⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-10 更新
Boosting Adverse Weather Crowd Counting via Multi-queue Contrastive Learning
Authors:Tianhang Pan, Xiuyi Jia
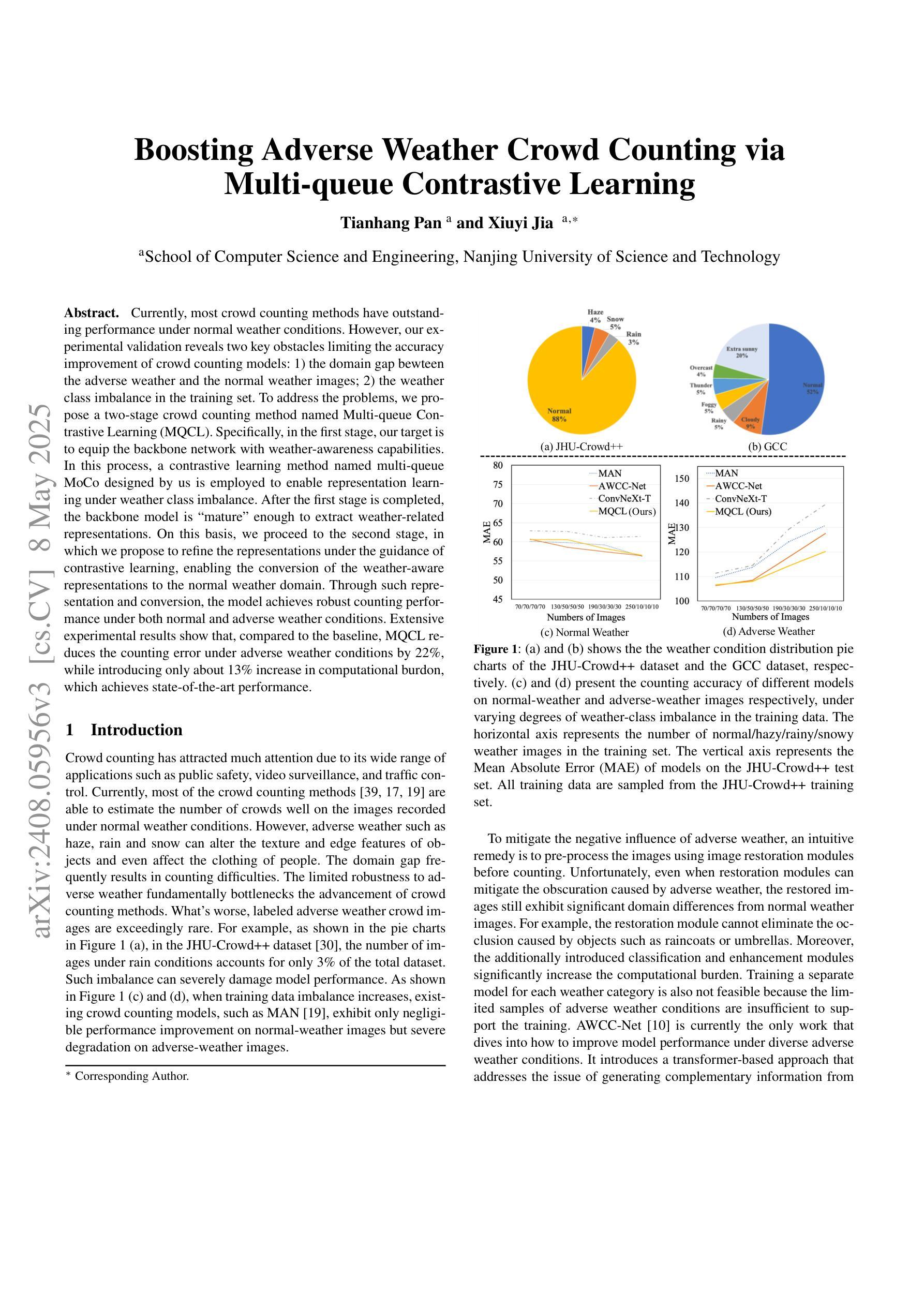
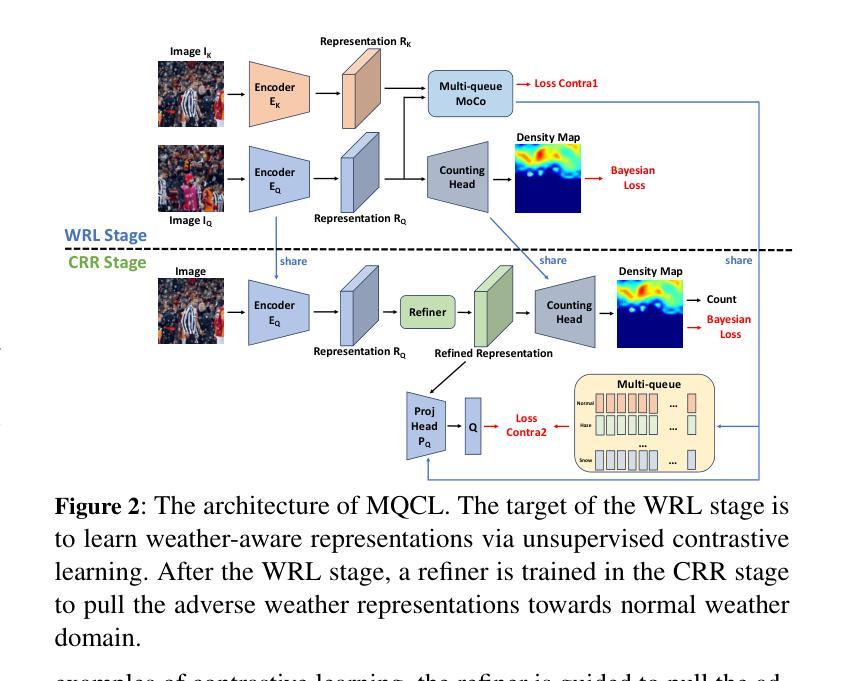
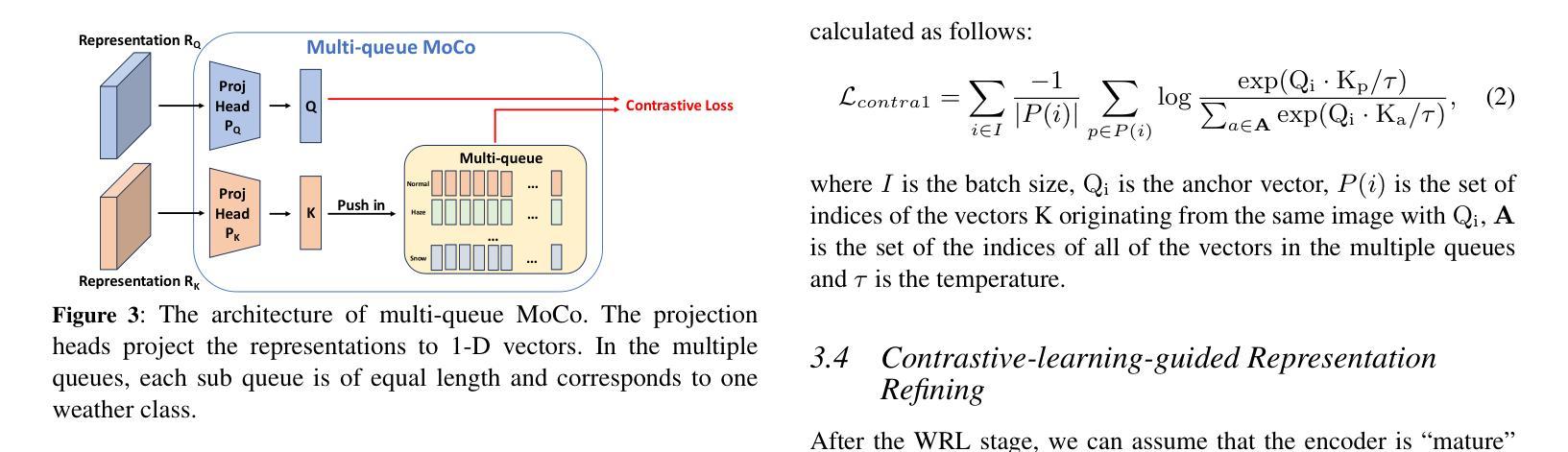
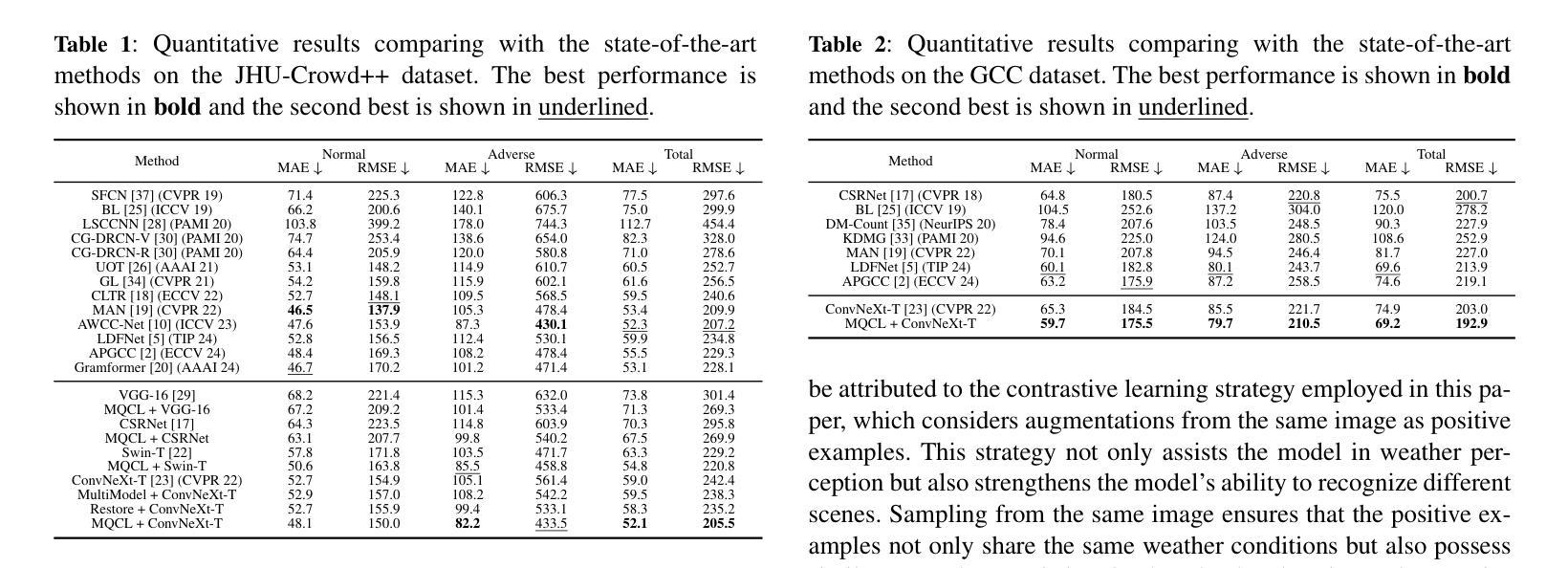
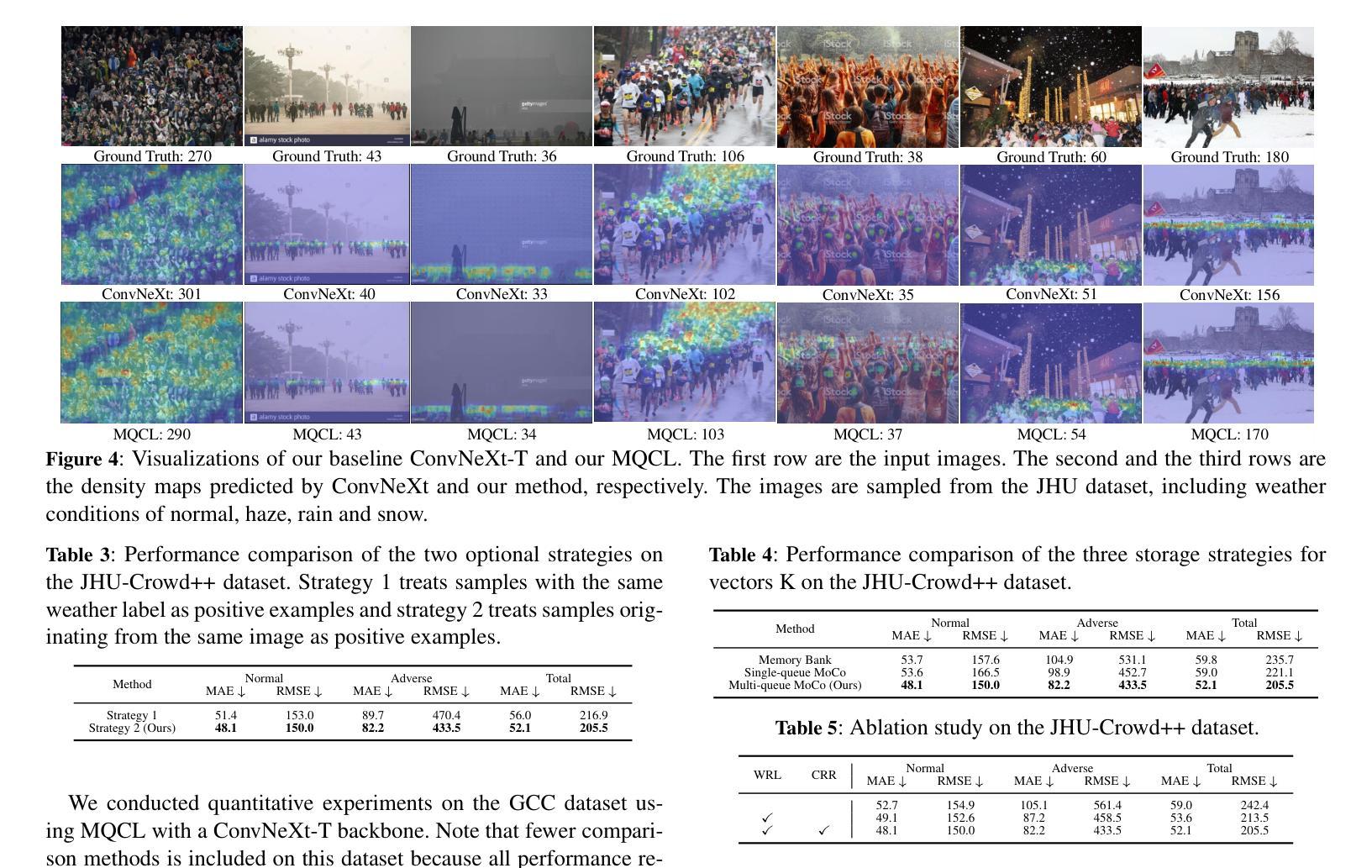
Currently, most crowd counting methods have outstanding performance under normal weather conditions. However, our experimental validation reveals two key obstacles limiting the accuracy improvement of crowd counting models: 1) the domain gap between the adverse weather and the normal weather images; 2) the weather class imbalance in the training set. To address the problems, we propose a two-stage crowd counting method named Multi-queue Contrastive Learning (MQCL). Specifically, in the first stage, our target is to equip the backbone network with weather-awareness capabilities. In this process, a contrastive learning method named multi-queue MoCo designed by us is employed to enable representation learning under weather class imbalance. After the first stage is completed, the backbone model is “mature” enough to extract weather-related representations. On this basis, we proceed to the second stage, in which we propose to refine the representations under the guidance of contrastive learning, enabling the conversion of the weather-aware representations to the normal weather domain. Through such representation and conversion, the model achieves robust counting performance under both normal and adverse weather conditions. Extensive experimental results show that, compared to the baseline, MQCL reduces the counting error under adverse weather conditions by 22%, while introducing only about 13% increase in computational burden, which achieves state-of-the-art performance.
当前,大多数人群计数方法在正常天气条件下表现突出。然而,我们的实验验证揭示了限制人群计数模型精度提升的两个关键障碍:1)恶劣天气和正常天气图像之间的域差距;2)训练集中的天气类别不平衡。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种两阶段的人群计数方法,名为多队列对比学习(MQCL)。具体来说,在第一阶段,我们的目标是使主干网络具备天气感知能力。在此过程中,我们采用了一种名为多队列MoCo的对比学习方法,以在天气类别不平衡的情况下进行表征学习。完成第一阶段后,主干模型已经足够“成熟”,可以提取与天气相关的表征。在此基础上,我们进入第二阶段,建议大家在对比学习的指导下对表征进行精炼,使天气感知表征能够转换为正常天气域。通过这样表征和转换,模型在正常和恶劣天气条件下均实现了稳健的计数性能。广泛的实验结果表明,与基线相比,MQCL在恶劣天气条件下的计数误差降低了22%,同时计算负担仅增加了约13%,实现了最新技术水平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 5 figures
Summary
针对人群计数方法在恶劣天气条件下性能下降的问题,提出一种两阶段的人群计数方法——多队列对比学习(MQCL)。首先通过多队列MoCo对比学习方法增强网络对天气的感知能力,然后在第一阶段完成的基础上进行精细化对比学习,实现天气感知表示向正常天气域的转换。该方法在正常和恶劣天气条件下均实现了稳健的计数性能,与基线相比,计数误差降低了22%,计算负担仅增加了约13%,达到先进水平。
Key Takeaways
- 当前人群计数方法在正常天气条件下表现良好,但在恶劣天气下存在准确性问题。
- 存在的关键问题包括:域差距(正常天气与恶劣天气图像)和训练集中的天气类别不平衡。
- 提出了一种两阶段的人群计数方法——多队列对比学习(MQCL)。
- 第一阶段目标是为骨干网络配备天气感知能力,采用多队列MoCo对比学习方法进行表示学习,以应对天气类不平衡问题。
- 第二阶段在已完成第一阶段的基础上,通过对比学习对表示进行精细化,实现天气感知表示向正常天气域的转换。
- MQCL方法在正常和恶劣天气条件下均实现了稳健的计数性能。
点此查看论文截图