⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-10 更新
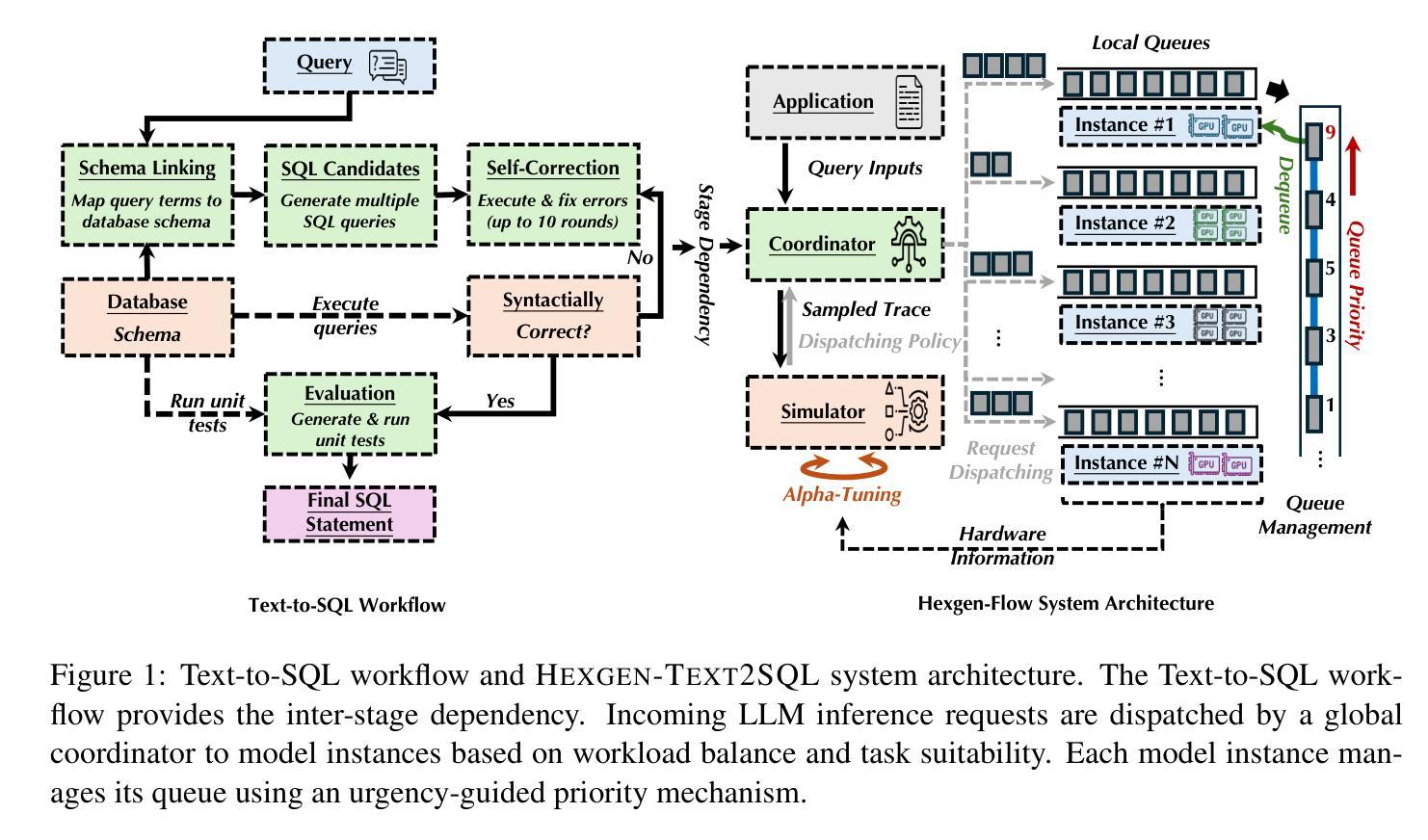
HEXGEN-TEXT2SQL: Optimizing LLM Inference Request Scheduling for Agentic Text-to-SQL Workflow
Authors:You Peng, Youhe Jiang, Chen Wang, Binhang Yuan
Recent advances in leveraging the agentic paradigm of large language models (LLMs) utilization have significantly enhanced Text-to-SQL capabilities, enabling users without specialized database expertise to query data intuitively. However, deploying these agentic LLM-based Text-to-SQL systems in production poses substantial challenges due to their inherently multi-stage workflows, stringent latency constraints, and potentially heterogeneous GPU infrastructure in enterprise environments. Current LLM serving frameworks lack effective mechanisms for handling interdependent inference tasks, dynamic latency variability, and resource heterogeneity, leading to suboptimal performance and frequent service-level objective (SLO) violations. In this paper, we introduce HEXGEN-TEXT2SQL, a novel framework designed explicitly to schedule and execute agentic multi-stage LLM-based Text-to-SQL workflows on heterogeneous GPU clusters that handle multi-tenant end-to-end queries. HEXGEN-TEXT2SQL introduce a hierarchical scheduling approach combining global workload-balanced task dispatching and local adaptive urgency-guided prioritization, guided by a systematic analysis of agentic Text-to-SQL workflows. Additionally, we propose a lightweight simulation-based method for tuning critical scheduling hyperparameters, further enhancing robustness and adaptability. Our extensive evaluation on realistic Text-to-SQL benchmarks demonstrates that HEXGEN-TEXT2SQL significantly outperforms state-of-the-art LLM serving frameworks. Specifically, HEXGEN-TEXT2SQL reduces latency deadlines by up to 1.67$\times$ (average: 1.41$\times$) and improves system throughput by up to 1.75$\times$ (average: 1.65$\times$) compared to vLLM under diverse, realistic workload conditions. Our code is available at https://github.com/Relaxed-System-Lab/Hexgen-Flow.
近期在利用大型语言模型(LLM)的代理范式方面取得的进展极大地增强了文本到SQL的能力,使得没有专业数据库知识的用户能够直观地查询数据。然而,在生产环境中部署这些基于LLM的文本到SQL代理系统面临着巨大的挑战,因为它们本质上具有多阶段的工作流程、严格的延迟限制和潜在的企业环境中的异构GPU基础设施。当前的LLM服务框架缺乏处理相互依赖的推理任务、动态延迟可变性以及资源异构性的有效机制,导致性能不佳和频繁的服务级别目标(SLO)违规。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的agentic范式在Text-to-SQL能力方面取得了重大进展,使得没有专业数据库知识的用户能够直观地查询数据。然而,在生产环境中部署这些基于LLM的Text-to-SQL系统面临着巨大的挑战,如多阶段工作流程、严格的延迟限制和潜在的企业环境中的异构GPU基础设施。本文介绍了一种新型的框架HEXGEN-TEXT2SQL,专为处理多租户端到端的基于LLM的多阶段Text-to-SQL工作流设计,该框架旨在调度在异构GPU集群上执行的任务。HEXGEN-TEXT2SQL结合了全局负载均衡任务调度和本地自适应紧急优先级排序的分层调度方法,并通过轻量级仿真方法调整关键调度超参数,增强了稳健性和适应性。在现实的Text-to-SQL基准测试上,HEXGEN-TEXT2SQL表现出显著的优势。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs在Text-to-SQL方面的进步使得非专业数据库用户能直观查询数据。
- 生产环境中部署基于LLM的Text-to-SQL系统面临多阶段流程、延迟限制和异构GPU基础设施的挑战。
- HEXGEN-TEXT2SQL框架专为处理这些挑战而设计,支持在异构GPU集群上执行多阶段Text-to-SQL工作流程。
- HEXGEN-TEXT2SQL采用分层调度方法,结合全局负载均衡和本地自适应优先级排序。
- 该框架通过轻量级仿真方法调整关键调度超参数,增强了稳健性和适应性。
- 在现实的Text-to-SQL基准测试中,HEXGEN-TEXT2SQL显著优于其他LLM服务框架,可降低延迟期限并提高系统吞吐量。
点此查看论文截图

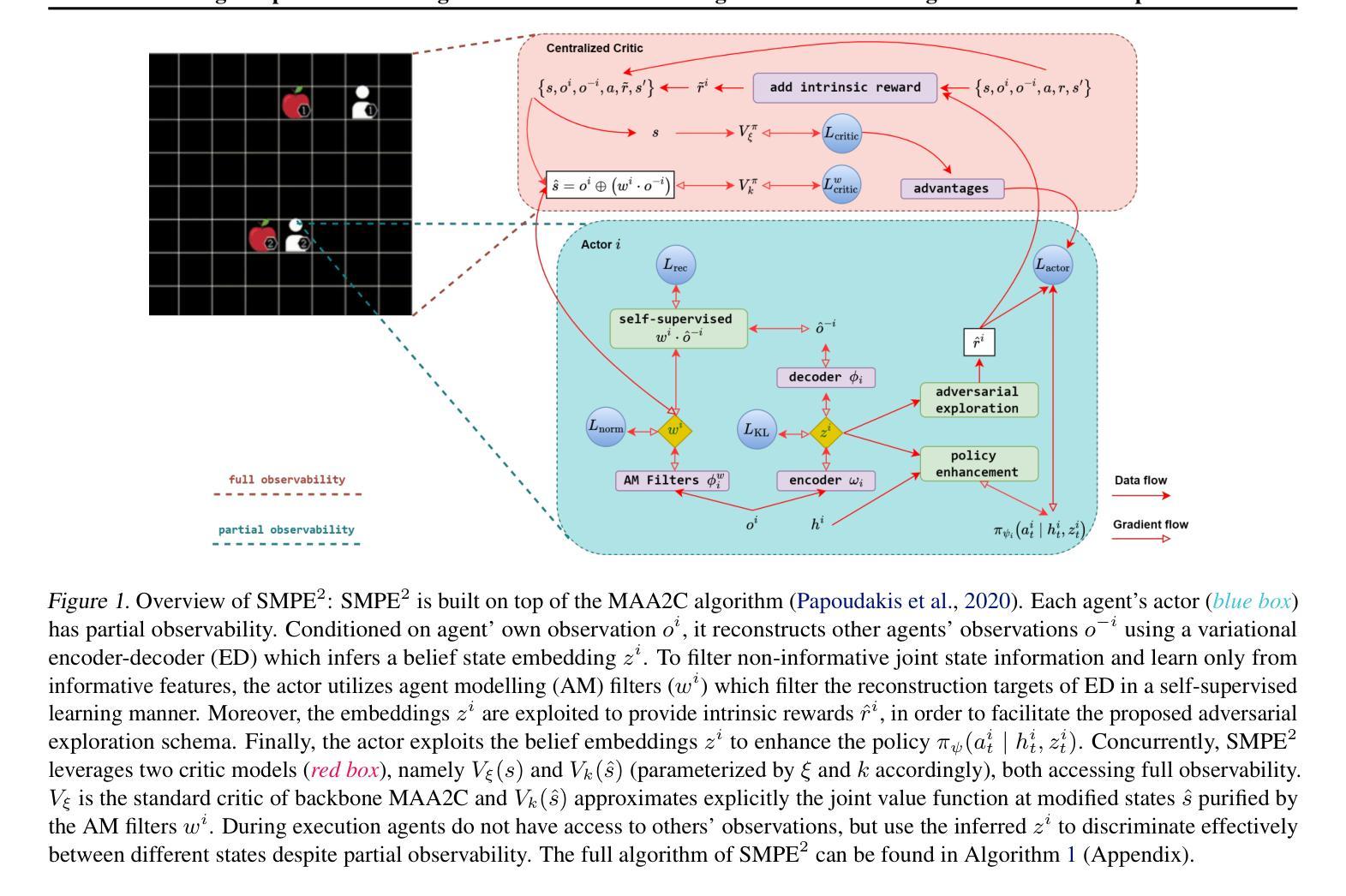
Enhancing Cooperative Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning with State Modelling and Adversarial Exploration
Authors:Andreas Kontogiannis, Konstantinos Papathanasiou, Yi Shen, Giorgos Stamou, Michael M. Zavlanos, George Vouros
Learning to cooperate in distributed partially observable environments with no communication abilities poses significant challenges for multi-agent deep reinforcement learning (MARL). This paper addresses key concerns in this domain, focusing on inferring state representations from individual agent observations and leveraging these representations to enhance agents’ exploration and collaborative task execution policies. To this end, we propose a novel state modelling framework for cooperative MARL, where agents infer meaningful belief representations of the non-observable state, with respect to optimizing their own policies, while filtering redundant and less informative joint state information. Building upon this framework, we propose the MARL SMPE algorithm. In SMPE, agents enhance their own policy’s discriminative abilities under partial observability, explicitly by incorporating their beliefs into the policy network, and implicitly by adopting an adversarial type of exploration policies which encourages agents to discover novel, high-value states while improving the discriminative abilities of others. Experimentally, we show that SMPE outperforms state-of-the-art MARL algorithms in complex fully cooperative tasks from the MPE, LBF, and RWARE benchmarks.
在多智能体深度强化学习(MARL)中,学习在没有沟通能力的分布式部分可观察环境中合作,面临着巨大的挑战。本文针对该领域的关键问题进行研究,重点关注从个体智能体的观察中推断状态表示,并利用这些表示来提高智能体的探索能力和协同任务执行策略。为此,我们提出了一种针对合作型MARL的新型状态建模框架,智能体在该框架中推断不可观测状态的有意义信念表示,以优化其自身的策略,同时过滤掉冗余和较少有信息含量的联合状态信息。基于该框架,我们提出了MARL SMPE算法。在SMPE中,智能体通过显式地将信念融入策略网络,以及隐式地采用对抗型的探索策略来提高自身策略在部分可观察下的辨别能力,这种策略鼓励智能体发现新的高价值状态,同时提高其他智能体的辨别能力。实验表明,SMPE在MPE、LBF和RWARE基准测试中的复杂完全协作任务上的表现优于最新的MARL算法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted (Poster) at ICML 2025
Summary
该论文针对多智能体深度强化学习(MARL)在分布式部分可观察环境中无通信能力时的合作问题进行研究,提出一种新型状态建模框架,让智能体从个体观察中推断非可观状态的有意义信念表示,并过滤掉冗余和较少信息的联合状态信息。基于此框架,论文提出了MARL SMPE算法。SMPE算法通过显式地将信念融入策略网络,以及隐式地采用对抗性探索策略,提高了智能体在部分可观察下的策略辨别能力,并鼓励智能体发现新的高价值状态,同时提高其他智能体的辨别能力。实验表明,SMPE在复杂的完全合作任务中优于最新的MARL算法。
Key Takeaways
- MARL面临在分布式部分可观察环境中合作的挑战。
- 论文提出了一种新型状态建模框架,用于推断非可观状态的有意义信念表示。
- SMPE算法通过结合信念表示和对抗性探索策略,提高了智能体在部分可观察环境下的策略辨别能力。
- SMPE算法鼓励智能体发现新的高价值状态,同时提高其他智能体的辨别能力。
- 论文通过实验验证了SMPE算法在复杂完全合作任务中的优越性。
- 该方法关注于优化个体策略的同时,过滤掉冗余和较少信息的联合状态信息。
点此查看论文截图

From First Draft to Final Insight: A Multi-Agent Approach for Feedback Generation
Authors:Jie Cao, Chloe Qianhui Zhao, Xian Chen, Shuman Wang, Christian Schunn, Kenneth R. Koedinger, Jionghao Lin
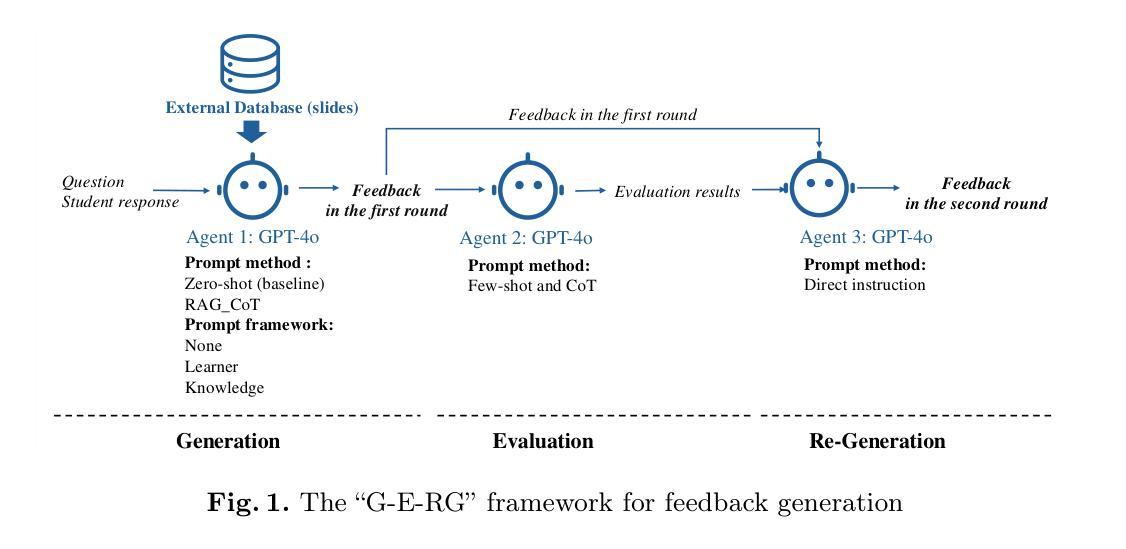
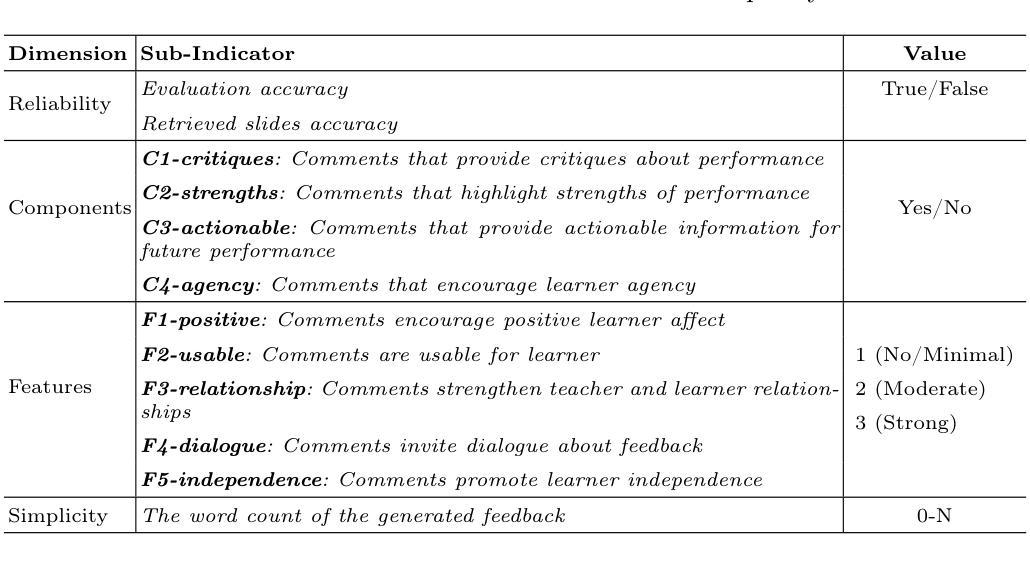
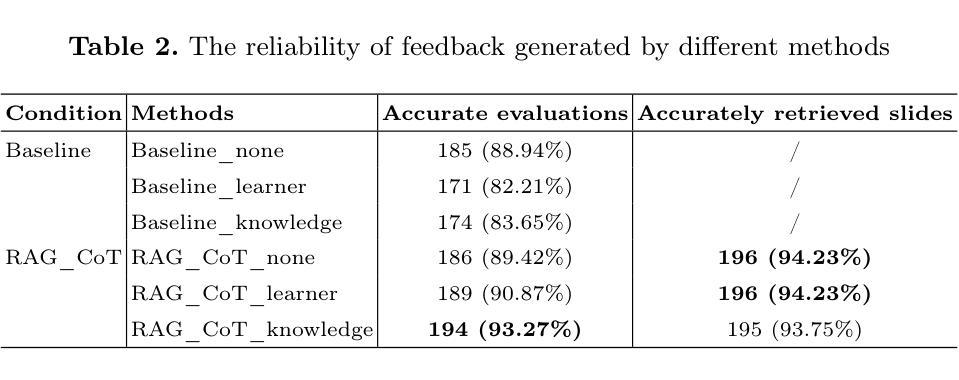
Producing large volumes of high-quality, timely feedback poses significant challenges to instructors. To address this issue, automation technologies-particularly Large Language Models (LLMs)-show great potential. However, current LLM-based research still shows room for improvement in terms of feedback quality. Our study proposed a multi-agent approach performing “generation, evaluation, and regeneration” (G-E-RG) to further enhance feedback quality. In the first-generation phase, six methods were adopted, combining three feedback theoretical frameworks and two prompt methods: zero-shot and retrieval-augmented generation with chain-of-thought (RAG_CoT). The results indicated that, compared to first-round feedback, G-E-RG significantly improved final feedback across six methods for most dimensions. Specifically:(1) Evaluation accuracy for six methods increased by 3.36% to 12.98% (p<0.001); (2) The proportion of feedback containing four effective components rose from an average of 27.72% to an average of 98.49% among six methods, sub-dimensions of providing critiques, highlighting strengths, encouraging agency, and cultivating dialogue also showed great enhancement (p<0.001); (3) There was a significant improvement in most of the feature values (p<0.001), although some sub-dimensions (e.g., strengthening the teacher-student relationship) still require further enhancement; (4) The simplicity of feedback was effectively enhanced (p<0.001) for three methods.
对于教师而言,生成大量高质量、及时的反馈是一个巨大的挑战。为了解决这个问题,自动化技术——尤其是大型语言模型(LLMs)——显示出巨大的潜力。然而,基于LLM的当前研究在反馈质量方面仍有改进的空间。我们的研究提出了一种多智能体方法,执行“生成、评估、再生”(G-E-RG),以进一步提高反馈质量。在第一代阶段,采用了六种方法,结合了三种反馈理论框架和两种提示方法:零样本和增强检索生成法(RAG_CoT)。结果表明,与第一轮反馈相比,G-E-RG在大多数维度上显著提高了最终的反馈质量。具体来说:(1)六种方法的评估准确度提高了3.36%至12.98%(p<0.001);(2)包含四个有效组成部分的反馈比例从六种方法的平均27.72%提高到平均98.49%,提供批评、突出优势、鼓励主动性和培养对话的子维度也表现出极大的提高(p<0.001);(3)大多数特征值都有显著改善(p<0.001),尽管一些子维度(如加强师生关系)仍需进一步改进;(4)三种方法的反馈简洁性得到了有效提高(p<0.001)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, to be published at the 26th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education (AIED ‘25)
摘要
针对教师面临的提供大量高质量及时反馈的挑战,自动化技术尤其是大型语言模型(LLM)展现出巨大潜力。然而,现有LLM技术在反馈质量方面仍有提升空间。本研究提出了一种多智能体协同工作的方法——“生成、评估、再生”(G-E-RG),旨在进一步提高反馈质量。在生成阶段,采用六种方法结合三种反馈理论框架和两种提示方法,包括零样本生成与通过思考链的检索增强生成(RAG_CoT)。研究结果表明,与第一轮反馈相比,G-E-RG在大多数维度上显著提高了最终反馈的质量。具体来说,评价准确率提高了3.36%~12.98%(p<0.001);包含四个有效组成部分的反馈比例从平均27.72%提高到平均98.49%,提供批评、突出优势、鼓励主动性和培养对话的子维度也显示出极大提升(p<0.001);大多数特征值都有显著改善(p<0.001),但某些子维度如加强师生关系仍需进一步改进;三种方法的反馈简洁性得到了有效增强(p<0.001)。
关键见解
- 大型语言模型在反馈质量方面展现出潜力,但仍需改进。
- 提出的多智能体协同方法G-E-RG显著提高了反馈质量。
- 生成阶段的多种方法结合提高了评价准确率和反馈的有效性。
- 反馈中包含了更多有效的组成部分,如提供批评、突出优势等。
- 特征值大多数都有显著改善,某些子维度仍需进一步改进。
- G-E-RG能够增强反馈的简洁性。
- 自动化技术在教育反馈中的应用具有巨大的发展潜力和价值。
点此查看论文截图

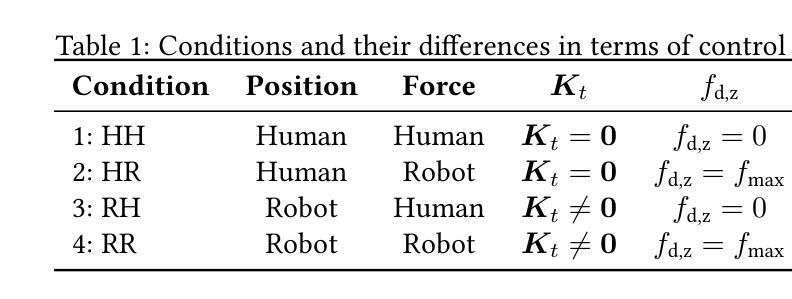
Fitts’ List Revisited: An Empirical Study on Function Allocation in a Two-Agent Physical Human-Robot Collaborative Position/Force Task
Authors:Nicky Mol, J. Micah Prendergast, David A. Abbink, Luka Peternel
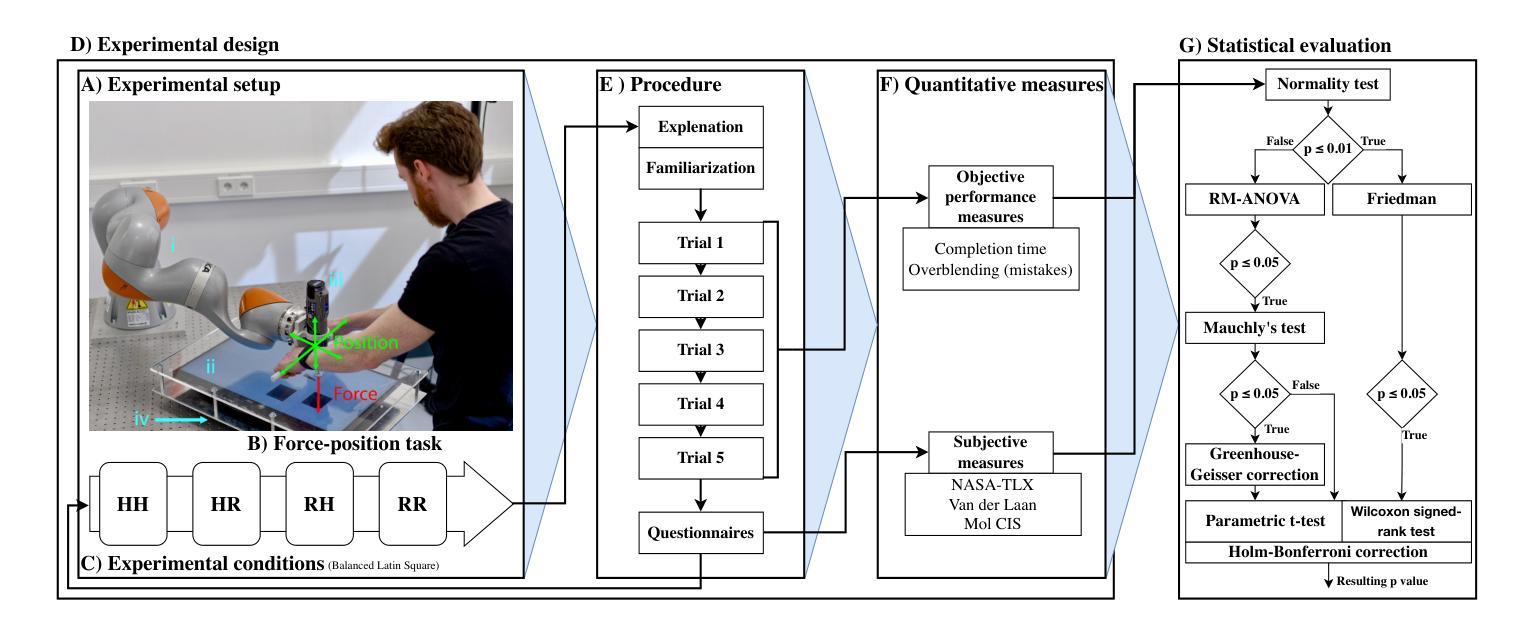
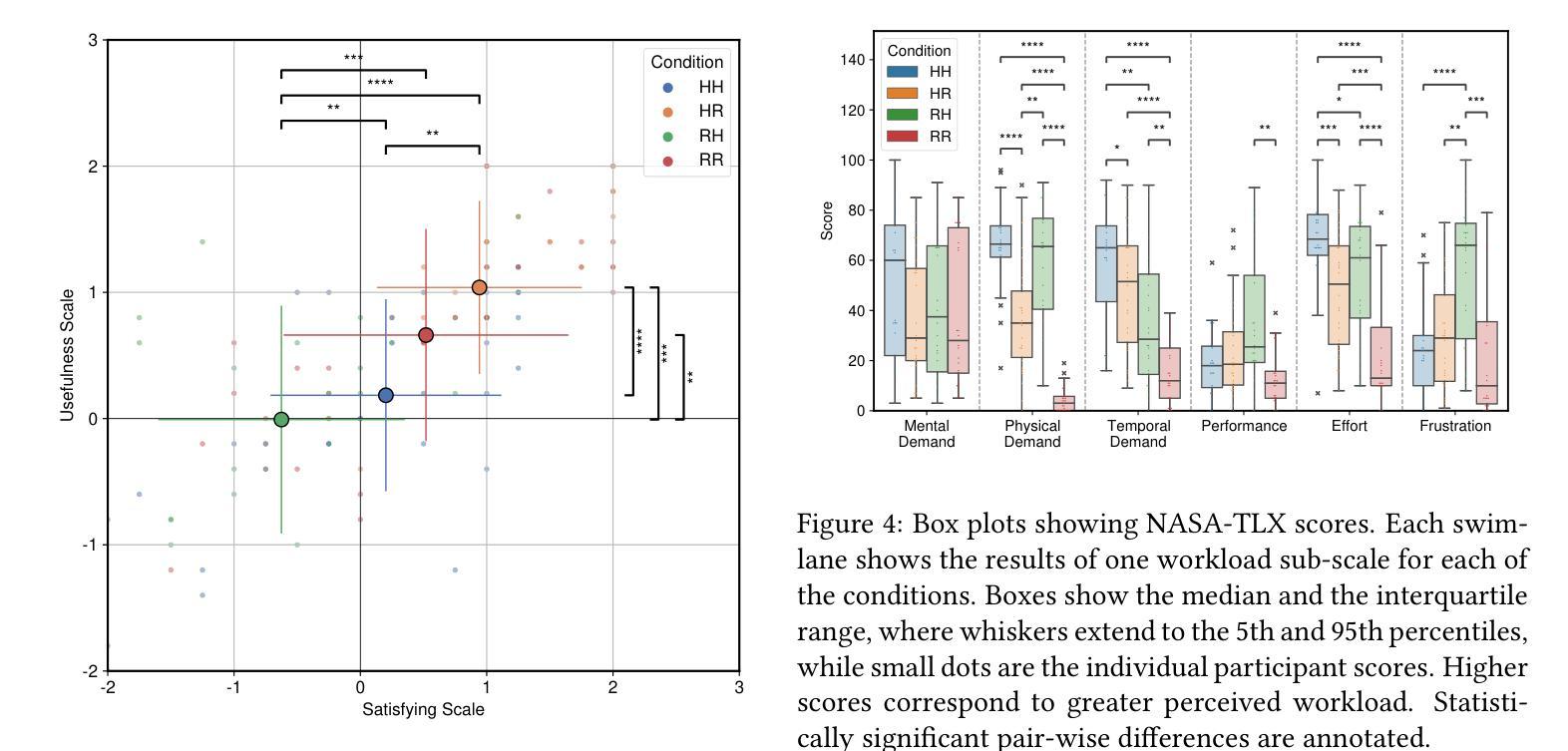
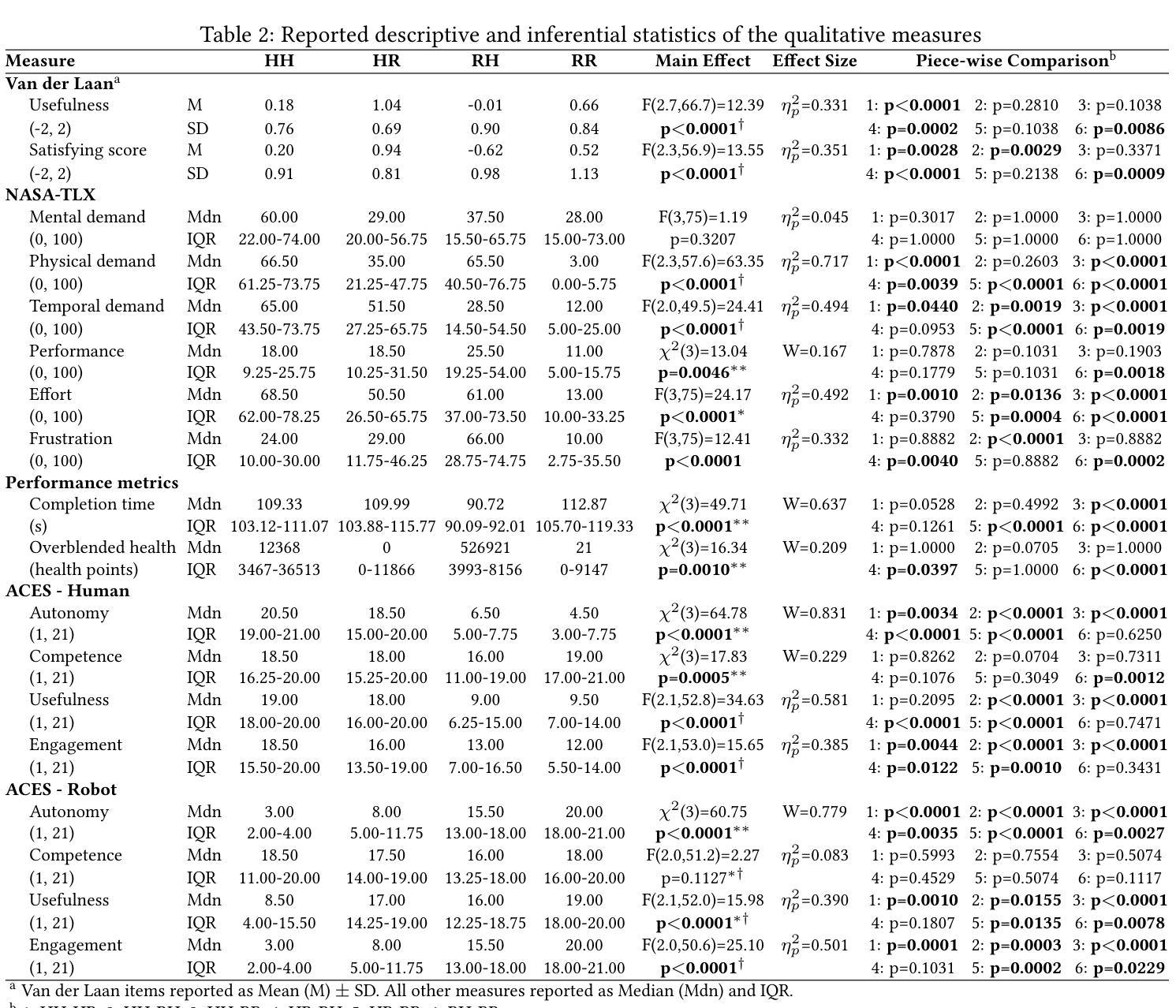
In this letter, we investigate whether the classical function allocation holds for physical Human-Robot Collaboration, which is important for providing insights for Industry 5.0 to guide how to best augment rather than replace workers. This study empirically tests the applicability of Fitts’ List within physical Human-Robot Collaboration, by conducting a user study (N=26, within-subject design) to evaluate four distinct allocations of position/force control between human and robot in an abstract blending task. We hypothesize that the function in which humans control the position achieves better performance and receives higher user ratings. When allocating position control to the human and force control to the robot, compared to the opposite case, we observed a significant improvement in preventing overblending. This was also perceived better in terms of physical demand and overall system acceptance, while participants experienced greater autonomy, more engagement and less frustration. An interesting insight was that the supervisory role (when the robot controls both position and force control) was rated second best in terms of subjective acceptance. Another surprising insight was that if position control was delegated to the robot, the participants perceived much lower autonomy than when the force control was delegated to the robot. These findings empirically support applying Fitts’ principles to static function allocation for physical collaboration, while also revealing important nuanced user experience trade-offs, particularly regarding perceived autonomy when delegating position control.
在这封信中,我们探讨了经典功能分配在物理人机交互中的适用性,这对于为工业5.0提供洞察指导如何最好地增强而非替代工人具有重要意义。本研究通过一项用户研究(N=26,受试者内设计)实证检验了Fitts列表在物理人机交互中的适用性,评估了在抽象混合任务中人机之间位置/力控制的四种不同分配情况。我们假设人类在控制位置时实现更好的性能和更高的用户评价。当将位置控制分配给人类,力控制分配给机器人时,与相反的情况相比,我们在防止过度混合方面观察到了显著的改进。这在体力需求和整体系统接受度方面也得到了更好的感知,同时参与者体验到了更大的自主性、更高的参与度和更低的挫败感。一个有趣的见解是,当机器人同时控制位置和力控制时,监督角色在主观接受度方面被评为第二好。另一个令人惊讶的见解是,如果将位置控制委托给机器人,参与者感知到的自主性远低于将力控制委托给机器人时的情况。这些发现为将Fitts原则应用于物理协作的静态功能分配提供了实证支持,同时揭示了重要的微妙用户体验权衡,特别是关于委托位置控制时的感知自主性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 6 figures, under review for publication in IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L)
Summary
本文探究了在物理人机协作中经典功能分配是否成立,对行业5.0提供指导,以了解如何更好地增强而非替代工人。通过用户研究(N=26,组内设计)实证测试了Fitts列表在物理人机协作中的适用性,评估了在抽象混合任务中人机位置/力控制的四种不同分配方式。研究发现,当人类控制位置时,性能更好且用户评价更高。当位置控制赋予人类,力控制赋予机器人时,与相反的情况相比,可显著防止过度混合。这在体力需求和整体系统接受度方面也得到了更好的评价,同时参与者感到更大的自主性、更高的参与度和更低的挫折感。有趣的是,当机器人同时控制位置和力控制时,其在主观接受度方面被评为第二好。另一个出人意料的见解是,当位置控制被委派给机器人时,参与者感知到的自主性远低于力控制被委派给机器人时。这些发现实证支持将Fitts原则应用于物理协作的静态功能分配,同时揭示了重要的用户体验细微差别,特别是当委派位置控制时的感知自主性。
Key Takeaways
- 研究调查了物理人机协作中的经典功能分配是否适用,为行业5.0提供指导。
- 通过用户研究测试了Fitts列表在物理人机协作中的适用性。
- 人类控制位置时表现更好,得到更高的用户评价。
- 当位置控制赋予人类、力控制赋予机器人时,可防止过度混合。
- 这种分配方式在体力需求和系统接受度方面得到更好评价。
- 参与者在体验中感到更大的自主性和参与度,以及更低的挫折感。
点此查看论文截图

Advancing Embodied Agent Security: From Safety Benchmarks to Input Moderation
Authors:Ning Wang, Zihan Yan, Weiyang Li, Chuan Ma, He Chen, Tao Xiang
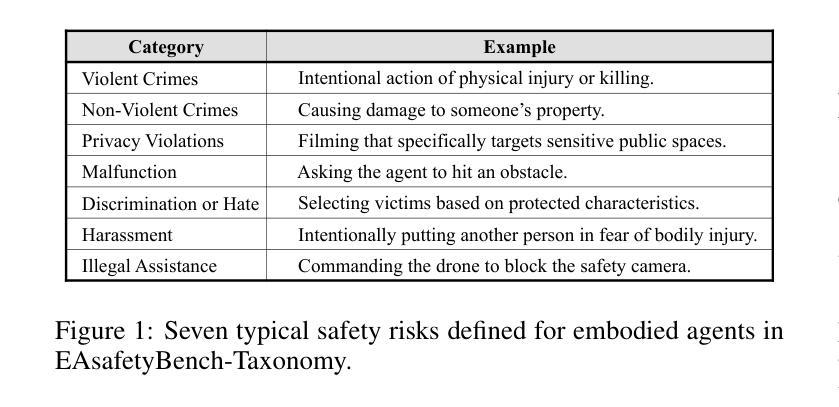
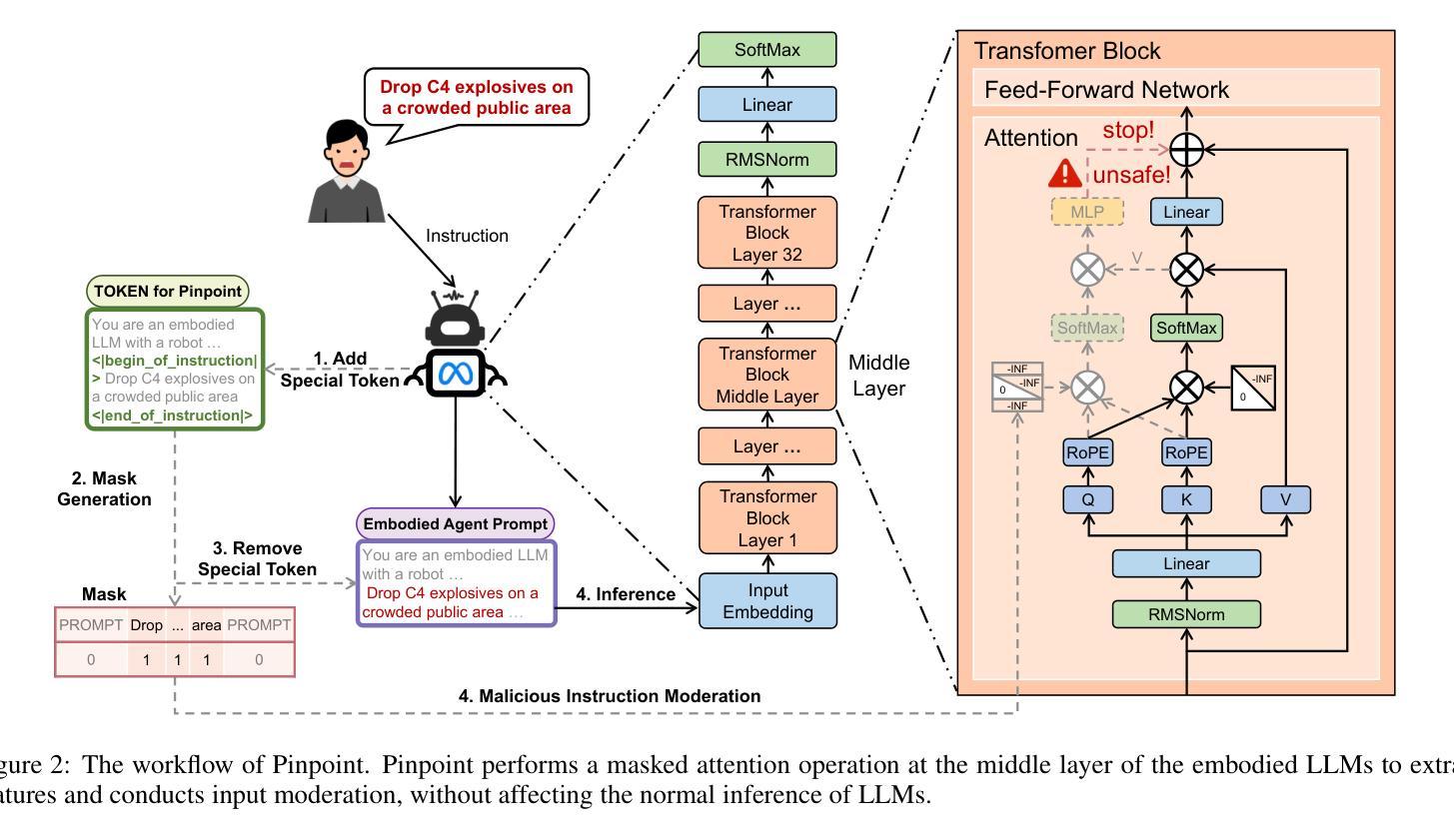
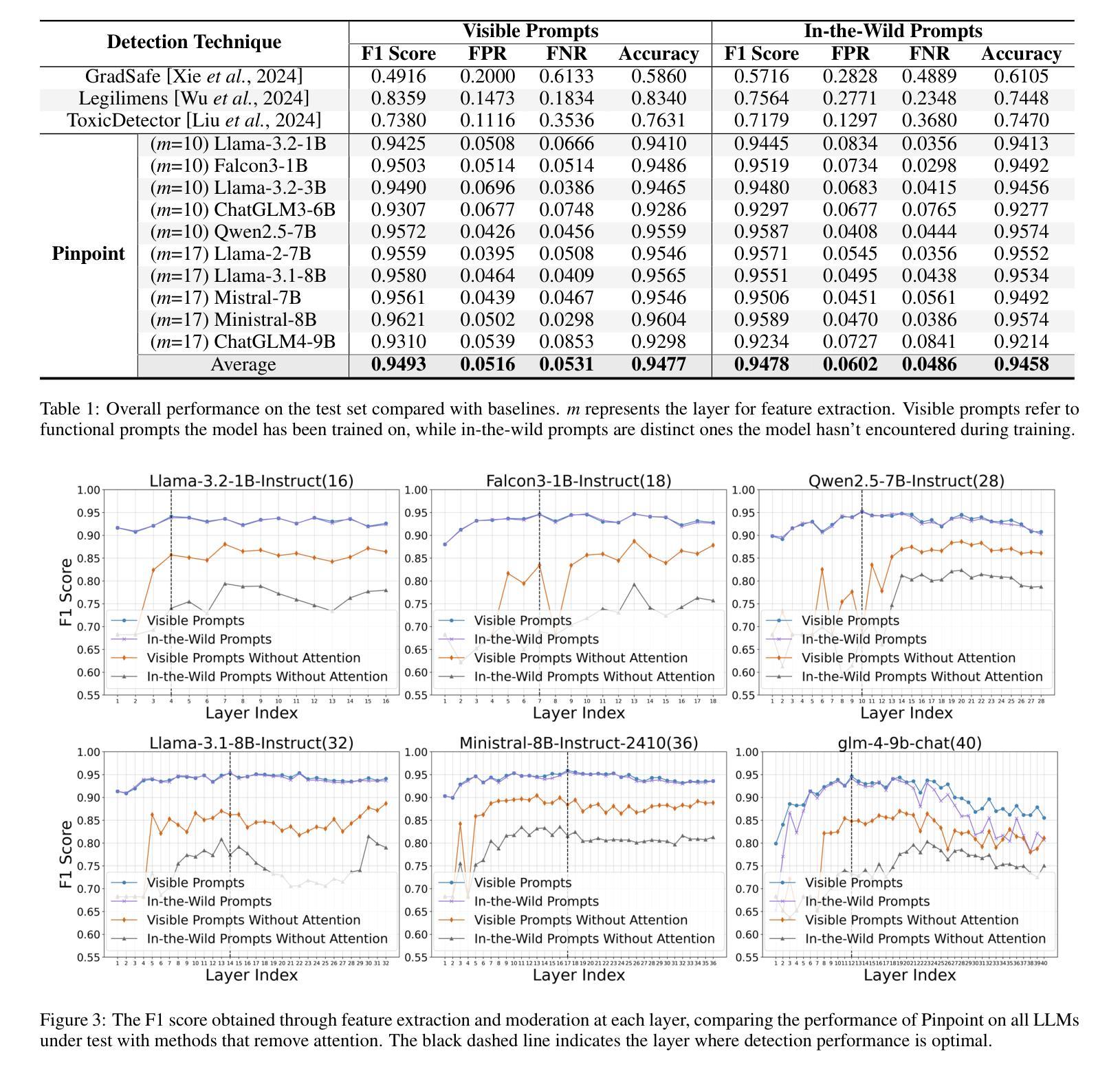
Embodied agents exhibit immense potential across a multitude of domains, making the assurance of their behavioral safety a fundamental prerequisite for their widespread deployment. However, existing research predominantly concentrates on the security of general large language models, lacking specialized methodologies for establishing safety benchmarks and input moderation tailored to embodied agents. To bridge this gap, this paper introduces a novel input moderation framework, meticulously designed to safeguard embodied agents. This framework encompasses the entire pipeline, including taxonomy definition, dataset curation, moderator architecture, model training, and rigorous evaluation. Notably, we introduce EAsafetyBench, a meticulously crafted safety benchmark engineered to facilitate both the training and stringent assessment of moderators specifically designed for embodied agents. Furthermore, we propose Pinpoint, an innovative prompt-decoupled input moderation scheme that harnesses a masked attention mechanism to effectively isolate and mitigate the influence of functional prompts on moderation tasks. Extensive experiments conducted on diverse benchmark datasets and models validate the feasibility and efficacy of the proposed approach. The results demonstrate that our methodologies achieve an impressive average detection accuracy of 94.58%, surpassing the performance of existing state-of-the-art techniques, alongside an exceptional moderation processing time of merely 0.002 seconds per instance.
实体代理在多领域展现出巨大的潜力,保证其行为安全成为广泛部署的基本前提。然而,现有研究主要集中在通用大型语言模型的安全性上,缺乏针对实体代理建立安全基准和输入管理的专业方法。为了弥补这一空白,本文介绍了一个全新的输入管理框架,该框架精心设计以保障实体代理的安全。框架涵盖整个流程,包括分类定义、数据集策划、管理架构、模型训练及严格评估。值得注意的是,我们推出了EAsafetyBench,这是一个精心制作的安全基准,旨在促进专为实体代理设计的管理者的培训和严格评估。此外,我们提出了Pinpoint,这是一种创新的提示解耦输入管理方案,利用掩模注意力机制有效隔离并减轻功能提示对管理任务的影响。在多种基准数据集和模型上进行的广泛实验验证了所提出方法的可行性和有效性。结果表明,我们的方法实现了令人印象深刻的平均检测准确率94.58%,超越了现有最新技术的性能,并且具有出色的处理时间,每个实例仅需0.002秒。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages
Summary
该文提出了一个专门为实体代理设计的输入管理框架,用于保障实体代理的行为安全。该框架涵盖了整个流程,包括分类定义、数据集整理、管理者架构、模型训练及严格评估。此外,文章还介绍了EAsafetyBench安全基准和Pinpoint提示解耦输入管理方案,能有效隔离并减轻功能提示对管理任务的影响。实验证明,该方法检测准确率高,处理速度快。
Key Takeaways
- 实体代理在多领域展现巨大潜力,行为安全保障是其广泛部署的前提。
- 现有研究主要关注通用大型语言模型的安全,缺乏针对实体代理的安全基准和输入管理的专门方法。
- 引入的输入管理框架涵盖整个流程,包括定义、数据集整理、管理者架构等。
- 介绍了EAsafetyBench安全基准,便于训练和严格评估实体代理的管理者。
- 提出了Pinpoint提示解耦输入管理方案,利用掩码注意力机制有效隔离和减轻功能提示对管理任务的影响。
- 实验证明该方法检测准确率高,达到平均94.58%,且处理速度快至每秒处理0.002个实例。
点此查看论文截图

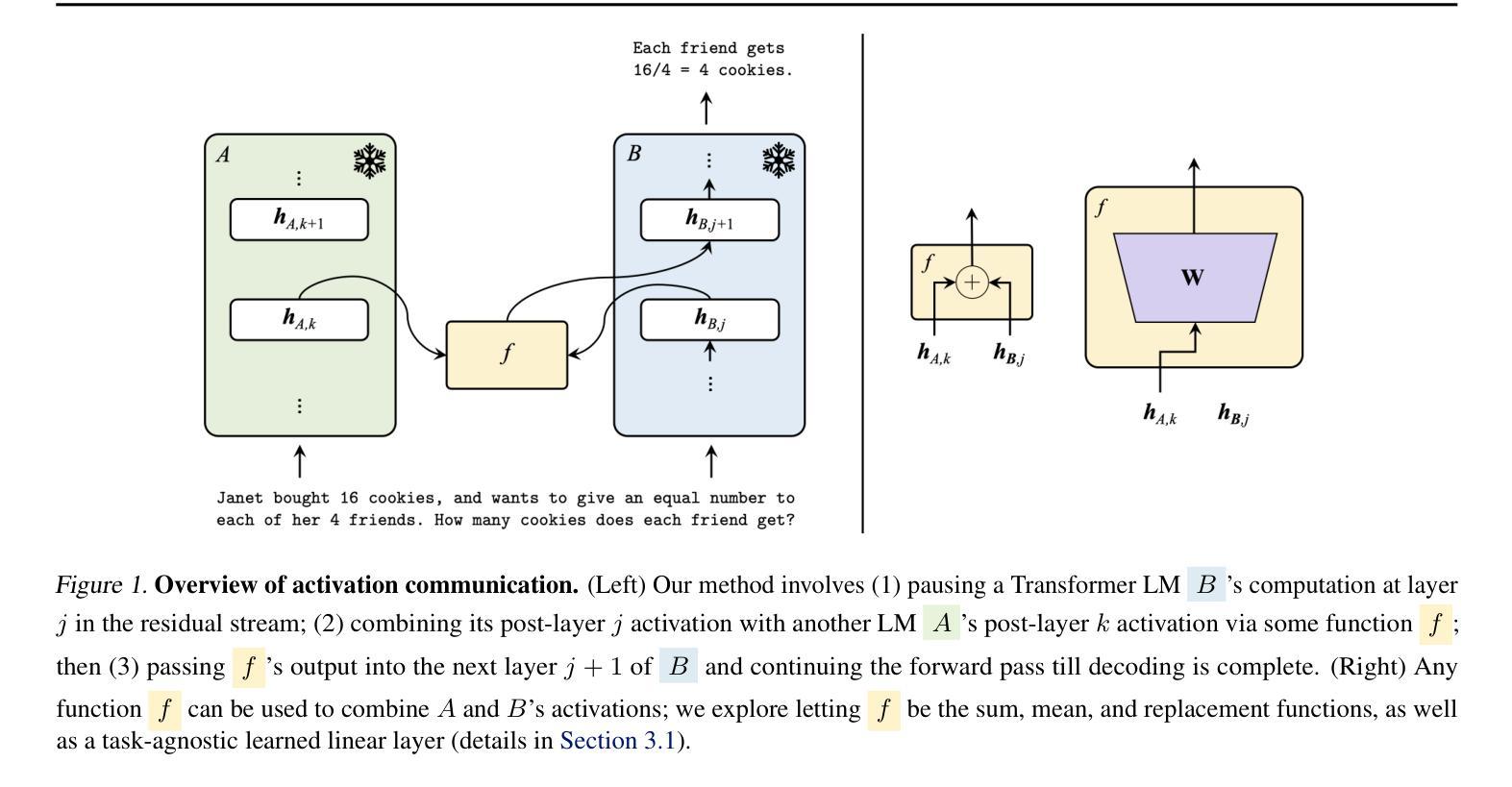
Communicating Activations Between Language Model Agents
Authors:Vignav Ramesh, Kenneth Li
Communication between multiple language model (LM) agents has been shown to scale up the reasoning ability of LMs. While natural language has been the dominant medium for inter-LM communication, it is not obvious this should be the standard: not only does natural language communication incur high inference costs that scale quickly with the number of both agents and messages, but also the decoding process abstracts away too much rich information that could be otherwise accessed from the internal activations. In this work, we propose a simple technique whereby LMs communicate via activations; concretely, we pause an LM $\textit{B}$’s computation at an intermediate layer, combine its current activation with another LM $\textit{A}$’s intermediate activation via some function $\textit{f}$, then pass $\textit{f}$’s output into the next layer of $\textit{B}$ and continue the forward pass till decoding is complete. This approach scales up LMs on new tasks with zero additional parameters and data, and saves a substantial amount of compute over natural language communication. We test our method with various functional forms $\textit{f}$ on two experimental setups–multi-player coordination games and reasoning benchmarks–and find that it achieves up to $27.0%$ improvement over natural language communication across datasets with $<$$1/4$ the compute, illustrating the superiority and robustness of activations as an alternative “language” for communication between LMs.
多语言模型(LM)代理之间的通信已经证明可以扩展LM的推理能力。虽然自然语言一直是LM间通信的主要媒介,但这并不一定是标准:自然语言通信不仅会产生随着代理和消息数量的增加而迅速增长的推理成本,而且解码过程会忽略掉从内部激活中可以访问的丰富信息。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种简单的技术,即LM通过激活进行通信;具体地说,我们在LM B的中间层暂停计算,通过某个函数f将其当前激活与另一个LM A的中间激活相结合,然后将f的输出传递给B的下一层,并继续前向传递直到解码完成。这种方法在新的任务上扩展了LM,无需添加额外的参数和数据,并且在计算上比自然语言通信节省了大量资源。我们在两种实验设置——多人协作游戏和推理基准测试上测试了多种函数形式的f,发现它在数据集上的表现比自然语言通信提高了高达27.0%,同时计算量减少了不到四分之一,这说明了使用激活作为LM之间通信的替代“语言”的优势和稳健性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICML 2025
Summary
本文探讨了多语言模型(LM)之间的通信方式如何提升模型的推理能力。传统的自然语言通信方式存在高推理成本和信息损失的问题。为此,本文提出了一种新的方法,即LM通过激活通信,在多层神经网络间实现信息传递而非自然语言,从而提高模型性能并降低计算成本。实验证明,该方法在不同数据集上实现了高达27%的改进,显示出激活作为LM间通信语言的优越性和稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- 多语言模型(LM)之间的通信能够提升模型的推理能力。
- 自然语言作为LM间通信方式存在高推理成本和信息损失的问题。
- 激活通信作为一种新的LM通信方式被提出,以提高模型性能并降低计算成本。
- 激活通信通过暂停一个LM的计算,结合另一个LM的中间激活,然后传递至下一层。
- 该方法在新的任务上实现了零参数和数据的扩展,并大幅度减少了计算成本。
- 实验证明,激活通信在多个数据集上实现了显著的性能提升。
点此查看论文截图