⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-05-10 更新
Hearing and Seeing Through CLIP: A Framework for Self-Supervised Sound Source Localization
Authors:Sooyoung Park, Arda Senocak, Joon Son Chung
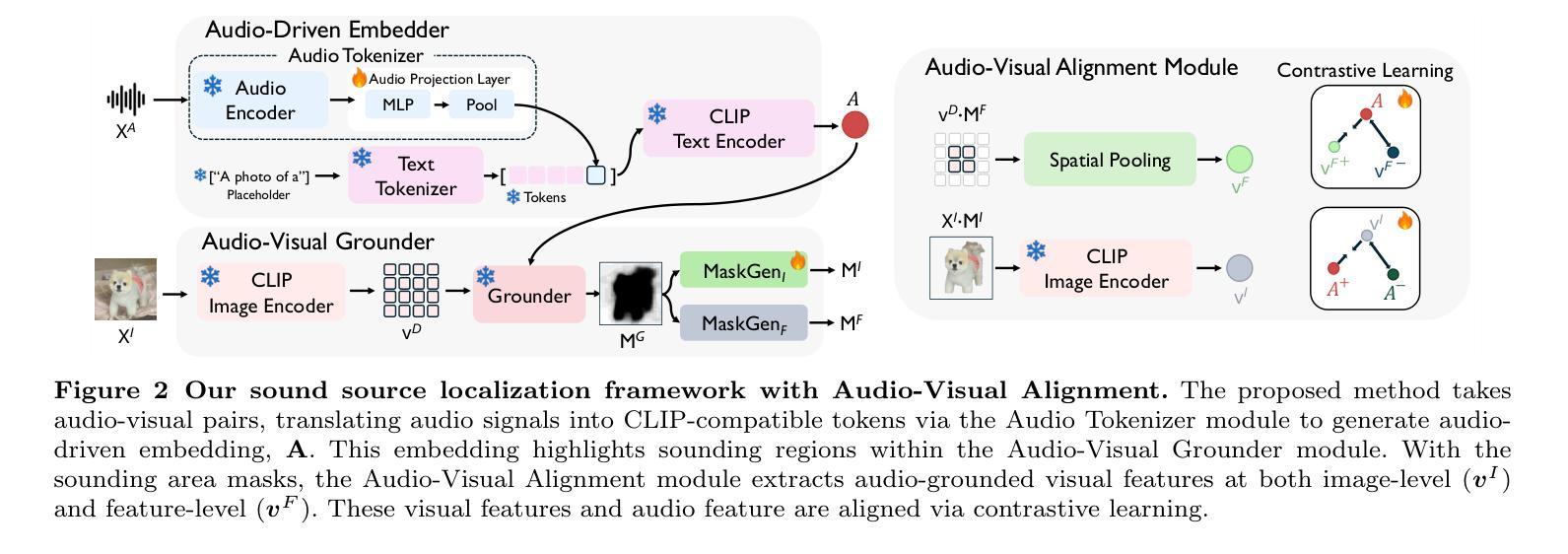
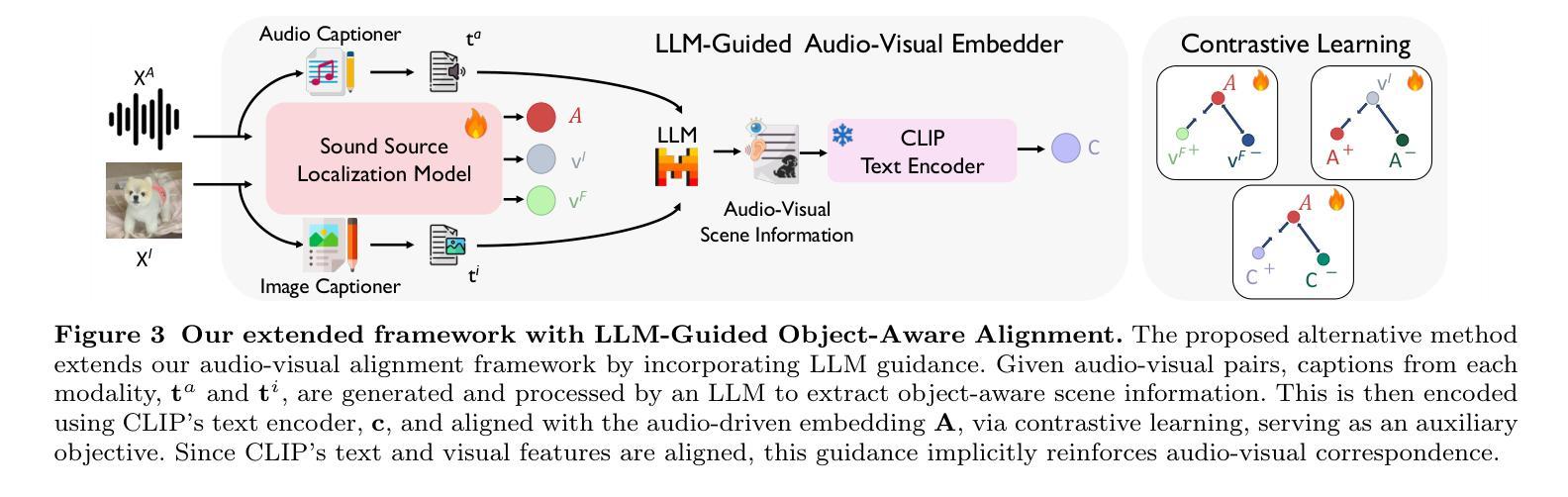
Large-scale vision-language models demonstrate strong multimodal alignment and generalization across diverse tasks. Among them, CLIP stands out as one of the most successful approaches. In this work, we extend the application of CLIP to sound source localization, proposing a self-supervised method operates without explicit text input. We introduce a framework that maps audios into tokens compatible with CLIP’s text encoder, producing audio-driven embeddings. These embeddings are used to generate sounding region masks, from which visual features are extracted and aligned with the audio embeddings through a contrastive audio-visual correspondence objective. Our findings show that alignment knowledge of pre-trained multimodal foundation model enables our method to generate more complete and compact localization for sounding objects. We further propose an LLM-guided extension that distills object-aware audio-visual scene understanding into the model during training to enhance alignment. Extensive experiments across five diverse tasks demonstrate that our method, in all variants, outperforms state-of-the-art approaches and achieves strong generalization in zero-shot settings.
大规模视觉语言模型表现出强大的跨不同任务的跨模态对齐和泛化能力。其中,CLIP是最成功的方法之一。在这项工作中,我们将CLIP的应用扩展到声音源定位,提出了一种无需明确文本输入的自监督方法。我们引入了一个框架,该框架将音频映射到与CLIP文本编码器兼容的令牌,从而产生音频驱动嵌入。这些嵌入用于生成声音区域掩码,从中提取视觉特征,并通过对比音频视觉对应目标进行与音频嵌入的对齐。我们的研究结果表明,预训练的多模态基础模型的对齐知识使我们的方法为发声对象生成更完整和紧凑的定位。我们进一步提出了一个由大型语言模型引导扩展的方法,在训练过程中将对象感知的音频视觉场景理解蒸馏到模型中,以增强对齐。在五个不同任务上的广泛实验表明,我们所有方法都优于最新技术,并在零样本设置中实现了强大的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Journal Extension of WACV 2024 paper (arXiv:2311.04066). Code is available at https://github.com/swimmiing/ACL-SSL
Summary
该文本介绍了将CLIP模型扩展到声音源定位的研究。研究团队提出了一种自监督方法,无需明确的文本输入即可生成音频驱动的嵌入。该研究将音频映射到与CLIP文本编码器兼容的标记,并通过对比音频视觉对应关系目标,从生成的音源区域掩模中提取视觉特征并与音频嵌入对齐。此外,该研究还提出了一种基于大型语言模型的扩展方法,通过训练期间将对象感知的音频视觉场景理解引导到模型中,以提高对齐效果。实验结果在五项不同任务上表现优于其他先进方法,并实现了零样本设置的强大泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- CLIP模型在多种任务上显示出强大的跨模态对齐和泛化能力。
- 研究将CLIP模型扩展到声音源定位,提出了一种自监督方法,无需文本输入即可生成音频驱动的嵌入。
- 通过对比音频视觉对应关系目标,从音源区域掩模中提取视觉特征并与音频嵌入对齐。
- 引入了一种基于大型语言模型的扩展方法,以提高音频视觉对齐效果。
- 方法在五项不同任务上的表现优于其他先进方法。
- 该方法实现了零样本设置的强大泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图