⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-10 更新
Significant reflection and absorption effects in the X-ray emission of the Intermediate Polar IGR J17195-4100
Authors:Elif Şafak, Şölen Balman, Gloria Sala
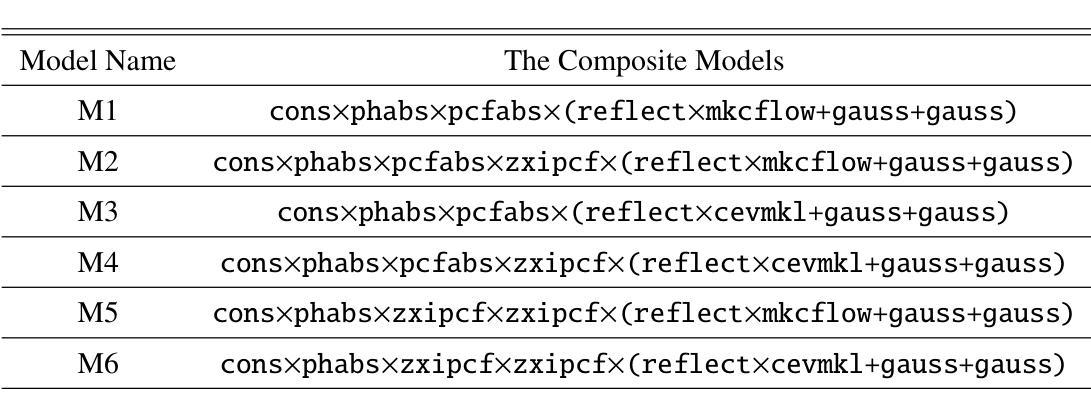
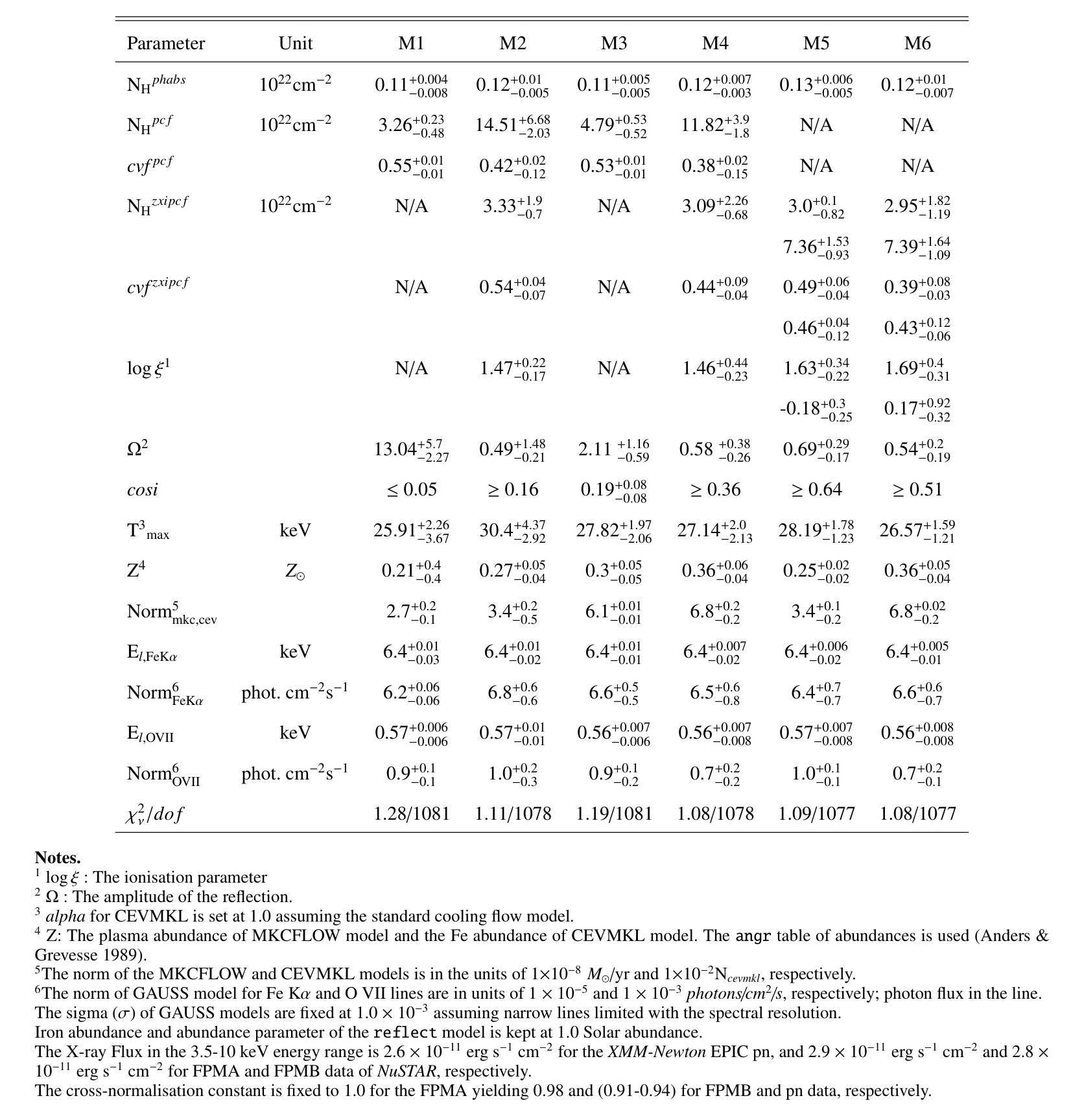
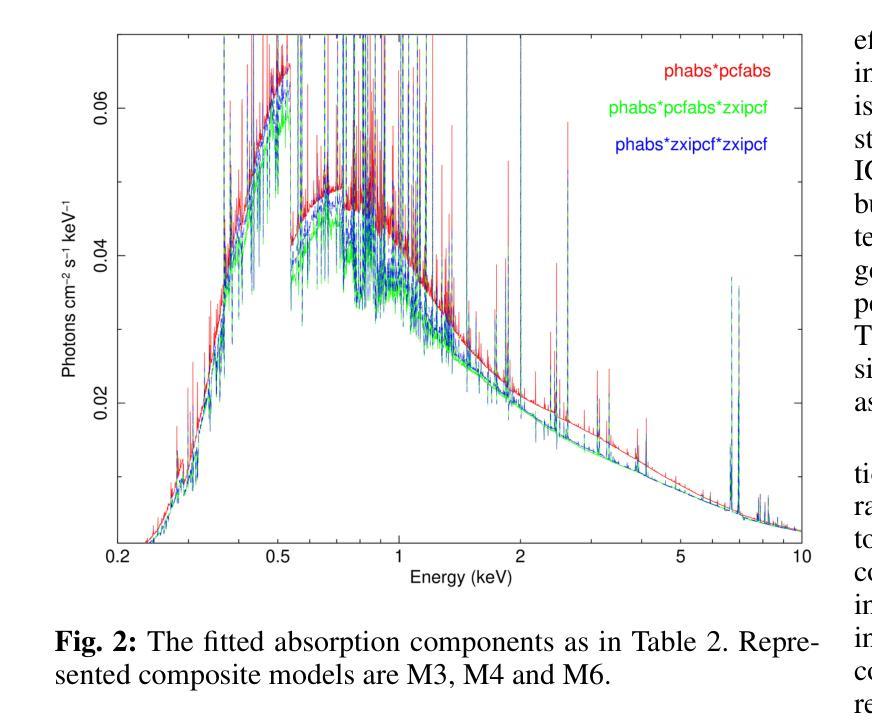
X-ray emission is from shock-heated plasma in magnetic cataclysmic variables, and is processed by absorption and scattering before reaching the observer. We investigate these effects in the X-ray emission of the Intermediate Polar IGR J17195-4100 by carrying out the X-ray spectral analysis, spin modulation and hardness ratio. We present high-sensitivity broadband X-ray spectral analysis by combining NuSTAR and XMM-Newton observations in the 0.3-78.0 keV energy range. The X-ray spectral analysis is performed using six composite models, including the angle-dependent reflection model (reflect), multi-temperature plasma emission models (CEVMKL, MKCFLOW), and photoionised and/or neutral partially covering absorption models (zxipcf, pcfabs) within XSPEC. We examine also the spin modulation in four energy ranges and the hardness ratio, to determine the absorption and scattering effects. We find that the spectrum is best modelled with a reflection amplitude ($\Omega$) of 0.58 $^{+0.38}{-0.26}$, an ionisation parameter, log($\xi$), of 1.46$^{+0.44}{-0.23}$ with an equivalent hydrogen column density of 3.09$^{+2.26}{-0.68}$ $\times$ 10$^{22}$ cm$^{-2}$, a neutral absorber, and a multi-temperature plasma temperature of 27.14$^{+2.0}{-2.13}$ keV. In addition, we detect effects of electron scattering in the NuSTAR band, leading to modulation amplitude of about a steady 9$%$ that increases up to 15$%$ after 20 keV. We stress that these effects significantly affect the X-ray emission of intermediate polars and should be considered to obtain a good representation of the intrinsic spectrum.
X射线发射来源于磁灾变变量的冲击加热等离子体,在到达观察者之前经过吸收和散射处理。我们通过进行X射线光谱分析、自转调制和硬度比来研究中间偏极IGR J17195-4100的X射线发射中的这些效应。我们通过结合NuSTAR和XMM-Newton在0.3-78.0 keV能量范围内的观测结果,进行了高灵敏度宽带X射线光谱分析。X射线光谱分析使用了六种复合模型,包括角度依赖反射模型(reflect)、多温度等离子体发射模型(CEVMKL、MKCFLOW),以及光离子化和/或部分中性覆盖吸收模型(zxipcf、pcfabs)。我们还研究了四个能量范围内的自转调制和硬度比,以确定吸收和散射效应。我们发现,光谱的最佳模型反射幅度(Ω)为0.58 $^{+0.38}{-0.26}$,电离参数log(ξ)为1.46^{+0.44}{-0.23},等效氢柱密度为3.09^{+2.26}{-0.68} × 10^{22} cm^{-2},中性吸收体和多温度等离子体温度为27.14^{+2.0}{-2.13} keV。此外,我们在NuSTAR波段检测到了电子散射效应,导致调制幅度约为稳定的9%,在20 keV后增加到15%。我们强调,这些效应对中间偏极的X射线发射产生了显著影响,应该考虑这些因素以获得内在谱的良好表示。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 Pages, 4 Figures, and 3 Tables, accepted to be published in the Astronomy & Astrophysics as it stands
Summary
磁灾变变量中的X射线发射源于等离子体冲击加热,经过吸收和散射后到达观测者。研究小组通过对中间极性的IGR J17195-4100的X射线发射进行光谱分析、自转调制和硬度比来研究这些影响。研究采用了高灵敏度宽带X射线光谱分析,结合了NuSTAR和XMM-Newton在0.3-78.0 keV能段的观测数据。发现X射线光谱与反射幅度、离子化参数、等效氢柱密度、中性吸收体和多温度等离子体温度等多个模型参数有关。此外,还检测到电子散射的影响,导致调制幅度在稳定状态下的9%增加至超过20keV时的约15%。这些影响对中间极性的X射线发射至关重要。
Key Takeaways
- X射线发射来源于磁灾变变量中的等离子体冲击加热,经过吸收和散射后到达观测者。
- 通过光谱分析、自转调制和硬度比对中间极性的IGR J17195-4100的X射线发射进行了研究。
- 高灵敏度宽带X射线光谱分析结合了NuSTAR和XMM-Newton在0.3-78.0 keV能段的观测数据。
- X射线光谱与反射幅度、离子化参数、等效氢柱密度等参数有关。
- 发现了中性吸收体和多温度等离子体温度的影响。
- 电子散射的影响导致调制幅度增加。
点此查看论文截图

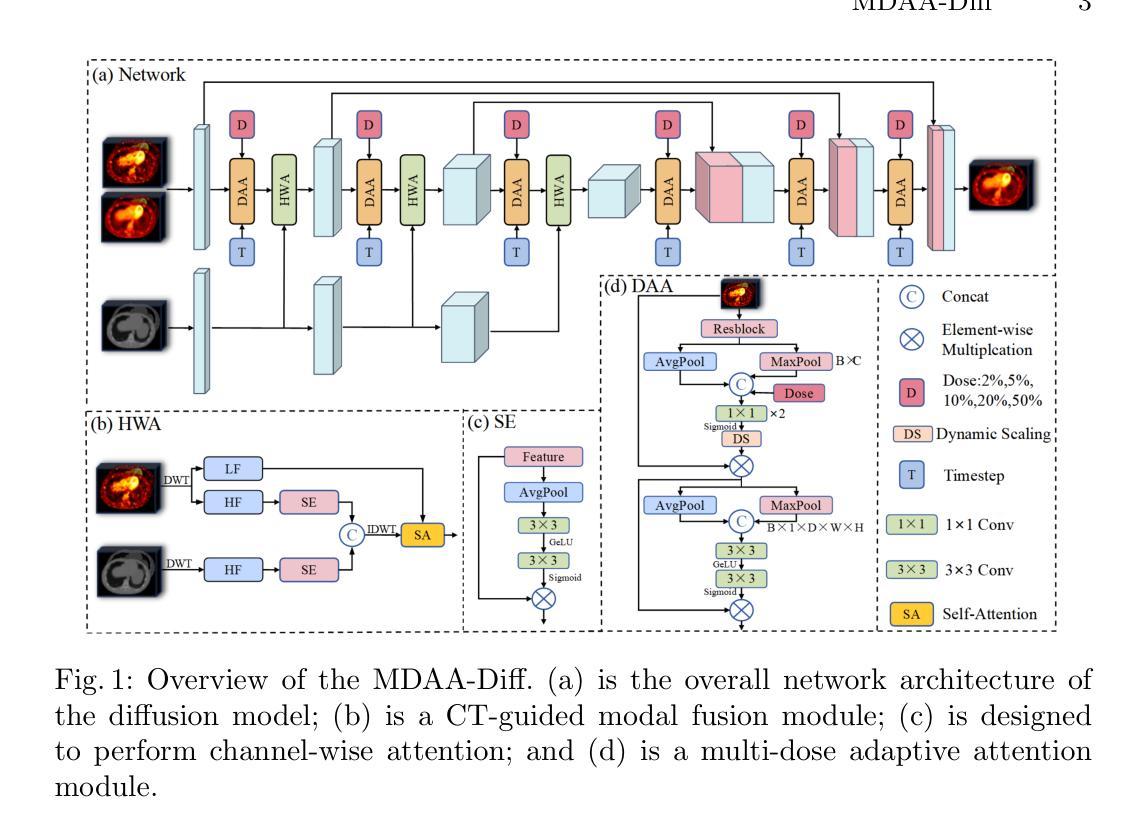
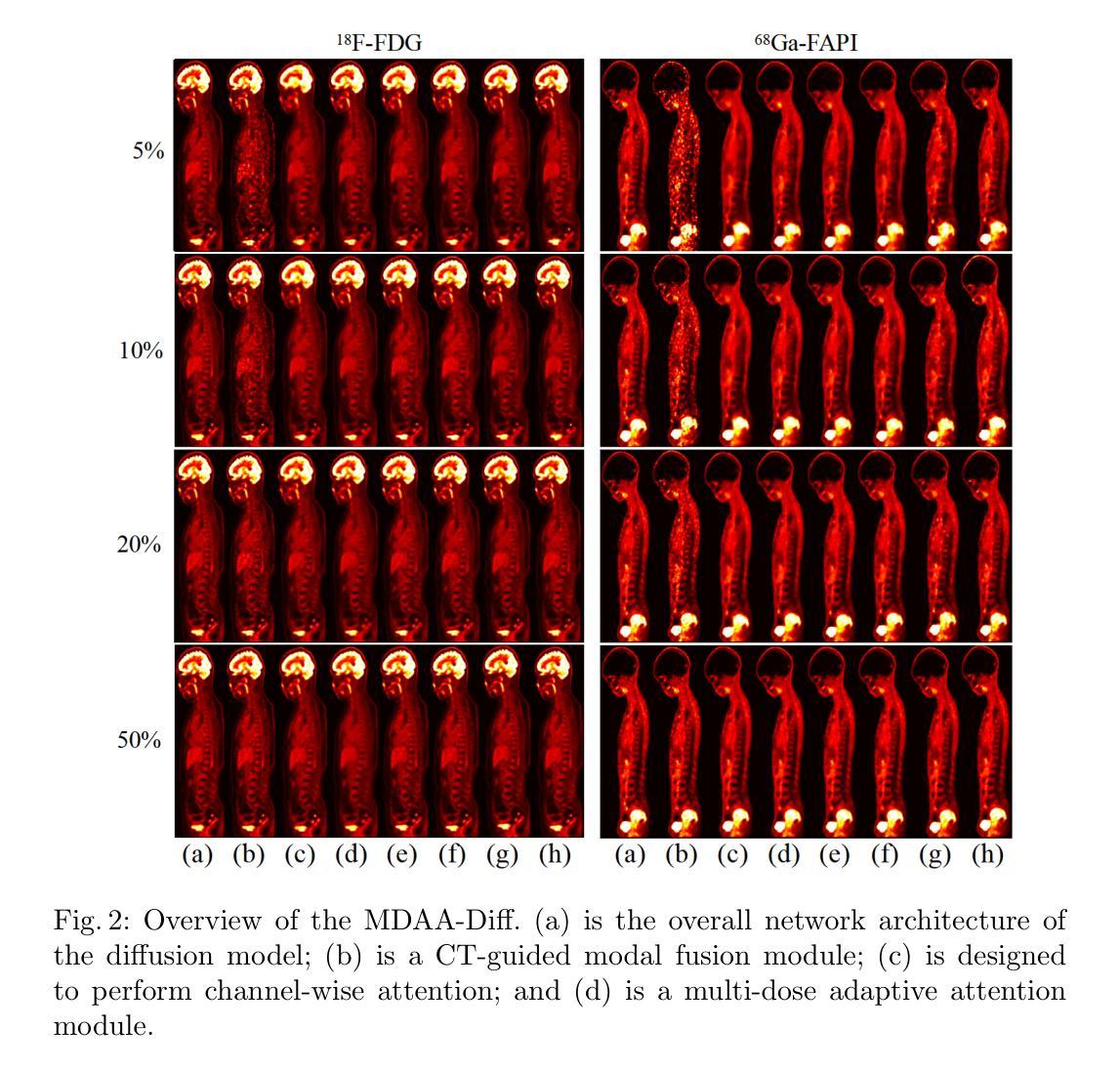
MDAA-Diff: CT-Guided Multi-Dose Adaptive Attention Diffusion Model for PET Denoising
Authors:Xiaolong Niu, Zanting Ye, Xu Han, Yanchao Huang, Hao Sun, Hubing Wu, Lijun Lu
Acquiring high-quality Positron Emission Tomography (PET) images requires administering high-dose radiotracers, which increases radiation exposure risks. Generating standard-dose PET (SPET) from low-dose PET (LPET) has become a potential solution. However, previous studies have primarily focused on single low-dose PET denoising, neglecting two critical factors: discrepancies in dose response caused by inter-patient variability, and complementary anatomical constraints derived from CT images. In this work, we propose a novel CT-Guided Multi-dose Adaptive Attention Denoising Diffusion Model (MDAA-Diff) for multi-dose PET denoising. Our approach integrates anatomical guidance and dose-level adaptation to achieve superior denoising performance under low-dose conditions. Specifically, this approach incorporates a CT-Guided High-frequency Wavelet Attention (HWA) module, which uses wavelet transforms to separate high-frequency anatomical boundary features from CT images. These extracted features are then incorporated into PET imaging through an adaptive weighted fusion mechanism to enhance edge details. Additionally, we propose the Dose-Adaptive Attention (DAA) module, a dose-conditioned enhancement mechanism that dynamically integrates dose levels into channel-spatial attention weight calculation. Extensive experiments on 18F-FDG and 68Ga-FAPI datasets demonstrate that MDAA-Diff outperforms state-of-the-art approaches in preserving diagnostic quality under reduced-dose conditions. Our code is publicly available.
获取高质量的正电子发射断层扫描(PET)图像需要注射高剂量放射性示踪剂,这增加了辐射暴露风险。从低剂量PET(LPET)生成标准剂量PET(SPET)已成为一种可能的解决方案。然而,以往的研究主要集中在单一低剂量PET去噪上,忽视了由患者间差异引起的剂量反应差异,以及从CT图像中获得的互补解剖约束。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新型的CT引导多剂量自适应注意力去噪扩散模型(MDAA-Diff)进行多剂量PET去噪。我们的方法结合了解剖指导和剂量水平适应,以在低剂量条件下实现卓越的去噪性能。具体来说,该方法采用CT引导高频小波注意力(HWA)模块,利用小波变换从CT图像中分离出高频解剖边界特征。这些提取的特征然后通过自适应加权融合机制融入PET成像,以增强边缘细节。此外,我们提出了剂量自适应注意力(DAA)模块,这是一种剂量调节增强机制,动态地将剂量水平融入通道空间注意力权重计算。在18F-FDG和68Ga-FAPI数据集上的大量实验表明,MDAA-Diff在降低剂量条件下保持诊断质量方面优于最新技术方法。我们的代码已公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文研究了低剂量PET图像的去噪问题。提出了一种新型的CT引导多剂量自适应注意力去噪扩散模型(MDAA-Diff),该模型结合了解剖学指导和剂量水平自适应,在低剂量条件下实现了卓越的去噪性能。该模型采用CT引导的高频小波注意力(HWA)模块和剂量自适应注意力(DAA)模块,能有效处理不同患者之间的剂量响应差异,并通过实验验证在降低剂量条件下能够保持诊断质量。
关键见解
- 提出了一种新型的CT引导多剂量自适应注意力去噪扩散模型(MDAA-Diff),用于处理低剂量PET图像的去噪问题。
- 模型结合了解剖学指导和剂量水平自适应,以提高低剂量条件下的去噪性能。
- 采用CT引导的高频小波注意力(HWA)模块,通过小波变换提取CT图像的高频解剖边界特征,并将其融入PET成像中,增强边缘细节。
- 提出了剂量自适应注意力(DAA)模块,这是一种根据剂量条件增强的机制,动态地将剂量水平纳入通道空间注意力权重的计算中。
- 通过对18F-FDG和68Ga-FAPI数据集的大量实验,证明MDAA-Diff在降低剂量条件下能够保持诊断质量,优于现有方法。
- 模型公开可用,为医学图像去噪提供了有力工具。
点此查看论文截图

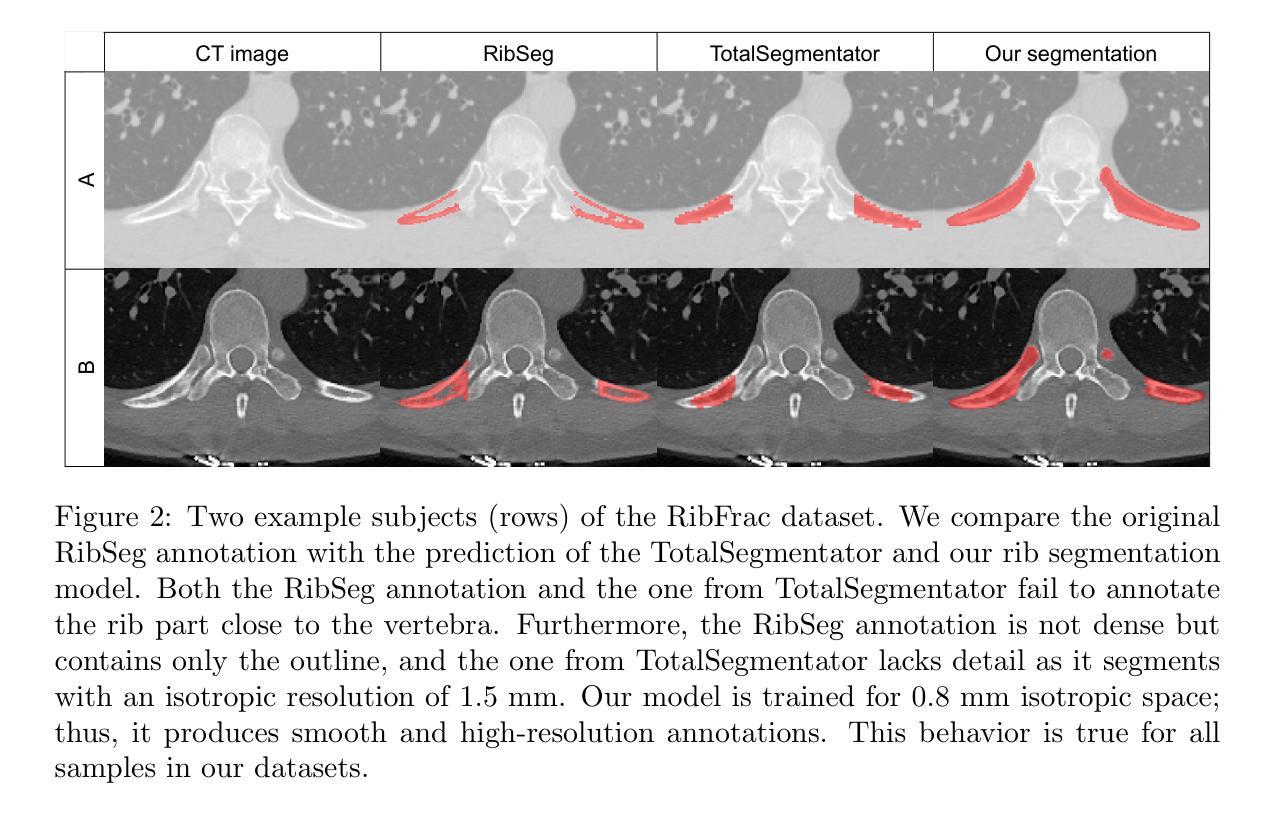
Automated Thoracolumbar Stump Rib Detection and Analysis in a Large CT Cohort
Authors:Hendrik Möller, Hanna Schön, Alina Dima, Benjamin Keinert-Weth, Robert Graf, Matan Atad, Johannes Paetzold, Friederike Jungmann, Rickmer Braren, Florian Kofler, Bjoern Menze, Daniel Rueckert, Jan S. Kirschke
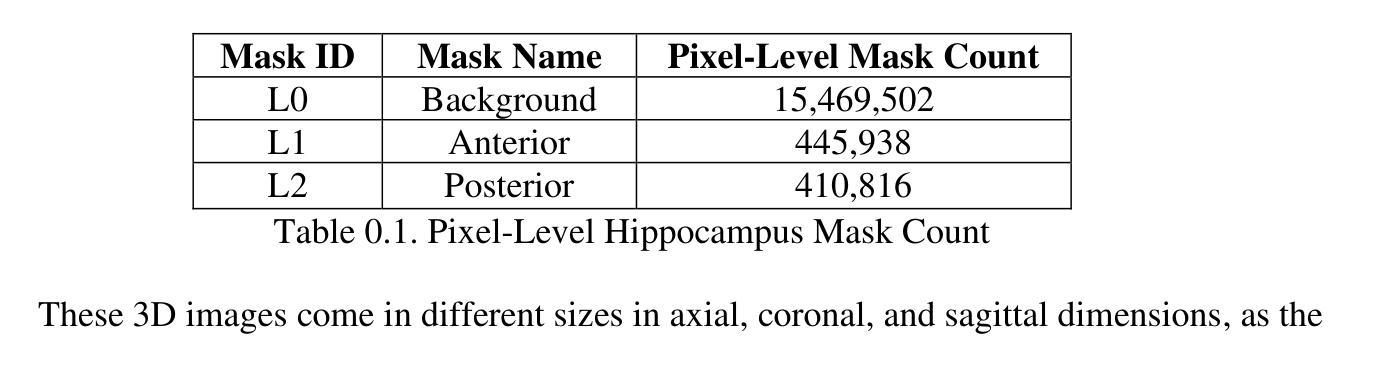
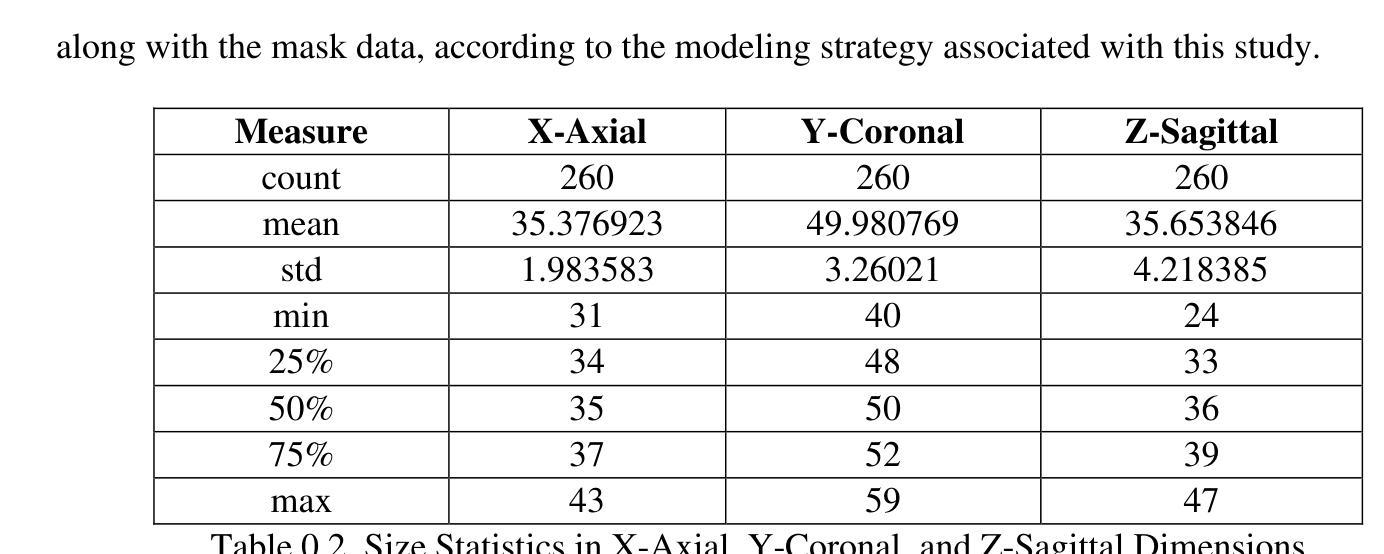
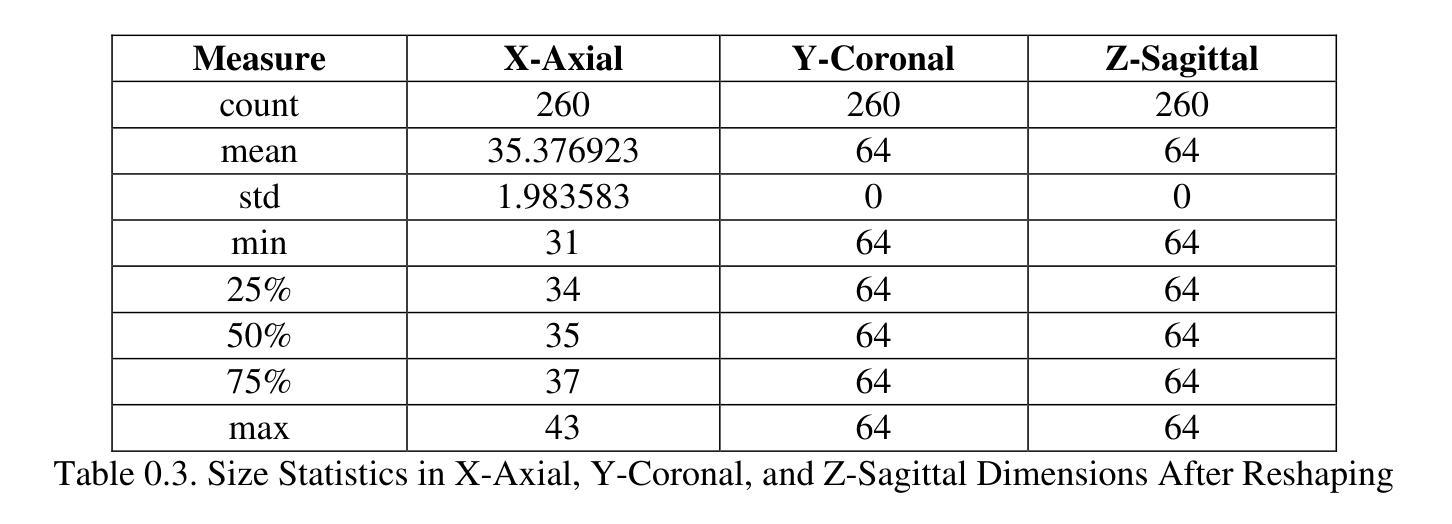
Thoracolumbar stump ribs are one of the essential indicators of thoracolumbar transitional vertebrae or enumeration anomalies. While some studies manually assess these anomalies and describe the ribs qualitatively, this study aims to automate thoracolumbar stump rib detection and analyze their morphology quantitatively. To this end, we train a high-resolution deep-learning model for rib segmentation and show significant improvements compared to existing models (Dice score 0.997 vs. 0.779, p-value < 0.01). In addition, we use an iterative algorithm and piece-wise linear interpolation to assess the length of the ribs, showing a success rate of 98.2%. When analyzing morphological features, we show that stump ribs articulate more posteriorly at the vertebrae (-19.2 +- 3.8 vs -13.8 +- 2.5, p-value < 0.01), are thinner (260.6 +- 103.4 vs. 563.6 +- 127.1, p-value < 0.01), and are oriented more downwards and sideways within the first centimeters in contrast to full-length ribs. We show that with partially visible ribs, these features can achieve an F1-score of 0.84 in differentiating stump ribs from regular ones. We publish the model weights and masks for public use.
胸腰椎残端肋骨是胸腰椎过渡椎或列举异常的重要指征之一。虽然一些研究手动评估这些异常并对其进行定性描述,但本研究旨在自动检测胸腰椎残端肋骨并对其形态进行定量分析。为此,我们训练了一个高分辨率的深度学习模型来进行肋骨分割,并显示出与现有模型的显著改进(Dice得分为0.997与0.779,p值<0.01)。此外,我们使用迭代算法和分段线性插值来评估肋骨的长度,成功率达到98.2%。在分析形态特征时,我们发现残端肋骨在椎体上更向后(-19.2 +- 3.8 vs -13.8 +- 2.5,p值<0.01),更薄(260.6 +- 103.4 vs. 563.6 +- 127.1,p值<0.01),并且在前几厘米内相比正常全长的肋骨,它们的方向更偏向于向下和侧向。我们证明了利用部分可见的肋骨特征,可以将残端肋骨与正常肋骨区分开来,并达到F1分数为0.84。我们公开了模型权重和掩膜供公众使用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究旨在自动化检测胸腰椎残端肋骨,并对其形态进行定量分析和评估。研究训练了高分辨率深度学习模型进行肋骨分割,并展现出相较于现有模型显著的改进(Dice得分0.997对比0.779,p值小于0.01)。通过迭代算法和分段线性插值评估肋骨长度,成功率达98.2%。分析形态学特征显示,残端肋骨在椎体上更向后(-19.2 ± 3.8 对比 -13.8 ± 2.5,p值小于0.01),更薄(260.6 ± 103.4 对比 563.6 ± 127.1,p值小于0.01),并且在前几厘米内向下和侧向倾斜与全长肋骨相比。这些特征可用于区分残端肋骨和正常肋骨,部分可见肋骨的F1分数可达0.84。公开使用模型权重和掩膜。
Key Takeaways
- 研究旨在自动化检测胸腰椎残端肋骨并进行形态定量评估。
- 高分辨率深度学习模型用于肋骨分割,显著优于现有模型。
- 通过迭代算法和分段线性插值准确评估肋骨长度。
- 残端肋骨在椎体位置、厚度、方向性与全长肋骨有显著不同。
- 这些差异可用于区分残端肋骨和正常肋骨。
- 部分可见肋骨的识别准确率较高(F1分数0.84)。
点此查看论文截图

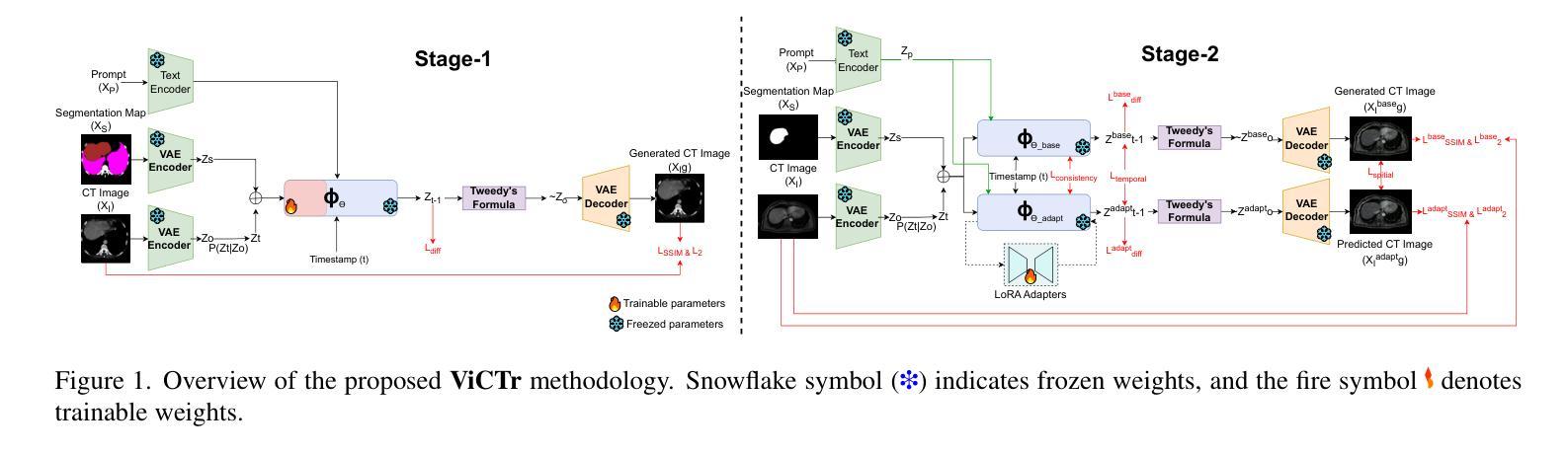
ViCTr: Vital Consistency Transfer for Pathology Aware Image Synthesis
Authors:Onkar Susladkar, Gayatri Deshmukh, Yalcin Tur, Ulas Bagci
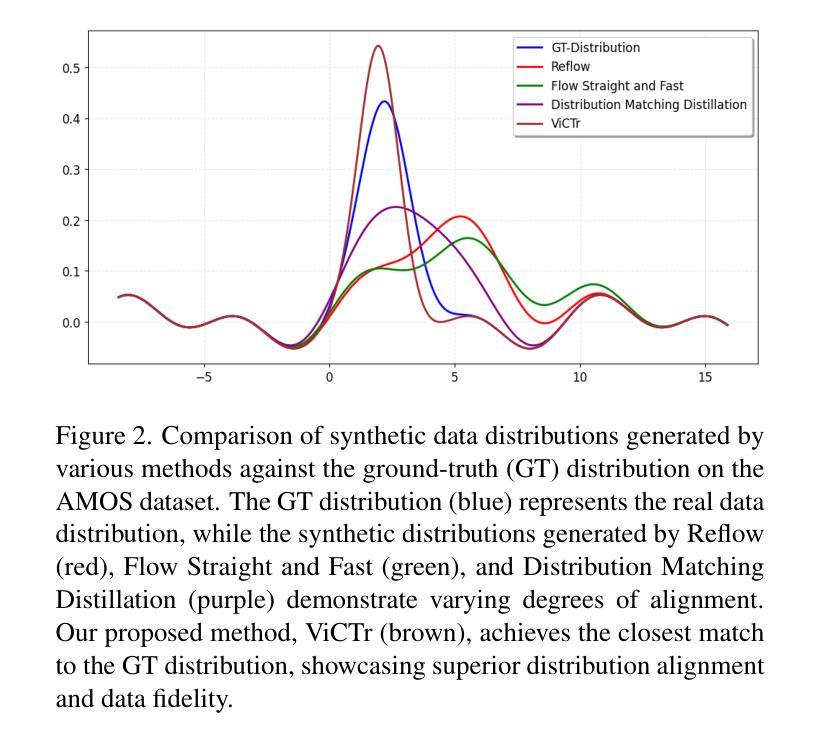
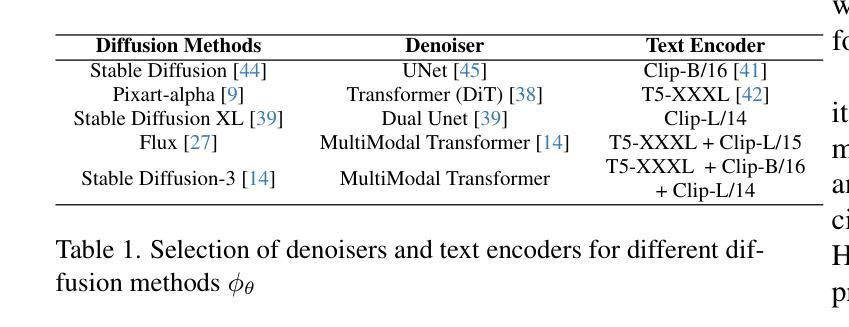
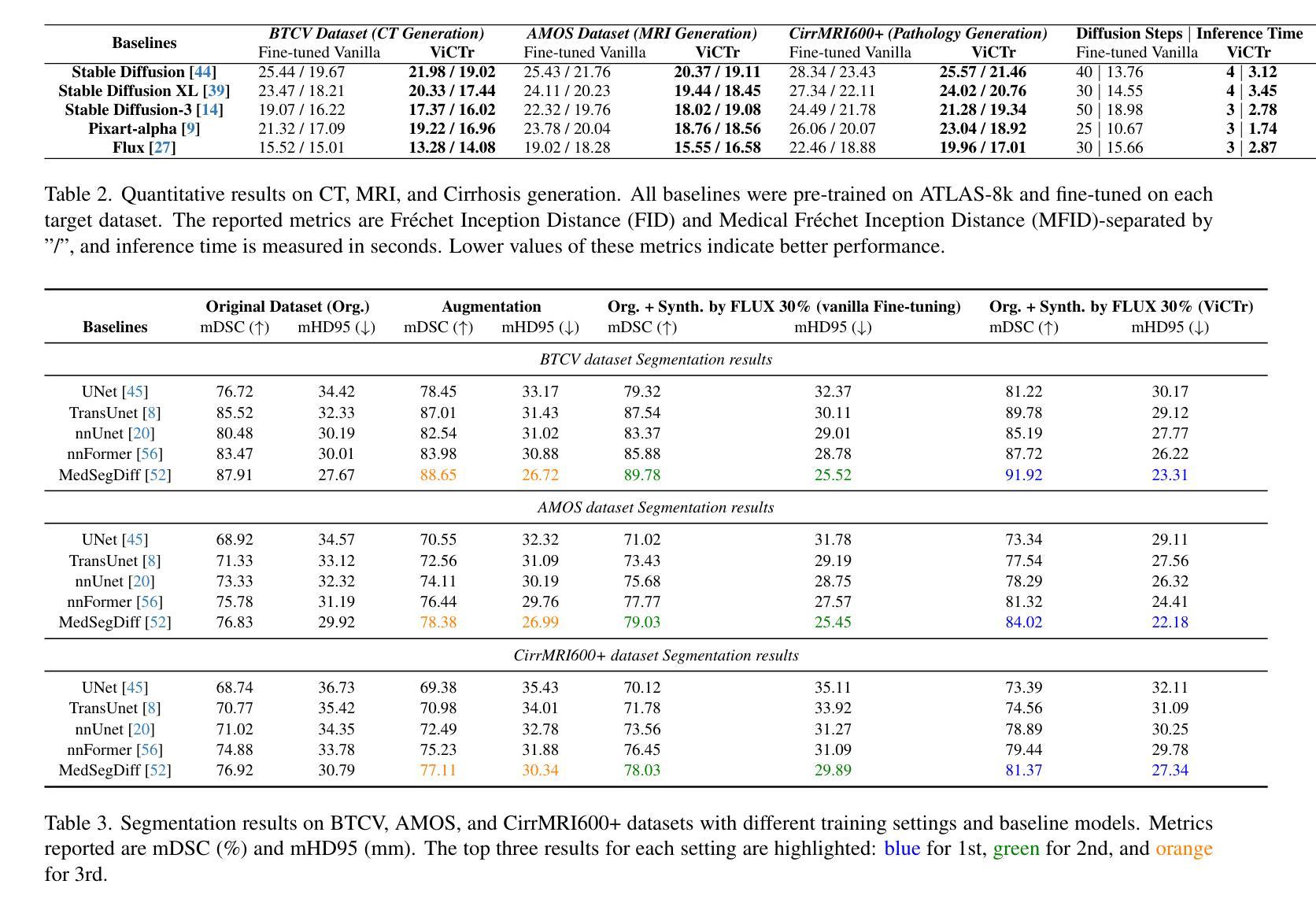
Synthesizing medical images remains challenging due to limited annotated pathological data, modality domain gaps, and the complexity of representing diffuse pathologies such as liver cirrhosis. Existing methods often struggle to maintain anatomical fidelity while accurately modeling pathological features, frequently relying on priors derived from natural images or inefficient multi-step sampling. In this work, we introduce ViCTr (Vital Consistency Transfer), a novel two-stage framework that combines a rectified flow trajectory with a Tweedie-corrected diffusion process to achieve high-fidelity, pathology-aware image synthesis. First, we pretrain ViCTr on the ATLAS-8k dataset using Elastic Weight Consolidation (EWC) to preserve critical anatomical structures. We then fine-tune the model adversarially with Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) modules for precise control over pathology severity. By reformulating Tweedie’s formula within a linear trajectory framework, ViCTr supports one-step sampling, reducing inference from 50 steps to just 4, without sacrificing anatomical realism. We evaluate ViCTr on BTCV (CT), AMOS (MRI), and CirrMRI600+ (cirrhosis) datasets. Results demonstrate state-of-the-art performance, achieving a Medical Frechet Inception Distance (MFID) of 17.01 for cirrhosis synthesis 28% lower than existing approaches and improving nnUNet segmentation by +3.8% mDSC when used for data augmentation. Radiologist reviews indicate that ViCTr-generated liver cirrhosis MRIs are clinically indistinguishable from real scans. To our knowledge, ViCTr is the first method to provide fine-grained, pathology-aware MRI synthesis with graded severity control, closing a critical gap in AI-driven medical imaging research.
医学图像合成仍然是一个充满挑战的任务,由于有限的标注病理数据、模态域差异以及表示弥散性病理(如肝硬化)的复杂性。现有方法往往难以在保持解剖结构真实性的同时准确建模病理特征,经常依赖于从自然图像中得出的先验知识或低效的多步采样。在这项工作中,我们引入了ViCTr(关键一致性转移),这是一个结合校正流轨迹和Tweedie校正扩散过程的新型两阶段框架,以实现高保真、病理感知的图像合成。首先,我们在ATLAS-8k数据集上预训练ViCTr,使用弹性权重整合(EWC)来保留关键的解剖结构。然后,我们使用低阶适应(LoRA)模块对模型进行对抗微调,以精确控制病理严重程度。ViCTr通过在线性轨迹框架内重新制定Tweedie公式,支持一步采样,将推理从50步减少到仅4步,而不损失解剖结构真实性。我们在BTCV(CT)、AMOS(MRI)和CirrMRI600+(肝硬化)数据集上评估了ViCTr。结果表明,其性能达到了最新水平,肝硬化合成的医疗Frechet Inception距离(MFID)达到了17.01,比现有方法降低了28%,在使用数据增强时,nnUNet分割提高了3.8%的mDSC。放射科医生评审表明,ViCTr生成的肝硬化MRI图像与真实扫描图像在临床上无法区分。据我们所知,ViCTr是第一种提供精细、病理感知的MRI合成方法,具有分级严重程度控制功能,填补了人工智能驱动医学成像研究中的一个关键空白。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为ViCTr的新型两阶段框架,用于合成医学图像。该框架结合了校正流轨迹和Tweedie校正扩散过程,实现了高保真、病理感知的图像合成。通过预训练和微调,ViCTr能够在保持解剖结构的同时,精确控制病理严重程度。评估结果表明,ViCTr在合成肝脏硬化图像方面表现出卓越性能,实现了医疗领域最先进的成果。
Key Takeaways
- ViCTr是一个新型的两阶段框架,用于医学图像合成。
- 框架结合了校正流轨迹和Tweedie校正扩散过程,以实现高保真和病理感知的图像合成。
- 通过在ATLAS-8k数据集上进行预训练,ViCTr能够保持关键的解剖结构。
- 使用Low-Rank Adaptation(LoRA)模块对模型进行微调,可精确控制病理严重程度。
- ViCTr将推理步骤从50步减少到仅4步,同时保持解剖结构的现实性。
- 在多个数据集上的评估结果表明,ViCTr在合成肝脏硬化图像方面达到最先进的性能。
点此查看论文截图

MoRe-3DGSMR: Motion-resolved reconstruction framework for free-breathing pulmonary MRI based on 3D Gaussian representation
Authors:Tengya Peng, Ruyi Zha, Qing Zou
This study presents an unsupervised, motion-resolved reconstruction framework for high-resolution, free-breathing pulmonary magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), utilizing a three-dimensional Gaussian representation (3DGS). The proposed method leverages 3DGS to address the challenges of motion-resolved 3D isotropic pulmonary MRI reconstruction by enabling data smoothing between voxels for continuous spatial representation. Pulmonary MRI data acquisition is performed using a golden-angle radial sampling trajectory, with respiratory motion signals extracted from the center of k-space in each radial spoke. Based on the estimated motion signal, the k-space data is sorted into multiple respiratory phases. A 3DGS framework is then applied to reconstruct a reference image volume from the first motion state. Subsequently, a patient-specific convolutional neural network is trained to estimate the deformation vector fields (DVFs), which are used to generate the remaining motion states through spatial transformation of the reference volume. The proposed reconstruction pipeline is evaluated on six datasets from six subjects and bench-marked against three state-of-the-art reconstruction methods. The experimental findings demonstrate that the proposed reconstruction framework effectively reconstructs high-resolution, motion-resolved pulmonary MR images. Compared with existing approaches, it achieves superior image quality, reflected by higher signal-to-noise ratio and contrast-to-noise ratio. The proposed unsupervised 3DGS-based reconstruction method enables accurate motion-resolved pulmonary MRI with isotropic spatial resolution. Its superior performance in image quality metrics over state-of-the-art methods highlights its potential as a robust solution for clinical pulmonary MR imaging.
本研究提出了一种基于三维高斯表示(3DGS)的无监督、运动解析重建框架,用于高分辨率、自由呼吸的肺部磁共振成像(MRI)。该方法利用3DGS解决运动解析三维同向肺部MRI重建的挑战,通过在体素之间进行数据平滑处理,实现连续的空间表示。肺部MRI数据采用黄金角径向采样轨迹采集,从每个径向射线的k空间中心提取呼吸运动信号。基于估计的运动信号,将k空间数据按多个呼吸阶段进行排序。然后应用一个基于图像结构的三维高表示法重建出一个基准图像体积的第一运动状态。接着训练病人特定的卷积神经网络来估计变形向量场(DVFs),并通过对参考体积的空间变换生成剩余的运动状态。该重建流程在六个不同主题的六组数据集上进行了评估,并与三种最新重建方法进行了比较。实验结果表明,所提出的重建框架可以有效地重建出高分辨率的运动解析肺部MR图像。与现有方法相比,它在图像质量和信号噪声比以及对比噪声比方面表现出更高的优越性。这种基于无监督的3DGS重建方法能够实现精确的运动解析肺部MRI,具有同向空间分辨率。其在图像质量指标上的卓越性能突出表明了其在临床肺部MRI中的稳健解决方案潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本研究提出了一种无监督的、基于运动解析的重建框架,用于高分辨率的自由呼吸肺部磁共振成像(MRI)。该框架采用三维高斯表示(3DGS)技术,解决了运动解析的三维立体肺部MRI重建问题。通过三维高斯表示,数据在体素间得以平滑处理,实现连续的空间表示。该研究使用黄金角径向采样轨迹进行肺部MRI数据采集,从每个径向射线的k空间中心提取呼吸运动信号。基于估计的运动信号,将k空间数据按多个呼吸阶段进行排序。然后,使用3DGS框架重建参考图像体积的第一个运动状态。随后,训练患者特定的卷积神经网络来估计变形矢量场(DVFs),用于通过参考体积的空间变换生成其余的运动状态。该重建流程在六个数据集上进行了评估,并与三种最先进的重建方法进行了比较。实验结果表明,所提出的重建框架有效地重建了高分辨率的运动解析肺部MR图像。与现有方法相比,它在图像质量和信号噪声比以及对比噪声比方面表现出优越性。这项无监督的基于三维高斯表示的重建方法能够实现精确的运动解析肺部MRI,具有各向同性的空间分辨率。其在图像质量指标上的卓越性能突显了其在临床肺部MRI中的稳健解决方案的潜力。
关键见解
- 本研究提出了一种无监督的重建框架,用于高分辨率的自由呼吸肺部磁共振成像(MRI)。
- 采用了三维高斯表示(3DGS)技术,以解决运动解析的三维立体肺部MRI重建的挑战。
- 通过黄金角径向采样轨迹采集数据,并从k空间的中心提取呼吸运动信号。
- 提出了基于估计的运动信号的k空间数据排序方法。
- 使用患者特定的卷积神经网络估计变形矢量场(DVFs),用于生成运动状态。
- 该方法实现了高图像质量,表现在较高的信号噪声比和对比噪声比。
点此查看论文截图

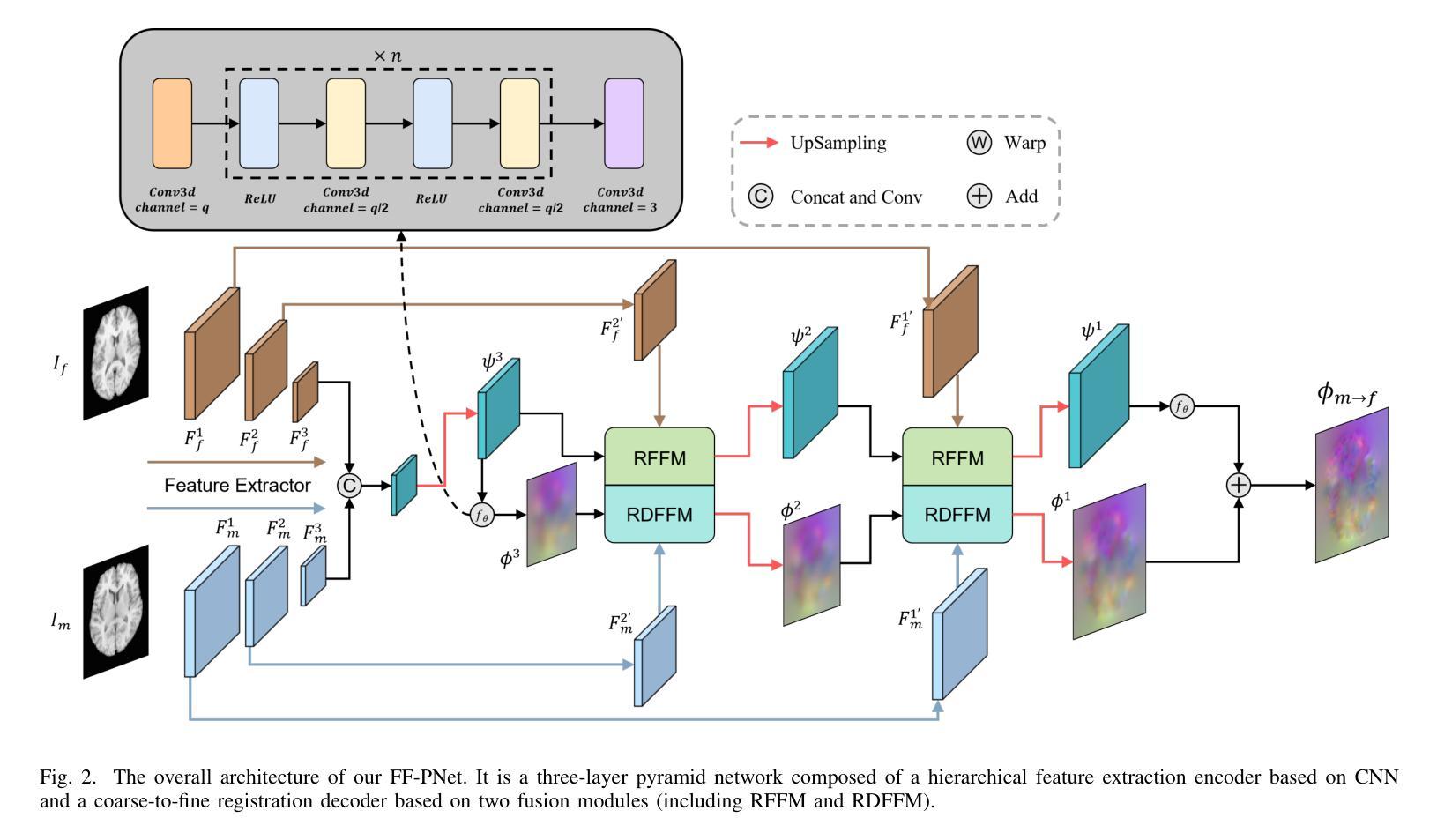
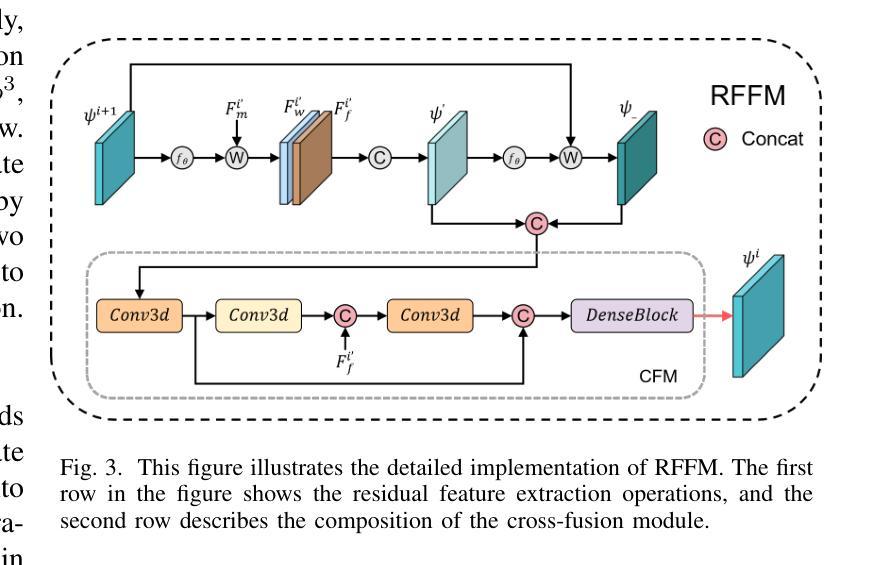
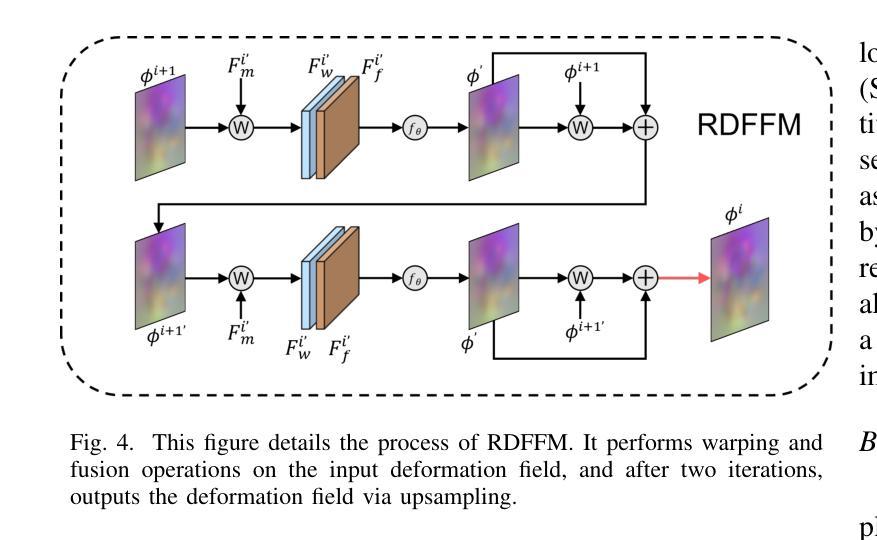
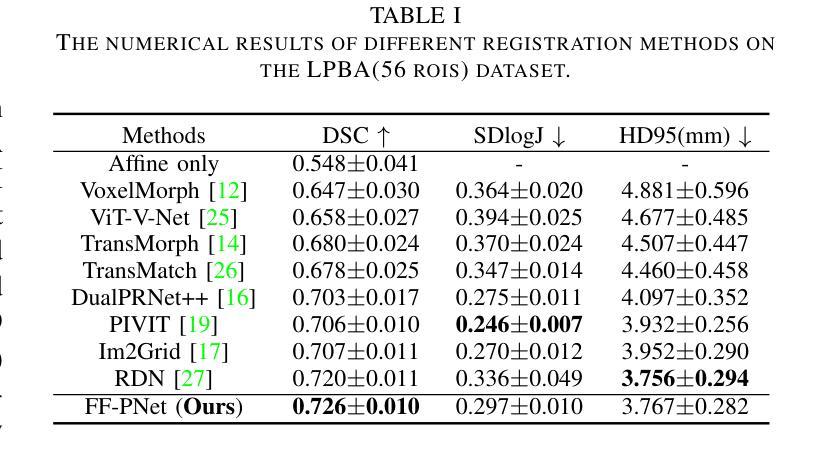
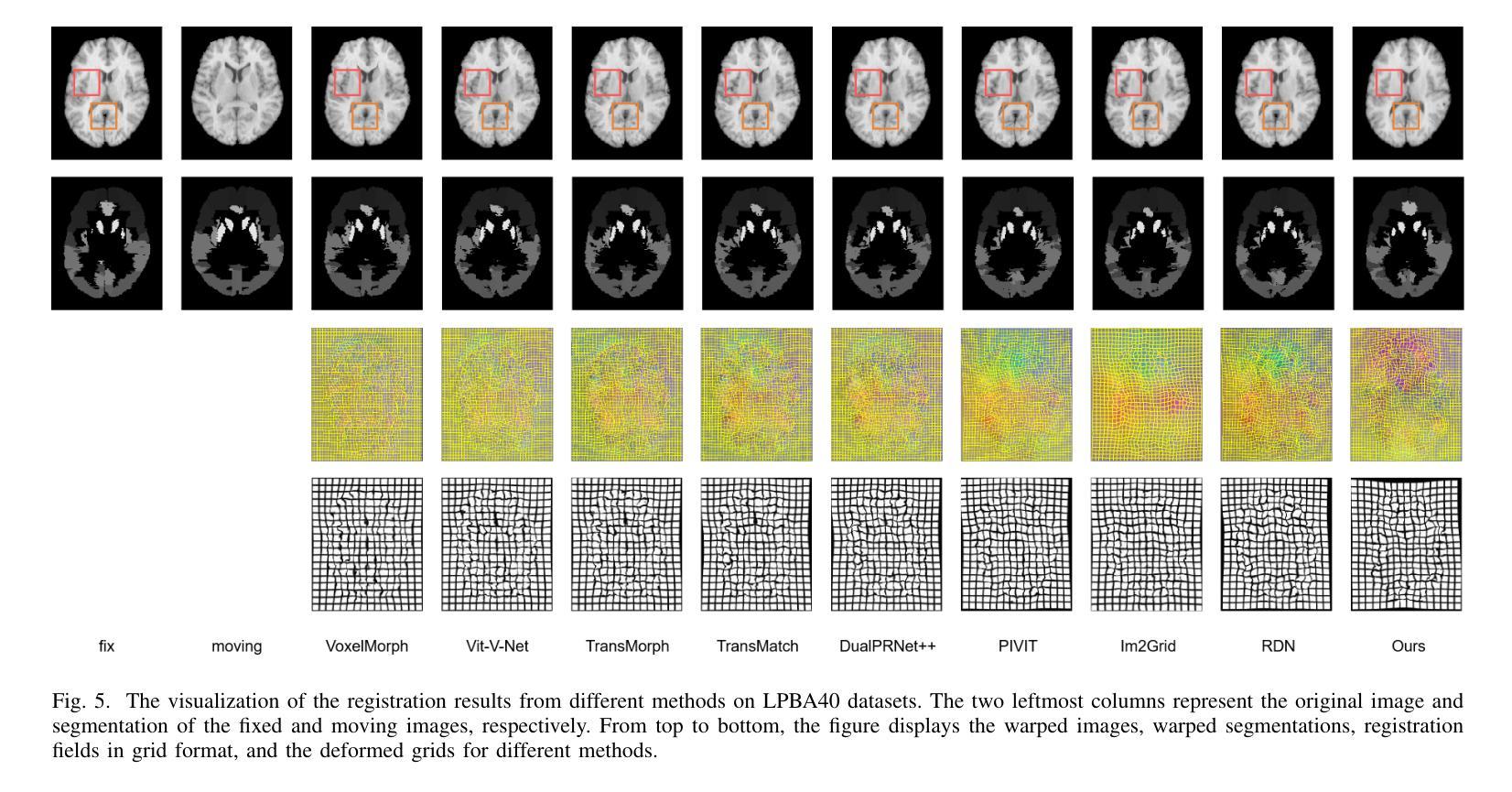
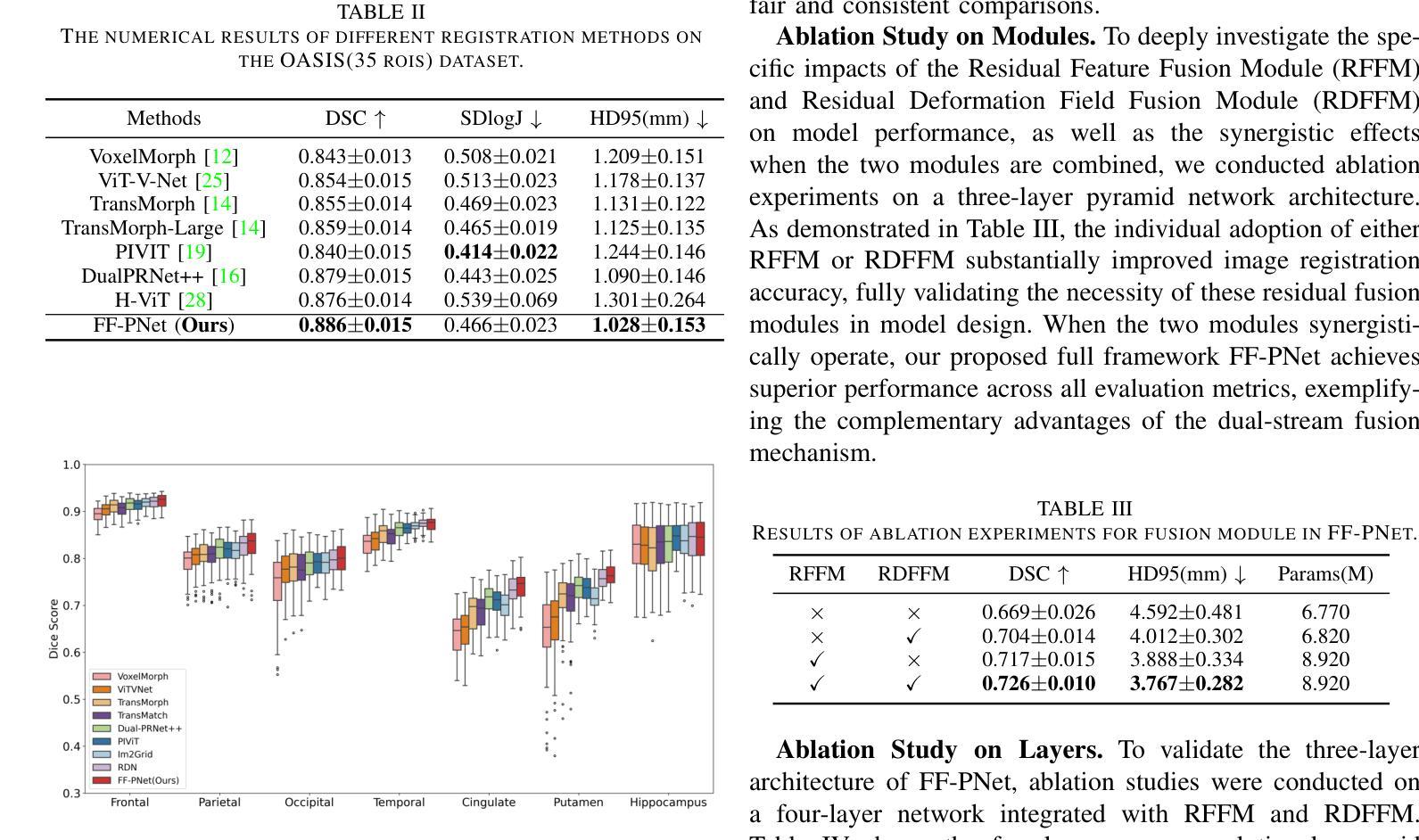
FF-PNet: A Pyramid Network Based on Feature and Field for Brain Image Registration
Authors:Ying Zhang, Shuai Guo, Chenxi Sun, Yuchen Zhu, Jinhai Xiang
In recent years, deformable medical image registration techniques have made significant progress. However, existing models still lack efficiency in parallel extraction of coarse and fine-grained features. To address this, we construct a new pyramid registration network based on feature and deformation field (FF-PNet). For coarse-grained feature extraction, we design a Residual Feature Fusion Module (RFFM), for fine-grained image deformation, we propose a Residual Deformation Field Fusion Module (RDFFM). Through the parallel operation of these two modules, the model can effectively handle complex image deformations. It is worth emphasizing that the encoding stage of FF-PNet only employs traditional convolutional neural networks without any attention mechanisms or multilayer perceptrons, yet it still achieves remarkable improvements in registration accuracy, fully demonstrating the superior feature decoding capabilities of RFFM and RDFFM. We conducted extensive experiments on the LPBA and OASIS datasets. The results show our network consistently outperforms popular methods in metrics like the Dice Similarity Coefficient.
近年来,可变形医学图像配准技术取得了重大进展。然而,现有模型在粗粒度和细粒度特征的并行提取方面仍然存在效率不足。为解决这一问题,我们构建了一个基于特征和变形场(FF-PNet)的新金字塔配准网络。对于粗粒度特征提取,我们设计了残差特征融合模块(RFFM),对于细粒度图像变形,我们提出了残差变形场融合模块(RDFFM)。这两个模块的并行操作使得模型能够有效地处理复杂的图像变形。值得一提的是,FF-PNet的编码阶段仅采用传统的卷积神经网络,没有任何注意力机制或多层感知器,但在配准精度上仍实现了显著的改进,充分展示了RFFM和RDFFM的优秀特征解码能力。我们在LPBA和OASIS数据集上进行了大量实验。结果表明,我们的网络在Dice相似系数等指标上始终优于流行的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像配准技术近年来取得显著进展,但仍存在粗粒度和细粒度特征并行提取效率不高的问题。为此,我们构建了一个基于特征和变形场的新颖金字塔配准网络(FF-PNet)。为粗粒度特征提取设计了残差特征融合模块(RFFM),为细粒度图像变形提出了残差变形场融合模块(RDFFM)。这两个模块的并行操作使得模型能够更有效地处理复杂的图像变形。该网络在编码阶段仅使用传统的卷积神经网络,未采用任何注意力机制或多层感知器,但在配准精度上取得了显著的提升,充分展示了RFFM和RDFFM的优秀特征解码能力。在LPBA和OASIS数据集上的实验结果表明,我们的网络在Dice相似系数等指标上表现优于流行的方法。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像配准技术虽有所进步,但在粗粒度和细粒度特征的并行提取效率上仍有提升空间。
- 提出了基于特征和变形场的新颖金字塔配准网络(FF-PNet)。
- 设计了残差特征融合模块(RFFM)用于粗粒度特征提取。
- 提出了残差变形场融合模块(RDFFM)用于处理细粒度图像变形。
- FF-PNet在编码阶段仅使用传统卷积神经网络,不使用注意力机制或多层感知器。
- FF-PNet在配准精度上取得了显著的提升,展示了RFFM和RDFFM的优秀特征解码能力。
点此查看论文截图

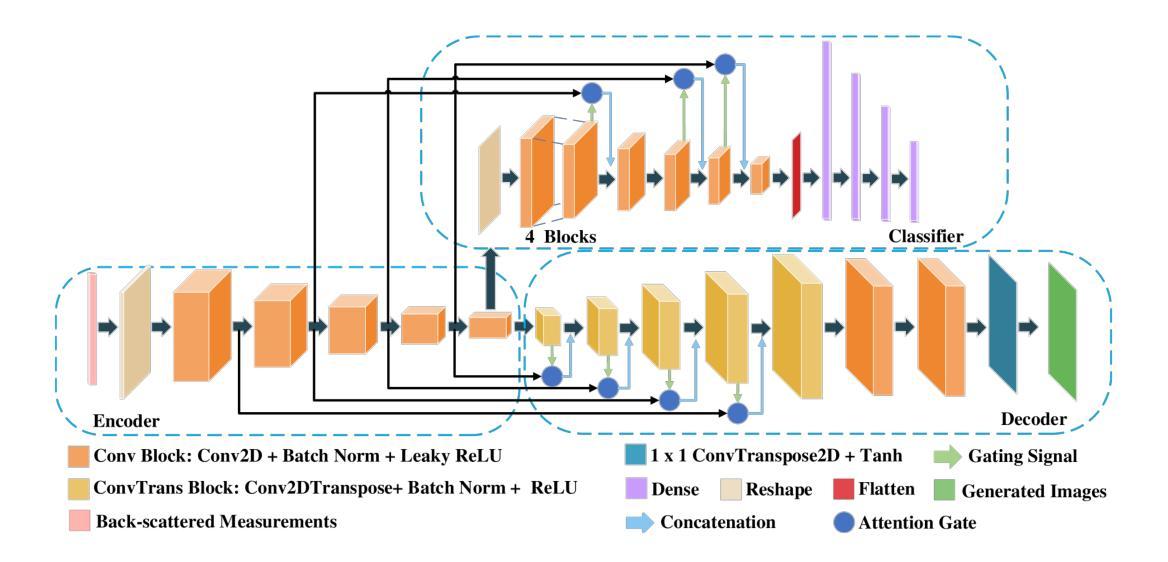
Integrated Image Reconstruction and Target Recognition based on Deep Learning Technique
Authors:Cien Zhang, Jiaming Zhang, Jiajun He, Okan Yurduseven
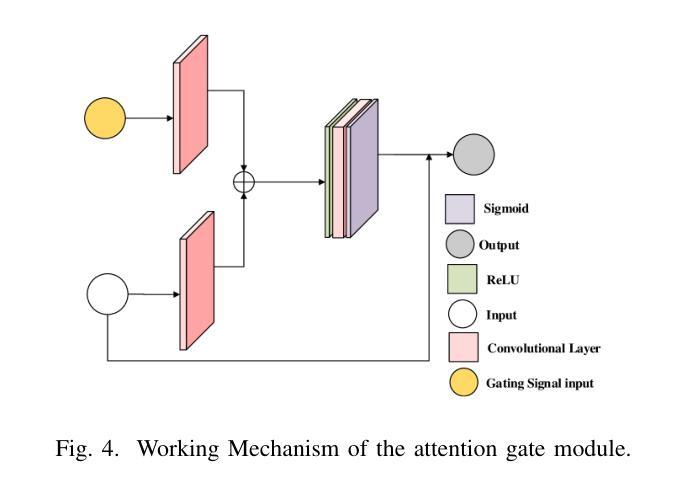
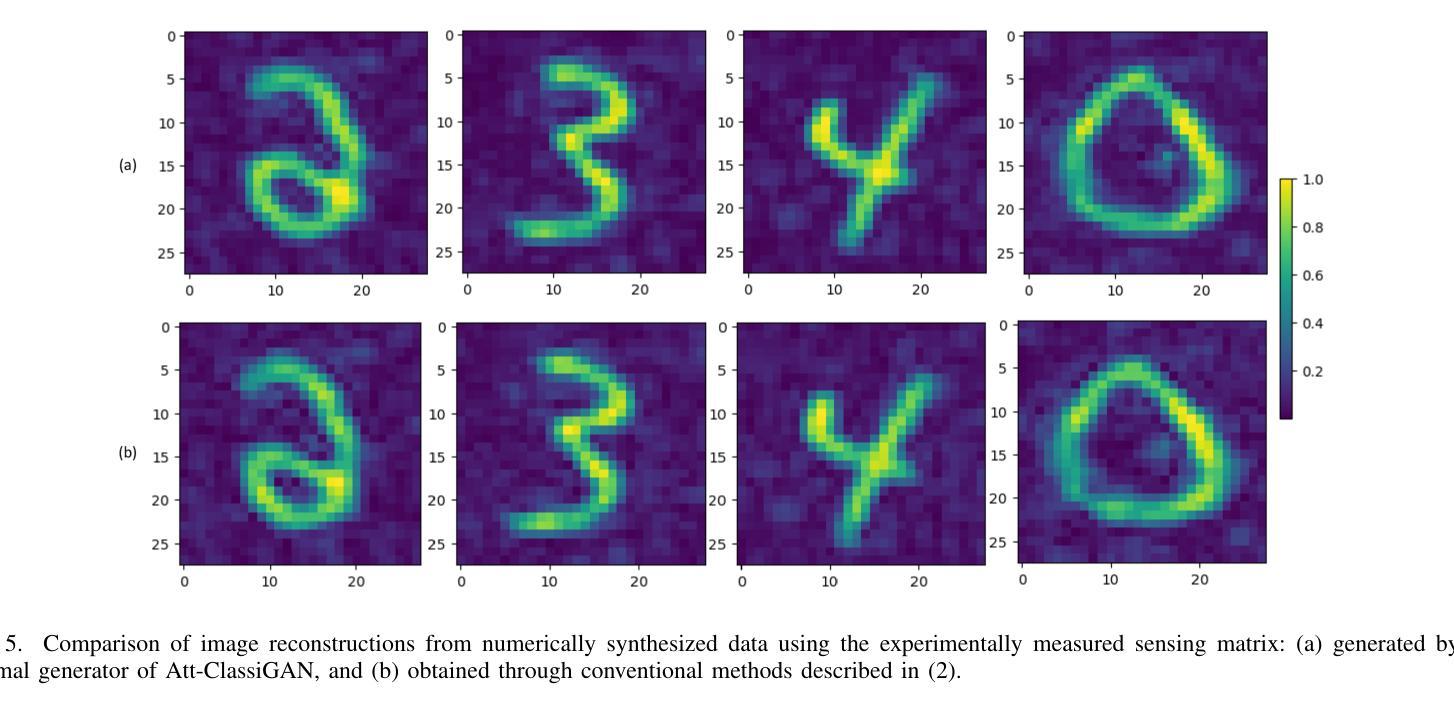
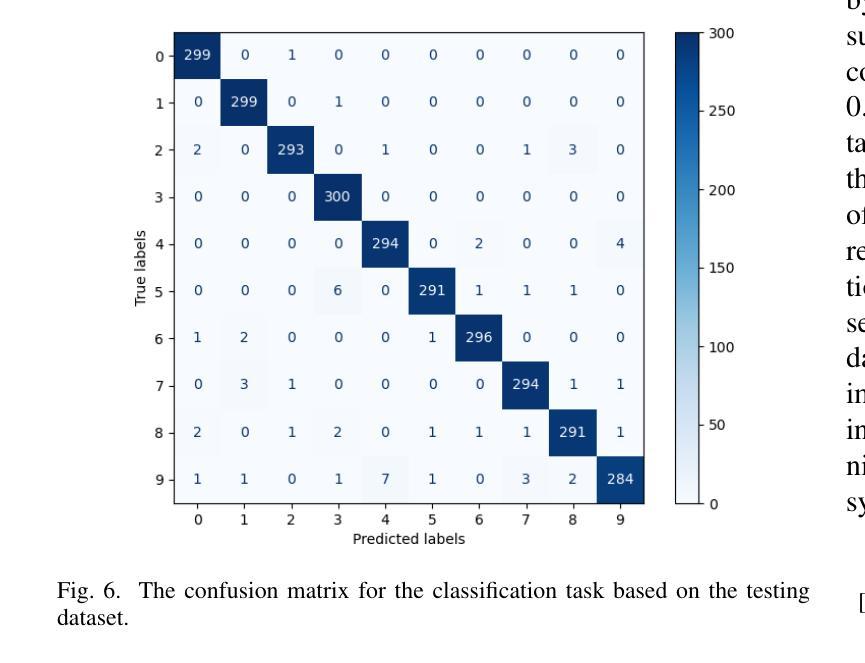
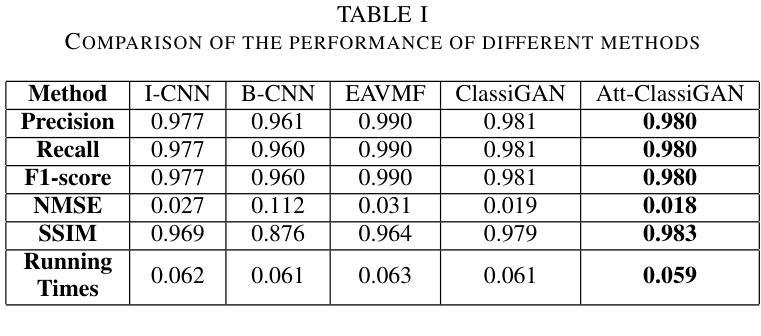
Computational microwave imaging (CMI) has gained attention as an alternative technique for conventional microwave imaging techniques, addressing their limitations such as hardware-intensive physical layer and slow data collection acquisition speed to name a few. Despite these advantages, CMI still encounters notable computational bottlenecks, especially during the image reconstruction stage. In this setting, both image recovery and object classification present significant processing demands. To address these challenges, our previous work introduced ClassiGAN, which is a generative deep learning model designed to simultaneously reconstruct images and classify targets using only back-scattered signals. In this study, we build upon that framework by incorporating attention gate modules into ClassiGAN. These modules are intended to refine feature extraction and improve the identification of relevant information. By dynamically focusing on important features and suppressing irrelevant ones, the attention mechanism enhances the overall model performance. The proposed architecture, named Att-ClassiGAN, significantly reduces the reconstruction time compared to traditional CMI approaches. Furthermore, it outperforms current advanced methods, delivering improved Normalized Mean Squared Error (NMSE), higher Structural Similarity Index (SSIM), and better classification outcomes for the reconstructed targets.
计算微波成像(CMI)作为一种替代传统微波成像的技术,引起了人们的关注。它克服了传统微波成像技术的一些局限性,如硬件密集的物理层和缓慢的数据采集速度等。尽管具有这些优势,但CMI仍然面临显著的计算瓶颈,特别是在图像重建阶段。在这种情况下,图像恢复和对象分类都呈现出巨大的处理需求。为了解决这些挑战,我们之前的工作引入了ClassiGAN,这是一个生成式深度学习模型,旨在仅使用反射信号同时重建图像和分类目标。在这项研究中,我们在ClassiGAN中融入了注意力门模块,以此为基础构建了一个新的框架。这些模块旨在改进特征提取并提高对相关信息识别的能力。通过动态关注重要特征并抑制不相关特征,注意力机制提高了整体模型性能。所提出的架构(称为Att-ClassiGAN)与传统CMI方法相比,显著减少了重建时间。此外,它在改进了归一化均方误差(NMSE)、提高了结构相似性指数(SSIM)以及为重建目标提供了更好的分类结果方面,表现出超越当前先进方法的能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to The 2025 15th IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Communications and Computing (ICSPCC 2025)
Summary
本文介绍了计算微波成像(CMI)作为一种替代传统微波成像技术的新方法,虽然具有解决硬件密集的物理层和慢数据采集获取速度等限制的优势,但在图像重建阶段仍面临重要的计算瓶颈。为应对这些挑战,研究者在先前工作的基础上引入了ClassiGAN,这是一种生成深度学习模型,能够同时重建图像并分类目标,仅使用后向散射信号。本研究在ClassiGAN框架的基础上,融入了注意力门模块,旨在优化特征提取,提高相关信息的识别能力。通过动态关注重要特征并抑制不相关特征,提高了模型的总体性能。提出的架构Att-ClassiGAN与传统CMI方法相比,显著减少了重建时间,并且在改进归一化均方误差(NMSE)、结构相似性指数(SSIM)和重建目标的分类结果方面表现优越。
Key Takeaways
- 计算微波成像(CMI)作为传统微波成像技术的替代方法,具有解决硬件密集和慢数据采集等限制的优势。
- CMI在图像重建阶段仍面临计算瓶颈,图像恢复和目标分类存在重大处理需求。
- ClassiGAN是一种生成深度学习模型,能够同时重建图像和分类目标,使用背散射信号。
- 研究在ClassiGAN框架中融入注意力门模块,以提高特征提取和相关信息识别的性能。
- 注意力机制通过动态关注重要特征并抑制不相关特征,提高了模型总体性能。
- 提出的Att-ClassiGAN架构与传统CMI方法相比,显著减少了重建时间。
点此查看论文截图

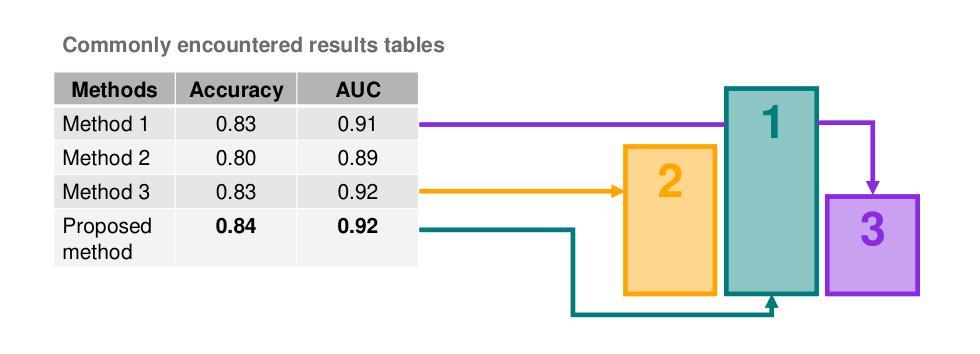
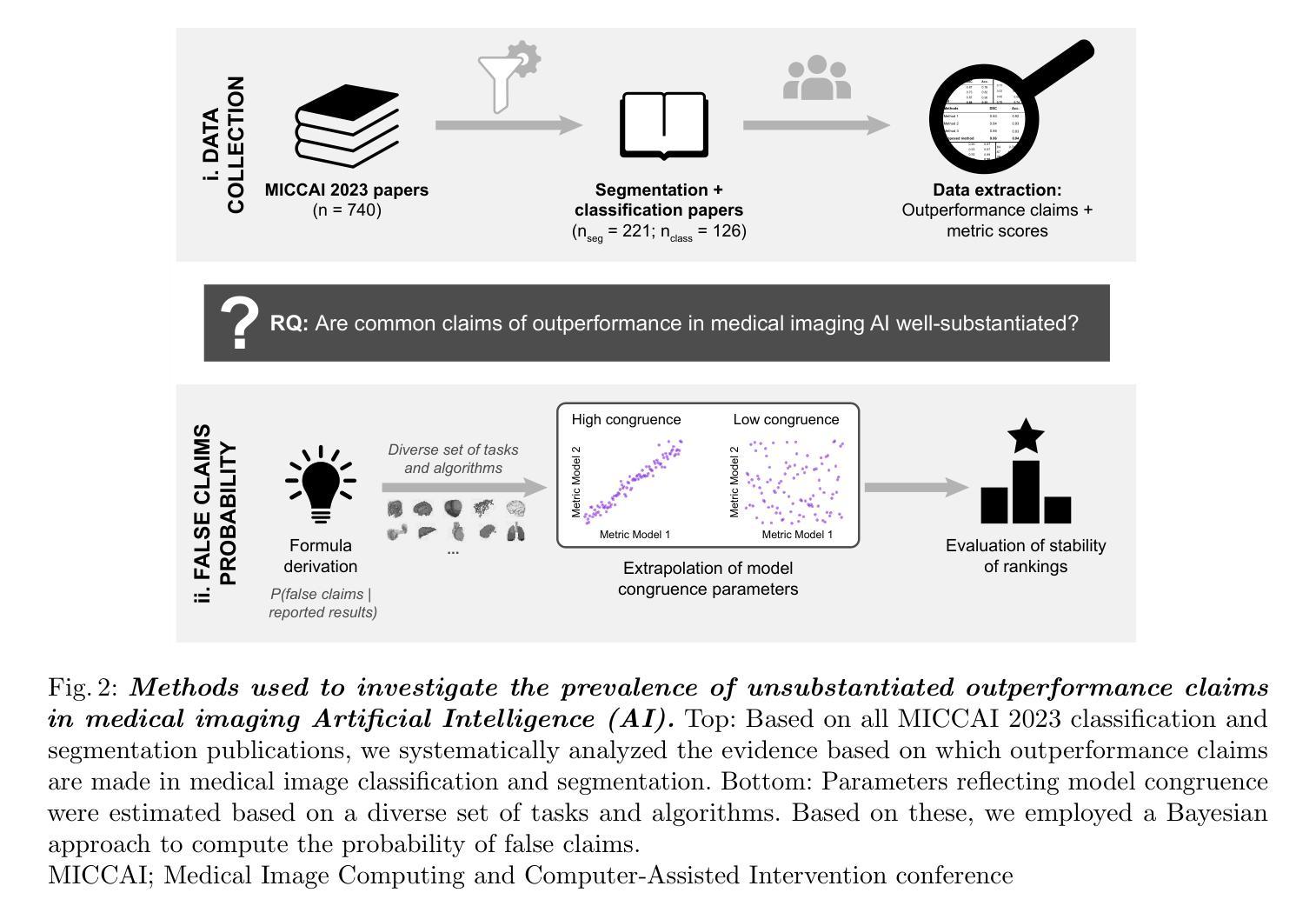
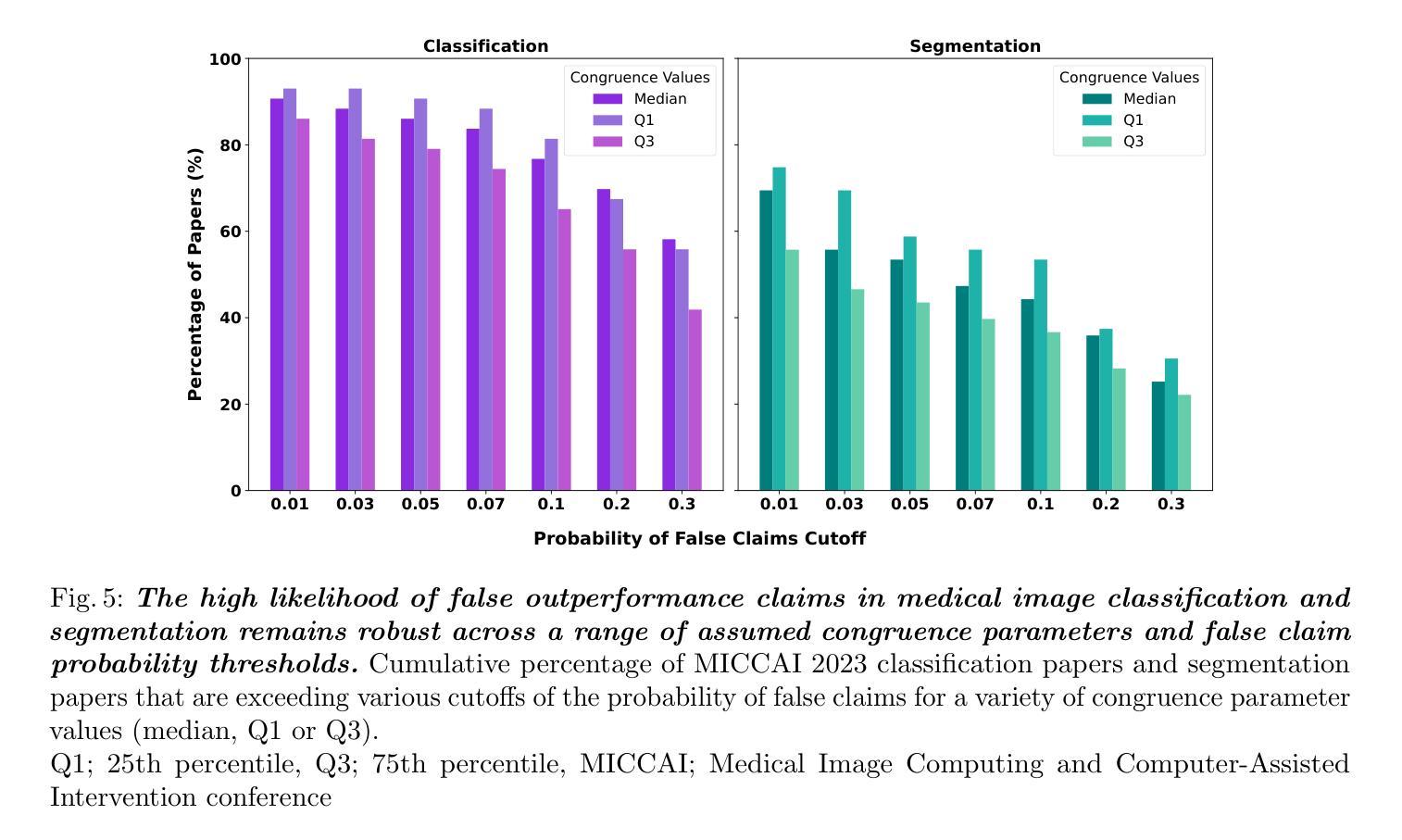
False Promises in Medical Imaging AI? Assessing Validity of Outperformance Claims
Authors:Evangelia Christodoulou, Annika Reinke, Pascaline Andrè, Patrick Godau, Piotr Kalinowski, Rola Houhou, Selen Erkan, Carole H. Sudre, Ninon Burgos, Sofiène Boutaj, Sophie Loizillon, Maëlys Solal, Veronika Cheplygina, Charles Heitz, Michal Kozubek, Michela Antonelli, Nicola Rieke, Antoine Gilson, Leon D. Mayer, Minu D. Tizabi, M. Jorge Cardoso, Amber Simpson, Annette Kopp-Schneider, Gaël Varoquaux, Olivier Colliot, Lena Maier-Hein
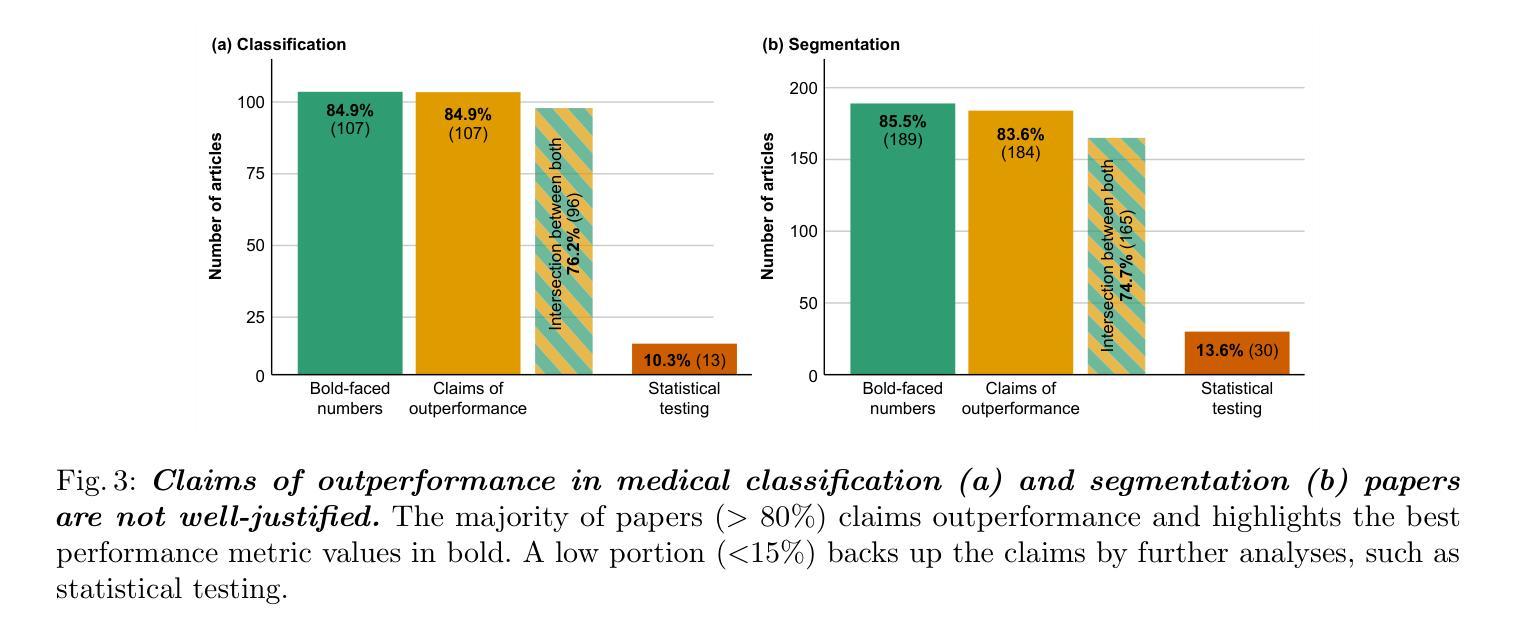
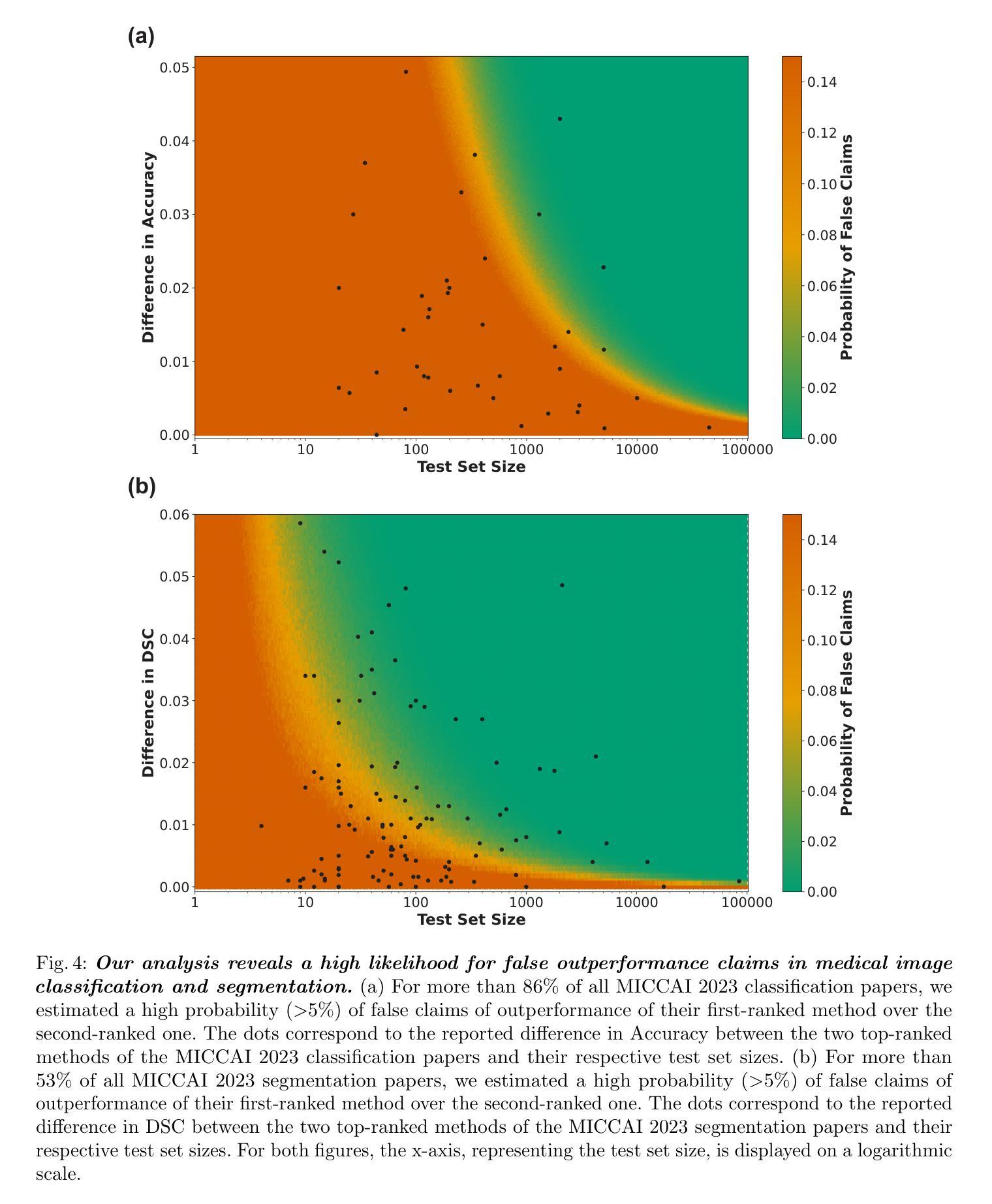
Performance comparisons are fundamental in medical imaging Artificial Intelligence (AI) research, often driving claims of superiority based on relative improvements in common performance metrics. However, such claims frequently rely solely on empirical mean performance. In this paper, we investigate whether newly proposed methods genuinely outperform the state of the art by analyzing a representative cohort of medical imaging papers. We quantify the probability of false claims based on a Bayesian approach that leverages reported results alongside empirically estimated model congruence to estimate whether the relative ranking of methods is likely to have occurred by chance. According to our results, the majority (>80%) of papers claims outperformance when introducing a new method. Our analysis further revealed a high probability (>5%) of false outperformance claims in 86% of classification papers and 53% of segmentation papers. These findings highlight a critical flaw in current benchmarking practices: claims of outperformance in medical imaging AI are frequently unsubstantiated, posing a risk of misdirecting future research efforts.
在医学影像人工智能(AI)研究中,性能对比是根本,通常基于通用性能指标上的相对改进来提出优越性主张。然而,此类主张往往仅依赖于经验平均性能。在本文中,我们通过分析具有代表性的医学影像论文,探究新提出的方法是否真正优于最新技术。我们基于贝叶斯方法量化错误主张的概率,该方法利用报告结果和实证估计的模型一致性来估计方法的相对排名是否可能偶然发生。根据我们的结果,在引入新方法时,大多数(> 80%)的论文主张性能优越。我们的分析还显示,分类论文中有高达86%和分割论文中有高达53%存在高概率(> 5%)的虚假性能优越主张。这些发现突显了当前基准测试实践中的一个关键缺陷:医学影像AI的优越性能主张往往缺乏依据,存在误导未来研究努力的风险。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文调查了医学成像人工智能领域新提出的方法是否真正超越了现有技术。通过基于贝叶斯方法的统计分析,发现大多数论文在引入新方法时声称性能有所提升,但存在较高的虚假声称概率。分类论文中的虚假声称概率更高。这揭示了当前基准测试实践中的一个关键缺陷:医学成像人工智能性能提升的声称往往缺乏依据,可能导致未来研究工作的误导。
Key Takeaways
- 医学成像AI研究领域,性能比较是基础研究的核心,但基于经验均值性能的相对改进来声称优越性可能存在缺陷。
- 新方法超越现有技术的声称在多数医学成像论文中普遍存在。
- 基于贝叶斯方法的统计分析揭示了虚假性能提升声称的高概率。
- 分类论文中的虚假声称概率高于分割论文。
- 当前基准测试实践存在关键缺陷,即性能提升声称缺乏实质依据。
- 虚假声称可能导致未来研究工作的误导。
点此查看论文截图

Advancing 3D Medical Image Segmentation: Unleashing the Potential of Planarian Neural Networks in Artificial Intelligence
Authors:Ziyuan Huang, Kevin Huggins, Srikar Bellur
Our study presents PNN-UNet as a method for constructing deep neural networks that replicate the planarian neural network (PNN) structure in the context of 3D medical image data. Planarians typically have a cerebral structure comprising two neural cords, where the cerebrum acts as a coordinator, and the neural cords serve slightly different purposes within the organism’s neurological system. Accordingly, PNN-UNet comprises a Deep-UNet and a Wide-UNet as the nerve cords, with a densely connected autoencoder performing the role of the brain. This distinct architecture offers advantages over both monolithic (UNet) and modular networks (Ensemble-UNet). Our outcomes on a 3D MRI hippocampus dataset, with and without data augmentation, demonstrate that PNN-UNet outperforms the baseline UNet and several other UNet variants in image segmentation.
我们的研究提出了PNN-UNet方法,这是一种构建深度神经网络的方法,在3D医学图像数据背景下复制了平板虫神经网络(PNN)结构。平板虫的大脑结构通常包括两条神经索,其中大脑起到协调作用,而神经索在生物神经系统中起到略微不同的作用。因此,PNN-UNet由Deep-UNet和Wide-UNet作为神经索组成,密集连接的自动编码器则充当大脑的角色。这种独特的架构相较于单一(UNet)和网络模块(Ensemble-UNet)具有优势。我们在带有和不带有数据增强的3D MRI海马体数据集上的结果证明,PNN-UNet在图像分割方面的性能优于基准UNet和其他几个UNet变体。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 36 pages, 8 figures, 21 tables
Summary
本文研究了PNN-UNet方法,该方法用于构建深度神经网络,以模拟平面动物神经网络(PNN)结构处理3D医学图像数据。PNN-UNet包括Deep-UNet和Wide-UNet作为神经索,并配备一个密集连接的自动编码器作为大脑。这种独特架构在图像分割方面优于单一UNet和模块化网络Ensemble-UNet,对3D MRI海马体数据集的结果验证了PNN-UNet的优越性。
Key Takeaways
- PNN-UNet是一种结合了Deep-UNet和Wide-UNet结构的深度神经网络方法。
- PNN-UNet设计灵感来源于平面动物的神经网络结构,具有独特的架构。
- PNN-UNet在处理3D医学图像数据时表现出优秀的性能。
- 通过在3D MRI海马体数据集上进行实验,验证了PNN-UNet在图像分割方面的优越性。
- PNN-UNet相比传统UNet和其他UNet变体有更高的性能。
- 数据增强在PNN-UNet的性能提升中可能起到了关键作用。
点此查看论文截图

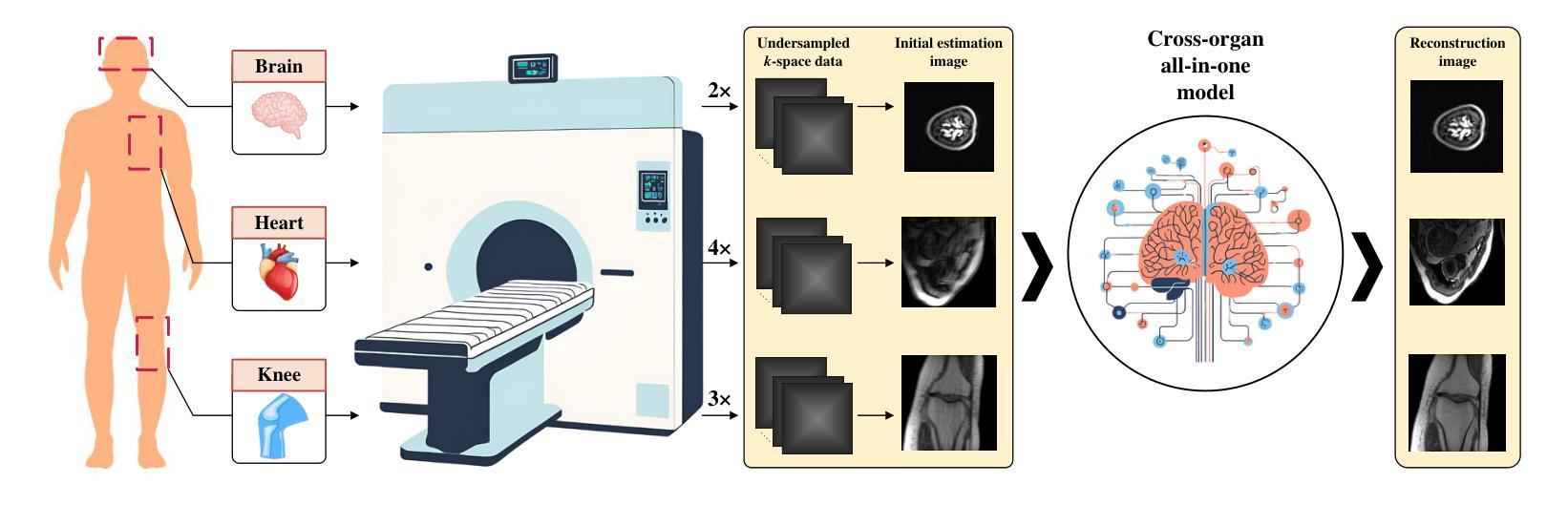
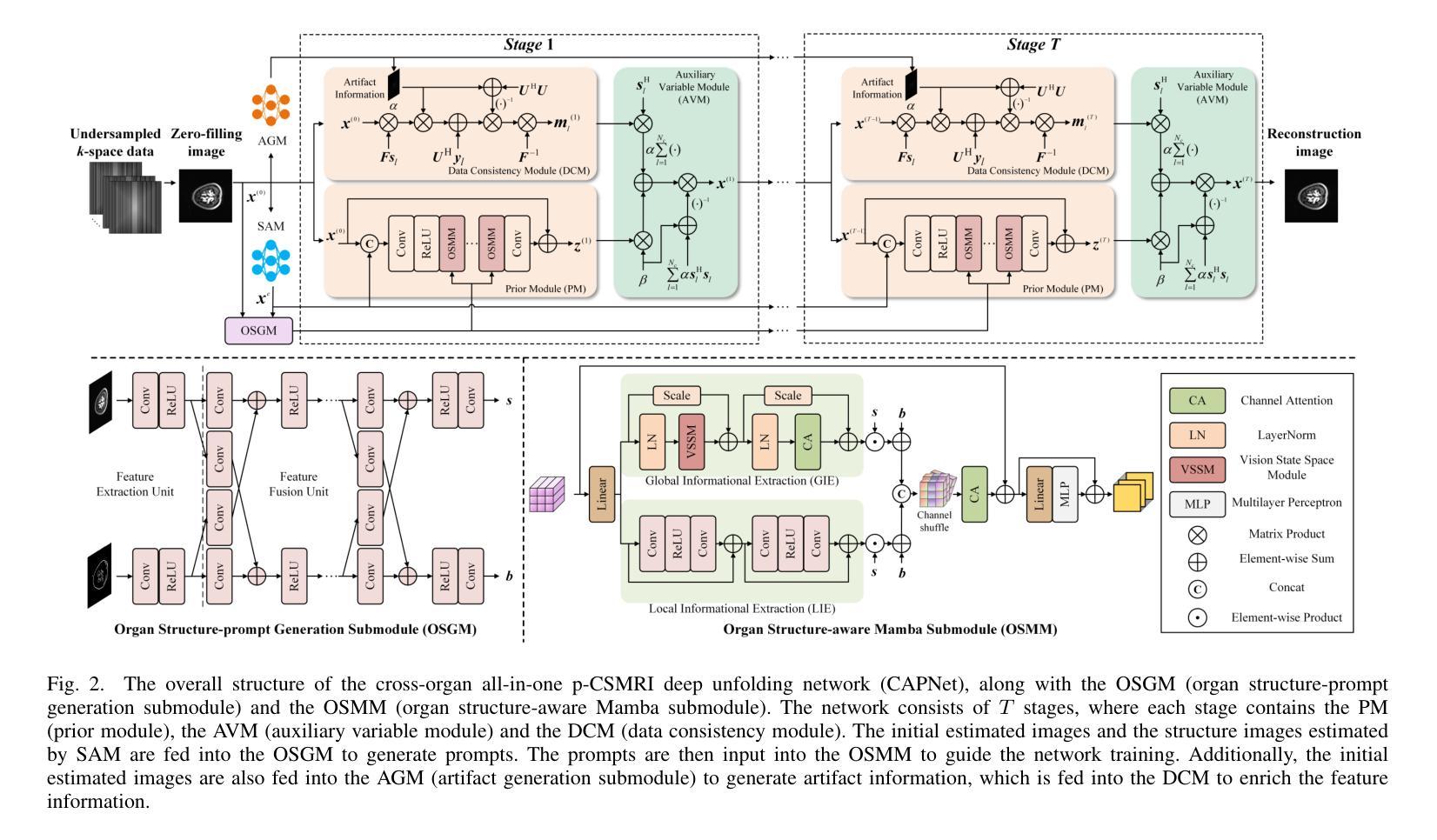
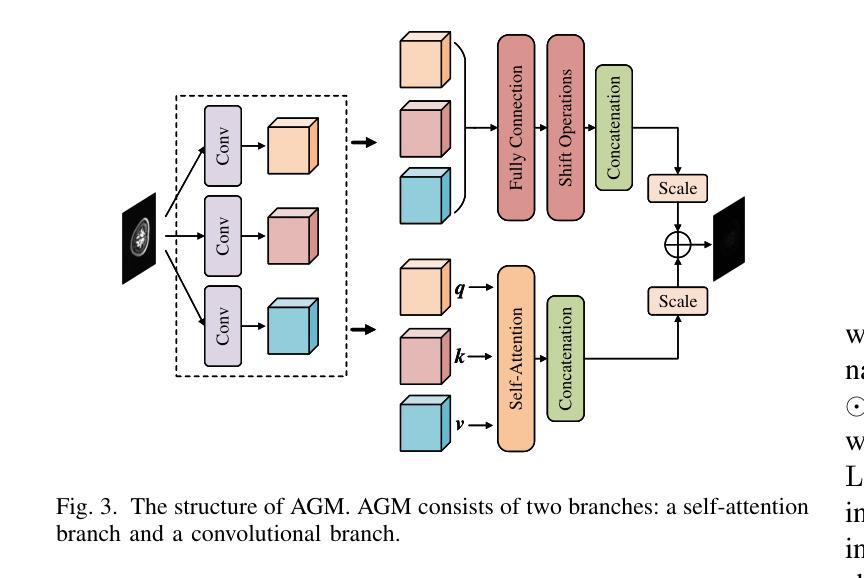
Cross-organ all-in-one parallel compressed sensing magnetic resonance imaging
Authors:Baoshun Shi, Zheng Liu, Xin Meng, Yan Yang
Recent advances in deep learning-based parallel compressed sensing magnetic resonance imaging (p-CSMRI) have significantly improved reconstruction quality. However, current p-CSMRI methods often require training separate deep neural network (DNN) for each organ due to anatomical variations, creating a barrier to developing generalized medical image reconstruction systems. To address this, we propose CAPNet (cross-organ all-in-one deep unfolding p-CSMRI network), a unified framework that implements a p-CSMRI iterative algorithm via three specialized modules: auxiliary variable module, prior module, and data consistency module. Recognizing that p-CSMRI systems often employ varying sampling ratios for different organs, resulting in organ-specific artifact patterns, we introduce an artifact generation submodule, which extracts and integrates artifact features into the data consistency module to enhance the discriminative capability of the overall network. For the prior module, we design an organ structure-prompt generation submodule that leverages structural features extracted from the segment anything model (SAM) to create cross-organ prompts. These prompts are strategically incorporated into the prior module through an organ structure-aware Mamba submodule. Comprehensive evaluations on a cross-organ dataset confirm that CAPNet achieves state-of-the-art reconstruction performance across multiple anatomical structures using a single unified model. Our code will be published at https://github.com/shibaoshun/CAPNet.
基于深度学习的并行压缩感知磁共振成像(p-CSMRI)的最新进展显著提高了重建质量。然而,由于解剖结构的变化,当前的p-CSMRI方法通常需要为每个器官训练单独的深度神经网络(DNN),这成为开发通用医学图像重建系统的障碍。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了CAPNet(跨器官全合一深度展开p-CSMRI网络),这是一个统一框架,通过三个专用模块实现p-CSMRI迭代算法:辅助变量模块、先验模块和数据一致性模块。我们认识到p-CSMRI系统通常对不同器官采用不同的采样比率,导致器官特定的伪影模式,因此我们引入了一个伪影生成子模块,该模块提取并将伪影特征集成到数据一致性模块中,以增强整体网络的判别能力。对于先验模块,我们设计了一个器官结构提示生成子模块,该模块利用从分割任何模型(SAM)中提取的结构特征来创建跨器官提示。这些提示通过器官结构感知的Mamba子模块战略性地融入先验模块。在跨器官数据集上的综合评估证实,CAPNet使用单个统一模型在多个解剖结构上实现了最先进的重建性能。我们的代码将在[https://github.com/shibaoshun/CAPNet上发布。](https://github.com/shibaoshun/CAPNet%E4%B8%8A%E5%8F%91%E5%B8%A该程序地址于后)。这个提议希望通过在先验信息不足的情境中解决实际应用的问题来实现超越原有图像质量边界的重大进展。这是生物医学图像领域的核心部分目前发展至能大大提升性能的实际需要问题的重要性的一个显著例子。我们相信我们的工作将推动医学图像重建领域的发展,并促进其在临床环境中的实际应用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于深度学习的并行压缩感知磁共振成像(p-CSMRI)最新进展显著提高了重建质量。然而,由于器官解剖结构差异,当前p-CSMRI方法需要为每个器官训练单独的深度神经网络(DNN),这阻碍了通用医疗图像重建系统的开发。为解决这个问题,提出一种统一的跨器官p-CSMRI网络CAPNet,通过辅助变量模块、先验模块和数据一致性模块三个专业模块实现p-CSMRI迭代算法。CAPNet引入缺陷生成子模块,提取和整合不同器官的缺陷特征,增强网络的整体判别能力。同时,设计器官结构提示生成子模块,利用从分割任何模型(SAM)中提取的结构特征创建跨器官提示。通过跨器官数据集的综合评估,证明CAPNet使用单一统一模型即可在多个解剖结构上实现最先进的重建性能。
Key Takeaways
- 最新p-CSMRI进展提高了重建质量。
- 现有方法需为每个器官训练单独的DNN,阻碍通用医疗图像重建系统开发。
- CAPNet是一个统一的跨器官p-CSMRI网络,通过三个专业模块实现p-CSMRI迭代算法。
- CAPNet引入缺陷生成子模块,增强网络判别能力。
- 设计器官结构提示生成子模块,利用SAM提取的结构特征。
- CAPNet在多个解剖结构上实现最先进的重建性能。
- 代码将发布在https://github.com/shibaoshun/CAPNet。
点此查看论文截图

Rethinking Boundary Detection in Deep Learning-Based Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Yi Lin, Dong Zhang, Xiao Fang, Yufan Chen, Kwang-Ting Cheng, Hao Chen
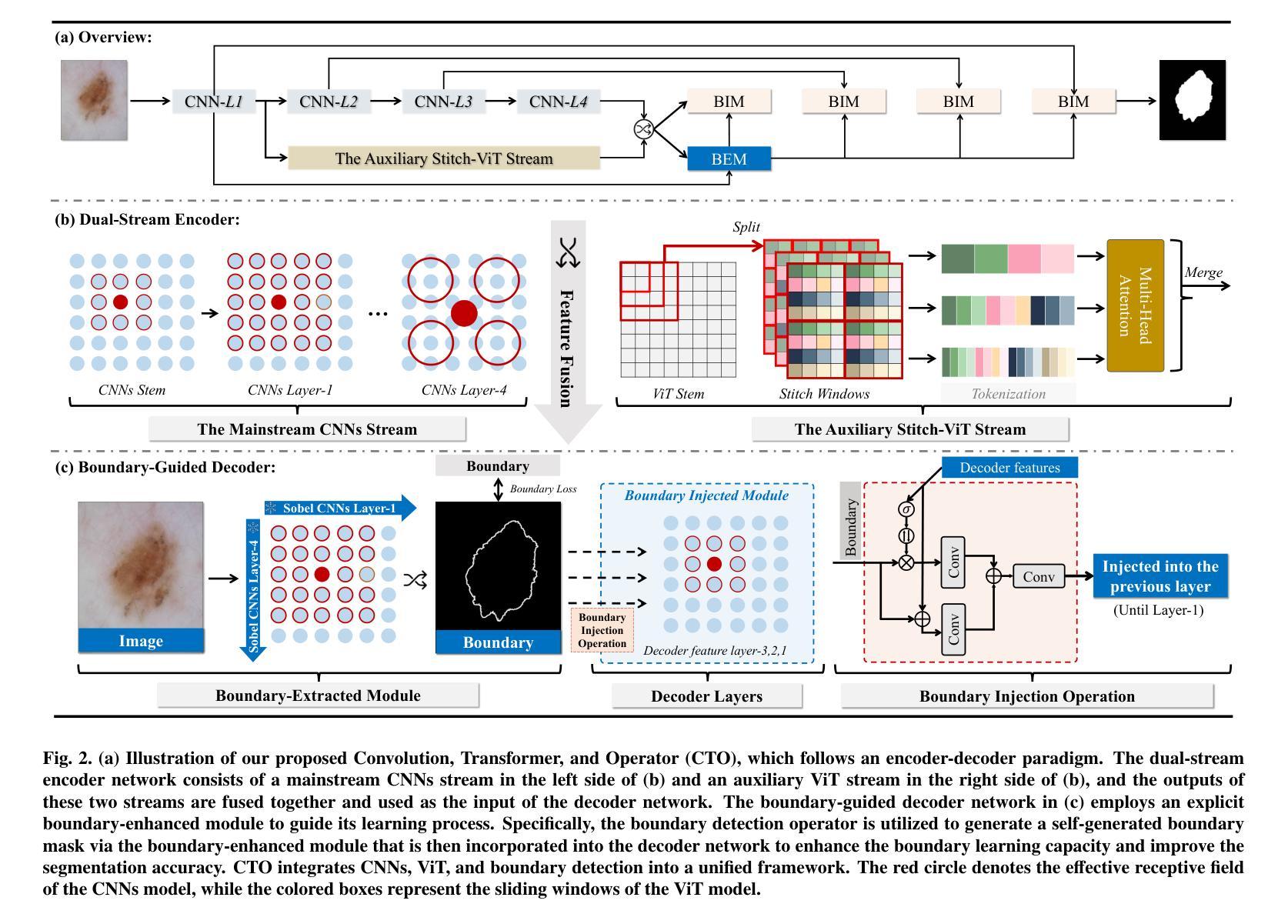
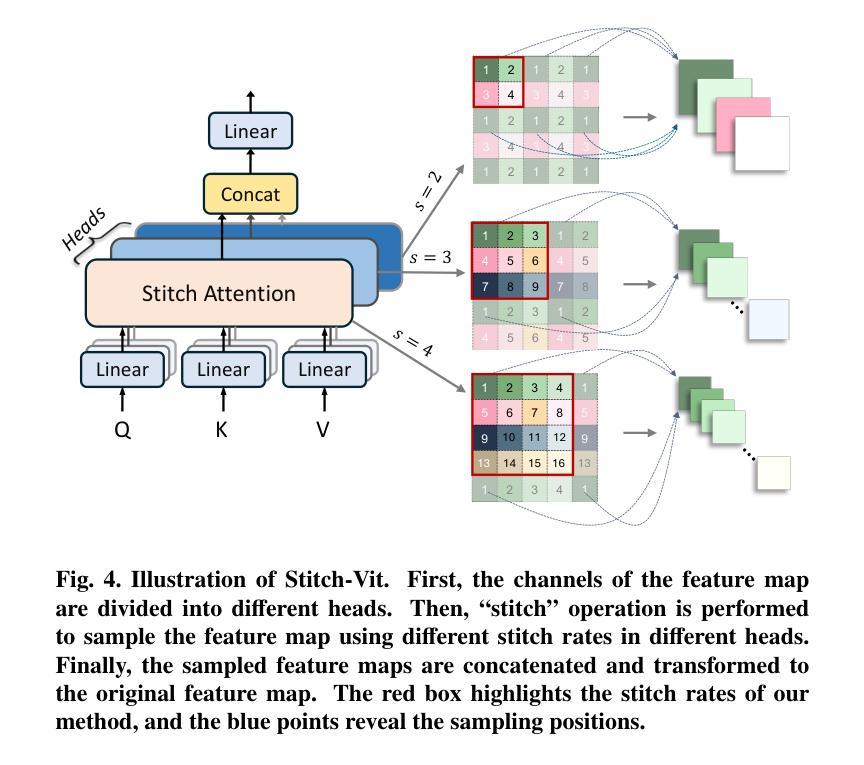
Medical image segmentation is a pivotal task within the realms of medical image analysis and computer vision. While current methods have shown promise in accurately segmenting major regions of interest, the precise segmentation of boundary areas remains challenging. In this study, we propose a novel network architecture named CTO, which combines Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), Vision Transformer (ViT) models, and explicit edge detection operators to tackle this challenge. CTO surpasses existing methods in terms of segmentation accuracy and strikes a better balance between accuracy and efficiency, without the need for additional data inputs or label injections. Specifically, CTO adheres to the canonical encoder-decoder network paradigm, with a dual-stream encoder network comprising a mainstream CNN stream for capturing local features and an auxiliary StitchViT stream for integrating long-range dependencies. Furthermore, to enhance the model’s ability to learn boundary areas, we introduce a boundary-guided decoder network that employs binary boundary masks generated by dedicated edge detection operators to provide explicit guidance during the decoding process. We validate the performance of CTO through extensive experiments conducted on seven challenging medical image segmentation datasets, namely ISIC 2016, PH2, ISIC 2018, CoNIC, LiTS17, and BTCV. Our experimental results unequivocally demonstrate that CTO achieves state-of-the-art accuracy on these datasets while maintaining competitive model complexity. The codes have been released at: https://github.com/xiaofang007/CTO.
医学图像分割是医学图像分析和计算机视觉领域中的一项重要任务。虽然当前方法在主要区域的分割方面显示出了一定的潜力,但对边界区域的精确分割仍然具有挑战性。本研究提出了一种新型网络架构CTO,该架构结合了卷积神经网络(CNN)、视觉Transformer(ViT)模型和明确的边缘检测算子,以应对这一挑战。CTO在分割精度上超越了现有方法,并在精度和效率之间达到了更好的平衡,无需额外的数据输入或标签注入。具体来说,CTO遵循典型的编码器-解码器网络范式,具有双编码器网络流,主流是CNN流,用于捕捉局部特征,辅助流是StitchViT流,用于整合长距离依赖关系。此外,为了提高模型对边界区域的学习能力,我们引入了一个边界引导解码器网络,该网络使用由专用边缘检测算子生成的二进制边界掩膜,为解码过程提供明确指导。我们在七个具有挑战性的医学图像分割数据集上验证了CTO的性能,即ISIC 2016、PH2、ISIC 2018、CoNIC、LiTS17和BTCV。我们的实验结果明确证明,CTO在这些数据集上达到了最先进的准确性,同时保持了具有竞争力的模型复杂度。相关代码已发布在:https://github.com/xiaofang007/CTO。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by Medical Image Analysis
摘要
本文提出一种新型的医学图像分割网络架构CTO,结合卷积神经网络(CNN)、视觉转换器(ViT)模型和边缘检测算子,旨在解决边界区域精确分割的挑战。CTO在分割精度上超越了现有方法,并在精度和效率之间达到更好的平衡,无需额外的数据输入或标签注入。CTO遵循典型的编码器-解码器网络范式,具有双流编码器网络,包括主流CNN流用于捕捉局部特征和辅助StitchViT流用于整合长程依赖关系。为增强模型对边界区域的学习能力,引入边界引导解码器网络,采用由专用边缘检测算子生成的二进制边界掩膜,为解码过程提供明确指导。在七个具有挑战性的医学图像分割数据集上的实验结果表明,CTO取得了最先进的准确度,同时保持了竞争性的模型复杂度。
关键见解
- 医学图像分割是医学图像分析和计算机视觉中的重要任务。
- 现有方法在精确分割边界区域方面面临挑战。
- 提出了一种新型网络架构CTO,结合CNN、ViT模型和边缘检测算子,以解决这一挑战。
- CTO超越了现有方法的分割精度,并在精度和效率之间达到了更好的平衡。
- CTO遵循典型的编码器-解码器网络范式,具有双流编码器网络和边界引导解码器网络。
- 实验在七个医学图像分割数据集上进行,证明了CTO的优越性能。
- CTO的代码已发布在相关仓库。
点此查看论文截图


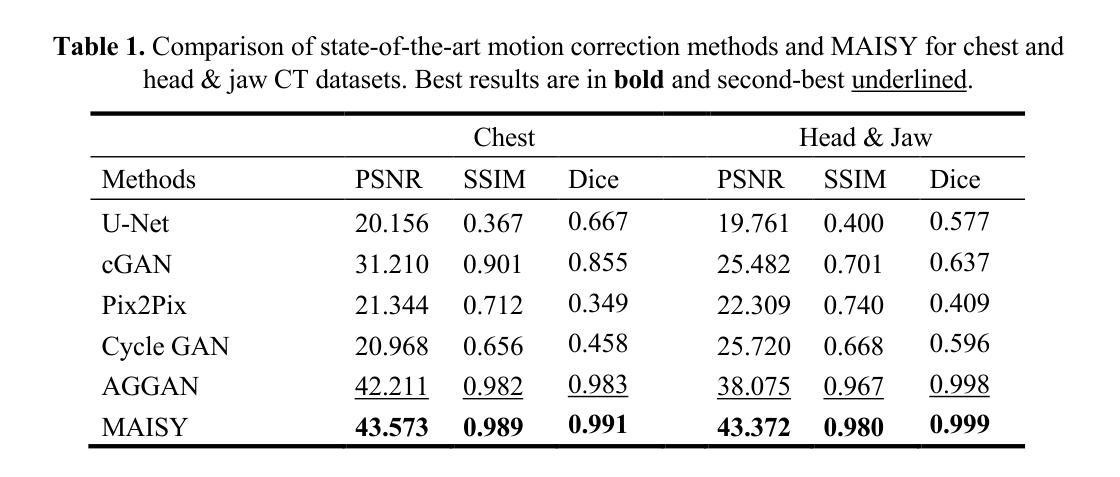
MAISY: Motion-Aware Image SYnthesis for Medical Image Motion Correction
Authors:Andrew Zhang, Hao Wang, Shuchang Ye, Michael Fulham, Jinman Kim
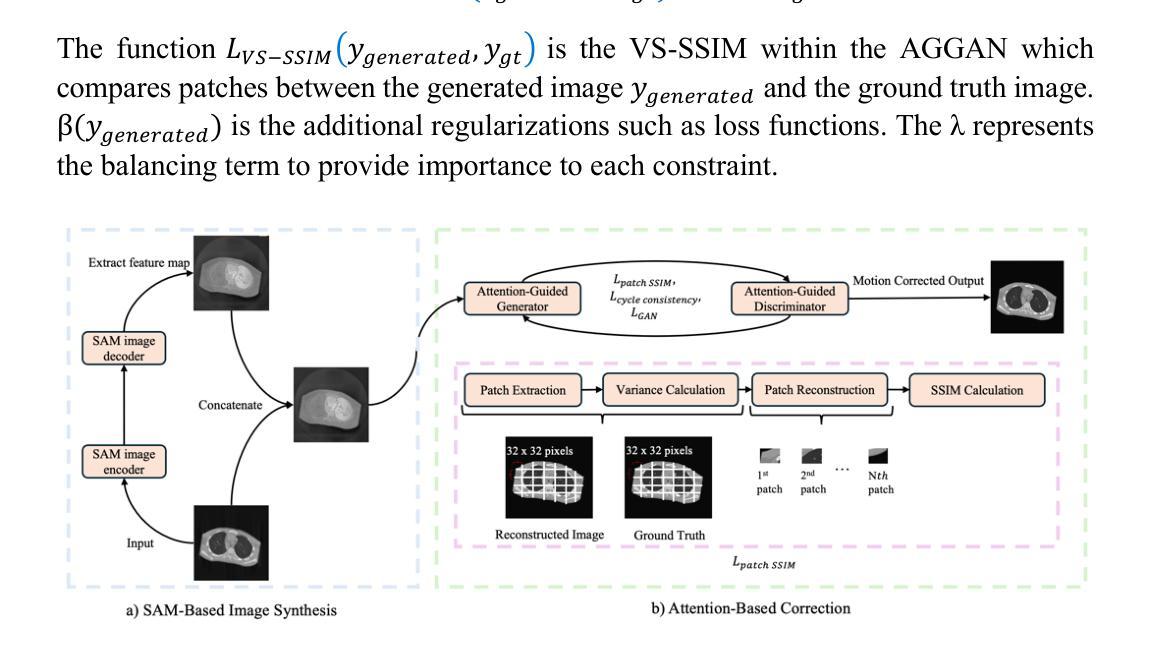
Patient motion during medical image acquisition causes blurring, ghosting, and distorts organs, which makes image interpretation challenging. Current state-of-the-art algorithms using Generative Adversarial Network (GAN)-based methods with their ability to learn the mappings between corrupted images and their ground truth via Structural Similarity Index Measure (SSIM) loss effectively generate motion-free images. However, we identified the following limitations: (i) they mainly focus on global structural characteristics and therefore overlook localized features that often carry critical pathological information, and (ii) the SSIM loss function struggles to handle images with varying pixel intensities, luminance factors, and variance. In this study, we propose Motion-Aware Image SYnthesis (MAISY) which initially characterize motion and then uses it for correction by: (a) leveraging the foundation model Segment Anything Model (SAM), to dynamically learn spatial patterns along anatomical boundaries where motion artifacts are most pronounced and, (b) introducing the Variance-Selective SSIM (VS-SSIM) loss which adaptively emphasizes spatial regions with high pixel variance to preserve essential anatomical details during artifact correction. Experiments on chest and head CT datasets demonstrate that our model outperformed the state-of-the-art counterparts, with Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR) increasing by 40%, SSIM by 10%, and Dice by 16%.
患者在医学图像采集过程中的运动会导致图像模糊、出现鬼影和器官扭曲,这使得图像解读具有挑战性。当前最先进的算法使用基于生成对抗网络(GAN)的方法,它们能够通过结构相似性指数度量(SSIM)损失学习受损图像与其真实值之间的映射,从而有效地生成无运动图像。然而,我们发现了以下局限性:(i)它们主要关注全局结构特征,因此忽略了通常携带关键病理信息的局部特征;(ii)SSIM损失函数在处理像素强度、亮度因素和方差各异的图像时遇到困难。在这项研究中,我们提出了运动感知图像合成(MAISY),它首先表征运动,然后利用运动进行校正:通过(a)利用分段任何模型(SAM)的基础模型,动态学习解剖边界处的空间模式,这些空间模式是运动伪影最明显的位置;(b)引入方差选择性SSIM(VS-SSIM)损失,该损失能够自适应地强调具有高像素方差的区域,在伪影校正过程中保留关键的解剖细节。对胸部和头部CT数据集的实验表明,我们的模型性能超过了最先进的同类模型,峰值信号与噪声比(PSNR)提高了40%,结构相似性指数度量(SSIM)提高了10%,Dice系数提高了16%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了在医学图像获取过程中患者运动引起的图像模糊、鬼影和器官扭曲问题,使得图像解读具有挑战性。当前最先进的算法主要关注全局结构特征,忽略了携带重要病理信息的局部特征。本研究提出了Motion-Aware Image SYnthesis(MAISY)模型,通过动态学习空间模式并对高像素方差的空间区域进行自适应强调,以纠正运动引起的伪影并保留关键解剖细节。实验表明,该模型在胸部和头部CT数据集上的性能优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 患者运动在医学图像采集过程中会导致图像模糊、鬼影和器官扭曲,增加了图像解读的难度。
- 当前最先进的算法使用GAN和SSIM损失来生成无运动图像,但仍存在对局部特征和像素强度变化的处理不足的问题。
- MAISY模型利用Segment Anything Model(SAM)动态学习空间模式,针对运动伪影最明显的解剖边界进行特征提取。
- MAISY模型引入了Variance-Selective SSIM(VS-SSIM)损失,能够自适应强调高像素方差的空间区域,以保留关键解剖细节。
- 实验结果表明,MAISY模型在胸部和头部CT数据集上的性能优于现有技术。
- MAISY模型通过纠正运动伪影,提高了图像质量,表现为Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio(PSNR)增加40%,Structural Similarity Index Measure(SSIM)增加10%,Dice系数增加16%。
点此查看论文截图

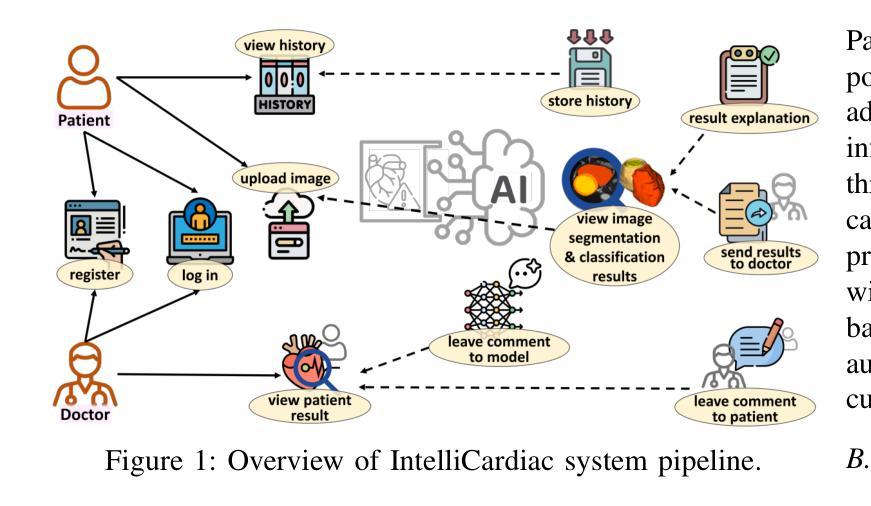
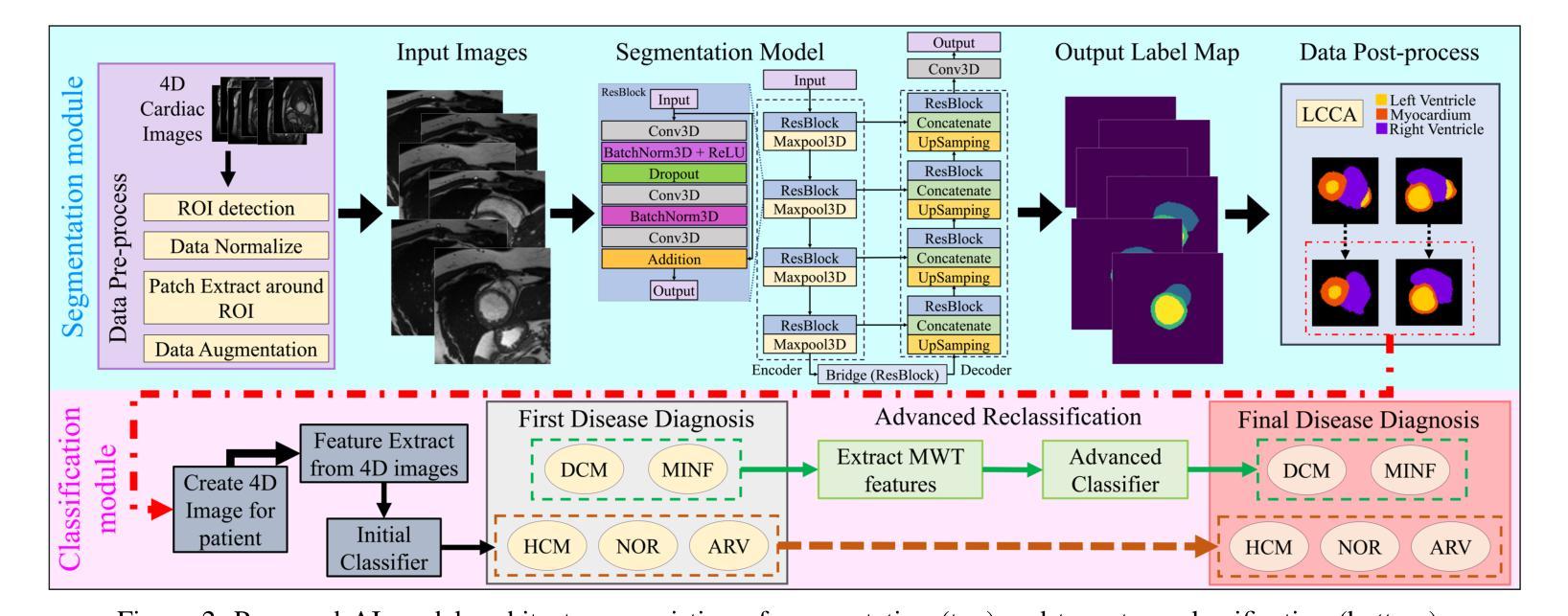
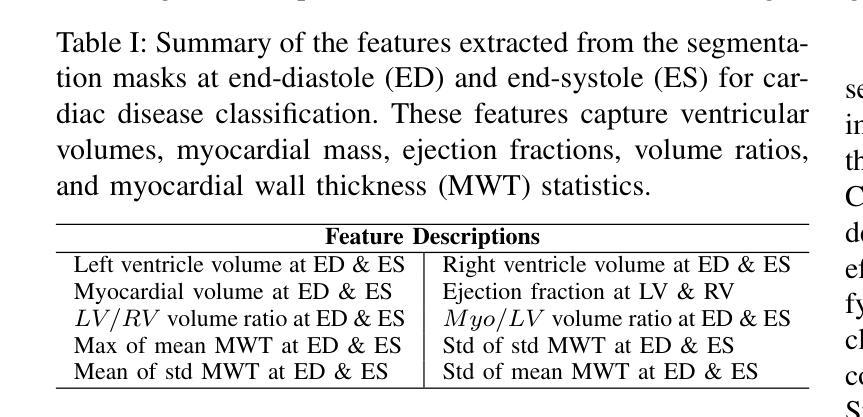
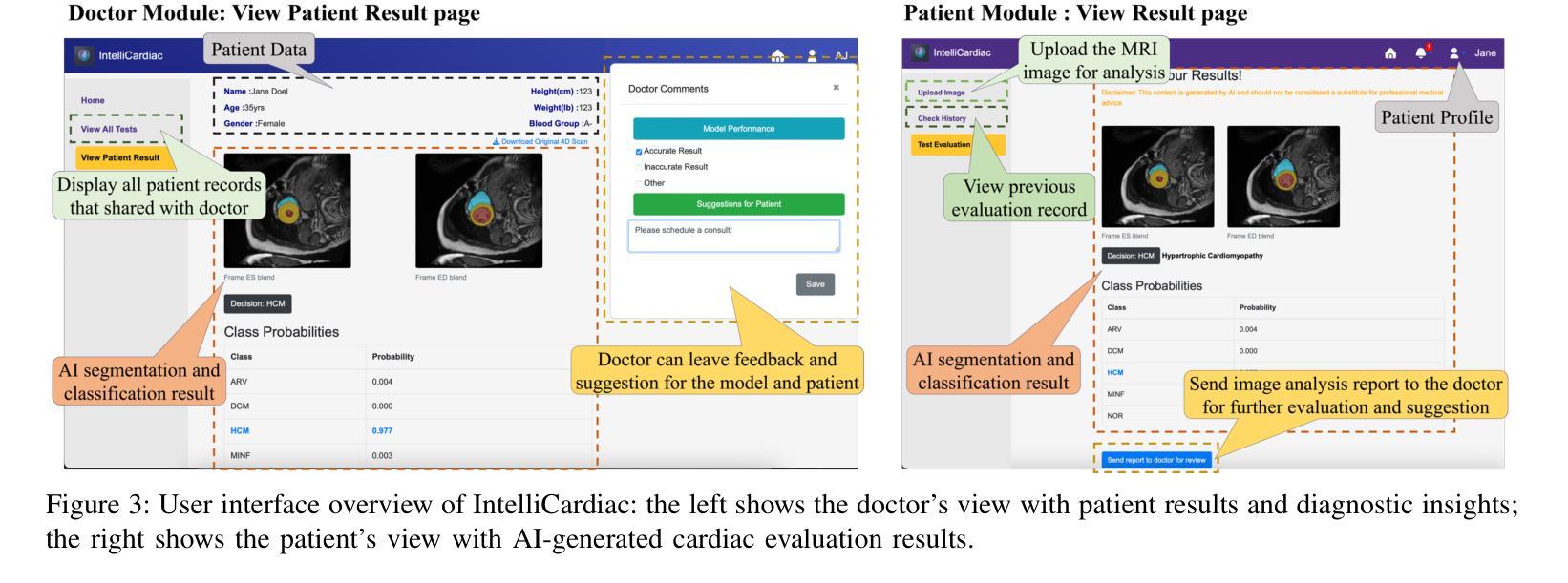
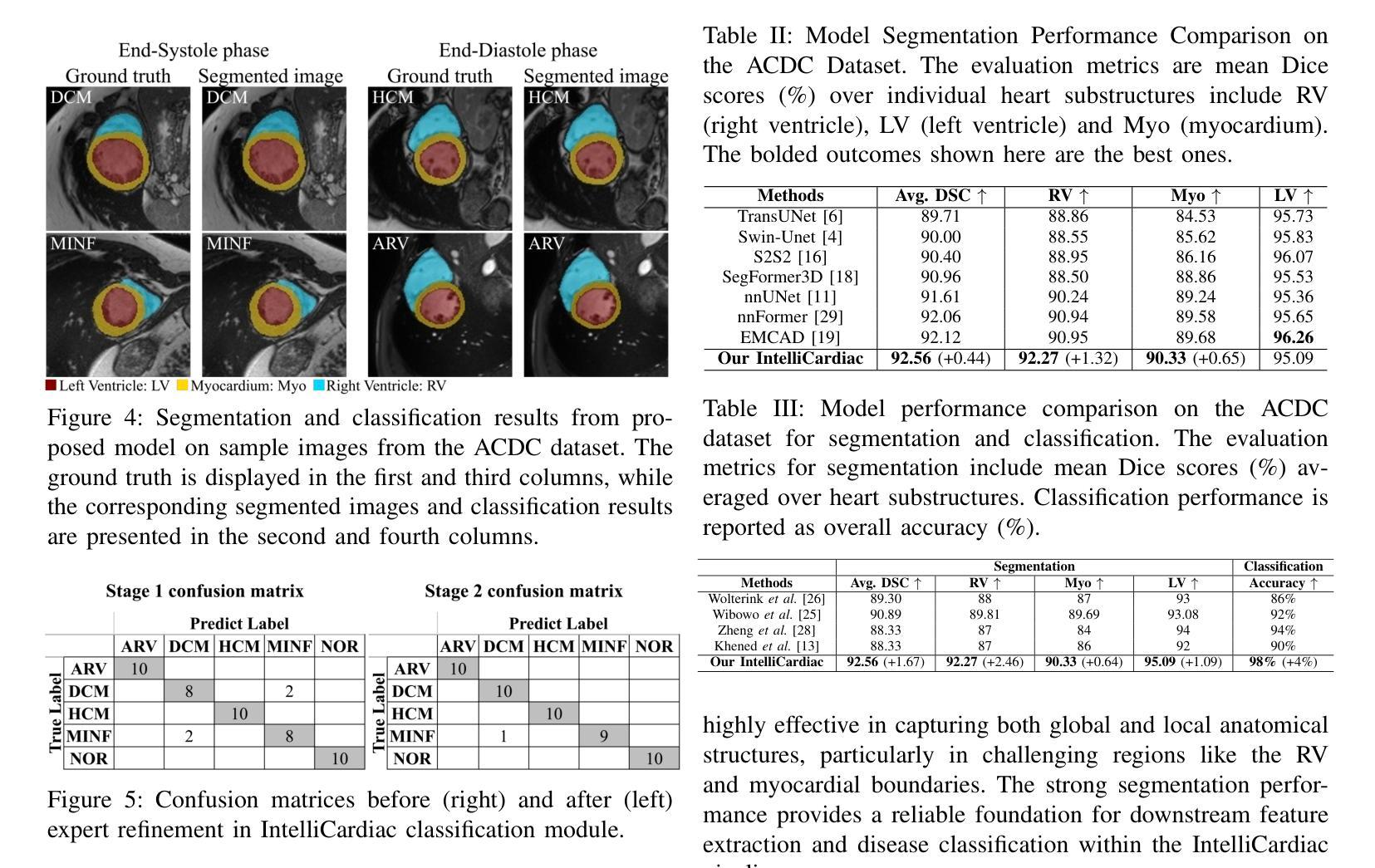
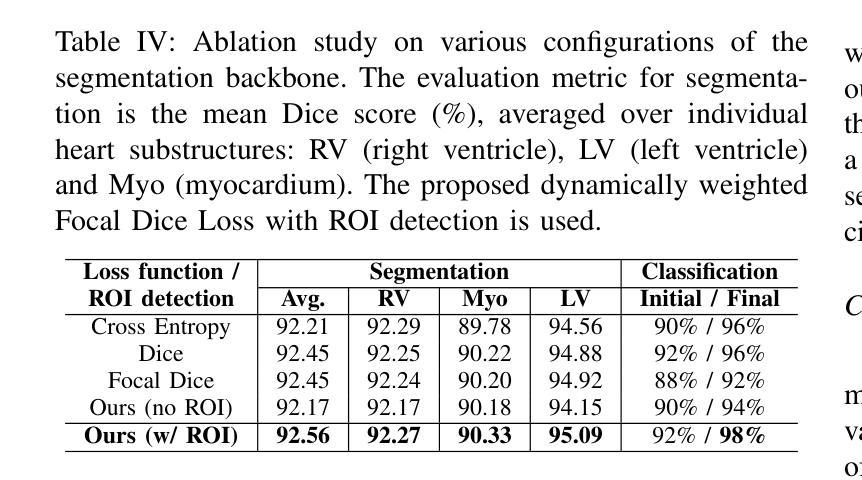
IntelliCardiac: An Intelligent Platform for Cardiac Image Segmentation and Classification
Authors:Ting Yu Tsai, An Yu, Meghana Spurthi Maadugundu, Ishrat Jahan Mohima, Umme Habiba Barsha, Mei-Hwa F. Chen, Balakrishnan Prabhakaran, Ming-Ching Chang
Precise and effective processing of cardiac imaging data is critical for the identification and management of the cardiovascular diseases. We introduce IntelliCardiac, a comprehensive, web-based medical image processing platform for the automatic segmentation of 4D cardiac images and disease classification, utilizing an AI model trained on the publicly accessible ACDC dataset. The system, intended for patients, cardiologists, and healthcare professionals, offers an intuitive interface and uses deep learning models to identify essential heart structures and categorize cardiac diseases. The system supports analysis of both the right and left ventricles as well as myocardium, and then classifies patient’s cardiac images into five diagnostic categories: dilated cardiomyopathy, myocardial infarction, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, right ventricular abnormality, and no disease. IntelliCardiac combines a deep learning-based segmentation model with a two-step classification pipeline. The segmentation module gains an overall accuracy of 92.6%. The classification module, trained on characteristics taken from segmented heart structures, achieves 98% accuracy in five categories. These results exceed the performance of the existing state-of-the-art methods that integrate both segmentation and classification models. IntelliCardiac, which supports real-time visualization, workflow integration, and AI-assisted diagnostics, has great potential as a scalable, accurate tool for clinical decision assistance in cardiac imaging and diagnosis.
精确且有效地处理心脏成像数据对于心血管疾病的识别和管理至关重要。我们推出IntelliCardiac,这是一个全面的基于网页的医学图像处理平台,用于自动分割4D心脏图像和疾病分类。我们利用在公共可访问的ACDC数据集上训练的AI模型建立此系统。该系统面向患者、心脏病专家和医疗保健专业人员,提供直观界面,并使用深度学习模型来识别心脏关键结构并对心脏病进行分类。该系统支持右心室和左心室以及心肌的分析,然后将患者的心脏图像分类为五种诊断类别:扩张型心肌病、心肌梗死、肥厚型心肌病、右心室异常和无疾病。IntelliCardiac将基于深度学习的分割模型与两步分类流程相结合。分割模块的整体准确度达到92.6%。分类模块根据分割的心脏结构特征进行训练,在五个类别中达到98%的准确率。这些结果超过了现有最先进的集成分割和分类模型的方法的性能。IntelliCardiac支持实时可视化、工作流程集成和人工智能辅助诊断,作为心脏成像和诊断的临床决策支持工具,具有可扩展性和准确性,具有巨大的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了IntelliCardiac这一基于网页的医学图像处理平台,该平台可对心脏4D图像进行自动分割并对疾病进行分类。它采用深度学习模型,可对心脏关键结构进行识别,并对五种常见的心脏疾病进行分类。此平台可实现实时可视化、工作流程集成和人工智能辅助诊断,为临床决策提供支持。
Key Takeaways
- IntelliCardiac是一个基于网页的医学图像处理平台,专门用于处理心脏成像数据。
- 平台可实现心脏4D图像的自动分割和疾病分类。
- 利用深度学习模型识别心脏关键结构。
- 平台支持对右心室和左心室的分析,以及心肌的分析。
- 可将患者的心脏图像分类为五种诊断类别:扩张型心肌病、心肌梗死、肥厚型心肌病、右心室异常和无疾病。
- IntelliCardiac的分割模型总体准确度为92.6%,分类模型准确度为98%。
点此查看论文截图

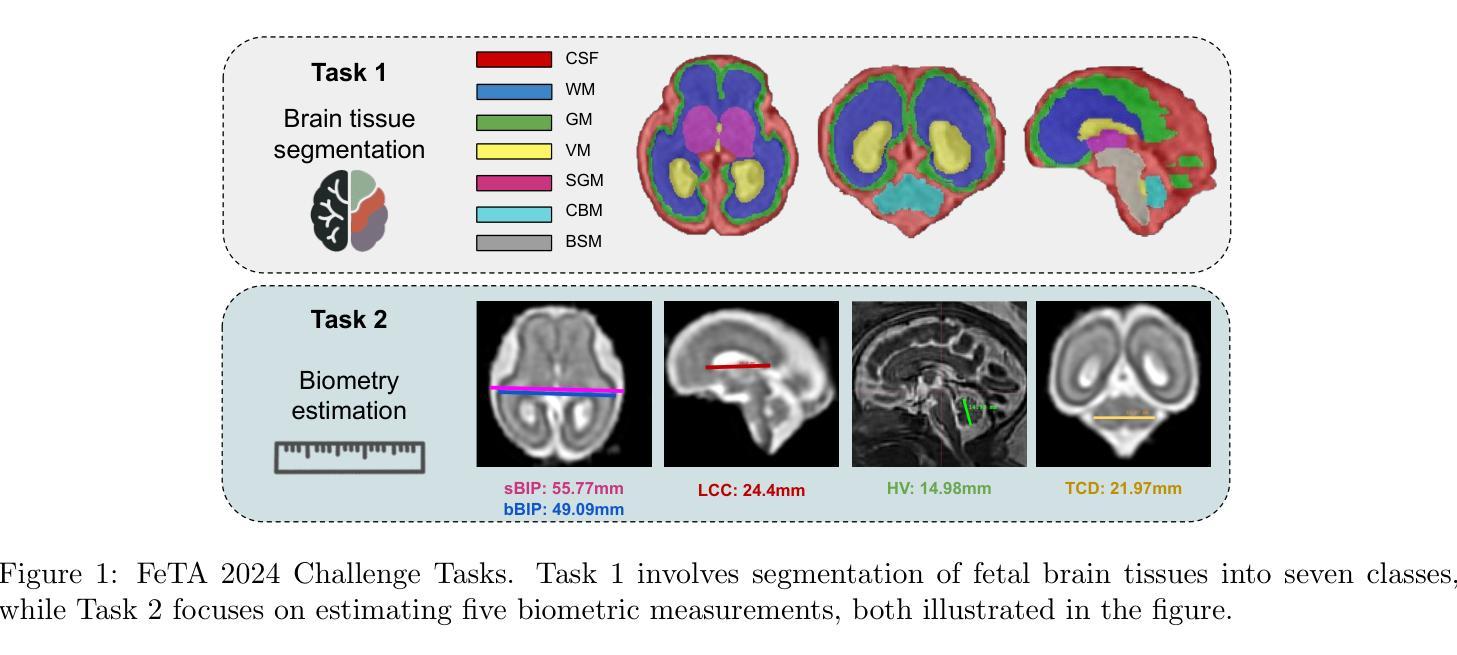
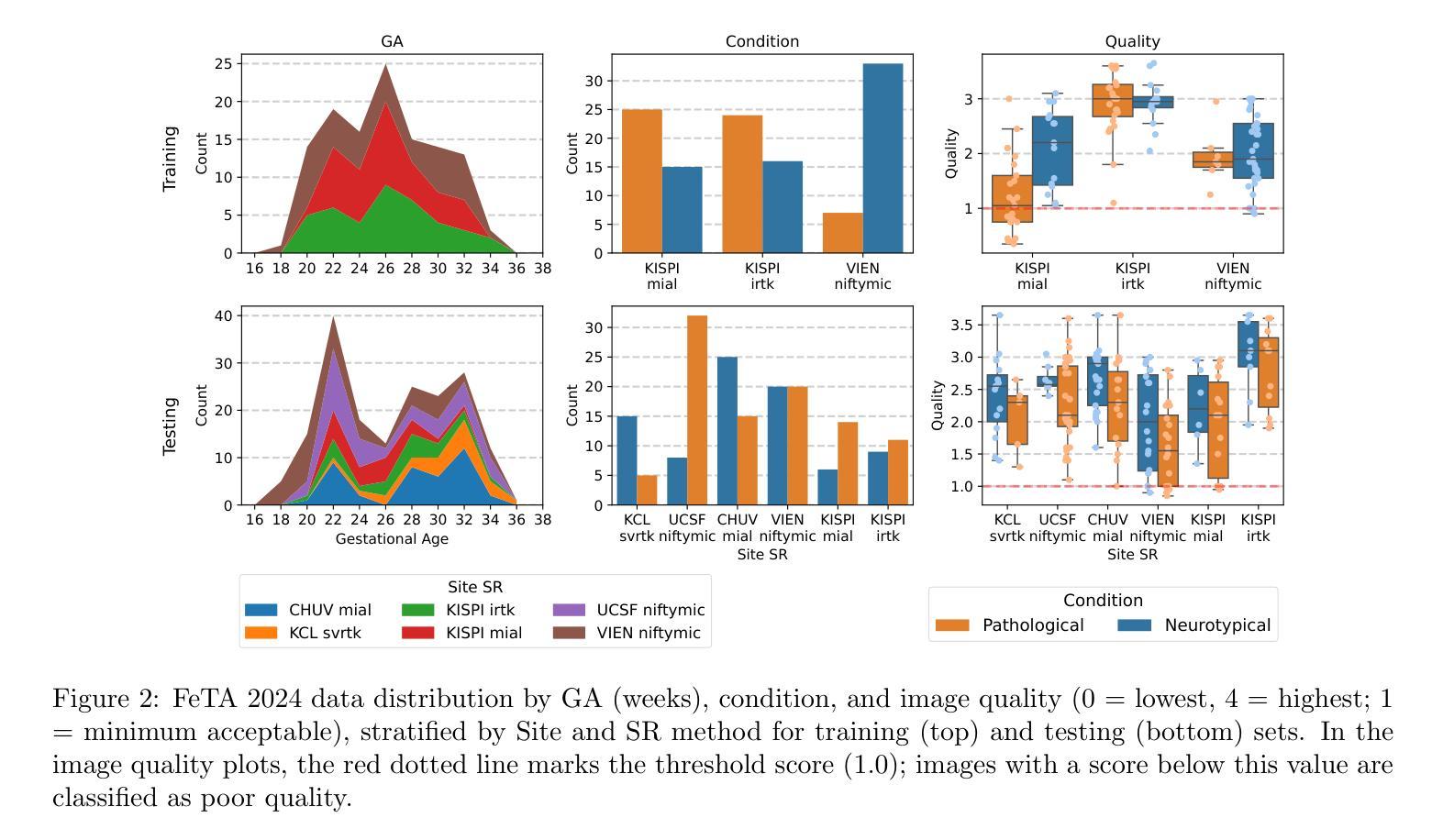
Advances in Automated Fetal Brain MRI Segmentation and Biometry: Insights from the FeTA 2024 Challenge
Authors:Vladyslav Zalevskyi, Thomas Sanchez, Misha Kaandorp, Margaux Roulet, Diego Fajardo-Rojas, Liu Li, Jana Hutter, Hongwei Bran Li, Matthew Barkovich, Hui Ji, Luca Wilhelmi, Aline Dändliker, Céline Steger, Mériam Koob, Yvan Gomez, Anton Jakovčić, Melita Klaić, Ana Adžić, Pavel Marković, Gracia Grabarić, Milan Rados, Jordina Aviles Verdera, Gregor Kasprian, Gregor Dovjak, Raphael Gaubert-Rachmühl, Maurice Aschwanden, Qi Zeng, Davood Karimi, Denis Peruzzo, Tommaso Ciceri, Giorgio Longari, Rachika E. Hamadache, Amina Bouzid, Xavier Lladó, Simone Chiarella, Gerard Martí-Juan, Miguel Ángel González Ballester, Marco Castellaro, Marco Pinamonti, Valentina Visani, Robin Cremese, Keïn Sam, Fleur Gaudfernau, Param Ahir, Mehul Parikh, Maximilian Zenk, Michael Baumgartner, Klaus Maier-Hein, Li Tianhong, Yang Hong, Zhao Longfei, Domen Preloznik, Žiga Špiclin, Jae Won Choi, Muyang Li, Jia Fu, Guotai Wang, Jingwen Jiang, Lyuyang Tong, Bo Du, Andrea Gondova, Sungmin You, Kiho Im, Abdul Qayyum, Moona Mazher, Steven A Niederer, Andras Jakab, Roxane Licandro, Kelly Payette, Meritxell Bach Cuadra
Accurate fetal brain tissue segmentation and biometric analysis are essential for studying brain development in utero. The FeTA Challenge 2024 advanced automated fetal brain MRI analysis by introducing biometry prediction as a new task alongside tissue segmentation. For the first time, our diverse multi-centric test set included data from a new low-field (0.55T) MRI dataset. Evaluation metrics were also expanded to include the topology-specific Euler characteristic difference (ED). Sixteen teams submitted segmentation methods, most of which performed consistently across both high- and low-field scans. However, longitudinal trends indicate that segmentation accuracy may be reaching a plateau, with results now approaching inter-rater variability. The ED metric uncovered topological differences that were missed by conventional metrics, while the low-field dataset achieved the highest segmentation scores, highlighting the potential of affordable imaging systems when paired with high-quality reconstruction. Seven teams participated in the biometry task, but most methods failed to outperform a simple baseline that predicted measurements based solely on gestational age, underscoring the challenge of extracting reliable biometric estimates from image data alone. Domain shift analysis identified image quality as the most significant factor affecting model generalization, with super-resolution pipelines also playing a substantial role. Other factors, such as gestational age, pathology, and acquisition site, had smaller, though still measurable, effects. Overall, FeTA 2024 offers a comprehensive benchmark for multi-class segmentation and biometry estimation in fetal brain MRI, underscoring the need for data-centric approaches, improved topological evaluation, and greater dataset diversity to enable clinically robust and generalizable AI tools.
准确对胎儿脑组织进行分割和生物测定分析是研究胎儿在母体内脑发育的重要前提。FeTA Challenge 2024通过引入生物测定预测作为新任务,推动了胎儿脑部自动化MRI分析的发展,同时辅以组织分割。我们的多样化多中心测试集首次包含来自新低场(0.55T)MRI数据集的数据。评估指标也扩展到包括拓扑特定的欧拉特征差异(ED)。有十六支队伍提交了分割方法,其中大多数在高场和低场扫描中表现一致。然而,纵向趋势表明,分割精度可能已达到一个瓶颈,结果现在已接近不同评估人员之间的差异。ED指标发现了传统指标未能捕获到的拓扑差异,同时低场数据集获得了最高的分割得分,突显了当与高质量重建相结合时,经济实惠的成像系统的潜力。有七支队伍参与了生物测定任务,但大多数方法未能超越一个简单基线,该基线仅根据胎龄进行预测测量,这突显了仅从图像数据中提取可靠生物测定估计的挑战性。域偏移分析确定了图像质量是影响模型泛化的最重要因素,超分辨率流程也发挥了重要作用。其他因素,如胎龄、病理和采集地点,虽然影响较小但仍可衡量。总体而言,FeTA 2024为多类分割和胎儿脑部MRI中的生物测定估计提供了全面的基准测试,这突显了以数据为中心的方法、改进拓扑评估和更大的数据集多样性的需求,以实现临床稳健和可推广的人工智能工具。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了FeTA Challenge 2024在胎儿脑部MRI分析方面的进展,包括组织分割和生物计量预测两项任务。研究使用了多中心测试集,并引入了拓扑特性差异作为新的评估指标。尽管大多数团队在分割任务上表现出色,但生物计量预测仍面临挑战。研究强调了数据中心方法、更先进的拓扑评估和更丰富的数据集多样性的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- FeTA Challenge 2024扩展了胎儿脑部MRI分析,引入生物计量预测作为新任务,同时使用多中心测试集和新的拓扑特性差异评估指标。
- 大多数团队在分割任务上表现稳定,但生物计量预测仍面临挑战,简单的基线方法在某些情况下表现良好。
- 低场MRI数据集获得最高分割分数,凸显出高质量重建与价格合理的成像系统结合的重要性。
- 域转移分析表明图像质量是影响模型泛化的最重要因素,超分辨率管道也发挥了重要作用。
- 其他因素如妊娠周数、病理情况和采集地点对模型性能也有一定影响。
- 研究强调了数据中心方法的重要性,并指出需要改进拓扑评估和增加数据集多样性以实现临床稳健和可推广的人工智能工具。
点此查看论文截图

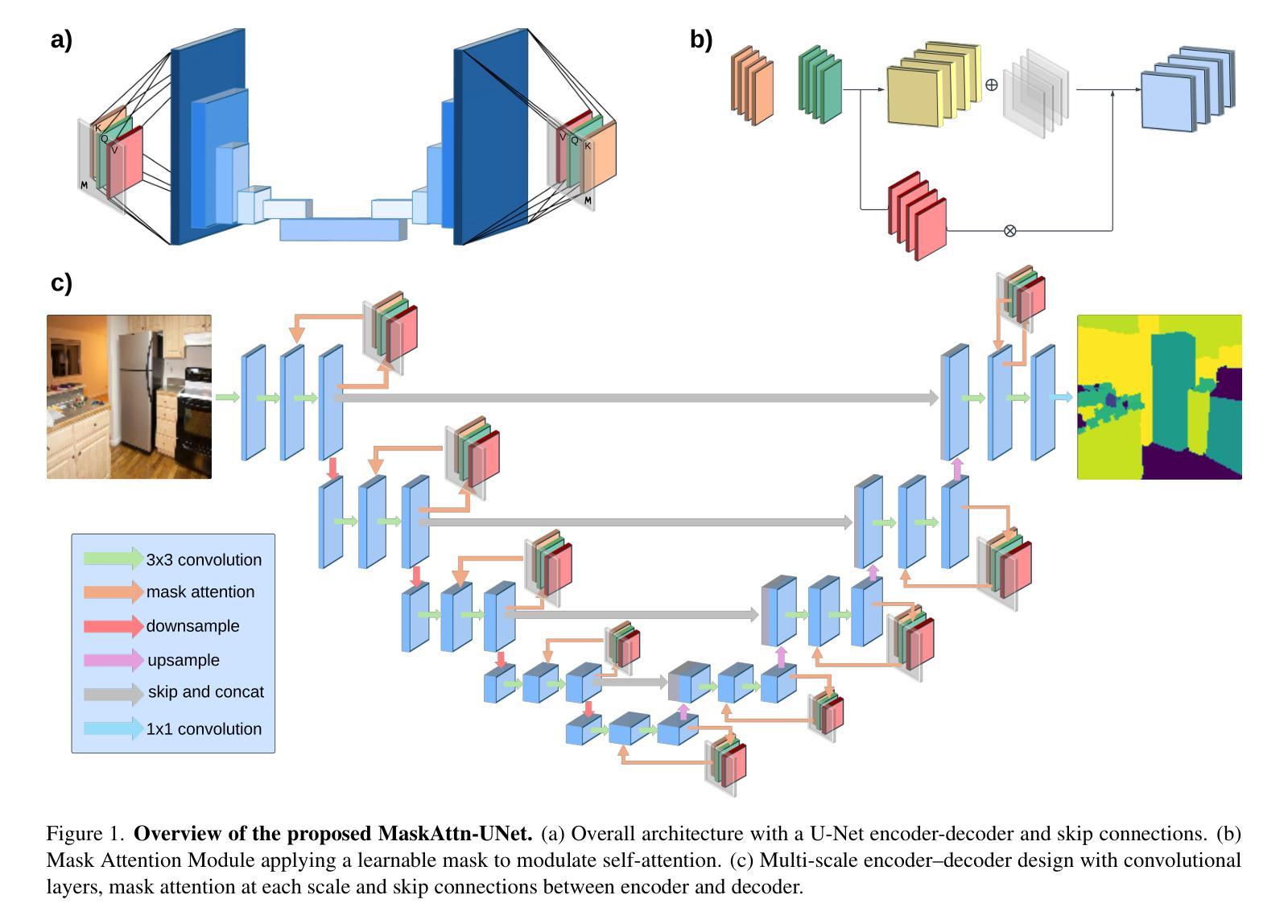
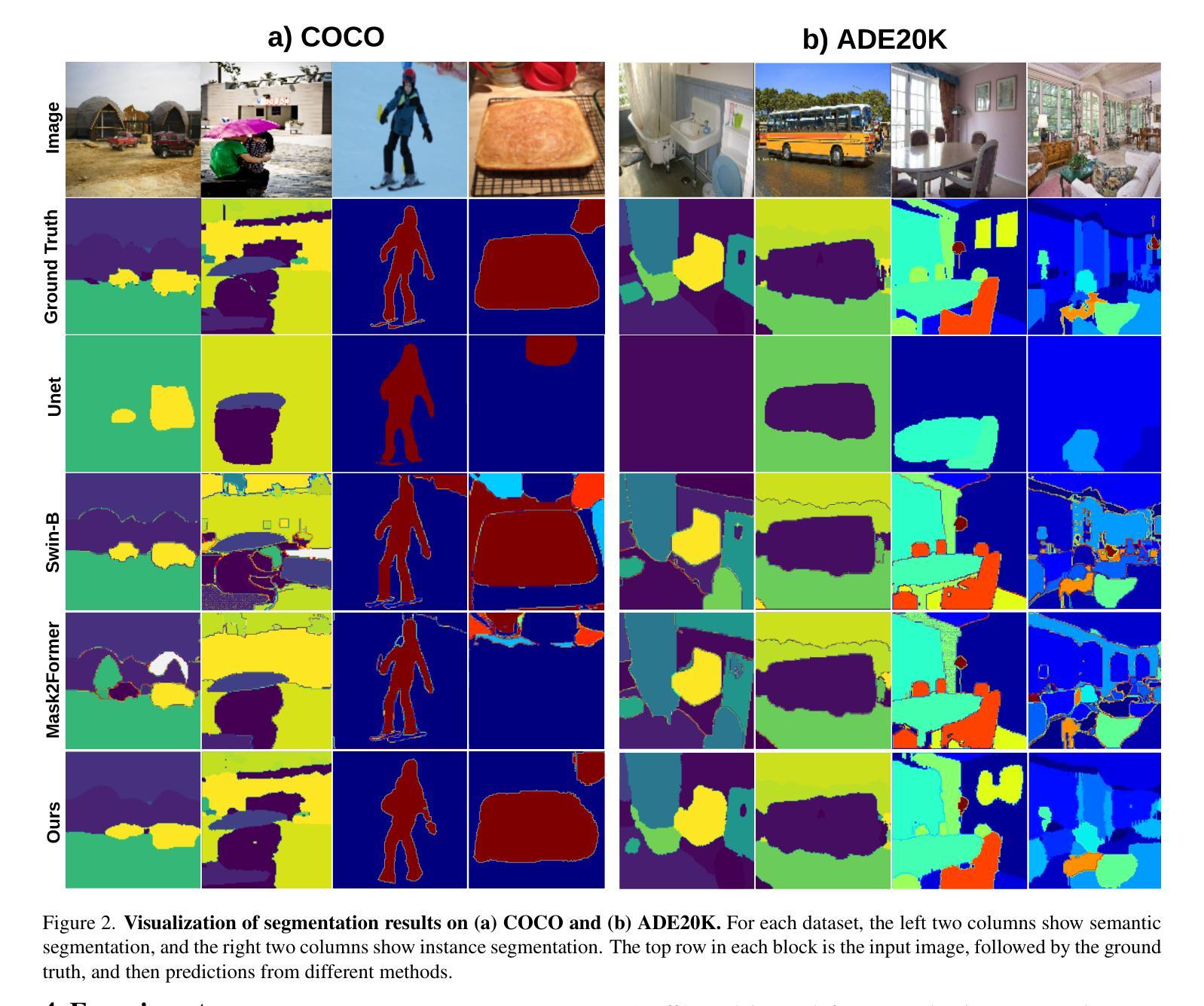
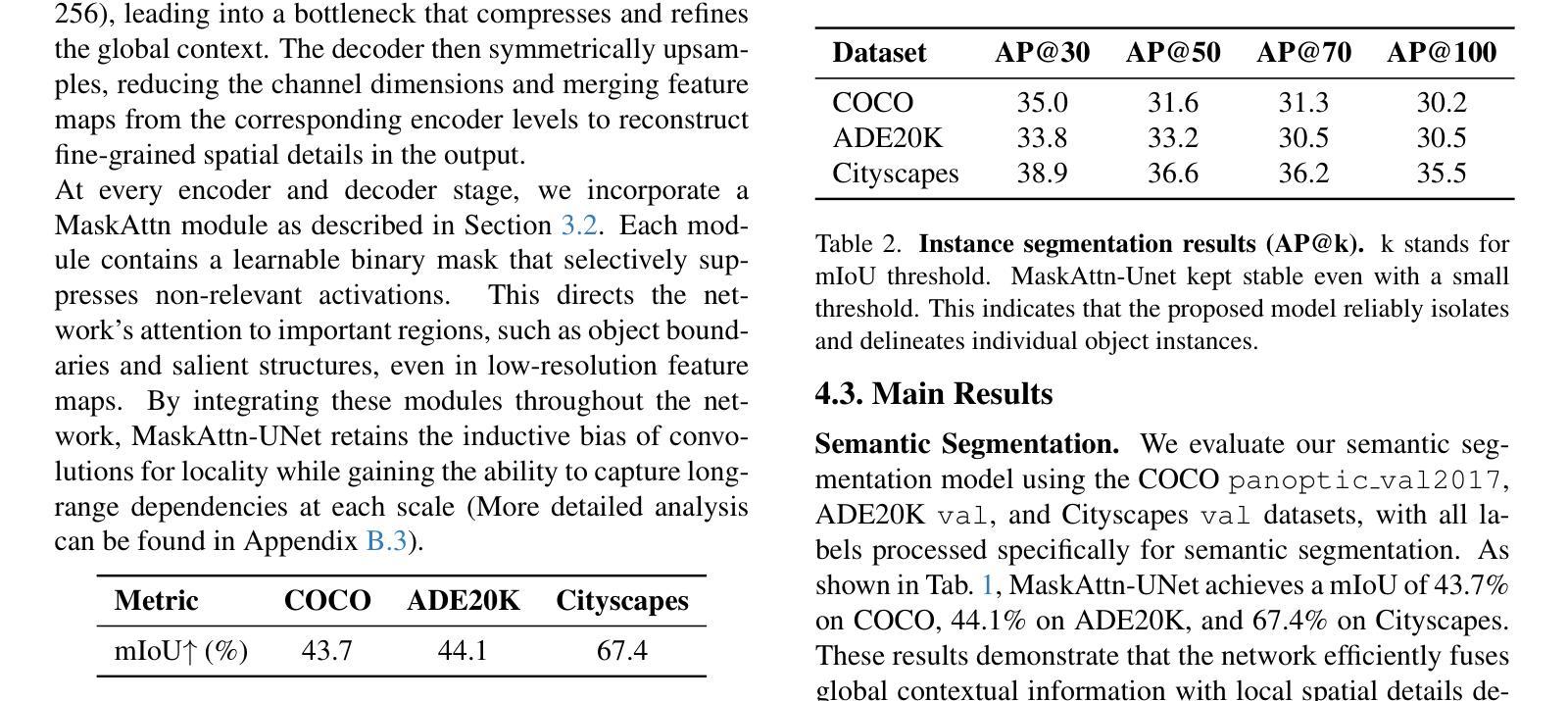
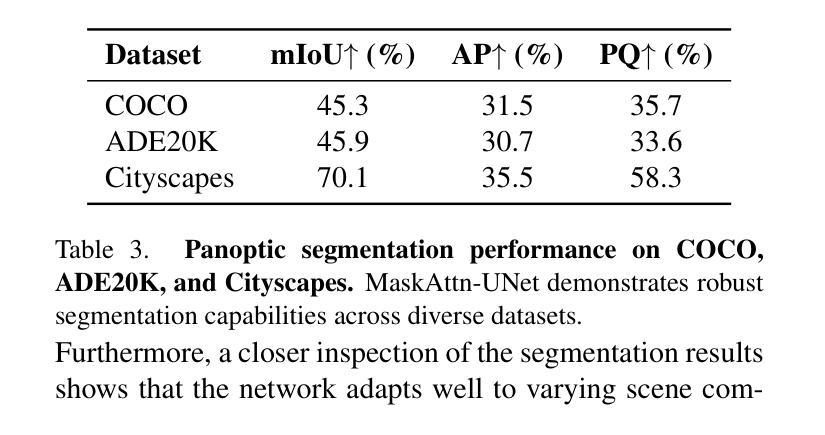
MaskAttn-UNet: A Mask Attention-Driven Framework for Universal Low-Resolution Image Segmentation
Authors:Anzhe Cheng, Chenzhong Yin, Yu Chang, Heng Ping, Shixuan Li, Shahin Nazarian, Paul Bogdan
Low-resolution image segmentation is crucial in real-world applications such as robotics, augmented reality, and large-scale scene understanding, where high-resolution data is often unavailable due to computational constraints. To address this challenge, we propose MaskAttn-UNet, a novel segmentation framework that enhances the traditional U-Net architecture via a mask attention mechanism. Our model selectively emphasizes important regions while suppressing irrelevant backgrounds, thereby improving segmentation accuracy in cluttered and complex scenes. Unlike conventional U-Net variants, MaskAttn-UNet effectively balances local feature extraction with broader contextual awareness, making it particularly well-suited for low-resolution inputs. We evaluate our approach on three benchmark datasets with input images rescaled to 128x128 and demonstrate competitive performance across semantic, instance, and panoptic segmentation tasks. Our results show that MaskAttn-UNet achieves accuracy comparable to state-of-the-art methods at significantly lower computational cost than transformer-based models, making it an efficient and scalable solution for low-resolution segmentation in resource-constrained scenarios.
低分辨率图像分割在现实世界应用中至关重要,例如机器人技术、增强现实和大规模场景理解等。在这些应用中,由于计算资源限制,往往无法获得高分辨率数据。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了MaskAttn-UNet,这是一种增强传统U-Net架构的新型分割框架,它采用掩膜注意力机制。我们的模型能够有选择地突出重要区域,同时抑制无关背景,从而提高复杂和混乱场景的分割精度。不同于传统的U-Net变体,MaskAttn-UNet有效地平衡了局部特征提取和更广泛的上下文意识,使其特别适合低分辨率输入。我们在三个基准数据集上评估了我们的方法,将输入图像缩放到128x128,并在语义、实例和全景分割任务上展示了具有竞争力的性能。我们的结果表明,MaskAttn-UNet的准确度与最新方法相当,而且与基于变压器的模型相比,计算成本显著降低,因此在资源受限的场景中,它是低分辨率分割的高效且可扩展的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对低分辨率图像分割在机器人、增强现实和大规模场景理解等实际应用中的挑战,提出了MaskAttn-UNet模型。该模型通过掩膜注意力机制增强传统U-Net架构,选择性强调重要区域并抑制无关背景,提高复杂场景中的分割精度。在三个基准数据集上评估,对输入图像进行128x128缩放,实现语义、实例和全景分割任务的竞争力表现,计算成本低,适用于资源受限场景。
Key Takeaways
- 低分辨率图像分割在机器人、增强现实和大规模场景理解中具有重要性。
- MaskAttn-UNet模型是基于传统U-Net架构的改进,引入掩膜注意力机制。
- MaskAttn-UNet模型能选择性强调重要区域,抑制无关背景,提高复杂场景分割精度。
- MaskAttn-UNet模型在三个基准数据集上表现良好,适用于多种分割任务。
- MaskAttn-UNet模型对输入图像进行缩放至128x128,具有计算成本低的优势。
- MaskAttn-UNet模型的性能与当前先进方法相当,特别适用于资源受限场景。
点此查看论文截图

Quaternionic Reweighted Amplitude Flow for Phase Retrieval in Image Reconstruction
Authors:Ren Hu, Pan Lian
Quaternionic signal processing provides powerful tools for efficiently managing color signals by preserving the intrinsic correlations among signal dimensions through quaternion algebra. In this paper, we address the quaternionic phase retrieval problem by systematically developing novel algorithms based on an amplitude-based model. Specifically, we propose the Quaternionic Reweighted Amplitude Flow (QRAF) algorithm, which is further enhanced by three of its variants: incremental, accelerated, and adapted QRAF algorithms. In addition, we introduce the Quaternionic Perturbed Amplitude Flow (QPAF) algorithm, which has linear convergence. Extensive numerical experiments on both synthetic data and real images, demonstrate that our proposed methods significantly improve recovery performance and computational efficiency compared to state-of-the-art approaches.
四元信号处理技术提供了强大的工具,能够通过四元代数保留信号维度之间的内在关联,从而有效地管理彩色信号。在本文中,我们解决了四元相位恢复问题,系统地开发了基于振幅模型的新型算法。具体来说,我们提出了四元重加权振幅流(QRAF)算法,该算法有三种变体:增量型、加速型和适应型QRAF算法。此外,我们还介绍了具有线性收敛性的四元扰动振幅流(QPAF)算法。在合成数据和真实图像上的大量数值实验表明,与最新方法相比,我们提出的方法在恢复性能和计算效率方面都有显著提高。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于四元数信号处理的新型算法,针对四元数相位恢复问题提出了Quaternionic Reweighted Amplitude Flow(QRAF)算法及其增量、加速和自适应版本。同时引入了具有线性收敛性的Quaternionic Perturbed Amplitude Flow(QPAF)算法,实验表明这些方法在恢复性能和计算效率上均优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 四元数信号处理通过保留信号维度之间的内在相关性,为有效管理彩色信号提供了强大的工具。
- 本文解决了四元数相位恢复问题,提出了基于振幅模型的全新算法。
- 介绍了Quaternionic Reweighted Amplitude Flow (QRAF) 算法及其增量、加速和自适应版本,这些版本增强了算法的性能。
- 引入了Quaternionic Perturbed Amplitude Flow (QPAF) 算法,具有线性收敛性。
- 通过大量的数值实验,在合成数据和真实图像上验证了所提方法相较于现有技术在恢复性能和计算效率上的优越性。
- 这些算法对于处理彩色信号具有重要的实用价值和应用前景。
点此查看论文截图

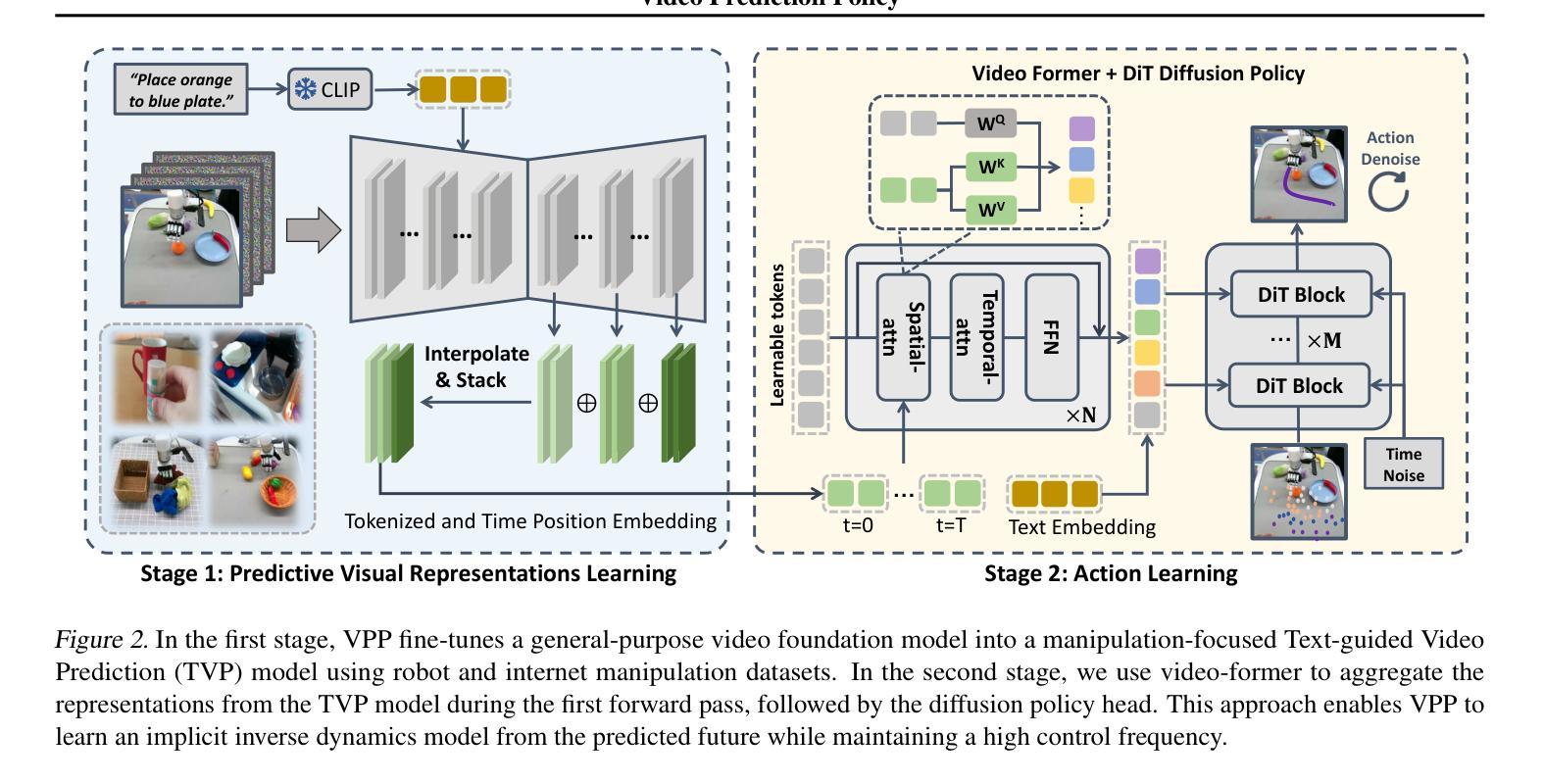
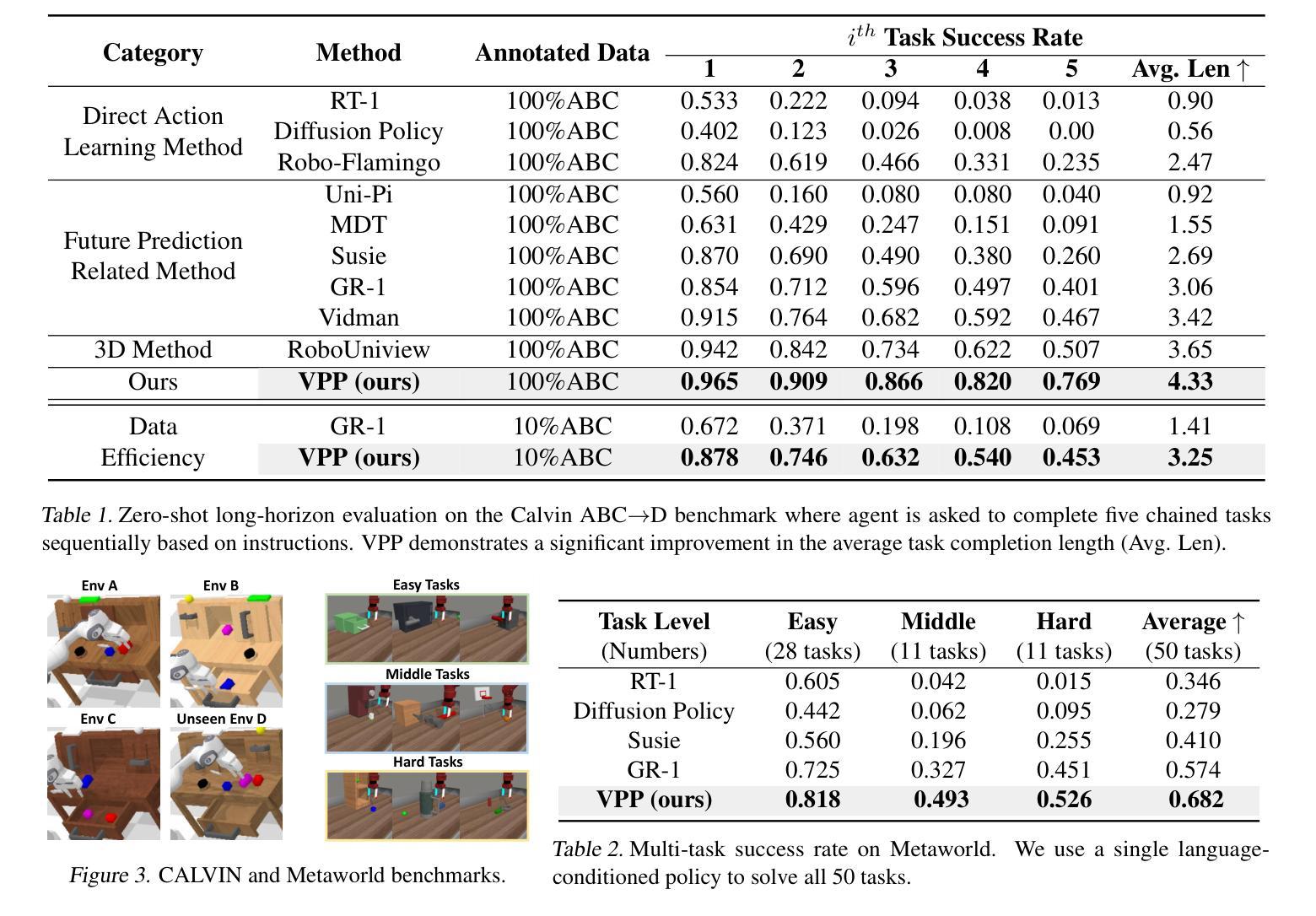
Video Prediction Policy: A Generalist Robot Policy with Predictive Visual Representations
Authors:Yucheng Hu, Yanjiang Guo, Pengchao Wang, Xiaoyu Chen, Yen-Jen Wang, Jianke Zhang, Koushil Sreenath, Chaochao Lu, Jianyu Chen
Visual representations play a crucial role in developing generalist robotic policies. Previous vision encoders, typically pre-trained with single-image reconstruction or two-image contrastive learning, tend to capture static information, often neglecting the dynamic aspects vital for embodied tasks. Recently, video diffusion models (VDMs) demonstrate the ability to predict future frames and showcase a strong understanding of physical world. We hypothesize that VDMs inherently produce visual representations that encompass both current static information and predicted future dynamics, thereby providing valuable guidance for robot action learning. Based on this hypothesis, we propose the Video Prediction Policy (VPP), which learns implicit inverse dynamics model conditioned on predicted future representations inside VDMs. To predict more precise future, we fine-tune pre-trained video foundation model on robot datasets along with internet human manipulation data. In experiments, VPP achieves a 18.6% relative improvement on the Calvin ABC-D generalization benchmark compared to the previous state-of-the-art, and demonstrates a 31.6% increase in success rates for complex real-world dexterous manipulation tasks. Project page at https://video-prediction-policy.github.io
视觉表示在开发通用机器人策略中起着至关重要的作用。之前的视觉编码器通常通过单图像重建或两图像对比学习进行预训练,它们更倾向于捕捉静态信息,往往会忽略对实体任务至关重要的动态方面。最近,视频扩散模型(VDMs)展示了预测未来帧的能力,并展示了对物理世界的强烈理解。我们假设VDMs天生就能产生包含当前静态信息和预测未来动态的视觉表示,从而为机器人动作学习提供有价值的指导。基于这一假设,我们提出了视频预测策略(VPP),它学习基于VDMs内部预测未来表示的隐式逆动力学模型。为了预测更精确的未来,我们在机器人数据集和互联网人类操作数据上对预训练的视频基础模型进行了微调。在实验中,VPP在Calvin ABC-D泛化基准测试上相对于之前的最先进水平实现了18.6%的相对改进,并在复杂的现实世界灵巧操作任务上成功率提高了3.视投影页面见:[https://video-prediction-policy.github io]现在提供上述论文的翻译以供审核。如果您有任何修改意见或建议,请随时告知。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML 2025 Spotlight Paper. The first two authors contribute equally
Summary
视觉表示在开发通用机器人策略中扮演关键角色。传统视觉编码器主要捕捉静态信息,忽略了动态方面,这对于实体任务至关重要。视频扩散模型(VDMs)能预测未来帧,展现了强大的物理世界理解力。我们假设VDMs产生的视觉表示包含当前静态信息和预测的未来动态,为机器人动作学习提供宝贵指导。基于此假设,我们提出视频预测策略(VPP),它学习基于VDMs内预测未来表示的隐逆动力学模型。在机器人数据集和互联网人类操作数据上微调预训练视频基础模型以预测更精确的未来。实验中,VPP在Calvin ABC-D泛化基准测试上相对于之前的最优策略实现了18.6%的相对改进,并在复杂的真实世界精细操作任务上成功率提高了31.6%。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉表示对于机器人策略的学习至关重要,涵盖静态和动态信息。
- 传统视觉编码器主要捕捉静态信息,可能忽略动态方面,影响机器人任务执行。
- 视频扩散模型(VDMs)能预测未来帧,展现出对物理世界的强烈理解。
- VDMs产生的视觉表示包含当前和未来的动态信息,对机器人动作学习有指导价值。
- 提出的视频预测策略(VPP)基于预测的未来表示学习隐逆动力学模型。
- 对预训练视频基础模型进行微调,以提高对未来预测的精确度。
- VPP在泛化性能和复杂机器人任务上的成功率相较于之前的方法有显著提升。
点此查看论文截图

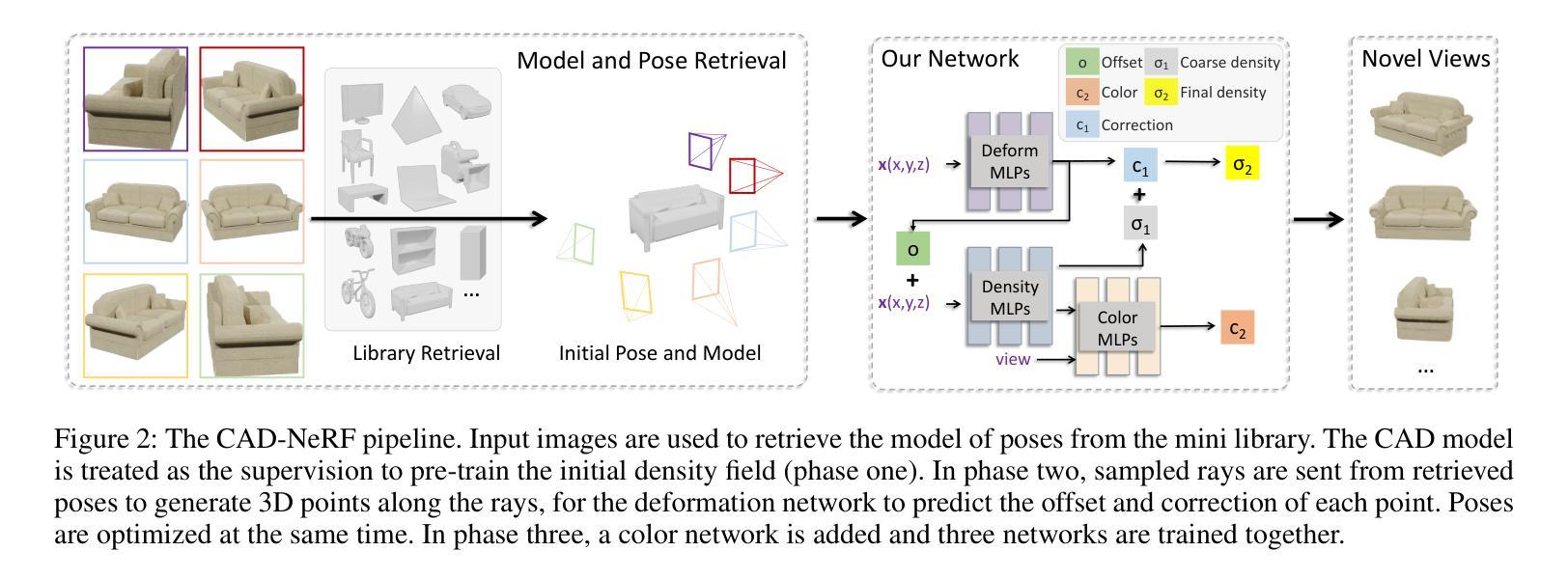
CAD-NeRF: Learning NeRFs from Uncalibrated Few-view Images by CAD Model Retrieval
Authors:Xin Wen, Xuening Zhu, Renjiao Yi, Zhifeng Wang, Chenyang Zhu, Kai Xu
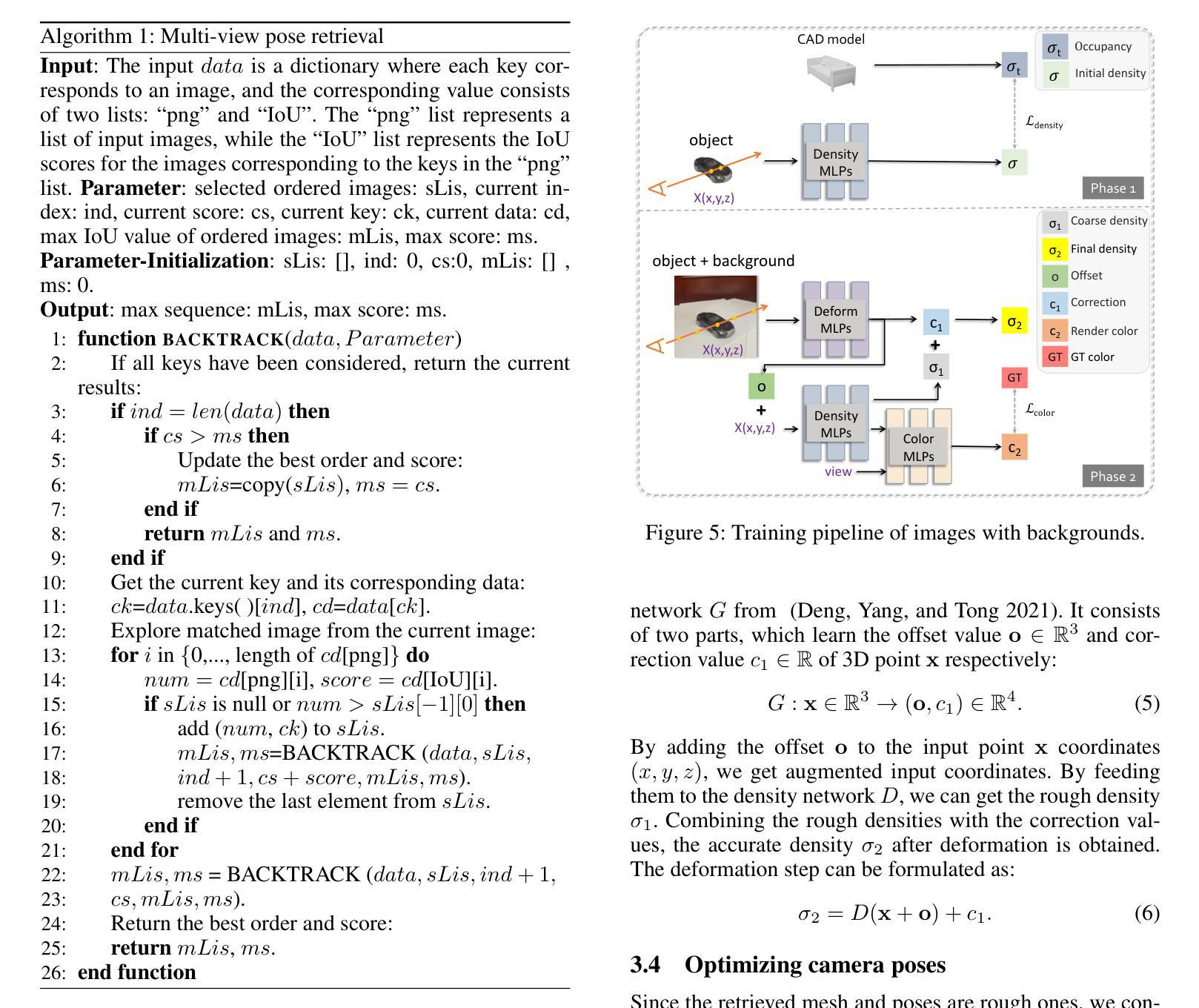
Reconstructing from multi-view images is a longstanding problem in 3D vision, where neural radiance fields (NeRFs) have shown great potential and get realistic rendered images of novel views. Currently, most NeRF methods either require accurate camera poses or a large number of input images, or even both. Reconstructing NeRF from few-view images without poses is challenging and highly ill-posed. To address this problem, we propose CAD-NeRF, a method reconstructed from less than 10 images without any known poses. Specifically, we build a mini library of several CAD models from ShapeNet and render them from many random views. Given sparse-view input images, we run a model and pose retrieval from the library, to get a model with similar shapes, serving as the density supervision and pose initializations. Here we propose a multi-view pose retrieval method to avoid pose conflicts among views, which is a new and unseen problem in uncalibrated NeRF methods. Then, the geometry of the object is trained by the CAD guidance. The deformation of the density field and camera poses are optimized jointly. Then texture and density are trained and fine-tuned as well. All training phases are in self-supervised manners. Comprehensive evaluations of synthetic and real images show that CAD-NeRF successfully learns accurate densities with a large deformation from retrieved CAD models, showing the generalization abilities.
从多视角图像重建是3D视觉中的一个长期存在的问题,神经辐射场(NeRFs)在此展示了巨大的潜力,并能呈现真实感的新视角渲染图像。目前,大多数NeRF方法都需要准确的相机姿态或大量输入图像,甚至两者都需要。从少数视角图像无姿态地重建NeRF是一个具有挑战性和高度不适定的问题。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了CAD-NeRF方法,该方法可从不到10张的图像中进行重建,而无需任何已知的姿态。具体地,我们从ShapeNet构建了几个CAD模型的迷你库,并从许多随机视角进行渲染。给定稀疏视角的输入图像,我们从库中运行模型和姿态检索,以获得具有相似形状的模型,作为密度监督和姿态初始化的基础。这里我们提出了一种多视角姿态检索方法,以避免各视角间的姿态冲突,这是在未校准的NeRF方法中的新且未见的问题。然后,通过CAD指导训练物体的几何形状。密度场的变形和相机姿态会进行联合优化。然后训练和微调纹理和密度。所有的训练阶段都是自监督的。对合成图像和真实图像的综合评估表明,CAD-NeRF成功地从检索到的CAD模型中学习到准确的密度,并展示了泛化能力,即使存在大的变形。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The article has been accepted by Frontiers of Computer Science (FCS)
Summary
基于少量图像(少于10张)且无姿态信息的情况下,重建NeRF模型是困难的且高度不适定的问题。为解决这个问题,我们提出了CAD-NeRF方法,该方法利用ShapeNet中的多个CAD模型库进行重建,并从库中检索模型和姿态。我们提出了多视角姿态检索方法来避免视角间的姿态冲突。训练阶段采用自我监督方式,通过CAD指导训练物体几何形状,联合优化密度场的变形和相机姿态,再训练和优化纹理和密度。在合成和真实图像上的综合评估显示,CAD-NeRF成功学习到了准确的密度信息,并展示了从检索的CAD模型中的大变形能力,证明了其泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- CAD-NeRF可以在缺少相机姿态和仅使用少量图像的情况下进行重建。
- 利用ShapeNet中的CAD模型库进行模型检索,为重建提供密度监督和姿态初始化。
- 提出多视角姿态检索方法来解决未校准NeRF方法中的新且未见的问题——姿态冲突。
- 训练阶段采用自我监督方式,通过CAD指导训练物体几何形状。
- 联合优化密度场的变形和相机姿态,再训练和优化纹理和密度。
- 在合成和真实图像上的评估表明CAD-NeRF具有准确学习密度信息的能力,并展示了良好的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图


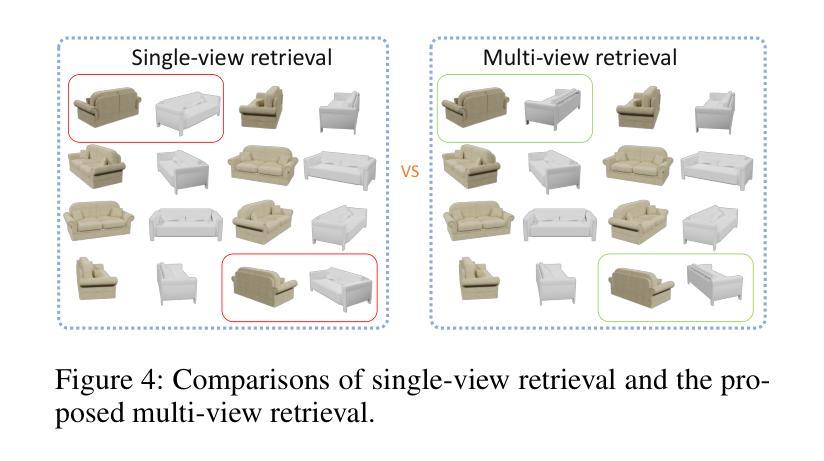
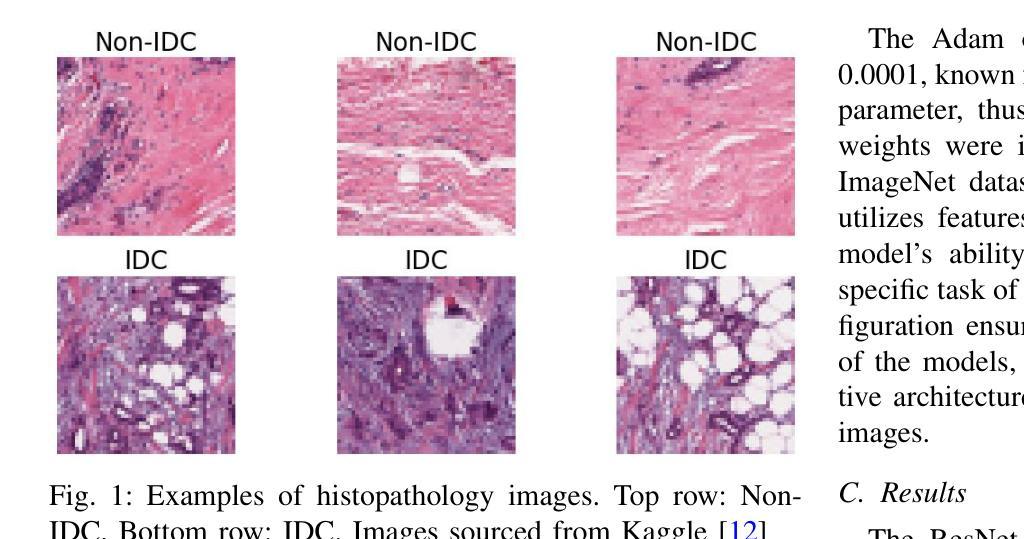
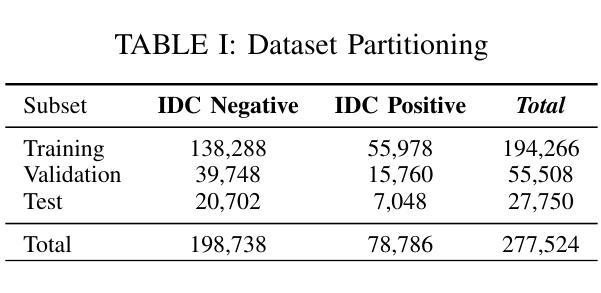
Evaluating Deep Learning Models for Breast Cancer Classification: A Comparative Study
Authors:Sania Eskandari, Ali Eslamian, Nusrat Munia, Amjad Alqarni, Qiang Cheng
This study evaluates the effectiveness of deep learning models in classifying histopathological images for early and accurate detection of breast cancer. Eight advanced models, including ResNet-50, DenseNet-121, ResNeXt-50, Vision Transformer (ViT), GoogLeNet (Inception v3), EfficientNet, MobileNet, and SqueezeNet, were compared using a dataset of 277,524 image patches. The Vision Transformer (ViT) model, with its attention-based mechanisms, achieved the highest validation accuracy of 94%, outperforming conventional CNNs. The study demonstrates the potential of advanced machine learning methods to enhance precision and efficiency in breast cancer diagnosis in clinical settings.
本研究评估了深度学习模型在分类病理图像以早期和准确检测乳腺癌方面的有效性。研究使用包含ResNet-50、DenseNet-121、ResNeXt-50、Vision Transformer(ViT)、GoogLeNet(Inception v3)、EfficientNet、MobileNet和SqueezeNet在内的八种先进模型进行了对比。通过使用含有277,524个图像块的数据集,通过测试得出Vision Transformer(ViT)模型使用其基于注意力的机制获得了最高的验证精度,达到94%,并优于传统的卷积神经网络(CNN)。该研究展示了先进的机器学习方法在增强乳腺癌诊断的精确性和效率方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 4 pages, 2 figures, 2 tables
Summary
本研究评估了深度学习模型在分类病理图像以早期和准确检测乳腺癌方面的有效性。比较了ResNet-50、DenseNet-121、ResNeXt-50、Vision Transformer(ViT)、GoogLeNet(Inception v3)、EfficientNet、MobileNet和SqueezeNet等八种先进模型。使用包含277,524个图像补丁的数据集进行测试,其中基于注意力机制的Vision Transformer(ViT)模型验证准确率最高,达到94%,优于传统卷积神经网络(CNN)。研究证明了先进机器学习方法在增强乳腺癌诊断的精确性和效率方面的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 研究评估了深度学习模型在乳腺癌病理图像分类中的有效性。
- 对比了八种深度学习模型,包括ResNet、DenseNet、ResNeXt、Vision Transformer、GoogLeNet、EfficientNet、MobileNet和SqueezeNet。
- Vision Transformer(ViT)模型在验证准确率上表现最佳,达到94%。
- ViT模型基于注意力机制,优于传统卷积神经网络(CNN)。
- 研究数据集包含大量的图像补丁,共计277,524个。
- 深度学习模型在乳腺癌诊断中有望提高精确性和效率。
点此查看论文截图
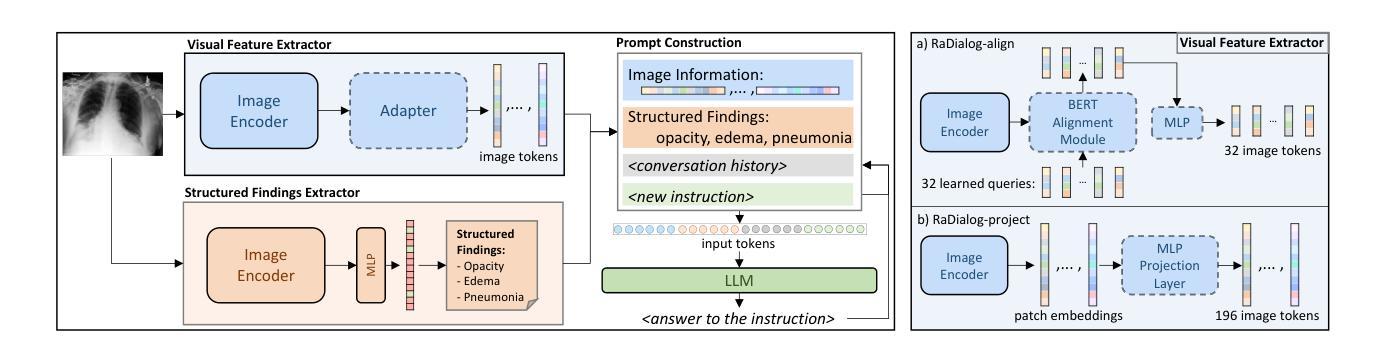
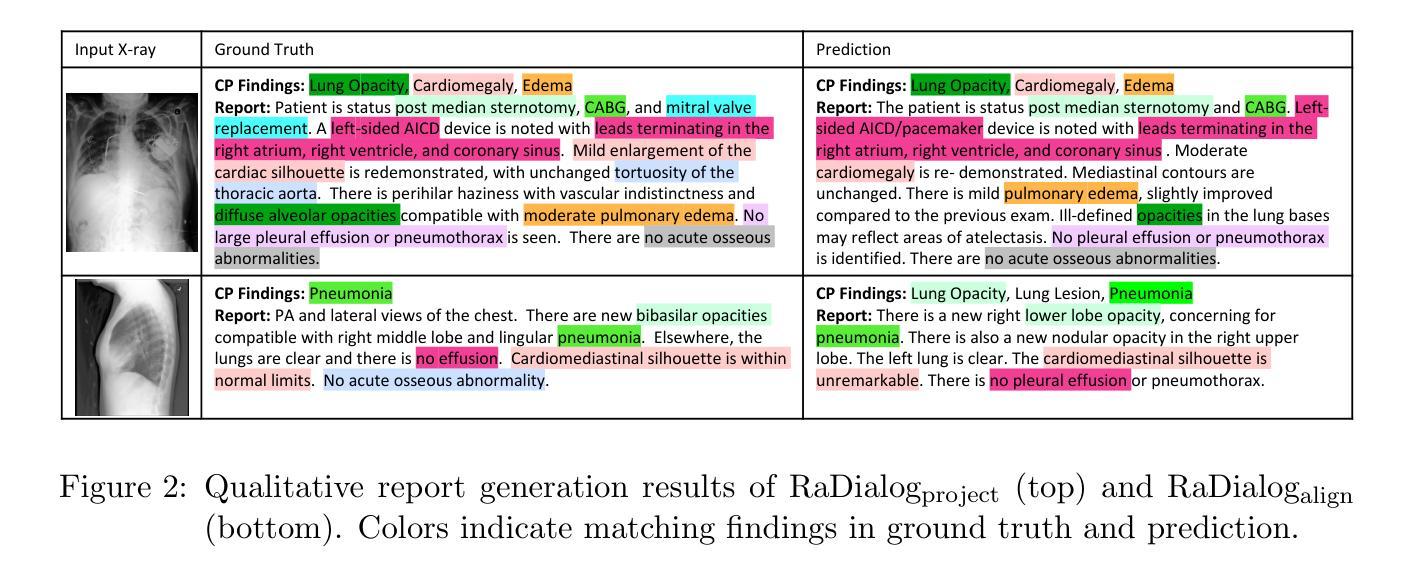
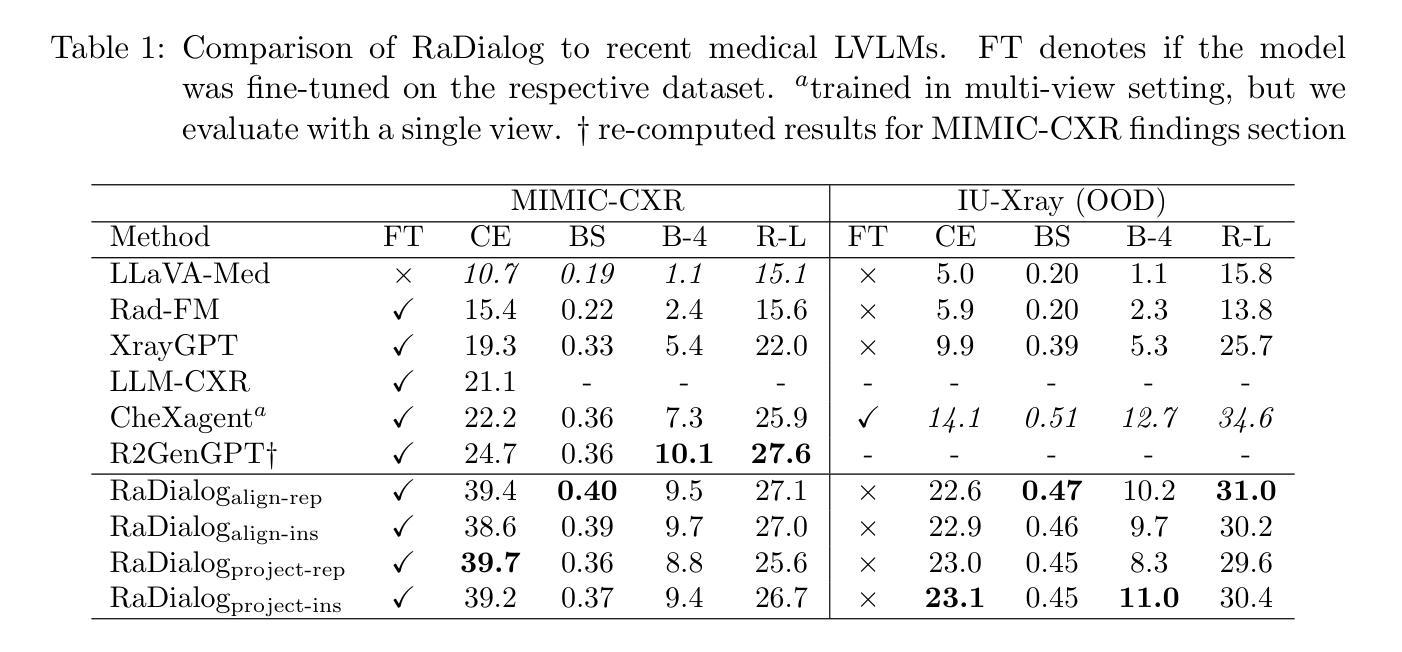
RaDialog: A Large Vision-Language Model for Radiology Report Generation and Conversational Assistance
Authors:Chantal Pellegrini, Ege Özsoy, Benjamin Busam, Nassir Navab, Matthias Keicher
Conversational AI tools that can generate and discuss clinically correct radiology reports for a given medical image have the potential to transform radiology. Such a human-in-the-loop radiology assistant could facilitate a collaborative diagnostic process, thus saving time and improving the quality of reports. Towards this goal, we introduce RaDialog, the first thoroughly evaluated and publicly available large vision-language model for radiology report generation and interactive dialog. RaDialog effectively integrates visual image features and structured pathology findings with a large language model (LLM) while simultaneously adapting it to a specialized domain using parameter-efficient fine-tuning. To keep the conversational abilities of the underlying LLM, we propose a comprehensive, semi-automatically labeled, image-grounded instruct dataset for chest X-ray radiology tasks. By training with this dataset, our method achieves state-of-the-art clinical correctness in report generation and shows impressive abilities in interactive tasks such as correcting reports and answering questions, serving as a foundational step toward clinical dialog systems. Our code is available on github: https://github.com/ChantalMP/RaDialog.
能够针对给定的医学图像生成并讨论临床上正确的放射学报告的对谈式人工智能工具具有改变放射学的潜力。这样的人机交互放射学助理可以促进协作诊断过程,从而节省时间并提高报告质量。为此,我们引入了RaDialog,这是首个经过全面评估且面向公众的大型视觉语言模型,可用于放射学报告生成和交互式对话。RaDialog有效地整合了视觉图像特征、结构化病理检查结果与大型语言模型(LLM),同时使用参数高效的微调方法使其适应专业领域。为了保持底层LLM的对话能力,我们为胸部X射线放射学任务提出了一个综合的、半自动标注的、以图像为基础的指令数据集。通过在此数据集上进行训练,我们的方法在报告生成方面达到了先进的临床正确性,并在纠正报告和回答问题等交互任务中表现出了令人印象深刻的能力,这作为迈向临床对话系统的基础一步。我们的代码可在github上获取:https://github.com/ChantalMP/RaDialog 。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication at MIDL 2025
Summary
对话式人工智能工具具有生成和讨论特定医学图像的临床正确放射学报告的能力,可为放射学带来变革。此类人类参与的放射学助理可推动协作诊断过程,从而节省时间并提高报告质量。为此目标,我们推出了RaDialog,这是首个全面评估并公开发布的用于放射学报告生成和交互式对话的大型视觉语言模型。RaDialog有效地整合了视觉图像特征、结构化病理发现与大型语言模型(LLM),同时采用高效的参数微调策略使其适应专业领域。为了保持底层LLM的对话能力,我们为胸部X射线放射学任务提出了一个综合的、半自动标记的图像基础指令数据集。通过此数据集进行训练,我们的方法在报告生成方面达到了临床正确性的最新水平,并在纠正报告和回答问题等交互任务方面表现出了令人印象深刻的能力,这可作为临床对话系统的基础一步。
Key Takeaways
- 对话式AI工具在放射学领域具有巨大潜力,能够生成和讨论临床正确的放射学报告。
- RaDialog是首个用于放射学报告生成和交互式对话的大型视觉语言模型。
- RaDialog集成了视觉图像特征、结构化病理发现与大型语言模型。
- RaDialog通过参数高效的微调策略适应专业领域。
- 为了训练模型,提出一个综合的、半自动标记的图像基础指令数据集,专注于胸部X射线放射学任务。
- RaDialog在报告生成方面达到了临床正确性的最新水平。
- RaDialog在交互任务中表现出色,如报告纠正和问答,为临床对话系统奠定了基础。
点此查看论文截图