⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-10 更新
SVAD: From Single Image to 3D Avatar via Synthetic Data Generation with Video Diffusion and Data Augmentation
Authors:Yonwoo Choi
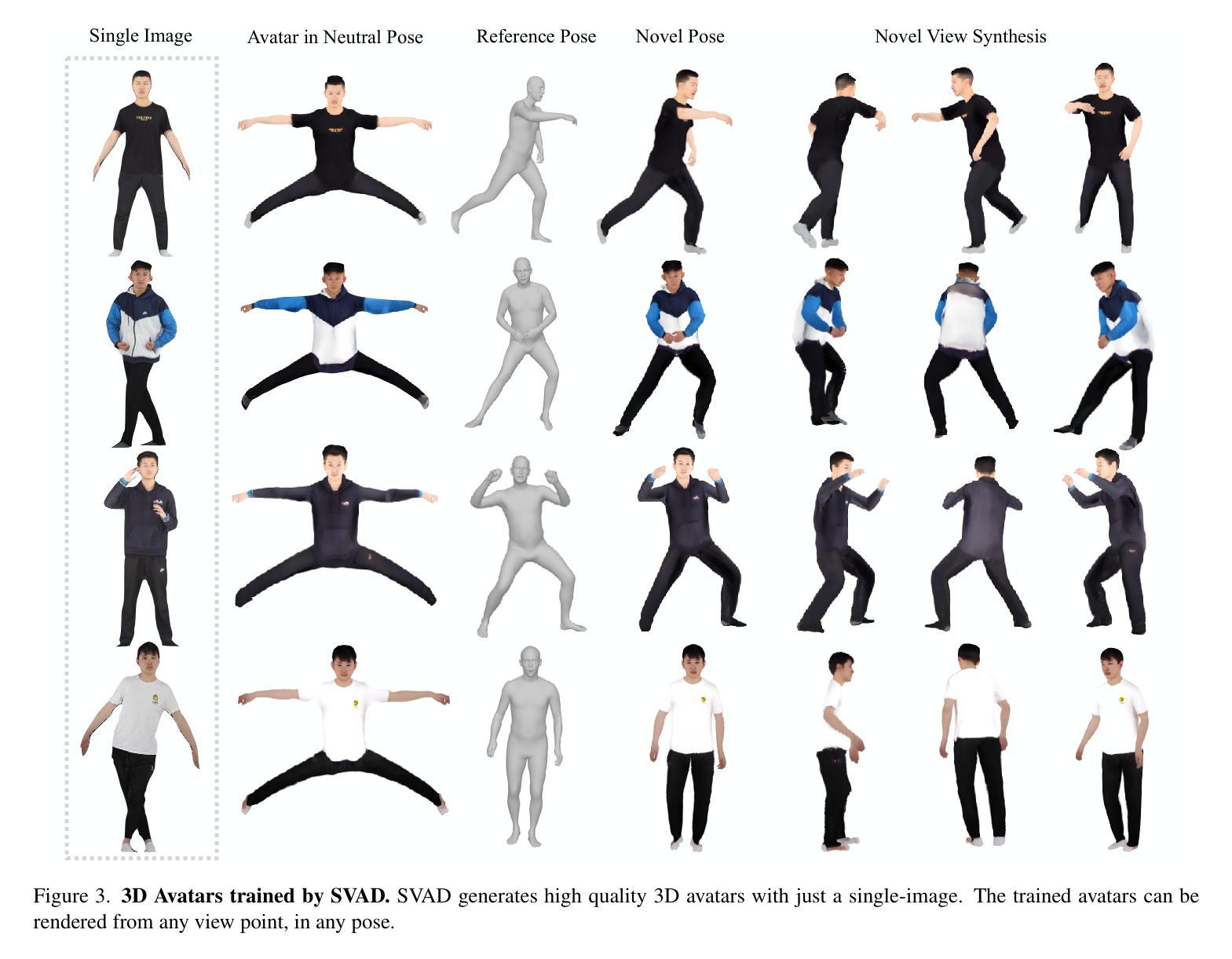
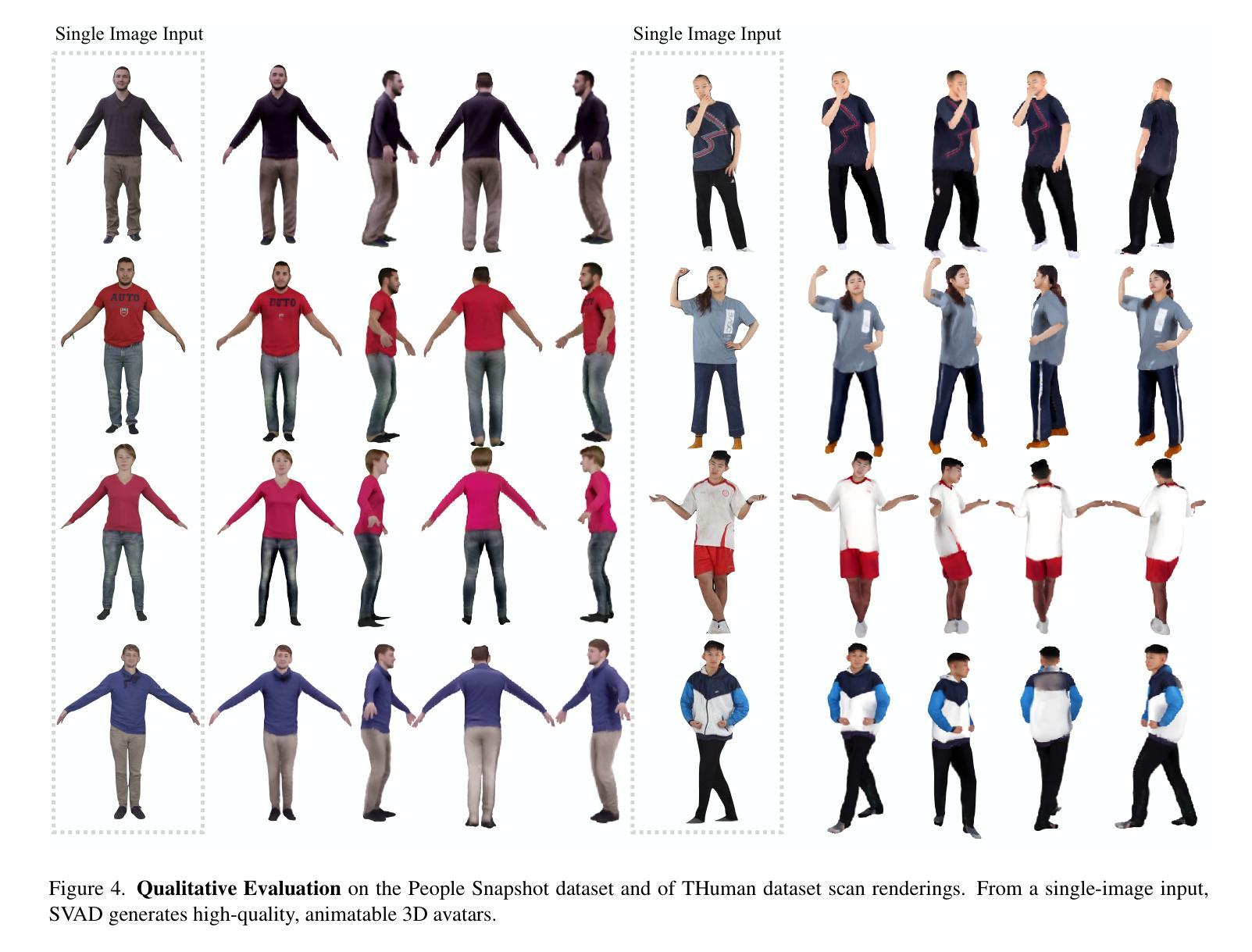
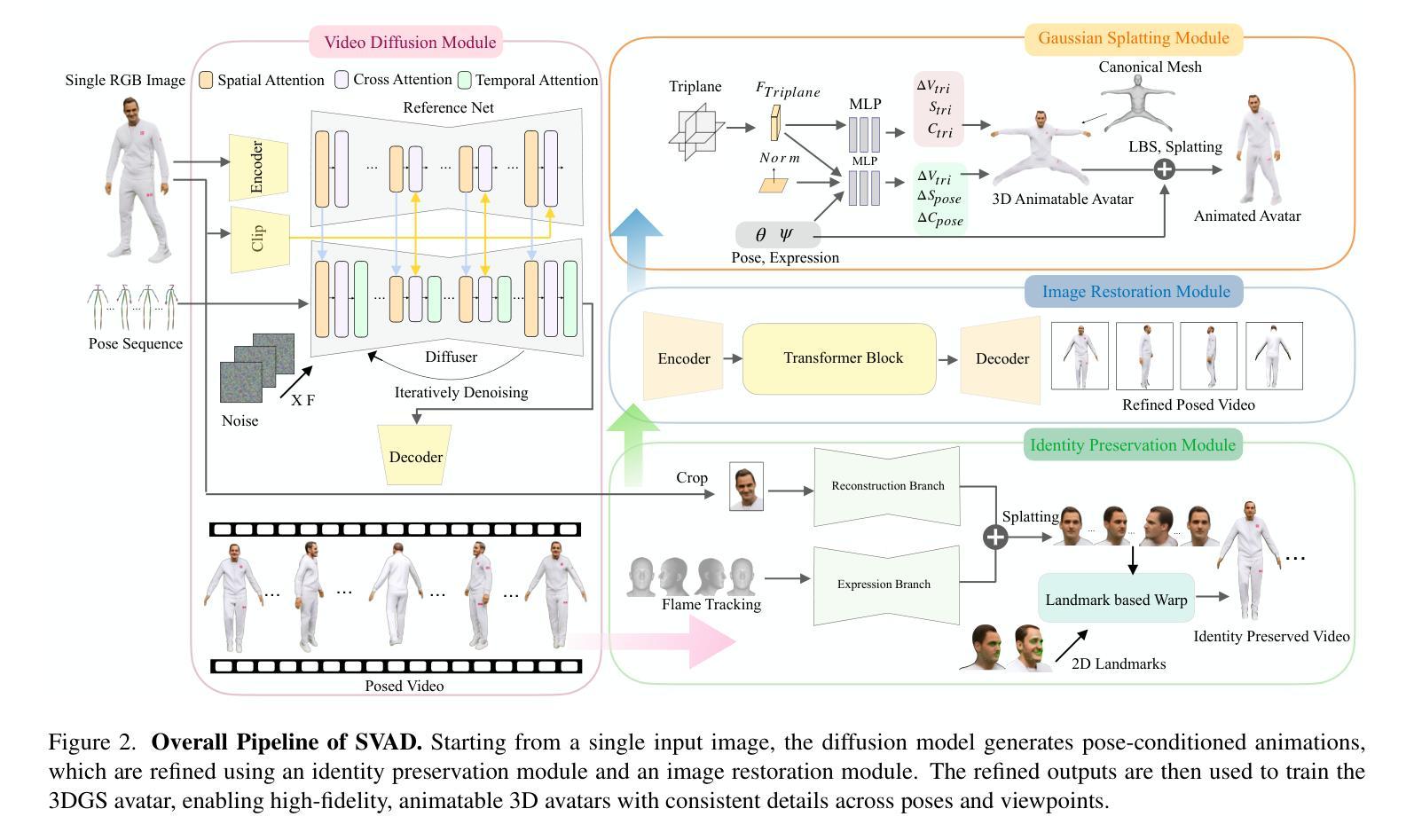
Creating high-quality animatable 3D human avatars from a single image remains a significant challenge in computer vision due to the inherent difficulty of reconstructing complete 3D information from a single viewpoint. Current approaches face a clear limitation: 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) methods produce high-quality results but require multiple views or video sequences, while video diffusion models can generate animations from single images but struggle with consistency and identity preservation. We present SVAD, a novel approach that addresses these limitations by leveraging complementary strengths of existing techniques. Our method generates synthetic training data through video diffusion, enhances it with identity preservation and image restoration modules, and utilizes this refined data to train 3DGS avatars. Comprehensive evaluations demonstrate that SVAD outperforms state-of-the-art (SOTA) single-image methods in maintaining identity consistency and fine details across novel poses and viewpoints, while enabling real-time rendering capabilities. Through our data augmentation pipeline, we overcome the dependency on dense monocular or multi-view training data typically required by traditional 3DGS approaches. Extensive quantitative, qualitative comparisons show our method achieves superior performance across multiple metrics against baseline models. By effectively combining the generative power of diffusion models with both the high-quality results and rendering efficiency of 3DGS, our work establishes a new approach for high-fidelity avatar generation from a single image input.
创建高质量的可动画三维人类角色(Avatar)从单张图像中仍然是计算机视觉领域的一大挑战,因为从单一视角重建完整的三维信息存在固有的难度。当前的方法存在一个明显的局限性:三维高斯平铺(3DGS)技术虽然能产生高质量的结果,但需要多个视角或视频序列,而视频扩散模型虽然可以从单个图像生成动画,但在保持一致性和身份识别方面存在困难。我们提出了一种新方法SVAD,它结合了现有技术的优势来解决这些局限性。我们的方法通过视频扩散生成合成训练数据,通过身份识别和图像恢复模块对其进行增强,并利用这些经过改进的数据来训练三维高斯平铺角色。全面的评估表明,SVAD在保持身份一致性和精细细节方面优于当前单图像方法,并在新型姿势和视角之间展现出卓越性能,同时实现了实时渲染功能。通过我们的数据增强流程,我们克服了传统三维高斯平铺方法通常对密集的单眼或多视角训练数据的依赖。大量的定量和定性对比显示,我们的方法在多个指标上均优于基线模型。通过有效地结合扩散模型的生成能力与三维高斯平铺的高质量结果和渲染效率,我们的工作建立了一种从单张图像输入生成高质量角色(Avatar)的新方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by CVPR 2025 SyntaGen Workshop, Project Page: https://yc4ny.github.io/SVAD/
Summary:
基于单张图像创建高质量的动态三维人类角色一直是计算机视觉领域的一大挑战。现有方法存在局限性:三维高斯贴片法(3DGS)虽然能生成高质量结果但需要多视角或视频序列,而视频扩散模型虽能从单张图像生成动画但缺乏一致性和身份保留。我们提出SVAD方法,结合现有技术的优势解决这些问题。我们的方法通过视频扩散生成合成训练数据,通过身份保留和图像恢复模块进行增强,并利用这些数据训练三维高斯贴片角色。评估显示,SVAD在维持身份一致性和细节方面优于单图像方法,在新姿态和视角上表现优异,并具备实时渲染能力。我们的数据增强流程克服了传统三维高斯贴片方法通常需要的密集单目或多视角训练数据的依赖。对比基线模型,我们的方法在多个指标上表现出卓越性能。
Key Takeaways:
- 当前创建高质量的三维人类角色从单张图像仍面临挑战,需要克服完整三维信息从单一视角重建的困难。
- 现有方法如三维高斯贴片法(3DGS)和视频扩散模型存在局限性。
- SVAD方法结合视频扩散和现有技术优点,生成合成训练数据并通过身份保留和图像恢复模块增强数据质量。
- SVAD在维持身份一致性和细节方面优于单图像方法,表现优异于新姿态和视角的渲染。
- SVAD具备实时渲染能力,提高用户体验和性能。
- 通过数据增强流程,SVAD克服了传统三维高斯贴片方法对密集训练数据的依赖。
点此查看论文截图



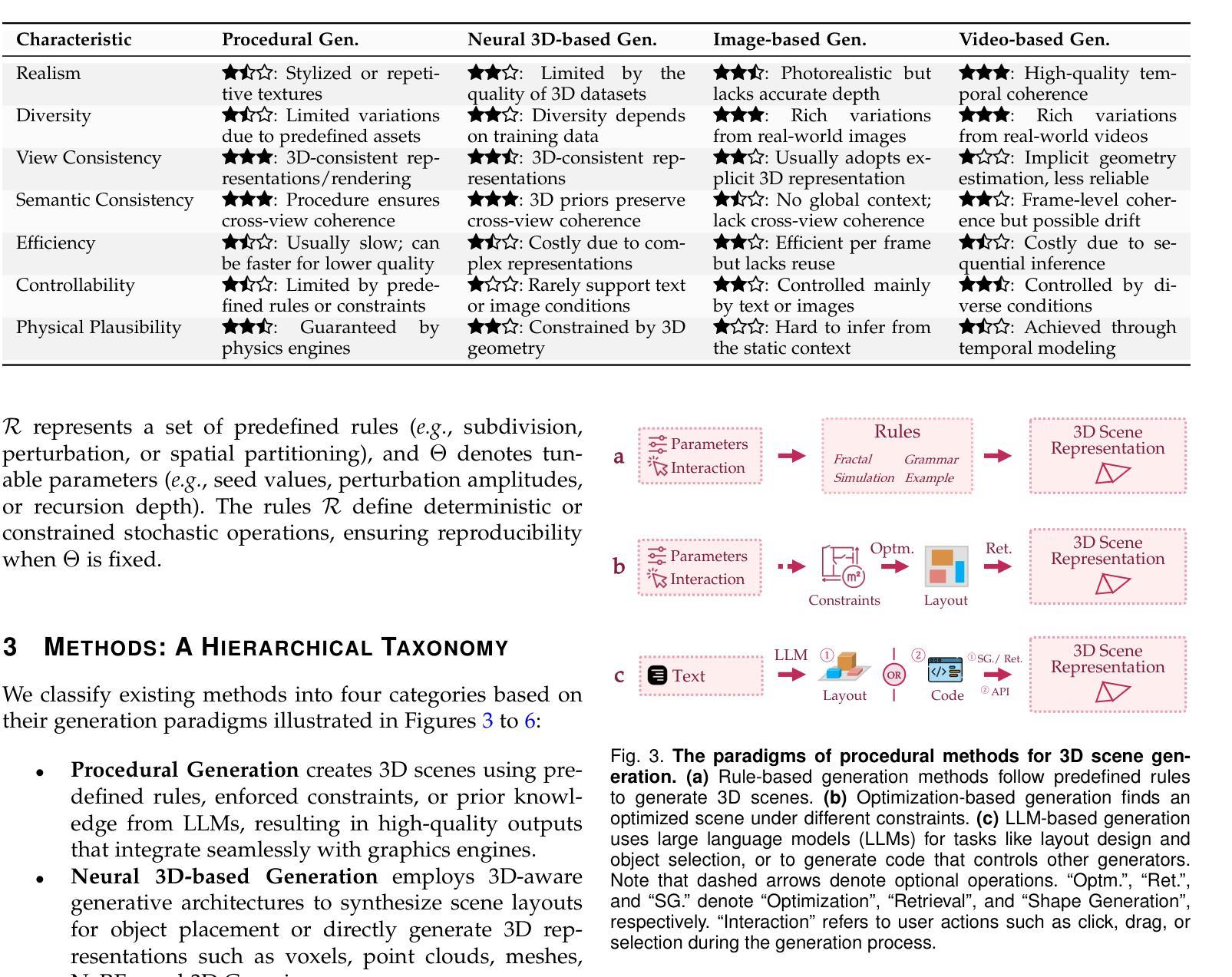
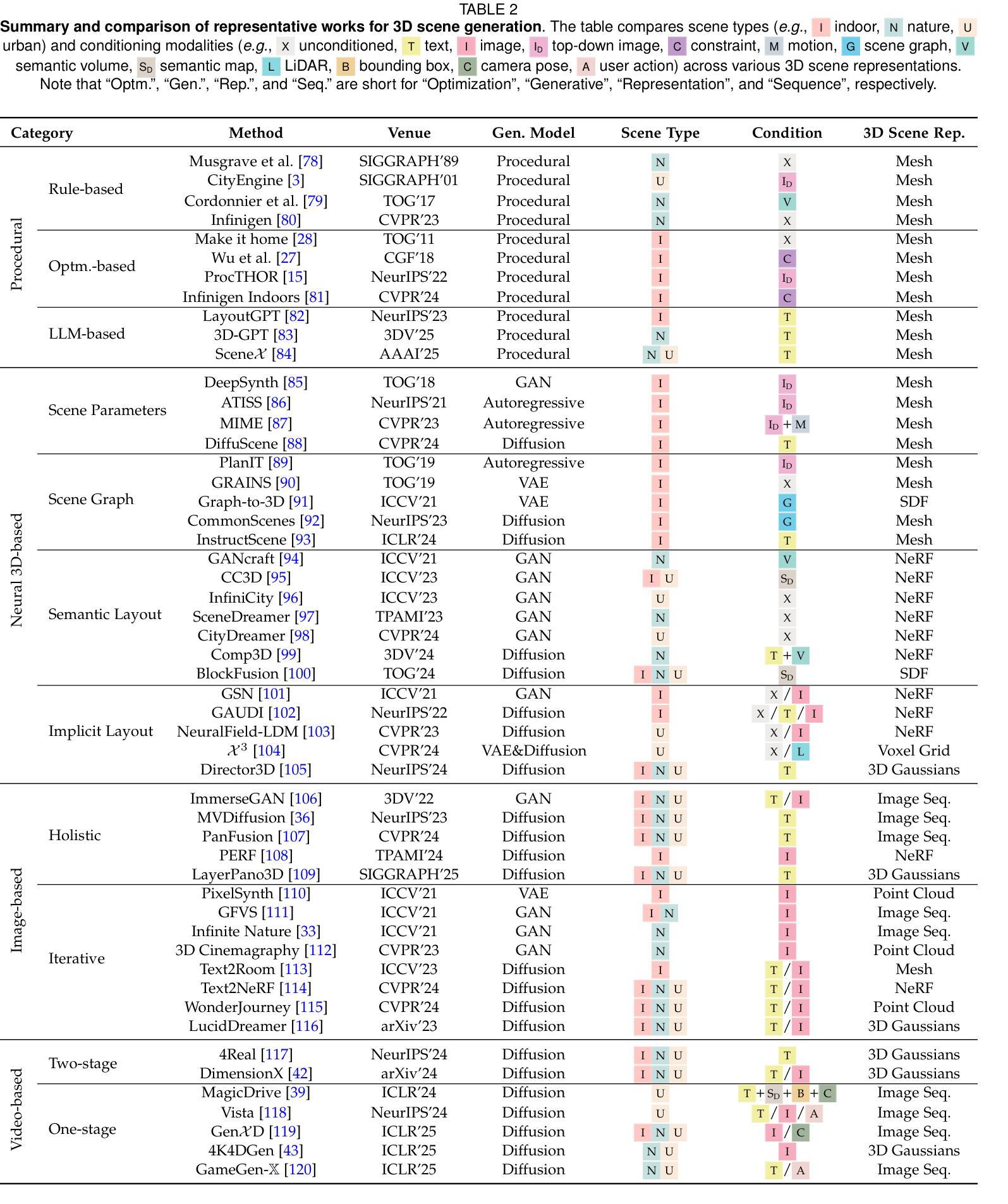
3D Scene Generation: A Survey
Authors:Beichen Wen, Haozhe Xie, Zhaoxi Chen, Fangzhou Hong, Ziwei Liu
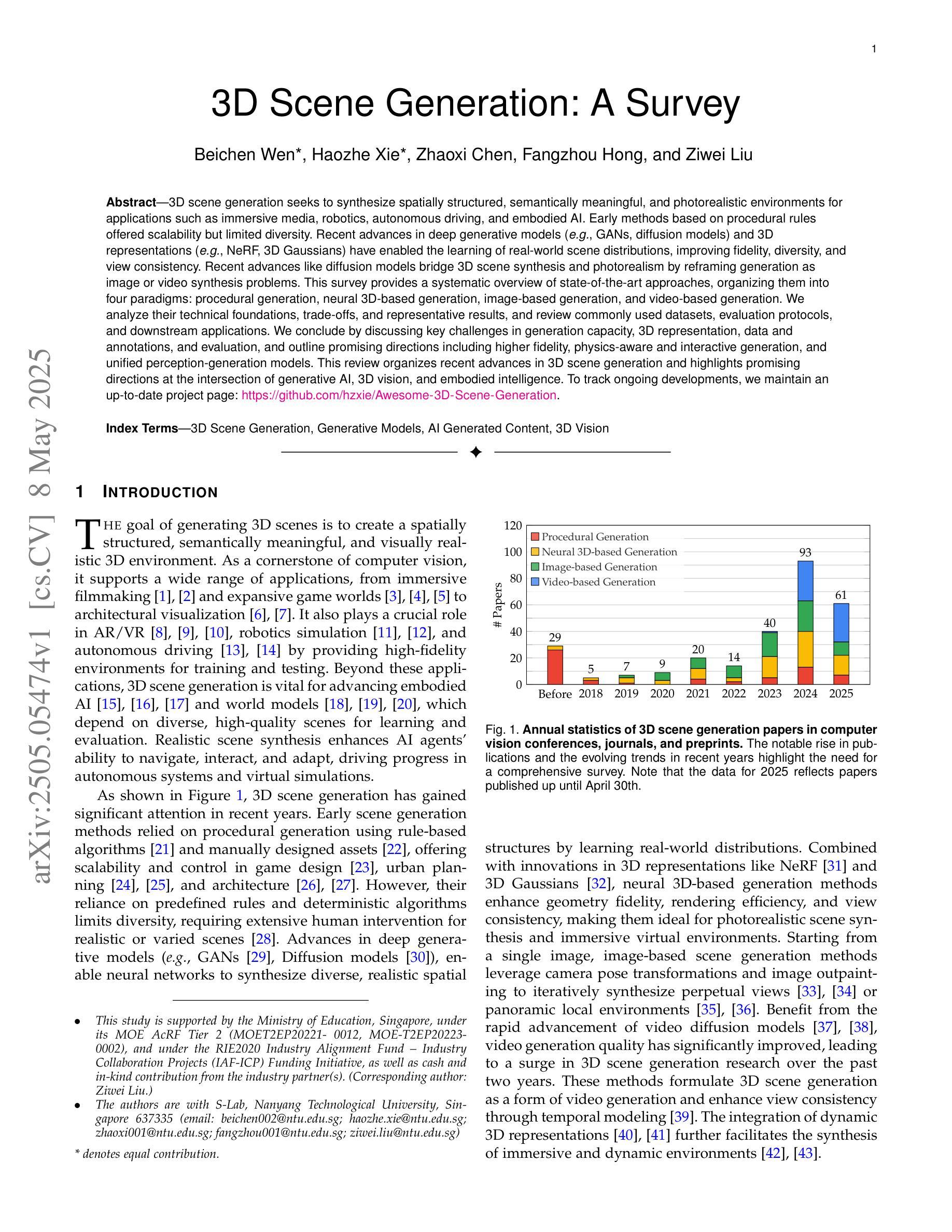
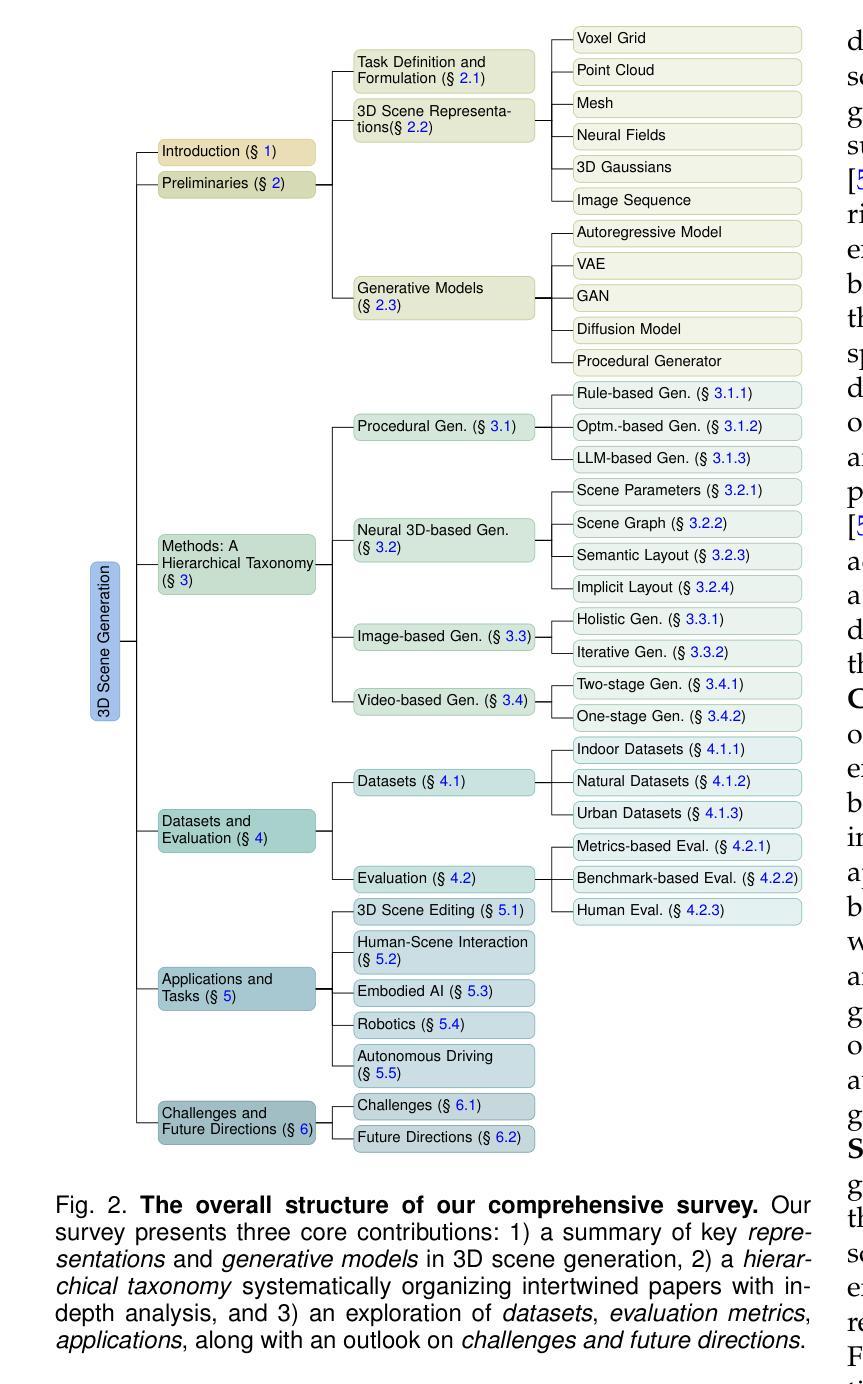
3D scene generation seeks to synthesize spatially structured, semantically meaningful, and photorealistic environments for applications such as immersive media, robotics, autonomous driving, and embodied AI. Early methods based on procedural rules offered scalability but limited diversity. Recent advances in deep generative models (e.g., GANs, diffusion models) and 3D representations (e.g., NeRF, 3D Gaussians) have enabled the learning of real-world scene distributions, improving fidelity, diversity, and view consistency. Recent advances like diffusion models bridge 3D scene synthesis and photorealism by reframing generation as image or video synthesis problems. This survey provides a systematic overview of state-of-the-art approaches, organizing them into four paradigms: procedural generation, neural 3D-based generation, image-based generation, and video-based generation. We analyze their technical foundations, trade-offs, and representative results, and review commonly used datasets, evaluation protocols, and downstream applications. We conclude by discussing key challenges in generation capacity, 3D representation, data and annotations, and evaluation, and outline promising directions including higher fidelity, physics-aware and interactive generation, and unified perception-generation models. This review organizes recent advances in 3D scene generation and highlights promising directions at the intersection of generative AI, 3D vision, and embodied intelligence. To track ongoing developments, we maintain an up-to-date project page: https://github.com/hzxie/Awesome-3D-Scene-Generation.
三维场景生成旨在合成具有空间结构、语义和逼真的环境,用于沉浸式媒体、机器人技术、自动驾驶和人工智能等应用。早期基于程序规则的方法虽然具有良好的可扩展性,但多样性有限。最近深度生成模型(例如GANs,扩散模型)和三维表示(例如NeRF,三维高斯分布)的最新进展已经能够学习真实场景分布,提高了逼真度、多样性和视图一致性。最近的扩散模型等进展通过重新构建生成问题为图像或视频合成问题,从而连接了三维场景合成和逼真度。这篇综述提供了对最新方法的系统概述,将它们组织成四种范式:程序生成、基于神经的三维生成、基于图像的生成和基于视频的生成。我们分析了它们的技术基础、权衡和代表性结果,并回顾了常用的数据集、评估协议和下游应用。最后,我们讨论了生成能力、三维表示、数据和注释以及评估方面的关键挑战,并概述了具有前景的方向,包括更高的逼真度、物理感知和交互式生成以及统一的感知生成模型。这篇综述整理了三维场景生成的最新进展,并强调了生成人工智能、三维视觉和身体智能交叉领域的具有前景的方向。要了解最新进展,请访问我们的项目页面:https://github.com/hzxie/Awesome-3D-Scene-Generation。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://github.com/hzxie/Awesome-3D-Scene-Generation
摘要
该文综述了最新的三维场景生成技术,介绍了四种范式:程序生成、基于神经的三维生成、基于图像生成和基于视频生成。分析了它们的技术基础、权衡和代表性成果,并讨论了数据集、评估协议和下游应用。文章总结了关键挑战,包括生成能力、三维表征、数据和注释以及评估,并指出了高保真、物理感知交互生成和统一感知生成模型等有希望的研究方向。
关键见解
- 3D场景生成旨在合成具有空间结构、语义意义和逼真度的环境,用于沉浸式媒体、机器人技术、自动驾驶和嵌入式人工智能等领域。
- 早期的方法基于程序规则,虽然提供了可扩展性,但多样性有限。
- 最近的深度生成模型(如GANs、扩散模型)和3D表示(如NeRF、3D高斯)的进步,使得学习真实场景分布成为可能,提高了逼真度、多样性和视角一致性。
- 扩散模型等新技术将3D场景合成与逼真度相结合,通过将生成问题重新构建为图像或视频合成问题来实现。
- 文章概述了当前的研究现状,指出了关键挑战,包括生成能力、3D表示、数据和注释以及评估。
- 文章强调了有希望的研究方向,包括更高逼真度、物理感知和交互式生成,以及统一的感知生成模型。
点此查看论文截图
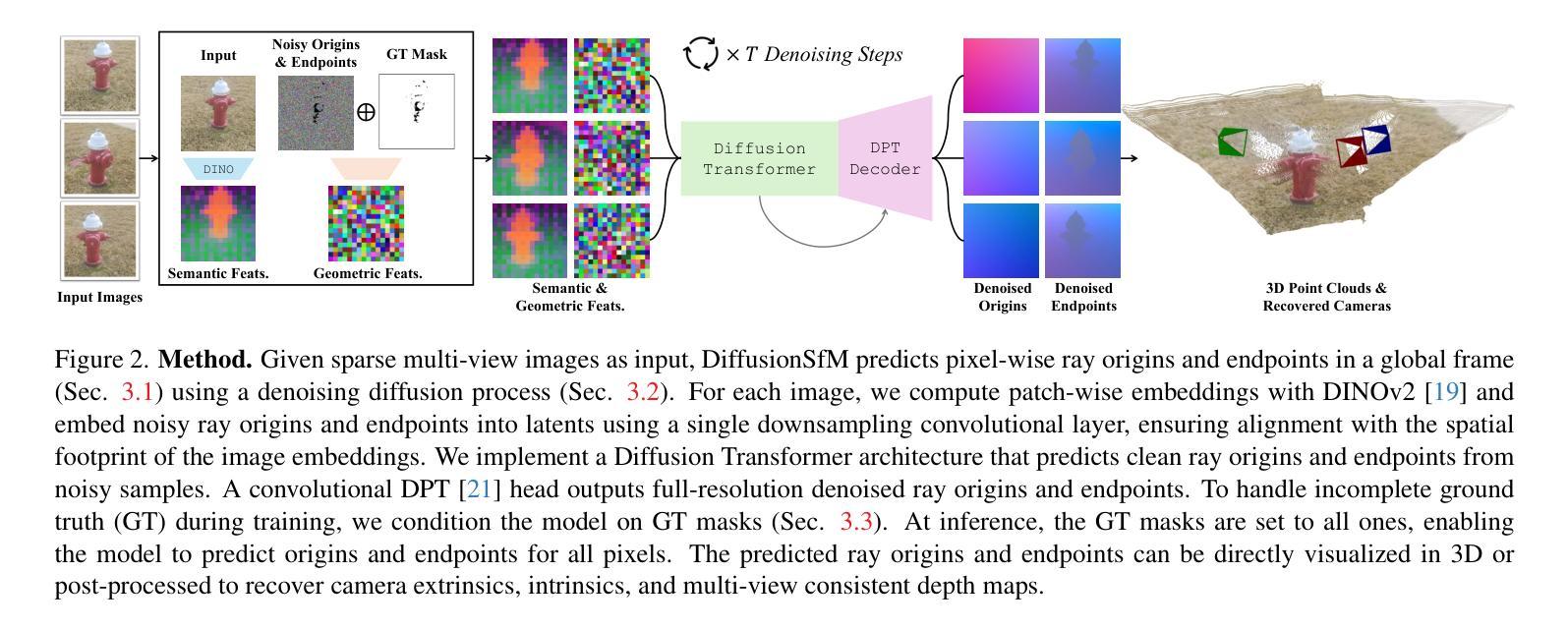
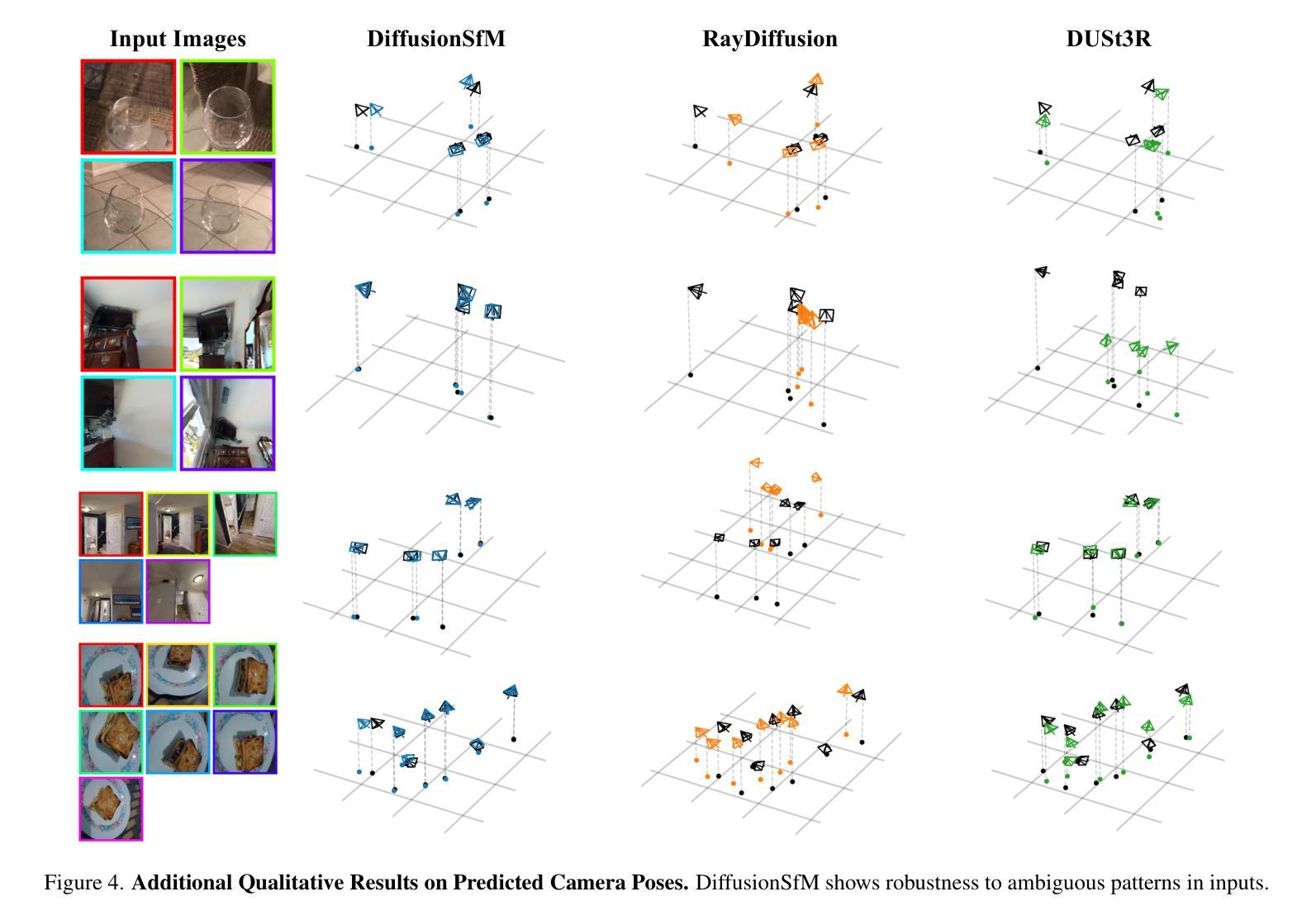
DiffusionSfM: Predicting Structure and Motion via Ray Origin and Endpoint Diffusion
Authors:Qitao Zhao, Amy Lin, Jeff Tan, Jason Y. Zhang, Deva Ramanan, Shubham Tulsiani
Current Structure-from-Motion (SfM) methods typically follow a two-stage pipeline, combining learned or geometric pairwise reasoning with a subsequent global optimization step. In contrast, we propose a data-driven multi-view reasoning approach that directly infers 3D scene geometry and camera poses from multi-view images. Our framework, DiffusionSfM, parameterizes scene geometry and cameras as pixel-wise ray origins and endpoints in a global frame and employs a transformer-based denoising diffusion model to predict them from multi-view inputs. To address practical challenges in training diffusion models with missing data and unbounded scene coordinates, we introduce specialized mechanisms that ensure robust learning. We empirically validate DiffusionSfM on both synthetic and real datasets, demonstrating that it outperforms classical and learning-based approaches while naturally modeling uncertainty.
当前的结构化运动(SfM)方法通常采用两阶段管道,结合学习或几何配对推理,随后进行全局优化步骤。相比之下,我们提出了一种数据驱动的多视角推理方法,该方法直接从多视角图像推断3D场景几何和相机姿态。我们的框架,DiffusionSfM,将场景几何和相机参数化为全局框架中的像素级射线起点和终点,并采用基于变压器的去噪扩散模型从多视角输入进行预测。为了解决在训练扩散模型时面临的实际挑战,例如数据缺失和无界场景坐标,我们引入了专业机制以确保稳健学习。我们在合成和真实数据集上实证验证了DiffusionSfM,表明其在建模不确定性方面具有优势,并超越了经典的和基于学习的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025. Project website: https://qitaozhao.github.io/DiffusionSfM
Summary
本文提出了一种数据驱动的多视角推理方法,直接由多视角图像推断三维场景几何和相机姿态。新方法采用扩散SfM框架,将场景几何和相机参数化为全局坐标系中的像素级射线起点和终点,并使用基于变压器的去噪扩散模型从多视角输入进行预测。为解决训练扩散模型时面临的缺失数据和无限场景坐标问题,引入了专门机制以确保稳健学习。经验证,DiffusionSfM在合成和真实数据集上的表现均优于传统和基于学习的方法,并能自然地建模不确定性。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散SfM提出了一种新的多视角推理方法,直接推断三维场景几何和相机姿态。
- 方法结合像素级射线起点和终点参数化场景几何和相机,在全局坐标系中进行表示。
- 采用基于变压器的去噪扩散模型进行预测。
- 引入专门机制解决训练扩散模型时的缺失数据和无限场景坐标问题。
- 扩散SfM在合成和真实数据集上的表现均优于传统和基于学习的方法。
- 扩散SfM能自然地建模不确定性。
点此查看论文截图


Mogao: An Omni Foundation Model for Interleaved Multi-Modal Generation
Authors:Chao Liao, Liyang Liu, Xun Wang, Zhengxiong Luo, Xinyu Zhang, Wenliang Zhao, Jie Wu, Liang Li, Zhi Tian, Weilin Huang
Recent progress in unified models for image understanding and generation has been impressive, yet most approaches remain limited to single-modal generation conditioned on multiple modalities. In this paper, we present Mogao, a unified framework that advances this paradigm by enabling interleaved multi-modal generation through a causal approach. Mogao integrates a set of key technical improvements in architecture design, including a deep-fusion design, dual vision encoders, interleaved rotary position embeddings, and multi-modal classifier-free guidance, which allow it to harness the strengths of both autoregressive models for text generation and diffusion models for high-quality image synthesis. These practical improvements also make Mogao particularly effective to process interleaved sequences of text and images arbitrarily. To further unlock the potential of unified models, we introduce an efficient training strategy on a large-scale, in-house dataset specifically curated for joint text and image generation. Extensive experiments show that Mogao not only achieves state-of-the-art performance in multi-modal understanding and text-to-image generation, but also excels in producing high-quality, coherent interleaved outputs. Its emergent capabilities in zero-shot image editing and compositional generation highlight Mogao as a practical omni-modal foundation model, paving the way for future development and scaling the unified multi-modal systems.
关于图像理解和生成的综合模型方面的最新进展令人印象深刻。然而,大多数方法仍然局限于单一模态的生成条件下,根据多个模态的条件生成内容。在本文中,我们介绍了Mogao,这是一个推进这一范式的一体化框架,它通过因果方法实现了交替多模态生成。Mogao集成了架构设计中的一系列关键技术改进,包括深度融合设计、双视觉编码器、交替旋转位置嵌入和无模态分类器引导等,这允许它充分利用自回归模型在文本生成和扩散模型在高质量图像合成方面的优势。这些实际的改进也使得Mogao在处理任意文本和图像的交替序列时特别有效。为了解锁综合模型的潜力,我们在专门为联合文本和图像生成设计的大规模内部数据集上引入了一种有效的训练策略。大量实验表明,Mogao不仅在多模态理解和文本到图像生成方面达到了最新技术性能水平,而且在生成高质量连贯的交替输出方面也表现出卓越性能。它在零样本图像编辑和组合生成方面的能力突显了Mogao作为一个实用的全模态基础模型,为未来的发展和扩展统一多模态系统铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Mogao Technical Report
Summary
多模态生成是图像理解和生成领域的一个热门话题。本文提出了一种名为Mogao的统一框架,通过一系列关键技术改进,如深度融合设计、双重视觉编码器、交替旋转位置嵌入和多模态无分类器引导等,实现了多模态生成。Mogao结合了自回归文本生成模型和扩散模型的优点,用于高质量图像合成。此外,还引入了一种大规模内建数据集的培训策略,为统一模型提供了更多潜力。实验表明,Mogao在多模态理解和文本到图像生成方面达到了最新技术水平,并能产生高质量连贯的交错输出。其零样本图像编辑和组合生成能力使其成为实用的多模态基础模型。
Key Takeaways
- Mogao是一个统一框架,实现了多模态生成,能够处理文本和图像的交错序列。
- 该框架通过一系列关键技术改进,如深度融合设计、双重视觉编码器等实现先进性能。
- Mogao结合了自回归文本生成模型和扩散模型的优点,用于高质量图像合成。
- 引入了一种大规模内建数据集的培训策略,提高模型的性能。
- Mogao在多模态理解和文本到图像生成方面达到了最新技术水平。
- 该模型能够产生高质量连贯的交错输出,并具有零样本图像编辑和组合生成能力。
点此查看论文截图



Diffusion Model Quantization: A Review
Authors:Qian Zeng, Chenggong Hu, Mingli Song, Jie Song
Recent success of large text-to-image models has empirically underscored the exceptional performance of diffusion models in generative tasks. To facilitate their efficient deployment on resource-constrained edge devices, model quantization has emerged as a pivotal technique for both compression and acceleration. This survey offers a thorough review of the latest advancements in diffusion model quantization, encapsulating and analyzing the current state of the art in this rapidly advancing domain. First, we provide an overview of the key challenges encountered in the quantization of diffusion models, including those based on U-Net architectures and Diffusion Transformers (DiT). We then present a comprehensive taxonomy of prevalent quantization techniques, engaging in an in-depth discussion of their underlying principles. Subsequently, we perform a meticulous analysis of representative diffusion model quantization schemes from both qualitative and quantitative perspectives. From a quantitative standpoint, we rigorously benchmark a variety of methods using widely recognized datasets, delivering an extensive evaluation of the most recent and impactful research in the field. From a qualitative standpoint, we categorize and synthesize the effects of quantization errors, elucidating these impacts through both visual analysis and trajectory examination. In conclusion, we outline prospective avenues for future research, proposing novel directions for the quantization of generative models in practical applications. The list of related papers, corresponding codes, pre-trained models and comparison results are publicly available at the survey project homepage https://github.com/TaylorJocelyn/Diffusion-Model-Quantization.
大型文本到图像模型的最新成功经验实证了扩散模型在生成任务中的卓越性能。为了在资源受限的边缘设备上有效部署这些模型,模型量化作为压缩和加速的关键技术应运而生。本文全面回顾了扩散模型量化的最新进展,分析和评估了这个快速发展领域的当前最新状态。首先,我们概述了扩散模型量化所面临的关键挑战,包括基于U-Net架构和扩散变压器(DiT)的挑战。然后,我们全面介绍了流行的量化技术,并深入讨论了它们的基本原理。随后,我们从定性和定量两个角度对代表性的扩散模型量化方案进行了详细分析。从定量角度看,我们使用公认的数据集对各种方法进行了严格评估,全面评价了该领域最新、最有影响力的研究。从定性角度看,我们对量化误差的影响进行了分类和归纳,并通过视觉分析和轨迹检查阐明了这些影响。最后,我们概述了未来研究的前景,为实际应用中生成模型的量化提出了新颖的研究方向。相关论文列表、相应代码、预训练模型和比较结果可在调查项目主页https://github.com/TaylorJocelyn/Diffusion-Model-Quantization上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 40 pages, 8 figures
Summary
本文主要探讨了扩散模型量化技术的最新进展与挑战,包括U-Net架构和Diffusion Transformers(DiT)中的挑战。文章概述了关键量化技术的原理和性能评估,同时从定性和定量两个角度分析了代表性的扩散模型量化方案。此外,文章还展望了未来研究方向,为实际应用中生成模型的量化提供了新思路。相关资源已公开在调查项目主页上。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在生成任务中表现出卓越性能,其量化技术是实现在资源受限的边缘设备上高效部署的关键。
- 面临的关键挑战包括U-Net架构和Diffusion Transformers(DiT)的量化难题。
- 流行的量化技术得到了全面的审查和分析,展示了当前该领域的最新发展。
- 从定量和定性两个角度对代表性的扩散模型量化方案进行了深入分析。
- 通过广泛认可的数据集对多种方法进行了严格基准测试,评估了最新研究成果。
- 量化误差的影响通过视觉分析和轨迹检查得到了详细阐述和分类。
点此查看论文截图

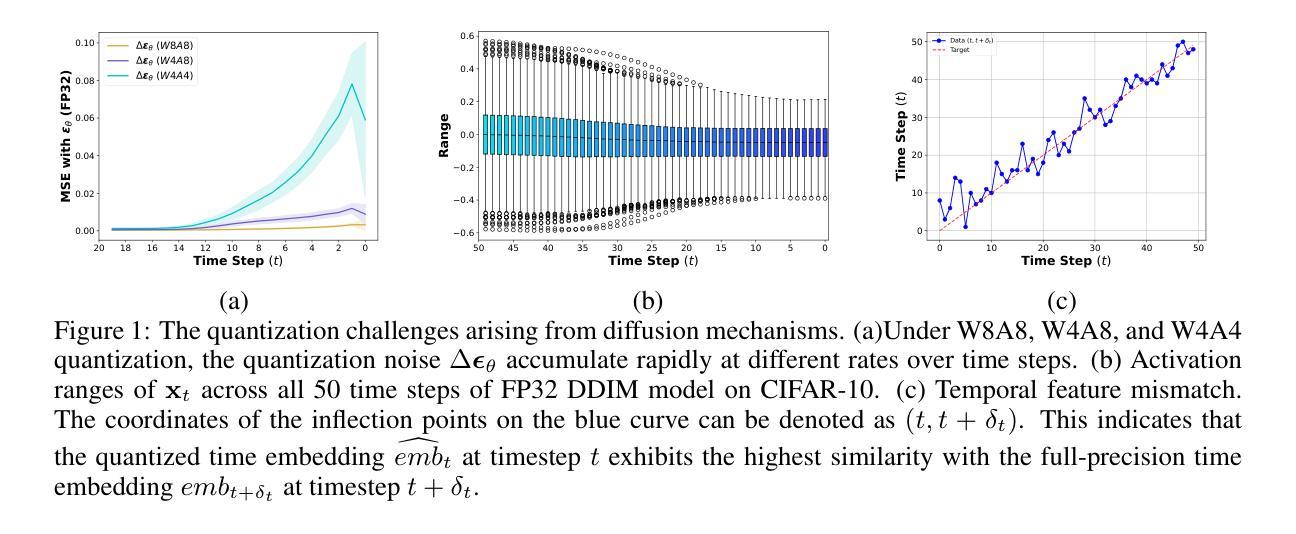
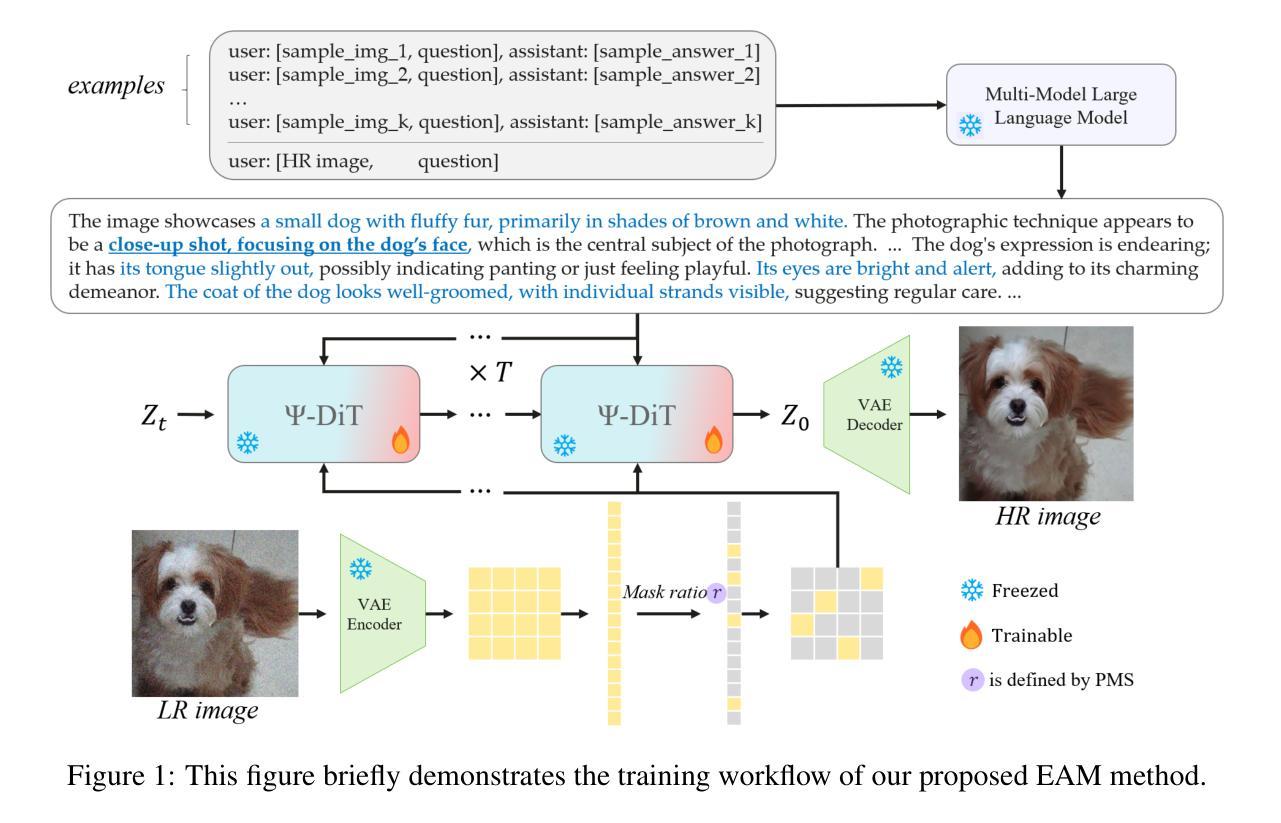
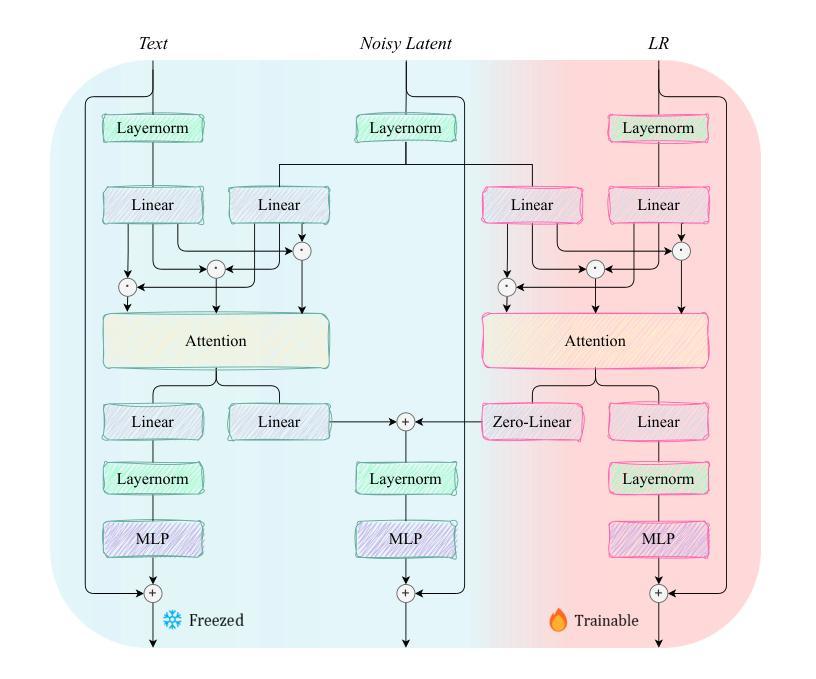
EAM: Enhancing Anything with Diffusion Transformers for Blind Super-Resolution
Authors:Haizhen Xie, Kunpeng Du, Qiangyu Yan, Sen Lu, Jianhong Han, Hanting Chen, Hailin Hu, Jie Hu
Utilizing pre-trained Text-to-Image (T2I) diffusion models to guide Blind Super-Resolution (BSR) has become a predominant approach in the field. While T2I models have traditionally relied on U-Net architectures, recent advancements have demonstrated that Diffusion Transformers (DiT) achieve significantly higher performance in this domain. In this work, we introduce Enhancing Anything Model (EAM), a novel BSR method that leverages DiT and outperforms previous U-Net-based approaches. We introduce a novel block, $\Psi$-DiT, which effectively guides the DiT to enhance image restoration. This block employs a low-resolution latent as a separable flow injection control, forming a triple-flow architecture that effectively leverages the prior knowledge embedded in the pre-trained DiT. To fully exploit the prior guidance capabilities of T2I models and enhance their generalization in BSR, we introduce a progressive Masked Image Modeling strategy, which also reduces training costs. Additionally, we propose a subject-aware prompt generation strategy that employs a robust multi-modal model in an in-context learning framework. This strategy automatically identifies key image areas, provides detailed descriptions, and optimizes the utilization of T2I diffusion priors. Our experiments demonstrate that EAM achieves state-of-the-art results across multiple datasets, outperforming existing methods in both quantitative metrics and visual quality.
利用预训练的文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型来指导盲超分辨率(BSR)已成为该领域的主要方法。虽然T2I模型传统上依赖于U-Net架构,但最近的进展表明,扩散变压器(DiT)在这个领域取得了显著更高的性能。在这项工作中,我们介绍了增强任何东西模型(EAM),这是一种新型的BSR方法,它利用DiT并超越了之前的U-Net基于的方法。我们引入了一个新型块Ψ-DiT,它有效地指导DiT进行图像恢复。此块采用低分辨率潜在值作为可分离的流程注入控制,形成一个三流架构,有效地利用预训练DiT中的先验知识。为了充分利用T2I模型的先验指导能力并增强其在BSR中的泛化能力,我们引入了一种渐进式遮挡图像建模策略,这也降低了训练成本。此外,我们提出了一种主题感知的提示生成策略,该策略在一个上下文学习框架中采用健壮的多模式模型。该策略自动识别关键图像区域,提供详细描述,并优化T2I扩散先验的利用。我们的实验表明,EAM在多个数据集上实现了最新结果,在定量指标和视觉质量方面都超越了现有方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于预训练的文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型指导盲超分辨率(BSR)已成为该领域的主流方法。本文介绍了一种新型的BSR方法——增强型任何东西模型(EAM),该模型利用扩散变压器(DiT)并超越了传统的U-Net方法。EAM引入了一个名为Ψ-DiT的新模块,它有效地引导DiT进行图像恢复。此外,本文还提出了一种渐进式遮掩图像建模策略,以充分利用T2I模型的先验指导能力,并增强其推广性。此外,本文还提出了一种基于主体感知的提示生成策略,该策略采用强大的多模态模型进行上下文学习框架。实验表明,EAM在多数据集上取得了最先进的成果,在定量指标和视觉质量上均优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- EAM模型是一种新型的盲超分辨率(BSR)方法,基于预训练的文本到图像扩散模型。
- EAM利用扩散变压器(DiT)技术超越传统的U-Net模型,提高了图像恢复的性能。
- Ψ-DiT模块的引入有效地引导了DiT进行图像恢复过程。
- 采用了渐进式遮掩图像建模策略,以提高模型的先验指导能力和泛化性能。
- 提出了一种基于主体感知的提示生成策略,采用多模态模型和上下文学习框架进行优化。
- EAM在多个数据集上取得了最先进的成果表现。
点此查看论文截图

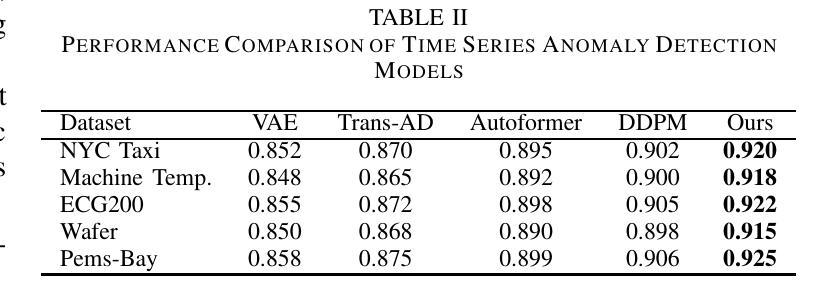
Research on Anomaly Detection Methods Based on Diffusion Models
Authors:Yi Chen
Anomaly detection is a fundamental task in machine learning and data mining, with significant applications in cybersecurity, industrial fault diagnosis, and clinical disease monitoring. Traditional methods, such as statistical modeling and machine learning-based approaches, often face challenges in handling complex, high-dimensional data distributions. In this study, we explore the potential of diffusion models for anomaly detection, proposing a novel framework that leverages the strengths of diffusion probabilistic models (DPMs) to effectively identify anomalies in both image and audio data. The proposed method models the distribution of normal data through a diffusion process and reconstructs input data via reverse diffusion, using a combination of reconstruction errors and semantic discrepancies as anomaly indicators. To enhance the framework’s performance, we introduce multi-scale feature extraction, attention mechanisms, and wavelet-domain representations, enabling the model to capture fine-grained structures and global dependencies in the data. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets, including MVTec AD and UrbanSound8K, demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art anomaly detection techniques, achieving superior accuracy and robustness across diverse data modalities. This research highlights the effectiveness of diffusion models in anomaly detection and provides a robust and efficient solution for real-world applications.
异常检测是机器学习和数据挖掘中的一项基本任务,在网络安全、工业故障诊断和临床疾病监测等领域有着广泛的应用。传统的方法,如统计建模和基于机器学习的方法,在处理复杂的高维数据分布时常常面临挑战。本研究探索了扩散模型在异常检测中的潜力,提出了一种新的框架,该框架利用扩散概率模型(DPMs)的优势,有效地识别图像和音频数据中的异常值。该方法通过扩散过程对正常数据的分布进行建模,并通过反向扩散重建输入数据,使用重建误差和语义差异作为异常指标。为了提高框架的性能,我们引入了多尺度特征提取、注意机制和波域表示,使模型能够捕捉数据的精细结构和全局依赖性。在MVTec AD和UrbanSound8K等基准数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的方法优于最新的异常检测技术,在多种数据模态上实现了较高的准确性和稳健性。该研究突出了扩散模型在异常检测中的有效性,为实际应用提供了稳健高效的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 3 table
摘要
本研究探索了扩散模型在异常检测中的潜力,提出了一种利用扩散概率模型(DPMs)优势的新框架,有效识别图像和音频数据中的异常值。该研究通过扩散过程对正常数据分布进行建模,并通过反向扩散重建输入数据,使用重建误差和语义差异作为异常指标。为提高框架性能,引入了多尺度特征提取、注意机制和小波域表示,使模型能够捕捉数据中的精细结构和全局依赖性。在MVTec AD和UrbanSound8K等基准数据集上的实验表明,该方法优于最先进的异常检测技术,在多种数据模态上实现了较高的准确性和鲁棒性。该研究突出了扩散模型在异常检测中的有效性,为实际应用提供了稳健高效的解决方案。
要点速记
- 异常检测是机器学习和数据挖掘中的基本任务,在网络安全、工业故障诊断和临床疾病监测等领域有广泛应用。
- 传统方法如统计建模和机器学习在处理复杂、高维数据分布时面临挑战。
- 本研究探索了扩散模型在异常检测中的潜力,提出了一种新的框架。
- 框架利用扩散概率模型(DPMs)通过扩散过程对正常数据建模,并通过反向扩散重建数据,使用重建误差和语义差异作为异常指标。
- 引入多尺度特征提取、注意机制和小波域表示,提高框架性能。
- 在基准数据集上的实验表明,该方法优于其他先进技术,具有高度的准确性和鲁棒性。
- 研究强调了扩散模型在异常检测中的有效性,为实际应用提供了解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

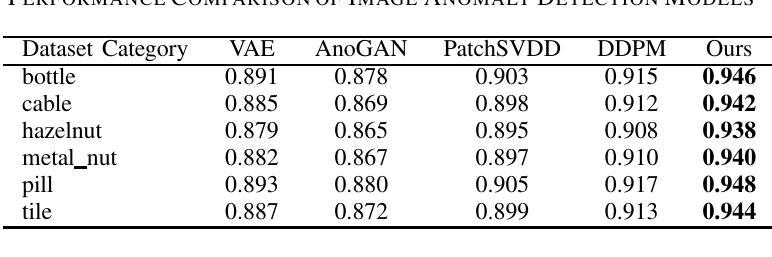
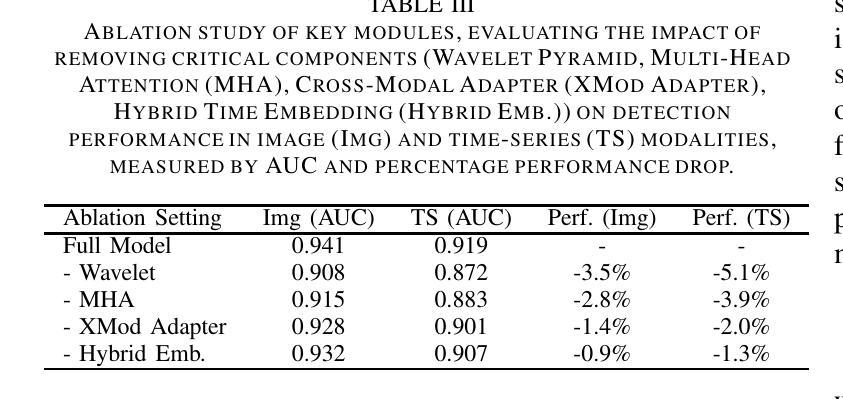
MDAA-Diff: CT-Guided Multi-Dose Adaptive Attention Diffusion Model for PET Denoising
Authors:Xiaolong Niu, Zanting Ye, Xu Han, Yanchao Huang, Hao Sun, Hubing Wu, Lijun Lu
Acquiring high-quality Positron Emission Tomography (PET) images requires administering high-dose radiotracers, which increases radiation exposure risks. Generating standard-dose PET (SPET) from low-dose PET (LPET) has become a potential solution. However, previous studies have primarily focused on single low-dose PET denoising, neglecting two critical factors: discrepancies in dose response caused by inter-patient variability, and complementary anatomical constraints derived from CT images. In this work, we propose a novel CT-Guided Multi-dose Adaptive Attention Denoising Diffusion Model (MDAA-Diff) for multi-dose PET denoising. Our approach integrates anatomical guidance and dose-level adaptation to achieve superior denoising performance under low-dose conditions. Specifically, this approach incorporates a CT-Guided High-frequency Wavelet Attention (HWA) module, which uses wavelet transforms to separate high-frequency anatomical boundary features from CT images. These extracted features are then incorporated into PET imaging through an adaptive weighted fusion mechanism to enhance edge details. Additionally, we propose the Dose-Adaptive Attention (DAA) module, a dose-conditioned enhancement mechanism that dynamically integrates dose levels into channel-spatial attention weight calculation. Extensive experiments on 18F-FDG and 68Ga-FAPI datasets demonstrate that MDAA-Diff outperforms state-of-the-art approaches in preserving diagnostic quality under reduced-dose conditions. Our code is publicly available.
获取高质量的发射正电子断层扫描(PET)图像需要注射高剂量放射性示踪剂,这增加了辐射暴露的风险。从低剂量PET(LPET)生成标准剂量PET(SPET)已成为一种可能的解决方案。然而,以往的研究主要集中在单一低剂量PET去噪上,忽视了两个关键因素:由患者间差异引起的剂量反应差异,以及从CT图像中得出的互补解剖约束。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新型的CT引导多剂量自适应注意力去噪扩散模型(MDAA-Diff),用于多剂量PET去噪。我们的方法结合了解剖指导和剂量水平适应,以在低剂量条件下实现卓越的去噪性能。具体来说,该方法采用CT引导的高频小波注意力(HWA)模块,利用小波变换从CT图像中分离出高频解剖边界特征。然后,通过自适应加权融合机制将这些提取的特征融入到PET成像中,以增强边缘细节。此外,我们提出了剂量自适应注意力(DAA)模块,这是一种剂量调节增强机制,动态地将剂量水平集成到通道空间注意力权重计算中。在18F-FDG和68Ga-FAPI数据集上的大量实验表明,MDAA-Diff在降低剂量条件下保存诊断质量方面优于现有先进技术。我们的代码公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:针对PET成像中高剂量带来的辐射风险问题,研究人员提出一种新型CT引导的多剂量自适应注意力去噪扩散模型(MDAA-Diff)。该模型结合解剖学指导和剂量水平自适应技术,在低剂量条件下实现出色的去噪性能。它通过小波变换提取CT图像的高频解剖边界特征,并融入PET成像中增强边缘细节。同时,剂量自适应注意力模块能够根据剂量水平动态调整通道空间注意力权重计算。实验证明,MDAA-Diff在减少剂量条件下能保留诊断质量,优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways:
- PET成像中需要高剂量放射线追踪剂以提高图像质量,但增加了辐射暴露风险。
- 提出一种新型CT引导的多剂量自适应注意力去噪扩散模型(MDAA-Diff),用于从低剂量PET生成标准剂量PET(SPET)。
- MDAA-Diff模型结合了解剖学指导和剂量水平自适应技术。
- 使用小波变换提取CT图像的高频解剖边界特征,并通过自适应加权融合机制融入PET成像中,以增强边缘细节。
- 剂量自适应注意力模块能根据剂量水平动态调整注意力权重计算。
- 实验证明MDAA-Diff在减少剂量条件下能保留诊断质量,优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图

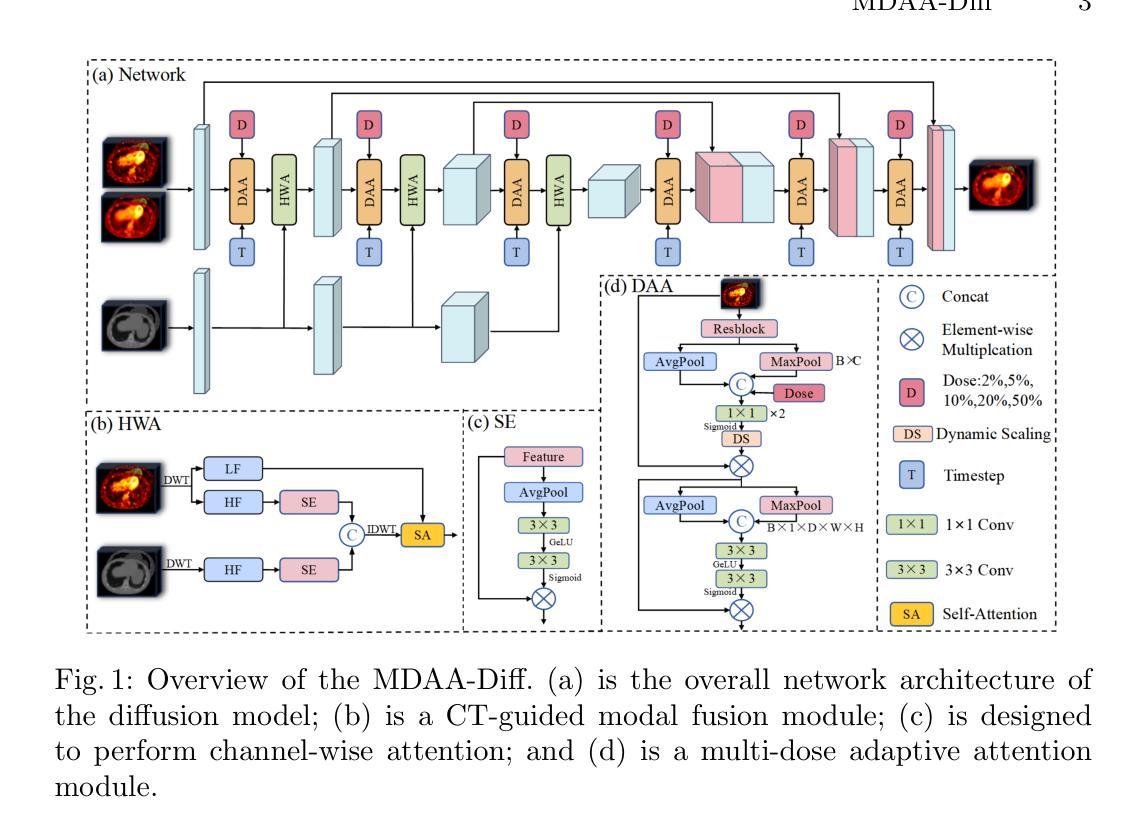
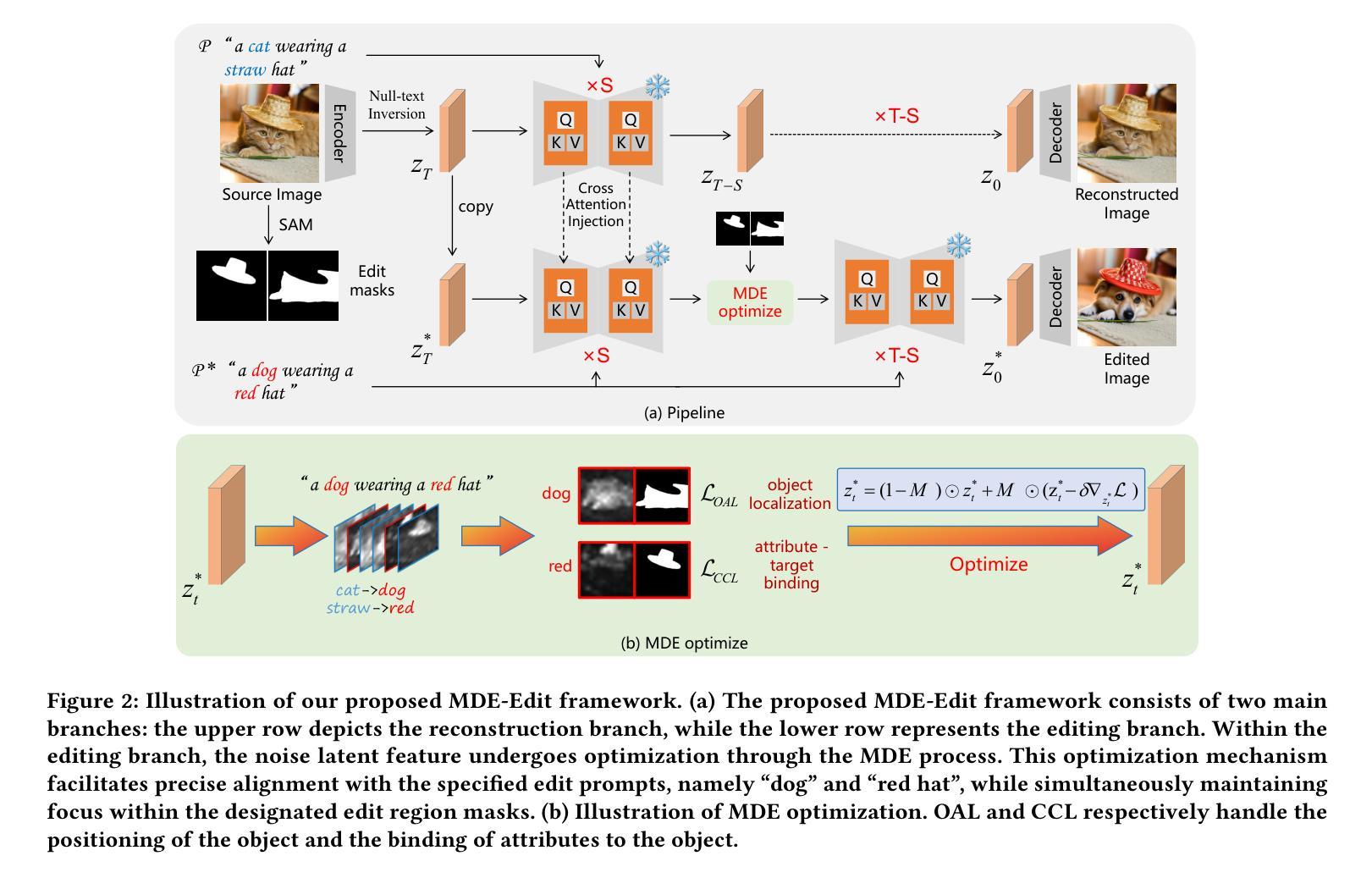
MDE-Edit: Masked Dual-Editing for Multi-Object Image Editing via Diffusion Models
Authors:Hongyang Zhu, Haipeng Liu, Bo Fu, Yang Wang
Multi-object editing aims to modify multiple objects or regions in complex scenes while preserving structural coherence. This task faces significant challenges in scenarios involving overlapping or interacting objects: (1) Inaccurate localization of target objects due to attention misalignment, leading to incomplete or misplaced edits; (2) Attribute-object mismatch, where color or texture changes fail to align with intended regions due to cross-attention leakage, creating semantic conflicts (\textit{e.g.}, color bleeding into non-target areas). Existing methods struggle with these challenges: approaches relying on global cross-attention mechanisms suffer from attention dilution and spatial interference between objects, while mask-based methods fail to bind attributes to geometrically accurate regions due to feature entanglement in multi-object scenarios. To address these limitations, we propose a training-free, inference-stage optimization approach that enables precise localized image manipulation in complex multi-object scenes, named MDE-Edit. MDE-Edit optimizes the noise latent feature in diffusion models via two key losses: Object Alignment Loss (OAL) aligns multi-layer cross-attention with segmentation masks for precise object positioning, and Color Consistency Loss (CCL) amplifies target attribute attention within masks while suppressing leakage to adjacent regions. This dual-loss design ensures localized and coherent multi-object edits. Extensive experiments demonstrate that MDE-Edit outperforms state-of-the-art methods in editing accuracy and visual quality, offering a robust solution for complex multi-object image manipulation tasks.
多对象编辑旨在在复杂的场景中修改多个对象或区域,同时保持结构连贯性。在涉及重叠或交互对象的场景中,此任务面临重大挑战:(1)由于注意力错位导致目标对象定位不准确,从而导致编辑不完整或错位;(2)属性对象不匹配,由于跨注意力泄漏,颜色或纹理变化未能与意图区域对齐,从而产生语义冲突(例如,颜色渗入非目标区域)。现有方法难以应对这些挑战:依赖全局跨注意力机制的方法受到注意力稀释和对象间空间干扰的影响,而基于掩膜的方法由于在多对象场景中的特征纠缠而无法将属性绑定到几何精确的区域。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了一种无需训练、在推理阶段进行优化的方法,能够在复杂的多对象场景中实现精确的定位图像操作,名为MDE-Edit。MDE-Edit通过两个关键损失优化扩散模型中的噪声潜在特征:对象对齐损失(OAL)将多层跨注意力与分割掩膜对齐,以实现精确的对象定位;颜色一致性损失(CCL)在掩膜内放大目标属性注意力,同时抑制泄漏到相邻区域。这种双重损失设计确保了局部化和连贯的多对象编辑。大量实验表明,MDE-Edit在编辑准确性和视觉质量方面优于最新方法,为复杂的多对象图像操作任务提供了稳健的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 7 figures
Summary
本文提出了在复杂多对象场景中进行精确局部图像编辑的方法MDE-Edit,旨在解决多对象编辑中的挑战,如目标对象定位不准确、属性对象不匹配等问题。通过采用对象对齐损失(OAL)和颜色一致性损失(CCL)来优化扩散模型中的噪声潜在特征,实现精准的对象定位及属性编辑,同时抑制对相邻区域的干扰。实验证明,MDE-Edit在编辑准确性和视觉质量上超越了现有方法,为复杂多对象图像操作任务提供了稳健的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 多对象编辑面临目标对象定位不准确和属性对象不匹配等挑战。
- 现有方法在处理这些挑战时存在局限性,如全局交叉注意机制面临注意力分散和空间干扰问题,而基于掩膜的方法在复杂多对象场景中特征纠缠。
- MDE-Edit通过优化扩散模型中的噪声潜在特征来解决这些问题。
- MDE-Edit采用对象对齐损失(OAL)进行精准对象定位。
- 颜色一致性损失(CCL)用于放大目标属性注意力,同时抑制相邻区域的泄漏。
- 双损失设计确保局部化和连贯的多对象编辑。
点此查看论文截图


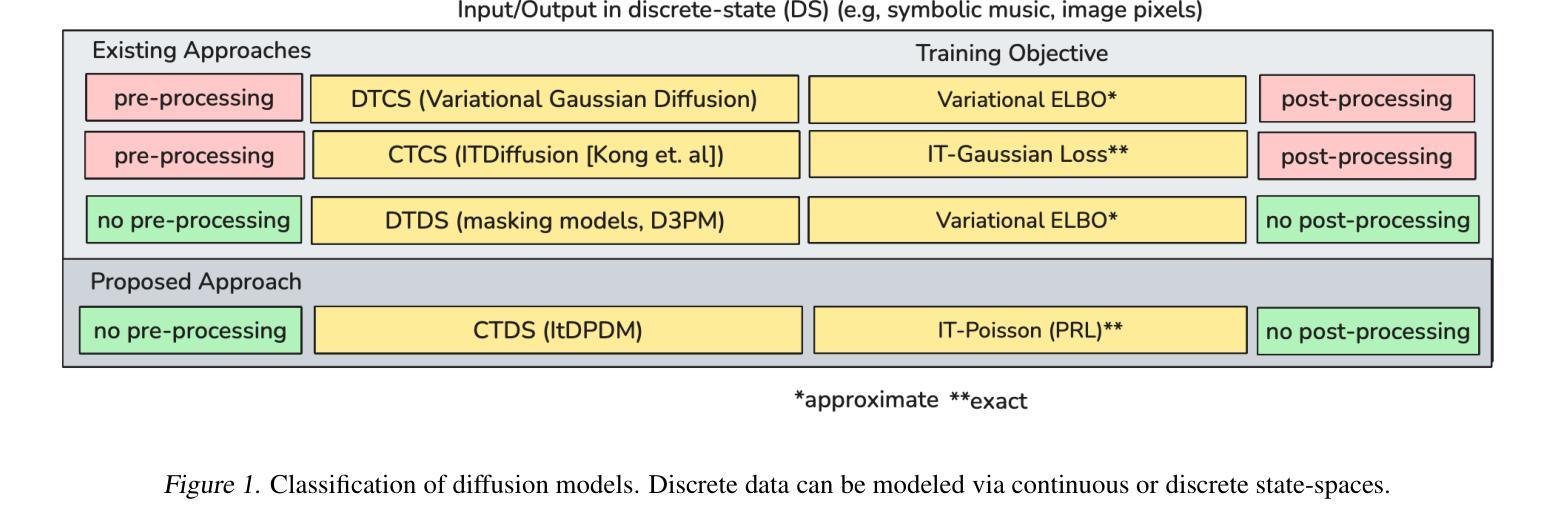
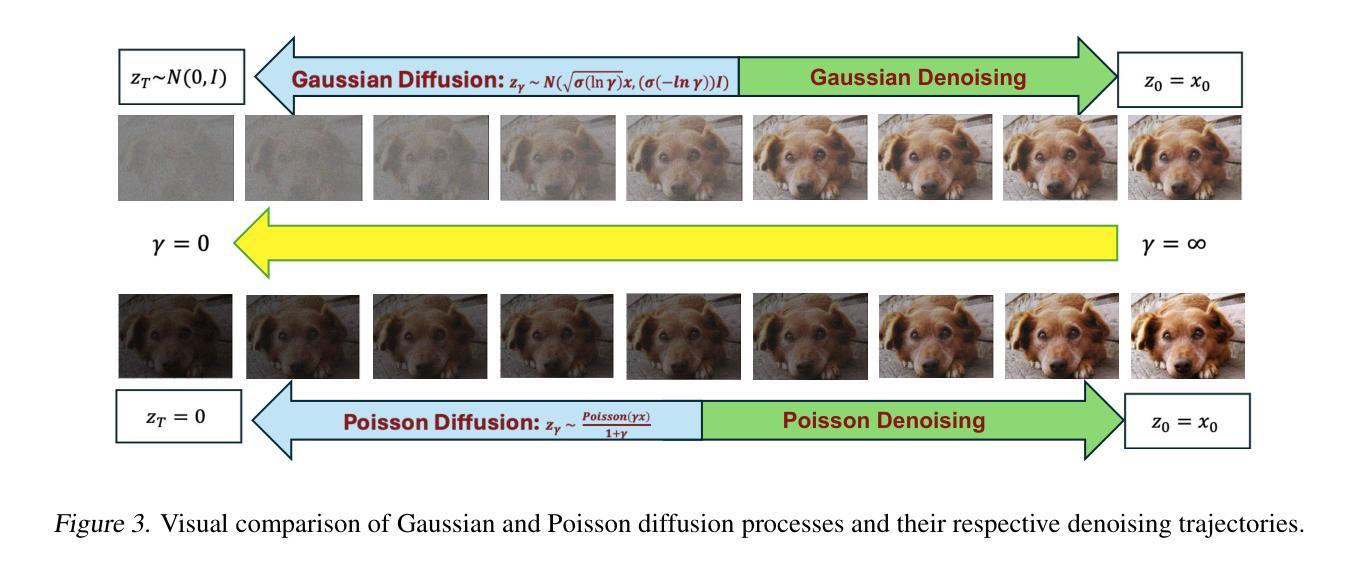
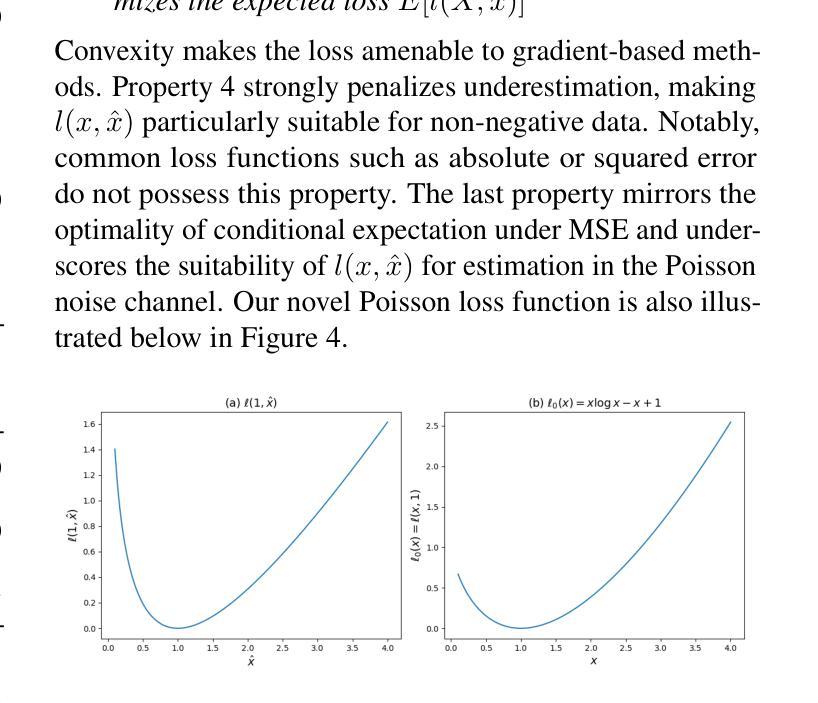
ItDPDM: Information-Theoretic Discrete Poisson Diffusion Model
Authors:Sagnik Bhattacharya, Abhiram R. Gorle, Ahmed Mohsin, Ahsan Bilal, Connor Ding, Amit Kumar Singh Yadav, Tsachy Weissman
Existing methods for generative modeling of discrete data, such as symbolic music tokens, face two primary challenges: (1) they either embed discrete inputs into continuous state-spaces or (2) rely on variational losses that only approximate the true negative log-likelihood. Previous efforts have individually targeted these limitations. While information-theoretic Gaussian diffusion models alleviate the suboptimality of variational losses, they still perform modeling in continuous domains. In this work, we introduce the Information-Theoretic Discrete Poisson Diffusion Model (ItDPDM), which simultaneously addresses both limitations by directly operating in a discrete state-space via a Poisson diffusion process inspired by photon arrival processes in camera sensors. We introduce a novel Poisson Reconstruction Loss (PRL) and derive an exact relationship between PRL and the true negative log-likelihood, thereby eliminating the need for approximate evidence lower bounds. Experiments conducted on the Lakh MIDI symbolic music dataset and the CIFAR-10 image benchmark demonstrate that ItDPDM delivers significant improvements, reducing test NLL by up to 80% compared to prior baselines, while also achieving faster convergence.
现有针对离散数据(如符号音乐标记)生成建模的方法面临两个主要挑战:(1)它们要么将离散输入嵌入到连续状态空间中,要么(2)依赖于仅近似真实负对数似然的变化损失。之前的努力已经分别针对这些局限性进行了改进。虽然信息理论高斯扩散模型缓解了变化损失的次优性,但它们仍然在连续域中进行建模。在这项工作中,我们引入了信息理论离散泊松扩散模型(ItDPDM),该模型通过受相机传感器中光子到达过程启发的泊松扩散过程,直接在离散状态空间中解决这两个局限性。我们引入了一种新型的泊松重建损失(PRL),并推导了PRL和真实负对数似然之间的精确关系,从而消除了对近似证据下界的需求。在Lakh MIDI符号音乐数据集和CIFAR-10图像基准测试上进行的实验表明,ItDPDM提供了显著改进,与先前基准相比,测试NLL降低了高达80%,同时实现了更快的收敛速度。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Pre-print
Summary
本文介绍了信息理论离散泊松扩散模型(ItDPDM),该模型通过泊松扩散过程直接在离散状态空间中进行操作,解决了当前生成离散数据建模的两个主要挑战。ItDPDM引入了新型的泊松重建损失(PRL),并与真正的负对数似然建立了精确关系,无需使用近似的证据下界。在Lakh MIDI符号音乐数据集和CIFAR-10图像基准测试上进行的实验表明,ItDPDM在测试NLL上较先前基线降低了高达80%,同时实现了更快的收敛速度。
Key Takeaways
- ItDPDM解决了生成离散数据建模的两个主要挑战:嵌入离散输入到连续状态空间和使用变分损失来近似真实负对数似然。
- ItDPDM通过泊松扩散过程直接在离散状态空间中进行操作,受到相机传感器中光子到达过程的启发。
- ItDPDM引入了新型的泊松重建损失(PRL)。
- PRL和真实负对数似然之间建立了精确关系,无需使用近似的证据下界。
- 在Lakh MIDI符号音乐数据集上的实验表明,ItDPDM在测试NLL上较先前方法降低了显著比例。
- 在CIFAR-10图像基准测试上,ItDPDM实现了更快的收敛速度。
- ItDPDM的优异性能证明了其在实际应用中的潜力。
点此查看论文截图


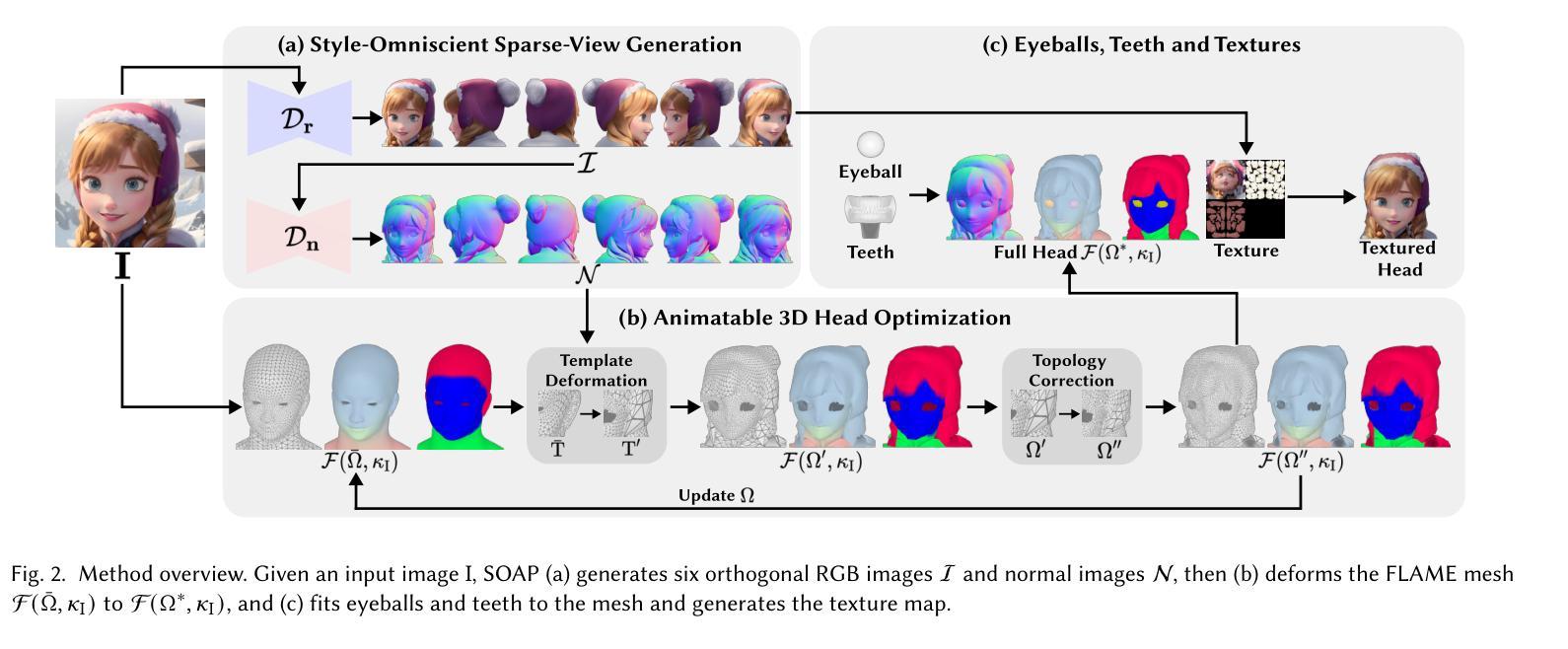
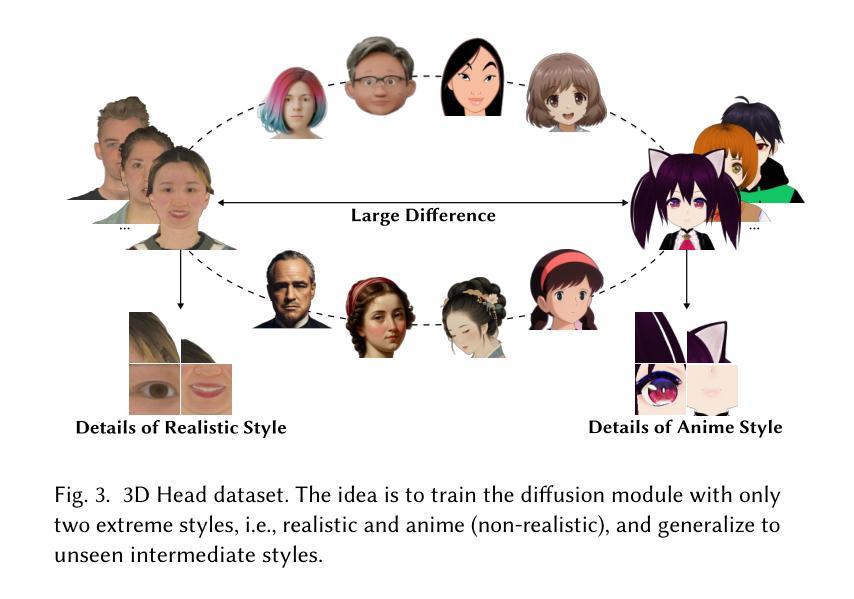
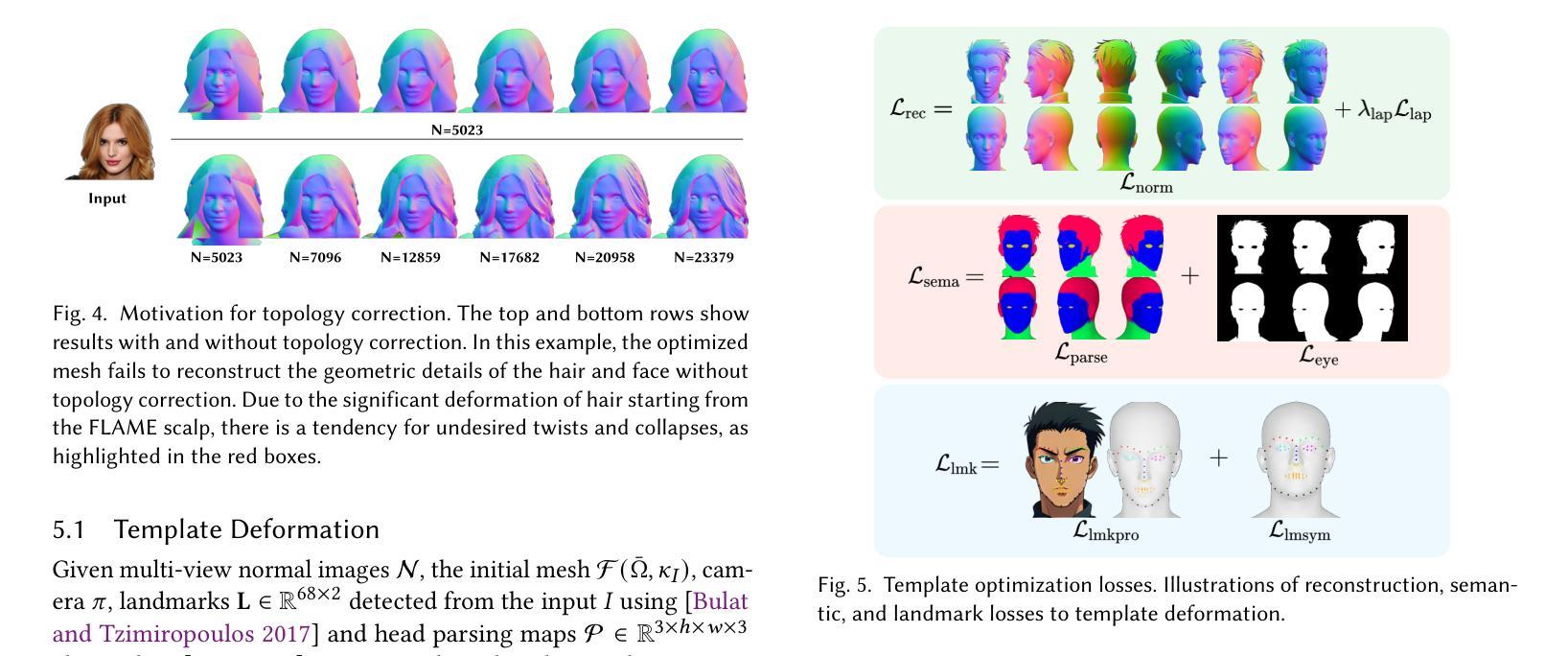
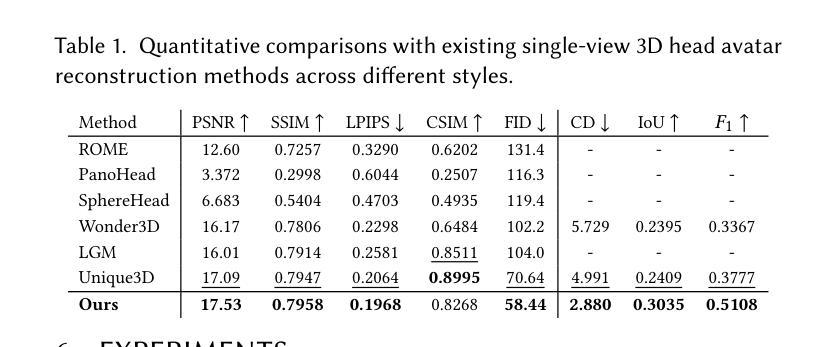
SOAP: Style-Omniscient Animatable Portraits
Authors:Tingting Liao, Yujian Zheng, Adilbek Karmanov, Liwen Hu, Leyang Jin, Yuliang Xiu, Hao Li
Creating animatable 3D avatars from a single image remains challenging due to style limitations (realistic, cartoon, anime) and difficulties in handling accessories or hairstyles. While 3D diffusion models advance single-view reconstruction for general objects, outputs often lack animation controls or suffer from artifacts because of the domain gap. We propose SOAP, a style-omniscient framework to generate rigged, topology-consistent avatars from any portrait. Our method leverages a multiview diffusion model trained on 24K 3D heads with multiple styles and an adaptive optimization pipeline to deform the FLAME mesh while maintaining topology and rigging via differentiable rendering. The resulting textured avatars support FACS-based animation, integrate with eyeballs and teeth, and preserve details like braided hair or accessories. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of our method over state-of-the-art techniques for both single-view head modeling and diffusion-based generation of Image-to-3D. Our code and data are publicly available for research purposes at https://github.com/TingtingLiao/soap.
从单张图片创建可动画的3D头像仍然存在挑战,因为涉及到风格(写实、卡通、动漫)的局限,以及处理配件和发型等难度。虽然3D扩散模型推动了单视图重建在一般物体上的应用,但输出往往缺乏动画控制或由于领域差距而产生伪影。我们提出了SOAP,这是一个风格全面的框架,可以从任何肖像生成装配、拓扑一致的头像。我们的方法利用了在24K 3D头像上训练的多元视图扩散模型,采用自适应优化管道来变形FLAME网格,同时通过可微分渲染保持拓扑和装配。得到的纹理头像支持基于FACs的动画,可以与眼球和牙齿集成,并保留如辫子头发或配件等细节。大量实验表明,我们的方法在单视图头部建模和基于扩散的图像到3D生成方面均优于现有技术。我们的代码和数据可供研究目的在https://github.com/TingtingLiao/soap上公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于单幅图像创建可动画的3D头像面临风格多样性和配件处理难题。最新3D扩散模型虽提升了一般物体的单视角重建效果,但在创建动画控制和克服域差异时仍有局限。本研究提出了SOAP框架,能够生成可动的、结构一致的头像,适用于各种肖像图像。通过利用多视角扩散模型与24K 3D头像数据库训练,结合自适应优化管道和可微分渲染技术,实现FLAME网格变形并保持拓扑结构。生成的纹理头像支持基于面部动作编码系统的动画,能融入眼球和牙齿细节,并保留如辫子或配件等细节。实验证明,此方法在单视角头部建模和基于扩散的图像到3D转换领域均优于现有技术。相关代码和数据已公开发布以供研究使用。
Key Takeaways
- SOAP框架能够生成多种风格的3D头像,解决了单图像创建动画3D头像的风格多样性难题。
- 该方法利用多视角扩散模型训练,提高了对一般物体的单视角重建效果。
- SOAP通过自适应优化管道和可微分渲染技术,实现了FLAME网格变形并保持拓扑结构一致性。
- 生成的头像支持基于面部动作编码系统的动画,能自然融入眼球和牙齿细节。
- 该方法能够保留头像的精细细节,如辫子、配件等。
- 实验证明,SOAP在单视角头部建模和图像到3D转换方面均优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图

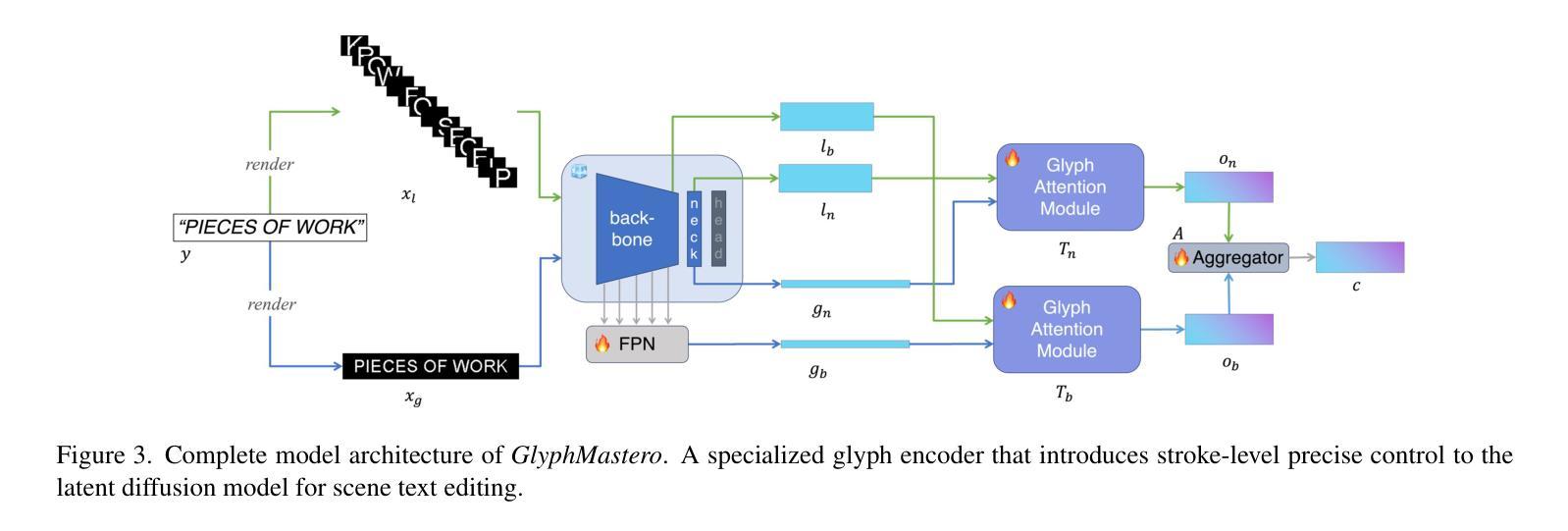
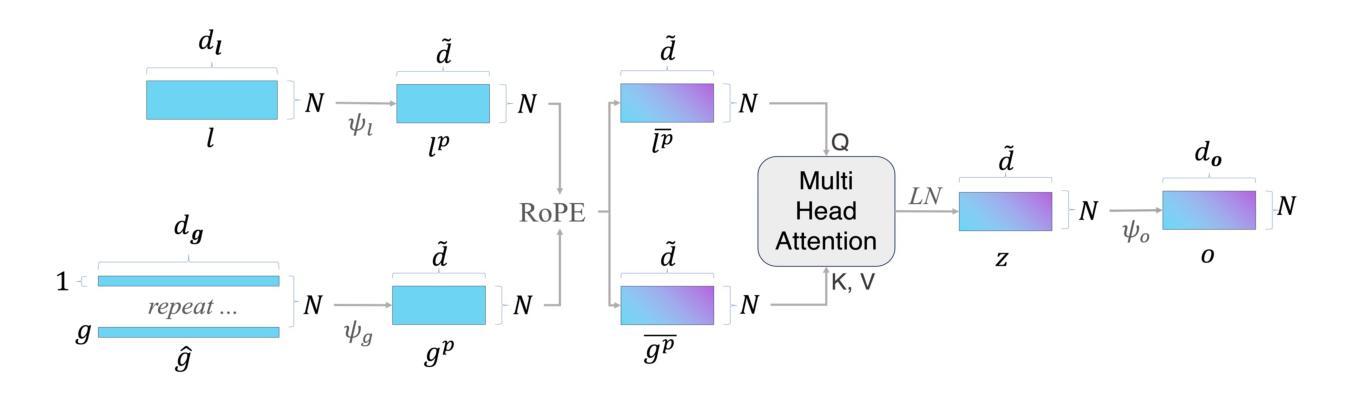
GlyphMastero: A Glyph Encoder for High-Fidelity Scene Text Editing
Authors:Tong Wang, Ting Liu, Xiaochao Qu, Chengjing Wu, Luoqi Liu, Xiaolin Hu
Scene text editing, a subfield of image editing, requires modifying texts in images while preserving style consistency and visual coherence with the surrounding environment. While diffusion-based methods have shown promise in text generation, they still struggle to produce high-quality results. These methods often generate distorted or unrecognizable characters, particularly when dealing with complex characters like Chinese. In such systems, characters are composed of intricate stroke patterns and spatial relationships that must be precisely maintained. We present GlyphMastero, a specialized glyph encoder designed to guide the latent diffusion model for generating texts with stroke-level precision. Our key insight is that existing methods, despite using pretrained OCR models for feature extraction, fail to capture the hierarchical nature of text structures - from individual strokes to stroke-level interactions to overall character-level structure. To address this, our glyph encoder explicitly models and captures the cross-level interactions between local-level individual characters and global-level text lines through our novel glyph attention module. Meanwhile, our model implements a feature pyramid network to fuse the multi-scale OCR backbone features at the global-level. Through these cross-level and multi-scale fusions, we obtain more detailed glyph-aware guidance, enabling precise control over the scene text generation process. Our method achieves an 18.02% improvement in sentence accuracy over the state-of-the-art multi-lingual scene text editing baseline, while simultaneously reducing the text-region Fr'echet inception distance by 53.28%.
场景文本编辑是图像编辑的一个子领域,它要求在修改图像中的文本时保持与周围环境的风格一致性和视觉连贯性。虽然基于扩散的方法在文本生成方面展现出了一定的潜力,但它们仍然难以产生高质量的结果。这些方法通常会产生扭曲或无法识别的字符,特别是当处理中文等复杂字符时。在这样的系统中,字符由复杂的笔画模式和空间关系组成,必须精确保持。我们提出了GlyphMastero,这是一种专门的字形编码器,旨在引导潜在扩散模型以笔画级精度生成文本。我们的关键见解是,现有方法虽然使用预训练的OCR模型进行特征提取,但未能捕捉文本结构的层次性——从单个笔画到笔画级交互再到整体字符级结构。为了解决这一问题,我们的字形编码器通过新型字形注意模块明确地建模并捕捉局部级别单个字符与全局级别文本行之间的跨级交互。同时,我们的模型实现了特征金字塔网络,以在全局级别融合多尺度OCR主干特征。通过这些跨级别和多尺度融合,我们获得了更详细的字形感知指导,实现对场景文本生成过程的精确控制。我们的方法在句子准确性方面比最新的多语言场景文本编辑基线提高了18.02%,同时降低了文本区域Fr’echet inception距离53.28%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025
Summary
本文介绍了场景文本编辑的挑战,提出了一种基于扩散模型的文本生成方法GlyphMastero。该方法通过专门的字形编码器指导潜在扩散模型,以笔画级别的精度生成文本。其关键洞察力是现有方法未能捕捉文本的层次结构,如从单个笔画到笔画级交互再到整体字符级结构。为解决这一问题,GlyphMastero通过其新颖的字形注意力模块显式地建模和捕捉局部级别的单个字符和全局级别的文本行之间的跨级别交互。此外,该方法实现了一个特征金字塔网络,以在全局层面上融合多尺度OCR主干特征。通过这些跨级别和多尺度的融合,GlyphMastero获得了更详细的字形感知指导,实现对场景文本生成过程的精确控制。该方法在句子准确度上较当前最佳的多语言场景文本编辑基线提高了18.02%,同时降低了文本区域的Fréchet inception距离达53.28%。
Key Takeaways
- 场景文本编辑是图像编辑的一个子领域,旨在修改图像中的文本,同时保持风格一致性和与周围环境的视觉连贯性。
- 扩散模型在文本生成方面显示出潜力,但在处理复杂字符(如中文)时生成结果常出现失真或无法识别。
- GlyphMastero是一个基于扩散模型的专门字形编码器,旨在以笔画级别的精度生成文本。
- GlyphMastero通过字形注意力模块显式地建模和捕捉文本的层次结构。
- GlyphMastero实现了特征金字塔网络,融合多尺度OCR主干特征,以在全局层面上获得更详细的字形感知指导。
- GlyphMastero在句子准确度上较现有方法有明显提升。
点此查看论文截图


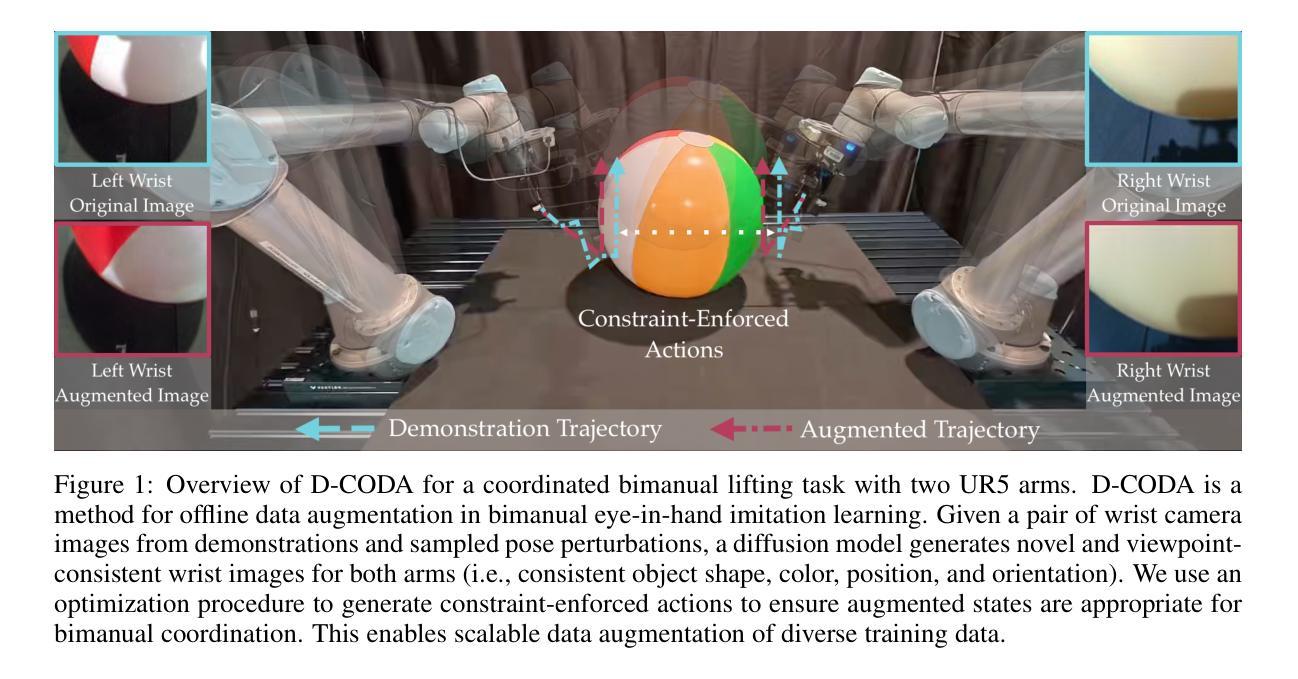
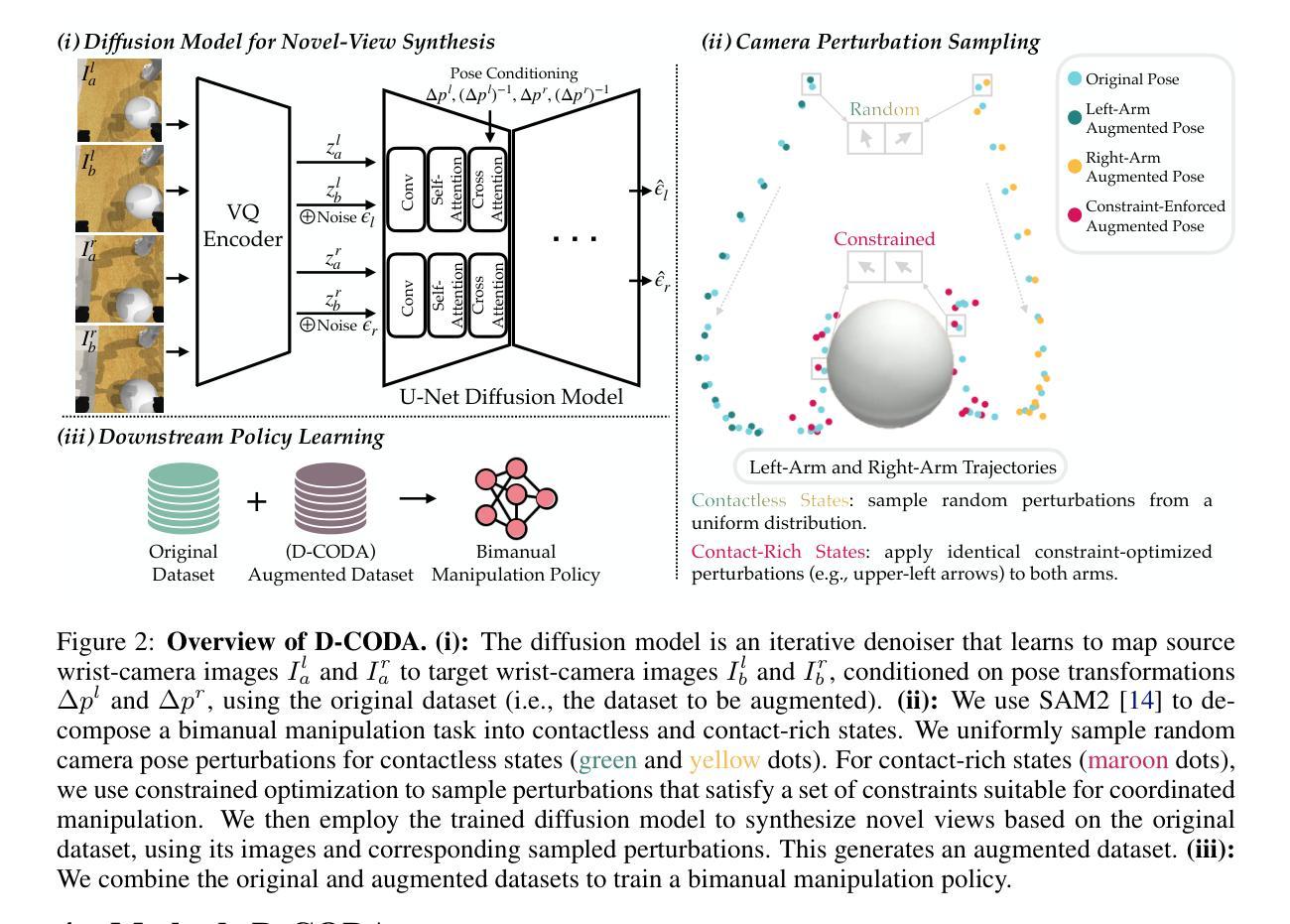
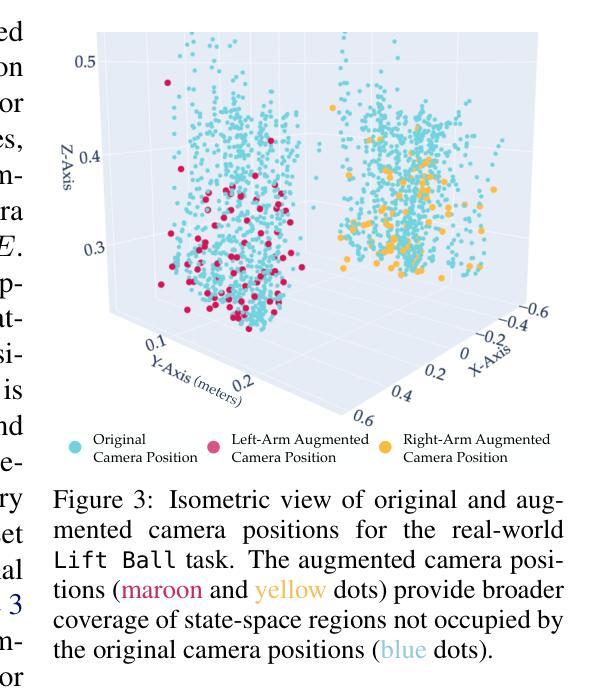
D-CODA: Diffusion for Coordinated Dual-Arm Data Augmentation
Authors:I-Chun Arthur Liu, Jason Chen, Gaurav Sukhatme, Daniel Seita
Learning bimanual manipulation is challenging due to its high dimensionality and tight coordination required between two arms. Eye-in-hand imitation learning, which uses wrist-mounted cameras, simplifies perception by focusing on task-relevant views. However, collecting diverse demonstrations remains costly, motivating the need for scalable data augmentation. While prior work has explored visual augmentation in single-arm settings, extending these approaches to bimanual manipulation requires generating viewpoint-consistent observations across both arms and producing corresponding action labels that are both valid and feasible. In this work, we propose Diffusion for COordinated Dual-arm Data Augmentation (D-CODA), a method for offline data augmentation tailored to eye-in-hand bimanual imitation learning that trains a diffusion model to synthesize novel, viewpoint-consistent wrist-camera images for both arms while simultaneously generating joint-space action labels. It employs constrained optimization to ensure that augmented states involving gripper-to-object contacts adhere to constraints suitable for bimanual coordination. We evaluate D-CODA on 5 simulated and 3 real-world tasks. Our results across 2250 simulation trials and 300 real-world trials demonstrate that it outperforms baselines and ablations, showing its potential for scalable data augmentation in eye-in-hand bimanual manipulation. Our project website is at: https://dcodaaug.github.io/D-CODA/.
学习双手协调操作是一项挑战,因为它具有高维度和需要两只手臂紧密协调的特点。眼在手上的模仿学习使用手腕安装的相机,通过专注于任务相关视角来简化感知。然而,收集各种示范仍然成本高昂,这激发了对可扩展数据增强的需求。虽然先前的工作已经在单臂设置中考虑了视觉增强,但将这些方法扩展到双手操作需要生成两只手臂的视角一致的观察结果,并产生既有效又可行的相应动作标签。在这项工作中,我们提出了用于眼在手上的双手模仿学习的数据增强方法——扩散协调双臂数据增强(D-CODA)。这是一种离线数据增强方法,训练扩散模型合成新颖、视角一致的两臂手腕相机图像,同时生成关节空间动作标签。它采用约束优化,确保涉及夹持器与物体接触点的增强状态符合双手协调的约束条件。我们在五个模拟任务和三个真实世界任务上评估了D-CODA。在2250次模拟试验和300次真实试验的结果表明,它在基线测试和消融测试中表现优越,显示出在眼在手上的双手操作中的可扩展数据增强的潜力。我们的项目网站地址为:https://dcodaaug.github.io/D-CODA/。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
眼手协同模仿学习通过手腕安装的相机简化感知过程,聚焦于任务相关视角。但收集多样化演示成本高昂,需要可扩展的数据增强技术。针对眼手协同双臂操作的数据增强问题,本文提出一种名为Diffusion for COordinated Dual-arm Data Augmentation(D-CODA)的方法。该方法训练扩散模型合成新颖、视角一致的双臂手腕相机图像,同时生成关节空间动作标签。采用约束优化确保增强状态中的夹持器与物体接触符合双臂协同操作的约束条件。在模拟和真实任务上的评估显示,D-CODA表现优于基准方法和消融实验,显示出其在眼手协同双臂操作中的数据增强的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 眼手模仿学习面临的挑战包括高维度和双臂紧密协调的需求。
- 数据收集成本高昂,需要可扩展的数据增强技术来解决这一问题。
- D-CODA方法针对眼手协同双臂操作的数据增强进行定制。
- D-CODA训练扩散模型来合成新颖、视角一致的双臂图像。
- 该方法同时生成关节空间动作标签,确保动作的有效性和可行性。
- 通过约束优化,确保合成的数据与双臂协同操作的实际约束一致。
点此查看论文截图

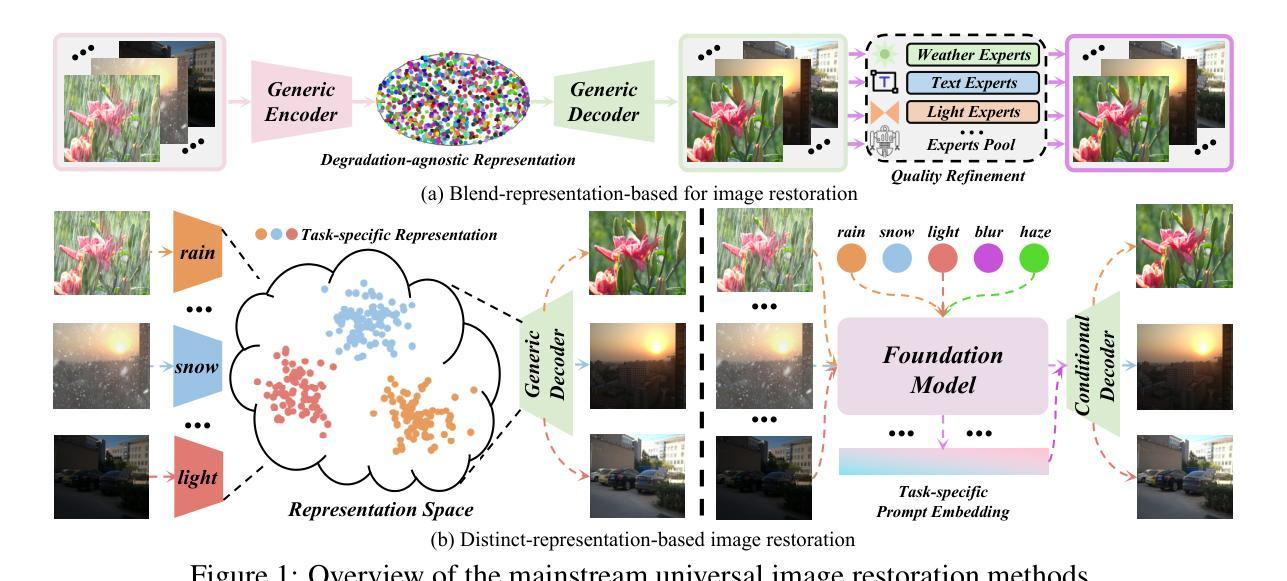
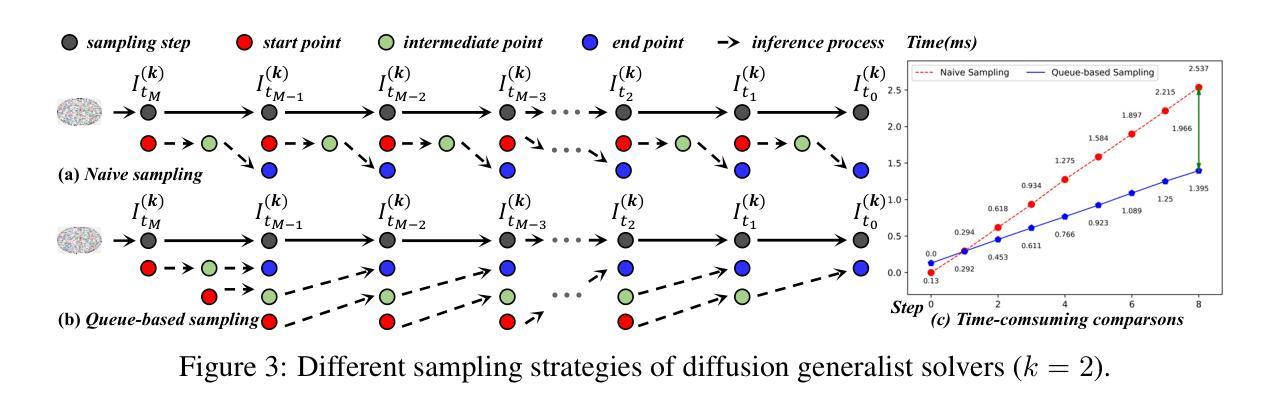
DGSolver: Diffusion Generalist Solver with Universal Posterior Sampling for Image Restoration
Authors:Hebaixu Wang, Jing Zhang, Haonan Guo, Di Wang, Jiayi Ma, Bo Du
Diffusion models have achieved remarkable progress in universal image restoration. While existing methods speed up inference by reducing sampling steps, substantial step intervals often introduce cumulative errors. Moreover, they struggle to balance the commonality of degradation representations and restoration quality. To address these challenges, we introduce \textbf{DGSolver}, a diffusion generalist solver with universal posterior sampling. We first derive the exact ordinary differential equations for generalist diffusion models and tailor high-order solvers with a queue-based accelerated sampling strategy to improve both accuracy and efficiency. We then integrate universal posterior sampling to better approximate manifold-constrained gradients, yielding a more accurate noise estimation and correcting errors in inverse inference. Extensive experiments show that DGSolver outperforms state-of-the-art methods in restoration accuracy, stability, and scalability, both qualitatively and quantitatively. Code and models will be available at https://github.com/MiliLab/DGSolver.
扩散模型在通用图像修复方面取得了显著的进步。虽然现有方法通过减少采样步骤来加速推理,但较大的步骤间隔通常会引入累积误差。此外,它们很难在退化表示的共同性和修复质量之间取得平衡。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了DGSolver,这是一种带有通用后验采样的扩散通用求解器。我们首先为通用扩散模型推导出精确的常微分方程,并使用基于队列的加速采样策略定制高阶求解器,以提高准确性和效率。然后,我们融入通用后验采样,以更好地近似流形约束梯度,从而得到更准确的噪声估计并纠正反向推理中的错误。大量实验表明,无论是在定性还是定量上,DGSolver在修复准确性、稳定性和可扩展性方面都优于最新方法。相关代码和模型将在https://github.com/MiliLab/DGSolver上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:针对通用扩散模型在图像恢复中的挑战,提出了名为DGSolver的通用扩散求解器,采用精确常微分方程、高阶求解器和基于队列的加速采样策略,提高准确性和效率。同时引入通用后采样以更好地近似流形约束梯度,改善噪声估计和反向推理中的误差。实验证明,DGSolver在恢复准确性、稳定性和可扩展性方面均优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways:
- 扩散模型在通用图像恢复中取得了显著进展。
- 现有方法通过减少采样步骤来加速推理,但会导致累积误差。
- 提出了名为DGSolver的通用扩散求解器,采用精确常微分方程和高阶求解器。
- DGSolver使用基于队列的加速采样策略,以提高准确性和效率。
- 引入通用后采样以更好地近似流形约束梯度。
- DGSolver改善了噪声估计和反向推理中的误差。
点此查看论文截图

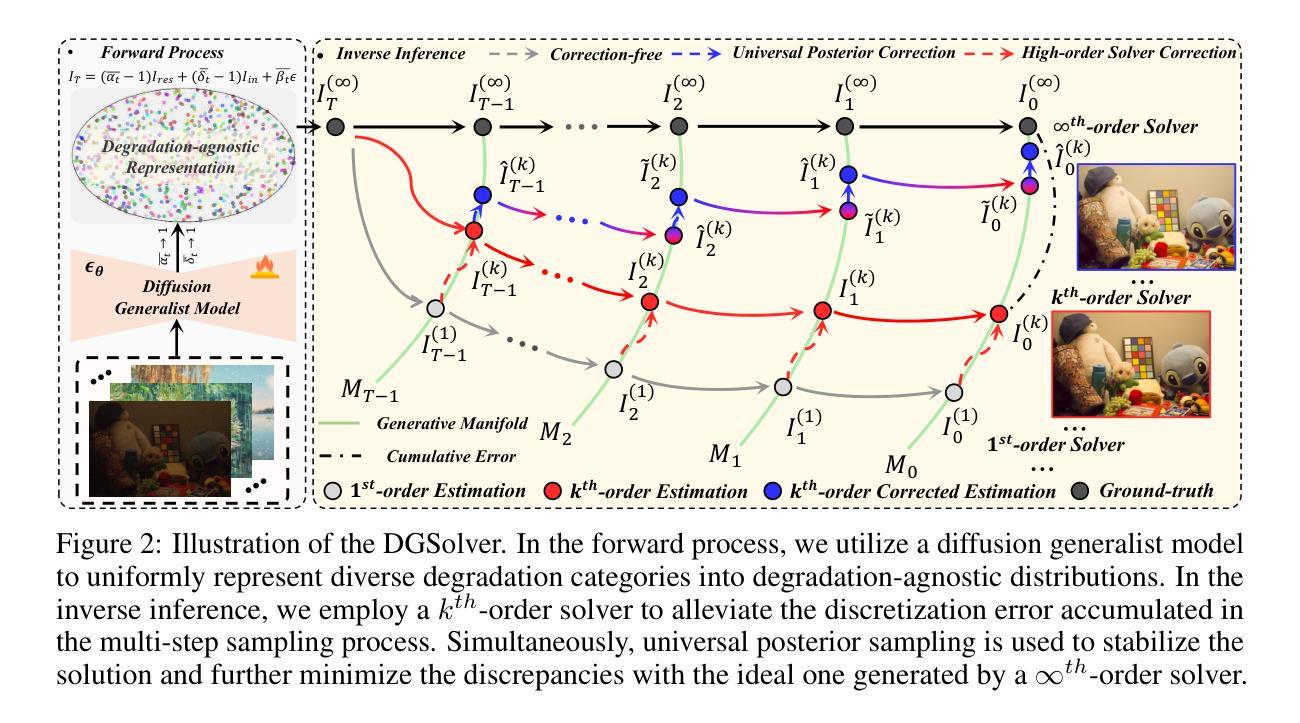
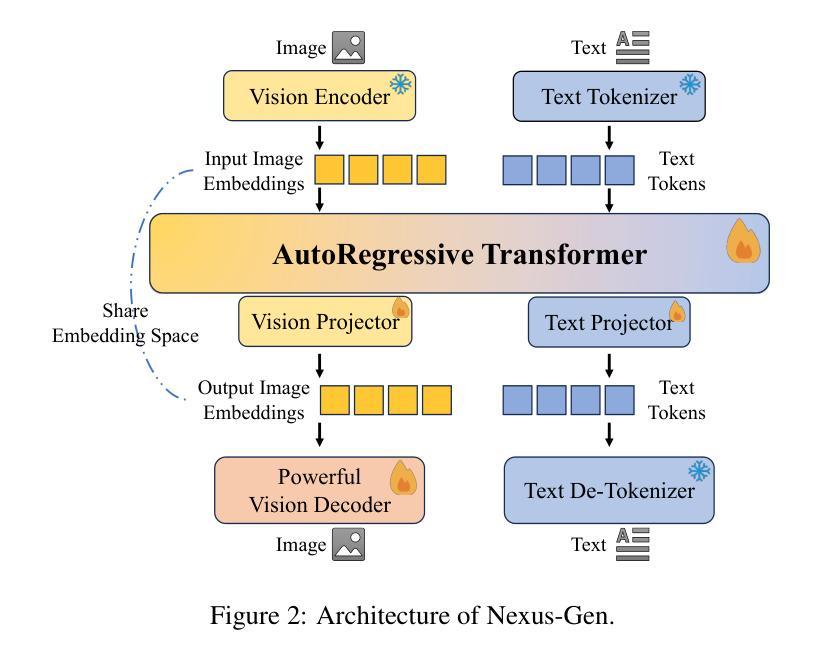
Nexus-Gen: A Unified Model for Image Understanding, Generation, and Editing
Authors:Hong Zhang, Zhongjie Duan, Xingjun Wang, Yuze Zhao, Weiyi Lu, Zhipeng Di, Yixuan Xu, Yingda Chen, Yu Zhang
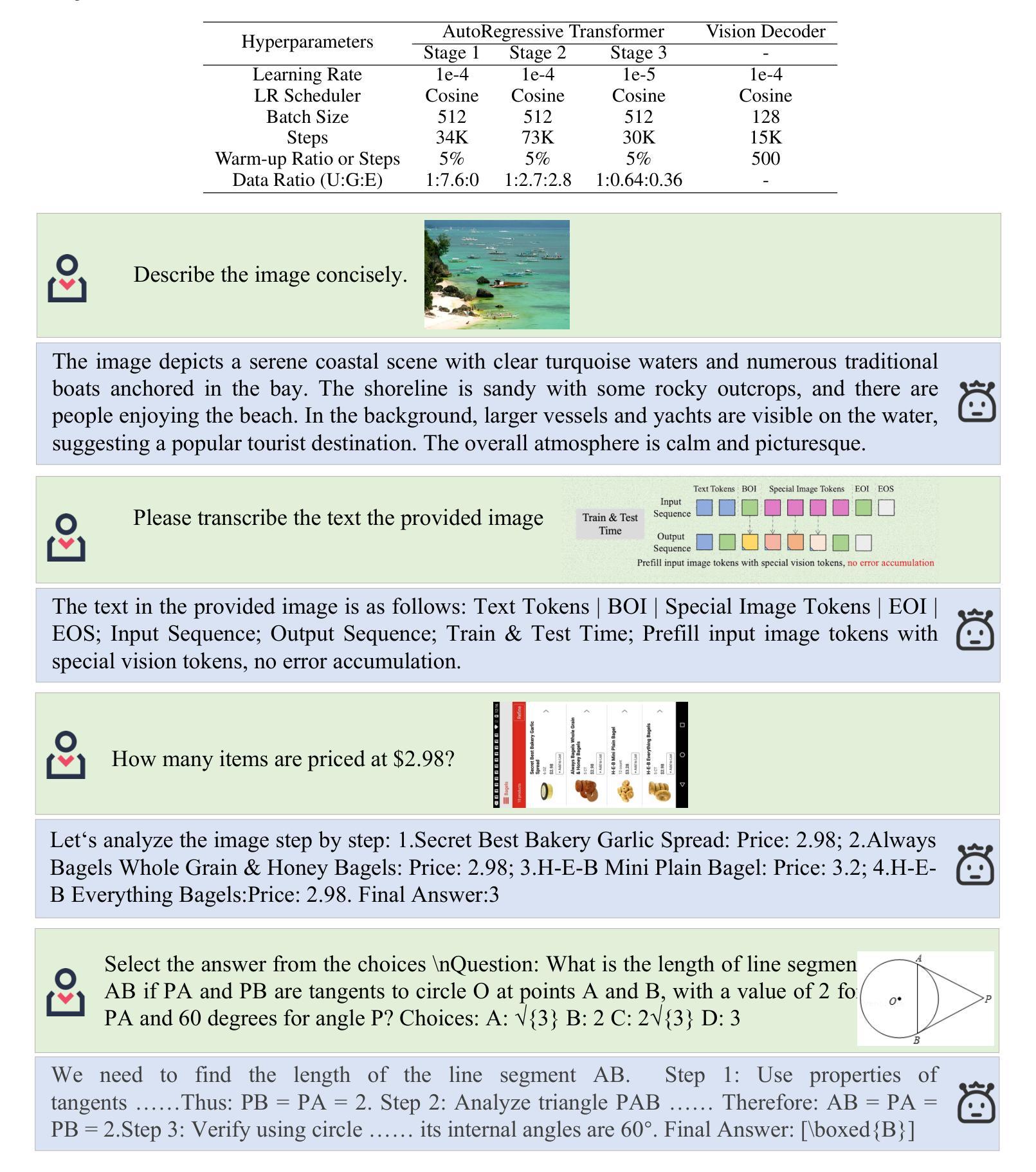
Unified multimodal large language models (MLLMs) aim to integrate multimodal understanding and generation abilities through a single framework. Despite their versatility, existing open-source unified models exhibit performance gaps against domain-specific architectures. To bridge this gap, we present Nexus-Gen, a unified model that synergizes the language reasoning capabilities of LLMs with the image synthesis power of diffusion models. To align the embedding space of the LLM and diffusion model, we conduct a dual-phase alignment training process. (1) The autoregressive LLM learns to predict image embeddings conditioned on multimodal inputs, while (2) the vision decoder is trained to reconstruct high-fidelity images from these embeddings. During training the LLM, we identified a critical discrepancy between the autoregressive paradigm’s training and inference phases, where error accumulation in continuous embedding space severely degrades generation quality. To avoid this issue, we introduce a prefilled autoregression strategy that prefills input sequence with position-embedded special tokens instead of continuous embeddings. Through dual-phase training, Nexus-Gen has developed the integrated capability to comprehensively address the image understanding, generation and editing tasks. All models, datasets, and codes are published at https://github.com/modelscope/Nexus-Gen.git to facilitate further advancements across the field.
统一多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)旨在通过单一框架整合多模态理解和生成能力。尽管它们具有多功能性,但现有的开源统一模型与领域特定架构之间存在性能差距。为了弥补这一差距,我们推出了Nexus-Gen,这是一款将大型语言模型的语言推理能力与扩散模型的图像合成能力相结合的统一模型。为了对齐大型语言模型和扩散模型的嵌入空间,我们进行了双阶段对齐训练过程。(1) 自回归大型语言模型学习根据多模态输入预测图像嵌入,而(2)视觉解码器则训练从这些嵌入重建高保真图像。在训练大型语言模型的过程中,我们发现自回归范式的训练阶段和推理阶段之间存在关键差异,连续嵌入空间中的误差累积会严重降低生成质量。为了避免这个问题,我们引入了一种预填充自回归策略,该策略用位置嵌入的特殊令牌预填充输入序列,而不是连续嵌入。通过双阶段训练,Nexus-Gen已具备全面解决图像理解、生成和编辑任务的综合能力。所有模型、数据集和代码都发布在https://github.com/modelscope/Nexus-Gen.git上,以促进该领域的进一步发展。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
统一多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)旨在通过单一框架整合多模态理解和生成能力。现有开源统一模型在针对特定领域的架构方面存在性能差距。为了缩小这一差距,我们推出了Nexus-Gen,一个将大型语言模型的语言推理能力与扩散模型的图像合成能力相结合的统一模型。我们通过双阶段对齐训练过程来对齐大型语言模型和扩散模型的嵌入空间:一是自回归大型语言模型学习基于多模态输入的图像嵌入预测,二是视觉解码器从这些嵌入中重建高质量图像。在训练大型语言模型时,我们发现自回归范式在训练和推理阶段之间存在关键差异,连续嵌入空间中的误差累积严重降低了生成质量。为了避免这个问题,我们引入了一种预填充自回归策略,该策略用位置嵌入的特殊令牌预填充输入序列,而不是连续嵌入。通过双阶段训练,Nexus-Gen已具备全面解决图像理解、生成和编辑任务的综合能力。所有模型、数据集和代码均已发布在https://github.com/modelscope/Nexus-Gen.git,以促进该领域的进一步发展。
Key Takeaways
- 统一多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)结合了多模态理解和生成能力。
- 现有开源统一模型在特定领域方面存在性能差距。
- Nexus-Gen旨在缩小性能差距,结合了大型语言模型和扩散模型的能力。
- 通过双阶段对齐训练过程对齐大型语言模型和扩散模型的嵌入空间。
- 在训练大型语言模型时发现了自回归范式的训练和推理阶段差异。
- 引入预填充自回归策略以避免连续嵌入空间中的误差累积。
点此查看论文截图


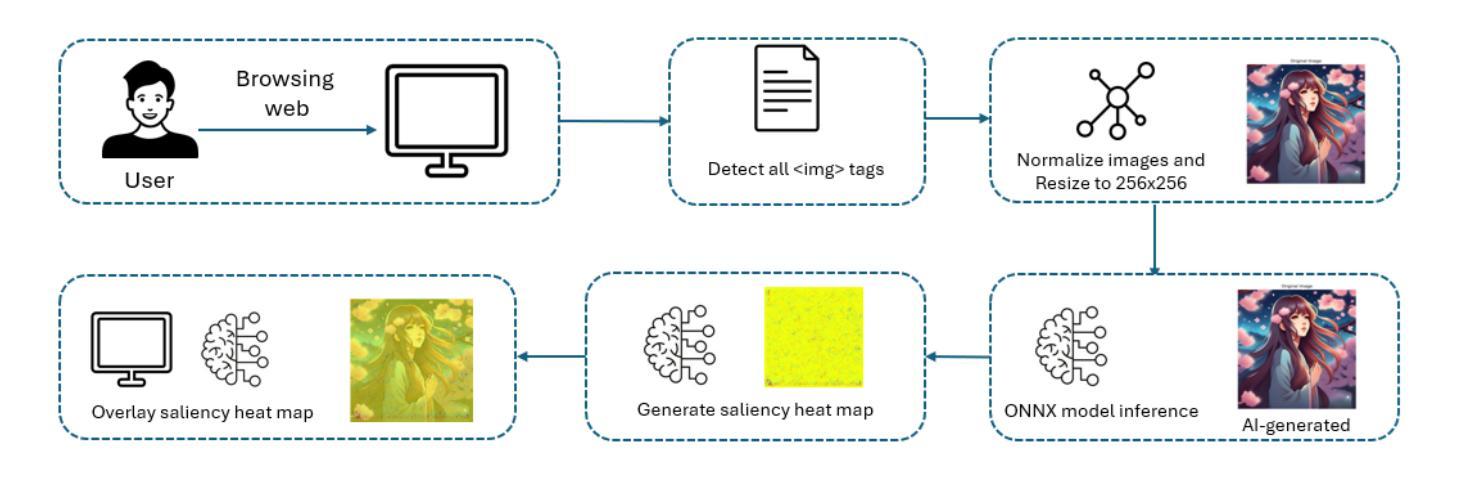
DejAIvu: Identifying and Explaining AI Art on the Web in Real-Time with Saliency Maps
Authors:Jocelyn Dzuong
The recent surge in advanced generative models, such as diffusion models and generative adversarial networks (GANs), has led to an alarming rise in AI-generated images across various domains on the web. While such technologies offer benefits such as democratizing artistic creation, they also pose challenges in misinformation, digital forgery, and authenticity verification. Additionally, the uncredited use of AI-generated images in media and marketing has sparked significant backlash from online communities. In response to this, we introduce DejAIvu, a Chrome Web extension that combines real-time AI-generated image detection with saliency-based explainability while users browse the web. Using an ONNX-optimized deep learning model, DejAIvu automatically analyzes images on websites such as Google Images, identifies AI-generated content using model inference, and overlays a saliency heatmap to highlight AI-related artifacts. Our approach integrates efficient in-browser inference, gradient-based saliency analysis, and a seamless user experience, ensuring that AI detection is both transparent and interpretable. We also evaluate DejAIvu across multiple pretrained architectures and benchmark datasets, demonstrating high accuracy and low latency, making it a practical and deployable tool for enhancing AI image accountability. The code for this system can be found at https://github.com/Noodulz/dejAIvu.
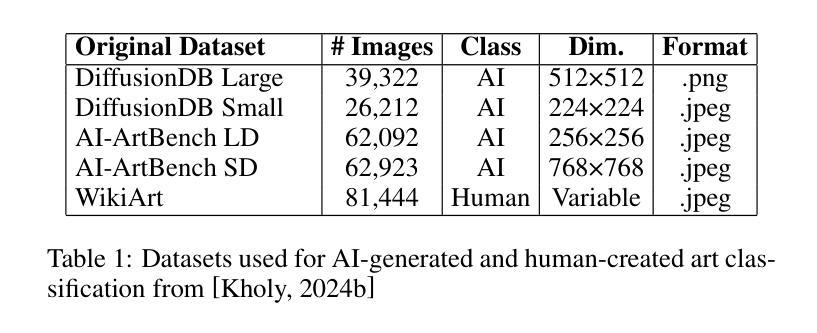
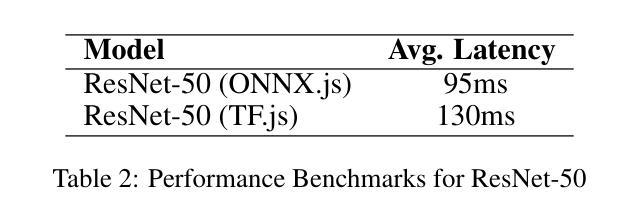
近期先进的生成模型,如扩散模型和生成对抗网络(GANs)的激增,导致网上各个领域AI生成的图像数量惊人地增长。虽然这些技术带来了民主化艺术创作等好处,但它们也带来了虚假信息、数字伪造和身份验证的挑战。此外,媒体和营销中未经授权使用AI生成的图像引发了在线社区的强烈反对。为了应对这一问题,我们推出了DejAIvu,这是一款Chrome网页扩展程序,结合实时AI生成图像检测与用户浏览网页时的基于显著性的解释性。DejAIvu使用优化的ONNX深度学习模型,自动分析网站上的图像(如Google Images),通过模型推理识别AI生成的内容,并通过覆盖显著性热图来突出AI相关伪影。我们的方法结合了高效的浏览器内推理、基于梯度的显著性分析和无缝用户体验,确保AI检测既透明又易解释。我们还对DejAIvu进行了跨多个预训练架构和基准数据集的评估,证明了其高准确性和低延迟性,使其成为增强AI图像责任制的实用且可部署的工具。该系统的代码可在https://github.com/Noodulz/dejAIvu找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, 3 figures. Accepted to IJCAI 2025 Demo Track. Revised version will be uploaded soon
Summary:
最近先进的生成模型如扩散模型和生成对抗网络(GANs)的兴起,导致网上各领域AI生成的图像激增。虽然这些技术带来了民主化艺术创作等好处,但也带来了虚假信息、数字伪造和身份认证等挑战。未经授权使用AI生成的图像在媒体和营销中引发了在线社区的强烈反对。为了应对这一问题,我们推出了DejAIvu,这是一款Chrome网页扩展程序,结合了实时AI生成的图像检测与用户浏览网页时的显著性解释。它通过优化后的深度学习模型分析网站上的图像,识别AI生成的内容,并叠加显著性热度图来突出显示AI相关的伪影。我们的方法确保了AI检测的透明性和可解释性,同时实现了高效的浏览器内推理、基于梯度的显著性分析和无缝用户体验。我们还评估了DejAIvu在多架构预训练模型和基准数据集上的性能,表现出高准确性和低延迟性,使其成为增强AI图像责任制的实用和可部署工具。
Key Takeaways:
- 先进的生成模型如扩散模型和GANs导致网上AI生成的图像激增。
- AI生成技术虽有助于民主化艺术创作,但也带来虚假信息、数字伪造等问题。
- 未经授权使用AI生成的图像在媒体和营销中引发社区反对。
- DejAIvu是一款Chrome网页扩展程序,能实时检测AI生成的图像并显示显著性热度图。
- DejAIvu结合了实时AI图像检测、显著性分析和无缝用户体验。
- DejAIvu在多架构预训练模型和基准数据集上表现出高准确性和低延迟性。
点此查看论文截图


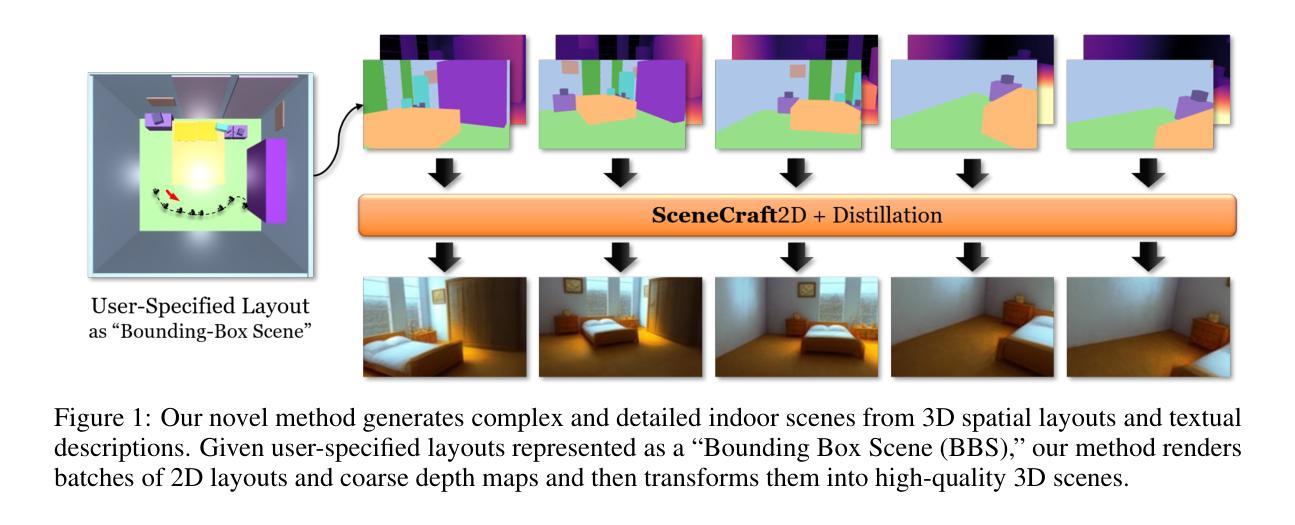
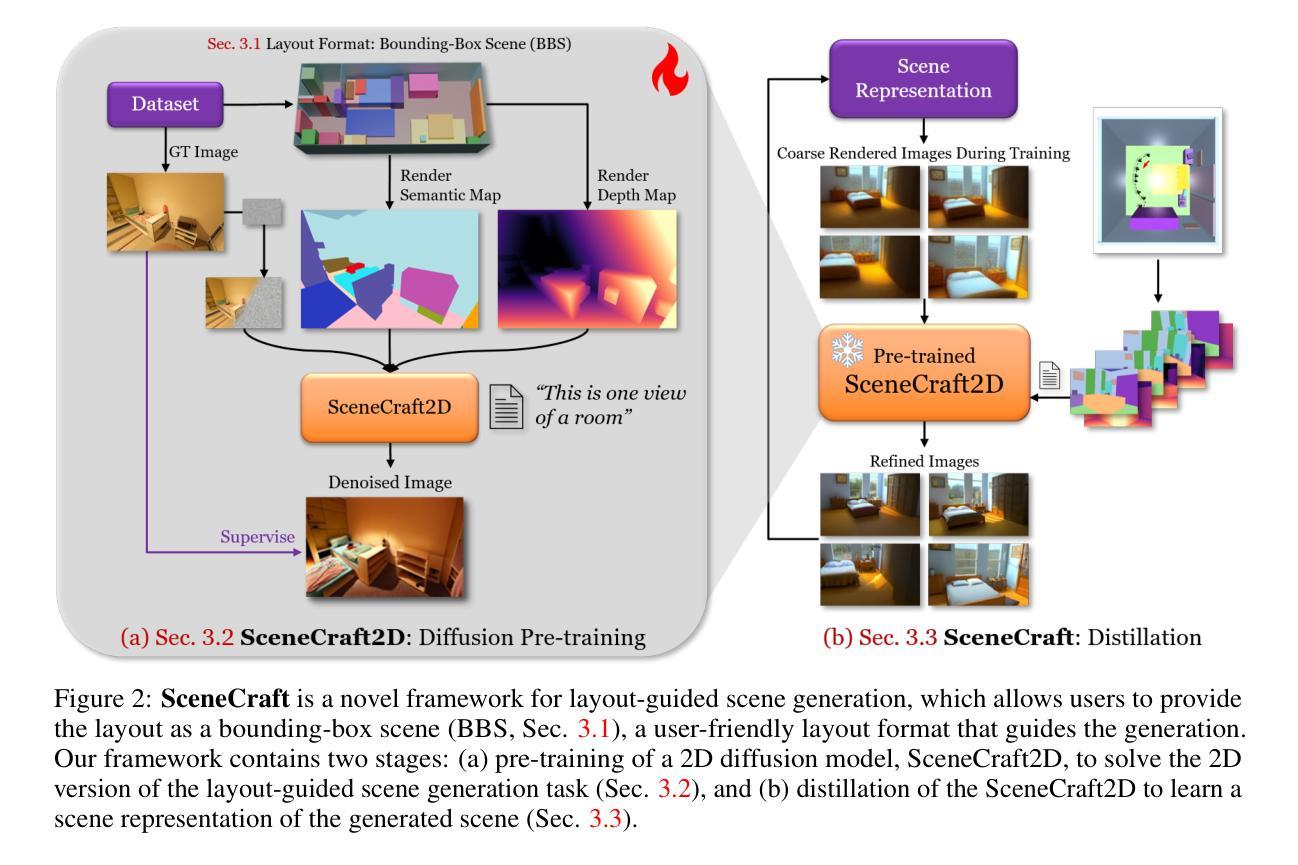
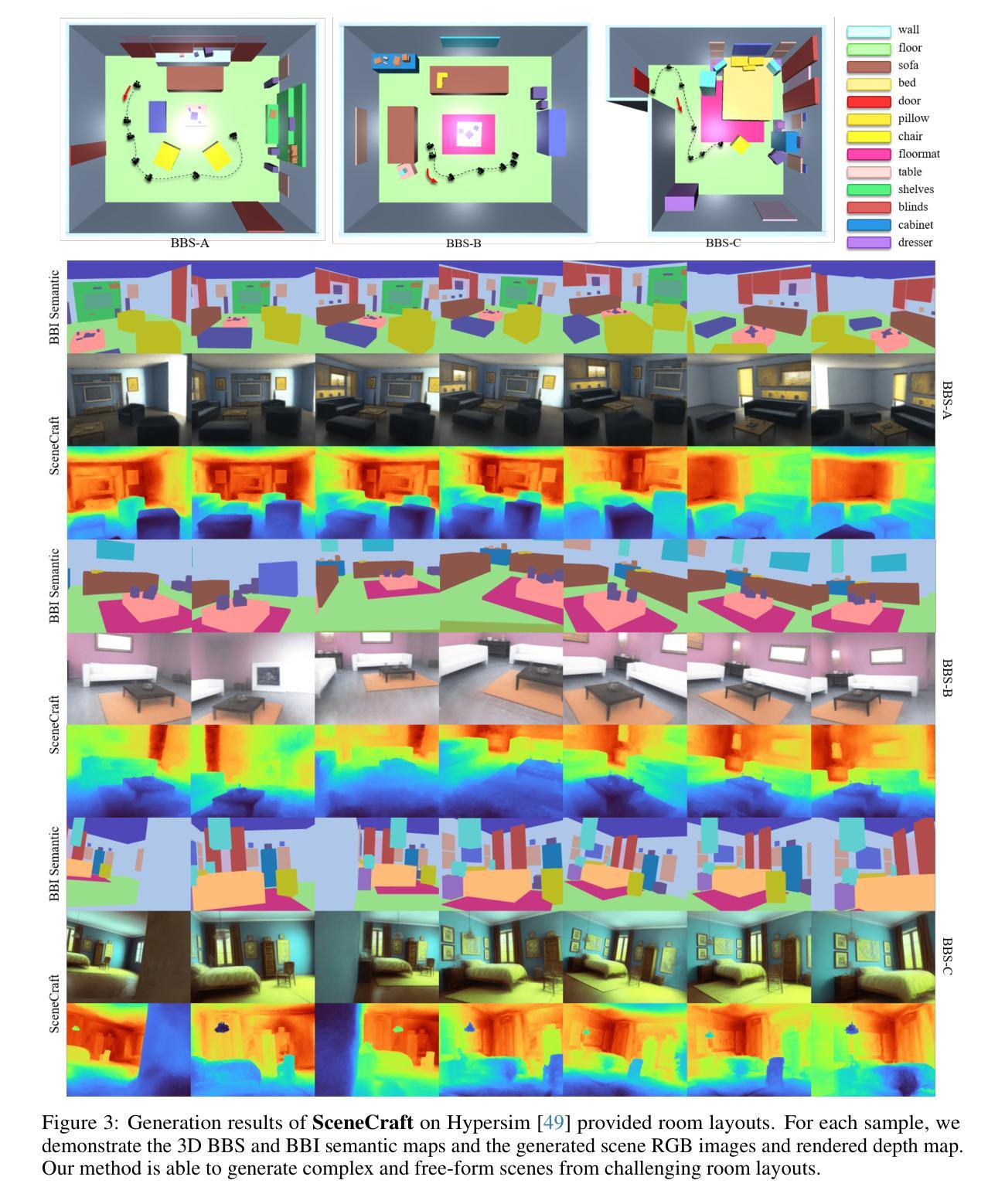
SceneCraft: Layout-Guided 3D Scene Generation
Authors:Xiuyu Yang, Yunze Man, Jun-Kun Chen, Yu-Xiong Wang
The creation of complex 3D scenes tailored to user specifications has been a tedious and challenging task with traditional 3D modeling tools. Although some pioneering methods have achieved automatic text-to-3D generation, they are generally limited to small-scale scenes with restricted control over the shape and texture. We introduce SceneCraft, a novel method for generating detailed indoor scenes that adhere to textual descriptions and spatial layout preferences provided by users. Central to our method is a rendering-based technique, which converts 3D semantic layouts into multi-view 2D proxy maps. Furthermore, we design a semantic and depth conditioned diffusion model to generate multi-view images, which are used to learn a neural radiance field (NeRF) as the final scene representation. Without the constraints of panorama image generation, we surpass previous methods in supporting complicated indoor space generation beyond a single room, even as complicated as a whole multi-bedroom apartment with irregular shapes and layouts. Through experimental analysis, we demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms existing approaches in complex indoor scene generation with diverse textures, consistent geometry, and realistic visual quality. Code and more results are available at: https://orangesodahub.github.io/SceneCraft
使用传统的3D建模工具创建符合用户规格的复杂3D场景一直是一项繁琐且具有挑战性的任务。尽管一些先进的方法已经实现了自动文本到3D的生成,但它们通常仅限于规模较小的场景,对形状和纹理的控制有限。我们推出了SceneCraft,这是一种生成详细室内场景的新方法,它符合用户提供的文本描述和空间布局偏好。我们的方法的核心是基于渲染的技术,该技术将3D语义布局转换为多视角的2D代理地图。此外,我们设计了一个语义和深度约束的扩散模型,以生成多视角图像,用于学习作为最终场景表示的神经辐射场(NeRF)。我们不受全景图像生成的约束,在支持复杂室内空间生成方面超越了之前的方法,不仅限于单个房间,甚至可以生成整个多卧室公寓的不规则形状和布局。通过实验分析,我们证明我们的方法在生成具有多样纹理、一致几何结构和逼真视觉质量的复杂室内场景方面显著优于现有方法。代码和更多结果可在以下网址找到:SceneCraft。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NeurIPS 2024. Code: https://github.com/OrangeSodahub/SceneCraft Project Page: https://orangesodahub.github.io/SceneCraft
Summary
基于文本描述和用户提供的空间布局偏好,SceneCraft方法能够生成详细的室内场景。该方法采用基于渲染的技术,将3D语义布局转换为多视角的2D代理地图,并设计了一个语义和深度条件下的扩散模型来生成多视角图像。最终场景表示为神经辐射场(NeRF)。该方法支持复杂的室内空间生成,包括超过单房间的空间,如复杂的多卧室公寓,具有不规则形状和布局。在纹理多样、几何一致和视觉真实感方面,该方法显著优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- SceneCraft是一种基于文本描述和用户偏好生成详细室内场景的方法。
- 该方法采用渲染技术将3D语义布局转换为多视角的2D代理地图。
- SceneCraft设计了一个语义和深度条件下的扩散模型来生成多视角图像。
- 最终场景表示为神经辐射场(NeRF)。
- 该方法支持复杂的室内空间生成,包括超过单房间的空间,具有不规则形状和布局。
- SceneCraft在纹理多样、几何一致性和视觉真实感方面显著优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图
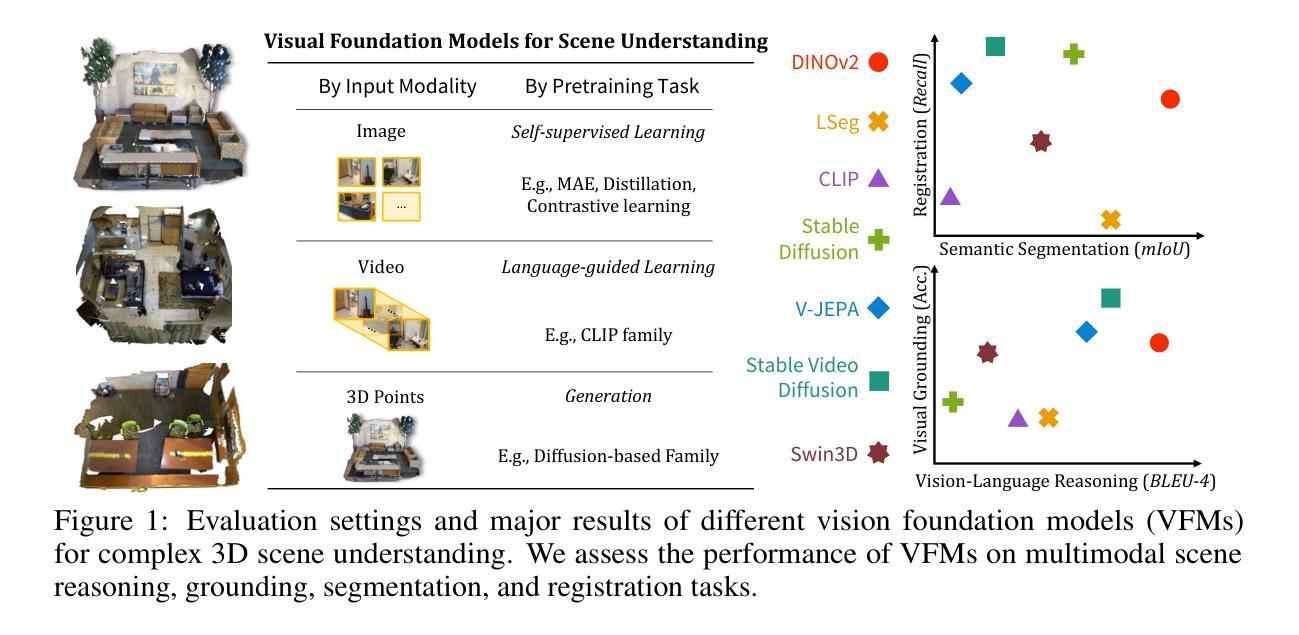
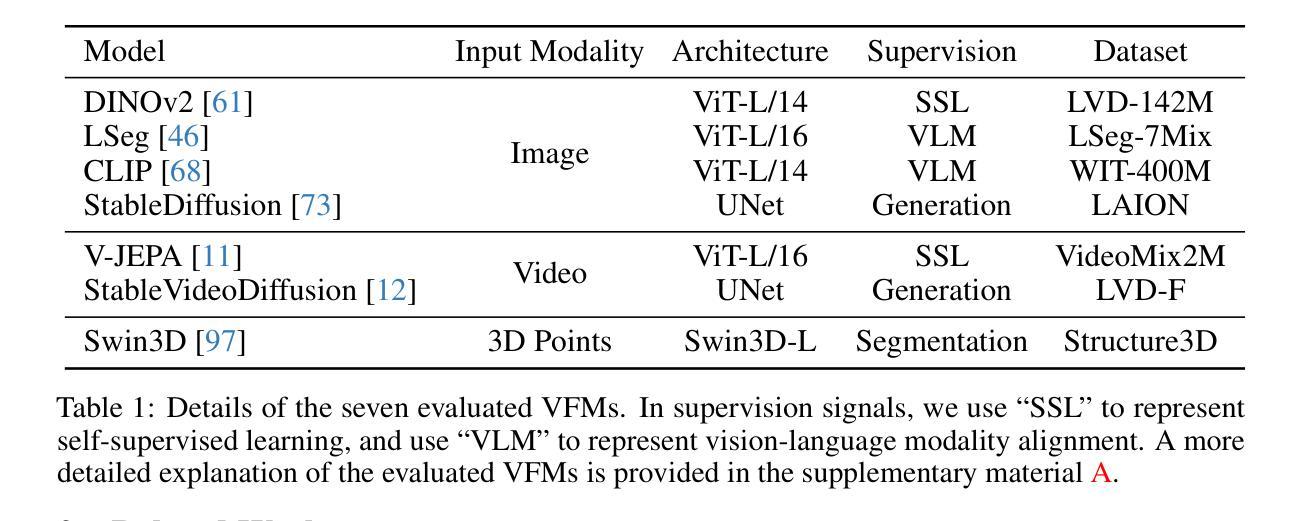
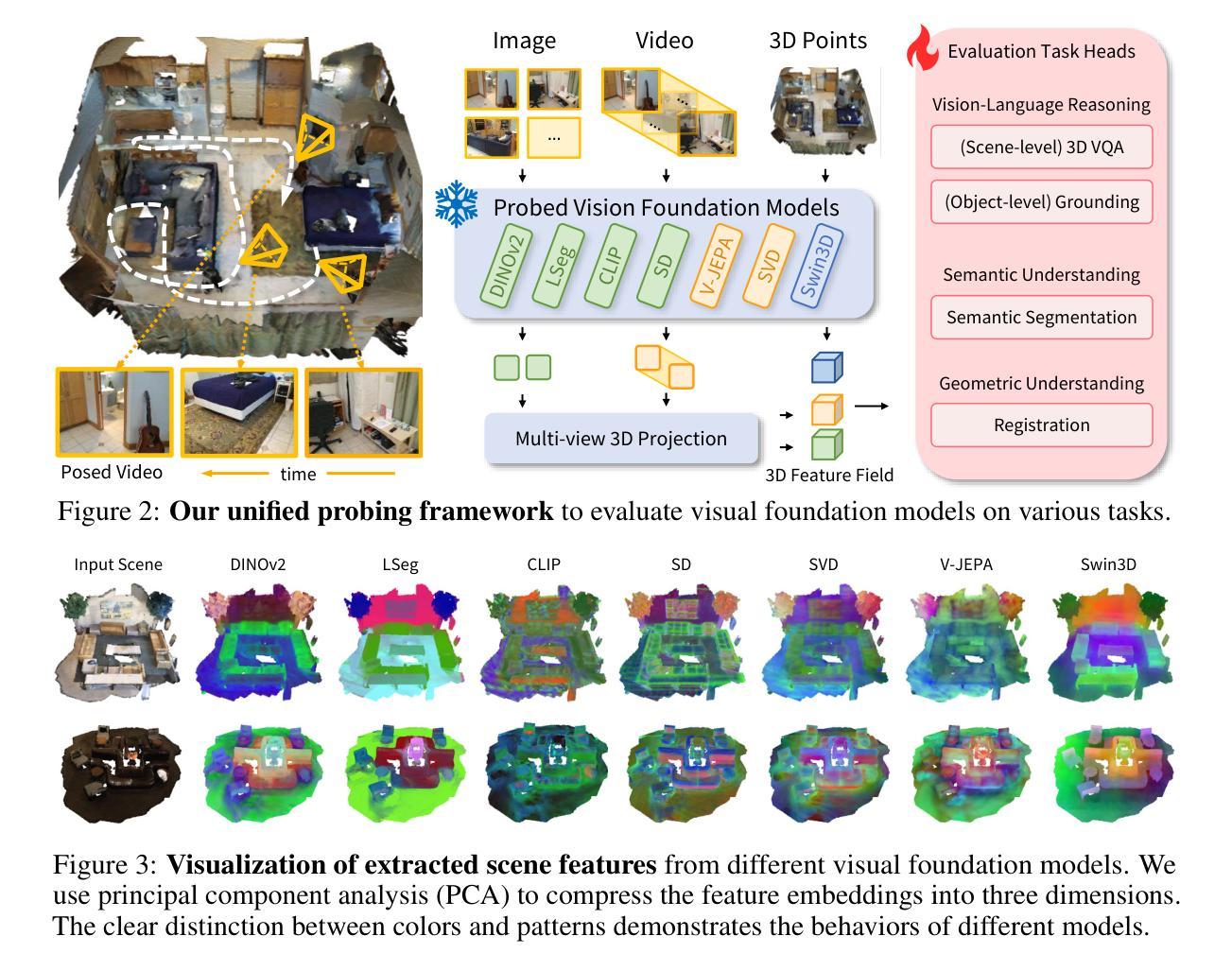
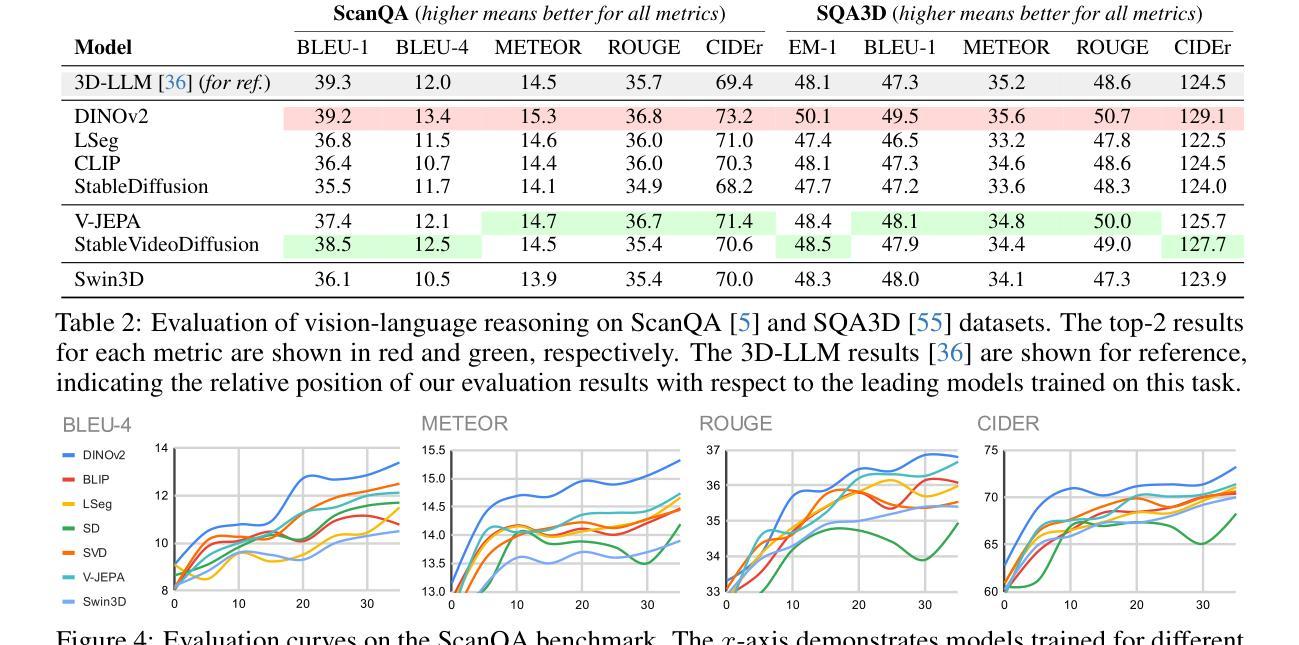
Lexicon3D: Probing Visual Foundation Models for Complex 3D Scene Understanding
Authors:Yunze Man, Shuhong Zheng, Zhipeng Bao, Martial Hebert, Liang-Yan Gui, Yu-Xiong Wang
Complex 3D scene understanding has gained increasing attention, with scene encoding strategies playing a crucial role in this success. However, the optimal scene encoding strategies for various scenarios remain unclear, particularly compared to their image-based counterparts. To address this issue, we present a comprehensive study that probes various visual encoding models for 3D scene understanding, identifying the strengths and limitations of each model across different scenarios. Our evaluation spans seven vision foundation encoders, including image-based, video-based, and 3D foundation models. We evaluate these models in four tasks: Vision-Language Scene Reasoning, Visual Grounding, Segmentation, and Registration, each focusing on different aspects of scene understanding. Our evaluations yield key findings: DINOv2 demonstrates superior performance, video models excel in object-level tasks, diffusion models benefit geometric tasks, and language-pretrained models show unexpected limitations in language-related tasks. These insights challenge some conventional understandings, provide novel perspectives on leveraging visual foundation models, and highlight the need for more flexible encoder selection in future vision-language and scene-understanding tasks. Code: https://github.com/YunzeMan/Lexicon3D
复杂的三维场景理解已经越来越受到关注,场景编码策略在其中起着至关重要的作用。然而,对于各种场景的最佳场景编码策略仍不清楚,尤其是与基于图像的对应物相比。为了解决这一问题,我们进行了一项全面的研究,探讨了用于三维场景理解的各种视觉编码模型,识别了不同场景编码模型在不同场景下的优点和局限性。我们的评估涵盖了七种视觉基础编码器,包括基于图像、基于视频和三维基础模型。我们在四个任务中评估了这些模型:视觉语言场景推理、视觉定位、分割和注册,每个任务都侧重于场景理解的不同方面。我们的评估得出了重要发现:DINOv2表现出卓越的性能,视频模型在对象级任务上表现出色,扩散模型有利于几何任务,而语言预训练模型在语言相关任务中显示出意外的局限性。这些见解挑战了一些传统理解,为利用视觉基础模型提供了新的视角,并强调了未来在视觉语言和场景理解任务中需要更灵活的编码器选择。代码地址:https://github.com/YunzeMan/Lexicon3D
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NeurIPS 2024. Project page: https://yunzeman.github.io/lexicon3d Github: https://github.com/YunzeMan/Lexicon3D
Summary
本文主要探讨三维场景理解中的视觉编码策略。针对此,作者对七种视觉编码模型进行了全面研究,并在四个任务中进行了评估:视觉语言场景推理、视觉定位、分割和注册。研究发现DINOv2表现优异,视频模型在对象级任务上表现出优势,扩散模型在几何任务上有所助益,而语言预训练模型在语言相关任务上显示出意外局限。这些见解为利用视觉基础模型和未来视觉语言及场景理解任务的编码器选择提供了新的视角和挑战。
Key Takeaways
- 对视觉编码模型进行了全面的三维场景理解研究。
- 在视觉语言场景推理、视觉定位、分割和注册等四个任务中评估了多种视觉编码模型。
- 发现DINOv2在多个任务中表现优越。
- 视频模型在对象级任务上具有优势。
- 扩散模型对几何任务有积极影响。
- 语言预训练模型在某些任务中存在局限。
点此查看论文截图