⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-10 更新
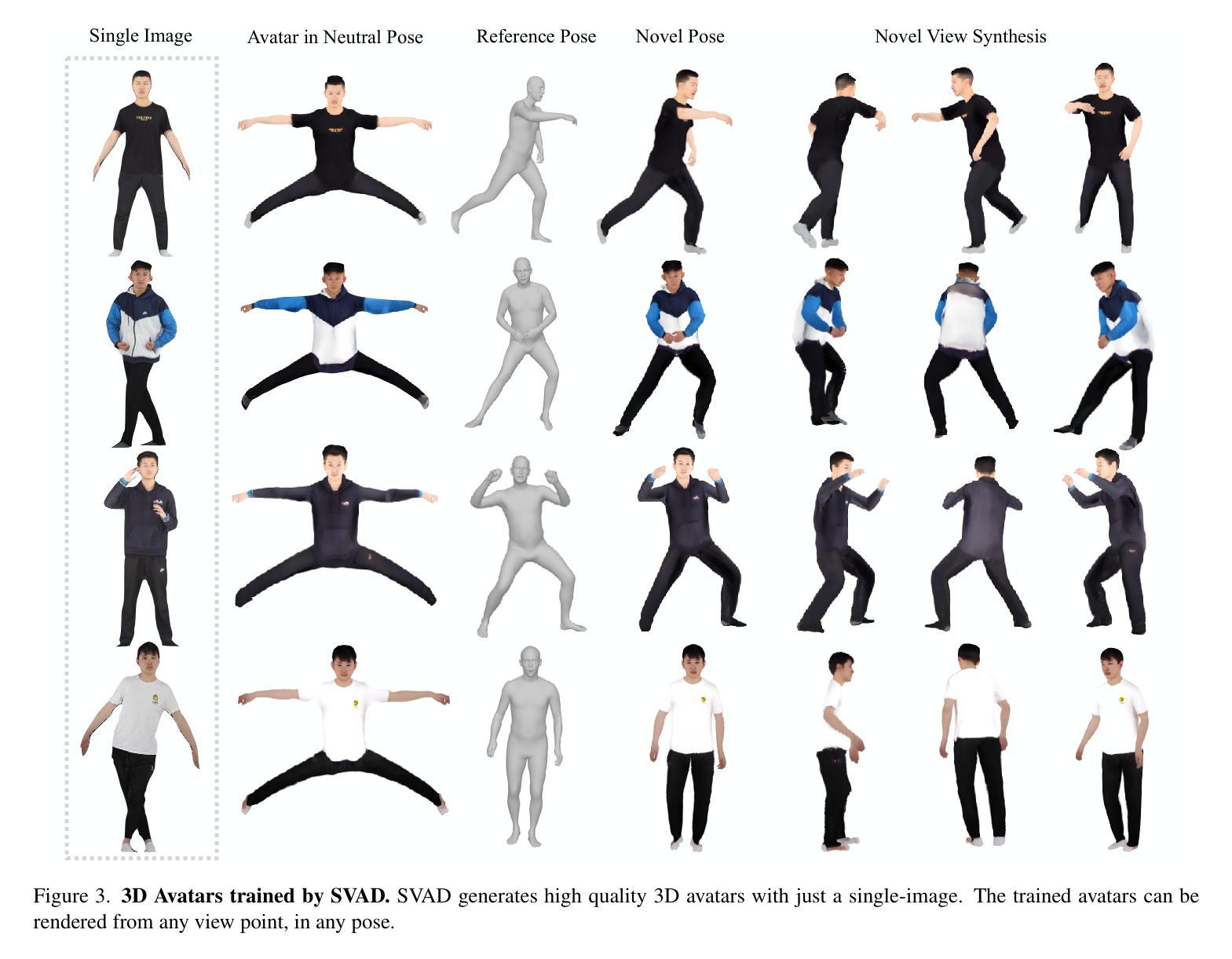
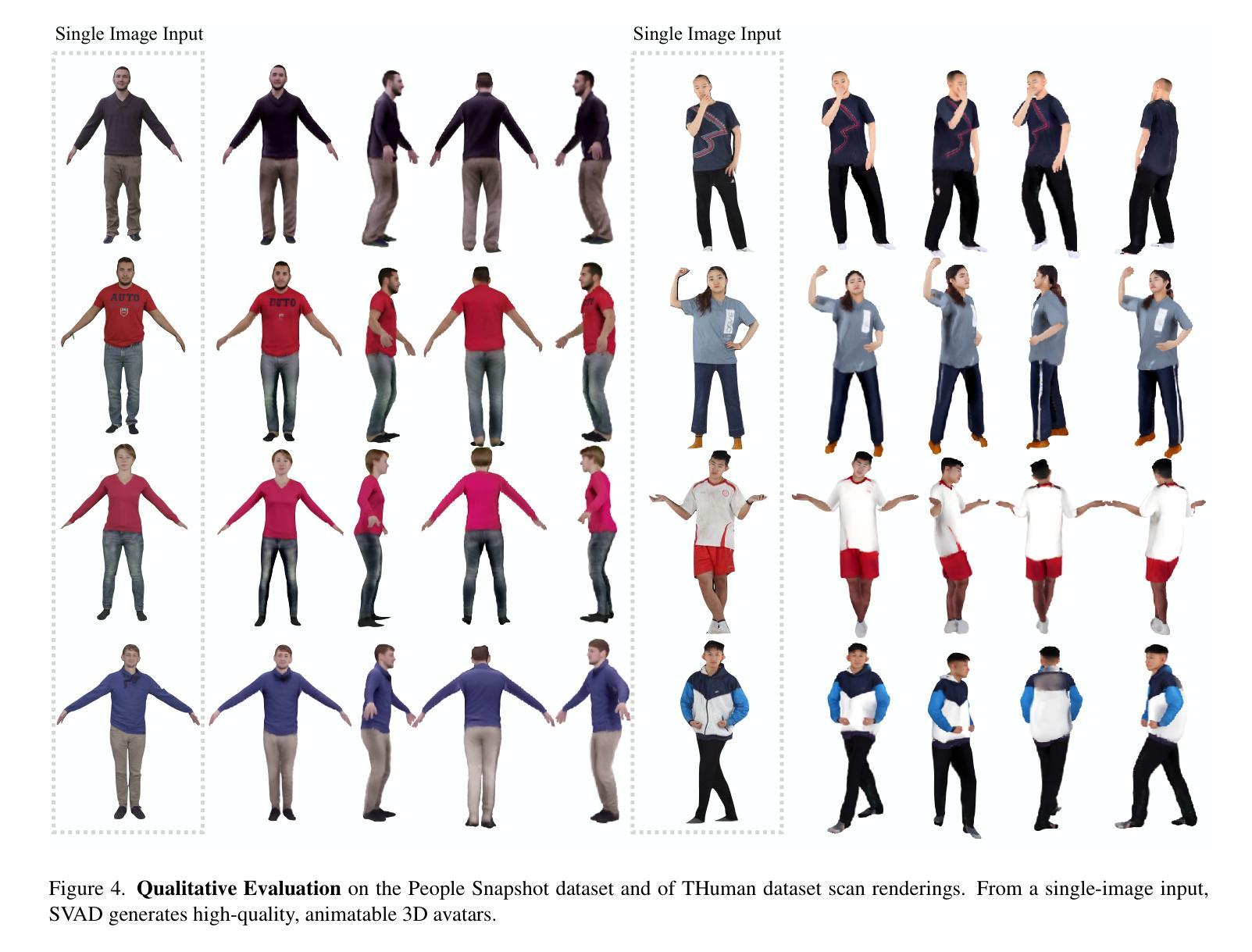
SVAD: From Single Image to 3D Avatar via Synthetic Data Generation with Video Diffusion and Data Augmentation
Authors:Yonwoo Choi
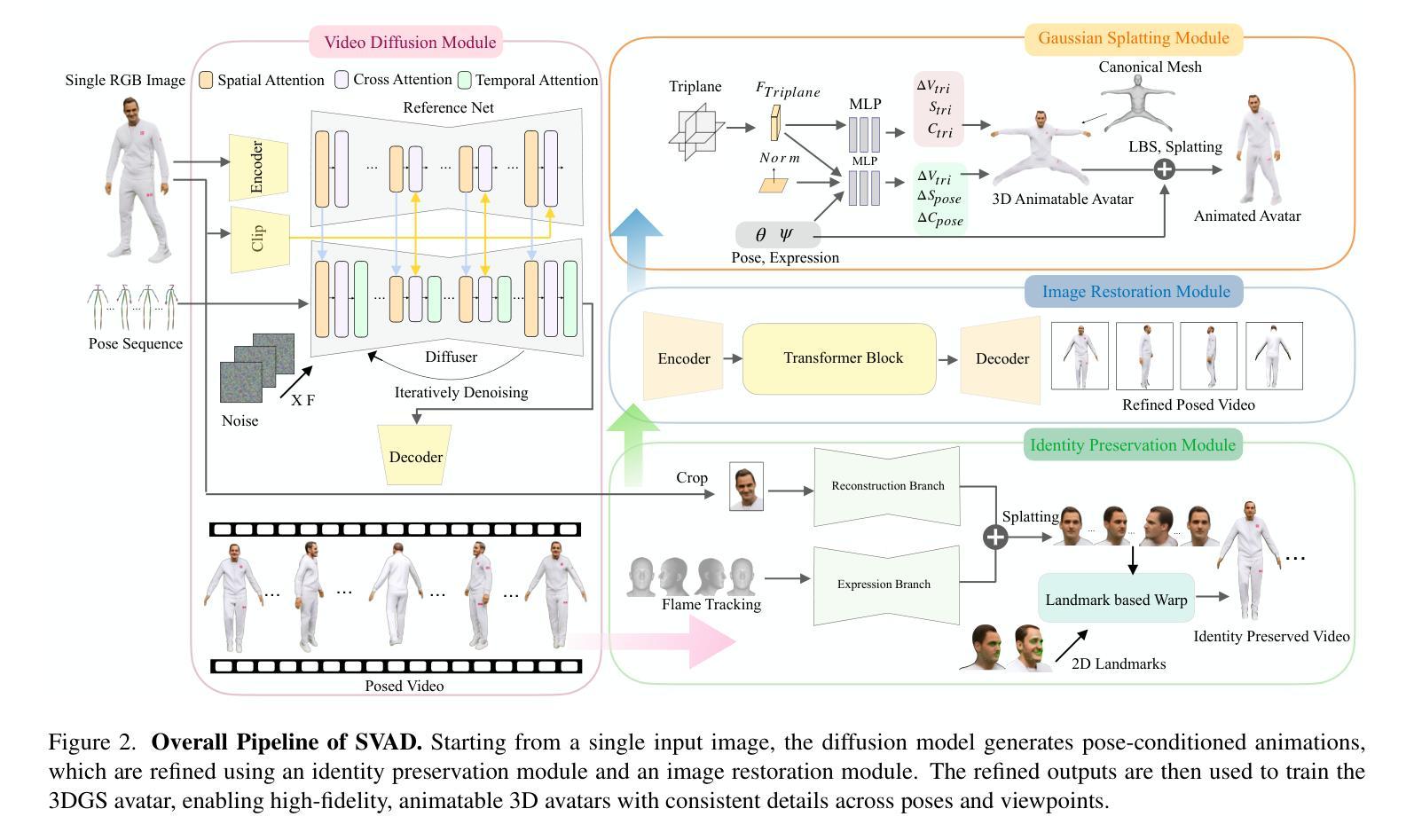
Creating high-quality animatable 3D human avatars from a single image remains a significant challenge in computer vision due to the inherent difficulty of reconstructing complete 3D information from a single viewpoint. Current approaches face a clear limitation: 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) methods produce high-quality results but require multiple views or video sequences, while video diffusion models can generate animations from single images but struggle with consistency and identity preservation. We present SVAD, a novel approach that addresses these limitations by leveraging complementary strengths of existing techniques. Our method generates synthetic training data through video diffusion, enhances it with identity preservation and image restoration modules, and utilizes this refined data to train 3DGS avatars. Comprehensive evaluations demonstrate that SVAD outperforms state-of-the-art (SOTA) single-image methods in maintaining identity consistency and fine details across novel poses and viewpoints, while enabling real-time rendering capabilities. Through our data augmentation pipeline, we overcome the dependency on dense monocular or multi-view training data typically required by traditional 3DGS approaches. Extensive quantitative, qualitative comparisons show our method achieves superior performance across multiple metrics against baseline models. By effectively combining the generative power of diffusion models with both the high-quality results and rendering efficiency of 3DGS, our work establishes a new approach for high-fidelity avatar generation from a single image input.
从单一图像创建高质量的可动画3D人类角色,仍然是计算机视觉领域的一个重大挑战。这是由于从单一视角重建完整的3D信息的固有难度所致。当前的方法存在一个明显的局限性:3D高斯喷溅(3DGS)方法虽然能产生高质量的结果,但需要多个视角或视频序列,而视频扩散模型虽然可以从单个图像生成动画,但在一致性和身份保持方面却存在困难。我们提出了SVAD这一新方法,它通过利用现有技术的互补优势来解决这些局限性。我们的方法通过视频扩散生成合成训练数据,通过身份保持和图像恢复模块对其进行增强,并利用这些精细数据训练3DGS角色。综合评估表明,SVAD在保持身份一致性、精细细节以及新型姿势和视角方面,优于最先进的单图像方法,同时实现了实时渲染功能。通过我们的数据增强流程,我们克服了传统3DGS方法通常对密集单眼或多视角训练数据的依赖。大量的定量和定性对比显示,我们的方法在多个指标上优于基线模型。通过有效地结合扩散模型的生成能力与3DGS的高质量结果和渲染效率,我们的工作建立了一种从单个图像输入生成高保真角色的新方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR 2025 SyntaGen Workshop, Project Page: https://yc4ny.github.io/SVAD/
Summary
该文本介绍了在计算机视觉领域创建高质量的可动画三维人类头像的重大挑战。现有方法存在局限性,如需要多视角或视频序列,或面临一致性及身份保持问题。本文提出了一种新方法SVAD,结合现有技术的优势,生成合成训练数据,增强身份保持和图像恢复模块,并利用这些数据训练三维高斯喷涂(3DGS)头像。新方法可在保持身份一致性和细节方面优于单图像方法,并具备实时渲染能力。通过数据增强管道,克服了传统3DGS方法对密集单目或多视角训练数据的依赖。本文结合了扩散模型的生成能力与3DGS的高质量结果和渲染效率,为从单张图像生成高质量头像提供了新的方法。
Key Takeaways
- 当前创建单一图像的高质量可动画三维人类头像是一大挑战。
- 现有方法如3DGS和视频扩散模型存在局限性。
- SVAD方法结合视频扩散模型的生成能力与身份保持和图像恢复模块来生成合成训练数据。
- SVAD利用这些数据训练三维高斯喷涂(3DGS)头像,实现高质量结果和实时渲染能力。
- SVAD通过数据增强管道克服了对密集单目或多视角训练数据的依赖。
- SVAD在保持身份一致性和细节方面优于单图像方法。
点此查看论文截图



3D Scene Generation: A Survey
Authors:Beichen Wen, Haozhe Xie, Zhaoxi Chen, Fangzhou Hong, Ziwei Liu
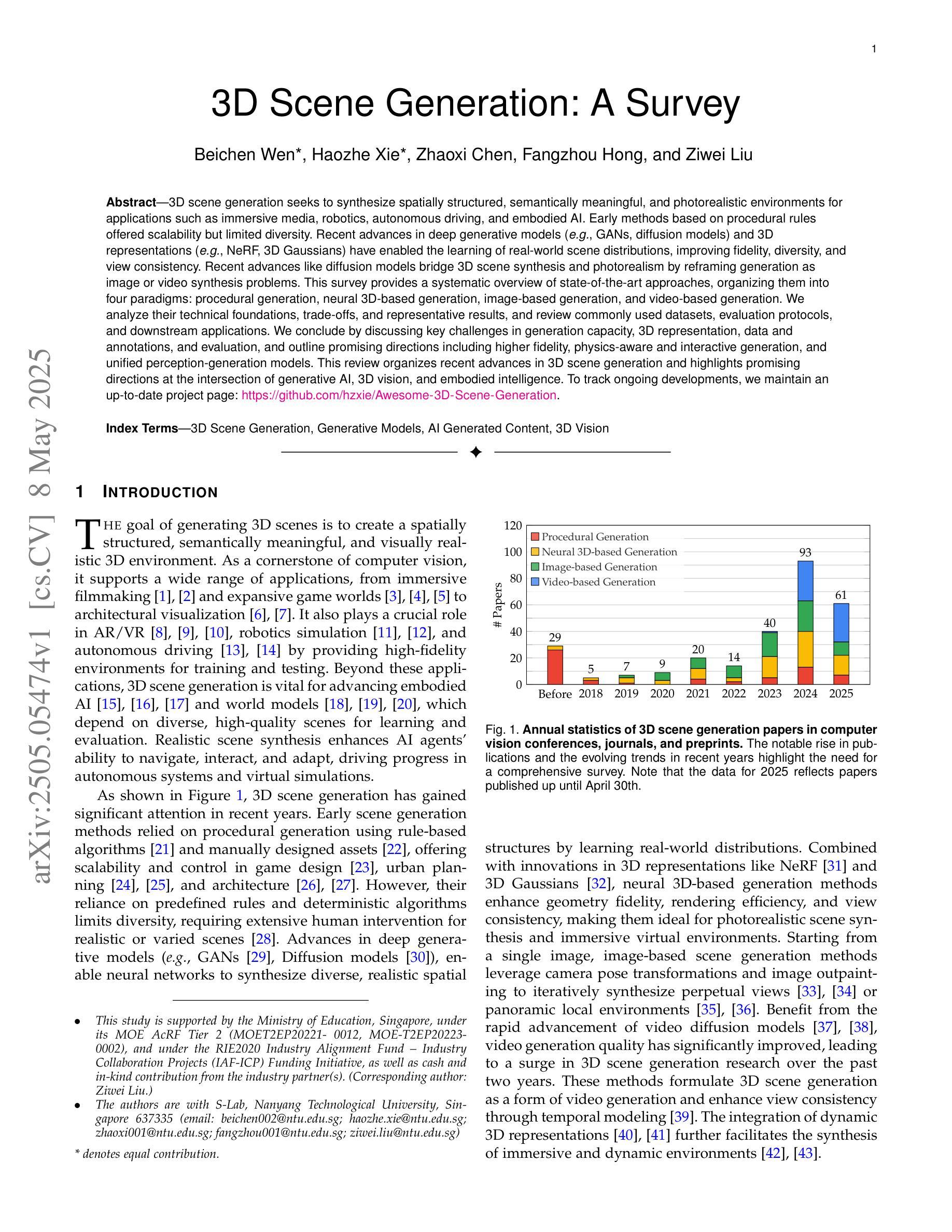
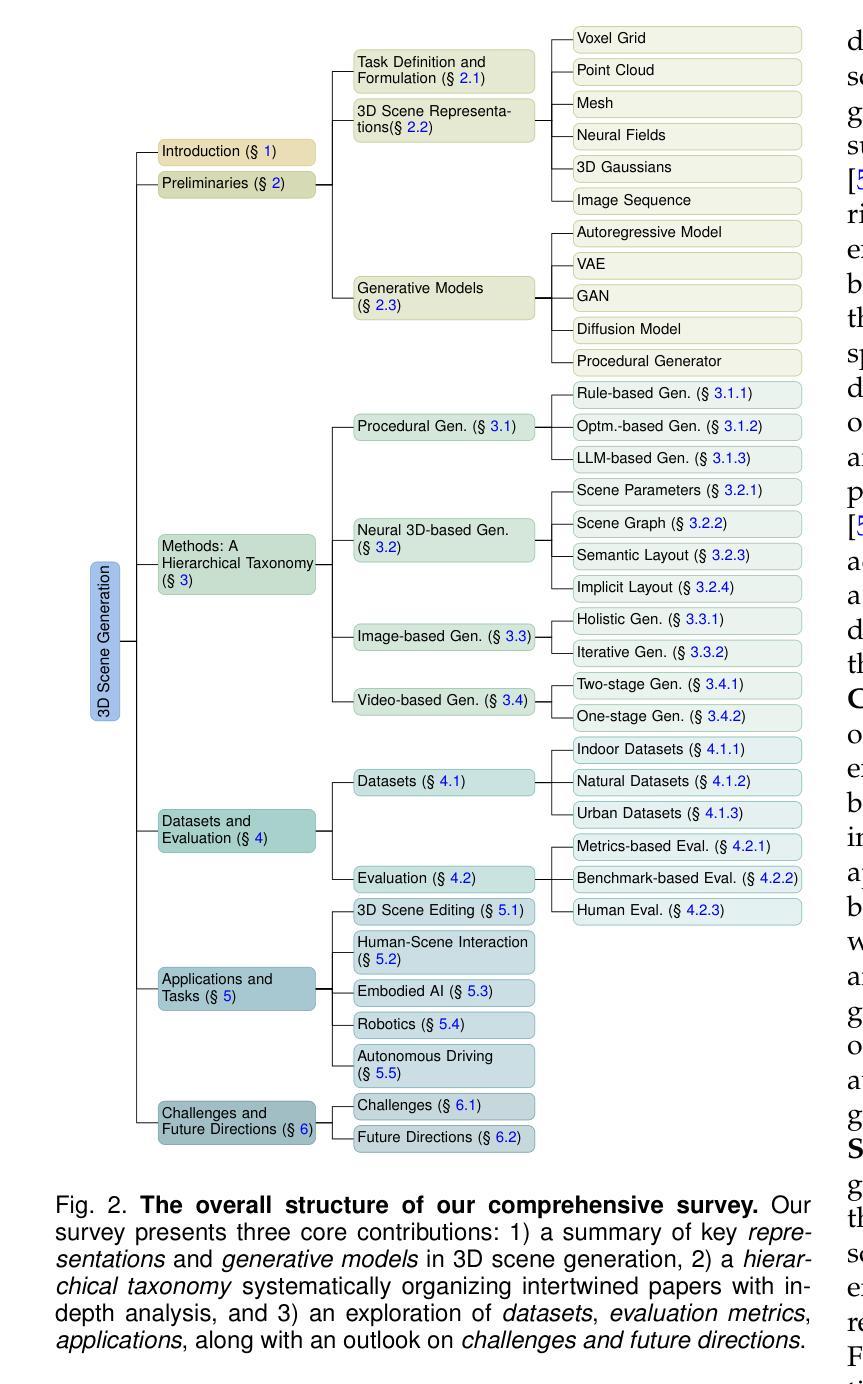
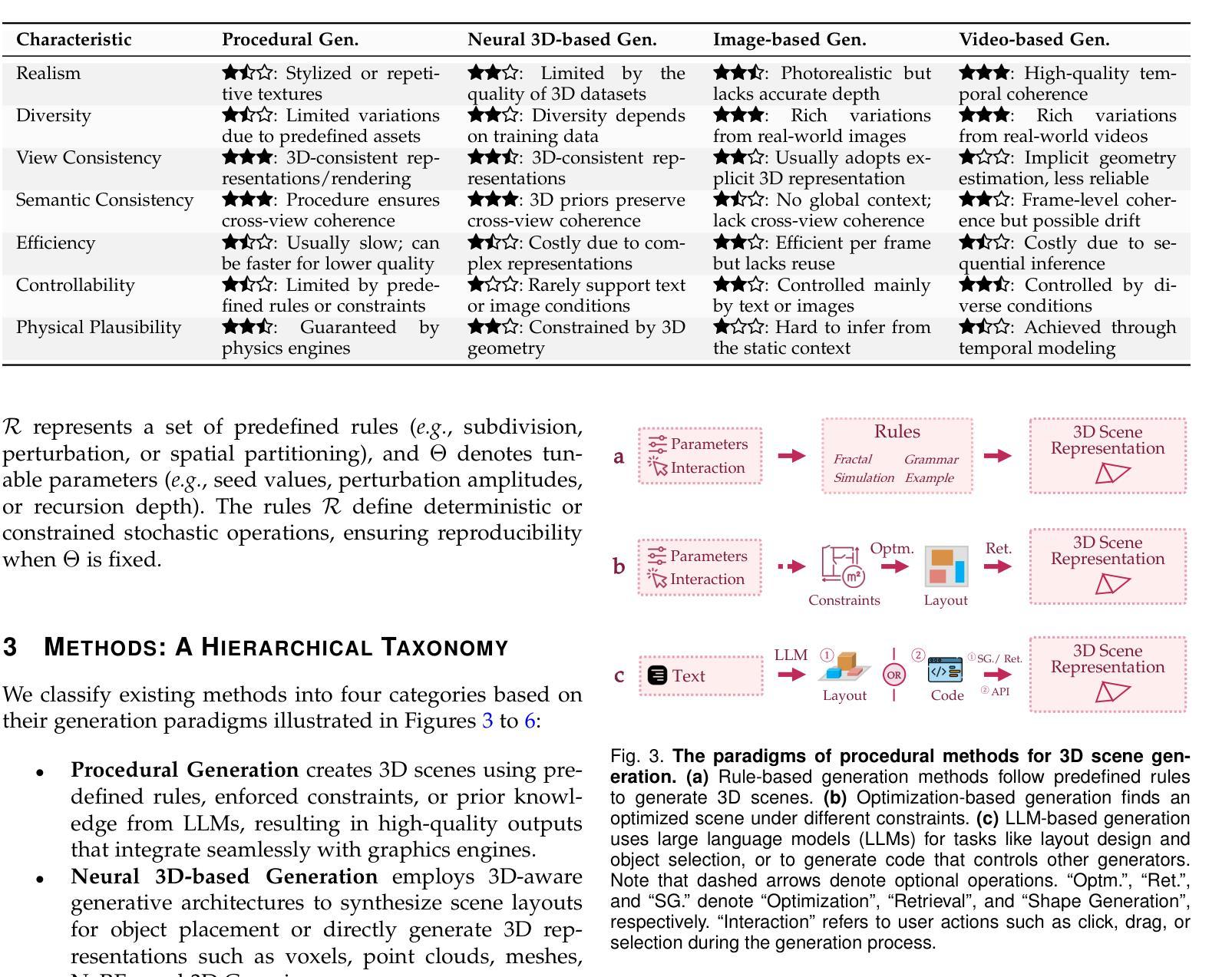
3D scene generation seeks to synthesize spatially structured, semantically meaningful, and photorealistic environments for applications such as immersive media, robotics, autonomous driving, and embodied AI. Early methods based on procedural rules offered scalability but limited diversity. Recent advances in deep generative models (e.g., GANs, diffusion models) and 3D representations (e.g., NeRF, 3D Gaussians) have enabled the learning of real-world scene distributions, improving fidelity, diversity, and view consistency. Recent advances like diffusion models bridge 3D scene synthesis and photorealism by reframing generation as image or video synthesis problems. This survey provides a systematic overview of state-of-the-art approaches, organizing them into four paradigms: procedural generation, neural 3D-based generation, image-based generation, and video-based generation. We analyze their technical foundations, trade-offs, and representative results, and review commonly used datasets, evaluation protocols, and downstream applications. We conclude by discussing key challenges in generation capacity, 3D representation, data and annotations, and evaluation, and outline promising directions including higher fidelity, physics-aware and interactive generation, and unified perception-generation models. This review organizes recent advances in 3D scene generation and highlights promising directions at the intersection of generative AI, 3D vision, and embodied intelligence. To track ongoing developments, we maintain an up-to-date project page: https://github.com/hzxie/Awesome-3D-Scene-Generation.
三维场景生成旨在合成具有空间结构、语义和逼真的环境,为沉浸式媒体、机器人技术、自动驾驶和人工智能等应用提供支持。早期基于程序规则的方法提供了可扩展性但限制了多样性。最近深度生成模型(如GANs和扩散模型)和三维表示(如NeRF和三维高斯)的进步使得学习真实场景分布成为可能,提高了逼真度、多样性和视角一致性。最近的扩散模型等技术通过将生成重新构建为图像或视频合成问题,从而实现了三维场景合成与逼真性的结合。这篇综述系统地概述了当前先进技术的方法,将它们归纳为四种范式:程序生成、基于神经的三维生成、基于图像的生成和基于视频的生成。我们分析了它们的技术基础、权衡和代表性成果,并回顾了常用的数据集、评估协议和下游应用。最后,我们讨论了生成能力、三维表示、数据和注释以及评估方面的关键挑战,并概述了具有前景的方向,包括更高的逼真度、物理感知和交互式生成以及统一的感知生成模型。这篇综述整理了三维场景生成的最新进展,并强调了生成人工智能、三维视觉和人工智能交叉领域的具有前景的方向。要了解最新进展,请访问我们的项目页面:https://github.com/hzxie/Awesome-3D-Scene-Generation。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://github.com/hzxie/Awesome-3D-Scene-Generation
Summary
这篇论文综述了当前三维场景生成的前沿技术,概述了四种主要方法:基于过程的生成、基于神经的三维生成、基于图像的生成和基于视频的生成。文章分析了它们的技术基础、优缺点及典型成果,并讨论了生成能力、三维表征、数据和标注、评估中的关键挑战,以及未来发展方向,包括更高保真度、物理感知和交互式生成以及统一的感知生成模型等。
Key Takeaways
- 3D场景生成旨在合成用于沉浸式媒体、机器人技术、自动驾驶和嵌入式人工智能等应用的空间结构、语义丰富和逼真的环境。
- 早期基于过程规则的方法虽然具有良好的可扩展性,但多样性有限。
- 深度生成模型(如GANs和扩散模型)和3D表示(如NeRF和3D高斯)的最新进展推动了学习现实场景分布的能力,提高了逼真度、多样性和视图一致性。
- 扩散模型等最新技术通过重新构建图像或视频合成问题,将3D场景合成与逼真性联系起来。
- 文章概述了当前研究的主要挑战,包括生成能力、3D表征技术和评价协议等。
- 文章强调了未来发展方向,包括提高保真度、物理感知和交互式生成以及统一的感知生成模型等。
点此查看论文截图
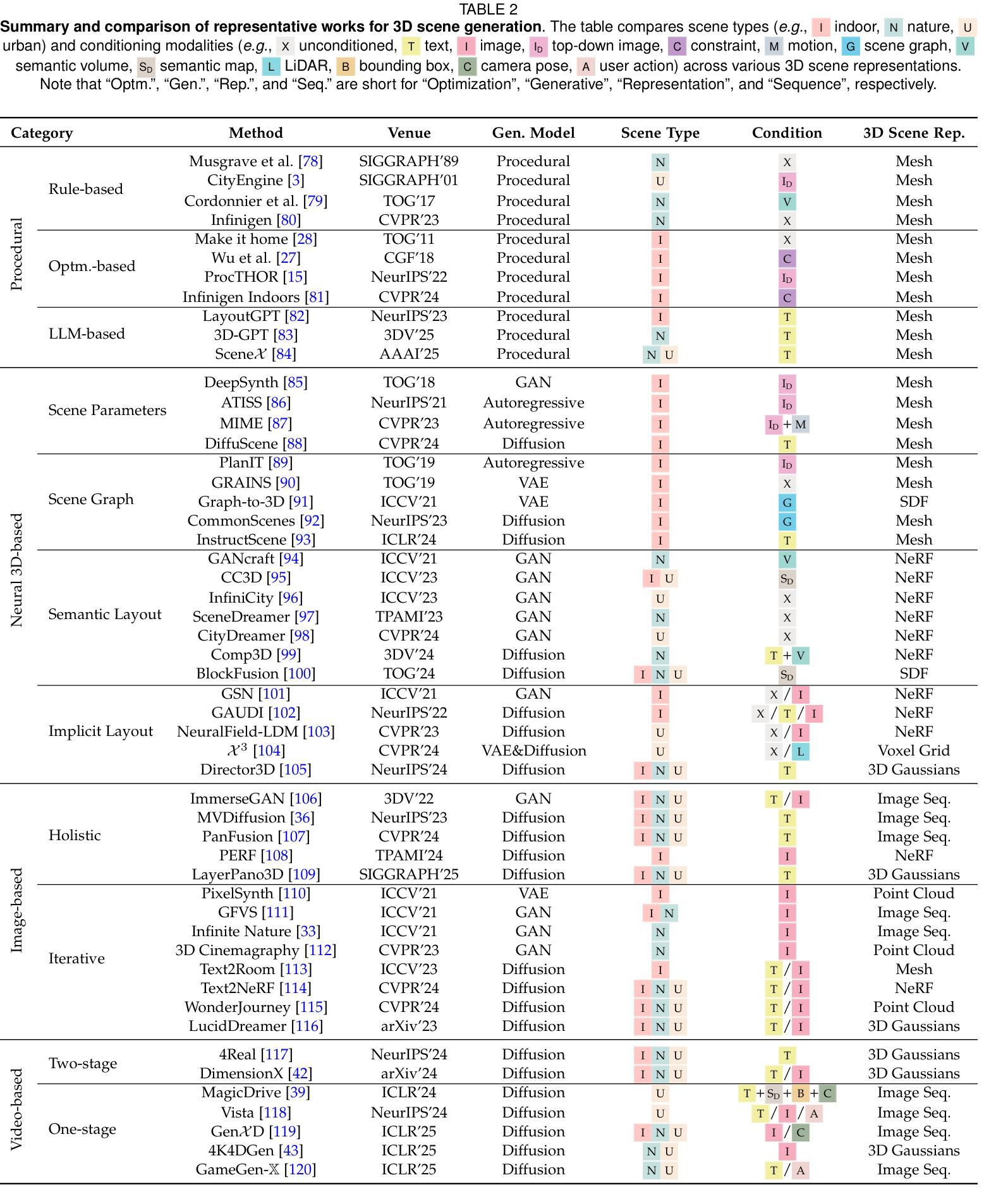
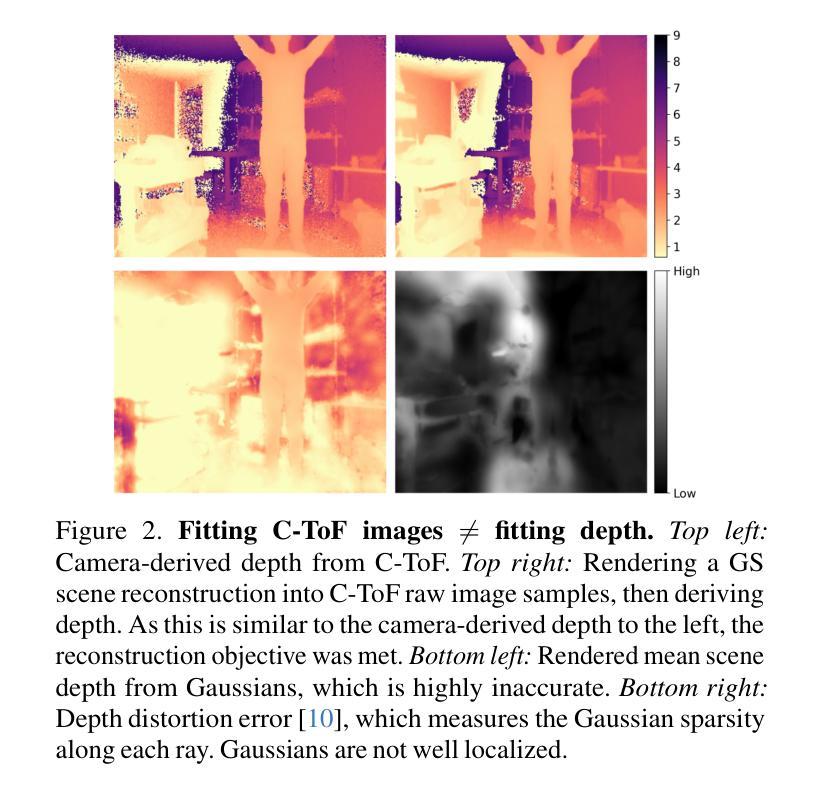
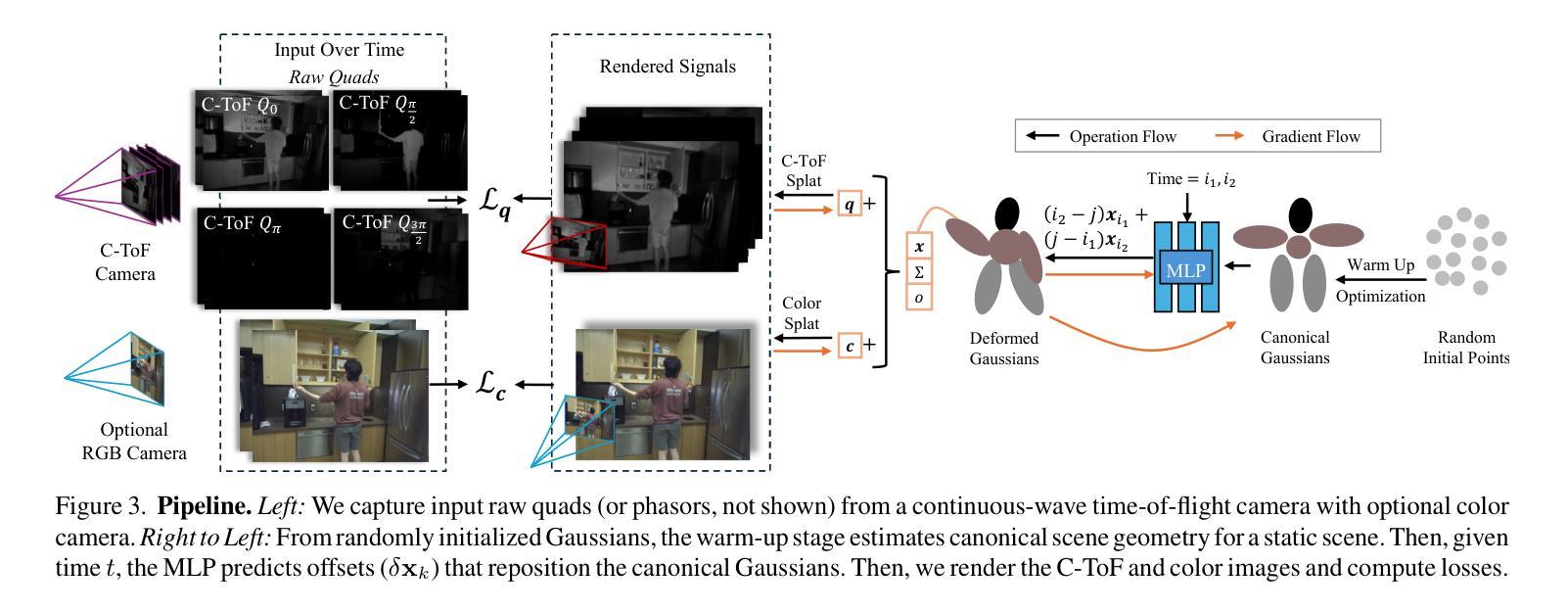
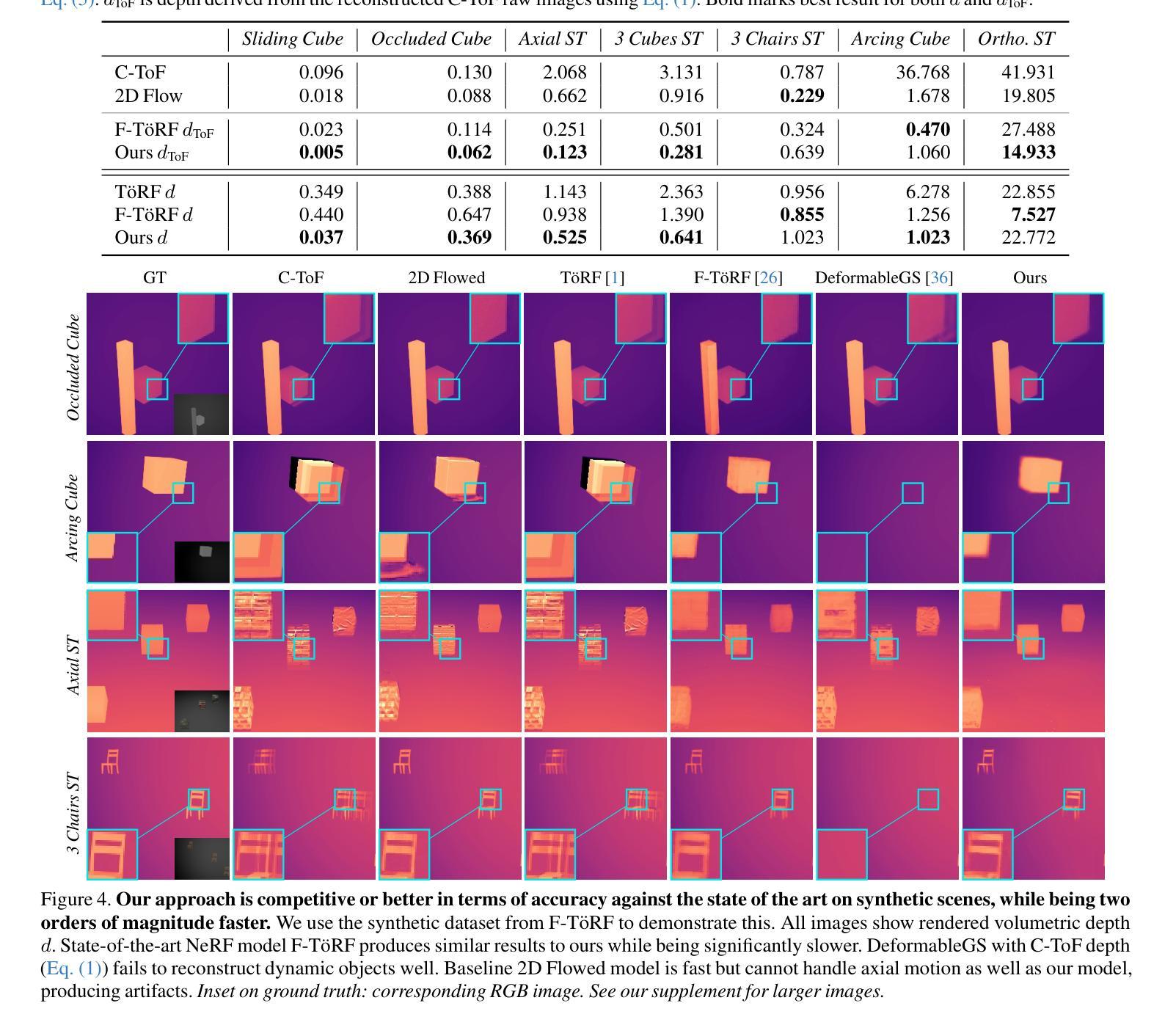
Time of the Flight of the Gaussians: Optimizing Depth Indirectly in Dynamic Radiance Fields
Authors:Runfeng Li, Mikhail Okunev, Zixuan Guo, Anh Ha Duong, Christian Richardt, Matthew O’Toole, James Tompkin
We present a method to reconstruct dynamic scenes from monocular continuous-wave time-of-flight (C-ToF) cameras using raw sensor samples that achieves similar or better accuracy than neural volumetric approaches and is 100x faster. Quickly achieving high-fidelity dynamic 3D reconstruction from a single viewpoint is a significant challenge in computer vision. In C-ToF radiance field reconstruction, the property of interest-depth-is not directly measured, causing an additional challenge. This problem has a large and underappreciated impact upon the optimization when using a fast primitive-based scene representation like 3D Gaussian splatting, which is commonly used with multi-view data to produce satisfactory results and is brittle in its optimization otherwise. We incorporate two heuristics into the optimization to improve the accuracy of scene geometry represented by Gaussians. Experimental results show that our approach produces accurate reconstructions under constrained C-ToF sensing conditions, including for fast motions like swinging baseball bats. https://visual.cs.brown.edu/gftorf
我们提出了一种利用单眼连续波飞行时间(C-ToF)相机的原始传感器样本重建动态场景的方法,该方法可以达到或超过神经体积方法的准确性,并且速度提高了100倍。从单一视角快速实现高保真动态3D重建是计算机视觉领域的一个重大挑战。在C-ToF辐射场重建中,感兴趣的深度属性并不能直接测量,这造成了额外的挑战。在使用基于原始场景的快速表示方法(如用于产生满意结果的3D高斯涂斑法)时,这个问题会对优化产生很大且被低估的影响。我们采用了两种启发式方法来优化高斯表示的场景几何的准确性。实验结果表明,我们的方法在受限的C-ToF感应条件下能产生准确的重建效果,包括快速运动如挥动棒球棒等。具体链接。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种利用单目连续波飞行时间(C-ToF)相机原始传感器样本重建动态场景的方法,该方法在保持与神经体积方法相似或更高的准确性的同时,速度提高了100倍。对于从单一视角快速实现高保真动态3D重建这一计算机视觉领域的重大挑战,该方法解决了C-ToF辐射场重建中深度信息未直接测量的问题,并采用两种启发式优化策略提高了高斯表示的几何场景的准确性。实验结果表明,该方法在受限的C-ToF传感条件下对快速运动场景也能进行准确重建。
Key Takeaways
- 方法使用单目连续波飞行时间(C-ToF)相机实现动态场景的快速重建。
- 该方法具有与神经体积方法相似的准确性,但速度提高了100倍。
- 在C-ToF辐射场重建中解决了深度信息未直接测量的问题。
- 采用两种启发式优化策略提高高斯表示的几何场景的准确性。
- 实验结果证明,该方法能处理快速运动场景的重建,如摇摆的棒球棍。
- 该方法适用于受限的C-ToF传感条件。
点此查看论文截图


MoRe-3DGSMR: Motion-resolved reconstruction framework for free-breathing pulmonary MRI based on 3D Gaussian representation
Authors:Tengya Peng, Ruyi Zha, Qing Zou
This study presents an unsupervised, motion-resolved reconstruction framework for high-resolution, free-breathing pulmonary magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), utilizing a three-dimensional Gaussian representation (3DGS). The proposed method leverages 3DGS to address the challenges of motion-resolved 3D isotropic pulmonary MRI reconstruction by enabling data smoothing between voxels for continuous spatial representation. Pulmonary MRI data acquisition is performed using a golden-angle radial sampling trajectory, with respiratory motion signals extracted from the center of k-space in each radial spoke. Based on the estimated motion signal, the k-space data is sorted into multiple respiratory phases. A 3DGS framework is then applied to reconstruct a reference image volume from the first motion state. Subsequently, a patient-specific convolutional neural network is trained to estimate the deformation vector fields (DVFs), which are used to generate the remaining motion states through spatial transformation of the reference volume. The proposed reconstruction pipeline is evaluated on six datasets from six subjects and bench-marked against three state-of-the-art reconstruction methods. The experimental findings demonstrate that the proposed reconstruction framework effectively reconstructs high-resolution, motion-resolved pulmonary MR images. Compared with existing approaches, it achieves superior image quality, reflected by higher signal-to-noise ratio and contrast-to-noise ratio. The proposed unsupervised 3DGS-based reconstruction method enables accurate motion-resolved pulmonary MRI with isotropic spatial resolution. Its superior performance in image quality metrics over state-of-the-art methods highlights its potential as a robust solution for clinical pulmonary MR imaging.
本研究提出了一种基于三维高斯表示(3DGS)的无监督、动态解析重建框架,用于高分辨率、自由呼吸的肺部磁共振成像(MRI)。该方法利用3DGS解决动态解析的3D立体肺部MRI重建的挑战,通过在体素之间进行数据平滑处理,实现连续的空间表示。肺部MRI数据采集采用金角径向采样轨迹,从每个径向射线的k空间中心提取呼吸运动信号。基于估计的运动信号,将k空间数据分为多个呼吸阶段。然后应用3DGS框架从第一个运动状态重建参考图像体积。随后,训练患者特定的卷积神经网络来估计变形矢量场(DVF),用于通过参考体积的空间变换生成其余的运动状态。该重建流水线在六个受试者数据集上进行了评估,并与三种最先进的重建方法进行了基准测试。实验结果表明,该重建框架有效地重建了高分辨率的肺部MRI图像序列。与现有方法相比,它在信号噪声比和对比噪声比方面表现出更高的图像质量。这种基于无监督的3DGS重建方法可实现精确的动态解析肺部MRI,具有立体空间分辨率。其在图像质量指标上的卓越性能,突出了其在临床肺部MRI成像中的稳健解决方案潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究提出了一种基于三维高斯表示(3DGS)的无监督、动态解析重建框架,用于高分辨、自由呼吸的肺部磁共振成像(MRI)。该研究利用3DGS解决动态解析的3D立体肺部MRI重建难题,通过优化数据在体素间的平滑处理,实现连续的空间表示。该研究采用黄金角径向采样轨迹进行肺部MRI数据采集,从每个径向射线的k空间中心提取呼吸运动信号。基于估计的运动信号,将k空间数据按多个呼吸阶段排序。使用3DGS框架从第一个运动状态重建参考图像体积。然后,训练患者特定的卷积神经网络来估计变形矢量场(DVFs),用于通过参考体积的空间变换生成其余的运动状态。该重建流程在六个来自六个受试者的数据集上进行了评估,并与三种最先进的重建方法进行了比较。实验结果表明,所提出的重建框架有效地重建了高分辨、动态解析的肺部MR图像。相较于现有方法,它在图像质量和噪声比方面表现更优。该无监督的基于3DGS的重建方法可实现准确的动态解析肺部MRI,具有各向同性分辨率。其在图像质量指标上的卓越性能表明其在临床肺部MR成像中的稳健解决方案潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究提出了一种基于三维高斯表示(3DGS)的无监督重建框架,用于自由呼吸的肺部磁共振成像(MRI)。
- 利用3DGS解决动态解析的肺部MRI重建难题,实现数据在连续空间内的平滑表示。
- 采用黄金角径向采样轨迹进行肺部MRI数据采集,并从k空间中心提取呼吸运动信号。
- 基于估计的运动信号,将k空间数据分为多个呼吸阶段,并使用3DGS框架从第一个运动状态重建参考图像体积。
- 利用卷积神经网络估计变形矢量场(DVFs),用于生成其余运动状态。
- 该方法在实验数据集上的表现优于三种最先进的重建方法,具有更高的图像质量和噪声比。
点此查看论文截图

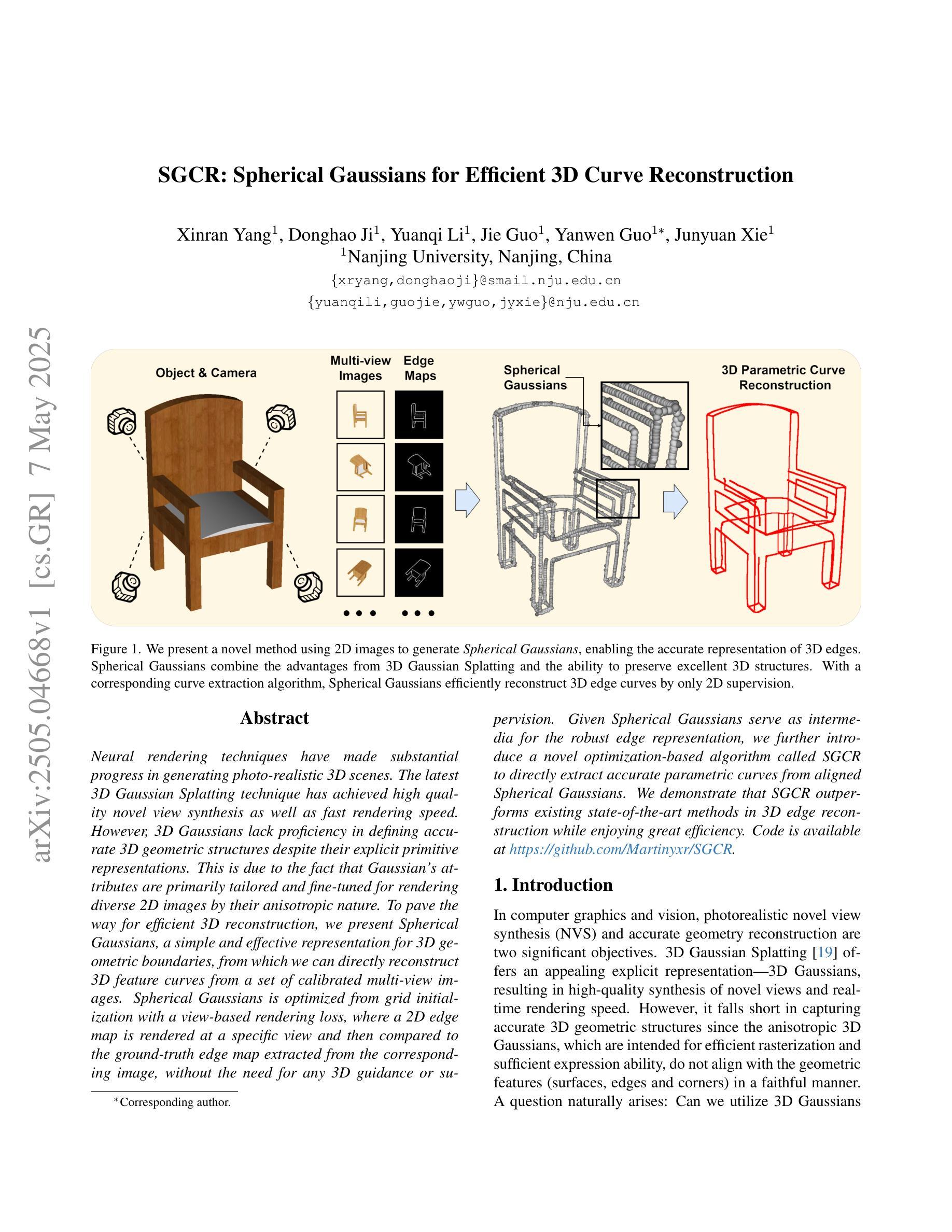
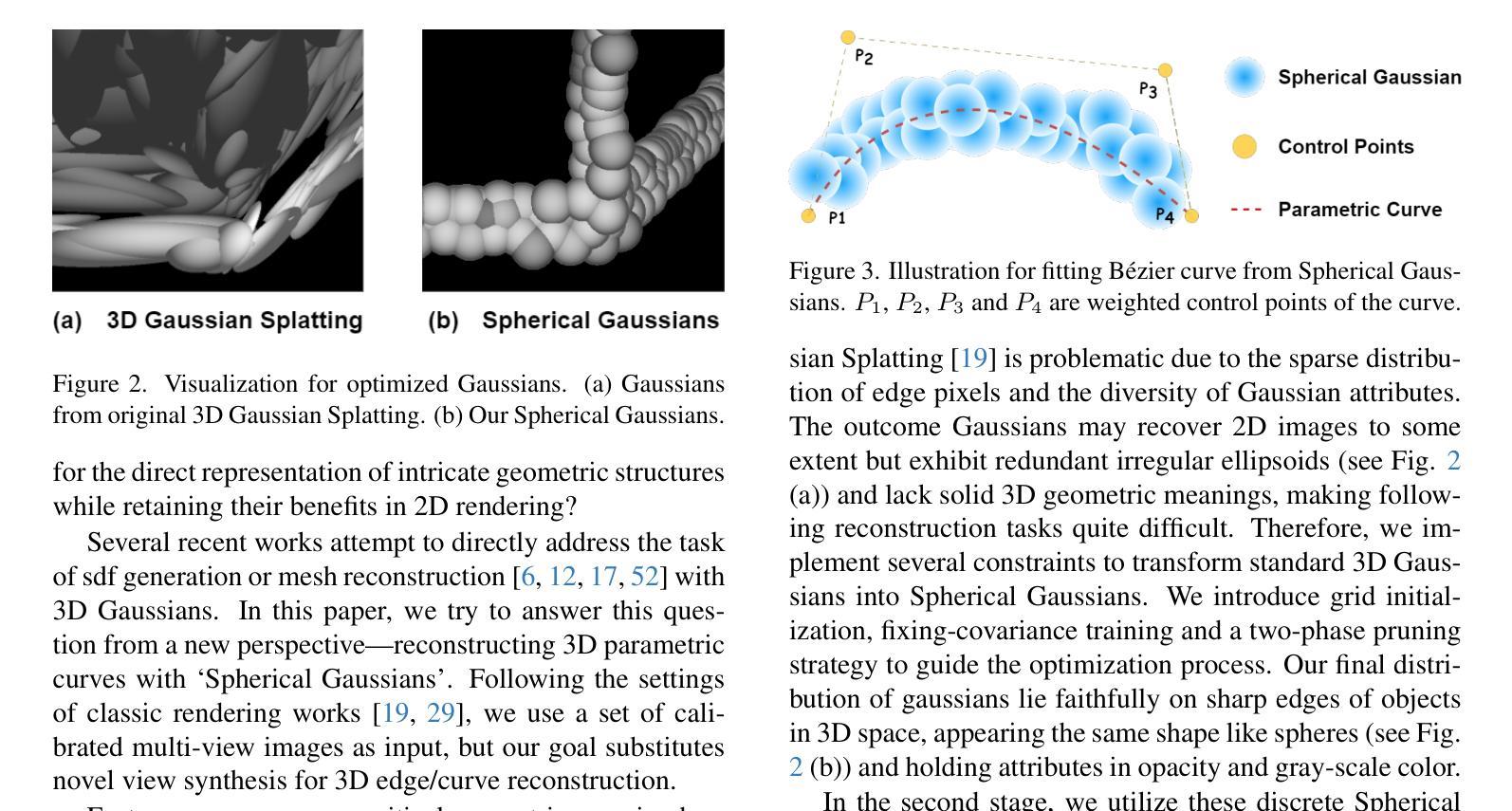
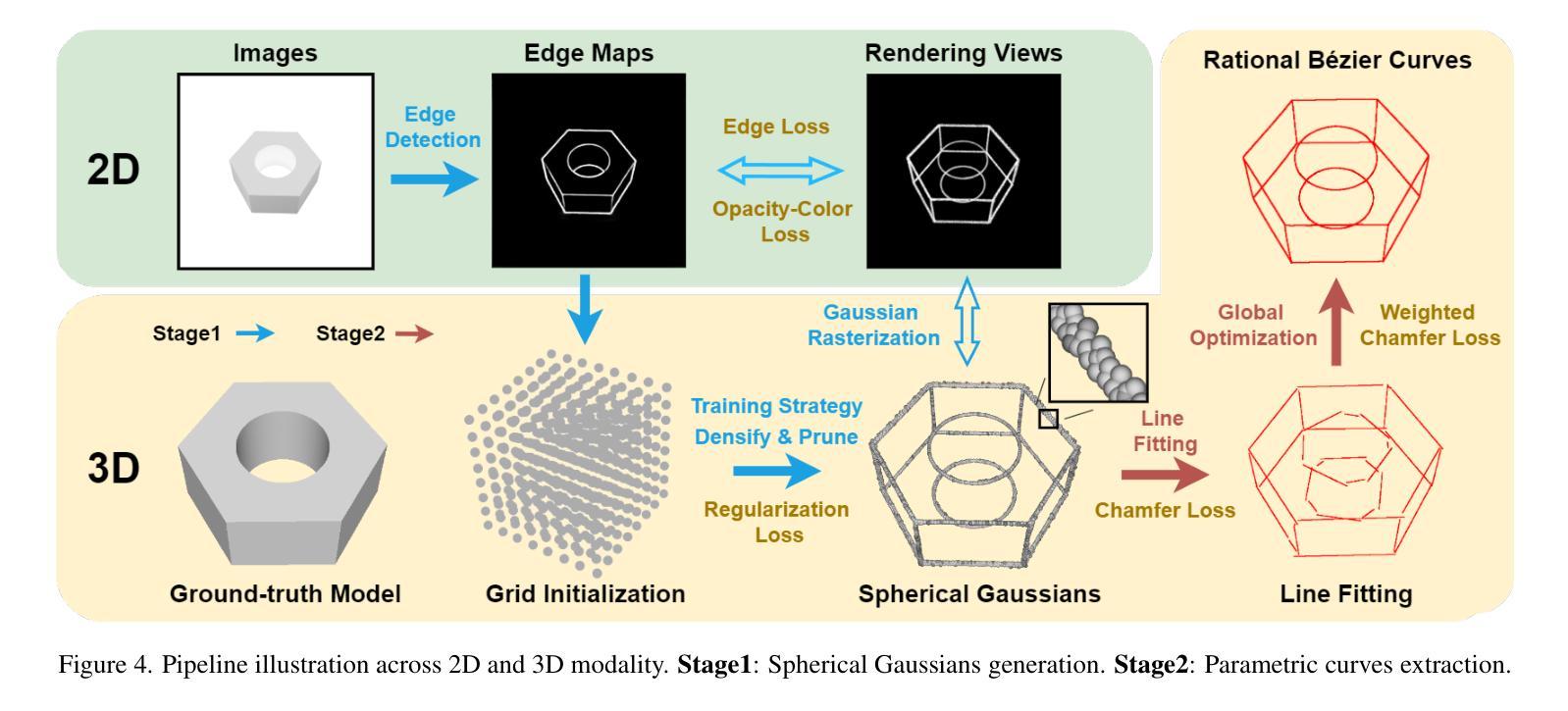
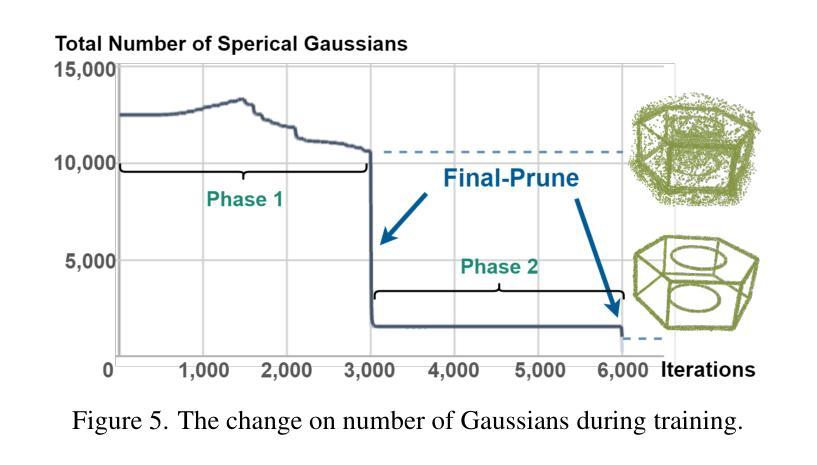
SGCR: Spherical Gaussians for Efficient 3D Curve Reconstruction
Authors:Xinran Yang, Donghao Ji, Yuanqi Li, Jie Guo, Yanwen Guo, Junyuan Xie
Neural rendering techniques have made substantial progress in generating photo-realistic 3D scenes. The latest 3D Gaussian Splatting technique has achieved high quality novel view synthesis as well as fast rendering speed. However, 3D Gaussians lack proficiency in defining accurate 3D geometric structures despite their explicit primitive representations. This is due to the fact that Gaussian’s attributes are primarily tailored and fine-tuned for rendering diverse 2D images by their anisotropic nature. To pave the way for efficient 3D reconstruction, we present Spherical Gaussians, a simple and effective representation for 3D geometric boundaries, from which we can directly reconstruct 3D feature curves from a set of calibrated multi-view images. Spherical Gaussians is optimized from grid initialization with a view-based rendering loss, where a 2D edge map is rendered at a specific view and then compared to the ground-truth edge map extracted from the corresponding image, without the need for any 3D guidance or supervision. Given Spherical Gaussians serve as intermedia for the robust edge representation, we further introduce a novel optimization-based algorithm called SGCR to directly extract accurate parametric curves from aligned Spherical Gaussians. We demonstrate that SGCR outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods in 3D edge reconstruction while enjoying great efficiency.
神经渲染技术在生成逼真的三维场景方面取得了重大进展。最新的三维高斯平铺技术实现了高质量的新型视图合成以及快速的渲染速度。然而,尽管三维高斯具有明确的原始表示,但它们在定义准确的三维几何结构方面并不熟练。这是由于高斯属性主要是为了利用其各向异性来渲染各种二维图像而定制和精细调整的。为了为高效的3D重建铺平道路,我们提出了球形高斯(Spherical Gaussians),这是一种用于三维几何边界的简单有效的表示方法,我们可以直接从一组校准的多视图图像重建三维特征曲线。球形高斯通过基于视图的渲染损失从网格初始化进行优化,其中在特定视图上呈现二维边缘图,然后将其与从相应图像中提取的真实边缘图进行比较,无需任何三维指导或监督。由于球形高斯充当稳健边缘表示的媒介,我们进一步引入了一种基于优化的新算法SGCR(球面高斯曲线重建算法),该算法直接从对齐的球形高斯中提取准确的参数曲线。我们证明了SGCR在三维边缘重建方面的表现优于现有先进技术,同时具有很高的效率。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2025, 8 pages
Summary
最新的三维高斯涂抹技术虽可实现高质量的新型视图合成和快速渲染速度,但在定义准确的3D几何结构方面存在不足。为此,我们提出球形高斯,这是一种简单有效的三维几何边界表示方法,可从一系列校准的多视图图像中直接重建三维特征曲线。我们进一步引入了一种基于优化的算法SGCR,可从对齐的球形高斯中提取准确的参数曲线。SGCR在三维边缘重建中表现优于现有方法,同时具有高效性。
Key Takeaways
- 神经渲染技术在生成逼真的三维场景方面取得了重大进展。
- 最新三维高斯涂抹技术实现了高质量的新型视图合成和快速渲染。
- 现有的三维几何结构定义存在不足,主要局限在二维图像渲染上。
- 提出球形高斯作为新的三维几何边界表示方法,适用于从多视图图像重建三维特征曲线。
- 球形高斯通过网格初始化优化,采用基于视图的渲染损失进行渲染。
- 引入了一种新的优化算法SGCR,可从对齐的球形高斯中提取准确的参数曲线。
点此查看论文截图
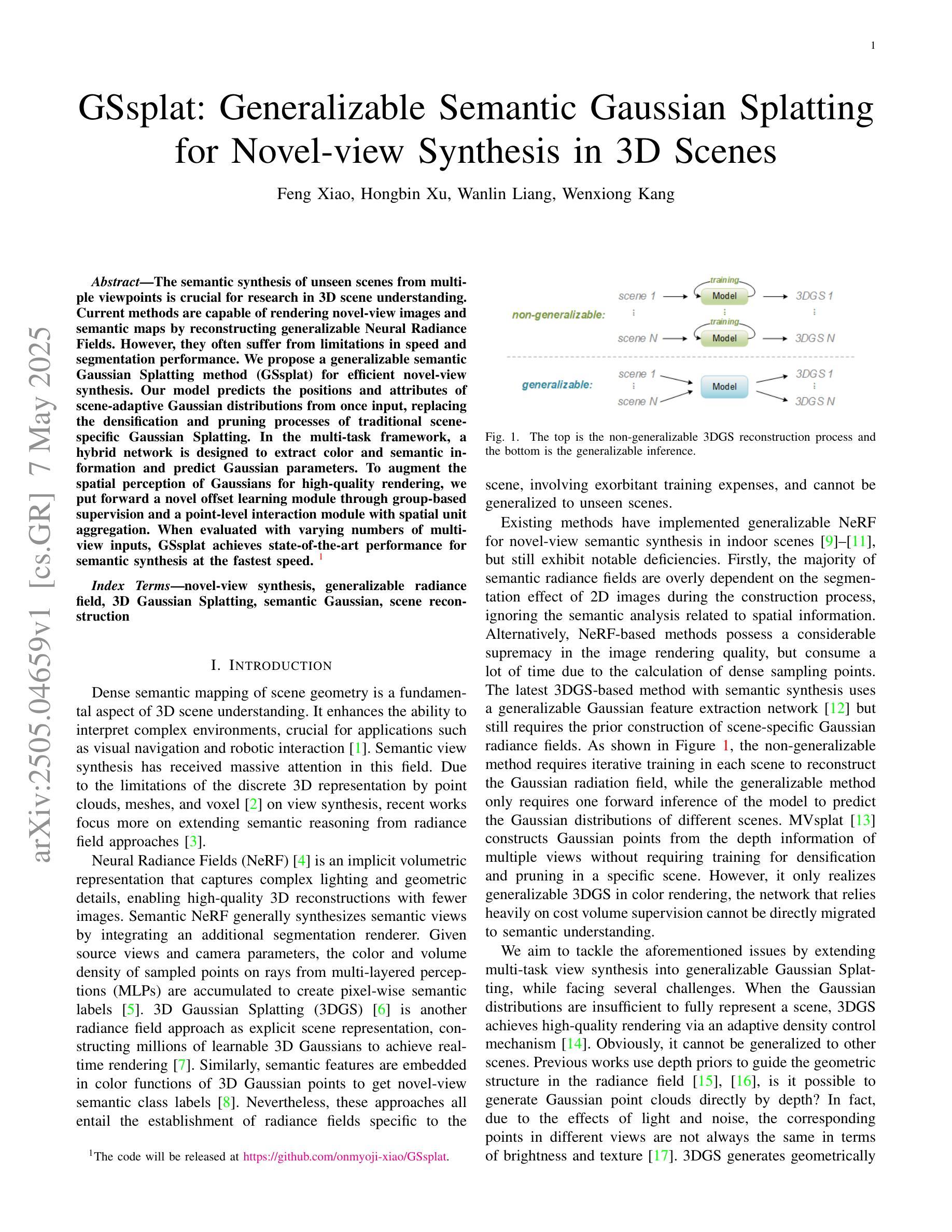
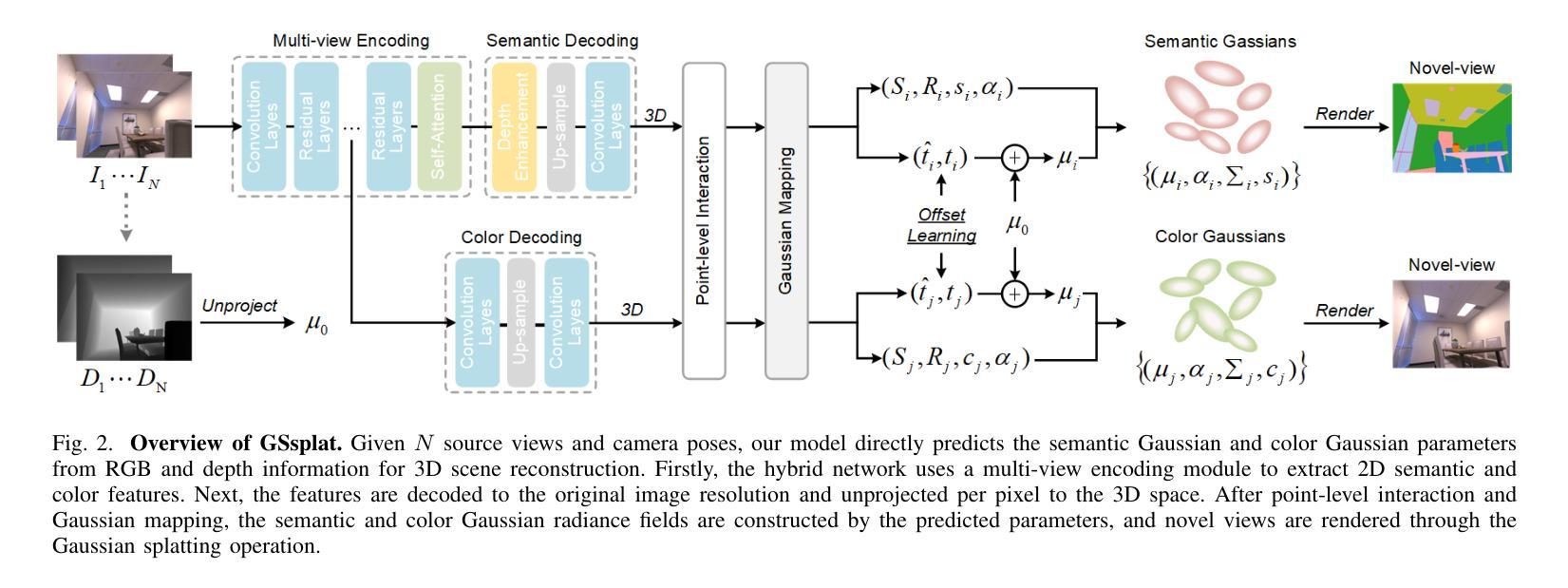
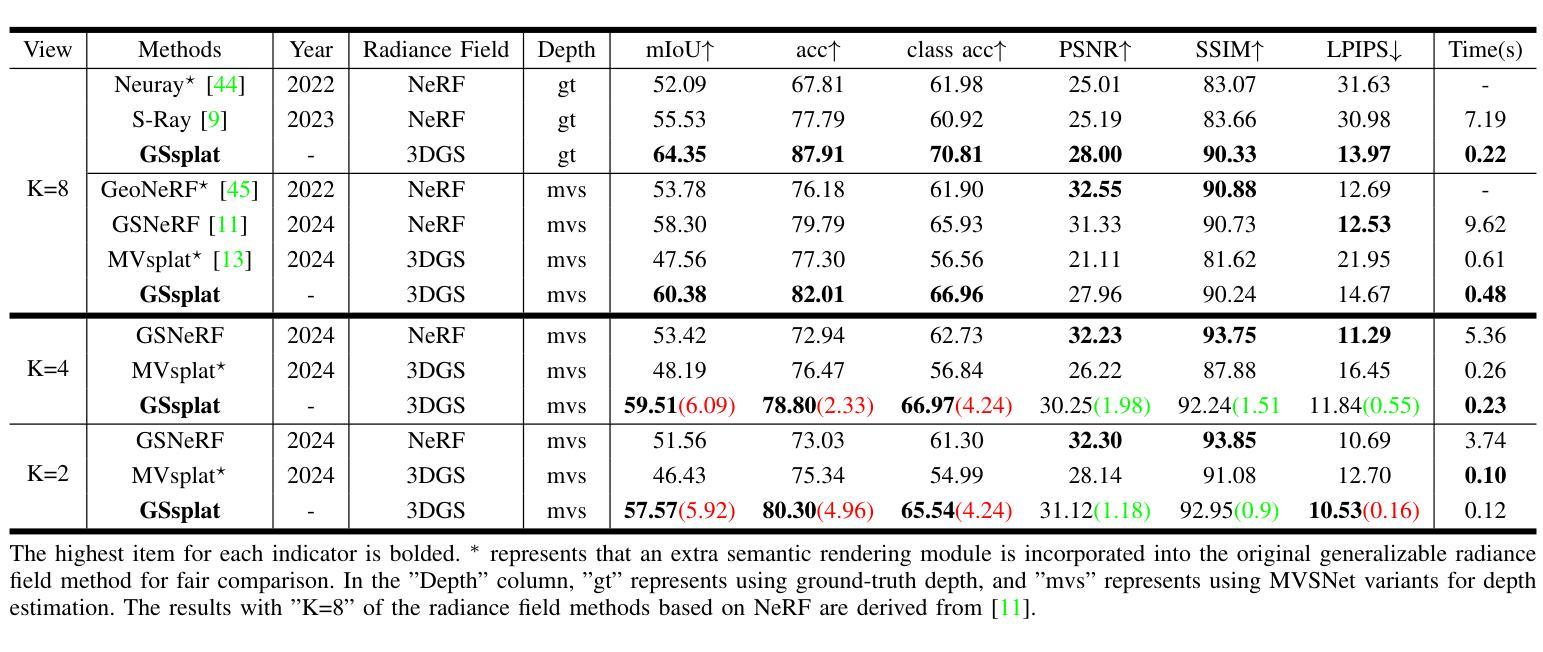
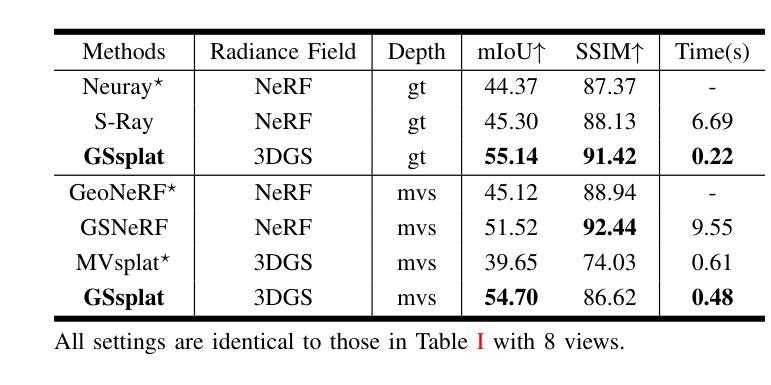
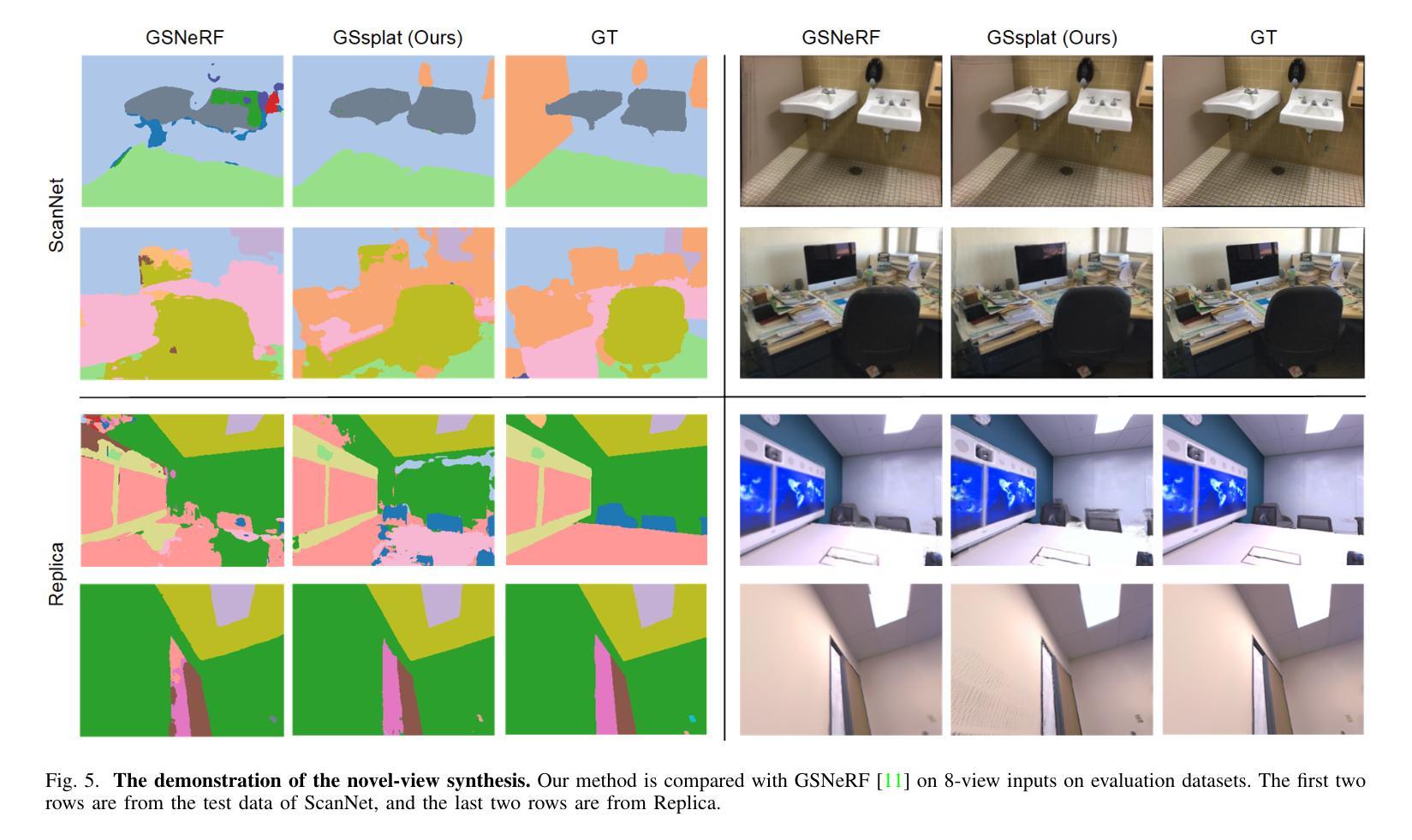
GSsplat: Generalizable Semantic Gaussian Splatting for Novel-view Synthesis in 3D Scenes
Authors:Feng Xiao, Hongbin Xu, Wanlin Liang, Wenxiong Kang
The semantic synthesis of unseen scenes from multiple viewpoints is crucial for research in 3D scene understanding. Current methods are capable of rendering novel-view images and semantic maps by reconstructing generalizable Neural Radiance Fields. However, they often suffer from limitations in speed and segmentation performance. We propose a generalizable semantic Gaussian Splatting method (GSsplat) for efficient novel-view synthesis. Our model predicts the positions and attributes of scene-adaptive Gaussian distributions from once input, replacing the densification and pruning processes of traditional scene-specific Gaussian Splatting. In the multi-task framework, a hybrid network is designed to extract color and semantic information and predict Gaussian parameters. To augment the spatial perception of Gaussians for high-quality rendering, we put forward a novel offset learning module through group-based supervision and a point-level interaction module with spatial unit aggregation. When evaluated with varying numbers of multi-view inputs, GSsplat achieves state-of-the-art performance for semantic synthesis at the fastest speed.
在三维场景理解研究中,从未见过的场景从多个视角进行语义合成至关重要。当前的方法能够通过重建可概括的神经辐射场来生成新型视角图像和语义地图。然而,它们在速度和分割性能上往往存在局限性。我们提出了一种通用的语义高斯飞溅方法(GSsplat)来进行高效的新型视角合成。我们的模型从一次输入预测场景自适应高斯分布的位置和属性,取代了传统场景特定高斯飞溅的密集化和修剪过程。在多任务框架下,设计了一个混合网络来提取颜色和语义信息并预测高斯参数。为了提高高斯的空间感知以进行高质量渲染,我们提出了通过基于组的监督和点级交互模块与空间单位聚合相结合的新型偏移学习模块。在多种不同数量的多视角输入进行评估时,GSsplat在语义合成方面实现了最快速度和最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了基于神经网络辐射场(Neural Radiance Fields)的三维场景理解中的语义合成问题。针对现有方法的速度和分割性能方面的局限性,提出了一种通用的语义高斯Splatting方法(GSsplat)。该方法通过一次输入预测场景自适应高斯分布的位置和属性,实现高效的新型视角合成。在混合任务框架中设计了一个混合网络来提取颜色和语义信息并预测高斯参数。为了提高高斯的空间感知能力以实现高质量渲染,提出了新型偏移学习模块和基于空间单位聚合的点级交互模块。实验表明,GSsplat在多视角输入不同数量的情况下,实现了语义合成的最佳性能,同时速度最快。
Key Takeaways
- 三维场景理解中的语义合成是从多个视角对未见场景进行理解的关键。
- 当前方法通过重建可概括的神经网络辐射场进行新型视角图像和语义地图的渲染。
- 现有方法存在速度和分割性能方面的局限性。
- 提出的GSsplat方法通过一次输入预测场景自适应高斯分布的位置和属性,实现高效的新型视角合成。
- GSsplat设计了混合网络来提取颜色和语义信息,并预测高斯参数。
- 为了提高高斯的空间感知能力,引入了偏移学习模块和点级交互模块。
点此查看论文截图

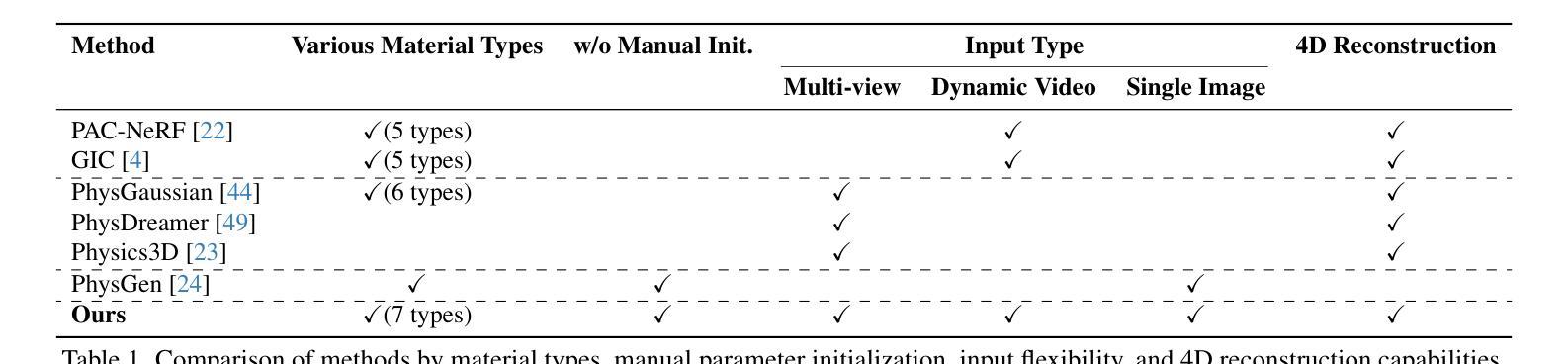
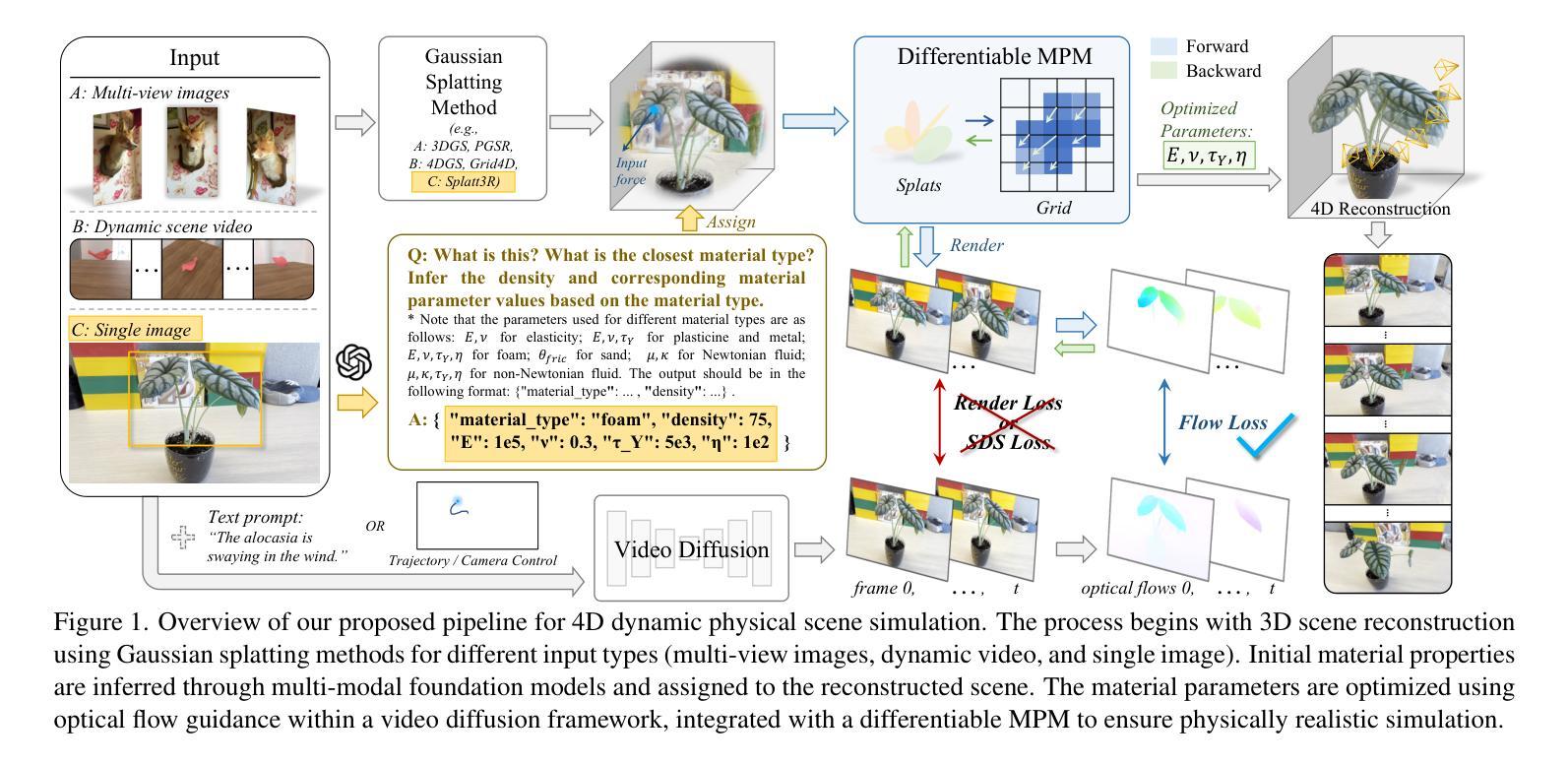
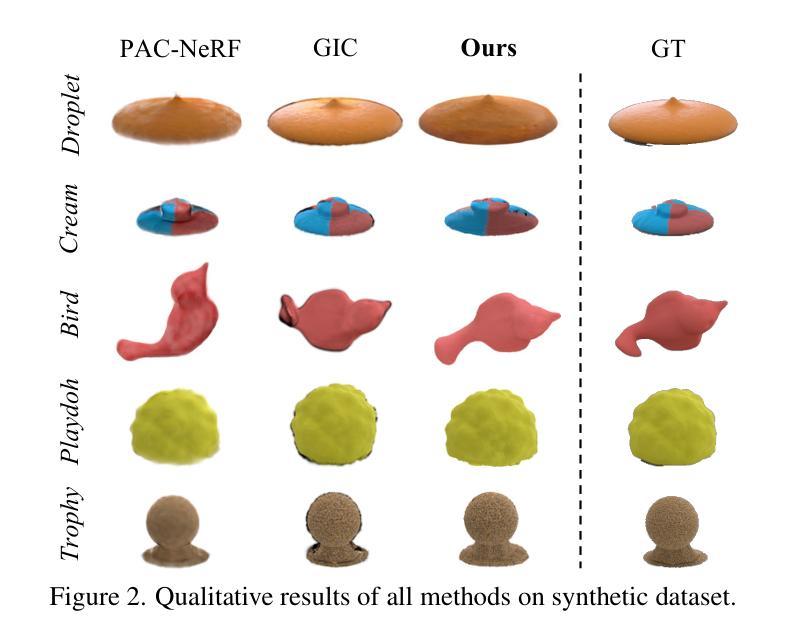
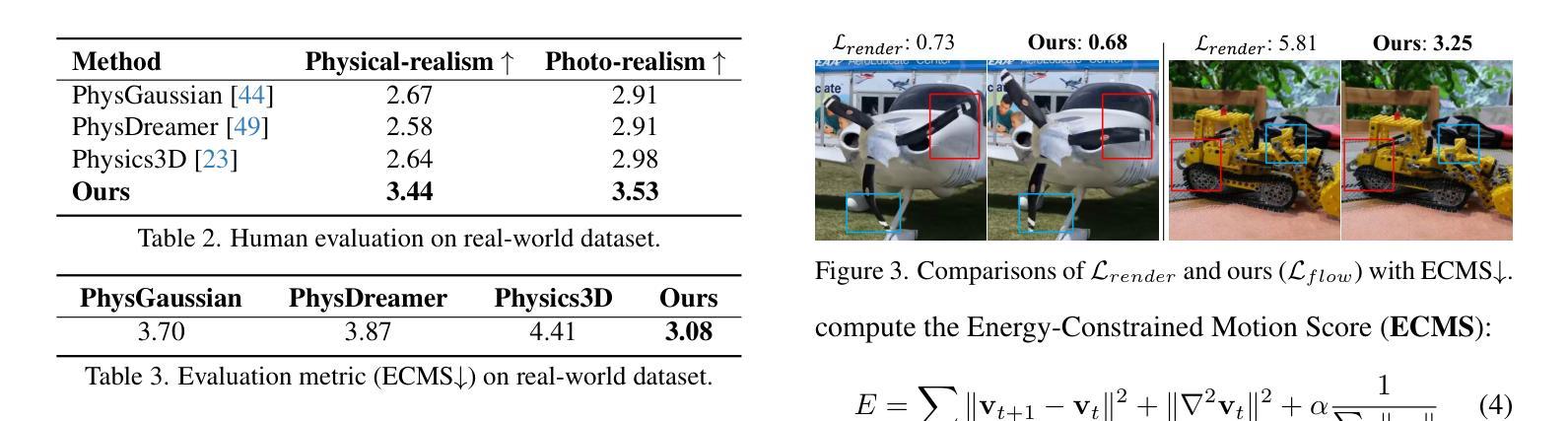
PhysFlow: Unleashing the Potential of Multi-modal Foundation Models and Video Diffusion for 4D Dynamic Physical Scene Simulation
Authors:Zhuoman Liu, Weicai Ye, Yan Luximon, Pengfei Wan, Di Zhang
Realistic simulation of dynamic scenes requires accurately capturing diverse material properties and modeling complex object interactions grounded in physical principles. However, existing methods are constrained to basic material types with limited predictable parameters, making them insufficient to represent the complexity of real-world materials. We introduce PhysFlow, a novel approach that leverages multi-modal foundation models and video diffusion to achieve enhanced 4D dynamic scene simulation. Our method utilizes multi-modal models to identify material types and initialize material parameters through image queries, while simultaneously inferring 3D Gaussian splats for detailed scene representation. We further refine these material parameters using video diffusion with a differentiable Material Point Method (MPM) and optical flow guidance rather than render loss or Score Distillation Sampling (SDS) loss. This integrated framework enables accurate prediction and realistic simulation of dynamic interactions in real-world scenarios, advancing both accuracy and flexibility in physics-based simulations.
真实场景的动态模拟需要准确捕捉各种材料属性,并基于物理原理对复杂的物体交互进行建模。然而,现有方法仅限于具有有限可预测参数的基本材料类型,无法代表真实世界材料的复杂性。我们引入了PhysFlow,这是一种利用多模态基础模型和视频扩散来实现增强的4D动态场景模拟的新方法。我们的方法利用多模态模型通过图像查询识别材料类型并初始化材料参数,同时推断3D高斯斑点用于详细的场景表示。我们进一步使用可微分的物质点法(MPM)和光流指导,而不是渲染损失或评分蒸馏采样(SDS)损失,来完善这些材料参数。这一综合框架能够准确预测和模拟真实场景中的动态交互,提高基于物理的模拟的准确性和灵活性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025. Homepage: https://zhuomanliu.github.io/PhysFlow/
Summary
现实动态场景的模拟需要准确捕捉各种材料属性并基于物理原理模拟复杂的物体交互。现有方法受限于基本材料类型和有限的可预测参数,无法代表真实世界的复杂性。我们引入了PhysFlow,这是一种利用多模态基础模型和视频扩散来实现增强的四维动态场景模拟的新方法。我们的方法使用多模态模型通过图像查询识别材料类型并初始化材料参数,同时推断三维高斯斑点进行详细的场景表示。我们进一步使用可区分的物质点法(MPM)和光流指导的视频扩散来优化这些材料参数,而不是使用渲染损失或评分蒸馏采样(SDS)损失。这一综合框架为实现真实场景中动态交互的准确预测和模拟提供了可能,提高了物理模拟的准确性和灵活性。
Key Takeaways
- 现实动态场景模拟需要捕捉材料属性和复杂物体交互。
- 现有模拟方法存在对材料类型和可预测参数的局限性。
- PhysFlow利用多模态基础模型和视频扩散增强四维动态场景模拟。
- 多模态模型可识别材料类型并初始化材料参数,通过图像查询进行。
- 使用三维高斯斑点进行详细的场景表示。
- 通过可区分的物质点法(MPM)和光流指导的视频扩散优化材料参数。
点此查看论文截图