⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-10 更新
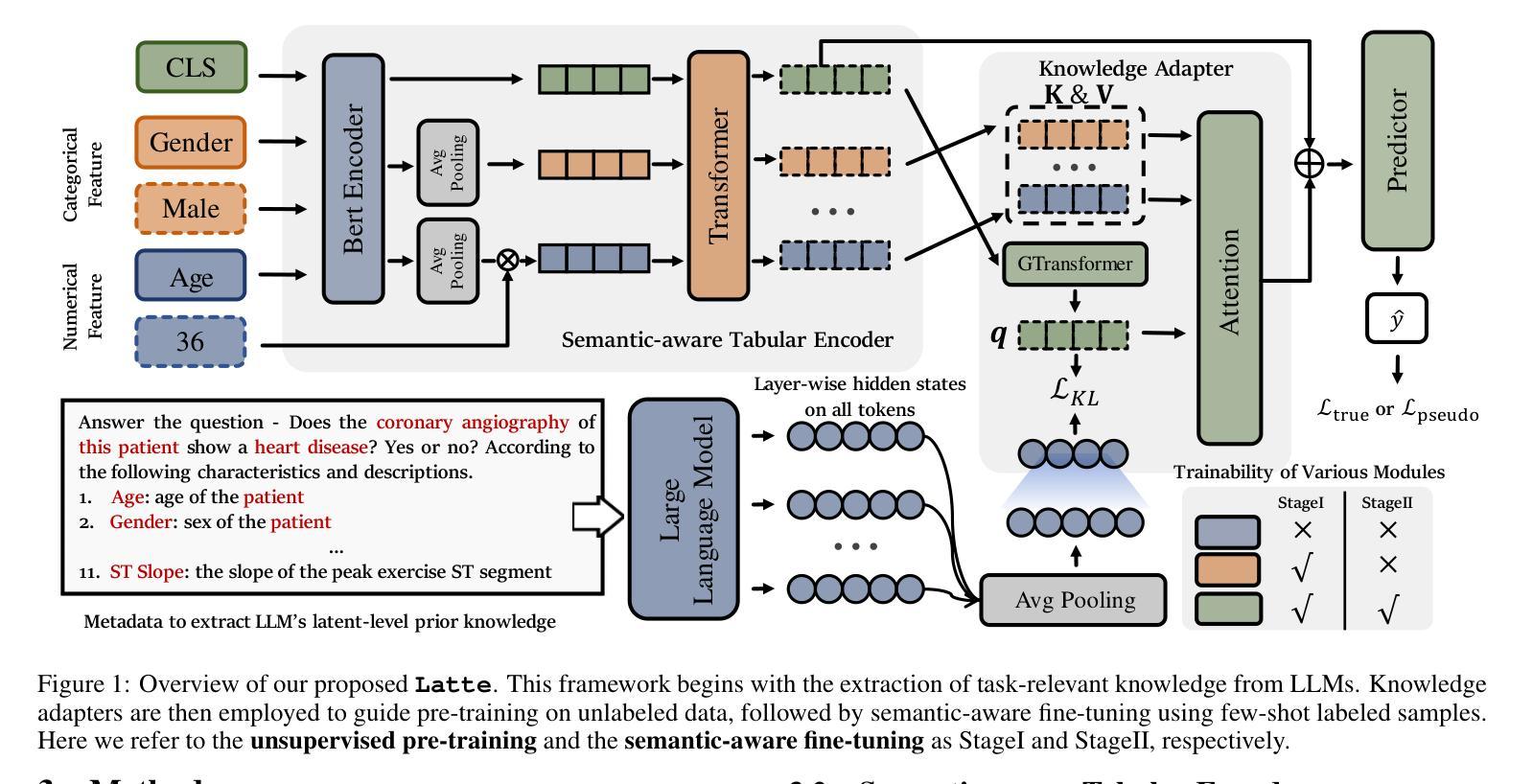
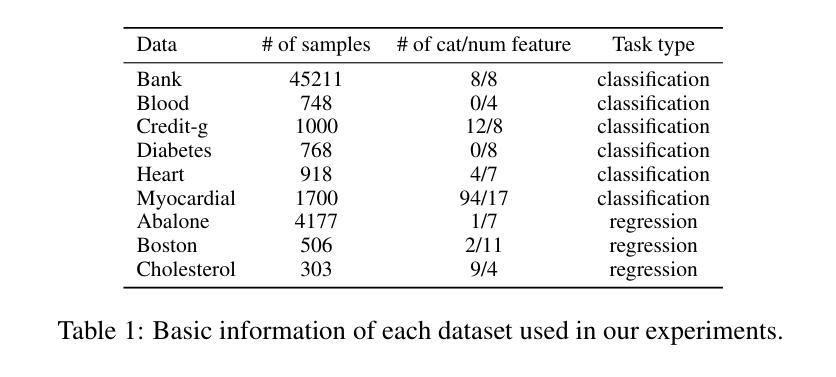
Latte: Transfering LLMs` Latent-level Knowledge for Few-shot Tabular Learning
Authors:Ruxue Shi, Hengrui Gu, Hangting Ye, Yiwei Dai, Xu Shen, Xin Wang
Few-shot tabular learning, in which machine learning models are trained with a limited amount of labeled data, provides a cost-effective approach to addressing real-world challenges. The advent of Large Language Models (LLMs) has sparked interest in leveraging their pre-trained knowledge for few-shot tabular learning. Despite promising results, existing approaches either rely on test-time knowledge extraction, which introduces undesirable latency, or text-level knowledge, which leads to unreliable feature engineering. To overcome these limitations, we propose Latte, a training-time knowledge extraction framework that transfers the latent prior knowledge within LLMs to optimize a more generalized downstream model. Latte enables general knowledge-guided downstream tabular learning, facilitating the weighted fusion of information across different feature values while reducing the risk of overfitting to limited labeled data. Furthermore, Latte is compatible with existing unsupervised pre-training paradigms and effectively utilizes available unlabeled samples to overcome the performance limitations imposed by an extremely small labeled dataset. Extensive experiments on various few-shot tabular learning benchmarks demonstrate the superior performance of Latte, establishing it as a state-of-the-art approach in this domain
少样本表格学习(Few-Shot Tabular Learning)是指利用有限量标记数据来训练机器学习模型,为解决现实世界挑战提供具有成本效益的方法。大型语言模型(LLM)的出现引发了利用预训练知识来促进少样本表格学习的兴趣。尽管已有方法取得了一些有前景的结果,但它们要么依赖于测试时的知识提取,这引入了不必要的延迟,要么依赖于文本级别的知识,这导致了不可靠的特征工程。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了Latte,这是一个训练时的知识提取框架,它将LLM中的潜在先验知识转移出来以优化更通用的下游模型。Latte能够实现通用知识指导的下游表格学习,促进不同特征值之间信息的加权融合,同时降低对有限标记数据过度拟合的风险。此外,Latte与现有的无监督预训练模式兼容,并能有效利用可用的未标记样本,以克服由于极小的标记数据集而带来的性能限制。在各种少样本表格学习基准测试上的广泛实验表明,Latte的性能卓越,已成为该领域的最前沿方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
少量标注数据的表格学习提供了一种具有成本效益的方法来解决现实世界的问题。利用大型语言模型(LLM)的潜在先验知识,提出一种名为Latte的训练时间知识提取框架,以优化更通用的下游模型。Latte通过加权融合不同特征值的信息,减少了对有限标注数据的过度拟合风险,并可与现有的无监督预训练范式兼容,有效利用可用的未标注样本。
Key Takeaways
- Few-shot tabular learning利用有限的标注数据来训练机器学习模型,为现实世界的问题解决提供了成本效益高的方法。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)的潜在先验知识在few-shot表格学习中具有应用价值。
- Latte框架是一种训练时间的知识提取方法,能够转移LLM中的潜在知识来优化下游模型。
- Latte通过加权融合不同特征值的信息,提高了模型的泛化能力,并降低了过度拟合的风险。
- Latte与现有的无监督预训练范式兼容,可以充分利用未标注的样本数据。
- Latte在多种few-shot表格学习基准测试上表现出卓越的性能。
点此查看论文截图

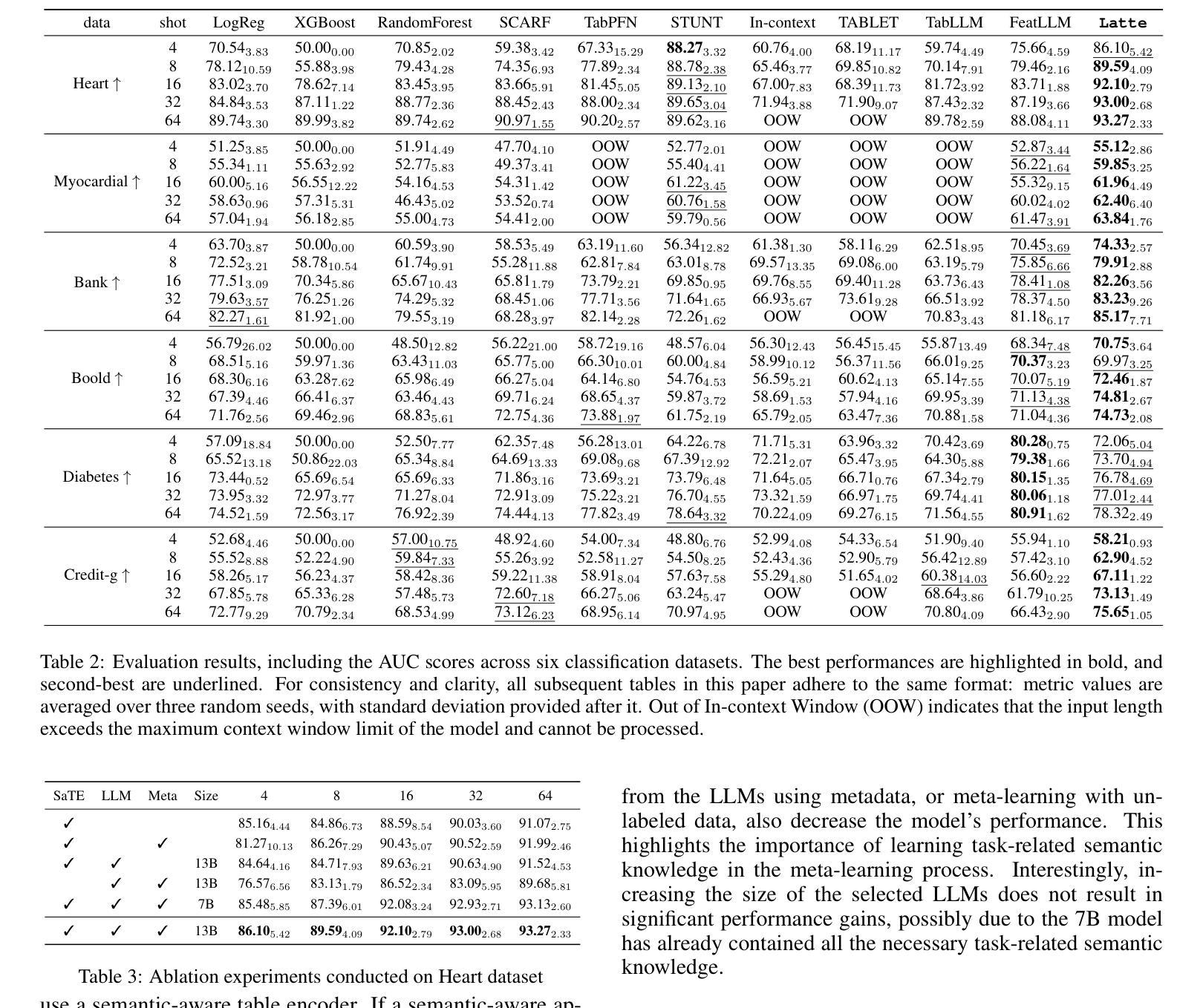
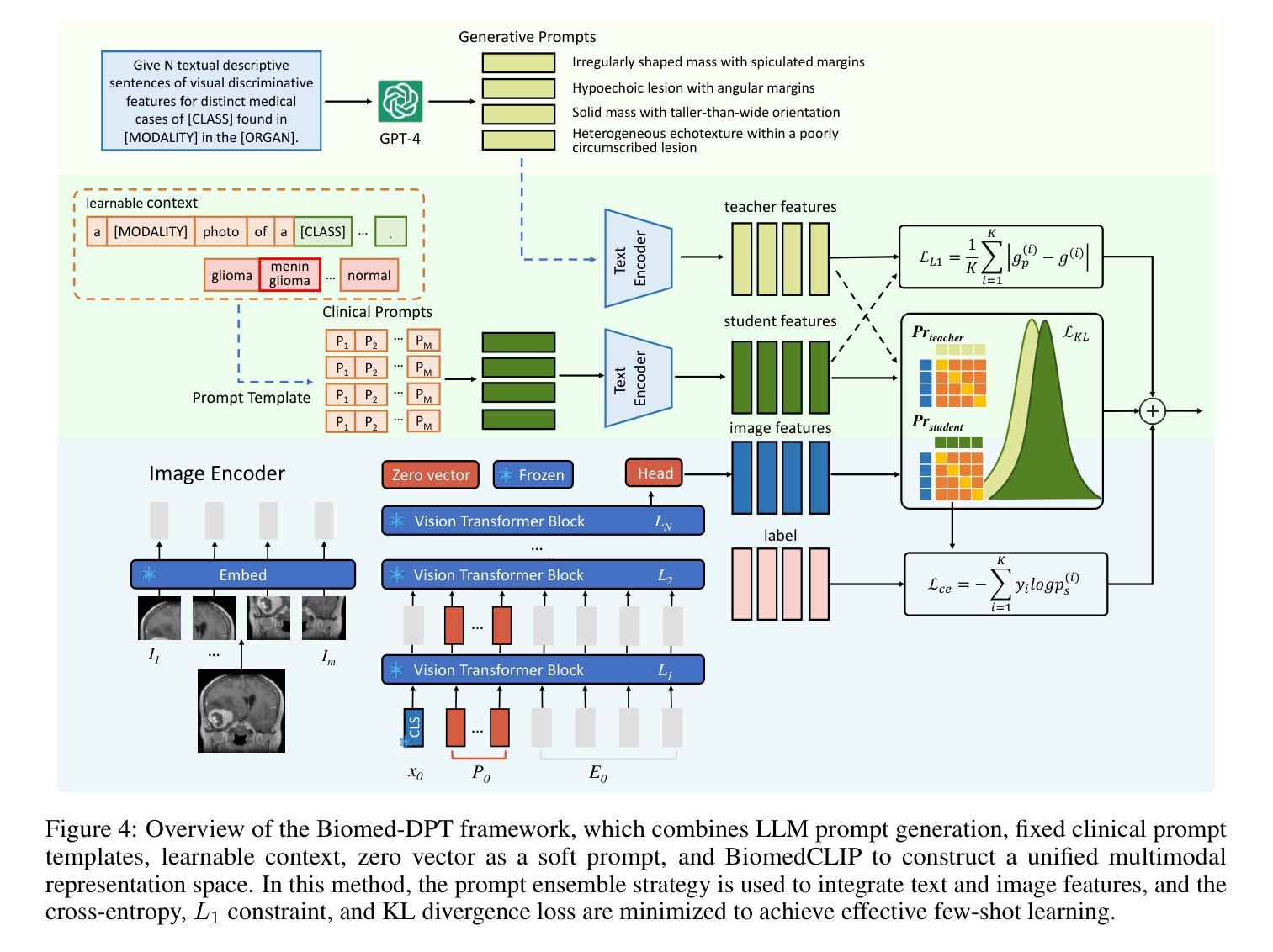
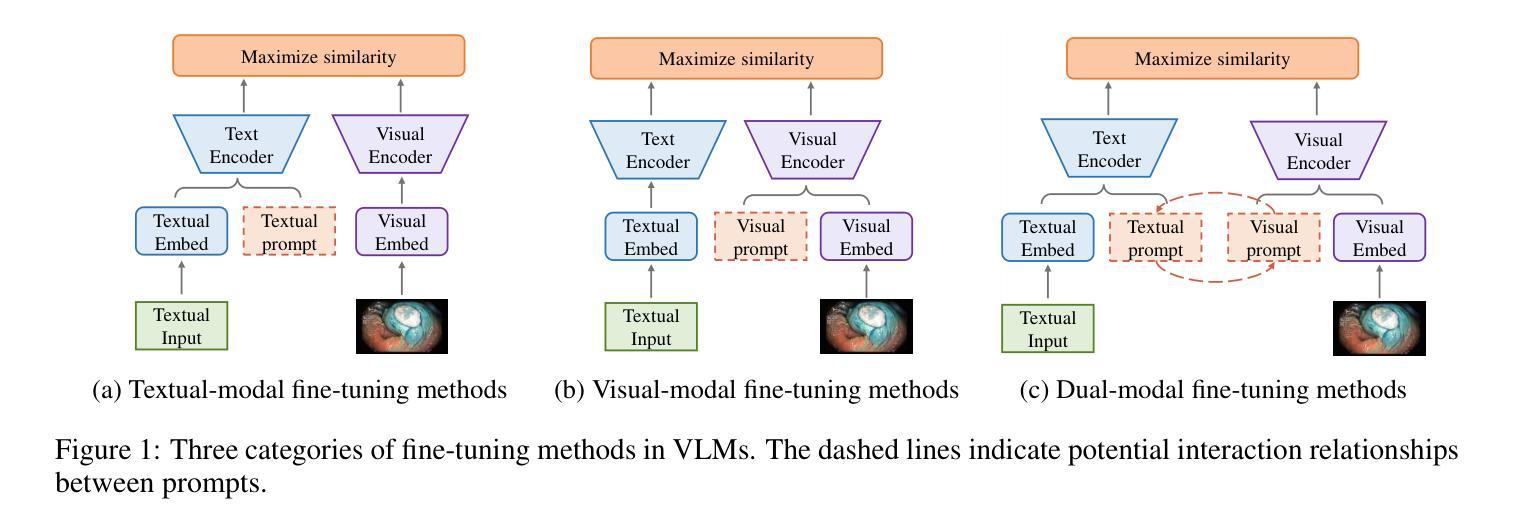
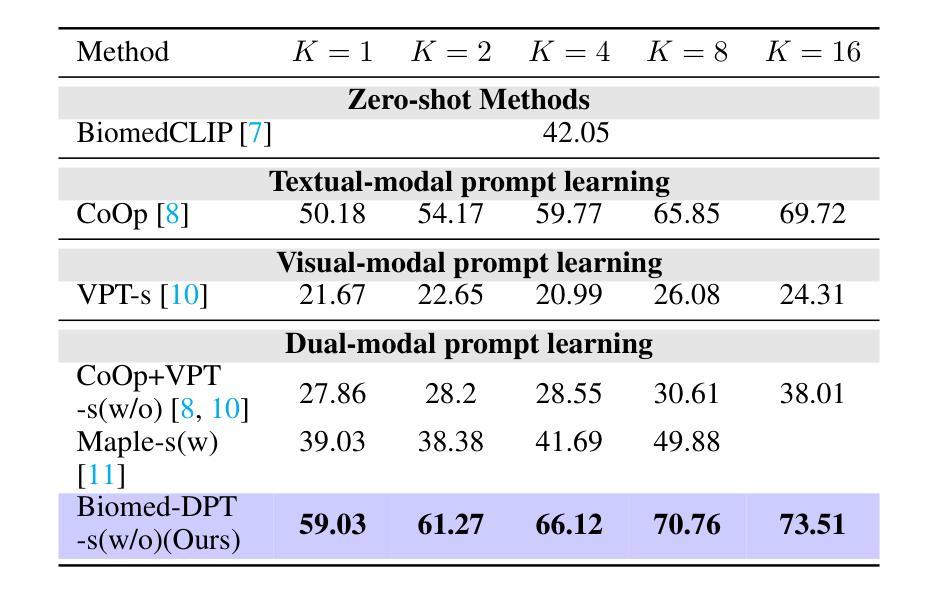
Biomed-DPT: Dual Modality Prompt Tuning for Biomedical Vision-Language Models
Authors:Wei Peng, Kang Liu, Jianchen Hu, Meng Zhang
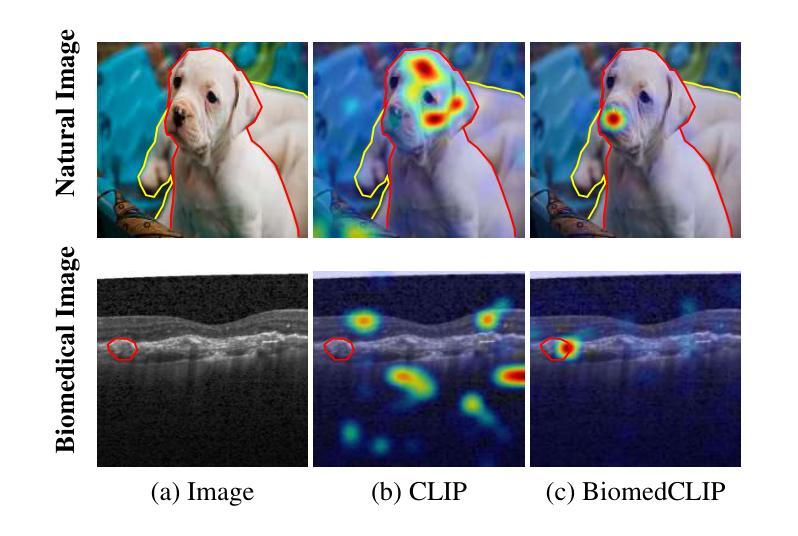
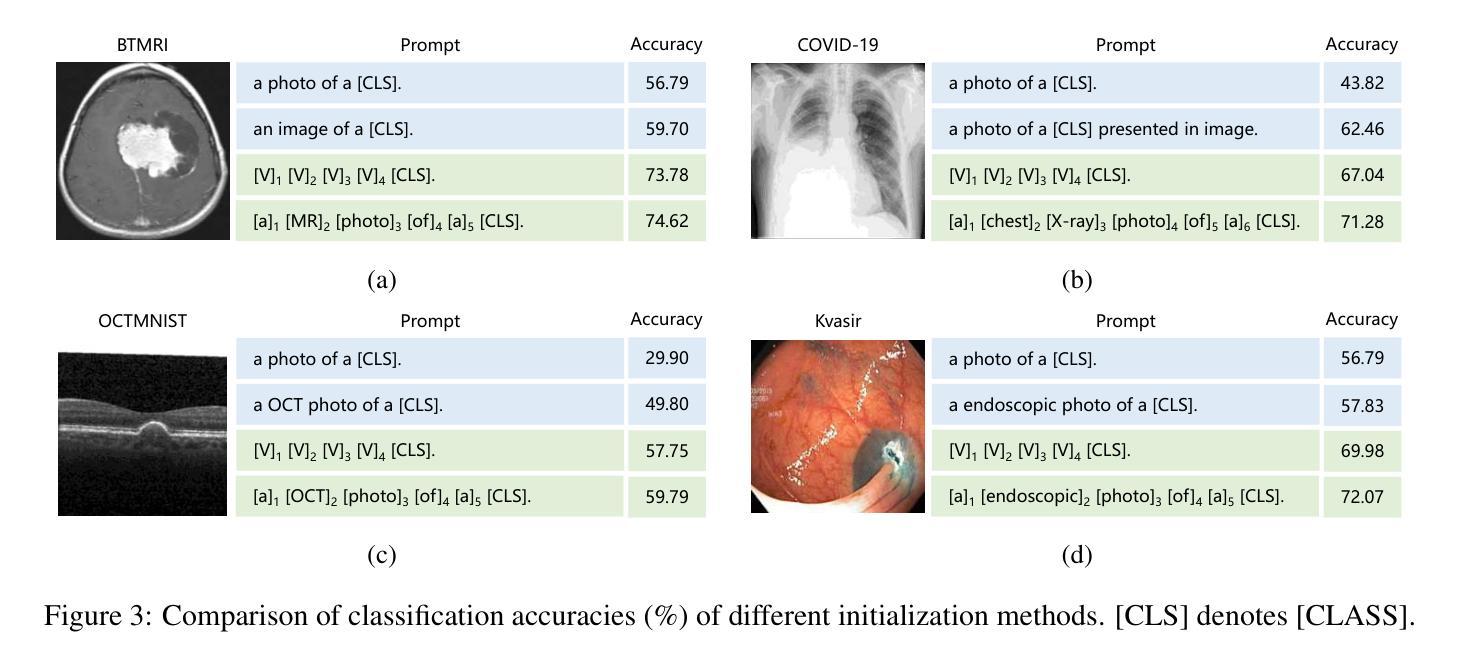
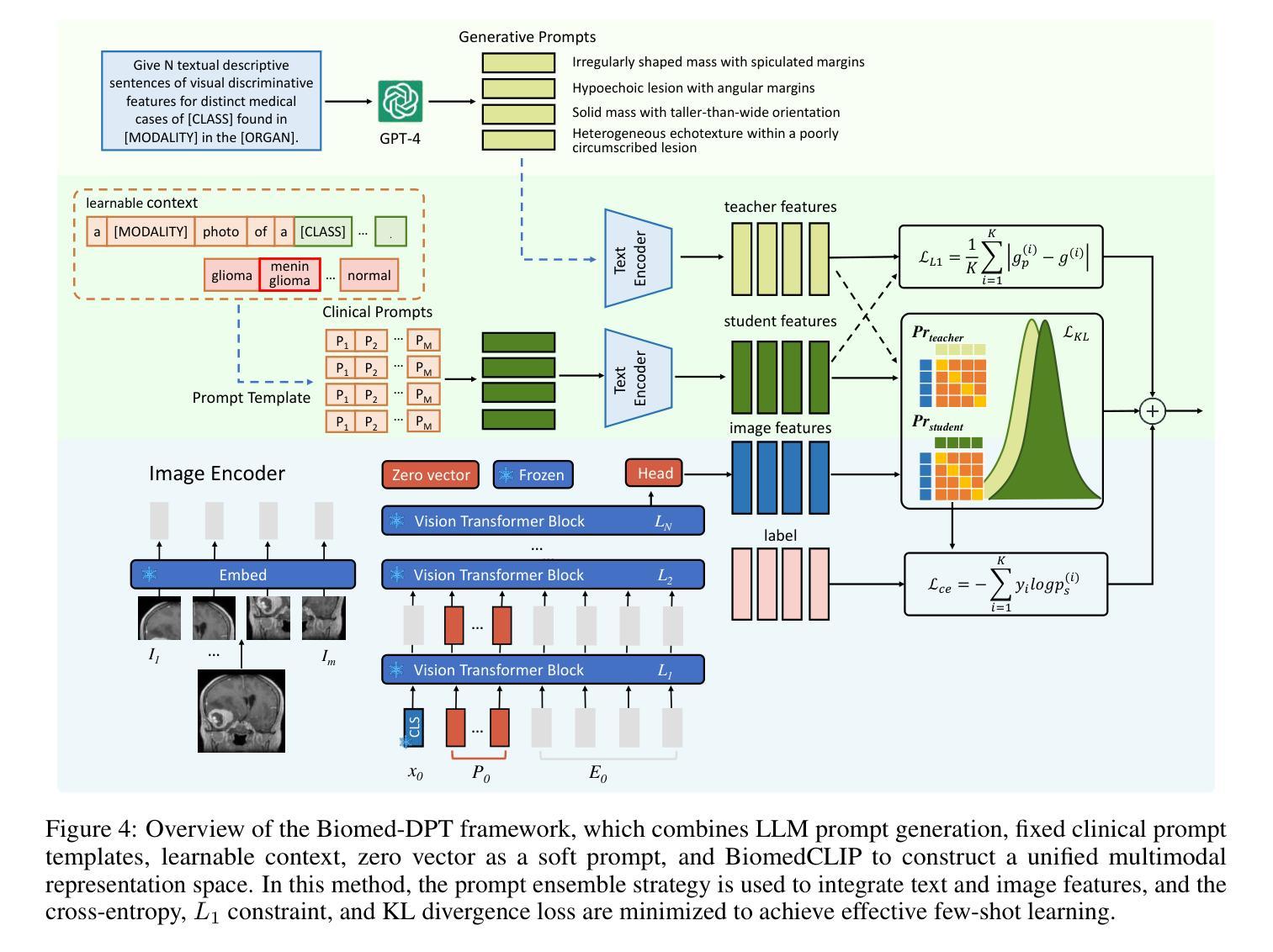
Prompt learning is one of the most effective paradigms for adapting pre-trained vision-language models (VLMs) to the biomedical image classification tasks in few shot scenarios. However, most of the current prompt learning methods only used the text prompts and ignored the particular structures (such as the complex anatomical structures and subtle pathological features) in the biomedical images. In this work, we propose Biomed-DPT, a knowledge-enhanced dual modality prompt tuning technique. In designing the text prompt, Biomed-DPT constructs a dual prompt including the template-driven clinical prompts and the large language model (LLM)-driven domain-adapted prompts, then extracts the clinical knowledge from the domain-adapted prompts through the knowledge distillation technique. In designing the vision prompt, Biomed-DPT introduces the zero vector as a soft prompt to leverage attention re-weighting so that the focus on non-diagnostic regions and the recognition of non-critical pathological features are avoided. Biomed-DPT achieves an average classification accuracy of 66.14% across 11 biomedical image datasets covering 9 modalities and 10 organs, with performance reaching 78.06% in base classes and 75.97% in novel classes, surpassing the Context Optimization (CoOp) method by 6.20%, 3.78%, and 8.04%, respectively. Our code are available at \underline{https://github.com/Kanyooo/Biomed-DPT}.
提示学习是在少量场景中将预训练的视觉语言模型(VLMs)适应生物医学图像分类任务的最有效范式之一。然而,当前大多数提示学习方法仅使用文本提示,而忽略了生物医学图像中的特定结构(如复杂的解剖结构和微妙的病理特征)。在本研究中,我们提出了生物医学DPT(Biomed-DPT),这是一种知识增强的双模态提示调整技术。在设计文本提示时,Biomed-DPT构建了一个双提示,包括模板驱动的临床提示和大型语言模型(LLM)驱动的域适应提示,然后通过知识蒸馏技术从域适应提示中提取临床知识。在设计视觉提示时,Biomed-DPT引入了零向量作为软提示,以利用注意力重新加权,从而避免关注非诊断区域和识别非关键病理特征。Biomed-DPT在涵盖9种模态和10个器官的11个生物医学图像数据集上实现了平均分类准确率66.14%,其中基础类的性能达到78.06%,新型类的性能达到75.97%,分别超越了上下文优化(CoOp)方法6.20%、3.78%和8.04%。我们的代码可在https://github.com/Kanyooo/Biomed-DPT上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
生物医学图像分类任务中,基于提示学习是预训练视觉语言模型的有效范式之一。然而,当前大多数提示学习方法仅使用文本提示,忽略了生物医学图像中的特定结构。本文提出Biomed-DPT,一种知识增强的双模态提示调整技术。设计文本提示时,Biomed-DPT构建包括模板驱动的临床提示和大型语言模型驱动领域自适应提示的双重提示,并通过知识蒸馏技术提取领域自适应提示中的临床知识。在视觉提示设计上,Biomed-DPT引入零向量作为软提示,利用注意力重新加权,避免关注非诊断区域和识别非关键病理特征。Biomed-DPT在涵盖九种模态和十个器官的11个生物医学图像数据集上取得了平均分类准确率66.14%,其中基础类别和新颖类别的性能分别达到了78.06%和75.97%,超过了CoOp方法。
Key Takeaways
- 提示学习是适应预训练视觉语言模型进行生物医学图像分类的有效方法。
- 当前提示学习方法多忽略生物医学图像中的特定结构。
- Biomed-DPT是一种知识增强的双模态提示调整技术,结合临床提示和大型语言模型。
- Biomed-DPT通过知识蒸馏提取临床知识。
- 在视觉提示设计上,Biomed-DPT引入零向量避免关注非诊断区域和识别非关键病理特征。
- Biomed-DPT在多个生物医学图像数据集上取得了较高的分类准确率。
点此查看论文截图

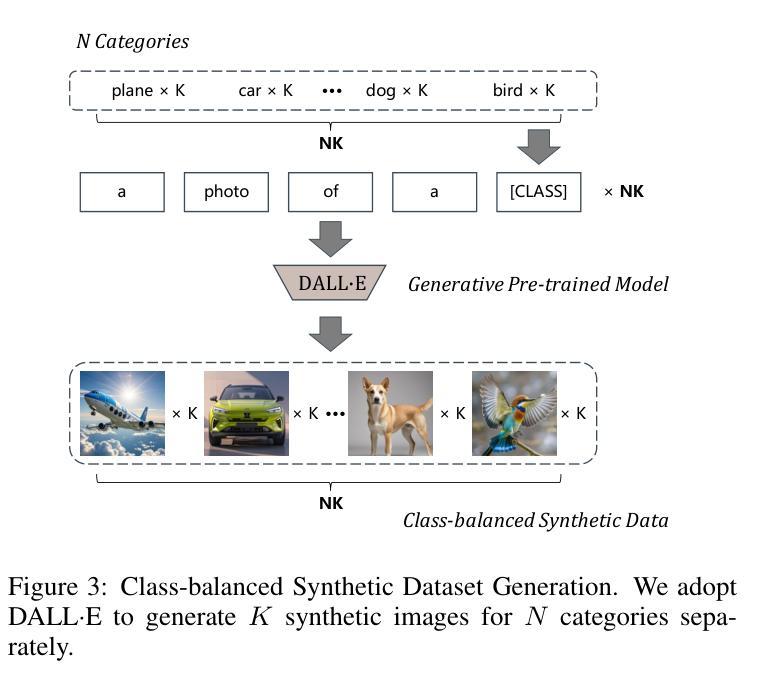
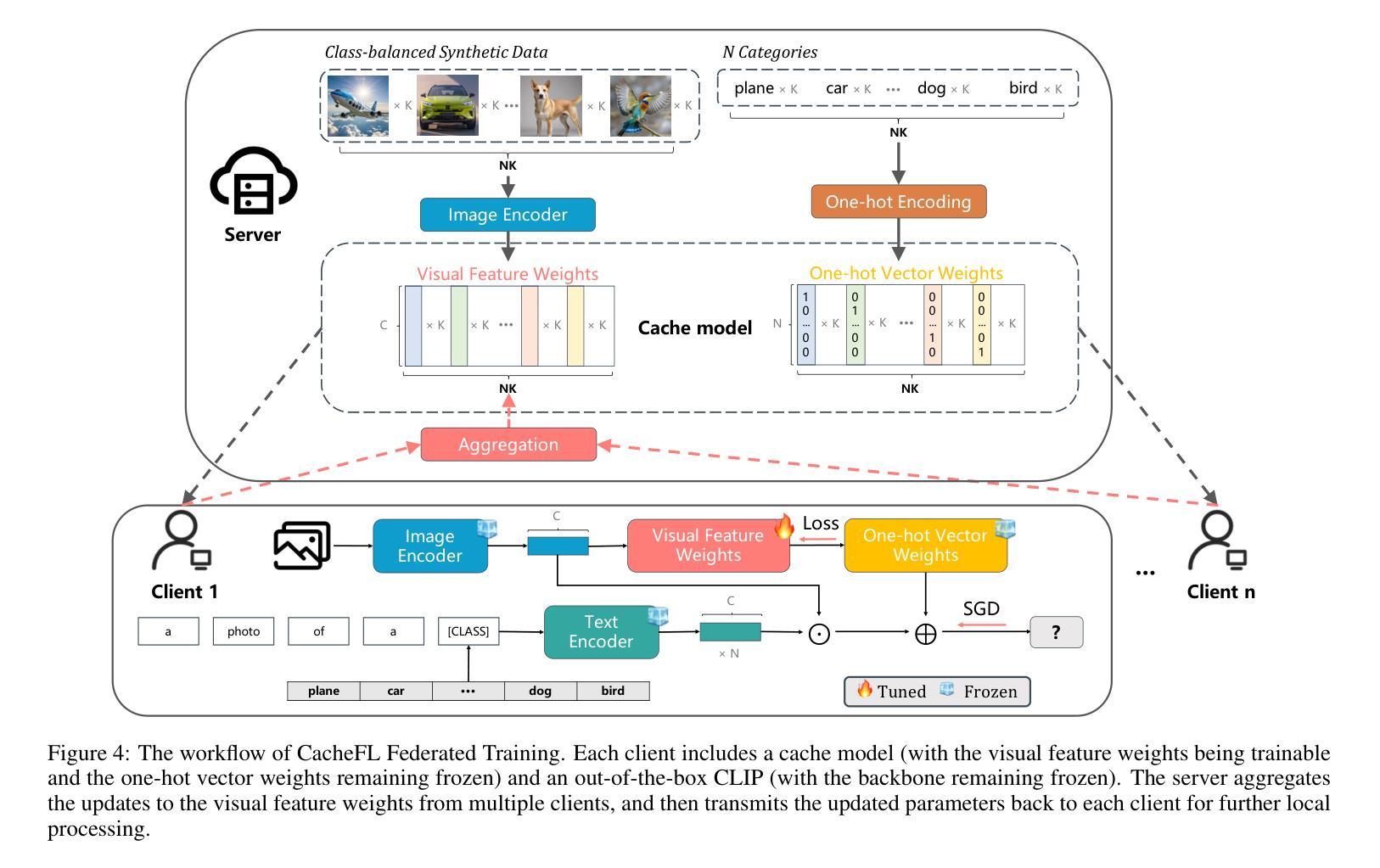
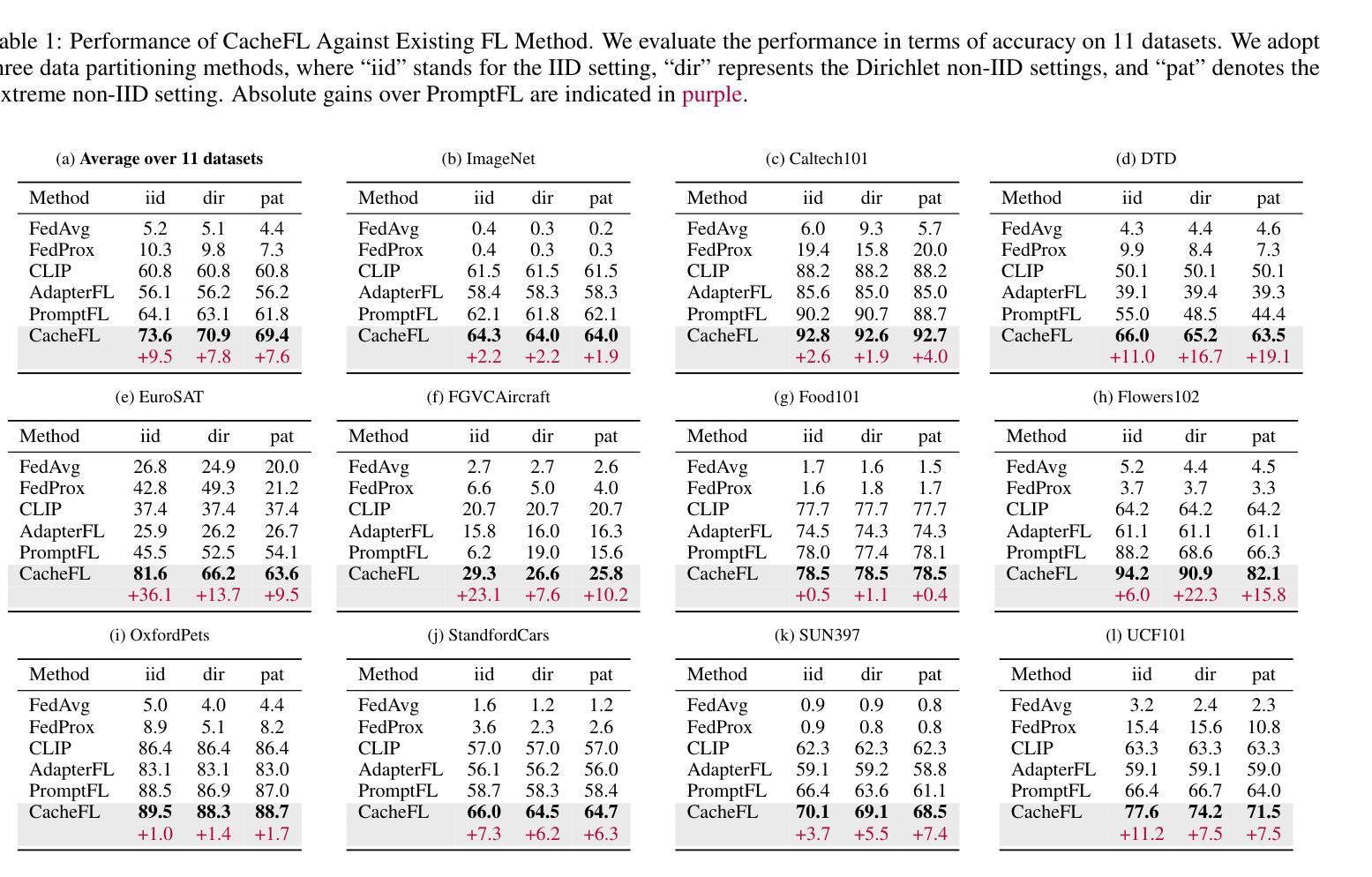
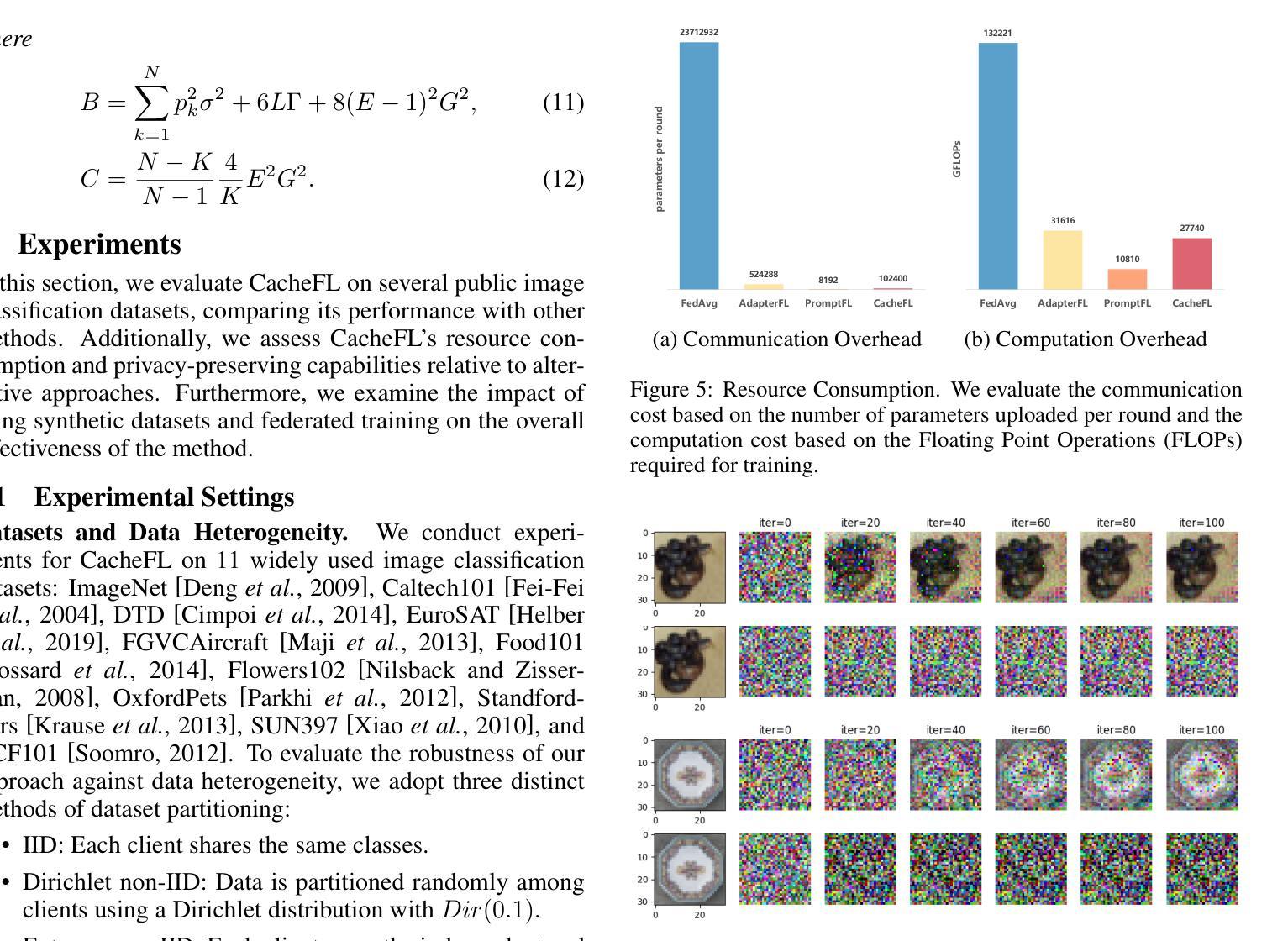
CacheFL: Efficient Federated Cache Model Fine-Tuning for Vision-Language Models
Authors:Mengjun Yi, Hanwen Zhang, Hui Dou, Jian Zhao, Furao Shen
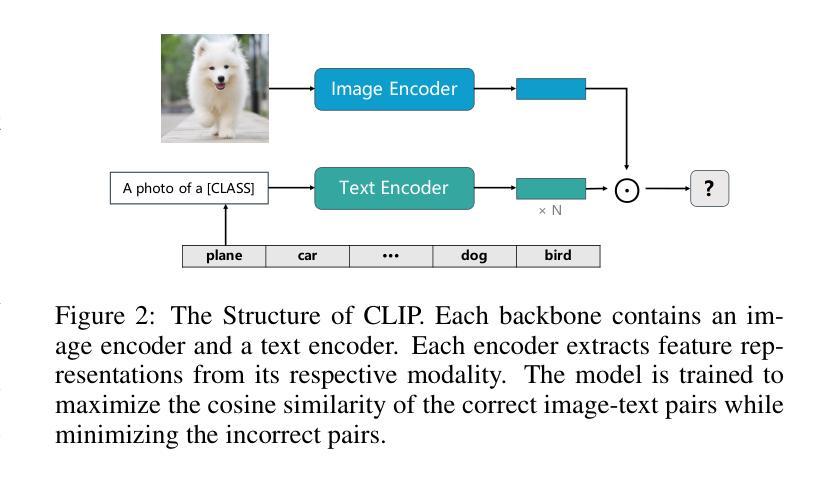
Large pre-trained Vision-Language Models (VLMs), such as Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP), have exhibited remarkable zero-shot performance across various image classification tasks. Fine-tuning these models on domain-specific datasets further enhances their effectiveness for downstream applications. However, fine-tuning in cloud environments raises significant concerns regarding data security and privacy. Federated Learning (FL) offers a decentralized solution by enabling model training across local clients without centralizing sensitive data, but the high communication and computation costs of transmitting full pre-trained models during training limit its scalability. Additionally, non-Independent and Identically Distributed (non-IID) data across local clients can negatively impact model convergence and performance. To address these challenges, we propose CacheFL, a novel federated learning method that replaces traditional full model fine-tuning with lightweight cache model fine-tuning. The cache model is initialized using a class-balanced dataset generated by a generative pre-trained model, effectively mitigating the impact of non-IID data. This cache model is then distributed to local clients for fine-tuning, and the updated parameters from each client are aggregated on the server and redistributed. With the updated cache model, the classification performance of CLIP is improved after just a few epochs. By limiting the training and communication to the cache model, CacheFL significantly reduces resource demands while ensuring data privacy and security. Extensive experiments conducted on ImageNet and 10 additional datasets demonstrate that CacheFL outperforms traditional approaches in terms of classification accuracy, resource efficiency, and privacy preservation.
大型预训练视觉语言模型(VLMs),如对比语言图像预训练(CLIP),在各种图像分类任务中表现出了出色的零样本性能。在特定领域数据集上对这些模型进行微调,可以进一步提高其下游应用的有效性。然而,在云环境中进行微调引发了关于数据安全和隐私的重大担忧。联邦学习(FL)通过支持本地客户端的模型训练,无需集中敏感数据,提供了分散的解决方案。但在训练过程中传输完整的预训练模型的高通信和计算成本限制了其可扩展性。此外,本地客户端之间的非独立同分布(non-IID)数据可能对模型收敛和性能产生负面影响。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了CacheFL,这是一种新型的联邦学习方法,它用轻量级的缓存模型微调取代了传统的全模型微调。缓存模型使用由生成式预训练模型生成的类别平衡数据集进行初始化,有效地减轻了非IID数据的影响。然后,该缓存模型将分发给本地客户端进行微调,从每个客户端更新的参数将在服务器上聚合并重新分发。仅通过几个周期,使用更新后的缓存模型,CLIP的分类性能就得到了提高。通过将训练和通信限制在缓存模型上,CacheFL在降低资源需求的同时,确保了数据隐私和安全。在ImageNet和另外10个数据集上进行的广泛实验表明,CacheFL在分类精度、资源效率和隐私保护方面优于传统方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型预训练视听模型,如对比语言图像预训练(CLIP),在各种图像分类任务中表现出出色的零样本性能。对这些模型进行领域特定数据集的微调可进一步提高其下游应用的效果。然而,在云环境中进行微调引发了关于数据安全和隐私的重大担忧。联邦学习(FL)提供了一种去中心化的解决方案,通过在本地客户端进行模型训练,而不集中敏感数据。但传输完整的预训练模型进行训练导致的通信和计算成本高昂,限制了其可扩展性。此外,本地客户端的非独立同分布(non-IID)数据可能给模型收敛和性能带来负面影响。为解决这些挑战,我们提出了CacheFL这一新型的联邦学习方法,它将传统的全模型微调替换为轻量级的缓存模型微调。缓存模型使用由生成式预训练模型生成的类别平衡数据集进行初始化,有效减轻了非IID数据的影响。缓存模型然后分发到本地客户端进行微调,来自每个客户端的更新参数在服务器上聚合并重新分发。通过仅对缓存模型进行训练和通信,CacheFL在降低资源需求的同时确保了数据隐私和安全。在ImageNet和另外10个数据集上进行的广泛实验表明,CacheFL在分类精度、资源效率和隐私保护方面优于传统方法。
Key Takeaways
- 大型预训练视听模型如CLIP在图像分类任务中表现出优秀的零样本性能。
- 模型的微调在特定领域数据集上能够提升其在下游应用中的效果。
- 云环境中模型微调存在数据安全和隐私的担忧。
- 联邦学习(FL)提供了一种去中心化的训练方式,但全模型传输导致的通信和计算成本高。
- CacheFL方法通过轻量级的缓存模型微调来提高效率和性能。
- 缓存模型使用类别平衡数据集初始化,减轻非IID数据的影响。
点此查看论文截图

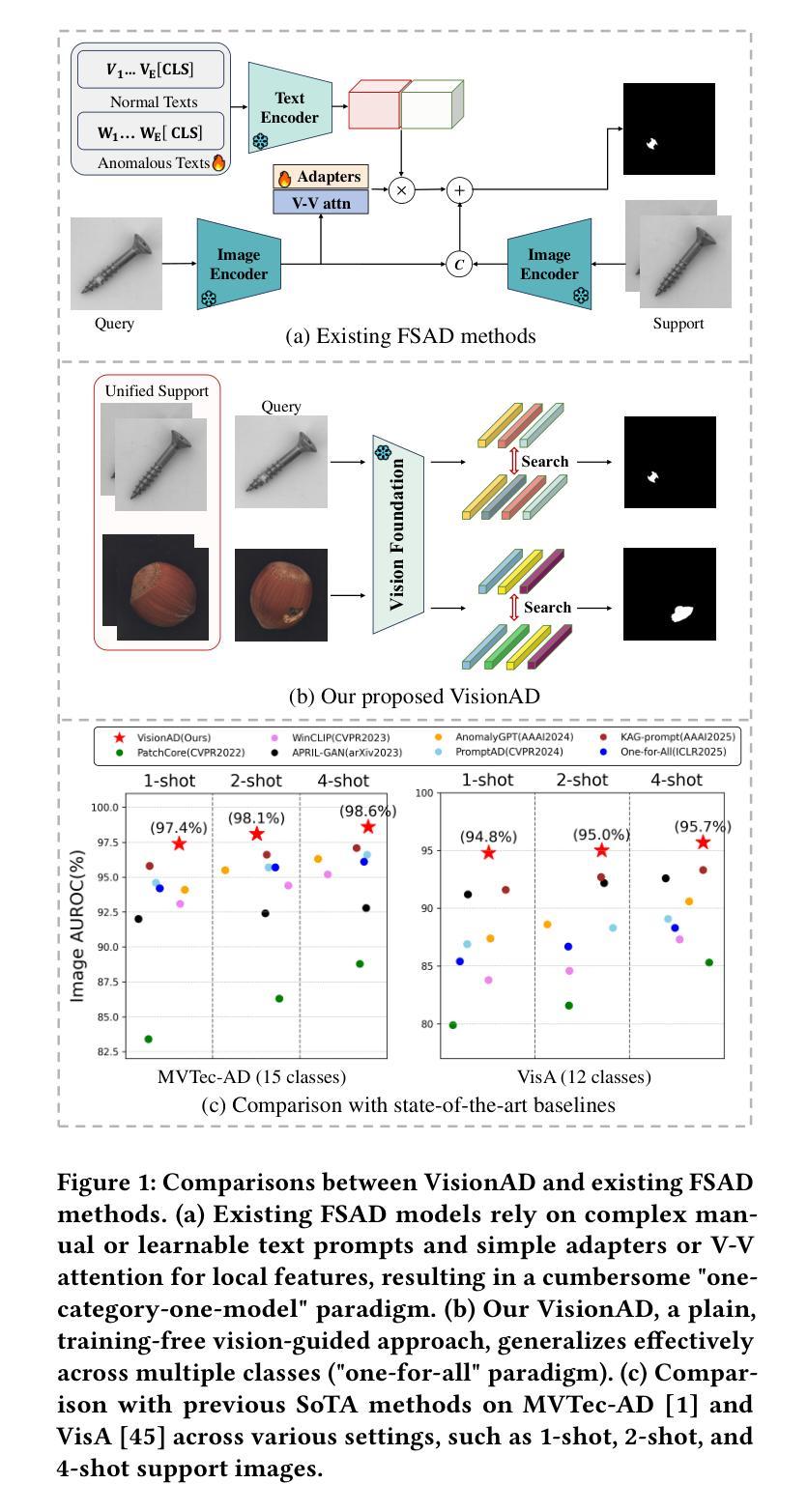
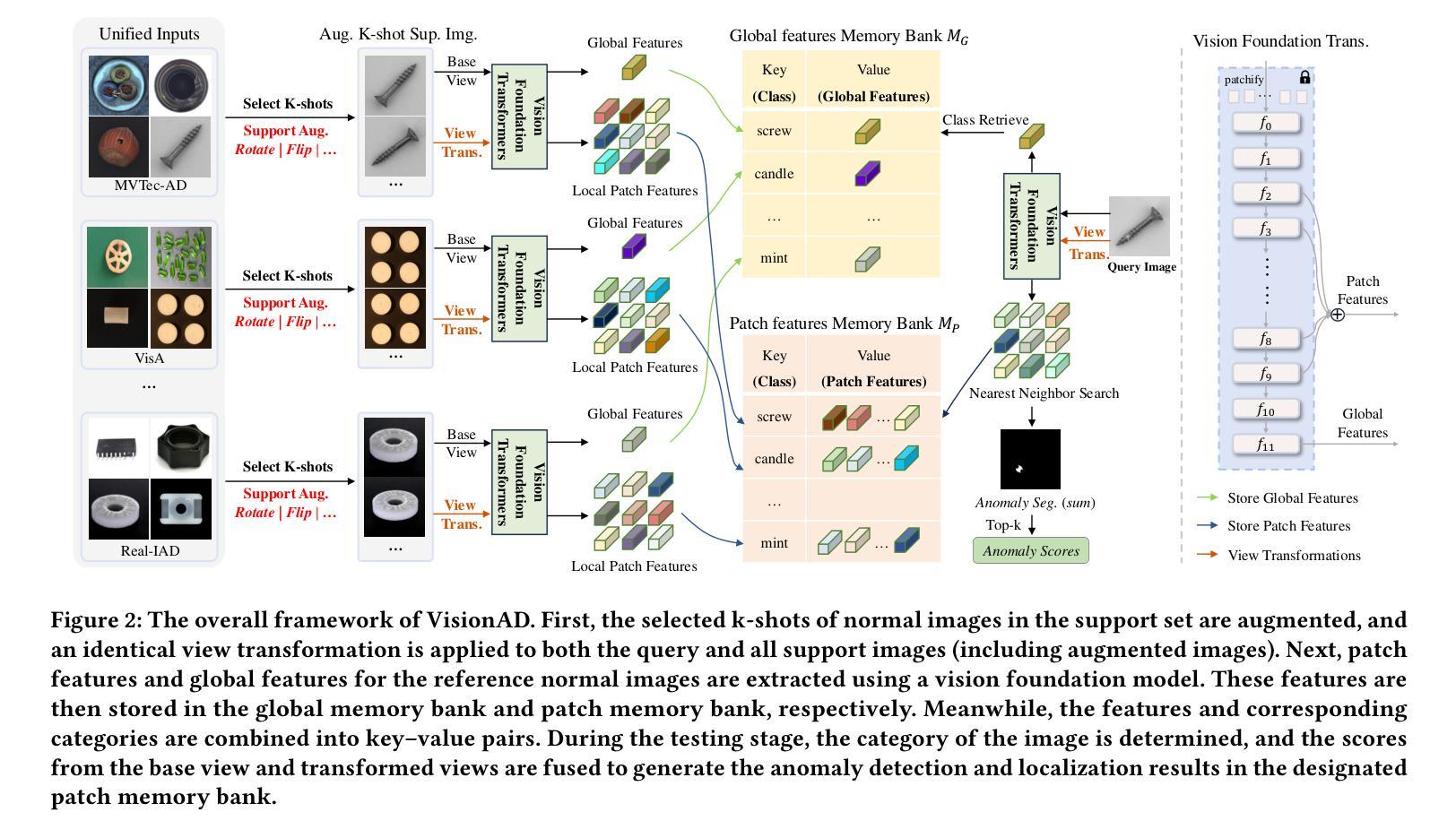
Search is All You Need for Few-shot Anomaly Detection
Authors:Qishan Wang, Jia Guo, Shuyong Gao, Haofen Wang, Li Xiong, Junjie Hu, Hanqi Guo, Wenqiang Zhang
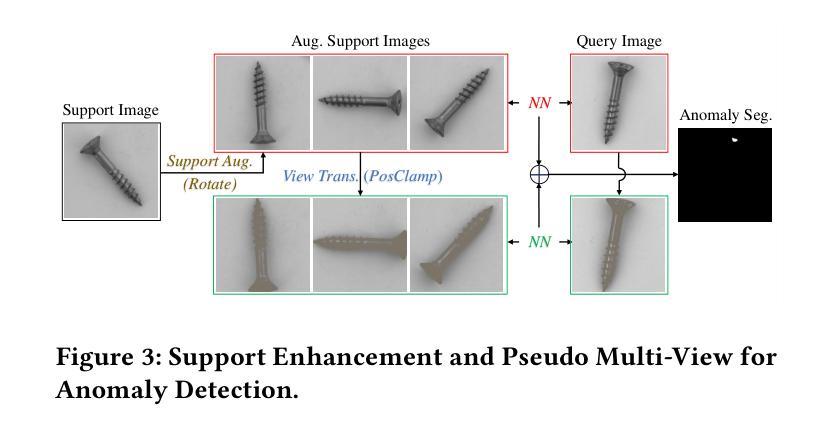
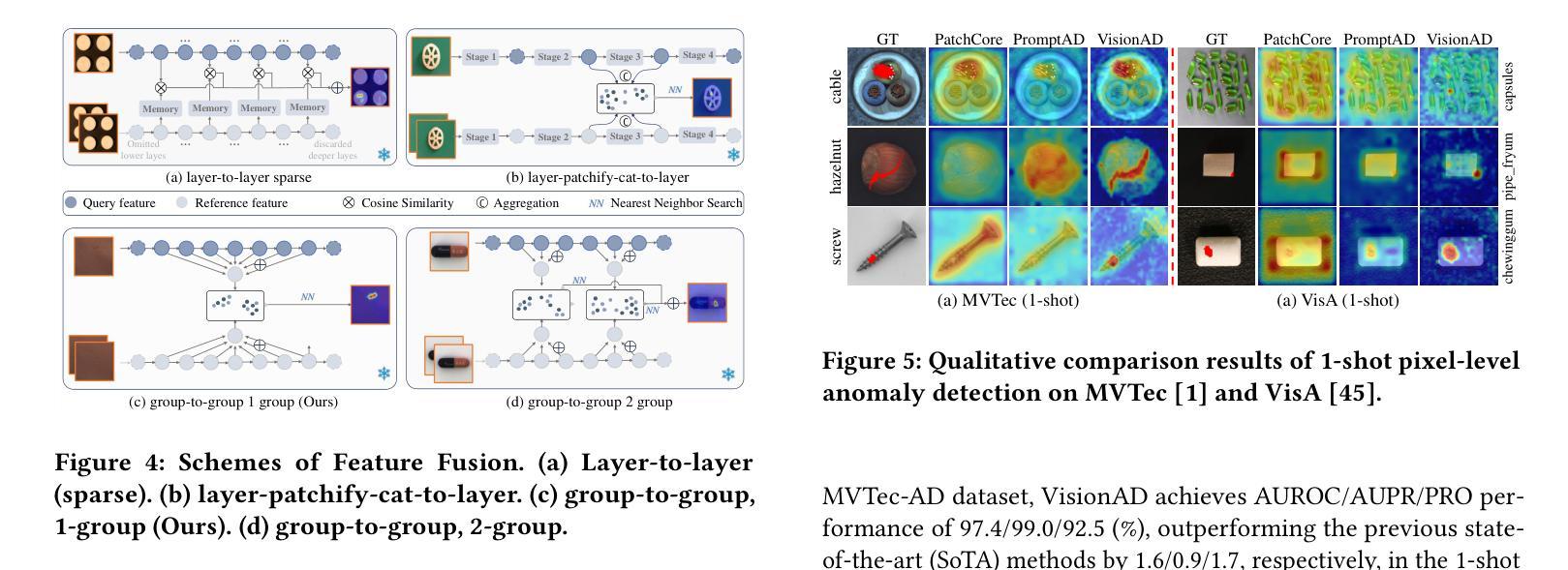
Few-shot anomaly detection (FSAD) has emerged as a crucial yet challenging task in industrial inspection, where normal distribution modeling must be accomplished with only a few normal images. While existing approaches typically employ multi-modal foundation models combining language and vision modalities for prompt-guided anomaly detection, these methods often demand sophisticated prompt engineering and extensive manual tuning. In this paper, we demonstrate that a straightforward nearest-neighbor search framework can surpass state-of-the-art performance in both single-class and multi-class FSAD scenarios. Our proposed method, VisionAD, consists of four simple yet essential components: (1) scalable vision foundation models that extract universal and discriminative features; (2) dual augmentation strategies - support augmentation to enhance feature matching adaptability and query augmentation to address the oversights of single-view prediction; (3) multi-layer feature integration that captures both low-frequency global context and high-frequency local details with minimal computational overhead; and (4) a class-aware visual memory bank enabling efficient one-for-all multi-class detection. Extensive evaluations across MVTec-AD, VisA, and Real-IAD benchmarks demonstrate VisionAD’s exceptional performance. Using only 1 normal images as support, our method achieves remarkable image-level AUROC scores of 97.4%, 94.8%, and 70.8% respectively, outperforming current state-of-the-art approaches by significant margins (+1.6%, +3.2%, and +1.4%). The training-free nature and superior few-shot capabilities of VisionAD make it particularly appealing for real-world applications where samples are scarce or expensive to obtain. Code is available at https://github.com/Qiqigeww/VisionAD.
少量样本异常检测(FSAD)在工业检测中是一项至关重要且充满挑战的任务,只需要少量的正常图像即可完成正常分布建模。尽管现有方法通常采用多模态基础模型,结合语言和视觉模式进行提示引导异常检测,但这些方法往往需要进行复杂的提示工程和大量的手动调整。在本文中,我们证明了一个简单的最近邻搜索框架可以在单类和多类FSAD场景中超越最新技术性能。我们提出的方法VisionAD由四个简单但至关重要的组件构成:(1)可扩展的视觉基础模型,用于提取通用和判别特征;(2)双增强策略——支持增强以提高特征匹配的适应性,查询增强以解决单视图预测的遗漏;(3)多层特征融合,以最小的计算开销捕获低频全局上下文和高频局部细节;(4)类感知视觉内存库,实现高效的一对多类检测。在MVTec-AD、VisA和Real-IAD基准测试上的广泛评估表明,VisionAD具有卓越的性能。仅使用1张正常图像作为支持,我们的方法在图像级AUROC得分上分别实现了97.4%、94.8%和70.8%的显著成绩,显著超越了当前的最先进方法(+1.6%、+3.2%和+1.4%)。VisionAD的无训练性质和优越的少量样本能力使其成为在现实世界应用中特别吸引人的选择,尤其是在样本稀缺或难以获取的情况下。相关代码可通过https://github.com/Qiqigeww/VisionAD获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本论文提出了一种基于最近邻搜索框架的通用少样本异常检测框架VisionAD。其主要贡献包括利用可扩展的视觉基础模型提取特征、双重增强策略提高特征匹配适应性及解决单视图预测缺陷、多层级特征融合捕捉全局与局部细节信息,以及建立类感知视觉记忆库实现多类检测效率。在MVTec-AD等数据集上,使用仅一个正常图像作为支持样本,VisionAD实现了显著的性能提升。
Key Takeaways
- VisionAD利用最近邻搜索框架在少样本异常检测中表现优异。
- VisionAD包含四个关键组件:可扩展视觉基础模型、双重增强策略、多层级特征融合和类感知视觉记忆库。
- VisionAD在MVTec-AD等数据集上实现了显著的性能提升,使用仅一个正常图像作为支持样本。
- VisionAD具有无需训练的优势,特别适用于样本稀缺或昂贵的真实世界应用。
- VisionAD具有高效的多类检测能力。
- VisionAD通过结合语言与视觉模态的提示引导异常检测,减少了复杂的手动调整需求。
点此查看论文截图

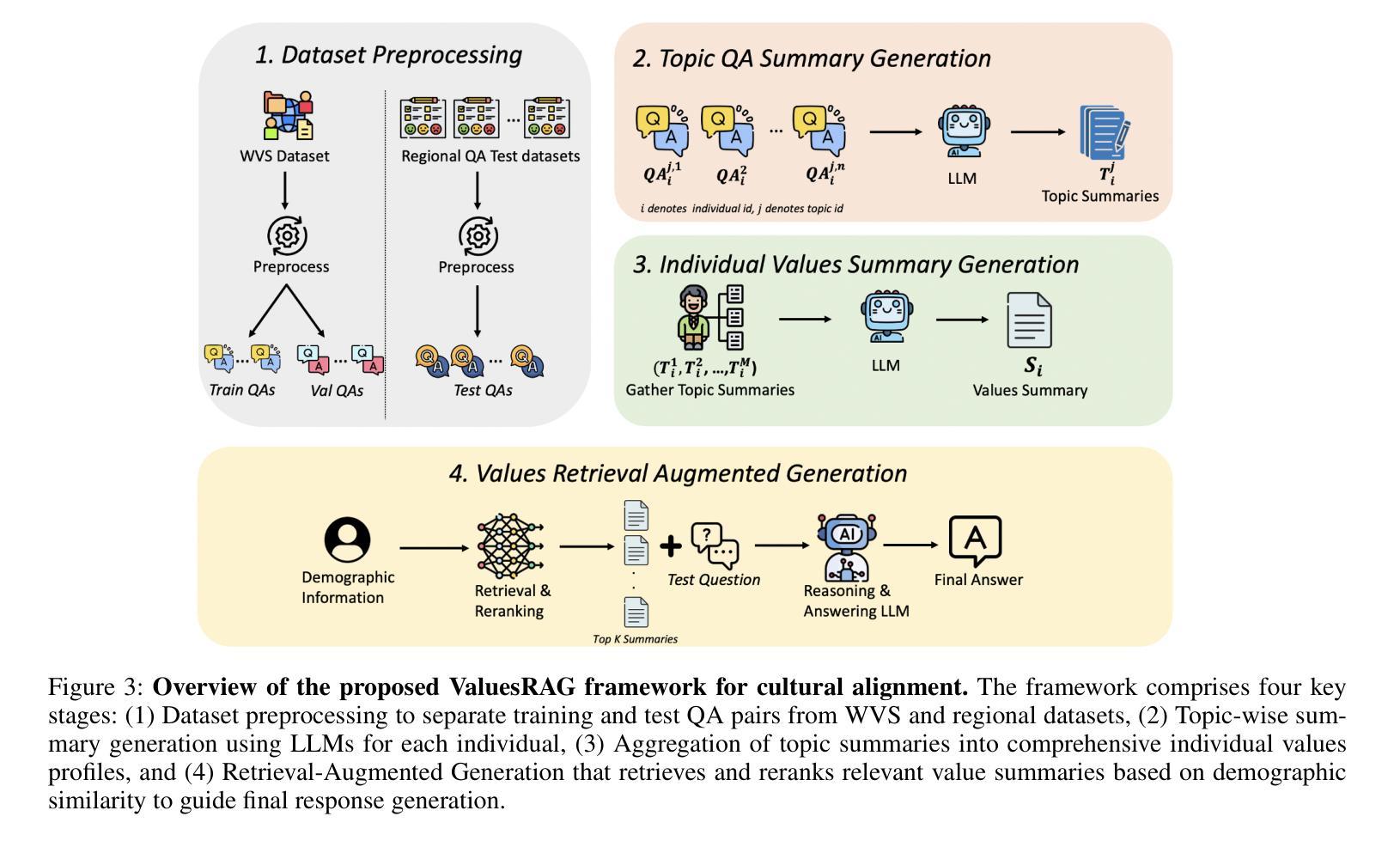
ValuesRAG: Enhancing Cultural Alignment Through Retrieval-Augmented Contextual Learning
Authors:Wonduk Seo, Zonghao Yuan, Yi Bu
Ensuring cultural values alignment in Large Language Models (LLMs) remains a critical challenge, as these models often embed Western-centric biases from their training data, leading to misrepresentations and fairness concerns in cross-cultural applications. Existing approaches such as role assignment and few-shot learning struggle to address these limitations effectively due to their reliance on pre-trained knowledge, limited scalability, and inability to capture nuanced cultural values. To address these issues, we propose ValuesRAG, a novel and effective framework that applies Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) with In-Context Learning (ICL) to integrate cultural and demographic knowledge dynamically during text generation. Leveraging the World Values Survey (WVS) dataset, ValuesRAG first generates summaries of values for each individual. We subsequently curate several representative regional datasets to serve as test datasets and retrieve relevant summaries of values based on demographic features, followed by a reranking step to select the top-k relevant summaries. We evaluate ValuesRAG using 6 diverse regional datasets and show that it consistently outperforms baselines: including zero-shot, role-assignment, few-shot, and hybrid methods, both in main experiments and ablation settings. Notably, ValuesRAG achieves the best overall performance over prior methods, demonstrating its effectiveness in fostering culturally aligned and inclusive AI systems. Our findings underscore the potential of dynamic retrieval-based methods to bridge the gap between global LLM capabilities and localized cultural values.
确保大型语言模型(LLM)中的文化价值观对齐仍然是一个关键挑战,因为这些模型通常从其训练数据中嵌入西方中心主义的偏见,导致跨文化应用中的误解和公平性问题。现有方法,如角色分配和少样本学习,由于依赖预训练知识、可扩展性有限以及无法捕捉微妙的文化价值观,难以有效地解决这些局限性。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了ValuesRAG,这是一个将检索增强生成(RAG)与上下文学习(ICL)相结合的新型有效框架,用于在文本生成过程中动态整合文化和人口统计数据知识。借助世界价值观调查(WVS)数据集,ValuesRAG首先为每个人生成价值观摘要。随后,我们精心挑选了几个具有代表性的区域数据集作为测试数据集,并根据人口统计特征检索相关的价值观摘要,然后进行重新排序以选择前k个最相关的摘要。我们使用6个不同的区域数据集对ValuesRAG进行了评估,结果表明,与零样本、角色分配、少样本和混合方法相比,无论是在主要实验还是消融设置中,ValuesRAG始终表现出更高的性能。值得注意的是,ValuesRAG在先前的方法中取得了最佳的整体性能,证明了其在促进文化对齐和包容性人工智能系统方面的有效性。我们的研究结果表明了动态检索方法在弥合全球LLM能力与本地化文化价值观之间的差距方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF preprint
Summary
训练数据中的西方中心偏见导致大型语言模型(LLM)在跨文化应用中存在误表示和公平性担忧的问题。ValuesRAG是一个结合检索增强生成(RAG)和上下文学习(ICL)的新框架,旨在动态集成文化和人口统计知识来进行文本生成,以解决这一问题。它利用世界价值观调查(WVS)数据集为每个个体生成价值观摘要,并根据人口统计特征检索相关的价值观摘要,然后进行重新排序。评估表明,ValuesRAG在多个区域数据集上的表现均优于包括零样本、角色分配、小样本和混合方法在内的基线方法,证明了其在促进文化对齐和包容性人工智能系统方面的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在跨文化应用中面临文化价值观对齐的挑战,存在西方中心偏见问题。
- 现有方法如角色分配和少样本学习无法有效解决这个问题,因为它们依赖预训练知识,具有有限的扩展能力,并且无法捕捉细微的文化价值观。
- ValuesRAG框架结合了检索增强生成(RAG)和上下文学习(ICL),能够动态集成文化和人口统计知识来进行文本生成。
- ValuesRAG利用世界价值观调查(WVS)数据集为每个个体生成价值观摘要,并通过检索和重新排序选择与人口统计特征相关的摘要。
- ValuesRAG在多个区域数据集上的表现优于其他方法,证明了其在促进文化对齐和包容性人工智能系统方面的有效性。
- ValuesRAG的实现为动态检索方法弥合全球LLM能力和本地化文化价值观之间的差距提供了潜力。
点此查看论文截图