⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-09 更新
SwinLip: An Efficient Visual Speech Encoder for Lip Reading Using Swin Transformer
Authors:Young-Hu Park, Rae-Hong Park, Hyung-Min Park
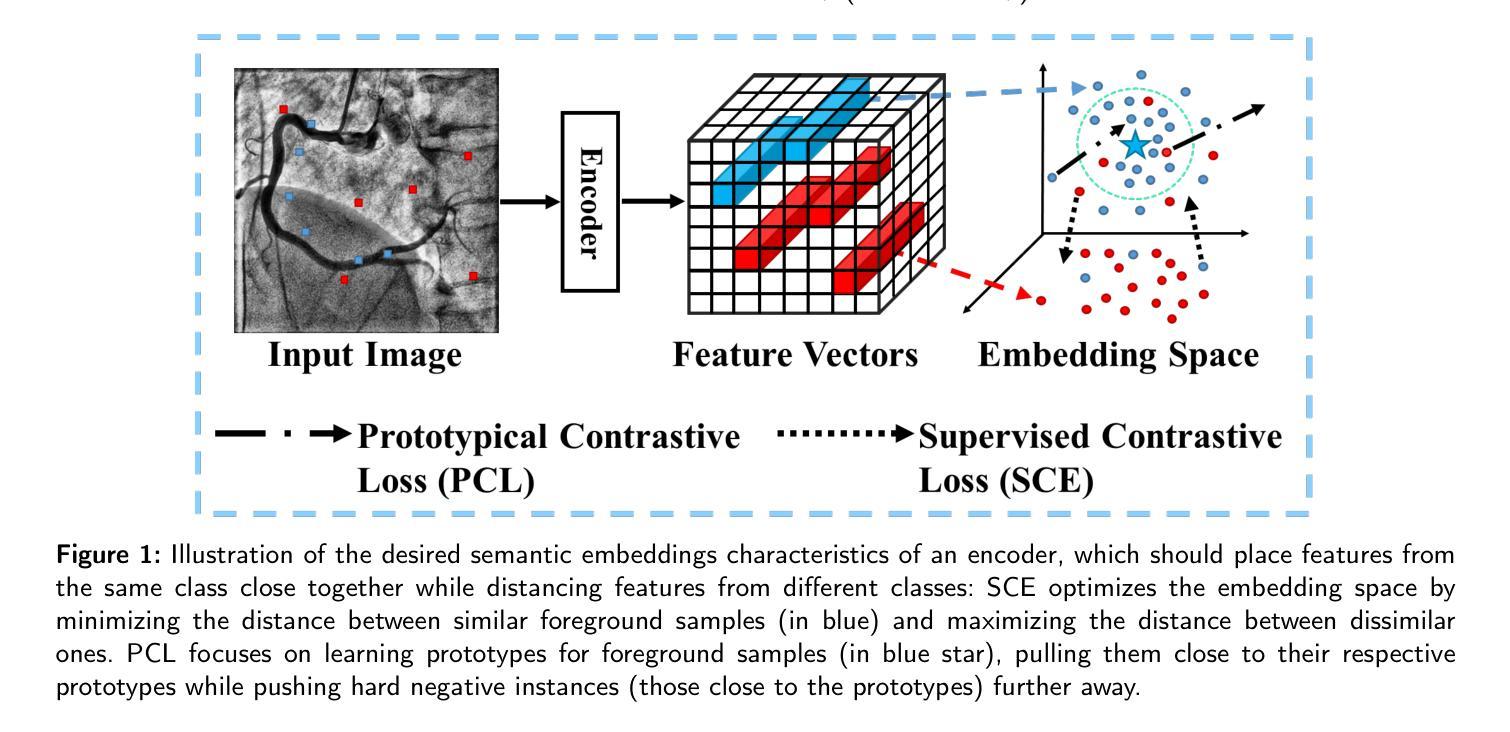
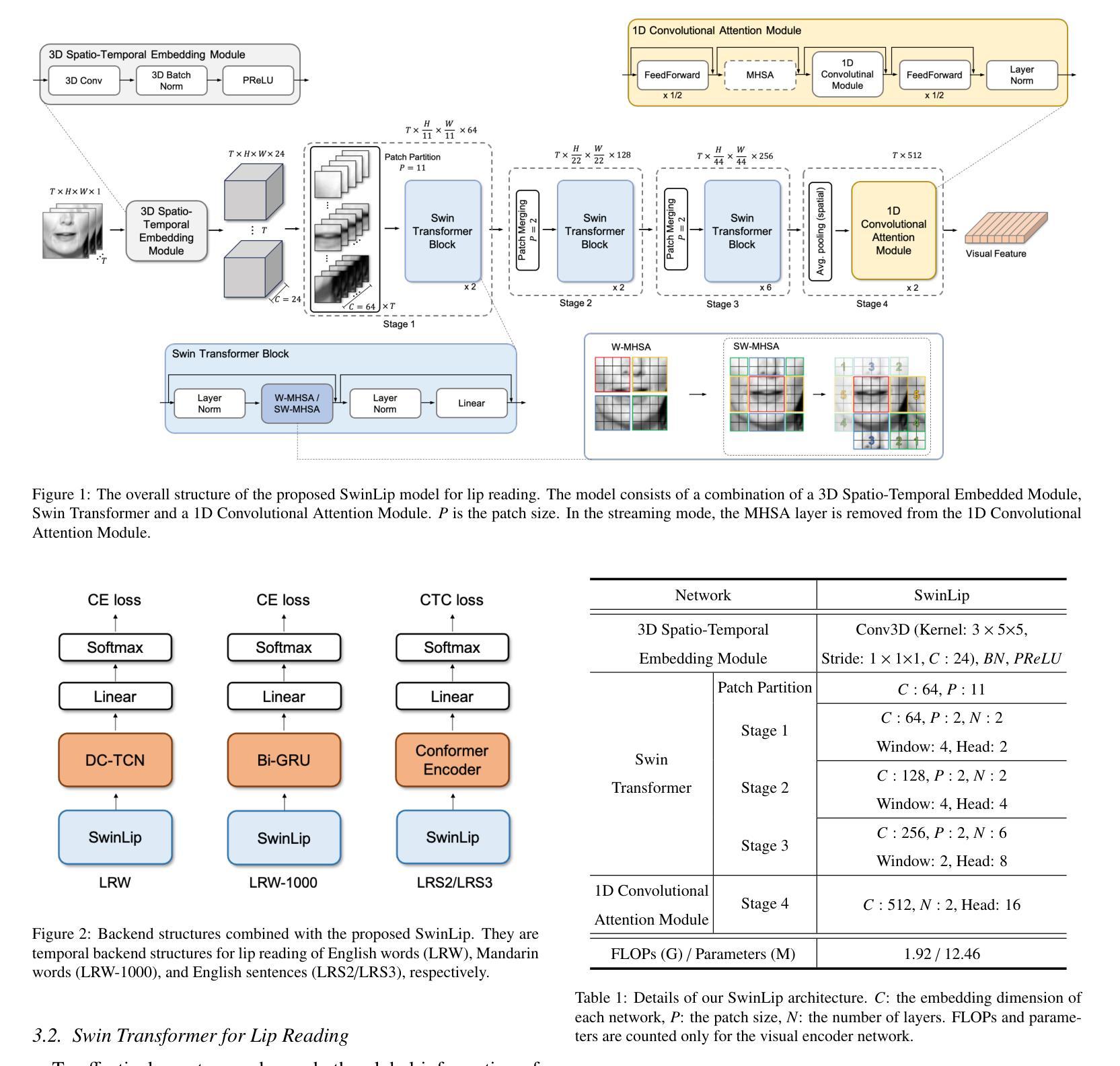
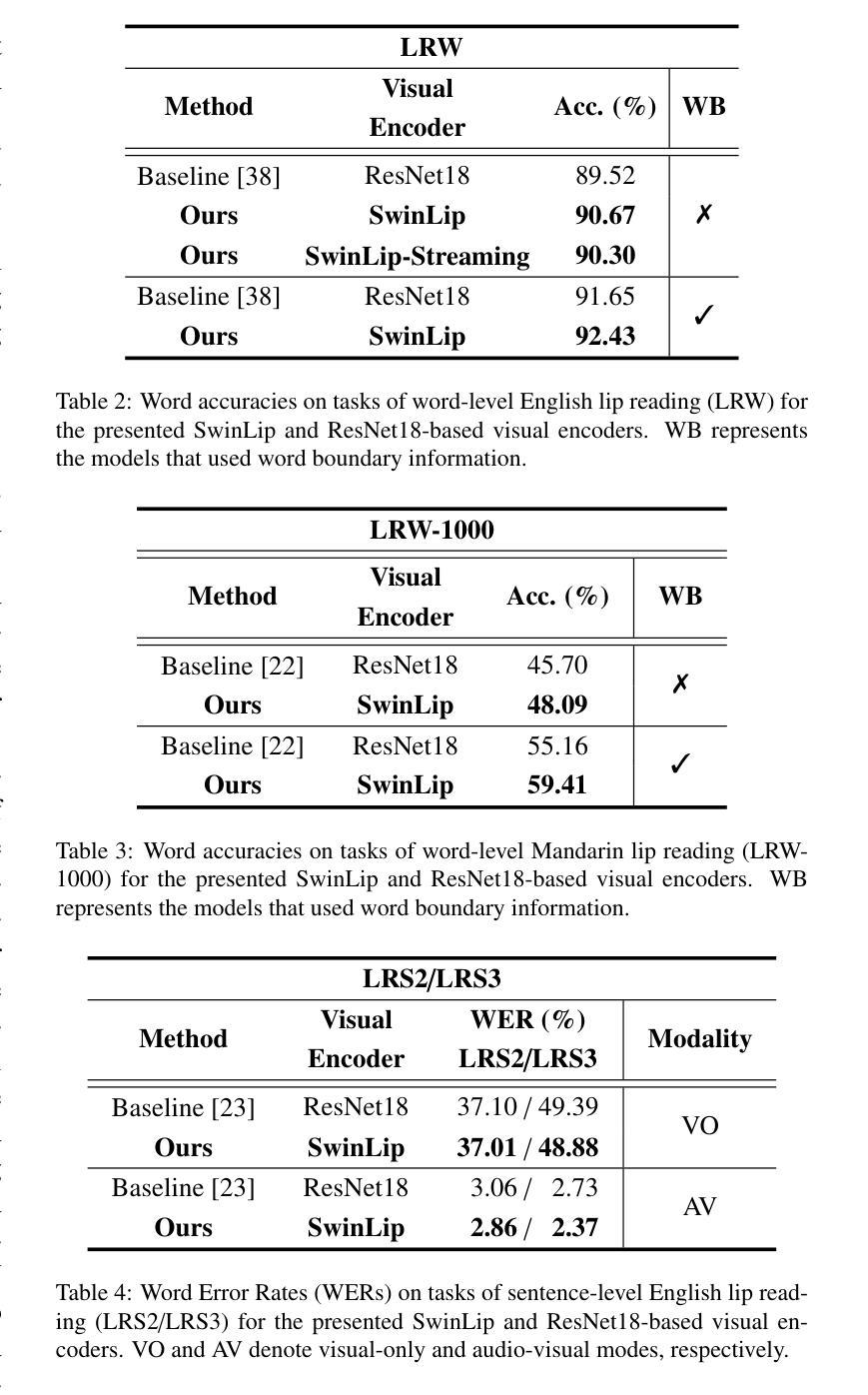
This paper presents an efficient visual speech encoder for lip reading. While most recent lip reading studies have been based on the ResNet architecture and have achieved significant success, they are not sufficiently suitable for efficiently capturing lip reading features due to high computational complexity in modeling spatio-temporal information. Additionally, using a complex visual model not only increases the complexity of lip reading models but also induces delays in the overall network for multi-modal studies (e.g., audio-visual speech recognition, speech enhancement, and speech separation). To overcome the limitations of Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)-based models, we apply the hierarchical structure and window self-attention of the Swin Transformer to lip reading. We configure a new lightweight scale of the Swin Transformer suitable for processing lip reading data and present the SwinLip visual speech encoder, which efficiently reduces computational load by integrating modified Convolution-augmented Transformer (Conformer) temporal embeddings with conventional spatial embeddings in the hierarchical structure. Through extensive experiments, we have validated that our SwinLip successfully improves the performance and inference speed of the lip reading network when applied to various backbones for word and sentence recognition, reducing computational load. In particular, our SwinLip demonstrated robust performance in both English LRW and Mandarin LRW-1000 datasets and achieved state-of-the-art performance on the Mandarin LRW-1000 dataset with less computation compared to the existing state-of-the-art model.
本文提出了一种高效的用于唇读的视觉语音编码器。尽管最近的唇读研究大多基于ResNet架构,并且取得了显著的成功,但由于建模时空信息的计算复杂性高,它们并不足以有效地捕获唇读特征。此外,使用复杂的视觉模型不仅增加了唇读模型的复杂性,而且还可能导致多模态研究(例如音频-视觉语音识别、语音增强和语音分离)的整体网络延迟。为了克服基于卷积神经网络(CNN)的模型的局限性,我们将Swin Transformer的层次结构和窗口自注意力应用于唇读。我们配置了适合处理唇读数据的新颖轻量级Swin Transformer规模,并推出了SwinLip视觉语音编码器,它通过整合修改后的卷积增强Transformer(Conformer)时间嵌入与分层结构中的传统空间嵌入,有效地减少了计算负载。通过大量实验,我们验证了将SwinLip应用于各种骨干网进行单词和句子识别时,成功提高了唇读网络的性能和推理速度,并减少了计算负载。特别是,我们的SwinLip在英语LRW和普通话LRW-1000数据集上均表现出稳健的性能,与现有的最先进的模型相比,在普通话LRW-1000数据集上实现了更少的计算量而达到最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种高效的视觉语音编码器,用于唇读。针对基于ResNet架构的唇读研究在捕捉时空信息时存在高计算复杂性的问题,采用Swin Transformer的层次结构和窗口自注意力机制改进。通过配置Swin Transformer的新轻量级规模,并整合修改后的Conformer时序嵌入和传统空间嵌入,提出SwinLip视觉语音编码器。实验证明,SwinLip在多种骨架网络上的单词和句子识别性能有所提高,且计算负载较小。特别是在中英文数据集上表现出卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文提出了一种针对唇读的视觉语音编码器SwinLip。
- SwinLip基于Swin Transformer,有效克服CNN模型在捕捉时空信息时的高计算复杂性。
- SwinLip通过整合Conformer时序嵌入和传统空间嵌入,提高了唇读性能并降低了计算负载。
- SwinLip在不同骨架网络上表现出卓越性能,适用于多种语音识别任务。
- 在中英文数据集上的实验证明SwinLip具有优异性能,特别是在Mandarin LRW-1000数据集上达到业界最佳水平。
- SwinLip对于多模态研究(如音频-视觉语音识别、语音增强和语音分离)具有潜力。
点此查看论文截图

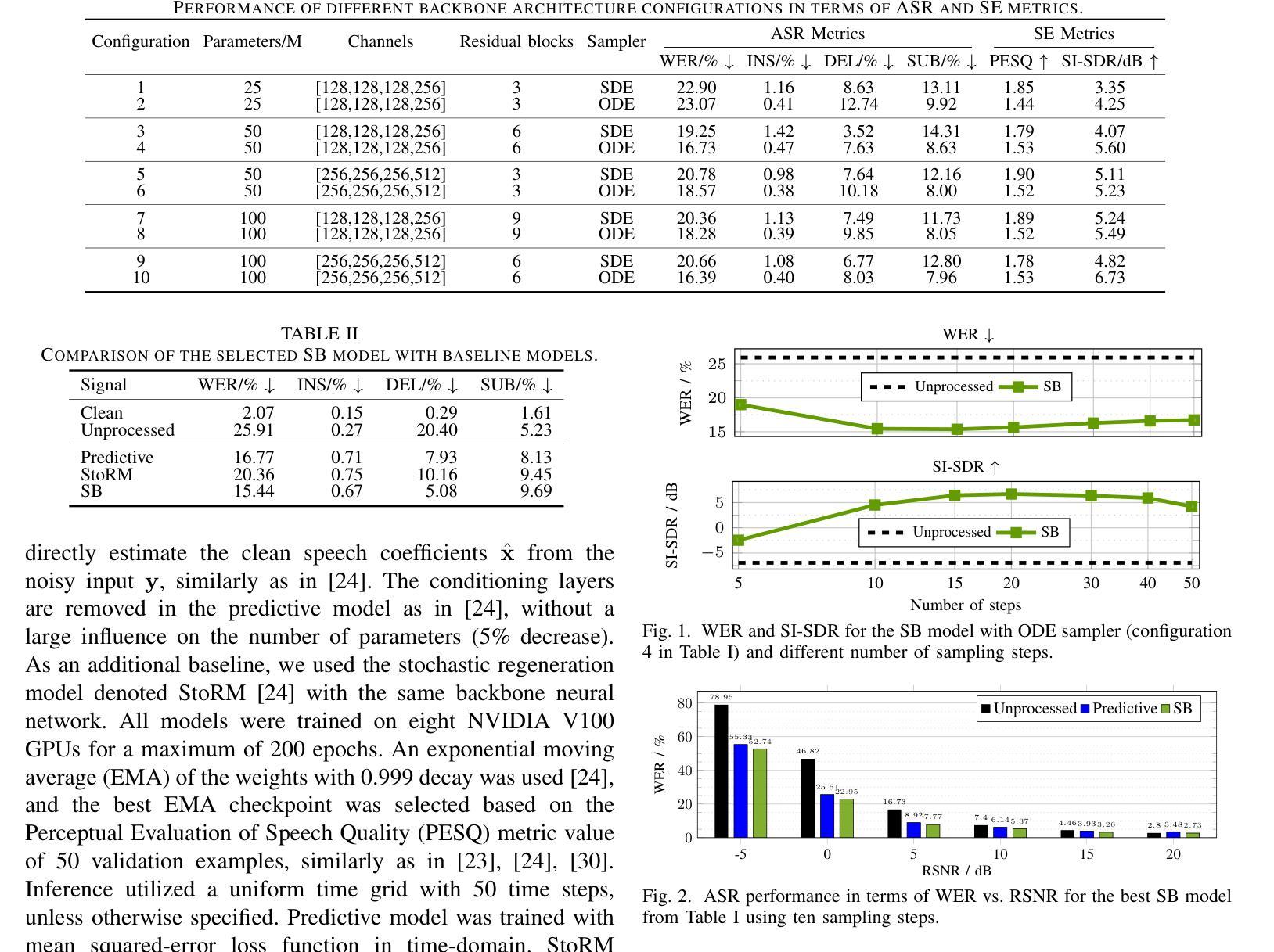
Robust Speech Recognition with Schrödinger Bridge-Based Speech Enhancement
Authors:Rauf Nasretdinov, Roman Korostik, Ante Jukić
In this work, we investigate application of generative speech enhancement to improve the robustness of ASR models in noisy and reverberant conditions. We employ a recently-proposed speech enhancement model based on Schr"odinger bridge, which has been shown to perform well compared to diffusion-based approaches. We analyze the impact of model scaling and different sampling methods on the ASR performance. Furthermore, we compare the considered model with predictive and diffusion-based baselines and analyze the speech recognition performance when using different pre-trained ASR models. The proposed approach significantly reduces the word error rate, reducing it by approximately 40% relative to the unprocessed speech signals and by approximately 8% relative to a similarly sized predictive approach.
在这项工作中,我们研究了生成性语音增强在噪声和回声条件下提高ASR模型稳健性的应用。我们采用了一种基于Schrödinger桥的最近提出的语音增强模型,该模型与基于扩散的方法相比表现出良好的性能。我们分析了模型缩放和不同采样方法对ASR性能的影响。此外,我们将所考虑的模型与预测和基于扩散的基线进行了比较,并分析了使用不同预训练ASR模型时的语音识别性能。所提出的方法显著降低了单词错误率,与未处理的语音信号相比降低了约40%,与类似规模的预测方法相比降低了约8%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages. Published in ICASSP 2025
Summary:本研究探讨了生成式语音增强在提高抗噪声和回声的自动语音识别模型稳健性方面的应用。研究采用基于Schrödinger桥的语音增强模型,相较于扩散模型展现出较好的性能。分析了模型缩放和不同采样方法对自动语音识别性能的影响,并与预测模型和扩散模型进行了比较。该方法显著降低了词错误率,相较于未处理语音信号降低了约40%,相较于类似规模的预测方法降低了约8%。
Key Takeaways:
- 研究关注生成式语音增强在提升自动语音识别模型稳健性方面的应用。
- 采用基于Schrödinger桥的语音增强模型,相较于扩散模型性能优越。
- 分析了模型缩放和采样方法对自动语音识别性能的影响。
- 与预测模型和扩散模型的比较显示,该方法在词错误率上表现更优秀。
- 该方法显著降低了词错误率,相较于未处理语音信号降低了约40%。
- 相较于类似规模的预测方法,该方法降低了约8%的词错误率。
点此查看论文截图


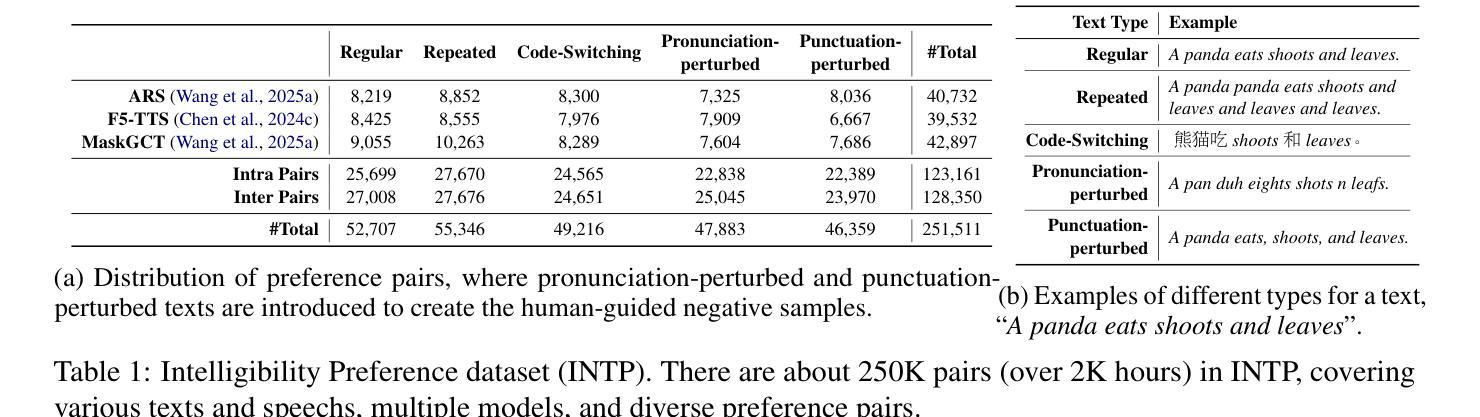
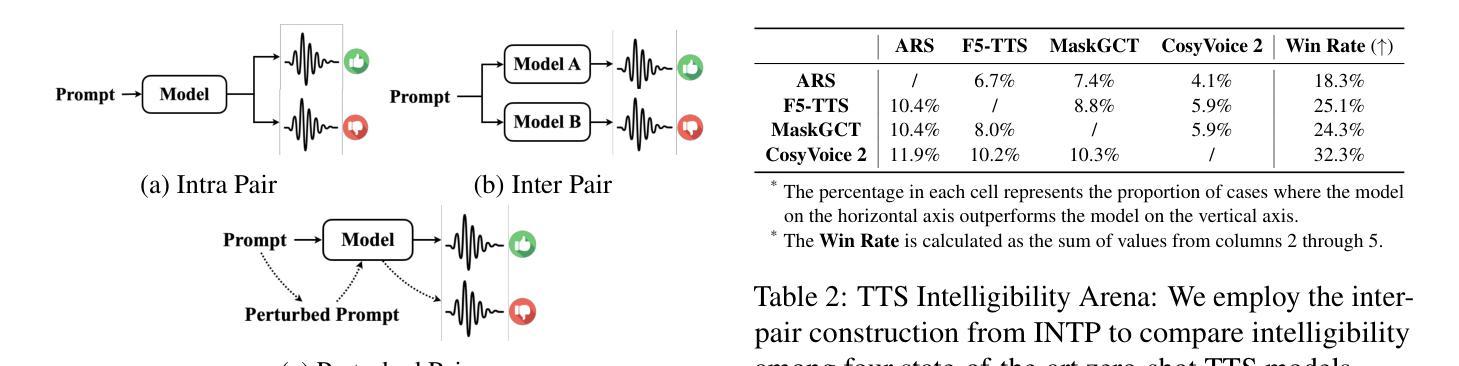
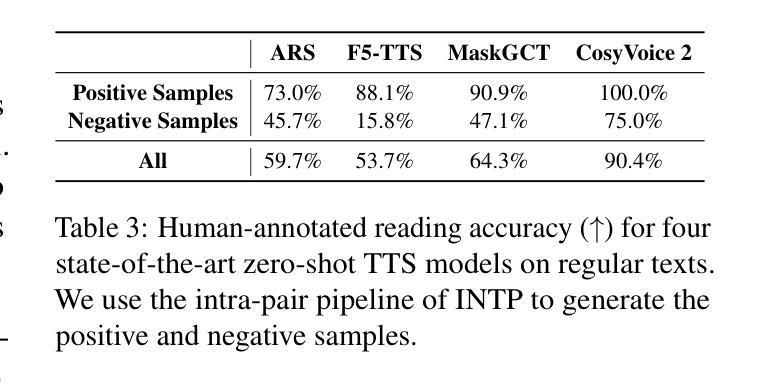
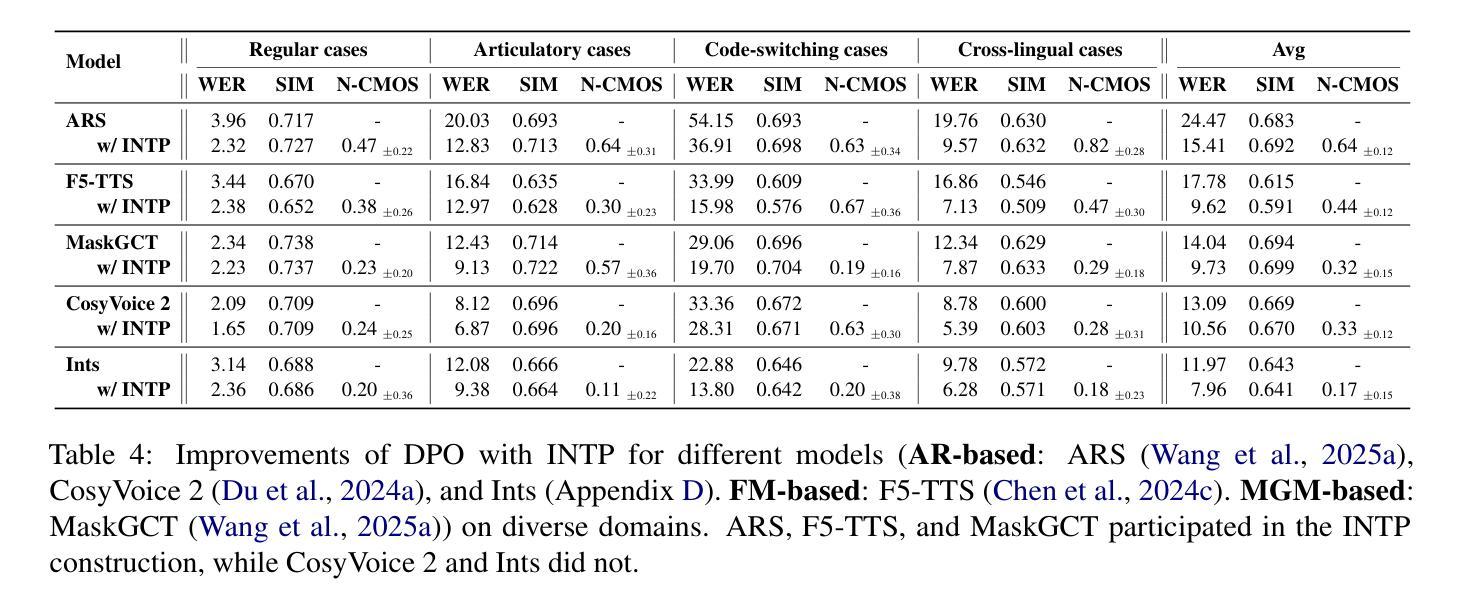
Advancing Zero-shot Text-to-Speech Intelligibility across Diverse Domains via Preference Alignment
Authors:Xueyao Zhang, Yuancheng Wang, Chaoren Wang, Ziniu Li, Zhuo Chen, Zhizheng Wu
Modern zero-shot text-to-speech (TTS) systems, despite using extensive pre-training, often struggle in challenging scenarios such as tongue twisters, repeated words, code-switching, and cross-lingual synthesis, leading to intelligibility issues. To address these limitations, this paper leverages preference alignment techniques, which enable targeted construction of out-of-pretraining-distribution data to enhance performance. We introduce a new dataset, named the Intelligibility Preference Speech Dataset (INTP), and extend the Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) framework to accommodate diverse TTS architectures. After INTP alignment, in addition to intelligibility, we observe overall improvements including naturalness, similarity, and audio quality for multiple TTS models across diverse domains. Based on that, we also verify the weak-to-strong generalization ability of INTP for more intelligible models such as CosyVoice 2 and Ints. Moreover, we showcase the potential for further improvements through iterative alignment based on Ints. Audio samples are available at https://intalign.github.io/.
现代零样本文本到语音(TTS)系统尽管进行了大量的预训练,但在如绕口令、重复词汇、代码切换和跨语言合成等挑战性场景中仍然面临可理解性问题。为了解决这些局限性,本文采用偏好对齐技术,该技术能够构建超出预训练分布的数据,以提高性能。我们引入了一个新的数据集,名为可理解性偏好语音数据集(INTP),并将直接偏好优化(DPO)框架扩展到适应多种TTS架构。经过INTP对齐后,除了可理解性外,我们还观察到多个TTS模型在不同领域的自然性、相似性和音频质量的总体改进。基于此,我们还验证了INTP对于如CosyVoice 2和Ints等更具理解能力的模型的从弱到强的泛化能力。此外,我们展示了通过基于Ints的迭代对齐实现进一步改进的潜力。音频样本可在https://intalign.github.io/获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文为了解决现代零点击文本转语音系统在挑战场景下的可理解性问题,引入了偏好对齐技术。该技术能构建超出预训练分布范围的数据以改善性能。为此,作者提出了一个名为“INTP”(Intelligibility Preference Speech Dataset)的数据集,扩展了Direct Preference Optimization框架以适应多样的TTS架构。在INTP对齐后,不仅提升了语音的可理解性,还观察到了包括自然度、相似性和音质在内的整体改进。此外,作者还验证了INTP对于CosyVoice 2和Ints等模型的弱到强泛化能力,并展示了通过迭代对齐进一步提升潜力的可能性。
Key Takeaways
- 现代TTS系统在特定挑战场景下存在可理解性问题。
- 偏好对齐技术被引入以解决这些问题,该技术能够构建超出预训练分布范围的数据。
- 提出了名为INTP的新数据集,用于提高TTS系统的性能。
- 扩展了Direct Preference Optimization框架以适应不同的TTS架构。
- INTP对齐后,不仅提高了语音的可理解性,还改善了整体音质和其他方面的表现。
- INTP对于某些TTS模型具有弱到强的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

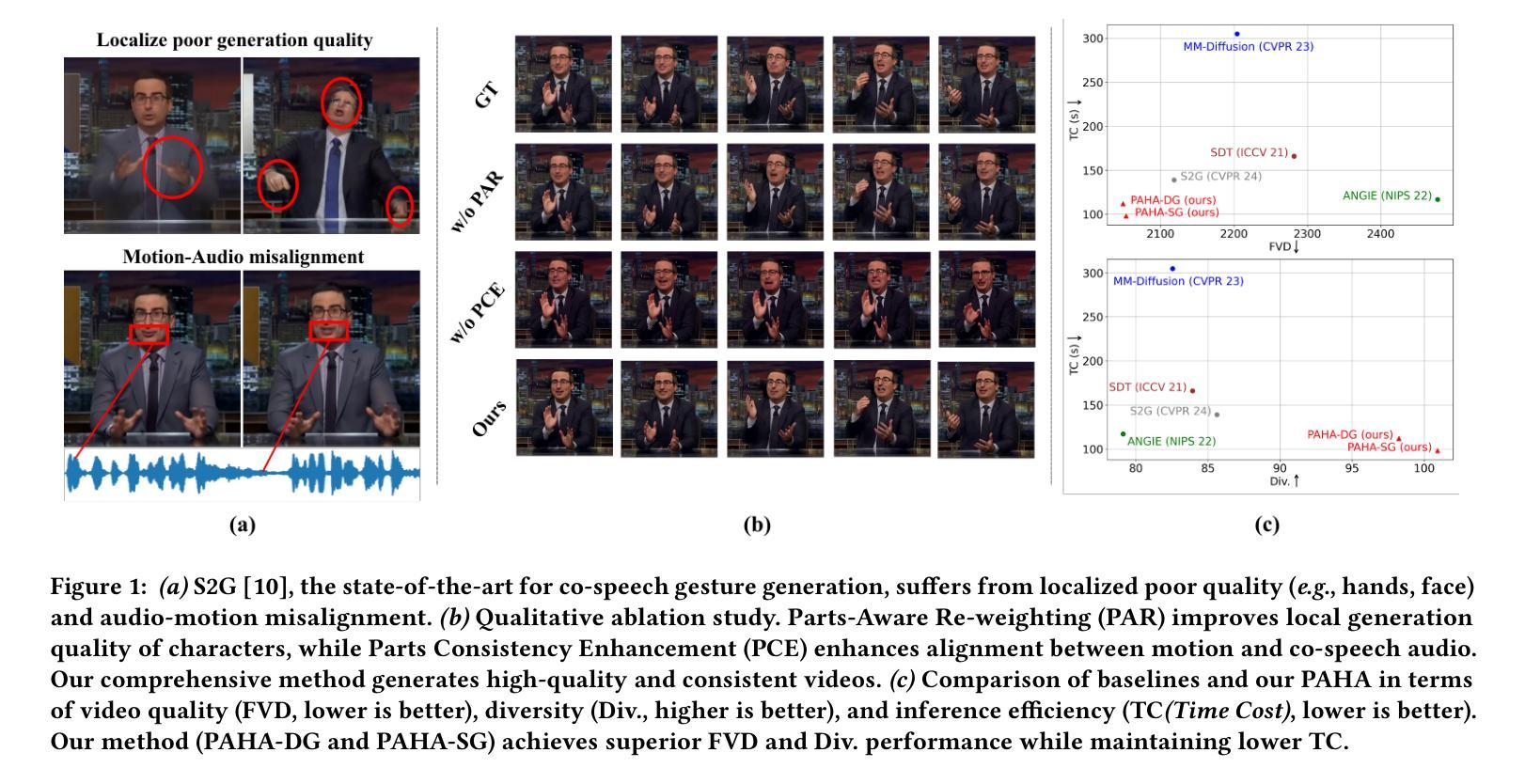
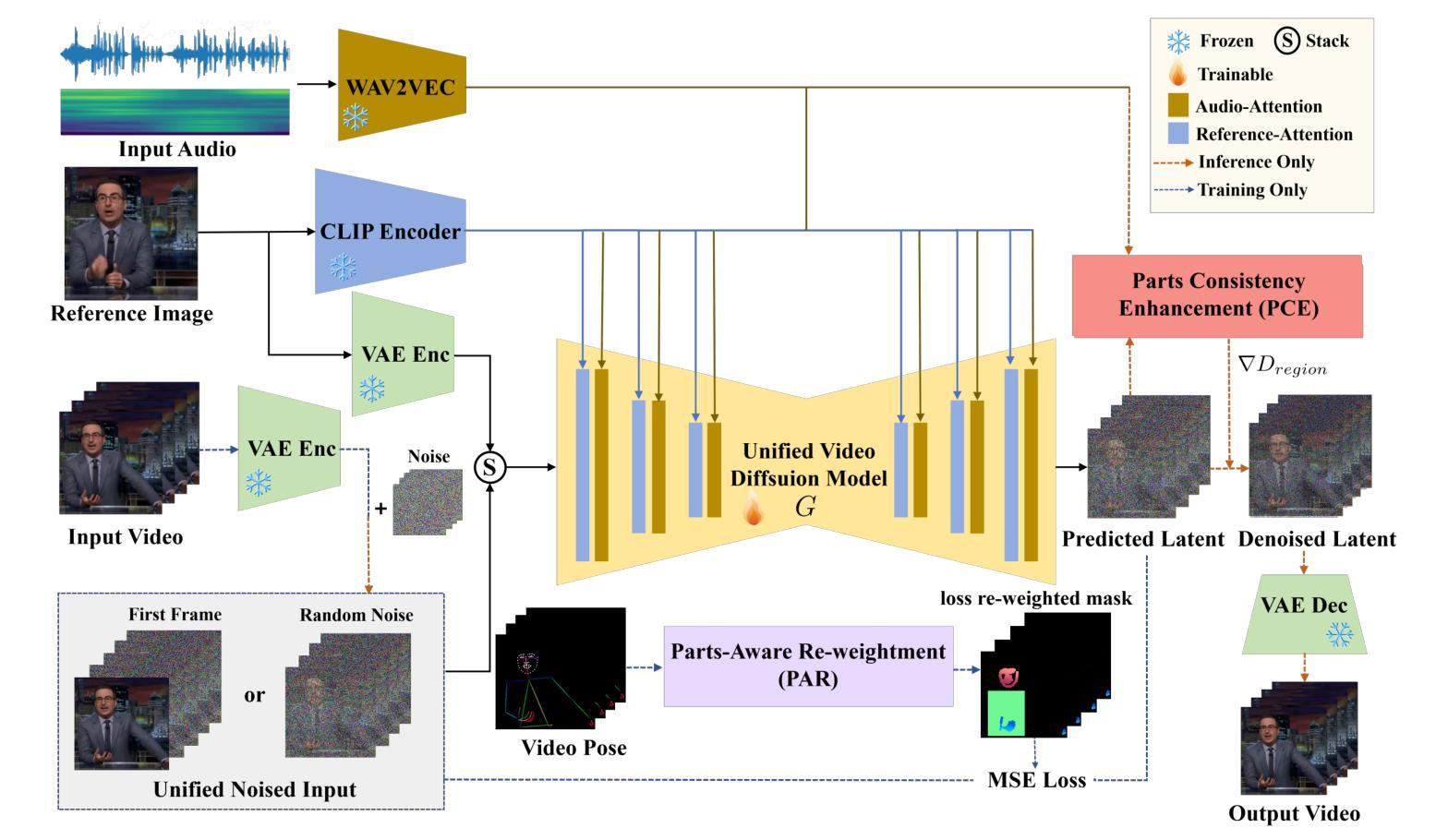
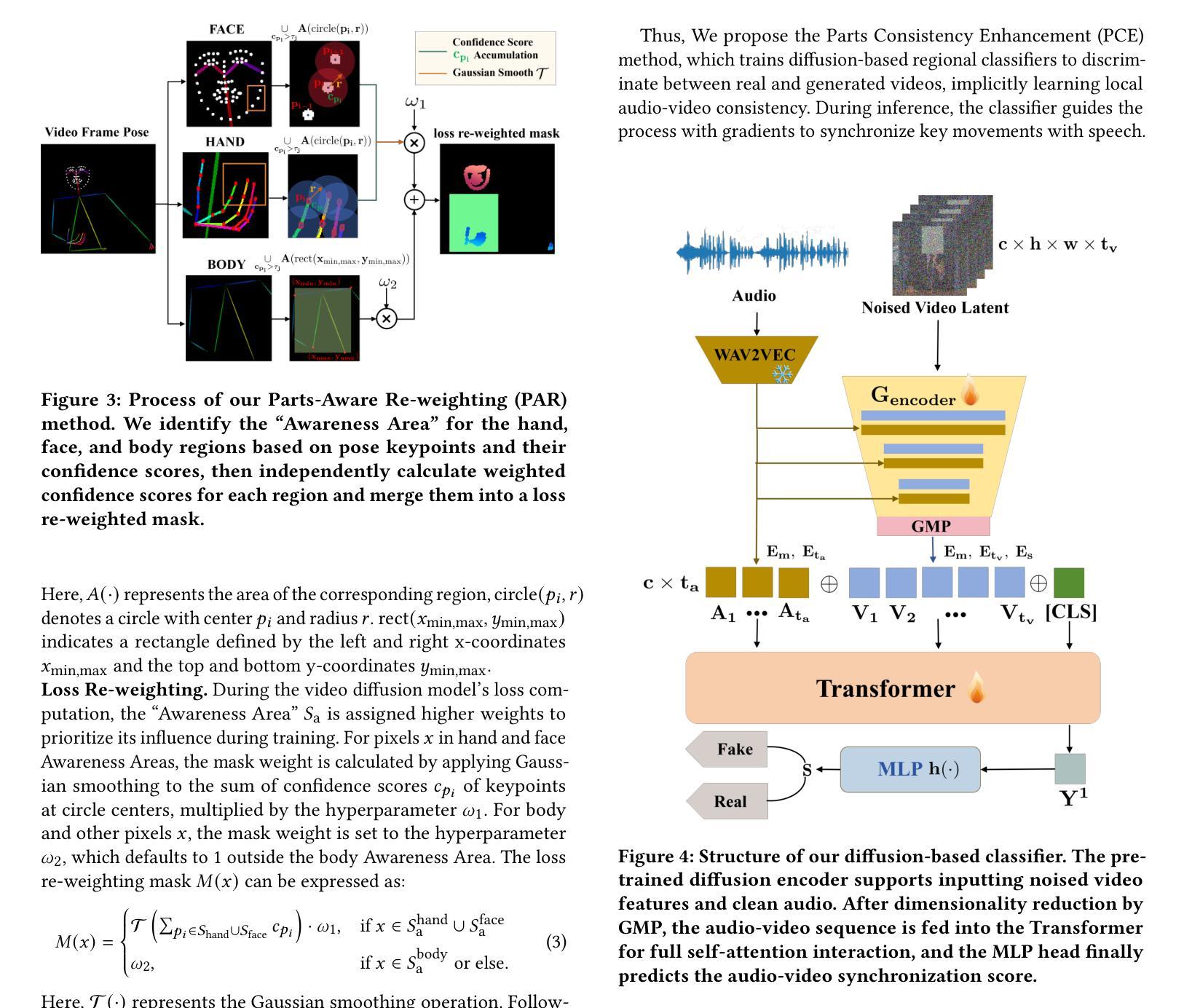
PAHA: Parts-Aware Audio-Driven Human Animation with Diffusion Model
Authors:Y. B. Wang, S. Z. Zhou, J. F. Wu, T. Hu, J. N. Zhang, Y. Liu
Audio-driven human animation technology is widely used in human-computer interaction, and the emergence of diffusion models has further advanced its development. Currently, most methods rely on multi-stage generation and intermediate representations, resulting in long inference time and issues with generation quality in specific foreground regions and audio-motion consistency. These shortcomings are primarily due to the lack of localized fine-grained supervised guidance. To address above challenges, we propose PAHA, an end-to-end audio-driven upper-body human animation framework with diffusion model. We introduce two key methods: Parts-Aware Re-weighting (PAR) and Parts Consistency Enhancement (PCE). PAR dynamically adjusts regional training loss weights based on pose confidence scores, effectively improving visual quality. PCE constructs and trains diffusion-based regional audio-visual classifiers to improve the consistency of motion and co-speech audio. Afterwards, we design two novel inference guidance methods for the foregoing classifiers, Sequential Guidance (SG) and Differential Guidance (DG), to balance efficiency and quality respectively. Additionally, we build CNAS, the first public Chinese News Anchor Speech dataset, to advance research and validation in this field. Extensive experimental results and user studies demonstrate that PAHA significantly outperforms existing methods in audio-motion alignment and video-related evaluations. The codes and CNAS dataset will be released upon acceptance.
音频驱动的人类动画技术广泛应用于人机交互领域,扩散模型的兴起进一步推动了其发展。目前,大多数方法依赖于多阶段生成和中间表示,导致推理时间长,特定前景区域生成质量和音频运动一致性存在问题。这些缺点主要是由于缺乏局部精细监督指导。为了解决上述挑战,我们提出了PAHA,这是一个基于扩散模型的端到端音频驱动人体上半身动画框架。我们引入了两种关键方法:零件感知重新加权(PAR)和零件一致性增强(PCE)。PAR根据姿势置信度分数动态调整区域训练损失权重,有效提高视觉效果。PCE构建并训练基于扩散的区域音频视觉分类器,以提高运动和语音音频的一致性。之后,我们为前述分类器设计了两种新型推理指导方法,即顺序指导(SG)和差分指导(DG),以分别平衡效率和质量。此外,我们构建了CNAS,即首个公开的中文新闻主播语音数据集,以推动该领域的研究和验证。大量的实验和用户研究结果表明,PAHA在音频运动对齐和视频相关评估方面显著优于现有方法。代码和CNAS数据集将在接受后发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于扩散模型的音频驱动人体动画技术取得了突破性进展。针对当前方法的缺陷,如推理时间长、前景区域生成质量问题和音频运动一致性差等,提出了PAHA框架及PAR和PCE两大方法。通过动态调整区域训练损失权重和构建基于扩散的区域音频视觉分类器,提高了运动一致性及音频与动作匹配度。此外,还设计了两种新型推理引导方法SG和DG,并创建了首个中文新闻主播语音数据集CNAS。实验和用户研究证明PAHA在音频运动对齐和视频相关评估方面显著优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 音频驱动人体动画技术在人机交互中的广泛应用。
- 扩散模型的出现进一步推动了该领域的发展。
- 当前方法存在推理时间长、特定前景区域生成质量问题和音频运动一致性差等缺点。
- PAHA框架通过PAR和PCE两大方法解决了上述问题。
- PAR通过动态调整区域训练损失权重提高了视觉质量。
- PCE构建了基于扩散的区域音频视觉分类器,增强了运动一致性及音频与动作的匹配度。
- 提出了两种新型推理引导方法SG和DG以平衡效率和质量。
- 创建了首个中文新闻主播语音数据集CNAS。
- PAHA在音频运动对齐和视频相关评估方面显著优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

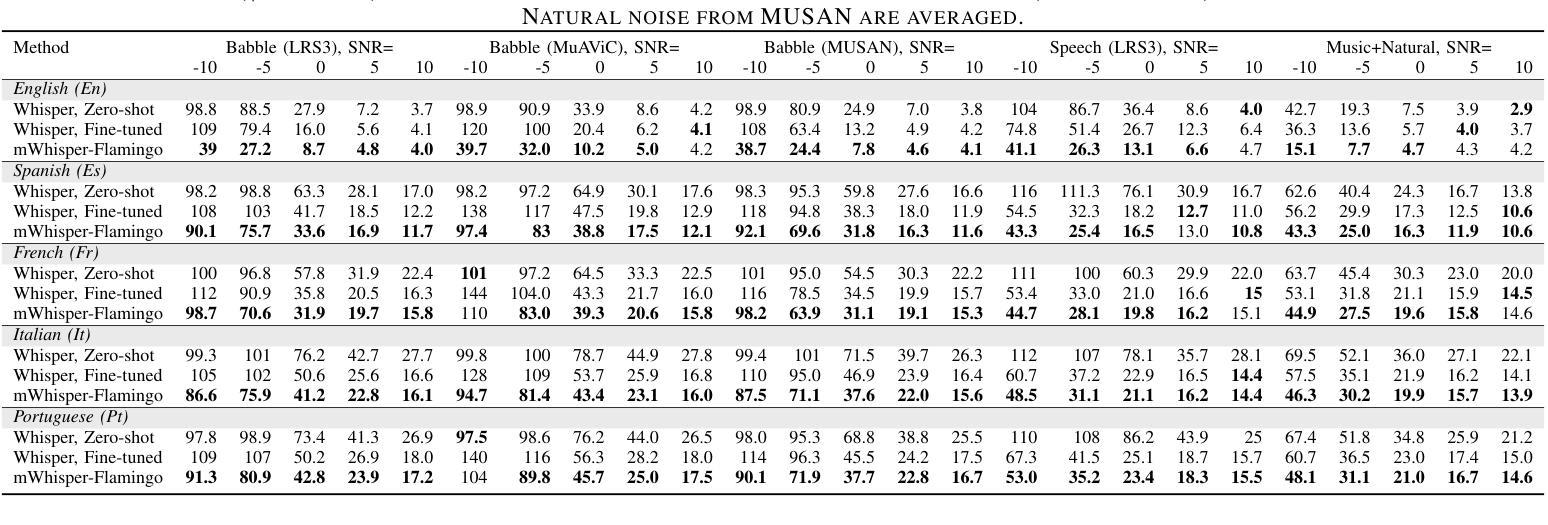
mWhisper-Flamingo for Multilingual Audio-Visual Noise-Robust Speech Recognition
Authors:Andrew Rouditchenko, Samuel Thomas, Hilde Kuehne, Rogerio Feris, James Glass
Audio-Visual Speech Recognition (AVSR) combines lip-based video with audio and can improve performance in noise, but most methods are trained only on English data. One limitation is the lack of large-scale multilingual video data, which makes it hard to train models from scratch. In this work, we propose mWhisper-Flamingo for multilingual AVSR which combines the strengths of a pre-trained audio model (Whisper) and video model (AV-HuBERT). To enable better multi-modal integration and improve the noisy multilingual performance, we introduce decoder modality dropout where the model is trained both on paired audio-visual inputs and separate audio/visual inputs. mWhisper-Flamingo achieves state-of-the-art WER on MuAViC, an AVSR dataset of 9 languages. Audio-visual mWhisper-Flamingo consistently outperforms audio-only Whisper on all languages in noisy conditions.
视听语音识别(AVSR)结合了基于唇语的视频和音频,可以提高降噪性能,但大多数方法仅针对英语数据进行训练。一个局限性在于缺乏大规模的多语言视频数据,这使得从头开始训练模型变得困难。在这项工作中,我们提出了用于多语言AVSR的mWhisper-Flamingo,它结合了预训练音频模型(Whisper)和视频模型(AV-HuBERT)的优点。为了更有效地进行多模式集成并提高降噪的多语言性能,我们引入了解码器模态丢弃训练策略,该策略对配对后的音频-视频输入和单独的音频/视频输入进行训练。mWhisper-Flamingo在MuAViC这一包含九种语言的AVSR数据集上实现了最先进的词错误率(WER)。在嘈杂条件下,视听mWhisper-Flamingo在所有语言上的表现均优于仅使用音频的Whisper。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in Signal Processing Letters. Code at https://github.com/roudimit/whisper-flamingo
Summary
该文本介绍了音频视觉语音识别(AVSR)结合唇语视频和音频在噪声环境中的性能提升。然而,大多数方法仅针对英语数据进行训练,缺乏大规模的多语言视频数据是训练模型的难点。本研究提出了多语言AVSR的mWhisper-Flamingo模型,结合了预训练音频模型(Whisper)和视频模型(AV-HuBERT)的优势。通过引入解码器模态丢弃技术,模型能够在配对音频视觉输入和单独音频/视觉输入上进行训练,实现更好的多模态集成并提升噪声多语言环境的表现。mWhisper-Flamingo在MuAViC数据集上实现了词错误率(WER)的领先水平,该数据集包含9种语言。在噪声条件下,视听mWhisper-Flamingo在所有语言上的表现均优于仅使用音频的Whisper模型。
Key Takeaways
- 音频视觉语音识别(AVSR)可以通过结合唇语视频和音频在噪声环境中提升性能。
- 大多数AVSR模型仅针对英语数据进行训练,缺乏多语言视频数据。
- mWhisper-Flamingo模型结合了预训练音频模型(Whisper)和视频模型(AV-HuBERT)的优势。
- 通过解码器模态丢弃技术,模型能够在配对音频视觉输入和单独音频/视觉输入上进行训练。
- mWhisper-Flamingo在MuAViC数据集上实现了词错误率(WER)的领先水平。
- 视听mWhisper-Flamingo在所有语言上的表现均优于仅使用音频的Whisper模型。
- mWhisper-Flamingo模型具备处理多种语言的能力,有助于扩大其在不同文化背景下的应用。
点此查看论文截图