajevo公开访问,以促进未来研究。
Key Takeaways
- 轨迹预测是模拟人类行为的关键任务,特别是在社交机器人和自动驾驶导航领域。
- 传统基于手工规则的方法准确性不足,而深度学习方法存在计算成本高、缺乏可解释性和泛化问题。
- TrajEvo框架利用大语言模型(LLM)自动设计轨迹预测规则,通过进化算法优化预测规则。
- TrajEvo采用跨代精英采样和统计反馈环机制,提高预测性能并促进LLM分析替代预测。
- TrajEvo在ETH-UCY数据集上表现优于传统启发式方法。
- TrajEvo在未见过的SDD数据集上显著优于启发式和深度学习方法,显示出其良好的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图


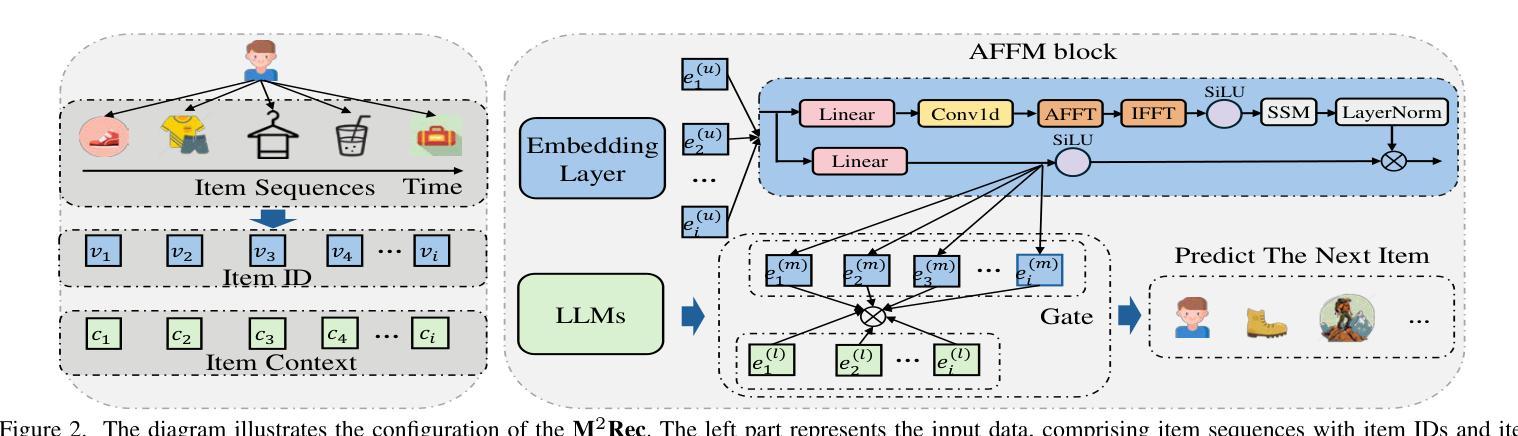
M2Rec: Multi-scale Mamba for Efficient Sequential Recommendation
Authors:Qianru Zhang, Liang Qu, Honggang Wen, Dong Huang, Siu-Ming Yiu, Nguyen Quoc Viet Hung, Hongzhi Yin
Sequential recommendation systems aim to predict users’ next preferences based on their interaction histories, but existing approaches face critical limitations in efficiency and multi-scale pattern recognition. While Transformer-based methods struggle with quadratic computational complexity, recent Mamba-based models improve efficiency but fail to capture periodic user behaviors, leverage rich semantic information, or effectively fuse multimodal features. To address these challenges, we propose \model, a novel sequential recommendation framework that integrates multi-scale Mamba with Fourier analysis, Large Language Models (LLMs), and adaptive gating. First, we enhance Mamba with Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) to explicitly model periodic patterns in the frequency domain, separating meaningful trends from noise. Second, we incorporate LLM-based text embeddings to enrich sparse interaction data with semantic context from item descriptions. Finally, we introduce a learnable gate mechanism to dynamically balance temporal (Mamba), frequency (FFT), and semantic (LLM) features, ensuring harmonious multimodal fusion. Extensive experiments demonstrate that \model\ achieves state-of-the-art performance, improving Hit Rate@10 by 3.2% over existing Mamba-based models while maintaining 20% faster inference than Transformer baselines. Our results highlight the effectiveness of combining frequency analysis, semantic understanding, and adaptive fusion for sequential recommendation. Code and datasets are available at: https://anonymous.4open.science/r/M2Rec.
序列推荐系统的目标是基于用户的交互历史预测其下一个偏好,但现有方法在效率和多尺度模式识别方面面临关键局限。虽然基于Transformer的方法面临二次计算复杂度的问题,最近的基于Mamba的模型提高了效率,但无法捕捉用户周期性行为,利用丰富的语义信息,或有效地融合多模态特征。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了M2Rec模型,这是一种新的序列推荐框架,它将多尺度Mamba与傅里叶分析、大型语言模型(LLM)和自适应门控机制相结合。首先,我们通过快速傅里叶变换(FFT)增强Mamba,以显式地模拟频率域中的周期性模式,将有意义的趋势与噪声区分开。其次,我们融入基于LLM的文本嵌入,以丰富稀疏交互数据,加入项目描述的语义上下文。最后,我们引入了一种可学习的门控机制,以动态平衡时间(Mamba)、频率(FFT)和语义(LLM)特征,确保和谐的多模态融合。大量实验表明,M2Rec模型达到了最新的性能水平,在现有基于Mamba的模型的基础上,Hit Rate@10提高了3.2%,同时保持比Transformer基准测试快20%的推理速度。我们的结果突出了结合频率分析、语义理解和自适应融合在序列推荐中的有效性。相关代码和数据集可通过https://anonymous.4open.science/r/M2Rec获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本文提出一种新型的顺序推荐框架,该框架集成了多尺度Mamba、傅里叶分析、大型语言模型(LLM)和自适应门控机制。它通过快速傅里叶变换(FFT)增强Mamba,以显式建模频率域中的周期性模式,同时融入LLM文本嵌入,丰富稀疏交互数据并加入项目描述的语义上下文。此外,引入了一种可学习的门控机制,动态平衡时间(Mamba)、频率(FFT)和语义(LLM)特征,确保和谐的多模式融合。实验表明,该模型在现有Mamba模型的基础上提高了Hit Rate@10达3.2%,同时保持比Transformer基线更快的推理速度。
Key Takeaways:
- 顺序推荐系统基于用户交互历史预测其下一个偏好。
- 现有方法面临效率和多尺度模式识别方面的关键限制。
- 提出的模型集成了多尺度Mamba、傅里叶分析、LLM和自适应门控机制。
- 使用快速傅里叶变换(FFT)增强Mamba,以显式建模频率域中的周期性模式。
- 融入LLM文本嵌入,丰富稀疏交互数据并加入项目描述的语义上下文。
- 引入可学习的门控机制,动态平衡时间、频率和语义特征。
- 模型在性能上实现了显著的提升,且在推理速度上也具有优势。
点此查看论文截图

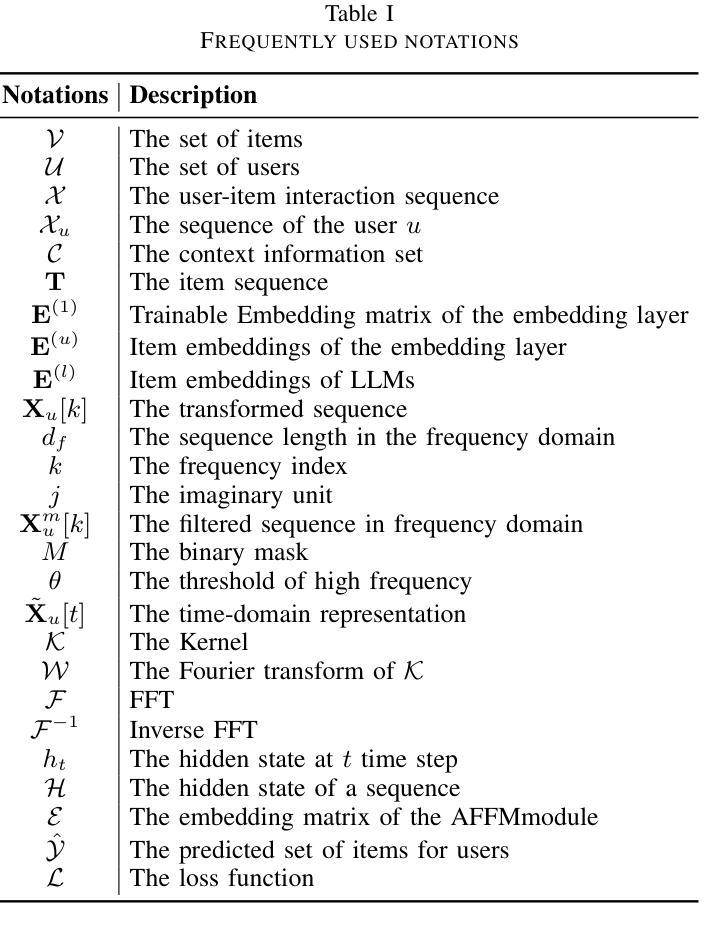

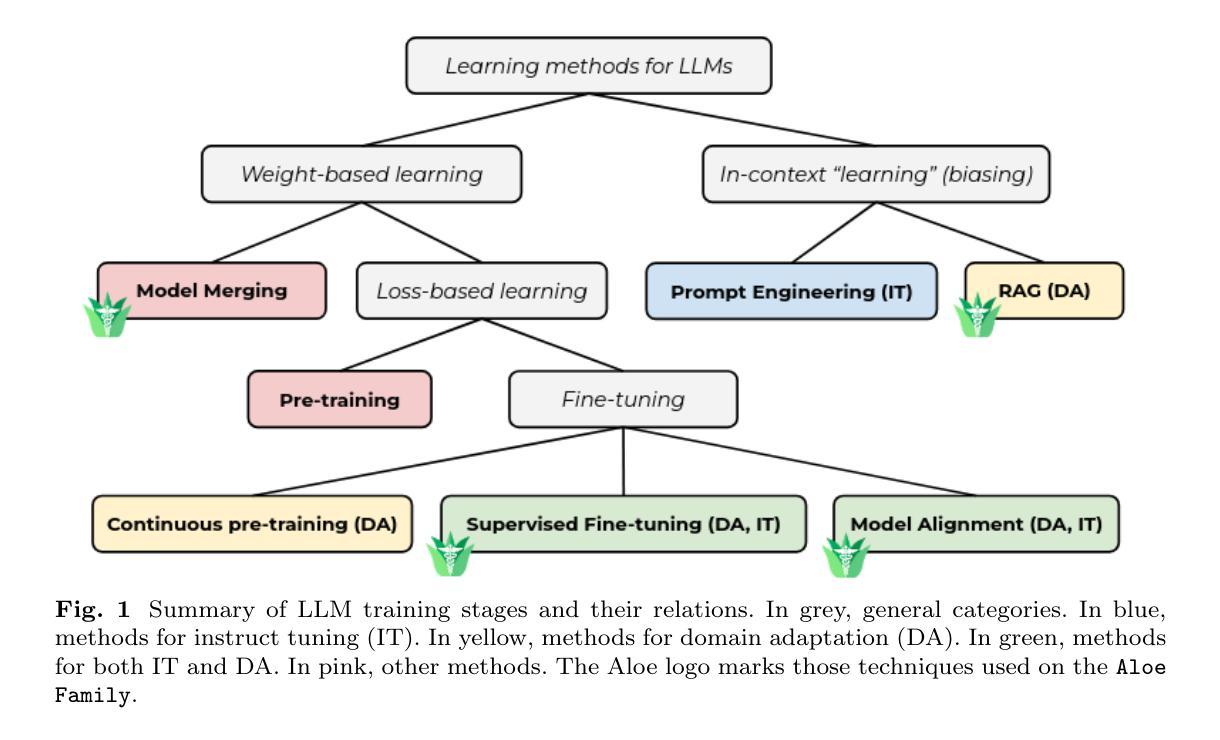
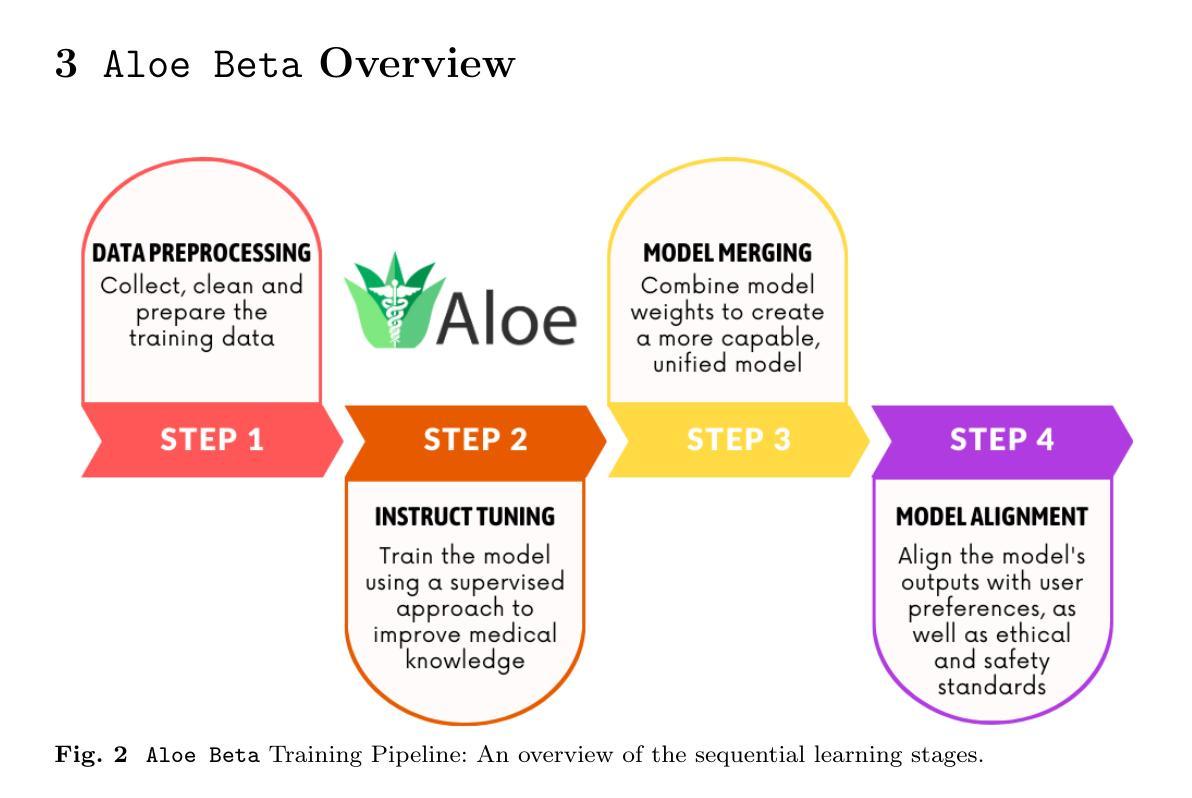
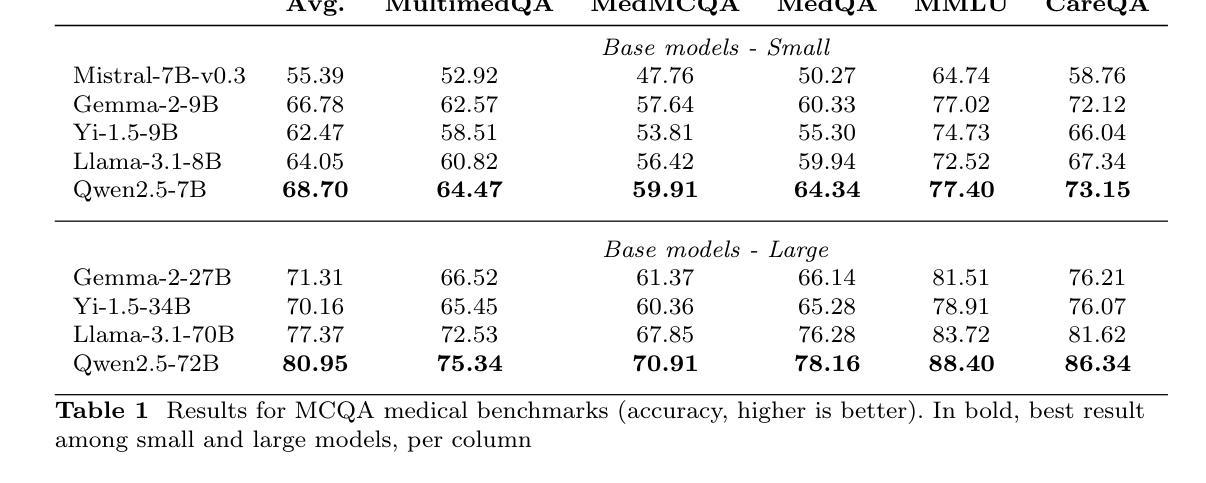
The Aloe Family Recipe for Open and Specialized Healthcare LLMs
Authors:Dario Garcia-Gasulla, Jordi Bayarri-Planas, Ashwin Kumar Gururajan, Enrique Lopez-Cuena, Adrian Tormos, Daniel Hinjos, Pablo Bernabeu-Perez, Anna Arias-Duart, Pablo Agustin Martin-Torres, Marta Gonzalez-Mallo, Sergio Alvarez-Napagao, Eduard Ayguadé-Parra, Ulises Cortés
Purpose: With advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) for healthcare, the need arises for competitive open-source models to protect the public interest. This work contributes to the field of open medical LLMs by optimizing key stages of data preprocessing and training, while showing how to improve model safety (through DPO) and efficacy (through RAG). The evaluation methodology used, which includes four different types of tests, defines a new standard for the field. The resultant models, shown to be competitive with the best private alternatives, are released with a permisive license. Methods: Building on top of strong base models like Llama 3.1 and Qwen 2.5, Aloe Beta uses a custom dataset to enhance public data with synthetic Chain of Thought examples. The models undergo alignment with Direct Preference Optimization, emphasizing ethical and policy-aligned performance in the presence of jailbreaking attacks. Evaluation includes close-ended, open-ended, safety and human assessments, to maximize the reliability of results. Results: Recommendations are made across the entire pipeline, backed by the solid performance of the Aloe Family. These models deliver competitive performance across healthcare benchmarks and medical fields, and are often preferred by healthcare professionals. On bias and toxicity, the Aloe Beta models significantly improve safety, showing resilience to unseen jailbreaking attacks. For a responsible release, a detailed risk assessment specific to healthcare is attached to the Aloe Family models. Conclusion: The Aloe Beta models, and the recipe that leads to them, are a significant contribution to the open-source medical LLM field, offering top-of-the-line performance while maintaining high ethical requirements. This work sets a new standard for developing and reporting aligned LLMs in healthcare.
目的:随着医疗领域的大型语言模型(LLM)的进步,对保护公众利益的开源模型的需求应运而生。这项工作通过对数据预处理和训练的关键阶段进行优化,为开源医疗LLM领域做出贡献,同时展示了如何通过DPO提高模型的安全性和通过RAG提高模型的效力。所使用的评估方法,包括四种不同类型的测试,为该领域定义了新的标准。所得到的模型被证明与最佳私有替代模型具有竞争力,并以许可许可的形式发布。
方法:Aloe Beta建立在强大的基础模型上,如Llama 3.1和Qwen 2. 5,并使用自定义数据集增强公共数据合成思维链示例。模型通过直接偏好优化进行对齐,强调在越狱攻击存在的情况下道德和政策对齐的性能。评估包括封闭式、开放式、安全性和人类评估,以最大化结果的可靠性。
结果:在整个管道中提出了建议,这些建议得到了Aloe家族稳健性能的支撑。这些模型在医疗基准测试和医疗领域表现出竞争力,并经常受到医疗保健专业人士的青睐。在偏见和毒性方面,Aloe Beta模型在安全方面得到显着改善,显示出对看不见的越狱攻击的韧性。为了负责任地发布,Aloe家族模型附带了针对医疗的详细风险评估。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:2405.01886
Summary
本文介绍了Aloe Beta模型在医疗领域大型语言模型(LLM)方面的贡献。通过优化数据预处理和训练的关键阶段,提高模型安全性和有效性。使用四种不同类型的测试来评估模型性能,并证明其与最佳私有替代品的竞争力。最终模型以许可形式发布,为公众利益做出贡献。
Key Takeaways
- Aloe Beta模型优化了数据预处理和训练的关键阶段,提高了大型语言模型(LLM)在医疗领域的性能。
- 通过直接偏好优化(DPO)提高模型安全性,通过RAG提高模型有效性。
- 使用四种不同类型的测试来评估模型性能,为医疗领域的LLM设定了新的评估标准。
- Aloe Beta模型表现出与最佳私有模型相当的竞争力,被医疗保健专业人士广泛接受。
- 在偏见和毒性方面,Aloe Beta模型显著提高了安全性,并对未曾遇到的攻击表现出韧性。
- 发布模型时进行了详细的风险评估,以确保对公众负责。
点此查看论文截图

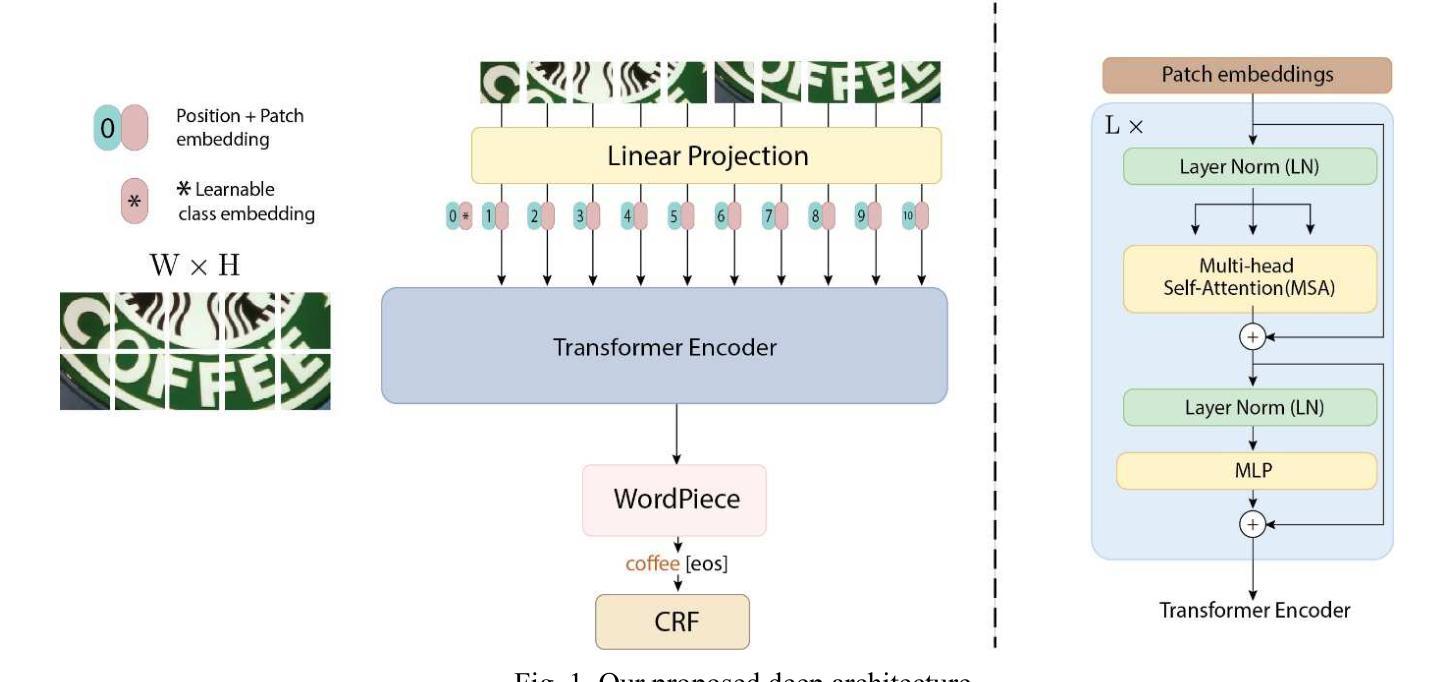
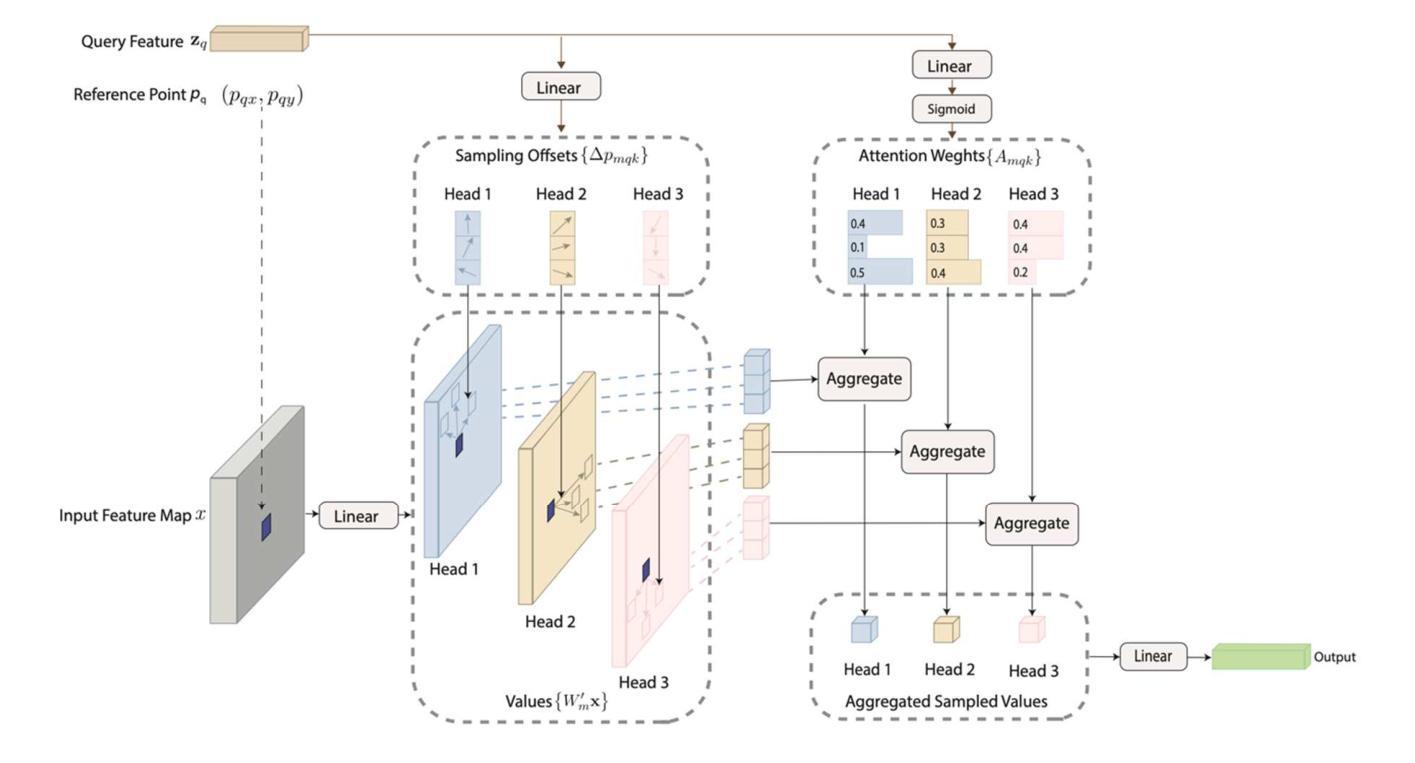
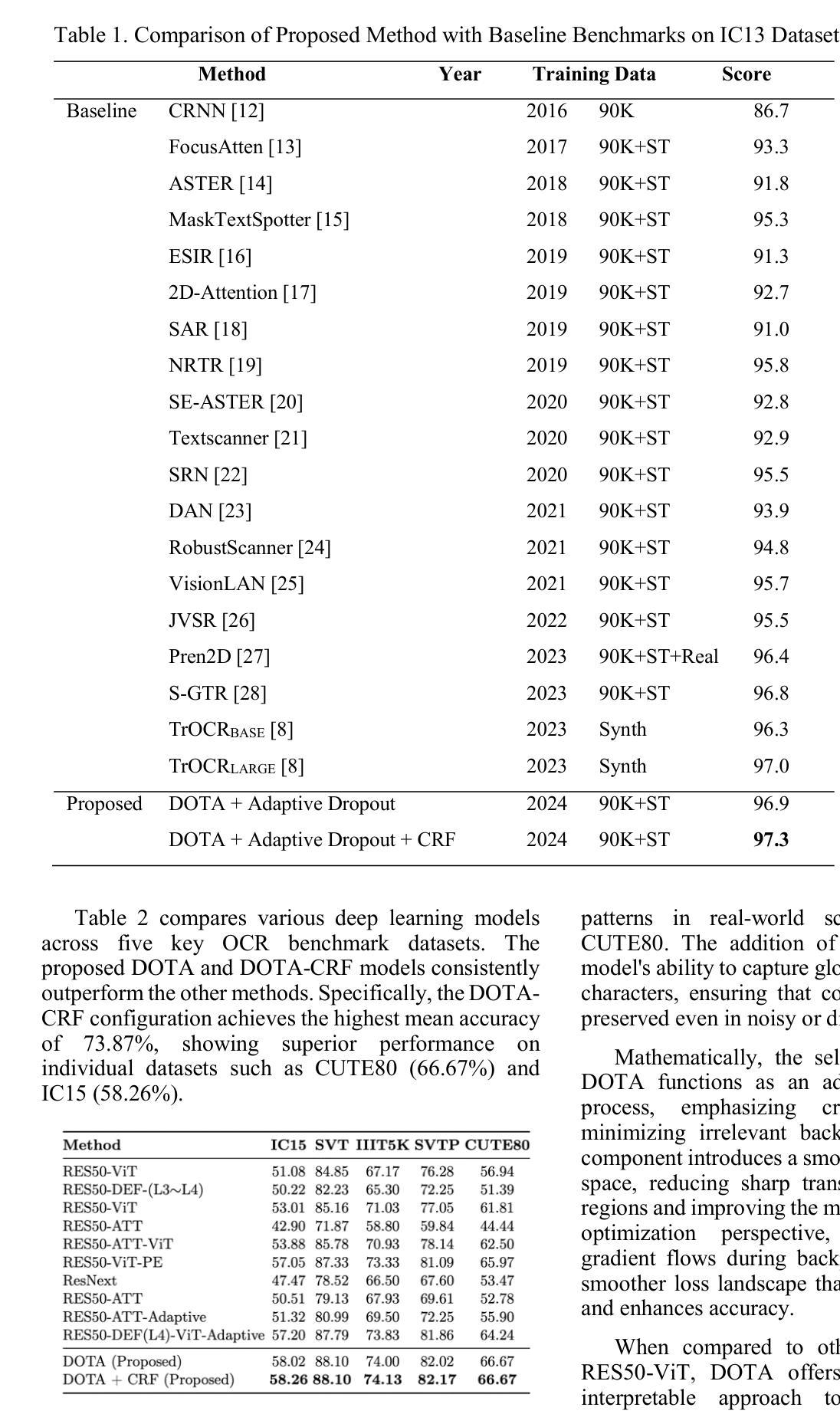
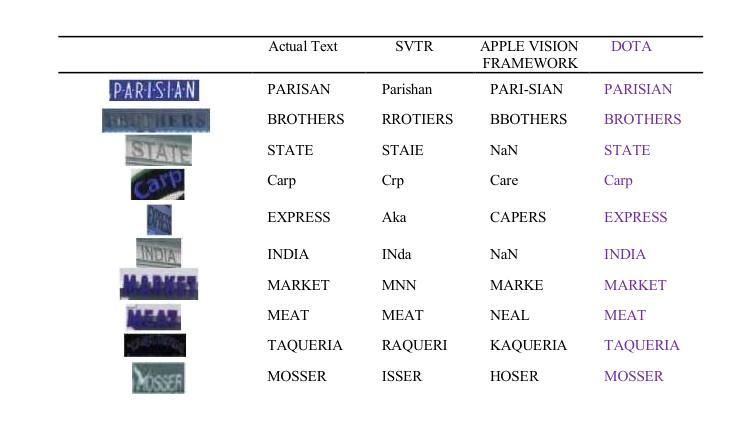
DOTA: Deformable Optimized Transformer Architecture for End-to-End Text Recognition with Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Authors:Naphat Nithisopa, Teerapong Panboonyuen
Text recognition in natural images remains a challenging yet essential task, with broad applications spanning computer vision and natural language processing. This paper introduces a novel end-to-end framework that combines ResNet and Vision Transformer backbones with advanced methodologies, including Deformable Convolutions, Retrieval-Augmented Generation, and Conditional Random Fields (CRF). These innovations collectively enhance feature representation and improve Optical Character Recognition (OCR) performance. Specifically, the framework substitutes standard convolution layers in the third and fourth blocks with Deformable Convolutions, leverages adaptive dropout for regularization, and incorporates CRF for more refined sequence modeling. Extensive experiments conducted on six benchmark datasets IC13, IC15, SVT, IIIT5K, SVTP, and CUTE80 validate the proposed method’s efficacy, achieving notable accuracies: 97.32% on IC13, 58.26% on IC15, 88.10% on SVT, 74.13% on IIIT5K, 82.17% on SVTP, and 66.67% on CUTE80, resulting in an average accuracy of 77.77%. These results establish a new state-of-the-art for text recognition, demonstrating the robustness of the approach across diverse and challenging datasets.
文本识别在自然图像中仍然是一项具有挑战但必不可少的任务,广泛应用于计算机视觉和自然语言处理领域。本文介绍了一种新型端到端框架,它结合了ResNet和Vision Transformer的主干网,并采用了先进的方法,包括可变形卷积、检索增强生成和条件随机场(CRF)。这些创新共同提高了特征表示能力,并提高了光学字符识别(OCR)的性能。具体来说,该框架在第三和第四块中用可变形卷积替代了标准卷积层,利用自适应丢弃进行正则化,并引入了CRF进行更精细的序列建模。在IC13、IC15、SVT、IIIT5K、SVTP和CUTE80六个基准数据集上进行的广泛实验验证了所提出方法的有效性,取得了显著的准确率:IC13上97.32%,IC15上58.26%,SVT上88.10%,IIIT5K上74.13%,SVTP上82.17%,CUTE80上66.67%,平均准确率为77.77%。这些结果建立了文本识别的新世界纪录,证明了该方法在多样化和具有挑战性的数据集上的稳健性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种新型端到端框架,结合了ResNet和Vision Transformer技术,并采用了可变形卷积、检索增强生成和条件随机场等先进方法,提高了自然图像中的文本识别性能。该框架在多个基准数据集上进行了广泛实验,取得了显著成果。
Key Takeaways
- 论文提出了一种新型端到端框架,用于自然图像中的文本识别。
- 框架结合了ResNet和Vision Transformer技术,增强了特征表示能力。
- 采用了可变形卷积、检索增强生成和条件随机场等方法,提高了光学字符识别(OCR)性能。
- 框架在六个基准数据集上进行了广泛实验,取得了平均准确率77.77%的显著成果。
- 该框架在IC13、IC15、SVT、IIIT5K、SVTP和CUTE80等数据集上的准确率分别为97.32%、58.26%、88.10%、74.13%、82.17%和66.67%。
- 论文实现了在自然图像文本识别领域的最新成果。
点此查看论文截图


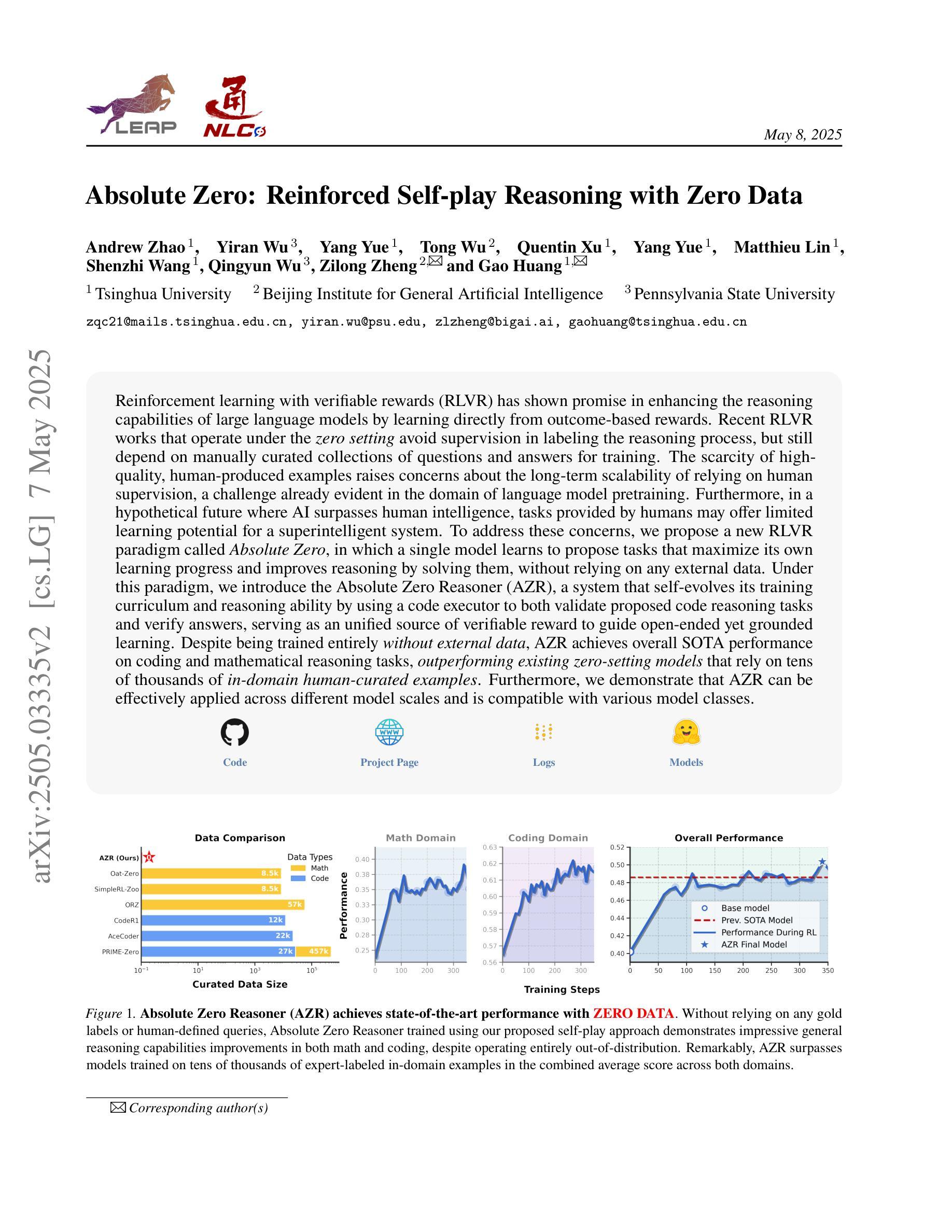
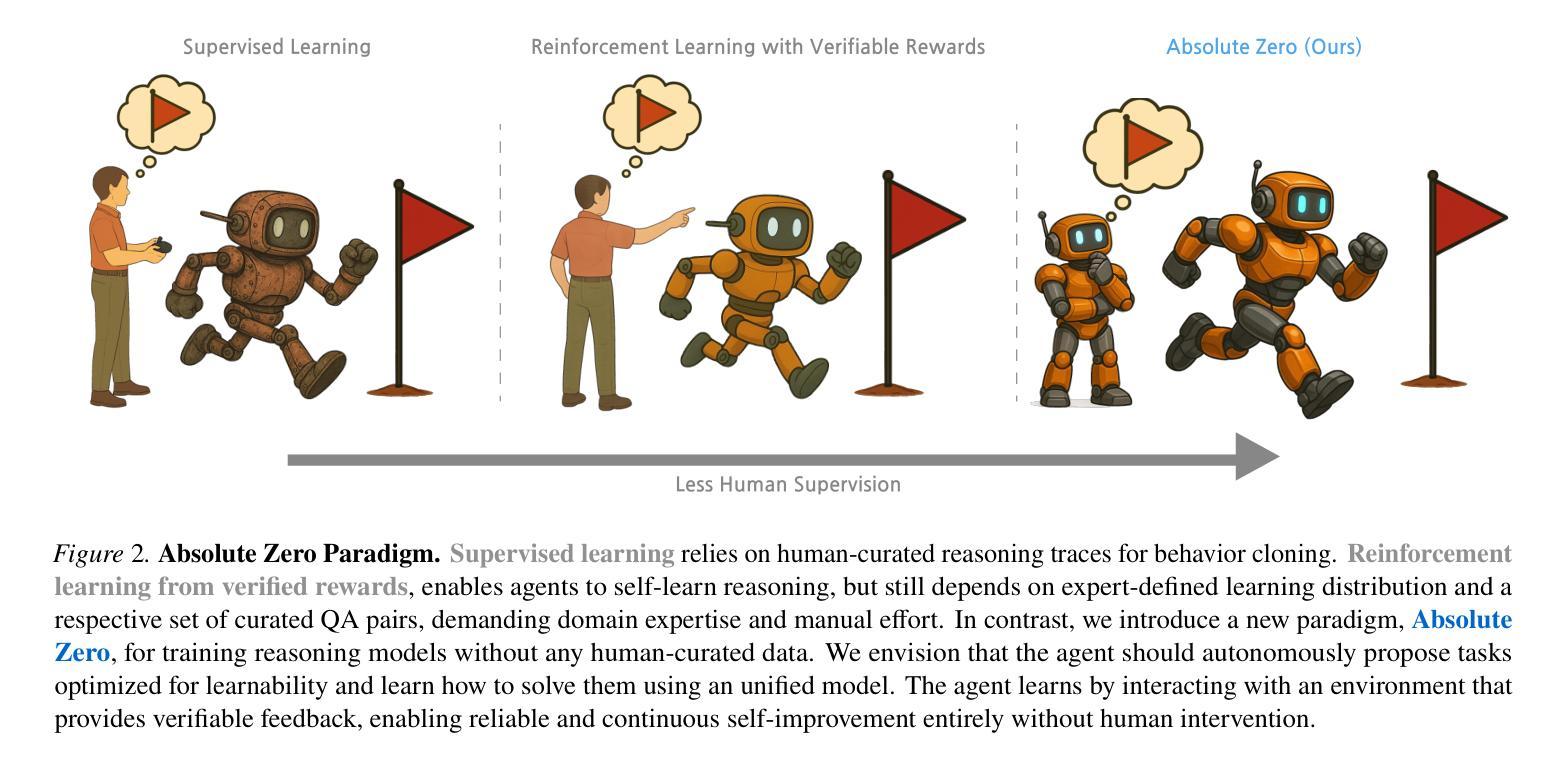
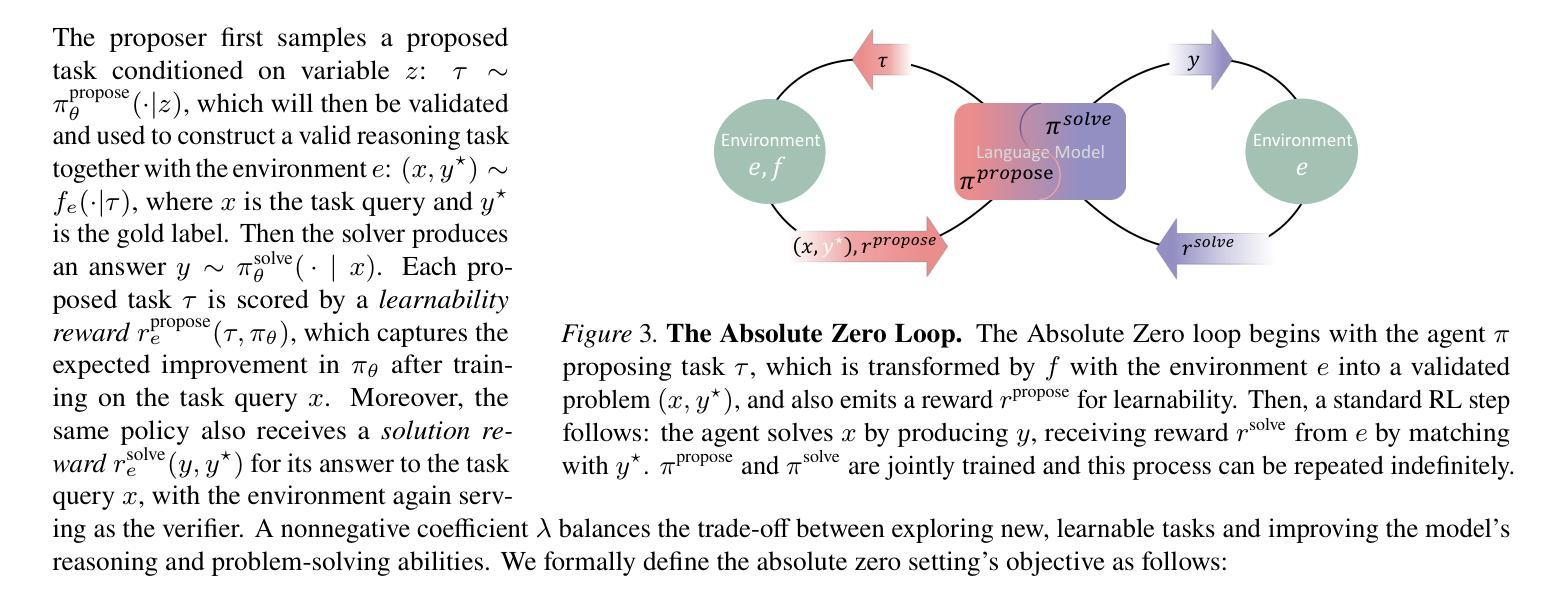
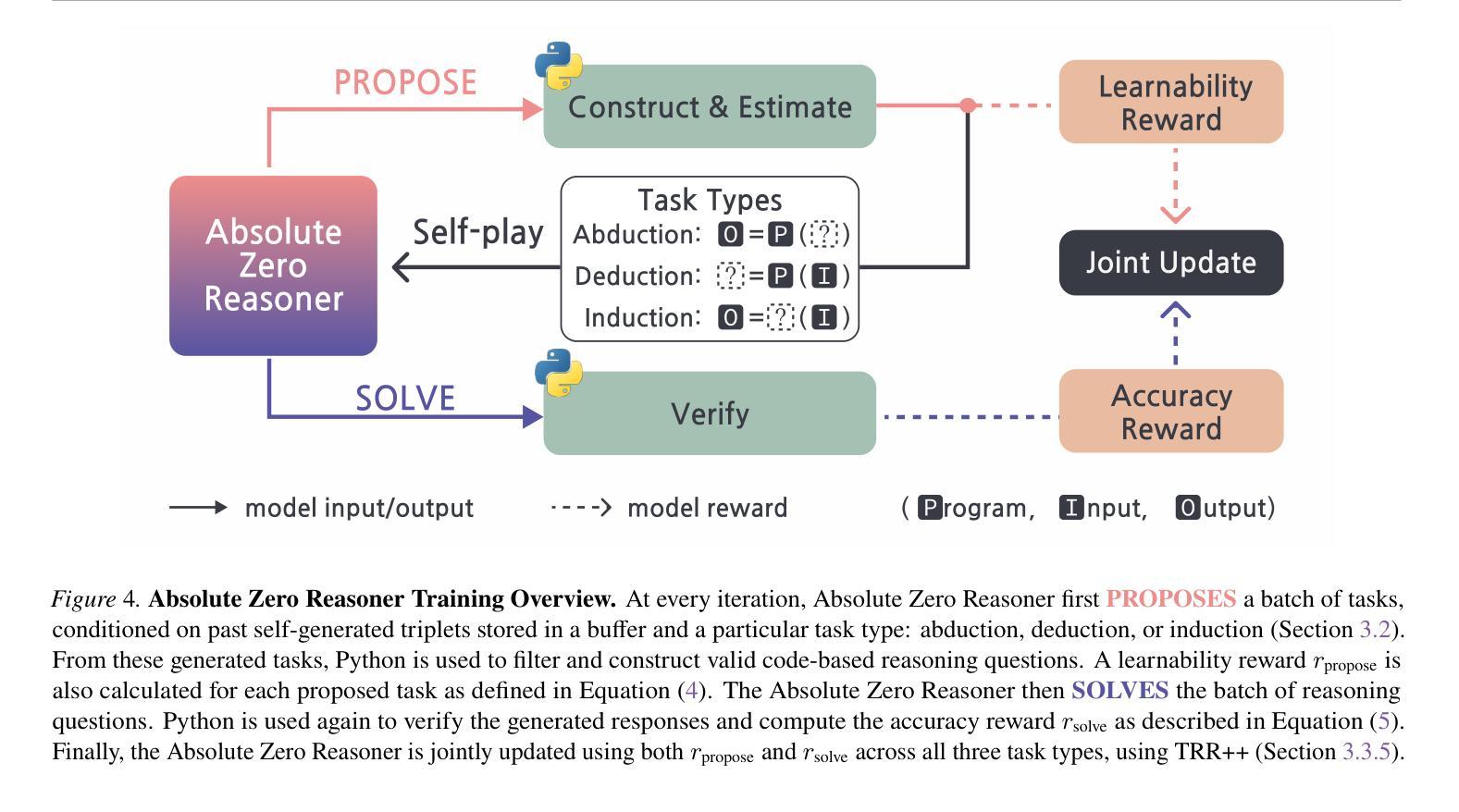
Absolute Zero: Reinforced Self-play Reasoning with Zero Data
Authors:Andrew Zhao, Yiran Wu, Yang Yue, Tong Wu, Quentin Xu, Yang Yue, Matthieu Lin, Shenzhi Wang, Qingyun Wu, Zilong Zheng, Gao Huang
Reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards (RLVR) has shown promise in enhancing the reasoning capabilities of large language models by learning directly from outcome-based rewards. Recent RLVR works that operate under the zero setting avoid supervision in labeling the reasoning process, but still depend on manually curated collections of questions and answers for training. The scarcity of high-quality, human-produced examples raises concerns about the long-term scalability of relying on human supervision, a challenge already evident in the domain of language model pretraining. Furthermore, in a hypothetical future where AI surpasses human intelligence, tasks provided by humans may offer limited learning potential for a superintelligent system. To address these concerns, we propose a new RLVR paradigm called Absolute Zero, in which a single model learns to propose tasks that maximize its own learning progress and improves reasoning by solving them, without relying on any external data. Under this paradigm, we introduce the Absolute Zero Reasoner (AZR), a system that self-evolves its training curriculum and reasoning ability by using a code executor to both validate proposed code reasoning tasks and verify answers, serving as an unified source of verifiable reward to guide open-ended yet grounded learning. Despite being trained entirely without external data, AZR achieves overall SOTA performance on coding and mathematical reasoning tasks, outperforming existing zero-setting models that rely on tens of thousands of in-domain human-curated examples. Furthermore, we demonstrate that AZR can be effectively applied across different model scales and is compatible with various model classes.
通过从结果奖励中直接学习,强化学习与可验证奖励(RLVR)在提升大型语言模型的推理能力方面展现出巨大的潜力。最近的一些RLVR工作在零样本设置下运行,避免了监督标注推理过程,但仍然依赖于手动整理的问题和答案集合进行训练。高质量、人类生产样本的稀缺性引发了对长期依赖人工监督的可行性的担忧,这一挑战在语言模型预训练领域已经显而易见。此外,在人工智能超越人类智能的假设未来中,人类提供的任务可能为超级智能系统提供有限的学习潜力。为了解决这些担忧,我们提出了一种新的RLVR范式,称为“绝对零”,其中单个模型学会提出能最大化其自身学习进度的任务,并通过解决这些任务提高推理能力,无需依赖任何外部数据。在这种范式下,我们引入了绝对零推理器(AZR),这是一个通过代码执行器验证提出的代码推理任务和答案的系统,该执行器作为可验证奖励的统一来源,指导开放但基于实际的学习,自我进化其训练课程和推理能力。尽管完全未经外部数据训练,AZR在编码和数学推理任务上实现了总体最佳性能,优于依赖数万领域内人工整理样本的现有零样本模型。此外,我们证明了AZR可以有效应用于不同的模型规模,并与各种模型类别兼容。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
强化学习与可验证奖励(RLVR)在提高大型语言模型的推理能力方面展现出潜力,通过直接从结果导向的奖励中学习。最新的RLVR工作在零样本设置下避免了监督标注推理过程,但仍依赖于手动整理的问题和答案集合进行训练。对高质量人类生成例子的稀缺性,以及对长期依赖人类监督的可持续性担忧,促使我们提出一种新的RLVR范式——绝对零(Absolute Zero)。在此范式下,单一模型学习提出任务以最大化自身学习进度并通过解决这些任务提高推理能力,无需依赖任何外部数据。我们介绍了绝对零推理器(AZR),一个通过代码执行器验证提出的代码推理任务和答案的系统,作为验证奖励的统一来源,指导开放式但基于现实的学习。尽管完全不依赖外部数据进行训练,AZR在编程和数学推理任务上实现了领先同类研究的性能表现,并能在不同模型规模和类别中有效应用。
Key Takeaways
- 强化学习与可验证奖励(RLVR)能够提高大型语言模型的推理能力。
- 在零样本设置下训练的模型可以避免对监督标注的依赖,但仍需要手动整理的任务数据。
- 对高质量人类生成例子的稀缺性和长期依赖人类监督的可持续性存在担忧。
- 提出新的RLVR范式——绝对零(Absolute Zero),允许模型自我进化其训练课程和推理能力,无需依赖外部数据。
- 引入绝对零推理器(AZR),通过代码执行器验证任务和答案,作为验证奖励的统一来源。
- AZR在编程和数学推理任务上实现了卓越性能,优于依赖大量人类整理数据的模型。
点此查看论文截图

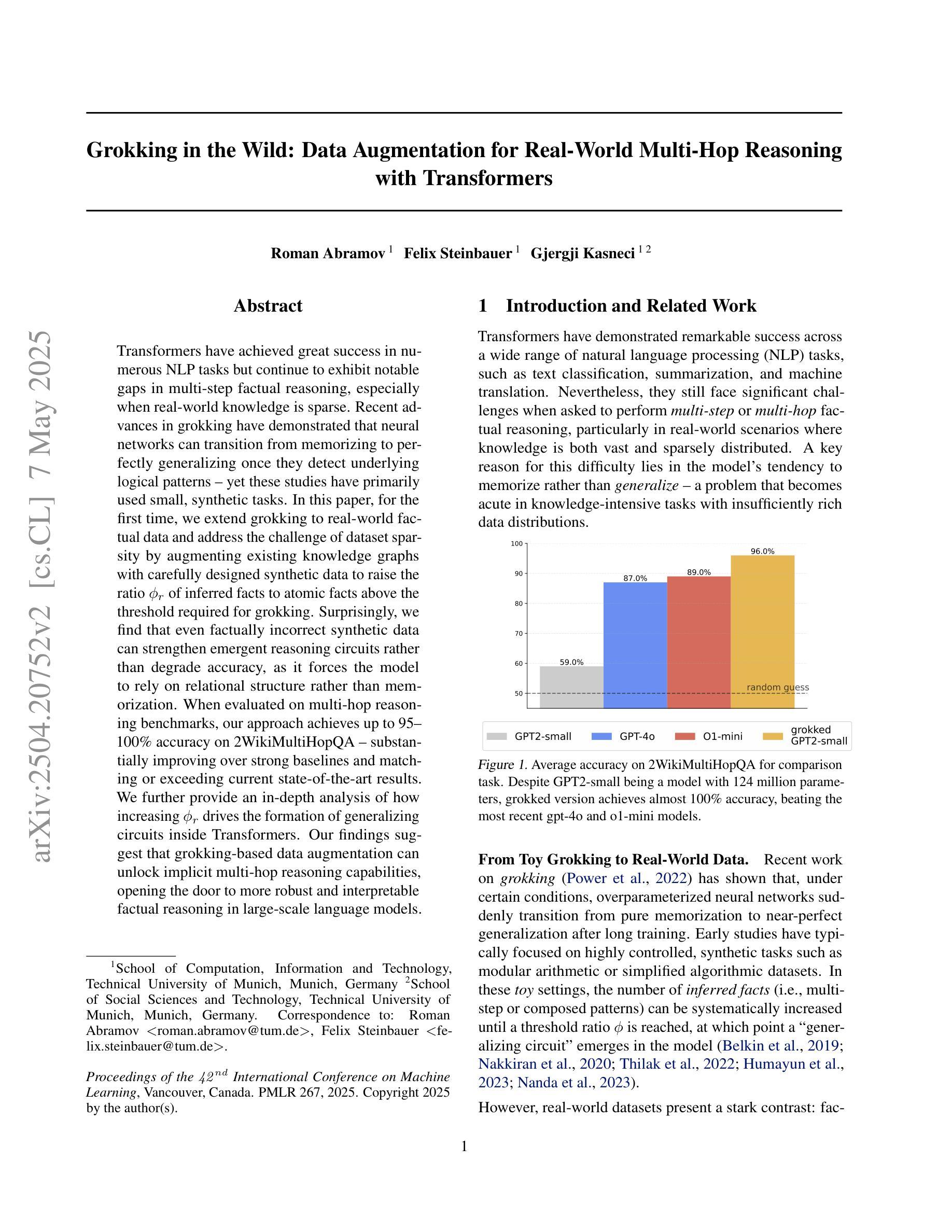
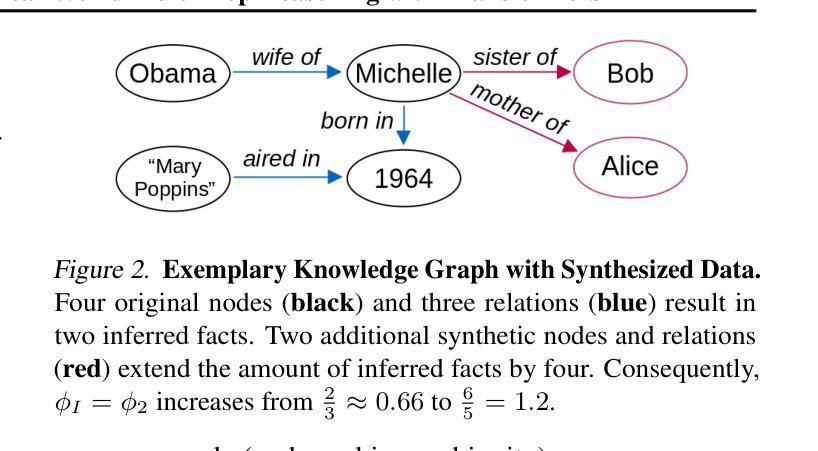
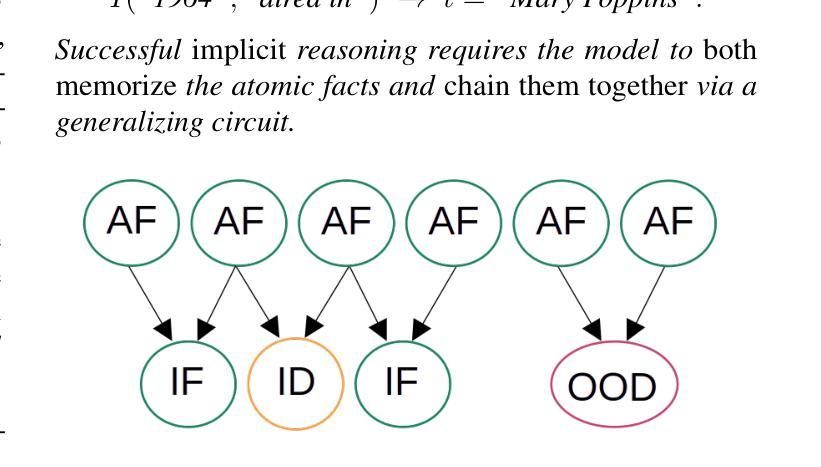
Grokking in the Wild: Data Augmentation for Real-World Multi-Hop Reasoning with Transformers
Authors:Roman Abramov, Felix Steinbauer, Gjergji Kasneci
Transformers have achieved great success in numerous NLP tasks but continue to exhibit notable gaps in multi-step factual reasoning, especially when real-world knowledge is sparse. Recent advances in grokking have demonstrated that neural networks can transition from memorizing to perfectly generalizing once they detect underlying logical patterns - yet these studies have primarily used small, synthetic tasks. In this paper, for the first time, we extend grokking to real-world factual data and address the challenge of dataset sparsity by augmenting existing knowledge graphs with carefully designed synthetic data to raise the ratio $\phi_r$ of inferred facts to atomic facts above the threshold required for grokking. Surprisingly, we find that even factually incorrect synthetic data can strengthen emergent reasoning circuits rather than degrade accuracy, as it forces the model to rely on relational structure rather than memorization. When evaluated on multi-hop reasoning benchmarks, our approach achieves up to 95-100% accuracy on 2WikiMultiHopQA - substantially improving over strong baselines and matching or exceeding current state-of-the-art results. We further provide an in-depth analysis of how increasing $\phi_r$ drives the formation of generalizing circuits inside Transformers. Our findings suggest that grokking-based data augmentation can unlock implicit multi-hop reasoning capabilities, opening the door to more robust and interpretable factual reasoning in large-scale language models.
Transformer在许多NLP任务中取得了巨大成功,但在多步骤事实推理方面仍存在明显差距,特别是在现实世界知识稀缺的情况下。最近的grokking研究表明,一旦神经网络发现潜在的逻辑模式,它们就可以从记忆转向完全泛化。然而,这些研究主要使用小型合成任务。在本文中,我们首次将grokking扩展到现实世界的事实数据,并通过精心设计的合成数据增强现有知识图谱来解决数据集稀疏性的挑战,从而提高推断事实与原子事实的比率$\phi_r$,使其超过实现grokking所需的阈值。令人惊讶的是,我们发现即使是事实错误的合成数据也可以加强新兴推理电路,而不是降低准确性,因为它迫使模型依赖关系结构而不是记忆。在评估多跳推理基准测试时,我们的方法在2WikiMultiHopQA上达到了高达95-100%的准确率,大幅超越了强大的基线并匹配或超过了当前最新的结果。我们还深入分析了如何提高$\phi_r$来驱动Transformer内部泛化电路的形成。我们的研究结果表明,基于grokking的数据增强可以解锁隐式的多跳推理能力,为大规模语言模型中的更稳健和可解释的事实推理打开了大门。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML) 2025
Summary
本文扩展了grokking至真实世界的事实数据,通过增强现有知识图谱与精心设计合成数据来解决数据集稀疏性的挑战。研究发现,即使事实上不正确合成数据也能加强新兴推理电路,而非降低准确度,这促使模型依赖关系结构而非记忆。在跨步推理基准测试上,该方法在2WikiMultiHopQA上达到95-100%的准确率,大幅超越强基线并匹配或超越当前最新结果。
Key Takeaways
- 论文将grokking扩展到真实世界的事实数据,解决数据集稀疏性问题。
- 通过增强知识图谱与合成数据,提高推断事实与原子事实比率$\phi_r$,达到grokking所需的阈值。
- 事实上不正确合成数据能加强模型的新兴推理电路,使其更依赖关系结构而非记忆。
- 在多步推理基准测试上取得高达95-100%的准确率,表现优异。
- 该方法匹配或超越当前最新技术结果。
- 增加$\phi_r$有助于在Transformer中形成通用电路。
点此查看论文截图

Adaptive Rank Allocation: Speeding Up Modern Transformers with RaNA Adapters
Authors:Roberto Garcia, Jerry Liu, Daniel Sorvisto, Sabri Eyuboglu
Large Language Models (LLMs) are computationally intensive, particularly during inference. Neuron-adaptive techniques, which selectively activate neurons in Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) layers, offer some speedups but suffer from limitations in modern Transformers. These include reliance on sparse activations, incompatibility with attention layers, and the use of costly neuron masking techniques. To address these issues, we propose the Adaptive Rank Allocation framework and introduce the Rank and Neuron Allocator (RaNA) adapter. RaNA adapters leverage rank adapters, which operate on linear layers by applying both low-rank matrix decompositions and adaptive masking to efficiently allocate compute without depending on activation sparsity. This enables RaNA to be generally applied to MLPs and linear components of attention modules, while eliminating the need for expensive maskers found in neuron-adaptive methods. Notably, when compared to neuron adapters, RaNA improves perplexity by up to 7 points and increases accuracy by up to 8 percentage-points when reducing FLOPs by $\sim$44% in state-of-the-art Transformer architectures. These results position RaNA as a robust solution for improving inference efficiency in modern Transformer architectures.
大型语言模型(LLM)计算密集,特别是在推理阶段。神经元自适应技术通过选择性激活多层感知器(MLP)层中的神经元提供了一些加速,但在现代Transformer中受到一些限制。这些限制包括依赖于稀疏激活、与注意力层不兼容以及使用成本高昂的神经元掩蔽技术。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了自适应排名分配框架,并引入了Rank和Neuron Allocator(RaNA)适配器。RaNA适配器利用排名适配器,通过低阶矩阵分解和自适应掩蔽在线性层上运行,可以有效地分配计算,而不依赖于激活稀疏性。这使得RaNA可以广泛应用于MLP和注意力模块的线性组件,同时消除了神经元自适应方法中发现的昂贵掩蔽器的需求。值得注意的是,与神经元适配器相比,RaNA在减少44%浮点运算(FLOPs)的情况下,困惑度降低了高达7点,准确率提高了高达8个百分点,这在最先进的Transformer架构中表现优异。这些结果将RaNA定位为提高现代Transformer架构推理效率的一种稳健解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
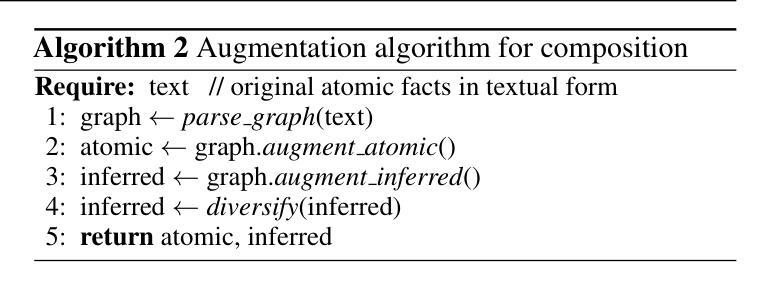
PDF 16 pages, 5 figures. ICLR 2025
Summary
大规模语言模型(LLM)在推理过程中计算密集,神经元自适应技术虽能提供一定的加速,但在现代Transformer架构中存在局限性。针对这些问题,我们提出了自适应排名分配框架和引入RaNA适配器。RaNA适配器利用排名适配器,通过低阶矩阵分解和自适应掩码在线性层上运行,以有效地分配计算资源,而无需依赖激活稀疏性。这使得RaNA可广泛应用于MLP和注意力模块的线性组件,消除了神经元自适应方法中昂贵的掩码器的需求。在减少约44%的浮点运算(FLOPs)的同时,RaNA在先进的Transformer架构中改善了困惑度达7点,准确率提高高达8个百分点,显示出其在提高现代Transformer架构推理效率方面的稳健解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- LLM在推理过程中计算密集,需要高效计算方法优化。
- 神经元自适应技术虽然可以提供加速,但在现代Transformer架构中存在局限性。
- 提出自适应排名分配框架和RaNA适配器以改进此问题。
- RaNA利用排名适配器,结合低阶矩阵分解和自适应掩码,有效分配计算资源。
- RaNA可广泛应用于MLP和注意力模块的线性组件。
- RaNA不需要昂贵的掩码器,与神经元自适应方法相比具有优势。
点此查看论文截图

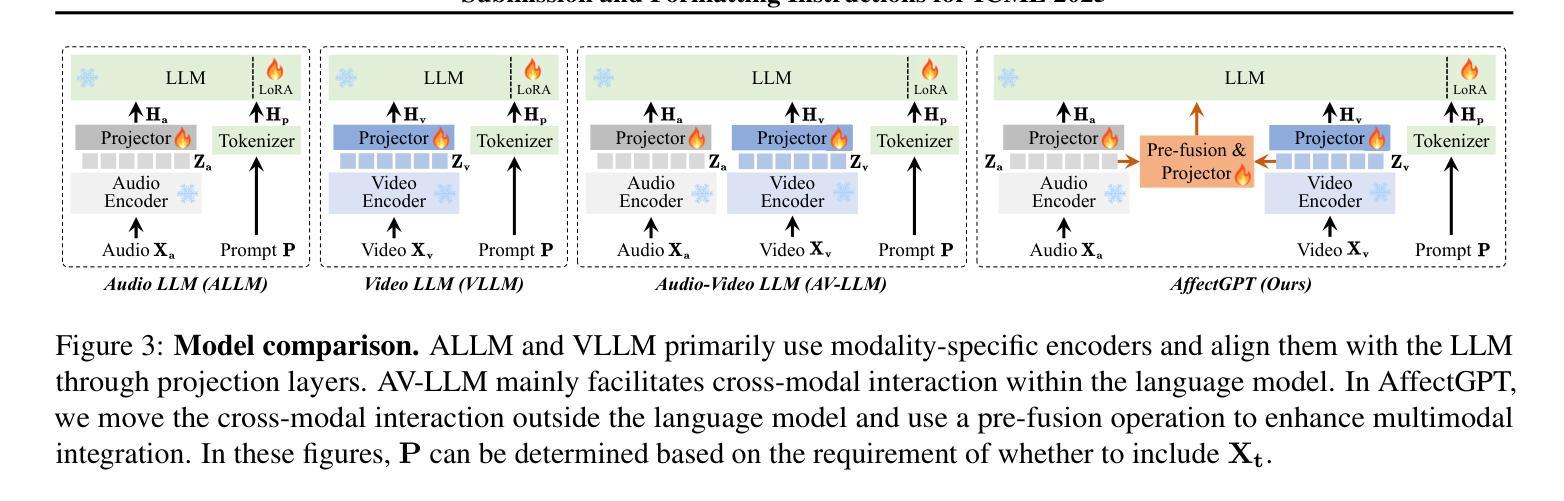
AffectGPT: A New Dataset, Model, and Benchmark for Emotion Understanding with Multimodal Large Language Models
Authors:Zheng Lian, Haoyu Chen, Lan Chen, Haiyang Sun, Licai Sun, Yong Ren, Zebang Cheng, Bin Liu, Rui Liu, Xiaojiang Peng, Jiangyan Yi, Jianhua Tao
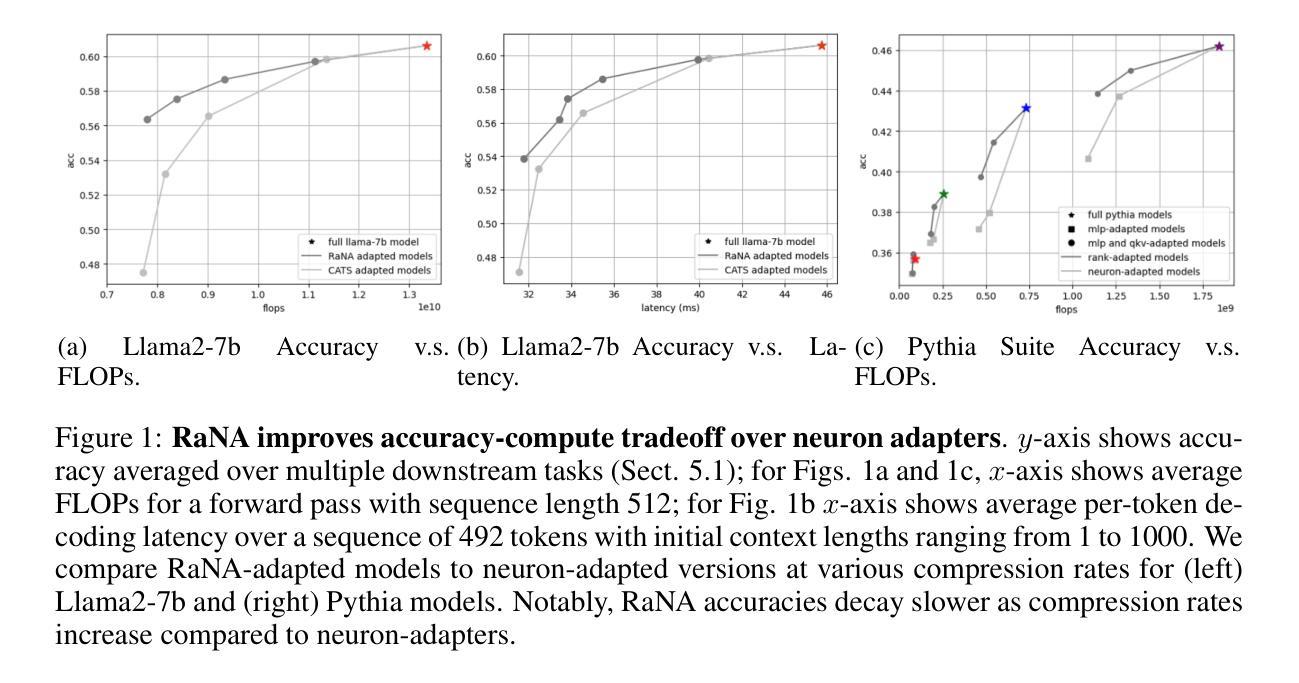
The emergence of multimodal large language models (MLLMs) advances multimodal emotion recognition (MER) to the next level, from naive discriminative tasks to complex emotion understanding with advanced video understanding abilities and natural language description. However, the current community suffers from a lack of large-scale datasets with intensive, descriptive emotion annotations, as well as a multimodal-centric framework to maximize the potential of MLLMs for emotion understanding. To address this, we establish a new benchmark for MLLM-based emotion understanding with a novel dataset (MER-Caption) and a new model (AffectGPT). Utilizing our model-based crowd-sourcing data collection strategy, we construct the largest descriptive emotion dataset to date (by far), featuring over 2K fine-grained emotion categories across 115K samples. We also introduce the AffectGPT model, designed with pre-fusion operations to enhance multimodal integration. Finally, we present MER-UniBench, a unified benchmark with evaluation metrics tailored for typical MER tasks and the free-form, natural language output style of MLLMs. Extensive experimental results show AffectGPT’s robust performance across various MER tasks. We have released both the code and the dataset to advance research and development in emotion understanding: https://github.com/zeroQiaoba/AffectGPT.
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的出现将多模态情感识别(MER)提升到了一个新的水平,从简单的辨别任务发展到了具有先进视频理解能力和自然语言描述功能的复杂情感理解。然而,当前社区缺乏大规模、情感标注密集且描述性的数据集,以及以多模态为中心、能最大化MLLM在情感理解潜力的框架。为了解决这一问题,我们建立了基于MLLM的情感理解新基准,包括一个新型数据集(MER-Caption)和一个新模型(AffectGPT)。通过基于模型的众包数据收集策略,我们构建了迄今为止最大的描述性情感数据集,涵盖超过2K个精细情感类别,跨越11.5万样本。我们还介绍了AffectGPT模型的设计,该模型通过预融合操作增强多模态集成。最后,我们推出了MER-UniBench统一基准测试,它包含针对典型MER任务的评估指标和MLLM的自由形式自然语言输出风格。广泛的实验结果表明AffectGPT在各种MER任务中的稳健性能。我们已经发布了代码和数据集,以促进情感理解的研究和发展:https://github.com/zeroQiaoba/AffectGPT。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的出现推动了多模态情感识别(MER)的发展,从简单的判别任务到复杂的情感理解,具备了高级视频理解能力和自然语言描述能力。然而,由于缺乏具有描述性情感注释的大规模数据集以及多模态中心框架来最大限度地发挥MLLMs在情感理解方面的潜力,当前的研究面临挑战。为此,我们建立了基于MLLM的情感理解新基准,并提出了新的数据集(MER-Caption)和新模型(AffectGPT)。我们利用基于模型的众包数据收集策略,构建了迄今为止最大的描述性情感数据集,包含超过2K个精细粒度的情感类别和超过11万样本。我们还介绍了专为增强多模态融合而设计的AffectGPT模型。最后,我们推出了MER-UniBench统一基准,其评估指标适用于典型的MER任务以及MLLMs的自然语言输出风格。实验结果广泛证明了AffectGPT在各种MER任务中的稳健性能。
Key Takeaways:
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在多模态情感识别(MER)领域展现出优异潜力,支持从复杂视频理解到自然语言描述的先进情感理解。
- 当前缺乏具备描述性情感注释的大规模数据集和多模态中心框架,限制了MLLMs在情感理解方面的应用。
- 建立了新的基于MLLM的情感理解基准,包括新的数据集MER-Caption和模型AffectGPT。
- MER-Caption数据集是迄今为止最大的描述性情感数据集,包含大量精细粒度的情感类别和样本。
- AffectGPT模型设计旨在增强多模态融合,提高情感理解的性能。
- 推出了MER-UniBench统一基准,适应典型的MER任务以及MLLMs的自然语言输出风格。
点此查看论文截图


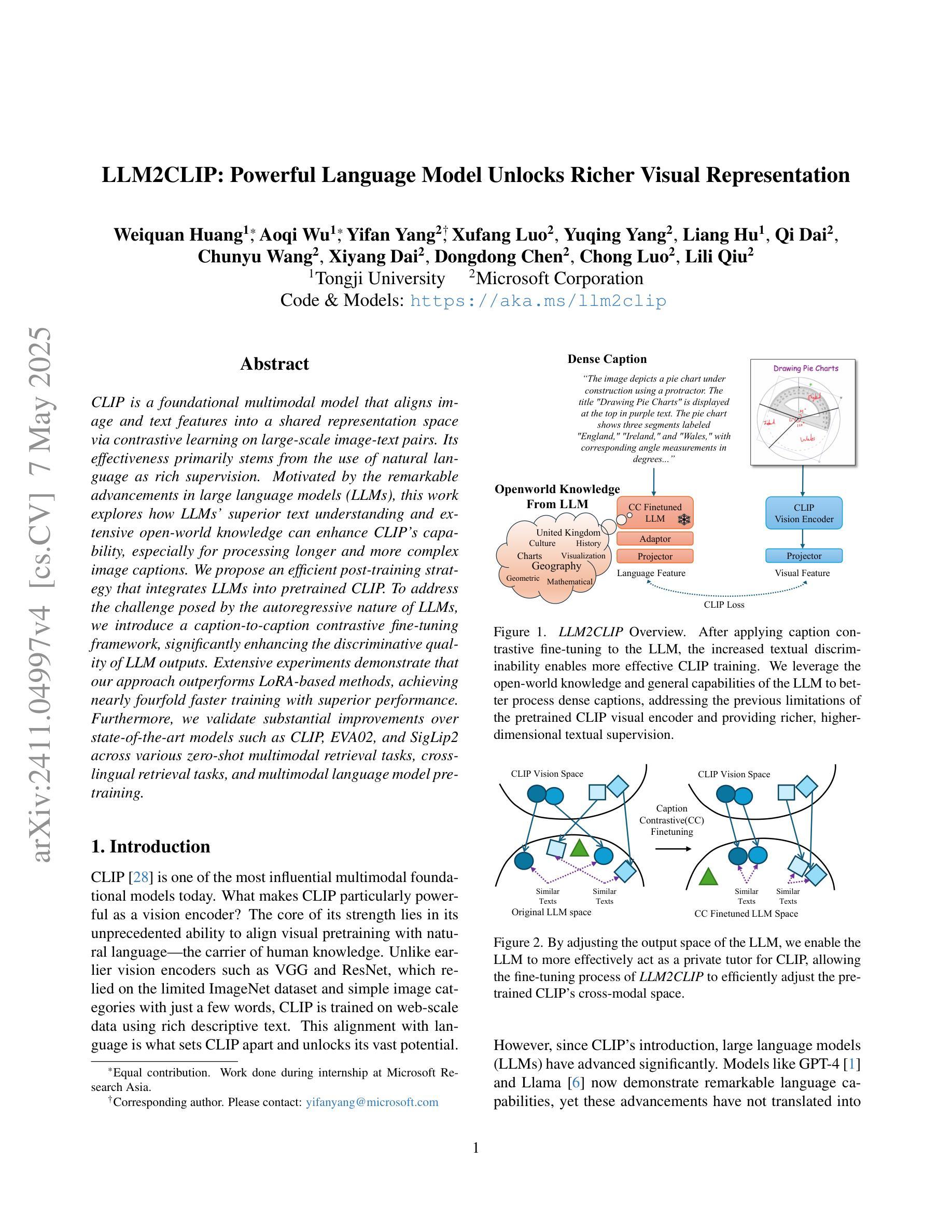
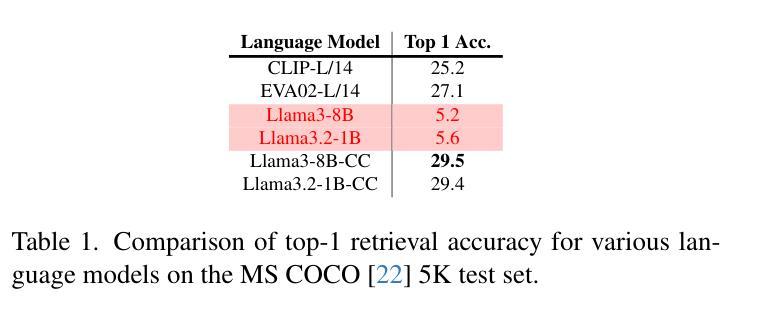
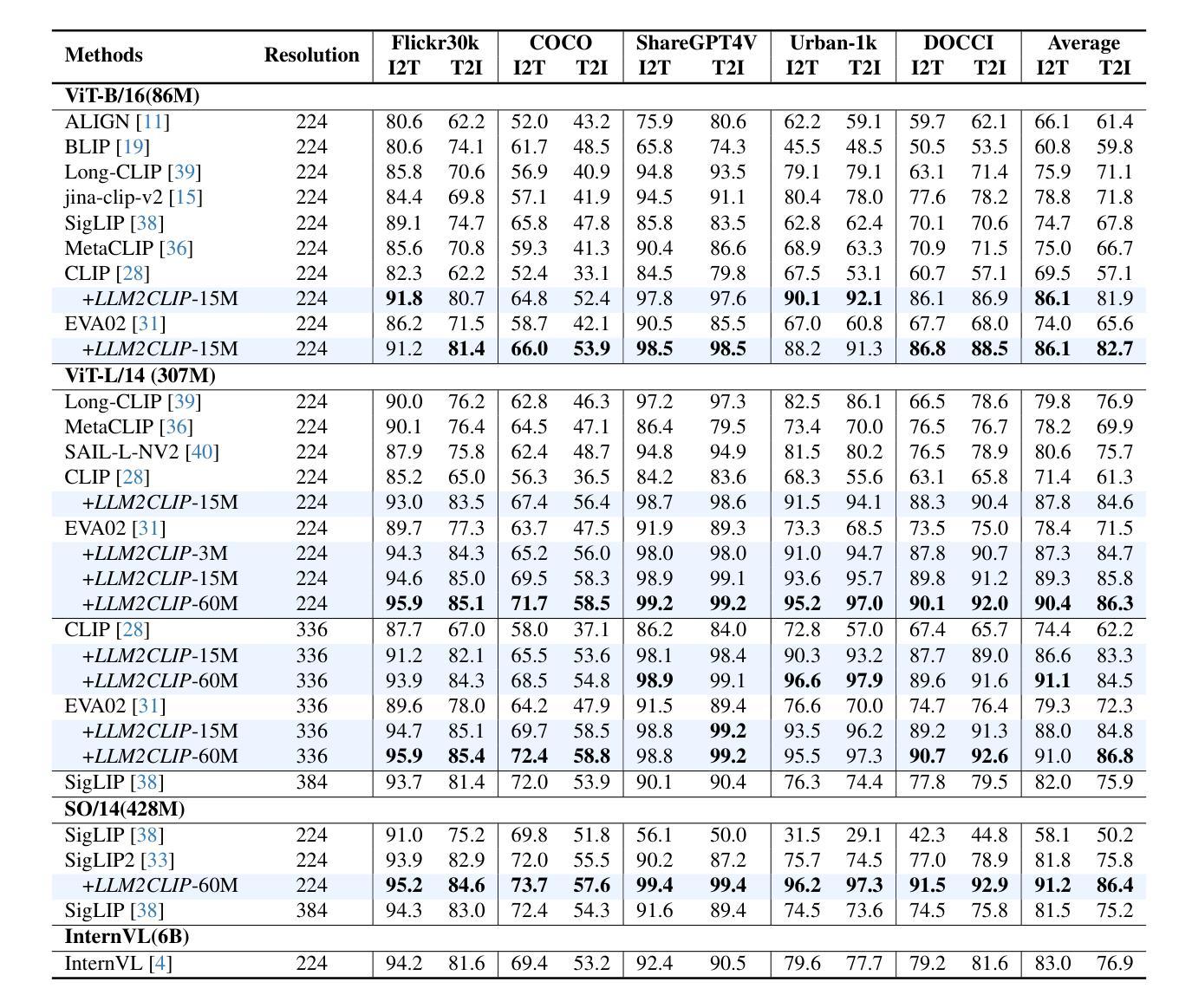
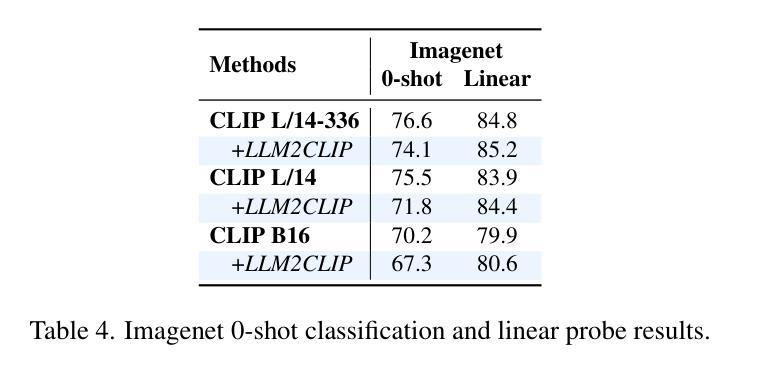
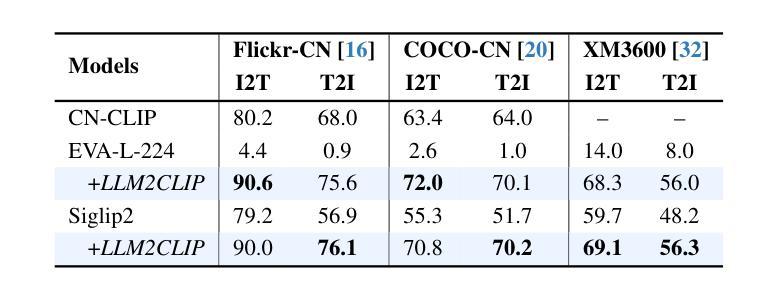
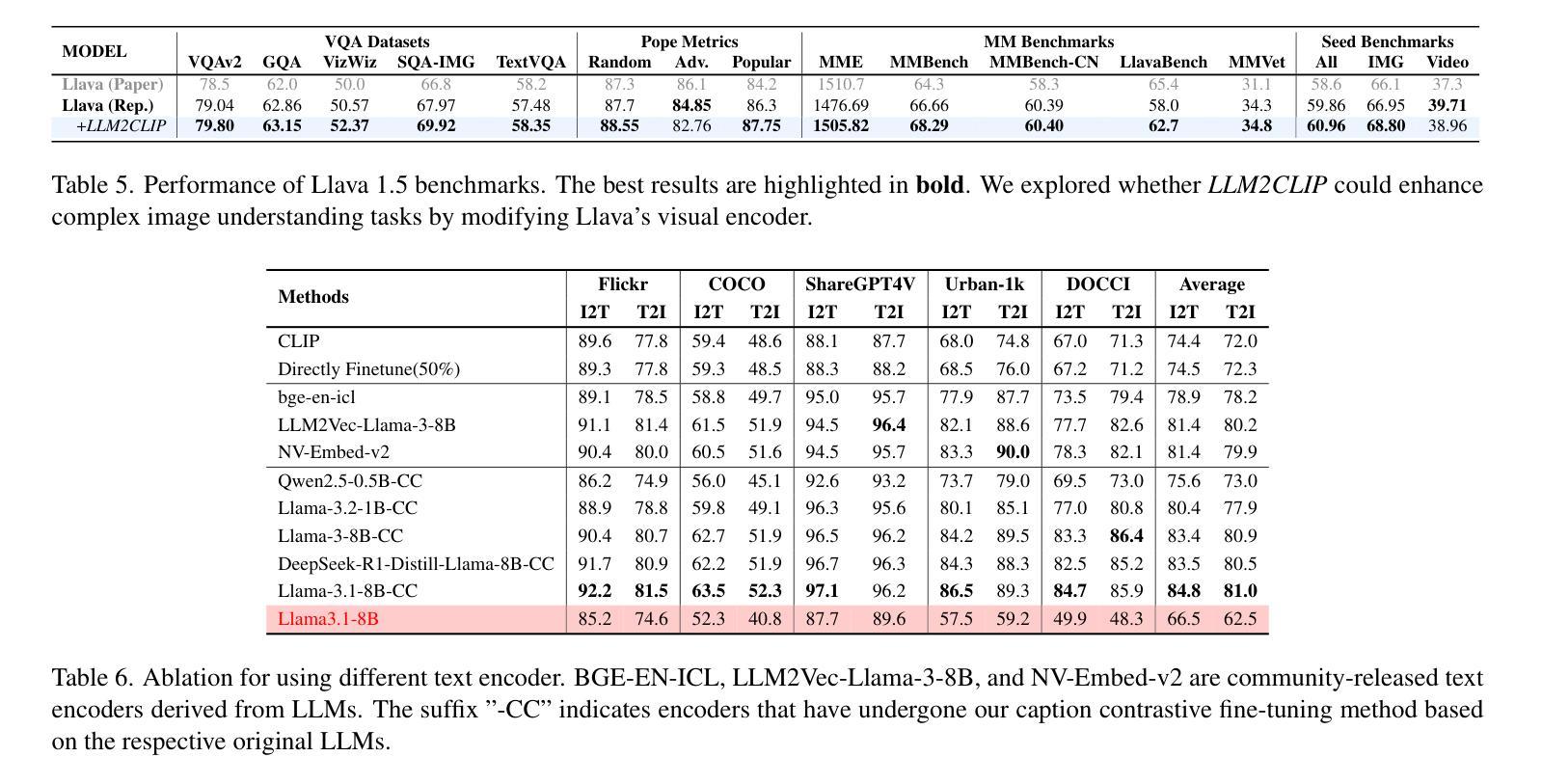
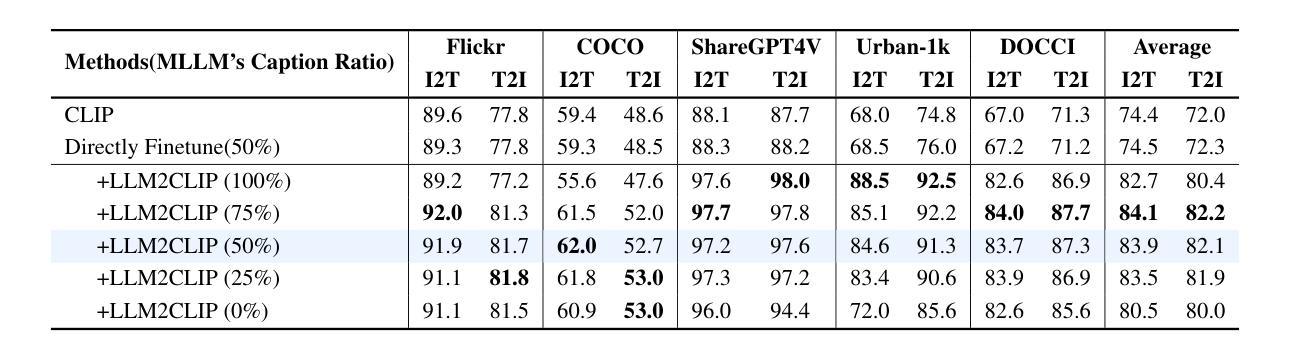
LLM2CLIP: Powerful Language Model Unlocks Richer Visual Representation
Authors:Weiquan Huang, Aoqi Wu, Yifan Yang, Xufang Luo, Yuqing Yang, Liang Hu, Qi Dai, Chunyu Wang, Xiyang Dai, Dongdong Chen, Chong Luo, Lili Qiu
CLIP is a foundational multimodal model that aligns image and text features into a shared representation space via contrastive learning on large-scale image-text pairs. Its effectiveness primarily stems from the use of natural language as rich supervision. Motivated by the remarkable advancements in large language models (LLMs), this work explores how LLMs’ superior text understanding and extensive open-world knowledge can enhance CLIP’s capability, especially for processing longer and more complex image captions. We propose an efficient post-training strategy that integrates LLMs into pretrained CLIP. To address the challenge posed by the autoregressive nature of LLMs, we introduce a caption-to-caption contrastive fine-tuning framework, significantly enhancing the discriminative quality of LLM outputs. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach outperforms LoRA-based methods, achieving nearly fourfold faster training with superior performance. Furthermore, we validate substantial improvements over state-of-the-art models such as CLIP, EVA02, and SigLip2 across various zero-shot multimodal retrieval tasks, cross-lingual retrieval tasks, and multimodal language model pretraining.
CLIP是一种基础的多模态模型,它通过大规模图像文本对上的对比学习,将图像和文本特征对齐到共享表示空间。其有效性主要源于使用丰富的自然语言监督。受大型语言模型(LLM)显著进步的启发,这项工作探索了LLMs出色的文本理解和丰富的开放世界知识如何增强CLIP的能力,特别是处理更长更复杂的图像标题。我们提出了一种高效的后训练策略,将LLMs集成到预训练的CLIP中。为了解决LLMs的自回归性质所带来的挑战,我们引入了一种标题到标题的对比微调框架,显著提高了LLM输出的辨别质量。大量实验表明,我们的方法优于基于LoRA的方法,训练速度近乎提高了四倍,且性能更优。此外,我们在各种零样本多模态检索任务、跨语言检索任务和多媒体语言模型预训练任务上,验证了与最新模型(如CLIP、EVA02和SigLip2)相比的实质性改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于CLIP模型的多模态模型通过对比学习在大规模图文对上对齐图像和文本特征,形成共享表示空间。本文探索了大型语言模型(LLMs)如何增强CLIP处理较长、更复杂图像字幕的能力,并提出将LLMs集成到预训练CLIP中的高效后训练策略。实验证明,该方法在零样本多模态检索任务、跨语言检索任务和跨模态语言模型预训练等方面实现了显著改进。
Key Takeaways
- CLIP是一个基础多模态模型,通过将图像和文本特征映射到共享表示空间进行对比学习。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)具有出色的文本理解和丰富的开放世界知识,可以强化CLIP的处理能力。
- 提出了一种高效的后训练策略,将LLMs集成到预训练的CLIP模型中。
- 引入了字幕对比微调框架来解决LLMs的自回归性质带来的挑战。
- 实验证明该方法优于基于LoRA的方法,实现了更快的训练和更高的性能。
点此查看论文截图

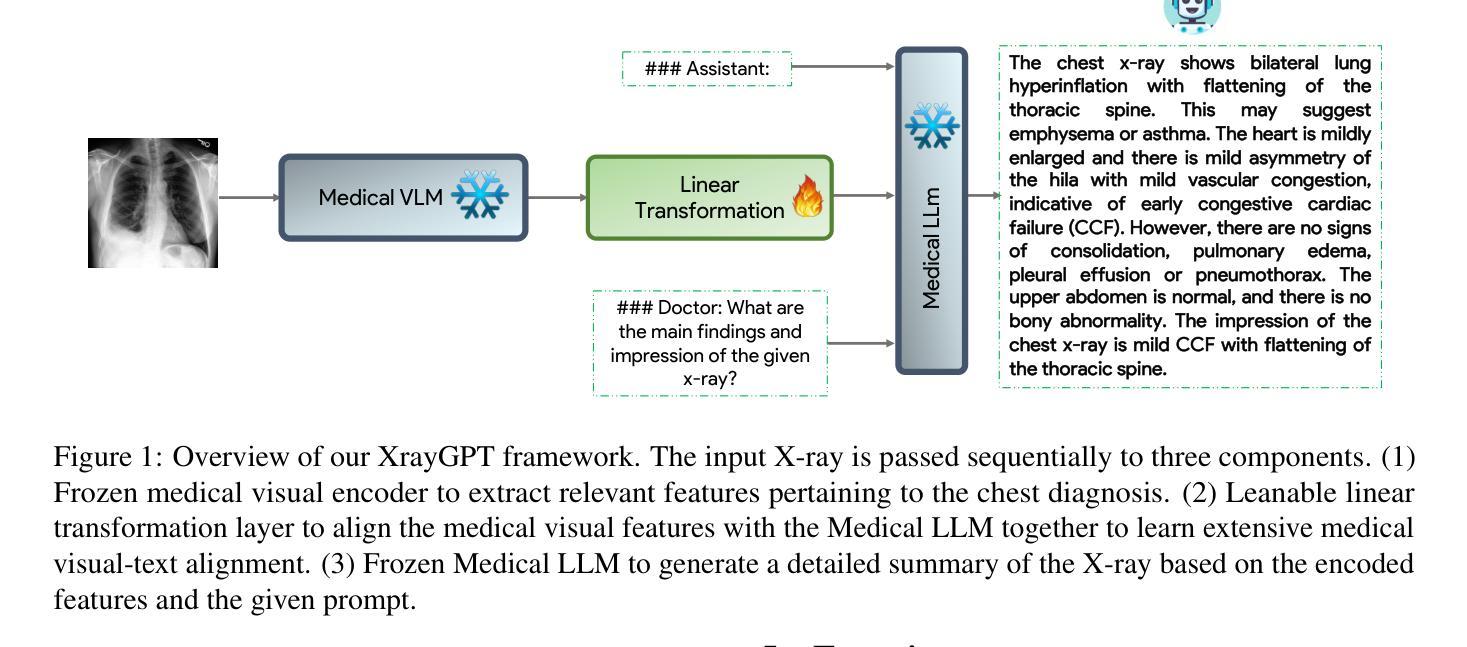
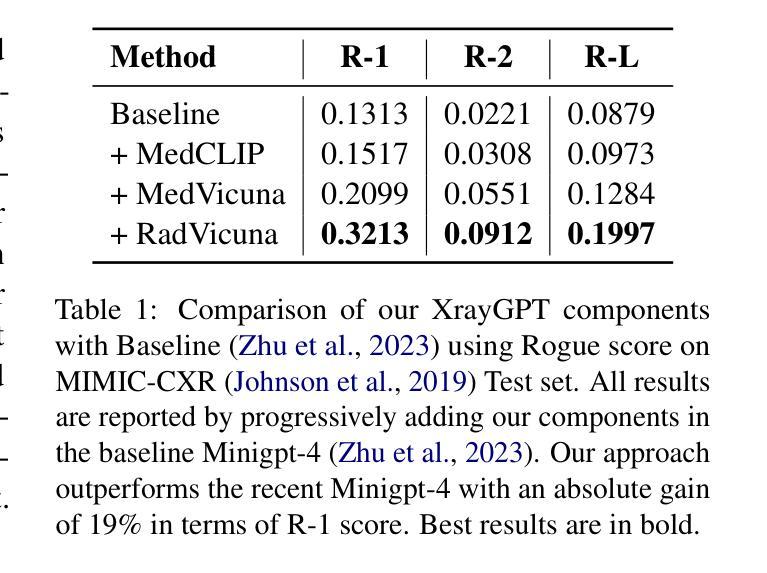
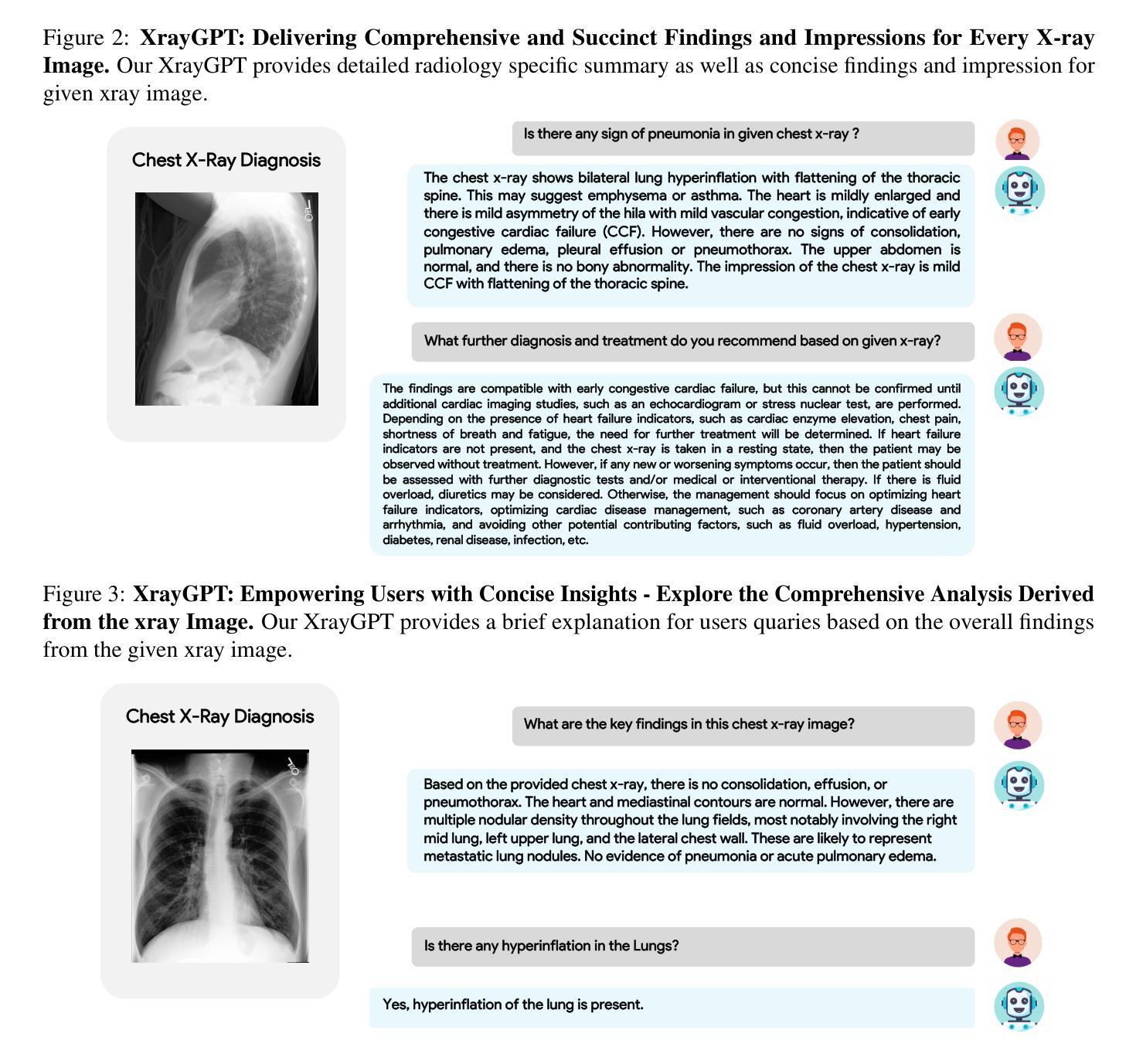
XrayGPT: Chest Radiographs Summarization using Medical Vision-Language Models
Authors:Omkar Thawakar, Abdelrahman Shaker, Sahal Shaji Mullappilly, Hisham Cholakkal, Rao Muhammad Anwer, Salman Khan, Jorma Laaksonen, Fahad Shahbaz Khan
The latest breakthroughs in large vision-language models, such as Bard and GPT-4, have showcased extraordinary abilities in performing a wide range of tasks. Such models are trained on massive datasets comprising billions of public image-text pairs with diverse tasks. However, their performance on task-specific domains, such as radiology, is still under-investigated and potentially limited due to a lack of sophistication in understanding biomedical images. On the other hand, conversational medical models have exhibited remarkable success but have mainly focused on text-based analysis. In this paper, we introduce XrayGPT, a novel conversational medical vision-language model that can analyze and answer open-ended questions about chest radiographs. Specifically, we align both medical visual encoder (MedClip) with a fine-tuned large language model (Vicuna), using a simple linear transformation. This alignment enables our model to possess exceptional visual conversation abilities, grounded in a deep understanding of radiographs and medical domain knowledge. To enhance the performance of LLMs in the medical context, we generate ~217k interactive and high-quality summaries from free-text radiology reports. These summaries serve to enhance the performance of LLMs through the fine-tuning process. Our approach opens up new avenues the research for advancing the automated analysis of chest radiographs. Our open-source demos, models, and instruction sets are available at: https://github.com/mbzuai-oryx/XrayGPT.
最新的大型视觉语言模型(如Bard和GPT-4)的突破展现出在各种任务上的超凡能力。这些模型经过大规模数据集的训练,包含数十亿张公共图像和文本对,涵盖多样化的任务。然而,它们在特定任务领域(如放射学)的表现仍待研究,并且由于缺乏复杂的生物医学图像理解能力,其表现可能受到限制。另一方面,对话式医疗模型已经取得了显著的成就,但主要侧重于基于文本的分析。在本文中,我们介绍了XrayGPT,这是一种新型对话式医疗视觉语言模型,能够分析并回答有关胸部X光片的开放性问题。具体来说,我们通过简单的线性变换,将医疗视觉编码器(MedClip)与经过微调的大型语言模型(Vicuna)进行对齐。这种对齐使我们的模型拥有出色的视觉对话能力,基于对X光片和医学领域知识的深刻理解。为了提高LLMs在医学背景下的性能,我们从自由文本放射学报告中生成了约21.7万条交互式和高质量摘要。这些摘要通过微调过程增强了LLMs的性能。我们的方法为推进胸部X光片的自动化分析研究开辟了新途径。我们的开源演示、模型和指令集可在https://github.com/mbzuai-oryx/XrayGPT获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ACL 2024-BIONLP Workshop. Code: https://github.com/mbzuai-oryx/XrayGPT
Summary:最新大型视觉语言模型如Bard和GPT-4展现出卓越的多任务性能,但在特定领域如放射学中的表现仍待研究。文章介绍了一种新型对话医学视觉语言模型XrayGPT,该模型通过融合医学视觉编码器MedClip和微调的大型语言模型Vicuna,对胸部X射线图像进行开放问答分析。为提高LLMs在医学语境下的性能,研究团队生成了约21.7万份来自放射报告的交互式高质量摘要。
Key Takeaways:
- 大型视觉语言模型如Bard和GPT-4具有广泛的任役能力,但在医学领域的表现仍需深入研究。
- XrayGPT是一种新型的对话医学视觉语言模型,能分析和回答关于胸部X射线图像的开放性问题。
- XrayGPT融合了医学视觉编码器MedClip和微调的大型语言模型Vicuna,实现出色的视觉对话能力。
- 研究团队通过生成来自放射报告的交互式高质量摘要,增强了LLMs在医学语境下的性能。
- XrayGPT的研究开放了新的途径,推动了胸部X射线图像的自动化分析的发展。
- XrayGPT的开源演示、模型和指令集可供公众访问和使用。
点此查看论文截图