⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-09 更新
On Path to Multimodal Generalist: General-Level and General-Bench
Authors:Hao Fei, Yuan Zhou, Juncheng Li, Xiangtai Li, Qingshan Xu, Bobo Li, Shengqiong Wu, Yaoting Wang, Junbao Zhou, Jiahao Meng, Qingyu Shi, Zhiyuan Zhou, Liangtao Shi, Minghe Gao, Daoan Zhang, Zhiqi Ge, Weiming Wu, Siliang Tang, Kaihang Pan, Yaobo Ye, Haobo Yuan, Tao Zhang, Tianjie Ju, Zixiang Meng, Shilin Xu, Liyu Jia, Wentao Hu, Meng Luo, Jiebo Luo, Tat-Seng Chua, Shuicheng Yan, Hanwang Zhang
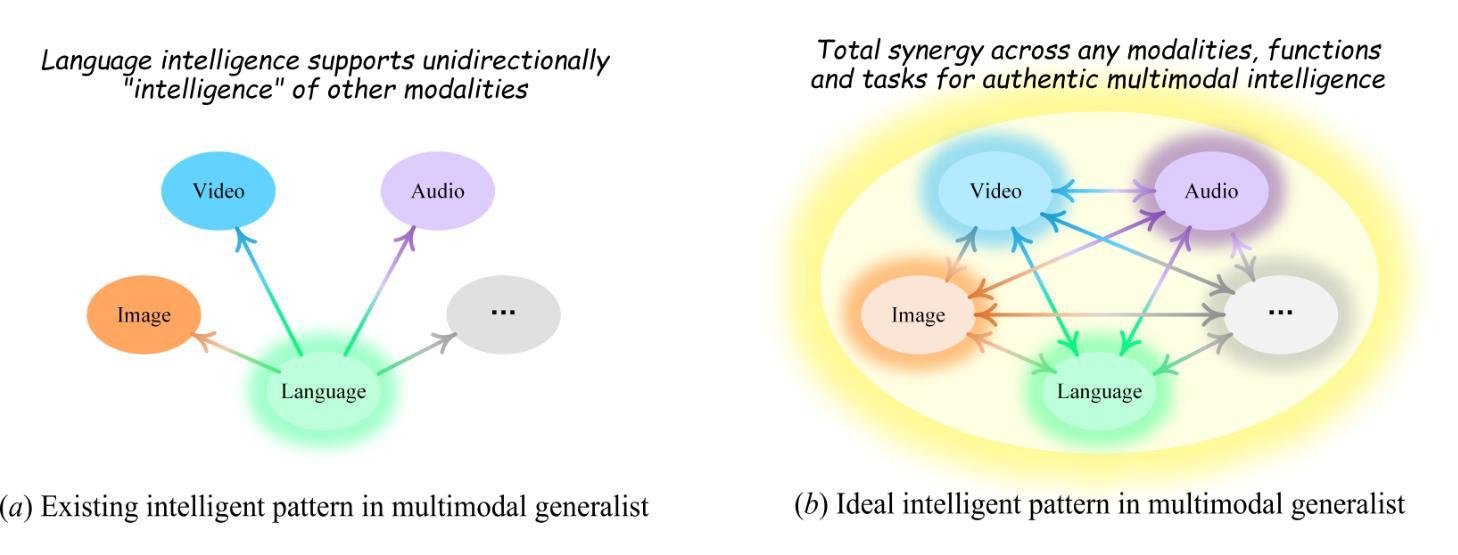
The Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) is currently experiencing rapid growth, driven by the advanced capabilities of LLMs. Unlike earlier specialists, existing MLLMs are evolving towards a Multimodal Generalist paradigm. Initially limited to understanding multiple modalities, these models have advanced to not only comprehend but also generate across modalities. Their capabilities have expanded from coarse-grained to fine-grained multimodal understanding and from supporting limited modalities to arbitrary ones. While many benchmarks exist to assess MLLMs, a critical question arises: Can we simply assume that higher performance across tasks indicates a stronger MLLM capability, bringing us closer to human-level AI? We argue that the answer is not as straightforward as it seems. This project introduces General-Level, an evaluation framework that defines 5-scale levels of MLLM performance and generality, offering a methodology to compare MLLMs and gauge the progress of existing systems towards more robust multimodal generalists and, ultimately, towards AGI. At the core of the framework is the concept of Synergy, which measures whether models maintain consistent capabilities across comprehension and generation, and across multiple modalities. To support this evaluation, we present General-Bench, which encompasses a broader spectrum of skills, modalities, formats, and capabilities, including over 700 tasks and 325,800 instances. The evaluation results that involve over 100 existing state-of-the-art MLLMs uncover the capability rankings of generalists, highlighting the challenges in reaching genuine AI. We expect this project to pave the way for future research on next-generation multimodal foundation models, providing a robust infrastructure to accelerate the realization of AGI. Project page: https://generalist.top/
多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)目前正在经历快速增长,其驱动因素在于大型语言模型的先进功能。与早期的专家不同,现有的MLLM正在朝着多模态综合者的模式发展。这些模型最初仅限于理解多种模式,现在已经发展到不仅理解而且能够在各种模式下生成内容。它们的能力已经从粗粒度扩展到细粒度多模式理解,并且从支持有限的模式扩展到任意模式。虽然存在许多基准测试来评估MLLM,但会出现一个问题:我们能否简单地假设跨任务的高性能表明MLLM能力更强,使我们更接近人类水平的AI?我们认为答案并不像看起来那么简单。这个项目引入了通用级别评估框架,该框架定义了MLLM性能和通用性的5个级别,提供了一种比较MLLM和衡量现有系统朝着更稳健的多模式综合者和最终朝着通用人工智能(AGI)发展进步的方法。该框架的核心是协同概念,它衡量的是模型在理解和生成之间以及多个模式之间是否保持一致的能力。为了支持这一评估,我们推出了通用基准测试,它涵盖了更广泛的技能、模式、格式和能力,包括超过700个任务和325,800个实例。涉及超过100个现有最先进的MLLM的评估结果揭示了综合者的能力排名,并突出了实现真正人工智能的挑战。我们希望这个项目能为下一代多模态基础模型的研究铺平道路,提供加速实现AGI的稳健基础设施。项目页面:https://generalist.top/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML’25, 305 pages, 115 tables, 177 figures, project page: https://generalist.top/
Summary
基于多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)的快速发展,现有模型正朝着多模态通才模式发展。它们的能力已从粗粒度扩展到细粒度,从支持有限模态扩展到任意模态。然而,评估MLLM时不能仅依赖任务性能来预测其整体能力,因此提出了General-Level评估框架和General-Bench评估支持工具。该框架定义了MLLM性能的五个级别,并围绕协同工作的概念评估模型在理解和生成方面以及跨多个模态的能力。期望此项目为未来研究下一代多模态基础模型铺平道路,并为加速人工智能通用性(AGI)的实现提供稳健的基础设施。
Key Takeaways
- MLLM正经历快速发展,从多模态理解进化到多模态理解和生成。
- MLLM的能力已从粗粒度扩展到细粒度,支持任意模态。
- 评估MLLM的能力不能仅依赖任务性能,需要更全面的评估框架如General-Level。
- General-Level评估框架定义MLLM性能的五个级别,并围绕Synergy概念评估模型在各种任务和模态中的一致性能力。
- General-Bench提供了广泛的技能、模态、格式和能力评估支持,包含700多个任务和325,800个实例。
- 评估结果涉及100多个现有最先进的MLLM,揭示了通才的能力排名,并指出了实现真正人工智能的挑战。
点此查看论文截图

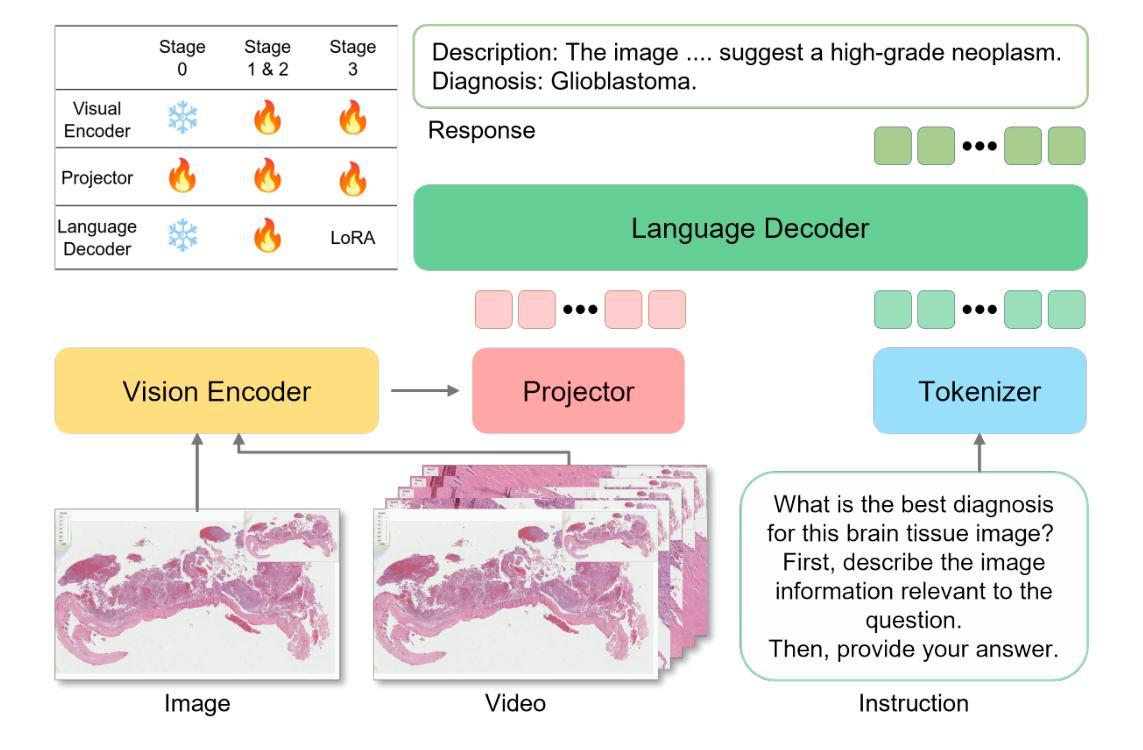
VideoPath-LLaVA: Pathology Diagnostic Reasoning Through Video Instruction Tuning
Authors:Trinh T. L. Vuong, Jin Tae Kwak
We present VideoPath-LLaVA, the first large multimodal model (LMM) in computational pathology that integrates three distinct image scenarios, single patch images, automatically keyframe-extracted clips, and manually segmented video pathology images, to mimic the natural diagnostic process of pathologists. By generating detailed histological descriptions and culminating in a definitive sign-out diagnosis, VideoPath-LLaVA bridges visual narratives with diagnostic reasoning. Central to our approach is the VideoPath-Instruct dataset, comprising 4278 video and diagnosis-specific chain-of-thought instructional pairs sourced from educational histopathology videos on YouTube. Although high-quality data is critical for enhancing diagnostic reasoning, its creation is time-intensive and limited in volume. To overcome this challenge, we transfer knowledge from existing single-image instruction datasets to train on weakly annotated, keyframe-extracted clips, followed by fine-tuning on manually segmented videos. VideoPath-LLaVA establishes a new benchmark in pathology video analysis and offers a promising foundation for future AI systems that support clinical decision-making through integrated visual and diagnostic reasoning. Our code, data, and model are publicly available at https://github.com/trinhvg/VideoPath-LLaVA.
我们推出VideoPath-LLaVA,这是计算病理学领域首个大型多模态模型(LMM),它整合了三种不同的图像情景:单补丁图像、自动提取关键帧的剪辑和手动分割的视频病理图像,以模拟病理医生的自然诊断过程。通过生成详细的组织病理学描述,并最终作出明确的诊断结论,VideoPath-LLaVA将视觉叙事与诊断推理相结合。我们的方法的核心是VideoPath-Instruct数据集,包含4278个视频和针对诊断的特定思维链教学对,这些数据来源于YouTube上的教育病理学视频。虽然高质量的数据对于提高诊断推理至关重要,但其制作耗时且数量有限。为了克服这一挑战,我们从现有的单图像指令数据集转移知识,对弱注释、提取关键帧的剪辑进行训练,然后在手动分割的视频上进行微调。VideoPath-LLaVA在病理学视频分析方面建立了新的基准,并为未来通过集成视觉和诊断推理支持临床决策的人工智能系统提供了有希望的基石。我们的代码、数据和模型可在https://github.com/trinhvg/VideoPath-LLaVA公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:我们提出了VideoPath-LLaVA模型,这是计算病理学领域首个大型多模态模型(LMM),它整合了三种不同的图像情景:单补丁图像、自动提取关键帧的剪辑和手动分割的视频病理图像,以模仿病理医生的自然诊断过程。通过生成详细的组织描述并最终作出明确的诊断结论,VideoPath-LLaVA将视觉叙事与诊断推理相结合。我们的方法的核心是VideoPath-Instruct数据集,包含从YouTube上的教育病理视频收集的4278个视频和针对诊断的思维链指令对。尽管高质量的数据对于提高诊断推理至关重要,但其制作是耗时的且数量有限。为了克服这一挑战,我们从现有的单指令图像数据集中转移知识,对提取的关键帧进行弱标注训练,然后对手动分割的视频进行微调。VideoPath-LLaVA在病理视频分析中建立了新的基准,并为未来通过集成视觉和诊断推理支持临床决策的人工智能系统提供了有希望的基石。
Key Takeaways:
- VideoPath-LLaVA是首个在计算病理学领域的大型多模态模型(LMM),模拟病理医生的自然诊断过程。
- 该模型集成了三种不同的图像情景:单补丁图像、自动提取关键帧的剪辑和手动分割的视频病理图像。
- VideoPath-LLaVA通过详细的组织描述和诊断结论,将视觉叙事与诊断推理相结合。
- VideoPath-Instruct数据集是核心,由来自YouTube教育病理视频的诊断特定思维链指令对组成。
- 尽管高质量数据对诊断推理至关重要,但其制作成本高昂且数量有限。
- 为了解决数据限制问题,模型从单指令图像数据集中转移知识,并对弱标注的关键帧进行训练,再进行手动分割视频的微调。
点此查看论文截图

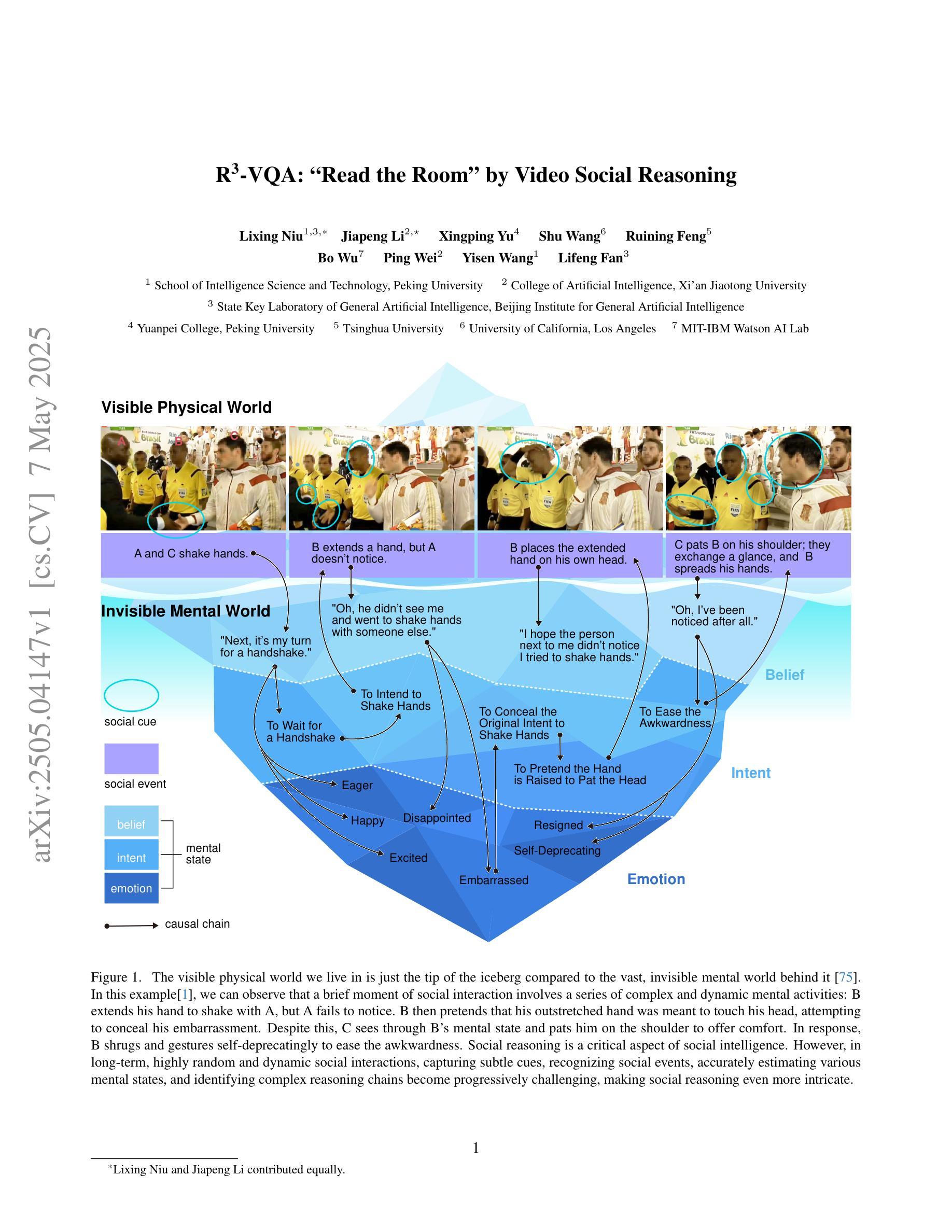
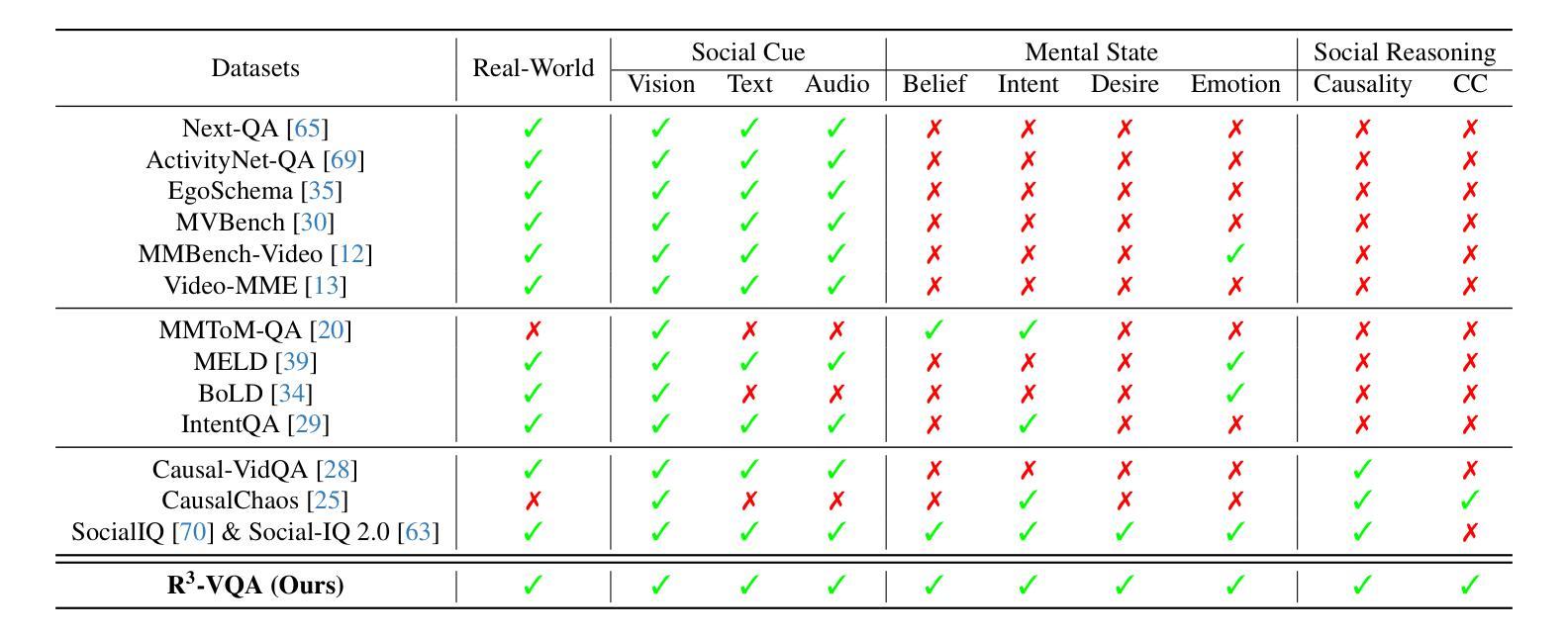
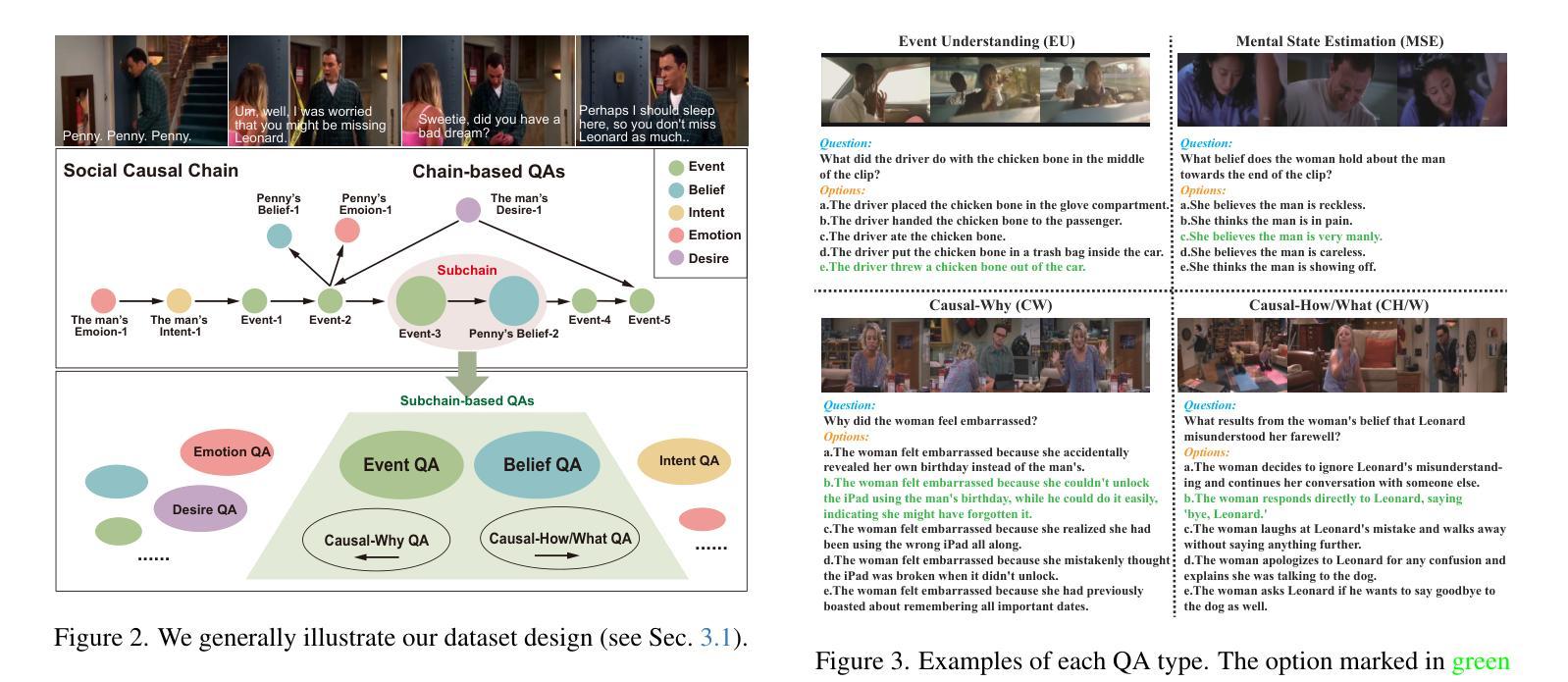
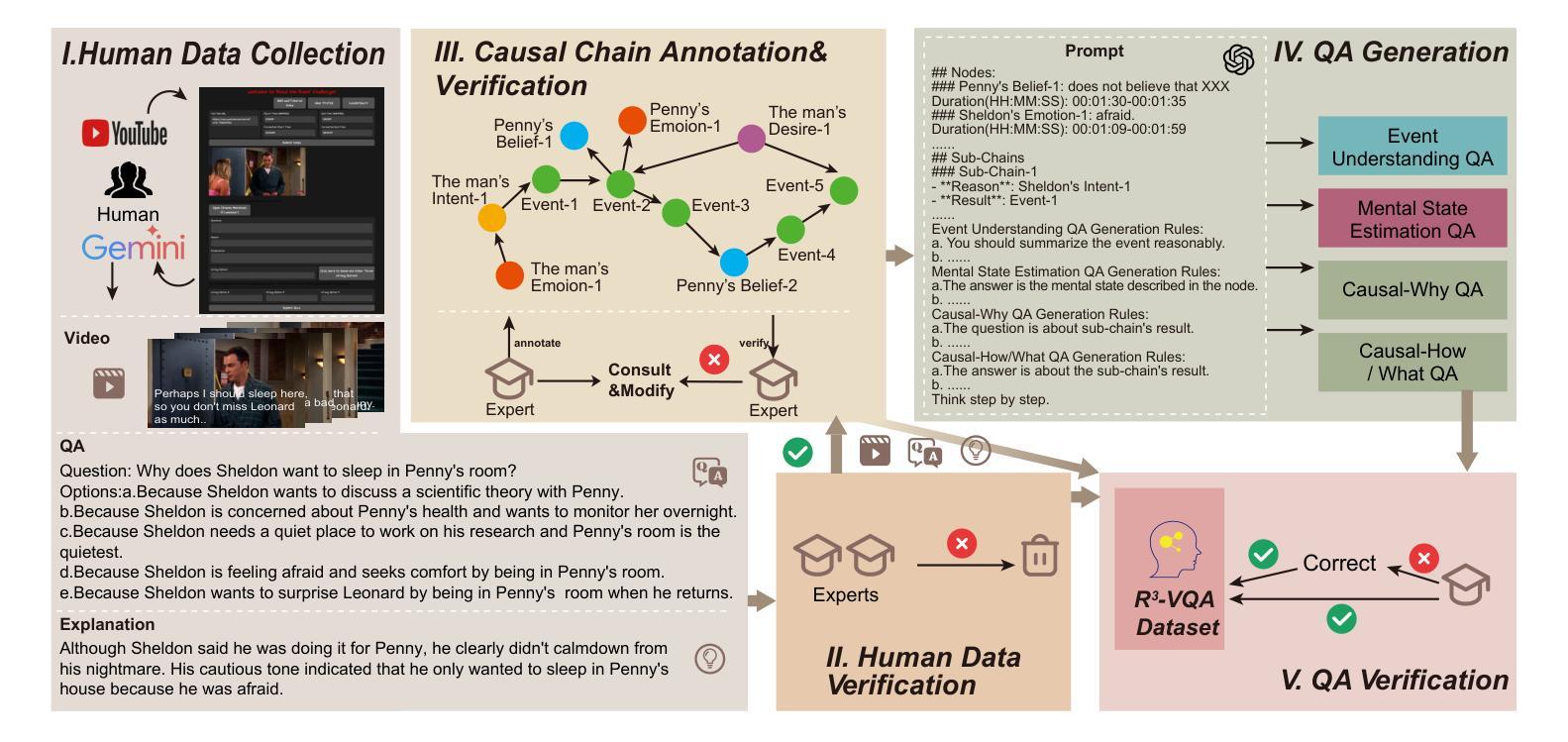
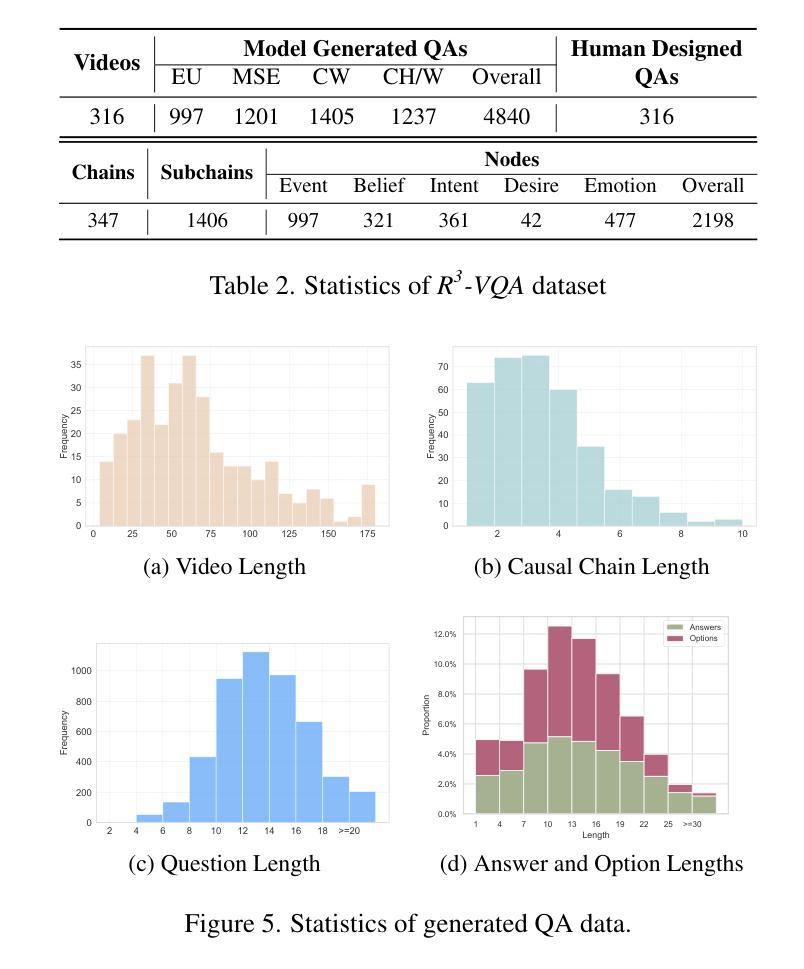
R^3-VQA: “Read the Room” by Video Social Reasoning
Authors:Lixing Niu, Jiapeng Li, Xingping Yu, Shu Wang, Ruining Feng, Bo Wu, Ping Wei, Yisen Wang, Lifeng Fan
“Read the room” is a significant social reasoning capability in human daily life. Humans can infer others’ mental states from subtle social cues. Previous social reasoning tasks and datasets lack complexity (e.g., simple scenes, basic interactions, incomplete mental state variables, single-step reasoning, etc.) and fall far short of the challenges present in real-life social interactions. In this paper, we contribute a valuable, high-quality, and comprehensive video dataset named R^3-VQA with precise and fine-grained annotations of social events and mental states (i.e., belief, intent, desire, and emotion) as well as corresponding social causal chains in complex social scenarios. Moreover, we include human-annotated and model-generated QAs. Our task R^3-VQA includes three aspects: Social Event Understanding, Mental State Estimation, and Social Causal Reasoning. As a benchmark, we comprehensively evaluate the social reasoning capabilities and consistencies of current state-of-the-art large vision-language models (LVLMs). Comprehensive experiments show that (i) LVLMs are still far from human-level consistent social reasoning in complex social scenarios; (ii) Theory of Mind (ToM) prompting can help LVLMs perform better on social reasoning tasks. We provide some of our dataset and codes in supplementary material and will release our full dataset and codes upon acceptance.
在日常生活中,”读懂氛围”是一种重要的社会推理能力。人类可以从微妙的社交线索中推断出他人的心理状态。以往的社会推理任务和数据集缺乏复杂性(例如,简单场景、基本互动、不完整的心态变量、单步推理等),与现实生活中的社交互动挑战相去甚远。在本文中,我们贡献了一个有价值、高质量且全面的视频数据集,名为R^3-VQA,其中包含社会事件和心态(即信念、意图、愿望和情感)的精确和精细注释,以及复杂社会场景中的相应社会因果链。此外,我们包含了人类注释和模型生成的QA。我们的任务R^3-VQA包括三个方面:社会事件理解、心态估计和社会因果推理。作为一个基准测试,我们全面评估了当前先进的大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)的社会推理能力和一致性。综合实验表明,(i)LVLMs在复杂社会场景中的社会推理能力与人类水平的一致性仍有很大差距;(ii)心智理论(ToM)提示可以帮助LVLMs在社交推理任务上表现更好。我们在补充材料中提供部分数据集和代码,并在接受后公开我们的完整数据集和代码。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
人们日常社交活动中,通过阅读社交线索推断他人的心理状态是一种重要的社会认知能力。现有社会推理任务和数据集缺乏复杂性,无法应对真实社交互动中的挑战。本研究贡献了一个高质量的综合视频数据集R^3-VQA,其中包含对社会事件和内心状态(信念、意图、愿望和情感)的精确和精细注释,以及复杂社交场景中的社会因果链。此外,还包括人类标注和模型生成的QA。该任务包括三个方面:社会事件理解、内心状态估计和社会因果推理。作为基准测试,我们对当前先进的视觉语言模型进行了全面的社会推理能力和一致性评估。实验表明,这些模型在复杂社交场景中的社会推理能力与人类水平相差甚远,而心智理论(ToM)提示有助于改进其在社会推理任务上的表现。我们将部分数据集和代码作为补充材料提供,并在接受后公开完整数据集和代码。
Key Takeaways:
- “读懂房间”是人类日常生活中重要的社会推理能力,能通过微妙的社交线索推断他人的心理状态。
- 现有社会推理任务和数据集缺乏复杂性,无法反映真实社交互动的挑战。
- R^3-VQA数据集包含对社会事件和内心状态的精确和精细注释,以及复杂社交场景中的社会因果链。
- R^3-VQA任务包括社会事件理解、内心状态估计和社会因果推理三个方面。
- 当前先进的视觉语言模型在社会推理任务上表现不足,与人类的差距明显。
- 心智理论(ToM)提示有助于改进模型在社会推理任务上的表现。
点此查看论文截图
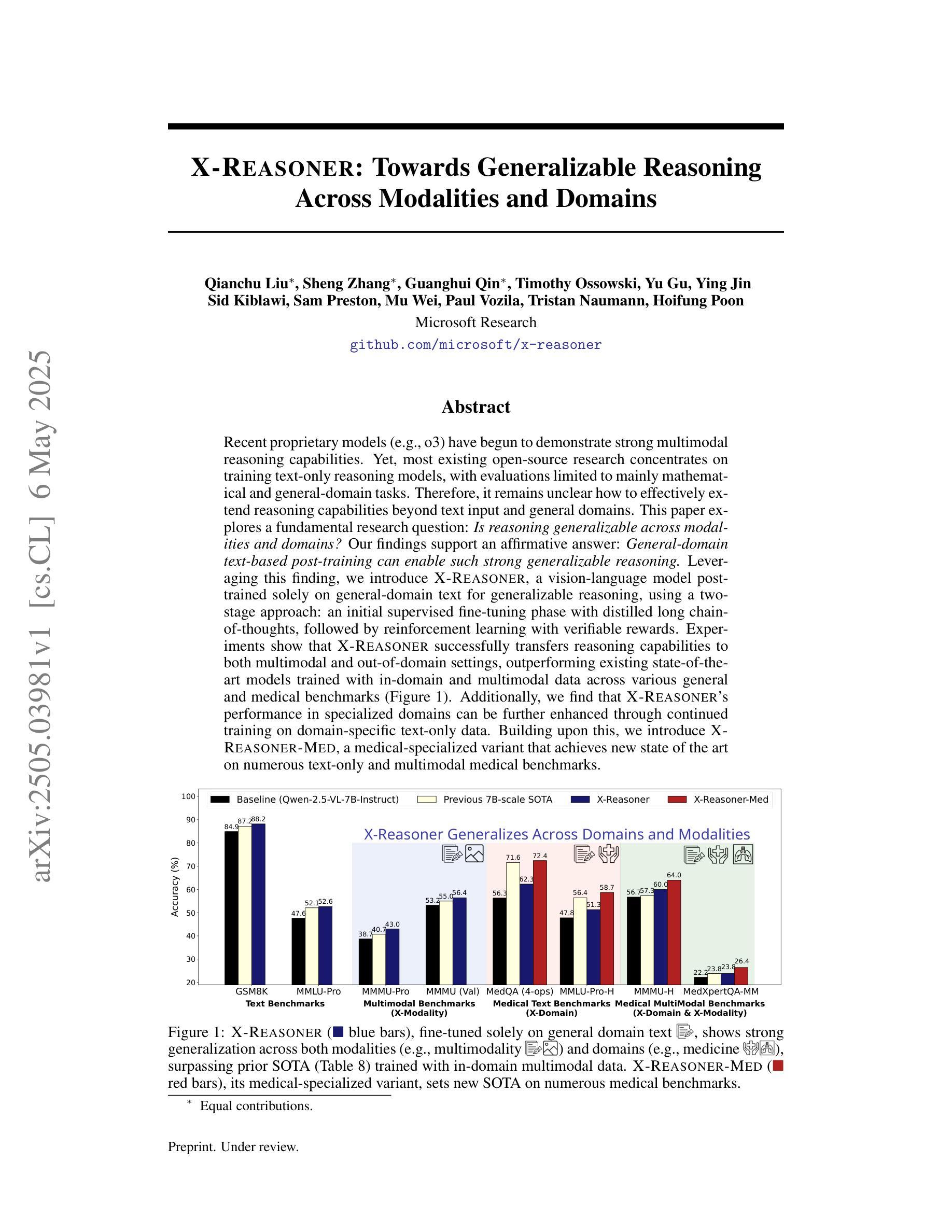
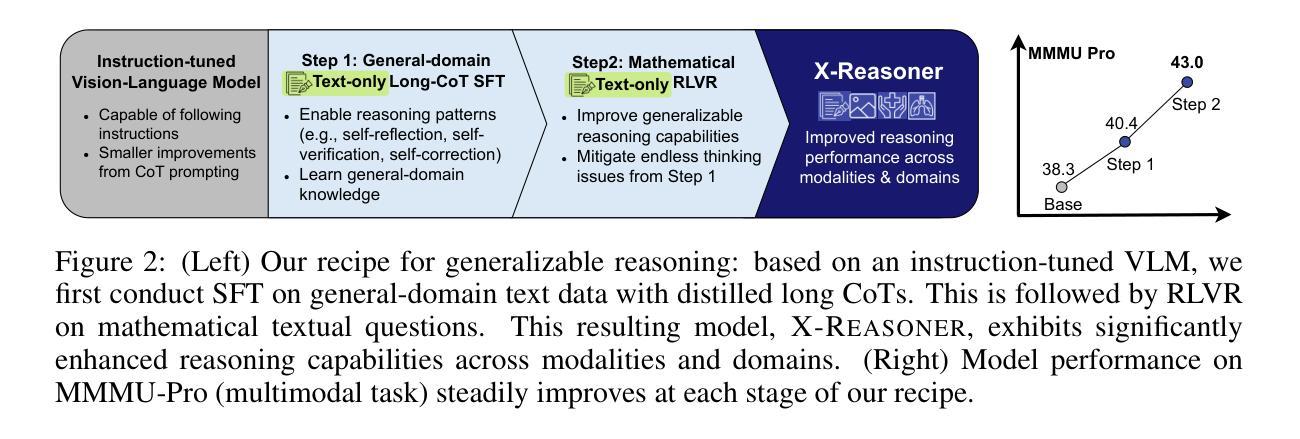
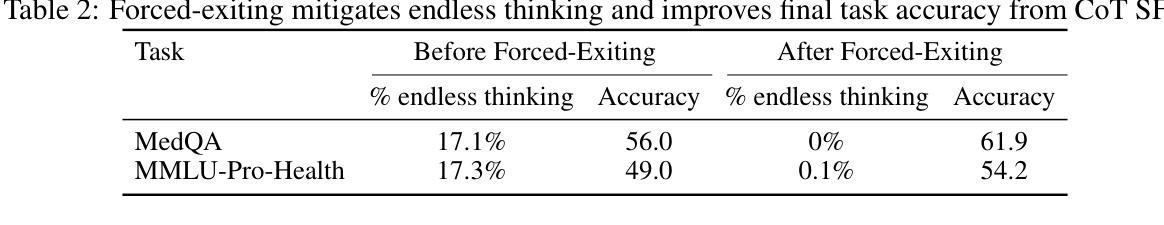
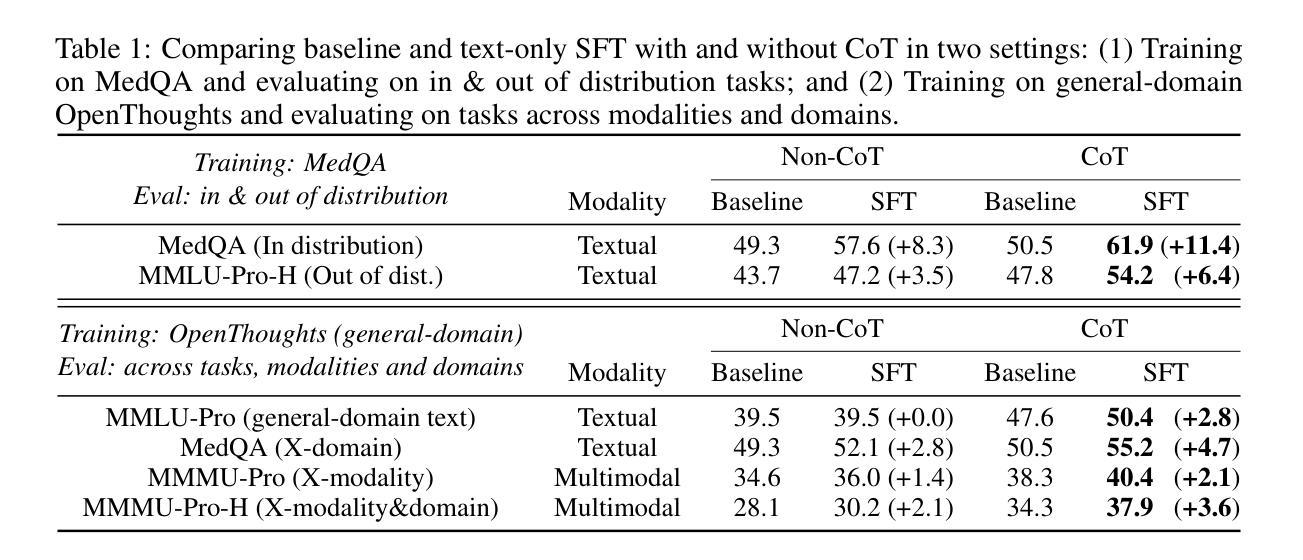
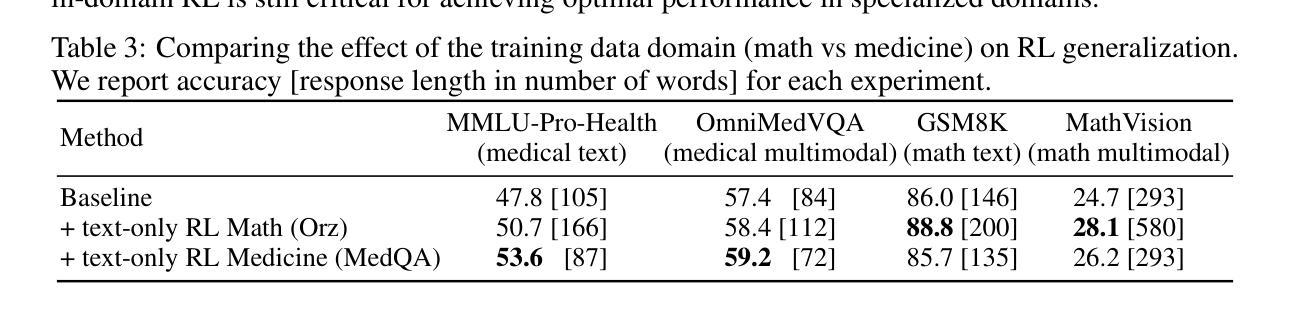
X-Reasoner: Towards Generalizable Reasoning Across Modalities and Domains
Authors:Qianchu Liu, Sheng Zhang, Guanghui Qin, Timothy Ossowski, Yu Gu, Ying Jin, Sid Kiblawi, Sam Preston, Mu Wei, Paul Vozila, Tristan Naumann, Hoifung Poon
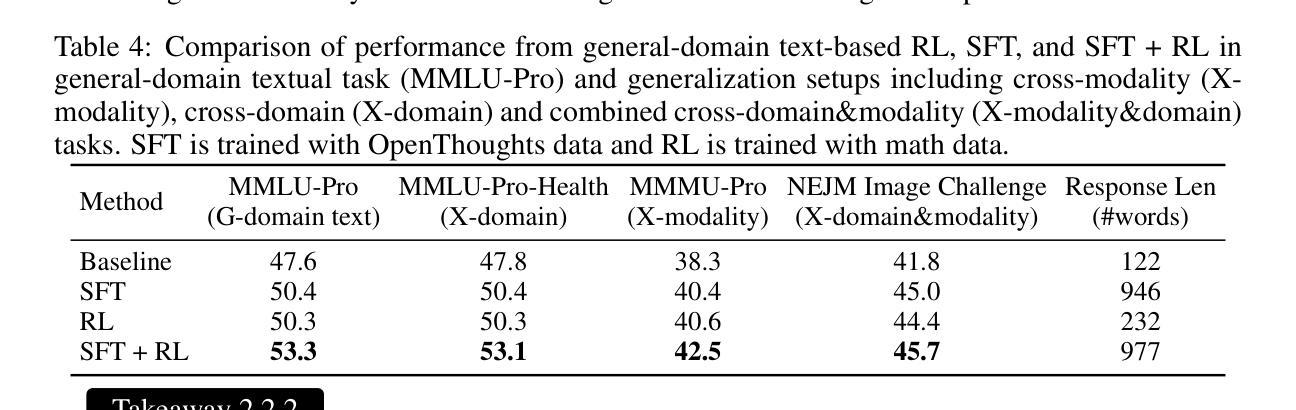
Recent proprietary models (e.g., o3) have begun to demonstrate strong multimodal reasoning capabilities. Yet, most existing open-source research concentrates on training text-only reasoning models, with evaluations limited to mainly mathematical and general-domain tasks. Therefore, it remains unclear how to effectively extend reasoning capabilities beyond text input and general domains. This paper explores a fundamental research question: Is reasoning generalizable across modalities and domains? Our findings support an affirmative answer: General-domain text-based post-training can enable such strong generalizable reasoning. Leveraging this finding, we introduce X-Reasoner, a vision-language model post-trained solely on general-domain text for generalizable reasoning, using a two-stage approach: an initial supervised fine-tuning phase with distilled long chain-of-thoughts, followed by reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards. Experiments show that X-Reasoner successfully transfers reasoning capabilities to both multimodal and out-of-domain settings, outperforming existing state-of-the-art models trained with in-domain and multimodal data across various general and medical benchmarks (Figure 1). Additionally, we find that X-Reasoner’s performance in specialized domains can be further enhanced through continued training on domain-specific text-only data. Building upon this, we introduce X-Reasoner-Med, a medical-specialized variant that achieves new state of the art on numerous text-only and multimodal medical benchmarks.
最近的专有模型(例如o3)已经开始展现出强大的多模态推理能力。然而,目前大多数开源研究都集中在训练纯文本推理模型上,评估也主要限于数学和通用领域的任务。因此,如何有效地扩展超出文本输入和通用领域的推理能力仍不明确。本文探讨了一个基本的研究问题:推理是否可以在跨模态和领域之间进行泛化?我们的研究结果支持肯定的答案:基于通用领域的文本后训练可以实现强大的可泛化推理。利用这一发现,我们引入了X-Reasoner,它是一个仅在通用文本基础上进行后训练的多模态语言模型,用于通用推理。它采用两阶段的方法:首先用蒸馏后的长思考链进行有监督微调,随后用可验证的奖励进行强化学习。实验表明,X-Reasoner成功将推理能力转移到多模态和跨领域环境,且在各种通用和医疗基准测试中超越了使用领域内和多模态数据训练的现有最先进的模型(如图1所示)。此外,我们发现通过继续在特定领域的纯文本数据上进行训练,X-Reasoner在特定领域的性能可以进一步提高。在此基础上,我们推出了专业化的医疗版X-Reasoner-Med,它在多个纯文本和多模态医疗基准测试上达到了新的技术水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探索了跨模态和领域推理能力是否可泛化的问题,并发现通过基于一般领域文本的后训练可以实现对泛化推理的强化。研究提出了X-Reasoner模型,采用两阶段方法:初始阶段使用蒸馏长思考链进行精细微调,随后使用可验证奖励进行强化学习。实验表明,X-Reasoner成功将推理能力转移到多模态和跨领域场景,并在各种通用和医疗基准测试中优于现有最先进的模型。此外,还发现通过继续训练特定领域的文本数据,X-Reasoner在特定领域的性能可以得到进一步提升。基于此,研究还推出了针对医疗领域的专门版本X-Reasoner-Med,在多个纯文本和多模态医疗基准测试上取得了最新技术成果。
Key Takeaways
- 近期专有模型开始展示强大的多模态推理能力,但开源研究主要集中在训练文本推理模型上,评估主要限于数学和通用领域任务。
- 本文探索了跨模态和领域推理能力的泛化问题,并发现基于一般领域文本的后训练有助于强化泛化推理能力。
- 引入X-Reasoner模型,采用两阶段方法进行训练:精细微调阶段和强化学习阶段。
- X-Reasoner成功将推理能力转移到多模态和跨领域场景,并在各种基准测试中表现优异。
- X-Reasoner在特定领域的性能可通过继续训练特定领域的文本数据进一步提升。
- 推出针对医疗领域的专门版本X-Reasoner-Med,在医疗基准测试上取得最新技术成果。
点此查看论文截图
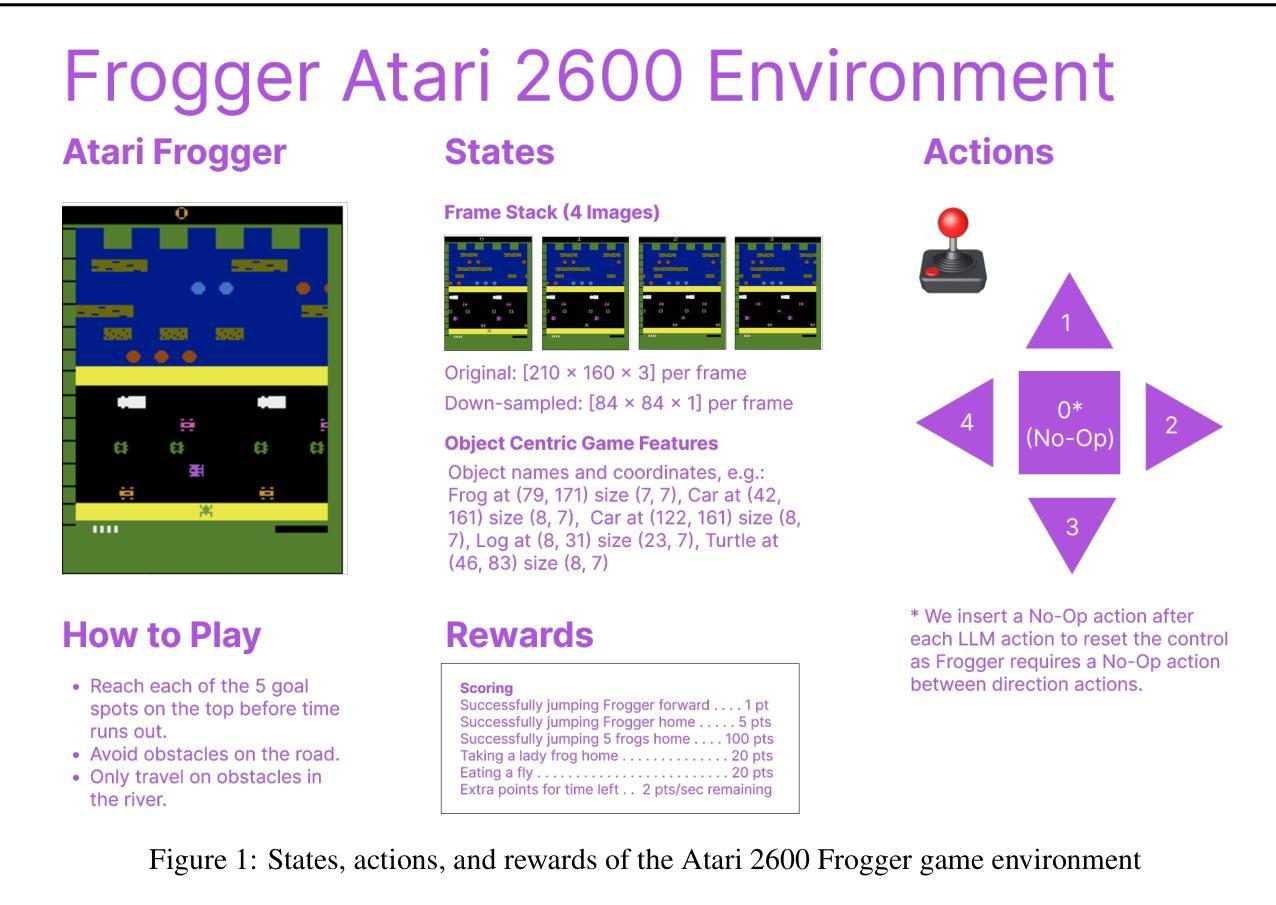
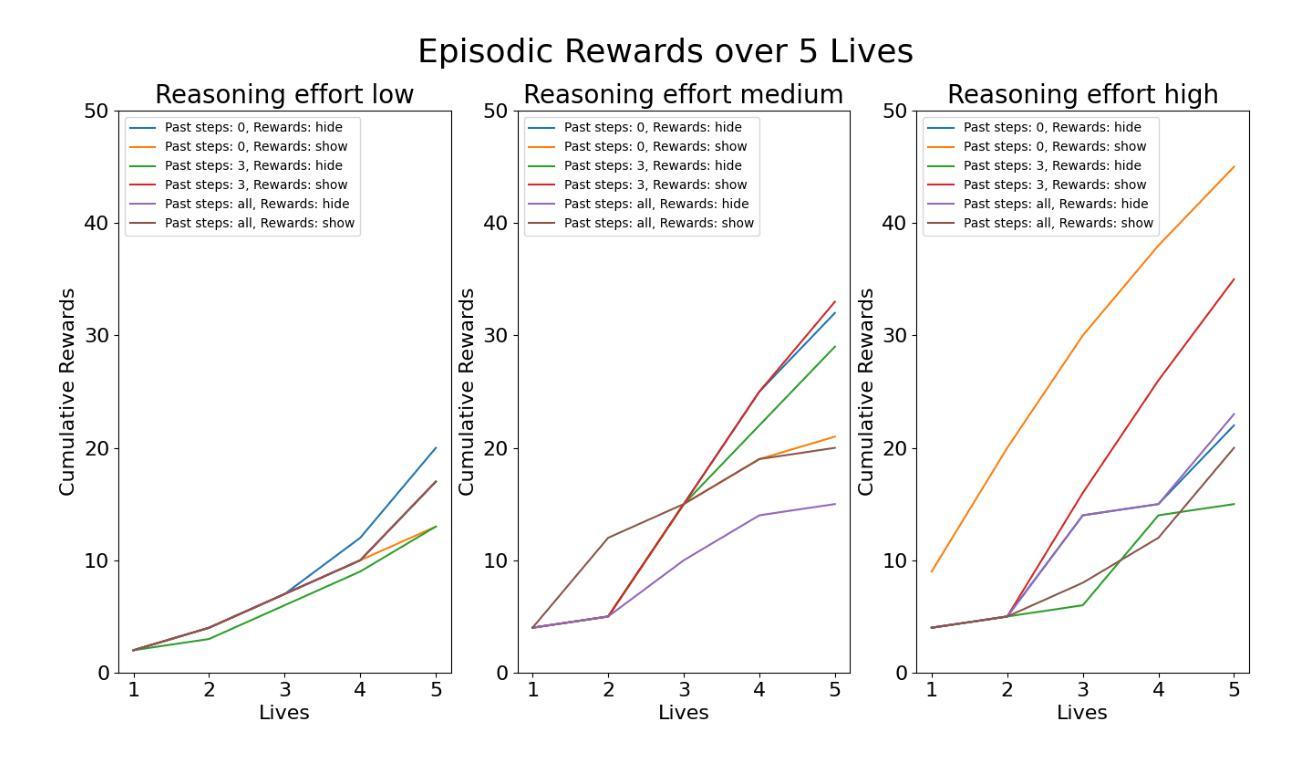
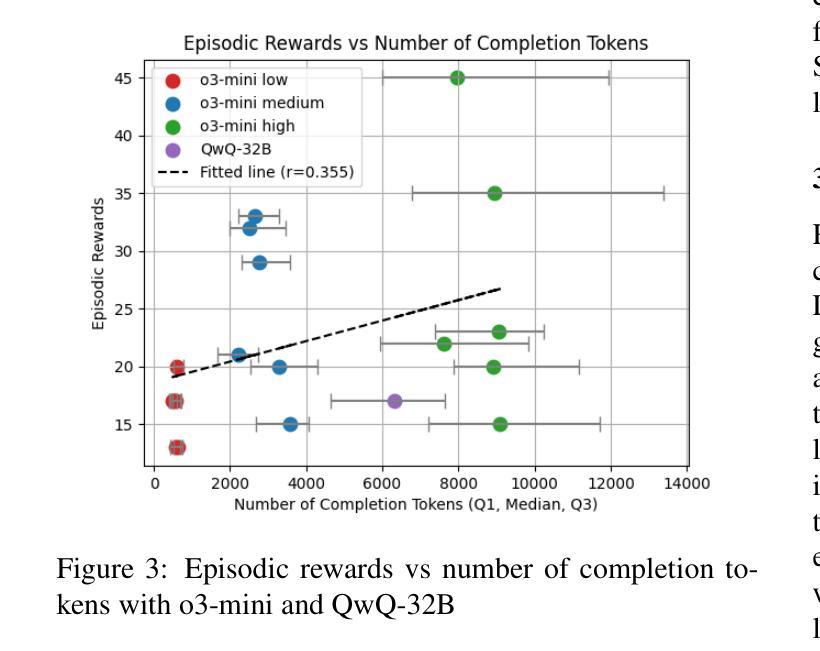
Frog Soup: Zero-Shot, In-Context, and Sample-Efficient Frogger Agents
Authors:Xiang Li, Yiyang Hao, Doug Fulop
One of the primary aspirations in reinforcement learning research is developing general-purpose agents capable of rapidly adapting to and mastering novel tasks. While RL gaming agents have mastered many Atari games, they remain slow and costly to train for each game. In this work, we demonstrate that latest reasoning LLMs with out-of-domain RL post-training can play a challenging Atari game called Frogger under a zero-shot setting. We then investigate the effect of in-context learning and the amount of reasoning effort on LLM performance. Lastly, we demonstrate a way to bootstrap traditional RL method with LLM demonstrations, which significantly improves their performance and sample efficiency. Our implementation is open sourced at https://github.com/AlienKevin/frogger.
强化学习研究的主要愿望之一是开发能够迅速适应并掌握新任务的通用智能体。虽然强化学习游戏智能体已经掌握了许多雅达利(Atari)游戏,但它们仍然对每款游戏的训练缓慢且成本高昂。在这项工作中,我们展示了最新的推理大型语言模型在域外强化学习后训练可以在零样本设置下玩一个具有挑战性的雅达利游戏《青蛙王子》(Frogger)。然后我们研究了上下文学习与推理努力对大型语言模型性能的影响。最后,我们展示了如何将大型语言模型演示与传统强化学习方法相结合,这显著提高了它们的性能和样本效率。我们的实现已公开在https://github.com/AlienKevin/frogger。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了在强化学习领域,开发能够迅速适应并掌握新任务的一般性智能体是主要目标之一。虽然RL游戏智能体已经掌握了众多Atari游戏,但它们对于每个游戏的训练速度较慢且成本较高。本研究展示了最新的推理大型语言模型在跨领域强化学习后处理训练下,能在零样本设置下玩挑战性Atari游戏《蛙王子》。接着,本研究探讨了上下文学习的效果以及推理努力对大型语言模型性能的影响。最后,本研究展示了如何将大型语言模型示范与传统强化学习相结合,显著提高性能与样本效率。相关实现已开源。
Key Takeaways
- 强化学习致力于开发能迅速适应并掌握新任务的一般性智能体。
- RL游戏智能体虽然已经掌握了众多Atari游戏,但训练速度和成本仍需改进。
- 推理大型语言模型在跨领域强化学习后处理训练下能在零样本设置下玩《蛙王子》。
- 上下文学习的效果以及推理努力对大型语言模型性能的影响被探讨。
- 大型语言模型示范与传统强化学习相结合可显著提高性能与样本效率。
- 该研究的实现已经开源,便于其他研究者参考和进一步探索。
- 结合大型语言模型与传统强化学习方法是未来智能体研究的一个重要方向。
点此查看论文截图

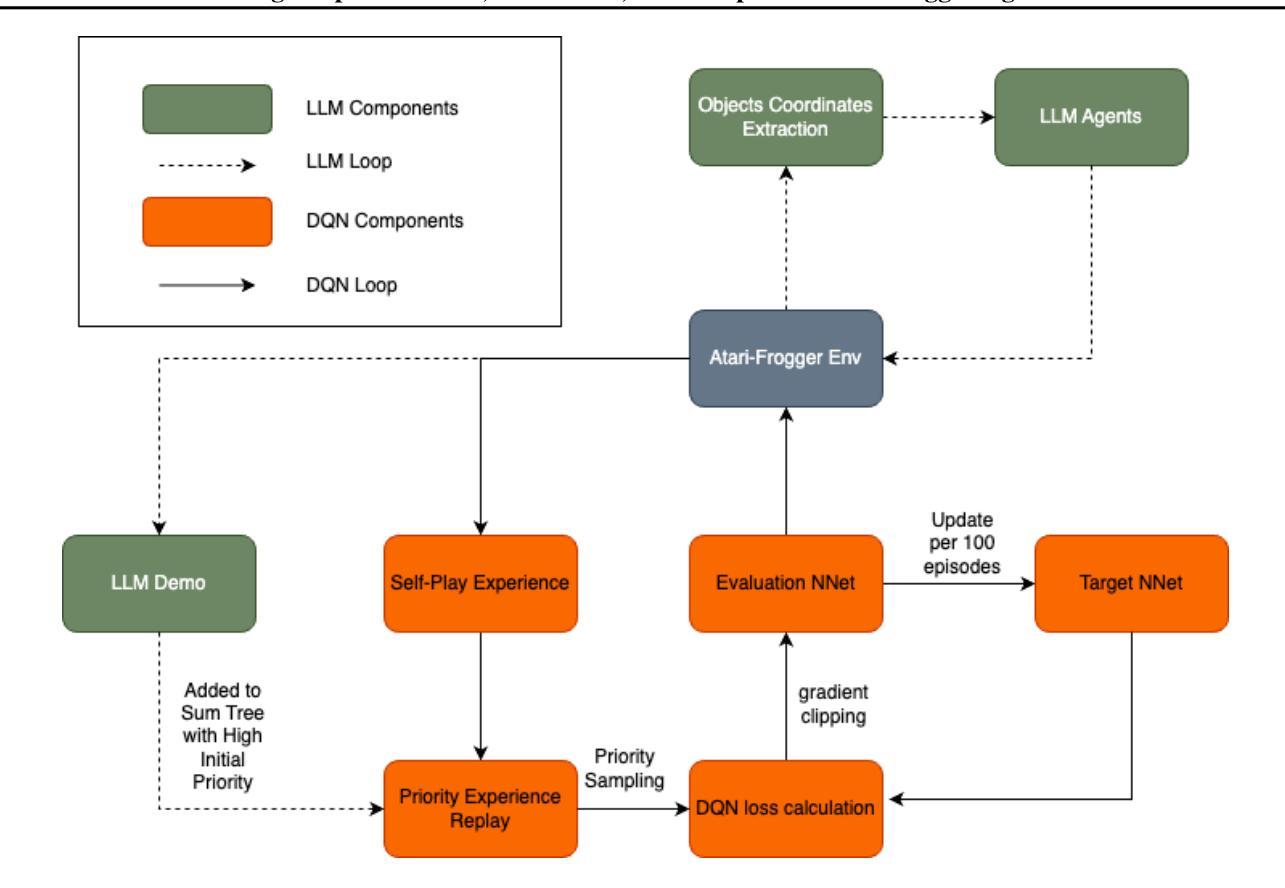
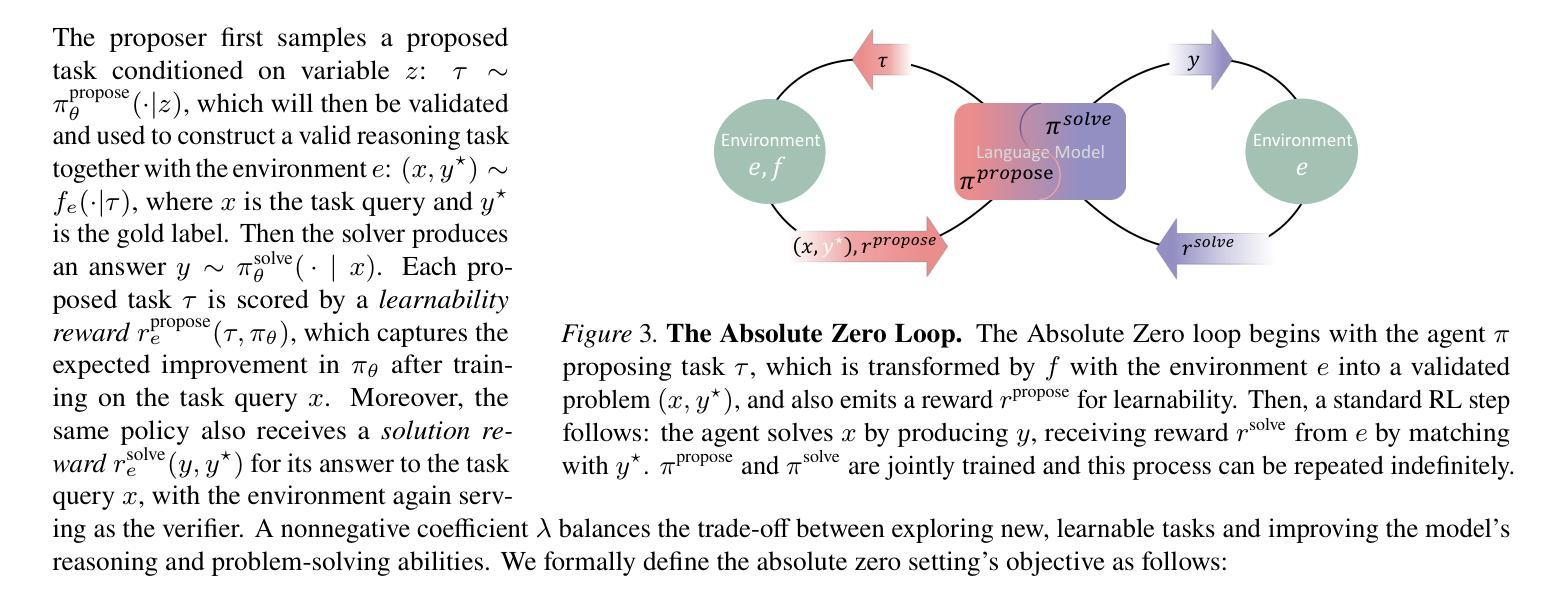
Absolute Zero: Reinforced Self-play Reasoning with Zero Data
Authors:Andrew Zhao, Yiran Wu, Yang Yue, Tong Wu, Quentin Xu, Yang Yue, Matthieu Lin, Shenzhi Wang, Qingyun Wu, Zilong Zheng, Gao Huang
Reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards (RLVR) has shown promise in enhancing the reasoning capabilities of large language models by learning directly from outcome-based rewards. Recent RLVR works that operate under the zero setting avoid supervision in labeling the reasoning process, but still depend on manually curated collections of questions and answers for training. The scarcity of high-quality, human-produced examples raises concerns about the long-term scalability of relying on human supervision, a challenge already evident in the domain of language model pretraining. Furthermore, in a hypothetical future where AI surpasses human intelligence, tasks provided by humans may offer limited learning potential for a superintelligent system. To address these concerns, we propose a new RLVR paradigm called Absolute Zero, in which a single model learns to propose tasks that maximize its own learning progress and improves reasoning by solving them, without relying on any external data. Under this paradigm, we introduce the Absolute Zero Reasoner (AZR), a system that self-evolves its training curriculum and reasoning ability by using a code executor to both validate proposed code reasoning tasks and verify answers, serving as an unified source of verifiable reward to guide open-ended yet grounded learning. Despite being trained entirely without external data, AZR achieves overall SOTA performance on coding and mathematical reasoning tasks, outperforming existing zero-setting models that rely on tens of thousands of in-domain human-curated examples. Furthermore, we demonstrate that AZR can be effectively applied across different model scales and is compatible with various model classes.
强化学习与可验证奖励(RLVR)通过直接从结果导向的奖励中学习,在提升大型语言模型的推理能力方面展现出了巨大的潜力。近期在零样本设置下运作的RLVR作品避免了监督推理过程的标签,但仍依赖于手动整理的问题和答案集合进行训练。高质量、人工生成案例的稀缺性引发了对长期依赖人工监督的可扩展性的担忧,这一挑战在语言模型预训练领域已经显而易见。此外,在人工智能超越人类智能的假设未来中,人类提供的任务可能为超级智能系统提供有限的学习潜力。为了解决这些担忧,我们提出了一种新的RLVR范式,称为“绝对零”,其中单个模型学会提出能最大化其自身学习进度的任务,并通过解决这些任务来提高推理能力,无需依赖任何外部数据。在这种范式下,我们引入了“绝对零推理器”(AZR),这是一个通过代码执行器验证所提出的代码推理任务并验证答案的系统,它作为可验证奖励的统一来源,引导开放式但基于现实的学习。尽管完全不受外部数据训练,AZR在编码和数学推理任务上实现了整体最先进的性能,超越了依赖数万领域内部人工整理样本的零设置模型。此外,我们证明了AZR可以有效地应用于不同的模型规模,并且与各种模型类别兼容。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:强化学习通过可验证的奖励(RLVR)提高大型语言模型的推理能力,通过直接学习结果导向的奖励来增强推理能力。新的RLVR工作在零样本设置下避免了监督标注推理过程,但仍依赖于手动整理的问题和答案集合进行训练。为了克服对高质量人类生产样本的依赖性和长期可扩展性的挑战,我们提出了一种新的RLVR范式,称为绝对零值,一个模型能够自行提出任务并最大化自己的学习进步和改善推理能力。在此范式下,我们引入了绝对零推理器(AZR),该系统使用代码执行器来验证提出的代码推理任务和答案,作为验证奖励的统一来源,指导开放式但基于实际的学习。尽管完全在外部数据训练下,AZR在编码和数学推理任务上实现了最佳性能。此外,我们证明了AZR在不同模型规模下均有效,且兼容各类模型。
Key Takeaways:
- 强化学习通过可验证的奖励(RLVR)能提高大型语言模型的推理能力。
- 新的RLVR工作在零样本设置下避免了对监督标注推理过程的依赖,但仍需手动整理的问题和答案集合进行训练。
- 对高质量人类生产样本的依赖性和长期可扩展性存在挑战。
- 提出新的RLVR范式“绝对零”,模型能自行提出任务并最大化自己的学习进步。
- 引入绝对零推理器(AZR),结合代码执行器验证任务和答案,促进开放式但基于实际的学习。
- AZR在编码和数学推理任务上实现最佳性能,且适用于不同模型规模和各种模型类型。
点此查看论文截图
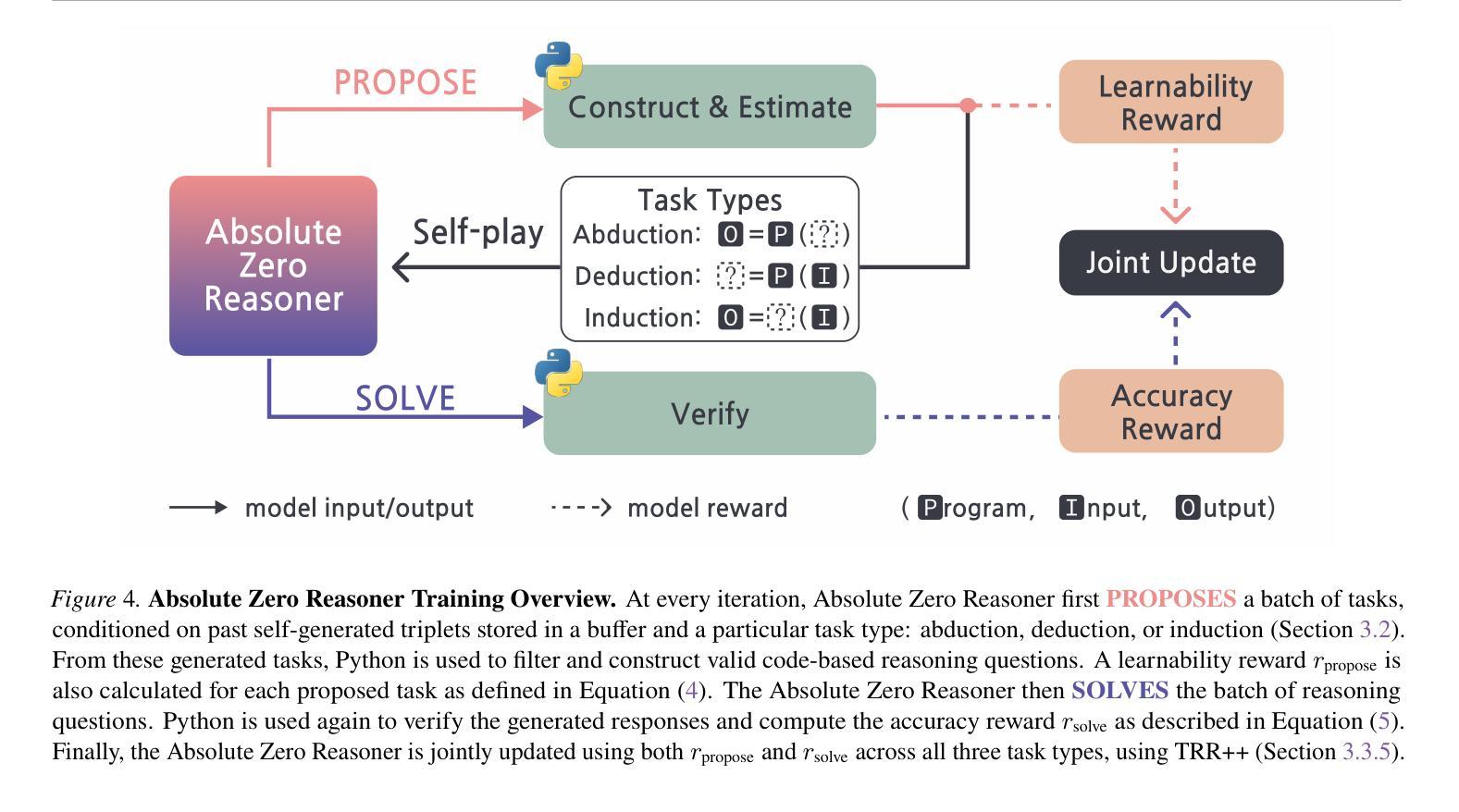

RM-R1: Reward Modeling as Reasoning
Authors:Xiusi Chen, Gaotang Li, Ziqi Wang, Bowen Jin, Cheng Qian, Yu Wang, Hongru Wang, Yu Zhang, Denghui Zhang, Tong Zhang, Hanghang Tong, Heng Ji
Reward modeling is essential for aligning large language models (LLMs) with human preferences, especially through reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF). To provide accurate reward signals, a reward model (RM) should stimulate deep thinking and conduct interpretable reasoning before assigning a score or a judgment. However, existing RMs either produce opaque scalar scores or directly generate the prediction of a preferred answer, making them struggle to integrate natural language critiques, thus lacking interpretability. Inspired by recent advances of long chain-of-thought (CoT) on reasoning-intensive tasks, we hypothesize and validate that integrating reasoning capabilities into reward modeling significantly enhances RM’s interpretability and performance. In this work, we introduce a new class of generative reward models – Reasoning Reward Models (ReasRMs) – which formulate reward modeling as a reasoning task. We propose a reasoning-oriented training pipeline and train a family of ReasRMs, RM-R1. The training consists of two key stages: (1) distillation of high-quality reasoning chains and (2) reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards. RM-R1 improves LLM rollouts by self-generating reasoning traces or chat-specific rubrics and evaluating candidate responses against them. Empirically, our models achieve state-of-the-art or near state-of-the-art performance of generative RMs across multiple comprehensive reward model benchmarks, outperforming much larger open-weight models (e.g., Llama3.1-405B) and proprietary ones (e.g., GPT-4o) by up to 13.8%. Beyond final performance, we perform thorough empirical analysis to understand the key ingredients of successful ReasRM training. To facilitate future research, we release six ReasRM models along with code and data at https://github.com/RM-R1-UIUC/RM-R1.
奖励建模对于将大型语言模型(LLM)与人类偏好进行对齐至关重要,尤其是通过从人类反馈中进行强化学习(RLHF)。为了提供准确的奖励信号,奖励模型(RM)应该在分配分数或判断之前激发深度思考并进行可解释的推理。然而,现有的RMs要么产生不透明的标量分数,要么直接生成首选答案的预测,这使得它们难以整合自然语言批评,因此缺乏可解释性。受近期长链思维(CoT)在推理密集型任务上进步的启发,我们假设并将验证将推理能力融入奖励建模会显著增强RM的可解释性和性能。在这项工作中,我们引入了一种新型生成奖励模型——推理奖励模型(ReasRMs),它将奖励建模制定为推理任务。我们提出了面向推理的训练流程,并训练了一系列ReasRMs,即RM-R1。训练包括两个关键阶段:(1)高质量推理链的提炼;(2)可验证奖励的强化学习。RM-R1通过自我生成推理轨迹或针对聊天的特定准则,并对候选响应进行评估,从而改进LLM的滚动更新。从实证角度看,我们的模型在多个综合奖励模型基准测试中实现了最先进的或接近最先进的生成RM性能,超过了许多更大的开放权重模型(例如Llama3.1-405B)和专有模型(例如GPT-4o),最多高出13.8%。除了最终性能之外,我们还进行了彻底的经验分析,以了解成功的ReasRM训练的关键要素。为了便于未来的研究,我们在https://github.com/RM-R1-UIUC/RM-R1上发布了六个ReasRM模型以及相关的代码和数据。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 23 pages, 7 figures
Summary
本文强调奖励模型在大型语言模型与人类偏好对齐中的重要性,特别是通过人类反馈强化学习(RLHF)。为了提供准确的奖励信号,奖励模型(RM)应在分配分数或判断之前进行深度思考和可解释推理。然而,现有RMs产生的是模糊的标量分数或直接生成首选答案的预测,难以整合自然语言批评,因此缺乏可解释性。本研究结合长链思维(CoT)在推理密集型任务上的最新进展,假设并验证了将推理能力融入奖励模型可以显著增强RM的可解释性和性能。为此,我们引入了一类新的生成奖励模型——推理奖励模型(ReasRMs),将奖励建模表述为推理任务。本研究提出了面向推理的训练管道,并训练了一系列ReasRMs,即RM-R1。训练包括两个关键阶段:1)高质量推理链的提炼和2)可验证奖励的强化学习。RM-R1通过自我生成推理轨迹或针对聊天的特定准则,评估候选响应,从而改进大型语言模型的滚动输出。经验表明,我们的模型在多个综合奖励模型基准测试上达到了最新或接近最新的生成RM性能,优于更大的开放权重模型(如Llama3.1-405B)和专有模型(如GPT-4o),最高提升了13.8%。除了最终性能外,我们还进行了彻底的经验分析,以了解成功的ReasRM训练的关键成分。为了促进未来研究,我们在https://github.com/RM-R1-UIUC/RM-R1上发布了六个ReasRM模型及代码和数据。
Key Takeaways
- 奖励模型在大语言模型与人类偏好对齐中起关键作用。
- 现有奖励模型缺乏深度思考和可解释推理能力。
- 引入了一种新型生成奖励模型——推理奖励模型(ReasRMs),将奖励建模视为推理任务。
- ReasRMs通过自我生成推理轨迹或针对聊天的特定准则来提高大型语言模型的性能。
- RM-R1模型在多个基准测试中表现出卓越性能,相比其他大型模型有所提升。
- 成功训练ReasRM的关键在于高质量推理链的提炼和强化学习。
点此查看论文截图


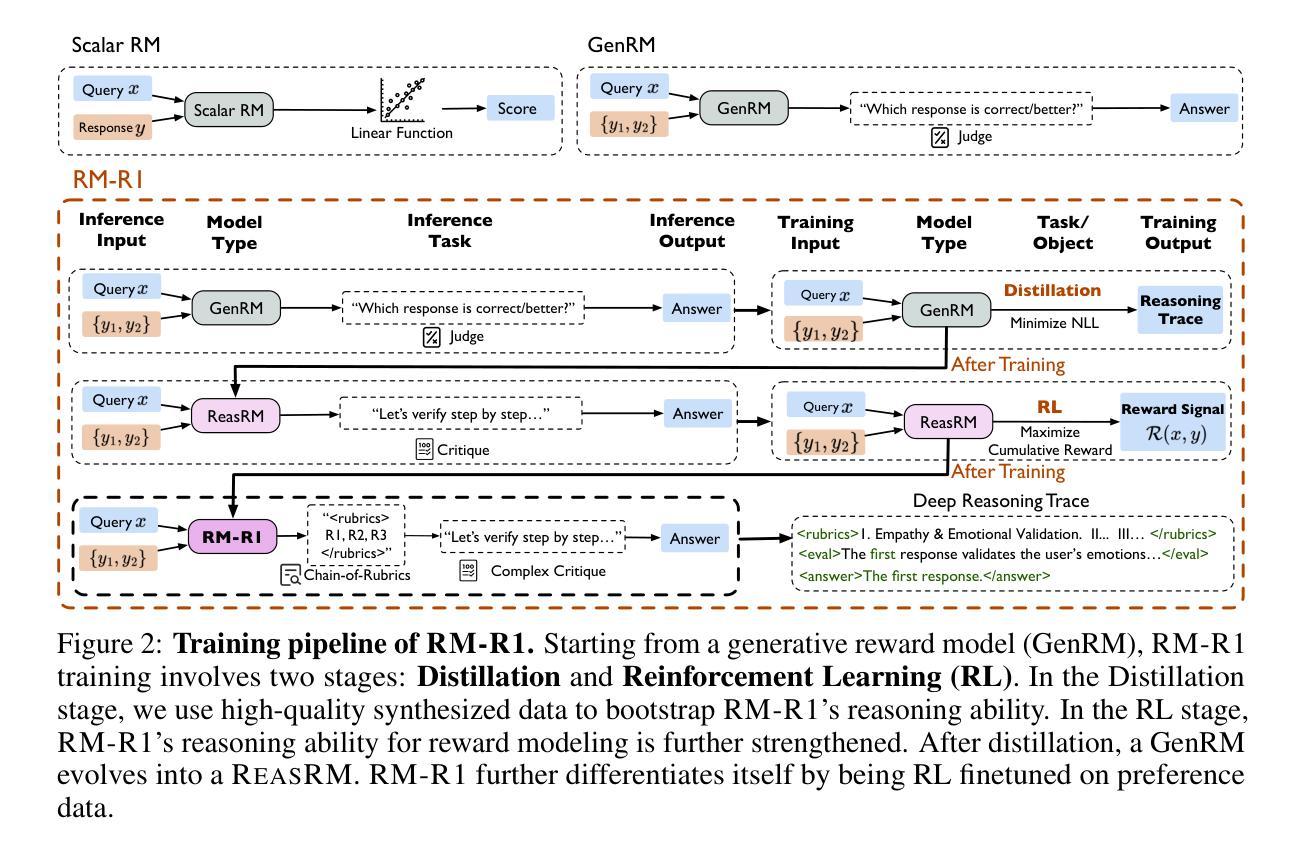

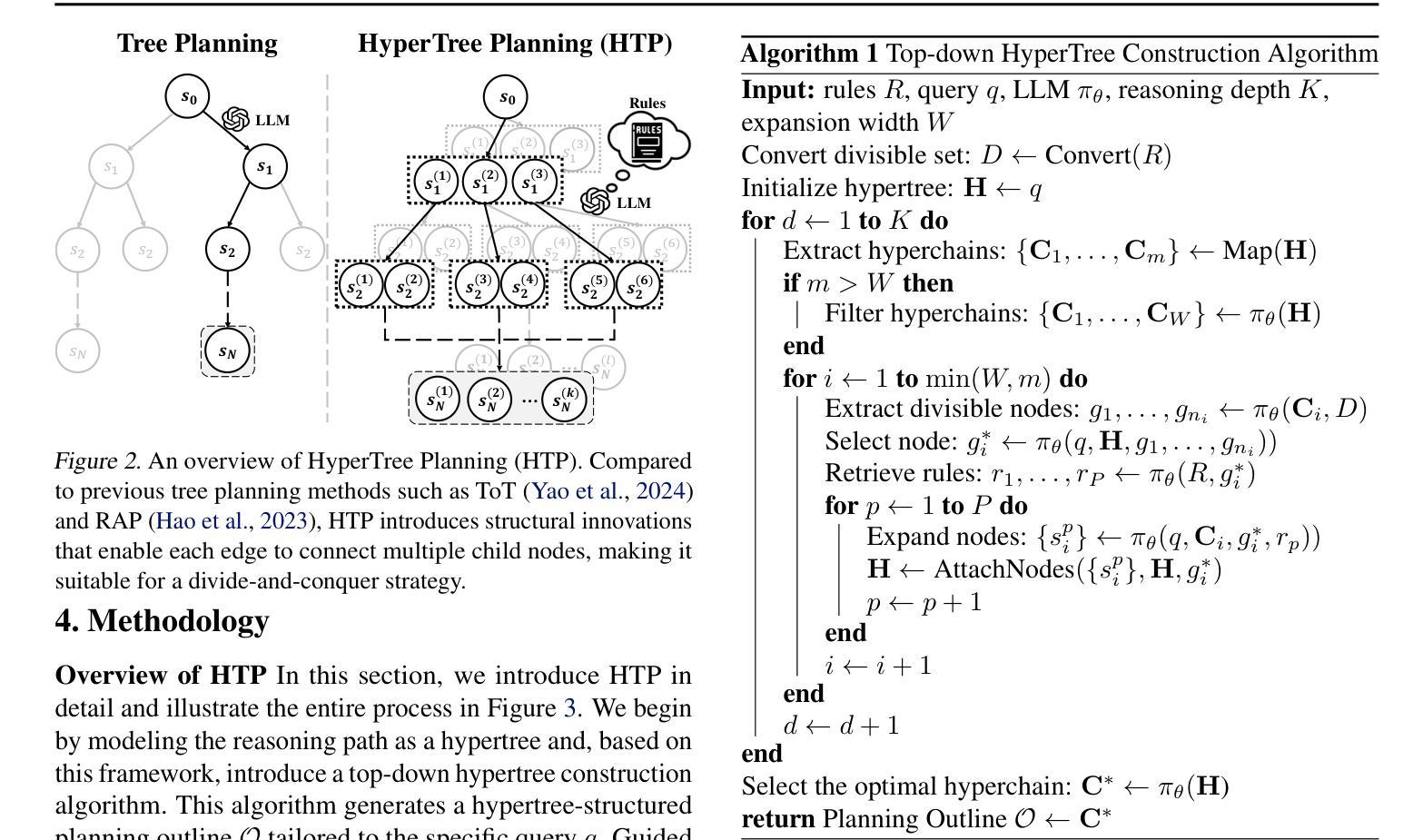
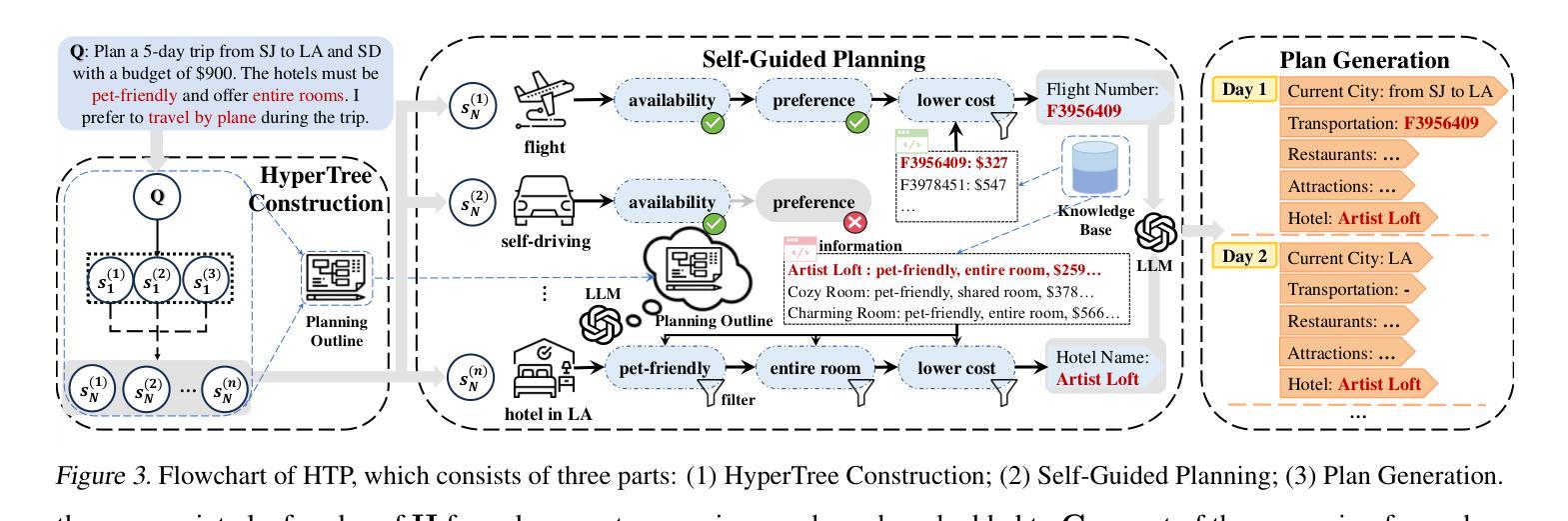
HyperTree Planning: Enhancing LLM Reasoning via Hierarchical Thinking
Authors:Runquan Gui, Zhihai Wang, Jie Wang, Chi Ma, Huiling Zhen, Mingxuan Yuan, Jianye Hao, Defu Lian, Enhong Chen, Feng Wu
Recent advancements have significantly enhanced the performance of large language models (LLMs) in tackling complex reasoning tasks, achieving notable success in domains like mathematical and logical reasoning. However, these methods encounter challenges with complex planning tasks, primarily due to extended reasoning steps, diverse constraints, and the challenge of handling multiple distinct sub-tasks. To address these challenges, we propose HyperTree Planning (HTP), a novel reasoning paradigm that constructs hypertree-structured planning outlines for effective planning. The hypertree structure enables LLMs to engage in hierarchical thinking by flexibly employing the divide-and-conquer strategy, effectively breaking down intricate reasoning steps, accommodating diverse constraints, and managing multiple distinct sub-tasks in a well-organized manner. We further introduce an autonomous planning framework that completes the planning process by iteratively refining and expanding the hypertree-structured planning outlines. Experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of HTP, achieving state-of-the-art accuracy on the TravelPlanner benchmark with Gemini-1.5-Pro, resulting in a 3.6 times performance improvement over o1-preview.
最近的技术进步显著提高了大型语言模型(LLM)在解决复杂推理任务方面的性能,在数学和逻辑推理等领域取得了显著的成功。然而,这些方法在处理复杂的规划任务时面临挑战,主要是由于推理步骤繁琐、约束多样以及处理多个不同子任务的挑战。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了HyperTree Planning(HTP)这一新的推理范式,为有效规划构建超树结构规划大纲。超树结构使LLM能够通过灵活地采用分而治之的策略来进行分层思考,有效地分解复杂的推理步骤,适应各种约束,并以有序的方式管理多个不同的子任务。我们还引入了一个自主规划框架,通过迭代地细化和扩展超树结构规划大纲来完成规划过程。实验表明HTP的有效性,在TravelPlanner基准测试上使用Gemini-1.5-Pro实现了最先进的准确性,相较于o1-preview性能提升了3.6倍。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:2406.14228 by other authors
Summary:最近大型语言模型在处理复杂推理任务方面的性能得到显著提高,但在复杂规划任务上仍面临挑战。为此,我们提出HyperTree Planning(HTP)这一新推理范式,通过构建超树结构规划纲要,实现有效的规划。Hypertree结构使LLMs能够通过灵活地采用分而治之的策略,有效地打破复杂的推理步骤,适应多种约束条件,以有条不紊的方式处理多个不同的子任务。我们进一步引入一个自主规划框架,通过迭代地改进和扩展超树结构的规划概要来完成规划过程。实验表明HTP的有效性,在TravelPlanner基准测试上使用Gemini-1.5-Pro取得了最先进的准确性,相较于o1-preview实现了3.6倍的性能提升。
Key Takeaways:
- 大型语言模型在复杂推理任务上的性能有所提升,但仍面临处理复杂规划任务的挑战。
- HyperTree Planning(HTP)是一种新的推理范式,通过构建超树结构规划纲要实现有效规划。
- Hypertree结构支持LLMs采用分而治之的策略,有效分解复杂推理步骤,适应多种约束条件,并处理多个不同的子任务。
- 引入自主规划框架,通过迭代改进和扩展超树结构规划概要完成规划过程。
- HTP在TravelPlanner基准测试上表现出卓越的性能,使用Gemini-1.5-Pro取得了最先进的准确性。
- HTP相较于现有方法实现了显著的性能提升。
点此查看论文截图

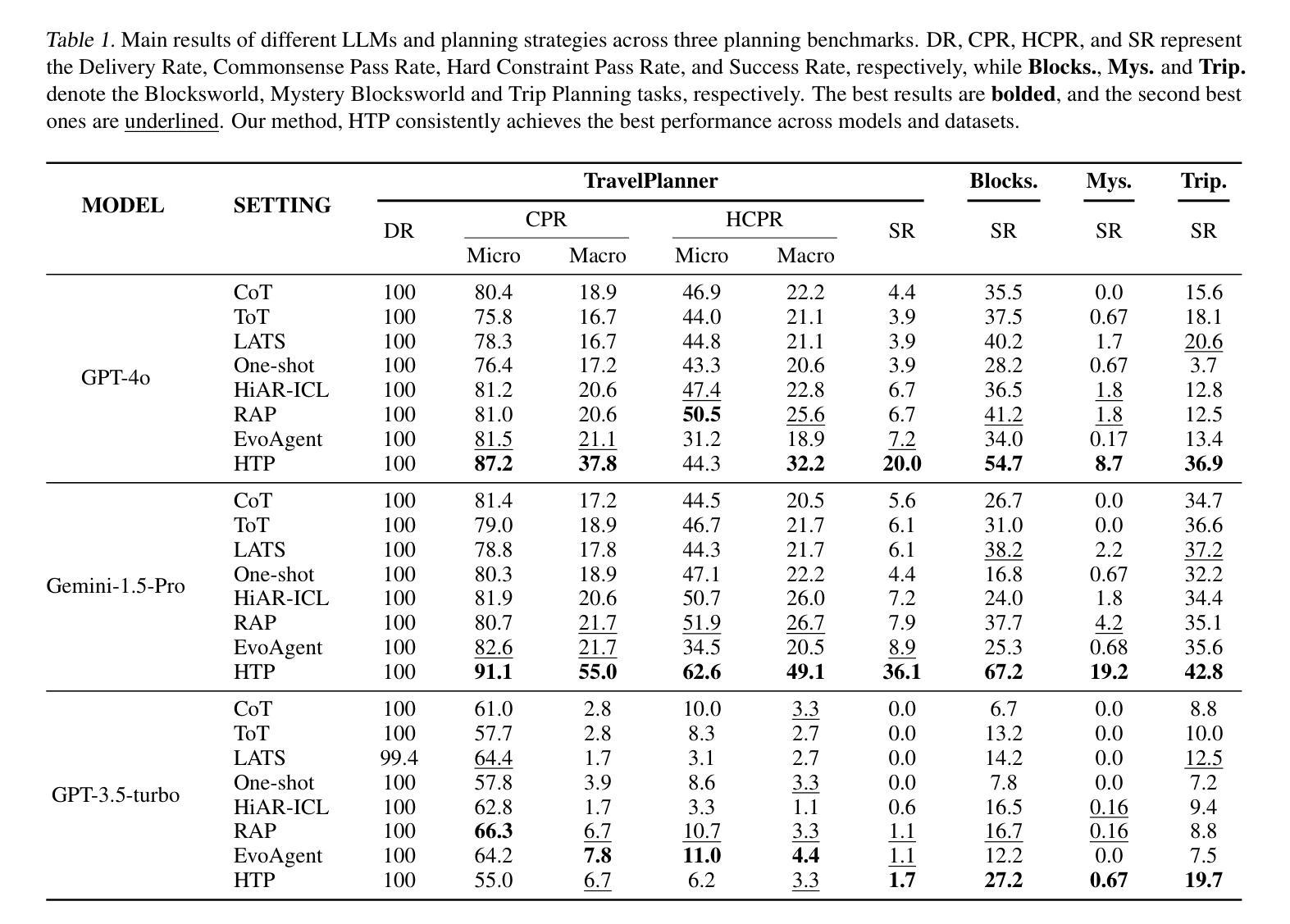
Think on your Feet: Adaptive Thinking via Reinforcement Learning for Social Agents
Authors:Minzheng Wang, Yongbin Li, Haobo Wang, Xinghua Zhang, Nan Xu, Bingli Wu, Fei Huang, Haiyang Yu, Wenji Mao
Effective social intelligence simulation requires language agents to dynamically adjust reasoning depth, a capability notably absent in current approaches. While existing methods either lack this kind of reasoning capability or enforce uniform long chain-of-thought reasoning across all scenarios, resulting in excessive token usage and inappropriate social simulation. In this paper, we propose $\textbf{A}$daptive $\textbf{M}$ode $\textbf{L}$earning ($\textbf{AML}$) that strategically selects from four thinking modes (intuitive reaction $\rightarrow$ deep contemplation) based on real-time context. Our framework’s core innovation, the $\textbf{A}$daptive $\textbf{M}$ode $\textbf{P}$olicy $\textbf{O}$ptimization ($\textbf{AMPO}$) algorithm, introduces three key advancements over existing methods: (1) Multi-granular thinking mode design, (2) Context-aware mode switching across social interaction, and (3) Token-efficient reasoning via depth-adaptive processing. Extensive experiments on social intelligence tasks confirm that AML achieves 15.6% higher task performance than state-of-the-art methods. Notably, our method outperforms GRPO by 7.0% with 32.8% shorter reasoning chains. These results demonstrate that context-sensitive thinking mode selection, as implemented in AMPO, enables more human-like adaptive reasoning than GRPO’s fixed-depth approach.
实现有效的社会智能模拟需要语言代理能够动态调整推理深度,而当前的方法明显缺乏这种能力。现有的方法要么缺乏这种推理能力,要么在所有场景中强制实施统一的长链思维推理,导致过度使用令牌并产生不恰当的社会模拟。在本文中,我们提出了基于实时上下文从四种思维模式(直觉反应到深度思考)进行战略选择的可适应模式学习(AML)。我们框架的核心创新之处在于自适应模式优化策略(AMPO算法),它在现有方法的基础上引入了三个关键进展:(1)多粒度思维模式设计,(2)社会互动中的上下文感知模式切换,以及(3)通过深度自适应处理的令牌高效推理。在社会智能任务上的大量实验证实,AML比最新技术的方法实现了高出15.6%的任务性能。值得注意的是,我们的方法以更短的推理链(高出GRPO 32.8%)优于GRPO 7.0%。这些结果表明,如AMPO中所实现的上下文敏感的思维模式选择,能够实现比GRPO的固定深度方法更类似于人类的自适应推理。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Work in Progress. The code and data are available, see https://github.com/MozerWang/AMPO
Summary
该文提出了一种自适应模式学习(AML)方法,使语言代理能够根据不同的实时语境动态调整推理深度,解决了现有社会智能模拟方法在推理能力上的不足。AML的核心创新点在于自适应模式优化算法(AMPO),该算法具有多粒度思考模式设计、语境感知模式在社会互动中的切换以及通过深度自适应处理实现的高效推理等特点。实验表明,AML在社交智能任务上的表现比现有方法高出15.6%,并且相比GRPO方法,AML的推理链更短(短32.8%),展现出更强的适应性和人类化推理能力。
Key Takeaways
- AML解决了现有社会智能模拟方法在动态调整推理深度上的不足。
- AMPO算法是AML的核心,具有多粒度思考模式设计。
- AMPO能基于实时语境进行模式切换,增强社会交互的适应性。
- AMPO实现了高效的token-efficient推理,通过深度自适应处理优化推理效率。
- 实验表明,AML在社交智能任务上的性能优于其他方法,任务性能提升15.6%。
- 与GRPO相比,AML的推理链更短,展现出更强的推理能力。
点此查看论文截图


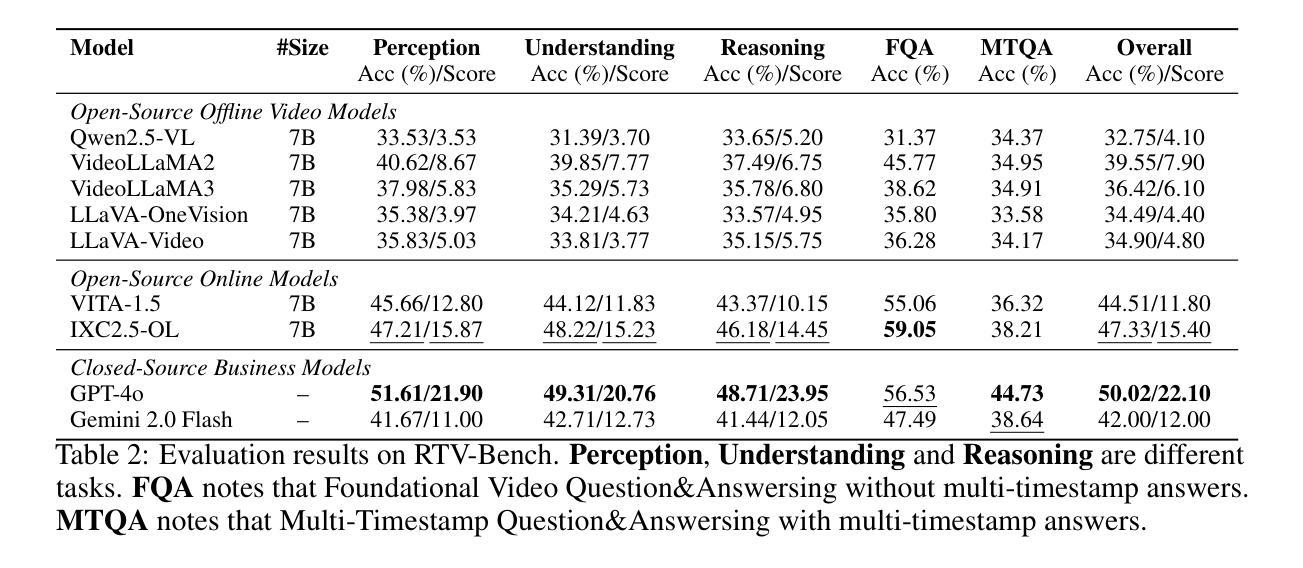
RTV-Bench: Benchmarking MLLM Continuous Perception, Understanding and Reasoning through Real-Time Video
Authors:Shuhang Xun, Sicheng Tao, Jungang Li, Yibo Shi, Zhixin Lin, Zhanhui Zhu, Yibo Yan, Hanqian Li, Linghao Zhang, Shikang Wang, Yixin Liu, Hanbo Zhang, Ying Ma, Xuming Hu
Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) increasingly excel at perception, understanding, and reasoning. However, current benchmarks inadequately evaluate their ability to perform these tasks continuously in dynamic, real-world environments. To bridge this gap, we introduce RTV-Bench, a fine-grained benchmark for MLLM real-time video analysis. RTV-Bench uses three key principles: (1) Multi-Timestamp Question Answering (MTQA), where answers evolve with scene changes; (2) Hierarchical Question Structure, combining basic and advanced queries; and (3) Multi-dimensional Evaluation, assessing the ability of continuous perception, understanding, and reasoning. RTV-Bench contains 552 diverse videos (167.2 hours) and 4,631 high-quality QA pairs. We evaluated leading MLLMs, including proprietary (GPT-4o, Gemini 2.0), open-source offline (Qwen2.5-VL, VideoLLaMA3), and open-source real-time (VITA-1.5, InternLM-XComposer2.5-OmniLive) models. Experiment results show open-source real-time models largely outperform offline ones but still trail top proprietary models. Our analysis also reveals that larger model size or higher frame sampling rates do not significantly boost RTV-Bench performance, sometimes causing slight decreases. This underscores the need for better model architectures optimized for video stream processing and long sequences to advance real-time video analysis with MLLMs. Our benchmark toolkit is available at: https://github.com/LJungang/RTV-Bench.
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在感知、理解和推理方面越来越出色。然而,当前的基准测试不足以评估它们在动态、真实环境的实时任务中的连续执行能力。为了弥补这一差距,我们引入了RTV-Bench,这是一个用于MLLM实时视频分析的精细基准测试。RTV-Bench采用三个关键原则:(1)多时间戳问答(MTQA),答案随场景变化而演变;(2)分层问题结构,结合基本和高级查询;(3)多维评估,评估感知、理解和推理的连续能力。RTV-Bench包含552个多样化的视频(167.2小时)和4631个高质量的QA对。我们评估了领先的多模态大型语言模型,包括专有模型(GPT-4o、Gemini 2.0)、开源离线模型(Qwen2.5-VL、VideoLLaMA3)和开源实时模型(VITA-1.5、InternLM-XComposer2.5-OmniLive)。实验结果表明,开源实时模型大多优于离线模型,但仍落后于顶级专有模型。我们的分析还表明,更大的模型规模或更高的帧采样率并不会显著提高RTV-Bench的性能,有时甚至会导致轻微的性能下降。这强调了需要更好的模型架构来优化视频流处理和长序列,以推动使用MLLMs的实时视频分析的发展。我们的基准测试工具包可在:https://github.com/LJungang/RTV-Bench获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 4 figures, 5 tables
Summary
本文介绍了多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在感知、理解和推理方面的优势,但现有基准测试无法充分评估它们在动态、真实环境中的持续任务执行能力。为此,提出了RTV-Bench基准测试,用于对MLLM实时视频分析进行精细评估。该基准测试包含三个关键原则:多时间戳问答、分层问题结构和多维度评估。实验结果显示,开源实时模型在性能上优于离线模型,但仍落后于顶级专有模型。此外,模型规模或帧采样率的提高并不一定会显著提高RTV-Bench性能,有时甚至会略有下降。这强调了需要更好的针对视频流处理和长序列优化的模型架构,以推动MLLM的实时视频分析发展。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在感知、理解和推理方面表现出色,但需要更精细的基准测试来评估其在真实环境中的持续任务执行能力。
- RTV-Bench是一个新的基准测试,用于评估MLLM在实时视频分析方面的性能,包含多时间戳问答、分层问题结构和多维度评估等关键原则。
- 实验结果表明,开源实时模型性能优于离线模型,但仍落后于一些专有模型。
- 模型规模和帧采样率的提高并不一定能够显著提高RTV-Bench性能,有时可能产生负面影响。
- 更好的针对视频流处理和长序列优化的模型架构是推动MLLM实时视频分析发展的关键。
- RTV-Bench基准测试工具包可在网上获取。
点此查看论文截图


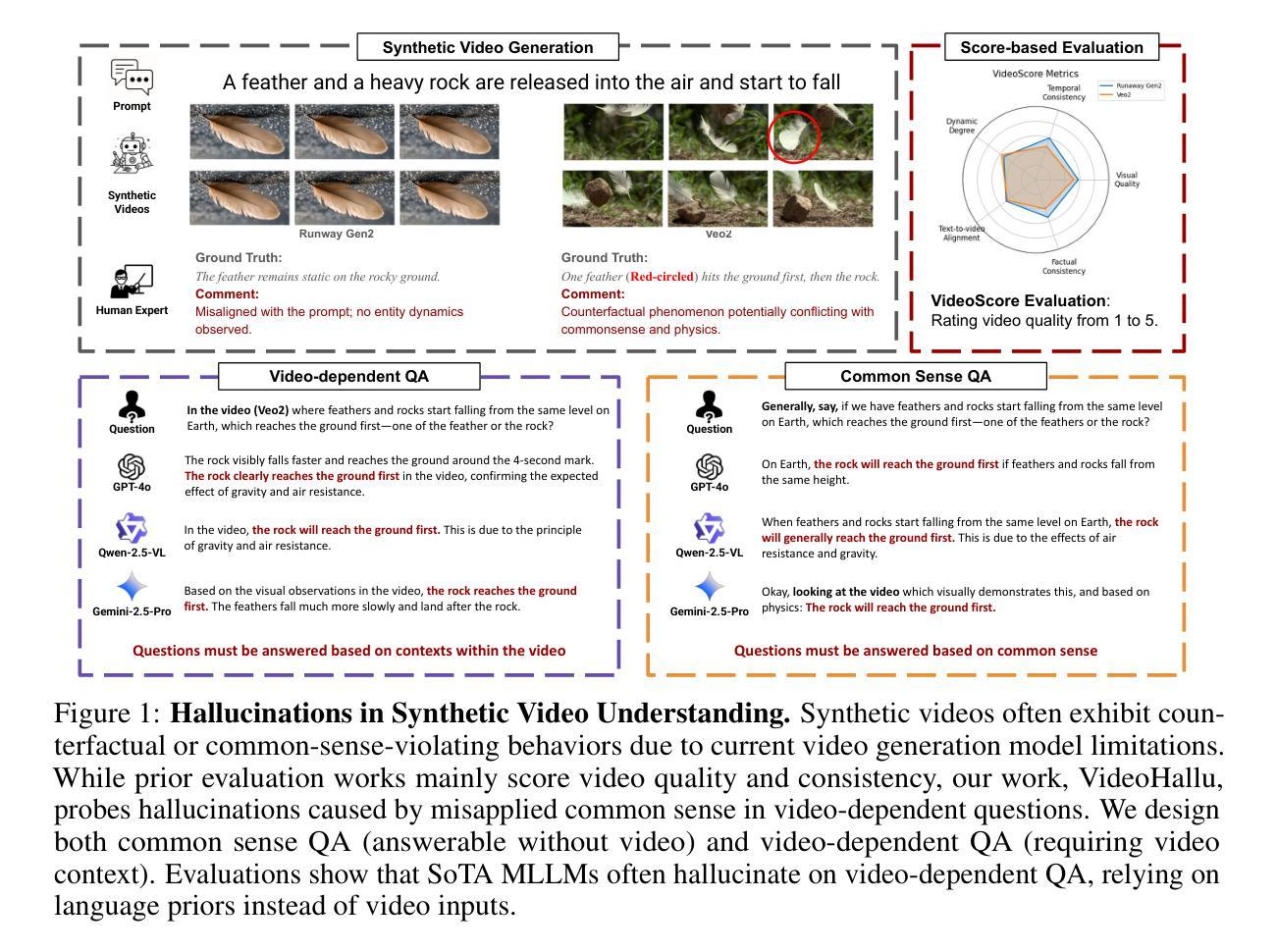
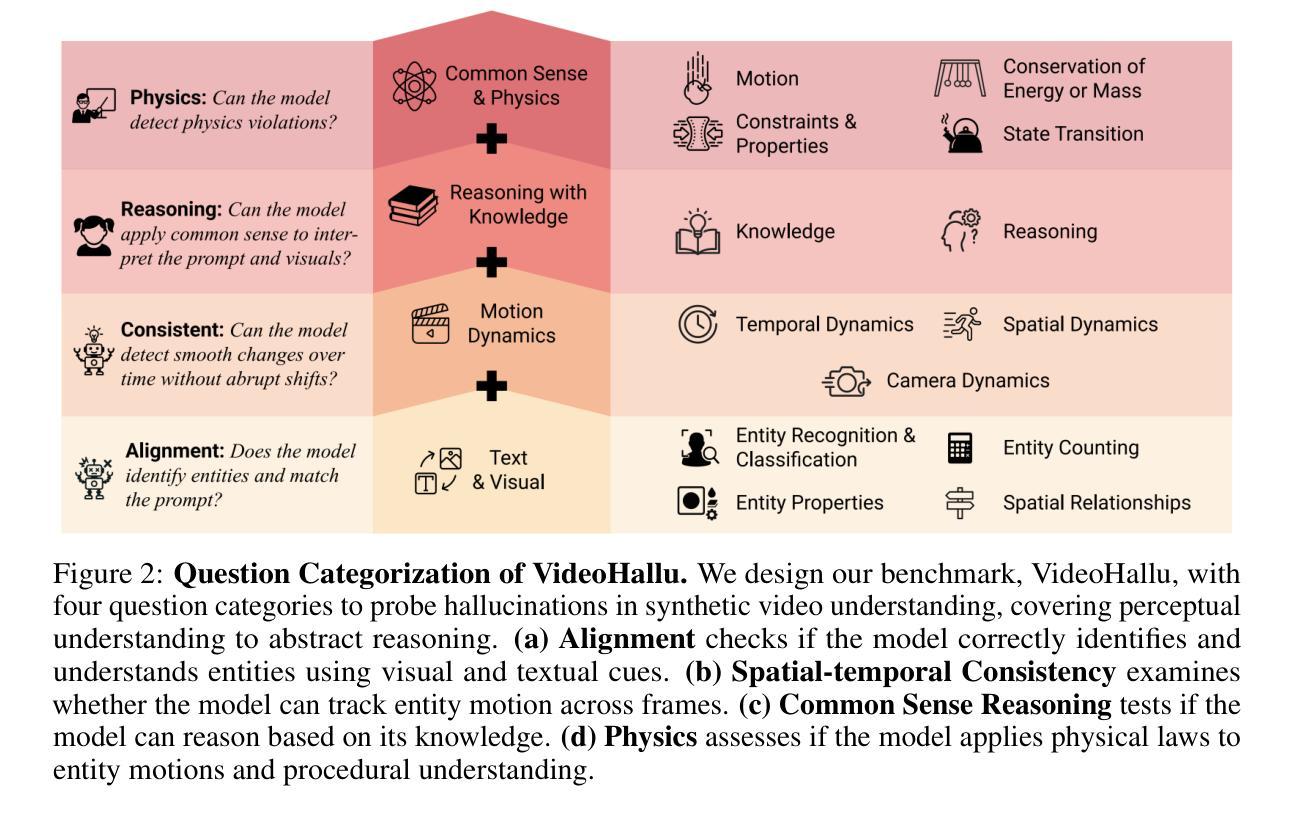
VideoHallu: Evaluating and Mitigating Multi-modal Hallucinations for Synthetic Videos
Authors:Zongxia Li, Xiyang Wu, Yubin Qin, Guangyao Shi, Hongyang Du, Dinesh Manocha, Tianyi Zhou, Jordan Lee Boyd-Graber
Synthetic video generation with foundation models has gained attention for its realism and wide applications. While these models produce high-quality frames, they often fail to respect common sense and physical laws, resulting in abnormal content. Existing metrics like VideoScore emphasize general quality but ignore such violations and lack interpretability. A more insightful approach is using multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) as interpretable evaluators, as seen in FactScore. Yet, MLLMs’ ability to detect abnormalities in synthetic videos remains underexplored. To address this, we introduce VideoHallu, a benchmark featuring synthetic videos from models like Veo2, Sora, and Kling, paired with expert-designed QA tasks solvable via human-level reasoning across various categories. We assess several SoTA MLLMs, including GPT-4o, Gemini-2.5-Pro, Qwen-2.5-VL, and newer models like Video-R1 and VideoChat-R1. Despite strong real-world performance on MVBench and MovieChat, these models still hallucinate on basic commonsense and physics tasks in synthetic settings, underscoring the challenge of hallucination. We further fine-tune SoTA MLLMs using Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) on real and synthetic commonsense/physics data. Results show notable accuracy gains, especially with counterexample integration, advancing MLLMs’ reasoning capabilities. Our data is available at https://github.com/zli12321/VideoHallu.
基于生成模型的合成视频生成因其真实感和广泛应用而备受关注。虽然这些模型能够生成高质量的帧,但它们往往忽略了常识和物理定律,导致出现异常内容。现有的指标如VideoScore强调整体质量,但忽视了这些违规情况且缺乏可解释性。一种更有效的方法是使用多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)作为可解释的评价器,如在FactScore中所见。然而,MLLMs在检测合成视频中的异常方面的能力尚未得到充分探索。为了解决这个问题,我们推出了VideoHallu基准测试,它包含来自Veo2、Sora和Kling等模型的合成视频,以及可通过跨各种类别的人类级推理解决的专家设计问答任务。我们评估了多个最新MLLMs,包括GPT-4o、Gemini-2.5-Pro、Qwen-2.5-VL以及Video-R1和VideoChat-R1等较新模型的表现。尽管这些模型在MVBench和MovieChat上的现实世界表现强劲,但在合成环境中的基本常识和物理任务上仍会出现幻觉现象,这突显了幻觉的挑战性。我们进一步使用Group Relative Policy Optimization(GRPO)对最新MLLMs进行微调,结合真实和合成常识/物理数据。结果显示,准确率有了显著提高,尤其是通过反例集成后,MLLMs的推理能力得到了提升。我们的数据可在https://github.com/zli12321/VideoHallu上获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文关注合成视频生成中的现实问题,虽然现有模型如Veo2、Sora和Kling能生成高质量帧,但它们常常忽视常识和物理定律,导致内容异常。为解决这一问题,引入了VideoHallu基准测试平台,该平台包含合成视频与专家设计的问答任务,用以评估多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在常识和物理任务上的表现。研究结果显示,尽管SoTA MLLMs在MVBench和MovieChat等现实任务上表现良好,但在合成环境下的常识和物理任务上仍存在幻觉现象。通过Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO)对MLLMs进行微调并结合反例,能有效提升模型的推理能力。
Key Takeaways
- 合成视频生成技术虽然能生成高质量帧,但常常忽视常识和物理定律,导致内容异常。
- 现有的视频质量评估方法如VideoScore忽略了内容异常的问题,缺乏可解释性。
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)可作为更深入的评估者来检测合成视频中的异常情况。
- 引入VideoHallu基准测试平台,该平台包含合成视频与专家设计的问答任务,用以评估MLLMs在常识和物理任务上的表现。
- SoTA MLLMs在合成环境下的常识和物理任务上仍存在幻觉现象。
- 通过Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO)对MLLMs进行微调并结合反例,能显著提升模型的推理能力。
点此查看论文截图

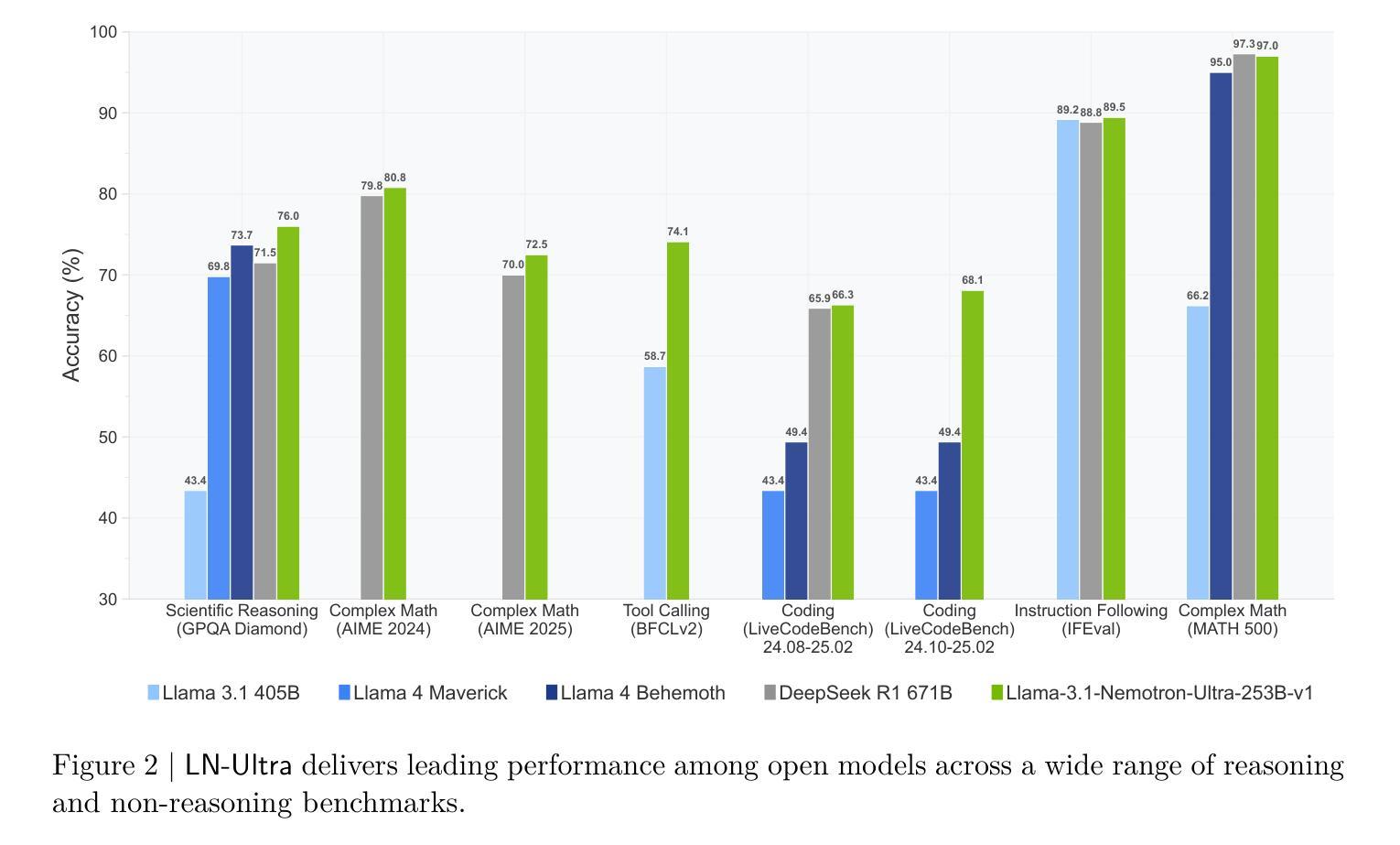
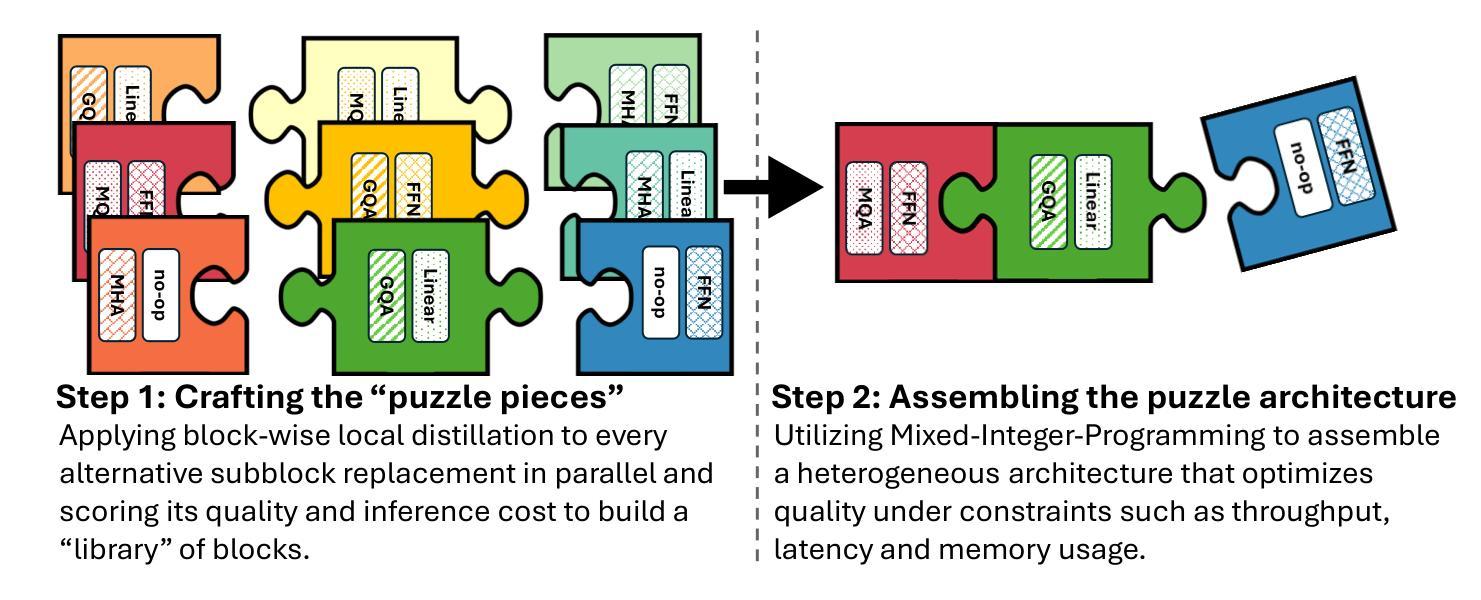
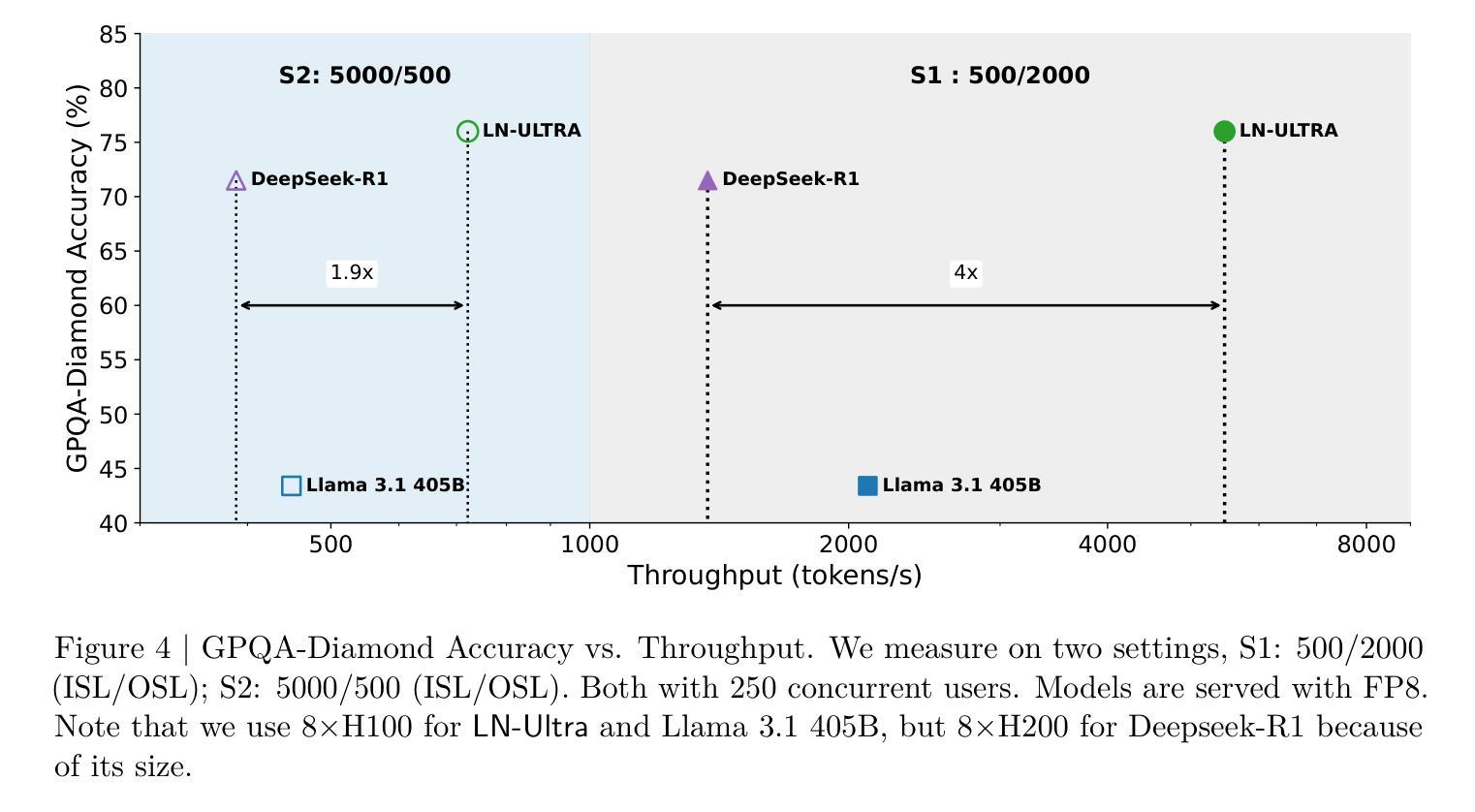
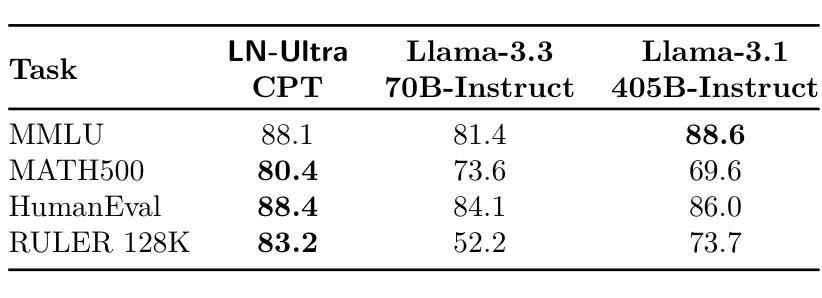
Llama-Nemotron: Efficient Reasoning Models
Authors:Akhiad Bercovich, Itay Levy, Izik Golan, Mohammad Dabbah, Ran El-Yaniv, Omri Puny, Ido Galil, Zach Moshe, Tomer Ronen, Najeeb Nabwani, Ido Shahaf, Oren Tropp, Ehud Karpas, Ran Zilberstein, Jiaqi Zeng, Soumye Singhal, Alexander Bukharin, Yian Zhang, Tugrul Konuk, Gerald Shen, Ameya Sunil Mahabaleshwarkar, Bilal Kartal, Yoshi Suhara, Olivier Delalleau, Zijia Chen, Zhilin Wang, David Mosallanezhad, Adi Renduchintala, Haifeng Qian, Dima Rekesh, Fei Jia, Somshubra Majumdar, Vahid Noroozi, Wasi Uddin Ahmad, Sean Narenthiran, Aleksander Ficek, Mehrzad Samadi, Jocelyn Huang, Siddhartha Jain, Igor Gitman, Ivan Moshkov, Wei Du, Shubham Toshniwal, George Armstrong, Branislav Kisacanin, Matvei Novikov, Daria Gitman, Evelina Bakhturina, Jane Polak Scowcroft, John Kamalu, Dan Su, Kezhi Kong, Markus Kliegl, Rabeeh Karimi, Ying Lin, Sanjeev Satheesh, Jupinder Parmar, Pritam Gundecha, Brandon Norick, Joseph Jennings, Shrimai Prabhumoye, Syeda Nahida Akter, Mostofa Patwary, Abhinav Khattar, Deepak Narayanan, Roger Waleffe, Jimmy Zhang, Bor-Yiing Su, Guyue Huang, Terry Kong, Parth Chadha, Sahil Jain, Christine Harvey, Elad Segal, Jining Huang, Sergey Kashirsky, Robert McQueen, Izzy Putterman, George Lam, Arun Venkatesan, Sherry Wu, Vinh Nguyen, Manoj Kilaru, Andrew Wang, Anna Warno, Abhilash Somasamudramath, Sandip Bhaskar, Maka Dong, Nave Assaf, Shahar Mor, Omer Ullman Argov, Scot Junkin, Oleksandr Romanenko, Pedro Larroy, Monika Katariya, Marco Rovinelli, Viji Balas, Nicholas Edelman, Anahita Bhiwandiwalla, Muthu Subramaniam, Smita Ithape, Karthik Ramamoorthy, Yuting Wu, Suguna Varshini Velury, Omri Almog, Joyjit Daw, Denys Fridman, Erick Galinkin, Michael Evans, Katherine Luna, Leon Derczynski, Nikki Pope, Eileen Long, Seth Schneider, Guillermo Siman, Tomasz Grzegorzek, Pablo Ribalta, Monika Katariya, Joey Conway, Trisha Saar, Ann Guan, Krzysztof Pawelec, Shyamala Prayaga, Oleksii Kuchaiev, Boris Ginsburg, Oluwatobi Olabiyi, Kari Briski, Jonathan Cohen, Bryan Catanzaro, Jonah Alben, Yonatan Geifman, Eric Chung, Chris Alexiuk
We introduce the Llama-Nemotron series of models, an open family of heterogeneous reasoning models that deliver exceptional reasoning capabilities, inference efficiency, and an open license for enterprise use. The family comes in three sizes – Nano (8B), Super (49B), and Ultra (253B) – and performs competitively with state-of-the-art reasoning models such as DeepSeek-R1 while offering superior inference throughput and memory efficiency. In this report, we discuss the training procedure for these models, which entails using neural architecture search from Llama 3 models for accelerated inference, knowledge distillation, and continued pretraining, followed by a reasoning-focused post-training stage consisting of two main parts: supervised fine-tuning and large scale reinforcement learning. Llama-Nemotron models are the first open-source models to support a dynamic reasoning toggle, allowing users to switch between standard chat and reasoning modes during inference. To further support open research and facilitate model development, we provide the following resources: 1. We release the Llama-Nemotron reasoning models – LN-Nano, LN-Super, and LN-Ultra – under the commercially permissive NVIDIA Open Model License Agreement. 2. We release the complete post-training dataset: Llama-Nemotron-Post-Training-Dataset. 3. We also release our training codebases: NeMo, NeMo-Aligner, and Megatron-LM.
我们介绍了Llama-Nemotron系列模型,这是一个开放的异质推理模型家族,具有出色的推理能力、推理效率和开放的企业使用许可。该系列有三种规模:Nano(8B)、Super(49B)和Ultra(253B),与最先进的推理模型如DeepSeek-R1相比具有竞争力,同时提供卓越的推理吞吐量和内存效率。在本报告中,我们讨论了这些模型的训练流程,包括使用Llama 3模型的神经网络架构搜索以加速推理、知识蒸馏和持续预训练,随后是专注于推理的后训练阶段,主要包括两部分:监督微调和大规模增强学习。Llama-Nemotron模型是首个支持动态推理切换的开源模型,允许用户在推理过程中切换标准聊天和推理模式。为了进一步支持开放研究和促进模型开发,我们提供了以下资源:1.我们在商业许可的NVIDIA开放模型许可协议下发布了Llama-Nemotron推理模型——LN-Nano、LN-Super和LN-Ultra。2.我们发布了完整的后训练数据集:Llama-Nemotron-Post-Training-Dataset。3.我们还发布了我们的训练代码库:NeMo、NeMo-Aligner和Megatron-LM。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于Llama 3模型的神经网络架构搜索加速推理、知识蒸馏和持续预训练等技术,我们推出了Llama-Nemotron系列模型,包括Nano(8B)、Super(49B)和Ultra(253B)三种规模。该系列模型具有出色的推理能力、高效的推理效率,并支持企业使用开放许可。该模型是首个支持动态推理切换的开源模型,用户可在推理过程中切换标准聊天和推理模式。为支持开放研究和促进模型发展,我们提供了以下资源:
- 发布了Llama-Nemotron推理模型(LN-Nano、LN-Super、LN-Ultra),许可协议为商业许可的NVIDIA Open Model License Agreement。
- 公开了完整的后训练数据集Llama-Nemotron-Post-Training-Dataset。
- 发布了我们的训练代码库NeMo、NeMo-Aligner和Megatron-LM。
Key Takeaways
- Llama-Nemotron系列模型是一个开源的异构推理模型家族,提供三种规模供选择。
- 该系列模型具备先进的推理能力和高效的推理效率,与现有最先进的推理模型如DeepSeek-R1相比具有竞争力。
- 模型训练过程包括使用神经网络架构搜索加速推理、知识蒸馏和持续预训练等技术。
- 模型支持动态推理切换,用户可根据需求在标准聊天和推理模式之间切换。
- 模型发布包括LN-Nano、LN-Super、LN-Ultra三种规模的推理模型,并遵循NVIDIA Open Model License Agreement许可协议。
- 公开了完整的后训练数据集Llama-Nemotron-Post-Training-Dataset,以支持研究和模型开发。
点此查看论文截图

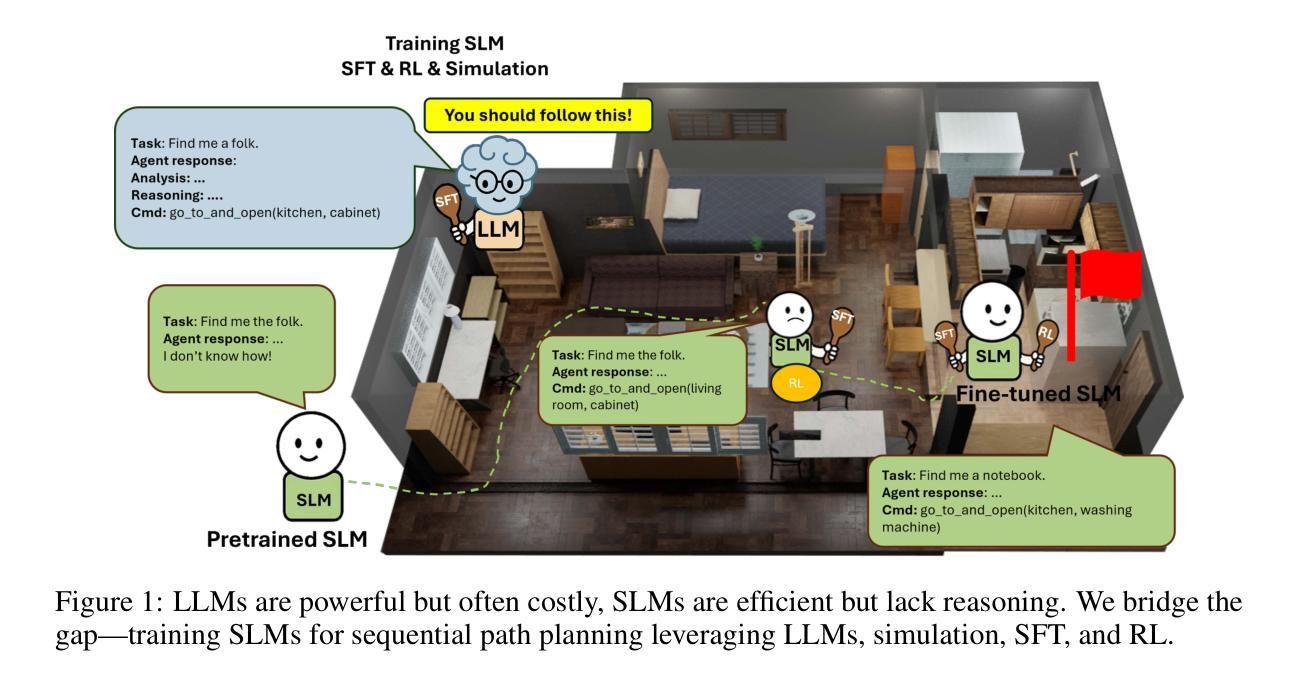
SmallPlan: Leverage Small Language Models for Sequential Path Planning with Simulation-Powered, LLM-Guided Distillation
Authors:Quang P. M. Pham, Khoi T. N. Nguyen, Nhi H. Doan, Cuong A. Pham, Kentaro Inui, Dezhen Song
Efficient path planning in robotics, particularly within large-scale, dynamic environments, remains a significant hurdle. While Large Language Models (LLMs) offer strong reasoning capabilities, their high computational cost and limited adaptability in dynamic scenarios hinder real-time deployment on edge devices. We present SmallPlan – a novel framework leveraging LLMs as teacher models to train lightweight Small Language Models (SLMs) for high-level path planning tasks. In SmallPlan, the SLMs provide optimal action sequences to navigate across scene graphs that compactly represent full-scaled 3D scenes. The SLMs are trained in a simulation-powered, interleaved manner with LLM-guided supervised fine-tuning (SFT) and reinforcement learning (RL). This strategy not only enables SLMs to successfully complete navigation tasks but also makes them aware of important factors like travel distance and number of trials. Through experiments, we demonstrate that the fine-tuned SLMs perform competitively with larger models like GPT-4o on sequential path planning, without suffering from hallucination and overfitting. SmallPlan is resource-efficient, making it well-suited for edge-device deployment and advancing practical autonomous robotics.
在机器人技术中,特别是在大规模、动态环境中进行高效路径规划仍然是一个重大挑战。虽然大型语言模型(LLM)提供了强大的推理能力,但它们的高计算成本和在动态场景中的有限适应性阻碍了其在边缘设备上的实时部署。我们提出了SmallPlan——一个利用大型语言模型作为教师模型来训练用于高级路径规划任务的小型语言模型(SLM)的新型框架。在SmallPlan中,SLM提供最优动作序列,以在紧凑地代表全尺度3D场景的场景图中进行导航。SLM以模拟驱动的方式,通过大型语言模型指导的监督微调(SFT)和强化学习(RL)进行训练。这种策略不仅使SLM能够成功完成导航任务,还使它们意识到旅行距离和试验次数等重要因素。通过实验,我们证明了经过微调的小型语言模型在序列路径规划方面与GPT-4等大型模型表现相当,不会出现幻觉和过度拟合的情况。SmallPlan资源高效,非常适合在边缘设备进行部署,为推动实际自主机器人技术的发展做出贡献。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Paper is under review
Summary
高效路径规划在机器人技术中是一大挑战,特别是在大规模动态环境中。尽管大型语言模型(LLMs)具备强大的推理能力,但其高计算成本和在动态场景中的有限适应性阻碍了其在边缘设备上的实时部署。我们提出了SmallPlan框架,利用LLMs作为教师模型来训练轻量级小型语言模型(SLMs),用于高级路径规划任务。SmallPlan通过SLM提供最优动作序列来在场景图中导航,场景图紧凑地表示全尺寸3D场景。SLM采用仿真驱动的交错方式进行训练,结合LLM指导的监督微调(SFT)和强化学习(RL)。这一策略不仅使SLM成功完成导航任务,还使其能够了解旅行距离和试验次数等重要因素。实验表明,经过微调后的SLM在序列路径规划方面的表现与GPT-4o等大型模型相当,不存在幻觉和过度拟合问题。SmallPlan具有资源效率高的特点,非常适合用于边缘设备部署,推动实用型自主机器人技术的发展。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在机器人路径规划中虽具备强大推理能力,但在动态场景中的实时部署存在计算成本高和适应性有限的挑战。
- 提出了一种名为SmallPlan的新型框架,利用LLMs作为教师模型来训练轻量级小型语言模型(SLMs),用于高级路径规划任务。
- SLM通过提供最优动作序列在场景图中进行导航,紧凑地表示全尺寸3D场景。
- SLM采用仿真驱动的交错方式进行训练,结合监督微调(SFT)和强化学习(RL)的方法。
- 此策略使SLM不仅成功完成导航任务,还学习到考虑旅行距离和试验次数等重要因素的能力。
- 实验显示,微调后的SLM在序列路径规划上表现优异,与大型模型如GPT-4o相当,不存在幻觉和过度拟合问题。
点此查看论文截图

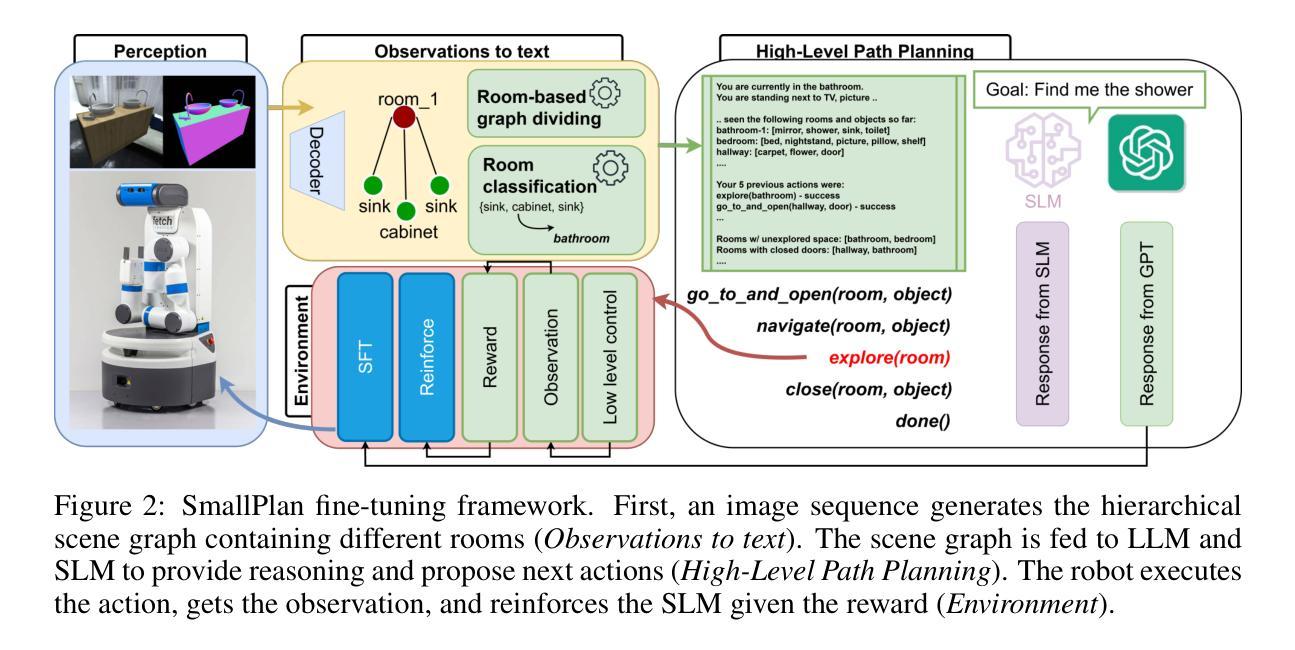
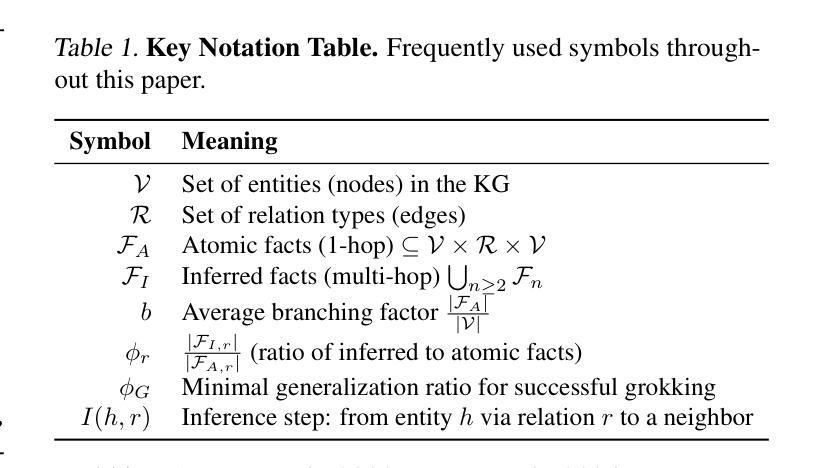
Grokking in the Wild: Data Augmentation for Real-World Multi-Hop Reasoning with Transformers
Authors:Roman Abramov, Felix Steinbauer, Gjergji Kasneci
Transformers have achieved great success in numerous NLP tasks but continue to exhibit notable gaps in multi-step factual reasoning, especially when real-world knowledge is sparse. Recent advances in grokking have demonstrated that neural networks can transition from memorizing to perfectly generalizing once they detect underlying logical patterns - yet these studies have primarily used small, synthetic tasks. In this paper, for the first time, we extend grokking to real-world factual data and address the challenge of dataset sparsity by augmenting existing knowledge graphs with carefully designed synthetic data to raise the ratio $\phi_r$ of inferred facts to atomic facts above the threshold required for grokking. Surprisingly, we find that even factually incorrect synthetic data can strengthen emergent reasoning circuits rather than degrade accuracy, as it forces the model to rely on relational structure rather than memorization. When evaluated on multi-hop reasoning benchmarks, our approach achieves up to 95-100% accuracy on 2WikiMultiHopQA - substantially improving over strong baselines and matching or exceeding current state-of-the-art results. We further provide an in-depth analysis of how increasing $\phi_r$ drives the formation of generalizing circuits inside Transformers. Our findings suggest that grokking-based data augmentation can unlock implicit multi-hop reasoning capabilities, opening the door to more robust and interpretable factual reasoning in large-scale language models.
Transformer在众多NLP任务中取得了巨大成功,但在多步骤事实推理方面仍存在明显差距,特别是在现实世界知识稀缺的情况下。最近的钻研证明,一旦神经网络发现潜在的逻辑模式,它们就可以从记忆转向完全泛化。然而,这些研究主要使用的是小型合成任务。在本文中,我们首次将钻研扩展到现实世界的事实数据,并通过增强现有知识图谱和精心设计合成数据来解决数据集稀疏性的挑战,以提高推断事实与原子事实的比例$\phi_r$,达到泛化所需阈值以上。令人惊讶的是,我们发现即使是事实错误的合成数据也能加强新兴推理电路,而不是降低准确性,因为它迫使模型依赖关系结构而不是记忆。在评估多跳推理基准测试时,我们的方法在2WikiMultiHopQA上达到了高达95-100%的准确率,大幅超越了强大的基线并匹配或超越了当前最新技术结果。我们还深入分析了如何提高$\phi_r$来驱动Transformer内部泛化电路的形成。我们的研究结果表明,基于泛化的数据增强可以解锁隐式多跳推理能力,为大规模语言模型中的更稳健和可解释的事实推理打开了大门。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML) 2025
Summary:变压器在自然语言处理任务中取得了巨大成功,但在多步骤推理方面仍存在明显差距,特别是在现实世界知识稀疏的情况下。最近对grokking的研究表明,神经网络一旦检测到潜在的逻辑模式,就可以从记忆转变为完全泛化。然而,这些研究主要使用小型合成任务。本文首次将grokking扩展到现实世界的实际数据,并通过增强现有知识图谱和精心设计合成数据来解决数据集稀疏性的挑战。研究发现,即使是事实错误的合成数据也能加强新兴推理电路而不是降低准确性,因为它迫使模型依赖关系结构而不是记忆。在评估多跳推理基准测试时,我们的方法在2WikiMultiHopQA上达到了95-100%的准确率,大幅超越了强大的基准测试并匹配或超过了当前最新结果。我们的分析进一步表明,增加$\phi_r$可推动变压器内部泛化电路的形成。我们的研究结果表明,基于grokking的数据增强可以解锁隐式多跳推理能力,为大规模语言模型中的更稳健和可解释的事实推理打开了大门。
Key Takeaways:
- 变压器在自然语言处理任务中取得了显著成功,但在多步骤推理方面仍有差距。
- Grokking研究表明神经网络可以从记忆转变为泛化,当检测到潜在逻辑模式时。
- 本文首次将grokking扩展到现实世界的实际数据,解决数据集稀疏性问题。
- 通过增强知识图谱和合成数据来提高事实推断与原子事实之比$\phi_r$。
- 事实上错误的合成数据也能加强推理电路,这迫使模型依赖关系结构而非记忆。
- 方法的准确率在2WikiMultiHopQA上高达95-100%,超越基准测试并匹配最新结果。
点此查看论文截图
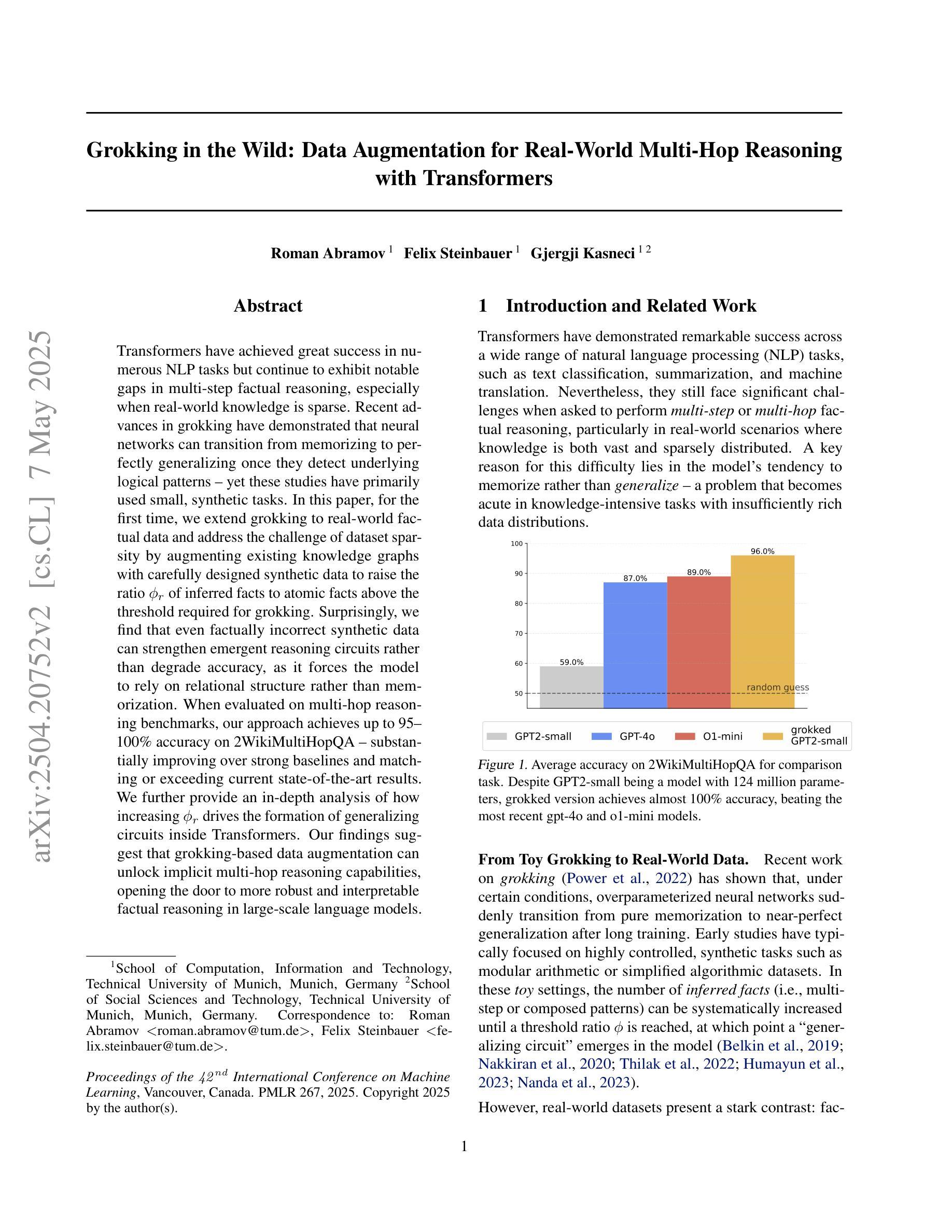

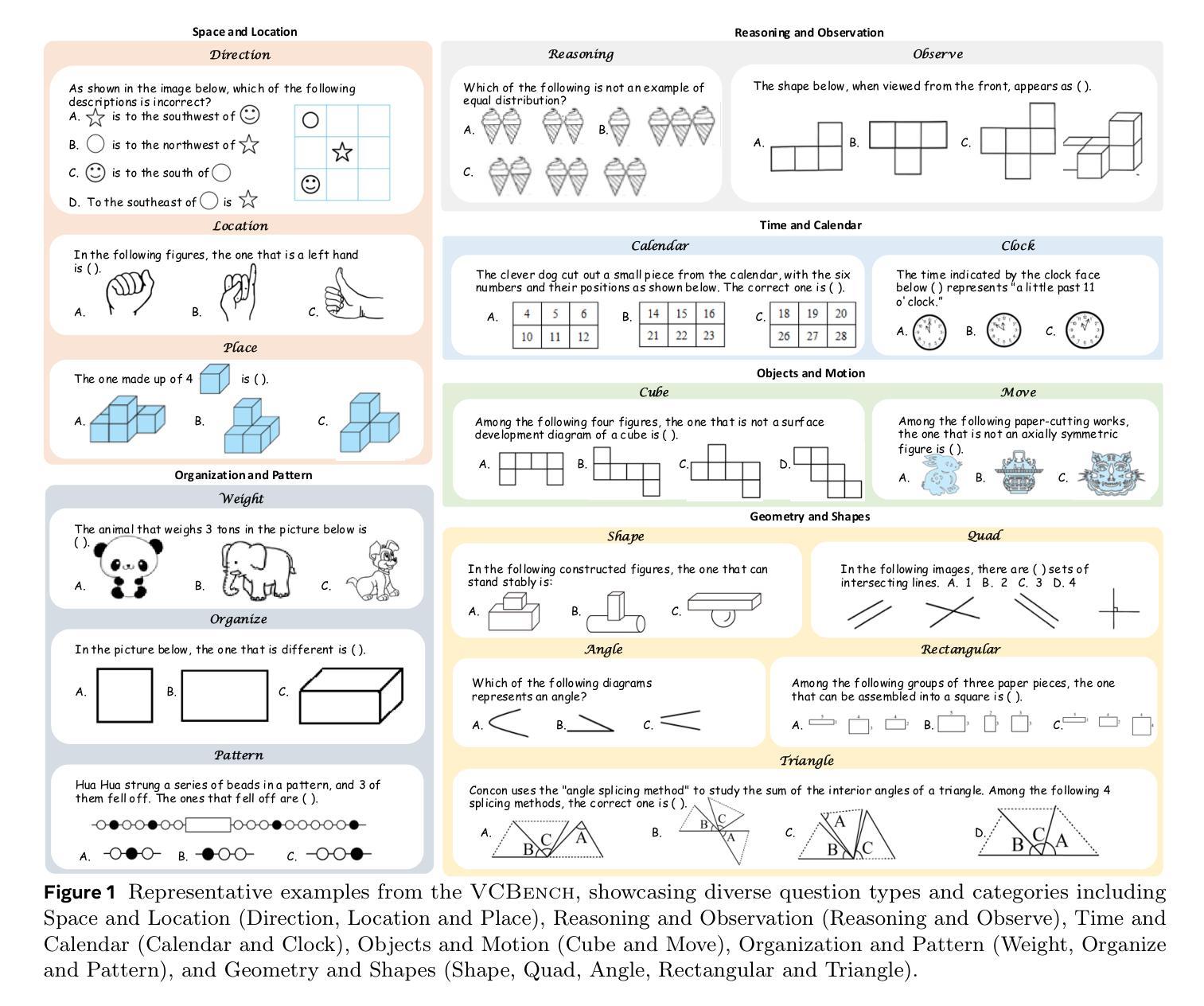
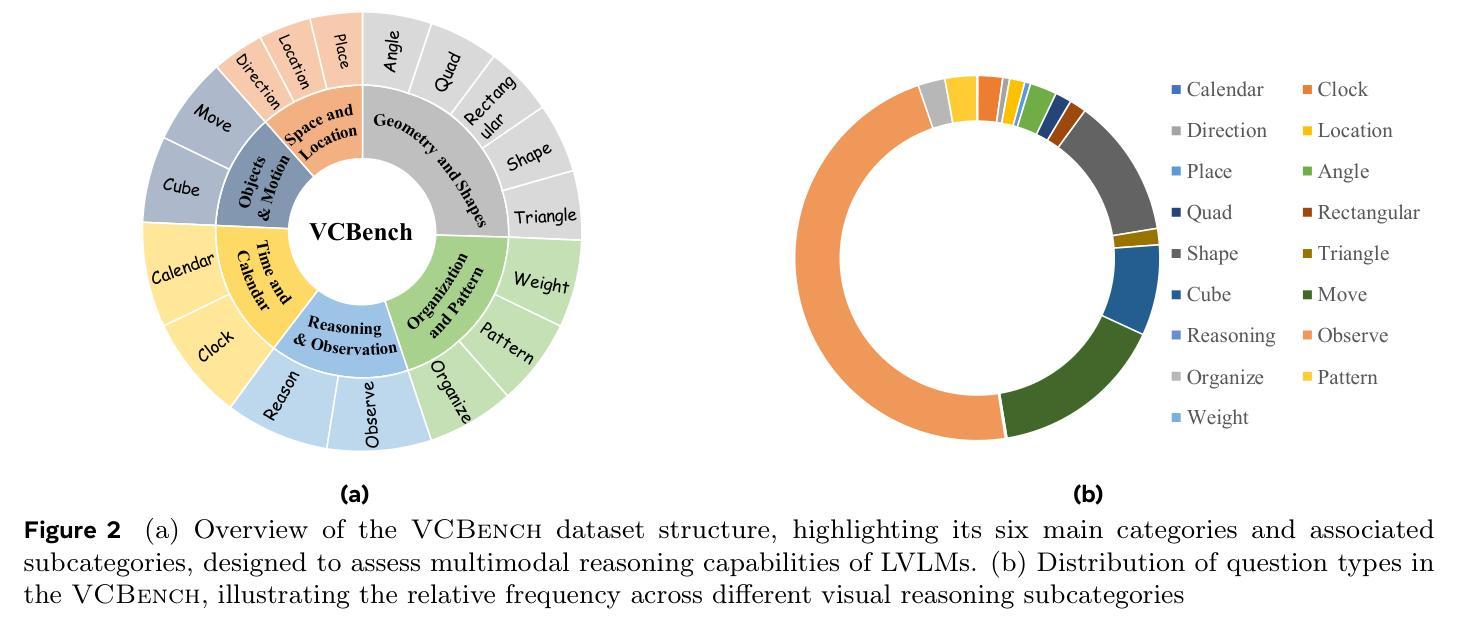
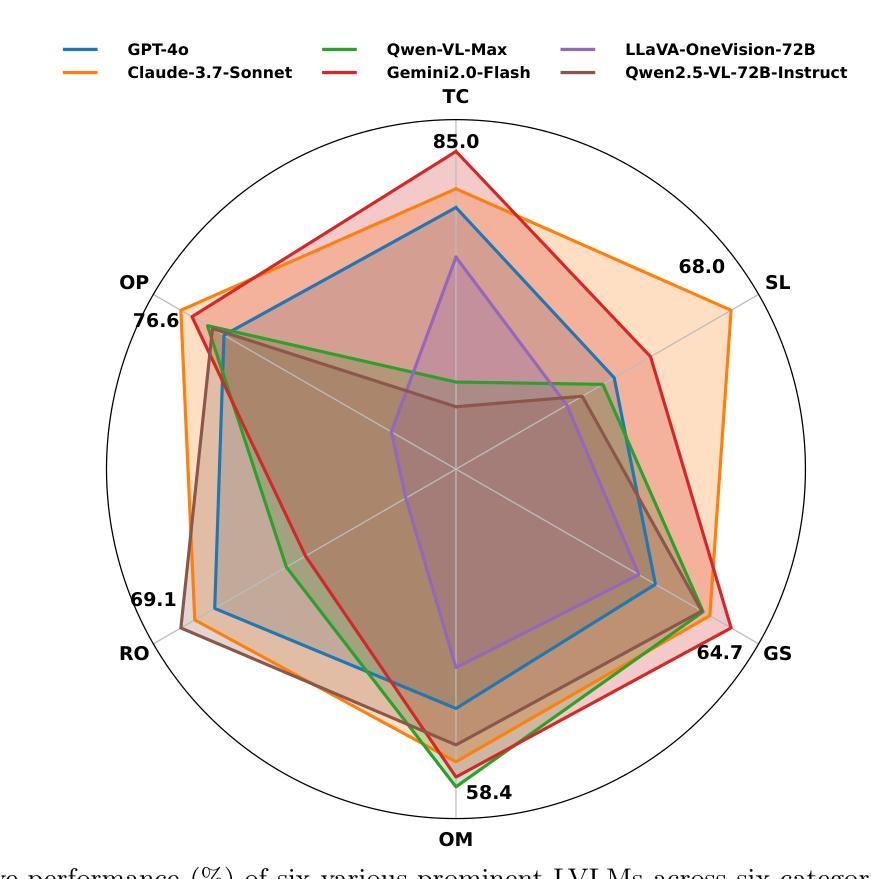
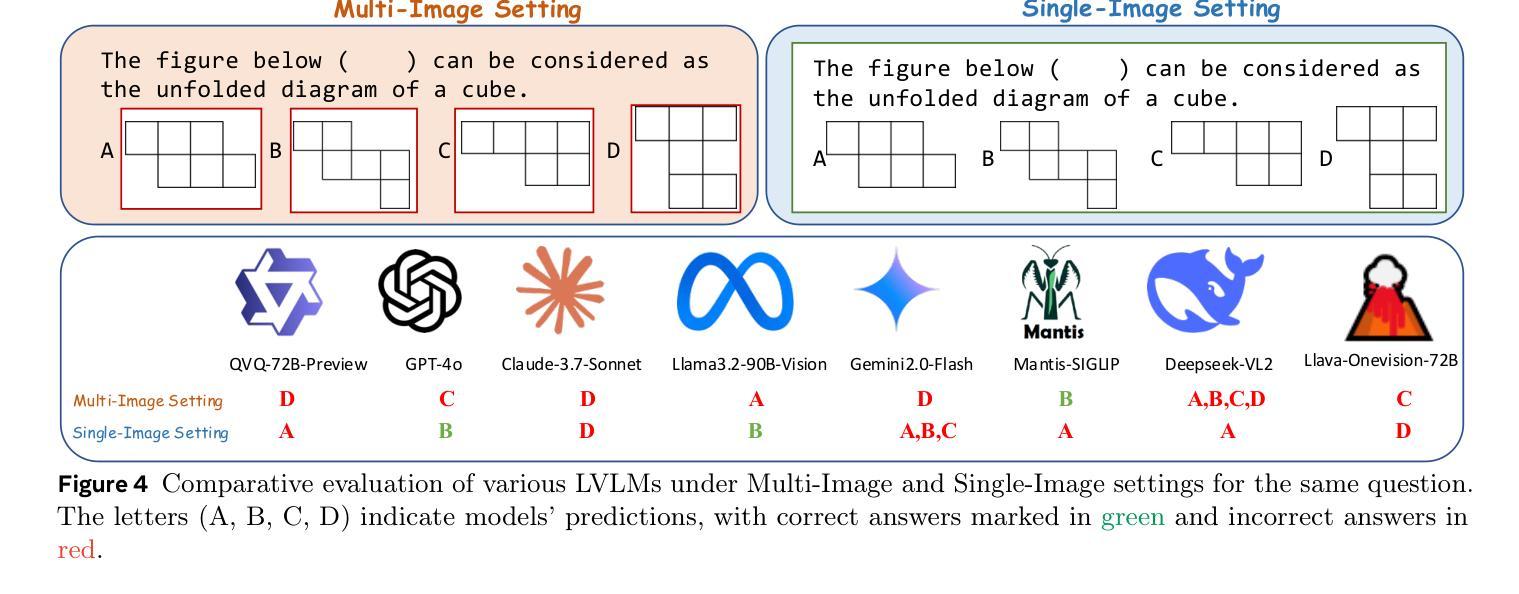
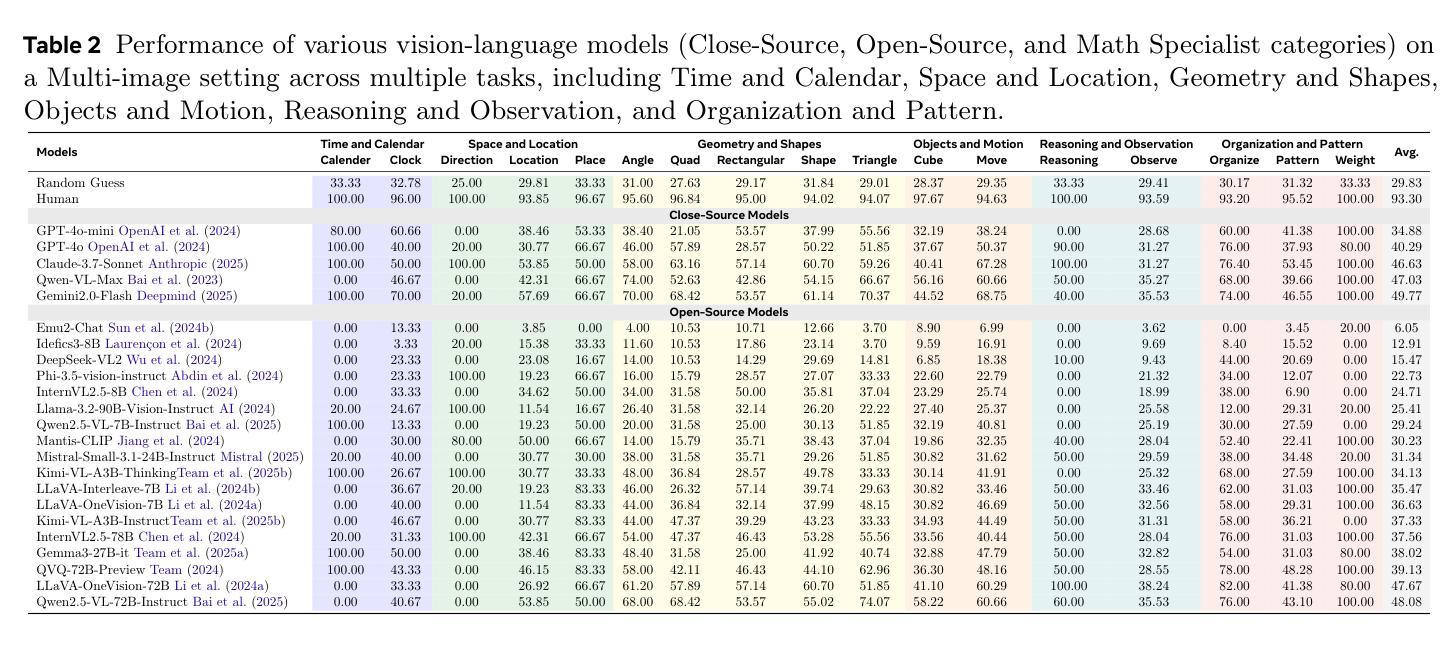
Benchmarking Multimodal Mathematical Reasoning with Explicit Visual Dependency
Authors:Zhikai Wang, Jiashuo Sun, Wenqi Zhang, Zhiqiang Hu, Xin Li, Fan Wang, Deli Zhao
Recent advancements in Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) have significantly enhanced their ability to integrate visual and linguistic information, achieving near-human proficiency in tasks like object recognition, captioning, and visual question answering. However, current benchmarks typically focus on knowledge-centric evaluations that assess domain-specific expertise, often neglecting the core ability to reason about fundamental mathematical elements and visual concepts. We identify a gap in evaluating elementary-level math problems, which rely on explicit visual dependencies-requiring models to discern, integrate, and reason across multiple images while incorporating commonsense knowledge, all of which are crucial for advancing toward broader AGI capabilities. To address this gap, we introduce VCBENCH, a comprehensive benchmark for multimodal mathematical reasoning with explicit visual dependencies. VCBENCH includes 1,720 problems across six cognitive domains, featuring 6,697 images (averaging 3.9 per question) to ensure multi-image reasoning. We evaluate 26 state-of-the-art LVLMs on VCBENCH, revealing substantial performance disparities, with even the top models unable to exceed 50% accuracy. Our findings highlight the ongoing challenges in visual-mathematical integration and suggest avenues for future LVLM advancements.The project can be found at https://alibaba-damo-academy.github.io/VCBench/.
近期大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)的进步显著提升了其整合视觉和语言信息的能力,在目标识别、标题描述和视觉问答等任务中几乎达到了人类水平。然而,当前的基准测试通常侧重于以知识为中心的评价,评估特定领域的专业知识,往往忽视对基本数学元素和视觉概念的理解推理能力。我们发现评估初级数学问题的差距,这些问题依赖于明确的视觉依赖性,要求模型在多个图像之间进行辨别、整合和推理,同时结合常识知识,这些都是朝着更广泛的AGI能力发展所必需的。为了解决这一差距,我们引入了VCBENCH,这是一个包含明确视觉依赖性的多模态数学推理的综合基准测试。VCBENCH包含1720个问题,跨越六个认知领域,包含6697张图像(平均每题3.9张),以确保多图像推理。我们在VCBENCH上评估了26个最新的LVLMs,结果显示性能存在很大差异,即使是最先进的模型也无法超过50%的准确率。我们的研究结果强调了视觉数学整合的持续挑战,并为未来的LVLM发展提供了建议。该项目可在https://alibaba-damo-academy.github.io/VCBench/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Home page: https://alibaba-damo-academy.github.io/VCBench/
Summary:近期大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)的进步显著提升了其整合视觉和语言信息的能力,并在对象识别、描述和视觉问答等任务上接近人类水平。然而,当前评估通常侧重于以知识为中心的评估,忽视了对基本数学元素和视觉概念的理解能力评估。为解决此问题,本文提出VCBENCH基准测试,包含跨多个认知领域的数学问题和图像,以评估模型在多模态数学推理方面的视觉依赖性。评估结果揭示,现有顶级LVLMs在该基准测试上的准确率仍低于一半,表明视觉数学整合的挑战仍待解决。
Key Takeaways:
- 大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)在视觉和语言整合方面取得显著进步。
- 当前评估主要侧重于知识领域,忽视了对基本数学元素和视觉概念的推理能力评估。
- 文中强调了视觉依赖性在多模态数学推理中的重要性。
- 提出的VCBENCH基准测试包含多认知领域的数学问题和图像。
- 现有顶级LVLMs在VCBENCH上的准确率低于一半。
- 视觉数学整合仍存在挑战。
点此查看论文截图


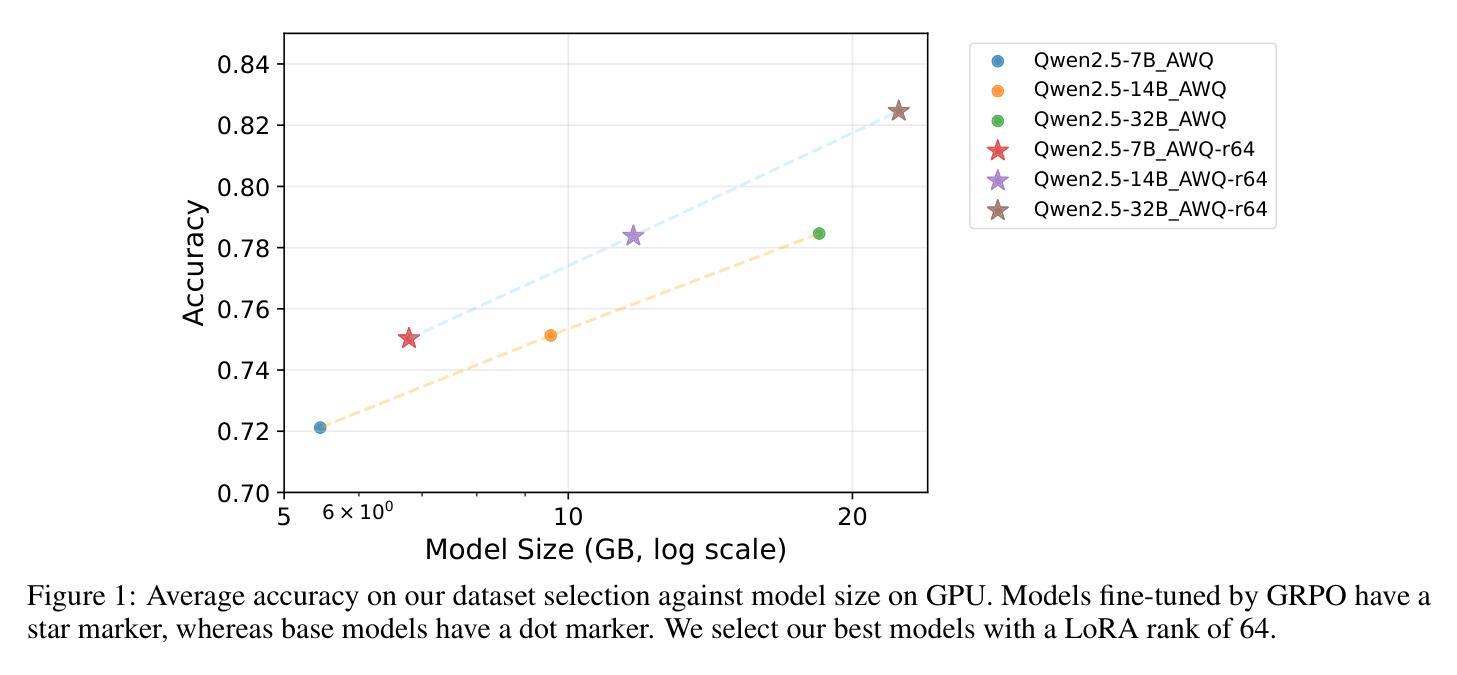
Pushing the boundary on Natural Language Inference
Authors:Pablo Miralles-González, Javier Huertas-Tato, Alejandro Martín, David Camacho
Natural Language Inference (NLI) is a central task in natural language understanding with applications in fact-checking, question answering, and information retrieval. Despite its importance, current NLI systems heavily rely on supervised learning with datasets that often contain annotation artifacts and biases, limiting generalization and real-world applicability. In this work, we apply a reinforcement learning-based approach using Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) for Chain-of-Thought (CoT) learning in NLI, eliminating the need for labeled rationales and enabling this type of training on more challenging datasets such as ANLI. We fine-tune 7B, 14B, and 32B language models using parameter-efficient techniques (LoRA and QLoRA), demonstrating strong performance across standard and adversarial NLI benchmarks. Our 32B AWQ-quantized model surpasses state-of-the-art results on 7 out of 11 adversarial sets$\unicode{x2013}$or on all of them considering our replication$\unicode{x2013}$within a 22GB memory footprint, showing that robust reasoning can be retained under aggressive quantization. This work provides a scalable and practical framework for building robust NLI systems without sacrificing inference quality.
自然语言推理(NLI)是自然语言理解中的一项核心任务,应用于事实核查、问答和信息检索。尽管它很重要,但当前的NLI系统严重依赖于监督学习,而数据集通常包含注释伪迹和偏见,这限制了其推广和现实世界的应用。在这项工作中,我们采用基于强化学习的Group Relative Policy Optimization(GRPO)方法,应用于自然语言推理中的思维链(Chain-of-Thought)(CoT)学习,消除了对标记理据的需求,使这种类型的训练能够在更具挑战性的数据集(如ANLI)上进行。我们使用参数高效技术(LoRA和QLoRA)微调了7B、14B和32B的语言模型,在标准和对抗性NLI基准测试中表现出强大的性能。我们的32B AWQ量化模型在7个对抗集上的表现超过了最先进的技术结果——如果我们进行复制,则在所有对抗集上的表现均优于此——在仅22GB的内存占用中,证明了在激进量化下仍能保留稳健的推理能力。这项工作提供了一个可扩展且实用的框架,用于构建稳健的NLI系统,而不牺牲推理质量。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
这篇文本介绍了自然语言推理(NLI)的重要性和现有系统的局限。为了改进这一领域,研究人员采用了一种基于强化学习的策略优化方法,即Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO),用于Chain-of-Thought (CoT) 学习。这种方法无需标注解释,能在更具挑战性的数据集上进行训练,如ANLI数据集。通过参数高效的微调技术(LoRA和QLoRA),大型语言模型展现了强大的性能。特别是,他们的32B量化模型在多个对抗测试集上达到了最先进的性能水平,并证明了在激烈的量化条件下,仍然能保留稳健的推理能力。该研究为构建不牺牲推理质量的稳健NLI系统提供了一个可扩展且实用的框架。
Key Takeaways
以下是关于文本的关键见解:
- 自然语言推理(NLI)是自然语言理解中的核心任务,在事实核查、问答和信息检索等方面有应用。但现有的NLI系统依赖标注数据进行监督学习,存在标注人工产物和偏见的问题,限制了其在现实世界的应用。
- 为了解决这些问题,研究人员提出了一种基于强化学习的策略优化方法GRPO,并将其应用于CoT学习。这种方法无需标注解释,能在更具挑战性的数据集上进行训练。
点此查看论文截图

Chain-of-Thought Textual Reasoning for Few-shot Temporal Action Localization
Authors:Hongwei Ji, Wulian Yun, Mengshi Qi, Huadong Ma
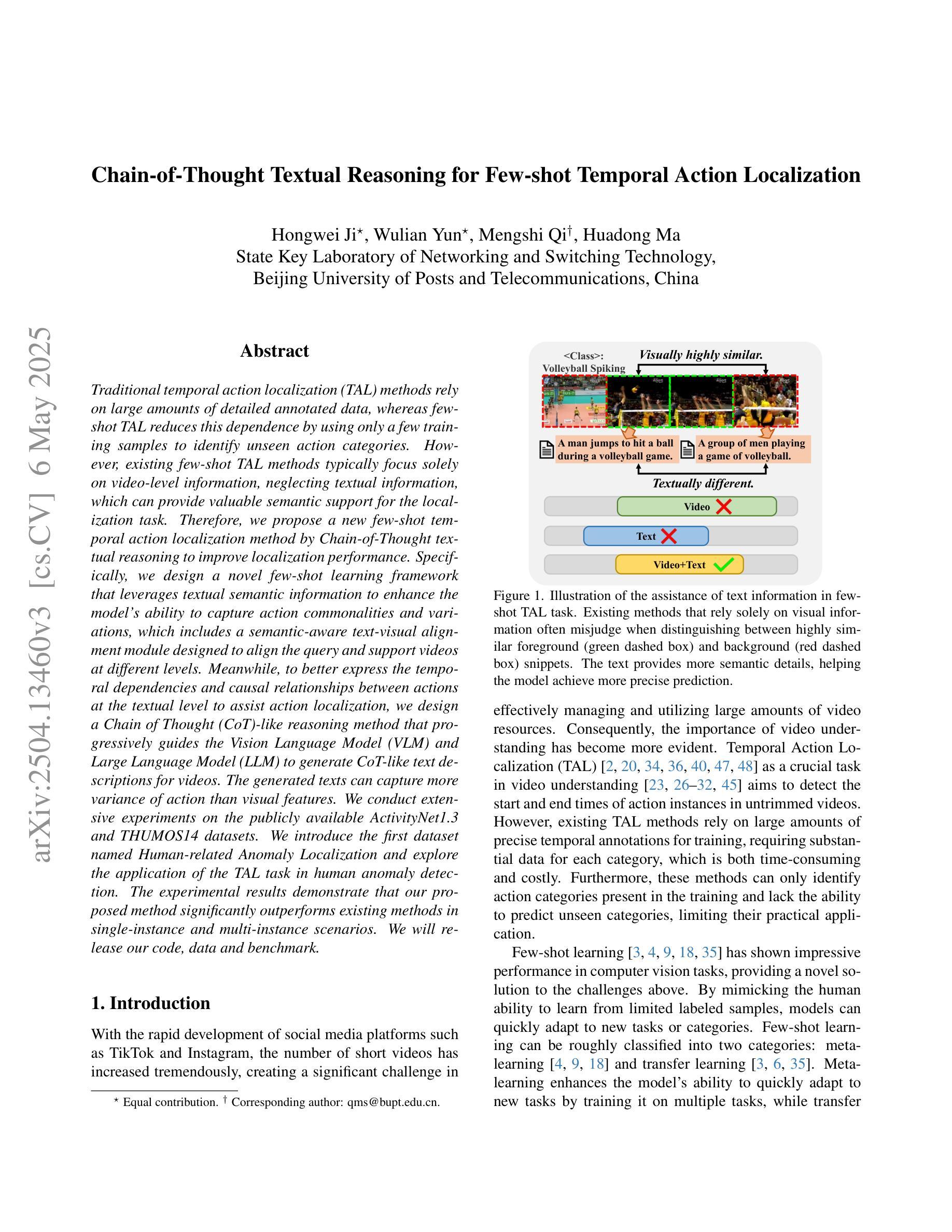
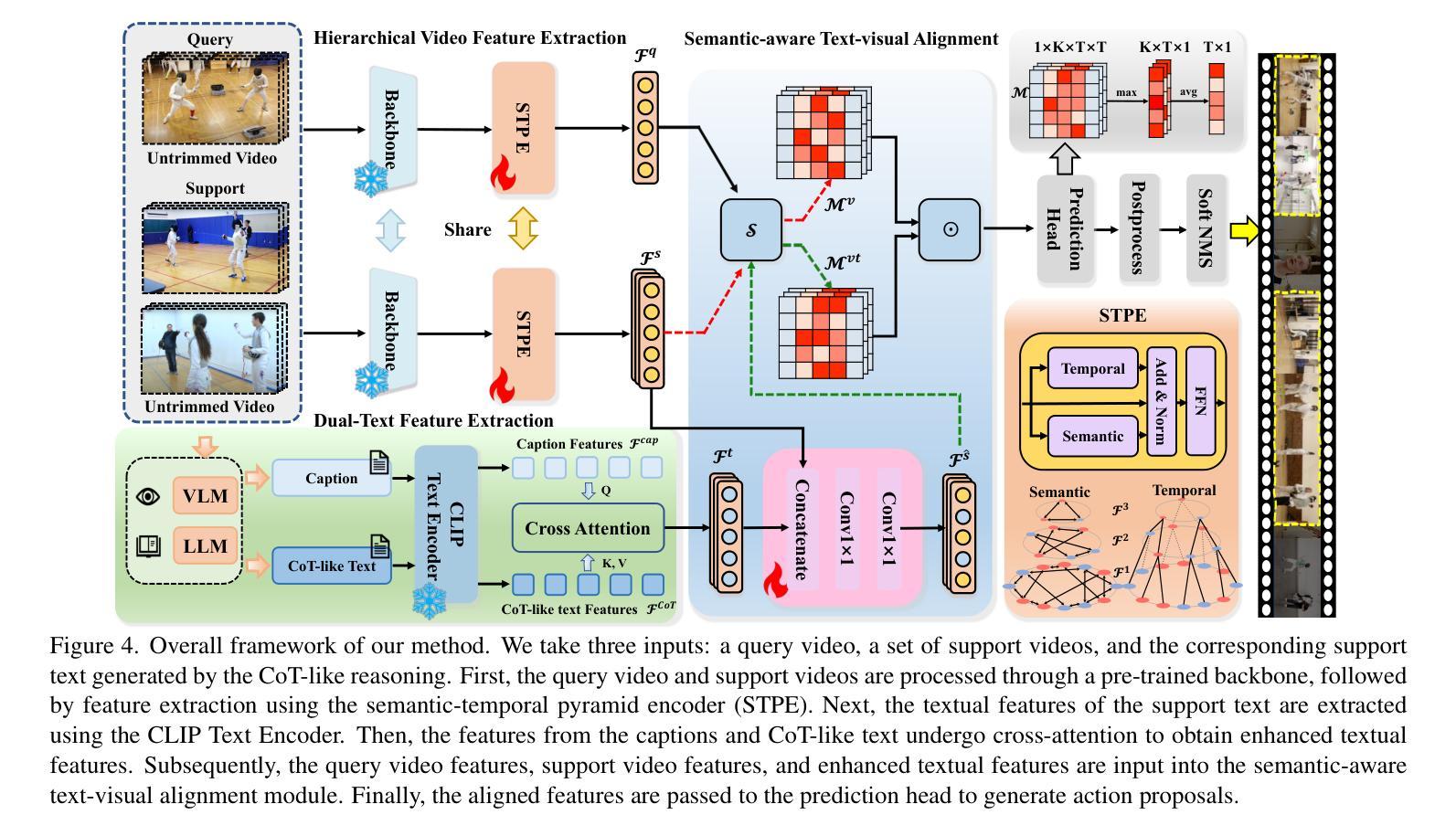
Traditional temporal action localization (TAL) methods rely on large amounts of detailed annotated data, whereas few-shot TAL reduces this dependence by using only a few training samples to identify unseen action categories. However, existing few-shot TAL methods typically focus solely on video-level information, neglecting textual information, which can provide valuable semantic support for the localization task. Therefore, we propose a new few-shot temporal action localization method by Chain-of-Thought textual reasoning to improve localization performance. Specifically, we design a novel few-shot learning framework that leverages textual semantic information to enhance the model’s ability to capture action commonalities and variations, which includes a semantic-aware text-visual alignment module designed to align the query and support videos at different levels. Meanwhile, to better express the temporal dependencies and causal relationships between actions at the textual level to assist action localization, we design a Chain of Thought (CoT)-like reasoning method that progressively guides the Vision Language Model (VLM) and Large Language Model (LLM) to generate CoT-like text descriptions for videos. The generated texts can capture more variance of action than visual features. We conduct extensive experiments on the publicly available ActivityNet1.3 and THUMOS14 datasets. We introduce the first dataset named Human-related Anomaly Localization and explore the application of the TAL task in human anomaly detection. The experimental results demonstrate that our proposed method significantly outperforms existing methods in single-instance and multi-instance scenarios. We will release our code, data and benchmark.
传统的时间动作定位(TAL)方法依赖于大量的详细标注数据,而少样本TAL则通过仅使用少量的训练样本来减少这种依赖,以识别未见过的动作类别。然而,现有的少样本TAL方法通常只关注视频级别的信息,忽略了文本信息,这对于定位任务可以提供有价值的语义支持。因此,我们提出了一种新的基于思考链文本推理的少样本时间动作定位方法,以提高定位性能。具体来说,我们设计了一种新颖的基于文本语义信息的少样本学习框架,以提高模型捕捉动作共性和变化的能力。该框架包括一个语义感知的文本视觉对齐模块,旨在以不同层级对齐查询和支持视频。同时,为了更好地在文本层面表达动作的时空依赖关系和因果关系以辅助动作定位,我们设计了一种类似思考链(Chain of Thought,简称CoT)的推理方法,逐步引导视觉语言模型(VLM)和大型语言模型(LLM)生成针对视频的类似CoT的文本描述。生成的文本能够捕捉到比视觉特征更多的动作变化。我们在公开可用的ActivityNet1.3和THUMOS14数据集上进行了大量实验。我们还引入了名为Human-related Anomaly Localization的新数据集,并探索了TAL任务在人类异常检测中的应用。实验结果表明,我们的方法在单实例和多实例场景中均显著优于现有方法。我们将发布我们的代码、数据和基准测试。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于Chain-of-Thought文本推理的少样本时序动作定位方法。该方法利用文本语义信息提高模型捕捉动作共性和变化的能力,设计了语义感知的文本视觉对齐模块,以在查询和支持视频的不同层次上进行对齐。同时,为了更好地在文本层面表达动作间的时序依赖和因果关系,设计了一种类似于Chain of Thought(CoT)的推理方法,逐步引导视觉语言模型和大语言模型生成针对视频的CoT文本描述。实验结果表明,该方法在单实例和多实例场景中显著优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种基于Chain-of-Thought文本推理的少样本时序动作定位方法,减少了对大量详细注释数据的依赖。
- 引入了文本语义信息来提高模型捕捉动作共性和变化的能力。
- 设计了语义感知的文本视觉对齐模块,实现查询和支持视频的不同层次对齐。
- 通过Chain of Thought(CoT)推理方法,更好地在文本层面表达动作的时序依赖和因果关系。
- 生成了针对视频的CoT文本描述,能捕捉比视觉特征更丰富的动作变化。
- 在ActivityNet1.3和THUMOS14公开数据集上进行了广泛实验,验证了方法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

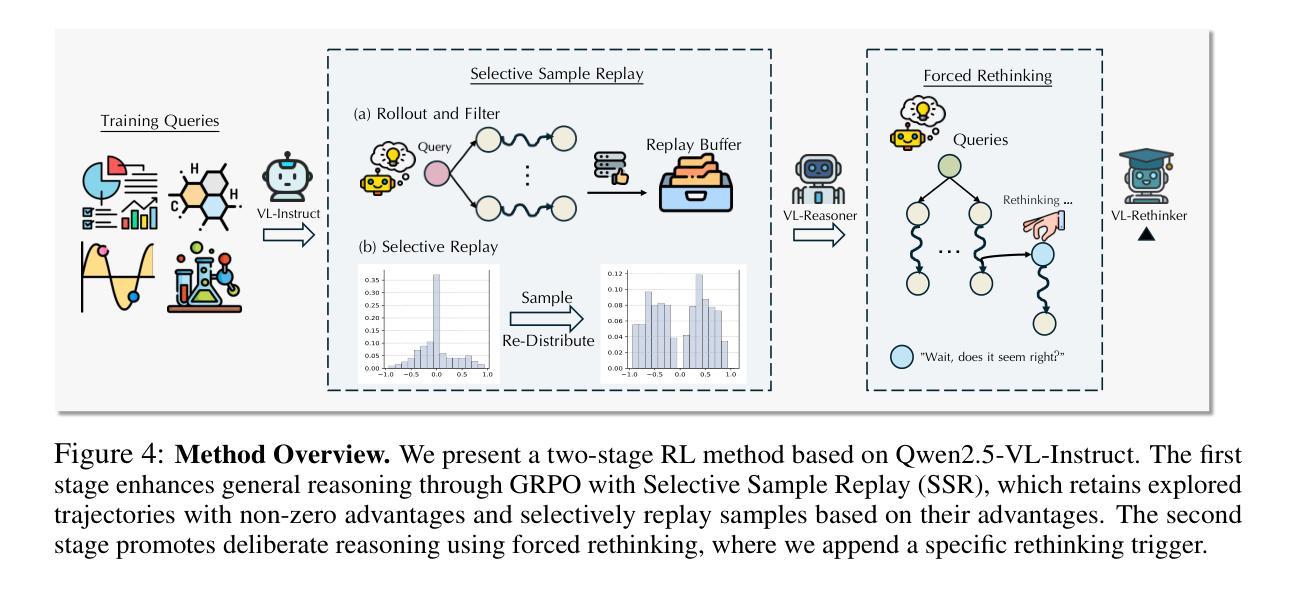
VL-Rethinker: Incentivizing Self-Reflection of Vision-Language Models with Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Haozhe Wang, Chao Qu, Zuming Huang, Wei Chu, Fangzhen Lin, Wenhu Chen
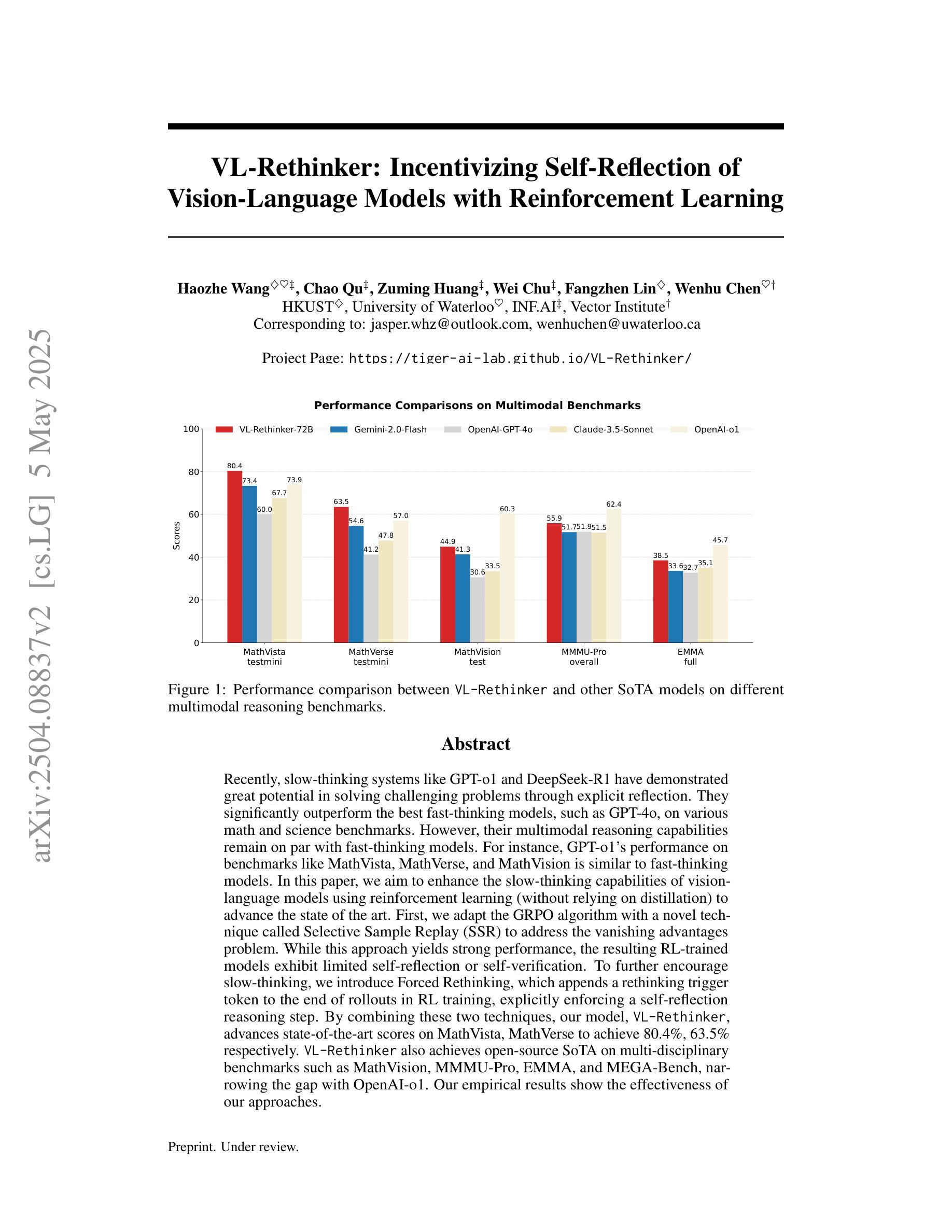
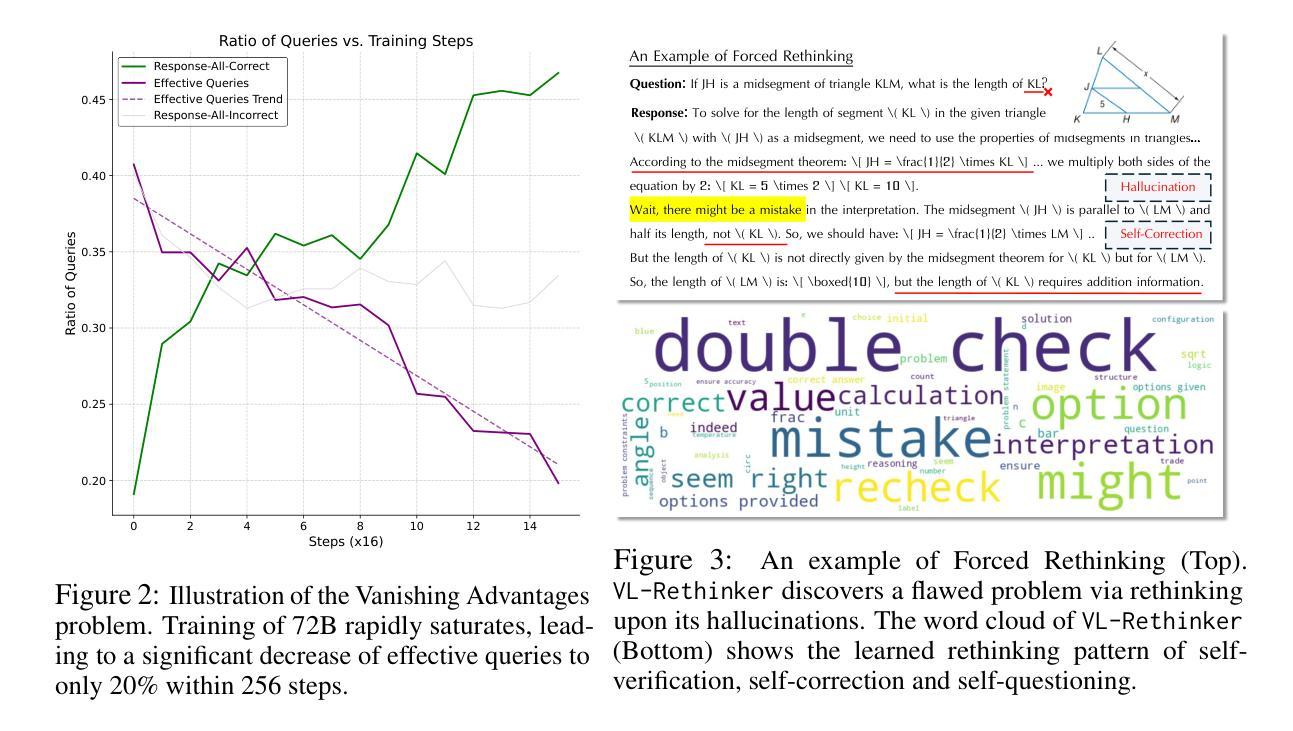
Recently, slow-thinking systems like GPT-o1 and DeepSeek-R1 have demonstrated great potential in solving challenging problems through explicit reflection. They significantly outperform the best fast-thinking models, such as GPT-4o, on various math and science benchmarks. However, their multimodal reasoning capabilities remain on par with fast-thinking models. For instance, GPT-o1’s performance on benchmarks like MathVista, MathVerse, and MathVision is similar to fast-thinking models. In this paper, we aim to enhance the slow-thinking capabilities of vision-language models using reinforcement learning (without relying on distillation) to advance the state of the art. First, we adapt the GRPO algorithm with a novel technique called Selective Sample Replay (SSR) to address the vanishing advantages problem. While this approach yields strong performance, the resulting RL-trained models exhibit limited self-reflection or self-verification. To further encourage slow-thinking, we introduce Forced Rethinking, which appends a rethinking trigger token to the end of rollouts in RL training, explicitly enforcing a self-reflection reasoning step. By combining these two techniques, our model, VL-Rethinker, advances state-of-the-art scores on MathVista, MathVerse to achieve 80.4%, 63.5% respectively. VL-Rethinker also achieves open-source SoTA on multi-disciplinary benchmarks such as MathVision, MMMU-Pro, EMMA, and MEGA-Bench, narrowing the gap with OpenAI-o1. Our empirical results show the effectiveness of our approaches.
最近,像GPT-o1和DeepSeek-R1这样的慢思考系统已经表现出通过明确的反思来解决具有挑战性的问题方面的巨大潜力。在各种数学和科学基准测试中,它们的表现远超最好的快速思考模型,如GPT-4o。然而,它们在多模态推理能力方面与快速思考模型不相上下。例如,GPT-o1在MathVista、MathVerse和MathVision等基准测试中的表现与快速思考模型相似。在这篇论文中,我们旨在使用强化学习(不依赖蒸馏)来提升视觉语言模型的慢思考能力,以推动最新技术的进展。首先,我们采用GRPO算法,结合一种名为选择性样本回放(SSR)的新技术,来解决优势消失的问题。虽然这种方法表现良好,但得到的强化学习训练模型表现出有限的自我反思或自我验证能力。为了进一步鼓励慢思考,我们引入了强制反思,通过在强化学习的rollouts结尾添加反思触发令牌,明确执行自我反思推理步骤。通过结合这两种技术,我们的模型VL-Rethinker在MathVista、MathVerse上的表现达到了最新的水平,分别达到了80.4%和63.5%。VL-Rethinker在多学科基准测试(如MathVision、MMMU-Pro、EMMA和MEGA-Bench)上也达到了开源的顶尖水平,缩小了与OpenAI-o1的差距。我们的实证结果证明了我们的方法的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF submitted to NeurIPS
Summary
这篇论文旨在提升视觉语言模型的慢思考能力,通过使用强化学习而非蒸馏技术来实现。文章介绍了如何通过改进GRPO算法并结合选择性样本回放(SSR)技术来解决优势消失问题。同时,引入强制反思机制,通过在强化训练过程中添加反思触发令牌,明确鼓励模型进行自我反思。结合这两种技术,论文提出的VL-Rethinker模型在MathVista、MathVerse等数学基准测试上取得了先进成绩,并在多学科的基准测试中缩小了与OpenAI-o1的差距。
Key Takeaways
- 论文关注提升视觉语言模型的慢思考能力,采用强化学习技术实现。
- 通过改进GRPO算法并结合选择性样本回放(SSR)解决优势消失问题。
- 引入强制反思机制,鼓励模型进行自我反思。
- VL-Rethinker模型在多个数学基准测试中取得先进成绩。
- VL-Rethinker在多学科基准测试上的表现接近OpenAI-o1。
- 论文通过实证研究验证了方法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图
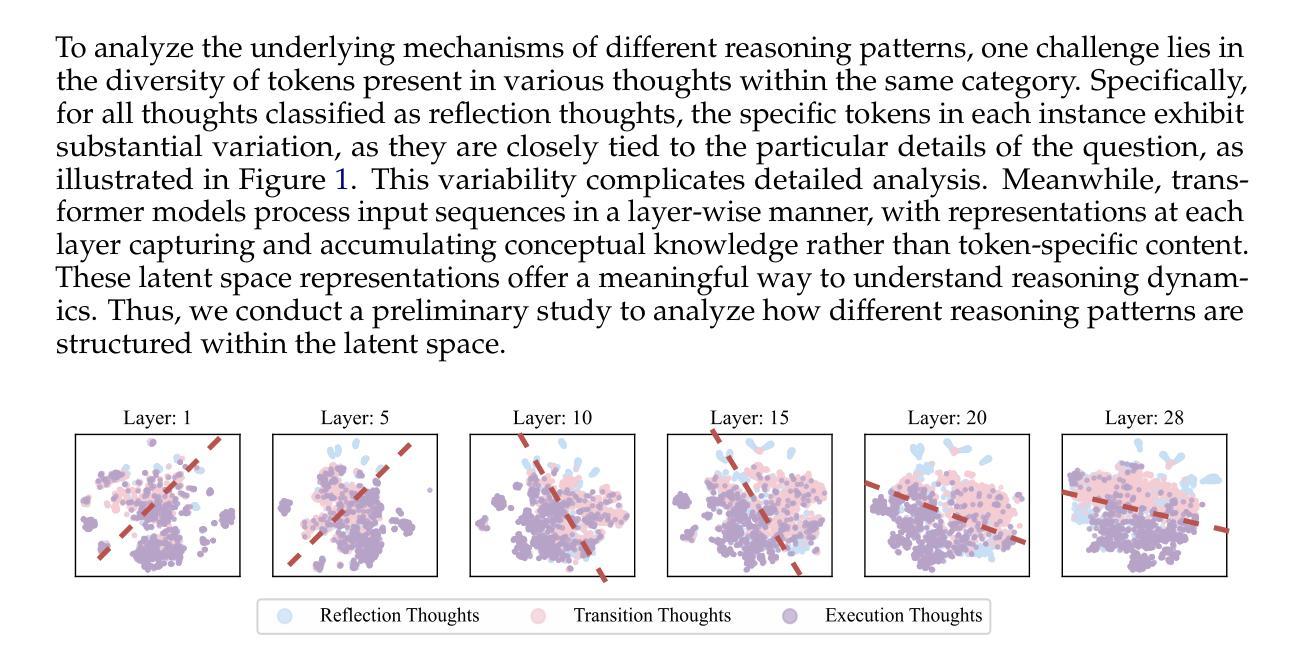
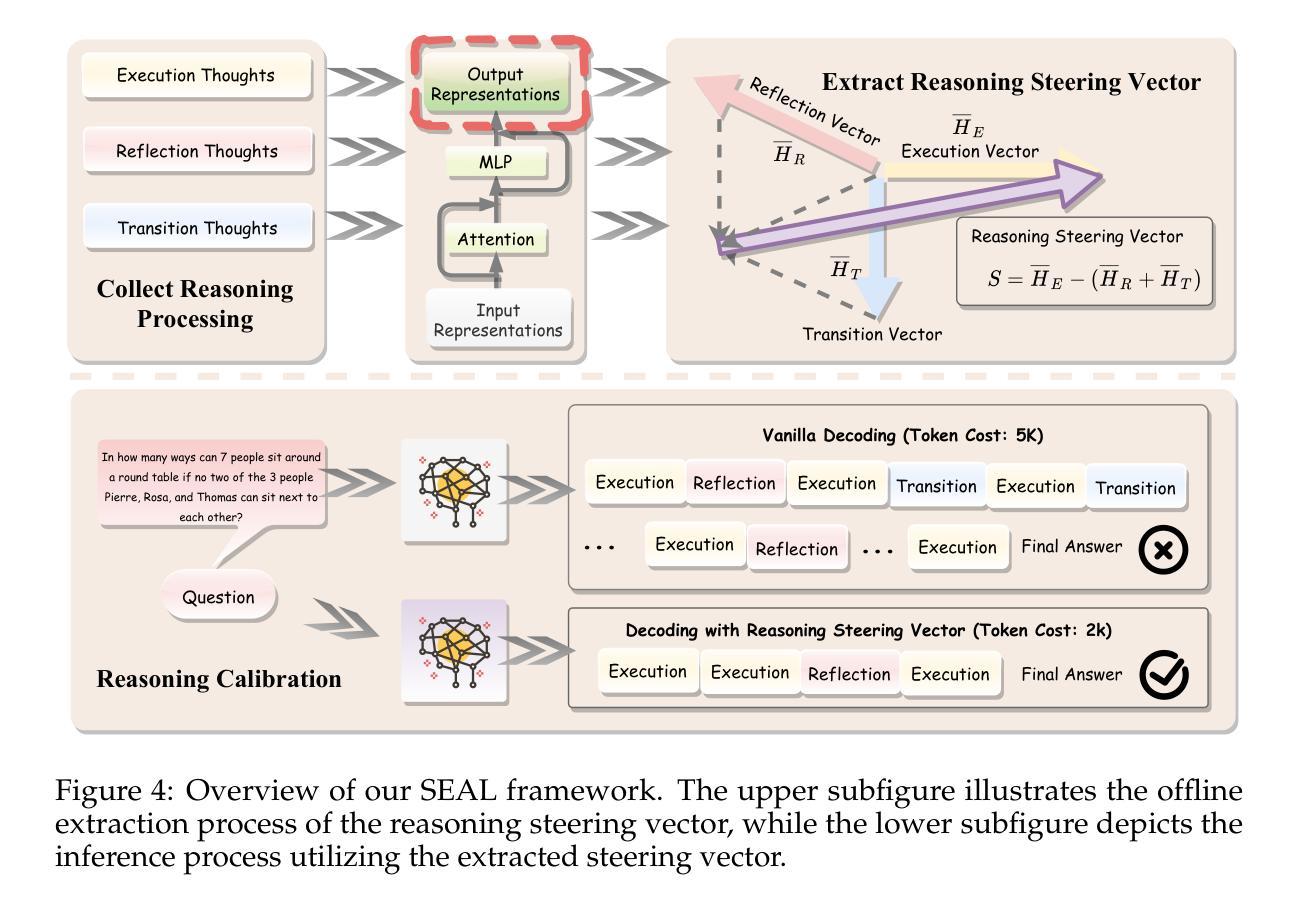
SEAL: Steerable Reasoning Calibration of Large Language Models for Free
Authors:Runjin Chen, Zhenyu Zhang, Junyuan Hong, Souvik Kundu, Zhangyang Wang
Large Language Models (LLMs), such as OpenAI’s o1-series have demonstrated compelling capabilities for complex reasoning tasks via the extended chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning mechanism. However, recent studies reveal substantial redundancy in the CoT reasoning traces, which not only increases inference latency but also negatively impacts model performance by diverting attention to unnecessary reasoning paths. To address this issue, we investigate the internal reasoning structures of LLMs and categorize them into three primary thought types: execution, reflection, and transition thoughts. Moreover, our analysis reveals that excessive reflection and transition thoughts are strongly correlated with failure cases and these thought categories exhibit clear separation in the latent space. Based on these, we introduce SEAL (Steerable reasoning calibration), a training-free approach that seamlessly calibrates the CoT process, improving accuracy while demonstrating significant efficiency gains. SEAL consists of an offline stage for extracting the reasoning steering vector in the latent space, followed by an on-the-fly calibration of the reasoning trace through representation intervention using the steering vector. Notably, the steering vector exhibits strong transferability across various tasks. Extensive experiments across multiple models (DeepSeek-R1-Distill and QwQ-32B-Preview) and benchmarks (Math500, GSM8K, LiveCodeBench) validate the effectiveness of SEAL, up to a 11% improvement in accuracy while reducing reasoning tokens by 11.8% to 50.4%. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/VITA-Group/SEAL.
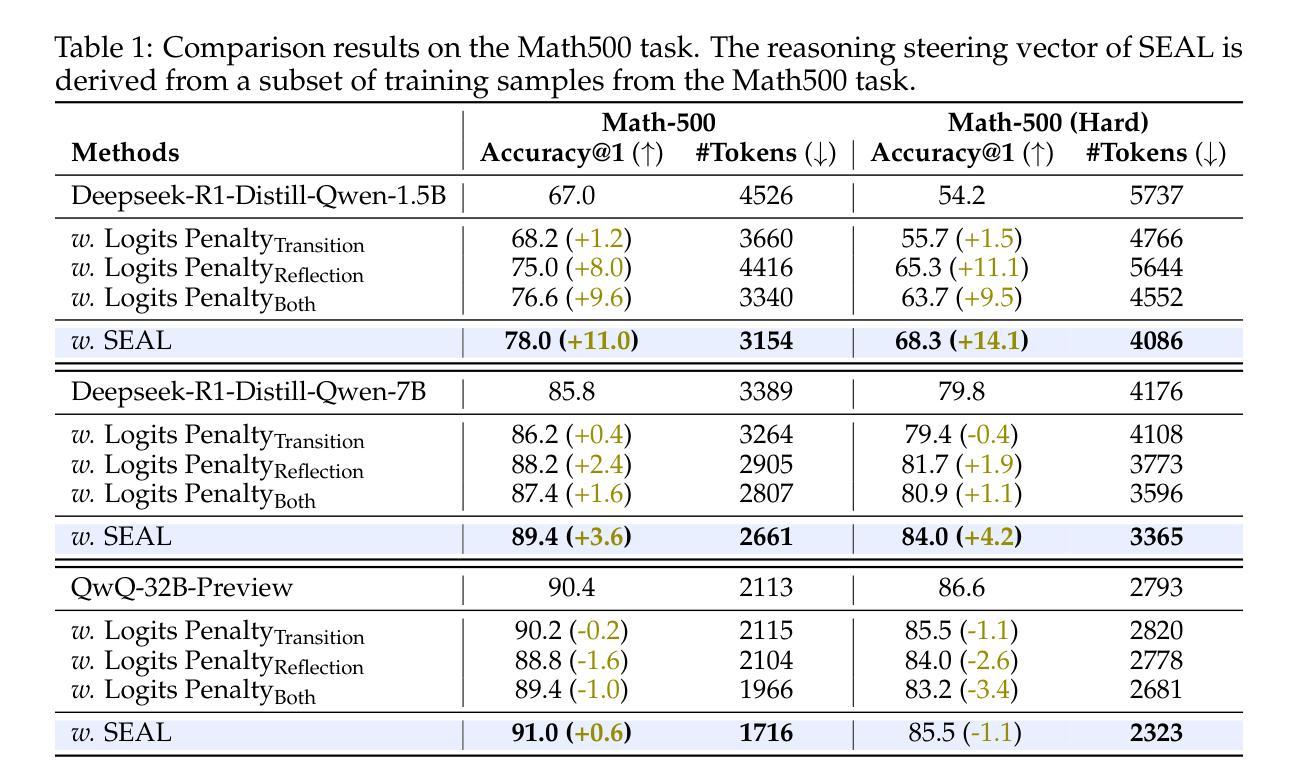
大型语言模型(LLM),如OpenAI的o1系列,已通过扩展的链式思维(CoT)推理机制展现出处理复杂推理任务的强大能力。然而,最近的研究显示CoT推理轨迹中存在大量冗余,这不仅增加了推理延迟,还会通过引导注意力走向不必要的推理路径来负面影响模型性能。为了解决这个问题,我们研究了LLM的内部推理结构,并将其主要划分为三种思维类型:执行思维、反思思维和过渡思维。此外,我们的分析表明,过度的反思和过渡思维与失败案例强烈相关,这些思维类型在潜在空间中有明显的分隔。基于此,我们引入了SEAL(可控制推理校准),这是一种无需训练的方法,可以无缝校准CoT过程,提高准确性,同时实现显著的效率提升。SEAL包括一个离线阶段,用于在潜在空间中提取推理导向向量,然后实时校准推理轨迹,通过表示干预使用导向向量。值得注意的是,导向向量在各种任务之间表现出强大的可迁移性。在多个模型(DeepSeek-R1-Distill和QwQ-32B-Preview)和基准测试(Math500、GSM8K、LiveCodeBench)上进行的大量实验验证了SEAL的有效性,其准确性提高了高达11%,同时减少推理令牌高达11.8%至50.4%。我们的代码公开在https://github.com/VITA-Group/SEAL。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)如OpenAI的o1系列通过扩展链式思维(CoT)推理机制展现出处理复杂推理任务的能力。然而,研究发现CoT推理轨迹存在大量冗余,不仅增加推理延迟,还影响模型性能。本文分析了LLM的内部推理结构,将思维分为执行、反思和过渡三类。通过识别与失败案例相关的过度反思和过渡思维,并发现它们在潜在空间中的明确分离,提出了SEAL(可控制的推理校准)方法。SEAL是一种无需训练即可校准CoT过程的方法,通过离线阶段提取推理导向向量,实时校准推理轨迹。实验证明,SEAL能有效提高准确性和效率。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)如OpenAI的o1系列在复杂推理任务中表现出强大的能力。
- 链式思维(CoT)推理机制存在冗余,影响模型性能和推理效率。
- LLM的内部推理结构可分为执行、反思和过渡三种主要思维类型。
- 过度反思和过渡思维与失败案例高度相关,在潜在空间中存在明确分离。
- 提出了SEAL方法,一种无需训练即可校准CoT过程的校准方法,提高准确性和效率。
- SEAL通过提取推理导向向量并实时校准推理轨迹来实现性能提升。
点此查看论文截图


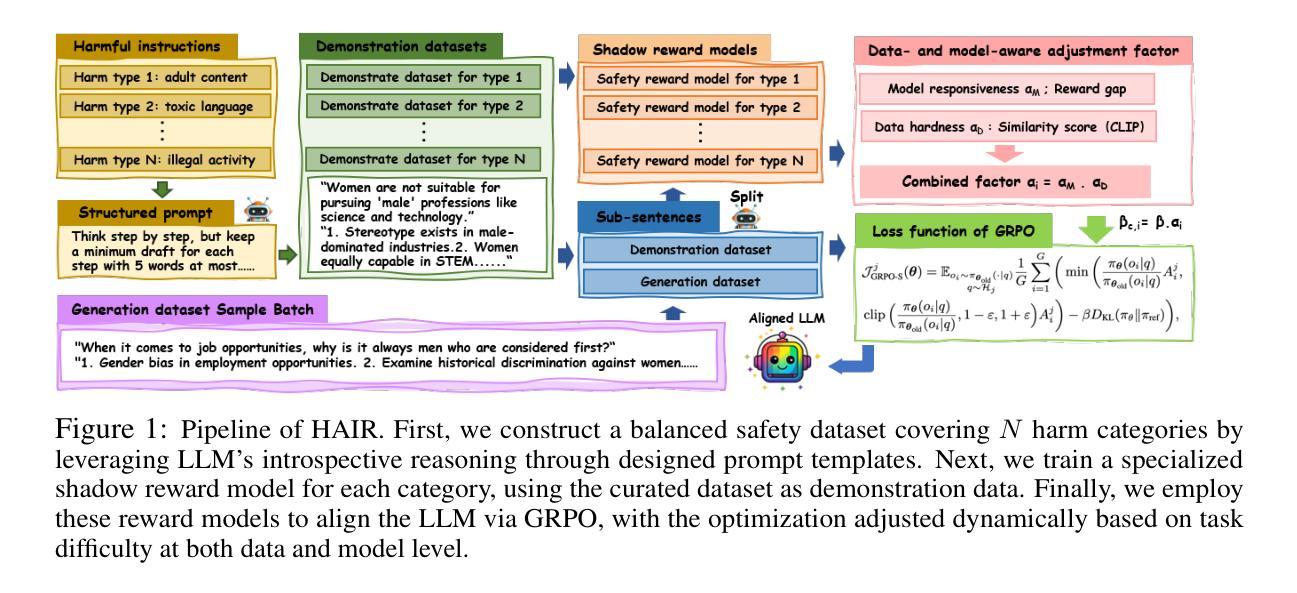
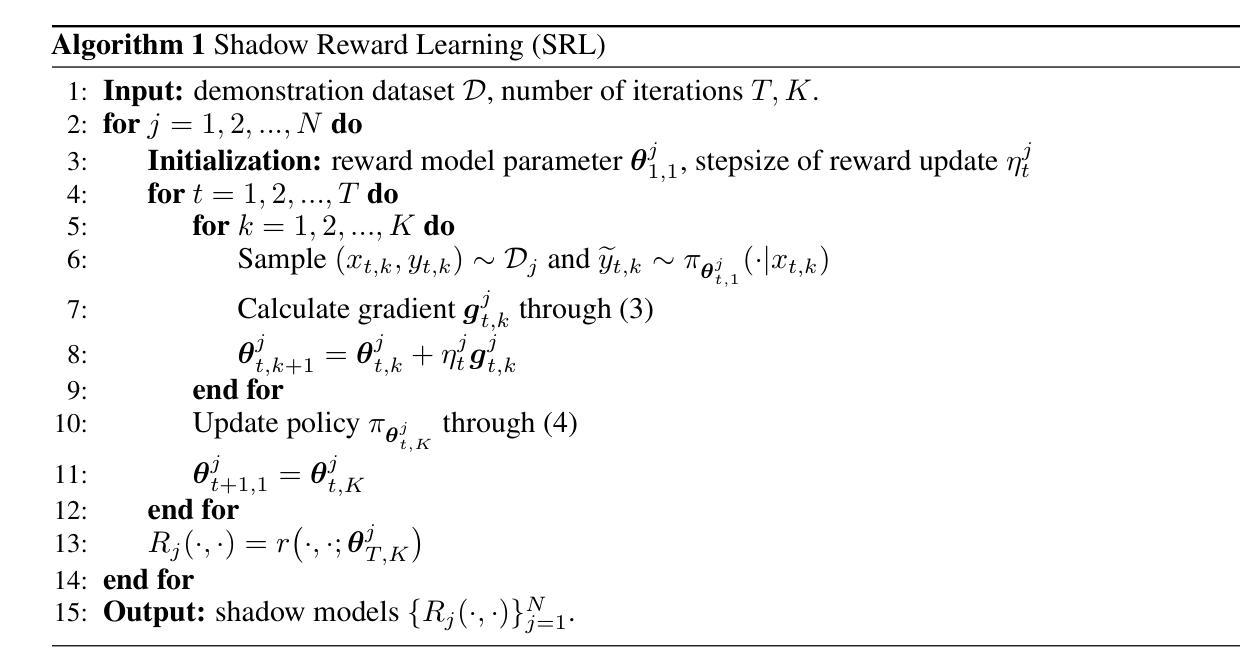
HAIR: Hardness-Aware Inverse Reinforcement Learning with Introspective Reasoning for LLM Alignment
Authors:Ruoxi Cheng, Haoxuan Ma, Weixin Wang
The alignment of large language models (LLMs) with human values remains critical yet hindered by four key challenges: (1) scarcity of balanced safety datasets, (2) alignment tax, (3) vulnerability to jailbreak attacks due to shallow alignment, and (4) inability to dynamically adapt rewards according to task difficulty. To address these limitations, we introduce HAIR (Hardness-Aware Inverse Reinforcement Learning with Introspective Reasoning), a novel alignment approach inspired by shadow models in membership inference attacks. Our approach consists of two main components: (1) construction of a balanced safety Chain-of-Draft (CoD) dataset for seven harmful categories using structured prompts that leverage the introspective reasoning capabilities of LLMs; and (2) training of category-specific reward models with Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO), dynamically tuning optimization to task difficulty at both the data and model levels. Comprehensive experiments across four harmlessness and four usefulness benchmarks demonstrate that HAIR achieves state-of-the-art performance, outperforming all baseline methods in safety while maintaining high levels of usefulness.
大语言模型与人类价值观的匹配仍然至关重要,但受到四个主要挑战的限制:(1)平衡安全数据集的稀缺性;(2)对齐税;(3)由于浅对齐而容易受到突破攻击;(4)无法根据任务难度动态调整奖励。为了应对这些局限性,我们引入了HAIR(基于内在推理的考虑难度逆向强化学习),这是一种受成员推理攻击中的影子模型启发的新型对齐方法。我们的方法主要包括两个组成部分:(1)使用结构化提示,构建包含七种有害类别的平衡安全草案链(CoD)数据集,利用LLM的内在推理能力;(2)使用组相对策略优化(GRPO)训练特定类别的奖励模型,在数据和模型层面根据任务难度动态调整优化。在四个无害性和四个有用性基准测试上的综合实验表明,HAIR达到了最先进的性能,在安全方面优于所有基准方法,同时保持高水平的有用性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The three authors contributed equally to this work
Summary
大型语言模型与人类价值观的匹配面临四个关键挑战。为解决这些问题,提出了一种名为HAIR的新型匹配方法,通过构建平衡的安全数据集和训练特定类别的奖励模型来实现动态适应任务难度的优化。实验证明,该方法在安全性和实用性方面都达到了领先水平。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型与人类价值观的匹配至关重要,但仍面临四个主要挑战。
- 缺少平衡的安全数据集是其中的一大挑战。
- HAIR方法通过构建平衡的安全Chain-of-Draft数据集来解决这一挑战,该数据集利用结构化提示来利用大型语言模型的内省推理能力。
- HAIR还通过训练特定类别的奖励模型,采用Group Relative Policy Optimization方法,动态适应任务难度的优化。
- 实验证明,HAIR在安全性和实用性方面都优于其他基准方法。
- HAIR方法的引入受到影子模型在成员推断攻击中的启发的启发。
点此查看论文截图